Asked by: Casey Hilpert
Score: 4.6/5
(11 votes)
Some of the functions of word processing software include: Creating, editing, saving and printing documents. Copying, pasting, moving and deleting text within a document. Formatting text, such as font type, bolding, underlining or italicizing.
What are the features of word processor class 10?
What are the four features of word processor?
- – Creating, editing, saving and printing documents.
- – Copying, pasting, moving and deleting text within a document.
- – Formatting text, such as font type, bolding, underlining or italicizing.
- – Creating and editing tables.
What are the features and advantages of word processing?
What are the advantages of word processing?
- It is faster and easier than writing by hand.
- You can store documents on your computer, which you cannot do on a typewriter.
- There are more formatting choices with a word processor (the spelling, grammar and language tools).
- You can print copies of your documents.
What are the types of word processing?
Types of Word Processing Applications
- Microsoft Word. One of the most well-known and widely used word processing applications on the market is Microsoft Word. …
- WordPerfect. WordPerfect is a word processing application from Corel Corp.. …
- Lotus Word Pro. …
- iWork Pages. …
- And the Rest.
What are the four functions of word processing?
There are four primary functions of word processors: composing, editing, saving and printing.
28 related questions found
What are the main features of word processing?
What are the main features of word processor?
- Creating, editing, saving and printing documents.
- Copying, pasting, moving and deleting text within a document.
- Formatting text, such as font type, bolding, underlining or italicizing.
- Creating and editing tables.
What are the 10 advantages of word processing?
1) It is faster and easier than writing by hand. 2) You can store documents on your computer, which you cannot do on a typewriter. … 3) There are more formatting choices with a word processor (the spelling, grammar and language tools). 4) You can print copies of your documents.
What are the benefits of word processing?
Improving Efficiency and Accuracy. Besides simply saving time, word processing offers ways to improve workers’ efficiency and accuracy. Word processors contain software to automatically correct common errors and identify misspellings, improving overall speed and reducing errors.
What are 10 features of Microsoft word?
10 Supremely Useful Features in Microsoft Word
- Convert a List to a Table.
- Convert a Bulleted List to SmartArt.
- Create a Custom Tab.
- Quick Selection Methods.
- Add Placeholder Text.
- Changing Case.
- Quick Parts.
- Touch/ Mouse Mode in Word 2013.
What is called word processing?
Word Processing refers to the act of using a computer to create, edit, save and print documents. In order to perform word processing, specialized software (known as a Word Processor) is needed. … The editing and formatting capabilities of the word processor demonstrate the application’s true power.
What is the function of word processor?
A word processor (WP) is a device or computer program that provides for input, editing, formatting, and output of text, often with some additional features.
What do you mean by word processing explain its features?
A word processor is software or a device that allows users to create, edit, and print documents . It enables you to write text, store it electronically. … The word processor is one of the most frequently used software programs on a computer, with Microsoft Word being the most popular word processor.
What are 3 new features in Microsoft Word?
Word 2019 gives you new ways to work with documents, like improved digital pen features, book-like page navigation, Learning Tools, and translation.
What are the latest features of Microsoft Word?
Let’s take a look at three of the most useful new features found in Microsoft Word.
- Resume Assistant (Office 365 only) One of the most difficult aspects of putting together your resume is finding just the right wording to use. …
- Translate Text. …
- Turn Text to Speech.
What are the components of Microsoft Word?
The basics of the Word window
- Title bar. This displays the document name followed by a program name.
- Menu bar. This contains a list of options to manage and customize documents.
- Standard toolbar. …
- Formatting toolbar. …
- Ruler. …
- Insertion point. …
- End-of-document marker. …
- Help.
What are the benefits of word processing in education?
- 1 Spelling. Word processors contain an electronic spell checker. …
- 2 Security. Teachers and students gain a sense of security about losing assignments. …
- 3 Legibility. Teachers benefit by receiving a readable copy that is easy to grade. …
- 4 Publishing. …
- 5 Mobility.
What is the disadvantage of word processing?
