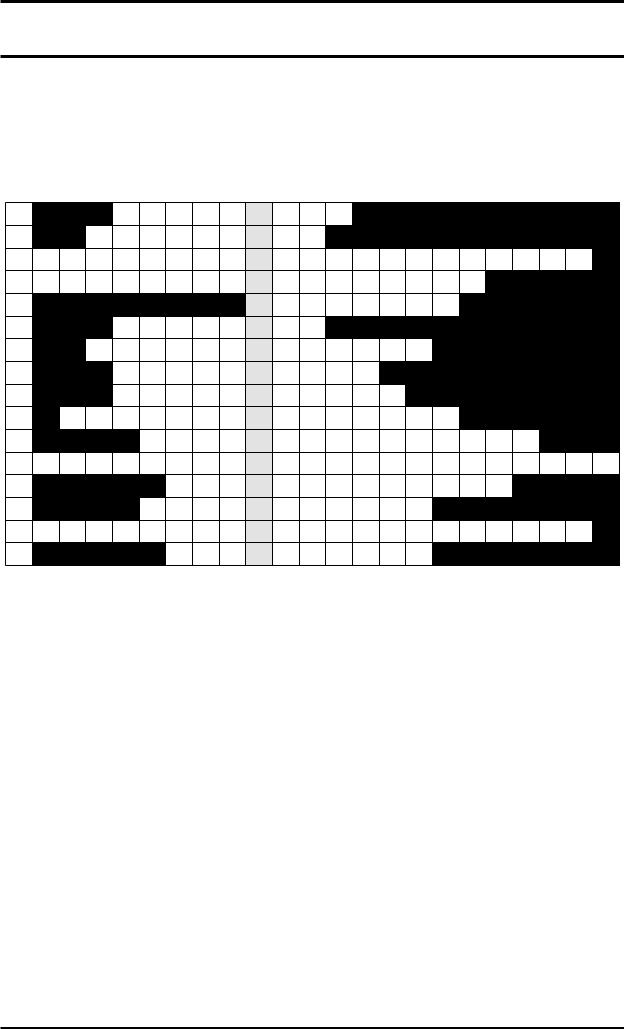
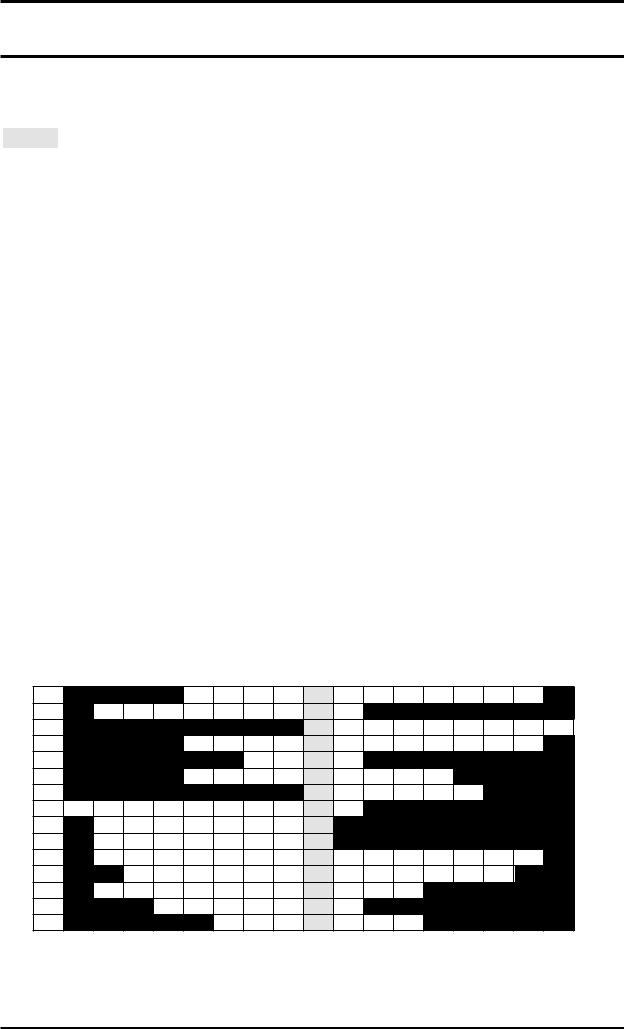
Complete the sentences below with a verb from the left-hand box, and a particle from the right-hand box, to make phrasal verbs. The meaning of each phrasal verb is explained in brackets at the end of each sentence. Write your answers in the crossword grid on the third page (you will not need to put a gap between the verb and the particle). The first one has been done as an example.
Note that you will need to use some of the verbs and particles more than once, and in some cases you will need to change their form (for example, to past simple). Also note that in some cases, more than one answer may be possible, but only one will fit into the crossword grid.
Verbs
|
back break |
bring build burn |
call |
||||
|
cancel |
carry |
cut fall |
fight |
fill |
find |
|
|
gear get |
give |
hand hold |
opt |
phase |
||
|
put run stand |
take turn |
|||||
|
( = across in the crossword grid, |
= down) |
Particles
across against ahead back behind down in into off on out over up with
|
1 |
Your suggestions sound good. Let’s |
run |
with |
them for a while. (informal: to decide |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
to carry out an idea or project) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
2 |
The unions are |
the proposed redundancies. (to struggle to try to overcome |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
something) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
3 |
The manager tried to |
to the workforce the reasons why some people were |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
being made redundant. (to make someone understand something) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
4 |
He |
the job he was offered. (to refuse something, such as an offer of help) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
5 |
There isn’t enough work, so we have to |
some of you |
for the day. (to reduce |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
employee’s hours of work because of shortage of work) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
6 |
We don’t know if they will agree to our terms, and we won’t |
until next week. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
(to discover a fact or piece of information) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
7 |
The workers refused to |
any of their rights. (to hand something to someone, or |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
to lose something, often as the result of pressure from someone) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
8 |
The new system of pension contributions will be |
over the next two months. (to |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
introduce / bring something in gradually) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
9 |
We expect negotiations to |
into the night. (to continue) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
10 |
If she decides to take early retirement, she’ll probably |
her responsibilities to her |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
deputy. (to pass your work responsibilities to someone else) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
11 |
The management have refused to |
to pressure from the unions. (to yield or to |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
surrender) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
12 |
After an agreement was reached, the union |
the strike. (to stop a planned course |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
of action or an event) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
13 |
Mr Smith is currently |
for the chairman, who is ill. (to take someone’s place) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
14 |
Despite serious personal problems, he has |
the same job for the last six years. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
(to manage to do a difficult job, usually over a long period of time) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
15 |
You must |
all the forecasts |
the budget. (to add something to something else that is |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
being set up) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
32
For reference see Dictionary of Business — 4th edition (A&C Black Publishers Ltd, 978-0-713-67918-2)
книга выложена группой vk.com/englishlibrary

|
16 |
The company was |
and separate divisions sold off. (to split something large into |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
small sections) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
17 |
We may decide to |
the price of some of our brands to help increase demand. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
(to reduce) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
17 |
We plan to |
a new model of the car for the motor show. (to produce something |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
new) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
18 |
Payment will be |
until the contract has been signed. (to wait, to not go forward) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
19 |
Make sure you don’t make any mistakes when you |
the application form. (to |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
write the required information in the spaces on a form) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
20 |
Negotiations between management and the unions |
after six hours. (to stop a |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
negotiation, usually because no agreement has been made) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
20 |
At the meeting, the chairman |
the subject of redundancy payments. (to refer to |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
something for the first time) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
21 |
The company is |
itself |
for expansion into the African market. (informal: to get ready) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
22 |
We have installed networked computers to |
on paperwork. (to reduce the |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
amount of something used) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
23 |
Don’t work too hard or you’ll |
yourself |
(informal: to become tired and incapable |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
of further work because of stress) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
24 |
We had to cancel the project when our German partners |
. (to stop being a part |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
of a deal or arrangement) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
25 |
After several years with the company, she |
a new post with one of our |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
competitors. (to start a new job) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
26 |
The contract signing was |
because of disagreements over some of the terms |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
and conditions. (to delay) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
27 |
He |
well in his new job, and was soon promoted. (to succeed) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
28 |
It’s very important to |
your duties to the best of your ability. (to do what is |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
necessary for your job) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
29 |
If you complain, you might |
your money |
. (to receive something which you had |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
before) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
30 |
The accounts department |
the draft accounts in time for the meeting. (to |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
produce something) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
31 |
If you want to |
in your job, you’ll need to show more commitment. (to advance |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
in your career) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
32 |
The meeting has been |
for two weeks. (to arrange for something to take place |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
later than planned) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
33 |
We are planning to |
most of our work to freelancers. (to send or give a job to |
someone else, usually not in your company)
|
34 |
Do you think they’ll |
when they realise how hard the project is? (to decide not |
|||||||||||||||
|
to do something) |
|||||||||||||||||
|
35 |
Have the managers agreed to |
more staff for the Witney office? (to employ) |
|||||||||||||||
|
36 |
Higher costs have |
the increased sales revenue. (to balance or act against each |
|||||||||||||||
|
other and so make each other invalid) |
|||||||||||||||||
|
37 |
In the last six months we have |
our rivals. (to have fewer sales or make less |
|||||||||||||||
|
profit than another company) |
|||||||||||||||||
33
For reference see Dictionary of Business — 4th edition (A&C Black Publishers Ltd, 978-0-713-67918-2)
книга выложена группой vk.com/englishlibrary

|
1 R |
2 |
3 |
|||
|
U |
|||||
|
4 |
N |
5 |
6 |
||
|
W |
|||||
|
7 |
I |
8 |
9 |
||
|
T |
10 |
||||
|
H |
|||||
|
11 |
|||||
|
12 |
|||||
|
13 |
|||||
|
14 |
15 |
16 |
|||
|
17 |
|||||
|
18 |
|||||
|
19 |
|||||
|
20 |
|||||
|
21 |
|||||
|
22 |
|||||
|
23 |
|||||
|
24 |
|||||
|
25 |
26 |
||||
|
27 |
|||||
|
28 |
29 |
||||
|
30 |
31 |
||||
|
32 |
|||||
|
33 |
|||||
|
34 |
35 |
||||
|
36 |
|||||
|
37 |
|||||
|
34 |
|||||
|
For reference see Dictionary of Business — 4th edition (A&C Black Publishers Ltd, 978-0-713-67918-2) |
|||||
|
книга выложена группой vk.com/englishlibrary |
PhrasalUnitverbs00002
Match the questions on the left with the most appropriate answers on the right. The answers contain a definition or an explanation of the phrasal verbs in bold on the left.
1.Would you advise against moving the head office to Edinburgh?
2.Did you manage to turn the company round?
3.Do you think the staff will walk out when they hear the news?
4.Did you manage to get through to the complaints department?
5.Shall we put back the meeting until everyone can come?
6.Were the management willing to improve on their previous offer?
7.Would the staff be prepared to hold out for a 10% pay rise?
8.Will we be able to hold him to the contract?
9.Can we clock off yet?
10.Have you taken over the company?
11.Are they hoping to build up a profitable business?
12.Did you sort out the accounts problem with the auditor?
13.Have our reps called in to give us their sales figures.
14.Can we pay you half now, and make up the difference next month?
15.Can we get along all right with only half the staff we had before?
16.Do you think the company will close down its branch in Banbury?
17.Are you worried that our partners will go back on their agreement?
18.Did you get my notice? I handed it in on Tuesday.
19.Can you follow up our proposal as soon as possible?
20.Do you think it’s time that AZ Products were phased out as a supplier of spare parts?
A.Yes, they thought they might be able to do a bit better as long as we were prepared to work harder.
B.Possibly. We’ll stop using them gradually while we start using other sources.
C.Well, we haven’t actually bought it yet, but we’ve made an offer to buy most of the shares.
D.No, we didn’t receive anything in writing.
E.Possibly. It won’t be the first time they’ve not done something that they’ve promised.
F.Yes, I don’t think we should do that for the time being.
G.Well, another £60 a week is an improvement, I suppose, but they won’t want to wait too long.
H.Yes, I’ve had three phone calls already this afternoon.
I.Fine. Credit us with the outstanding balance on your next statement.
J.Well, there has already been some gradual expansion, but it’s going to take time.
K.Of course. We’ll be examining it in detail at the next meeting.
L.Well, I certainly think it’s a good idea to move it to a later date.
M.Yes, it was making a loss, but now it’s a very profitable organisation.
N.I hope so. We’ve been promised that the terms we’ve set out will be honoured.
O.I don’t know, but if they do, that’s the third one they’ll have shut this year.
P.We should manage, although everyone will have to work a bit harder.
Q.Yes, it’s time to leave. Let’s go home.
R.Probably, but we really don’t want everyone to stop working and leave in protest.
S.Yes. Everything has been put in order at last.
T.No, they weren’t answering the phone.
35
For reference see Dictionary of Business — 4th edition (A&C Black Publishers Ltd, 978-0-713-67918-2)
книга выложена группой vk.com/englishlibrary

ProductionUnit 0000 and operations
Exercise 1: Complete each sentence 1 – 15 with two words to make an expression connected with production and operations. The first word should come from the left-hand box, and the second word should come from the right-hand box. Each sentence is followed by a definition of the expression you need. Use each word once only.
|
assembly capacity finished |
lead |
allocation |
capacity chain |
costs |
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
manufacturing offshore optimum |
defects |
goods |
line |
materials |
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
planned |
product |
purchasing |
random |
obsolescence planning |
power |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
raw |
resource |
supply |
zero |
production |
recall |
sampling |
time |
||||||||||||||||||
|
1. |
Unless our supplier reduces its |
, we will have to radically change the way we |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
operate. (the length of time that lapses between placing an order for something and receiving it) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
2. |
The recession has led to a drop in overall |
, which means that we will have to |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
reduce output on some of our less popular lines. (the quantity of goods or services which can be bought |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
by a group of people, a sector, an organisation, etc) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
3. |
We are currently operating at |
, which means that we can afford to keep |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
prices lower for our clients. (the most efficient level of production or output, with the result that production |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
costs are kept to a minimum) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
4. |
She works on an |
in a factory that makes electronic goods. (a production system |
where a product moves slowly through a factory as new parts are added to it)
5.We do not allow visitors to come onto the factory floor, but you can view our range of
in the showroom. (complete products that are ready to sell)
6. The company had to put out a to its customers when several potentially
dangerous faults were discovered. (the removal from sale of an item that might be dangerous to the people who have bought it)
7.We will be unable to compete successfully in the domestic market unless we reduce our costs by
|
taking advantage of |
. (the manufacture of goods in another country for import to the |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
domestic market) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
8. |
Our company builds |
into most of its electronic products, so that our customers |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
are forced or obliged to update them more often. (designing products so that they have a limited lifespan |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
and so need to be replaced more often) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
9. |
We make packaging for frozen food, and are an important part of the |
for the |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
industry. (the manufacturers, wholesalers, distributors, etc, who make, deliver and sell products to |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
customers) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
10. |
None of our products are allowed to leave the factory unless there are |
present. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
(having no faults) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
11. |
Without effective |
, we will not be able to produce enough goods to keep up |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
with demand. (assigning people and machines to projects in a way that optimises production and results) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
12. |
The manufacture of most items relies on a reliable source of |
such as wood, |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
iron ore or crude petroleum. (basic items which have to be treated in some way before they can be used) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
13. |
If |
can be kept to a minimum, we can keep market prices at a minimum. (the |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
money needed to make a product) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
36
For reference see Dictionary of Business — 4th edition (A&C Black Publishers Ltd, 978-0-713-67918-2)
книга выложена группой vk.com/englishlibrary

Unit 0000
14.We don’t check every item before we send it for sale. We usually find that
gives us a good idea of quality. (testing a few items from one batch of products before they are sent for sale)
15. Our company takes very seriously: we never start a project without working out
how many people it will need, and the equipment they will require. (measuring the amount of work that can be done within a certain amount of time, and how many people, machines, etc, it will need)
Exercise 2: Look at the definitions in sentences 1 – 16, and decide what is being described in each case. The words you need are in the box (you will need to use some of these words more than once). There are 8 words that do not match any of the definitions.
Write your answers in the appropriate space in the table on the next page. In cases where more than one word is needed, do not put any gaps between those words in the table. If you complete it correctly, you will reveal a three-word expression in the shaded vertical column that refers to a production system where work is split up into clearly defined tasks and areas of responsibility.
|
and |
backlog |
bar |
batch |
centralised |
continuous |
coding |
demand |
|||||
|
development |
down |
error |
first |
global goods |
in |
improvement |
||||||
|
intermediate |
just logistics |
made |
maintenance |
margin |
of |
operating |
||||||
|
order |
out |
outsourcing |
packaging |
parts |
preventive |
pricing |
production |
|||||
|
research |
sourcing |
spare |
stockout |
supplier |
supply |
time |
to |
|||||
1.The process of attaching machine-readable lines on a product, product part or package, which can then be read by a computer. (2 words)
2.The task of managing the movement, storage and processing of materials and information in a supply chain. (1 word)
3.The servicing of factory machines and other equipment that is carried out before a fault develops. (2 words)
4.Goods that are bought for use in the production of other products. (2 words)
5.A situation where a particular component or part has been used up and has not been replenished (often as a result of poor inventory control). (1 word)
6.A period during which a machine is not available because it is being serviced or has broken down. (2 words)
7.An allowance made for the possibility of mistakes (for example, a miscalculation in a calculation) (3 words)
8.A production system in which goods are made or purchased just before they are needed. (3 words)
9.An item that is produced in response to the request of a particular client or customer. (3 words)
10.A method of stock control in which the stock of a product in store is used before more recently produced or purchased stock. (4 words)
11.The amount of goods available for sale and the level of consumer need for those goods. (3 words)
12.Finding out facts and information before making a new product, or improving a current one. (3 words)
13.A contract in which the supplier charges the customer the same price for delivery of goods anywhere in the world. (2 words)
37
For reference see Dictionary of Business — 4th edition (A&C Black Publishers Ltd, 978-0-713-67918-2)
книга выложена группой vk.com/englishlibrary
Unit 0000
14.The practice of obtaining services from other companies rather than using in-house services (including production services) (1 word)
15.Making production processes and products better over a period of time in order to increase quality and reduce waste. (2 words)
16.Pieces of machinery that are used to replace parts of a machine that are broken or faulty. (2 words)
|
1 |
|
2 |
|
3 |
|
4 |
|
5 |
|
6 |
|
7 |
|
8 |
|
9 |
|
10 |
|
11 |
|
12 |
|
13 |
|
14 |
|
15 |
|
16 |
Exercise 3: Here are some more word pairs associated with production and operations. Match a word on the left with its ‘partner’ on the right. There are two words on the left that do not have a partner.
|
automatic |
assembly |
|
|
batch |
||
|
book |
||
|
buffer |
||
|
capacity |
||
|
bottleneck |
||
|
control |
||
|
buying |
||
|
centralised |
floor |
|
|
cluster |
forwarder |
|
|
contract |
line |
|
|
forward |
manager |
|
|
freight |
manufacturing |
|
|
list |
price |
|
|
order |
production |
|
|
paced |
purchasing |
|
|
quality |
sampling |
|
|
shop |
scheduling |
|
|
surplus |
stock |
|
|
warehousing |
||
38
For reference see Dictionary of Business — 4th edition (A&C Black Publishers Ltd, 978-0-713-67918-2)
книга выложена группой vk.com/englishlibrary

