Содержание
- Ways to format a worksheet
- Excel Formatting
- Formatting
- Styling Commands in Ribbon
- Styling Commands, Right Clicking Cells
- Chapter summary
- Apply Conditional Formatting – Multiple Sheets in Excel & Google Sheets
- Apply Conditional Formatting to Multiple Sheets
- Copy-Paste
- Format Painter
- Create a Macro to Apply Conditional Formatting Rule
- Apply Conditional Formatting to Multiple Sheets in Google Sheets
- Copy Conditional Formatting From One Cell
- Copy-Paste
- Paint Format
Ways to format a worksheet
In Excel, formatting worksheet (or sheet) data is easier than ever. You can use several fast and simple ways to create professional-looking worksheets that display your data effectively. For example, you can use document themes for a uniform look throughout all of your Excel spreadsheets, styles to apply predefined formats, and other manual formatting features to highlight important data.
A document theme is a predefined set of colors, fonts, and effects (such as line styles and fill effects) that will be available when you format your worksheet data or other items, such as tables, PivotTables, or charts. For a uniform and professional look, a document theme can be applied to all of your Excel workbooks and other Office release documents.
Your company may provide a corporate document theme that you can use, or you can choose from a variety of predefined document themes that are available in Excel. If needed, you can also create your own document theme by changing any or all of the theme colors, fonts, or effects that a document theme is based on.
Before you format the data on your worksheet, you may want to apply the document theme that you want to use, so that the formatting that you apply to your worksheet data can use the colors, fonts, and effects that are determined by that document theme.
For information on how to work with document themes, see Apply or customize a document theme.
A style is a predefined, often theme-based format that you can apply to change the look of data, tables, charts, PivotTables, shapes, or diagrams. If predefined styles don’t meet your needs, you can customize a style. For charts, you can customize a chart style and save it as a chart template that you can use again.
Depending on the data that you want to format, you can use the following styles in Excel:
Cell styles To apply several formats in one step, and to ensure that cells have consistent formatting, you can use a cell style. A cell style is a defined set of formatting characteristics, such as fonts and font sizes, number formats, cell borders, and cell shading. To prevent anyone from making changes to specific cells, you can also use a cell style that locks cells.
Excel has several predefined cell styles that you can apply. If needed, you can modify a predefined cell style to create a custom cell style.
Some cell styles are based on the document theme that is applied to the entire workbook. When you switch to another document theme, these cell styles are updated to match the new document theme.
For information on how to work with cell styles, see Apply, create, or remove a cell style.
Table styles To quickly add designer-quality, professional formatting to an Excel table, you can apply a predefined or custom table style. When you choose one of the predefined alternate-row styles, Excel maintains the alternating row pattern when you filter, hide, or rearrange rows.
For information on how to work with table styles, see Format an Excel table.
PivotTable styles To format a PivotTable, you can quickly apply a predefined or custom PivotTable style. Just like with Excel tables, you can choose a predefined alternate-row style that retains the alternate row pattern when you filter, hide, or rearrange rows.
For information on how to work with PivotTable styles, see Design the layout and format of a PivotTable report.
Chart styles You apply a predefined style to your chart. Excel provides a variety of useful predefined chart styles that you can choose from, and you can customize a style further if needed by manually changing the style of individual chart elements. You cannot save a custom chart style, but you can save the entire chart as a chart template that you can use to create a similar chart.
For information on how to work with chart styles, see Change the layout or style of a chart.
To make specific data (such as text or numbers) stand out, you can format the data manually. Manual formatting is not based on the document theme of your workbook unless you choose a theme font or use theme colors — manual formatting stays the same when you change the document theme. You can manually format all of the data in a cell or range at the same time, but you can also use this method to format individual characters.
For information on how to format data manually, see Format text in cells.
To distinguish between different types of information on a worksheet and to make a worksheet easier to scan, you can add borders around cells or ranges. For enhanced visibility and to draw attention to specific data, you can also shade the cells with a solid background color or a specific color pattern.
If you want to add a colorful background to all of your worksheet data, you can also use a picture as a sheet background. However, a sheet background cannot be printed — a background only enhances the onscreen display of your worksheet.
