Excel Method
This method is different than many you will see. Others use a loop to write each cell and write the cells with text data type.
This method creates an object array from a DataTable or DataGridView and then writes the array to Excel. This means I can write to Excel without a loop and retain data types.
I extracted this from my library and I think I changed it enough to work with this code only, but more minor tweaking might be necessary. If you get errors just let me know and I’ll correct them for you. Normally, I create an instance of my class and call these methods. If you would like to use my library then use this link to download it and if you need help just let me know.
https://zomp.co/Files.aspx?ID=zExcel
After copying the code to your solution you will use it like this.
In your button code add this and change the names to your controls.
WriteDataGrid("Sheet1", grid)
To open your file after exporting use this line
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("The location and filename of your file")
In the WriteArray method you’ll want to change the line that saves the workbook to where you want to save it. Probably makes sense to add this as a parameter.
wb.SaveAs("C:MyWorkbook.xlsx")
Public Function WriteArray(Sheet As String, ByRef ObjectArray As Object(,)) As String
Try
Dim xl As Excel.Application = New Excel.Application
Dim wb As Excel.Workbook = xl.Workbooks.Add()
Dim ws As Excel.Worksheet = wb.Worksheets.Add()
ws.Name = Sheet
Dim range As Excel.Range = ws.Range("A1").Resize(ObjectArray.GetLength(0), ObjectArray.GetLength(1))
range.Value = ObjectArray
range = ws.Range("A1").Resize(1, ObjectArray.GetLength(1) - 1)
range.Interior.Color = RGB(0, 70, 132) 'Con-way Blue
range.Font.Color = RGB(Drawing.Color.White.R, Drawing.Color.White.G, Drawing.Color.White.B)
range.Font.Bold = True
range.WrapText = True
range.HorizontalAlignment = Excel.XlHAlign.xlHAlignCenter
range.VerticalAlignment = Excel.XlVAlign.xlVAlignCenter
range.Application.ActiveWindow.SplitColumn = 0
range.Application.ActiveWindow.SplitRow = 1
range.Application.ActiveWindow.FreezePanes = True
wb.SaveAs("C:MyWorkbook.xlsx")
wb.CLose()
xl.Quit()
xl = Nothing
wb = Nothing
ws = Nothing
range = Nothing
ReleaseComObject(xl)
ReleaseComObject(wb)
ReleaseComObject(ws)
ReleaseComObject(range)
Return ""
Catch ex As Exception
Return "WriteArray()" & Environment.NewLine & Environment.NewLine & ex.Message
End Try
End Function
Public Function WriteDataGrid(SheetName As String, ByRef dt As DataGridView) As String
Try
Dim l(dt.Rows.Count + 1, dt.Columns.Count) As Object
For c As Integer = 0 To dt.Columns.Count - 1
l(0, c) = dt.Columns(c).HeaderText
Next
For r As Integer = 1 To dt.Rows.Count
For c As Integer = 0 To dt.Columns.Count - 1
l(r, c) = dt.Rows(r - 1).Cells(c)
Next
Next
Dim errors As String = WriteArray(SheetName, l)
If errors <> "" Then
Return errors
End If
Return ""
Catch ex As Exception
Return "WriteDataGrid()" & Environment.NewLine & Environment.NewLine & ex.Message
End Try
End Function
Public Function WriteDataTable(SheetName As String, ByRef dt As DataTable) As String
Try
Dim l(dt.Rows.Count + 1, dt.Columns.Count) As Object
For c As Integer = 0 To dt.Columns.Count - 1
l(0, c) = dt.Columns(c).ColumnName
Next
For r As Integer = 1 To dt.Rows.Count
For c As Integer = 0 To dt.Columns.Count - 1
l(r, c) = dt.Rows(r - 1).Item(c)
Next
Next
Dim errors As String = WriteArray(SheetName, l)
If errors <> "" Then
Return errors
End If
Return ""
Catch ex As Exception
Return "WriteDataTable()" & Environment.NewLine & Environment.NewLine & ex.Message
End Try
End Function
I actually don’t use this method in my Database program because it’s a slow method when you have a lot of rows/columns. I instead create a CSV from the DataGridView. Writing to Excel with Excel Automation is only useful if you need to format the data and cells otherwise you should use CSV. You can use the code after the image for CSV export.