Recruitment 1: Job advertisingUnit0000
Complete the conversation with words or expressions from the box.
|
advance |
application |
basic salary |
benefits |
candidate |
colleagues |
|||||
|
commencing |
commission |
covering letter CV |
drive (noun) experience |
|||||||
|
incentive |
increment interview leading (adjective) |
motivate |
post |
qualified |
||||||
|
relocation allowance responsibilities |
rewards package |
team |
vacancy |
|||||||
|
Sandra: |
What are you reading? |
|||||||||
|
Terry: |
I’m looking at the jobs pages in the paper. There’s something here I like the sound of. |
|||||||||
|
Modus International, a 1.__________ supplier of car parts, has a 2. __________ for |
||||||||||
|
the 3. __________ of Sales Manager in their Brighton office. |
||||||||||
|
Sandra: |
That sounds like your kind of job. When does it begin? |
|||||||||
|
Terry: |
Let me see. Er, 4. __________ April 1st, it says here. That’s in three weeks’ time. |
|||||||||
|
Sandra: |
You’d better get your 5. __________ in, if you’re interested. What else does it say |
|||||||||
|
about the job? |
||||||||||
|
Terry: |
It says that the successful 6. __________ should be suitably 7. __________ and |
|||||||||
|
should have had extensive 8. __________ in sales management. |
||||||||||
|
Sandra: |
That sounds perfect. You’ve got a University degree in Business Management, and |
|||||||||
|
you’ve been working in sales for more than five years. |
||||||||||
|
Terry: |
I suppose so. It also says that he or she should be able to work as part of a |
|||||||||
|
9. __________, and should have 10. __________ and the ability to 11. __________ |
||||||||||
|
and inspire his or her 12. __________. |
||||||||||
|
Sandra: |
Well, that’s great! You’ve always got on with the people you work with, and |
|||||||||
|
everyone is always saying how you’re able to encourage people to work harder. |
||||||||||
|
Terry: |
That’s true. It also says that the 13. __________ include liaising with colleagues |
|||||||||
|
around the country, training new staff and presenting a full report to the board of |
||||||||||
|
directors twice a year. |
||||||||||
|
Sandra: |
It all sounds quite good. What’s the company offering in return? |
|||||||||
|
Terry: |
The 14. __________ they’re offering looks |
very |
attractive. |
It includes a |
||||||
|
15. __________ of £25000 per annum… |
||||||||||
|
Sandra: |
What does that mean? |
|||||||||
|
Terry: |
Well, that’s the minimum amount of money that you can earn during the year. In |
|||||||||
|
addition to that, they’re offering 10% 16. __________ on all sales made. |
||||||||||
|
Sandra: |
Well, that’s a good 17. __________. The more you work, the more you sell. |
|||||||||
|
And the more you sell, the more money you’ll make! |
||||||||||
|
Terry: |
Exactly. There’s also a guaranteed annual 18. __________ of £1500, and a |
|||||||||
|
19. __________ of £2500. |
||||||||||
|
Sandra: |
What’s that for? |
|||||||||
|
Terry: |
To pay me for moving to the area, finding somewhere to live, and so on. Oh, and |
|||||||||
|
there are other 20. __________, such as a company car, free medical and dental |
||||||||||
|
insurance and free meals in the canteen. It also says that there is room to |
||||||||||
|
21. __________, so I might end up with an even better job within the company. |
||||||||||
|
Sandra: |
So what should you do if you’re interested in applying for the job? |
|||||||||
|
Terry: |
It says I should send my 22. __________, together with a 23. __________, to their |
|||||||||
|
head office in Sheffield. If the company is interested, they’ll contact me to arrange an |
||||||||||
|
24. __________ at one of their offices nearer home. |
||||||||||
39
For reference see Dictionary of Business — 4th edition (A&C Black Publishers Ltd, 978-0-713-67918-2)
книга выложена группой vk.com/englishlibrary

RecruitmentUnit 0000 2: The recruitment process
This text about the recruitment process below has been divided into three parts. Complete each part with the words and expressions in the boxes. The first answer for each part has been done for you. Some of the words and expressions have already appeared in Recruitment 1 on the previous page.
Part 1
|
affirmative recruitment |
applicants |
appointments |
benefits |
description |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
disabilities discrimination equal opportunities |
experience |
externally |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
institutional agency |
increments |
internally job centres |
journals |
leave |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
personal qualities |
private recruitment agency |
qualifications |
recruit |
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
recruitment agency |
rewards |
situations vacant |
staff |
vacancy |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
When a company or organisation has a 1. vacancy for a job, and it needs to 2. |
a new |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
member of 3. |
, it usually advertises the post. It does this 4. |
(for example, in the |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
company magazine or on a company notice board) or 5. |
, either in the 6. |
or |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
7. |
section of a newspaper, in specialist trade 8. |
or through a 9. |
which helps people to find employment. There are two main types of agency. The first of these is the
10., usually found in a school or university. These work closely with employers to let potential
employees know about the jobs that are on offer (also included in this category are 11. , which
are provided by the state, and which can be found in most main towns in Britain and other countries).
|
The second is the 12. |
, which are independent companies, and employers have to pay these |
|||||||||||||||||
|
agencies for each employee they successfully provide. |
||||||||||||||||||
|
A job advertisement has to give an accurate 13. |
of the job and what it requires from the |
|||||||||||||||||
|
14. |
(the people who are interested in the post). These requirements might include |
|||||||||||||||||
|
15. |
||||||||||||||||||
|
(academic, vocational and professional), work 16. |
in similar lines of work, |
|||||||||||||||||
|
and certain 17. |
(for example, it might say that you need to be practical, professional and have |
|||||||||||||||||
|
a sense of humour). The advertisement will also specify what 18. |
(basic salary, commission, |
|||||||||||||||||
|
regular 19. |
, etc) and 20. |
(paid 21. |
||||||||||||||||
|
, free medical insurance, company |
car, etc) the company can offer in return. The advertisement must be careful it does not break
|
employment laws concerning sex and racial 22. |
: some companies emphasise in their job |
|||||||
|
advertisements that they are 23. |
employers (or 24. |
employers in the USA), which |
||||||
|
means that they will employ people regardless of their sex, skin colour, religion, 25. |
, etc. |
Part 2
|
application |
aptitude |
board |
candidates covering |
CV |
|
|
group-situational |
health screening |
in-basket |
introduction |
medical |
|
|
one-to-one |
pre-selection |
psychometric |
short-list turn down |
||
40
For reference see Dictionary of Business — 4th edition (A&C Black Publishers Ltd, 978-0-713-67918-2)
книга выложена группой vk.com/englishlibrary

Unit 0000
|
The job advertisement will usually ask people interested in the post to send their 1. |
CV |
with |
|||||||||||||
|
a 2. |
letter or a letter of 3. |
, or they will ask people to write or call for an 4. |
|||||||||||||
|
form. The managers of the company will look at these, and go through a 5. |
procedure, |
||||||||||||||
|
where they choose or 6. |
applicants. They then prepare a 7. |
of possible 8. |
|||||||||||||
: these are the people who will then be invited for an interview. Interviews usually take one of two
forms. The first is the 9. interview, with one applicant and one employer talking together. The second is the 10. interview, with one applicant being interviewed by several people at once.
There may also be tests to see whether the applicant is suitable for the post. There are several of these, including 11. tests (which consider psychological aspects of the applicant), 12.
tests, (which test the applicant’s skills and knowledge, and his / her potential for acquiring more skills
|
and knowledge), 13. |
tests (where several applicants are put into an imaginary situation |
|||
|
and decide how to deal with it), and 14. |
tests (in which an applicant has to deal with a |
number of imaginary tasks similar to those s/he would face in the job). Applicants may also have to go
|
for a 15. |
test (also called a 16. |
) to see whether they are healthy enough to do |
||
|
their job. |
Part 3
appearance circumstances disposition fixed-term follow-up
|
induction programme |
intelligence interests offered open-ended |
|
potential probationary |
references seven-point plan skills temporary |
Many employers use a 1. seven-point plan when they recruit for a new post. They look at different
|
aspects of the applicant to decide whether or not s/he has the correct 2. |
for the job. These |
|||||||||||||||||
|
include physical 3. |
(for example, is the applicant smart and well-presented?), educational |
|||||||||||||||||
|
qualifications, general 4. |
, special 5. |
, hobbies and outside 6.________, mental |
||||||||||||||||
|
and emotional 7. |
and family 8. |
. |
||||||||||||||||
|
If a candidate gets through the above stages, s/he will be asked to provide 9. |
from people |
|||||||||||||||||
|
who know him / her, and if these are positive, s/he is then 10. |
the post. Before s/he |
|||||||||||||||||
|
actually starts working, s/he may go through an 11. |
to learn more about the company and |
the post. Sometimes, s/he may be given a 12.________ contract and have to complete a 13.
period, where the employers make sure that s/he is suitable for the job before being offered an 14. or 15. contract. After s/he has been with the company for a while, there might be a 16. session, to assess how s/he is getting on in the post.
41
For reference see Dictionary of Business — 4th edition (A&C Black Publishers Ltd, 978-0-713-67918-2)
книга выложена группой vk.com/englishlibrary
RecruitmentUnit 0000 3: Contract of employment and job description
Exercise 1: In this contract of employment, there are a lot of vocabulary mistakes. Either a word is spelt incorrectly, the form of the word is wrong, or a wrong word has been used. Identify and correct these words. Some of the mistakes occur more than once in the contract.
|
1. |
Term and conditionals of employment |
|||||
|
2. |
Name of employ: |
|||||
|
Dilligaf Toys plc |
||||||
|
3. |
Name of employed: |
Sarah Ramus |
||||
|
4. |
Job titel: |
Regional Production Manager. |
||||
|
5. |
Job descriptive: |
To oversee the work of the Production Department. |
||||
|
6. |
Job locally: |
. |
Head Office, London. Branches in South and South-East. |
|||
|
7. |
Celery: |
£35,000 per anum (payable monthly in rears) |
||||
|
8. |
Started date: |
1 August 2007. |
||||
|
9. |
Hours of labour: |
Full time. 9.00 – 5.00 Monday until Friday. |
||||
|
10. |
Undertime: |
Extra hours worked will be paid at the normal hourly rat. |
||||
|
. |
. |
Saturdays will be paid at time x 1 ½, Sundays at time x2. |
||||
|
11. |
Holiday enticement: |
21 days per anum, plus bank holidays. |
||||
|
12. |
Absent from work: |
. |
If for any reason you cannot come to work, you should |
|||
|
. |
telephone the central manager as soon as possible. |
|||||
|
13. |
Pension sceme: |
The company operates its own pension sceme which is |
||||
|
. |
open to all employs. |
|||||
|
14. |
Dissiplinary and |
Information on these procedures are provided in the |
||||
|
g |
grieving procedures: |
staff handybook, together with information on all |
||||
|
. |
company police. |
|||||
|
15. |
Probbation: |
. |
All appointments are subjective to three months’ |
|||
|
. |
probbation, during which time employees may be |
|||||
|
. |
terminated with two weeks’ note on either side. |
|||||
|
16. |
Terminator: |
After successful completion of the probbation period, |
||||
|
. |
the note period will be three months. |
|||||
|
17. |
Referrals: |
All apointments are subject to satisfactory referrals. |
||||
|
18. Singed |
Sarah Ramus |
Date: |
21 June 2007 |
|
Exercise 2: Read this informal discussion, in which the person who signed the contract in Exercise 1 is telling their friend about their new job. Complete the gaps with an appropriate word or expression from the box. Some of these words appeared in Exercise 1.
42
For reference see Dictionary of Business — 4th edition (A&C Black Publishers Ltd, 978-0-713-67918-2)
книга выложена группой vk.com/englishlibrary

Unit 0000
|
accountability |
agree |
based |
branches |
commission |
consult |
deal with |
||||||
|
delegate |
departments |
ensure |
evaluate |
full-time |
head office |
hours inspect |
||||||
|
key responsibilities |
leave (noun) |
negotiate |
nine to five |
per annum |
produce |
|||||||
|
recommend |
report to |
responsible |
salary |
supervise |
title |
visit |
||||||
|
James: |
Hi, Sarah. How’s the new job going? |
|||||||||||
|
Sarah: |
Oh, not too bad. I’m still trying to find my feet, though. |
|||||||||||
|
James: |
Tell me a bit about it. |
|||||||||||
|
Sarah: |
Well, my official job ___________ is Regional Production Manager, which means that my |
|||||||||||
|
main ___________ is to ___________ the work of the production department. |
||||||||||||
|
James: |
Where are you ___________? |
|||||||||||
|
Sarah: |
Most of my work is done at the ___________ in central London, but I also have to |
|||||||||||
|
spend time at our various ___________ and ___________ in the area. There are |
||||||||||||
|
several of these in the South and South-East. |
||||||||||||
|
James: |
Who do you ___________? |
|||||||||||
|
Sarah: |
The Central Production Manager. Tom Atkinson, his name is. I’ve only met him a couple of |
|||||||||||
|
times, but he seems nice enough. We meet once a month to |
___________ each other on |
|||||||||||
|
major issues. We ___________ the current state of production, and I ___________ any |
||||||||||||
|
changes that I think need to be made |
||||||||||||
|
James: |
And what about the ___________? |
|||||||||||
|
Sarah: |
Pretty typical for this kind of job. I’m on a ___________ contract, which means I work from |
|||||||||||
|
Monday to Friday, ___________. And occasionally I have to go in at the weekend, too. I get |
||||||||||||
|
21 days___________ a year, plus bank holidays. |
||||||||||||
|
James: |
Not bad. And your ___________? If you don’t mind me asking? |
|||||||||||
|
Sarah: |
No, not at all. I get £35,000 ___________, plus expenses, ___________ for reaching |
|||||||||||
|
targets, overtime pay and so on. |
||||||||||||
|
James: |
That’s pretty good for a job that just involves checking things are running smoothly. |
|||||||||||
|
Sarah: |
Well, there’s more to my job than just that. I do have several other ___________. |
|||||||||||
|
James: |
Such as? |
|||||||||||
|
Sarah: |
First of all I have to ___________ product specifications with sales departments and time |
|||||||||||
|
schedules with the stock control department. Then I need to ___________ that the |
||||||||||||
|
product is manufactured according to agreed specifications, and I also have to |
||||||||||||
|
___________ the quality of the finished product. |
||||||||||||
|
James: |
That’s all? |
|||||||||||
|
Sarah: |
No. I also need to ___________ with our suppliers on prices for our base materials, |
|||||||||||
|
___________ those suppliers on a regular basis to check the quality of the base |
||||||||||||
|
materials… |
||||||||||||
|
James: |
Do you have a car for that? |
|||||||||||
|
Sarah: |
Oh yes, the company provides me with one. I also have to ___________ problems as they |
|||||||||||
|
arise on a day-to-day basis, and ___________ regular sales reports for the Directors. |
||||||||||||
|
James: |
Anything else? |
|||||||||||
|
Sarah: |
Well, on top of everything else, I’m ___________ for managing 10 machinists, 3 trainees, 2 |
|||||||||||
|
cleaners and 2 security guards. |
||||||||||||
|
James: |
That sounds like a lot of work for one person. Can you ___________ any of it? |
|||||||||||
|
Sarah: |
Unfortunately no. I have to do it all myself! |
43
For reference see Dictionary of Business — 4th edition (A&C Black Publishers Ltd, 978-0-713-67918-2)
книга выложена группой vk.com/englishlibrary

SalesUnit 0000and marketing 1
In the following sentences, the enthusiastic marketing manager of a mobile phone company is telling her team about the company’s latest model of mobile phone. However, each sentence contains a spelling mistake. Identify and correct the word in each case.
1.Everybody says that the market for mobile phones is very cowded, and there is no more room or demand for new products.
2.However, we believe we’ve found a nich in the market for something a little bit different: a mobile phone with an infra-red camera that lets you see in the dark. Impressive, eh?
3.However, this isn’t its only uniqe selling point.
4.It also has a huge range of other feachures, including a built-in navigation system, a scanner, a photo-editing suite, a dictionary and translator and even a thermometer.
5.We call it the ‘Ultimafone®’, and we’ve just applied for a patient so that no-one else can copy it.
6.It was conceived by our inovative designs team, led by the brilliant Kevin Anorak.
7.We plan to lunch it early in the New Year.
8.You’ll find the ‘Ultimafone®’ on page 1 of our latest mobile phones brocure.
9.As you can see, it’s the ultimate must-have opmarket accessory.
10.We made the decision to start making it after extensive reserch into what people wanted from a mobile phone in the 21st century.
11.Of course, we won’t sell many without a great deal of advertiseing.
12.As a result, we’re starting a major campain to let the public know all about it.
13.We’re going to premote the ‘Ultimafone®’ any way we can.
14.There are going to be comercials on all of the main radio stations and television channels.
15.In fact, we’re hoping to get at least five spouts on each of the major channels during prime-time viewing.
16.All the daily newspapers and major magazines will carry full-page advertisments.
17.There will be plenty of product pacement in some of the biggest films of the year.
18.You won’t be able to walk down the street without seeing one of our giant billyboards.
19.And you won’t even be able to visit the Internet without our plop-ups coming up on your screen all the time!
20.We’re also going to send mailshoots to everyone who has ever bought one of our phones in the past.
21.And naturally we’ll be making some sponsership deals with some of the country’s major sporting teams.
22.If we’re lucky, we might even get a famous rock star, actor or sports personality to endoarse it for us.
23.After all, you can’t beat an opinon leader for really helping to make a new product take off successfully.
44
For reference see Dictionary of Business — 4th edition (A&C Black Publishers Ltd, 978-0-713-67918-2)
книга выложена группой vk.com/englishlibrary

Unit 0000
24.There will also be big posters at every pont of sale (including department stores and music stores).
25.In fact, there probably won’t be a single major retale outlet anywhere in the country that doesn’t sell the ‘Ultimafone®’!
26.Our expert sales team — that’s you — will be there to give potential customers your pich and persuade them that the ‘Ultimafone®’ is just what they need.
27.There will be lots of special offers, including miscounts on phone and talk-time packages.
28.There will also be lots of giveways: free hands-free kits, free phone covers, free ringtones, and so on.
29.Sales won’t just be limited to the dommestic market.
30.We believe that the ‘Ultimafone®’ will really catch on in the expot market as well.
31.In fact, our overseas raps are already packing their suitcases and booking their flight tickets.
32.Eventually we hope to have the ‘Ultimafone®’ made under franshise in mainland Europe, the Far East and South America.
33.We’re so confident of the reliability of the ‘Ultimafone®’ that they will all carry a free 3- year guarantea.
34.That’s not bad, considering the where and tear that can be expected from the customers on an item such as this.
35.You might also like to know that in addition to the phone itself, there will be a whole range of ‘Ultimafone®’ merchantizing, including ‘Ultimafone®’ T-shirts, ‘Ultimafone®’ trainers and even ‘Ultimafone®’ biscuits!
36.They will all carry the soon-to-be famous ‘Ultimafone®’ brant name.
37.They will all display a distinctive ‘Ultimafone®’ loco.
38.And they will all come in an attractive, instantly-recognisable ‘Ultimafone®’ pakaging.
39.Our latest cattalog has the whole range!
40.We think it’s the best invention since the microchip, although obviously some people will tell you that it’s just hyp, and we’re making a lot of fuss about nothing.
41.They’ll say that the ‘Ultimafone®’ is nothing more than a fat, and that this time next year nobody will want one!
42.However, I just know it will sell well, and I bet our competiton is getting really worried!
43.In the war for new customers, we’re going to tramp them!
44.However, we mustn’t be too complacent. We will be trucking our buying public over the next year or so to see how they react to the ‘Ultimafone®’.
45.So get out there, and canvince as many people as possible that the ‘Ultimafone®’ is the only mobile phone they’ll ever need!
Also see Sales and marketing 2 on the next page.
45
For reference see Dictionary of Business — 4th edition (A&C Black Publishers Ltd, 978-0-713-67918-2)
книга выложена группой vk.com/englishlibrary
SalesUnit 0000and marketing 2
Rearrange the letters in bold in these definitions and explanations to make words connected with sales and marketing. Then write these words in the appropriate space in the grid. If you do this correctly, you will reveal a three-word idiomatic expression in the shaded vertical strip that marketing people use to describe people who are easy marketing targets because they are already thinking of buying a product or service.
1.The process of a product going out of date because of progress in design or technology, and therefore becoming less useful or valuable, is known as bencsoslecoe.
2.moonPtior is the means of conveying the message about a product or service to potential customers (for example, publicity, a sales campaign, television commercials, etc).
3.ehlaWoles is a word referring to the business of buying goods from manufacturers and selling them in large quantities to retailers, who then sell in smaller quantities to the public.
4.magencrkhiBn is the system of measuring the performance of a company against the performance of other companies in the same sector.
5.Unsolicited mail advertising, and especially email advertising, is known as amsp (named after a famous American brand of tinned meat).
6.The transfer of rights to manufacture or market a particular product to another individual or organisation through a legal arrangement or contract is called niligesnc.
7.The brand name of a product that is recognised around the world is known as a boglla brand.
8.A ephlrsadei is a retail outlet distributing, selling and servicing products (especially cars) on behalf of a manufacturer.
9.A wdorknma is the reduction of the price of something to less than its usual price.
10.When a new product or service is tested on a small group of consumers in order to try to find out the reactions of a larger group of consumers, this is known as pigslman.
11.The adding of new types of products to the range already made is known as avidfictionsier.
12.mingerkeaTlet is the selling of a product or service by telephone.
13.An organisation that delivers products to retailers on behalf of a manufacturer is called a isorditbtru.
14.A eberife is an informal word for a product or service that is given away, usually to encourage people to buy a bigger product or service, or to advertise that product or service (for example, a pen with the company name on).
15.In radio, television and cinema advertising, tamirei is the amount of time given to an advertisement.
|
1 |
|
2 |
|
3 |
|
4 |
|
5 |
|
6 |
|
7 |
|
8 |
|
9 |
|
10 |
|
11 |
|
12 |
|
13 |
|
14 |
|
15 |
Also see Sales and marketing 3 on the next page.
46
For reference see Dictionary of Business — 4th edition (A&C Black Publishers Ltd, 978-0-713-67918-2)
книга выложена группой vk.com/englishlibrary