If you want to write something down quickly, it can take more time to switch the computer on, open the word processor and set up the document. Sometimes pen and paper is faster.
How has word processing affected writing?
Some studies have shown positive effects towards the use of computer word processing programs. … Some latest word processors are even able put in text citations on student research papers Similarly, computer writing software are able to correct the mistakes and check for plagiarism of researched work.
What is editing in word processing?
Editing: Editing is the process of making changes or corrections in a document. It includes alterations to the text itself, moving or copying items to other locations and applying formatting options to the document itself and items within it.
Why is Microsoft Word black?
If you have enabled the Black Office theme, you will have a Switch Modes button on the View tab of the Ribbon. For more, see https://insider.office.com/it-it/blog/try-dark-mode-in-word.
Is Microsoft Word free?
The good news is, if you don’t need the full suite of Microsoft 365 tools, you can access a number of its apps online for free — including Word, Excel, PowerPoint, OneDrive, Outlook, Calendar and Skype. Here’s how to get them: Go to Office.com. Log in to your Microsoft account (or create one for free).
What is the Save As command in Word?
Save the current document: Press Ctrl + S to save the current document immediately. Open the Save As window: Press F12 to open the Save As dialog box to save the document with a specific filename or in a new folder. Close the current document: Press Ctrl + W to close the current document.
What are features of word processing package?
Typical features of a modern word processor include multiple font sets, spell checking, grammar checking, a built-in thesaurus, automatic text correction, web integration, HTML conversion, pre-formatted publication projects such as newsletters and to-do lists, and much more.
What is modern word processing?
A word processor, or word processing program, does exactly what the name implies. … Modern word processing programs, however, include features to customize the style of the text, change the page formatting, and may be able to add headers, footers, and page numbers to each page.
Is Excel a word processor?
Examples. Microsoft Word, OpenOffice Writer and WordPerfect are examples of word processing programs. … Microsoft Excel, OpenOffice Calc and Lotus 1-2-3 are examples of spreadsheet programs. Like the word processing applications, each spreadsheet program can open files created in another application.
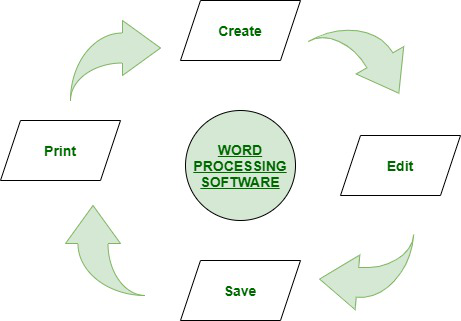
Some of the functions of word processing software include:
- Creating, editing, saving and printing documents.
- Copying, pasting, moving and deleting text within a document.
- Formatting text, such as font type, bolding, underlining or italicizing.
- Creating and editing tables.
What is word processing and its features?
A word processor is software or a device that allows users to create, edit, and print documents. It enables you to write text, store it electronically, display it on a screen, modify it by entering commands and characters from the keyboard, and print it. Of all computer applications, word processing is the most common.
What are the four features of word processor?
List four important feature of a word processor ? Name any two word processor
- – Creating, editing, saving and printing documents.
- – Copying, pasting, moving and deleting text within a document.
- – Formatting text, such as font type, bolding, underlining or italicizing.
- – Creating and editing tables.
What are the features and advantages of word processing?
Advantages of Word Processing
- Quality : It produces error free documents.
- Storage of Text : We can take any number of copies with word processor.
- Time Saving : We can get any number of copies of document in future without retyping.
- Security : We can protect the documents in word processing by giving passwords.
What is the importance of word processing?
Furthermore, word processing benefits the environment by reducing the amount of paperwork needed to perform daily tasks (e.g., archiving, sending out letters, sending meeting agendas). By sending documents via a secured email, the cost of postage and paper waste are reduced significantly.
What are the benefits of word processing in education?
With word processing software, students can easily review and revise their compositions, highlight key ideas, rearrange sentences or paragraphs to flow more logically, and try out alternative sentences or words to communicate their ideas better.