CSV Method
Private Sub DataGridToCSV(ByRef dt As DataGridView, Qualifier As String)
Dim TempDirectory As String = "A temp Directory"
System.IO.Directory.CreateDirectory(TempDirectory)
Dim oWrite As System.IO.StreamWriter
Dim file As String = System.IO.Path.GetRandomFileName & ".csv"
oWrite = IO.File.CreateText(TempDirectory & "" & file)
Dim CSV As StringBuilder = New StringBuilder()
Dim i As Integer = 1
Dim CSVHeader As StringBuilder = New StringBuilder()
For Each c As DataGridViewColumn In dt.Columns
If i = 1 Then
CSVHeader.Append(Qualifier & c.HeaderText.ToString() & Qualifier)
Else
CSVHeader.Append("," & Qualifier & c.HeaderText.ToString() & Qualifier)
End If
i += 1
Next
'CSV.AppendLine(CSVHeader.ToString())
oWrite.WriteLine(CSVHeader.ToString())
oWrite.Flush()
For r As Integer = 0 To dt.Rows.Count - 1
Dim CSVLine As StringBuilder = New StringBuilder()
Dim s As String = ""
For c As Integer = 0 To dt.Columns.Count - 1
If c = 0 Then
'CSVLine.Append(Qualifier & gridResults.Rows(r).Cells(c).Value.ToString() & Qualifier)
s = s & Qualifier & gridResults.Rows(r).Cells(c).Value.ToString() & Qualifier
Else
'CSVLine.Append("," & Qualifier & gridResults.Rows(r).Cells(c).Value.ToString() & Qualifier)
s = s & "," & Qualifier & gridResults.Rows(r).Cells(c).Value.ToString() & Qualifier
End If
Next
oWrite.WriteLine(s)
oWrite.Flush()
'CSV.AppendLine(CSVLine.ToString())
'CSVLine.Clear()
Next
'oWrite.Write(CSV.ToString())
oWrite.Close()
oWrite = Nothing
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start(TempDirectory & "" & file)
GC.Collect()
End Sub
This tutorial is all about how to Export DataGridView Data to Excel in VB.Net. In this tutorial, you will expect that I will teach you everything you need to learn on how to Export DataGridView Data to excel using visual basic.net.
What is Visual Basic’s purpose?
The third-generation programming language was created to aid developers in the creation of Windows applications. It has a programming environment that allows programmers to write code in.exe or executable files. They can also utilize it to create in-house front-end solutions for interacting with huge databases. Because the language allows for continuing changes, you can keep coding and revising your work as needed.
However, there are some limits to the Microsoft Visual Basic download. If you want to make applications that take a long time to process, this software isn’t for you. That implies you won’t be able to use VB to create games or large apps because the system’s graphic interface requires a lot of memory and space. Furthermore, the language is limited to Microsoft and does not support other operating systems.
With this tutorial, it can answer the question raised in StackOverflow.
So let’s get started:
Steps How to Export DataGridView to Excel In VB.Net
Step 1: First, Open the Visual Basic, Select File on the menu, then click New and create a new project.
Step 2: Then a New Project Dialog will appear. You can rename your project, depending on what you like to name it. After that click OK.
Step 3: Design your form just like this one I’ve shown you below.
Drag a Datagridview and a Button from the toolbox.
Step 4: Add a reference to Microsoft Excel 12.0 Object Library, In the project menu click on Project – Add Reference – go to COM tab,
Add Microsoft Excel 12.0 Object Library
Step 5: After that, add the following references above the Public Class Form1 Line.
Imports System.Data.OleDb Imports Excel = Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel
Step 6: Then add these following declarations below the Public Class Form1 line.
