We use different languages worldwide to communicate with each other. Every so often we wonder where a word came from. How did a particular word start being used as a common word worldwide and where did it actually originate from. So to find this out we will explore the world of languages and origin of words in this article. This article will cover websites which will let you know the origin of a word.
The study of origin of a word is known as Etymology. You will find that often there are popular tales behind the origin of a word. Most of these tales are just tales and not true, but knowing how the word came into being is equally interesting. So let’s look at these websites to know the origin of words below.
Online Etymology Dictionary
Online etymology dictionary explains you the origin of words and what they meant along with how they would have sounded years back. You would see a date beside each word. This date represents the earliest evidence of this word being used in some sort of written manuscript. Now you can either search for a word you are looking for by typing it in the search box given at the top of the page, otherwise you can browse the words alphabetically. The website has a huge collection of words in it. You can go through the words and find out there origins and meanings as well.
Word Origins by English Oxford Living Dictionaries
Word Origins by English Oxford Living Dictionaries is a good website to know about a words origin. You can check out origin of a word or a phrase. You can search for the word or a phrase you are looking for or can even browse the page to know origin of different words. The website apart from this has a dictionary, thesaurus, grammar helper, etc. As this app has a dictionary, it proves to be a good source for knowing the origin of a word. You can see trending words when you scroll down the page. You can also subscribe to the newsletter on this website to receive updates regarding new words, phrases, etc.
Wordorigins.org
The website Wordorigins.org will let you know the origin of words and phrases. The website has a big list of words which you can go through, or even search for a particular word that you are looking for. The website also has a blog and discussion forum where people can discuss there views. You can login and become a member of the website so you receive regular updates from the website. You can either start browsing words by going to the big list words tab, or by searching for a word. The big list of words is in alphabetical order and there are about 400 words in here. Each word has a interesting story or folklore related to it.
Words of the World
Words of the World is a website which lets you watch videos to let you know the origin of a word. The website explains which language a word originated from through a video. The home page of the website will have a list of words for which you can see a video explaining how the word originated. The words on the home page are given in the format as shown in the screenshot above, but they can also be turned into a neat list if you like. The website is supported by the University of Nottingham and thus is a trusted source.
Learning Nerd
Learning Nerd is another website which has a section on English etymology resources. The website lists references to origin of words like there are word origin dictionaries listed, words with Greek and Latin roots are under a different category, words originating from around the world can be found under international words, and then there is a section for miscellaneous words. You can also play etymology quizzes and listen to etymology podcasts as well. The website itself doesn’t have much information about word origins but will redirect you to another website for your word needs.
Learn That Word
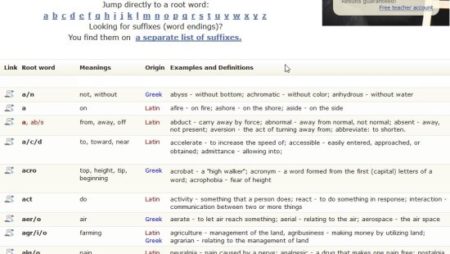
Learn That Word is another website which lists root words and prefixes. The website is pretty basic and a list of words can be seen right on the first page. The words are listed alphabetically, so you can even jump to a word that you are looking for easily. The website will list the root word, its meaning, its place of origin, and then definition and examples. This can be seen in the screenshot above.
These are the websites I found which let you know the origin of a word. Go through them and let me know which one you liked most. If you think there is a website which could be included in this article then leave a comment below.
Download Article
Download Article
The origin of the meaning and sound of words (etymology) is a fascinating and rewarding subject. The previous sentence alone has words of Latin, Greek, Anglo-Saxon, and Germanic origins! Investigating the linguistic root and history of a word can be an enjoyable pastime or a full-fledged profession that’ll help you understand why we say the things we do and why we say them in the way we do. It can also improve your vocabulary, enhance your spelling, and give you lots of fun facts to share that’ll impress your friends and colleagues.
