Phrase Processing Softwares, Capabilities and Terminologies. This text is a whole answer for get an advance data about Phrase processing, Sorts of phrase Processors, Totally different Terminologies in Phrase Processing, benefits and drawbacks of Phrase processing. Additionally, you will be taught that what are Working Schema of Phrase-processing, Options and features of word-processing.
What’s phrase processing?
Phrase Processing is an act of utilizing a pc for creating, modifying, saving and print of paperwork. With a purpose to carry out an exercise with phrase processing, particular applications required referred to as a Phrase Processor. e.g., Microsoft Phrase. As an alternative of Microsoft Phrase plenty of different phrase processing purposes are additionally getting used.
What’s phrase processor?
A phrase processor is a software program or program that offers with phrases. It additionally processes contents like paragraphs, pages, and full papers. Like some instance of phrase processors are Microsoft Phrase, WordPerfect, AppleWorks, OpenOffice.
Sorts of CSS and the right way to use CSS sorts in webpages styling
Background
Phrase processor did not develop out of laptop computer experience. Pretty, they superior from mechanical machines and solely later did they merge with the laptop self-discipline. The historic previous of Phrase processing is the story of the gradual automation of the bodily components of writing and modifying, after which to the refinement of the experience to make it accessible to companies and Folks.
The time interval Phrase processing appeared in American workplaces in early 1970s centered on the considered streamlining the work to typists, nevertheless the meaning shortly shifted in direction of the automation of the complete modifying cycle.
At first, the designers of Phrase processing strategies blended current utilized sciences with rising ones to develop stand-alone instruments, making a brand-new enterprise distinct from the rising world of the private laptop. The thought of Phrase processing arose from the additional fundamental data processing, which as a result of the 1950s had been the making use of of pc programs to enterprise administration
Phrase Processing refers again to the act of using a laptop to create, edit, save and print paperwork. With a view to hold out Phrase processing, specialised software program program (usually referred to as a Phrase Processor) is required.
Create web site format utilizing CSS
One occasion of a Phrase Processor is Microsoft Phrase, nevertheless completely different Phrase processing functions are moreover extensively used. Examples embrace: Microsoft Works Phrase Processor, Open Office Writer, Phrase Wonderful and Google Drive Doc.

Examples of phrase processor software program
- Microsoft Phrase
- LibreOffice
- Corel WordPerfect
- AbiWord.
- Google Docs
- Apple iWork
- Apple TextEdit
- Dropbox Paper.
- Google Docs.
Primary options and performance of phrase processing?
- Creation, modifying, saving and printing of paperwork.
- Copying, pasting of textual content.
- Shifting and deletion of textual content.
- Textual content Formatting like font sort, type, bolding, italicizing and underlining.
- Desk Creation and modifying.
Working Schema of Phrase Processing
These purposes allow clients to create every kind of paperwork along with (Phrase processing cycle nevertheless really not restricted to) tales, letters, memos, newsletters and brochures. Together with typing textual content material, the Phrase processor means which you can add content material materials harking back to photographs, tables, and charts to your paperwork along with decorative devices along with borders and clipart.
Learn how to create Desk, Paragraph, Marquee and their properties
The modifying and formatting capabilities of the Phrase processor present the making use of’s true power. Textual content material could be inserted, edited, moved, copied or deleted inside your doc and the appears to be like of the textual content material could be modified in fairly just a few strategies. Most Phrase processors moreover offer you’re the facility to look at your spelling and grammar and plenty of have in-built dictionaries and completely different devices that will help you in your writing.
The remainder of this lesson will introduce you to a few the important concepts and options of Phrase Processing after which give you hyperlinks to tutorials which is in a position that will help you in rising your skills using Microsoft Phrase, the same old Phrase processing software program program software program at Broome Group College.
Phrase Processing Working Terminologies
Alignment
Alignment refers again to the means textual content material is organized inside the doc between the margins. In horizontal alignment, paragraphs of textual content material could be left aligned (flush in direction of the left margin), correct aligned (flush in direction of the becoming margin), or centered (each line all through the paragraph centered between the margins). There is a fourth alignment selection usually referred to as “justified”. Textual content material in a justified paragraph shall be unfold evenly all through the online web page and appear as a block with textual content material lining up on every the left and correct margins.
Software
One different Phrase for a software program program. In Phrase processing, the making use of is a Phrase Processor harking back to Microsoft Phrase.
Connecting CSS with Webpage Full Coding
AutoCorrect
This attribute is used to acceptable typos and misspelled phrases. When AutoCorrect is turned on, widespread errors are routinely modified using a default a list of phrases which could be saved inside the Phrase processing software program. The individual might often modify the report to include their very personal widespread misspellings.
Clipboard
The clipboard is a quick holding house the laptop makes use of for any merchandise that has been copied or decrease. When a merchandise harking back to textual content material is positioned on the clipboard, it might really then be pasted elsewhere inside the doc.
Devices will carry on the clipboard until they’re deleted or erased. The type whereby the clipboard is cleared is decided by the making use of getting used. Fairly often, the clipboard is cleared when one different merchandise is minimizing or copied or if the making use of is closed.
Copying
The strategy of copying will take a gift merchandise in a doc and creates a replica in a brand-new location inside the doc (and even in a single different doc). When a merchandise is copied, it is saved briefly on the clipboard able to be pasted elsewhere.
UOS Results of BA/BSc/ADP & B.Com 1st Annual Examination 2020
Cursor/ Insertion Stage
The cursor (additionally known as the insertion degree) is a flashing vertical bar on the show that signifies the place entered textual content material or objects shall be positioned inside the doc. To place the cursor to a brand-new location in your doc, you’d switch your mouse pointer to the brand-new location and click on on the left mouse button as quickly as. The flashing cursor must now appear inside the new location and any textual content material typed or object inserted shall be positioned there.
Reducing
The strategy of lowering is used to maneuver textual content material or objects in a doc. Chopping takes a gift merchandise in a doc, removes it from its current location and outlets it on the clipboard. The merchandise can then be pasted elsewhere inside the doc (and even in a single different doc) as long as it stays on the clipboard.
Doc
A Doc is the file that is created using a Phrase processor. Paperwork can embody many a number of sorts of devices harking back to textual content material, pictures, tables, charts, borders and clip paintings.
Enhancing
Modifying is the strategy of making modifications or corrections in a doc. It consists of alterations to the textual content material itself, shifting or copying devices to completely different locations and making use of formatting selections to the doc itself and devices inside it.
Footer
The footer is an area that appears on the bottom of every internet web page in a doc that will embody plenty of traces of textual content material. One widespread use of the footer is to insert the current internet web page amount on every internet web page inside the doc.
Font
A font is a set of letters and numbers of 1 specific typeface. The font consists of not solely the typeface, nevertheless completely different traits harking back to dimension, spacing and emphasis. An occasion of a font could be Arial, 12 degree, italic.
Formatting
The strategy of formatting a doc consists of specifying how the doc will look in its final form on the show and when printed. Widespread formatting selections embrace the font, font dimension, coloration, alignment, spacing, margins and completely different properties.
Header
The header is an area that appears on the excessive of every internet web page in a doc that will embody plenty of traces of textual content material. One widespread use of the header is to include particulars concerning the doc (such as a result of the title) on every internet web page inside the doc.
Highlighting
Highlighting (or Selecting) an object or house of textual content material is often the first step to making a change to that merchandise. When a merchandise is highlighted (or chosen) the next movement (whether or not or not or not it is formatting, deleting, copying, or lowering) will often solely impact that merchandise.
Devices are usually highlighted (chosen) using the mouse by clicking inside the starting place (and holding down the mouse button) and dragging to the highest of the world that you simply simply want to decide on.
Indent
The home between the margin of the online web page and the textual content material. Most Phrase processors allow for every left and correct indentation. One completely different widespread use of indention is what is named a “first line indent” the place solely the first line of a paragraph is indented and the remaining traces of textual content material lie straight in direction of the left margin of the online web page.
Insertion Stage / Cursor
The insertion degree (additionally known as the cursor) is a flashing vertical bar on the show that signifies the place entered textual content material or objects shall be positioned inside the doc. To place the insertion degree to a brand-new location in your doc, you’d switch your mouse pointer to the brand-new location and click on on the left mouse button as quickly as.
LND Reflective Notes Writing Technique for SED Lecturers
The flashing insertion degree must now appear inside the new location and any textual content material typed or object inserted shall be positioned there.
Panorama / Panorama
Internet web page orientation refers again to the means the rectangular internet web page is turned or positioned for viewing or printing. The two forms of orientation in Phrase processing are portrait and panorama. Portrait orientation is the place the height of the online web page is larger than the width. Panorama orientation, alternatively, has a better width than prime (the online web page is turned on its side).
Authorized Dimension
The time interval “Licensed” inside the internet web page format house of a Phrase processing software program refers again to the dimension of the paper getting used to print the doc. The scale of approved sized paper are 8.5 X 14 inches.
Letter Dimension
The time interval “Letter” inside the internet web page format house of a Phrase processing software program refers again to the dimension of the paper getting used to print the doc. The scale of letter sized paper are 8.5 X 11 inches.
Line Spacing: Line spacing refers again to the amount of white home between traces of textual content material in a paragraph. Usually used line spacing settings are single spaced and double spaced.
Margin
The margin is the white home between the sting of the online web page and the place textual content material or completely different devices could be positioned in your doc. Margin settings could be adjusted to include type of home throughout the perimeter of the online web page and left, correct, excessive and bottom margins could be modified independently of one another.
