Asked by: Samson Bogisich I
Score: 4.8/5
(36 votes)
Every spreadsheet in your Excel file will turn into a separate page in your PDF document. PDF is a static format, which means it doesn’t have any mathematic formulas. That’s why, when you convert from Excel to PDF, your Excel formulas will not be carried over into PDF.
How do you save an Excel file as a PDF with formulas?
How to Convert Excel Formulas to PDF
- Load the Excel worksheet containing the formulas you want to save in PDF format.
- Hit «Ctrl» + «~» to display the formulas in each cell (as opposed to the results of the formulas).
- Go to «File» then «Save As.»
- Enter a filename and choose «Portable Document Format *.
How do I put formulas into a PDF?
Select the Total Price box, go to Text Box Properties > Calculate, and select the third option. You’ll be able to input a formula into a text box by clicking the Edit button. For simple arithmetic computations, this formula box works very similarly to an Excel formula box.
How do I convert Excel to PDF and keep formatting?
Use a PDF tool to convert Excel sheets.
Open from any web browser and simply follow the steps below: Click Select A File and drag and drop your Excel sheet, or select the file and upload. Watch as Acrobat online services convert your Excel sheet to PDF automatically. Download the converted file as a PDF.
Can PDF pull data from Excel?
Yes, but you there are two things you need to do in Excel for this to work: The columns need to be named the same way as the field names in the PDF form. … This will fill the PDF form with the selected values: You do this for every record you have in your Excel file and save the PDF file to a new name.
38 related questions found
How do I extract data from a PDF table?
How to Extract table from PDF with Adobe Acrobat Pro DC
- Step 1: Open the PDF file.
- Step 2: Locate the table from which you want to extract data and drag a selection over the table as shown below.
- Step 3: Right-click and select “Export Selection As…”
- Step 4: Choose the export type.
- Step 1: Open the file with Adobe Reader.
How can I convert PDF to Excel for free?
Follow these easy steps to turn a PDF document into a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet: Click the Select a file button above or drag and drop a PDF into the drop zone. Select the PDF you want to convert to the XLSX file format. Watch Acrobat automatically convert the file to the Excel file format.
How do I save an Excel graph as a PDF?
With just the chart selected, go to File>Save As and select ‘PDF’ from the ‘Save as type’ dropdown. Name the file and click Save. The chart will be exported to a PDF file. You can export multiple charts from Excel to a single PDF file but you must take care to arrange them in the correct order in Excel first.
What is tic tie calculate?
TicTie Calculate helps tax and accounting offices create annotated workpapers directly from PDF documents — without the paper.
How do I calculate time in a PDF?
To answer your question: Time calculations require a script. There’s no built-in method in Acrobat to do it. You have to parse the in and out times as Date objects and then deduct one from the other to get the time difference between them.
How do you create a fillable PDF?
How to create fillable PDF files:
- Open Acrobat: Click the “Tools” tab and select “Prepare Form.”
- Select a file or scan a document: Acrobat will automatically analyse your document and add form fields.
- Add new form fields: Use the top toolbar and adjust the layout using tools in the right pane.
- Save your fillable PDF:
How do I insert an Excel file into Adobe?
Open the PDF file, on the left side, look for attachment icon, click on it and you will be able to open the Excel file embedded. You may also refer to Links and attachments in PDFs, Adobe Acrobat Let us know how it goes.
How do you create a dropdown list in Excel?
Create a drop-down list
- Select the cells that you want to contain the lists.
- On the ribbon, click DATA > Data Validation.
- In the dialog, set Allow to List.
- Click in Source, type the text or numbers (separated by commas, for a comma-delimited list) that you want in your drop-down list, and click OK.
How do you create a fillable form that will populate an Excel spreadsheet?
Below are the steps to create a new entry using the Data Entry Form in Excel:
- Select any cell in the Excel Table.
- Click on the Form icon in the Quick Access Toolbar.
- Enter the data in the form fields.
- Hit the Enter key (or click the New button) to enter the record in the table and get a blank form for next record.
How do you do a tick and tie in accounting?
It refers the action an accountant performs when he agrees one financial statement number to another.
…
Tic and Tie Examples
- Total assets equals total liabilities and equity (the balance sheet includes each of these)
- Net income on the income statement should agree with net income on the statement of changes in equity.
How do I download tic tie to Adobe?
You can download the software directly from our website, www.safesend.com/downloads/.
…
Installing and Activating TicTie & Calculate (TTC)
- If not already completed, Ensure Adobe Acrobat is closed before running the installer.
- Run the installer.
- Follow the onscreen instructions.
- Complete the download.
- Open Adobe Acrobat.
What is TicTie?
Tic, Tie & Calculate (TTC) is an Adobe Acrobat plug-in specifically designed for an accountant. It installs an accounting centric toolbar in Acrobat that allows you to organize and annotate digital . PDF files the same way an accountant would in the paper World.
How do I save an Excel table as an image?
Create a picture from cells, a chart, or an object in Excel
- Select the cells, or click the chart or object that you want to copy as a picture.
- On the Home tab, in the Clipboard group, click the arrow next to Copy, then click Copy as Picture.
- In the Copy Picture dialog box, do the following: …
- Click OK.
How do I save an Excel chart as an image?
Click the chart that you want to save as a picture. Choose Copy from the ribbon, or press CTRL+C on your keyboard . Switch to the application you want to copy the chart to. If you’re saving as a separate image file open your favorite graphics editor, such as Microsoft Paint.
How do I convert all columns to PDF in Excel?
Open an Excel workbook, switch to the File tab, click Print, and select Foxit Reader PDF Printer in the list of printers. Configure the settings. Under the Settings section, you have the following choices: Convert an active sheet, entire workbook or selection to PDF.
How do I convert a PDF to Excel in Adobe Reader?
Open a PDF file in Acrobat DC.
- Open a PDF file in Acrobat DC.
- Click the “Export PDF” tool in the right pane.
- Choose “spreadsheet” as your export format and then select “Microsoft Excel Workbook.”
- Click “Export.” If your PDF documents contain scanned text, Acrobat will run text recognition automatically.
How do I convert a PDF to Excel spreadsheet?
Convert PDF to Excel offline
- Open the PDF file in Adobe Acrobat DC.
- Go to Tools > click on Export PDF.
- Click on Convert to and choose Spreadsheet as your export format.
- Next, click on Export to save the new file in Excel format.
How do you use Vlookup function in Excel?