Dim connString As String = "Provider=Microsoft.ACE.OLEDB.12.0; Data Source=C:UsersCliveDocumentsVisual Studio 2008clive projectsExportdatagridtoexcelExportdatagridtoexcelbinDebugtest.accdb" Dim excelLocation As String = "C:UsersCliveDocumentsVisual Studio 2008clive projectsExportdatagridtoexcelExportdatagridtoexcelbinDebugtest.xlsx" Dim Conn As OleDbConnection Dim da As OleDbDataAdapter Dim ds As DataSet Dim tables As DataTableCollection Dim source1 As New BindingSource Dim APP As New Excel.Application Dim worksheet As Excel.Worksheet Dim workbook As Excel.Workbook
Step 7: Add this code to the form load event.
Private Sub Form1_Load(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles MyBase.Load
workbook = APP.Workbooks.Open(excelLocation)
worksheet = workbook.Worksheets("sheet1")
Conn = New OleDbConnection
Conn.ConnectionString = connString
ds = New DataSet
tables = ds.Tables
da = New OleDbDataAdapter("Select * from [tblbio]", Conn)
da.Fill(ds, "tblbio")
Dim view As New DataView(tables(0))
source1.DataSource = view
DataGridView1.DataSource = view
DataGridView1.AllowUserToAddRows = False
Step 8: Next, add this code to the export button.
Private Sub Btnexport_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles Btnexport.Click Dim columnsCount As Integer = DataGridView1.Columns.Count For Each column In DataGridView1.Columns worksheet.Cells(1, column.Index + 1).Value = column.Name Next For i As Integer = 0 To DataGridView1.Rows.Count - 1 Dim columnIndex As Integer = 0 Do Until columnIndex = columnsCount worksheet.Cells(i + 2, columnIndex + 1).Value = DataGridView1.Item(columnIndex, i).Value.ToString columnIndex += 1 Loop Next End Sub
Step 9: Finally, add the following code to save the excel file when closing the form.
Private Sub Form1_FormClosed(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As System.Windows.Forms.FormClosedEventArgs) Handles Me.FormClosed workbook.Save() workbook.Close() APP.Quit() End Sub
Step 10: Click F5 to run your project.
Output:
If you have any questions or suggestions about Export DataGridView Data to Excel using VB.Net please contact me through our contact page.
Download Export DataGridView Data to Excel using VB.Net Source code Here
Readers might read also:
- How to Read an Excel file using Visual Basic.Net
- How to Make Media Player Using Visual Basic.Net
- How to Create an Image Slideshow Using VB.Net with Picturebox
I have an application which opens one of several excel templates, fills a datagrid view with
Excel Named Range data. Once the data is modified in the application I neet to save it to an excel spreadsheet. I currently have the following working:
1. This sub writes 2 columns of data (Ingredient) and (Result) from those named ranges and places them in the datagrid
Private Sub CboBoxTypeCofA_SelectedIndexChanged(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles CboBoxTypeCofA.SelectedIndexChanged
WorkbookTemplate =
«»
CofABook = «»
CboBoxTypeCofA.Visible = False
Select Case CboBoxTypeCofA.SelectedItem
Case Is = «Nothing»
GoTo Nextline
‘ Msgbox will go here to require change the jump to nextline is temporary
Case Is = «Flax Seed Oil»
CofABook = «D:Flaxseedcofa_08.xls»
‘ Sets the name of the cofa template worksheet should be on a network mapped drive.
WorkbookTemplate = «D:Flaxseedtemplate.xls»
Case Is = «PS Shakes»
CofABook = «D:PSshakescofa_08.xls»
‘ Sets the name of the cofa template worksheet should be on a network mapped drive.
WorkbookTemplate = «D:PSshakestemplate.xls»
Case Is = «Zone Shakes»
CofABook = «D:Zoneshakescofa_08.xls»
WorkbookTemplate = «D:zoneshakestemplate.xls»
End Select
NextLine:
‘ this code opens the template worksheet and writes the CofA results found named range to the datagrid for the user to update.
connect = New System.Data.OleDb.OleDbConnection(«provider=Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;» & «data source=» & WorkbookTemplate & «;Extended Properties=Excel 8.0;»)
adapter = New System.Data.OleDb.OleDbDataAdapter(«select * from [Ingredient]», connect)
connect.Open()
adapter.Fill(dataset)
Me.DataGridView1.DataSource = dataset.Tables(0)
adapter.Fill(dataset.Tables(0))
adapter = New System.Data.OleDb.OleDbDataAdapter(«select * from [Found]», connect)
adapter.Fill(dataset)
Me.DataGridView1.DataSource = dataset.Tables(0)
adapter.Fill(dataset.Tables(0))
connect.Close()
2. This code takes other named ranges (single data items) from the same workbook and places them in controls on the form for update.