Menu Bar
The menu bar often appears on the excessive of the Phrase processing software program’s window and accommodates a listing of the first directions inside the kind of textual content material. Menu devices which could be widespread amongst plenty of functions embrace File, Edit, View and Help. In case you click on on brand-new one amongst these items, additional selections appear in a drop-down menu on the show.
Paragraph
In a Phrase processing doc, a brand-new paragraph is created each time the enter key on the keyboard is pressed. A paragraph could be made up of plenty of traces of textual content material, a single merchandise, or nothing the least bit. Microsoft Phrase has a view that may current you the place each paragraph in a doc begins or ends.
Paragraph Spacing
Paragraph spacing refers again to the amount of white home that is left between paragraphs after they enter secret’s hit. In distinction to line spacing, paragraph spacing does not impact the amount of home between traces of textual content material, nevertheless as an alternative, between one paragraph and the next.
Pasting
After textual content material or one different merchandise is minimizing or copied it is positioned on the clipboard. The strategy of pasting takes the merchandise on the keyboard and areas it in current location of the insertion degree.
Portrait
If the online web page format signifies Portrait internet web page orientation, the vertical fringe of the paper is larger than the horizontal edge. Portrait orientation is the commonest orientation in Phrase processing. Panorama (the place the horizontal edge is larger than the vertical edge) is the alternative selection.
Print Preview: Print Preview is a Phrase processing attribute that may current you what your doc will seem to be on a bit of paper if it has been to be printed.
Ruler
The rulers appear on the excessive and side of the doc all through the Phrase processing window and are used to level out the place of the margins, tabs, indents, columns, rows and completely different devices which could be set for the doc.
Scroll Bars: Since many paperwork are too prolonged to go well with legibly on a single laptop show, vertical and horizontal scroll bars are included to allow you to switch by the use of the doc and alter the world of the doc that is at current being seen on the show.
Selecting / Highlighting
Selecting (or Highlighting) an object or house of textual content material is often the first step to making a change to that merchandise. When a merchandise is chosen (or highlighted) the next movement (whether or not or not or not it is formatting, deleting, copying, or lowering) will often solely impact that merchandise.
Devices are usually chosen (or highlighted) using the mouse by clicking inside the starting place (and holding down the mouse button) and dragging to the highest of the world that you simply simply want to decide on.
Spelling / Grammar Checker
Most Phrase processing purposes embrace a utility that checks for proper spelling and grammar. Counting on the making use of getting used, these utilities may run routinely and warn you to errors as your form (harking back to in Microsoft Phrase) or require you to run the utility manually.
Each means, you often shall be given selections as your to if or to not accept the modifications immediate by the utility. The exception to this may very well be if AutoCorrect is turned on and the merchandise in question appears inside the AutoCorrect itemizing.
Tabs
Tabs are used to control the place of textual content material on an internet web page. Tab stops could be set all through the ruler on the excessive of the Phrase processing window. Together with the position of a tab (occasion: 2 inches in from the left margin), the type of tab could be set.
Widespread tab kinds embrace left, correct, centered and decimal. The tab form controls how the textual content material shall be aligned whether or not it’s pressured to that tab stop. When the tab secret’s pressed on the keyboard, the cursor will switch to the next tab stop location.
Desk
A desk is a gaggle of textual content material, data or completely different devices which could be organized in columns and rows.
Template
A template is a kick off point for a doc that accommodates preliminary formatting selections, settings, colours, format and placeholders. A typical clear doc begins with the “Common” template, nevertheless sometimes it is a time saver to start out with a preformatted template when making an additional superior doc (harking back to a brochure or flyer).
Up to date LND Booklet & LitNum Materials for MEA Monitoring
Instrument bar
A software program bar consists of buttons that current a shortcut technique of performing a usually used function. There are numerous completely completely different toolbars that exist in Phrase processing functions, each of which focuses on a specific topic or class.
Typeface
The typeface determines the type of the letters and numbers in a doc. Widespread typeface embrace Events New Roman and Arial. A set of letters and numbers of 1 specific typeface makes up a Font.
Undo
The “Undo” command could be utilized to reverse the ultimate movement (or sequence of actions) that you have carried out in a doc. When using the Undo command, each merchandise needs to be reversed sequentially, that implies that if you wish to undo the movement you took 7 actions up to now, you’d first must undo actions 1 by the use of 6 as properly.
Wizard
A wizard is an interactive attribute constructed into the Phrase processing software program (considerably in Microsoft Phrase) that may stroll you step-by-step by the use of a specialised course of. One occasion of a Wizard included in Microsoft Phrase is the Mail Merge Wizard which supplies assist with routinely creating letters, mailing labels or envelopes from a list of names and addresses.
Phrase Processing
Phrase Processing refers again to the act of using a laptop to create, edit, save and print paperwork.
Phrase Wrap
Phrase Wrap refers again to the function of a Phrase processor that may routinely drive textual content material to a brand-new line when the becoming margin is reached whereas typing. Phrase Wrap eliminates the need for pressing the Enter key on the keyboard on the end of every line.
Benefits of phrase processors
- Time saving, quickest and easiest method of writing.
- Paperwork storage facility in your pc.
- Variety of formatting selections like grammar, spelling checking and language instruments.
- Printing facility in your paperwork.
- Readability of studying as in comparison with handwriting.
Disadvantages
- Costly as everybody can’t afford a pc which is important in utilizing phrase processors
- It Is dependent upon energy when there’s a energy blackout. We can’t use phrase processors.
- Too many choices in lots of processors trigger problem for consumer.
ESSENTIAL WORD-PROCESSING FUNCTIONS
Essential word-processing options may very well be grouped into the courses of enter, manipulation, formatting, and output of textual content material.
Textual content material Enter
Typically, textual content material is entered into the phrase processor from a keyboard; completely different enter methods embrace:
- Copying textual content material from completely different functions (akin to from hypertext markup language [HTML] paperwork, e-mail messages, or on-line encyclopedias) and pasting it proper right into a word-processing doc
- Scanning printed paperwork and using optical-character-recognition (OCR) software program program to remodel the scanned paperwork into textual content material characters
- Using voice-recognition software program program to remodel spoken phrases into textual content material characters
Textual Content material Manipulation
Textual content material manipulation refers again to the “processing” part of phrase processing. Phrase processors current easy methods of deleting, inserting, copying, and shifting explicit individual characters, phrases, phrases, and paragraphs. Even complete pages of data with only a few clicks of a mouse button or with such keyboard shortcuts as Ctrl-C to repeat. Ctrl-X to cut, and Ctrl-V to stay or insert textual content material.
Textual content material may very well be mechanically checked for spelling and for conformance to main grammatical concepts as a result of the textual content material is entered and edited.
The find-and-replace operate in a phrase processor permits the patron to hunt for every prevalence of a selected character, phrase, or phrase inside a doc and substitute it with new textual content material.
Most phrase processors moreover embrace automated correction and automatic formatting of widespread errors and mechanical conventions as textual content material is entered from the keyboard.
For example, usually misspelled phrases may very well be mechanically corrected as shortly as a result of the misspelled phrases are entered; two areas entered after the tip of a sentence may very well be modified mechanically to no less than one space; a lowercase letter beginning a brand-new sentence may very well be capitalized mechanically.
Right typographic quotation marks (“good” or “curly” quote marks—” and “) and apostrophes (‘) may very well be inserted mechanically in its place of the straight typewriter-style quotation marks entered from the keyboard. Fractions and completely different symbols may very well be formatted mechanically as their keyboard equivalents are entered.
For example, when a fraction for one-half is entered as half, it is modified to the picture ½ two hyphens (––) are modified to an prolonged dash (—); and (c) is modified to ©.
Textual Content material Formatting
Phrase-processing software program program typically consists of “wizards” or “help” choices to produce automated formatting of widespread enterprise paperwork. For example, a letter wizard can assist the patron to appropriately format a enterprise letter, and a résumé wizard may assist the patron format a professional-looking résumé.
Templates are one different automated formatting operate. A template is a type of pre-formatted, fill-in-the-blank doc that is useful for sustaining a specific format each time a doc is created, notably when plenty of word-processing operators are involved.
A e-newsletter template, as an example, permits a shopper to entered the textual content material of e-newsletter articles, headlines, and graphics with out having to re-create the e-newsletter format for each concern of the e-newsletter.
Most likely the most-common formatting duties are typically carried out by the patron as a doc is created. Explicit individual character and phrase formatting consists of assortment of form dimension, form style, and typeface. Measurement is measured in elements, a unit of measure whereby 72 elements make up an inch. Typically, 11- or 12-point form is used for main enterprise paperwork.
Newsletters, annual research, and completely different such “designed” paperwork may use form as small as eight or 9 elements for the important textual content material and as big as 24, 36, or 48 elements (or additional) for elementary titles. Type sorts, akin to italics, underline, and daring, are merely chosen using keyboard shortcuts or by deciding on them from the important font menu.
Typefaces (typeface refers again to the look or design of the sort) could be present in 1000’s of kinds, along with such usually recognized faces as Events Roman, Arial, Helvetica, and Garamond.
Paragraph formatting consists of line spacing, meaning the amount of fresh space left between traces of form (single spacing and double spacing, as an example); paragraph spacing (the amount of fresh space that precedes or follows each paragraph); justification (all traces of form made even at every margin, or left uneven or ragged on the correct margin); and indentation (akin to a first-line indentation at first of each paragraph).