For information on how to use borders and colors, see:
For the optimal display of the data on your worksheet, you may want to reposition the text within a cell. You can change the alignment of the cell contents, use indentation for better spacing, or display the data at a different angle by rotating it.
Rotating data is especially useful when column headings are wider than the data in the column. Instead of creating unnecessarily wide columns or abbreviated labels, you can rotate the column heading text.
For information on how to change the alignment or orientation of data, see Reposition the data in a cell.
If you have already formatted some cells on a worksheet the way that you want, there are several ways to copy just those formats to other cells or ranges.
Home > Paste > Paste Special > Paste Formatting.
Home > Format Painter 
Right click command
Point your mouse at the edge of selected cells until the pointer changes to a crosshair.
Right click and hold, drag the selection to a range, and then release.
Select Copy Here as Formats Only.
Tip If you’re using a single-button mouse or trackpad on a Mac, use Control+Click instead of right click.
Data range formats are automatically extended to additional rows when you enter rows at the end of a data range that you have already formatted, and the formats appear in at least three of five preceding rows. The option to extend data range formats and formulas is on by default, but you can turn it on or off by:
Newer versions Selecting File > Options > Advanced > Extend date range and formulas (under Editing options).
Excel 2007 Selecting Microsoft Office Button 
Источник
Excel Formatting
Formatting
Excel has many ways to format and style a spreadsheet.
Why format and style your spreadsheet?
- Make it easier to read and understand
- Make it more delicate
Styling is about changing the looks of cells, such as changing colors, font, font sizes, borders, number formats, and so on.
The most used styling functions are:
There are two ways to access the styling commands in Excel:
- The Ribbon
- Formatting menu, by right clicking cells