-
1
Find a good etymological dictionary. To start informally studying etymology, buy or gain access to an authoritative dictionary that includes the linguistic origins of words in its definitions. The easiest way to tell that it does is if it has, “etymological” in the title. However, it may still include etymologies even if it does not include this in the title. Check a definition to see if there is a section labeled “origin” or “etymology.”[1]
- The most respected print dictionaries for English’s etymology include An Etymological Dictionary of Modern English, A Comprehensive Etymological Dictionary of the English Language, and The Oxford English Dictionary. The last also has an online subscription option.
- There is also a free, well-researched online dictionary that’s specifically dedicated to etymology, available here: http://www.etymonline.com/
-
2
Look for the roots. Etymologies seek the earliest origin of a word by tracing it back to its most basic components, that is, the simple words that were combined to create it in the first place. When you know the roots of a word, you can better understand how we arrived at the sound and meaning for the word that exist today.[2]
- For instance, the word “etymology” itself has Greek roots: “etymos,” which means, “true sense,” and “logia,” which means, “study of.”[3]
- Besides helping you to understand the origin of a word, knowing its roots can help you understand other words with similar roots. In the case of “etymology,” you’ll note that the root “logia,” which means “the study of,” appears in multiple other places in modern English, from “biology” to “astrology.”[4]
- Take note of any patterns you find, particularly if you’re working with the etymologies of multiple words. This will help streamline your studies.
Advertisement
- For instance, the word “etymology” itself has Greek roots: “etymos,” which means, “true sense,” and “logia,” which means, “study of.”[3]
-
3
Trace the word’s journey into English. Etymology traces not only the word’s origins but also how its meanings and spellings have developed over time. Sometimes that means that a word has traveled through more than one language on its journey into modern English.[5]
- Etymological dictionaries will usually present this trajectory in reverse-chronological order, starting with the most recent usage and showing where each iteration came from in turn.
- If we return to the word “etymology,” it entered into Old English as ethimolegia («facts of the origin and development of a word»), from Old French etimologie, ethimologie, from Latin etymologia, from Greek etymologia («analysis of a word to find its true origin»). So, it appeared in the written record of 3 languages (Greek, Latin, and French) before it entered into English.
-
4
Understand the dates. Most etymologies will include dates in their origins of words. These represent the first time a particular word appeared in a document written in English. (Keep in mind that a word may well have existed in spoken English a long time before that, but this is the date of the first written record of it that has survived.)[6]
- For example, “etymology” entered English in the 14th century but did not take on its modern spelling and definition until the 1640s.[7]
- For example, “etymology” entered English in the 14th century but did not take on its modern spelling and definition until the 1640s.[7]
-
5
Check the examples and sources. Thorough etymological dictionaries will often include documentary sources for each iteration of a word and/or examples of how a word has been used in context over time, usually through a phrase or sentence from a written document in English. This provides concrete historical evidence for the word’s origins while giving you insight into how its meaning has changed.
- For instance, the word “queen” comes from the Middle English “quene,” which can be seen in Chaucer’s Canterbury Tales, and the Old English “cwen,” which appears in Beowulf.[8]
- For instance, the word “queen” comes from the Middle English “quene,” which can be seen in Chaucer’s Canterbury Tales, and the Old English “cwen,” which appears in Beowulf.[8]
Advertisement
-
1
Look up words you’re curious about. Now that you know what to look for, start studying the etymology of those words that make you wonder, “Where did this come from?” It’s an entertaining way to get to know the historical meaning behind the things you say, and you’ll often be surprised about where they come from.
- It’s also edifying to look up those words that seem so normal that you’ve taken their origins for granted. For instance, if you study the etymology of a familiar word like “nostril,” you’ll find that it comes from Old English “nosu” (nose) and “pyrel” or “thrill” (hole). It’s literally a “nose hole.” You’ll also note that “pyrel” and “thrill” once sounded alike in English, which shows how far the language has developed phonically. That also means that the word “nostril” is surprisingly related to the word “thrilling.”