What are the basic elements of Microsoft Word?
MS- Word Window Elements:
- Title bar.
- Menu Bar.
- Toolbars.
- Workspace.
- Status Bar.
- Scroll Bars.
- Scroll Box.
- Task Pane.
How do you describe computer skills?
Computer skills are abilities and knowledge which allow you to use computers and related technology. They let you use word processing software, access the Internet, manage files, or create presentations. Advanced computer skills would let you access databases, use spreadsheets, and even code.
What are some common word processing applications?
Two of the most widely used examples of word processing software are Microsoft Word and Google Docs. Both Word and Google Docs provide the business writer with the formatting tools needed to create professional documents.
What are examples of word processing?
- Adobe InCopy.
- Corel WordPerfect (up to v. 9.0)
- Hangul.
- Ichitaro.
- Kingsoft Writer.
- Microsoft Word.
- Scrivener.
- StarOffice Writer.
What are the word processing tools?
5 Great Word Processing Tools For Writing Your Novel
- Microsoft Office. Microsoft Word is pretty much the standard in the traditional business world, and for good reason – it’s fairly easy to use, compatible across a wide range of platforms (there’s even an iphone app currently in the works!), and great customer service.
- Apache OpenOffice.
- Google Drive.
- iWork Pages.
- Scrivener.
How many types of word processing are there?
3 types
Which software is best for word processing?
- LibreOffice Writer. All-singing, all-dancing word processors for any text-based work.
- WPS Office Free Writer. A word processor with cloud storage and support for all text files.
- FocusWriter. The ideal word processor for first drafts, with no fussy formatting.
- FreeOffice TextMaker.
- Writemonkey.
What are Microsoft Word functions?
Given below are the basic functions of Microsoft Word:
- Creating text documents.
- Editing and Formatting the existing documents.
- Making a text document interactive with different features and tools.
- Graphical documents, comprising images.
- Used by Authors and Researchers.
- Detect grammatical errors in a text document.
Which one is not a function in MS Word?
The NOT function is a built-in function in Excel that is categorized as a Logical Function. It can be used as a worksheet function (WS) in Excel. As a worksheet function, the NOT function can be entered as part of a formula in a cell of a worksheet.
What are the basic functions of Microsoft Excel?
You may be familiar with common functions like sum, average, product, and count, but there are hundreds of functions in Excel, even for things like formatting text, referencing cells, calculating financial rates, and analyzing statistics.
What is MS Word and Excel?
Microsoft Word is a word processing program used for writing letters, memos, reports and paper presentations. Microsoft Excel is a spreadsheet program used for calculations, making charts and recording data about all sorts of business processes.
What is the full form of MS Excel?
Microsoft Excel is a spreadsheet developed by Microsoft for Windows, macOS, Android and iOS. It features calculation, graphing tools, pivot tables, and a macro programming language called Visual Basic for Applications (VBA). Excel forms part of the Microsoft Office suite of software.
What is the use of MS Office?
Microsoft Office has become a leading platform to drive productivity at home and in the workplace. Whether it’s managing email in Outlook, or building analysis spreadsheets in Excel, Office has made carrying out many computer based tasks easier for all of us.
Improve Article
Save Article
Like Article
Improve Article
Save Article
Like Article
Word Processing Software :
The word “word processor” means it processes words with pages and paragraphs. Word processors are of 3 types which are electronic, mechanical, and software.
The word processing software is used to apply the basic editing and design and also helps in manipulating the text to your pages whereas the word processor, is a device that provides editing, input, formatting, and output of the given text with some additional features.
It is a type of computer software application or an electronic device. In today’s generation, the word processor has become the word processing software or programs that are running on general-purpose computers.
Examples or Applications of a Word Processing Software :
- Wordpad
- Microsoft Word
- Lotus word pro
- Notepad
- WordPerfect (Windows only),
- AppleWorks (Mac only),
- Work pages
- OpenOffice Writer
Features :
- They are stand-alone devices that are dedicated to the function.