Sales and marketingUnit00003
Match each definition in sentences 1 – 32 with an appropriate word ‘pair’ connected with sales and marketing. The first word of each pair can be found hidden in the top box, and the second word can be found hidden in the bottom box. These words can be found by reading from left to right ( ), and / or from top to bottom ( ). The first one has been done as an example.
(Note that in some cases the same word may be needed more than once, but will only appear once in each grid).
|
C |
Q |
P |
W |
E |
P |
R |
O |
W |
N |
T |
Y |
U |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
R |
I |
R |
O |
P |
U |
M |
A |
P |
R |
I |
C |
E |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
I |
S |
E |
D |
C |
B |
A |
F |
R |
G |
A |
L |
H |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
S |
J |
M |
K |
O |
L |
I |
C |
O |
L |
D |
I |
L |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
I |
Z |
I |
S |
R |
I |
L |
U |
D |
X |
D |
E |
C |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
S |
V |
U |
A |
P |
C |
I |
S |
U |
B |
E |
N |
N |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
M |
Q |
M |
L |
O |
W |
N |
T |
C |
E |
D |
T |
N |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
R |
T |
P |
E |
R |
T |
G |
O |
T |
R |
A |
D |
E |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Y |
A |
R |
S |
A |
U |
B |
M |
A |
R |
K |
E |
T |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
I |
R |
E |
O |
T |
P |
R |
E |
W |
A |
R |
D |
W |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
A |
G |
S |
S |
E |
D |
A |
R |
L |
O |
S |
S |
O |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
F |
E |
S |
G |
H |
J |
N |
W |
H |
I |
T |
E |
R |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
K |
T |
R |
A |
D |
E |
D |
L |
H |
I |
G |
H |
K |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
F |
O |
C |
U |
S |
C |
O |
N |
S |
U |
M |
E |
R |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Z |
X |
B |
R |
E |
A |
K |
C |
V |
B |
N |
M |
Q |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
D |
G |
D |
Q |
W |
G |
O |
O |
D |
S |
L |
E |
A |
P |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
R |
R |
E |
P |
R |
E |
S |
S |
U |
R |
E |
R |
W |
L |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
I |
O |
L |
A |
H |
O |
U |
S |
E |
T |
A |
L |
A |
D |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
V |
U |
E |
B |
R |
A |
N |
D |
Y |
U |
D |
O |
R |
I |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
E |
P |
G |
A |
I |
O |
P |
C |
A |
R |
E |
Y |
E |
F |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
N |
F |
A |
N |
S |
C |
H |
E |
M |
E |
R |
A |
N |
F |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
A |
O |
T |
D |
V |
A |
L |
U |
E |
S |
W |
L |
E |
E |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
M |
R |
I |
O |
D |
L |
F |
A |
I |
R |
A |
T |
S |
R |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
A |
E |
O |
N |
F |
L |
E |
A |
D |
E |
R |
Y |
S |
E |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
R |
C |
N |
M |
B |
A |
S |
E |
I |
M |
A |
G |
E |
N |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
K |
A |
L |
E |
A |
D |
E |
R |
S |
H |
I |
P |
G |
T |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
E |
S |
E |
N |
S |
E |
N |
S |
I |
T |
I |
V |
E |
I |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
T |
T |
V |
T |
M |
A |
R |
K |
E |
T |
I |
N |
G |
A |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
H |
J |
E |
K |
R |
E |
L |
A |
T |
I |
O |
N |
G |
T |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
L |
Z |
N |
P |
R |
O |
T |
E |
C |
T |
I |
O |
N |
I |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
X |
M |
A |
N |
A |
G |
E |
M |
E |
N |
T |
C |
V |
O |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
R |
E |
L |
E |
A |
S |
E |
T |
O |
F |
F |
E |
R |
N |
1.An increase in the attractiveness to customers of a product or service which is achieved by adding something to it (for example, a computer might come with pre-loaded software, a printer, scanner, etc). = added value
2.A large exhibition and meeting for advertising and selling a specific type of product.
3.A long-term customer preference for a particular product or service (for example, someone who always buys Mazda cars because he thinks they are better than other cars on the market).
4.A carefully selected representative range of consumers used for the purposes of providing feedback on likes and preferences.
5.To reach the point at which revenue (the amount of money received for selling something) is equal to the costs of production.
47
For reference see Dictionary of Business — 4th edition (A&C Black Publishers Ltd, 978-0-713-67918-2)
книга выложена группой vk.com/englishlibrary

Unit 0000
6.A system that gives incentives to customers to continue using the same shop or service (for example, by collecting points that they can redeem on future purchases).
7.A competition between companies to get a larger market share by cutting prices.
8.Machines which are used in the kitchen, such as washing machines, refrigerators, etc.
9.An organisation that specialises in planning, creating and implementing direct mail campaigns for clients.
10.A marketing technique that promotes and emphasises a product’s difference from other products of a similar nature.
11.The activity of looking after customers so that they do not become dissatisfied.
12.A telephone call or sales visit where the sales person has no appointment and the client is not an established customer.
13.Actions taken by an organisation to protect itself when unexpected events or situations occur that could threaten its success or continued operation (for example, a competitor selling a better product at a lower price).
14.The regular customers of an organisation or professional person.
15.The selling of goods or services through a linked group of self-employed agents or representatives.
16.An item in a shop that is sold below cost price in order to attract customers into the shop.
17.A prediction of future sales based mainly on past sales performance.
18.A two-word adjective used to describe a sales technique in which a customer is forced to buy something that he / she does not really want.
19.The level of recognition that consumers have of a company name (or its products) and its specific category (for example, most people know that McDonalds® sell fast food, especially burgers).
20.The practice of building up and keeping contacts with customers, clients, the general public, etc.
21.A product or service which sells the most in a market.
22.A sheet giving news about something (for example, a new product) which is sent to newspapers and television and radio stations so that they can use the information.
23.A two-word adjective used to describe a product or service for which sales remain constant no matter what its price because it is essential to buyers.
24.The ending of the manufacture and sale of a product.
25.The safeguarding of customers’ interests in terms of quality, price and safety.
26.A group of manufacturers or suppliers who visit another country to increase export business.
27.An idea which a company would like the public to have of it.
28.The establishment of price levels in a market by a dominant company or brand.
29.The people to whom a company is planning to sell its goods or services.
30.A sales promotion technique in which customers are offered a ‘free gift’.
31.The name of a store which is used on products which are specially packed (and sometimes produced) for that store.
32.Using your knowledge of your customers in order to determine the corporate strategy of your company or organisation.
48
For reference see Dictionary of Business — 4th edition (A&C Black Publishers Ltd, 978-0-713-67918-2)
книга выложена группой vk.com/englishlibrary

Similar meaningsUnit1: Nouns0000
Exercise 1: Look at sentences 1 – 22. These can either be completed with a word from box A or a word with a similar meaning from box B. Identify both the words that could be used. In some cases, you will need to add an -s to one or both of the words when you put them into the sentence.
|
A |
B |
|||||||||
|
acclaim |
administration |
agenda |
acquisition |
advantage |
(personal) appeal |
|||||
|
appointment |
benefit |
charisma |
choice |
client |
closeness collaboration |
decline |
||||
|
code cooperation |
customer |
discipline |
defect |
employment evidence |
meeting |
|||||
|
discount |
drop |
fault |
liability |
option order patron personnel praise |
||||||
|
opposition |
proof proximity |
prerequisite receivership reduction |
||||||||
|
requirement |
staff |
takeover |
work |
resistance |
responsibility |
rule |
schedule |
|||
1.We have a very busy __________ / __________ today, so I suggest we start as soon as possible.
2.After two financially disastrous years, the company went into __________ / __________ .
3.We need to maintain __________ / __________ on the factory floor at all times, otherwise there are increased risks of an accident occurring.
4.Several employees were made redundant following EZPrint’s __________ / __________ of Colourcom.
5.There has been a sharp __________ / __________ in the number of people attending the staff development sessions.
6.The latest computer program has several __________ / __________ which need to be sorted out before it can be put onto the market.
7.There has been a lot of __________ / __________ to the new compulsory overtime plan.
8.Despite government reassurances, there is no __________ / __________ that standards of living have improved.
9.Repeated orders are eligible for a 10% __________ / __________ on wholesale prices.
10.The hotel is popular with business people because of its __________ / __________ to the central business district.
11.I can’t see you this afternoon because I have a / an __________ / __________ with the Board of Directors.
12.A lot of our regular __________ / __________ say that they are unhappy with the speed of our service.
13.When the company begins operations, it hopes to provide __________ / __________ for 300 people.
14.There are several __________ / __________ to working from home: you save on travel costs, for one thing.
15.If you want the job, a working knowledge of German is one of the main __________ / __________.
16.Our latest range of language-learning products has received widespread __________ /
__________ in the press, and is expected to help us become a market leader.
17.The company __________ / __________ state(s) that no employee can leave his or her work station without asking for permission.
18.The management accepts no __________ / __________ for any damage to vehicles in the car park.
19.There are two __________ / __________ available to us: close the company or move to another locality.
20.All __________ / __________ are requested to attend tomorrow’s meeting, which will begin at 2pm.
21.Thanks to our __________ / __________ with several affiliated companies, we have increased our turnover by 37%.
22.We believe that the new manager’s lack of __________ / __________ will have a negative effect on sales.
49
For reference see Dictionary of Business — 4th edition (A&C Black Publishers Ltd, 978-0-713-67918-2)
книга выложена группой vk.com/englishlibrary

Unit 0000
Exercise 2: Instructions as above.
|
A |
B |
||||||||||
|
achievement |
advertising |
assignment |
accomplishment |
change |
classification |
||||||
|
calibre |
category |
customer |
disparity |
complication condition |
difference |
||||||
|
ending |
entitlement |
notion |
outlet |
earnings |
expert |
final demand |
idea |
||||
|
priority |
problem |
proceeds |
proficiency |
intellect and ability |
job |
patron |
plan |
||||
|
question review |
revision |
specialist |
precedence |
publicity query right |
shop |
||||||
|
strategy |
term |
ultimatum |
skill |
termination |
write-up |
||||||
1.Our latest range of products has received several favourable __________ / __________ in the press, and should be a firm favourite with the 18 – 24 age group.
2.Our latest model is excellent, but without adequate __________ / __________, we won’t make enough to cover production costs.
3.__________ / __________ are requested not to smoke in the restaurant.
4.The hotel has several room __________ / __________, including five family rooms and two honeymoon suites.
5.Poor long-term sales figures resulted in the __________ / __________ of the contract and the closure of two offices.
6.If you leave the company, you will lose your __________ / __________ to a share of the profits.
7.We would very much appreciate having somebody of your __________ / __________ working for us: you would be of great benefit to the company.
8.We called in a health and safety __________ / __________ to examine the building for any potential problems.
9.He was given the __________ / __________ of dealing with the press and keeping the public informed about new developments.
10.The new manager has a strange __________ / __________ that all employees are potentially dishonest.
11.She hasn’t reached the required level of __________ / __________ in typing, and will have to repeat that section of the training course.
12.His promotion to director was a remarkable __________ / __________ for someone so young.
13.The bank gave us a / an __________ / __________: pay back the money or face immediate closure.
14.Despite several changes to the pay structure, there is still a __________ / __________ in pay between graduate trainees and non-graduates.
15.All __________ / __________ from the sale of the building will be re-invested in the company.
16.We advise you to read the __________ / __________ of the contract carefully, and contact us if you disagree with any of the points covered.
17.If you have any __________ / __________, please ask a member of staff.
18.Selfwood’s operates several __________ / __________ where you can buy a selection of our own goods along with a large range of branded varieties.
19.We had hoped that everything would run smoothly, but unfortunately there have been several
__________ / __________.
20.Our __________ / __________ is to wait for prices to fall before putting the product onto the market.
21.Advertising is currently our main concern, and it should take __________ / __________ over everything else.
22.Is it necessary to make any __________ / __________ to the plan, or should we keep it as it is?
50
For reference see Dictionary of Business — 4th edition (A&C Black Publishers Ltd, 978-0-713-67918-2)
книга выложена группой vk.com/englishlibrary

Similar meaningsUnit2: Verbs0000
Look at the words and expressions in italics, and then rearrange the letters in bold that follow each expression to make a word with the same or a similar meaning in the same context. Use these words to complete the crossword on the next page.
Across ( )
(4)Help a customer. ssaits
(9)Agree to do something. nnscoet
(11)Make something clearer. aylrifc
(12)Book a restaurant table. veerres
(13)Control a process or activity. ergateul
(14)Examine information in detail. alseyan
(16)Collect information. tgaehr
(17)Speak to an audience. rsedsad
(24)Choose something. celste
(26)Produce or make good sales of a product. ereengat
(28)Manage or organise a department. stainierdm
(30)Verify something is true. nmfcori
(33)Examine financial accounts. duita
(34)Give information or instructions to your staff. erbfi
(35)Tell somebody about an event that has happened. taeler
(37)Measure the effect of something. nafytqui
(39)Remove something from a sum of money. cdutde
(41)Require somebody to do something. lbioeg
(42)Increase your area of operations. iwned
(43)Take on new staff. mleyop
Down ( )
(1)Finish making plans for something. ilifsena
(2)Suggest something without saying it directly. yplim
(3)Ask somebody for advice. ucsotnl
(4)Make a process go faster. aeclrcteae
(5)Deal with a problem. leahdn
(6)Keep something for future use. etrina
(7)Come to an interview. teadnt
(8)Give or take a message to somebody. ecvyon
(9)Make up for something you have done wrong. pensacteom
(10)Reveal information to somebody. esolcsid
(12)Settle an argument or disagreement. veslroe
(15)Replace something with something similar. tetubstsui
(18)Firmly tell somebody your terms and conditions. tadteic
(19)Firmly state your opinion. sraset
(20)Promote a product. tiarseedv
(21)Prevent a strike from taking place. rvate
(22)Use up all your resources. etdeepl
(23)Recover lost money or property. airclem
(25)Approve of a decision. oresend
(27)To not allow smoking in a public place. hpobitir
(29)Have an effect on someone or something. ncfiunlee
(31)Give a contract to a company. radwa
(32)Try to do a difficult job. ptetmat
(36)Check facts to see if they are true. scenraiat
|
(38) |
Obtain or get information uciraqe |
|
(40) |
Account for something that has happened. pixlnae |
51
For reference see Dictionary of Business — 4th edition (A&C Black Publishers Ltd, 978-0-713-67918-2)
книга выложена группой vk.com/englishlibrary

Unit 0000
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
|
|
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
|
8 |
9 |
||
|
10 |
|||
|
11 |
|
12 |
||||
|
13 |
||||
|
14 |
15 |
|||
|
16 |
||||
|
17 |
18 |
|||
|
19 |
20 |
|||
|
21 |
22 |
|||
|
23 |
24 |
25 |
||
|
26 |
||||
|
27 |
28 |
29 |
||
|
30 |
||||
|
31 |
32 |
|||
|
33 |
||||
|
34 |
||||
|
35 |
36 |
|||
|
37 |
38 |
39 |
40 |
|
|
41 |
||||
|
42 |
||||
|
43 |
Note that using a word with a similar meaning to another word does not always mean using that word in exactly the same way. For example: you can ‘prevent a strike from taking place‘ or you can ‘avert a strike‘ (not ‘avert a strike from taking place‘); you can ‘suggest something without saying it directly‘ or you can ‘imply something‘ (not ‘imply something without saying it directly‘). In these examples, the words at the end are not necessary because their meaning is carried in the main verb. This is one reason why you should always record words in context, and with an example that shows how they are used, so that when you use them yourself, you use them correctly.
Also note that some of these verbs can be used in more than one way. For example, you can convey a message to someone, or you can convey goods from one place to another.
52
For reference see Dictionary of Business — 4th edition (A&C Black Publishers Ltd, 978-0-713-67918-2)
книга выложена группой vk.com/englishlibrary

Similar meanings 3: AdjectivesUnit0000
Exercise 1: Match the words and expressions in bold in sentences 1 – 20 with words with the same or a similar meaning. These words can be found in the box by reading from left to right, and from right to left, in the direction of the arrows. However, the words in the box are not in the same order as the sentences they match.
|
START B |
a |
b |
r |
u |
p |
t |
r |
e |
s |
o |
l |
u |
t |
e |
b |
a |
s |
i |
c |
||||
|
r |
c |
s |
u |
o |
l |
u |
p |
u |
r |
c |
s |
e |
v |
i |
s |
n |
e |
t |
x |
e |
|||
|
u |
c |
i |
a |
l |
m |
a n d a |
t |
o |
r |
y |
o u |
t |
d a |
t |
e |
||||||||
|
i |
t |
r |
e |
p |
t |
n |
a |
d n u b |
a |
t |
n |
a |
r |
b |
i |
v |
d |
||||||
|
n |
e |
n |
t |
d |
i |
s |
c |
o |
u |
r |
t |
e |
o u |
s |
o |
v |
e |
r |
a |
||||
|
t |
s |
i |
s |
n |
o |
c |
n |
i |
d |
e |
t |
c |
i |
r |
t |
s |
e |
r |
l |
l |
|||
|
e |
n |
t |
a |
d |
e |
q |
u |
a |
t |
e |
t |
h o |
r |
o u g h |
i |
n |
|||||||
|
FINISH |
w |
o |
r |
r |
a |
n |
y |
k |
s |
i |
r |
e |
l |
b |
i |
x |
e |
l |
f |
||||
1.We’ve carried out a comprehensive audit of our accounts, but haven’t found any irregularities.
2.Regular government health and safety inspections are compulsory.
3.Despite several USP’s* in our latest range, we can expect to face some determined competition from our rivals.
4.We are unable to make a decision at this time as we do not have enough information.
5.Your performance has become rather erratic recently, so we were wondering if you might benefit from going on a new training course.
6.I’m not sure why your order was delayed for so long, but I assure you I will carry out a full and detailed investigation.
7.We don’t need to know all the details: try to give us a general idea.
8.She’s a very successful saleswoman, but I don’t think she’s particularly honest and fair with her clients.
9.We have received a number of complaints about impolite sales people in our call centre.
10.Employee access to the office after 6pm is strictly limited and controlled.
11.People enjoy working in our department: the atmosphere in the office is really lively.
12.Our department manager does a good job, although he is often criticised for his old-fashioned business ideas.
13.There are plenty of opportunities for promotion within the company, provided you work hard enough.
14.At the end of her presentation, there were several relevant questions from the audience.
15.This schedule is too rigid. We need a bit of wiggle room** here.
16.The company is unwilling to invest in financially dangerous projects.
17.Free accommodation is provided for our employees. It is simple but adequate.
18.Our profit margin has been very small over the last six months.
19.We were ready to sign the contract when there was a sudden change of plan.
20.There has been a lot of talk of redundancies, so this afternoon’s meeting is very important for all those concerned.
*USP’s: unique selling points.
**wiggle room: an informal expression for time and flexibility.
53
For reference see Dictionary of Business — 4th edition (A&C Black Publishers Ltd, 978-0-713-67918-2)
книга выложена группой vk.com/englishlibrary
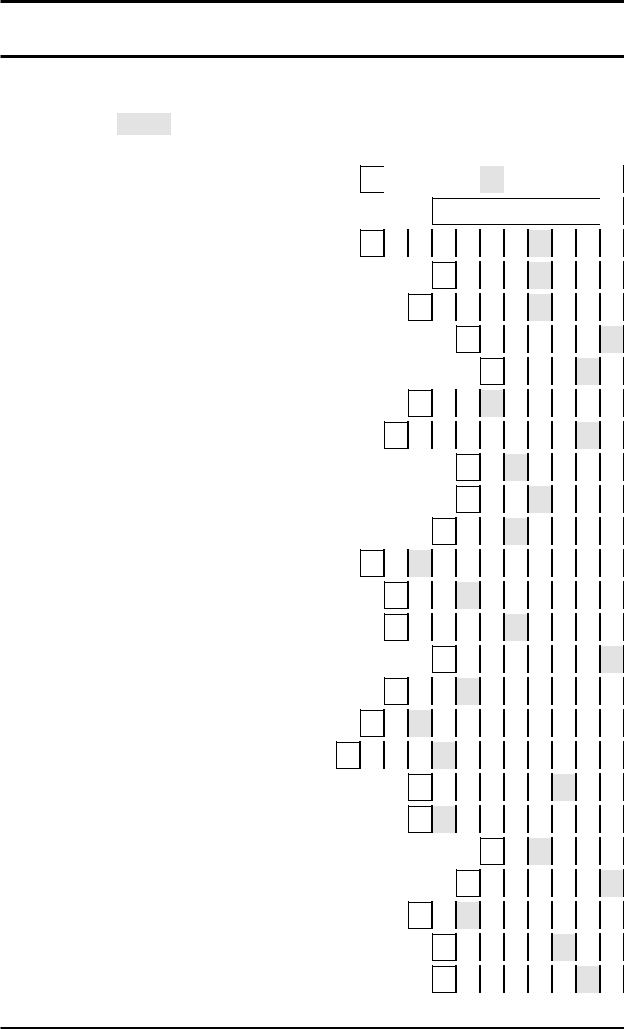
Unit 0000
Exercise 2: Rearrange the letters in bold to make words that have the same or a similar meaning to the words and expressions in italics. Write each word in the table on the right of the page. The shaded letter in each word is the first letter of the next word. The first
one has been done as an example.
1.A likely or possible job applicant. ecivrosppte
2.A product’s lasting appeal. ridugenn
3.Basic computer skills. utadirymren
4.A flourishing IT business. ringvith
5.An optional dress code. taurynlvo
6.A boring and repetitive job. outesdi
7.A constant and continuous price rise. saydte
8.A flow of unrelated ideas. spitdaear
9.A lucrative venture. opritleafb
10.A long meeting. glehnty
11.A small charge for postage and packing. monalin
12.A very important part of something. gainrtel
13.An outstanding presentation. nactexiolep
14.Two well-suited organisations. ticmpbleao
15.An observant secretary. cepetviper
16.A prompt start to a meeting. caputnlu
17.A valid reason for doing something. itemalegit
18.A hardworking staff member. iriustnusod
19.Punitive action. panscdiiylir
20.A creative idea. tivvenein
21.A significant event. naprotimt
22.A contemporary approach to management. omnedr
23.A varied programme of events. viseder
24.A well-run and productive department. fitefince
25.Easily changeable working hours. blleifex
26.An insolvent company. narubptk
54
For reference see Dictionary of Business — 4th edition (A&C Black Publishers Ltd, 978-0-713-67918-2)
книга выложена группой vk.com/englishlibrary