-
2
Follow up on surprising word origins. If what you find when you look into the etymology of a particular word does not make obvious sense today, do some research to figure out why its original meaning is what it is. If you’re writing a paper on etymology, briefly discuss these origins and why they are unexpected.
- For instance, you may wonder where a word like “disaster” came from. When you look it up, you’ll find that its Greek roots are the negative prefix “dis” and “astron” (star). So, it’s earliest meaning was something like “bad star.” This might be surprising until you consider Greek astrology and their strong belief that celestial bodies exerted control over our lives on Earth.[9]
- For instance, you may wonder where a word like “disaster” came from. When you look it up, you’ll find that its Greek roots are the negative prefix “dis” and “astron” (star). So, it’s earliest meaning was something like “bad star.” This might be surprising until you consider Greek astrology and their strong belief that celestial bodies exerted control over our lives on Earth.[9]
-
3
Recognize related words. Now that you know the origin of a particular word, you can use it to identify words with similar histories and therefore with related sounds and meanings.[10]
- In the case of etymology, there are not a lot of related words, but you can see that “etymological,” “etymologically,” and “etymologist” are all closely related forms. In the case of a word like “autopsy” with the Greek root “autos” (meaning, “self”), there’ll be a whole host of related words, from “autonomy” (self-governing) to “automobile” (self-moving) to “automatic” (self-acting).[11]
- In the case of etymology, there are not a lot of related words, but you can see that “etymological,” “etymologically,” and “etymologist” are all closely related forms. In the case of a word like “autopsy” with the Greek root “autos” (meaning, “self”), there’ll be a whole host of related words, from “autonomy” (self-governing) to “automobile” (self-moving) to “automatic” (self-acting).[11]
Advertisement
-
1
Get an etymology app. You can make studying etymology part of your daily routine by downloading a related app on one or more of your devices. That way, you can carry your hobby with you wherever you go. These apps can also help you understand how words have evolved from their origins and provide you with new perspectives.
- Etymology Explorer gives you engaging visual maps of word origins that are complete with full definitions, linguistic histories, and links to related words.[12]
- WordBook is a comprehensive dictionary app with a significant etymological component that provides the word origins and links to related words for thousands of entries.
- Etymology Explorer gives you engaging visual maps of word origins that are complete with full definitions, linguistic histories, and links to related words.[12]
-
2
Take a related MOOC. Sometimes there are free Massive Online Courses available on etymology. They’re taught by qualified professors at top universities and colleges, so you’re getting a dose of higher education on word history at no charge![13]
- The Open University has a free online course available on the history of the English Language that you can take at your own pace. It explores etymology alongside lexicography.[14]
- The Open University has a free online course available on the history of the English Language that you can take at your own pace. It explores etymology alongside lexicography.[14]
-
3
Go to the library. Search your local library’s online catalog for textbooks, dictionaries, studies, and other resources related to etymology. That way, you can expand your knowledge of the complex subject without paying lots of money to build your own collection of etymology books since academic books tend to be expensive.
- University libraries will probably have more etymology-related resources available than public libraries.
- This is also a great opportunity to delve into specific types of etymology that may interest you. For instance, you can get an etymology book associated with a specific language or dialect or with a particular field, like geography or medicine.
-
4
Do Internet research. A quick Internet search can yield tons of results about the etymologies of various words. You might even find some interesting discussion threads on the topic. You could also post a question to a forum site, like Quora, for more information.
- If you’re looking for more academic results, try using a site like Google Scholar.
-
5
Follow a related blog or podcast. There are many popular blogs and podcasts where you can read and listen to stories about etymology. Both offer a fun and informative way to keep up your hobby of studying etymology.
- For blogs, try the Oxford Etymologist, The Etyman Language Blog, or Omniglot Blog.
- For podcasts, try The Allusionist, Lexicon Valley, or The History of English.