- Their programs are running on general-purpose computers
- It is easy to use
- Helps in changing the shape and style of the characters of the paragraphs
- Basic editing like headers & footers, bullets, numbering is being performed by it.
- It has a facility for mail merge and preview.
Functions :
- It helps in Correcting grammar and spelling of sentences
- It helps in storing and creating typed documents in a new way.
- It provides the function of Creating the documents with basic editing, saving, and printing of it or same.
- It helps in Copy the text along with moving deleting and pasting the text within a given document.
- It helps in Formatting text like bold, underlining, font type, etc.
- It provides the function of creating and editing the formats of tables.
- It helps in Inserting the various elements from some other types of software.
Advantages :
- It benefits the environment by helping in reducing the amount of paperwork.
- The cost of paper and postage waste is being reduced.
- It is used to manipulate the document text like a report
- It provides various tools like copying, deleting and formatting, etc.
- It helps in recognizing the user interface feature
- It applies the basic design to your pages
- It makes it easier for you to perform repetitive tasks
- It is a fully functioned desktop publishing program
- It is time-saving.
- It is dynamic in nature for exchanging the data.
- It produces error-free documents.
- Provide security to our documents.
Disadvantages :
- It does not give you complete control over the look and feel of your document.
- It did not develop out of computer technology.
Like Article
Save Article
A
word processor (more formally known as document preparation system)
is a computer application used for the production (including
composition, editing, formatting, and possibly printing) of any sort
of printable material.
Word
processor may also refer to a type of stand-alone office machine,
popular in the 1970s and 1980s, combining the keyboard text-entry and
printing functions of an electric typewriter with a dedicated
processor (like a computer processor) for the editing of text.
Although features and design varied between manufacturers and models,
with new features added as technology advanced, word processors for
several years usually featured a monochrome display and the ability
to save documents on memory cards or diskettes. Later models
introduced innovations such as spell-checking programs, increased
formatting options, and dot-matrix printing. As the more versatile
combination of a personal computer and separate printer became
commonplace, most business-machine companies stopped manufacturing
the word processor as a stand-alone office machine. As of 2009 there
were only two U.S. companies, Classic and AlphaSmart, which still
made stand-alone word processors.[1] Many older machines, however,
remain in use.
Word
processors are descended from early text formatting tools (sometimes
called text justification tools, from their only real capability).
Word processing was one of the earliest applications for the personal
computer in office productivity.
Although
early word processors used tag-based markup for document formatting,
most modern word processors take advantage of a graphical user
interface providing some form of What You See Is What You Get
editing. Most are powerful systems consisting of one or more programs
that can produce any arbitrary combination of images, graphics and
text, the latter handled with type-setting capability.
Microsoft
Word is the most widely used word processing software. Microsoft
estimates that over 500,000,000 people use the Microsoft Office
suite,[2] which includes Word. Many other word processing
applications exist, including WordPerfect (which dominated the market
from the mid-1980s to early-1990s on computers running Microsoft’s
MS-DOS operating system) and open source applications OpenOffice.org
Writer, AbiWord, KWord, and LyX. Web-based word processors, such as
Google Docs, are a relatively new category.
Word processing
Characteristics
Word
processing typically implies the presence of text manipulation
functions that extend beyond a basic ability to enter and change
text, such as automatic generation of:
• batch
mailings using a form letter template and an address database (also
called mail merging);
• indices
of keywords and their page numbers;
• tables
of contents with section titles and their page numbers;
• tables
of figures with caption titles and their page numbers;
• cross-referencing
with section or page numbers;
• footnote
numbering;
• new
versions of a document using variables (e.g. model numbers, product
names, etc.)
Other
word processing functions include «spell checking»
(actually checks against wordlists), «grammar checking»
(checks for what seem to be simple grammar errors), and a «thesaurus»
function (finds words with similar or opposite meanings). Other
common features include collaborative editing, comments and
annotations, support for images and diagrams and internal
cross-referencing.