On the telephoneUnit0000
Exercise 1: Complete these dialogues with words and expressions from the box.
|
automated services call back |
camping on the line connect |
convenient |
|||||||
|
cut off dead |
direct line |
engaged |
extension |
get back hang on |
hash |
||||
|
hold the line hung up |
junk calls |
message |
on behalf of |
on hold |
|||||
|
put through |
speaking star |
switchboard tone |
voicemail |
zeroing out |
|||||
|
1. |
Caller: |
Could I speak to Jennifer Thompson in Accounts, please? |
|||||||
|
Receptionist: |
I’m afraid her line is ________ at the moment. Shall I get her to ________ |
you |
|||||||
|
________ (you need one expression for these two gaps)? |
|||||||||
|
2. |
Caller: |
Oh, hello, could you ________ me ________ (you need one expression for these two |
|||||||
|
gaps) to Ron Atkinson, please? |
|||||||||
|
Receptionist: |
Certainly. ________ please. |
||||||||
|
3. |
Caller: |
Hello. Adam Harrison, please. |
|||||||
|
Receptionist: |
He’s out of the office, I’m afraid, but I can ________ you and you can leave a |
||||||||
|
________ on his ________, if you like. |
|||||||||
|
Caller: |
No, that’s OK. I’ll try again later. When would be a ________ time? |
4.Speaker 1: Oh no, not again!
|
Speaker 2: |
What’s up? |
|
|
Speaker 1: |
I’m trying to call my credit card company, and I’ve got one of those stupid ________. |
|
|
Speaker 2: |
Well, try ________. You might get through to a real human being. |
|
|
Speaker 1: |
OK. Oh, the line’s gone ________. I’ve been ________. |
|
|
5. |
Answering |
Hello. This is Anthony Roberts. I’m not in the office at the moment, |
|
machine: |
but if you leave your name and number after the ________, I’ll ________ to you |
6.Speaker 1: Bob’s been on the phone for ages.
Speaker 2: I know. He’s calling our supplier, but they’ve put him ________. He’s been
________ for over ten minutes!
7.Speaker 1: (Answering the phone) Hello?
|
Recorded |
Hello there. I’m Sandy from Moneygrubbers International, and I’m delighted to |
|
message: |
tell you that you have been personally selected from a list of literally millions to |
|
receive a fantastic travel offer… |
|
|
Speaker 2: |
Who is it? |
|
Speaker 1: |
(putting down the phone): Oh, just one of those irritating ________. |
8.Mr Floyd: (Answering the phone) Hello?
Telemarketer: Oh, hello. Could I speak to Mr Floyd, please?
|
Mr Floyd: |
________. |
|
Telemarketer: |
Good evening, Mr Floyd. I’m Tim Spanner, and I’m calling ________ Superglaze |
|
Windows. I was wondering if… |
|
|
Mr Floyd: |
(Says nothing, but puts the phone down) |
|
Telemarketer: |
Oh dear. That’s the fifth one who’s ________ on me today. |
55
For reference see Dictionary of Business — 4th edition (A&C Black Publishers Ltd, 978-0-713-67918-2)
книга выложена группой vk.com/englishlibrary

Unit 0000
|
9. |
Caller: |
Hello. Could I have Sarah Knowles’ ________ please? |
|
Receptionist: |
Well, actually, she has a ________, which means you can by-pass the ________ the |
|
|
next time you call. If you ________ a moment, I’ll get you her number. |
10.Speaker 1: How do I access my messages on this phone?
Speaker 2: Press zero, then the ________ key. That’s the little asterisk at the bottom of the keypad. Then press zero again, followed by the ________ key.
Speaker 1: Which one’s that?
Speaker 2: The key with the four vertical and horizontal lines crossing one another.
Exercise 2. The popularity of SMS mobile phone text messaging has led to an increase in the use of certain abbreviations to communicate ideas (for example, ‘FYI‘ means ‘For your information‘). Many of these are used by business people, not only in SMS messages, but also in emails and handwritten notes and messages.
Look at these messages, and try to decide what the abbreviations in bold mean. Choose the words you need from the box. You will need to use some words more than once.
|
a |
am |
as |
back |
be |
business |
by crying |
eyes fact |
for |
glaze |
||||||
|
ha |
hand |
helps |
hope |
I |
in |
it |
it’s |
keep |
kidding |
lawyer |
loud |
||||
|
matter |
mind |
my |
not |
of on |
only |
opinion |
other |
out |
over |
||||||
|
own |
possible |
respect |
right |
simple |
soon |
stupid |
the |
this |
to |
||||||
|
way |
what |
with |
words |
worth |
your |
||||||||||
1.We didn’t make a profit last month. AAMOF, we lost almost £8000.
2.I need a reply from you urgently. Please call me ASAP.
3.Must go to a meeting now. BRB.
4.Thanks for sending the contract. BTW, have you received our latest catalogue?
5.I still haven’t received your reply. FCOL, what are you playing at?
6.I’m sorry the boss was so rude to you. FWIW, I think you’ve done a fantastic job.
7.Thanks for lending me your mobile, but I’m afraid I’ve dropped it down the loo.
HHOK! I’ll bring it right back.
8.Here’s the information you asked for (see attachment). HTH.
9.How should I know if our latest advertising campaign has broken the law. IANAL!
10.You asked me what we should do about the fall in sales. IMO, we should meet and discuss this problem face to face.
11.The papers we needed have finally arrived. IOW, we can get on with putting the project together at last.
12.One bit of advice for the report you’re writing: KISS!
13.Have you seen his report? It’s almost 200 pages long. Oh my god, MEGO!
14.This is my project, not yours! Hands off, and MYOB!
15.You could be wrong. OTOH, you’re probably right.
16.WRT your request for a day off next week, I’m afraid my answer is no.
56
For reference see Dictionary of Business — 4th edition (A&C Black Publishers Ltd, 978-0-713-67918-2)
книга выложена группой vk.com/englishlibrary

UnitTrade0000
Complete the sentences and definitions below with appropriate words, and use these words to complete the crossword grid on the next page. In each case, the first letter of each word you need is in the sentence / definition. The number and arrow after each gap show
|
you where to put the word in the grid: = across, |
= down. |
|
When you bring goods into a country you i________ (5 |
) them. When you send them out of a country |
|
you e________ (15 ) them. |
A group of manufacturers or suppliers who visit another country to increase their sales there is known as a trade d________ (32 ).
C________ (20 ) – also called f________ (26 ) – is a general word for goods which are transported in a ship, plane etc. It is usually carried in a c________ (14 ) (= a very large metal case of a standard size).
A bill of l________ (3 ) is a list of goods being transported, which the transporter gives to the person sending the goods, to show them that the goods have been loaded. The person receiving the goods should receive a p________ (16 ) list, showing them the goods that they should be receiving.
A letter of c________ (21 ) – often abbreviated to L/C – is a document issued by a bank on behalf of a customer authorising payment to a supplier when conditions specified in the document are met.
A p________-________ (24 ) invoice is an invoice sent to a buyer before the goods are sent, so that payment can be made (or so that goods can be sent to a consignee who is not the buyer). (note: write this as one word in your crossword grid: do not leave any spaces)
COD is a payment which is made for goods when they arrive. COD stands for cash on d________ (23 ). A group of goods sent for sale by road, sea or air is called a c________ (9 ).
CIF refers to the price a buyer has to pay for goods which have to be transported. It stands for c________ (28 ), i________ (5 ) and freight.
Goods sent by air are called a________ (31 ). Goods sent by sea are called s________ (33 ).
FOB stand for free on b________ (2 ). It refers to the price a buyer pays a seller for goods. The price includes all the seller’s costs until the goods are on the ship, plane, etc, for transportation.
|
Import d________ (11 ) – also sometimes called an import l________ (19 |
) – is a tax which has to |
|
|
be paid on goods coming into a country. A customs t________ (27 |
) is a list of those taxes that must be |
|
|
paid. |
||
|
A person or company which arranges shipping and c________ (29 |
) documents is called a f________ |
|
|
(13 ) agent. |
||
|
If tax on imported goods is not paid, those goods may be i________ (30 |
) (in other words, they are |
kept in a secure w________ (6 ) at or near the p________ (18 ) of entry until that tax is paid).
A c________ (21 ) agent arranges the import and delivery of goods at their port of d________ (10 ).
As soon as goods are allowed into a country by the customs officer, we can say that they have been c________ (1 ).
A record of the international trading position of a country in m________ (34 ) (= goods), excluding invisible trade, is called the b________ (22 ) of trade.
A w________ (4 ) price is a price paid by customers (for example, shops) who buy goods in large quantities. They sell these goods to individual customers (for example, shoppers) at a higher price which is called the r________ (7 ) price. Some offer d________ (17 ) to their customers, which means they pay a little less.
A l________ (25 ) agreement allows a company to market or produce goods or services owned by another company, and is a popular means for a company to penetrate the overseas market.
57
For reference see Dictionary of Business — 4th edition (A&C Black Publishers Ltd, 978-0-713-67918-2)
книга выложена группой vk.com/englishlibrary

Unit 0000
A q________ (35 ) is a limited amount of a good that can be brought into a country (usually as an incentive for people to buy home-produced versions of that good). This is an example of a trade b________ (12 ).
When goods are sold within one country, they are transported to their place of sale by a d________ (8 ).
|
1 |
2 |
|||
|
3 |
||||
|
4 |
5 |
|||
|
6 |
||||
|
7 |
8 |
9 |
||
|
10 |
||||
|
11 |
||||
|
12 |
13 |
|||
|
14 |
||||
|
15 |
||||
|
16 |
17 |
|||
|
18 |
19 |
|||
|
20 |
||||
|
21 |
||||
|
22 |
23 |
|||
|
24 |
25 |
|||
|
26 |
27 |
|||
|
28 |
||||
|
29 |
30 |
|||
|
31 |
||||
|
32 |
||||
|
33 |
||||
|
34 |
||||
|
35 |
||||
|
58 |
||||
|
For reference see Dictionary of Business — 4th edition (A&C Black Publishers Ltd, 978-0-713-67918-2) |
||||
|
книга выложена группой vk.com/englishlibrary |

BusinessUnittravel0000
Exercise 1: Choose the best word(s) or expression(s) to complete these sentences. In some cases, more than one option is possible.
1.(At the airport. A check-in assistant is talking to a passenger) I’m afraid your flight has been cancelled / delayed / crashed / double-booked. It won’t be leaving for another two hours.
2.(At the airport. An angry passenger is talking to her colleague) I don’t believe it. The airline has diverted / overbooked / rerouted / postponed our flight and have told me there are no more seats available for us. We’ll have to wait for the next one.
3.(A business executive is explaining why he prefers to fly business class) Flying business class is much more expensive than flying tourist / coach / economy / club class, but it’s much more comfortable and the food is better.
4.(An announcement is being made at a port) The ship will soon be ready for embarkation / boarding / disembarkation / climbing. Would passengers please ensure they have their tickets ready.
5.(At the airport, an announcement is being made to passengers arriving on a flight) Welcome to London Heathrow Airport. Could we remind transition / transitive / transitory / transit passengers to wait in the lounge until their next flight is ready.
6.(At the airport, an urgent announcement is being made over the PA system) Would the last remaining passenger for flight BZ112 to Thessalonica please proceed immediately to door / entrance / gate / pier 22, where their flight is about to depart.
7.(A travel agent is telling a traveller about his flight) Your flight to Istanbul is one way / indirect / direct / non-stop, so you won’t be landing anywhere else en route.
8.(At the airport, an assistant is helping a passenger to find the right terminal for her flight from London to Belfast)
Terminals 2 and 3 are the terminals for international flights. You need terminal 1 for domesticated / domestic / domesticity / domicile flights.
9.(At the station, an information desk assistant is explaining ticket prices to a passenger who wants to visit a town and return on the same day). A single / simple / one way / one direction ticket to Bradford costs £27.50. A return trip / round-trip / circle-trip / square-trip ticket will cost you £42.
10.(At the bank, a clerk is telling a customer why he can’t take out any more money with his American Express card). I’m really sorry, sir, but you have already exceeded your profit margin / loyalty points / credit limit / commission rates.
11.(On an aircraft, the captain is talking to his passengers) If you need anything during the flight, please do not hesitate to ask one of our cabin staff / gang / team / crew members.
12.(A radio announcement is being made for people travelling to a city for their job) Bad news for expatriates / commuters / immigrants / migrants, I’m afraid. Traffic on the M25 is backed up for12 miles at junction 9.
13.(An article in a magazine is talking about air travel) In a recent survey, Albion International Air Ltd was voted the world’s favourite carrier / airline / airliner / airways for its punctuality, comfort, quality of inflight catering and of course its standards of safety.
14.(A travel agent is explaining insurance policies to a customer) We advise you to take out our comprehensive / adhesive / apprehensive / defensive insurance policy which will cover you against all risks that are likely to happen.
15.(A car hire clerk is helping a customer choose a vehicle) The roads here are so bad and so full of holes that we very much recommend you hire a / an MPV / saloon / 4×4 / van.
59
For reference see Dictionary of Business — 4th edition (A&C Black Publishers Ltd, 978-0-713-67918-2)
книга выложена группой vk.com/englishlibrary

Unit 0000
Exercise 2: Choose the best word or expression from each pair in bold to complete this text. In some cases, both words / expressions are possible.
There are a few things that the well-prepared business traveller should sort out before they leave the country. First of all, they will need to prepare a / an (1) schedule / itinerary so that they know exactly where they will be and who they will seeing at various times on their (2) voyage / trip. Next, they should check their passport: have they got one, for a start, and is it still (3) validated / valid? Most countries will not let them in if their passport (4) runs out / expires within six months. Secondly, what about a (5) visa / visor? More and more countries require foreign visitors to have one, and this will cost money (and time and effort, too: in some cases, the traveller has to present himself or herself in person at the country’s (6) emmbassy / embassy). Thirdly, they will need to get (7) traveller’s cheques / traveling cheques and / or foreign (8) currancy / currency: if they choose the latter, they need to check the (9) exchange / changing rate to make sure they are getting a favourable (10) deal / bargain, and then in most cases they will need to pay (11) comission / commission / commision to the bank who supplies it. Finally, they should check that they have (12) insurence / insurance / insureance cover, that their (13) vaccinations / vaccinnations / vacinations are up to date, and that their mobile phone will work abroad (and if necessary, make arrangements with their (14) provider / provisor to ensure they can get connected to the (15) network / website when they arrive).
Exercise 3: Now try this quiz.
1.In which places would you check in?
2.You are told that you need to pay an excess baggage charge. What does this mean?
3.At the airport you are told you have been bumped from your flight. What does this mean?
4.You want an upgrade on your flight. What exactly do you want?
5.The flight you have booked includes free transfers. What are these?
6.You are travelling from Greece to the UK. Are you allowed a duty free allowance?
7.What is the correct word in bold in this question: ‘How much is the business class fee / fare from Washington to Rome?’
8.What is an e-ticket?
9.You are flying from Cape Town to London. Would you expect to suffer jet lag?
10.In a hotel, what is the difference between full-board, half-board and bed and breakfast accommodation?
11.In a hotel, what is the difference between a single room, a twin room, a double room and a suite?
12.The hotel you want to stay at insists on charging you the rack rate. What is this?
13.You are in your room in a large international hotel. Which department would you call if you wanted the following?
(a)someone to clean your room, bring you some towels and wash your shirts
(b)to make a general enquiry
(c)to report an electrical or plumbing problem
(d)to help you make a national or international phone call
(e)to have some food brought to your room
(f)to order a taxi or have your luggage taken from or to your room
14.Rearrange the letters in bold to make the names of things you might find in a hotel room (in addition to a bed, of course).
|
rwoarbed feas |
niim rab nlboyac |
ari tincnoniogdi ate dan fceeof fteiliacis |
|
|
nteeIntr scesac |
nori |
snioleitev |
oemrte ontolcr |
15.The room in your hotel was pokey, scruffy and draughty, the hotel staff were discourteous, officious and surly, and the hotel food was greasy, unappetising and repetitive. Would you stay at the hotel again?
16.In which situations would you expect to leave a tip?
60
For reference see Dictionary of Business — 4th edition (A&C Black Publishers Ltd, 978-0-713-67918-2)
книга выложена группой vk.com/englishlibrary

Word associationUnit0000
The four words in each set 1 — 28 below can be used with one other word (i.e., they collocate with that word). What is that word in each set? Choose your answers from the box. The first one has been done for you. Note that each word you choose from the box must work with all four words in the set.
|
brand |
business |
career |
contract |
corporate |
cost |
customer |
|||||||||||||
|
employment |
group |
health |
income |
industrial |
insurance |
job |
labour |
||||||||||||
|
management |
market |
minimum |
pension |
personal |
price |
private |
|||||||||||||
|
salary |
sales |
shift |
staff |
strike |
tax |
||||||||||||||
|
1. |
_pension_ scheme |
_pension_ contributions |
occupational _pension_ |
portable _pension_ |
|||||||||||||||
|
2. |
__________ address |
__________ cycle |
__________ expenses |
__________ plan |
|||||||||||||||
|
3. |
__________ application |
__________ description |
__________ opportunities |
__________ rotation |
|||||||||||||||
|
4. |
__________ freeze |
__________ war |
__________ fixing __________ ceiling |
||||||||||||||||
|
5. |
__________ climate |
__________ culture |
__________ governance |
__________ image |
|||||||||||||||
|
6. |
__________ accounting |
__________ analysis |
__________ factor |
marginal __________ |
|||||||||||||||
|
7. |
__________ allowance |
__________ bracket |
__________ exemption |
__________ threshold |
|||||||||||||||
|
8. |
__________ accident __________ action |
__________ relations __________ tribunal |
|||||||||||||||||
|
9. |
__________ age |
__________ pay |
__________ wage |
__________ salary |
|||||||||||||||
|
10. |
__________ review |
__________ structure |
annual __________ |
basic __________ |
|||||||||||||||
|
11. |
__________ call |
__________ notice |
unofficial __________ |
wildcat __________ |
|||||||||||||||
|
12. |
__________ transfer |
__________ work |
night __________ |
day __________ |
|||||||||||||||
|
13. |
__________ audit |
__________ committee __________ style |
__________ trainee |
||||||||||||||||
|
14. |
__________ cover |
__________ screening |
__________ insurance |
__________ report |
|||||||||||||||
|
15. |
__________ force |
__________ dispute |
skilled __________ |
manual __________ |
|||||||||||||||
|
16. |
__________ agency |
__________ law |
full-time __________ |
temporary __________ |
|||||||||||||||
|
17. |
__________ policy |
__________cover |
__________ broker |
national __________ |
|||||||||||||||
|
18. |
__________ expectations |
__________ ladder |
__________ opportunities |
__________ path |
|||||||||||||||
|
19. |
__________ leader |
__________ penetration |
__________ research |
__________ value |
|||||||||||||||
|
20. |
__________ tax |
__________ support |
earned __________ |
net __________ |
|||||||||||||||
|
21. |
__________ complaint |
__________ expectation |
__________ satisfaction |
__________ service |
|||||||||||||||
|
22. |
__________ enterprise |
__________ ownership |
__________ secretary |
__________ sector |
|||||||||||||||
|
23. |
__________ agency |
__________ appointment |
senior __________ |
skeleton __________ |
|||||||||||||||
|
24. |
__________ discussion |
__________ dynamics |
__________ interview |
focus __________ |
|||||||||||||||
|
25. |
__________ work |
__________ law |
__________ hire |
fixed-term __________ |
|||||||||||||||
|
26. |
__________ analysis |
__________ campaign |
__________ representative |
__________ team |
|||||||||||||||
|
27. |
__________ allowance |
__________ assistant |
__________ contract |
__________ development |
|||||||||||||||
|
28. |
__________ leader |
__________ loyalty |
__________ image |
own __________ |
61
For reference see Dictionary of Business — 4th edition (A&C Black Publishers Ltd, 978-0-713-67918-2)
книга выложена группой vk.com/englishlibrary

