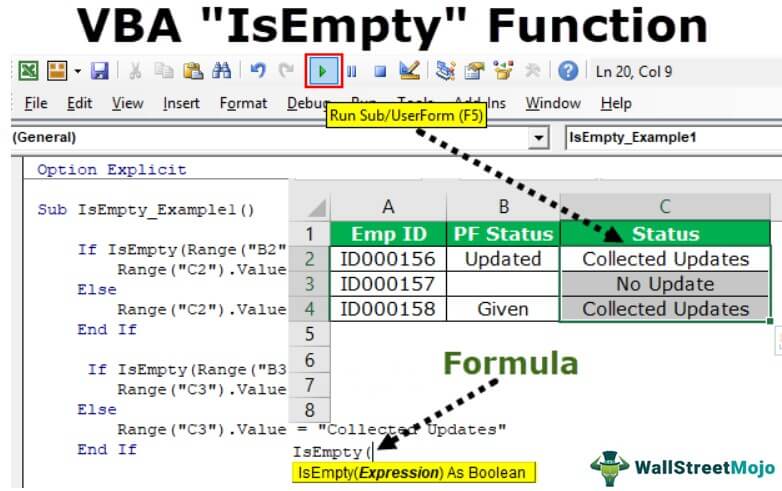
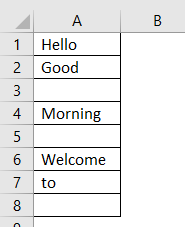
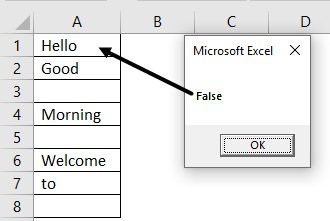
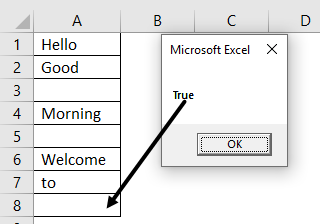
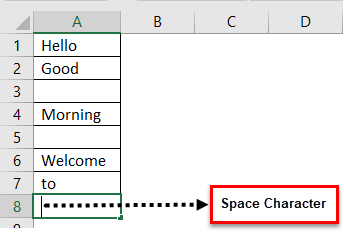
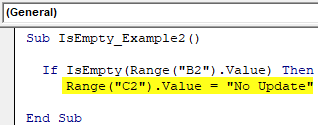
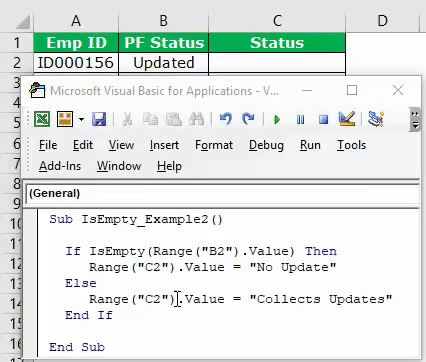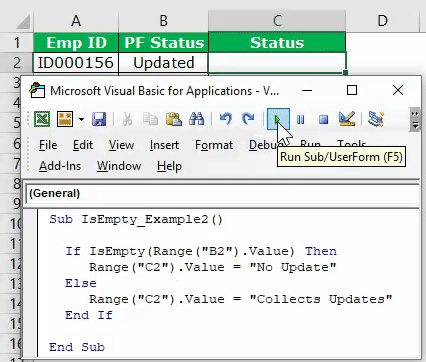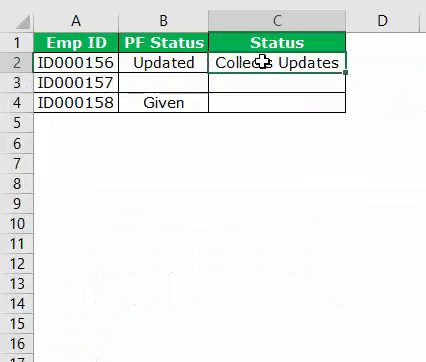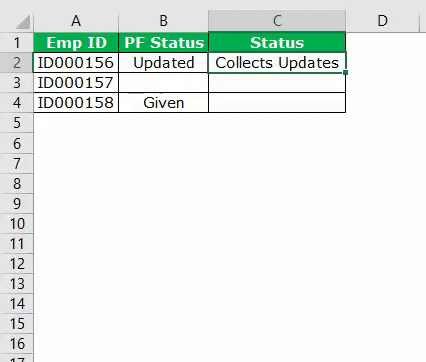
My sheet look like :
I have a function to get index of the LAST empty cell in column A:
NextRow = Range("A" & Rows.Count).End(xlUp).Row + 1
This function works to write on second array (Type2).
But now, i would like a function to get index of the FIRST empty cell in column A. So i went to this website: Select first empty cell and i tried to adapt code but it’s doesn’t work:
If Array= "Type1" Then
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = ActiveSheet
For Each cell In ws.Columns(1).Cells
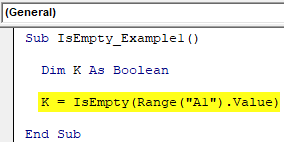
If IsEmpty(cell) = True Then NextRow = cell: Exit For 'ERROR 1004
Next cell
End If
If Array= "Type2" Then 'It s works
NextRow = Range("A" & Rows.Count).End(xlUp).Row + 1
End If
ActiveSheet.Range("A" & NextRow) = "TEST"
Could you help me to adapt my code to have NextRow = IndexOf FIRST empty cell in A ?
asked Oct 28, 2016 at 9:13
You could just use the same method you did to get the last one.
NextRow = Range("A1").End(xlDown).Row + 1
answered Oct 28, 2016 at 11:22
LissLiss
4413 silver badges8 bronze badges
1
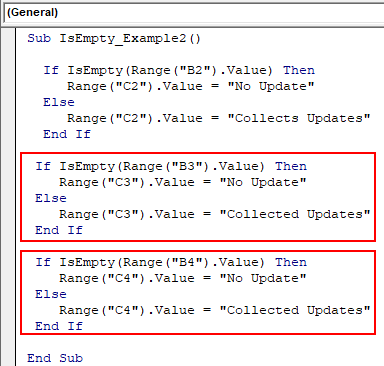
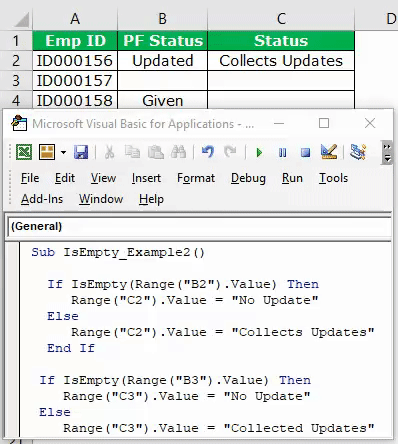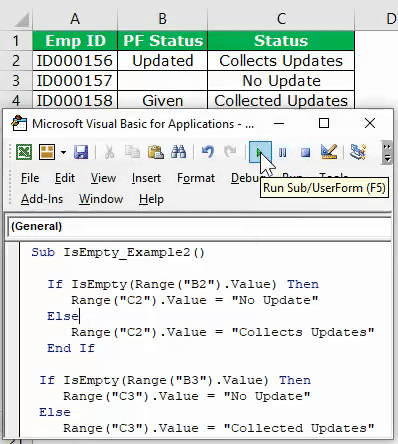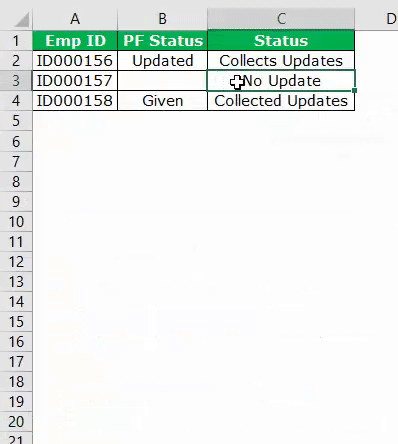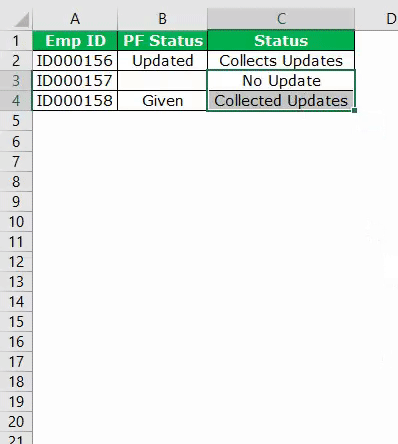
I do this and it’ works:
If Array= "Type1" Then
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = ActiveSheet
For Each cell In ws.Columns(1).Cells
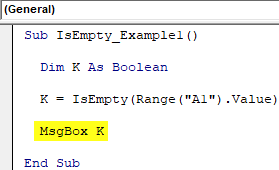
If IsEmpty(cell) = True Then
NextRow = cell.Row
Exit For
MsgBox NextRow
End If
Next cell
End If
If Array= "Type2" Then 'It s works
NextRow = Range("A" & Rows.Count).End(xlUp).Row + 1
End If
ActiveSheet.Range("A" & NextRow) = "TEST"
Vasily
5,7073 gold badges20 silver badges34 bronze badges
answered Oct 28, 2016 at 9:58
FerfaFerfa
2112 gold badges4 silver badges16 bronze badges
You should look bottom up for this.
And Find is better than xlUp.
Sub FindBlank()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim rng1 As Range
Set ws = ActiveSheet
Set rng1 = ws.Columns(1).Find("*", ws.[a1], xlFormulas, , xlByColumns, xlPrevious)
If Not rng1 Is Nothing Then
MsgBox "Last used cell is " & rng1.Address(0, 0)
Else
MsgBox ws.Name & " row1 is completely empty", vbCritical
End If
End Sub
answered Oct 31, 2016 at 8:02
brettdjbrettdj
54.6k16 gold badges113 silver badges176 bronze badges
I took a similar approach to some of the answers, but with the goal of repeatedly looking down the column until I could guarantee that there was no more populated cells below.
I turned this into a small function that I put in a standard module:-
Public Function getFirstBlankRowNumberOnSheet(sht As Worksheet, Optional startingRef As String = "A1") As Long 'may get more than 32767 rows in a spreadsheet (but probably not!)
Dim celTop As Range
Dim celBottom As Range
On Error Resume Next
Set celTop = sht.Range(startingRef)
Do
Set celBottom = celTop.End(xlDown)
Set celTop = celBottom.Offset(1) 'This will throw an error when the bottom cell is on the last available row (1048576)
Loop Until IsEmpty(celBottom.value)
getFirstBlankRowNumberOnSheet = celTop.Row
End Function
This will throw an error if there happens to be content in the row #1048576! The particulars of this are dependent on the Excel version I suppose in terms of maximum row cont allowed.
answered Jun 12, 2020 at 21:39

This VBA Find Tutorial is accompanied by an Excel workbook containing the data and macros I use in the examples below. You can get free access to this example workbook by clicking the button below.
Use the following Table of Contents to navigate to the Section you’re interested in.
Related Excel VBA and Macro Training Materials
The following VBA and Macro training materials may help you better understand and implement the contents below:
- Tutorials about general VBA constructs and structures:
- Tutorials for Beginners:
- Macros.
- VBA.
- Enable and disable macros.
- The Visual Basic Editor (VBE).
- Procedures:
- Sub procedures.
- Function procedures.
- Work with:
- Objects.
- Properties.
- Methods.
- Variables.
- Data types.
- R1C1-style references.
- Worksheet functions.
- Loops.
- Arrays.
- Refer to:
- Sheets and worksheets.
- Cell ranges.
- Tutorials for Beginners:
- Tutorials with practical VBA applications and macro examples:
- Find the last row or last column.
- Set or get a cell’s or cell range’s value.
- Check if a cell is empty.
- Use the VLookup function.
- The comprehensive and actionable Books at The Power Spreadsheets Library:
- Excel Macros for Beginners Book Series.
- VBA Fundamentals Book Series.
#1. Excel VBA Find (Cell with) Value in Cell Range
VBA Code to Find (Cell with) Value in Cell Range
To find a cell with a numeric value in a cell range, use the following structure/template in the applicable statement:
CellRangeObject.Find(What:=SearchedValue, After:=SingleCellRangeObject, LookIn:=xlValues, LookAt:=xlWhole, SearchOrder:=XlSearchOrderConstant, SearchDirection:=XlSearchDirectionConstant)
The following Sections describe the main elements in this structure.
CellRangeObject
A Range object representing the cell range you search in.
Find
The Range.Find method:
- Finds specific information (the numeric value you search for) in a cell range (CellRangeObject).
- Returns a Range object representing the first cell where the information is found.
What:=SearchedValue
The What parameter of the Range.Find method specifies the data to search for.
To find a cell with a numeric value in a cell range, set the What parameter to the numeric value you search for (SearchedValue).
After:=SingleCellRangeObject
The After parameter of the Range.Find method specifies the cell after which the search begins. This must be a single cell in the cell range you search in (CellRangeObject).
If you omit specifying the After parameter, the search begins after the first cell (in the upper left corner) of the cell range you search in (CellRangeObject).
To find a cell with a numeric value in a cell range, set the After parameter to a Range object representing the cell after which the search begins.
LookIn:=xlValues
The LookIn parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the type of data to search in.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlFindLookIn enumeration.
To find a cell with a numeric value in a cell range, set the LookIn parameter to xlValues. xlValues refers to values.
LookAt:=xlWhole
The LookAt parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies against which of the following the data you are searching for is matched:
- The entire/whole searched cell contents.
- Any part of the searched cell contents.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlLookAt enumeration.
To find a cell with a numeric value in a cell range, set the LookAt parameter to xlWhole. xlWhole matches the data you are searching for against the entire/whole searched cell contents.
SearchOrder:=XlSearchOrderConstant
The SearchOrder parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the order in which the applicable cell range (CellRangeObject) is searched:
- By rows.
- By columns.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlSearchOrder enumeration.
To find a cell with a numeric value in a cell range, set the SearchOrder parameter to either of the following, as applicable:
- xlByRows (SearchOrder:=xlByRows): To search by rows.
- xlByColumns (SearchOrder:=xlByColumns): To search by columns.
SearchDirection:=XlSearchDirectionConstant
The SearchDirection parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the search direction:
- Search for the previous match.
- Search for the next match.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlSearchDirection enumeration.
To find a cell with a numeric value in a cell range, set the SearchDirection parameter to either of the following, as applicable:
- xlNext (SearchDirection:=xlNext): To search for the next match.
- xlPrevious (SearchDirection:=xlPrevious): To search for the previous match.
Macro Example to Find (Cell with) Value in Cell Range
The following macro (User-Defined Function) example does the following:
- Accepts two arguments:
- MyRange: The cell range you search in.
- MyValue: The numeric value you search for.
- Finds MyValue in MyRange.
- Returns a string containing the address (as an A1-style relative reference) of the first cell in the cell range (MyRange) where the numeric value (MyValue) is found.
Function FindValueInCellRange(MyRange As Range, MyValue As Variant) As String
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-find/
'This UDF:
'(1) Accepts 2 arguments: MyRange and MyValue
'(2) Finds a value passed as argument (MyValue) in a cell range passed as argument (MyRange)
'(3) Returns the address (as an A1-style relative reference) of the first cell in the cell range (MyRange) where the value (MyValue) is found
With MyRange
FindValueInCellRange = .Find(What:=MyValue, After:=.Cells(.Cells.Count), LookIn:=xlValues, LookAt:=xlWhole, SearchOrder:=xlByRows, SearchDirection:=xlNext).Address(RowAbsolute:=False, ColumnAbsolute:=False)
End With
End Function
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Find (Cell with) Value in Cell Range
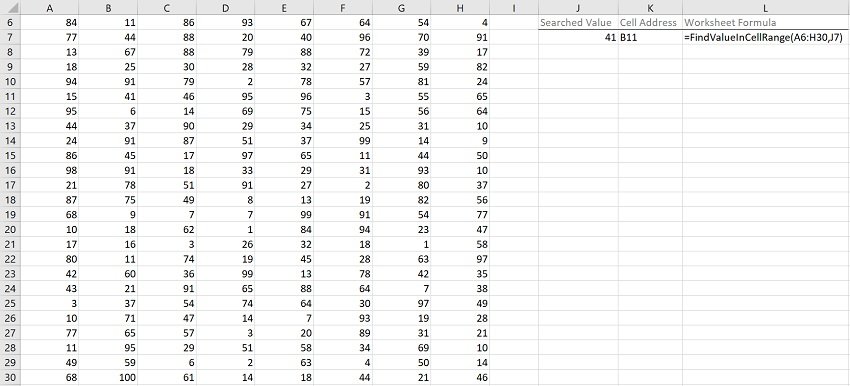
The following image illustrates the effects of using the macro (User-Defined Function) example. In this example:
- Columns A through H (cells A6 to H30) contain randomly generated values.
- Cell J7 contains the searched value (41).
- Cell K7 contains the worksheet formula that works with the macro (User-Defined Function) example. This worksheet formula returns the address (as an A1-style relative reference) of the first cell in the cell range (MyRange) where the numeric value (MyValue) is found. This is cell B11.
- Cell L7 displays the worksheet formula used in cell K7 (=FindValueInCellRange(A6:H30,J7)).
- The cell range where the search is carried out contains cells A6 to H30 (A6:H30).
- The searched value is stored in cell J7 (J7).
#2. Excel VBA Find (Cell with) Value in Table
VBA Code to Find (Cell with) Value in Table
To find a cell with a numeric value in an Excel Table, use the following structure/template in the applicable statement:
ListObjectObject.DataBodyRange.Find(What:=SearchedValue, After:=SingleCellRangeObject, LookIn:=xlValues, LookAt:=xlWhole, SearchOrder:=XlSearchOrderConstant, SearchDirection:=XlSearchDirectionConstant)
The following Sections describe the main elements in this structure.
ListObjectObject
A ListObject object representing the Excel Table you search in.
DataBodyRange
The ListObject.DataBodyRange property returns a Range object representing the cell range containing an Excel Table’s values (excluding the headers).
Find
The Range.Find method:
- Finds specific information (the numeric value you search for) in a cell range (containing the applicable Excel Table’s values).
- Returns a Range object representing the first cell where the information is found.
What:=SearchedValue
The What parameter of the Range.Find method specifies the data to search for.
To find a cell with a numeric value in an Excel Table, set the What parameter to the numeric value you search for (SearchedValue).
After:=SingleCellRangeObject
The After parameter of the Range.Find method specifies the cell after which the search begins. This must be a single cell in the cell range you search in (containing the applicable Excel Table’s values).
If you omit specifying the After parameter, the search begins after the first cell (in the upper left corner) of the cell range you search in (containing the applicable Excel Table’s values).
To find a cell with a numeric value in an Excel Table, set the After parameter to a Range object representing the cell after which the search begins.
LookIn:=xlValues
The LookIn parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the type of data to search in.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlFindLookIn enumeration.
To find a cell with a numeric value in an Excel Table, set the LookIn parameter to xlValues. xlValues refers to values.
LookAt:=xlWhole
The LookAt parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies against which of the following the data you are searching for is matched:
- The entire/whole searched cell contents.
- Any part of the searched cell contents.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlLookAt enumeration.
To find a cell with a numeric value in an Excel Table, set the LookAt parameter to xlWhole. xlWhole matches the data you are searching for against the entire/whole searched cell contents.
SearchOrder:=XlSearchOrderConstant
The SearchOrder parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the order in which the applicable cell range (containing the applicable Excel Table’s values) is searched:
- By rows.
- By columns.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlSearchOrder enumeration.
To find a cell with a numeric value in an Excel Table, set the SearchOrder parameter to either of the following, as applicable:
- xlByRows (SearchOrder:=xlByRows): To search by rows.
- xlByColumns (SearchOrder:=xlByColumns): To search by columns.
SearchDirection:=XlSearchDirectionConstant
The SearchDirection parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the search direction:
- Search for the previous match.
- Search for the next match.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlSearchDirection enumeration.
To find a cell with a numeric value in an Excel Table, set the SearchDirection parameter to either of the following, as applicable:
- xlNext (SearchDirection:=xlNext): To search for the next match.
- xlPrevious (SearchDirection:=xlPrevious): To search for the previous match.
Macro Example to Find (Cell with) Value in Table
The following macro (User-Defined Function) example does the following:
- Accepts 3 arguments:
- MyWorksheetName: The name of the worksheet where the Excel Table you search in is stored.
- MyValue: The numeric value you search for.
- MyTableIndex: The index number of the Excel Table (stored in the worksheet named MyWorksheetName) you search in. MyTableIndex is an optional argument with a default value of 1.
- Finds MyValue in the applicable Excel Table’s values (excluding the headers).
- Returns a string containing the address (as an A1-style relative reference) of the first cell in the applicable Excel Table where the numeric value (MyValue) is found.