Read more about the Ribbon in the Excel overview chapter.
Styling Commands in Ribbon
The Ribbon can be expanded by clicking the arrow/caret-down icon on the right side. This gives access to more commands:
Styling Commands, Right Clicking Cells
You can also right-click on any cell to style it:
Styling commands can be accessed from both views.
Chapter summary
Formatting is used to make spreadsheets more readable. There are many ways to add styles. The most common ones are; Color, Font, Number format and Grids.
Источник
Apply Conditional Formatting – Multiple Sheets in Excel & Google Sheets
This tutorial demonstrates how to apply conditional formatting to multiple sheets in Excel and Google Sheets.
In the latest versions of Excel, you can no longer select multiple sheets and then apply a conditional formatting rule to all the sheets at once. You need to do one sheet first, then copy the conditional formatting between sheets. Or, you can write a macro to repeat the conditional formatting on each sheet.
Apply Conditional Formatting to Multiple Sheets
Copy-Paste
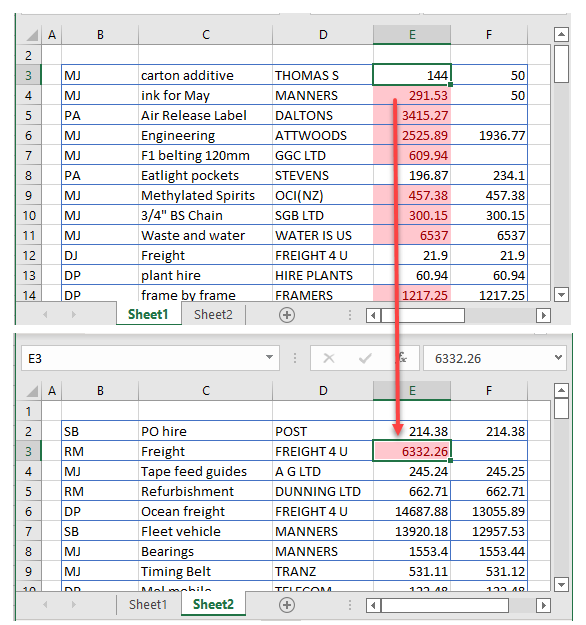
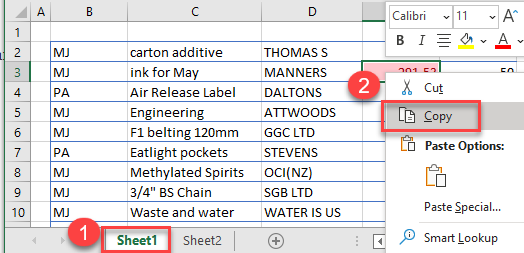
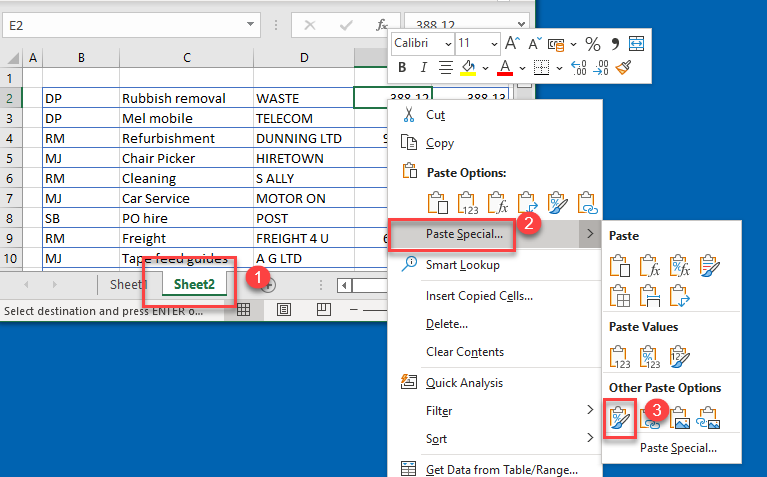
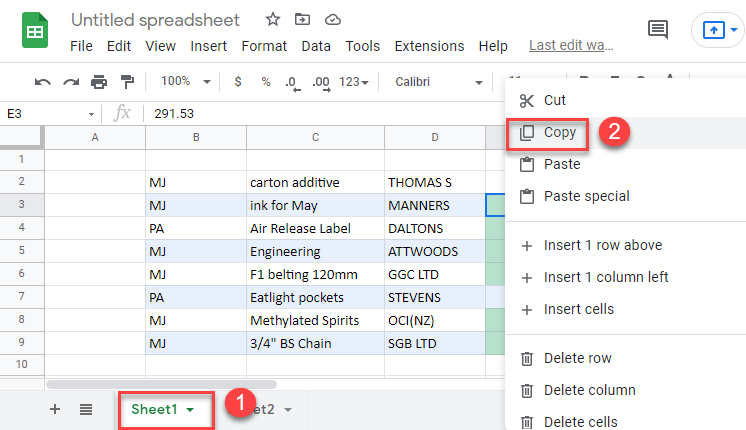
- Select the sheet with the conditional formatting applied and right-click the cell with conditional formatting rule. Then click Copy (or use the keyboard shortcut CTRL + C).
- Next, click on the destination sheet and select the destination cell or cells. Right-click and choose Paste Special > Paste Format.
Format Painter
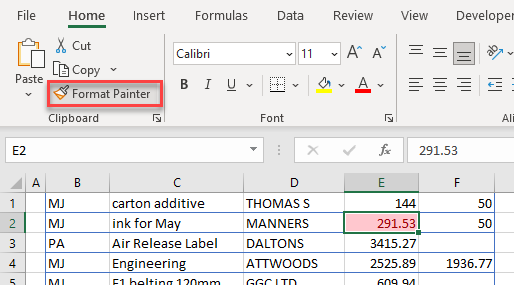
You can also copy the conditional formatting rule from one sheet to another with the Format Painter feature.
- Select the cell in the source sheet that has a conditional formatting rule and then, in the Ribbon, select Home > Clipboard > Format Painter.
- Click on the destination sheet and click on the cells or cell where you wish to apply the format.
Create a Macro to Apply Conditional Formatting Rule
While creating a new conditional formatting rule in Excel, you can record a macro to mimic the steps you take.