oExcel = CreateObject(
«Excel.Application»)
‘ Create the template workbook object
oBook = oExcel.Workbooks.Open(WorkbookTemplate)
TxtProductName.Text = oBook.names(«Productname»).referstorange.value
TxtLotnum.Text = oBook.Names(«Lotnum»).RefersToRange.Value
TxtQtyShipped.Text = oBook.names(«Qtyshipped»).referstorange.value
OldYear = oBook.names(«Year»).referstorange.value
oExcel.workbooks.Close()
oExcel.Quit()
This code works and the only problem is that after running the code the excel application does not close.
Now I need to write the completed updates from the datagrid view and the other controls back into a workbook.
Ive been searching around but have not found the proper way to do this and how to kill the oexcel application in the code above.
Thanks
Wnewcomb
Exporting data from a DataGridView to Excel is a useful skill to have, whether you’re working with data analysis, reporting, or any other task that involves manipulating large amounts of data. In this tutorial, we’ll walk you through the steps of exporting data from a DataGridView to Excel using VB.NET.
Prerequisites
Before we begin, you’ll need to have the following tools and software installed on your computer:
- Visual Studio
- Microsoft Excel
A DataGridView is a visual control for displaying data in a tabular format. It’s a common component of many Windows Forms applications, and it’s useful for displaying and editing large amounts of data.
Setting up the DataGridView
- Open Visual Studio and create a new Windows Forms project.
- Drag a DataGridView control onto your form from the Toolbox.
- Populate the DataGridView with data. You can do this by connecting to a database, loading a CSV file, or using any other method that suits your needs.
Exporting the DataGridView to Excel
To export the DataGridView to Excel, we’ll need to use the Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel library. This library provides us with the necessary objects and methods for working with Excel files in VB.NET.
- In your project, go to the Solution Explorer and right-click on “References.”
- Select “Add Reference” and browse to the location of the Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel library on your computer.
- Import the library by adding the following line to the top of your code file:
Imports Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel - Declare the following objects:
Dim xlApp As Excel.Application
Dim xlWorkbook As Excel.Workbook
Dim xlWorksheet As Excel.Worksheet
Dim xlRange As Excel.Range- Initialize the objects by adding the following code:
xlApp = New Excel.Application
xlWorkbook = xlApp.Workbooks.Add
xlWorksheet = xlWorkbook.Worksheets(1)
xlRange = xlWorksheet.Range("A1")- Iterate through the rows and columns of the DataGridView, and copy the data into the Excel worksheet. You can do this using a loop like this:
For i As Integer = 0 To dataGridView1.ColumnCount - 1
For j As Integer = 0 To dataGridView1.RowCount - 1
xlRange.Cells(j + 1, i + 1) = dataGridView1(i, j).Value.ToString()
Next
Next- Save the Excel workbook and close the objects by adding the following code:
xlWorkbook.SaveAs("C:pathtoyourfile.xlsx")
xlWorkbook.Close()
xlApp.Quit()Advanced Features
You can add some advanced features to the export process to make your Excel worksheet more useful and visually appealing. Here are a few ideas:
- Format the Excel worksheet with colors, fonts, and other formatting options
- Use the
AutoFit()method to automatically adjust the column widths to fit the data - Add charts or graphs to the worksheet to visualize the data in a more intuitive way
Conclusion
Exporting data from a DataGridView to Excel is a useful skill to have in your toolkit. By using the Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel library and following the steps outlined in this tutorial, you can easily copy data from a DataGridView into an Excel worksheet.