Function FindValueInTable(MyWorksheetName As String, MyValue As Variant, Optional MyTableIndex As Long = 1) As String
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-find/
'This UDF:
'(1) Accepts 3 arguments: MyWorksheetName, MyValue and MyTableIndex
'(2) Finds a value passed as argument (MyValue) in an Excel Table stored in a worksheet whose name is passed as argument (MyWorksheetName). The index number of the Excel Table is either:
'(1) Passed as an argument (MyTableIndex); or
'(2) Assumed to be 1 (if MyTableIndex is omitted)
'(3) Returns the address (as an A1-style relative reference) of the first cell in the Excel Table (stored in the MyWorksheetName worksheet and whose index is MyTableIndex) where the value (MyValue) is found
With ThisWorkbook.Worksheets(MyWorksheetName).ListObjects(MyTableIndex).DataBodyRange
FindValueInTable = .Find(What:=MyValue, After:=.Cells(.Cells.Count), LookIn:=xlValues, LookAt:=xlWhole, SearchOrder:=xlByRows, SearchDirection:=xlNext).Address(RowAbsolute:=False, ColumnAbsolute:=False)
End With
End Function
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Find (Cell with) Value in Table
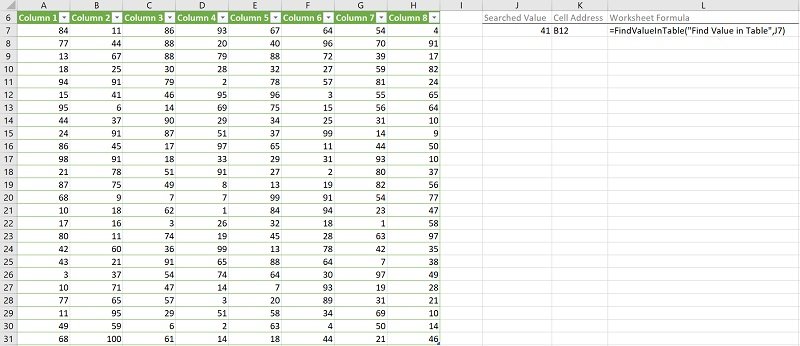
The following image illustrates the effects of using the macro (User-Defined Function) example. In this example:
- Columns A through H (cells A6 to H31) contain an Excel Table with randomly generated values.
- Cell J7 contains the searched value (41).
- Cell K7 contains the worksheet formula that works with the macro (User-Defined Function) example. This worksheet formula returns the address (as an A1-style relative reference) of the first cell in the Excel Table where the numeric value (MyValue) is found. This is cell B12.
- Cell L7 displays the worksheet formula used in cell K7 (=FindValueInTable(“Find Value in Table”,J7)).
- The name of the worksheet where the Excel Table is stored is “Find Value in Table” (“Find Value in Table”).
- The searched value is stored in cell J7 (J7).
- The index number of the Excel Table is 1 (by default).
#3. Excel VBA Find (Cell with) Value in Column
VBA Code to Find (Cell with) Value in Column
To find a cell with a numeric value in a column, use the following structure/template in the applicable statement:
RangeObjectColumn.Find(What:=SearchedValue, After:=SingleCellRangeObject, LookIn:=xlValues, LookAt:=xlWhole, SearchOrder:=xlByRows, SearchDirection:=XlSearchDirectionConstant)
The following Sections describe the main elements in this structure.
RangeObjectColumn
A Range object representing the column you search in.
Find
The Range.Find method:
- Finds specific information (the numeric value you search for) in a cell range (RangeObjectColumn).
- Returns a Range object representing the first cell where the information is found.
What:=SearchedValue
The What parameter of the Range.Find method specifies the data to search for.
To find a cell with a numeric value in a column, set the What parameter to the numeric value you search for (SearchedValue).
After:=SingleCellRangeObject
The After parameter of the Range.Find method specifies the cell after which the search begins. This must be a single cell in the column you search in (RangeObjectColumn).
If you omit specifying the After parameter, the search begins after the first cell of the column you search in (RangeObjectColumn).
To find a cell with a numeric value in a column, set the After parameter to a Range object representing the cell after which the search begins.
LookIn:=xlValues
The LookIn parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the type of data to search in.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlFindLookIn enumeration.
To find a cell with a numeric value in a column, set the LookIn parameter to xlValues. xlValues refers to values.
LookAt:=xlWhole
The LookAt parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies against which of the following the data you are searching for is matched:
- The entire/whole searched cell contents.
- Any part of the searched cell contents.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlLookAt enumeration.
To find a cell with a numeric value in a column, set the LookAt parameter to xlWhole. xlWhole matches the data you are searching for against the entire/whole searched cell contents.
SearchOrder:=xlByRows
The SearchOrder parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the order in which the applicable column (RangeObjectColumn) is searched:
- By rows.
- By columns.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlSearchOrder enumeration.
To find a cell with a numeric value in a column, set the SearchOrder parameter to xlByRows. xlByRows results in the Range.Find method searching by rows.
SearchDirection:=XlSearchDirectionConstant
The SearchDirection parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the search direction:
- Search for the previous match.
- Search for the next match.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlSearchDirection enumeration.
To find a cell with a numeric value in a column, set the SearchDirection parameter to either of the following, as applicable:
- xlNext (SearchDirection:=xlNext): To search for the next match.
- xlPrevious (SearchDirection:=xlPrevious): To search for the previous match.
Macro Example to Find (Cell with) Value in Column
The following macro (User-Defined Function) example does the following:
- Accepts two arguments:
- MyColumn: The column you search in.
- MyValue: The numeric value you search for.
- Finds MyValue in MyColumn.
- Returns a string containing the address (as an A1-style relative reference) of the first cell in the column (MyColumn) where the numeric value (MyValue) is found.
Function FindValueInColumn(MyColumn As Range, MyValue As Variant) As String
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-find/
'This UDF:
'(1) Accepts 2 arguments: MyColumn and MyValue
'(2) Finds a value passed as argument (MyValue) in a column passed as argument (MyColumn)
'(3) Returns the address (as an A1-style relative reference) of the first cell in the column (MyColumn) where the value (MyValue) is found
With MyColumn
FindValueInColumn = .Find(What:=MyValue, After:=.Cells(.Cells.Count), LookIn:=xlValues, LookAt:=xlWhole, SearchOrder:=xlByRows, SearchDirection:=xlNext).Address(RowAbsolute:=False, ColumnAbsolute:=False)
End With
End Function
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Find (Cell with) Value in Column
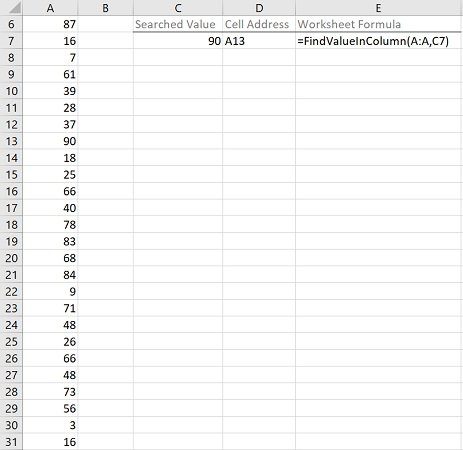
The following image illustrates the effects of using the macro (User-Defined Function) example. In this example:
- Column A (cells A6 to A31) contains randomly generated values.
- Cell C7 contains the searched value (90).
- Cell D7 contains the worksheet formula that works with the macro (User-Defined Function) example. This worksheet formula returns the address (as an A1-style relative reference) of the first cell in the column (MyColumn) where the numeric value (MyValue) is found. This is cell A13.
- Cell E7 displays the worksheet formula used in cell D7 (=FindValueInColumn(A:A,C7)).
- The column where the search is carried out is column A (A:A).
- The searched value is stored in cell C7 (C7).
#4. Excel VBA Find (Cell with) Value in Table Column
VBA Code to Find (Cell with) Value in Table Column
To find a cell with a numeric value in an Excel Table column, use the following structure/template in the applicable statement:
ListColumnObject.DataBodyRange.Find(What:=SearchedValue, After:=SingleCellRangeObject, LookIn:=xlValues, LookAt:=xlWhole, SearchOrder:=XlSearchOrderConstant, SearchDirection:=XlSearchDirectionConstant)
The following Sections describe the main elements in this structure.
ListColumnObject
A ListColumn object representing the Excel Table column you search in.
DataBodyRange
The ListColumn.DataBodyRange property returns a Range object representing the cell range containing an Excel Table column’s values (excluding the header).
Find
The Range.Find method:
- Finds specific information (the numeric value you search for) in a cell range (containing the applicable Excel Table column’s values).
- Returns a Range object representing the first cell where the information is found.
What:=SearchedValue
The What parameter of the Range.Find method specifies the data to search for.
To find a cell with a numeric value in an Excel Table column, set the What parameter to the numeric value you search for (SearchedValue).
After:=SingleCellRangeObject
The After parameter of the Range.Find method specifies the cell after which the search begins. This must be a single cell in the cell range you search in (containing the applicable Excel Table column’s values).
If you omit specifying the After parameter, the search begins after the first cell of the cell range you search in (containing the applicable Excel Table column’s values).
To find a cell with a numeric value in an Excel Table column, set the After parameter to a Range object representing the cell after which the search begins.
LookIn:=xlValues
The LookIn parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the type of data to search in.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlFindLookIn enumeration.
To find a cell with a numeric value in an Excel Table column, set the LookIn parameter to xlValues. xlValues refers to values.
LookAt:=xlWhole
The LookAt parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies against which of the following the data you are searching for is matched:
- The entire/whole searched cell contents.
- Any part of the searched cell contents.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlLookAt enumeration.
To find a cell with a numeric value in an Excel Table column, set the LookAt parameter to xlWhole. xlWhole matches the data you are searching for against the entire/whole searched cell contents.
SearchOrder:=XlSearchOrderConstant
The SearchOrder parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the order in which the applicable cell range (containing the applicable Excel Table column’s values) is searched:
- By rows.
- By columns.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlSearchOrder enumeration.
To find a cell with a numeric value in an Excel Table column, set the SearchOrder parameter to either of the following, as applicable:
- xlByRows (SearchOrder:=xlByRows): To search by rows.
- xlByColumns (SearchOrder:=xlByColumns): To search by columns.
SearchDirection:=XlSearchDirectionConstant
The SearchDirection parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the search direction:
- Search for the previous match.
- Search for the next match.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlSearchDirection enumeration.
To find a cell with a numeric value in an Excel Table column, set the SearchDirection parameter to either of the following, as applicable:
- xlNext (SearchDirection:=xlNext): To search for the next match.
- xlPrevious (SearchDirection:=xlPrevious): To search for the previous match.
Macro Example to Find (Cell with) Value in Table Column
The following macro (User-Defined Function) example does the following:
- Accepts 4 arguments:
- MyWorksheetName: The name of the worksheet where the Excel Table (containing the column you search in) is stored.
- MyColumnIndex: The index/column number of the column you search in (in the applicable Excel Table).
- MyValue: The numeric value you search for.
- MyTableIndex: The index number of the Excel Table (stored in the worksheet named MyWorksheetName) containing the column you search in. MyTableIndex is an optional argument with a default value of 1.
- Finds MyValue in the applicable Excel Table column’s values (excluding the header).
- Returns a string containing the address (as an A1-style relative reference) of the first cell in the applicable Excel Table column where the numeric value (MyValue) is found.
Function FindValueInTableColumn(MyWorksheetName As String, MyColumnIndex As Long, MyValue As Variant, Optional MyTableIndex As Long = 1) As String
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-find/
'This UDF:
'(1) Accepts 4 arguments: MyWorksheetName, MyColumnIndex, MyValue and MyTableIndex
'(2) Finds a value passed as argument (MyValue) in an Excel Table column, where:
'(1) The table column's index is passed as argument (MyColumnIndex); and
'(2) The Excel Table is stored in a worksheet whose name is passed as argument (MyWorksheetName). The index number of the Excel Table is either:
'(1) Passed as an argument (MyTableIndex); or
'(2) Assumed to be 1 (if MyTableIndex is omitted)
'(3) Returns the address (as an A1-style relative reference) of the first cell in the applicable Excel Table column where the value (MyValue) is found
With ThisWorkbook.Worksheets(MyWorksheetName).ListObjects(MyTableIndex).ListColumns(MyColumnIndex).DataBodyRange
FindValueInTableColumn = .Find(What:=MyValue, After:=.Cells(.Cells.Count), LookIn:=xlValues, LookAt:=xlWhole, SearchOrder:=xlByRows, SearchDirection:=xlNext).Address(RowAbsolute:=False, ColumnAbsolute:=False)
End With
End Function
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Find (Cell with) Value in Table Column
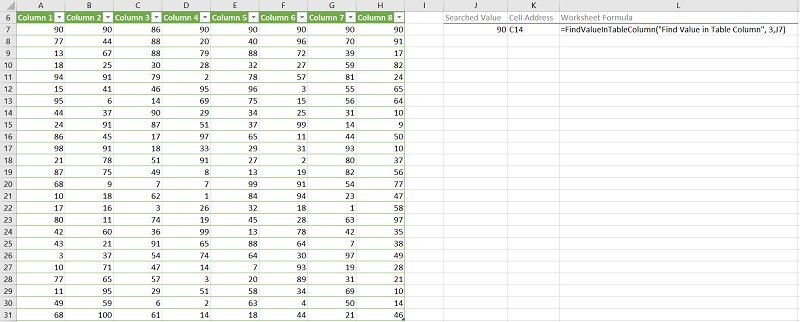
The following image illustrates the effects of using the macro (User-Defined Function) example. In this example:
- Columns A through H (cells A6 to H31) contain an Excel Table with randomly generated values. Cells in the first row (row 7) contain the searched value (90), except for the cell in the searched column (Column 3).
- Cell J7 contains the searched value (90).
- Cell K7 contains the worksheet formula that works with the macro (User-Defined Function) example. This worksheet formula returns the address (as an A1-style relative reference) of the first cell in the applicable Excel Table column (Column 3) where the numeric value (MyValue) is found. This is cell C14.
- Cell L7 displays the worksheet formula used in cell K7 (=FindValueInTableColumn(“Find Value in Table Column”,3, J7)).
- The name of the worksheet where the Excel Table is stored is “Find Value in Table Column” (“Find Value in Table Column”).
- The index number of the Excel Table column is 3 (3).
- The searched value is stored in cell J7 (J7).
- The index number of the Excel Table is 1 (by default).
#5. Excel VBA Find Minimum Value in Cell Range
VBA Code to Find Minimum Value in Cell Range
To find the minimum value in a cell range, use the following structure/template in the applicable statement:
Application.Min(CellRangeObject)
The following Sections describe the main elements in this structure.
Application.Min
The WorksheetFunction.Min method returns the minimum value in a set of values.
CellRangeObject
The WorksheetFunction.Min method accepts up to thirty parameters (Arg1 to Arg30). These are the values for which you want to find the minimum value.
To find the minimum value in a cell range, pass a Range object (CellRangeObject) representing the cell range whose minimum value you want to find as method parameter.
Macro Example to Find Minimum Value in Cell Range
The following macro (User-Defined Function) example does the following:
- Accepts 1 argument (MyRange): The cell range whose minimum value you search for.
- Finds and returns the minimum value in the cell range (MyRange).
Function FindMinimumValueInCellRange(MyRange As Range) As Double
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-find/
'This UDF:
'(1) Accepts 1 argument: MyRange
'(2) Finds the minimum value in the cell range passed as argument (MyRange)
FindMinimumValueInCellRange = Application.Min(MyRange)
End Function
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Find Minimum Value in Cell Range
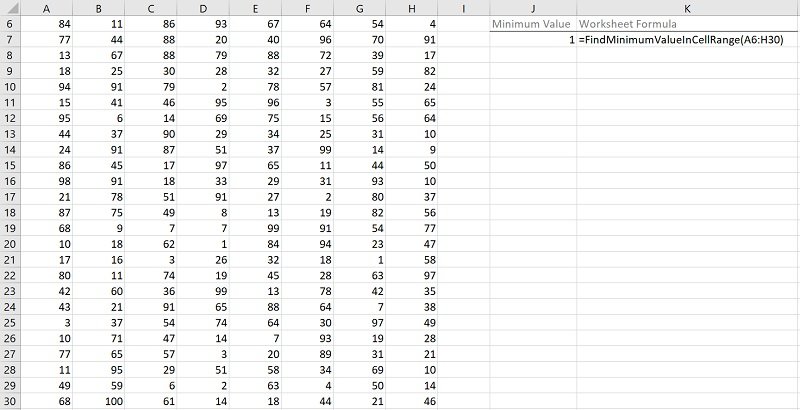
The following image illustrates the effects of using the macro (User-Defined Function) example. In this example:
- Columns A through H (cells A6 to H30) contain randomly generated values.
- Cell J7 contains the worksheet formula that works with the macro (User-Defined Function) example. This worksheet formula returns the minimum value in the cell range (MyRange). This is the number 1.
- Cell K7 displays the worksheet formula used in cell J7 (=FindMinimumValueInCellRange(A6:H30)). The cell range where the search is carried out contains cells A6 to H30 (A6:H30).
#6. Excel VBA Find (Cell with) String (or Text) in Cell Range
VBA Code to Find (Cell with) String (or Text) in Cell Range
To find a cell with a string (or text) in a cell range, use the following structure/template in the applicable statement:
CellRangeObject.Find(What:=SearchedString, After:=SingleCellRangeObject, LookIn:=XlFindLookInConstant, LookAt:=XlLookAtConstant, SearchOrder:=XlSearchOrderConstant, SearchDirection:=XlSearchDirectionConstant, MatchCase:=BooleanValue)
The following Sections describe the main elements in this structure.
CellRangeObject
A Range object representing the cell range you search in.
Find
The Range.Find method:
- Finds specific information (the string or text you search for) in a cell range (CellRangeObject).
- Returns a Range object representing the first cell where the information is found.
What:=SearchedString
The What parameter of the Range.Find method specifies the data to search for.
To find a cell with a string (or text) in a cell range, set the What parameter to the string (or text) you search for (SearchedString).
After:=SingleCellRangeObject
The After parameter of the Range.Find method specifies the cell after which the search begins. This must be a single cell in the cell range you search in (CellRangeObject).
If you omit specifying the After parameter, the search begins after the first cell (in the upper left corner) of the cell range you search in (CellRangeObject).
To find a cell with a string (or text) in a cell range, set the After parameter to a Range object representing the cell after which the search begins.
LookIn:=XlFindLookInConstant
The LookIn parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the type of data to search in.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlFindLookIn enumeration.
To find a cell with a string (or text) in a cell range, set the LookIn parameter to either of the following, as applicable:
- xlFormulas (LookIn:=xlFormulas): To search in the applicable cell range’s formulas.
- xlValues (LookIn:=xlValues): To search in the applicable cell range’s values.
LookAt:=XlLookAtConstant
The LookAt parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies against which of the following the data you are searching for is matched:
- The entire/whole searched cell contents.
- Any part of the searched cell contents.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlLookAt enumeration.
To find a cell with a string (or text) in a cell range, set the LookAt parameter to either of the following, as applicable:
- xlWhole (LookAt:=xlWhole): To match against the entire/whole searched cell contents.
- xlPart (LookAt:=xlPart): To match against any part of the searched cell contents.
SearchOrder:=XlSearchOrderConstant
The SearchOrder parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the order in which the applicable cell range (CellRangeObject) is searched:
- By rows.
- By columns.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlSearchOrder enumeration.
To find a cell with a string (or text) in a cell range, set the SearchOrder parameter to either of the following, as applicable:
- xlByRows (SearchOrder:=xlByRows): To search by rows.
- xlByColumns (SearchOrder:=xlByColumns): To search by columns.
SearchDirection:=XlSearchDirectionConstant
The SearchDirection parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the search direction:
- Search for the previous match.
- Search for the next match.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlSearchDirection enumeration.
To find a cell with a string (or text) in a cell range, set the SearchDirection parameter to either of the following, as applicable:
- xlNext (SearchDirection:=xlNext): To search for the next match.
- xlPrevious (SearchDirection:=xlPrevious): To search for the previous match.
MatchCase:=BooleanValue
The MatchCase parameter of the Range.Find method specifies whether the search is:
- Case-sensitive; or
- Case-insensitive.
The default value of the MatchCase parameter is False.
To find a cell with a string (or text) in a cell range, set the MatchCase parameter to either of the following, as applicable:
- True (MatchCase:=True): To carry out a case-sensitive search.
- False (MatchCase:=False): To carry out a case-insensitive search.
Macro Example to Find (Cell with) String (or Text) in Cell Range
The following macro (User-Defined Function) example does the following:
- Accepts two arguments:
- MyRange: The cell range you search in.
- MyString: The string (or text) you search for.
- Finds MyString in MyRange. The search is case-insensitive.
- Returns a string containing the address (as an A1-style relative reference) of the first cell in the cell range (MyRange) where the string or text (MyString) is found.
Function FindStringInCellRange(MyRange As Range, MyString As Variant) As String
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-find/
'This UDF:
'(1) Accepts 2 arguments: MyRange and MyString
'(2) Finds a string passed as argument (MyString) in a cell range passed as argument (MyRange). The search is case-insensitive
'(3) Returns the address (as an A1-style relative reference) of the first cell in the cell range (MyRange) where the string (MyString) is found
With MyRange
FindStringInCellRange = .Find(What:=MyString, After:=.Cells(.Cells.Count), LookIn:=xlValues, LookAt:=xlWhole, SearchOrder:=xlByRows, SearchDirection:=xlNext, MatchCase:=False).Address(RowAbsolute:=False, ColumnAbsolute:=False)
End With
End Function
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Find (Cell with) String (or Text) in Cell Range
The following image illustrates the effects of using the macro (User-Defined Function) example. In this example:
- Columns A through H (cells A6 to H30) contain randomly generated words.
- Cell J7 contains the searched string or text (Excel).
- Cell K7 contains the worksheet formula that works with the macro (User-Defined Function) example. This worksheet formula returns the address (as an A1-style relative reference) of the first cell in the cell range (MyRange) where the string or text (MyString) is found. This is cell F20.
- Cell L7 displays the worksheet formula used in cell K7 (=FindStringInCellRange(A6:H30,J7)).
- The cell range where the search is carried out contains cells A6 to H30 (A6:H30).
- The searched string or text is stored in cell J7 (J7).