Advertisement
-
1
Take a course for credit. Many colleges and universities offer traditional and online courses related to etymology. There will not be a broad array of related courses available, but there is likely to be one or two at most higher education institutions. The best place to look for classes related to etymology are in the Classics, English, and Linguistics departments.
- Keep in mind that you will have to be enrolled at a college or university in order to take a course through them. Most courses taken for credit will require you to be accepted as a student through a formal application process and to pay a tuition fee.
-
2
Apply for a linguistics degree program. No colleges or universities currently offer degrees specifically in etymology. However, many higher ed institutions do have Linguistics Departments that offer bachelor’s, master’s, and/or doctoral degrees. Getting a degree in Linguistics is the best preparation you can have for becoming a professional word historian.[15]
- The QS World University Rankings publishes an annual list of the top international programs in Linguistics according to their strengths in research and reputation along with their student and faculty ratio and diversity.[16]
- The QS World University Rankings publishes an annual list of the top international programs in Linguistics according to their strengths in research and reputation along with their student and faculty ratio and diversity.[16]
-
3
Get a related job or internship. Study etymology in a hands-on way. There isn’t too much call for professional etymologists these days. However, if you’d like to pursue a career in word history, the best way to go about it is to seek an editorial position with a quality dictionary, like the Oxford English Dictionary.[17]
- Dictionaries require constant updates to word definitions and etymologies, which means they always need new editorial staff. Search for job openings at dictionaries that interest you. They could be anything from the Oxford English Dictionary to Dictionary.com.
Advertisement
Add New Question
-
Question
Why is it important to know the etymology of words?
Katherine Demby is an Academic Consultant based in New York City. Katherine specializes in tutoring for the LSAT, GRE, SAT, ACT, and academic subjects for high school and college students. She holds a BA in History and Political Science from the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill and a JD from Yale Law School. Katherine is also a freelance writer and editor.
Academic Tutor
Expert Answer
Besides the fact that it’s super interesting, knowledge of etymology will make it much easier to identify words you don’t know. It’s especially helpful when it comes to standardized tests, and reading.
-
Question
What’s the easiest way to find where a word comes from?
Katherine Demby is an Academic Consultant based in New York City. Katherine specializes in tutoring for the LSAT, GRE, SAT, ACT, and academic subjects for high school and college students. She holds a BA in History and Political Science from the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill and a JD from Yale Law School. Katherine is also a freelance writer and editor.
Academic Tutor
Expert Answer
Look it up in an etymological dictionary! You can buy a hardcover copy, or you can just hop online and search a digital dictionary. That’s going to be the fastest way.
-
Question
What should I start studying first if I want to learn etymology?
Katherine Demby is an Academic Consultant based in New York City. Katherine specializes in tutoring for the LSAT, GRE, SAT, ACT, and academic subjects for high school and college students. She holds a BA in History and Political Science from the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill and a JD from Yale Law School. Katherine is also a freelance writer and editor.
Academic Tutor
Expert Answer
Start by working through the super common prefixes and suffixes. Once you’ve identified one, you can make inferences about other words with the same prefix or suffix. For example, matri- comes from the Latin word mater, which means «mother.» So, once you know that you can immediately figure certain things out about maternity, matricide, matrimony, or matriarchal. They’re all related to motherhood or women!
See more answers
Ask a Question
200 characters left
Include your email address to get a message when this question is answered.
Submit
Advertisement
Video
-
Read! The more you read, the more words you see. When you learn and see these words used, you will recognize other words that look similar or are used similarly. This can be a great starting point for another quick etymology study.
-
Try looking up all sorts of words, from the anatomical («wrist, bicep, knee, digit» etc) to the zany such as slang words (but be aware that some, if they are too new, may not yet have made it into the dictionary).
Advertisement
-
Since etymology is not a perfect science, not all etymologies of a given word will be the same. Some of their roots and histories may even be disputed. Check out more than one etymological definition to see how different etymologists have interpreted a word’s history.