Word
processors can be distinguished from several other, related forms of
software:
Text
editors (modern examples of which include Notepad, BBEdit, Kate,
Gedit), were the precursors of word processors. While offering
facilities for composing and editing text, they do not format
documents. This can be done by batch document processing systems,
starting with TJ-2 and RUNOFF and still available in such systems as
LaTeX (as well as programs that implement the paged-media extensions
to HTML and CSS). Text editors are now used mainly by programmers,
website designers, computer system administrators, and, in the case
of LaTeX by mathematicians and scientists (for complex formulas and
for citations in rare languages). They are also useful when fast
startup times, small file sizes, editing speed and simplicity of
operation are preferred over formatting.
Later
desktop publishing programs were specifically designed to allow
elaborate layout for publication, but often offered only limited
support for editing. Typically, desktop publishing programs allowed
users to import text that was written using a text editor or word
processor.
Almost
all word processors enable users to employ styles, which are used to
automate consistent formatting of text body, titles, subtitles,
highlighted text, and so on.
Styles
greatly simplify managing the formatting of large documents, since
changing a style automatically changes all text that the style has
been applied to. Even in shorter documents styles can save a lot of
time while formatting. However, most help files refer to styles as an
‘advanced feature’ of the word processor, which often discourages
users from using styles regularly.
Document
statistics
Most
current word processors can calculate various statistics pertaining
to a document. These usually include:
• Character
count, word count, sentence count, line count, paragraph count, page
count.
• Word,
sentence and paragraph length.
• Editing
time.
Errors
are common; for instance, a dash surrounded by spaces — like either
of these — may be counted as a word.
Typical
usage
Word
processors have a variety of uses and applications within the
business world, home, and education.
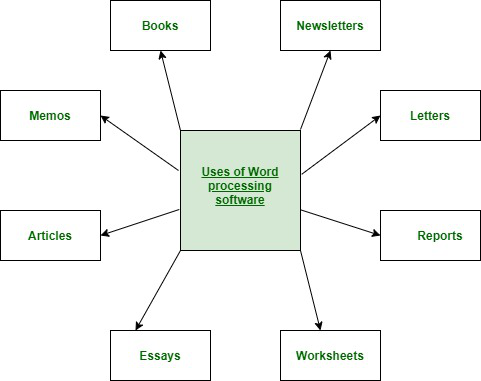
Business
Within
the business world, word processors are extremely useful tools.
Typical uses include:
• legal
copies
• letters
and letterhead
• memos
• reference
documents
Businesses
tend to have their own format and style for any of these. Thus,
versatile word processors with layout editing and similar
capabilities find widespread use in most businesses.
Education
Many
schools have begun to teach typing and word processing to their
students, starting as early as elementary school. Typically these
skills are developed throughout secondary school in preparation for
the business world. Undergraduate students typically spend many hours
writing essays. Graduate and doctoral students continue this trend,
as well as creating works for research and publication.
Home
While
many homes have word processors on their computers, word processing
in the home tends to be educational, planning or business related,
dealing with assignments or work being completed at home, or
occasionally recreational, e.g. writing short stories. Some use word
processors for letter writing, résumé creation, and card creation.
However, many of these home publishing processes have been taken over
by desktop publishing programs specifically oriented toward home use.
which are better suited to these types of documents.
History
Toshiba
JW-10, the first word processor for the Japanese language (1971-1978
IEEE milestones)
Examples
of standalone word processor typefaces c. 1980-1981
Brother
WP-1400D editing electronic typewriter (1994)
The
term word processing was invented by IBM in the late 1960s. By 1971
it was recognized by the New York Times as a «buzz word».[3]
A 1974 Times article referred to «the brave new world of Word
Processing or W/P. That’s International Business Machines talk…
I.B.M. introduced W/P about five years ago for its Magnetic Tape
Selectric Typewriter and other electronic razzle-dazzle.»