#7. Excel VBA Find (Cell with) String (or Text) in Column
VBA Code to Find (Cell with) String (or Text) in Column
To find a cell with a string (or text) in a column, use the following structure/template in the applicable statement:
RangeObjectColumn.Find(What:=SearchedString, After:=SingleCellRangeObject, LookIn:=XlFindLookInConstant, LookAt:=XlLookAtConstant, SearchOrder:=xlByRows, SearchDirection:=XlSearchDirectionConstant, MatchCase:=BooleanValue)
The following Sections describe the main elements in this structure.
RangeObjectColumn
A Range object representing the column you search in.
Find
The Range.Find method:
- Finds specific information (the string or text you search for) in a cell range (RangeObjectColumn).
- Returns a Range object representing the first cell where the information is found.
What:=SearchedString
The What parameter of the Range.Find method specifies the data to search for.
To find a cell with a string (or text) in a column, set the What parameter to the string (or text) you search for (SearchedString).
After:=SingleCellRangeObject
The After parameter of the Range.Find method specifies the cell after which the search begins. This must be a single cell in the column you search in (RangeObjectColumn).
If you omit specifying the After parameter, the search begins after the first cell of the column you search in (RangeObjectColumn).
To find a cell with a string (or text) in a column, set the After parameter to a Range object representing the cell after which the search begins.
LookIn:=XlFindLookInConstant
The LookIn parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the type of data to search in.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlFindLookIn enumeration.
To find a cell with a string (or text) in a column, set the LookIn parameter to either of the following, as applicable:
- xlFormulas (LookIn:=xlFormulas): To search in the applicable column’s formulas.
- xlValues (LookIn:=xlValues): To search in the applicable column’s values.
LookAt:=XlLookAtConstant
The LookAt parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies against which of the following the data you are searching for is matched:
- The entire/whole searched cell contents.
- Any part of the searched cell contents.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlLookAt enumeration.
To find a cell with a string (or text) in a column, set the LookAt parameter to either of the following, as applicable:
- xlWhole (LookAt:=xlWhole): To match against the entire/whole searched cell contents.
- xlPart (LookAt:=xlPart): To match against any part of the searched cell contents.
SearchOrder:=xlByRows
The SearchOrder parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the order in which the applicable column (RangeObjectColumn) is searched:
- By rows.
- By columns.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlSearchOrder enumeration.
To find a cell with a string (or text) in a column, set the SearchOrder parameter to xlByRows. xlByRows results in the Range.Find method searching by rows.
SearchDirection:=XlSearchDirectionConstant
The SearchDirection parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the search direction:
- Search for the previous match.
- Search for the next match.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlSearchDirection enumeration.
To find a cell with a string (or text) in a column, set the SearchDirection parameter to either of the following, as applicable:
- xlNext (SearchDirection:=xlNext): To search for the next match.
- xlPrevious (SearchDirection:=xlPrevious): To search for the previous match.
MatchCase:=BooleanValue
The MatchCase parameter of the Range.Find method specifies whether the search is:
- Case-sensitive; or
- Case-insensitive.
The default value of the MatchCase parameter is False.
To find a cell with a string (or text) in a column, set the MatchCase parameter to either of the following, as applicable:
- True (MatchCase:=True): To carry out a case-sensitive search.
- False (MatchCase:=False): To carry out a case-insensitive search.
Macro Example to Find (Cell with) String (or Text) in Column
The following macro (User-Defined Function) example does the following:
- Accepts two arguments:
- MyColumn: The column you search in.
- MyString: The string (or text) you search for.
- Finds MyString in MyColumn. The search is case-insensitive.
- Returns a string containing the address (as an A1-style relative reference) of the first cell in the column (MyColumn) where the string or text (MyString) is found.
Function FindStringInColumn(MyColumn As Range, MyString As Variant) As String
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-find/
'This UDF:
'(1) Accepts 2 arguments: MyColumn and MyString
'(2) Finds a string passed as argument (MyString) in a column passed as argument (MyColumn). The search is case-insensitive
'(3) Returns the address (as an A1-style relative reference) of the first cell in the column (MyColumn) where the string (MyString) is found
With MyColumn
FindStringInColumn = .Find(What:=MyString, After:=.Cells(.Cells.Count), LookIn:=xlValues, LookAt:=xlWhole, SearchOrder:=xlByRows, SearchDirection:=xlNext, MatchCase:=False).Address(RowAbsolute:=False, ColumnAbsolute:=False)
End With
End Function
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Find (Cell with) String (or Text) in Column
The following image illustrates the effects of using the macro (User-Defined Function) example. In this example:
- Column A (cells A6 to A30) contains randomly generated words.
- Cell C7 contains the searched string or text (Excel).
- Cell D7 contains the worksheet formula that works with the macro (User-Defined Function) example. This worksheet formula returns the address (as an A1-style relative reference) of the first cell in the column (MyColumn) where the string or text (MyString) is found. This is cell A21.
- Cell E7 displays the worksheet formula used in cell D7 (=FindStringInColumn(A:A,C7)).
- The column where the search is carried out is column A (A:A).
- The searched string or text is stored in cell C7 (C7).

#8. Excel VBA Find String (or Text) in Cell
VBA Code to Find String (or Text) in Cell
To find a string (or text) in a cell, use the following structure/template in the applicable statement:
InStr(StartingPosition, SearchedCell.Value, SearchedString, VbCompareMethodConstant)
The following Sections describe the main elements in this structure.
InStr
The InStr function returns a number. This number specifies the position of the first occurrence of a string or text (SearchedString) in another string (the string stored in SearchedCell).
StartingPosition
The Start argument of the InStr function is:
- An optional argument.
- A numeric expression specifying the starting position for the string (or text) search.
If you omit specifying the Start argument, the search begins at the first character of the searched string (the string stored in SearchedCell).
To find a string (or text) in a cell, set the Start argument to the position (in the string stored in SearchedCell) where the string (or text) search starts.
SearchedCell.Value
The String1 argument of the InStr function represents the string expression the InStr function searches in.
To find a string (or text) in a cell, set the String1 argument to the value/string stored in the searched cell. For these purposes:
- “SearchedCell” is a Range object representing the searched cell.
- “Value” refers to the Range.Value property. The Range.Value property returns the value/string stored in the searched cell (SearchedCell).
SearchedString
The String2 argument of the InStr function represents the string expression (or text) the InStr function searches for.
To find a string (or text) in a cell, set the String2 argument to the string (or text) you search for.
VbCompareMethodConstant
The Compare argument of the InStr function:
- Is an optional argument.
- Specifies the type of string comparison carried out by the InStr function.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the vbCompareMethod enumeration.
If you omit specifying the Compare argument, the type of string comparison is determined by the Option Compare statement. The Option Compare statement declares the default string comparison method at a module level. The default string comparison method is binary (vbBinaryCompare).
To find a string (or text) in a cell, set the Compare argument to either of the following, as applicable:
- vbBinaryCompare: Performs a binary comparison. vbBinaryCompare:
- Results in a case-sensitive search.
- May be (slightly) faster than vbTextCompare.
- vbTextCompare: Performs a textual comparison. vbTextCompare:
- Results in a case-insensitive search.
- May be (slightly) slower than vbBinaryCompare.
- Is more prone to errors/bugs than vbBinaryCompare.
Macro Example to Find String (or Text) in Cell
The following macro (User-Defined Function) example does the following:
- Accepts three arguments:
- MyCell: The cell you search in.
- MyString: The string (or text) you search for.
- MyStartingPosition: The starting position for the string (or text) search. MyStartingPosition is an optional argument with a default value of 1.
- Finds MyString in the value/string stored in MyCell.
- Returns the following:
- If MyString is not found in the value/string stored in MyCell, the string “String not found in cell”.
- If MyString is found in the value/string stored in MyCell, the position of the first occurrence of MyString in the value/string stored in MyCell.
Function FindStringInCell(MyCell As Range, MyString As Variant, Optional MyStartingPosition As Variant = 1) As Variant
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-find/
'This UDF:
'(1) Accepts three arguments: MyCell, MyString and MyStartingPosition (optional argument with a default value of 1)
'(2) Finds a string passed as argument (MyString) in the value/string stored in a cell passed as argument (MyCell)
'(3) Returns the following (as applicable):
'If MyString is not found in the value/string stored in MyCell: The string "String not found in cell"
'If MyString is found in the value/string stored in MyCell: The position of the first occurrence of MyString in the value/string stored in MyCell
'Obtain position of first occurrence of MyString in the value/string stored in MyCell
FindStringInCell = InStr(MyStartingPosition, MyCell.Value, MyString, vbBinaryCompare)
'If MyString is not found in the value/string stored in MyCell, return the string "String not found in cell"
If FindStringInCell = 0 Then FindStringInCell = "String not found in cell"
End Function
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Find String (or Text) in Cell
The following image illustrates the effects of using the macro (User-Defined Function) example. In this example:
- Column A (cells A7 to A31) contains randomly generated words.
- Column B (cells B7 to B31) contains a 2-character string (ar).
- Column C (cells C7 to C31) contains worksheet formulas working with the macro (User-Defined Function) example. These worksheet formulas return either of the following (as applicable):
- The string “String not found in cell”, if the string (or text) specified in the applicable cell of column B is not found in the applicable cell of column A.
- The position of the first occurrence of the string (or text) specified in the applicable cell of column B in the applicable cell of column A, if the string (or text) specified in the applicable cell of column B is found in the applicable cell of column A.
- Column D (cells D7 to D31) displays the worksheet formulas used in column C (=FindStringInCell(CellInColumnA,CellInColumnB)).
- The cell where the search is carried out is in column A (CellInColumnA).
- The searched string or text is stored in column B (CellInColumnB).

#9. Excel VBA Find String (or Text) in String
VBA Code to Find String (or Text) in String
To find a string (or text) in a string, use the following structure/template in the applicable statement:
InStr(StartingPosition, SearchedString, SearchedText, VbCompareMethodConstant)
The following Sections describe the main elements in this structure.
InStr
The InStr function returns a number. This number specifies the position of the first occurrence of a string or text (SearchedText) in another string (SearchedString).
StartingPosition
The Start argument of the InStr function is:
- An optional argument.
- A numeric expression specifying the starting position for the string (or text) search.
If you omit specifying the Start argument, the search begins at the first character of the searched string (SearchedString).
To find a string (or text) in a string, set the Start argument to the position (in SearchedString) where the string (or text) search starts.
SearchedString
The String1 argument of the InStr function represents the string expression the InStr function searches in.
To find a string (or text) in a string, set the String1 argument to the searched string.
SearchedText
The String2 argument of the InStr function represents the string expression (or text) the InStr function searches for.
To find a string (or text) in a string, set the String2 argument to the string (or text) you search for.
VbCompareMethodConstant
The Compare argument of the InStr function:
- Is an optional argument.
- Specifies the type of string comparison carried out by the InStr function.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the vbCompareMethod enumeration.
If you omit specifying the Compare argument, the type of string comparison is determined by the Option Compare statement. The Option Compare statement declares the default string comparison method at a module level. The default string comparison method is binary (vbBinaryCompare).
To find a string (or text) in a string, set the Compare argument to either of the following, as applicable:
- vbBinaryCompare: Performs a binary comparison. vbBinaryCompare:
- Results in a case-sensitive search.
- May be (slightly) faster than vbTextCompare.
- vbTextCompare: Performs a textual comparison. vbTextCompare:
- Results in a case-insensitive search.
- May be (slightly) slower than vbBinaryCompare.
- Is more prone to errors/bugs than vbBinaryCompare.
Macro Example to Find String (or Text) in String
The following macro (User-Defined Function) example does the following:
- Accepts three arguments:
- MyString: The string you search in.
- MyText: The string (or text) you search for.
- MyStartingPosition: The starting position for the string (or text) search. MyStartingPosition is an optional argument with a default value of 1.
- Finds MyText in MyString.
- Returns the following:
- If MyText is not found in MyString, the string “Text not found in string”.
- If MyText is found in MyString, the position of the first occurrence of MyText in MyString.
Function FindTextInString(MyString As Variant, MyText As Variant, Optional MyStartingPosition As Variant = 1) As Variant
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-find/
'This UDF:
'(1) Accepts three arguments: MyString, MyText and MyStartingPosition (optional argument with a default value of 1)
'(2) Finds text (a string) passed as argument (MyText) in a string passed as argument (MyString)
'(3) Returns the following (as applicable):
'If MyText is not found in MyString: The string "Text not found in string"
'If MyText is found in MyString: The position of the first occurrence of MyText in MyString
'Obtain position of first occurrence of MyText in MyString
FindTextInString = InStr(MyStartingPosition, MyString, MyText, vbBinaryCompare)
'If MyText is not found in MyString, return the string "Text not found in string"
If FindTextInString = 0 Then FindTextInString = "Text not found in string"
End Function
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Find String (or Text) in String
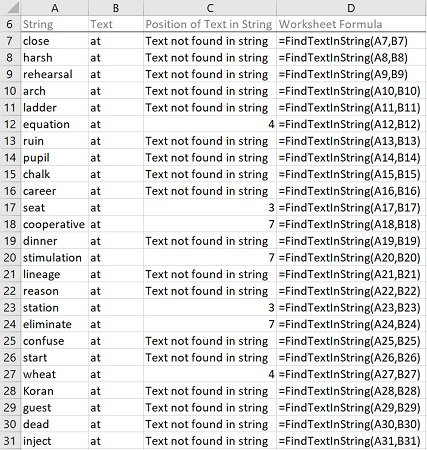
The following image illustrates the effects of using the macro (User-Defined Function) example. In this example:
- Column A (cells A7 to A31) contains randomly generated words.
- Column B (cells B7 to B31) contains text (at).
- Column C (cells C7 to C31) contains worksheet formulas working with the macro (User-Defined Function) example. These worksheet formulas return either of the following (as applicable):
- The string “Text not found in string”, if the string (or text) specified in the applicable cell of column B is not found in the string specified in the applicable cell of column A.
- The position of the first occurrence of the string (or text) specified in the applicable cell of column B in the string specified in the applicable cell of column A, if the string (or text) specified in the applicable cell of column B is found in the string specified in the applicable cell of column A.
- Column D (cells D7 to D31) displays the worksheet formulas used in column C (=FindTextInString(CellInColumnA,CellInColumnB)).
- The string where the search is carried out is stored in column A (CellInColumnA).
- The searched string (or text) is stored in column B (CellInColumnB).
#10. Excel VBA Find Character in String
VBA Code to Find Character in String
To find a character in a string, use the following structure/template in the applicable statement:
InStr(StartingPosition, SearchedString, SearchedCharacter, VbCompareMethodConstant)
The following Sections describe the main elements in this structure.
InStr
The InStr function returns a number. This number specifies the position of the first occurrence of a string or text (SearchedCharacter) in another string (SearchedString).
StartingPosition
The Start argument of the InStr function is:
- An optional argument.
- A numeric expression specifying the starting position for the character search.
If you omit specifying the Start argument, the search begins at the first character of the searched string (SearchedString).
To find a character in a string, set the Start argument to the position (in SearchedString) where the character search starts.
SearchedString
The String1 argument of the InStr function represents the string expression the InStr function searches in.
To find a character in a string, set the String1 argument to the searched string.
SearchedCharacter
The String2 argument of the InStr function represents the string expression (or text) the InStr function searches for.
To find a character in a string, set the String2 argument to the character you search for.
VbCompareMethodConstant
The Compare argument of the InStr function:
- Is an optional argument.
- Specifies the type of string comparison carried out by the InStr function.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the vbCompareMethod enumeration.
If you omit specifying the Compare argument, the type of string comparison is determined by the Option Compare statement. The Option Compare statement declares the default string comparison method at a module level. The default string comparison method is binary (vbBinaryCompare).
To find a character in a string, set the Compare argument to either of the following, as applicable:
- vbBinaryCompare: Performs a binary comparison. vbBinaryCompare:
- Results in a case-sensitive search.
- May be (slightly) faster than vbTextCompare.
- vbTextCompare: Performs a textual comparison. vbTextCompare:
- Results in a case-insensitive search.
- May be (slightly) slower than vbBinaryCompare.
- Is more prone to errors/bugs than vbBinaryCompare.
Macro Example to Find Character in String
The following macro (User-Defined Function) example does the following:
- Accepts three arguments:
- MyString: The string you search in.
- MyCharacter: The character you search for.
- MyStartingPosition: The starting position for the character search. MyStartingPosition is an optional argument with a default value of 1.
- Finds MyCharacter in MyString.
- Returns the following:
- If MyCharacter is not found in MyString, the string “Character not found in string”.
- If MyCharacter is found in MyString, the position of the first occurrence of MyCharacter in MyString.
Function FindCharacterInString(MyString As Variant, MyCharacter As Variant, Optional MyStartingPosition As Variant = 1) As Variant
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-find/
'This UDF:
'(1) Accepts three arguments: MyString, MyCharacter and MyStartingPosition (optional argument with a default value of 1)
'(2) Finds a character passed as argument (MyCharacter) in a string passed as argument (MyString)
'(3) Returns the following (as applicable):
'If MyCharacter is not found in MyString: The string "Character not found in string"
'If MyCharacter is found in MyString: The position of the first occurrence of MyCharacter in MyString
'Obtain position of first occurrence of MyCharacter in MyString
FindCharacterInString = InStr(MyStartingPosition, MyString, MyCharacter, vbBinaryCompare)
'If MyCharacter is not found in MyString, return the string "Character not found in string"
If FindCharacterInString = 0 Then FindCharacterInString = "Character not found in string"
End Function
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Find Character in String
The following image illustrates the effects of using the macro (User-Defined Function) example. In this example:
- Column A (cells A7 to A31) contains randomly generated words.
- Column B (cells B7 to B31) contains a character (a).
- Column C (cells C7 to C31) contains worksheet formulas working with the macro (User-Defined Function) example. These worksheet formulas return either of the following (as applicable):
- The string “Character not found in string”, if the character specified in the applicable cell of column B is not found in the string specified in the applicable cell of column A.
- The position of the first occurrence of the character specified in the applicable cell of column B in the string specified in the applicable cell of column A, if the character specified in the applicable cell of column B is found in the string specified in the applicable cell of column A.
- Column D (cells D7 to D31) displays the worksheet formulas used in column C (=FindCharacterInString(CellInColumnA,CellInColumnB)).
- The string where the search is carried out is stored in column A (CellInColumnA).
- The searched character is stored in column B (CellInColumnB).

#11. Excel VBA Find Column with Specific Header
VBA Code to Find Column with Specific Header
To find a column with a specific header, use the following structure/template in the applicable statement:
HeaderRowRangeObject.Find(What:=SearchedHeader, After:=SingleCellRangeObject, LookIn:=xlValues, LookAt:=xlWhole, SearchOrder:=xlByColumns, SearchDirection:=XlSearchDirectionConstant, MatchCase:=BooleanValue)
The following Sections describe the main elements in this structure.
HeaderRowRangeObject
A Range object representing the cell range containing the headers you search in.
Find
The Range.Find method:
- Finds specific information (the header you search for) in a cell range (HeaderRowRangeObject).
- Returns a Range object representing the first cell where the information is found.
What:=SearchedHeader
The What parameter of the Range.Find method specifies the data to search for.
To find a column with a specific header, set the What parameter to the header you search for (SearchedHeader).
After:=SingleCellRangeObject
The After parameter of the Range.Find method specifies the cell after which the search begins. This must be a single cell in the cell range containing the headers you search in (HeaderRowRangeObject).
If you omit specifying the After parameter, the search begins after the first cell of the cell range you search in (HeaderRowRangeObject).
To find a column with a specific header, set the After parameter to a Range object representing the cell after which the search begins.
LookIn:=xlValues
The LookIn parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the type of data to search in.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlFindLookIn enumeration.
To find a column with a specific header, set the LookIn parameter to xlValues. xlValues refers to values.
LookAt:=xlWhole
The LookAt parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies against which of the following the data you are searching for is matched:
- The entire/whole searched cell contents.
- Any part of the searched cell contents.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlLookAt enumeration.
To find a column with a specific header, set the LookAt parameter to xlWhole. xlWhole matches the data you are searching for against the entire/whole searched cell contents.
SearchOrder:=xlByColumns
The SearchOrder parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the order in which the applicable cell range (HeaderRowRangeObject) is searched:
- By rows.
- By columns.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlSearchOrder enumeration.
To find a column with a specific header, set the SearchOrder parameter to xlByColumns. xlByColumns searches by columns.
SearchDirection:=XlSearchDirectionConstant
The SearchDirection parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the search direction:
- Search for the previous match.
- Search for the next match.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlSearchDirection enumeration.
To find a column with a specific header, set the SearchDirection parameter to either of the following, as applicable:
- xlNext (SearchDirection:=xlNext): To search for the next match.
- xlPrevious (SearchDirection:=xlPrevious): To search for the previous match.
MatchCase:=BooleanValue
The MatchCase parameter of the Range.Find method specifies whether the search is:
- Case-sensitive; or
- Case-insensitive.
The default value of the MatchCase parameter is False.
To find a column with a specific header, set the MatchCase parameter to either of the following, as applicable:
- True (MatchCase:=True): To carry out a case-sensitive search.
- False (MatchCase:=False): To carry out a case-insensitive search.
Macro Example to Find Column with Specific Header
The following macro (User-Defined Function) example does the following:
- Accepts two arguments:
- MyRange: The cell range whose first row contains the headers you search in.
- MyHeader: The header you search for.
- Finds MyHeader in the first row of MyRange.
- Returns the number of the column containing the first cell in the header row where the header (MyHeader) is found.