Internet web page and overall-document formatting consists of setting margins (typically 1-inch margins are used on the best, bottom, and all sides of such main enterprise paperwork as letters, research, and memos).
Creating columns like these utilized in a newspaper or e-newsletter, and creating headers and footers (information such as a result of the online web page amount or a chapter title that is repeated on the prime or bottom of each internet web page of a doc).
Most phrase processors moreover current explicit format choices for formatting outlines, tables, envelopes, and mailing labels.
Textual Content material Output
As quickly as textual content material has been created, edited, and formatted proper right into a accomplished digital doc, it needs to be put into some tangible form or lasting digital form to be of smart revenue. That output course of usually begins with the saving of the doc on the laptop’s exhausting drive, a floppy disk, a CD, or a memory machine akin to a flash drive.
36 Lesson Plans Booklet for LitNum Hour Grade 3
Saving the doc, really, is an train that must occur ceaselessly in the midst of the creation and modifying processes to guard in opposition to loss on account of points akin to electrical-power failure, laptop malfunctions, and operator error.
Printing a doc on paper is the most typical output method; completely different output methods embrace faxing a doc immediately from the phrase processor by use of a laptop modem, sending the doc to a special explicit individual by e-mail, and altering the word-processing doc to quite a few completely different digital codecs for on-line viewing or for eventual printing from completely different functions.
For example, word-processing paperwork are ceaselessly remodeled to HTML for use as Web pages, to transportable doc format (PDF) data information, and to rich textual content material format (RTF) data information for use in numerous laptop purposes (considerably completely different word-processing purposes).
ADVANCED WORD-PROCESSING FEATURES
Although most word-processing clients are prone to be taught and use primarily the important word-processing choices, fairly just a few more-advanced choices could be present in most phrase processors to make phrase processing quite a bit less complicated to complete in a lot much less time.
Taking the time to be taught some superior word-processing choices and capabilities usually has a extreme payoff by the use of productiveness and professionalism.
Among the many more-common superior word-processing choices and capabilities are described briefly underneath:
Varieties
Varieties are user-created formatting directions that allow good administration over repetitive formatting buildings inside a doc. For example, using a “style” for each type of heading in a report will assure fixed formatting of the headings and may eliminate the need for a shopper to manually format each heading because it’s created.
Macros and Merging
Macros are saved keystrokes, or items of modifying and formatting directions, which may be replayed each time wished. They will improve productiveness and take quite a lot of the tedium out of repetitive word-processing duties.
Merging is the strategy of using lists of such information as names, addresses, phone numbers, product descriptions or model numbers, and so forth to fill in designated fields or blanks in paperwork to create mass mailings, deal with labels, directories, and catalogs.
Mannequin Administration
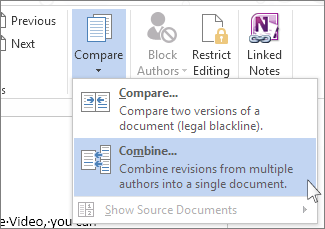
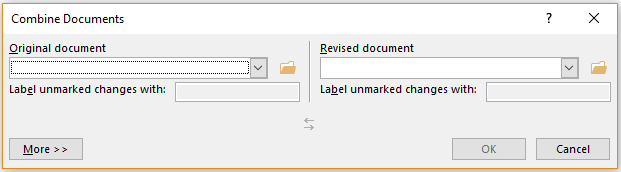
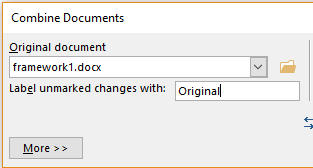
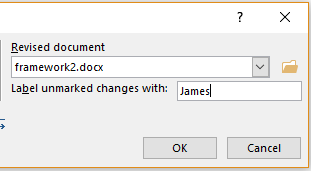
Mannequin-control choices allow a shopper to hint the numerous ranges of modifying {{that a}} doc may cross by, along with variations created by plenty of clients involved inside the creation and modifying of a doc. Related choices akin to the facility to hint modifications made in a doc enable plenty of clients to analysis instructed doc modifications and to easily settle for or reject proposed modifications.
Computerized References and Indexes
Paperwork that embraces tables of contents, cross-references, indexes, footnotes, endnotes, and captions will revenue from the aptitude of a phrase processor to mechanically generate and format these items.
Desktop-Publishing Capabilities
Expert-looking paperwork akin to newsletters, commercials, annual research, brochures, and enterprise enjoying playing cards may very well be designed with most stylish word-processing software program program.
Graphical photos from clip-art collections, digital photos, and scanned photos, and drawings created with graphics purposes, may very well be built-in merely into word-processing paperwork. Pages and paragraphs may very well be enclosed with decorative borders. Background photos and colours may very well be added to pages inside a doc.
Graphical part akin to traces, packing containers, arrows, and ingenious textual headings may very well be created shortly and easily inside most word-processing purposes.
Although phrase processors are often not as delicate as desktop-publishing software program program or page-layout purposes of their capabilities for setting form and for working with graphical parts, they are often utilized to create partaking, professional-looking paperwork that transcend the important format and formatting of letters, memos, and research.
Using a word-processing program to create designed paperwork is often preferable to using a high- end desktop-publishing program, however, because of word-processing clients aren’t required to show into proficient in using one different program and since paperwork inside an organization or division are created and maintained using the similar software program.
Word Processing
Word processing means to use a computer to create, edit, format and print documents. The great advantage of word processing over using a typewriter is that you can make changes without retyping the entire document
Word Processor
A word processor is computer application software that enables a user to create a document,editand format, store it electronically and print
Uses of Word Processing
Some of the functions of word processing software include:
- Creating, editing, saving and printing documents.
- Copying, pasting, moving and deleting text within a document.
- Formatting text, such as font type, bolding, underlining or italicizing.
- Creating and editing tables.
- Inserting elements from other software, such as illustrations or photographs.
- Correcting spelling and grammar.
Application of Word Processor
A word processor can be used for creating documents like :
- Memo
- Letters
- Resumes
- Examinations
- Books
- Invitations
- Invoices
- Postcard etc
EXERCISE
Define the following terms
1. Word processing
2. Word processor
Examples Of Word Processor
The examples of word processor include the following
- Word star
- Microsoft Word
- Word Perfect
- Word Pad etc.
Features of the word processor
The basic features of the word processors are
- Insert Text : allow you to insert text anywhere
- Delete text : allows you to erase text , characters, words or lines
- Cut ,copy , paste : cut allows you to move an item in a copy mode, copy allows you to duplicate while paste allows you to insert an item that has already being cut or copied
- Page size and Margin : this allows you to adjust your page size and margins
- Search and replace: this allow you to search for a particular word with the option of replacing it with another word .
Other features of the standard Word processor are :
- File management
- Font specification
- Headers , footers and page numbers
- Layouts
- Macros
- Spell checkers
- Thesaurus
- Table of content and index.
Office Application
The Microsoft Office suite incorporates the following:
- Word Processori.e. Ms Word
- Spread sheet i.e. Ms Excel
- Presentation Package i.e. Ms PowerPoint
- Database Package i.e. Ms Access
- Web Page/ website development package i.e Front Page
Entering Text
To enter text, just begin typing from the keyboard at the insertion point. The insertion point moves to the right as you type. When you come to the end of the line continue to type as you don’t need to press ENTER key before it automatically goes to the next line.
Moving around the document
Use the following combination of keys to move around the document
| Key combinations | Movement |
| Home | Move to the beginning of the line |
| End | Move to the end of the line |
| Ctrl + right arrow | Move one word to the right |
| Ctrl + left arrow | Move one word to the left |
| Ctrl + up arrow | Moves to the previous paragraph |
| Page up | Move up one window |
| Page down | Move down one window |
| Ctrl + Pgup | Move up one page |
| Ctrl + Pgdn | Move down one page |
| Ctrl + home | Move to the top of the document |
| Ctrl + End | Move to the bottom of the document |
Selecting Text with the Mouse
The mouse is an excellent tool for selecting text in your document during the editing process. The following steps guides you in text selection
- Double clicking : double a word to select it
- Triple clicking : triple in a paragraph to select it
- Ctrl + click : is used for selecting a sentence
Font formatting in Word processing
Formatting : this is the manipulation carried out on the font . this is also called text called Text Formatting.
The various text formatting includes :
- Changing font : font is a collection of letters ,numbers ,and special characters that contains the same type face, thickness and size.
- Changing font sizes : font sizes of characters can be increased up to 72
- Font Attribute : the following can be carried out on the font
- Bold
- Italic
- Underline
- Font colours: the colour of the characters can be changed to a suitable one
Page Setup
The following can be done under page setup
- Settings Margins
- Setting Paper size
- Page orientation
EXERCISE
State the features of the word processor
EXERCISE
State the procedures on how to
1. load the Ms word2. close the ms word
Some of the functions of word processing software include:
- Creating, editing, saving and printing documents.
- Copying, pasting, moving and deleting text within a document.
- Formatting text, such as font type, bolding, underlining or italicizing.
- Creating and editing tables.
What is word processing and its features?
A word processor is software or a device that allows users to create, edit, and print documents. It enables you to write text, store it electronically, display it on a screen, modify it by entering commands and characters from the keyboard, and print it. Of all computer applications, word processing is the most common.
What are the four features of word processor?
List four important feature of a word processor ? Name any two word processor
- – Creating, editing, saving and printing documents.
- – Copying, pasting, moving and deleting text within a document.