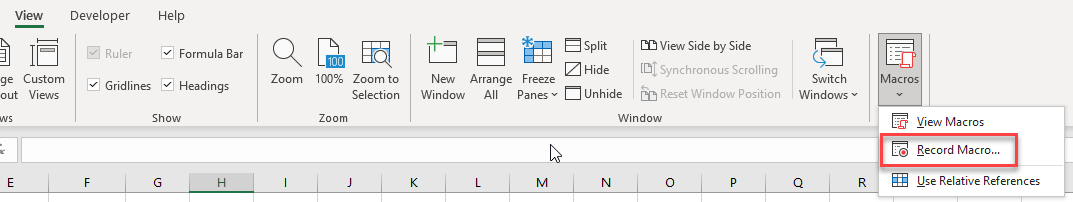
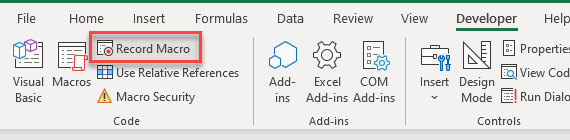
- In the Ribbon, select View > Macros > Record Macro.
OR, in the Ribbon, select Developer > Code > Record Macro.
Note: If you don’t see the Developer Ribbon, you’ll need to enable it.
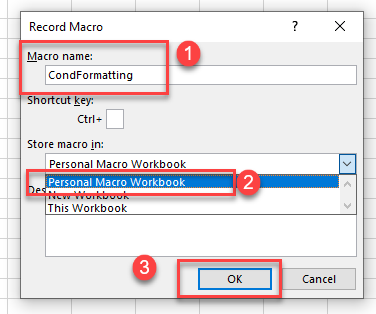
- In the Record Macro dialog box, (1) type in a name for your macro and (2) make sure you select Personal Macro Workbookfrom the drop-down list. Then, (3) click OK to start recording.
- Once you have clicked OK, you can follow the steps to create the conditional formatting rule you require, and then click the stop button at the bottom of the screen to stop recording the macro.
- To run the macro on a different sheet, switch to that sheet and select the cell or cells you wish to apply the conditional formatting to.
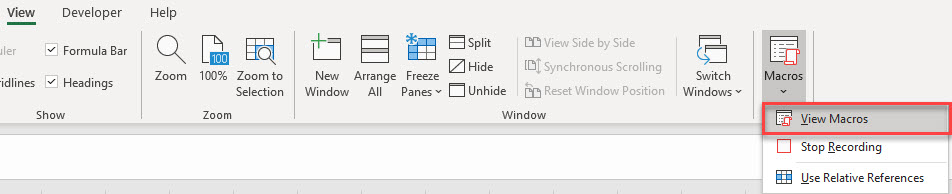
- In the Ribbon, select View > Macros > View Macros.
OR Developer > Visual Basic > Macros
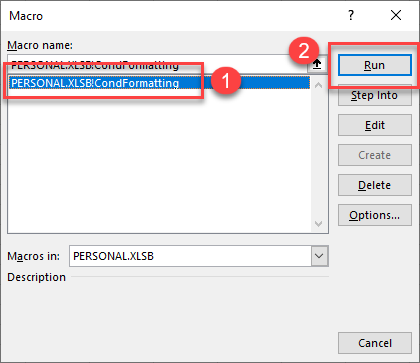
- Click on the Macro in the Macro name list and then select Run.
- You can run the macro on as many sheets as you require.
Note: You can view the code by selecting the macro in the Macro dialog box (shown above) and selecting Edit. This takes you to the Visual Basic Editor and enables you to view and/or edit your VBA code.
Apply Conditional Formatting to Multiple Sheets in Google Sheets
You can apply conditional formatting to multiple sheets in Google Sheets in the same way as you do in Excel.
Copy Conditional Formatting From One Cell
Copy-Paste
If you already have a cell or column with a Conditional Formatting rule set up, you can use Copy-Paste to copy the rule to another sheet.