Function FindColumnWithSpecificHeader(MyRange As Range, MyHeader As Variant) As Long
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-find/
'This UDF:
'(1) Accepts 2 arguments: MyRange and MyHeader
'(2) Finds a header passed as argument (MyHeader) in the first row (the header row) of a cell range passed as argument (MyRange). The search is case-insensitive
'(3) Returns the number of the column containing the first cell in the header row where the header (MyHeader) is found
With MyRange.Rows(1)
FindColumnWithSpecificHeader = .Find(What:=MyHeader, After:=.Cells(.Cells.Count), LookIn:=xlValues, LookAt:=xlWhole, SearchOrder:=xlByColumns, SearchDirection:=xlNext, MatchCase:=False).Column
End With
End Function
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Find Column with Specific Header
The following image illustrates the effects of using the macro (User-Defined Function) example. In this example:
- Columns A through H (cells A6 to H31) contain data with the following characteristics:
- Headers in its first row (row 6).
- Randomly generated values.
- Cell J7 contains the searched header (Column 3).
- Cell K7 contains the worksheet formula that works with the macro (User-Defined Function) example. This worksheet formula returns the column number of the first cell in the header row (cells A6 to H6) of the cell range (MyRange) where the header (MyHeader) is found. This is column 3 (C).
- Cell L7 displays the worksheet formula used in cell K7 (=FindColumnWithSpecificHeader(A6:H31,J7)).
- The cell range whose first row contains the headers where the search is carried out contains cells A6 to H31 (A6:H31).
- The searched header is stored in cell J7 (J7).

#12. Excel VBA Find Next or Find All
VBA Code to Find Next or Find All
To (i) find the next appearance of specific information or (ii) find all appearances of specific information, use the following structure/template in the applicable procedure:
Dim FoundCell As Range
Dim FirstFoundCellAddress As String
Set FoundCell = SearchedRangeObject.Find(What:=SearchedData, After:=SingleCellRangeObject, LookIn:=XlFindLookInConstant, LookAt:=XlLookAtConstant, SearchOrder:=XlSearchDirectionConstant, SearchDirection:=xlNext, MatchCase:=BooleanValue)
If Not FoundCell Is Nothing Then
FirstFoundCellAddress = FoundCell.Address
Do
Statements
Set FoundCell = SearchedRangeObject.FindNext(After:=FoundCell)
Loop Until FoundCell.Address = FirstFoundCellAddress
End If
The following Sections describe the main elements in this structure.
Lines #1 and #2: Dim FoundCell As Range | Dim FirstFoundCellAddress As String
Dim
The Dim statement:
- Declares variables.
- Allocates storage space.
FoundCell | FirstFoundCellAddress
The names of the variables declared with the Dim statement.
- FoundCell holds/represents the cell where the searched data is found.
- FirstFoundCellAddress holds/represents the address of the first cell where the searched data is found.
As Range | As String
The data type of the variables declared with the Dim statement.
- FoundCell is of the Range object data type. The Range object represents a cell or cell range.
- FirstFoundCellAddress is of the String data type. The String data type (generally) holds textual data.
Line #3: Set FoundCell = SearchedRangeObject.Find(What:=SearchedData, After:=SingleCellRangeObject, LookIn:=XlFindLookInConstant, LookAt:=XlLookAtConstant, SearchOrder:=XlSearchDirectionConstant, SearchDirection:=xlNext, MatchCase:=BooleanValue)
Set
The Set statement assigns an object reference to an object variable.
FoundCell
Object variable holding/representing the cell where the searched data is found.
=
The assignment operator assigns an object reference (returned by the Range.Find method) to an object variable (FoundCell).
SearchedRangeObject
A Range object representing the cell range you search in.
Find
The Range.Find method:
- Finds specific information (the data you search for) in a cell range (SearchedRangeObject).
- Returns a Range object representing the first cell where the information is found.
What:=SearchedData
The What parameter of the Range.Find method specifies the data to search for.
To (i) find the next appearance of specific information or (ii) find all appearances of specific information, set the What parameter to the data you search for (SearchedData).
After:=SingleCellRangeObject
The After parameter of the Range.Find method specifies the cell after which the search begins. This must be a single cell in the cell range you search in (SearchedRangeObject).
If you omit specifying the After parameter, the search begins after the first cell (in the upper left corner) of the cell range you search in (SearchedRangeObject).
To (i) find the next appearance of specific information or (ii) find all appearances of specific information, set the After parameter to a Range object representing the cell after which the search begins.
LookIn:=XlFindLookInConstant
The LookIn parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the type of data to search in.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlFindLookIn enumeration.
To (i) find the next appearance of specific information or (ii) find all appearances of specific information, set the LookIn parameter to any of the following, as applicable:
- xlCommentsThreaded (LookIn:=xlCommentsThreaded): To search in the applicable cell range’s threaded comments.
- xlValues (LookIn:=xlValues): To search in the applicable cell range’s values.
- xlComments (LookIn:=xlComments): To search in the applicable cell range’s comments/notes.
- xlFormulas (LookIn:=xlFormulas): To search in the applicable cell range’s formulas.
LookAt:=XlLookAtConstant
The LookAt parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies against which of the following the data you are searching for is matched:
- The entire/whole searched cell contents.
- Any part of the searched cell contents.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlLookAt enumeration.
To (i) find the next appearance of specific information or (ii) find all appearances of specific information, set the LookAt parameter to either of the following, as applicable:
- xlWhole (LookAt:=xlWhole): To match against the entire/whole searched cell contents.
- xlPart (LookAt:=xlPart): To match against any part of the searched cell contents.
SearchOrder:=XlSearchDirectionConstant
The SearchOrder parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the order in which the applicable cell range (SearchedRangeObject) is searched:
- By rows.
- By columns.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlSearchOrder enumeration.
To (i) find the next appearance of specific information or (ii) find all appearances of specific information, set the SearchOrder parameter to either of the following, as applicable:
- xlByRows (SearchOrder:=xlByRows): To search by rows.
- xlByColumns (SearchOrder:=xlByColumns): To search by columns.
SearchDirection:=xlNext
The SearchDirection parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the search direction:
- Search for the previous match.
- Search for the next match.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlSearchDirection enumeration.
To (i) find the next appearance of specific information or (ii) find all appearances of specific information, set the SearchDirection parameter to xlNext. xlNext results in the Range.Find method searching for the next match.
MatchCase:=BooleanValue
The MatchCase parameter of the Range.Find method specifies whether the search is:
- Case-sensitive; or
- Case-insensitive.
The default value of the MatchCase parameter is False.
To (i) find the next appearance of specific information or (ii) find all appearances of specific information, set the MatchCase parameter to either of the following, as applicable:
- True (MatchCase:=True): To carry out a case-sensitive search.
- False (MatchCase:=False): To carry out a case-insensitive search.
Lines #4 and 10: If Not FoundCell Is Nothing Then | End If
If … Then | End If
The If… Then… Else statement:
- Conditionally executes a set of statements (lines #5 to #9);
- Depending on an expression’s value (Not FoundCell Is Nothing).
Not FoundCell Is Nothing
The condition of an If… Then… Else statement is an expression evaluating to True or False. If the expression returns True, the applicable set of statements (lines #5 to #9) is executed.
In this expression:
- Not FoundCell:
- The Not operator performs a logical negation on an expression.
- FoundCell is the object variable holding/representing the cell where the searched data is found.
- The Range.Find method (in line #3) returns Nothing if no match is found. Therefore:
- If the Range.Find method finds no match:
- FoundCell is Nothing.
- Not FoundCell is not Nothing.
- If the Range.Find method finds a match:
- FoundCell is not Nothing.
- Not FoundCell is Nothing.
- If the Range.Find method finds no match:
- Is: The Is operator is an object reference comparison operator.
- Nothing: Nothing allows you to disassociate a variable from the data it previously represented. The Range.Find method (in line #3) returns Nothing if no match is found.
Line #5: FirstFoundCellAddress = FoundCell.Address
FirstFoundCellAddress
Variable holding/representing the address of the first cell where the searched data is found.
=
The assignment operator assigns the result returned by an expression (FoundCell.Address) to a variable (FirstFoundCellAddress).
FoundCell
Object variable holding/representing the cell where the searched data is found.
At this point, FoundCell holds/represents the first cell where the searched data is found (by line #3).
Address
The Range.Address property returns a String representing the applicable cell range’s (FoundCell’s) reference.
Lines #6 and #9: Do | Loop Until FoundCell.Address = FirstFoundCellAddress
Do | Loop Until…
The Do… Loop Until statement repeats a set of statements until a condition becomes True.
FoundCell.Address = FirstFoundCellAddress
The condition of a Do… Loop Until statement is an expression evaluating to True or False. The applicable set of statements (lines #7 and #8) are:
- (Always) executed once, even if the condition is never met; and
- Repeatedly executed until the condition returns True.
In this expression:
- FoundCell.Address:
- FoundCell is an object variable holding/representing the cell where the searched data is found.
- The Range.Address property returns a String representing the applicable cell range’s (FoundCell’s) reference.
- =: The equal to comparison operator returns True or False as follows:
- True if both expressions (FoundCell.Address and FirstFoundCellAddress) are equal.
- False if the expressions (FoundCell.Address and FirstFoundCellAddress) are not equal.
- FirstFoundCellAddress: Variable holding/representing the address of the first cell where the searched data is found.
This condition is tested (only) after the procedure finds (and works with) the first cell where the searched data is found. Therefore, the condition (only) returns True after the Range.FindNext method (line #8) wraps around to the first cell where the searched data is found (after finding all other cells where the searched data is found).
Line #7: Statements
Set of statements to be repeatedly executed for each cell where the searched data is found.
Line #8: Set FoundCell = SearchedRangeObject.FindNext(After:=FoundCell)
Set
The Set statement assigns an object reference to an object variable.
FoundCell
Object variable holding/representing the cell where the searched data is found.
=
The assignment operator assigns an object reference (returned by the Range.FindNext method) to an object variable (FoundCell).
SearchedRangeObject
A Range object representing the cell range you search in.
FindNext
The Range.FindNext method:
- Continues the search that was begun by the Range.Find method (line #3).
- Finds the next cell matching the conditions specified by the Range.Find method (line #3).
- Returns a Range object representing the next cell where the information is found.
After:=FoundCell
The After parameter of the Range.FindNext method specifies the cell after which the search restarts.
To (i) find the next appearance of specific information or (ii) find all appearances of specific information, set the After parameter to the object variable holding/representing the cell where the searched data is found.
Macro Example to Find Next or Find All
The following macro example does the following:
- Find:
- All cells whose value is 10;
- In the cell range containing cells A6 to H30 in the “Find Next All” worksheet in the workbook where the procedure is stored.
- Set the interior/fill color of all found cells to light green.
Sub FindNextAll()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-find/
'This procedure:
'(1) Finds all cells whose value is 10 in cells A6 to H30 of the "Find Next All" worksheet in this workbook
'(2) Sets the found cells' interior/fill color to light green
'Declare variable to hold/represent searched value
Dim MyValue As Long
'Declare variable to hold/represent address of first cell where searched value is found
Dim FirstFoundCellAddress As String
'Declare object variable to hold/represent cell range where search takes place
Dim MyRange As Range
'Declare object variable to hold/represent cell where searched value is found
Dim FoundCell As Range
'Specify searched value
MyValue = 10
'Identify cell range where search takes place
Set MyRange = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Find Next All").Range("A6:H30")
'Find first cell where searched value is found
With MyRange
Set FoundCell = .Find(What:=MyValue, After:=.Cells(.Cells.Count), LookIn:=xlValues, LookAt:=xlWhole, SearchOrder:=xlByRows, SearchDirection:=xlNext)
End With
'Test whether searched value is found in cell range where search takes place
If Not FoundCell Is Nothing Then
'Store address of first cell where searched value is found
FirstFoundCellAddress = FoundCell.Address
Do
'Set interior/fill color of applicable cell where searched value is found to light green
FoundCell.Interior.Color = RGB(63, 189, 133)
'Find next cell where searched value is found
Set FoundCell = MyRange.FindNext(After:=FoundCell)
'Loop until address of current cell where searched value is found is equal to address of first cell where searched value was found
Loop Until FoundCell.Address = FirstFoundCellAddress
End If
End Sub
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Find Next or Find All
The following image illustrates the effects of executing the macro example. In this example:
- Cells A6 to H30 contain randomly generated values.
- A text box (Find all cells where value = 10) executes the macro example when clicked.
After the macro is executed, Excel sets the interior/fill color of all cells whose value is 10 to light green.
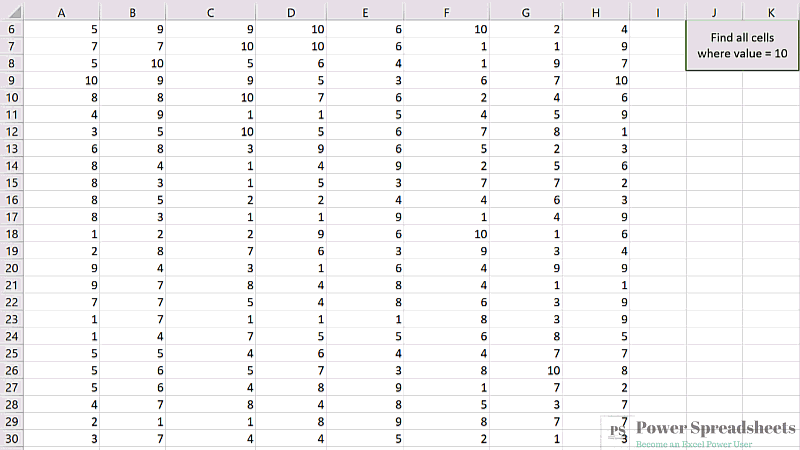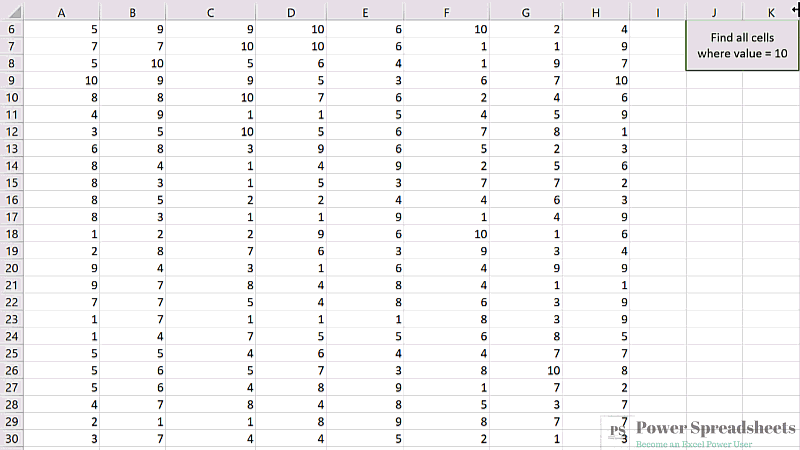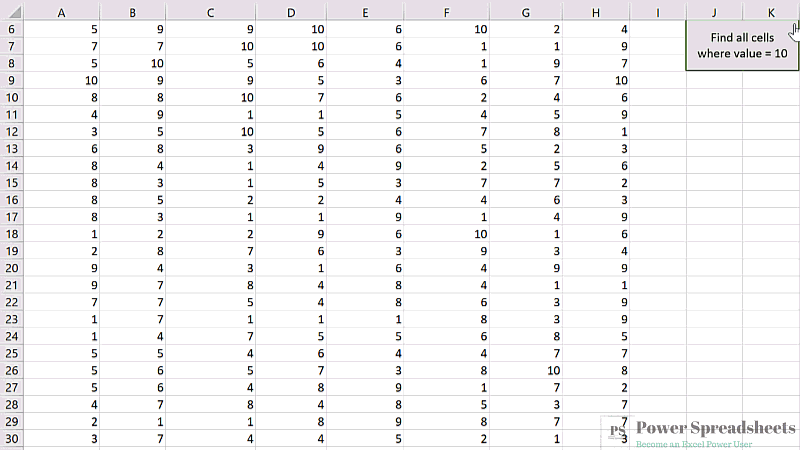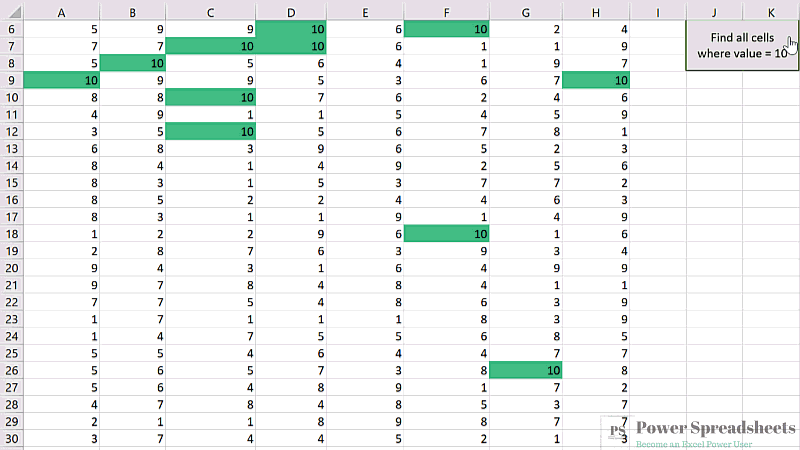
#13. Excel VBA Find Last Row with Data in Cell Range
VBA Code to Find Last Row with Data in Cell Range
To find the last row with data in a cell range, use the following structure/template in the applicable procedure:
If Application.CountA(SearchedCellRangeObject) = 0 Then
LastRowVariable = ValueIfCellRangeEmpty
Else
LastRowVariable = SearchedCellRangeObject.Find(What:="*", LookIn:=xlFormulas, LookAt:=xlPart, SearchOrder:=xlByRows, SearchDirection:=xlPrevious).Row
End If
The following Sections describe the main elements in this structure.
Lines #1, #3 and #5: If Application.CountA(SearchedCellRangeObject) = 0 Then | Else | End If
If… Then … Else… End If
The If… Then… Else statement:
- Conditionally executes a set of statements (line #2 or line #4);
- Depending on an expression’s value (Application.CountA(SearchedCellRangeObject) = 0).
Application.CountA(SearchedCellRangeObject) = 0
The condition of an If… Then… Else statement is an expression evaluating to True or False.
- If the expression returns True, a set of statements (line #2) is executed.
- If the expression returns False, a different set of statements (line #4) is executed.
In this expression:
- Application.CountA(…): The WorksheetFunction.CountA method counts the number of cells in a cell range (SearchedCellRangeObject) that are not empty.
- SearchedCellRangeObject: A Range object representing the cell range whose last row you search.
- =: The equal to comparison operator returns True or False as follows:
- True if both expressions (Application.CountA(SearchedCellRangeObject) and 0) are equal.
- False if the expressions (Application.CountA(SearchedCellRangeObject) and 0) are not equal.
- 0: The number 0. The WorksheetFunction.CountA method returns 0 if all cells in SearchedCellRangeObject are empty.
Line #2: LastRowVariable = ValueIfCellRangeEmpty
Assignment statement assigning:
- ValueIfCellRangeEmpty; to
- LastRowVariable.
In this expression:
- LastRowVariable: Variable of (usually) the Long data type holding/representing the number of the last row with data in the cell range whose last row you search (SearchedCellRangeObject).
- =: Assignment operator. Assigns a value (ValueIfCellRangeEmpty) to a variable (LastRowVariable).
- ValueIfCellRangeEmpty: Value assigned to LastRowVariable when SearchedCellRangeObject is empty and the WorksheetFunction.CountA method returns 0.
Line #4: LastRowVariable = SearchedCellRangeObject.Find(What:=”*”, LookIn:=xlFormulas, LookAt:=xlPart, SearchOrder:=xlByRows, SearchDirection:=xlPrevious).Row
LastRowVariable
Variable of (usually) the Long data type holding/representing the number of the last row with data in the cell range whose last row you search (SearchedCellRangeObject).
=
The assignment operator assigns a value (SearchedCellRangeObject.Find(What:=”*”, LookIn:=xlFormulas, LookAt:=xlPart, SearchOrder:=xlByRows, SearchDirection:=xlPrevious).Row) to a variable (LastRowVariable).
SearchedCellRangeObject
A Range object representing the cell range whose last row you search.
Find
The Range.Find method:
- Finds specific information in a cell range (SearchedCellRangeObject).
- Returns a Range object representing the first cell where the information is found.
What:=”*”
The What parameter of the Range.Find method specifies the data to search for.
To find the last row with data in a cell range, set the What parameter to any character sequence. The asterisk (*) acts as a wildcard and results in Range.Find searching for any character sequence.
LookIn:=xlFormulas
The LookIn parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the type of data to search in.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlFindLookIn enumeration.
To find the last row with data in a cell range, set the LookIn parameter to xlFormulas. xlFormulas refers to formulas.
LookAt:=xlPart
The LookAt parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies against which of the following the data you are searching for is matched:
- The entire/whole searched cell contents.
- Any part of the searched cell contents.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlLookAt enumeration.
To find the last row with data in a cell range, set the LookAt parameter to xlPart. xlPart matches the data you are searching for (any character sequence as specified by the What parameter) against any part of the searched cell contents.
SearchOrder:=xlByRows
The SearchOrder parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the order in which the applicable cell range (SearchedCellRangeObject) is searched:
- By rows.
- By columns.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlSearchOrder enumeration.
To find the last row with data in a cell range, set the SearchOrder parameter to xlByRows. xlByRows results in the Range.Find method searching by rows.
SearchDirection:=xlPrevious
The SearchDirection parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the search direction:
- Search for the previous match.
- Search for the next match.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlSearchDirection enumeration.
To find the last row with data in a cell range, set the SearchDirection parameter to xlPrevious. xlPrevious results in the Range.Find method searching for the previous match.
Row
The Range.Row property returns the number of the first row of the first area in a cell range.