- – Formatting text, such as font type, bolding, underlining or italicizing.
- – Creating and editing tables.
What are the features and advantages of word processing?
Advantages of Word Processing
- Quality : It produces error free documents.
- Storage of Text : We can take any number of copies with word processor.
- Time Saving : We can get any number of copies of document in future without retyping.
- Security : We can protect the documents in word processing by giving passwords.
What is the importance of word processing?
Furthermore, word processing benefits the environment by reducing the amount of paperwork needed to perform daily tasks (e.g., archiving, sending out letters, sending meeting agendas). By sending documents via a secured email, the cost of postage and paper waste are reduced significantly.
What are the benefits of word processing in education?
With word processing software, students can easily review and revise their compositions, highlight key ideas, rearrange sentences or paragraphs to flow more logically, and try out alternative sentences or words to communicate their ideas better.
What are the basic elements of Microsoft Word?
MS- Word Window Elements:
- Title bar.
- Menu Bar.
- Toolbars.
- Workspace.
- Status Bar.
- Scroll Bars.
- Scroll Box.
- Task Pane.
How do you describe computer skills?
Computer skills are abilities and knowledge which allow you to use computers and related technology. They let you use word processing software, access the Internet, manage files, or create presentations. Advanced computer skills would let you access databases, use spreadsheets, and even code.
What are some common word processing applications?
Two of the most widely used examples of word processing software are Microsoft Word and Google Docs. Both Word and Google Docs provide the business writer with the formatting tools needed to create professional documents.
What are examples of word processing?
- Adobe InCopy.
- Corel WordPerfect (up to v. 9.0)
- Hangul.
- Ichitaro.
- Kingsoft Writer.
- Microsoft Word.
- Scrivener.
- StarOffice Writer.
What are the word processing tools?
5 Great Word Processing Tools For Writing Your Novel
- Microsoft Office. Microsoft Word is pretty much the standard in the traditional business world, and for good reason – it’s fairly easy to use, compatible across a wide range of platforms (there’s even an iphone app currently in the works!), and great customer service.
- Apache OpenOffice.
- Google Drive.
- iWork Pages.
- Scrivener.
How many types of word processing are there?
3 types
Which software is best for word processing?
- LibreOffice Writer. All-singing, all-dancing word processors for any text-based work.
- WPS Office Free Writer. A word processor with cloud storage and support for all text files.
- FocusWriter. The ideal word processor for first drafts, with no fussy formatting.
- FreeOffice TextMaker.
- Writemonkey.
What are Microsoft Word functions?
Given below are the basic functions of Microsoft Word:
- Creating text documents.
- Editing and Formatting the existing documents.
- Making a text document interactive with different features and tools.
- Graphical documents, comprising images.
- Used by Authors and Researchers.
- Detect grammatical errors in a text document.
Which one is not a function in MS Word?
The NOT function is a built-in function in Excel that is categorized as a Logical Function. It can be used as a worksheet function (WS) in Excel. As a worksheet function, the NOT function can be entered as part of a formula in a cell of a worksheet.
What are the basic functions of Microsoft Excel?
You may be familiar with common functions like sum, average, product, and count, but there are hundreds of functions in Excel, even for things like formatting text, referencing cells, calculating financial rates, and analyzing statistics.
What is MS Word and Excel?
Microsoft Word is a word processing program used for writing letters, memos, reports and paper presentations. Microsoft Excel is a spreadsheet program used for calculations, making charts and recording data about all sorts of business processes.
What is the full form of MS Excel?
Microsoft Excel is a spreadsheet developed by Microsoft for Windows, macOS, Android and iOS. It features calculation, graphing tools, pivot tables, and a macro programming language called Visual Basic for Applications (VBA). Excel forms part of the Microsoft Office suite of software.
What is the use of MS Office?
Microsoft Office has become a leading platform to drive productivity at home and in the workplace. Whether it’s managing email in Outlook, or building analysis spreadsheets in Excel, Office has made carrying out many computer based tasks easier for all of us.
Word Processing
Andrew Prestage, in Encyclopedia of Information Systems, 2003
I. An Introduction to Word Processing
Word processing is the act of using a computer to transform written, verbal, or recorded information into typewritten or printed form. This chapter will discuss the history of word processing, identify several popular word processing applications, and define the capabilities of word processors.
Of all the computer applications in use, word processing is by far the most common. The ability to perform word processing requires a computer and a special type of computer software called a word processor. A word processor is a program designed to assist with the production of a wide variety of documents, including letters, memoranda, and manuals, rapidly and at relatively low cost. A typical word processor enables the user to create documents, edit them using the keyboard and mouse, store them for later retrieval, and print them to a printer. Common word processing applications include Microsoft Notepad, Microsoft Word, and Corel WordPerfect.
Word processing technology allows human beings to freely and efficiently share ideas, thoughts, feelings, sentiments, facts, and other information in written form. Throughout history, the written word has provided mankind with the ability to transform thoughts into printed words for distribution to hundreds, thousands, or possibly millions of readers around the world. The power of the written word to transcend verbal communications is best exemplified by the ability of writers to share information and express ideas with far larger audiences and the permanency of the written word.
The increasingly large collective body of knowledge is one outcome of the permanency of the written word, including both historical and current works. Powered by decreasing prices, increasing sophistication, and widespread availability of technology, the word processing revolution changed the landscape of communications by giving people hitherto unavailable power to make or break reputations, to win or lose elections, and to inspire or mislead through the printed word.
Read full chapter
URL:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B0122272404001982
Computers and Effective Security Management1
Charles A. Sennewald, Curtis Baillie, in Effective Security Management (Sixth Edition), 2016
Word Processing
Word processing software can easily create, edit, store, and print text documents such as letters, memoranda, forms, employee performance evaluations (such as those in Appendix A), proposals, reports, security surveys (such as those in Appendix B), general security checklists, security manuals, books, articles, press releases, and speeches. A professional-looking document can be easily created and readily updated when necessary.
The length of created documents is limited only by the storage capabilities of the computer, which are enormous. Also, if multiple copies of a working document exist, changes to it should be promptly communicated to all persons who use the document. Specialized software, using network features, can be programmed to automatically route changes to those who need to know about updates.
Read full chapter
URL:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780128027745000241
Globalization
Jennifer DeCamp, in Encyclopedia of Information Systems, 2003
II.D.2.c. Rendering Systems
Special word processing software is usually required to correctly display languages that are substantially different from English, for example:
- 1.
-
Connecting characters, as in Arabic, Persian, Urdu, Hindi, and Hebrew
- 2.
-
Different text direction, as in the right-to-left capability required in Arabic, Persian, Urdu, and Hindi, or the right-to-left and top-to-bottom capability in formal Chinese
- 3.
-
Multiple accents or diacritics, such as in Vietnamese or in fully vowelled Arabic
- 4.
-
Nonlinear text entry, as in Hindi, where a vowel may be typed after the consonant but appears before the consonant.
Alternatives to providing software with appropriate character rendering systems include providing graphic files or elaborate formatting (e.g., backwards typing of Arabic and/or typing of Arabic with hard line breaks). However, graphic files are cumbersome to download and use, are space consuming, and cannot be electronically searched except by metadata. The second option of elaborate formatting often does not look as culturally appropriate as properly rendered text, and usually loses its special formatting when text is added or is upgraded to a new system. It is also difficult and time consuming to produce. Note that Microsoft Word 2000 and Office XP support the above rendering systems; Java 1.4 supports the above rendering systems except for vertical text.
Read full chapter
URL:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B0122272404000800
Text Entry When Movement is Impaired
Shari Trewin, John Arnott, in Text Entry Systems, 2007
15.3.2 Abbreviation Expansion
Popular word processing programs often include abbreviation expansion capabilities. Abbreviations for commonly used text can be defined, allowing a long sequence such as an address to be entered with just a few keystrokes. With a little investment of setup time, those who are able to remember the abbreviations they have defined can find this a useful technique. Abbreviation expansion schemes have also been developed specifically for people with disabilities (Moulton et al., 1999; Vanderheiden, 1984).
Automatic abbreviation expansion at phrase/sentence level has also been investigated: the Compansion (Demasco & McCoy, 1992; McCoy et al., 1998) system was designed to process and expand spontaneous language constructions, using Natural Language Processing to convert groups of uninflected content words automatically into full phrases or sentences. For example, the output sentence “John breaks the window with the hammer” might derive from the user input text “John break window hammer” using such an approach.
With the rise of text messaging on mobile devices such as mobile (cell) phones, abbreviations are increasingly commonplace in text communications. Automatic expansion of many abbreviations may not be necessary, however, depending on the context in which the text is being used. Frequent users of text messaging can learn to recognize a large number of abbreviations without assistance.
Read full chapter
URL:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780123735911500152
Case Studies
Brett Shavers, in Placing the Suspect Behind the Keyboard, 2013
Altered evidence and spoliation
Electronic evidence in the form of word processing documents which were submitted by a party in litigation is alleged to have been altered. Altered electronic evidence has become a common claim with the ability to determine the changes becoming more difficult. How do you know if an email has been altered? What about a text document?
Case in Point
Odom v Microsoft and Best Buy, 2006
The Odom v Microsoft and Best Buy litigation primarily focused on Internet access offered to customers in which the customers were automatically billed for Internet service without their consent. One of the most surprising aspects of this case involved the altering of electronic evidence by an attorney for Best Buy. The attorney, Timothy Block, admitted to altering documents prior to producing the documents in discovery to benefit Best Buy.