-
The internet contains many false etymologies and origins, so be sure that you’re doing research using an authoritative dictionary. An example is CANOE — the Committee to Assign Naval Origins to Everything (not a real committee!) — which gives an entirely spurious explanation as to the origins of «brass monkey weather.»
-
Because our written record of languages is incomplete and many languages do not have a written record, etymology is not a perfect science. It can only attempt to recreate the history of words based on the limited evidence that we have available.
Advertisement
References
About This Article
Thanks to all authors for creating a page that has been read 112,952 times.
Reader Success Stories
-
Simone Kaplan
May 14, 2019
«I am currently studying for a spelling bee. This helped me learn language patterns. Thank you very much!»
Did this article help you?
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow’s weekly email newsletter
Subscribe
You’re all set!
For example what is the origin of name Catherine?
Etymology Dictionary says that:
it’s from French Catherine, from Medieval Latin Katerina, from Latin Ecaterina, from Greek Aikaterine. The -h- was introduced 16c., probably a folk etymology from Greek katheros «pure.» The initial Greek vowel is preserved in Russian form Ekaterina.
As the name of a type of pear, attested from 1640s. Catherine wheel (early 13c.) is named for St. Catherine of Alexandria, legendary virgin martyr from the time of Maximinus who was tortured on a spiked wheel. Her name day is Nov. 25. A popular saint in the Middle Ages, which accounts for the popularity of the given name.
So the origin of this word is
Greek? or Latin? or French?
How to find out?
asked Oct 22, 2014 at 15:44
7
Borrowing happens in stages. The English name Catherine is borrowed from French, the French from Latin, the Latin from Greek. From an English point of view the origin is French.
answered Oct 22, 2014 at 17:36
fdbfdb
23.2k1 gold badge33 silver badges66 bronze badges
3
Borrowing can also go back and forth. The word «flirt» is used in
French, both as a noun (for the act or for the person) and as a verb
(«flirter»). It was clearly borrowed, a few decades ago, from English.
But in English, it is said (among other possible origins) to possibly
derives from the French «conter fleurette», borrowed a long time
ago (16th century). I will not get into the etymology of «conter fleurette», since a
quick scan of the web shows many not so compatible views of it.
answered Oct 23, 2014 at 22:36
baboubabou
1,48711 silver badges18 bronze badges
Which origin?
If you’re looking for which language a word first emerged, you’d be looking for the ultimate origin.
So in the case of the name Catherine, we can say that it is ultimately from Greek Aikaterine.
But sometimes we aren’t so interested in the ultimate origin so much as an intermediate one, especially when we try to understand how the spelling or pronunciation has changed over time.
There isn’t really a specific name for this, but a term I like to use among friends is vectoral origin. Can we determine which language has transmitted a particular word to another?
Catherine was directly loaned into English through the French Catherine, hence the identical spelling and similar pronunciation.
All of the steps you can find in a dictionary altogether constitute the origin of a word, or at least a speculation thereof.
answered Dec 20, 2020 at 10:05
madprogramermadprogramer
7351 gold badge5 silver badges20 bronze badges
607
Previews
12
Favorites
Purchase options
Better World Books
DOWNLOAD OPTIONS
No suitable files to display here.
14 day loan required to access EPUB and PDF files.
IN COLLECTIONS
Books to Borrow
Books for People with Print Disabilities
Internet Archive Books
Scanned in China
Uploaded by
AngelaC-loader
on October 28, 2010
Wiki User
∙ 10y ago
Best Answer
Copy
The larger dictionaries discuss the origins of the words that
they define. And of course, lots of information is available my
means of an internet search. Many of the questions asked on this
site could be answered more rapidly and in greater detail, by
resorting to the Google search engine.
Wiki User
∙ 10y ago
This answer is:
Study guides
Add your answer:
Earn +
20
pts
Q: How do you find the origin of any word?