When searching for the last row with data in a cell range, the Range.Row property returns the row number of the cell represented by the Range object returned by the Range.Find method (Find(What:=”*”, LookIn:=xlFormulas, LookAt:=xlPart, SearchOrder:=xlByRows, SearchDirection:=xlPrevious)).
Macro Example to Find Last Row with Data in Cell Range
The following macro (User-Defined Function) example does the following:
- Accepts one argument (MyRange). This is the cell range whose last row you search.
- Tests whether MyRange is empty and proceeds accordingly:
- If MyRange is empty, returns the number 0 as the number of the last row with data in MyRange.
- If MyRange isn’t empty:
- Finds the last row with data in MyRange; and
- Returns the number of the last row with data in MyRange.
Function FindLastRow(MyRange As Range) As Long
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-find/
'This UDF:
'(1) Accepts 1 argument: MyRange
'(2) Tests whether MyRange is empty
'(3) If MyRange is empty, returns 0 as the number of the last row with data in MyRange
'(4) If MyRange is not empty:
'(1) Finds the last row with data in MyRange by searching for the last cell with any character sequence
'(2) Returns the number of the last row with data in MyRange
'Test if MyRange is empty
If Application.CountA(MyRange) = 0 Then
'If MyRange is empty, assign 0 to FindLastRow
FindLastRow = 0
Else
'If MyRange isn't empty, find the last cell with any character sequence by:
'(1) Searching for the previous match;
'(2) Across rows
FindLastRow = MyRange.Find(What:="*", LookIn:=xlFormulas, LookAt:=xlPart, SearchOrder:=xlByRows, SearchDirection:=xlPrevious).Row
End If
End Function
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Find Last Row with Data in Cell Range
The following image illustrates the effects of using the macro (User-Defined Function) example. In this example:
- Columns A through H (cells A6 to H30) contain data.
- Cell J7 contains the worksheet formula that works with the macro (User-Defined Function) example. This worksheet formula returns the number of the last row with data in the cell range (MyRange). This is row 30.
- Cell K7 displays the worksheet formula used in cell J7 (=FindLastRow(A:H)). The cell range whose last row is searched contains columns A through H (A:H).
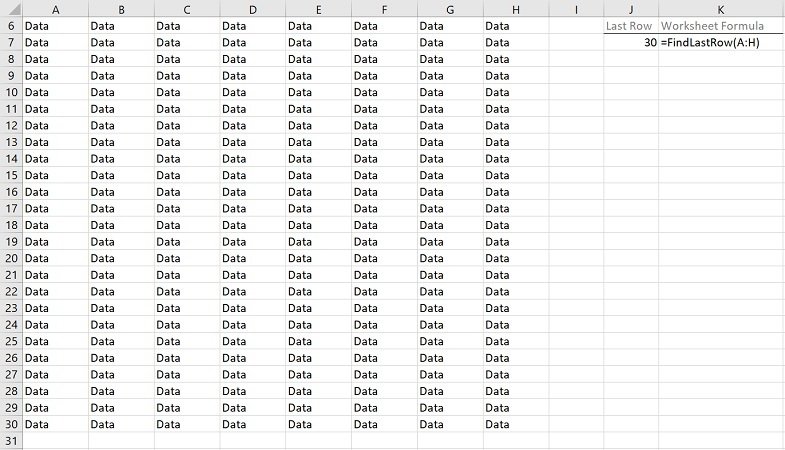
#14. Excel VBA Find Last Column with Data in Cell Range
VBA Code to Find Last Column with Data in Cell Range
To find the last column with data in a cell range, use the following structure/template in the applicable procedure:
If Application.CountA(SearchedCellRangeObject) = 0 Then
LastColumnVariable = ValueIfCellRangeEmpty
Else
LastColumnVariable = SearchedCellRangeObject.Find(What:="*", LookIn:=xlFormulas, LookAt:=xlPart, SearchOrder:=xlByColumns, SearchDirection:=xlPrevious).Column
End If
The following Sections describe the main elements in this structure.
Lines #1, #3 and #5: If Application.CountA(SearchedCellRangeObject) = 0 Then | Else | End If
If… Then … Else… End If
The If… Then… Else statement:
- Conditionally executes a set of statements (line #2 or line #4);
- Depending on an expression’s value (Application.CountA(SearchedCellRangeObject) = 0).
Application.CountA(SearchedCellRangeObject) = 0
The condition of an If… Then… Else statement is an expression evaluating to True or False.
- If the expression returns True, a set of statements (line #2) is executed.
- If the expression returns False, a different set of statements (line #4) is executed.
In this expression:
- Application.CountA(…): The WorksheetFunction.CountA method counts the number of cells in a cell range (SearchedCellRangeObject) that are not empty.
- SearchedCellRangeObject: A Range object representing the cell range whose last column you search.
- =: The equal to comparison operator returns True or False as follows:
- True if both expressions (Application.CountA(SearchedCellRangeObject) and 0) are equal.
- False if the expressions (Application.CountA(SearchedCellRangeObject) and 0) are not equal.
- 0: The number 0. The WorksheetFunction.CountA method returns 0 if all cells in SearchedCellRangeObject are empty.
Line #2: LastColumnVariable = ValueIfCellRangeEmpty
Assignment statement assigning:
- ValueIfCellRangeEmpty; to
- LastColumnVariable.
In this expression:
- LastColumnVariable: Variable of (usually) the Long data type holding/representing the number of the last column with data in the cell range whose last column you search (SearchedCellRangeObject).
- =: Assignment operator. Assigns a value (ValueIfCellRangeEmpty) to a variable (LastColumnVariable).
- ValueIfCellRangeEmpty: Value assigned to LastColumnVariable when SearchedCellRangeObject is empty and the WorksheetFunction.CountA method returns 0.
Line #4: LastColumnVariable = SearchedCellRangeObject.Find(What:=”*”, LookIn:=xlFormulas, LookAt:=xlPart, SearchOrder:=xlByColumns, SearchDirection:=xlPrevious).Column
LastColumnVariable
Variable of (usually) the Long data type holding/representing the number of the last column with data in the cell range whose last column you search (SearchedCellRangeObject).
=
The assignment operator assigns a value (SearchedCellRangeObject.Find(What:=”*”, LookIn:=xlFormulas, LookAt:=xlPart, SearchOrder:=xlByColumns, SearchDirection:=xlPrevious).Column) to a variable (LastColumnVariable).
SearchedCellRangeObject
A Range object representing the cell range whose last column you search.
Find
The Range.Find method:
- Finds specific information in a cell range (SearchedCellRangeObject).
- Returns a Range object representing the first cell where the information is found.
What:=”*”
The What parameter of the Range.Find method specifies the data to search for.
To find the last column with data in a cell range, set the What parameter to any character sequence. The asterisk (*) acts as a wildcard and results in Range.Find searching for any character sequence.
LookIn:=xlFormulas
The LookIn parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the type of data to search in.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlFindLookIn enumeration.
To find the last column with data in a cell range, set the LookIn parameter to xlFormulas. xlFormulas refers to formulas.
LookAt:=xlPart
The LookAt parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies against which of the following the data you are searching for is matched:
- The entire/whole searched cell contents.
- Any part of the searched cell contents.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlLookAt enumeration.
To find the last column with data in a cell range, set the LookAt parameter to xlPart. xlPart matches the data you are searching for (any character sequence as specified by the What parameter) against any part of the searched cell contents.
SearchOrder:=xlByColumns
The SearchOrder parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the order in which the applicable cell range (SearchedCellRangeObject) is searched:
- By rows.
- By columns.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlSearchOrder enumeration.
To find the last column with data in a cell range, set the SearchOrder parameter to xlByColumns. xlByColumns results in the Range.Find method searching by columns.
SearchDirection:=xlPrevious
The SearchDirection parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the search direction:
- Search for the previous match.
- Search for the next match.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlSearchDirection enumeration.
To find the last column with data in a cell range, set the SearchDirection parameter to xlPrevious. xlPrevious results in the Range.Find method searching for the previous match.
Column
The Range.Column property returns the number of the first column of the first area in a cell range.
When searching for the last column with data in a cell range, the Range.Column property returns the column number of the cell represented by the Range object returned by the Range.Find method (Find(What:=”*”, LookIn:=xlFormulas, LookAt:=xlPart, SearchOrder:=xlByColumns, SearchDirection:=xlPrevious)).
Macro Example to Find Last Column with Data in Cell Range
The following macro (User-Defined Function) example does the following:
- Accepts one argument (MyWorksheetName). This is the name of the worksheet whose last column you search.
- Tests whether the worksheet named MyWorksheetName is empty and proceeds accordingly:
- If the worksheet named MyWorksheetName is empty, returns the number 0 as the number of the last column with data in the worksheet.
- If the worksheet named MyWorksheetName isn’t empty:
- Finds the last column with data in the worksheet; and
- Returns the number of the last column with data in the worksheet.
Function FindLastColumn(MyWorksheetName As String) As Long
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-find/
'This UDF:
'(1) Accepts 1 argument: MyWorksheetName
'(2) Tests whether the worksheet named MyWorksheetName is empty
'(3) If the worksheet named MyWorksheetName is empty, returns 0 as the number of the last column with data in the worksheet
'(4) If the worksheet named MyWorksheetName is not empty:
'(1) Finds the last column with data in the worksheet by searching for the last cell with any character sequence
'(2) Returns the number of the last column with data in the worksheet
'Declare object variable to hold/represent all cells in the worksheet named MyWorksheetName
Dim MyRange As Range
'Identify all cells in the worksheet named MyWorksheetName
Set MyRange = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets(MyWorksheetName).Cells
'Test if MyRange is empty
If Application.CountA(MyRange) = 0 Then
'If MyRange is empty, assign 0 to FindLastColumn
FindLastColumn = 0
Else
'If MyRange isn't empty, find the last cell with any character sequence by:
'(1) Searching for the previous match;
'(2) Across columns
FindLastColumn = MyRange.Find(What:="*", LookIn:=xlFormulas, LookAt:=xlPart, SearchOrder:=xlByColumns, SearchDirection:=xlPrevious).Column
End If
End Function
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Find Last Column with Data in Cell Range
The following image illustrates the effects of using the macro (User-Defined Function) example. In this example:
- Columns A through H (cells A6 to H30) in the worksheet named “Find Last Column Data” contain data.
- Columns A through H of the “Find Last Column Data” worksheet contain exactly the same data as that in the “Find Last Column Formula” worksheet (displayed in the image below).
- The “Find Last Column Data” worksheet contains no data in columns J or K whereas the “Find Last Column Formula” worksheet (displayed in the image below) does.
- Cell J7 contains the worksheet formula that works with the macro (User-Defined Function) example. This worksheet formula returns the number of the last column with data in the worksheet (named “Find Last Column Data”). This is column H or 8.
- Cell K7 displays the worksheet formula used in cell J7 (=FindLastColumn(“Find Last Column Data”)). The name of the worksheet whose last column is searched is “Find Last Column Data”.
#15. Excel VBA Find Last Non Empty Cell in Column
VBA Code to Find Last Non Empty Cell in Column
To find the last non empty cell in a column, use the following structure/template in the applicable statement:
WorksheetObject.Range(ColumnLetter & WorksheetObject.Rows.Count).End(xlUp)
The following Sections describe the main elements in this structure.
WorksheetObject
A Worksheet object representing the worksheet containing the column whose last non empty cell you want to find.
Range
The Worksheet.Range property returns a Range object representing a cell or cell range.
ColumnLetter
The letter of the column whose last non empty cell you want to find.
&
The concatenation operator joins two strings and creates a new string.
WorksheetObject
A Worksheet object representing the worksheet containing the column whose last non empty cell you want to find.
Rows
The Worksheet.Rows property returns a Range object representing all rows in the applicable worksheet (containing the column whose last non empty cell you want to find).
Count
The Range.Count property returns the number of objects in a collection (the number of rows in the worksheet containing the column whose last non empty cell you want to find).
End(xlUp)
The Range.End property returns a Range object representing the cell at the end of the region containing the source range. In other words: The Range.End property is the rough equivalent of using the “Ctrl + Arrow Key” or “End, Arrow Key” keyboard shortcuts.
The Range.End property accepts one parameter: Direction. Direction:
- Specifies the direction in which to move.
- Can take the any of the built-in constants/values from the XlDirection enumeration.
To find the last non empty cell in a column, set the Direction parameter to xlUp. xlUp:
- Results in moving up, to the top of the data region.
- Is the rough equivalent of the “Ctrl + Up Arrow” or “End, Up Arrow” keyboard shortcuts.
Macro Example to Find Last Non Empty Cell in Column
The following macro (User-Defined Function) example does the following:
- Accepts one argument (MyColumn): The letter of the column (in the worksheet where the UDF is used) whose last non empty cell you want to find.
- Finds the last non empty cell in the applicable column.
- Returns a string containing the address (as an A1-style relative reference) of the last non empty cell in the applicable column.
Function FindLastNonEmptyCellColumn(MyColumn As String) As String
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-find/
'This UDF:
'(1) Accepts 1 argument: MyColumn
'(2) Finds the last non empty cell in the column whose letter is passed as argument (MyColumn) in the worksheet where the UDF is used
'(3) Returns the address (as an A1-style relative reference) of the last non empty cell found in the column whose letter is passed as argument (MyColumn) in the worksheet where the UDF is used
With Application.Caller.Parent
FindLastNonEmptyCellColumn = .Range(MyColumn & .Rows.Count).End(xlUp).Address(RowAbsolute:=False, ColumnAbsolute:=False)
End With
End Function
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Find Last Non Empty Cell in Column
The following image illustrates the effects of using the macro (User-Defined Function) example. In this example:
- Column A (cells A6 to A30) contains data.
- Cell C7 contains the letter of the column whose last non empty cell is sought (A).
- Cell D7 contains the worksheet formula that works with the macro (User-Defined Function) example. This worksheet formula returns the address (as an A1-style relative reference) of the last non empty cell in column A (MyColumn). This is cell A30
- Cell E7 displays the worksheet formula used in cell D7 (=FindLastNonEmptyCellColumn(C7)). The letter of the column whose last non empty cell is sought is stored in cell C7 (C7).
#16. Excel VBA Find Empty (or Blank) Cells
VBA Code to Find Empty (or Blank) Cells
To find all empty (or blank) cells in a cell range, use the following structure/template in the applicable procedure:
Dim BlankCellsObjectVariable As Range
On Error Resume Next
Set BlankCellsObjectVariable = RangeObjectWithBlankCells.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeBlanks)
On Error GoTo 0
If Not BlankCellsObjectVariable Is Nothing Then
StatementsIfBlankCells
End If
The following Sections describe the main elements in this structure.
Line #1: Dim BlankCellsObjectVariable As Range
Dim
The Dim statement:
- Declares variables.
- Allocates storage space.
BlankCellsObjectVariable
The name of the variable declared with the Dim statement.
BlankCellsObjectVariable holds/represents the empty (or blank) cells found.
As Range
The data type of the variable declared with the Dim statement.
BlankCellsObjectVariable is declared as of the Range object data type. The Range object represents a cell or cell range.
Line #2: On Error Resume Next
The On Error Resume Next statement specifies that, when a run-time error occurs, control passes to the statement immediately following that statement where the error occurred. Therefore, procedure execution continues.
Line #3 returns an error (Run time error ‘1004′: No cells were found) if the cell range where you search for empty (or blank) cells doesn’t contain any empty (or blank) cells.
Line #3: Set BlankCellsObjectVariable = RangeObjectWithBlankCells.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeBlanks)
Set
The Set statement assigns an object reference to an object variable.
BlankCellsObjectVariable
Object variable holding/representing the empty (or blank) cells found.
=
The assignment operator assigns an object reference (returned by the Range.SpecialCells method) to an object variable (BlankCellsObjectVariable).
RangeObjectWithBlankCells
A Range object representing the cell range you search in for empty (or blank) cells.
SpecialCells
The Range.SpecialCells method returns a Range object representing all cells matching a specified:
- Type; and
- Value.
xlCellTypeBlanks
The Type parameter of the Range.SpecialCells method:
- Specifies the cells to include in the Range object returned by the Range.SpecialCells method.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlCellType enumeration.
To find all empty (or blank) cells in a cell range, set the Type parameter to xlCellTypeBlanks. xlCellTypeBlanks results in the Range.SpecialCells method including blank/empty cells in the Range object it returns.
Line #4: On Error GoTo 0
The On Error GoTo 0 statement disables error handling (originally enabled by line #2).
Line #5 and #7: If Not BlankCellsObjectVariable Is Nothing Then | End If
If… Then | End If
The If… Then… Else statement:
- Conditionally executes a set of statements (line #6);
- Depending on an expression’s value (Not BlankCellsObjectVariable Is Nothing).
Not BlankCellsObjectVariable Is Nothing
The condition of an If… Then… Else statement is an expression evaluating to True or False. If the expression returns True, the applicable set of statements (line #6) is executed.
In this expression:
- Not BlankCellsObjectVariable:
- The Not operator performs a logical negation on an expression.
- BlankCellsObjectVariable is the object variable holding/representing the empty (or blank) cells found.
- BlankCellsObjectVariable holds/represents Nothing if no empty (or blank) cells are found. Therefore:
- If the Range.SpecialCells method finds no empty (or blank) cells:
- BlankCellsObjectVariable is Nothing.
- Not BlankCellsObjectVariable is not Nothing.
- If the Range.SpecialCells method finds empty (or blank) cells:
- BlankCellsObjectVariable is not Nothing.
- Not BlankCellsObjectVariable is Nothing.
- If the Range.SpecialCells method finds no empty (or blank) cells:
- Is: The Is operator is an object reference comparison operator.
- Nothing: Nothing allows you to disassociate a variable from the data it previously represented. BlankCellsObjectVariable holds/represents Nothing if no empty (or blank) cells are found.
Line #6: StatementsIfBlankCells
Statements conditionally executed by the If… Then… Else statement if the applicable condition (Not BlankCellsObjectVariable Is Nothing) returns True (the Range.SpecialCells method finds empty or blank cells).
Macro Example to Find Empty (or Blank) Cells
The following macro example does the following:
- Find all empty (or blank) cells in the cell range containing cells A6 to H30 in the “Find Blank Cells” worksheet in the workbook where the procedure is stored.
- Set the interior/fill color of all found empty (or blank) cells to light green.
Sub FindBlankCells()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-find/
'This procedure:
'(1) Finds all blank cells in cells A6 to H30 of the "Find Blank Cells" worksheet in this workbook
'(2) Sets the found cells' interior/fill color to light green
'Declare object variable to hold/represent blank cells
Dim MyBlankCells As Range
'Enable error-handling
On Error Resume Next
'Identify blank cells in searched cell range
Set MyBlankCells = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Find Blank Cells").Range("A6:H30").SpecialCells(xlCellTypeBlanks)
'Disable error-handling
On Error GoTo 0
'Test whether blank cells were found in searched cell range
If Not MyBlankCells Is Nothing Then
'Set interior/fill color of blank cells found to light green
MyBlankCells.Interior.Color = RGB(63, 189, 133)
End If
End Sub
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Find Empty (or Blank) Cells
The following image illustrates the effects of using the macro example. In this example:
- Columns A through H (cells A6 to H30) contain:
- Data; and
- A few empty cells (with light green interior/fill).
- A text box (Find all blank cells) executes the macro example when clicked.
After the macro is executed, Excel sets the interior/fill color of all empty (or blank) cells to light green.

#17. Excel VBA Find First Empty (or Blank) Cell in Cell Range
VBA Code to Find First Empty (or Blank) Cell in Cell Range
To find the first empty (or blank) cell in a cell range, use the following structure/template in the applicable procedure:
For Each iCell In CellRangeObject
If IsEmpty(iCell) Then
StatementsForFirstEmptyCell
Exit For
End If
Next iCell
The following Sections describe the main elements in this structure.
Lines #1 and #6: For Each iCell In CellRangeObject | Next iCell
For Each … In … | Next …
The For Each… Next statement repeats a series of statements for each element (iCell, an individual cell) in a collection (CellRangeObject).
iCell
Object variable (of the Range data type) used to iterate/loop through each element of the collection (CellRangeObject).
CellRangeObject
A Range object representing the cell range you search in.
The series of statements repeated by the For Each… Next statement are repeated for each individual element (iCell) in CellRangeObject.
Lines #2 and #5: If IsEmpty(iCell) Then | End If
If… Then | End If
The If… Then Else statement:
- Conditionally executes a set of statements (lines #3 and #4);
- Depending on an expression’s value (IsEmpty(iCell)).
IsEmpty(iCell)
The condition of an If… Then… Else statement is an expression evaluating to True or False. If the expression returns True, the applicable set of statements (lines #3 and #4) are executed.
In this expression:
- As a general rule, the IsEmpty function returns a Boolean value (True or False) indicating whether a variable is initialized. You can (also) use the IsEmpty function to test whether a cell is empty (or blank).
- iCell is an object variable representing the individual cell the For Each… Next statement is currently working with (iterating through).
- IsEmpty(iCell) returns True or False as follows:
- True if the cell (currently) represented by iCell is empty (or blank).
- False if the cell (currently) represented by iCell isn’t empty. A cell isn’t considered to be empty if, for example, it contains a worksheet formula returning a zero-length string (“”).
Line #3: StatementsForFirstEmptyCell
Statements conditionally executed by the If… Then… Else statement if the applicable condition (IsEmpty(iCell)) returns True (the cell currently represented by iCell is empty or blank).
Line #4: Exit For
The Exit For statement:
- Exits a For Each… Next loop.
- Transfers control to the statement following the Next statement (line #6).
Macro Example to Find First Empty (or Blank) Cell in Cell Range
The following macro (User-Defined Function) example does the following:
- Accepts one argument (MyRange): The cell range whose first empty cell you search for.