IBM
defined the term in a broad and vague way as «the combination of
people, procedures, and equipment which transforms ideas into printed
communications,» and originally used it to include dictating
machines and ordinary, manually-operated Selectric typewriters. By
the early seventies, however, the term was generally understood to
mean semiautomated typewriters affording at least some form of
electronic editing and correction, and the ability to produce perfect
«originals.» Thus, the Times headlined a 1974 Xerox product
as a «speedier electronic typewriter», but went on to
describe the product, which had no screen, as «a word processor
rather than strictly a typewriter, in that it stores copy on magnetic
tape or magnetic cards for retyping, corrections, and subsequent
printout.»
Electromechanical
paper-tape-based equipment such as the Friden Flexowriter had long
been available; the Flexowriter allowed for operations such as
repetitive typing of form letters (with a pause for the operator to
manually type in the variable information)[8], and when equipped with
an auxiliary reader, could perform an early version of «mail
merge». Circa 1970 it began to be feasible to apply electronic
computers to office automation tasks. IBM’s Mag Tape Selectric
Typewriter (MTST) and later Mag Card Selectric (MCST) were early
devices of this kind, which allowed editing, simple revision, and
repetitive typing, with a one-line display for editing single lines.
The
New York Times, reporting on a 1971 business equipment trade show,
said
The
«buzz word» for this year’s show was «word
processing,» or the use of electronic equipment, such as
typewriters; procedures and trained personnel to maximize office
efficiency. At the IBM exhibition a girl [sic] typed on an electronic
typewriter. The copy was received on a magnetic tape cassette which
accepted corrections, deletions, and additions and then produced a
perfect letter for the boss’s signature….
In
1971, a third of all working women in the United States were
secretaries, and they could see that word processing would have an
impact on their careers. Some manufacturers, according to a Times
article, urged that «the concept of ‘word processing’ could be
the answer to Women’s Lib advocates’ prayers. Word processing will
replace the ‘traditional’ secretary and give women new administrative
roles in business and industry.»
The
1970s word processing concept did not refer merely to equipment, but,
explicitly, to the use of equipment for «breaking down
secretarial labor into distinct components, with some staff members
handling typing exclusively while others supply administrative
support. A typical operation would leave most executives without
private secretaries. Instead one secretary would perform various
administrative tasks for three or more secretaries.» A 1971
article said that «Some [secretaries] see W/P as a career ladder
into management; others see it as a dead-end into the automated
ghetto; others predict it will lead straight to the picket line.»
The National Secretaries Association, which defined secretaries as
people who «can assume responsibility without direct
supervision,» feared that W/P would transform secretaries into
«space-age typing pools.» The article considered only the
organizational changes resulting from secretaries operating word
processors rather than typewriters; the possibility that word
processors might result in managers creating documents without the
intervention of secretaries was not considered—not surprising in an
era when few but secretaries possessed keyboarding skills.
In
the early 1970s, computer scientist Harold Koplow was hired by Wang
Laboratories to program calculators. One of his programs permitted a
Wang calculator to interface with an IBM Selectric typewriter, which
was at the time used to calculate and print the paperwork for auto
sales.
In
1974, Koplow’s interface program was developed into the Wang 1200
Word Processor, an IBM Selectric-based text-storage device. The
operator of this machine typed text on a conventional IBM Selectric;
when the Return key was pressed, the line of text was stored on a
cassette tape. One cassette held roughly 20 pages of text, and could
be «played back» (i.e., the text retrieved) by printing the
contents on continuous-form paper in the 1200 typewriter’s «print»
mode. The stored text could also be edited, using keys on a simple,
six-key array. Basic editing functions included Insert, Delete, Skip
(character, line), and so on.
The
labor and cost savings of this device were immediate, and remarkable:
pages of text no longer had to be retyped to correct simple errors,
and projects could be worked on, stored, and then retrieved for use
later on. The rudimentary Wang 1200 machine was the precursor of the
Wang Office Information System (OIS), introduced in 1976, whose
CRT-based system was a major breakthrough in word processing
technology. It displayed text on a CRT screen, and incorporated
virtually every fundamental characteristic of word processors as we
know them today. It was a true office machine, affordable by
organizations such as medium-sized law firms, and easily learned and
operated by secretarial staff.