Investigative Tips: All evidence needs to be validated for authenticity. The weight given in legal hearings depends upon the veracity of the evidence. Many electronic files can be quickly validated through hash comparisons. An example seen in Figure 11.4 shows two files with different file names, yet their hash values are identical. If one file is known to be valid, perhaps an original evidence file, any file matching the hash values would also be a valid and unaltered copy of the original file.
Figure 11.4. Two files with different file names, but having the same hash value, indicating the contents of the files are identical.
Alternatively, Figure 11.5 shows two files with the same file name but having different hash values. If there were a claim that both of these files are the same original files, it would be apparent that one of the files has been modified.
Figure 11.5. Two files with the same file names, but having different hash values, indicating the contents are not identical.
Finding the discrepancies or modifications of an electronic file can only be accomplished if there is a comparison to be made with the original file. Using Figure 11.5 as an example, given that the file having the MD5 hash value of d41d8cd98f00b204e9800998ecf8427e is the original, and where the second file is the alleged altered file, a visual inspection of both files should be able to determine the modifications. However, when only file exists, proving the file to be unaltered is more than problematic, it is virtually impossible.
In this situation of having a single file to verify as original and unaltered evidence, an analysis would only be able to show when the file was modified over time, but the actual modifications won’t be known. Even if the document has “track changed” enabled, which logs changes to a document, that would only capture changes that were tracked, as there may be more untracked and unknown changes.
As a side note to hash values, in Figure 11.5, the hash values are completely different, even though the only difference between the two sample files is a single period added to the text. Any modification, no matter how minor, results in a drastic different hash value.
The importance in validating files in relation to the identification of a suspect that may have altered a file is that the embedded metadata will be a key point of focus and avenue for case leads. As a file is created, copied, modified, and otherwise touched, the file and system metadata will generally be updated.
Having the dates and times of these updates should give rise to you that the updates occurred on some computer system. This may be on one or more computers even if the file existed on a flash drive. At some point, the flash drive was connected to a computer system, where evidence on a system may show link files to the file. Each of these instances of access to the file is an opportunity to create a list of possible suspects having access to those systems in use at each updated metadata fields.
In the Microsoft Windows operating systems, Volume Shadow Copies may provide an examiner with a string of previous versions of a document, in which the modifications between each version can be determined. Although not every change may have been incrementally saved by the Volume Shadow Service, such as if the file was saved to a flash drive, any previous versions that can be found will allow to find some of the modifications made.
Where a single file will determine the outcome of an investigation or have a dramatic effect on the case, the importance of ‘getting it right’ cannot be overstated. Such would be the case of a single file, modified by someone in a business office, where many persons had common access to the evidence file before it was known to be evidence. Finding the suspect that altered the evidence file may be simple if you were at the location close to the time of occurrence. Interviews of the employees would be easier as most would remember their whereabouts in the office within the last few days. Some may be able to tell you exactly where other employees were in the office, even point the suspect out directly.
But what if you are called in a year later? How about 2 or more years later? What would be the odds employees remembering their whereabouts on a Monday in July 2 years earlier? To identify a suspect at this point requires more than a forensic analysis of a computer. It will probably require an investigation into work schedules, lunch schedules, backup tapes, phone call logs, and anything else to place everyone somewhere during the time of the file being altered.
Potentially you may even need to examine the hard drive of a copy machine and maybe place a person at the copy machine based on what was copied at the time the evidence file was being modified. When a company’s livelihood is at stake or a person’s career is at risk, leave no stone unturned. If you can’t place a suspect at the scene, you might be able to place everyone else at a location, and those you can’t place, just made your list of possible suspects.
Read full chapter
URL:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9781597499859000113
When, How, and Why Do We Trust Technology Too Much?
Patricia L. Hardré, in Emotions, Technology, and Behaviors, 2016
Trusting Spelling and Grammar Checkers
We often see evidence that users of word processing systems trust absolutely in spelling and grammar checkers. From errors in business letters and on resumes to uncorrected word usage in academic papers, this nonstrategy emerges as epidemic. It underscores a pattern of implicit trust that if a word is not flagged as incorrect in a word processing system, then it must be not only spelled correctly but also used correctly. The overarching error is trusting the digital checking system too much, while the underlying functional problem is that such software identifies gross errors (such as nonwords) but cannot discriminate finer nuances of language requiring judgment (like real words used incorrectly). Users from average citizens to business executives have become absolutely comfortable with depending on embedded spelling and grammar checkers that are supposed to autofind, trusting the technology so much that they often do not even proofread. Like overtrust of security monitoring, these personal examples are instances of reduced vigilance due to their implicit belief that the technology is functionally flawless, that if the technology has not found an error, then an error must not exist.
Read full chapter
URL:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780128018736000054
Establishing a C&A Program
Laura Taylor, Matthew Shepherd Technical Editor, in FISMA Certification and Accreditation Handbook, 2007
Template Development
Certification Packages consist of a set of documents that all go together and complement one another. A Certification Package is voluminous, and without standardization, it takes an inordinate amount of time to evaluate it to make sure all the right information is included. Therefore, agencies should have templates for all the documents that they require in their Certification Packages. Agencies without templates should work on creating them. If an agency does not have the resources in-house to develop these templates, they should consider outsourcing this initiative to outside consultants.
A template should be developed using the word processing application that is the standard within the agency. All of the relevant sections that the evaluation team will be looking for within each document should be included. Text that will remain constant for a particular document type also should be included. An efficient and effective C&A program will have templates for the following types of C&A documents:
- ▪
-
Categorization and Certification Level Recommendation
- ▪
-
Hardware and Software Inventory
- ▪
-
Self-Assessment
- ▪
-
Security Awareness and Training Plan
- ▪
-
End-User Rules of Behavior
- ▪
-
Incident Response Plan
- ▪
-
Security Test and Evaluation Plan
- ▪
-
Privacy Impact Assessment
- ▪
-
Business Risk Assessment
- ▪
-
Business Impact Assessment
- ▪
-
Contingency Plan
- ▪
-
Configuration Management Plan
- ▪
-
System Risk Assessment
- ▪
-
System Security Plan
- ▪
-
Security Assessment Report
The later chapters in this book will help you understand what should be included in each of these types of documents. Some agencies may possibly require other types of documents as required by their information security program and policies.
Templates should include guidelines for what type of content should be included, and also should have built-in formatting. The templates should be as complete as possible, and any text that should remain consistent and exactly the same in like document types should be included. Though it may seem redundant to have the exact same verbatim text at the beginning of, say, each Business Risk Assessment from a particular agency, each document needs to be able to stand alone and make sense if it is pulled out of the Certification Package for review. Having similar wording in like documents also shows that the packages were developed consistently using the same methodology and criteria.
With established templates in hand, it makes it much easier for the C&A review team to understand what it is that they need to document. Even expert C&A consultants need and appreciate document templates. Finding the right information to include the C&A documents can by itself by extremely difficult without first having to figure out what it is that you are supposed to find—which is why the templates are so very important. It’s often the case that a large complex application is distributed and managed throughout multiple departments or divisions and it can take a long time to figure out not just what questions to ask, but who the right people are who will know the answers.
Read full chapter
URL:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9781597491167500093
Speech Recognition
John-Paul Hosom, in Encyclopedia of Information Systems, 2003
I.B. Capabilities and Limitations of Automatic Speech Recognition
ASR is currently used for dictation into word processing software, or in a “command-and-control” framework in which the computer recognizes and acts on certain key words. Dictation systems are available for general use, as well as for specialized fields such as medicine and law. General dictation systems now cost under $100 and have speaker-dependent word-recognition accuracy from 93% to as high as 98%. Command-and-control systems are more often used over the telephone for automatically dialing telephone numbers or for requesting specific services before (or without) speaking to a human operator. Telephone companies use ASR to allow customers to automatically place calls even from a rotary telephone, and airlines now utilize telephone-based ASR systems to help passengers locate and reclaim lost luggage. Research is currently being conducted on systems that allow the user to interact naturally with an ASR system for goals such as making airline or hotel reservations.
Despite these successes, the performance of ASR is often about an order of magnitude worse than human-level performance, even with superior hardware and long processing delays. For example, recognition of the digits “zero” through “nine” over the telephone has word-level accuracy of about 98% to 99% using ASR, but nearly perfect recognition by humans. Transcription of radio broadcasts by world-class ASR systems has accuracy of less than 87%. This relatively low accuracy of current ASR systems has limited its use; it is not yet possible to reliably and consistently recognize and act on a wide variety of commands from different users.
Read full chapter
URL:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B0122272404001647
Prototyping
Rex Hartson, Pardha Pyla, in The UX Book (Second Edition), 2019
20.7 Software Tools for Making Wireframes
Wireframes can be sketched using any drawing or word processing software package that supports creating and manipulating shapes. While many applications suffice for simple wireframing, we recommend tools designed specifically for this purpose. We use Sketch, a drawing app, to do all the drawing. Craft is a plug-in to Sketch that connects it to InVision, allowing you to export Sketch screen designs to InVision to incorporate hotspots as working links.
In the “Build mode” of InVision, you work on one screen at a time, adding rectangular overlays that are the hotspots. For each hotspot, you specify what other screen you go to when someone clicks on that hotspot in “Preview mode.” You get a nice bonus using InVision: In the “operate” mode, you, or the user, can click anywhere in an open space in the prototype and it highlights all the available links. These tools are available only on Mac computers, but similar tools are available under Windows.