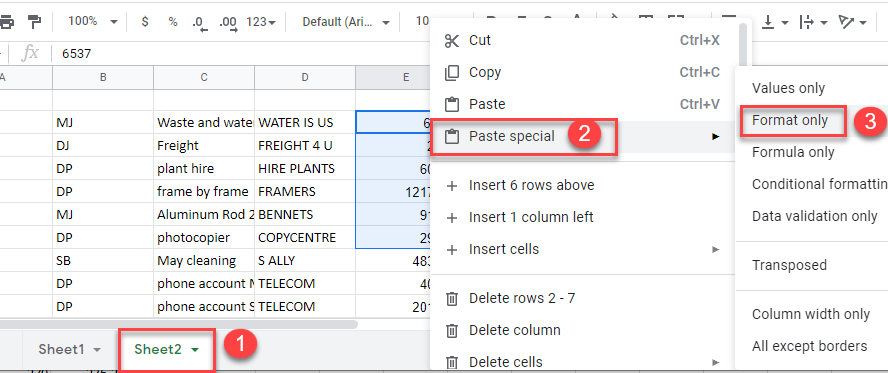
- Right-click on a cell that has the conditional formatting rule applied to it and click Copy (or use the keyboard shortcut CTRL + C).
- Select the sheet you require and then select the cell or cells in that sheet where you wish to apply the conditional formatting rule. Select Paste special > Format only (or use the keyboard shortcut CTRL + ALT + V).
The conditional formatting rule will then be applied to the entire column you have selected.
Paint Format
If you already have a cell or column with a conditional formatting rule set up, you can use Paint Format to copy the rule to another column.
- Select the cell with the relevant conditional formatting rule. Then in the Menu, select Paint Format.
- Select the destination sheet, then highlight the cells to copy the conditional formatting rule to.
Источник
Excel for Microsoft 365 Excel 2021 Excel 2019 Excel 2016 Excel 2013 Excel 2010 Excel 2007 More…Less
In Excel, formatting worksheet (or sheet) data is easier than ever. You can use several fast and simple ways to create professional-looking worksheets that display your data effectively. For example, you can use document themes for a uniform look throughout all of your Excel spreadsheets, styles to apply predefined formats, and other manual formatting features to highlight important data.
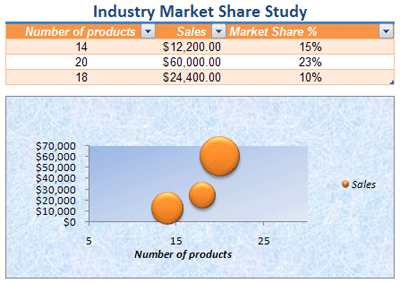
A document theme is a predefined set of colors, fonts, and effects (such as line styles and fill effects) that will be available when you format your worksheet data or other items, such as tables, PivotTables, or charts. For a uniform and professional look, a document theme can be applied to all of your Excel workbooks and other Office release documents.
Your company may provide a corporate document theme that you can use, or you can choose from a variety of predefined document themes that are available in Excel. If needed, you can also create your own document theme by changing any or all of the theme colors, fonts, or effects that a document theme is based on.
Before you format the data on your worksheet, you may want to apply the document theme that you want to use, so that the formatting that you apply to your worksheet data can use the colors, fonts, and effects that are determined by that document theme.
For information on how to work with document themes, see Apply or customize a document theme.
A style is a predefined, often theme-based format that you can apply to change the look of data, tables, charts, PivotTables, shapes, or diagrams. If predefined styles don’t meet your needs, you can customize a style. For charts, you can customize a chart style and save it as a chart template that you can use again.
Depending on the data that you want to format, you can use the following styles in Excel:
-
Cell styles To apply several formats in one step, and to ensure that cells have consistent formatting, you can use a cell style. A cell style is a defined set of formatting characteristics, such as fonts and font sizes, number formats, cell borders, and cell shading. To prevent anyone from making changes to specific cells, you can also use a cell style that locks cells.
Excel has several predefined cell styles that you can apply. If needed, you can modify a predefined cell style to create a custom cell style.
Some cell styles are based on the document theme that is applied to the entire workbook. When you switch to another document theme, these cell styles are updated to match the new document theme.
For information on how to work with cell styles, see Apply, create, or remove a cell style.
-
Table styles To quickly add designer-quality, professional formatting to an Excel table, you can apply a predefined or custom table style. When you choose one of the predefined alternate-row styles, Excel maintains the alternating row pattern when you filter, hide, or rearrange rows.
