Excel for Microsoft 365 Excel for Microsoft 365 for Mac Excel for the web Excel 2021 Excel 2021 for Mac Excel 2019 Excel 2019 for Mac Excel 2016 Excel 2016 for Mac Excel 2013 Excel 2010 Excel 2007 Excel for Mac 2011 Excel Starter 2010 More…Less
This article describes the formula syntax and usage of the DAY function in Microsoft Excel. For information about the DAYS function, see DAYS function.
Description
Returns the day of a date, represented by a serial number. The day is given as an integer ranging from 1 to 31.
Syntax
DAY(serial_number)
The DAY function syntax has the following arguments:
-
Serial_number Required. The date of the day you are trying to find. Dates should be entered by using the DATE function, or as results of other formulas or functions. For example, use DATE(2008,5,23) for the 23rd day of May, 2008. Problems can occur if dates are entered as text.
Remarks
Microsoft Excel stores dates as sequential serial numbers so they can be used in calculations. By default, January 1, 1900 is serial number 1, and January 1, 2008 is serial number 39448 because it is 39,448 days after January 1, 1900.
Values returned by the YEAR, MONTH and DAY functions will be Gregorian values regardless of the display format for the supplied date value. For example, if the display format of the supplied date is Hijri, the returned values for the YEAR, MONTH and DAY functions will be values associated with the equivalent Gregorian date.
Example
Copy the example data in the following table, and paste it in cell A1 of a new Excel worksheet. For formulas to show results, select them, press F2, and then press Enter. If you need to, you can adjust the column widths to see all the data.
|
Date |
||
|---|---|---|
|
15-Apr-11 |
||
|
Formula |
Description (Result) |
Result |
|
=DAY(A2) |
Day of the date in cell A2 (15) |
15 |
Need more help?
Want more options?
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.
Summary
The Excel DAY function returns the day of the month as a number between 1 to 31 from a given date. You can use the DAY function to extract a day number from a date into a cell. You can also use the DAY function to extract and feed a day value into another function, like the DATE function.
Purpose
Get the day as a number (1-31) from a date
Return value
A number (1-31) representing the day component in a date.
Arguments
- date — A valid Excel date.
Syntax
Usage notes
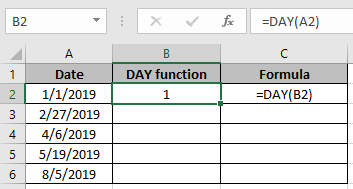
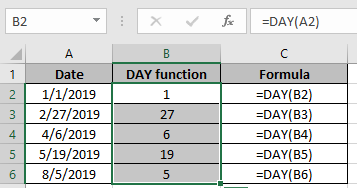
The DAY function returns the day value in a given date as a number between 1 to 31 from a given date. For example, with the date January 15, 2019 in cell A1:
=DAY(A1) // returns 15
You can use the DAY function to extract a day number from a date into a cell. You can also use the DAY function to extract and feed a day value into another function, like the DATE function. For example, to change the year of a date in cell A1 to 2020, but leave the month and day as-is, you can use a formula like this:
=DATE(2020,MONTH(A1),DAY(A1))
See below for more examples of formulas that use the DAY function.
Note: in Excel’s date system, dates are serial numbers. January 1, 1900 is number 1 and later dates are larger numbers. To display date values in a human-readable date format, apply a number format of your choice.
Notes
- The date argument must be a valid Excel date.
- The DAY function returns #VALUE! if date is not valid.
Author
Dave Bruns
Hi — I’m Dave Bruns, and I run Exceljet with my wife, Lisa. Our goal is to help you work faster in Excel. We create short videos, and clear examples of formulas, functions, pivot tables, conditional formatting, and charts.
There are hundreds and hundreds of Excel sites out there. I’ve been to many and most are an exercise in frustration. Found yours today and wanted to let you know that it might be the simplest and easiest site that will get me where I want to go.
Get Training
Quick, clean, and to the point training
Learn Excel with high quality video training. Our videos are quick, clean, and to the point, so you can learn Excel in less time, and easily review key topics when needed. Each video comes with its own practice worksheet.
View Paid Training & Bundles
Help us improve Exceljet
The DAY function has a simple purpose when used by itself. It gives you the «day» component (i.e., a number from 1-31) of a date inside a cell. However, the DAY function allows us to play around with dates in our worksheets by using it with some logical arguments or other functions, as will see in the examples section.
But first, let’s get some basics out of the way.