- In the Formula Bar, type =VLOOKUP().
- In the parentheses, enter your lookup value, followed by a comma. …
- Enter your table array or lookup table, the range of data you want to search, and a comma: (H2,B3:F25,
- Enter column index number. …
- Enter the range lookup value, either TRUE or FALSE.
How do I enable data from a PDF in Excel?
Import Data from a PDF to Excel Steps
- Step 1: Get Data from PDF — It’s as easy as going to the Data tab of the ribbon > Get Data > From File > From PDF:
- Step 2: Locate the PDF File you want to import to Excel — Browse to the location the PDF is saved > click Import:
How do I extract data from a PDF in R?
How to Extract and Clean Data From PDF Files in R
- Why PDF files?
- Two techniques to extract raw text from PDF files. Use pdftools::pdf_text. Use the tm package.
- Extract the right information. Clean the headers and footers on all pages. Get the two columns together. Find the rows of the speakers.
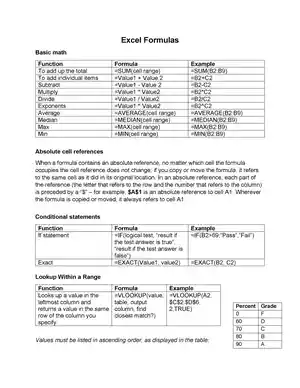
What do you understand about the Advanced Excel Formulas and Basic Excel Functions?
This Blog will give you the Excel formulas PDF/list of the Key Functions of Excel. Excel Formulas PDF is a list of the most useful or extensively used excel formulas in day-to-day working life with Excel. These formulas, we can use in Excel 2013. 2016 as well as 2019.
PDF GUIDE BOOKS
- Download Excel Shortcuts for Windows & Mac
- Basic to Advanced Excel Formulas PDF Guide
This Book will help you to get Excel Skills & Boost your career.
The Excel Functions covered here are: VLOOKUP, INDEX, MATCH, RANK, AVERAGE, SMALL, LARGE, LOOKUP, ROUND, COUNTIFS, SUMIFS, FIND, DATE, and many more. Let’s dive right in…
Compatibility Excel Formulas & Functions
|
Functions |
Excel Formulas |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
CONCATENATE |
=CONCATENATE(text1,text2,…) |
Joins several text items into one text item. Easier to use ‘&’ instead of the function usually. |
|
FLOOR |
=FLOOR(number,significance) |
Rounds a number down, toward zero |
|
BINOMDIST |
=BINOMDIST(number_s,trials,probability_s,cumulative) |
Returns the individual term binomial distribution probability |
|
CHIDIST |
=CHIDIST(x,deg_freedom) |
Returns the one-tailed probability of the chi-squared distribution |
|
CHIINV |
=CHITEST(actual_range,expected_range) |
Returns the test for independence |
|
CONFIDENCE |
=CONFIDENCE(alpha,standard_dev,size) |
Returns the confidence interval for a population mean |
|
FTEST |
=FTEST(array1,array2) |
|
|
LOGINV |
=LOGINV(probability,mean,standard_dev) |
Returns the inverse of the lognormal cumulative distribution |
|
LOGNORMDIST |
=LOGNORMDIST(x,mean,standard_dev) |
Returns the cumulative lognormal distribution |
|
MODE |
=MODE(number1,number2,…) |
Returns the most common value in a data set |
|
NORMDIST |
=NORMDIST(x,mean,standard_dev,cumulative) |
Returns the normal cumulative distribution |
|
NORMINV |
=NORMINV(probability,mean,standard_dev) |
Returns the inverse of the normal cumulative distribution |
|
NORMSDIST |
=NORMSDIST(z) |
Returns the standard normal cumulative distribution |
|
NORMSINV |
=NORMSINV(probability) |
Returns the inverse of the standard normal cumulative distribution |
|
PERCENTILE |
=PERCENTILE(array,k) |
Returns the k-th percentile of values in a range |
|
PERCENTRANK |
=PERCENTRANK(array,x,significance) |
Returns the percentage rank of a value in a data set |
|
POISSON |
=POISSON(x,mean,cumulative) |
Returns the Poisson distribution |
|
QUARTILE |
=QUARTILE(array,quart) |
Returns the quartile of a data set |
|
RANK |
=RANK(number,ref,order) |
Returns the rank of a number in a list of numbers |
|
STDEV |
=STDEV(number1,number2,…) |
Estimates standard deviation based on a sample |
|
STDEVP |
=STDEVP(number1,number2,…) |
Calculates standard deviation based on the entire population |
|
TDIST |
=TDIST(x,deg_freedom,tails) |
Returns the Student’s t-distribution |
|
TINV |
=TINV(probability,deg_freedom) |
Returns the inverse of the Student’s t-distribution |
|
VAR |
=VAR(number1,number2,…) |
Estimates variance based on a sample |
|
VARP |
=VARP(number1,number2,…) |
Calculates variance based on the entire population |
|
FINV |
=FINV(probability,deg_freedom1,deg_freedom2) |
Returns the inverse of the F probability distribution |
|
FORECAST |
=FORECAST(x,known_y’s,known_x’s) |
Returns a value along a linear trend |
|
BETADIST |
=BETADIST(x,alpha,beta,A,B) |
Returns the beta cumulative distribution function |
|
BETAINV |
=BETAINV(probability,alpha,beta,A,B) |
Returns the inverse of the cumulative distribution function for a specified beta distribution |
|
COVAR |
=COVAR(array1,array2) |
Returns covariance, the average of the products of paired deviations |
|
CRITBINOM |
=CRITBINOM(trials,probability_s,alpha) |
Returns the smallest value for which the cumulative binomial distribution is less than or equal to a criterion value |
|
EXPONDIST |
=EXPONDIST(x,lambda,cumulative) |
Returns the exponential distribution |
|
POISSON |
=POISSON(x,mean,cumulative) |
Returns the Poisson distribution |
|
FDIST |
=FDIST(x,deg_freedom1,deg_freedom2) |
Returns the F probability distribution |
|
GAMMADIST |
=GAMMADIST(x,alpha,beta,cumulative) |
Returns the gamma distribution |
|
GAMMAINV |
=GAMMAINV(probability,alpha,beta) |
Returns the inverse of the gamma cumulative distribution |
|
HYPGEOMDIST |
=HYPGEOMDIST(sample_s,number_sample,population_s,number_pop) |
Returns the hypergeometric distribution |
|
NEGBINOMDIST |
=NEGBINOMDIST(number_f,number_s,probability_s) |
Returns the negative binomial distribution |
|
TTEST |
=TTEST(array1,array2,tails,type) |
Returns the probability associated with a Student’s t-test |
|
WEIBULL |
=WEIBULL(x,alpha,beta,cumulative) |
Calculates variance based on the entire population, including numbers, text, and logical values |
|
ZTEST |
=ZTEST(array,x,sigma) |
Returns the one-tailed probability-value of a z-test |
PDF GUIDE BOOKS
- Download Excel Shortcuts for Windows & Mac
- Basic to Advanced Excel Formulas PDF Guide
This Book will help you to get Excel Skills & Boost your career.