For information on how to work with table styles, see Format an Excel table.
-
PivotTable styles To format a PivotTable, you can quickly apply a predefined or custom PivotTable style. Just like with Excel tables, you can choose a predefined alternate-row style that retains the alternate row pattern when you filter, hide, or rearrange rows.
For information on how to work with PivotTable styles, see Design the layout and format of a PivotTable report.
-
Chart styles You apply a predefined style to your chart. Excel provides a variety of useful predefined chart styles that you can choose from, and you can customize a style further if needed by manually changing the style of individual chart elements. You cannot save a custom chart style, but you can save the entire chart as a chart template that you can use to create a similar chart.
For information on how to work with chart styles, see Change the layout or style of a chart.
To make specific data (such as text or numbers) stand out, you can format the data manually. Manual formatting is not based on the document theme of your workbook unless you choose a theme font or use theme colors — manual formatting stays the same when you change the document theme. You can manually format all of the data in a cell or range at the same time, but you can also use this method to format individual characters.
For information on how to format data manually, see Format text in cells.
To distinguish between different types of information on a worksheet and to make a worksheet easier to scan, you can add borders around cells or ranges. For enhanced visibility and to draw attention to specific data, you can also shade the cells with a solid background color or a specific color pattern.
If you want to add a colorful background to all of your worksheet data, you can also use a picture as a sheet background. However, a sheet background cannot be printed — a background only enhances the onscreen display of your worksheet.
For information on how to use borders and colors, see:
Apply or remove cell borders on a worksheet
Apply or remove cell shading
Add or remove a sheet background
For the optimal display of the data on your worksheet, you may want to reposition the text within a cell. You can change the alignment of the cell contents, use indentation for better spacing, or display the data at a different angle by rotating it.
Rotating data is especially useful when column headings are wider than the data in the column. Instead of creating unnecessarily wide columns or abbreviated labels, you can rotate the column heading text.
For information on how to change the alignment or orientation of data, see Reposition the data in a cell.
If you have already formatted some cells on a worksheet the way that you want, there are several ways to copy just those formats to other cells or ranges.
Clipboard commands
-
Home > Paste > Paste Special > Paste Formatting.
-
Home > Format Painter
.
Right click command
-
Point your mouse at the edge of selected cells until the pointer changes to a crosshair.
-
Right click and hold, drag the selection to a range, and then release.
-
Select Copy Here as Formats Only.
Tip If you’re using a single-button mouse or trackpad on a Mac, use Control+Click instead of right click.
Range Extension
Data range formats are automatically extended to additional rows when you enter rows at the end of a data range that you have already formatted, and the formats appear in at least three of five preceding rows. The option to extend data range formats and formulas is on by default, but you can turn it on or off by:
-
Newer versions Selecting File > Options > Advanced > Extend date range and formulas (under Editing options).
-
Excel 2007 Selecting Microsoft Office Button
> Excel Options > Advanced > Extend date range and formulas (under Editing options)).
Need more help?
In this article, we will learn How to format all worksheets in one go in Excel.
Scenario:
When working with multiple worksheets in Excel. Before proceeding to the analysis in excel, first we need to get the right format of cells. For example learning the products data of a super store having multiple sheets. For these problems we use the shortcut to do the task.
Ctrl + Click to select multiple sheets in Excel
To select multiple sheets at once. Go to excel sheet tabs and click all required sheets holding the Ctrl key.
Then format any of the selected sheets and the formatting done on the sheet will be copied to all. Only formatting not the data itself.
Example :
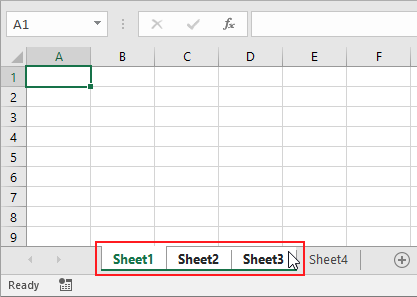
All of these might be confusing to understand. Let’s understand how to use the function using an example. Here we have 4 worksheets and we need to edit the formatting of Sheet1 , Sheet2 and Sheet3.