Syntax
The syntax of the DAY function is as follows:
=DAY(serial_number)
Arguments:
serial_number – The DAY function has just one argument, where you will need to enter a date, either in the form of a serial number or cell reference.
Important Characteristics of the DAY function
- The DAY function extracts the day from a given date and returns it into a cell.
- The DAY function can be nested inside another function to relay the return (for example, in the DATE function).
- If the cell referenced in the
serial_numberargument does not contain a valid Excel date, the function will return a #VALUE! error.
Examples of the DAY function
Now let’s have a look at some of the examples of the DAY function in Excel.
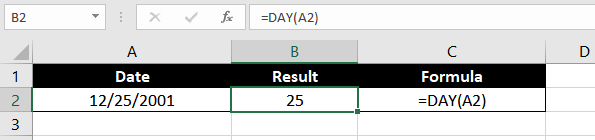
Example 1 – Plain-vanilla DAY formula
Let’s use the DAY function to extract a day from a date without adding any other complexities. Here is the formula we will use:
=DAY(A2)
No rocket science, right? We have a date in cell A2, and we use the DAY function to extract the day from that date, which is ’25.’
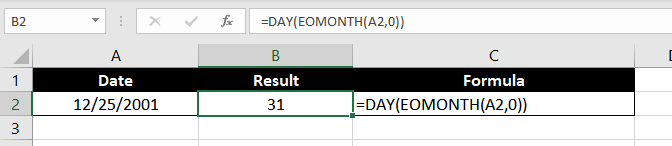
Example 2 – Finding the Number of Days in a Month with DAY function
The formula we will use here is pretty simple. It has a 2-step process and involves 2 functions: DAY and EOMONTH.
We know how the DAY function works. Let’s talk about the EOMONTH function.
The EOMONTH function has 2 arguments. In the first argument, you must supply a date, and in the second argument, you must supply the number of months you want to add to that date.
The EOMONTH function returns the last date of the month, after adding the specified number of months to the given date. For example, if we supply the start date as «12/25/2001» and enter 1 in the second argument, the EOMONTH function will return 01/31/2002.
Alright, now that we have the EOMONTH function covered, let’s look at the formula for finding the number of days in a given month:
=DAY(EOMONTH(A2, 0))
Since our start date is 12/25/2001, the EOMONTH will return 12/31/2001. Also, we know that the DAY function returns the day component of a date, and therefore, it will return ’31,’ i.e. the number of days in December.
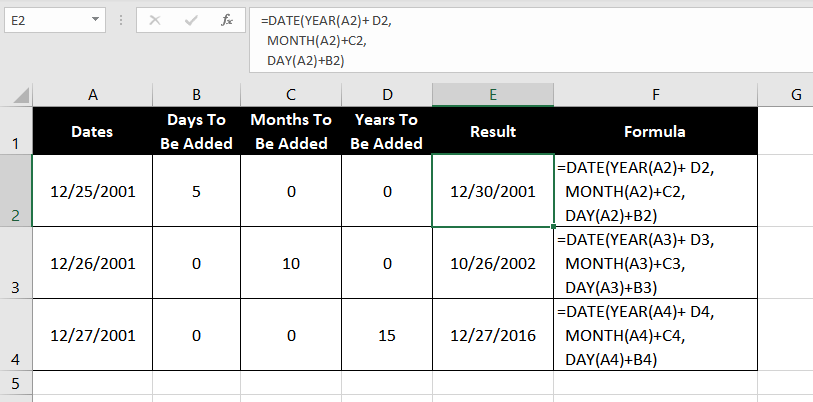
Example 3 – Adding Days, Months, or Years with DAY and DATE function
Okay, so let’s say we have a list of dates and a list of days/months/years that we want to add to those dates.
To accomplish this, we will nest the YEAR, MONTH & DAY functions inside the DATE function and add the relevant argument with the corresponding year, month or day to be added. So the formula would be :
=DATE(YEAR(A2) + D2, MONTH(A2) + C2, DAY(A2) + B2)
Essentially, we are trying to add 0 years (from cell D2 to the first argument), 0 months (from cell C2 to the second argument), and 5 days (from cell B2 to the third argument) of the date function. When this formula is dragged down using the fill-handle it populates the correct formula against each row and gives us the suitable output.
Note that instead of putting a number for the years, months, or days to be added in a separate cell, we could just use the number in the formula after the ‘+’ sign instead of referencing the cell.