The
Wang was not the first CRT-based machine nor were all of its
innovations unique to Wang. In the early 1970s Linolex, Lexitron and
Vydec introduced pioneering word-processing systems with CRT display
editing. A Canadian electronics company, Automatic Electronic
Systems, had introduced a product with similarities to Wang’s product
in 1973, but went into bankruptcy a year later. In 1976, refinanced
by the Canada Development Corporation, it returned to operation as
AES Data, and went on to successfully market its brand of word
processors worldwide until its demise in the mid-1980s. Its first
office product, the AES-90, combined for the first time a CRT-screen,
a floppy-disk and a microprocessor,[citation needed] that is, the
very same winning combination that would be used by IBM for its PC
seven years later. The AES-90 software was able to handle French and
English typing from the start, displaying and printing the texts
side-by-side, a Canadian government requirement. The first eight
units were delivered to the office of the then Prime Minister, Pierre
Elliot Trudeau, in February 1974. Despite these predecessors, Wang’s
product was a standout, and by 1978 it had sold more of these systems
than any other vendor.
In
the early 1980’s, AES Data Inc. introduced a networked word processor
system, called MULTIPLUS, offering multi-tasking and up to 8
workstations all sharing the resources of a centralized computer
system, a precursor to today’s networks. It followed with the
introduction of SuperPlus and SuperPlus IV systems which also offered
the CP/M operating system answering client needs. AES Data word
processors were placed side-by-side with CP/M software, like
Wordstar, to highlight ease of use.
The
phrase «word processor» rapidly came to refer to CRT-based
machines similar to Wang’s. Numerous machines of this kind emerged,
typically marketed by traditional office-equipment companies such as
IBM, Lanier (marketing AES Data machines, re-badged), CPT, and
NBI.[13] All were specialized, dedicated, proprietary systems, with
prices in the $10,000 ballpark. Cheap general-purpose computers were
still the domain of hobbyists.
Some
of the earliest CRT-based machines used cassette tapes for
removable-memory storage until floppy diskettes became available for
this purpose — first the 8-inch floppy, then the 5-1/4-inch (drives
by Shugart Associates and diskettes by Dysan).
Printing
of documents was initially accomplished using IBM Selectric
typewriters modified for ASCII-character input. These were later
replaced by application-specific daisy wheel printers (Diablo, which
became a Xerox company, and Qume — both now defunct.) For quicker
«draft» printing, dot-matrix line printers were optional
alternatives with some word processors.
With
the rise of personal computers, and in particular the IBM PC and PC
compatibles, software-based word processors running on
general-purpose commodity hardware gradually displaced dedicated word
processors, and the term came to refer to software rather than
hardware. Some programs were modeled after particular dedicated WP
hardware. MultiMate, for example, was written for an insurance
company that had hundreds of typists using Wang systems, and spread
from there to other Wang customers. To adapt to the smaller PC
keyboard, MultiMate used stick-on labels and a large plastic clip-on
template to remind users of its dozens of Wang-like functions, using
the shift, alt and ctrl keys with the 10 IBM function keys and many
of the alphabet keys.
Other
early word-processing software required users to memorize
semi-mnemonic key combinations rather than pressing keys labelled
«copy» or «bold.» (In fact, many early PCs lacked
cursor keys; WordStar famously used the E-S-D-X-centered «diamond»
for cursor navigation, and modern vi-like editors encourage use of
hjkl for navigation.) However, the price differences between
dedicated word processors and general-purpose PCs, and the value
added to the latter by software such as VisiCalc, were so compelling
that personal computers and word processing software soon became
serious competition for the dedicated machines. Word Perfect,
XyWrite, Microsoft Word, Wordstar, Workwriter and dozens of other
word processing software brands competed in the 1980s. Development of
higher-resolution monitors allowed them to provide limited WYSIWYG —
What You See Is What You Get, to the extent that typographical
features like bold and italics, indentation, justification and
margins were approximated on screen.