Write your answer…
Submit
Still have questions?
Related questions
People also asked
- Definition & Examples
- When & How to Use Etymology
- Quiz
I. What is Etymology?
Etymology is not a rhetorical or literary device. “Etymology is the investigation of word histories.” Every word in every language has a unique origin and history; words can be born in many ways, and often their histories are quite adventurous and informative. Etymology investigates and documents the lives (mainly the origins) of words.
The etymology of a word may include many things. A word’s birthday is usually given as the date of the first known usage of the word in print. If a word, like “selfie” was created within historical times, it’s origin is described. Most words are developed over hundreds of years out of previous words, going back into the ancient past, so an etymology tries to trace that development back as far as it can, usually ending with the oldest dead language that we actually have records of. Most words had slightly or very different meanings in the ancient languages they came from, which is documented as well.
Etymologies can be simple or complex. Much like the lives of people, it depends upon how much a word has traveled and what adventures it has had. Here are examples of each:
Example 1
The etymology of the word ‘etymology’ is complex, as follows:
- ethimolegia “facts of the origin and development of a word,”
- from Old French etimologie, ethimologie (14c., Modern French étymologie)
- from Greek etymologia “analysis of a word to find its true origin,” properly “study of the true sense (of a word)”
Example 2
The etymology of “show-and-tell” is much more simple:
show-and-tell (n.) elementary school teaching tool, 1948, American English.
III. Types of Etymology
Words are born and develop in many ways.
Many words begin with ‘roots’; a root’ is the central piece of most words, the part of the word that carries most of the meaning.
Example
The root of ‘English’ is ‘Engl’ which came from the ancient Germanic tribe, the Angles, who spoke a language that later became English. The -ish is just a suffix, that means “language of” in this case.
There are 1,000’s of word-roots in English (or any language). About half of English word-roots come from ancient Germanic languages, because those languages evolved into English, however the other half of English word-roots come from ancient Latin and French because England was conquered by the Norman French 1,000 years ago and English speakers had to learn most of their vocabulary, which became part of English. Contrary to what a lot of people think, though, English is not descended from Latin. It’s just that most of our more educated-sounding words were borrowed from Norman French, Latin, or Greek, because they were high-status languages.
As they grow, words can change physically and they can change in meaning. They can also give birth to new words or be adopted from far places and foreign languages. In an etymology, you will find the origins of a word and see when, where and why these changes took place.
Words develop through many processes. Here are four of the most general processes:
a. Modifications
Once people begin to use a word, they may change it, perhaps to make it easier to say, or to make it sound more different from other words, or other reasons. They may also form new words by modifying old words. ‘Selfie’ is a good example.
b. Semantic Changes
The meanings of words can change over time.
Metaphors: Technology gives us many new words through metaphor such as keyboard, mouse, and desktop.
Euphemisms: what is socially acceptable changes and then, words must, too.
- Housecleaner instead of maid.
- Server instead of waiter or waitress
Functional shift: how words get new parts of speech.
- A soldier > to soldier on
- A load > to upload
- To drive > a drive
Generalization: extending the particular to the general.
- Fanatic (religious zealot) to sports fanatic
Semantic shift: word meanings slide in meaning, as in . . .
- Mood comes from Old English mod, which meant mind or spirit
- Dream in Old English meant a festive atmosphere
c. Generation
As words are used, subtle differences become permanent changes and even new words, themselves:
- Baby talk: Jammies, bye-bye, tummy
- Blends or ‘portmanteau’ words: Spanglish, labradoodle
- Coinages (purposely invented words): Workaholic, blog
- Combining forms: Mini, clipped from miniature and added to everything: minicomputer, minivan
- Compounding: Do and Undo
- Eponyms (words named after people): Alzheimer’s disease
- Nonsense words: Supercalifragilisticexpialidocious, jabberwocky
- Onomatopoeia (words that sound like their meaning): Slam, crack, bump
- Phrasal verbs (getting by, down, in, off, on, over, and out): Tune in, clean up, buzz off
- Prefixing and suffixing: Pre-heat, legal-ize, re-educate-ion
- Reduplication (the doubling of a syllable or word element to strengthen or emphasize meaning): Flip-flop
d. Borrowing
Words are frequently adopted from foreign languages, usually with some changes in their sound:
- Many borrowed words are names of things or foods that have been brought into our culture from another: bar mitzvah, feng shui, yoga, taco, sushi.