Cube Excel Formulas & Functions
|
Functions |
Excel Formulas |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
CUBEKPIMEMBER |
=CUBEKPIMEMBER(connection,kpi_name,kpi_property,caption) |
Returns a key performance indicator (KPI) name, property, and measure, and displays the name and property in the cell. A KPI is a quantifiable measurement, such as monthly gross profit or quarterly employee turnover, used to monitor an organization’s performance. |
|
CUBEMEMBER |
=CUBEMEMBER(connection,member_expression,caption) |
Returns a member or tuple in a cube hierarchy. Use to validate that the member or tuple exists in the cube. |
|
CUBEMEMBERPROPERTY |
=CUBEMEMBERPROPERTY(connection,member_expression,property) |
Returns the value of a member property in the cube. Use to validate that a member name exists within the cube and to return the specified property for this member. |
|
CUBERANKEDMEMBER |
=CUBERANKEDMEMBER(connection,set_expression,rank,caption) |
Returns the nth, or ranked, member in a set. Use to return one or more elements in a set, such as the top sales performer or top 10 students. |
|
CUBESET |
=CUBESET(connection,set_expression,caption,sort_order,sort_by) |
Defines a calculated set of members or tuples by sending a set expression to the cube on the server, which creates the set, and then returns that set to Microsoft Office Excel. |
|
CUBESETCOUNT |
=CUBESETCOUNT(set) |
Returns the number of items in a set. |
|
CUBEVALUE |
=CUBEVALUE(connection,member_expression1,…) |
Returns an aggregated value from a cube |
Database Excel Formulas & Functions
|
Functions |
Excel Formulas |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
DGET |
=DGET(database,field,criteria) |
Extracts from a database a single record that matches the specified criteria |
|
DSUM |
=DSUM(database,field,criteria) |
Adds the numbers in the field column of records in the database that match the criteria |
|
DAVERAGE |
=DAVERAGE(database,field,criteria) |
Returns the average of selected database entries |
|
DCOUNT |
=DCOUNT(database,field,criteria) |
Counts the cells that contain numbers in a database |
|
DCOUNTA |
=DCOUNTA(database,field,criteria) |
Counts nonblank cells in a database |
|
DMAX |
=DMAX(database,field,criteria) |
Returns the maximum value from selected database entries |
|
DMIN |
=DMIN(database,field,criteria) |
Returns the minimum value from selected database entries |
|
DPRODUCT |
=DPRODUCT(database,field,criteria) |
Multiplies the values in a particular field of records that match the criteria in a database |
|
DSTDEV |
=DSTDEV(database,field,criteria) |
Estimates the standard deviation based on a sample of selected database entries |
|
DSTDEVP |
=DSTDEVP(database,field,criteria) |
Calculates the standard deviation based on the entire population of selected database entries |
|
DVAR |
=DVAR(database,field,criteria) |
Estimates variance based on a sample from selected database entries |
|
DVARP |
=DVARP(database,field,criteria) |
Calculates variance based on the entire population of selected database entries |
Date & Time Excel Formulas & Functions
|
Functions |
Excel Formulas |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
DATE |
=DATE(year,month,day) |
Returns the serial number of a particular date |
|
DATEVALUE |
=DATEVALUE(date_text) |
Converts a date in the form of text to a serial number |
|
DAY |
=DAY(serial_number) |
Converts a serial number to a day of the month |
|
HOUR |
=HOUR(serial_number) |
Converts a serial number to an hour |
|
MINUTE |
=MINUTE(serial_number) |
Converts a serial number to a minute |
|
MONTH |
=MONTH(serial_number) |
Converts a serial number to a month |
|
NOW |
=NOW() |
Returns the serial number of the current date and time |
|
SECOND |
=SECOND(serial_number) |
Converts a serial number to a second |
|
TIME |
=TIME(hour,minute,second) |
Returns the serial number of a particular time |
|
TIMEVALUE |
=TIMEVALUE(time_text) |
Converts a time in the form of text to a serial number |
|
TODAY |
=TODAY() |
Returns the serial number of today’s date |
|
YEAR |
=YEAR(serial_number) |
Converts a serial number to a year |
|
DAYS360 |
=DAYS360(start_date,end_date,method) |
Calculates the number of days between two dates based on a 360-day year |
|
EDATE |
=EDATE(start_date,months) |
Returns the serial number of the date that is the indicated number of months before or after the start date |
|
EOMONTH |
=EOMONTH(start_date,months) |
Returns the serial number of the last day of the month before or after a specified number of months |
|
NETWORKDAYS |
=NETWORKDAYS(start_date,end_date,[holidays]) |
Returns the number of whole workdays between two dates |
|
NETWORKDAYS.INTL |
=NETWORKDAYS.INTL(start_date,end_date,[weekend],[holidays]) |
Returns the number of whole workdays between two dates using parameters to indicate which and how many days are weekend days |
|
WEEKDAY |
=WEEKDAY(serial_number,[return_type]) |
Converts a serial number to a day of the week |
|
WEEKNUM |
=WEEKNUM(serial_number,[return_type]) |
Converts a serial number to a number representing where the week falls numerically with a year |
|
WORKDAY |
=WORKDAY(start_date, days, [holidays]) |
Returns the serial number of the date before or after a specified number of workdays |
|
WORKDAY.INTL |
=WORKDAY.INTL(start_date,days,weekend,holidays) |
Returns the serial number of the date before or after a specified number of workdays using parameters to indicate which and how many days are weekend days |
|
YEARFRAC |
=YEARFRAC(start_date,end_date,basis) |
Returns the year fraction representing the number of whole days between start_date and end_date |
PDF GUIDE BOOKS
- Download Excel Shortcuts for Windows & Mac
- Basic to Advanced Excel Formulas PDF Guide
This Book will help you to get Excel Skills & Boost your career.