The
mid-to-late 1980s saw the spread of laser printers, a «typographic»
approach to word processing, and of true WYSIWYG bitmap displays with
multiple fonts (pioneered by the Xerox Alto computer and Bravo word
processing program), PostScript, and graphical user interfaces
(another Xerox PARC innovation, with the Gypsy word processor which
was commercialised in the Xerox Star product range). Standalone word
processors adapted by getting smaller and replacing their CRTs with
small character-oriented LCD displays. Some models also had
computer-like features such as floppy disk drives and the ability to
output to an external printer. They also got a name change, now being
called «electronic typewriters» and typically occupying a
lower end of the market, selling for under $200 USD.
MacWrite,
Microsoft Word and other word processing programs for the bit-mapped
Apple Macintosh screen, introduced in 1984, were probably the first
true WYSIWYG word processors to become known to many people until the
introduction of Microsoft Windows. Dedicated
word processors eventually became museum pieces.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Word_processor
Соседние файлы в предмете [НЕСОРТИРОВАННОЕ]
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
A word processor program is a computer program that provides word processing functions. Originally a separate type of application to desktop publishing, the two program types now overlap, with many word processors now including what were once desktop publishing functions.
History[edit]
The first known electronic word processor program was Electric Pencil, released in 1976, as a tool for programmers to write documentation and manuals for their code. Electric pencil featured basic formatting and navigation, and supported external devices such as cassette recorders and printers. Electric Pencil II was released shortly after, targeting the CP/M operating system. Several other word processing programs were released shortly after, including EasyWriter and WordStar.[1]
A screenshot of WordStar 3.0 in use
WordStar was created in four months by Seymour Rubinstein after founding MicroPro International in 1978. WordStar is commonly attributed as the first WYSIWYG (what you see is what you get) editor, as the WordStar editor replicated the printed output. Inspired by the success of WordStar, many competitors began to release their offerings, including WordPerfect in 1979, MultiMate in 1982, and Microsoft Word in 1983.[1][2]
List of word processors[edit]
Notable programs include:
- Electric Pencil (1976)
- WordStar (1978)
- WordPerfect (1979)
- EasyWriter (1979)
- IBM DisplayWrite (1981)
- MultiMate (1982)
- Volkswriter (1982)
- Microsoft Word (1983)
- Lotus Manuscript (1986)
- TextMaker (1987)
- Sprint (word processor) (1987)
- IBM Lotus Word Pro (1988)
- InPage (1994)
- WordPad (1995)
- TextEdit (1996)
- Ability Write (1996)
- KWord (1998)
- AbiWord (1998)
- Adobe InCopy (1999)
- Atlantis Word Processor (2000)
- Jarte (2001)
- Pages (2005)
- JWPce (2005)
- Google Docs (2006)
- Scrivener (software) (2007)
- WordGrinder (2007)
- PolyEdit (2010)
- LibreOffice Writer (2011)
- Apache OpenOffice Writer (2012)
- Calligra Words (2012)
A word processing function is an essential part of any office suite, and may be provided as a stand-alone program (for example Word in Microsoft Office) or as a function of a more general program (for example LibreOffice Writer in LibreOffice) or other (for example
TextMaker in SoftMaker). With the emergence of the internet, different cloud-based word processor programs began to emerge, which allow people to work faster and more efficiently.
See also[edit]
- Word processor
- Word processor (electronic device)
References[edit]
- ^ a b Bergin, Thomas J. (October 2006). «The Origins of Word Processing Software for Personal Computers: 1976-1985». IEEE Annals of the History of Computing. 28 (4): 32–47. doi:10.1109/MAHC.2006.76. ISSN 1934-1547. S2CID 18895790. Retrieved 29 June 2022.
- ^ Bergin, Thomas J. (October 2006). «The Proliferation and Consolidation of Word Processing Software: 1985-1995». IEEE Annals of the History of Computing. 28 (4): 48–63. doi:10.1109/MAHC.2006.77. ISSN 1934-1547. S2CID 20785663. Retrieved 29 June 2022.