WorkingUnit 0000hours and time off work
Exercise 1: Complete sentences 1 – 26 with words and expressions from the box. Note that some of the sentences refer to shift work (when employees work for a period and then are replaced by others). Other sentences refer to flexible work systems, where employees can start or stop work at different hours of the day, provided they work a certain number of hours a day or week.
|
allowed time |
clock off |
core time |
double time |
fixed hours |
||||
|
Flexible Work Regulations |
flexileader flexilagger flexitime full-time |
|||||||
|
graveyard shift |
homeworking |
job rotation |
job-share |
overtime |
part-time |
|||
|
roster |
rotating shifts shift differentials |
shift transfer |
time and a half |
|||||
|
time-keeping |
time sheet |
twilight shift |
unsocial hours |
work-life balance |
||||
1.___________ is the fact of being on time for work (for example, ‘He was reprimanded for bad
___________’).
2.___________ is paid time which the management agrees an employee can spend on rest, cleaning or meals, not working.
3.___________ is a form of employment in which two or more people do a single job or take on a specific role within a company, each person working part-time.
4.___________ is a short form of the expression flexible time.
5.A company or organisation that puts a lot of emphasis on flexibility in its employment practices is known informally as a ___________.
6.A company or organisation that puts too little emphasis on flexibility in its working practices is known informally as a ___________.
7.An employee who works ___________ works at times such as in the evening, at night or during public holidays when most people are not at work.
8.Employees who work ___________ work for the normal working time (i.e. about 8 hours a day 5 days a week).
9.Employees who work ___________ do not work for the whole working week (for example, they might only work 4 hours a day instead of 8).
10.A time for which work is paid at twice the normal rate (for example, at weekends or on public holidays) is called ___________.
11.___________ is the normal rate of pay plus 50% extra (for example, when an employee does overtime or works evenings).
12.Hours worked more than the normal working hours are called ___________.
13.___________ is a period when employees working under a flexible time system must be present at work.
14.The act of changing an employee’s shift or working hours is called ___________.
15If a company does not operate a flexible time system, we say that the employees work ___________
hours.
16.___________ refers to a system where employees take turns in working different shifts.
17.The ___________ is an informal expression for the night shift.
18.___________ is a working method where employees work at home (usually on computer terminals), and send the finished material back to the office by email.
62
For reference see Dictionary of Business — 4th edition (A&C Black Publishers Ltd, 978-0-713-67918-2)
книга выложена группой vk.com/englishlibrary

Unit 0000
19.A duty ___________ is a list of times showing when each employee is on duty at those times.
20.When you record the time you leave work by putting a card into a special machine, you ___________.
21.A ___________ is a record of when employees arrive at and leave work, or one which shows how much time an employee spends on different jobs each day.
22.In Britain, parents who have children under 6, or disabled children under 18, have a legal right to have their working hours arranged to help them with their responsibilities. This right is known as
___________.
23.The ability to devote a sensible amount of time to doing your job, making sure that you have enough time left over to do other things (for example, spend time with your family) is referred to as ___________.
24.___________ are payments made to an employee in addition to their basic pay to compensate them for the inconvenience of the pattern of shift work.
25.The ___________ is another name for the evening shift, just before it gets dark.
26.When an employee is moved systematically from one job to another, this is known as ___________.
Exercise 2: Complete these sentences with an appropriate word or words, and write these words in the grid on the next page. If you do this correctly, you will reveal a hidden expression in the shaded vertical strip which means time off work granted to an employee to deal with personal or family problems. Some of the letters have already been put into the grid to help you.
Several of the sentences use the word leave. In these cases, leave is a noun for permission to be away from work (e.g., ‘He isn’t here, he’s on leave’). Employees can be or go on leave.
1.A certificate from a doctor to show that an employee has been ill is called a ___________ certificate.
2.A holiday from work which is fixed by law is called a ___________ holiday.
3.A period when a woman is away from work to have a baby (but is still paid) is called ___________
leave.
4.Leave during which an employee receives no money is called ___________ leave.
5.A period of leave during which an employee is not allowed into the company offices is known informally as___________ leave.
6.A period of paid or unpaid time off work for the purposes of research, study or travel is called a
___________.
7.The percentage of a workforce which is away from work with no good excuse is called the
___________ rate.
8.A day when all employees in the country are allowed to take a day off work is called a
___________ ___________.
9.A period of paid leave given by some companies to staff who have completed several years of service is called ___________-___________ leave.
10.A person’s right to something (for example, their right to a paid holiday from work) is called an
___________.
63
For reference see Dictionary of Business — 4th edition (A&C Black Publishers Ltd, 978-0-713-67918-2)
книга выложена группой vk.com/englishlibrary

Unit 0000
11.If an employee is away from work without permission and without a good reason, we can say that s/he has taken ___________ absence from work.
12.When an employee is sick and has to wait three days before s/he can claim sick pay, these days are known as ___________ days.
13.If an employee has permission to be away from work, s/he has leave of ___________.
14.When an employee gets time off from work instead of pay (for example, if they work overtime and get some time off work instead of overtime pay), we say that they take time off ___________
___________.
15.A short period of leave given to a father to be away from work when his partner has a baby is called
___________ leave.
16.Paid time off from work given to an employee to help him / her deal with personal affairs is called
___________ leave.
17.A holiday or period when people are not working is called a ___________ (especially in the USA).
18.A payment made by the government or by a private insurance company to someone who is ill and cannot work is called sickness ___________.
|
1. |
D |
L |
|||||||||||||||
|
2. |
T |
T |
|||||||||||||||
|
3. |
T |
R |
Y |
||||||||||||||
|
4. |
U |
D |
|||||||||||||||
|
5. |
G |
E |
N |
||||||||||||||
|
6. |
A |
B |
C |
||||||||||||||
|
7. |
A |
S |
E |
I |
|||||||||||||
|
8. |
U |
O |
A |
||||||||||||||
|
9. |
O |
G |
R |
C |
|||||||||||||
|
10. |
T |
M |
|||||||||||||||
|
11. |
U |
H |
S |
||||||||||||||
|
12. |
A |
I |
|||||||||||||||
|
13. |
N |
E |
|||||||||||||||
|
14. |
I |
E |
|||||||||||||||
|
15. |
P |
T |
|||||||||||||||
|
16. |
A |
S |
|||||||||||||||
|
17. |
C |
T |
|||||||||||||||
|
18. |
B |
F |
|||||||||||||||
64
For reference see Dictionary of Business — 4th edition (A&C Black Publishers Ltd, 978-0-713-67918-2)
книга выложена группой vk.com/englishlibrary

Workplace Unitproblems0000
Exercise 1: In the following sentences and paragraphs, one of the words in each of the word pairs in bold is wrong and one is right. Identify the most appropriate word in each case. You will find this easier to do if you read each paragraph through first so that you have a better idea of what it is about (Note that the wrong words are real English words, but do not fit into the context of the sentence / paragraph).
Paragraph (A)
If there is a (1) despite / dispute between the management and the union in a company which cannot be (2) restored / resolved, and as a result a (3) strike / stroke looks likely, a third party might be called in to (4) abdicate / arbitrate.
Paragraph (B)
Three managers have been accused of (1) fraught / fraud, (2) dissemination / discrimination,
(3) bullying / bumbling, (4) racy / racial (5) obtuse / abuse and (6) sectional / sexual (7) harassment
/arrestment . As a result two of them have been (8) fried / fired and one has been (9) suspected / suspended without pay. The first two are claiming (10) unfair / unfaithful (11) dismissive / dismissal and plan to (12) appeal / appal. The third has applied for a job with the government.
Paragraph (C)
We would like to point out that there have been several (1) breaches / beaches of the company’s ‘No smoking’ policy. We also have proof that several factory floor workers have been (2) neglecting / negotiating their duties, and there have also been several incidences of (3) insurrection / insubordination towards senior managers and intentional (4) damning / damage of company property. If this happens again, those responsible will be taken before a (5) disconcerting / disciplinary
(6) broad / board and could face (7) instant / instance (8) dismal / dismissal. We would like to stress that the company has a (9) nil-tolerant / zero tolerance policy towards those who misbehave or break the rules.
Paragraph (D)
The management are fully aware that because of staff (1) shortness / shortages we are all
(2)overstretched / oversubscribed at the moment, Mr Harrington, but we suggest that if you have a
(3)grievance / grievous, you put it to us in writing rather than encourage your colleagues to hold a sudden (4) walkout / walkabout. We’d like you to treat this as a (5) verbal / verdant (6) warming /
warning: the next time it happens, we will be obliged to ask for your (7) notice / note.
Paragraph (E)
What a terrible month! Sales have (1) droned / dropped by 40%, six employees have been made
(2) recumbent / redundant, two senior managers have (3) resigned / resided, our main supplier has gone (4) bankrolled / bankrupt, someone has (5) haggled / hacked into the company website and given us a (6) virus / viscous (with the result that the entire computer system has (7) crashed / cracked), and the coffee machine is still out of (8) odour / order.
65
For reference see Dictionary of Business — 4th edition (A&C Black Publishers Ltd, 978-0-713-67918-2)
книга выложена группой vk.com/englishlibrary

Unit 0000
Paragraph (F)
One problem that many companies face is that of their employees (1) plateauing / plating. This often happens when there is a lack of opportunity for promotion. In such situations, employees may feel they are lacking sufficient (2) simulation / stimulation, and as a result could lose their (3) motivation / motorisation and display less (4) indicative / initiative than before. This in turn can lead to reduced
(5) proclivity / productivity for the company concerned. A good manager should recognise the potential danger signs, and (6) implement / inclement any solutions that they think might help.
Paragraph (G)
An unhappy workforce should be easy for a good manager to spot. Basically, if staff (1) turnover / turnaround is high and staff (2) detention / retention is low, (3) conflict / conscript situations are frequent, there is frequent staff (4) absenteeism / abstention, poor (5) timeserving / timekeeping and (6) misconduct / misconception in the workplace, if (7) moral / morale seems generally low and if there is often the threat of (8) industrial / industrious action, it is time to act. The first thing to do is to (9) counsel / council employees and try to establish the cause of their (10) grievances / grief.
Exercise 2. Match the words in paragraphs A – G above with their definitions below.
1.The practice of staying away from work, often without a good reason.
2.Reaching a point where you cannot go any further in your job.
3.To give professional advice to someone on personal or professional issues.
4.The frequency within which employees people leave a job and are replaced by new employees.
5.Not needed for a job anymore.
6.A disagreement.
7.To be in a situation where you have too much to do.
8.To try to settle a disagreement between two or more people / groups.
9.The practice of treating people in different ways (because of their sex, race, religion, etc).
10.Regularly worrying or bothering someone.
11.A complaint.
12.The eagerness to work well.
13.Bad behaviour at work.
14.A failure to carry out the terms of an agreement, or the failure to follow rules.
15.The sudden stopping of work by employees when they leave their place of work because of a disagreement.
16.The decision or idea to start or do something.
17.The refusal to obey someone with more authority.
18.To ask someone formally to change a decision that you are not happy with.
19.Spoken.
20.To put something (for example, a plan) into action.
21.Official written information telling an employee that he / she is going to lose his / her job.
22.A feeling of confidence or satisfaction.
Also see Dispute resolution on pages 11–12.
66
For reference see Dictionary of Business — 4th edition (A&C Black Publishers Ltd, 978-0-713-67918-2)
книга выложена группой vk.com/englishlibrary
Answer key
|
Abbreviations (pages 1–2) |
|||||||||||||
|
Across: |
2. European |
4. buyout |
8. selling |
9. business |
|||||||||
|
11. |
technological |
13. Director |
14. investment |
||||||||||
|
15. |
mergers |
17. earnings |
19. earn |
20. Tax |
|||||||||
|
22. opportunities |
25. Executive |
26. vitae |
27. needs |
||||||||||
|
29. |
time |
32. price |
34. Financial |
37. questions |
|||||||||
|
38. injury |
39. index |
41. annum (do not confuse p.a. |
|||||||||||
|
with PA: a personal assistant) |
43. annual |
45. Commerce |
|||||||||||
|
49. information |
51. product |
52. secure |
54. domestic |
||||||||||
|
56. |
person (the plural is VIP’s: very important people / |
||||||||||||
|
persons) |
|||||||||||||
|
Down: |
1. quality |
3. parity |
5. public |
6. meeting |
|||||||||
|
7. relations |
10. credit |
12. Administration 15. methods |
|||||||||||
|
(or sometimes management) |
16. resources |
18. sale |
|||||||||||
|
21. profit |
23. possible |
24. central |
28. delivery |
30. first |
|||||||||
|
31. |
Qualification |
33. |
national |
35. |
Insurance |
||||||||
|
36. development 40. share |
42. thousand |
44. electronic |
|||||||||||
|
46. |
research |
47. postage |
48. Internet |
50. free |
|||||||||
|
53. you (the same pronunciation as the letter u) |
55. time |
Appraisals, training and development (pages 3–5)
Exercise 1:
The questions in this exercise are typical questions that might be asked at an appraisal / assessment interview (sometimes informally called job chats).
|
1. standards |
2. knowledge |
3. quality |
4. objectives |
|||
|
5. improvement |
6. strengths |
7. training |
8. progression |
|||
|
9. schedule |
10. challenging |
11. least |
12. workload |
|||
|
13. description |
14. |
defined |
15. |
advancement |
||
|
16. improving |
17. morale 18. relationship |
19. discipline |
||||
|
20. treatment |
21. promptly 22. complaints 23. progress |
|||||
|
24. praise 25. facilities |
26. provisions 27. recommend |
|||||
|
28. comments |
Normally before an appraisal, employees fill in a selfappraisal form. Note that appraisals / assessments are normally knowledge-based (what the employee knows),and performance-based (how well the employee has worked, and the results s/he has achieved). Appraisals can be two-way, with the employee telling the company how s/he feels about it, and his / her role in it. A good company will always listen to the feedback it receives from its employees.
Performance-based appraisals often use a method known as BARS (behaviourally-anchored rating scales), where performance is based on a typical performance criteria set for each individual employee.
Many companies have adopted the practice of 360degree appraisals. Colleagues above, below and at the same rank as the employee being appraised are asked to contribute their views on that employee before the interview takes place.
If an employee is not performing well in his / her current position, s/he might be given a remedial transfer. This means that s/he is transferred to a more suitable job. The informal expression is a turkey trot.
Note that many of the questions in this exercise might also be asked at an exit interview, when an employee is interviewed before s/he leaves the company. The questions would normally be expressed in the past tense, e.g., Did you think…?, Were you happy…?, etc. In
addition to the questions in the exercise, exit interviews might also ask the employee how s/he felt about the rewards, benefits and services offered by the company (holiday pay, sick pay, pension scheme, health insurance, life assurance, loan facilities, educational assistance, sports and social facilities, refreshment facilities, HR services, etc).
Exercise 2:
1. continuous personal development (also called continual personal development) 2. assertiveness training 3. experiential learning (also called learning by doing) 4. adventure training 5. in-tray learning 6. team-building (an employee who works well as part of
|
a team is called a team player) |
7. carousel learning |
||
|
8. sales training |
9. modern apprenticeship |
10. an |
induction course 11. off-the-job training (training which takes place on the company premises during work time is called on-the-job training or in-house / in-company training) 12. open learning 13. training needs analysis 14. total quality management (TQM)
Note: a trainer is somebody who trains staff, a trainee is somebody who learns how to do something.
Here are some other words and expressions that you might find useful:
|
adult education |
correspondence course team learning |
||
|
distance learning training needs |
performance appraisal |
||
|
staff appraisal |
individual learning |
autonomous learning |
|
|
learning curve |
learning style |
evaluation and assessment |
|
|
work-based learning |
INSET (in-service training) |
Investor in People (a national programme for employee development sponsored by the UK government) managerial grid
|
Changes (page 6–7) |
|||||||
|
Exercise 1: |
|||||||
|
1. widening |
2. sharp decline / fall |
3. general |
|||||
|
improvement |
4. expansion |
5. weakening |
6. tightening |
||||
|
up |
7. constant rise |
8. dramatic increase |
9. steady |
||||
|
decrease |
10. phased out |
11. build up |
12. cuts |
||||
|
13. deterioration 14. considerable growth |
15. upward |
||||||
|
trend |
16. marked progress |
17. upgrade |
18. streamline |
||||
|
19. Downsizing |
20. fluctuated |
21. amended |
|||||
|
22. restructure |
|||||||
|
Exercise 2: |
|||||||
|
1. exchanged |
2. adapt 3. outsourced (if you outsource |
a part of a company, you move part of the company operations from your home country to another country, or
|
from inside your company to |
another |
company) |
|
|
4. |
transformed 5. renovated |
6. switched |
7. vary |
|
8. |
expanded 9. dissolve (we could also use the phrasal |
verb break up) 10. revised (revised prices are usually increased, but they can also go down, as in the first part of this example)
Business colours (page 
1. (a) orange goods (= goods that are not bought as often as fast-moving items such as food products, but are replaced from time to time. (b) brown goods (= electrical equipment for home entertainment). (c) white goods (= machines that are used in the kitchen / utility room. White
книга выложена группой vk.com/englishlibrary

Answer key
goods can also refer to household linen, such as towels and sheets). (d) yellow goods (= high-priced goods which are kept in use for a relatively long time, and so are not replaced very often). (e) red goods (= fast-selling convenience goods, especially food products).
Note that items such as televisions, stereo systems and even clothes could also be classified as yellow goods, especially if they are very expensive.
2. (d) red tape. 3. These informal expressions refer to bank accounts. If an account is in the red, it is showing a debit or loss (e.g., less than £0). If an account is in the black, it is showing a profit, or (if used to refer to a company) having more assets than debt. 4. black (we can also say hidden economy, parallel economy or shadow economy). 5. Green taxes. 6. False. A bluechip investment is the purchase of low-risk shares in a company which is performing well. 7. (b) to blacklist (this can also be a noun: a blacklist). 8. Yes, provided it has received planning permission to do so. Compare greenfield site (= an area of land — usually in the country — that has not been built on before) with brownfield site (= an area of land, especially in an urban area, that had buildings on it in the past, and can be built on again). 9. A white-collar worker is someone who works in an office. A blue-collar worker is someone who works in a factory. 10. white-collar (see number 9 above). 11. Women. This is an informal and rather sexist expression for a job that is normally held by a woman (especially a young one). 12. a black market (often used in the expression a black market economy). 13. Probably a bad thing. Blue-sky ideas (also called blue-sky thinking) are extremely idealistic, ambitious, unrealistic and unconventional. 14. Unhappy: this is an informal expression for stocks and bonds that have no value. 15. All of these.
Contracts (pages 9–10)
Exercise 1:
Here is the complete text:
A contract can be defined as ‘an agreement between two or more parties to create legal obligations between them’. Some contracts are made ‘under seal‘: in other words, they are signed and sealed (stamped) by the parties involved. Most contracts are made verbally or in writing. The essential elements of a contract are: (a) that an offer made by one party should be accepted by the other; (b) consideration (the price in money, goods or some other reward, paid by one party in exchange for another party agreeing to do something); (c) the intention to create legal relations. The terms of a contract may be express (clearly stated) or implied (not clearly stated in the contract, but generally understood). A breach of contract by one party of their contractual liability entitles the other party to sue for damages or, in some cases, to seek specific performance. In such circumstances, the contract may be voided (in other words, it becomes invalid).
|
Exercise 2: |
|
|
1. 1. parts = parties 2. False |
3. C |
|
2. 1. terminator = termination |
2. True 3. obligated / |
|
required |
3. 1. un-negotiable = non-negotiable 2. True (amend = change or alter. The noun is an amendment. You can
|
make an amendment) |
3. oral / spoken / implied / |
|
understood |
(Note that if a contract is on paper, it is called a written contract)
4. 1. in beach of = in breach of (breach can also be a verb:
|
to breach a contract) |
2. abide by (in paragraph 1) |
||
|
3. |
False (they have only broken one of the clauses, or |
||
|
parts, of the contract) |
|||
|
5. |
1. period |
of notification |
= period of notice |
|
2. agreement |
3. True |
||
|
6. 1. anointment = appointment |
2. False (amalgamation |
comes from the verb to amalgamate: to join and become one. We can also say merger, from the verb to merge)
3.False (he is not allowed to have a controlling interest in the company, so his ability to buy stocks is restricted)
4.None (third parties are people or groups other than Mr Wiley and the amalgamation of AKL Publishing and Berryhill Books)
Dispute resolution (pages 11–12)
Exercise 1:
Here is the complete text:
A dispute is an argument or disagreement. In business and commerce, there are usually two types of dispute.
The first of these is an industrial dispute, which is between an employer and an employer’s representative, which in many cases is a trade union. These are usually the result of disagreements over pay, conditions of work and unfair dismissals, including redundancy (the layingoff of employees because they are not needed). The least favourable outcome of this type of dispute is usually industrial action, often in the form of a strike (where employees stop working). Alternatively, employees may stage a go-slow (where they work at less than their normal speed). They may also adopt a work-to-rule strategy, in which they strictly follow all the terms of their contract, and obey other regulations to the letter. They may also refuse to work overtime. The result of this is usually decreased productivity for the company.
The second type of dispute is a commercial dispute, which is a disagreement between two businesses. This is usually the result of a breach of contract (in which one or both sides fails to agree to, or abide by, the terms and conditions of a contract drawn up between them). In extreme cases, this may result in litigation (in which one side brings a suit against the other in a court of law), with the aim of getting financial compensation, or of legally obliging the other side to abide by their contractual obligations.
Disputes do not necessarily have to be settled in an imposed court case. Mediation (an attempt by a disinterested* third party to make two sides in an argument agree) is often quicker, more cost-effective and less stressful for the parties involved.
* Disinterested has a similar meaning to impartial (see exercise 2).
|
Exercise 2: |
||
|
1. alternative |
2. litigation (the verb is to litigate, the |
|
|
adjective is litigious) 3. voluntary / consent 4. |
impartial |
|
|
/ mediator (the verb is to mediate) 5. facilitator |
6. joint |
книга выложена группой vk.com/englishlibrary