For this we go step by step. First we go to the sheet tabs as shown below.
Select the Sheet1 and now select the Sheet2 with holding Ctrl key and then select Sheet3 keep holding the Ctrl key.
Now any format editing done on any of the selected three sheets will be copied to the other selected ones.
Here are all the observational notes using the formula in Excel.
Notes :
- This process is the most common practice.
- You can also copy format of any cell and apply to others using the Copy formatter option in Excel
Hope this article about How to format all worksheets in one go in Excel is explanatory. Find more articles on calculating values and related Excel formulas here. If you liked our blogs, share it with your friends on Facebook. And also you can follow us on Twitter and Facebook. We would love to hear from you, do let us know how we can improve, complement or innovate our work and make it better for you. Write to us at info@exceltip.com.
Related Articles :
50 Excel Shortcuts to Increase Your Productivity : Get faster at your tasks in Excel. These shortcuts will help you increase your work efficiency in Excel.
Replace text from end of a string starting from variable position : To replace text from the end of the string, we use the REPLACE function. The REPLACE function use the position of text in the string to replace.
How to Select Entire Column and Row Using Keyboard Shortcuts in Excel : Selecting cells is a very common function in Excel. Use Ctrl + Space to select columns and Shift + Space to select rows in Excel.
How to Insert Row Shortcut in Excel : Use Ctrl + Shift + = to open the Insert dialog box where you can insert row, column or cells in Excel.
How to Select Entire Column and Row Using Keyboard Shortcuts in Excel : Use Ctrl + Space to select whole column and Shift + Space to select whole row using keyboard shortcut in Excel
Excel Shortcut Keys for Merge and Center : This Merge and Center shortcut helps you quickly merge and unmerge cells.
Excel REPLACE vs SUBSTITUTE function: The REPLACE and SUBSTITUTE functions are the most misunderstood functions. To find and replace a given text we use the SUBSTITUTE function. Where REPLACE is used to replace a number of characters in string…
Popular Articles :
How to use the IF Function in Excel : The IF statement in Excel checks the condition and returns a specific value if the condition is TRUE or returns another specific value if FALSE.
How to use the VLOOKUP Function in Excel : This is one of the most used and popular functions of excel that is used to lookup value from different ranges and sheets.
How to use the SUMIF Function in Excel : This is another dashboard essential function. This helps you sum up values on specific conditions.
How to use the COUNTIF Function in Excel : Count values with conditions using this amazing function. You don’t need to filter your data to count specific values. Countif function is essential to prepare your dashboard.
Ctrl + Click to select multiple sheets in Excel Go to excel sheet tabs and click all required sheets holding the Ctrl key. Then format any of the selected sheets and the formatting done on the sheet will be copied to all. Only formatting not the data itself.
How do I make multiple worksheets format faster in Excel?
As a recap – here’s how to format multiple sheets at the same time:
- Ctrl + Click each sheet tab at the bottom of your worksheet (selected sheets will turn white).
- While selected, any formatting changes you make will happen in all of the selected sheets.
- Double-click each tab when you are done to un-select them.
How do I apply VBA code to all worksheets?
Run or execute the same macro on multiple worksheets at same time with VBA code
- Hold down the ALT + F11 keys to open the Microsoft Visual Basic for Applications window.
- Click Insert > Module, and paste the following macro in the Module Window.
How do you collect data from another workbook?
How to collect data from multiple sheets to a master sheet in…
- In a new sheet of the workbook which you want to collect data from sheets, click Data > Consolidate.
- In the Consolidate dialog, do as these: (1 Select one operation you want to do after combine the data in Function drop down list; (2 Click.
- Click OK. Now the data have been collect and sum in one sheet.
How do I collate data in Excel using macros?
Open the Excel file where you want to merge sheets from other workbooks and do the following:
- Press Alt + F8 to open the Macro dialog.
- Under Macro name, select MergeExcelFiles and click Run.
- The standard explorer window will open, you select one or more workbooks you want to combine, and click Open.
How do you compile data in Excel?