Information Excel Formulas & Functions
|
Functions |
Excel Formulas |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
CELL |
=CELL(info_type, [reference]) |
Returns information about the formatting, location, or contents of a cell |
|
ISBLANK |
=ISBLANK(value) |
Returns TRUE if the value is blank |
|
ISERROR |
=ISERROR(value) |
Returns TRUE if the value is any error value |
|
ISNONTEXT |
=ISNONTEXT(value) |
Returns TRUE if the value is not text |
|
ISNUMBER |
=ISNUMBER(value) |
Returns TRUE if the value is a number |
|
ISTEXT |
=ISTEXT(value) |
Returns TRUE if the value is text |
|
ERROR.TYPE |
=ERROR.TYPE(error_val) |
Returns a number corresponding to an error type |
|
INFO |
=INFO(type_text) |
Returns information about the current operating environment |
|
ISERR |
=ISERR(value) |
Returns TRUE if the value is any error value except #N/A |
|
ISEVEN |
=ISEVEN(number) |
Returns TRUE if the number is even |
|
ISLOGICAL |
=ISLOGICAL(value) |
Returns TRUE if the value is a logical value |
|
ISNA |
=ISNA(value) |
Returns TRUE if the value is the #N/A error value |
|
ISODD |
=ISODD(number) |
Returns TRUE if the number is odd |
|
ISREF |
=ISREF(value) |
Returns TRUE if the value is a reference |
|
N |
=N(value) |
Returns a value converted to a number |
|
NA |
=NA() |
Returns the error value #N/A |
|
TYPE |
=TYPE(value) |
Returns a number indicating the data type of a value |
Logical Excel Formulas & Functions
|
Functions |
Excel Formulas |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
AND |
=AND(logical1,logical2,…) |
Returns TRUE if all of its arguments are TRUE |
|
FALSE |
=FALSE |
Returns the logical value FALSE |
|
IF |
=IF(logical_test, [value_if_true], [value_if_false]) |
Specifies a logical test to perform |
|
IFERROR |
=IFERROR(value, value_if_error) |
Returns a value you specify if a formula evaluates to an error; otherwise, returns the result of the formula |
|
NOT |
=NOT(logical) |
Reverses the logic of its argument |
|
OR |
=OR(logical1,logical2,…) |
Returns TRUE if any argument is TRUE |
|
TRUE |
=TRUE |
Returns the logical value TRUE |
|
LOOKUP |
=LOOKUP(lookup_value, array)– 2 types |
Looks up values in a vector or array |
Lookup & Reference Excel Formulas
|
Functions |
Excel Formulas |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
ADDRESS |
=ADDRESS(row_num, column_num, [abs_num], [a1], [sheet_text]) |
Returns a reference as text to a single cell in a worksheet |
|
COLUMN |
=COLUMN([reference]) |
Returns the column number of a reference |
|
COLUMNS |
=COLUMNS(array) |
Returns the number of columns in a reference |
|
HLOOKUP |
=HLOOKUP(lookup_value,table_array,row_index_num,[range_lookup]) |
Looks in the top row of an array and returns the value of the indicated cell |
|
INDEX |
=INDEX(array,row_num,[column_num])– 2 types |
Uses an index to choose a value from a reference or array |
|
INDIRECT |
=INDIRECT(ref_text,a1) |
Returns a reference indicated by a text value |
|
MATCH |
=MATCH(lookup_value,lookup_array,match_type) |
Looks up values in a reference or array |
|
OFFSET |
=OFFSET(reference,rows,cols,height,width) |
Returns a reference offset from a given reference |
|
ROW |
=ROW([reference]) |
Returns the row number of a reference |
|
ROWS |
=ROWS(array) |
Returns the number of rows in a reference |
|
VLOOKUP |
=VLOOKUP(lookup_value,table_array,col_index_num,[range_lookup]) |
Looks in the first column of an array and moves across the row to return the value of a cell |
|
CHOOSE |
=CHOOSE(index_num,value1,value2,…) |
Chooses a value from a list of values |
|
GETPIVOTDATA |
=GETPIVOTDATA(data_field,pivot_table,field,item,…) |
Returns data stored in a PivotTable report |
|
HYPERLINK |
=HYPERLINK(link_location,friendly_name) |
Creates a shortcut or jump that opens a document stored on a network server, an intranet, or the Internet |
|
TRANSPOSE |
=TRANSPOSE(array) |
Returns the transpose of an array |
|
AREAS |
=AREAS(reference) |
Returns the number of areas in a reference |
Text Excel Formulas & Functions
|
Functions |
Excel Formulas |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
EXACT |
=EXACT(text1,text2) |
Checks to see if two text values are identical |
|
LOWER |
=LOWER(text) |
Converts text to lowercase |
|
PROPER |
=PROPER(text) |
Capitalizes the first letter in each word of a text value |
|
TRIM |
=TRIM(text) |
Removes spaces from text |
|
UPPER |
=UPPER(text) |
Converts text to uppercase |
|
CHAR |
=CHAR(number) |
Returns the character specified by the code number |
|
CLEAN |
=CLEAN(text) |
Removes all nonprintable characters from text |
|
CODE |
=CODE(text) |
Returns a numeric code for the first character in a text string |
|
DOLLAR |
=DOLLAR(number,decimals) |
Converts a number to text, using the $ (dollar) currency format |
|
FIXED |
=FIXED(number,decimals,no_commas) |
Formats a number as text with a fixed number of decimals |
|
PHONETIC |
=PHONETIC(reference) |
Extracts the phonetic (furigana) characters from a text string |
|
REPT |
=REPT(text,number_times) |
Repeats text a given number of times |
|
SUBSTITUTE |
=SUBSTITUTE(text,old_text,new_text,instance_num) |
Substitutes new text for old text in a text string |
|
T |
=T(value) |
Converts its arguments to text |
|
VALUE |
=VALUE(text) |
Converts a text argument to a number |
|
ASC |
=ASC(text) |
Changes full-width (double-byte) English letters or katakana within a character string to half-width (single-byte) characters |
|
BAHTTEXT |
=BAHTTEXT(number) |
Converts a number to text, using the ß (baht) currency format |
Most Common Excel Formulas & Functions
|
Functions |
Excel Formulas |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