Answer key
session / caucus 7. confidential/ disclosed 8. resolutions
|
/ practical / beneficial |
9. negotiations |
10. settlements / |
|
compromise / mutual |
11. bound |
12. prejudice |
|
13. binding / honour |
14. contractually |
15. arbitration |
16. tribunal 17. arbitrator 18. adjudication 19. public domain
Earnings, rewards and benefits 1 (pages 13–14)
|
1. |
wage / salary |
2. |
remuneration |
3. overtime |
||||
|
4. |
increment |
5. deduction |
6. dock |
7. minimum |
||||
|
8. |
double time |
9. time and a half |
10. pension plan |
|||||
|
11. |
rise (we can also say raise) |
12. advance / sub |
||||||
|
13. |
payslip |
14. bonus |
15. payroll |
16. package |
17. weighting (for example, a job advertisement might offer an annual salary of £30,000 + £4,000 London weighting) 18. leave entitlement 19. Income / expenditure 20. stock options (we can also say share options. Some companies have something called an ESOP:
|
an employee share ownership plan) |
21. incentive plans |
||||
|
22. |
rate |
23. redundancy pay |
24. discount |
||
|
25. |
relocation allowance |
26. danger |
27. gross |
||
|
28. |
net |
(also called take-home pay) |
29. index-linked |
||
|
30. |
commensurate (for example, Your |
salary will be |
commensurate with your experience and qualifications)
31. arrears 32. direct deposit 33. performance related
34. golden handshake (some companies also give new employees a golden hello when they accept a job with the company, and some companies may offer new employees a golden parachute, which guarantees them a special payment if they are made redundant)
Earnings, rewards and benefits 2 (page 15)
|
1. |
direct / extrinsic |
2. extrinsic |
/ direct |
3. basic |
|
|
4. performance-related |
5. commissions 6. recognition |
||||
|
7. |
Gainsharing |
8. motivation |
9. production bonus |
10. premium bonus 11. attendance bonus 12. acceptance bonus (informally called a golden hello) 13. Profit sharing
|
14. benefits |
15. extras |
16. pensions |
17. share |
|
18. insurance |
19. duvet days 20. fixed |
21. flexible |
(also known as a cafeteria-style benefits plan) 22. Incentive
|
23. indirect / intrinsic 24. intrinsic / indirect |
25. status |
|
|
26. satisfaction |
27. growth / development |
28. skill |
|
29. development |
30. security 31. comradeship |
Here are some other words and expressions that you might find useful:
|
salaried (the adjective of salary) |
earnings |
real earnings |
||||||
|
take-home pay |
well-paid |
low-paid |
pay packet |
|||||
|
pension contributions |
accrual rate |
hourly / daily rate |
||||||
|
occupational / company pension (scheme) |
remuneration |
|||||||
|
portable pension (scheme) |
per day / per diem |
perks |
||||||
|
increments a year / per annum |
wage / salary review |
|||||||
|
on-target earnings |
parity |
to erode wage differentials |
||||||
|
incentive |
basic / flat rate |
reward management |
||||||
|
broadbanding |
compensation package |
benefit in kind |
||||||
|
reward review |
exploding bonus |
health insurance |
||||||
|
holiday pay |
sick pay |
life assurance |
Formal words (pages 16–17)
Exercise 1:
1. analyse (spelt analyze in American English) 2. assessed at 3. averting 4. administer 5. assigned 6. annulled
|
7. audit 8. appealed to |
9. addressed |
10. award |
||
|
11. admonished |
12. |
awaiting |
13. |
adjusted |
|
14. adjourned 15. appointed |
||||
|
Exercise 2: |
||||
|
1. attend 2. advised |
3. assist |
4. amalgamated |
5. attempt |
6. assured 7. sequestered (we can also say sequestrated) 8. settle 9. tender 10. dismissed 11. engage (we can
|
also say employ, recruit or hire) |
12. waived |
13. present |
||
|
14. elected |
15. licensed |
|||
|
Exercise 3: |
||||
|
1. |
retain |
2. specify |
3. redeployed |
4. consulted |
|
5. |
undertaken 6. reinstated |
7. inquiring (note that in |
this sentence, inquiring must be followed by into: ‘We are inquiring into the background of the new supplier‘.
|
Inquiring can also be written enquiring) |
8. consented |
|
9. notified 10. briefed 11. outlined |
12. upgraded |
The word in the shaded vertical strip (and the one that can be used to replace the words in bold in number 13) is apportioning.
Business idioms (page 18–19)
|
Exercise 1: |
||
|
1. goes belly up 2. rat race |
3. turkey trot |
4. a people |
|
churner 5. an ohnosecond |
6. a dogsbody |
7. a sickie |
8. work rage (also called desk rage when applied to
|
people working in an office) 9. out of the loop |
10. a |
||
|
cushy number |
11. got the boot |
12. pencil-whip |
13. a |
|
helicopter view |
14. eye service |
15. a mushroom job |
16. a Mickey Mouse job 17. swinging the lead 18. a lemon
Exercise 2:
1. stress puppy (= someone who seems to enjoy being under pressure, but still complains about it) 2. shape up or ship out (= improve or leave) 3. empty suit (= someone — usually in a fairly high position — who doesn’t really contribute very much to a company or organisation) 4. kiss up to (= to be very nice and polite to someone in a position of power. It is a negative expression. We can also say schmooze up to or suck up to) 5. dead wood (= the employees who are losing a company money. We can use the expression to cut out the dead wood in this context) 6. glad hand (= to shake hands with people. We can also use the expression press the flesh) 7. seagull manager (= someone who is brought in to a company to deal with a problem or make changes, achieves nothing, annoys everyone and then leaves) 8. ear candy (= kind words of praise and encouragement) 9. wombat (an acronym: waste of money, brains and time. Basket case — see number 14. below — could also be used in this sentence if speaker B is talking about the boss) 10. dumbsizing (= to dismiss the best workers in a company. It is an adaptation of the word downsizing. If a company dismisses those workers who do not contribute much and are losing the company money, we could say that they smartsize) 11. happy camper (= someone who enjoys their job, although the expression is often used ironically) 12. wiggle room (= time to think before making an important decision) 13. busymeet (= a business meeting) 14. basket case (= a company or a person who is in such bad condition that they are beyond help) 15. trim the fat (= dismiss / lay off of those employees who do not work well or are surplus to requirement) 16. cash cow (= a product or service that makes a lot of money with a minimum amount of advertising)
книга выложена группой vk.com/englishlibrary

Answer key
|
IT and e-commerce (pages 20-22) |
|
|
Exercise 1: |
|
|
1. desktop |
2. laptop (also sometimes called a notebook) |
|
3. components |
4. CPU 5. hard drive |
6. hard disk |
||
|
7. |
memory |
8. software |
9. word |
processing |
|
10. |
spreadsheet |
11. DTP 12. load (we can also say |
||
|
install) 13. CD / DVD drive 14. USB port |
15. memory |
|||
|
stick 16. monitor |
17. keyboard |
18. printer |
19. scanner |
|
|
20. |
mouse 21. Internet (sometimes called the World |
Wide Web) 22. provider (also called an Internet Service
|
provider, or ISP) |
23. browser 24. download 25. chatrooms |
|
|
26. newsgroups |
27. website 28. log on 29. pop-up |
|
|
30. search engine 31. keywords |
32. links (also called |
|
|
hyperlinks or hypertext links) |
33. domain (name) |
|
|
34. homepage |
35. on-line 36. log out (we can also say |
|
|
log off) 37. bookmark 38. email |
39. password (most |
email providers also ask their subscribers to enter a
|
username, which is similar to a password) |
40. spam |
|
41. delete 42. attachment 43. virus |
44. crashing |
|
45. anti-virus software 46. update (it) |
Exercise 2:
1. A JPEG is a method of reducing, or compressing, computer files that contain images so that they can be sent quickly by email over the Internet (it is also the name of a file that is produced by this method) 2. A file is a set of information or a document that is stored under a particular name on a computer, a folder is a group of related programs or documents stored together on a computer 3. Freeware is free software available on the Internet, shareware is similar, but users are asked to make a voluntary monetary contribution for its use, or are encouraged to buy a more advanced version 4. Spyware is computer software that secretly records the websites you visit on your computer, and this information is then used by companies who try to sell you things 5. The Internet is a computer system, or network, that allows people in different parts of the world to exchange information (using websites and sending emails, etc). An intranet is a computer network that can only be used within a company or organisation. An extranet is similar to an intranet, but also allows access by others associated with that company or organisation (for example, suppliers, buyers, etc) 6. She has finished shopping and is now going to pay 7. (a) The user ‘signs’ the contract by clicking on a box or boxes to show that he / she agrees
|
with the |
terms and conditions |
8. Internet Service |
|
|
Provider |
9. (b) |
10. (c) (A company that only does |
business on the Internet is called a dot.com business. A company that does not have an Internet shopping facility is known as a bricks and mortar business) 11. Frequently
|
asked questions |
12. |
(a) |
13. Business to business |
|
14. An auto response |
16. |
15. (b) UCE = unsolicited |
|
|
commercial email |
Broadband is a class of |
transmission system that allows large amounts of data to be transferred at high speed over the Internet; an ISDN line is a digital telephone network that supports advanced communication services and can be used for high-speed data transmission 17. (b) 18. personal identification number, a private code number that only the user knows (also required when using a credit / debit card in a cash machine or in a shop) 19. They are forms of on-screen advertising 20. No. An anti-site, also called a hate-site or gripe-site, is a website set up by an unhappy (ex-) customer so that they can publicly say bad things about your company, and encourage other people to do the same 21. A hacker is someone who uses a computer to connect to other people’s computers secretly and often
illegally, so that they can find or change information. The verb is to hack 22. A firewall protects your computer or network, or certain files and folders on that computer / network, from being illegally accessed by a hacker (see number 21 above) 23. If a company is Amazoned, is has lost a large share of its market to a competitor because it has failed to develop an effective business strategy (especially if it has failed to utilise IT technology). This is an informal word, named after the Internet company Amazon.com, who very quickly took a large share of the book market before expanding into other areas 24. (e) Also called a heavy site. This is an informal expression 25. Phishing (pronounced like fishing) is an informal word which refers to sending emails that are designed to trick people into giving away personal information, such as bank account details. This information is then used to steal from those people. More advanced phishers set up bogus websites that look like real websites (especially ones that look like bank websites) that try to trick the unwary or gullible 26. You would probably feel rather unhappy, especially if you were the company’s website manager: a cobweb site is a website that contains a lot of out-of-date information, and if it looks like an angry fruit salad, it has an interface that is particularly unattractive to look at 27. Spider food is an informal expression that refers to words that are embedded in a web page to attract search engines. As a result, your website would receive a lot of visitors 28. You are if you were able to answer most of the questions in this exercise: someone who is buzzword compliant is familiar with the latest computer and IT terms and expressions. It is an informal expression.
Jobs and positions (pages 23–24)
|
Exercise 1: |
||||||||
|
1. Receptionist |
2. Human Resources Manager 3. Secretary |
|||||||
|
4. Girl |
Friday |
(this |
is rather |
a sexist |
expression) |
|||
|
5. Technical Support Consultant |
6. Company Director |
|||||||
|
7. Managing Director 8. Chief Executive Officer 9. Personal |
||||||||
|
Assistant |
10. Company Secretary |
11. Chairman |
||||||
|
12. Non-executive Director |
13. Production Manager |
|||||||
|
14. Assistant Manager |
15. Trainer |
|||||||
|
Exercise 2: |
||||||||
|
1. Accountant 2. External Auditor |
3. Area Manager |
|||||||
|
4. Marketing Manager |
5. Advertising Manager |
6. Sales |
||||||
|
Representative (often shortened to rep) |
7. Foreman |
|||||||
|
8. Trade Union Representative |
9. Official Mediator |
|||||||
|
10. Arbitrator 11. Graduate Trainee |
12. IT Consultant |
|||||||
|
13. Telesales Manager |
14. Official receiver |
15. Security |
||||||
|
Guard |
||||||||
|
Letters (pages 25–27) |
||||||||
|
(A): 6, 22, 46, 47, 56 |
(B): 5, 21, 35, 39, 40 |
(C): 3, 17, |
||||||
|
34, 41, 52 (D): 7, 16, 37, 43, 49 |
(E): 13 (this could also |
|||||||
|
fit in F), 33, 38, 48, 51 |
(F): 2, 9, 23, 29, 59 |
(G): 1, 8, |
||||||
|
25 (this could also fit in H), 26, 60 |
(H): 4, 12, 27, 42, 54 |
|||||||
|
(I): 10, 24, 32, 36, 55 |
(J): 11, 14, 30, 45, 58 |
(K): 15, |
||||||
|
18, 28, 44, 53 |
The following extracts do not match any of the letter types in the box:
19 (a reminder from a company to a client to pay them), 20 (a letter or email reserving a hotel room), 31 (a letter or email requesting something), 50 (a covering letter or note
книга выложена группой vk.com/englishlibrary

Answer key
sent with a catalogue and price list), 57 (an order from a client for some products).
Usage notes:
Begin all letters with Dear + the recipient’s family name (if you know it), or with Dear Sir / Madam if you don’t.
If you are not sure if a woman is married or single, begin it Dear Ms + her family name (this is now the accepted form of address even if you do know whether she is married or not).
Letters that begin with a name (e.g., Dear Mr Brown,
Dear Ms Smith) end with Yours sincerely. Letters that begin with Dear Sir / Madam end with Yours faithfully.
Use the active rather than the passive voice (for example, instead of «Your order has been received«, write «We have received your order«. Instead of «With reference to…«, write «I refer to…«, etc).
Ordinal numbers (for dates, e.g., the first of November, the seventh of April) are sometimes followed by letters (e.g., 1st November, 7th April), but this is less common now than it used to be. 1 November, 7 April, etc, is more common.
You should avoid using abbreviated dates (e.g., 12/11/05) in business letters.
Note that modern business letters should be brief. The message you want to communicate should be done in the most economical way, while remaining clear and polite (remember this acronym: KISS — Keep it short and simple)
Meetings and presentations (page 28)
|
1. open 2. welcoming |
3. participants |
4. attendance |
|||||||
|
5. supporting |
6. agenda |
7. progress |
8. schedule |
||||||
|
9. get through |
10. achieve |
11. goals |
12. objectives |
||||||
|
13. |
chair (we can also say preside over) 14. contribute |
||||||||
|
15. clarification |
16. interrupt |
17. issues |
18. address |
||||||
|
(= discuss/talk about) |
19. bringing |
up |
20. matters |
||||||
|
21. |
priority |
22. |
summarizing |
23. points |
|||||
|
24. |
recommendations |
25. open floor |
26. opinions |
||||||
|
27. |
closes |
28. notes |
29. minutes |
30. report |
|||||
|
31. complaints |
32. questions |
33. floor 34. discuss |
|||||||
|
35. |
conference |
36. |
venue |
37. speakers |
|||||
|
38. |
presentations |
39. delegates |
40. contingency |
41. implement
Money and finance (pages 29–30)
|
Exercise 1: |
|||||||
|
1. lend / borrow |
2. credit / debit |
3. insolvent / bankrupt |
|||||
|
4. dividend / royalty 5. shares / stocks |
6. gross / net |
||||||
|
7. |
deposit / withdraw |
8. tax /duty |
9. income / |
||||
|
expenditure 10. overpriced / exorbitant |
11. wage / |
||||||
|
salary |
12. invoice / receipt |
13. discount / refund |
|||||
|
14. refund / rebate 15. inflation / deflation |
16. pension |
||||||
|
/ |
redundancy |
pay |
17. |
statement / |
balance |
||
|
18. commission / interest |
19. compound / simple |
||||||
|
20. working capital / venture capital |
21. |
fund / |
|||||
|
underwrite 22. audit / budget |
23. subsidize / sponsor |
||||||
|
(or fund) 24. honour / default |
Note that many of the words in this exercise can be used in other ways. For example, the verb deposit in number 7 can also be a noun (a deposit), and the verb withdraw can be made into a noun (a withdrawal).
|
Exercise 2: |
||||
|
1. |
Business overheads |
2. Credit risk |
3. Pension plan |
|
|
4. |
Profit margin |
5. |
Exchange rate |
6. Cash flow |
7. Credit limit 8. Capital gains 9. Down payment
10.Risk management 11. Money laundering
|
12. Offshore banking |
13. Foreign currency |
14. Value |
||
|
added tax 15. Net operating income |
16. |
Operating |
||
|
profit |
17. |
Interest rate 18. Budgetary constraints |
||
|
19. Finance company |
20. Expense account |
21. Return |
||
|
on investment |
22. |
Rate of return |
23. |
Real assets |
24.Dynamic pricing 25. Management buyout
26.Budget deficit 27. Consumer spending
|
28. Income tax |
29. Golden handshake |
30. Price |
|
insensitive |
Numbers and symbols (page 31)
1. 2006 = two thousand and six (some people also say twenty oh six) / 1994 = nineteen ninety four 2. 24/7 = twenty four seven (= 24 hours a day, 7 days a week) 3. 8.4% = eight point four per cent 4. 3.45 = three forty five, or quarter to four 5. 1800 = eighteen hundred (hours) 6. 30 June = the thirtieth of June or June the thirtieth 7. 10/3/07 = the tenth of March two thousand and seven (in the UK) or the third of October two thousand and seven (in the USA). Alternatively, you could say the tenth of the third oh seven 8. 27½ = twenty seven and a half 9. ¾ = three quarters 10. 2m x 1m x 1m = two metres by one metre by one metre 11. £10.99 = ten pounds ninety nine (or ten pounds and ninety nine pence*) 12. £100.99 = one hundred pounds ninety nine (or one hundred pounds and ninety nine pence)
13.£120.75 = one hundred and twenty pounds seventy five (or one hundred and twenty pounds and seventy five pence) / £1120.75 = One thousand, one hundred and twenty pounds seventy five (or one thousand, one hundred and twenty pounds and seventy five pence)
14.ACB81 — 25/B = ACB eighty one dash (or hyphen) 25 slash (or stroke) B 15. 020 7921 3567 = oh two oh,
seven nine two one, three five six seven 16. 0845 601 5884 = oh eight four five, six oh one, five double eight four 17. 0800 231415 = oh eight hundred, two three one four one five (or oh eight hundred, twenty three, fourteen, fifteen)** 18. 999 = nine nine nine / 911 = nine one one 19. # = hash / 0 = zero / * = star 20. £200K = two hundred thousand pounds / mid-50’s = mid-fifties 21. $6M = six million dollars 22. M25 = M twenty five / M4 = M four / A329 = A three two nine (these are British road classifications. M = motorway. A = main road) 23. 2:1 = two to one (when talking about odds and ratios) 24. @snailmail.co.uk = at snailmail dot co dot u k 25. GR8 = great / 
*The British currency, called sterling, consists of pounds (£) and pence (p). £1 = 100p. Some people say pee instead of pence, but many people dislike this.
**For more information on how to say telephone numbers, see the information in the answer key for
Telephoning.
*** 
книга выложена группой vk.com/englishlibrary