- Loops through each individual cell in the cell range (MyRange) and tests whether the applicable cell is empty (or blank).
- Returns the following:
- If MyRange contains empty cells, the address (as an A1-style relative reference) of the first empty cell in the cell range (MyRange).
- If MyRange doesn’t contain empty cells, the string “No empty cells found in cell range”.
Function FindNextEmptyCellRange(MyRange As Range) As String
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-find/
'This UDF:
'(1) Accepts 1 argument: MyRange
'(2) Loops through each individual cell in the cell range (MyRange) and tests whether the applicable cell is empty
'(3) Returns the following (as applicable):
'If there are empty cells in MyRange: The address (as an A1-style relative reference) of the first empty cell
'If there are no empty cells in MyRange: The string "No empty cells found in cell range"
'Declare object variable to iterate/loop through all cells in the cell range (MyRange)
Dim iCell As Range
'Loop through each cell in the cell range (MyRange)
For Each iCell In MyRange
'If the current cell is empty:
'(1) Return the current cell's address (as an A1-style relative reference)
'(2) Exit the For Each... Next loop
If IsEmpty(iCell) Then
FindNextEmptyCellRange = iCell.Address(RowAbsolute:=False, ColumnAbsolute:=False)
Exit For
End If
Next iCell
'If no empty cells are found in the cell range (MyRange), return the string "No empty cells found in cell range"
If FindNextEmptyCellRange = "" Then FindNextEmptyCellRange = "No empty cells found in cell range"
End Function
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Find First Empty (or Blank) Cell in Cell Range
The following image illustrates the effects of using the macro (User-Defined Function) example. In this example:
- Columns A through H (cells A6 to H30) contain:
- Data; and
- A few empty cells (with light green interior/fill).
- Cell J7 contains the worksheet formula that works with the macro (User-Defined Function) example. This worksheet formula returns the address (as an A1-style relative reference) of the first empty cell in the cell range (MyRange). This is cell B7.
- Cell K7 displays the worksheet formula used in cell J7 (=FindNextEmptyCellRange(A6:H30)). The cell range where the search is carried out contains cells A6 to H30 (A6:H30).
#18. Excel VBA Find First Empty (or Blank) Cell in Column
VBA Code to Find First Empty (or Blank) Cell in Column
To find the first empty (or blank) cell in a column, use the following structure/template in the applicable statement:
ColumnRangeObject.Find(What:="", After:=ColumnRangeObject.Cells(ColumnRangeObject.Cells.Count), LookIn:=xlFormulas, LookAt:=xlWhole, SearchOrder:=xlByRows, SearchDirection:=xlNext)
The following Sections describe the main elements in this structure.
ColumnRangeObject
A Range object representing the column whose first empty (or blank) cell you search for.
Find
The Range.Find method:
- Finds specific information (the first empty or blank cell) in a cell range (ColumnRangeObject).
- Returns a Range object representing the first cell where the information is found.
What:=””
The What parameter of the Range.Find method specifies the data to search for.
To find the first empty (or blank) cell in a column, set the What parameter to a zero-length string (“”).
After:=ColumnRangeObject.Cells(ColumnRangeObject.Cells.Count)
The After parameter of the Range.Find method specifies the cell after which the search begins.
To find the first empty (or blank) cell in a column, set the After parameter to “ColumnRangeObject.Cells(ColumnRangeObject.Cells.Count)”. For these purposes:
- “ColumnRangeObject” is a Range object representing the column whose first empty (or blank) cell you search for.
- The Range.Cells property (Cells) returns a Range object representing all cells in the column whose first empty (or blank) cell you search for.
- The Range.Item property returns a Range object representing the last cell in the column whose first empty (or blank) cell you search for. For these purposes, the RowIndex parameter of the Range.Item property is set to the value returned by the Range.Count property (Count).
- The Range.Count property (Count) returns the number of cells in the Range object returned by the Range.Cells property (ColumnRangeObject.Cells).
LookIn:=xlFormulas
The LookIn parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the type of data to search in.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlFindLookIn enumeration.
To find the first empty (or blank) cell in a column, set the LookIn parameter to xlFormulas. xlFormulas refers to formulas.
LookAt:=xlWhole
The LookAt parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies against which of the following the data you are searching for is matched:
- The entire/whole searched cell contents.
- Any part of the searched cell contents.
- The LookAt parameter can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlLookAt enumeration.
To find the first empty (or blank) cell in a column, set the LookAt parameter to xlWhole. xlWhole matches the data you are searching for against the entire/whole searched cell contents.
SearchOrder:=xlByRows
The SearchOrder parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the order in which the applicable cell range (ColumnRangeObject) is searched:
- By rows.
- By columns.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlSearchOrder enumeration.
To find the first empty (or blank) cell in a column, set the SearchOrder parameter to xlByRows. xlByRows searches by rows.
SearchDirection:=xlNext
The SearchDirection parameter of the Range.Find method:
- Specifies the search direction:
- Search for the previous match.
- Search for the next match.
- Can take any of the built-in constants/values from the XlSearchDirection enumeration.
To find the first empty (or blank) cell in a column, set the SearchDirection parameter to xlNext. xlNext searches for the next match.
Macro Example to Find First Empty (or Blank) Cell in Column
The following macro (User-Defined Function) example does the following:
- Accepts one argument (MyColumn): The letter of the column (in the worksheet where the UDF is used) whose first empty (or blank) cell you search for.
- Finds the first empty (or blank) cell in the applicable column.
- Returns a string containing the address (as an A1-style relative reference) of the first empty (or blank) cell in the applicable column.
Function FindFirstEmptyCellColumn(MyColumn As String) As String
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-find/
'This UDF:
'(1) Accepts 1 argument: MyColumn
'(2) Finds the first empty (blank) cell in the column whose letter is passed as argument (MyColumn) in the worksheet where the UDF is used
'(3) Returns the address (as an A1-style relative reference) of the first empty (blank) cell in the column whose letter is passed as argument (MyColumn) in the worksheet where the UDF is used
With Application.Caller.Parent.Columns(MyColumn)
FindFirstEmptyCellColumn = .Find(What:="", After:=.Cells(.Cells.Count), LookIn:=xlFormulas, LookAt:=xlWhole, SearchOrder:=xlByRows, SearchDirection:=xlNext).Address(RowAbsolute:=False, ColumnAbsolute:=False)
End With
End Function
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Find First Empty (or Blank) Cell in Column
The following image illustrates the effects of using the macro (User-Defined Function) example. In this example:
- Column I (cells I1 to I25) contains:
- Data; and
- A few empty cells (with light green interior/fill).
- Cell A7 contains the letter of the column whose first empty (or blank) cell is sought (I).
- Cell B7 contains the worksheet formula that works with the macro (User-Defined Function) example. This worksheet formula returns the address (as an A1-style relative reference) of the first empty (or blank) cell in column I (MyColumn). This is cell I10.
- Cell C7 displays the worksheet formula used in cell B7 (=FindFirstEmptyCellColumn(A7)). The letter of the column whose first empty (or blank) cell is sought is stored in cell A7 (A7).
#19. Excel VBA Find Next Empty (or Blank) Cell in Column
VBA Code to Find Next Empty (or Blank) Cell in Column
To find the next empty (or blank) cell in a column, use the following structure/template in the applicable procedure:
If IsEmpty(RangeObjectSourceCell) Then
RangeObjectSourceCell.ActionForNextEmptyCell
ElseIf IsEmpty(RangeObjectSourceCell.Offset(1, 0)) Then
RangeObjectSourceCell.Offset(1, 0).ActionForNextEmptyCell
Else
RangeObjectSourceCell.End(xlDown).Offset(1, 0).ActionForNextEmptyCell
End If
The following Sections describe the main elements in this structure.
Lines #1, #3, #5 and #7: If IsEmpty(RangeObjectSourceCell) Then | ElseIf IsEmpty(RangeObjectSourceCell.Offset(1, 0)) Then | Else | End If
If… Then | ElseIf… Then | Else | End If
The If… Then… Else statement:
- Conditionally executes a set of statements (lines #2, #4 or #6);
- Depending on an expression’s value (IsEmpty(RangeObjectSourceCell) or IsEmpty(RangeObjectSourceCell.Offset(1, 0))).
IsEmpty(RangeObjectSourceCell)
The condition of an If… Then… Else statement is an expression evaluating to True or False. If the expression returns True, the applicable set of statements (line #2) is executed.
In this expression:
- As a general rule, the IsEmpty function returns a Boolean value (True or False) indicating whether a variable is initialized. You can (also) use the IsEmpty function to test whether a cell is empty (or blank).
- RangeObjectSourceCell is a Range object representing the cell where the search (for the next empty or blank cell in the column) begins.
- IsEmpty(RangeObjectSourceCell) returns True or False as follows:
- True if the cell represented by RangeObjectSourceCell is empty (or blank).
- False if the cell represented by RangeObjectSourceCell isn’t empty. A cell isn’t considered to be empty if, for example, it contains a worksheet formula returning a zero-length string (“”).
IsEmpty(RangeObjectSourceCell.Offset(1, 0))
The condition of an If… Then… Else statement is an expression evaluating to True or False. If the expression returns True, the applicable set of statements (line #4) is executed.
In this expression:
- As a general rule, the IsEmpty function returns a Boolean value (True or False) indicating whether a variable is initialized. You can (also) use the IsEmpty function to test whether a cell is empty (or blank).
- RangeObjectSourceCell is a Range object representing the cell where the search (for the next empty or blank cell in the column) begins.
- The Range.Offset property (Offset(1, 0)) returns a Range object representing a cell range at an offset from the source cell range. In this expression:
- The source cell range is the cell where the search (for the next empty or blank cell in the column) begins (RangeObjectSourceCell).
- The offset from the source cell range is as follows:
- 1 row downwards, as specified by the RowOffset parameter of the Range.Offset property (1).
- No column offsetting, as specified by the ColumnOffset parameter of the Range.Offset property (0).
- IsEmpty(RangeObjectSourceCell.Offset(1, 0)) returns True or False as follows:
- True if the cell represented by the Range object returned by the Range.Offset property is empty.
- False if the cell represented by the Range object returned by the Range.Offset property isn’t empty. A cell isn’t considered to be empty if, for example, it contains a worksheet formula returning a zero-length string (“”).
Line #2: RangeObjectSourceCell.ActionForNextEmptyCell
Statement conditionally executed by the If… Then… Else statement if the applicable condition (IsEmpty(RangeObjectSourceCell)) returns True.
RangeObjectSourceCell
A Range object representing the cell where the search (for the next empty or blank cell in the column) begins.
ActionForNextEmptyCell
VBA construct (usually a property or method) working with the applicable cell (represented by RangeObjectSourceCell).
Line #4: RangeObjectSourceCell.Offset(1, 0).ActionForNextEmptyCell
Statement conditionally executed by the If… Then… Else statement if the applicable condition (IsEmpty(RangeObjectSourceCell.Offset(1, 0))) returns True.
RangeObjectSourceCell
A Range object representing the cell where the search (for the next empty or blank cell in the column) begins.
Offset(1, 0)
The Range.Offset property (Offset(1, 0)) returns a Range object representing a cell range at an offset from the source cell range. For these purposes:
- The source cell range is the cell where the search (for the next empty or blank cell in the column) begins (RangeObjectSourceCell).
- The offset from the source cell range is as follows:
- 1 row downwards, as specified by the RowOffset parameter of the Range.Offset property (1).
- No column offsetting, as specified by the ColumnOffset parameter of the Range.Offset property (0).
ActionForNextEmptyCell
VBA construct (usually a property or method) working with the applicable cell (returned by the Range.Offset property).
Line #6: RangeObjectSourceCell.End(xlDown).Offset(1, 0).ActionForNextEmptyCell
Statement conditionally executed by the If… Then… Else statement if no previous condition (in lines #1 or #3) returns True.
RangeObjectSourceCell
A Range object representing the cell where the search (for the next empty or blank cell in the column) begins.
End(xlDown)
The Range.End property returns a Range object representing the cell at the end of the region containing the source range. In other words: The Range.End property is the rough equivalent of using the “Ctrl + Arrow Key” or “End, Arrow Key” keyboard shortcuts.
The Range.End property accepts one parameter: Direction. Direction:
- Specifies the direction in which to move.
- Can take the any of the built-in constants/values from the XlDirection enumeration.
To find the next empty (or blank) cell in a column, set the Direction parameter to xlDown. xlDown:
- Results in moving down, to the bottom of the data region.
- Is the rough equivalent of the “Ctrl + Down Arrow” or “End, Down Arrow” keyboard shortcuts.
Offset(1, 0)
The Range.Offset property (Offset(1, 0)) returns a Range object representing a cell range at an offset from the source cell range. For these purposes:
- The source cell range is the cell represented by the Range object returned by the Range.End property (End(xlDown)).
- The offset from the source cell range is as follows:
- 1 row downwards, as specified by the RowOffset parameter of the Range.Offset property (1).
- No column offsetting, as specified by the ColumnOffset parameter of the Range.Offset property (0).
ActionForNextEmptyCell
VBA construct (usually a property or method) working with the applicable cell (returned by the Range.Offset property).
Macro Example to Find Next Empty (or Blank) Cell in Column
The following macro (User-Defined Function) example does the following:
- Accepts one argument (MySourceCell): The cell where the search (for the next empty or blank cell in the column) begins.
- Finds the next empty (or blank) cell in the applicable column after MySourceCell.
- Returns a string containing the address (as an R1C1-style absolute reference) of the next empty (or blank) cell in the applicable column.
Function FindNextEmptyCellColumn(MySourceCell As Range) As String
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-find/
'This UDF:
'(1) Accepts 1 argument: MySourceCell
'(2) Finds the next empty/blank cell in the applicable column and after the cell passed as argument (MySourceCell)
'(3) Returns the address (as an R1C1-style absolute reference) of the next empty/blank cell in the applicable column and after the cell passed as argument (MySourceCell)
With MySourceCell(1)
'If first cell in cell range passed as argument (MySourceCell) is empty, obtain/return that cell's address
If IsEmpty(MySourceCell(1)) Then
FindNextEmptyCellColumn = .Address(ReferenceStyle:=xlR1C1)
'If cell below first cell in cell range passed as argument (MySourceCell) is empty, obtain/return that cell's address
ElseIf IsEmpty(.Offset(1, 0)) Then
FindNextEmptyCellColumn = .Offset(1, 0).Address(ReferenceStyle:=xlR1C1)
'Otherwise:
'(1) Find the next empty/blank cell in the applicable column and after the first cell in cell range passed as argument (MySourceCell)
'(2) Obtain/return the applicable cell's address
Else
FindNextEmptyCellColumn = .End(xlDown).Offset(1, 0).Address(ReferenceStyle:=xlR1C1)
End If
End With
End Function
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Find Next Empty (or Blank) Cell in Column
The following image illustrates the effects of using the macro (User-Defined Function) example. In this example:
- Column A (cells A6 to A30) contains:
- Data; and
- A few empty cells.
- Cell C7 contains the worksheet formula that works with the macro (User-Defined Function) example. This worksheet formula returns the address (as an R1C1-style absolute reference) of the next empty (or blank) cell in column A after cell A13 (MySourceCell). This cell R21C1 (or A21 as an A1-style relative reference).
- Cell D7 displays the worksheet formula used in cell C7 (=FindNextEmptyCellColumn(A13)). The cell where the search (for the next empty or blank cell in the column) begins is A13 (A13).
#20. Excel VBA Find Value in Array
VBA Code to Find Value in Array
To find a numeric value in a one-dimensional array, use the following structure/template in the applicable procedure:
Dim PositionOfValueInArray As Variant
Dim LoopCounter As Long
PositionOfValueInArray = OutputIfValueNotInArray
For LoopCounter = LBound(SearchedArray) To UBound(SearchedArray)
If SearchedArray(LoopCounter) = SearchedValue Then
PositionOfValueInArray = LoopCounter
Exit For
End If
Next LoopCounter
The following Sections describe the main elements in this structure.
Lines #1 and #2: Dim PositionOfValueInArray As Variant | Dim LoopCounter As Long
The Dim statement:
- Declares variables.
- Allocates storage space.
PositionOfValueInArray | LoopCounter
The names of the variables declared with the Dim statement.
- PositionOfValueInArray holds/represents:
- The position of the searched numeric value in the array, if the searched numeric value is found in the array.
- The default/fallback output/data, if the searched numeric value isn’t found in the array.
- LoopCounter represents the loop counter used in the For… Next loop in lines #4 to #9.
As Variant | As Long
The data type of the variables declared with the Dim statement.
- PositionOfValueInArray is of the Variant data type. The Variant data type can (generally) contain any type of data, except for fixed-length Strings.
- LoopCounter is of the Long data type. The Long data type can contain integers between -2,147,483,648 and 2,147,483,647.
Line #3: PositionOfValueInArray = OutputIfValueNotInArray
PositionOfValueInArray
Variable holding/representing:
- The position of the searched numeric value in the array, if the searched numeric value is found in the array.
- The default/fallback output/data, if the searched numeric value isn’t found in the array.
=
The assignment operator assigns the result returned by an expression (OutputIfValueNotInArray) to a variable (PositionOfValueInArray).
OutputIfValueNotInArray
Expression specifying the default/fallback output/data to be assigned to the PositionOfValueInArray variable if the searched numeric value isn’t found in the array.
Lines #4 and #9: For LoopCounter = LBound(SearchedArray) To UBound(SearchedArray) | Next LoopCounter
For… = … To … | Next…
The For… Next statement repeats a series of statements a specific number of times.
LoopCounter
Variable holding/representing the loop counter.
LBound(…) | UBound(…)
The LBound/UBound functions return the lower/upper bound of an array’s dimension. The LBound/UBound functions accept two arguments:
- ArrayName: The name of the array whose lower/upper bound you want to obtain.
- Dimension:
- An optional argument.
- The dimension (of the applicable array) whose lower/upper bound you want to obtain.
If you omit specifying the Dimension argument, the LBound/UBound functions return the lower/upper bound of the array’s first dimension.
The initial/final values of LoopCounter are set to the following:
- Initial value (Start) of LoopCounter: The output returned by the LBound function (LBound(SearchedArray)).
- Final value (End) of LoopCounter: The output returned by the UBound function (UBound(SearchedArray)).
SearchedArray
The array you search in.
SearchedArray is passed as the ArrayName argument of the LBound/UBound functions.
Lines #5 and #8: If SearchedArray(LoopCounter) = SearchedValue Then | End If
If… Then… End If
The If… Then… Else statement:
- Conditionally executes a set of statements (lines #6 and #7);
- Depending on an expression’s value (SearchedArray(LoopCounter) = SearchedValue).
SearchedArray(LoopCounter) = SearchedValue
The condition of an If… Then… Else statement is an expression evaluating to True or False.
- If the expression returns True, a set of statements (lines #6 and #7) is executed.
- If the expression returns False:
- No statements are executed.
- Execution continues with the statement following End If (line #8).
In this expression:
- SearchedArray: The array you search in.
- LoopCounter: Variable holding/representing the loop counter.
- SearchedArray(LoopCounter): Array element whose index number is LoopCounter.
- =: The equal to comparison operator returns True or False as follows:
- True if both expressions (SearchedArray(LoopCounter) and SearchedValue) are equal.
- False if the expressions (SearchedArray(LoopCounter) and SearchedValue) are not equal.
- SearchedValue: Numeric value you search for in the array (SearchedArray).
Line #6: PositionOfValueInArray = LoopCounter
PositionOfValueInArray
Variable holding/representing:
- The position of the searched numeric value in the array, if the searched numeric value is found in the array.
- The default/fallback output/data, if the searched numeric value isn’t found in the array.
=
The assignment operator assigns the result returned by an expression (LoopCounter) to a variable (PositionOfValueInArray).
LoopCounter
Variable holding/representing the loop counter.
Line #7: Exit For
The Exit For statement:
- Exits a For… Next loop.
- Transfers control to the statement following the Next statement (line #8).
Macro Example to Find Value in Array
The following macro (User-Defined Function) example does the following:
- Accepts two arguments:
- MyArray: The array you search in.
- MyValue: The numeric value you search for.
- Loops through each element in MyArray and tests whether the applicable element is equal to MyValue.
- Returns the following:
- If MyValue is not found in MyArray, the string “Value not found in array”.
- If MyValue is found in MyArray, the position/index number of MyValue in MyArray.
Function FindValueInArray(MyArray As Variant, MyValue As Variant) As Variant
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-find/
'This UDF:
'(1) Accepts 2 arguments: MyArray and MyValue
'(2) Loops through each element in the array (MyArray) and tests whether the applicable element is equal to the searched value (MyValue)
'(3) Returns the following (as applicable):
'If MyValue is not found in MyArray: The string "Value not found in array"
'If MyValue is found in MyArray: The position (index number) of MyValue in MyArray
'Declare variable to represent loop counter
Dim iCounter As Long
'Specify default/fallback value/string to be returned ("Value not found in array") if MyValue is not found in MyArray
FindValueInArray = "Value not found in array"
'Loop through each element in the array (MyArray)
For iCounter = LBound(MyArray) To UBound(MyArray)
'Test if the current array element is equal to MyValue
If MyArray(iCounter) = MyValue Then
'If the current array element is equal to MyValue:
'(1) Return the position (index number) of the current array element
'(2) Exit the For... Next loop
FindValueInArray = iCounter
Exit For
End If
Next iCounter
End Function
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Find Value in Array
To illustrate the effects of using the macro (User-Defined Function) example, I use the following macro. The following macro does the following:
- Declare an array (MySearchedArray).
- Fill the array with values (0, 10, 20, …, 90).
- Call the FindValueInArray macro (User-Defined Function) example to find the number “50” in the array.