I hope you found this tutorial helpful! For more information on working with Excel and VB.NET, check out the following resources:
- Microsoft’s documentation on the Excel interop library: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/dotnet/api/microsoft.office.interop.excel?view=excel-pia
- A tutorial on creating charts in Excel with VB.NET: https://www.c-sharpcorner.com/article/creating-charts-in-excel-using-vb-net/
-
KC Spectra is a dynamic and versatile author with a passion for storytelling. With a background in literature and creative writing, KC has a talent for crafting compelling characters and immersive worlds. Whether writing science fiction, fantasy, or contemporary fiction, KC brings a unique voice and fresh perspective to every project.
View all posts
In this article I will explain with an example, how to export DataGridView data to Excel file with formatting i.e. Colors and Styles in Windows Forms (WinForms) Applications using C# and VB.Net.
DataGridView cannot be exported directly to Excel file and hence need to generate a DataTable and export the DataTable to Excel file.
The DataTable will be exported to a formatted Excel file using ClosedXml library which is a wrapper of OpenXml.
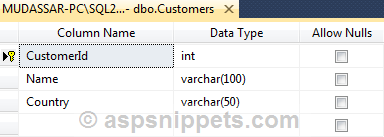
Database
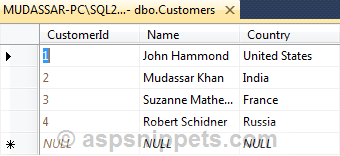
I have made use of the following table Customers with the schema as follows.
I have already inserted few records in the table.
Note: You can download the database table SQL by clicking the download link below.
Download DocumentFormat.OpenXml and ClosedXml Libraries
You can download the libraries using the following download locations.
Note: The DLL files of both OpenXml and ClosedXml are present in the attached sample.
Form Controls
I have added a DataGridView and a Button to the Windows Form.
Namespaces
You will need to import the following namespaces.
C#
using System.IO;
using System.Data;
using ClosedXML.Excel;
using System.Data.SqlClient;
VB.Net
Imports System.IO
Imports System.Data
Imports ClosedXML.Excel
Imports System.Data.SqlClient
Populating DataGridView
Inside the Form Load event, the DataGridView is populated with records from Customers table.
C#
private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
this.BindDataGridView();
}
private void BindDataGridView()
{
string constring = @»Data Source=.SQL2014;Initial Catalog=AjaxSamples;Integrated Security=true»;
using (SqlConnection con = new SqlConnection(constring))
{
using (SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand(«SELECT * FROM Customers», con))
{
cmd.CommandType = CommandType.Text;
using (SqlDataAdapter sda = new SqlDataAdapter(cmd))
{
using (DataTable dt = new DataTable())
{
sda.Fill(dt);
dataGridView1.DataSource = dt;
}
}
}
}
}
VB.Net
Private Sub Form1_Load(sender As System.Object, e As System.EventArgs) Handles MyBase.Load
Me.BindDataGridView()
End Sub
Private Sub BindDataGridView()
Dim constring As String = «Data Source=.SQL2014;Initial Catalog=AjaxSamples;Integrated Security=true»
Using con As New SqlConnection(constring)
Using cmd As New SqlCommand(«SELECT * FROM Customers», con)
cmd.CommandType = CommandType.Text
Using sda As New SqlDataAdapter(cmd)
Using dt As New DataTable()
sda.Fill(dt)
dataGridView1.DataSource = dt
End Using
End Using
End Using
End Using
End Sub
Exporting DataGridView data to Excel with formatting
Inside the Button Click event handler, first a DataTable is created with columns same as that of the DataGridView and a loop is executed over the DataGridView rows and all the data is added to the DataTable.
Then a Workbook object is created to which the DataTable is added as Worksheet using the Add method which accepts DataTable and the name of the Sheet as parameters.
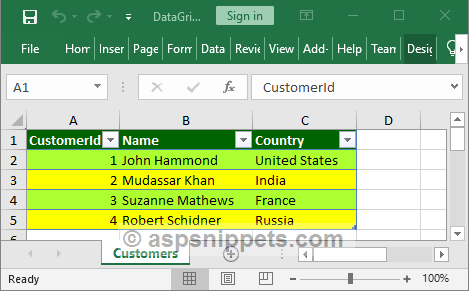
Once the DataTable is added as a Worksheet to the Workbook, the formatting is done by first setting the Header row background color and then applying background colors to the rows and the alternating rows of the Excel file.