Answer key
a smiling face to show happiness. Other emoticons include 

|
Phrasal verbs 1 (pages 32–34) |
||||||||
|
1. |
: run with |
2. |
: fighting against |
3. |
: get across |
|||
|
4. |
: turned down |
5. |
: stand off |
6. |
: find out |
|||
|
7. |
: give up |
8. |
: phased in |
9. |
: carry on |
|||
|
10. |
: hand over |
11. |
: give in |
12. |
: called off |
|||
|
13. |
: standing in |
14. |
: held down |
15. |
: build into |
|||
|
16. |
: broken up |
17. |
: bring down |
17. |
: bring out |
|||
|
18. |
: held back |
19. |
: fill in |
20. |
: broke down |
|||
|
20. |
: brought up |
21. |
: gearing up |
22. |
: cut down |
|||
|
23. |
: burn out |
24. |
: backed out |
25. |
: took up |
|||
|
26. |
: held up |
27. |
: got on |
28. |
: carry out |
|||
|
29. |
: get back |
30. |
: got out |
31. |
: get ahead |
|||
|
32. |
: put off |
33. |
: put out |
34. |
: opt out |
|||
|
35. |
: take on |
36. |
: cancelled out |
37. |
: fallen behind |
Note that some of the phrasal verbs in this exercise actually use two particles. For example: to cut down on something. The second particle appears in the sentence and has not been included in the crossword grid.
Phrasal verbs 2 (page 35)
There are a few possible matches, but these are the best options
|
1. F |
2. M |
3. R 4. T 5. L |
6. A 7. G 8. |
N |
9. Q |
||
|
10. C |
11. J |
12. S |
13. H |
14. I 15. P |
16. O |
||
|
17. E |
18. |
D |
19. K |
20. B |
Production and operations (pages 36–38)
Exercise 1:
1. lead time (also called cycle time) 2. purchasing power
|
3. optimum capacity |
4. assembly line (also called a |
||||||
|
production line) |
5. finished goods |
6. product recall |
|||||
|
7. offshore production |
8. |
planned |
obsolescence |
||||
|
9. supply chain |
10. zero defects |
11. resource allocation |
|||||
|
12. raw materials 13. manufacturing costs |
14. random |
||||||
|
sampling |
15. capacity planning |
||||||
|
Exercise 2: |
|||||||
|
1. bar coding |
2. logistics |
3. preventive maintenance |
|||||
|
(also called preventative maintenance) |
4. intermediate |
||||||
|
goods 5. stockout |
6. down time |
7. margin of error |
|||||
|
8. just in time (usually written just-in-time) |
9. made to |
||||||
|
order |
10. first in, first |
out |
(abbreviated to FIFO) |
11. supply and demand 12. research and development
|
(abbreviated to |
R and D) |
13. global pricing |
|
14. outsourcing |
15. continuous improvement 16. spare |
|
|
parts |
The phrase in the shaded vertical strip is division of labour.
Exercise 3:
There are a few combinations, but these are the best matches:
|
automatic assembly |
batch production |
buffer stock |
|
|
buying manager |
centralised purchasing |
cluster |
|
sampling |
contract manufacturing |
forward scheduling |
|||
|
freight forwarder |
list price |
order book |
paced line |
||
|
quality control |
shop floor |
(= factory floor, in a |
|||
|
production / operations context) |
surplus capacity |
||||
|
Recruitment 1: Job advertising (page 39) |
|||||
|
1. leading |
2. vacancy 3. post (we can also say position |
||||
|
or job) |
4. commencing 5. application (the verb is to |
||||
|
apply) |
6. candidate (we can also say applicant) |
||||
|
7. qualified 8. |
experience |
9. |
team |
10. drive |
11. motivate (the noun is motivation, the adjective is motivated) 12. colleagues (we sometimes use the informal word workmates) 13. responsibilities (we can also say duties) 14. rewards package (we can also say benefits package) 15. basic salary (note that a salary is the money, or pay, you receive every month or year for doing your job; a wage is money you receive every day or week for doing a job: see the section on ‘Rewards and benefits’ elsewhere in this book for more information) 16. commission 17. incentive 18. increment 19. relocation allowance 20. benefits (we can also say rewards) 21. advance 22. CV (= curriculum vitae. We can also say resumé. A CV lists your qualifications and experience in detail, and also provides important personal information — name, age, contact details, etc.) 23. covering letter 24. interview (A person attending an interview is called an interviewee; a person conducting an interview is called an interviewer)
Recruitment 2: The recruitment process (pages 40–41)
Part 1.
1. vacancy 2. recruit 3. staff 4. internally (an internal appointment) 5. externally 6. appointments / situations vacant (informally called the jobs pages or jobs section)
|
7. situations vacant / appointments |
8. |
journals |
||
|
9. recruitment agency 10. institutional agency |
11. job |
|||
|
centres 12. private recruitment agency |
13. description |
|||
|
14. applicants (from the verb to apply) |
15. qualifications |
|||
|
16. experience |
17. personal qualities |
18. rewards |
||
|
(sometimes called remuneration) |
19. increments |
|||
|
20. benefits 21. leave (or holiday) |
22. discrimination |
23.equal opportunities 24. affirmative recruitment
25.disabilities
In Britain, the Equal Opportunities Commission (EOC) is the government body set up to make sure that no sex discrimination exists in employment. The Commission for Racial Equality (CRE) is the statutory body set up to monitor racial matters in companies, and to issue guidelines on best practice. Official legislation ensures that nobody is discriminated against (for example, the Sex Discrimination Act of 1975, the Race Relations Act of 1976, and the Disability Discrimination Act of 1995). Companies have a vicarious liability to ensure that discrimination is not a feature of the workplace.
Part 2.
1. CV (= curriculum vitae) 2. covering 3. introduction 4. application 5. pre-selection 6. turn down 7. short-list
8.candidates 9. one-to-one 10. board 11. psychometric
12.aptitude (compare this with an ability test, which only tests the candidates current skills and knowledge) 13. group
situational 14. in-basket 15. medical (sometimes just called a medical) 16. health screening
книга выложена группой vk.com/englishlibrary

Answer key
A test should have face validity — it should be relevant, useful and give accurate results that indicate how well the employee will perform.
|
Part 3. |
|||||
|
1. |
seven-point plan |
2. |
potential |
3. |
appearance |
|
4. |
intelligence 5. skills |
6. interests |
7. disposition |
||
|
8. circumstances 9. references 10. offered |
11. induction |
||||
|
programme 12. temporary |
13. probationary 14. open- |
||||
|
ended / fixed-term |
15. fixed-term |
/ |
open-ended |
||
|
16. follow-up |
Recruitment 3: Contract of employment and job description (pages 42–43)
|
Exercise 1: |
|
|
1. Term = Terms, conditionals = conditions |
2. employ |
|
= employer 3. employed = employee |
4. titel = title |
5. descriptive = description 6. locally = location 7. Celery = Salary, anum = annum, rears = arrears 8. Started =
|
Starting (or Start) 9. labour = work, |
until = to (Monday |
|
through Friday in American English) |
10. Undertime = |
Overtime, rat = rate 11. enticement = entitlement, anum = annum 12. Absent = Absence (or Absenteeism from work) 13. sceme = scheme (x2), employs = employees 14. Dissiplinary = Disciplinary, grieving = grievance, handybook = handbook, police = policies 15. Probbation
|
= |
Probation (x2), subjective = subject, employees |
|
= |
employment, note = notice 16. Terminator |
=Termination, probbation = probation (or probationary), note = notice 17. Referrals = References (x2) (a person who writes a reference is called a referee), apointments
=appointments 18. singed = signed
Contracts of employment can be temporary, permanent, short term, long term, fixed-term or open-ended. Contracts contain express terms (those that both the employer and the employee agree on), and implied terms (these are not stated in the contract, but impose obligations on both the employer and the employee) Some contracts may contain a restrictive covenant (a clause which prevents an employee from doing something. For example, it may prevent the employee working for another similar company when s/he finishes work in his / her current company).
Contractual liability is a legal responsibility for something as stated in a contract.
Exercise 2:
Here is the complete conversation:
James: Hi, Sarah. How’s the new job going?
Sarah: Oh, not too bad. I’m still trying to find my feet, though.
James: Tell me a bit about it.
Sarah: Well, my official job title is Regional Production Manager, which means that my main accountability is to supervise the work of the production department.
James: Where are you based?
Sarah: Most of my work is done at the head office in central London, but I also have to spend time at our various branches and departments in the area. There are several of these in the South and South-East.
James: Who do you report to?
Sarah: The Central Production Manager. Tom Atkinson, his name is. I’ve only met him a couple of times, but he seems nice enough. We meet once a month to consult each other on major issues. We evaluate the current
state of production, and I recommend any changes that I think need to be made
James: And what about the hours?
Sarah: Pretty typical for this kind of job. I’m on a fulltime contract, which means I work from Monday to Friday, nine to five. And occasionally I have to go in at the weekend, too. I get 21 days leave a year, plus bank holidays.
James: Not bad. And your salary? If you don’t mind me asking?
Sarah: No, not at all. I get £35000 per annum, plus expenses, commission for reaching targets, overtime pay and so on.
James: That’s pretty good for a job that just involves checking things are running smoothly.
Sarah: Well, there’s more to my job than just that. I do have several other key responsibilities.
James: Such as?
Sarah: First of all I have to agree product specifications with sales departments and time schedules with the stock control department. Then I need to ensure that the product is manufactured according to agreed specifications, and I also have to inspect the quality of the finished product.
James: That’s all?
Sarah: No. I also need to negotiate with our suppliers on prices for our base materials, visit those suppliers on a regular basis to check the quality of the base materials… James: Do you have a car for that?
Sarah: Oh yes, the company provides me with one. I also have to deal with problems as they arise on a day-to- day basis, and produce regular sales reports for the Directors.
James: Anything else?
Sarah: Well, on top of everything else, I’m responsible for managing 10 machinists, 3 trainees, 2 cleaners and 2 security guards.
James: That sounds like a lot of work for one person. Can you delegate any of it?
Sarah: Unfortunately no. I have to do it all myself!
Sales and marketing 1 (pages 44–45)
|
1. cowded = crowded |
2. nich = niche |
3. uniqe |
|
|
= unique |
4. feachures = features 5. patient = patent |
||
|
6. inovative = innovative |
7. lunch = launch |
8. brocure |
|
|
= brochure |
9. opmarket = upmarket |
10. reserch |
|
|
= research |
11. advertiseing = advertising |
12. campain |
|
|
= campaign |
13. premote = promote 14. comercials |
= commercials 15. spouts = spots (an informal word) 16. advertisments = advertisements 17. pacement = placement 18. billyboards = billboards (we can also say
|
hoardings) |
19. plop-ups = pop-ups |
20. mailshoots |
|
= mailshots |
21. sponsership = sponsorship 22. endoarse |
|
|
= endorse |
23. opinon = opinion |
24. pont = point |
|
25. |
retale = retail 26. pich = pitch (an informal word) |
|||||||
|
27. |
miscounts = discounts |
28. giveways = giveaways |
||||||
|
29. dommestic = domestic |
30. expot = export 31. raps |
|||||||
|
= reps (= short form of representatives) |
32. franshise |
|||||||
|
= franchise |
33. guarantea = guarantee |
34. where |
||||||
|
= |
wear (part of an expression: |
wear |
and |
tear) |
||||
|
35. merchantizing = merchandizing |
36. brant = brand |
|||||||
|
37. loco = logo |
38. pakaging = packaging |
39. cattalog |
||||||
|
= catalogue |
40. hyp |
= |
hype |
41. |
fat = |
fad |
||
|
42. |
competiton = competition |
43. tramp = trump (an |
||||||
|
informal word) |
44. trucking = tracking |
45. canvince |
||||||
|
= convince |
книга выложена группой vk.com/englishlibrary

Answer key
Sales and marketing 2 (page 46)
1. obsolescence 2. Promotion (promotion is also the selling of a new product through the use of ‘free gifts’, by
|
giving special discounts, etc) 3. Wholesale |
4. bench- |
||
|
marking 5. Spam® |
6. licensing |
7. global |
8. dealer- |
|
ship 9. markdown |
10. sampling 11. diversification |
||
|
12. Telemarketing 13. distributor |
14. freebie |
15. airtime |
The expression in the shaded vertical strip is low-hanging fruit.
Sales and marketing 3 (pages 47–48)
|
1. added value 2. trade fair |
3. brand loyalty |
4. focus |
||||||
|
group 5. break even |
6. reward scheme |
7. price war |
||||||
|
(also called a price-cutting war) |
8. |
white goods |
||||||
|
9. |
mailing |
house |
10. |
product differentiation |
||||
|
11. customer care |
12. cold call 13. crisis management |
|||||||
|
14. |
client base (also called a client |
list) |
15. network |
|||||
|
marketing |
16. loss leader 17. sales forecast |
18. high |
||||||
|
pressure |
19. brand awareness |
20. public relations |
||||||
|
21. market leader |
22. press release |
23. price insensitive |
||||||
|
24. |
product abandonment |
25. consumer protection |
||||||
|
26. |
trade delegation |
27. corporate image |
28. price |
|||||
|
leadership |
29. target market |
30. premium offer |
||||||
|
31. own brand 32. market driven |
Note that, as with other exercises in this book, these words are not always exclusive to the area of sales and marketing, and may be relevant to other business areas.
Similar meanings 1: Nouns (pages 49–50)
|
Exercise 1: |
||||||||||
|
1. agenda / schedule |
2. administration / receivership |
|||||||||
|
3. discipline / order 4. takeover / acquisition |
5. drop / |
|||||||||
|
decline |
6. faults / defects |
7. opposition / resistance |
||||||||
|
8. proof / evidence 9. discount / reduction |
10. proximity |
|||||||||
|
/ closeness 11. appointment / meeting |
12. customers / |
|||||||||
|
clients |
13. |
work / |
employment |
14. |
benefits / |
|||||
|
advantages 15. requirements / prerequisites |
16. acclaim |
|||||||||
|
/ praise |
17. code / rules |
18. liability / responsibility |
||||||||
|
19. |
choices |
/ |
options |
20. staff |
/ |
personnel |
||||
|
21. cooperation / collaboration |
22. charisma / (personal) |
|||||||||
|
appeal |
||||||||||
|
Exercise 2: |
||||||||||
|
1. |
reviews / |
write-ups |
2. |
advertising |
/ publicity |
3. customers / patrons 4. categories / classifications (we
|
could also use plans here) |
5. ending / termination |
||||||||
|
6. entitlement / rights |
7. calibre / intellect and ability |
||||||||
|
8. specialist / expert |
9. assignment / job |
10. notion / |
|||||||
|
idea |
11. |
proficiency / |
skill |
12. achievement / |
|||||
|
accomplishment |
13. ultimatum / final demand |
||||||||
|
14. |
disparity |
/ difference |
15. proceeds |
/ |
earnings |
||||
|
16. |
terms |
/ |
conditions |
17. |
questions |
/ |
queries |
||
|
18. |
outlets |
/ |
shops |
19. problems / |
complications |
20.strategy / plan 21. priority / precedence
22.revisions / changes
Similar meanings 2: Verbs (pages 51–52)
|
Across: 4. assist 9. consent 11. clarify |
12. reserve |
||
|
13. regulate |
14. analyse |
16. gather |
17. address |
|
24. select |
26. generate |
28. administer |
30. confirm |
|
33. audit |
34. |
brief |
35. relate |
37. quantify |
|
39. deduct |
41. oblige 42. widen 43. employ |
|||
|
Down: 1. finalise |
2. imply |
3. consult |
4. accelerate |
|
|
5. handle |
6. |
retain |
7. attend |
8. convey |
|
9. compensate 10. disclose |
12. resolve |
15. substitute |
||
|
18. dictate |
19. assert |
20. advertise |
21. avert |
|
|
22. deplete |
23. reclaim |
25. endorse |
27. prohibit |
|
|
29. influence |
31. award |
32. attempt |
36. ascertain |
|
|
38. acquire |
40. explain |
Similar meanings 3: Adjectives (pages 53-54)
|
Exercise 1: |
||||||||||
|
1. |
extensive |
2. mandatory |
3. resolute |
4. adequate |
||||||
|
5. inconsistent |
6. thorough |
7. overall |
8. scrupulous |
|||||||
|
9. |
discourteous |
10. restricted |
11. vibrant 12. out- |
|||||||
|
dated |
13. abundant |
14. pertinent |
15. inflexible |
|||||||
|
16. risky |
17. basic 18. narrow |
19. abrupt |
20. crucial |
|||||||
|
Exercise 2: |
||||||||||
|
1. prospective |
2. enduring |
3. rudimentary |
4. thriving |
|||||||
|
5. |
voluntary |
6. tedious |
7. steady |
8. disparate |
||||||
|
9. |
profitable |
10. lengthy |
11. nominal |
12. integral |
||||||
|
13. exceptional |
14. compatible |
15. perceptive |
||||||||
|
16. punctual |
17. legitimate |
18. |
industrious |
|||||||
|
19. disciplinary |
20. inventive |
21. important |
22. modern |
|||||||
|
23. diverse 24. efficient |
25. flexible |
26. bankrupt |
On the telephone (pages 55–56)
Exercise 1:
1. engaged / call…back 2. put…through / Hold the line 3. connect / message / voicemail / convenient 4. automated services / zeroing out (= pressing the zero key in the hope that you will speak to someone) / dead / cut off 5. tone / get…back 6. on hold / camping on the line (= waiting on hold or a long time) 7. junk calls (= unsolicited cold calls from companies trying to sell you something) 8. Speaking (= I am the person you want to speak to) / on behalf of / hung up 9. extension / direct line / switchboard / hang on 10. star (= *) / hash (= #)
Exercise 2:
1. as a matter of fact 2. as soon as possible 3. be right back 4. by the way 5. for crying out loud (= an exclamation of frustration and anger) 6. for what it’s worth (= an expression used when giving your opinion about something, usually to someone who has received some bad news and you are trying to make them feel a bit
|
better) |
7. ha ha only kidding (humorous. Kidding |
|
= joking) |
8. hope this helps 9. I am not a lawyer (used |
humorously when someone asks you a complicated question, especially about legal matters) 10. in my opinion 11. in other words 12. keep it simple, stupid (humorous. It can also mean keep it short and simple) 13. my eyes glaze over (humorous, used for saying that
|
something is extremely boring) |
14. mind your own |
|
business (usually humorous) |
15. on the other hand |
|
16. with respect to |
Note that, sometimes, abbreviations use letters that are not used at the beginning of the word, but are instead pronounced like the word itself. For example, ‘CUL‘ means ‘See you later‘. Numbers are also used to represent words or parts of words. For example, ‘UR2L8‘ means ‘You are too late‘.
книга выложена группой vk.com/englishlibrary