- Display a message box with the value/string returned by the FindValueInArray macro (User-Defined Function) example.
Sub FindValueInArrayCaller()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-find/
'This procedure:
'(1) Declares an array and fills it with values (0, 10, 20, ..., 90)
'(2) Calls the FindValueInArray UDF to find the number "50" in the array
'(3) Displays a message box with the value/string returned by the FindValueInArray UDF
'Declare a zero-based array with 10 elements of the Long data type
Dim MySearchedArray(0 To 9) As Long
'Assign values to array elements
MySearchedArray(0) = 0
MySearchedArray(1) = 10
MySearchedArray(2) = 20
MySearchedArray(3) = 30
MySearchedArray(4) = 40
MySearchedArray(5) = 50
MySearchedArray(6) = 60
MySearchedArray(7) = 70
MySearchedArray(8) = 80
MySearchedArray(9) = 90
'Do the following:
'(1) Call the FindValueInArray UDF and search for the number "50" in MySearchedArray
'(2) Display a message box with the value/string returned by the FindValueInArray UDF
MsgBox FindValueInArray(MySearchedArray, 50)
End Sub
The following GIF illustrates the effects of using the macro above to call the macro (User-Defined Function) example.
As expected, this results in Excel displaying a message box with the number 5. This is the position of the searched numeric value (50) in the array.

Learn More About Excel VBA Find
Workbook Example Used in this Excel VBA Find Tutorial
This VBA Find Tutorial is accompanied by an Excel workbook containing the data and macros I use in the examples above. You can get free access to this example workbook by clicking the button below.
The Power Spreadsheets Library
The Books at The Power Spreadsheets Library are comprehensive and actionable guides for professionals who want to:
- Automate Excel;
- Save time for the things that really matter; and
- Open new career opportunities.
Learn more about The Power Spreadsheets Library here.
-
#1
Hi all,
I’m struggling my way through a macro with help from you all and am bringing in data from several sheets into a single sheet — what I need to do is to copy certain ranges (which I know how to select and do now) but then I need to paste it beneath the last active cell in column A which can vary.
So for instance if the first part of my macro copies in 450 entries into column A and the next part selects 100 entries it needs to paste those starting from A451 (the next empty cell).
The number of entries copied in will vary every time which is why I need a flexible way to do this.
As always help gratefuly appreciated!
Add Bullets to Range
Select range. Press Ctrl+1. On Number tab, choose Custom. Type Alt+7 then space then @ sign (using 7 on numeric keypad)
-
#2
Worksheets(«Sheet1»).Range(«A1»).End(xlDown).Row + 1
Literally copied and pasted from a google search. Does what you want?
-
#3
wow thanks for the quick reply — I’ve had mixed results with some of the googled stuff I’ve found — will try this in the morning!
-
#4
I’m having the same issue as Puppies72 — the user ‘wut’ has been banned I’m guess for posting silly replies….
any help on this would be great
-
#5
there are numerous ways of determining the last row or first blank row…
Range(«A» & Rows.Count).End(xlup).Offset(1).Row
Cells(Rows.Count,1).End(xlup).Offset(1).Row
UsedRange.Rows.Count
-
#6
My issue is a little more complex — the users all have a form on one worksheet within a workbook to fill in and send to me. I have a tracker that tracks information like name, ref number etc so I need the macro to copy that information from the the forms and paste it to a new row on the tracker. so it needs to check the next empty row and enter the informatin from the the form in the relivant cells — name, ref number, date etc
-
#7
My issue is a little more complex — the users all have a form on one worksheet within a workbook to fill in and send to me. I have a tracker that tracks information like name, ref number etc so I need the macro to copy that information from the the forms and paste it to a new row on the tracker. so it needs to check the next empty row and enter the informatin from the the form in the relivant cells — name, ref number, date etc
that doesn’t sound so complex…
Code:
Dim LastRow as Long
LastRow = Sheets("Sheet1").Cells(Rows.Count,1).End(xlup).Offset(1).Row
Sheets("Sheet2").Range("A1").Copy Sheets("Sheet1").Cells(LastRow,1)
-
#8
lol ok in my head it sounded more complex — I bow down to your superior coding skills
thanks a lot for the help — I’ll give this a whirl now
-
#9
that doesn’t sound so complex…
Code:
Dim LastRow as Long LastRow = Sheets("Sheet1").Cells(Rows.Count,1).End(xlup).Offset(1).Row Sheets("Sheet2").Range("A1").Copy Sheets("Sheet1").Cells(LastRow,1)
I might be out of my depth here as I still can’t work out a few things
The tracker I’m using is stored on my desktop (for ease) and it’s call AndyTrackerQ3.xls. Now the individual files being sent to me via email will have a different persons names on each form so tomsmith.xls terryjones.xls Neilgoodwin.xls might be all in one email — the idea being that I open a form check it click a button and it copies the info from cells AC74, AD74, AE74, AF74, AG74, AH74, AI74 into my tracker. The first available row that these will copy into would be starting C3, D4, E4, F4 , G4, H4, J4 and the next form I open would have to copy in the line below so C4, D5, E5, F5 etc or essentially just the next available row
<o></o
>
Hope what I’m trying to do/say makes sense!
-
#10
If you’re looking for a full solution, you’ll need to provide a lot more detail:
— which file (tracker or emailed file) will contain the macro?
— will both files be open when the macro is run?
— what are the relevant sheet names?
— is there a field in the tracker that lists the persons name? If so, which column?
— in your example, you said the data will be copied to C3, D4, E4 etc. Why is column C a different row to the other columns?
Sometimes, You may need to find and select the first blank cell or last blank cell in a column, these macros can help you.
Sub Macro1()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = ActiveSheet
For Each cell In ws.Columns(1).Cells
If IsEmpty(cell) = True Then cell.Select: Exit For
Next cell
End Sub
or
Sub Macro2()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = ActiveSheet
For Each cell In ws.Columns(1).Cells
If Len(cell) = 0 Then cell.Select: Exit For
Next cell
End Sub
First blank cell: before selection
First blank cell: after selection
Find and Select the Last Blank Cell in Column A
Sub Macro3()
'Step 1: Declare Your Variables.
Dim LastRow As Long
'Step 2: Capture the last used row number.
LastRow = Cells(Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row
'Step 3: Select the next row down
Cells(LastRow, 1).Offset(1, 0).Select
End Subor
Sub Macro4()
'Step 1: Declare Your Variables.
Dim LastBlankRow As Long
'Step 2: Capture the last used row number.
LastBlankRow = Cells(Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row + 1
'Step 3: Select the next row down
Cells(LastBlankRow, 1).Select
End Sub
Note: Some of the most common ways of finding last row which are highly unreliable and hence should never be used:
UsedRangexlDownCountA
Why we use Rows.Count not 65536?
This question is a classic scenario where the code will fail because the Rows.Count returns 65536 for Excel 2003 and earlier and 1048576 for Excel 2007 and later. The above fact that Excel 2007+ has 1048576 rows also emphasizes on the fact that we should always declare the variable which will hold the row value as Long instead of Integer else you will get an Overflow error.
How to use it
To use this macro, you can copy and paste it into a standard module:
- Activate the Visual Basic Editor by pressing ALT F11.
- Right-click the project/workbook name in the Project window.
- Choose Insert -> Module.
- Type or paste the code in the newly created module.
|
Подскажите как при помощи VBA определить наличие пустой ячейки (не заполненной = «» |
|
|
Юрий М Модератор Сообщений: 60570 Контакты см. в профиле |
Нашли, дальше что? Перебрать диапазон/массив и при нахождении пустой/нулевой выйти из цикла с сообщением. |
|
Антон Пользователь Сообщений: 617 |
#3 28.01.2014 01:20:21 посредством перебора каждого значения массива и сравнением )
Изменено: Антон — 28.01.2014 01:25:02 |
||
|
Да, если такие ячейки имеются вывести сообщение и прекратить дальнейшее выполнение макроса, если таких ячеек нет продолжить выполнение макроса. |
|
|
Юрий М Модератор Сообщений: 60570 Контакты см. в профиле |
#5 28.01.2014 01:28:51
|
||
|
Юрий М Модератор Сообщений: 60570 Контакты см. в профиле |
#7 28.01.2014 02:01:36 Без цикла, но и без адресов:
|
||
|
KuklP Пользователь Сообщений: 14868 E-mail и реквизиты в профиле. |
Я сам — дурнее всякого примера! … |
|
Max.il Пользователь Сообщений: 64 |
Юрий М, Юрий, добрый вечер. Развивая тему, если нужно проверить несколько ячеек, к примеру А3, Т16 и Т22, если они пустые — залить эту ячейку красным цветом. Если в ней есть что-то , пропустить. Если во всех ячейках есть данные, то просто прекратить выполнение макроса без вывода сообщения. |
|
Юрий М Модератор Сообщений: 60570 Контакты см. в профиле |
|
|
Max.il Пользователь Сообщений: 64 |
Юрий М,Нет, т.к. проверка должна осуществляться после макроса. |
|
Юрий М Модератор Сообщений: 60570 Контакты см. в профиле |
УФ сработает и после макроса. А макрос написать не смогу: нет у меня файла, где имеются перечисленные Вами ячейки )) |
|
Юрий М Модератор Сообщений: 60570 Контакты см. в профиле |
#13 27.05.2019 23:32:23 Нет ответа…
|
||
|
RAN Пользователь Сообщений: 7091 |
#14 27.05.2019 23:39:10
|
||||
|
Max.il Пользователь Сообщений: 64 |
RAN, Юрий М, Мужчины, спасибо, что помогаете . Искренняя благодарность. |
|
Николай Китаев Пользователь Сообщений: 2 |
#16 17.12.2021 13:26:01
Такая конструкция не работает: If cells(i,y).Value=»» then…. А так — должно работать: Изменено: Николай Китаев — 17.12.2021 14:07:17 |
||
|
Jack Famous Пользователь Сообщений: 10846 OS: Win 8.1 Корп. x64 | Excel 2016 x64: | Browser: Chrome |
Николай Китаев, с момента создания темы прошло почти 8 лет, а ТС был последний раз почти 2 года назад — в курсе? Во всех делах очень полезно периодически ставить знак вопроса к тому, что вы с давних пор считали не требующим доказательств (Бертран Рассел) ►Благодарности сюда◄ |
|
Ничего страшного. Можно считать, что памятка для себя. Тем более проверка вида cells(i,y).Value=»» не работает. |
|
|
БМВ Модератор Сообщений: 21376 Excel 2013, 2016 |
#19 17.12.2021 14:19:40
докажите. По вопросам из тем форума, личку не читаю. |
||
|
Jack Famous Пользователь Сообщений: 10846 OS: Win 8.1 Корп. x64 | Excel 2016 x64: | Browser: Chrome |
Если вас что-то не устраивает, то не нужно поднимать со дна старую тему, тем более, что спросить автора не получится — создайте свою и там всё подробно опишите и/или спросите И тут гляньте: VBA. UDF. Функция для проверки значения на строку нулевой длины «=»»» Во всех делах очень полезно периодически ставить знак вопроса к тому, что вы с давних пор считали не требующим доказательств (Бертран Рассел) ►Благодарности сюда◄ |
|
vikttur Пользователь Сообщений: 47199 |
#21 17.12.2021 23:29:31
И где К? ) |
||
IsEmpty is a worksheet function used to find out whether a given cell reference or a range of cells is empty or not. Since it is a worksheet function, we use the Application to use it in VBA. It is the worksheet method in VBA to use this function. This function comes under the logical lists of functions and returns “True” if the reference is empty.
VBA IsEmpty Function
VBA IsEmpty is a logical function that tests whether the selected is empty or not. Since it is a logical function, it will return the results in Boolean values, i.e., TRUE or FALSE.
If the selected cell is empty, it will return TRUE, or else it will return FALSE.
This article will show you how to use the ISEMPTY function in VBA to check the cells using VBA codesVBA code refers to a set of instructions written by the user in the Visual Basic Applications programming language on a Visual Basic Editor (VBE) to perform a specific task.read more.
Table of contents
- VBA IsEmpty Function
- What Does ISEMPTY Function Do in VBA?
- Examples of ISEMPTY Function in VBA
- Example #1
- Example #2 – Combination of VBA ISEMPTY with IF Condition
- Example #3 – Alternative to VBA ISEMPTY Function
- Recommended Articles
What Does ISEMPTY Function Do in VBA?
Often empty cells frustrate us from working efficiently on the worksheet. Finding the blank cells is not the hardest, but if empty cells hide them in the middle of the data, it takes a toll to find them.
To find the empty cells in Excel, we have the ” ISBLANK ” function as a worksheet function, but in VBA, it is called “ISEMPTY.”
It works similarly to the worksheet function “ISBLANK”. Now, look at the below formula of the “ISEMPTY” function.
As we can see in the above image, it returns the result as Boolean, i.e., TRUE or FALSE.
Examples of ISEMPTY Function in VBA
The following are examples of IsEmpty in VBA.
You can download this VBA IsEmpty Excel Template here – VBA IsEmpty Excel Template
Example #1
Now, we will see the first practical example of “ISEMPTY.” For this, take a look at the below image of the worksheet.
Now, we will apply Excel VBA ISEMPTY function to test all these.
Step 1: Define the variable as Boolean.
Code:
Sub IsEmpty_Example1() Dim K As Boolean End Sub
Step 2: Assign the value through VBA ISEMPTY function for this variable.
Code:
Sub IsEmpty_Example1() Dim K As Boolean K = IsEmpty( End Sub
Step 3: Expression is nothing but what is the cell we are testing. Now, we are testing the A1 cell.
Code:
Sub IsEmpty_Example1() Dim K As Boolean K = IsEmpty(Range("A1").Value) End Sub
Step 4: Show the value of this variable in the VBA Msgbox.
Code:
Sub IsEmpty_Example1() Dim K As Boolean K = IsEmpty(Range("A1").Value) MsgBox K End Sub
Run this code to check the result.
Since there is a value in cell A1, we got the result as FALSE.
Now, we will change the cell reference from A1 to A5.
Code:
Sub IsEmpty_Example1() Dim K As Boolean K = IsEmpty(Range("A5").Value) MsgBox K End Sub
Run this code to see the result.
We got the result as TRUE. The referenced cell A5 is an empty cell, so we got the result as “TRUE.”
Now, we will test cell A8.
Code:
Sub IsEmpty_Example1() Dim K As Boolean K = IsEmpty(Range("A8").Value) MsgBox K End Sub
Run this code to see the result.
We got the result as FALSE even though there is no value in cell A8.
Now, is it an error result from the ISEMPTY formula?
No… Absolutely No!
When examining cell A8, there was a space character inside the cell that is not easy to see with bare eyes.
So, the conclusion is even space is considered a character in Excel and VBA language.
Example #2 – Combination of VBA ISEMPTY with IF Condition
The real usage of the function “ISEMPTY” is admirable when we use it with other logical functions.
Especially when we use it with IF conditions, we can derive many useful results from it.
For this demonstration, take a look at the below example.
In the “Status” column, if the “PF Status” column is empty, we need the value “No Update.” If there is any value, we need the values as “Collected Updates.”
Remember here that we do not need the default result of TRUE or FALSE. We need our results here. We need to use Excel VBA ISEMPTY with IF conditions to have our results.
Step 1: Open IF condition.
Code:
Sub IsEmpty_Example2() If End Sub
Step 2: Inside the IF condition, open the ISEMPTY function.
Code:
Sub IsEmpty_Example2() If IsEmpty( End Sub
Step 3: The first logical test is cell B2 value is empty or not.
Code:
Sub IsEmpty_Example2() If IsEmpty(Range("B2").Value) Then End Sub
Step 4: If the logical test in excelA logical test in Excel results in an analytical output, either true or false. The equals to operator, “=,” is the most commonly used logical test.read more VBA is TRUE, i.e., if the cell is empty, we need the resultas “No Update” in cell C2.
Code:
Sub IsEmpty_Example2() If IsEmpty(Range("B2").Value) Then Range("C2").Value = "No Update" End Sub
Step 5: If the logical test is FALSE, we need the result in cell C2 as “Collected Updates.”
Code:
Sub IsEmpty_Example2() If IsEmpty(Range("B2").Value) Then Range("C2").Value = "No Update" Else Range("C2").Value = "Collects Updates" End If End Sub
We have completed it now.
Run the code to get the result.
We got the “Collected Updates” result because we have the non-empty cell in B2.
Now, similarly, apply the code for other cells to test.
Code:
Sub IsEmpty_Example2() If IsEmpty(Range("B2").Value) Then Range("C2").Value = "No Update" Else Range("C2").Value = "Collects Updates" End If If IsEmpty(Range("B3").Value) Then Range("C3").Value = "No Update" Else Range("C3").Value = "Collected Updates" End If If IsEmpty(Range("B4").Value) Then Range("C4").Value = "No Update" Else Range("C4").Value = "Collected Updates" End If End Sub
Run this code to have the results.
In cell C3, we got the result as “No Update” because there is no value in cell B3, i.e., an empty cell. Since the logical formula returned TRUE, we got the individual result.
Example #3 – Alternative to VBA ISEMPTY Function
We have an alternative to the ISEMPTY function; without applying the Excel VBA ISEMPTY function, we can test the cell.
For an example, look at the below code.
Code:
Sub IsEmpty_Example3() If Range("B2").Value = "" Then Range("C2").Value = "No Update" Else Range("C2").Value = "Collected Updates" End If End Sub
The line of code Range(“B2″).Value = ” ” means whether the cell B2 cell is equal to empty or not.
Double Quotes (“”) represent an empty cell or not if the empty result is TRUE or else FALSE.
Recommended Articles
This article has been a guide to VBA ISEMPTY function. Here, we learned how to use the VBA ISEMPTY function in Excel, the Combination of IsEmpty with the IF condition, some practical examples, and a downloadable Excel template. Below are some useful Excel articles related to VBA: –
- Boolean in VBA
- False Function in Excel
- OFFSET in VBA
- Date Function in VBA
Introduction to Cells
In Microsoft Excel, a cell is nothing but an intersection of a column and a row. This cell is referenced by its row number and column letter. A cell can hold a formula/data directly. It can be formatted with font styles and colors or background colors too.
In the image above, cell B4 is selected. It is the intersection of row number “4” and column letter “B.” Since the value of the cell does not start with an “=”, it means that the cell is holding some data directly. Here the data held is “110.”
Empty Cells in Excel
If the cell does not have any value, it is said to be empty. There’s a chance that a cell has the same font color and background color, but with some data. In that case, it may look empty but actually isn’t. So, to find this, we have to select the cell and check the formula bar.

Here the selected cell D9 looks blank but has a value “India.” It is not visible on the cell because the color of the font in that cell is white, which is equal to its background color.
ISBLANK Formula
Microsoft Excel offers a formula named ISBLANK which returns/provides a Boolean result stating whether the value of that cells is blank or not.
Syntax:
ISBLANK( <value> )
Where <value> can be a reference to a cell.


In the above images, the selected cells hold the formula as in the formula bar referring to the cells B7 (first image) and C8 (second image) respectively. The false and true values are returned depending on the values in the cells referred as parameters.
The selected cells hold the formula seen in the formula bar referring to the cells B7 (first image) and C8 (second image) respectively. The false and true values are returned depending on the values in the cells referred as parameters.
Range of Cells in Excel
In Excel a range is a set of continuous cells which can be a part of one or more columns or one or more rows or both. For example, in this image above Range(“A1:B12”) can be termed as a range.
Empty Cells in a Range
If there is a need to find the empty cells in a huge range of cells, it might be time consuming and tiring to select each cell and find this manually.
VBA to Find Empty Cells
VBA offers an inbuilt function called “IsEmpty” to do this for us.
Syntax
<Var> = IsEmpty ( <expression> )
Where <var> is any Boolean variable that can hold the end result value (return value) of the function and <expression> is any value that needs to be checked if empty.
For Example:
Select a Cell and Display if it is Empty
Sub empty_demo() ' select an empty cell Cells(1, 5).Select ' display a msg to cross check if the selected cell is empty MsgBox IsEmpty(Cells(1, 5).Value) End Sub
The same with a non-empty cell:
Sub empty_demo() ' select a non-empty cell Cells(1, 1).Select ' display a msg to cross check if the selected cell is empty MsgBox IsEmpty(Cells(1, 1).Value) End Sub
Another Simple Program to Check if a Cell is Empty
Sub demo2()
' check if the value of a particular cell is nothing or ""
' if there is a value, the value is displayed . If not, a statement is displayed
If Cells(3, 4).Value = "" Then
MsgBox "The cell in 3rd row and 4th col is empty"
Else
MsgBox Cells(3, 4).Value
End If
End Sub
This program looks if the value of a specific cell is empty using just the “”. The same can also be done on several cells using a loop/range.
VBA – Find Empty Cells in a Range
It is possible to find the cells that are empty in a range of cells. Once a range is defined, we can loop through each cell in the range. As we loop, we can check if the cell is empty.
Program to Count the Number of Empty Cells in a Range of Cells
In this program:
- We declare a count variable and initialize it to “0.” This will help us count the number of empty cells in a range.
- We define a range in an Excel worksheet.
- Then we loop through the cells in it using a “for each” loop. Inside the loop, we check if the cell is empty/blank using the inbuilt VBA function “ISEMPTY()”.
- If so, the value of the “cnt” variable is incremented by “1.” Once we come out of the loop, we display the value of “cnt” as the number of empty cells in the declared range.