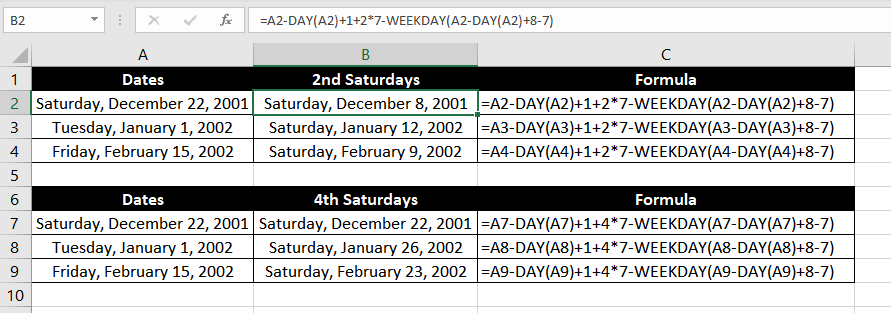
Example 4 – Fetch the nth Weekday in a Given Month
Let’s say we are trying to find out 2nd and 4th Saturdays in a month, for this we can make use of the DAY and WEEKDAY functions.
We’ll prepare the formula as:
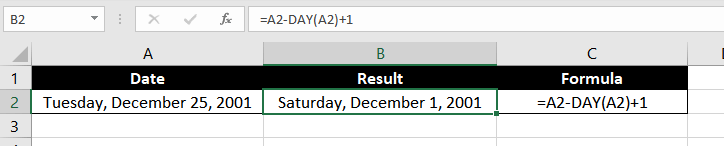
=A2 – DAY(A2) + 1 + n * 7 – WEEKDAY(A2 – DAY(A2) + 8 – 7)
Like we always do, let’s dismantle this formula and understand what each component contributes to the final output.
Step 1
A2 is the start date. From A2, we will subtract the date itself using the DAY function and then add 1.
Why?
Well, all we want to do in this part of the formula is bring the formula to the 1st day of the month. In our example, cell A2 contains the date 12/22/2001. Removing 22 days using the DAY function, and adding 1, gives us 12/01/2001.
Step 2
Great, so the next component of the formula is n * 7. ‘n’ here is the occurrence of the day in a given month that we want to compute. In our example, we want the 2nd and 4th Saturday of the given months, so we will set our n to ‘2’ and ‘4’. In effect, this computation will take us ‘n’ number of weeks into a given month.
We will now continue our discussion with the list of 2nd Saturdays, but the logic remains the same for both lists.
In step 1, we navigated to the 1st date of the month. Now, what should we add to this to reach the last day of the nth week? Just the number of weeks multiplied by the number of days in a week, right? So, we will add 14 days (2 * 7) for our list of 2nd Saturdays.
This brings our formula to 12/15/2001.
Step 3
The final step. Now that we have navigated n number of weeks into a given month, let’s navigate to the specific day we want.
While 12/15/2001 (as computed in Step 2) also happens to be a Saturday, it is the 3rd Saturday of the month.
So, we will use the WEEKDAY function to backtrack to the intended day. WEEKDAY returns a number from 1 to 7 in which 1 represents a Sunday, and 7 represents a Saturday.
In our example, the WEEKDAY function returns a ‘7.’
Why does WEEKDAY return 7?
The ‘7’ represents the weekday as on the first date in a given month since, within the WEEKDAY function, we navigate to the first day using the DAY function and then add 1.
So, let’s subtract 7 from 12/15/2001 to get our final output.
We get 12/08/2001, which is the 2nd Saturday; the first Saturday being 12/01/2001.
Example 5 – Get the First Day of the Month with DAY function
I sort of gave this away in the previous example, but let’s quickly recap through how we can compute the first day of the month using the DAY function.
We will use the following formula:
=A2 – DAY(A2) + 1
Does this look familiar? We used this formula in our previous example, too.
A2 is our start day. When we use the DAY function and reference cell A2 in the argument, we are essentially asking it to fetch the day component of the date.
In our example, our start date is December 25, and the DAY function returns 25. Subtracting 25 days from December 25 will give us November 30, so we add 1 and get our final output as 12/01/2001, i.e. the first day of the month.
That’s a wrap on DAY function. When you are done playing around with the DAY function and ace these formulas, we will have another exciting Excel function for you. Until then, keep crunching those numbers.
The DAY function in Excel is a date function in Excel that is used to calculate the day value from a given date. This function takes a date as an argument and returns a two-digit numeric value as an integer representing the day of the provided date. The method to use this function is as follows =Edate (Serial_number), the range for the output for this formula is from 1-31 as this is the range of the dates in Excel date format.