Beyond this discussion, it’s not wise to try to cover software tools for making prototypes in this kind of textbook. The field is changing fast and whatever we could say here would be out of date by the time you read this. Plus, it wouldn’t be fair to the numerous other perfectly good tools that didn’t get cited. To get the latest on software tools for prototyping, it’s better to ask an experienced UX professional or to do your research online.
Read full chapter
URL:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780128053423000205
Design Production
Rex Hartson, Partha S. Pyla, in The UX Book, 2012
9.5.3 How to Build Wireframes?
Wireframes can be built using any drawing or word processing software package that supports creating and manipulating shapes, such as iWork Pages, Keynote, Microsoft PowerPoint, or Word. While such applications suffice for simple wireframing, we recommend tools designed specifically for this purpose, such as OmniGraffle (for Mac), Microsoft Visio (for PC), and Adobe InDesign.
Many tools and templates for making wireframes are used in combination—truly an invent-as-you-go approach serving the specific needs of prototyping. For example, some tools are available to combine the generic-looking placeholders in wireframes with more detailed mockups of some screens or parts of screens. In essence they allow you to add color, graphics, and real fonts, as well as representations of real content, to the wireframe scaffolding structure.
In early stages of design, during ideation and sketching, you started with thinking about the high-level conceptual design. It makes sense to start with that here, too, first by wireframing the design concept and then by going top down to address major parts of the concept. Identify the interaction conceptual design using boxes with labels, as shown in Figure 9-4.
Take each box and start fleshing out the design details. What are the different kinds of interaction needed to support each part of the design, and what kinds of widgets work best in each case? What are the best ways to lay them out? Think about relationships among the widgets and any data that need to go with them. Leverage design patterns, metaphors, and other ideas and concepts from the work domain ontology. Do not spend too much time with exact locations of these widgets or on their alignment yet. Such refinement will come in later iterations after all the key elements of the design are represented.
As you flesh out all the major areas in the design, be mindful of the information architecture on the screen. Make sure the wireframes convey that inherent information architecture. For example, do elements on the screen follow a logical information hierarchy? Are related elements on the screen positioned in such a way that those relationships are evident? Are content areas indented appropriately? Are margins and indents communicating the hierarchy of the content in the screen?
Next it is time to think about sequencing. If you are representing a workflow, start with the “wake-up” state for that workflow. Then make a wireframe representing the next state, for example, to show the result of a user action such as clicking on a button. In Figure 9-6 we showed what happens when a user clicks on the “Related information” expander widget. In Figure 9-7 we showed what happens if the user clicks on the “One-up” view switcher button.
Once you create the key screens to depict the workflow, it is time to review and refine each screen. Start by specifying all the options that go on the screen (even those not related to this workflow). For example, if you have a toolbar, what are all the options that go into that toolbar? What are all the buttons, view switchers, window controllers (e.g., scrollbars), and so on that need to go on the screen? At this time you are looking at scalability of your design. Is the design pattern and layout still working after you add all the widgets that need to go on this screen?
Think of cases when the windows or other container elements such as navigation bars in the design are resized or when different data elements that need to be supported are larger than shown in the wireframe. For example, in Figures 9-5 and 9-6, what must happen if the number of photo collections is greater than what fits in the default size of that container? Should the entire page scroll or should new scrollbars appear on the left-hand navigation bar alone? How about situations where the number of people identified in a collection are large? Should we show the first few (perhaps ones with most number of associated photos) with a “more” option, should we use an independent scrollbar for that pane, or should we scroll the entire page? You may want to make wireframes for such edge cases; remember they are less expensive and easier to do using boxes and lines than in code.
As you iterate your wireframes, refine them further, increasing the fidelity of the deck. Think about proportions, alignments, spacing, and so on for all the widgets. Refine the wording and language aspects of the design. Get the wireframe as close to the envisioned design as possible within the constraints of using boxes and lines.
Read full chapter
URL:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780123852410000099
1.1 ESSENTIAL WORD-PROCESSING FUNCTIONS
Essential word-processing functions can be grouped into the categories of input, manipulation, formatting, and output of text.
Text Input
Typically, the text is entered into the word processor from a keyboard; other input methods include:
Copying text from other applications (such as from hypertext markup language [HTML] documents, e-mail messages, or online encyclopedias) and pasting it into a word-processing document
Scanning printed documents and using optical-character-recognition (OCR) software to convert the scanned documents into text characters
Using voice-recognition software to convert spoken words into text characters
Text Manipulation
Text manipulation refers to the “processing” part of word processing. Word processors provide easy methods of deleting, inserting, copying, and moving individual characters, words, phrases, and paragraphs—even entire pages of information—with a few clicks of a mouse button or with such keyboard shortcuts as Ctrl-C to copy, Ctrl-X to cut, and Ctrl-V to paste or insert text. Text can be automatically checked for spelling and for conformance to basic grammatical principles as the text is entered and edited.
The find-and-replace feature in a word processor allows the user to search for every occurrence of a particular character, word, or phrase within a document and replace it with new text. Most word processors also include automatic correction and automatic formatting of common errors and mechanical conventions as text is entered from the keyboard. For example, commonly misspelled words can be automatically corrected as soon as the misspelled words are entered; two spaces entered after the end of a sentence can be changed automatically to one space; a lowercase letter beginning a new sentence can be capitalized automatically. Proper typographic quotation marks (“smart” or “curly” quote marks—” and “) and apostrophes (‘) can be inserted automatically instead of the straight typewriter-style quotation marks entered from the keyboard. Fractions and other symbols can be formatted automatically as their keyboard equivalents are entered. For example, when a fraction for one-half is entered as 1/2, it is changed to the symbol ½ two hyphens (––) are changed to a long dash (—); and (c) is changed to ©.
Text Formatting
Word-processing software typically includes “wizards” or “help” features to provide automated formatting of common business documents. For example, a letter wizard can assist the user to properly format a business letter, and a resume wizard can help the user format a professional-looking resume. Templates are another automated formatting feature. A template is a type of pre-formatted, fill-in-the-blank document that is useful for maintaining a specific format each time a document is created, especially when multiple word-processing operators are involved. A newsletter template, for example, allows a user to enter the text of newsletter articles, headlines, and graphics without having to re-create the newsletter layout for each issue of the newsletter.
The most-common formatting tasks are typically performed by the user as a document is created. Individual character and word formatting include a selection of type size, type style, and typeface. Size is measured in points, a unit of measure in which 72 points make up an inch. Typically, 11- or 12-point type is used for basic business documents. Newsletters, annual reports, and other such “designed” documents may use type as small as 8 or 9 points for the basic text and as large as 24, 36, or 48 points (or more) for main titles. Typestyles, such as italics, underline, and bold, are easily selected using keyboard shortcuts or by selecting them from the basic font menu. Typefaces (typeface refers to the look or design of the type) are available in thousands of varieties, including such commonly known faces as Times Roman, Arial, Helvetica, and Garamond.
Paragraph formatting includes line spacing, meaning the amount of blank space left between lines of type (single spacing and double spacing, for example); paragraph spacing (the amount of blank space that precedes or follows each paragraph); justification (all lines of type made even at both margins, or left uneven or ragged at the right margin); and indentation (such as a first-line indentation at the beginning of each paragraph).
Page and overall-document formatting includes setting margins (typically 1-inch margins are used on the top, bottom, and both sides of such basic business documents as letters, reports, and memos), creating columns like those used in a newspaper or newsletter, and creating headers and footers (information such as the page number or a chapter title that is repeated at the top or bottom of each page of a document). Most word processors also provide special layout features for formatting outlines, tables, envelopes, and mailing labels.
Text Output
Once text has been created, edited, and formatted into a finished electronic document, it must be put into some tangible form or lasting electronic form to be of practical benefit. That output process usually starts with the saving of the document on the computer’s hard drive, a floppy disk, a CD, or a memory device such as a flash drive. Saving the document, in fact, is an activity that should take place frequently during the creation and editing processes to guard against loss due to problems such as electrical-power failure, computer malfunctions, and operator error.
Printing a document on paper is the most common output method; other output methods include faxing a document directly from the word processor by use of a computer modem, sending the document to another person by e-mail, and converting the word-processing document to various other electronic formats for online viewing or for eventual printing from other applications. For example, word-processing documents are frequently converted to HTML for use as Web pages, to portable document format (PDF) files, and to rich text format (RTF) files for use in other computer programs (particularly other word-processing programs).
Advanced word processing
Although most word-processing users tend to learn and use primarily the basic word-processing features, numerous more-advanced features are available in most word processors to make word processing much easier to complete in less time. Taking the time to learn some advanced word-processing features and functions usually has a high payoff in terms of productivity and professionalism.
Some of the more-common advanced word-processing features and functions are described briefly below:
Styles
Styles are user-created formatting commands that allow great control over repetitive formatting structures within a document. For example, using a “style” for each type of heading in a report will ensure consistent formatting of the headings and will eliminate the need for a user to manually format each heading as it is created.
Macros and Merging
Macros are stored keystrokes or sets of editing and formatting commands, that can be replayed whenever needed. Macros can boost productivity and take much of the tedium out of repetitive word-processing tasks. Merging is the process of using lists of such information as names, addresses, phone numbers, product descriptions or model numbers, and so on to fill in designated fields or blanks in documents to create mass mailings, address labels, directories, and catalogs.
Version Control
Version-control features allow a user to track the various stages of editing that a document may pass through, including versions created by multiple users involved in the creation and editing of a document. Related features such as the ability to track changes made in a document enable multiple users to review suggested document changes and to accept or reject proposed changes.