FIND |
=FIND(find_text,within_text,start_num) |
Finds one text value within another (case-sensitive) |
|
LEFT |
=LEFT(text,num_chars) |
Returns the leftmost characters from a text value |
|
LEN |
=LEN(text) |
Returns the number of characters in a text string |
|
MID |
=MID(text,start_num,num_chars) |
Returns a specific number of characters from a text string starting at the position you specify |
|
REPLACE |
=REPLACE(old_text,start_num,num_chars,new_text) |
Replaces characters within text |
|
RIGHT |
=RIGHT(text,num_chars) |
Returns the rightmost characters from a text value |
|
SEARCH |
=SEARCH(find_text,within_text,start_num) |
Finds one text value within another (not case-sensitive) |
Engineering Excel Formulas & Functions
|
Functions |
Excel Formulas |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
CONVERT |
=CONVERT(number,from_unit,to_unit) |
Converts a number from one measurement system to another |
|
DELTA |
=DELTA(number1,number2) |
Tests whether two values are equal |
|
ERF |
=ERF(lower_limit,upper_limit) |
Returns the error function |
|
ERFC |
=ERFC(x) |
Returns the complementary error function |
|
GESTEP |
=GESTEP(number,step) |
Tests whether a number is greater than a threshold value |
|
ERF.PRECISE |
=ERF.PRECISE(X) |
Returns the error function |
|
ERFC.PRECISE |
=ERFC.PRECISE(X) |
Returns the complementary ERF function integrated between x and infinity |
|
BESSELI |
=BESSELI(x,n) |
Returns the modified Bessel function In(x) |
|
BESSELJ |
=BESSELJ(x,n) |
Returns the Bessel function Jn(x) |
|
BESSELK |
=BESSELK(x,n) |
Returns the modified Bessel function Kn(x) |
|
BESSELY |
=BESSELY(x,n) |
Returns the Bessel function Yn(x) |
|
BIN2DEC |
=BIN2DEC(number) |
Converts a binary number to decimal |
|
BIN2HEX |
=BIN2HEX(number,places) |
Converts a binary number to hexadecimal |
|
DEC2OCT |
=DEC2OCT(number,places) |
Converts a decimal number to octal |
|
HEX2BIN |
=HEX2BIN(number,places) |
Converts a hexadecimal number to binary |
|
HEX2DEC |
=HEX2DEC(number) |
Converts a hexadecimal number to decimal |
|
HEX2OCT |
=HEX2OCT(number,places) |
Converts a hexadecimal number to octal |
|
IMABS |
=IMABS(inumber) |
Returns the absolute value (modulus) of a complex number |
|
IMAGINARY |
=IMAGINARY(inumber) |
Returns the imaginary coefficient of a complex number |
|
IMARGUMENT |
=IMARGUMENT(inumber) |
Returns the argument theta, an angle expressed in radians |
|
IMCONJUGATE |
=IMCONJUGATE(inumber) |
Returns the complex conjugate of a complex number |
|
IMCOS |
=IMCOS(inumber) |
Returns the cosine of a complex number |
|
IMDIV |
=IMDIV(inumber1,inumber2) |
Returns the quotient of two complex numbers |
|
IMEXP |
=IMEXP(inumber) |
Returns the exponential of a complex number |
|
IMLN |
=IMLN(inumber) |
Returns the natural logarithm of a complex number |
|
IMLOG10 |
=IMLOG10(inumber) |
Returns the base-10 logarithm of a complex number |
|
IMLOG2 |
=IMLOG2(inumber) |
Returns the base-2 logarithm of a complex number |
|
IMPOWER |
=IMPOWER(inumber,number) |
Returns a complex number raised to an integer power |
|
IMPRODUCT |
=IMPRODUCT(inumber1,inumber2,…) |
Returns the product of complex numbers |
|
IMREAL |
=IMREAL(inumber) |
Returns the real coefficient of a complex number |
|
IMSIN |
=IMSIN(inumber) |
Returns the sine of a complex number |
|
IMSQRT |
=IMSQRT(inumber) |
Returns the square root of a complex number |
|
IMSUB |
=IMSUB(inumber1,inumber2) |
Returns the difference between two complex numbers |
|
IMSUM |
=IMSUM(inumber1,inumber2,…) |
Returns the sum of complex numbers |
|
OCT2BIN |
=OCT2BIN(number,places) |
Converts an octal number to binary |
|
OCT2DEC |
=OCT2DEC(number) |
Converts an octal number to decimal |
|
OCT2HEX |
=OCT2HEX(number,places) |
Converts an octal number to hexadecimal |
Level up your Excel skills and transform your data into powerful insights. Join us in Corporate Excel Training in Mumbai, and Corporate Excel Training in Delhi for a comprehensive training session that covers everything from the basics to advanced techniques. Whether you’re a beginner or an intermediate user, this training will give you the skills and confidence to tackle any project with ease.
PDF GUIDE BOOKS
- Download Excel Shortcuts for Windows & Mac
- Basic to Advanced Excel Formulas PDF Guide
This Book will help you to get Excel Skills & Boost your career.
Excel Formulas List PDF Download
Excel Formulas List PDF download link is available below in the article, download PDF of Excel Formulas List using the direct link given at the bottom of content.
| PDF Name | Excel Formulas List PDF |
|---|---|
| No. of Pages | 12 |
| PDF Size | 0.44 MB |
| PDF Category | Education & Jobs |
| Published/Updated | January 6, 2023January 6, 2023 |
| Source / Credits | drive.google.com |
| Comments ✎ | 3 |
| pk |
50 People Like This
REPORT THIS PDF ⚐
Excel Formulas List PDF
Excel Formulas List PDF Download for free using the direct download link given at the bottom of this article.
Excel Formulas List PDF can be downloaded from the link given at the bottom of this page. Excel Formula Mean is calculated by adding a set of numbers and then dividing the sum by the count of those numbers. In Microsoft Excel, the mean can be calculated by using one of the following functions: AVERAGE – Returns the average number.
In Excel, a formula is an expression that operates on values in a range of cells or a cell. For example, =A1+A2+A3, which finds the sum of the range of values from cell A1 to cell A3. If you want to expert in Excel then you must know the Excel formula. Excel Formulas List PDF can be downloaded from the link given at the bottom of this page.