- There are also many words which you would not realize come from foreign cultures, such as slogan (Gaelic), coyote (Nahuatl), and avatar (Sanskrit)
IV. The Importance of Using Etymology
Etymology is important because by knowing it you can become a better wordsmith. If you understand where your words came from, you understand them better and may be able to sue them more effectively, precisely and beautifully. Knowing etymology will also often help you know the meanings of words you have never seen before. If you look at two people who are related, you can see their similar features and their family tree becomes obvious. In the same way, if you are familiar with word roots and know the etymologies of some words, you can infer the meanings of other words. In this way, your vocabulary can begin to grow on its own.
V. Examples of Etymology in Literature
This section might be more accurately entitled, “etymologists in literature.” The great literary writers created much of our language.
Example 1
No one has had quite the same influence on the English language as the playwright and poet William Shakespeare. His works are extensive examples of etymology at work. If you do a quick internet search, you will find pages and pages of websites devoted to words he created or adapted to more interesting purposes. It is said that he invented over 4,000 words! He could only do this by understanding the words he was borrowing from. By manipulating old words to new purposes and situations, he was able to creatively entertain his audiences in continually new ways. Here are just a few of the words he is credited with inventing:
- assassination
- bedroom
- courtship
- epileptic
- fashionable
- hob-nob
- luggage
- puking
Example 2
J.R.R. Tolkien was another of our language’s great etymologists. He is best known as the author of The Lord of the Rings trilogy and The Hobbit, but he was also a professor of linguistics and he used his knowledge of linguistics in a very different way from Shakespeare—to create realistic fictional languages, names, poetry, and cultures; much of them were closely based on Old English and Old Norse. He also worked on the staff of the Oxford English Dictionary.
Those are only a few examples. If you look at the works of any great author, you will find that they are masters of their language.
VI. Examples of Etymology in Popular Culture
Example 1
Journalism is a huge part of our popular culture, and the best journalists are excellent etymologists. They must understand both culture and language to do their jobs effectively. They must be able to communicate with people in all areas of society and make themselves understood.
Example 2
The technological field is one of the greatest fields for etymological development. New words are being invented every day to keep up with changing technology and its uses. Simply think of your computer and you will think of many new words and new ways words are being used: microchip, data processor, iPod, metadata, bandwidth, defrag, interface.
Example 3
Acronyms are one way that words are invented, which is incredibly popular in current culture. It seems that just about everything has to be shortened to fit into a text message or a two-second sound-bite: LOL, ROFL, OMG. In addition, every institution has its own acronym: UCLA, DOD, FDA. This trend is important to etymology because things that start out as acronyms often become normal words. The words scuba, laser, radar, awol and zip (zip code) are all acronyms that have been accepted as words. Here we can see etymology hard at work.
VII. Related Terms
There are a myriad of terms related to etymology. Go back to section III of this article and you will find an extensive list of them. But, in order to be thorough, here are a few more:
- Linguistics – “the scientific study of language”
- Lexicostatistics – “the statistical study of the vocabulary of a language, with special attention to the historical links with other languages”
- Derivation – “the process whereby new words are formed from existing words or bases by affixation; “’singer’ from ‘sing’ or ‘undo’ from ‘do’ are examples of derivations”
- Folk etymology – “change in the form of a words or phrase resulting from a mistaken assumption about its composition or meaning.” For example, cockroach did not come from cock+roach, but rather from the Spanish cucaracha.