Automatic References and Indexes
Documents that include tables of contents, cross-references, indexes, footnotes, endnotes, and captions will benefit from the capability of a word processor to automatically generate and format these items.
Desktop-Publishing Capabilities
Professional-looking documents such as newsletters, advertisements, annual reports, brochures, and business cards can be designed with most modern word-processing software.
Graphical images from clip-art collections, digital photographs, and scanned images, and drawings created with graphics programs, can be integrated easily into word-processing documents. Pages and paragraphs can be enclosed with decorative borders. Background images and colors can be added to pages within a document. Graphical elements such as lines, boxes, arrows, and artistic textual headings can be created quickly and easily within most word-processing programs.
Although word processors are generally not as sophisticated as desktop-publishing software or page-layout programs in their capabilities for setting type and for working with graphical elements, they can be used to create attractive, professional-looking documents that go beyond the basic layout and formatting of letters, memos, and reports. Using a word-processing program to create designed documents is often preferable to using a high- end desktop-publishing program, however, because word-processing users are not required to become proficient in using another program and because documents within an organization or department are created and maintained using the same application.
Word Processors
How many typewriters are you likely to find in an office today? Probably none, but in the mid-1960s they were plentiful. That was when IBM coined the term “word processing” to market their Magnetic Tape Selectric Typewriter, also known as the MTST. It was very different from other typewriters because it recorded words on magnetic tape and printed them on paper at the same time. Each tape could store many documents, making it possible to retrieve any of them for later printing, or for generating multiple copies of the same document. This was the first device to allow semi-automatic production of personalized letters: after the user typed the names and addresses, the machine took over and completed the task.
The MTST underwent many transformations, and in 1974 it used internal storage along with external storage on magnetic tapes or cards. However, fast typists could not reach their full potential because it was still a mechanical device. It was not until the introduction of CRT-based word processing equipment in 1976, with the Wang Computer System, that operators were released from the constraints of mechanical printing devices.
By the mid-1970s customer demand provided the thrust for a new industry: special-purpose computers dedicated to word processing. New vendors of word processors, such as Wang Laboratories, surpassed IBM in sales and product innovation. Word processors have undergone many transformations while evolving from dedicated units to multi-purpose personal computers that can perform several functions, including word processing, database management, and accessing the Internet. “Word processor” now refers primarily to the software used to create and manipulate text documents, rather than to the hardware on which the software is run.
Functions of Word Processing Systems
Most word processing systems provide, in a single software package, all the necessary tools that users need to produce a finished document, from entering and editing text, to formatting and proofreading it, and finally to saving and printing it. Here are the steps one would follow to create a document using a word processing program.
Entering Text.
A word processing document starts as an empty window on the computer screen with a flashing cursor bar that indicates your location in the document. As you type, the cursor moves to the right, and the characters are displayed on the screen and stored in the computer’s memory. You can fix your typing mistakes at any time by pressing the Delete or Backspace keys. Word processors are equipped with the “word wrap” feature, which automatically moves a word to the next line once a line has reached its full capacity. Therefore, the only time you need to press the Return or Enter key is when you want to begin a new line, such as at the end of a paragraph. On typewriters, a typist had to press the return key to begin a new line of text.
Editing Text.
Word processors make it easy for you to change and rearrange your work in many different ways. For example, you can easily:
Navigate to different parts of a document by scrolling;
Search for and replace specific words or phrases throughout a document;
Insert text at any point;
Delete text from any section;
Move text from one part of a document to another;
Copy text from one part and duplicate it in another section of the same document or to another document.
Formatting Text.
This refers to arranging a document so it will look the way you want it to once it is printed. All word processors allow you to format individual characters, lines, paragraphs, or whole documents. WYSIWYG (What You See Is What You Get) systems also give you a good view on the screen of what the final product will look like.
Formatting characters affect the size of the characters (point size), their style (typeface, sometimes called font), and whether they are underlined, written in italic, or displayed in bold, heavy type. The formatting of lines and paragraphs determines the spacing between lines of text, the placement of indents or tabs, and the finished length and position of the lines of type on a page. Document formatting applies to margin settings, as well as headers and footers—blocks of text that appear at the top and bottom of every page.
Other text formatting features give you the ability to:
Create documents with variable-width multiple columns;
Perform automatic footnoting;
Generate table-of-contents and indexing for books and other long works;
Create and format multi column tables;
Attach hidden text, pop-up notes, or audio notes that can be seen or heard by the user but do not show up in the final document;
Incorporate graphics created with other applications.
Additional Tools.
Word processing does not end with editing and formatting. Most high-end word processors also include a built-in outliner, spell checker, grammar and style checker, thesaurus, mail merger, and indexer. As word processors become more powerful, they take on many features previously found only in desktop publishing (DTP) software such as merging graphics, tables, and text into one document. Many word processors are capable of producing professional-quality books and periodicals, so the line between word processors and DTP programs is likely to fade with time.
1.2 identify how different types of information should be linked of integrated
Besides being able to link information from other Windows applications into your document, you can link other Word documents to your current document. This comes in real handy if you are working with a document that needs to pull information from other documents. For instance, you might have a contract that has standard clauses in it. These clauses may be stored in other documents and then be pulled into the contract as necessary. If you are using Word 97, this is done in the following manner:
1.Position the insertion point where you want the document inserted and linked.
2.Choose File from the Insert menu. Word displays the Insert File dialog box.
3.Specify a filename for the document you want to be inserted and linked.
4.Make sure the Link to File check box is selected.
5.Click on the OK button.
If you are using Word 2000, 2002, or 2003, the process is just a bit different:
1.Position the insertion point where you want the document inserted and linked.
2.Choose File from the Insert menu. Word displays the Insert File dialog box.
3.Specify a filename for the document you want to be inserted and linked.
4.Click your mouse on the pull-down arrow at the right side of the Insert button. Word 5.displays a menu of the different ways you can insert the document.
Choose Insert As Link from the menu.
This process results in Word displaying the other file, but the Include Text field is used instead of the actual text from the file. The advantage to adding links in this way instead of inserting the other file completely is that the original documents (the ones you are linked to) can be independently updated, and those changes are reflected in the document with the links.
1.3 Use appropriate techniques to information accurately and efficiently
Not all of us, but most use Microsoft Word for processing documents on a computer at work. One needs to know how to use the basic tools to format a document and also understand the uses and benefits of using templates and styles in documents.
In this section, we will look at the different types of information that we need to create a document, the techniques that one needs to use to enter information, the use of styles and templates, how to combine or merge documents, the different editing tools and how to store and retrieve documents effectively.
This hub is written to help candidates who will be or who are pursuing their NVQ Level 2 or Level 3 Diploma in Business and Administration or IT. The unit covered is word processor and candidates who are IT users will have to evidence knowledge, understanding and skills to use an application that is designed to create, edit and produce large text-based documents at an intermediate level.
Most part of this unit has to be evidenced by a candidate’s ability to demonstrate the skills (practical application) they possess and the techniques that they apply to use the software. This will be through direct observation by the assessor and / or through a devised test or task at their work place and / or evidenced through documents that they have already created.
I have tried my best to outline the basic knowledge that one should possess in order to use a word processor and this unit has been written based on the word processing application called Microsoft Word. I have tried my best to use screenshots wherever possible from Microsoft Word 2003 and some videos that will really help.
Microsoft Word is an office application that most organisations and companies use to process text based documents. Most of the companies still use Microsoft word 2003 and most part of the unit will be limited to tasks using Microsoft word 2003.
This is a Level 2 unit with a credit value of 4. For ease of going through, I have divided this Unit into three sections and also published them as three different sections. Please follow the links below for sections 2 and 3.
Section 2 – Create and modify layout and structures for word processing documents (Word Processing Software, Questions 2.1 to 2.4)
Section 3 – Use word processing software tools to format and present documents effectively to meet requirements (Word Processing Software, Questions 3.1 to 3.6)
In this part, that is Section 1, we will look at how to enter and combine text and other information accurately within word processing documents.
Enter and combine text and other information accurately within word processing documents
Note: All along the course of the unit, in all the three sections, I have added as many screenshots as possible. You will not be presenting screenshots if you are writing down answers for this unit, but you will be asked to perform a few tasks to test your knowledge and understanding of using a word processor, and the screenshots may come in handy!
1.4 Create ,use and modify appropriate templates for different type of documents
In Microsoft Word, templates are pre-designed documents that you or someone else (such as Microsoft) creates to use as a pattern for a project. The template could be for a business card, brochure, resume, presentation…the list goes on. Regardless of the purpose, templates provide the design consistency that any organization (or individual) needs to look professional. (You can also find templates for Excel, PowerPoint, and other applications, but in this article we’re focusing on Microsoft Word.)
The template contains a specific layout, style, design and, sometimes, fields and text that are common to every use of that template. Some templates are so complete (such as business cards), you only have to change the individual’s name, phone number, and email address. Others, such as business reports or brochures, could require that everything is changed except the layout and design.
Once you create a template, you can use it over and over. Remember that while you open a template to start a project, you save the project as another file type, such as the basic .docx Word format, for editing, sharing, printing, and more. The template file stays the same, unless or until you want to change it (more on that later).
Adobe
Steps to create a Sign template:
Sign in to Adobe Document Cloud at https://documentcloud.adobe.com with your Adobe ID and password, or with your social (Facebook or Google) account.