Finally the WorkBook is saved to the specified location on the disk.
C#
private void btnExportExcel_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
//Creating DataTable.
DataTable dt = new DataTable();
//Adding the Columns.
foreach (DataGridViewColumn column in dataGridView1.Columns)
{
dt.Columns.Add(column.HeaderText, column.ValueType);
}
//Adding the Rows.
foreach (DataGridViewRow row in dataGridView1.Rows)
{
dt.Rows.Add();
foreach (DataGridViewCell cell in row.Cells)
{
dt.Rows[dt.Rows.Count — 1][cell.ColumnIndex] = cell.Value.ToString();
}
}
//Exporting to Excel.
string folderPath = «C:\Excel\»;
if (!Directory.Exists(folderPath))
{
Directory.CreateDirectory(folderPath);
}
using (XLWorkbook wb = new XLWorkbook())
{
wb.Worksheets.Add(dt, «Customers»);
//Set the color of Header Row.
//A resembles First Column while C resembles Third column.
wb.Worksheet(1).Cells(«A1:C1»).Style.Fill.BackgroundColor = XLColor.DarkGreen;
for (int i = 1; i <= dt.Rows.Count; i++)
{
//A resembles First Column while C resembles Third column.
//Header row is at Position 1 and hence First row starts from Index 2.
string cellRange = string.Format(«A{0}:C{0}», i + 1);
if (i % 2 != 0)
{
wb.Worksheet(1).Cells(cellRange).Style.Fill.BackgroundColor = XLColor.GreenYellow;
}
else
{
wb.Worksheet(1).Cells(cellRange).Style.Fill.BackgroundColor = XLColor.Yellow;
}
}
//Adjust widths of Columns.
wb.Worksheet(1).Columns().AdjustToContents();
//Save the Excel file.
wb.SaveAs(folderPath + «DataGridViewExport.xlsx»);
}
}
VB.Net
Private Sub btnExportExcel_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles btnExportExcel.Click
‘Creating DataTable.
Dim dt As New DataTable()
‘Adding the Columns.
For Each column As DataGridViewColumn In dataGridView1.Columns
dt.Columns.Add(column.HeaderText, column.ValueType)
Next
‘Adding the Rows.
For Each row As DataGridViewRow In dataGridView1.Rows
dt.Rows.Add()
For Each cell As DataGridViewCell In row.Cells
dt.Rows(dt.Rows.Count — 1)(cell.ColumnIndex) = cell.Value.ToString()
Next
Next
‘Exporting to Excel.
Dim folderPath As String = «C:Excel»
If Not Directory.Exists(folderPath) Then
Directory.CreateDirectory(folderPath)
End If
Using wb As New XLWorkbook()
wb.Worksheets.Add(dt, «Customers»)
‘Set the color of Header Row.
‘A resembles First Column while C resembles Third column.
wb.Worksheet(1).Cells(«A1:C1»).Style.Fill.BackgroundColor = XLColor.DarkGreen
For i As Integer = 1 To dt.Rows.Count
‘A resembles First Column while C resembles Third column.
‘Header row is at Position 1 and hence First row starts from Index 2.
Dim cellRange As String = String.Format(«A{0}:C{0}», i + 1)
If i Mod 2 <> 0 Then
wb.Worksheet(1).Cells(cellRange).Style.Fill.BackgroundColor = XLColor.GreenYellow
Else
wb.Worksheet(1).Cells(cellRange).Style.Fill.BackgroundColor = XLColor.Yellow
End If
Next
‘Adjust widths of Columns.
wb.Worksheet(1).Columns().AdjustToContents()
‘Save the Excel file.
wb.SaveAs(folderPath & «DataGridViewExport.xlsx»)
End Using
End Sub
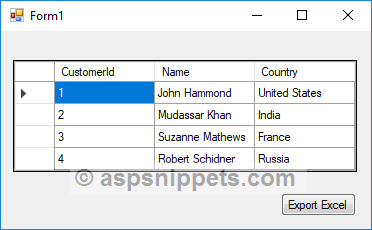
Screenshot
Downloads