Excel Formulas List PDF
| Excel Function | Shortcut Keys |
|---|---|
| Close a Workbook | Ctrl + W |
| Repeat Last Command Actions | F4 |
| Open Options | Alt + F + T |
| Open Help | F1 |
| Undo | Ctrl + Z |
| Redo | Ctrl + Y |
| Copy | Ctrl + C |
| Cut | Ctrl + X |
| Paste | Ctrl + V |
| Display Paste Special Dialogue Box | Ctrl + Alt + V |
| Find Box | Ctrl + F |
| Find and Replace | Ctrl + H |
| Find next match | Shift + F4 |
| Find Previous Match | Ctrl + Shift + F4 |
| Create an Embedded Chart | Alt + F1 – |
| Create Chart in new Worksheet | F11 |
| New Workbook | Ctrl + N |
| Open Workbook | Ctrl + O |
| Save Workbook | Ctrl + S |
| Save As | F12 |
| Print File | Ctrl + P |
| Open Print Preview | Ctrl + F2 |
| Close Workbook | Ctrl + F4 |
| Close Excel | Alt + F4 |
| Expand or close Ribbon | Ctrl + F1 |
| Activate Access Keys | Alt |
| Move to next control on Ribbon | Tab |
| Help | F1 |
| Select all contents of a worksheet. | Ctrl+A |
| Bold all cells in the highlighted section. | Ctrl+B |
| Fill the Content of the selected cell on top to bottom. CTRL + D (i.e. Ctrl+ Down) | Ctrl+D |
| “Search the current sheet. | Ctrl+F |
| Go to a certain area. | Ctrl+G |
| Find and replace. | Ctrl+H |
| Puts italics on all cells in the highlighted section. | Ctrl+I |
| Inserts a hyperlink. | Ctrl+K |
| Print the current sheet. | Ctrl+P |
| Fill Right. | Ctrl+R |
| Saves the open worksheet. | Ctrl+S |
| Underlines all cells in the highlighted section. | Ctrl+U |
| Pastes everything copied onto the clipboard. | Ctrl+V |
| Closes the current workbook. | Ctrl+W |
| Cuts all cells within the highlighted section. | Ctrl+X |
| Repeats the last entry. | Ctrl+Y |
| Undo the last action. | Ctrl+Z |
| Changes the format of the selected cells. | Ctrl+1 |
| Bolds all cells in the highlighted section. | Ctrl+2 |
| Puts italics all cells in the highlighted section. | Ctrl+3 |
| Underlines all cells in the highlighted section. | Ctrl+4 |
| Puts a strikethrough all cells in the highlighted section. | Ctrl+5 |
| Shows or hides objects. | Ctrl+6 |
| Shows or hides the toolbar. | Ctrl+7 |
| Toggles the outline symbols. | Ctrl+8 |
| Hides rows. | Ctrl+9 |
| Hides columns. | Ctrl+0 |
Excel Shortcuts List PDF (Top 50)
| Description | Excel Shortcuts |
|---|---|
| 1. To create a new workbook | Ctrl + N |
| 2. To open an existing workbook | Ctrl + O |
| 3. To save a workbook/spreadsheet | Ctrl + S |
| 4. To close the current workbook | Ctrl + W |
| 5. To close Excel | Ctrl + F4 |
| 6. To move to the next sheet | Ctrl + PageDown |
| 7. To move to the previous sheet | Ctrl + PageUp |
| 8. To go to the Data tab | Alt + A |
| 9. To go to the View tab | Alt + W |
| 10. To go the Formula tab | Alt + M |
| 11. To edit a cell | F2 |
| 12. To copy and paste cells | Ctrl + C, Ctrl + V |
| 13. To italicize and make the font bold | Ctrl + I, Ctrl + B |
| 14. To center align cell contents | Alt + H + A + C |
| 15. To fill color | Alt + H + H |
| 16. To add a border | Alt + H + B |
| 17. To remove outline border | Ctrl + Shift + _ |
| 18. To add an outline to the select cells | Ctrl + Shift + & |
| 19. To move to the next cell | Tab |
| 20. To move to the previous cell | Shift + Tab |
| 21. To select all the cells on the right | Ctrl + Shift + Right arrow |
| 22. To select all the cells on the left | Ctrl + Shift + Left Arrow |
| 23. To select the column from the selected cell to the end of the table | Ctrl + Shift + Down Arrow |
| 24. To select all the cells above the selected cell | Ctrl + Shift + Up Arrow |
| 25. To select all the cells below the selected cell | Ctrl + Shift + Down Arrow |
| 26. To add a comment to a cell | Shift + F2 |
| 27. To delete a cell comment | Shift + F10 + D |
| 28. To display find and replace | Ctrl + H |
| 29. To activate the filter | Ctrl + Shift + L, Alt + Down Arrow |
| 30. To insert the current date | Ctrl + ; |
| 31. To insert current time | Ctrl + Shift + : |
| 32. To insert a hyperlink | Ctrl + k |
| 33. To apply the currency format | Ctrl + Shift + $ |
| 34. To apply the percent format | Ctrl + Shift + % |
| 35. To go to the “Tell me what you want to do” box | Alt + Q |
| 36. To select the entire row | Shift + Space |
| 37. To select the entire column | Ctrl + Space |
| 38. To delete a column | Alt+H+D+C |
| 39. To delete a row | Shift + Space, Ctrl + – |
| 40. To hide selected row | Ctrl + 9 |
| 41. To unhide selected row | Ctrl + Shift + 9 |
| 42. To hide a selected column | Ctrl + 0 |
| 43. To unhide a selected column | Ctrl + Shift + 0 |
| 44. To group rows or columns | Alt + Shift + Right arrow |
| 45. To ungroup rows or columns | Alt + Shift + Left arrow |
| 46. To group pivot table items | Alt + Shift + Right arrow |
| 47. To ungroup pivot table items | Alt + Shift + Left arrow |
| 48. To hide pivot table items | Ctrl + – |
| 49. To create a pivot chart on the same sheet | Alt + F1 |
| 50. To create a pivot chart on a new worksheet | F11 |
MS Excel Formulas List
| SUM Excel Formula : | SUM(number1, [number2] ) |
| AVERAGE Excel Formula : | AVERAGE(number1, [number2], …) |
| MAX & MIN Excel Formula : | =MAX(A2:A5) =MIN(A2:A5) |
| COUNT & COUNTA Formula : | COUNT(value1, [value2], …) |
| IF Excel Formula : | IF(logical_test, [value_if_true], [value_if_false]) |
| TRIM Excel Formula : | = TRIM (A1) |
| LEN Excel Formula : | =LEN (text) |
| CONCATENATE Excel Formula : | CONCATENATE(text1, [text2], …) |
Sum Function
The sum function is the most used function when it comes to computing data on Excel. This function works to sum a group of numbers in a specific set of cells. This means you don’t need to type a long cumbrous formula just to calculate the sum of all the data you need. Because of its popularity, newer versions of Microsoft Excel have a button specifically for this function.