In the Quick Start section, click Create Sign Template.
Enter a name for the template.
Do one of the following to select a document and create a sign template:
- Drag-and-drop the file onto the highlighted area.
- Click Add Files, and then choose a file from Document Cloud, Creative Cloud, Box, Dropbox, or Google Drive. You can also choose a file from your computer. Click Attach.
Click Preview & Add Fields.
The document is now ready for adding fields. The form fields are automatically detected in the PDF. Click the 
Note: If you have added multiple documents, the documents are converted into PDFs and combined into a single file. The combined file is opened for you to add appropriate fields.
- To move a field, move your pointer closer to the field border until you see the drag handle, and then hold and move the field as required.
- To resize a field, use the blue triangular drag handle, and then hold and resize the field as required.
- To delete a field, select the field and hit the Delete key on the keyboard. Alternatively, you can right-click a field and select Delete.
For more information on adding form fields, see
-Prefill Agreement fields before sending
-Assign form fields to recipients
-Click Save. You get a confirmation message about the successful sign template creation.
1.5 Explain how to combine and merge information from other software or multiple documents
Word for Office 365 Word 2019 Word 2016 Word 2013 Word 2010 Word 2007
Merge two documents
-
Click Review > Compare > Combine.
A pop-up window lets you choose the Original document and the Revised document.
-
Under Original document, click the down arrow and choose the document you sent for review. If you need to browse to the file’s location, click the folder icon. Remember, this is the original document that you worked on without any changes or modifications.
-
Under Revised document, choose the document you want to merge.
-
In the Label unmarked changes with box, type a name or phrase so you’ll know who suggested the changes.
-
Click More to get more options for combining the documents.
-
Under Show changes in, click New document.
-
Click OK.
Word opens a new document that combines the original document and the copy you merged in. The screen is divided into three sections. One section shows the Revisions made, the middle section shows the combined document, and the third section,which is split in two, displays the Original document and Revised document.
If that’s too much information on the screen, click Compare > Show Source Documents > Hide Source Documents. Note the red vertical line that shows where changes were made.
-
When you’ve resolved the combined changes the way you want, save the document.
Tip: Next time, skip all of this by sharing the document on OneDrive and inviting people to add their edits and comments.
Merge in additional copies
If you want to merge in more copies, save the document that contains the combined changes of the first two copies. Then merge the additional copies into that document.
-
Click Review > Compare > Combine.
-
Under Original document, click the arrow and then click the document that contains the combined changes.
-
Under Revised document, click the next copy you want to merge in.
-
In the Label unmarked changes with box, type a name or phrase so you’ll know who suggested the changes.
-
Click More.
-
Under Show changes in, click Original document.
-
Click OK.
Add different documents to a file
If you want to combine multiple documents and make a single file, you can copy and paste all the documents’ contents into one file. Or you can open the first document, click Insert > Object > Text from File, and then browse to the documents you want to add, click them, and then click Insert.
Combine documents by copying and pasting
To merge two different documents into one file, copy the contents of one document and paste it into the other.
- Open both documents.
- In the document you want to add, choose Home > Select > Select All to select the whole document. Or press Ctrl+A.
- Choose Home > Copy. Or press Ctrl+C.
- In the second document, click where you want to add the copied content and choose Home > Paste > Merge Formatting to make the new content match what’s already there. Alternatively, you can press Ctrl+V to paste and select Merge Formatting in the paste button that appears below.
1.6 Combine and merge information within a document from a range of sources
Excel 2016 gives you a wide range of tools with which to format, summarize, and present your data. After you have created a workbook to hold data about a particular subject, you can create as many worksheets as you need to make that data easier to find within your workbook. To ensure that every year’s workbook has a similar appearance, you can create a workbook with the characteristics you want, and save it as a pattern, or template, for similar workbooks you will create in the future.
A consequence of organizing your data into different workbooks and worksheets is that you need ways to manage, combine, and summarize data from more than one Excel document. You can always copy data from one worksheet to another, but if the original value were to change, that change would not be reflected in the cell range to which you copied the data. Rather than remembering which cells you need to update when a value changes, you can create a link to the original cell. That way, Excel will update the value for you whenever you open the workbook. If multiple worksheets hold related values, you can use links to summarize those values in a single worksheet.
This chapter guides you through procedures related to using a workbook as a template for other workbooks, linking to data in other workbooks, and consolidating multiple sets of data into a single workbook.
Use workbooks as templates for other workbooks
After you decide on the type of data you want to store in a workbook and what that workbook should look like, you probably want to be able to create similar workbooks without adding all of the formatting and formulas again. For example, you might have established a design for your monthly sales-tracking workbook.
When you have settled on a design for your workbooks, you can save one of the workbooks as a template for similar workbooks you will create in the future. You can leave the workbook’s labels to aid in data entry, but you should remove any existing data from a workbook that you save as a template, both to avoid data entry errors and to remove any confusion as to whether the workbook is a template. You can also remove any worksheets you and your colleagues won’t need by right-clicking the tab of an unneeded worksheet and, on the shortcut menu that appears, clicking Delete.
1.7 Store and retrieve document and associated files effectively
There are a lot of ways to save a file on your computer, but some of them are not compatible- meaning they will not work with – the operating system on different computers. I make folders and keep my work on the desktop of my computer so I can find it easily.
When you click to save it it gives you different ways of saving it such as JPEG, or TIFF for photographs and Word Document or a PDF file for letters and writing.
I use JPEG and Word Doc usually as most people can read them as they are used a lot. To find a file you can use the search bar at the bottom left of the computer. Put the file name into it or whatever you think it is and it comes up with a list. Then you can click and drag the file onto the desktop to use it.
1.8 Use tools and techniques to work with multiple documents or users
Working on multiple documents is not an easy task. Especially, when you need to compare, edit and switch between them very frequently. But if you are working on MS Word, there are few interesting tools that could relieve you from this complexity.
We are going to talk about all such tools placed under the View tab, in the Window section. Let us explore each one and see which of these can come in handy for ya’ll.
ADD NEW WINDOW
How do you create a copy of the current document you are working on? Do you close your document, copy the original and paste the copy? Now, that isn’t the best way..Just navigate to View and click on the New Window button. This creates a clone of the current document and opens it in a new Window.
SWITCH WINDOWS
It may not always be pleasant to use the Alt + Tab combination to switch between windows for multiple MS Word documents that are open at the same time. It’s also time consuming to hover over the task bar and choose the required document. An easier and better way is to use the Switch Windows tool that shows all documents currently open.
ARRANGE ALL
I personally do not find it that useful but maybe you can put it to use. Clicking on this icon arranges all the copies of current document in horizontal splits. Take a look at the picture below.
SPLIT WINDOW
It is an awesome piece of tool to look at two different parts (or two different pages) of the same document at the same time. It splits the window (or rather the document) into two halves to help you through. You may choose the position of split by yourself.
VIEW SIDE BY SIDE
Have two documents to compare or edit at the same time. When you hit this button you will be asked to select a document you wish to compare the present with.
When done both the documents would appear as vertical splits like when you divide your desktop screen vertically.
Associated with this function are two more tools:-
Synchronous Scrolling: Though the name explains itself, let me tell you that you can switch it on or off by clicking on it. When it is on, scrolling one scrollbar will scroll both the documents together.
Reset Window Position: At any time you may feel the need to maximize one window or minimize the other. Wondering how to bring them back? Click on this button and they will be arranged in vertical splits again.
1.9 Customise interface to meet needs
Customising the user interface
The user interface of Smart Edit Writer has been set up in a particular way. Chapters, scenes and notes are stored on the left, the main tabbed word processor sits in the middle, and research and notes open to the right (along with your daily word counts). This basic structure will be maintained as we add new features to the software over the coming year.
On the Word Processor toolbar, there are options to Zoom in or out, enlarging the word processor or making it smaller. There is also an ability to widen the Document Tree and the Notes section by dragging the separator to the left or right. These are project wide settings. Changes to any of these settings will be maintained when you close and re-open a project. You should spend a little time configuring your look and feel, and be confident that Smart Edit Writer will adopt these changes every time it opens that project.
At the top right of the Smart Edit Writer window, next to the minimise button, there is a fourth button that opens a drop down menu. The options available in this drop down are:
Auto-hide Ribbon, Show Tabs and Show Tabs and Commands.
Selecting from these options along with closing the right and left sections gives a close approximation of full screen writing. This is an area we will probably add to in the future.
If you prefer to write on a dark background, you’ll find a “Use dark theme” option on the first page of the Settings dialog. Selecting this option will switch all of SmartEdit Writer over to a dark theme, allowing you to write white (-ish) text on a dark gray background.
If you do enable the dark theme, you’ll need to be careful about copying and pasting from Word documents or websites into a scene. In these cases you should use the “Paste Special” option on the toolbar and select “Unformatted Text” from the options available. If you paste formatted text into a dark themed page, you’ll end up with different colored fonts, as formatted text carries font color information of its own into your scene. This is a limitation that every word processor with dark themes faces, and it’s the price you pay for that dark background.
References
https://www.microsoftpressstore.com/articles/article.aspx?p=2447199
https://jamesorddrummer.wordpress.com/2014/05/08/unit-15-1-7-i-can-store-and-retrieve-files-effectively-in-line-with-local-guidelines-and-conventions-where-available/
https://www.guidingtech.com/11276/manage-or-work-with-multiple-documents-ms-word/
https://www.smart-edit.com/Writer/Knowledge/Page/Customisation/