Sub empty_demo()
' declare a range
Dim myrange
'declare a variable to store count
Dim cnt
' define the range and initialize count
myrange = Range("A1:A20")
cnt = 0
'loop through each cell of the range
For Each cell In myrange
' if the cell is empty , we increment the value of cnt variable by 1
If IsEmpty(cell) Then
cnt = cnt + 1
End If
Next cell
' display the number of empty cells
MsgBox "There are " &amp; cnt &amp; " empty cells in the mentioned range. "
End Sub
Color the Empty Cells in a Range of Cells Without Defining Any Range
In this program, instead of using a range, we use a nested “for loop” to iterate through every row in every column. The outer loop iterates through the columns while the inner loop iterates through the rows. The upper and lower bounds of the desired range/table are already provided in the “for loop” definition. Inside the inner loop, as in the previous example, we check if the cell is empty and add a number to the “cnt” variable’s value if so. Here, in addition, we also color those empty cells that are identified within the inner loop’s condition.
Sub empty_demo_1() ' declare variables to indicate, row, col and counter Dim r, c, cnt ' intialize the variables r = 1 c = 1 cnt = 0 ' loop through each col in the worksheet till we reach col no "2" For c = 1 To 2 ' loop through each row in the worksheet till we reach row no "20" For r = 1 To 20 ' if the cell ( intersection of the row and col) is empty , we increment the value of cnt variable by 1 If IsEmpty(Cells(r, c).Value) = True Then cnt = cnt + 1 ' Color the cells in yellow just to identify Cells(r, c).Interior.Color = 65535 End If Next r Next c ' display the number of empty cells MsgBox "There are " &amp;amp; cnt &amp;amp; " empty cells in the mentioned range. " End Sub
Using IsEmpty() for Variable Values
This program checks if a variable is empty and displays the result.
Sub demo3() ' declare a variable and do not initialize Dim var1 ' check if variable has value If IsEmpty(var1) = True Then ' statement if empty Debug.Print "Var1 is Empty" Else ' statement if not empty Debug.Print "Var1 has a value " &amp;amp; var1 End If End Sub
Output would be:
“Var1 is Empty”
Sub demo3() ' declare a variable and initialize it Dim var1 var1 = "This is a good day" ' check if variable has value If IsEmpty(var1) = True Then ' statement if empty Debug.Print "Var1 is Empty" Else ' statement if not empty Debug.Print "Var1 has a value. " &amp;amp; var1 End If
Output would be:
“Var1 has a value. This is a good day”
Conclusion
Apart from cells and variables, the IsEmpty() function offered by VBA can be used for arrays and many such objects. However, these are not elaborated here as the focus of this article is on checking if a cell is empty. The “” ( empty double quotes) can also be used to check if the cell(s) are empty. This is just a replacement for the IsEmpty() function and straightforward too. At times, we get stuck into a situation where nothing works out to validate if a cell is empty. In that case we can also try the len() function. The length of the cell value is “0” if it is actually empty.
Check out our other articles on the specific functions to know much about their usage.
Tagged with: Cells and Ranges, empty cells, Excel, Formulas, Functions and Formulas, isempty, Loop, Microsoft Excel, Range, VBA, VBA Boolean, VBA For Excel
Содержание
- Select first empty cell in column F starting from row 1. (without using offset )
- 15 Answers 15
- Excel VBA Check if Cell is Empty: Step-by-Step Guide and 4 Examples to Check if Cell Range is Empty with Macros
- Related VBA and Macro Tutorials
- #1: Check if Cell is Empty
- VBA Code to Check if Cell is Empty
- Process Followed by VBA Code to Check if Cell is Empty
- VBA Statement Explanation
- Line #1: If IsEmpty(Cell) Then
- Line #2: StatementsIfCellIsEmpty
- Line #3: Else
- Line #4: StatementsIfCellIsNotEmpty
- Line #5: End If
- Macro Example to Check if Cell is Empty
- Effects of Executing Macro Example to Check if Cell is Empty
- #2: Check if Active Cell is Empty
- VBA Code to Check if Active Cell is Empty
- Process Followed by VBA Code to Check if Active Cell is Empty
- VBA Statement Explanation
- Line #1: If IsEmpty(ActiveCell) Then
- Line #2: StatementsIfActiveCellIsEmpty
- Line #3: Else
- Line #4: StatementsIfActiveCellIsNotEmpty
- Line #5: End If
- Macro Example to Check if Active Cell is Empty
- Effects of Executing Macro Example to Check if Active Cell is Empty
- #3: Check if Range is Empty
- VBA Code to Check if Range is Empty
- Process Followed by VBA Code to Check if Range is Empty
- VBA Statement Explanation
- Line #1: If WorksheetFunction.CountA(CellRange) = 0 Then
- Line #2: StatementsIfRangeIsEmpty
- Line #3: Else
- Line #4: StatementsIfRangeIsNotEmpty
- Line #5: End If
- Macro Example to Check if Range is Empty
- Effects of Executing Macro Example to Check if Range is Empty
- #4: Check if Any Cell in Range is Empty
- VBA Code to Check if Any Cell in Range is Empty
- Process Followed by VBA Code to Check if Any Cell in Range is Empty
- VBA Statement Explanation
- Line #1: If WorksheetFunction.CountA(CellRange) Macro Example to Check if Any Cell in Range is Empty
- Effects of Executing Macro Example to Check if Any Cell in Range is Empty
- References to VBA Constructs Used in this VBA Tutorial
Select first empty cell in column F starting from row 1. (without using offset )
This is one query that I am really confused with. Coz I have looked for this so many times but I always find the codes related to finding the last used or first non empty cell. Tried at below codes. diff codes have been separated by the word «even»
Find the very last used cell in a Column:
Find the last cell, before a blank in a Row:
Find the very last used cell in a Row:
15 Answers 15
If all you’re trying to do is select the first blank cell in a given column, you can give this a try:
Code:
Before Selection — first blank cell to select:
After Selection:
In case any one stumbles upon this as I just have.
Find First blank cell in a column(I’m using column D but didn’t want to include D1)
NextFree is just a name, you could use sausages if you wanted.
If all you’re trying to do is select the first blank cell in a given column, you can give this a try:
If you’re using it relative to a column you’ve selected this works:
Code of Sam is good but I think it need some correction,
If you are looking for a one liner (not including designations and comments) try this
I adapted a bit the code of everyone, made it in a Function, made it faster (array), and added parameters :
This is a very fast and clean way of doing it. It also supports empty columns where as none of the answers above worked for empty columns.
If any column contains more than one empty cell continuously then this code will not work properly
I found this thread while trying to carry out a similar task. In the end, I used
Which works fine as long as there is a blank cell in the intersection of the specified range and the used range of the worksheet.
The areas property is not needed to find the absolute first blank in the range, but is useful for finding subsequent non consecutive blanks.
I think a Do Until -loop is cleaner, shorter and more appropriate here:
There is another way which ignores all empty cells before a nonempty cell and selects the last empty cell from the end of the first column. Columns should be addressed with their number eg. Col «A» = 1.
The next code is exactly as the above but can be understood better.
NextRow = Application.WorksheetFunction.CountA(Range(«A:A»)) + 1
I just wrote this one-liner to select the first empty cell found in a column based on a selected cell. Only works on first column of selected cells. Modify as necessary
.Find has a lot of options and returns Nothing if there are no empty cells found in your range:
.Find starts searching after the first cell in the range by default, so it would normally start in row 2. It will find the first empty cell starting in row 1, if its After argument is the last cell in the range. That’s because the search wraps.
This formula uses the built-in ISBLANK(range) function to match to the first empty row number in a column: =MATCH(TRUE,ISBLANK(F:F),0)
You can narrow down the range in the usual fashion, of course.
To count the number of non-blank entries up to that point, subtract 1: =MATCH(TRUE,ISBLANK(F:F),0)-1 which is useful (eg) for counting the number of entries in a dynamically changing table such as the number of transactions coming in on a csv or similar import. You can exclude header rows by subtracting the number of those; or by changing the range to (F1:Fxxxx) where xxxx is a number greater than the highest expected range.
Источник
Excel VBA Check if Cell is Empty: Step-by-Step Guide and 4 Examples to Check if Cell Range is Empty with Macros
In this VBA Tutorial, you learn how to check if a cell or range is empty.
This VBA Tutorial is accompanied by an Excel workbook containing the data and macros I use in the examples below. You can get immediate free access to this example workbook by subscribing to the Power Spreadsheets Newsletter.
Use the following Table of Contents to navigate to the section you’re interested in.
Table of Contents
The following VBA and Macro Tutorials may help you better understand and implement the contents below:
- Learn about commonly-used VBA terms here.
Learn about the Excel Object Model and how to refer to objects here.
Learn how to create references to cell ranges here.
Learn how to declare and work with variables here.
Learn about data types here.
You can find additional VBA and Macro Tutorials in the Archives.
#1: Check if Cell is Empty
VBA Code to Check if Cell is Empty
To check if a cell is empty with VBA, use a macro with the following statement structure:
Process Followed by VBA Code to Check if Cell is Empty
Execute StatementsIfCellIsEmpty or StatementsIfCellIsNotEmpty» width=»406″ height=»253″ data-srcset=»https://powerspreadsheets.com/wp-content/uploads/check-if-cell-is-empty.jpg 406w, https://powerspreadsheets.com/wp-content/uploads/check-if-cell-is-empty-300×187.jpg 300w» data-src=»https://powerspreadsheets.com/wp-content/uploads/check-if-cell-is-empty.jpg» data-sizes=»(max-width: 406px) 100vw, 406px» gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAAAAACH5BAEKAAEALAAAAAABAAEAAAICTAEAOw==»/>
VBA Statement Explanation
Line #1: If IsEmpty(Cell) Then
- VBA Construct: Opening statement of If… Then… Else statement.
Description: The If… Then… Else statement conditionally executes a group of statements depending on the value of an expression. For these purposes:
- The If… Then… Else statement tests the specified condition (IsEmpty(Cell)).
If the condition is met and returns True: StatementsIfCellIsEmpty are executed.
If the condition isn’t met and returns False: StatementsIfCellIsNotEmpty are executed.
Item: IsEmpty(…).
- VBA Construct: IsEmpty function.
Description: Generally, the IsEmpty function indicates whether a variable has been initialized. Nonetheless, you can also use IsEmpty to check if a cell is empty.
The IsEmpty function:
- Takes one parameter (expression) of the Variant data type. Within this macro structure, the parameter is a Range object (Cell).
Returns True if the variable is uninitialized or explicitly set to Empty. Otherwise, IsEmpty returns False.
Item: Cell.
- VBA Construct: Range object.
Description: Range object representing the cell you work with.
You can usually return a Range object with constructs such as the Worksheet.Range, Worksheet.Cells (with the Range.Item) or Range.Offset properties. If you explicitly declare an object variable to represent Cell, use the Range object data type.
Item: IsEmpty(Cell).
- VBA Construct: Condition of If… Then… Else statement.
Description: This condition is an expression that evaluates to True or False. The IsEmpty function (IsEmpty(Cell)) returns True or False, as follows:
- True: Cell is empty.
Line #2: StatementsIfCellIsEmpty
- Item: StatementsIfCellIsEmpty.
- VBA Construct: Statements within If… Then… Else statement.
Line #3: Else
- VBA Construct: Else clause of If… Then… Else statement.
Description: The statements below the Else clause (StatementsIfCellIsNotEmpty) are executed if the condition tested in the opening statement of the If… Then… Else statement (IsEmpty(Cell)) returns False. Within this macro structure, IsEmpty(Cell) returns False if Cell is not empty.
Line #4: StatementsIfCellIsNotEmpty
- Item: StatementsIfCellIsNotEmpty.
- VBA Construct: Else Statements within If… Then… Else statement.
Line #5: End If
- VBA Construct: Closing statement of If… Then… Else statement.
Macro Example to Check if Cell is Empty
The following macro example checks if cell A5 of the worksheet named “Check if Cell is Empty” (myCell) is empty and displays a message box confirming whether the cell is empty or not empty.
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Check if Cell is Empty
The following GIF illustrates the results of executing the macro example. Cell A5 (This cell isn’t empty) is not empty and the message box displayed confirms that this is the case.
#2: Check if Active Cell is Empty
VBA Code to Check if Active Cell is Empty
To check if the active cell is empty with VBA, use a macro with the following statement structure:
Process Followed by VBA Code to Check if Active Cell is Empty
Execute StatementsIfActiveCellIsEmpty or StatementsIfActiveCellIsNotEmpty» width=»447″ height=»237″ data-srcset=»https://powerspreadsheets.com/wp-content/uploads/check-if-active-cell-is-empty.jpg 447w, https://powerspreadsheets.com/wp-content/uploads/check-if-active-cell-is-empty-300×159.jpg 300w» data-src=»https://powerspreadsheets.com/wp-content/uploads/check-if-active-cell-is-empty.jpg» data-sizes=»(max-width: 447px) 100vw, 447px» gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAAAAACH5BAEKAAEALAAAAAABAAEAAAICTAEAOw==»/>
VBA Statement Explanation
Line #1: If IsEmpty(ActiveCell) Then
- VBA Construct: Opening statement of If… Then… Else statement.
Description: The If… Then… Else statement conditionally executes a group of statements depending on the value of an expression. For these purposes:
- The If… Then… Else statement tests the specified condition (IsEmpty(ActiveCell)).
If the condition is met and returns True: StatementsIfActiveCellIsEmpty are executed.
If the condition isn’t met and returns False: StatementsIfActiveCellIsNotEmpty are executed.
Item: IsEmpty(…).
- VBA Construct: IsEmpty function.
Description: Generally, the IsEmpty function indicates whether a variable has been initialized. Nonetheless, you can also use IsEmpty to check if a cell is empty.
The IsEmpty function:
- Takes one parameter (expression) of the Variant data type. Within this macro structure, the parameter is a Range object (ActiveCell).
Returns True if the variable is uninitialized or explicitly set to Empty. Otherwise, IsEmpty returns False.
Item: ActiveCell.
- VBA Construct: Application.ActiveCell property.
Description: The Application.ActiveCell property returns a Range object representing the active cell.
Item: IsEmpty(ActiveCell).
- VBA Construct: Condition of If… Then… Else statement.
Description: This condition is an expression that evaluates to True or False. The IsEmpty function (IsEmpty(ActiveCell)) returns True or False, as follows:
- True: Active cell is empty.
Line #2: StatementsIfActiveCellIsEmpty
- Item: StatementsIfActiveCellIsEmpty.
- VBA Construct: Statements within If… Then… Else statement.
Line #3: Else
- VBA Construct: Else clause of If… Then… Else statement.
Description: The statements below the Else clause (StatementsIfActiveCellIsNotEmpty) are executed if the condition tested in the opening statement of the If… Then… Else statement (IsEmpty(ActiveCell)) returns False. Within this macro structure, IsEmpty(ActiveCell) returns False if the active cell is not empty.
Line #4: StatementsIfActiveCellIsNotEmpty
- Item: StatementsIfActiveCellIsNotEmpty.
- VBA Construct: Else Statements within If… Then… Else statement.
Line #5: End If
- VBA Construct: Closing statement of If… Then… Else statement.
Macro Example to Check if Active Cell is Empty
The following macro example checks if the active cell is empty and displays a message box confirming whether the active cell is empty or not empty.
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Check if Active Cell is Empty
The following GIF illustrates the results of executing the macro example. The active cell (A6) is empty and the message box displayed confirms that this is the case.
#3: Check if Range is Empty
VBA Code to Check if Range is Empty
To check if a range is empty with VBA, use a macro with the following statement structure:
Process Followed by VBA Code to Check if Range is Empty
Execute StatementsIfRangeIsEmpty or StatementsIfRangeIsNotEmpty» width=»472″ height=»282″ data-srcset=»https://powerspreadsheets.com/wp-content/uploads/check-if-range-is-empty.jpg 472w, https://powerspreadsheets.com/wp-content/uploads/check-if-range-is-empty-300×179.jpg 300w» data-src=»https://powerspreadsheets.com/wp-content/uploads/check-if-range-is-empty.jpg» data-sizes=»(max-width: 472px) 100vw, 472px» gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAAAAACH5BAEKAAEALAAAAAABAAEAAAICTAEAOw==»/>
VBA Statement Explanation
Line #1: If WorksheetFunction.CountA(CellRange) = 0 Then
- VBA Construct: Opening statement of If… Then… Else statement.
Description: The If… Then… Else statement conditionally executes a group of statements depending on the value of an expression. For these purposes:
- The If… Then… Else statement tests the specified condition (WorksheetFunction.CountA(CellRange) = 0).
If the condition is met and returns True: StatementsIfRangeIsEmpty are executed.
If the condition isn’t met and returns False: StatementsIfRangeIsNotEmpty are executed.
Item: WorksheetFunction.CountA(…).
- VBA Construct: WorksheetFunction.CountA method.
Description: The WorksheetFunction.CountA method counts the number of cells that are not empty within the argument list (CellRange). For these purposes, a cell is deemed to not be empty if, for example, it contains an error value or empty text (“”).
Item: CellRange.
- VBA Construct: Range object.
Description: Range object representing the cell range you work with.
You can usually return a Range object with constructs such as the Worksheet.Range property. If you explicitly declare an object variable to represent CellRange, use the Range object data type.
Item: =.
- VBA Construct: = comparison operator.
Description: The = comparison operator compares the 2 expressions to determine whether they’re equal:
- The expression to the left of the = comparison operator (WorksheetFunction.CountA(CellRange)).
The expression to the right of the = comparison operator (0).
Item: WorksheetFunction.CountA(CellRange) = 0.
- VBA Construct: Condition of If… Then… Else statement.
Description: The condition is an expression that evaluates to True or False. The = comparison operator returns True or False as follows:
- True: If WorksheetFunction.CountA(CellRange) returns 0. This occurs when CellRange is empty.
Line #2: StatementsIfRangeIsEmpty
- Item: StatementsIfRangeIsEmpty.
- VBA Construct: Statements within If… Then… Else statement.
Line #3: Else
- VBA Construct: Else clause of If… Then… Else statement.
Description: The statements below the Else clause (StatementsIfRangeIsNotEmpty) are executed if the condition tested in the opening statement of the If… Then… Else statement (WorksheetFunction.CountA(CellRange) = 0) returns False. Within this macro structure, (WorksheetFunction.CountA(CellRange) = 0) returns False if CellRange is not empty.
Line #4: StatementsIfRangeIsNotEmpty
- Item: StatementsIfRangeIsNotEmpty.
- VBA Construct: Else Statements within If… Then… Else statement.
Line #5: End If
- VBA Construct: Closing statement of If… Then… Else statement.
Macro Example to Check if Range is Empty
The following macro example checks if the range composed of cells A7 through A11 of the worksheet named “Check if Cell is Empty” (myCellRange) is empty and displays a message box confirming whether the range is empty or not empty.
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Check if Range is Empty
The following GIF illustrates the results of executing the macro example. Cells A7 through A11 (with fill) are empty and the message box displayed confirms that this is the case.
#4: Check if Any Cell in Range is Empty
VBA Code to Check if Any Cell in Range is Empty
To check if any cell in a range is empty with VBA, use a macro with the following statement structure:
Process Followed by VBA Code to Check if Any Cell in Range is Empty
Execute StatementsIfAnyCellInRangeIsEmpty or StatementsIfNoCellInRangeIsEmpty» width=»547″ height=»314″ data-srcset=»https://powerspreadsheets.com/wp-content/uploads/check-if-any-cell-in-range-is-empty.jpg 547w, https://powerspreadsheets.com/wp-content/uploads/check-if-any-cell-in-range-is-empty-300×172.jpg 300w» data-src=»https://powerspreadsheets.com/wp-content/uploads/check-if-any-cell-in-range-is-empty.jpg» data-sizes=»(max-width: 547px) 100vw, 547px» gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAAAAACH5BAEKAAEALAAAAAABAAEAAAICTAEAOw==»/>
VBA Statement Explanation
Line #1: If WorksheetFunction.CountA(CellRange) Macro Example to Check if Any Cell in Range is Empty
The following macro example checks if the range composed of cells A13 through A17 of the worksheet named “Check if Cell is Empty” (myCellRange) contains any empty cells and displays a message box confirming whether the range contains or not any empty cells.
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Check if Any Cell in Range is Empty
The following GIF illustrates the results of executing the macro example. Cell A15 is empty. The message box displayed confirms that the cell range containing cells A13 to A17 (with fill) contains at least one empty cell (A15).
References to VBA Constructs Used in this VBA Tutorial
Use the following links to visit the appropriate webpage within the Microsoft Developer Network:
- Identify the cell or cell range you work with:
Test if a cell or cell range is empty:
Display a message box including, among others, the address of a cell or cell range:
Work with variables and data types:
Источник
Hi Katrina,
I’ll point you in this direction and give a few tips
Check out this bit of code
Sub FindLastCell()
Dim LastCell As Range
Dim LastCellColRef As Long
LastCellColRef = 2 'column number to look in when finding last cell
Set LastCell = Sheets("UNNEEDED").Cells(Rows.Count, LastCellColRef).End(xlUp).Offset(1, 0)
MsgBox LastCell.Address
Set LastCell = Nothing
End Sub
The first change I would make to this code is to replace the Sheets(«UNNEEDED») part with the underlying sheet number e.g Sheet2.cells or Sheet3.cells You can see that sheet number next to the name in the VBA editor window. The main reason is to prevent your code breaking if the sheet is renamed.
The Dim part is setting the variables to use in your code. This is a very important concept to learn about when writing VBA.
I’ve made LastCellColRef as a variable as this makes it clear that it is column 2 that is being searched in to find the last entry
Once you’ve SET your LastCell you can use it as a reference in your code
e.g.
Selection.Copy
LastCell.PasteSpecial xlPasteValues
Tips
Once you’ve set a variable, then at the end of your routine you should set it = nothing to clear it from memory.
Try to avoid cell referencing when writing VBA e.g. Range(«$A$2:$DM$8442), use named ranges instead.