TEXT Function
Text function is a useful tool that helps convert a date (or number) into a text string in a particular format. It falls in the category of string formulas that converts numerical values to a string. It is handy when users need to view numeric data in a readable format. Take note that the “TEXT” formula only works to convert numeric values to text.
You can download the Excel Formulas List in PDF format using the link given below.
Excel Formulas List PDF Download Link
3 more PDF of Excel Formulas List
Excel Formulas List with Examples PDF
Size: 0.31 | Pages: 9 | Source(s)/Credits: www.shastacoe.org | Language: English
Added on 26 Apr, 2022 by pk
Excel Formula List PDF
Size: 2.47 | Pages: 44 | Source(s)/Credits: www.shastacoe.org | Language: English
Added on 09 Mar, 2022 by pk
Excel Formulas List PDF
Size: 0.13 | Pages: 2 | Source(s)/Credits: drive.google.com | Language: English
Added on 08 Mar, 2022 by pk
REPORT THISIf the purchase / download link of Excel Formulas List PDF is not working or you feel any other problem with it, please REPORT IT by selecting the appropriate action such as copyright material / promotion content / link is broken etc. If Excel Formulas List is a copyright material we will not be providing its PDF or any source for downloading at any cost.
RELATED PDF FILES
@santhosh785
First of all, when you convert a worksheet to PDF, there is basically no way to keep the Excel formulas, let alone to influence the other values.
You can convert it to PDF, but then you need editing software, with an Adobe Reader you can almost only read and fill in fields.
So you need a subscription such as Adobe Pro DC to be able to make changes in the PDF.
There are also some free tools on the internet, with less or more success.
There you can perform simple calculations in given commands / menus or write / convert a formula yourself in Javascript and I would recommend Adobe Lefecycle Designer.
Basically it is not recommended that a PDF behaves like an Excel file.
The greatest advantage of a PDF file, besides being usable on any computer and preventing text manipulation by the end user, is that there are no costs for the reader. In contrast to Excel, you can use many advantages, for example simple and fast formatting, but the biggest advantage is the enormous time savings that anyone could / can achieve with it.
My recommendation, two different pairs of shoes should not be put on at the same time.
Thank you for your patience and time.
Nikolino
I know I don’t know anything (Socrates)
7 Quick Conversion Methods – Excel to PDF & PDF to Excel
Excel and PDF are the two most popular file types and you might need to convert one format to another from time to time.
This tutorial will cover exactly that – How to Convert Excel to PDF or PDF to Excel.
PDF files are a widely used format for electronic documents. They are used when you need to save a file without modification so that it can be easily shared and printed. By default, an Excel Workbook is saved as a .xlsx file type.
But you can easily convert Excel to PDF format. Similarly, you can easily create tables from the PDF document using Excel.
This article will cover the following two conversion methods in detail:
- Convert Excel to PDF
- Convert PDF to Excel
Let’s look at both ways one-by-one!
Make sure to download the Excel Workbook below and follow along:
Want to know how to convert excel to pdf and pdf to excel?
*** Watch our video and step by step guide below with free downloadable Excel workbook to practice ***
Watch it on YouTube and give it a thumbs-up!
Convert Excel to PDF
PDFs can be easily shared and can be viewed on any platform without a change in format. So, learning how to convert Excel to PDF is extremely essential!
There are 5 different methods in which you can convert Excel to PDF:
- #1 – Using Save as Option
- #2 – Using Export Option
- #3 – Export using Quick Access Toolbar
- #4 – Email PDF using Quick Access Toolbar
- #5 – Using VBA
#1 – Using Save As Option
Follow the step-by-step tutorial on how to convert Excel to PDF using the Save As option:
STEP 1: Select the Excel table that you want in the PDF Format.
STEP 2: Click on File Tab.
STEP 3: Select Save As > Browse.
STEP 4: In the Save As dialog box, select the location where you want to save the PDF file.
STEP 5: Under Save as type dropdown, select PDF.
STEP 6: Click on the Options button to customize the PDF file you want to create.
STEP 7: In the Options dialog box, Go to Publish what section and click on Selection. Then, Click OK.
This will help you to publish only what you have selected on the sheet. To publish the entire sheet, click on Active Sheet(s), and to publish the workbook click on the Entire Workbook.
STEP 8: Click Save.
This will save you Excel Table in PDF format.
#2 – Using Export Option
The Export option in Excel will provide you with a quicker way to save your file as PDF.
STEP 1:Go to the File Tab.
STEP 2: Click on Export > Create PDF/XPS Document > Create PDF/XPS Document button.
STEP 3: In the Publish as PDF or XPS dialog box, click on Publish.
#3 – Export using Quick Access Toolbar
If converting Excel to PDF is a regular task for you, you can add it to the Quick Access Toolbar (QAT). Follow the steps below to add Publish as PDF option to the QAT:
STEP 1: Right Click on the QAT to customize it.
STEP 2: In the Excel Options dialog box, select Quick Access Toolbar > Publish as PDF or XPS > Add.
STEP 3: This will add Publish as PDF under Customize Quick Access Toolbar. Now, Click OK.

STEP 5: Simply click on the icon, select the file location you want to save it at and click on Publish.
#4 – Email PDF using Quick Access Toolbar
If you want to attach an Excel file as PDF in an email, you can add it to the Quick Access Toolbar (QAT).
Follow the steps below to email PDF as QAT:
STEP 1: Right Click on the QAT to customize it.
STEP 2: In the Excel Options dialog box, select Quick Access Toolbar > E-mail as PDF Attachment > Add.
STEP 3: This will add E-mail as PDF Attachment under Customize Quick Access Toolbar. Now, Click OK.
STEP 4: This will add E-mail as PDF Attachment to Quick Access Toolbar.
#5 – Using VBA
You can also use VBA code to publish a range in Excel into PDF. This VBA will prompt you to provide the range you wish to export and then select the location, to automatically export Excel to PDF.