For example, suppose in the spreadsheet, in column A, we have a date of 15-Apr-2015, and we need to extract the day from the date in column B. In such a situation, we can use the DAY function in Excel. Using the function will return the value as 15 in column B.
Table of contents
- DAY Function in Excel
- Syntax
- Usage Notes
- How to Open DAY Function in Excel?
- Example #1
- Example #2
- Example #3
- Example #4
- Example #5
- Applications
- Common Problem
- Errors
- DAY Excel Function Video
- Recommended Articles
Syntax
- Date_value/serial_number: A valid Excel date with the serial number format for returning the day of the month.
- Return Value: The return value will be a numeric value between 1 and 31, representing the day component in a date.
Usage Notes
- The date inserted in the DAY formula must be a valid Excel date in the serial number format. For example, the date to be entered is Jan 1, 2000. Therefore, it is equal to the serial number 32526 in Microsoft Excel.
- We should also note that Microsoft Excel can only handle dates after 1/1/1900.
- The DAY formula in Excel is helpful in financial modelingFinancial modeling refers to the use of excel-based models to reflect a company’s projected financial performance. Such models represent the financial situation by taking into account risks and future assumptions, which are critical for making significant decisions in the future, such as raising capital or valuing a business, and interpreting their impact.read more in many business models.
How to Open DAY Function in Excel?
The following are the steps to open the DAY function in Excel:
- First, we must enter the desired DAY formula in Excel in the required cell to attain a return value on the argument.
- We can manually open the DAY formula in the Excel dialog box in the spreadsheet and enter the logical values to attain a return value.
- You may consider the screenshot below to see the DAY formula in Excel under the Date Time Function menu.
- We must click on the DAY function Excel. As a result, the dialog box shall open, where we can enter the arguments to attain a return value, i.e., the day of the given specific date in this case.
Let us look below at some of the examples of the DAY function. These examples will help you explore the use of the DAY function in Excel.
You can download this DAY Function Excel Template here – DAY Function Excel Template
Based on the above Excel spreadsheet, let us consider three examples and see the DAY formula return based on the function’s syntax.
Consider the screenshots of the above examples for a clear understanding.
Example #1
Example #2
Example #3
Example #4
Example #5
Applications
We can use the Microsoft DAY function for various purposes and applications within the spreadsheet. Some of the common applications of the DAY function in spreadsheets are given below:
- To get a series of dates by year
- To add years to date
- To get a series of dates by month
- To get a day from the date
- To add days to a specific date
- To get the first day of the month
Common Problem
Sometimes, we can face a problem that the result of the DAY function is not an integer value between 1 and 31, but it looks like a date. This problem can arise when the cell or column is formatted as a”Date” instead of “General.” We have to format the cell or column as “General.”
Errors
If we get any error from the DAY function, then it can be any one of the following:
- #NUM! – This error occurs in the DAY function when the supplied argument is a numeric value, but it is not recognized as a valid date.
- #VALUE! – This error occurs in the DAY function when the supplied argument is a text value and cannot be considered a valid date.
DAY Excel Function Video
Recommended Articles
This article has been a guide to the DAY Excel function. Here, we discuss the DAY formula in Excel and how to use it and examples, and a downloadable template. You may also look at these useful functions in Excel: –
- WEEKDAY Excel FunctionThe WEEKDAY function in excel returns the day corresponding to a specified date. The date is supplied as an argument to this function. read more
- TODAY Function in ExcelToday function is a date and time function that is used to find out the current system date and time in excel. This function does not take any arguments and auto-updates anytime the worksheet is reopened. This function just reflects the current system date, not the time.read more
- NOW In ExcelIn an excel worksheet, the NOW function is used to display the current system date and time. The syntax for using this function is quite simple =NOW ().read more
- TIME in ExcelTime is a time worksheet function in Excel that is used to calculate time based on the inputs provided by the user. The arguments can take the following formats: hours, minutes, and seconds.read more
- Recover Document in ExcelWhen an Excel document crashes unexpectedly while being worked on, certain amazing Excel workbook recovery techniques such as ‘Recover Unsaved Workbooks‘ and ‘Autosave‘ options come to the rescue of users.read more
Reader Interactions
Функция DAY (ДЕНЬ) используется в Excel, для того чтобы узнать порядковый номер дня месяца (в промежутке от 1 до 31) из любой даты.