Consolidate
- Open all three workbooks.
- Open a blank workbook.
- Choose the Sum function to sum the data.
- Click in the Reference box, select the range A1:E4 in the district1 workbook, and click Add.
- Repeat step 4 for the district2 and district3 workbook.
- Check Top row, Left column and Create links to source data.
- Click OK.
How do I merge data in Excel?
Combine data with the Ampersand symbol (&)
- Select the cell where you want to put the combined data.
- Type = and select the first cell you want to combine.
- Type & and use quotation marks with a space enclosed.
- Select the next cell you want to combine and press enter. An example formula might be =A2&” “&B2.
How do I combine two sets of data in Excel?
Use Excel’s chart wizard to make a combo chart that combines two chart types, each with its own data set.
- Select the two sets of data you want to use to create the graph.
- Choose the “Insert” tab, and then select “Recommended Charts” in the Charts group.
When a user inserts a PivotTable Where is it inserted?
above the first row of data in the worksheet.
What is the first step to creating a PivotTable click the Insert tab and insert PivotTable data or needs to be analyzed?
On the Insert tab, in the Tables group, click the PivotTable command, then select PivotTable . In the Create PivotTable dialog box, verify that Excel has selected the correct range, select where you want the pivot table to show up (you will almost always want to select New Worksheet ), and click OK .
What steps will add Slicers to a PivotTable Use the drop down menu to complete the steps?
Click. Insert Timeline, Insert Slicer, Active Field, Group. In the Insert Slicer dialog box, select the fields to create slicers for. Click OK.
How do I make a pivot chart?
Select a cell in your PivotTable. On the Insert tab, select the Insert Chart dropdown menu, and then click any chart option. The chart will now appear in the worksheet….Create a chart from a PivotTable
- Select a cell in your table.
- Select PivotTable Tools > Analyze > PivotChart .
- Select a chart.
- Select OK.
How do I edit a pivot chart?
Edit a pivot table. Click anywhere in a pivot table to open the editor. Add data—Depending on where you want to add data, under Rows, Columns, or Values, click Add. Change row or column names—Double-click a Row or Column name and enter a new name.
How do I create a sunburst chart in Excel?
Create a sunburst chart
- Select your data.
- Click Insert > Insert Hierarchy Chart > Sunburst. You can also use the All Charts tab in Recommended Charts to create a sunburst chart, although the sunburst chart will only be recommended when empty (blank) cells exist within the hierarchal structure. (
How do you insert a chart on its own sheet?
To insert a chart:
- Select the cells you want to chart, including the column titles and row labels. These cells will be the source data for the chart.
- From the Insert tab, click the desired Chart command.
- Choose the desired chart type from the drop-down menu.
- The selected chart will be inserted in the worksheet.
What is a sunburst diagram?
A Sunburst Diagram is used to visualize hierarchical data, depicted by concentric circles. The circle in the centre represents the root node, with the hierarchy moving outward from the center.
How do I change the size of my sunburst chart?
To change the type of your chart click on the Change Chart Type item in the Right-Click (Context) Menu or Design tab. In the Change Chart Type dialog, you can see the options for all chart types with the preview of your chart. Unfortunately, you don’t have any different options for your Sunburst chart.
Have you ever been frustrated by the amount of time it takes to format your Excel documents? Good news, there’s no need to keep wasting time by applying the same formatting styles over and over. With this easy trick you can select multiple sheets and format them all at once. It’s easy and will save you lots of frustration. Check out the video below:
As a recap – here’s how to format multiple sheets at the same time:
1. Ctrl + Click each sheet tab at the bottom of your worksheet (selected sheets will turn white).
2. While selected, any formatting changes you make will happen in all of the selected sheets.
3. Double-click each tab when you are done to un-select them.
Check out all all of our videos and subscribe to our official YouTube channel.
To take your Excel skills to another level check out these courses at TechRepublic Academy.
Technology Advice is able to offer our services for free because some vendors may pay us for web traffic or other sales opportunities. Our mission is to help technology buyers make better purchasing decisions, so we provide you with information for all vendors — even those that don’t pay us.