Answer key
When we say telephone numbers, we usually speak each number individually. For example: 020 7837 7324 is usually spoken as ‘Oh two oh / seven eight three seven / seven three two four‘.
If a number is doubled, we normally say ‘double‘ before it. For example: 0845 601 5884 is usually spoken as ‘Oh eight four five / six oh one / five double eight four‘
If a telephone number has one or more zeros after a number, and no numbers after it, we often say it as one number. For example: 0800 800 151 is often spoken as ‘Oh eight hundred / eight hundred / one five one‘.
Six-figure numbers are becoming increasingly spoken as three separate numbers. For example: 0800 201215 is spoken ‘Oh eight hundred / twenty / twelve / fifteen‘.
Trade (pages 57–58)
Here are the complete sentences, with the answers in bold.
When you bring goods into a country you import them. When you send them out of a country you export them.
A group of manufacturers or suppliers who visit another country to increase their sales there is known as a trade delegation.
Cargo — also called freight — is a general word for goods which are transported in a ship, plane etc. It is usually carried in a container (= a very large metal case of a standard size).
A bill of lading is a list of goods being transported, which the transporter gives to the person sending the goods, to show them that the goods have been loaded. The person receiving the goods should receive a packing list, showing them the goods that they should be receiving.
A letter of credit — often abbreviated to L/C — is a document issued by a bank on behalf of a customer authorising payment to a supplier when conditions specified in the document are met.
A pro-forma invoice is an invoice sent to a buyer before the goods are sent, so that payment can be made (or so that goods can be sent to a consignee who is not the buyer).
COD is a payment which is made for goods when they arrive. COD stands for cash on delivery.
A group of goods sent for sale by road, sea or air is called a consignment.
CIF refers to the price a buyer has to pay for goods which have to be transported. It stands for cost, insurance and freight.
Goods sent by air are called airfreight. Goods sent by sea are called seafreight.
FOB stand for free on board. It refers to the price a buyer pays a seller for goods. The price includes all the seller’s costs until the goods are on the ship, plane, etc, for transportation.
Import duty — also sometimes called an import levy — is a tax which has to be paid on goods coming into a country. A customs tariff is a list of those taxes that must be paid.
A person or company which arranges shipping and customs documents is called a forwarding agent.
If tax on imported goods is not paid, those goods may be impounded (in other words, they are kept in a secure warehouse at or near the port of entry until that tax is paid).
A clearing agent arranges the import and delivery of goods at their port of destination.
As soon as goods are allowed into a country by the customs officer, we can say that they have been cleared.
A record of the international trading position of a country in merchandise (= goods), excluding invisible trade, is called the balance of trade.
A wholesale price is a price paid by customers (for example, shops) who buy goods in large quantities. They sell these goods to individual customers (for example, shoppers) at a higher price which is called the retail price. Some offer discounts to their customers, which means they pay a little less
A licensing agreement allows a company to market or produce goods or services owned by another company, and is a popular means for a company to penetrate the overseas market.
A quota is a limited amount of a good that can be brought into a country (usually as an incentive for people to buy home-produced versions of that good). This is an example of a trade barrier.
When goods are sold within one country, they are transported to their place of sale by a distributor.
Business travel (pages 59–60)
|
Exercise 1: |
||
|
1. delayed |
2. overbooked |
3. tourist or coach or |
|
economy |
4. embarkation or boarding 5. transit 6. gate |
7. non-stop (a direct flight may land somewhere between its departure point and its destination, although the passengers do not need to change planes, and may not even need to leave the plane they are on. For example, a direct flight from London to Singapore may land, or stop
|
over, in Dubai for a couple of hours) |
8. |
domestic |
|
9. single or one-way / return trip or round-trip |
10. credit |
limit 11. crew 12. commuters 13. carrier or airline 14. comprehensive 15. 4×4 (pronounced four by four, also called an SUV)
Exercise 2:
1. schedule or itinerary 2. trip (voyage does not really work here, as this word usually refers to a long journey by
|
land or sea) |
3. valid (validate is a verb) |
4. runs out or |
||
|
expires (although expires is a better word) |
5. visa |
|||
|
6. embassy |
7. traveller’s |
cheques |
8. |
currency |
|
9. exchange |
10. deal 11. commission |
12. insurance |
||
|
13. vaccinations 14. provider |
15. network |
Exercise 3:
1. At the airport (at the check-in desk) or at a hotel (when you check into your room) 2. Your baggage weighs more than the allowed amount, and so you have to pay extra money for the airline to carry it 3. Your flight has been overbooked (see number 2 in Exercise 1) and your
|
seat has been given to someone else |
4. You want to |
|
move to a higher class of travel (for |
example, from |
economy class to business class) 5. Transport from the airport to your hotel or another place at your destination 6. No. Passengers flying between countries in the EU (the European Union) are not allowed a duty free allowance (ie, alcohol, cigarettes, perfume, etc, on which a special tax has to be paid) 7. fare 8. A ticket for a journey (especially one by aircraft) which is stored in a computer and is not given to the passenger (who usually has a receipt for the ticket instead) 9. No. Jet lag is usually experienced by people flying from west to east, and vice versa. Cape Town is in the same time zone as London, so passengers should not be affected by time changes 10. Full board accommodation means that the price of
книга выложена группой vk.com/englishlibrary

Answer key
Answer key
your room includes all meals; half board includes room, breakfast and your evening meal; bed and breakfast (B and B) includes your room and breakfast only. 11. A single room has one small bed, a twin room has two small beds, a double room has one large bed, a suite has one large bed and will also have a separate area with a sofa, armchair, etc, for relaxing 12. The full price for staying in a room, with no discount 13. (a) housekeeping, (b) reception, (c) maintenance, (d) switchboard, (e) room service, (f) concierge 14. wardrobe, safe, mini bar, balcony, air conditioning, tea and coffee facilities, Internet access, iron, television, remote control (for the television and / or air conditioning) 15. Probably not: the adjectives in italics are negative 16. In many situations where a service is provided, such as in a taxi, in a restaurant, at a hairdresser, at a hotel when the porter carries your bags to your room, etc.
|
Word association (page 61) |
|||||||||
|
1. pension |
2. business |
3. job |
4. price |
5. corporate |
|||||
|
6. cost |
7. tax |
8. industrial |
9. minimum |
10. salary |
|||||
|
11. strike |
12. shift |
13. management |
14. health |
||||||
|
15. labour |
16. employment |
17. insurance |
18. career |
||||||
|
19. market |
20. income |
21. customer |
22. private |
||||||
|
23. staff |
24. |
group |
25. |
contract |
26. sales |
||||
|
27. personal |
28. brand |
||||||||
|
Working hours and time off work (pages 62–64) |
|||||||||
|
Exercise 1: |
|||||||||
|
1. time-keeping |
2. |
allowed |
time |
3. job-share |
|||||
|
4. flexitime |
5. flexileader |
6. flexilagger |
7. unsocial |
||||||
|
hours |
8. full-time |
9. part-time |
10. double time |
||||||
|
11. time and a half |
12. overtime |
13. core time |
|||||||
|
14. shift transfer |
15. fixed hours 16. rotating shifts |
17. graveyard shift 18. homeworking (people who do this are sometimes referred to as open-collar workers) 19. roster 20. clock off (used informally even if you do not use a card and machine: «Right, that’s it. I’m clocking off for the day«. We can also say clock out. When we
|
arrive for work we clock on or clock in) |
21. time sheet |
|
22. Flexible Work Regulations (see |
note *1 below) |
23. work-life balance (see note *2 below) 24. shift differentials 25. twilight shift 26. job rotation
*1: In Britain, the Working Time Directive of 1998 (based on guidelines set by the European Union) sets out the following regulations: Employees should work no more than 48 hours a week, and should receive a minimum of 4 weeks’ paid leave a year. They should have a weekly rest period of at least 24 consecutive hours, a daily break of at least 20 minutes for every six hours worked, and a daily rest period of 11 consecutive hours. There are different directives for some groups (e.g., pilots, bus drivers, doctors, etc) whose jobs are more stressful, demand greater concentration, or whose performance might affect other people.
*2: Work-life balance is the subject of widespread debate
on how to allow employees more control over their working arrangements so that they have more time for their outside activities and responsibilities, but in a way that will still benefit the organisations they work for. Flexible working practices and family-friendly policies are two areas of work-life balance that are frequently the focus of debate.
|
Exercise 2: |
||
|
1. medical (also called a doctor’s certificate) |
2. statutory |
|
|
(SSP = statutory sick pay) |
3. maternity |
4. unpaid |
5. gardening 6. sabbatical (this word is especially used for teachers, university professors, etc, who take time away from their school or college) 7. absenteeism 8. public holiday (called a bank holiday in the UK, and a legal holiday in the USA) 9. long-service 10. entitlement 11. unauthorised (also spelt unauthorized. An employee who takes unauthorised leave is or goes AWOL: absent
|
without leave) |
12. waiting |
13. absence |
14. in lieu |
|
(usually abbreviated to TOIL) |
15. paternity |
16. casual |
|
|
17. vacation |
18. benefit |
The expression in the shaded vertical strip is compassionate leave.
|
Workplace problems (pages 65–66) |
|||||||
|
Exercise 1: |
|||||||
|
Paragraph (A) 1. dispute |
2. resolved 3. strike 4. arbitrate |
||||||
|
Paragraph (B) |
1. fraud |
2. discrimination |
3. bullying |
||||
|
4. racial |
5. abuse |
6. sexual |
7. harassment 8. fired |
||||
|
9. suspended |
10. unfair |
11. dismissal (we can also say |
|||||
|
wrongful dismissal) |
12. appeal |
||||||
|
Paragraph (C) 1. breaches |
2. neglecting (this can also be |
||||||
|
a noun: neglect of duties) |
3. insubordination |
4. damage |
|||||
|
5. disciplinary |
6. board |
7. instant |
8. dismissal |
||||
|
9. zero tolerance |
|||||||
|
Paragraph |
(D) 1. |
shortages |
2. overstretched |
||||
|
3. grievance |
4. walkout |
5. verbal 6. warning (after a |
verbal warning, an employee might receive a written warning) 7. notice (when a company asks you for your notice, they are politely telling you that they are going to force you to resign)
|
Paragraph (E) 1. dropped |
2. |
redundant |
3. resigned |
||||
|
4. bankrupt |
5. hacked 6. virus 7. crashed 8. order |
||||||
|
(out of order = broken / not working) |
|||||||
|
Paragraph (F) 1. plateauing |
2. stimulation |
3. motivation |
|||||
|
4. initiative |
5. productivity 6. implement |
||||||
|
Paragraph (G) 1. turnover |
2. retention |
3. conflict |
|||||
|
4. absenteeism |
5. timekeeping |
6. misconduct 7. morale |
|||||
|
8. industrial |
9. counsel |
10. grievances |
|||||
|
Exercise 2: |
|||||||
|
1. absenteeism |
2. plateauing |
3. counsel |
4. turnover |
||||
|
5. redundant |
6. dispute |
7. overstretched |
8. arbitrate |
||||
|
9. discrimination |
10. harassment |
11. grievance |
|||||
|
12. motivation |
13. misconduct |
14. breach |
15. walkout |
16. initiative 17. insubordination (usually used in a work
|
environment where there |
are |
strict rules and a strict |
||
|
hierarchy) |
18. appeal |
19. |
verbal |
20. implement |
|
21. notice |
22. morale |
76
Соседние файлы в предмете [НЕСОРТИРОВАННОЕ]
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
Все категории
- Фотография и видеосъемка
- Знания
- Другое
- Гороскопы, магия, гадания
- Общество и политика
- Образование
- Путешествия и туризм
- Искусство и культура
- Города и страны
- Строительство и ремонт
- Работа и карьера
- Спорт
- Стиль и красота
- Юридическая консультация
- Компьютеры и интернет
- Товары и услуги
- Темы для взрослых
- Семья и дом
- Животные и растения
- Еда и кулинария
- Здоровье и медицина
- Авто и мото
- Бизнес и финансы
- Философия, непознанное
- Досуг и развлечения
- Знакомства, любовь, отношения
- Наука и техника
12
_________ and detective stories, science fiction and comics. I would like to tell you about my favourite ____________. “ Harry Potter” is one of the most ________books I have ever read. In this story the children have dangerous ____________ and fight with the evil (зло) My favorite ___________ is Ron Weasley. He is very __________. This policeman put many _________ behind the bars. 3. Put the verbs into Past Simple: Mr. Johnson ………………. (find) 10$ in the park yesterday. Columbus ……………………… (discover) America. We ………………………… (watch) TV last night. Marry …………………….(send) an e-mail to her friend an hour ago. J. Rowling ……………………… (write) 8 books about Harry Potter and his friends. 4. Make up sentences using used to construction: I play football when I was 10. Matt not have a lot of free time when he was a student. Fiona wake up late before she found a job. Karl live with his parent when he was a student. They play computer games when they were 11.
1 ответ:
0
0
#1
Sherlock Holmes is famous for his neat appearance.
A mystery is a story about a crime or a strange event.
Agatha Christy created a lot of famous detectives.
The police started an investigation into the crime.
The young man hid behind some bushes.
Sherlock ran out after the criminal.
The detective put up a fight with the burglar.
The children hide an old chest.
There are a lot of small shops in the area.
It is an amazing book.
#2
enjoy adventure
book amazing
aventures
character funny
criminals
#3
fond
discovered
watched
sent
wrote
#4
When I was 10 I play football.
When he was a student Matt not have a lot of free time.
Fiona woke up late before she found a job.
Karl live with his parents when he was a student.
When they were 11 they play computer games.
Читайте также
1.Has Mary got a long green skirt?
2.Has the dog a big bone?
3.Have you got a nice sister?
4.Has you niece a husband?
5.Have Henry and Mark got a grandmother?
6.Has Alice got a father?
7.Has the man got a car?
8.Have they got three little dolls?
9.Have you got a green apple?
10.Has the cat a little fish?
Our country can participate in this international exposition
Сочинение мой любимый вид спорта — плаванье. <span>
hello! I want to tell you some information about me. Last time , I am fond of sport and i want to tell you about my favourite kind of sport. I am fond of swiimming. I go in for swimming and i like it so much. i attend the swimming pool, i train in the swimming pool twice a week. I like my trains. i have many friends there and we like to spend time together and speak about how sport influents in our health and life. Also i have my favourite swimmer. His name is Michael Phelps. I want to be like him.
</span> Сочинение мой любимый вид спорта — велоспорт.
hello! I want to tell you some information about me. Last time , I am fond of sport and i want to tell you about my favourite kind of sport. I am fond of cycling. I go in for cycling and i like it so much. i attend the cycling Club, i train in the cycling Club twice a week. I like my trains. i have many friends there and we like to spend time together and speak about how sport influents in our health and life.
1)I don’t want you to scream so loud. 2)I would like my sister to earn more. 3) John doesn’t expect that we come at 5 o’clock. 4)My mother doesn’t want me to become a seamstress. 5)All parents want their kids to be honest and bold.
9.В
10.В
11.В
12.С
13.В
14.В
АС
1. Choose the best word to fit the gap.
1 It’s important to understand how other cultures behave so you don’t cause .
A offence B problem C disaster D behaviour
2 In some countries it is quite to use the correct title when talking to business colleagues.
A offensive B likely C formal D tricky
3 Having good may help you to make deals more easily.
A entertaining B manners C demonstrations D handshaking
4 Ian has to be very organised as his work involves meeting tight .
A problems B responsibilities C challenges D deadlines
5 Lesley doesn’t like having to wait for other people to work for her.
A generate B solve C resolve D tackle
6 Paul enjoys working at Small World because he finds the stimulating.
A installation B environment C application D opportunity
7 If someone looks me straight in the eye without I tend to think they are honest.
A yawning B sighing C blinking D sniffing
8 Your body usually gives other people information about how you really feel.
A appearance B impression C language D relationship
9 Bob and Tony are business and have arranged to meet at the sales conference.
A delegates B customers C associates D officers
10 I’ve given the latest sales to Mr Allen but he hasn’t had a chance to look at them yet.
A systems B figures C worksheets D facts
Автор: Гость
Read the article. Choose the best word (A, B or C) for each space.
The World is Getting Hotter
The world is getting hotter because 1) ………. us! Our factories, cars, trains and planes 2) ………. the air dirty. When 3) ………. sun shines, everything gets hot and the dirt stops the hot air from going 4) ………. to the sky. Because the hot air has nowhere to go, 5) ………. gets hotter.
Already our world is 6) ………. than it was one hundred years ago. Hot countries may become drier and the people who live there will not be able to grow enough food. Ice in cold areas 7) ………. changing to water because of higher temperatures. When this happens, the seas become bigger. Some towns 
We can help 9) ………. we stop making the air dirty but we 10) ………. do something fast!
1) A. by B. for C. of
2) A. make B. making C. makes
3) A. a B. the C. an
4) A. on B. at C. up
5) A. everything B. all C. every
6) A. warm B. warmer C. warmest
7) A. are B. be C. is

9) A. so B. if C. but
10) A. must B. should C. can
3a Выберите лучшее слово (А, В, С или D) для каждого пропуска (1-8).
Ты с нетерпением 1) ждешь, когда пойдешь в школу или ты абсолютно боишься(dread) этого? Или, возможно, ты бы предпочел пойти в школу где-то еще! На этой неделе журнал Go рассмотрит, насколько разными бывают школы 2) в мире.
А.
В мире существует много видов школ. Некоторые дорогие, частные школы-интернаты, как, например Школа Регби в Англии, где была изобретена(inventend) игра регби! Также есть специальные школы, например школы драмы, танцевальные школы или 40 акробатических школ в Уцяо, в Китае. Это может звучать смешно, но как объясняет 13-летний Чжан Ли: «Наша тренировка(training) начинается 5:30 утра. Это очень тяжело, но эти навыки(skills) помогут мне 3) зарабатывать на жизнь, когда я закончу школу». Также в разных школах огромное количество учебных предметов. В Средней школе Холдена в США, предметы включают в себя рисование комиксов, уроки фотографии, написание песен и йогу.
В.
В школе в горах Аннапурна в Непале, занятия не начинаются раньше 10 утра потому, что многие ученики вынуждены пройти пешком час, чтобы добраться до школы. В Японии нет ничего необычного(unusual) в том, чтобы 4) тратить 2 часа или больше, чтобы добраться до школы на общественном транспорте(public trasport) «Это не так уж и плохо» — говорит 15-летний Кейко из Токио. «Иногда я учусь или сплю в поезде, и это хороший способ догнать моих друзей 5) по учебе».
С.
Средняя продолжительность учебного дня в Великобритании и США – 6 с половиной часов для учащихся средней школы. Ученикам в Корее и Греции, 6) однако не так повезло! После школы они посещают(attend) дополнительные занятия в частных школах. «Обычно, — говорит Джи Ким из Сеула, Южная Корея, — я не возвращаюсь домой раньше полуночи, но если я не буду упорно заниматься, я не 7) поступлю в хороший университет».
D.
Во всех школах есть правила, но иногда они действительно строгие(strict). В колледже Итон, очень известной школе-интернате для мальчиков в Англии, студенты носят изящную(smart), но очень старомодную форму(old-fashioned unifom) с длинным пиджаком, штанами и рубашкой; в Японии все должны участвовать(participate) в «о содзи» или уборке школы перед тем, как идти домой, в то время как в школе Саммерхилл в Англии, где студенты сами 
Е.
Итак, твоя школа лучше или хуже, чем школы в других частях мира? Неважно каков твой ответ, мы не должны забывать, что у 300 миллионов детей в мире нет школ, чтобы в них ходить. Так что если ты даже захочешь изменить какие-то вещи в своей школе, ты один из счастливчиков!
1-D
2-B
3-D
4-C
5-A
6-B
7-A
8-C
Task 1
11 b (some)
12 c (because)
13 a (more)
14 b (give)
15 a (during)
16 c (they)
17 b (have)
18 c (also)
Task 2
Read the text and put the verbs in brackets 19–31 in the correct tense. The first one is done for you.
Do you agree Happy Birthday to You (0) is (be) the world’s most famous song? It (19) is recognised by just about everyone. In fact somebody probably (20) is singing it somewhere in the world at this moment! But what are the origins of a tune which (21) has become so famous?
In 1893 two teachers Patty and Mildred J.Hill (22) wrote a song. They (23) called it Good Morning to You. They (24) taught it to their kindergarten pupils in Kentucky, USA. The children (25) found the song easy to learn and sing.
The present song (26) has the same tune but different words. Millions of people (27) have sung the song in many different languages since those days.
Not long ago it (28) was my birthday. My guests (29) gave me many presents. And I (30) heard (не употребляется в continuous) this wonderful song when I (31) blew out the candles on the cake.
Task 3
underground (BrE) — subway (AmE)
car park (BrE) — parking lot (AmE)
chips (BrE) — fries (AmE)
form (BrE) – grade (AmE)
petrol (BrE) – gas (AmE)
ground floor (BrE) — first floor (AmE)
shop (BrE) – store (AmE)
ill (BrE) — sick (AmE)
rubbish (BrE) — garbage (AmE)
wardrobe (BrE) – cabinet (AmE)
handbag (BrE) — purse (AmE)
TEST
YOUR VOCABULARY 4
9. Choose
the word 1
Choose the best
word to complete each sentence.
|
1 |
After hours of walking across |
||||||
|
A |
ghost |
B |
mirage |
C |
trick |
D |
mirror |
|
2 |
The boxer recovered, although |
||||||
|
A |
unconscious |
B |
asleep |
C |
stopped |
D |
ignorant |
|
3 |
Today’s football match has |
||||||
|
A |
put away |
B |
cancelled |
C |
decided |
D |
postponed |
|
4 |
If workers and bosses cannot |
||||||
|
A |
settle |
B |
decide |
C |
arbitrate |
D |
compromise |
|
5 |
The soldiers __________ around |
||||||
|
A |
walked |
B |
marched |
C |
strolled |
D |
ran |
|
6 |
The very idea of my sister |
||||||
|
A |
risky |
B |
dishonest |
C |
futile |
D |
absurd |
|
7 |
Heavy snow __________ the |
||||||
|
A |
cancelled |
B |
hindered |
C |
delayed |
D |
postponed |
|
8 |
According to the weather __________, |
||||||
|
A |
programme |
B |
information |
C |
forecast |
D |
news |
|
9 |
I liked her. She gave me the __________ |
||||||
|
A |
impression |
B |
thought |
C |
idea |
D |
picture |
|
10 |
The __________ of the ship now |
||||||
|
A |
crash |
B |
body |
C |
corpse |
D |
wreck |
Sometimes a
dictionary definition is not enough. You need to see words in action. Extensive
reading is the secret of success.
Answer key