Содержание
- Что функция возвращает
- Синтаксис
- Аргументы функции DAY (ДЕНЬ) в Excel
- Дополнительная информация
- Примеры использования функции DAY (ДЕНЬ) в Excel
- Пример №1. Получаем значение дня используя числовой аргумент
- Пример №2. Получаем значение дня из ячейки с датой
- Пример №3. Получаем значение дня текущей даты
- Пример №4. Получаем значение первого дня месяца
Что функция возвращает
Возвращает число в промежутке от 0 до 31, в зависимости от даты, из которой требуется извлечь данные. Например, возвращая данные для Февраля, формула вернет номер дня в промежутке от «0» до «29».
Синтаксис
=DAY(serial_number)
=ДЕНЬ(дата_в_числовом_формате)
Аргументы функции DAY (ДЕНЬ) в Excel
- serial_number (дата_в_числовом_формате): Это порядковый номер дня. Он может быть результатом вычисления формулы, ссылкой на ячейку, которая содержит дату или данные введенные вручную.
Дополнительная информация
Помимо введенных в ручную чисел, функция DAY (ДЕНЬ) также будет работать с:
- результатами вычислений;
- датой введенной в текстовом формате (в кавычках);
- датой, указанной в текстовом формате;
- Excel отразит любую дату начиная с 1 Января 1900 года на Windows и с 1904 года на Mac.
Примеры использования функции DAY (ДЕНЬ) в Excel
Пример №1. Получаем значение дня используя числовой аргумент
На примере выше в качестве аргумента мы используем число “42736”. Это порядковый номер даты “1 января 2017”. Так как 1 января это первый день месяца, то результатом вычисления будет “1”.
Пример №2. Получаем значение дня из ячейки с датой

На примере выше, функция принимает значение ячейки с конкретной датой и возвращает номер дня месяца этой даты. Обратите внимание, что если вы используете формат даты, который не распознается Excel, он покажет ошибку.
Пример №3. Получаем значение дня текущей даты
Вы можете легко получить текущее значение дня с помощью функции TODAY (СЕГОДНЯ) в качестве исходных данных. Функция TODAY (СЕГОДНЯ) возвращает текущую дату, а DAY (ДЕНЬ), в свою очередь, использует эти данные, чтобы вернуть порядковый номер дня этого месяца.
На примере выше, функция TODAY(СЕГОДНЯ) возвращает 12-02-2017. Функция DAY (ДЕНЬ) принимает значение функции TODAY (СЕГОДНЯ) как вводные данные и возвращает значение “12” как порядковый номер дня этого месяца.
Пример №4. Получаем значение первого дня месяца
Вы также можете вычислить значение первого дня любого месяца.
На примере выше, значение дня для даты в ячейке “A2” — “15-03-2017” равно “15”. Для того чтобы узнать номер первого дня месяца этой даты, нам нужно вычесть из нее значение дня (получим “0”, т.к. все даты хранятся в Excel как порядковые номера) и прибавить “1”, чтобы получить первый день месяца.
Обратите внимание, что даты в ячейках D2 и D3 отформатированы как даты. Может случиться так, что, когда вы используете эту формулу, вы можете получить серийный номер (например, “42795” за 1 марта 2017 года). Затем вы можете просто отформатировать его в качестве даты.
How to Use the DAY function in Excel
Get the day of a date in numeric form
What to Know
- Syntax for function: DAY(serial_number).
- Enter date in spreadsheet > select cell > select Formulas > Date & Time > DAY > Serial_number > choose cell.
- If not working, select date column > right-click and select Format Cells > Number tab > Number > OK.
This article explains how to use the DAY function in Microsoft Excel to return a date as a serial number using an integer between 1 and 31.
How to Use the DAY function in Excel
The syntax for the DAY function is DAY(serial_number).
The only argument for the DAY function is serial_number, which is required. This serial number field refers to the date of the day you are trying to find.
Dates are serial numbers in Excel’s internal system. Beginning with January 1, 1900 (which is number 1), each serial number is assigned in ascending numerical order. For example, January 1, 2008 is serial number 39448 because it is 39447 days after January 1, 1900.
Excel uses the serial number entered to determine which day of the month the date falls on. The day is returned as an integer ranging from 1 to 31.
-
Enter a date in an Excel spreadsheet using the DATE function. You can also use dates appearing as the result of other formulas or functions.
If dates are entered as text, the DAY function might not work as it should.
-
Select the cell where you want the day of the date to appear.
-
Select Formulas. In Excel Online, select the Insert Function button next to the formula bar to open the Insert Function dialog box.
-
Select Date & Time to open the Function drop-down list. In Excel Online, choose Date & Time in the Pick a Category list.