Copy Source Code
‘MyExcelOnline.com – PrintSelectionToPDF
Sub PrintSelectionToPDF()‘Declaration of Variables
Dim rng As Range
Dim strFilePath As String
Dim strFile As String
Dim file As Variant‘Check first if a range has been selected
If Selection.Count = 1 Then
Set rng = Application.InputBox(“Please select a range”, “Get Range”, Type:=8)
Else
Set rng = Selection
End If‘Create the filename with the path – the default filename is ExceltoPdf.pdf
strFile = “ExceltoPdf.pdf”
strFile = ThisWorkbook.Path & “” & strFile‘We open a save prompt for the username to select the location and filename
file = Application.GetSaveAsFilename(InitialFileName:=strFile, FileFilter:=”PDF Files (*.pdf), *.pdf”, Title:=”Select location for the PDF file”)‘Start the export process of the selected range
If file <> “False” Then
rng.ExportAsFixedFormat Type:=xlTypePDF, Filename:=file, Quality:=xlQualityStandard, IncludeDocProperties:=True, IgnorePrintAreas:=False, OpenAfterPublish:=False
MsgBox “PDF file has been successfully created: ” & strFile
Else
MsgBox “Unable to create PDF file”, vbOKOnly, “No File Selected”
End IfEnd Sub
Follow the steps below to use this VBA code to Export selection to PDF:
STEP 1: Press Alt + F11 to open VBA Editor.
STEP 2: Right Click on the sheet name and then select Insert > Module.
STEP 3: Copy-paste the VBA code from above into here.
STEP 4: Press Ctrl + S to save the file and then click No.
STEP 5: In the Save as dialog box, choose Excel macro-enabled workbook from the drop-down list and click the Save button.
STEP 6: Press Alt + F8 to open the Macro dialog box.
STEP 7: Select the Macro PrintSelectionToPDF that is located in All Open Workbooks and click Run.
STEP 8: In the dialog box, type the required range – A1: F8.
STEP 9: Select the location and press Save.
This is how you can convert the range A1: F8 in excel to PDF.
Convert PDF to Excel
PDF does not allow users to make edits on the data so it might be useful to learn how to convert the data from PDF to Excel. If you have a table saved in PDF, you can easily get that imported in Excel and work on it easily.
The two methods for converting PDF to Excel are:
- #1 – Copy and Paste
- #2 – Import Data from PDF to Excel
#1 – Copy and Paste
The most simple method to convert PDF to Excel is to copy & paste the data. Let’s look at an example to understand this better.
Follow the steps below for a detailed tutorial on PDF to Excel converter:
STEP 1: Press Ctrl + A and Ctrl + C to select the entire data and copy the data in PDF.
STEP 2: Open the Excel File and simply press Ctrl + V to paste the data in Excel.
Even though, you have got the data in Excel it is not formatted in the way you want. You can use different functions of Excel to format that like Text to Column, Index Formula, OFFSET Formula, etc.
In this example, you need to transpose every 5th row into a single row using OFFSET Formula.
STEP 3: In the blank cell C1, start with the OFFSET formula to transpose the data
=OFFSET($A$1
This will provide Excel with the starting point to extract data from i.e cell A1.
STEP 4: Now, type the second argument the provides Excel with the number of rows, up or down, that you want the top-left cell of the result to refer to.
=OFFSET($A$1,COLUMNS($A1:A1)-1+(ROWS($1:1)-1)*5, Here:
- COLUMNS ($A1: A1) will count the columns in the defined range and it will expand by keeping the first reference frozen ($A1) and the second reference (A1) relative. When you will drag the formula right, the column count will increase.
- Similarly, ROWS ($1:1) will count the rows in the defined range and it will expand by keeping the first reference frozen ($1) and the second reference (1) relative. When you will drag the formula down, the row count will increase.
- Moreover, we are multiplying (ROWS($1:1)-1) with 5 because we want to transpose every 5 rows from 1 column to multiple columns.
- Lastly, say if we want to transpose data from cell A1 to C1. We need to subtract 1 from both COLUMNS and ROWS function Excel to say in the same row and column from the starting point i.e. A1.
STEP 5: Type the third argument the provides Excel with the number of columns, to the left or right, that you want the top-left cell of the result to refer to.
Since the entire data is in the same column i.e. Column A, the third argument will be 0.
=OFFSET($A$1,COLUMNS($A1:A1)-1+(ROWS($1:1)-1)*5,0)
STEP 6: Drag this formula right till Column G.
STEP 7: Again, drag down till row 46 to incorporate the entire table.
STEP 8: Change the Date & Currency format, make the header bold and insert borders.
Your Data Table is ready!
Let’s look at how Excel retrieves a value using this formula in a particular cell (say E4).
=OFFSET($A$1,COLUMNS($A4:C4)-1+(ROWS($1:4)-1)*5,0)
=OFFSET($A$1, 4-1+(ROWS($1:4)-1)*5,0)
=OFFSET($A$1, 3+(4-1)*5,0
=OFFSET($A$1,18,0)
=John Michaloudis
#2 – Import Data from PDF to Excel
In most cases, you will be able to simply copy & paste the data and format it to get the desired result. But if that is not working for you, use the Import Data method in Excel.
Follow the steps below to import data from PDF to Excel (For Excel 365 only):
STEP 1: Go to Data Tab > Get Data > From File > From PDF.
STEP 2: In the Import Data dialog box, select the location of the PDF file, and click on Import.
STEP 3: In the dialog box, select the table from the left panel and click on Load.
This will convert the table from PDF to Excel!
Conclusion
In this article, you have learned how to swap between the two most commonly used file formats – Excel & PDF.
When you need a file in PDF format for sharing or printing – Convert Excel to PDF by using either the Save as or Export option.
Similarly, when you need to make edits in a PDF file – Convert PDF to Excel by using either the copy-paste technique or the Import Data feature in Excel 365.
You can learn more about how to import or export files in Excel by going through this
tutorial by Microsoft.
HELPFUL RESOURCE:
Make sure to download our FREE PDF on the 333 Excel keyboard Shortcuts here:
You can learn more about how to use Excel by viewing our FREE Excel webinar training on Formulas, Pivot Tables, and Macros & VBA!
You can follow our YouTube channel to learn more about How To Merge Cells in Excel!
👉 Click Here To Join Our Excel Academy Online Course & Access 1,000+ Excel Tutorials On Formulas, Macros, VBA, Pivot Tables, Dashboards, Power BI, Power Query, Power Pivot, Charts, Microsoft Office Suite + MORE!