-
Select DAY in the list to bring up the function’s dialog box.
-
Make sure the Serial_number field is selected and then choose the cell containing the date you want to use.
-
Choose OK to apply the function and view the number representing the day of the date.
DAY Function Not Working
If your results are not appearing as numbers but rather as dates, it is likely a simple formatting issue. Problems could occur if the numbers are formatted as text rather than dates. Checking the format for the cells containing the serial number portion of the DAY function syntax (and then changing the format, if necessary) is the most likely way to resolve an error or incorrect result.
-
Select the column containing the dates.
-
Right-click anywhere on the selected cells and select Format Cells.
-
Make sure the Number tab is selected and choose Number in the Category list.
-
Select OK to apply the changes and close the dialog. Your results will appear as integers instead of dates.
When to Use the DAY Function in Excel
The DAY function is useful for financial analysis, primarily in a business setting. For instance, a retail organization might want to determine what day of the month has the highest number of customers or when most shipments arrive.
You can also extract a value using the DAY function inside of a larger formula. For instance, in this sample worksheet, the DAY function helps determine how many days are in the listed months.
The formula entered in cell G3 is
=DAY(EOMONTH(F3,0))
The DAY function provides the day component and EOMONTH (end of month) gives you the last day of the month for that date. The syntax for EOMONTH is EOMONTH(start_date, months). So the start date argument is the DAY entry and the number of months is 0, resulting in a list showing the number of days in the months presented.
Be careful not to confuse the DAY function with the DAYS function. The DAYS function, which uses the syntax DAYS(end_date, start_date) returns the number of days between a start date and an end date.
Thanks for letting us know!
Get the Latest Tech News Delivered Every Day
Subscribe
In this article, we will learn about the DAY function in Excel.
DAY function in Excel returns just the number from 1-31 corresponding to the date in the argument.
Syntax:
=DAY(date)
Note: Date should be a valid date
Let’s understand this function using the example shown below
Here we have dates. We will use the function on the below shown data set.
Use the Formula:
=DAY(A2)
Note: Date should be a valid date
As you can see in the above snapshot, we have a date as a number from the date.
Copy the formula in the remaining cells to get the new amount for the rest of the data.
Date(value) can be extracted using the above procedure
Hope you understood how to use the DAY function in Excel. Explore more articles on Mathematical formulation in Excel here. Mention your queries in the comment box below. We will help you with it.
Related Articles:
How to Use TODAY Function in Excel
How to use the Excel TIME function
How to use the NOW Function in Excel
How to use the WEEKDAY Function in Excel
How to use the MONTH Function in Excel
How to Use the YEAR Function in Excel
Popular Articles:
The VLOOKUP Function in Excel
COUNTIF in Excel 2016
How to Use SUMIF Function in Excel
Функция
ДЕНЬ()
, английский вариант DAY(),
возвращает день, соответствующий заданной дате. День определяется как целое число в диапазоне от 1 до 31.
Синтаксис функции
ДЕНЬ
(
дата
)
Дата
— дата, день которой необходимо найти.
Примеры
Используемая в качестве аргумента Дата должна быть в формате воспринимаемым EXCEL. Следующие формулы будут работать:
=ДЕНЬ(«28.02.2011») =ДЕНЬ(«28/02/2011») =ДЕНЬ(«28-02-2011») =ДЕНЬ(«28-фев-2011») =ДЕНЬ(«28-февраль-2011») =ДЕНЬ(«28 февраль 2011») =ДЕНЬ(«2011.02.28»)
=ДЕНЬ(40602)
В EXCEL даты хранятся в виде последовательности чисел (1, 2, 3, …), что позволяет выполнять над ними вычисления. По умолчанию день 1 января 1900 г. имеет номер 1, а 28 февраля 2011 г. — номер 40602, так как интервал между этими датами составляет 40 602 дня. О том как EXCEL хранит дату и время, читайте эту
статью
.
=ДЕНЬ(A1)
Если в ячейке
А1
введена дата в одном из вышеуказанных форматов, то формулой будет возвращен день (28).
Следующие формулы вернут ошибку #ЗНАЧ!
=ДЕНЬ(«28-февраля-2011») =ДЕНЬ(«28 02 2011»)
Использование с функцией
ДАТА()
Для того, чтобы прибавить к дате 28.02.2011, содержащейся в ячейке
А1
, например, 5 лет, можно использовать следующую формулу:
=ДАТА(ГОД(A1)+5;МЕСЯЦ(A1);ДЕНЬ(A1)).