Хитрости »
1 Май 2011 162370 просмотров
Как защитить лист от пользователя, но не от макроса?
Иногда бывает полезно защитить данные на листе от изменений другими пользователями, но при этом так же надо будет работать с данными на листе из VBA(т.е. вносить изменения с помощью кода). Обычная защита листа, конечно, подходит, хоть и есть небольшой недостаток: надо перед каждым обращением к листу снимать с него защиту, выполнять необходимые действия и защищать заново:
Sub Write_in_ProtectSheet() 'снимаем защиту с листа Worksheets("Лист1").Unprotect 'если лист защищен с паролем 1234: Worksheets("Лист1").Unprotect "1234" 'действия на листе.Например,изменение значения ячейки А1 Cells("A1").Value = "www.excel-vba.ru" 'устанавливаем защиту на лист Worksheets("Лист1").Protect 'если лист был защищен с паролем 1234: Worksheets("Лист1").Protect "1234" End Sub
Но есть метод проще.
Если выполнить ниже приведенную строчку кода, то пользователю невозможно будет изменить данные на листе(кроме тех, которые Вы сами разрешите), однако код VBA(макрос) сможет преспокойно вносить любые изменения, не снимая защиту.
Sub Protect_for_User_Non_for_VBA() ActiveSheet.Protect Password:="1111", UserInterfaceOnly:=True End Sub
Основную роль здесь играет параметр UserInterfaceOnly. Если его установить в True, то это говорит Excel-ю, что коды VBA могут выполнять действия по изменению ячеек, не снимая защиты методом Unprotect. Однако сама защита листа при этом не снимается и вручную изменить данные ячеек, не сняв защиту с листа, невозможно.
Код выше устанавливает такую защиту только на активный лист книги. Но можно указать лист явно(например установить защиту на лист с именем Лист1 в активной книге и лист, идущий вторым по порядку в книге(Sheets(2))):
Sub Protect_for_User_Non_for_VBA() Sheets(2).Protect Password:="1111", UserInterfaceOnly:=True Sheets("Лист1").Protect Password:="1111", UserInterfaceOnly:=True End Sub
Так же приведенный код можно еще чуть модернизировать и разрешить пользователю помимо изменения ячеек еще и использовать автофильтр:
Sub Protect_for_User_Non_for_VBA() Sheets(2).Protect Password:="1111", UserInterfaceOnly:=True 'на лист "Лист1" поставим защиту и разрешим пользоваться фильтром Sheets("Лист1").Protect Password:="1111", AllowFiltering:=True, UserInterfaceOnly:=True End Sub
Можно разрешить и другие действия(выделение незащищенных ячеек, выделение защищенных ячеек, форматирование ячеек, вставку строк, вставку столбцов и т.д. Чуть подробнее про доступные параметры можно узнать в статье Защита листов и ячеек в MS Excel). А как будет выглядеть строка кода с разрешенными параметрами можно узнать, записав макрорекордером установку защиты листа с нужными параметрами:
После этого получится строка вроде такой:
ActiveSheet.Protect DrawingObjects:=True, Contents:=True, Scenarios:=True _ , AllowInsertingColumns:=True, AllowInsertingRows:=True, AllowFiltering:=True
здесь я разрешил использовать автофильтр(AllowFiltering:=True), вставлять строки(AllowInsertingRows:=True) и столбцы(AllowInsertingColumns:=True).Чтобы добавить возможность изменять данные ячеек только через код VBA, останется добавить параметр UserInterfaceOnly:=True:
ActiveSheet.Protect DrawingObjects:=True, Contents:=True, Scenarios:=True _ , AllowInsertingColumns:=True, AllowInsertingRows:=True, AllowFiltering:=True, UserInterfaceOnly:=True
и так же неплохо бы добавить и пароль для снятия защиты, т.к. запись макрорекордером не записывает пароль:
ActiveSheet.Protect DrawingObjects:=True, Contents:=True, Scenarios:=True _ , AllowInsertingColumns:=True, AllowInsertingRows:=True, AllowFiltering:=True, UserInterfaceOnly:=True, Password:="1111"
Этот метод всем хорош, все отлично, но. Параметр UserInterfaceOnly сбрасывается сразу после закрытия книги. Т.е. если установить таким образом защиту на лист и закрыть книгу, то при следующем открытии защиты этой уже не будет — останется лишь стандартная защита. Поэтому, если необходимо такую защиту видеть постоянно, то данный макрос лучше всего прописывать на событие открытия книги(модуль ЭтаКнига(ThisWorkbook)).
Сделать это можно таким кодом:
Private Sub Workbook_Open() Sheets("Лист1").Protect Password:="1111", UserInterfaceOnly:=True End Sub
Этот код сработает только после того, как книга будет открыта. А это значит, чтобы увидеть результат необходимо после записи этого кода в ЭтаКнига сохранить книгу, закрыть её и открыть заново. Тогда в сам момент открытия книги код сработает и установит на «Лист1» правильную защиту.
Часто так же бывает необходимо устанавливать одинаковую защиту на все листы книги. Сделать это можно таким кодом, который так же должен быть размещен в модуле ЭтаКнига(ThisWorkbook):
Private Sub Workbook_Open() Dim wsSh As Object For Each wsSh In Me.Sheets Protect_for_User_Non_for_VBA wsSh Next wsSh End Sub Sub Protect_for_User_Non_for_VBA(wsSh As Worksheet) wsSh.Protect Password:="1111", UserInterfaceOnly:=True End Sub
Плюс во избежание ошибок лучше перед установкой защиты снимать ранее установленную(если она была):
Sub Protect_for_User_Non_for_VBA(wsSh As Worksheet) wsSh.Unrotect "1111" wsSh.Protect Password:="1111", UserInterfaceOnly:=True End Sub
Ну и если надо такую защиту установить только на конкретные листы, то убираем цикл и вызываем процедуру только для нужных листов. Если известны их имена, то можно прибегнуть к использованию массивов:
Private Sub Workbook_Open() Dim arr, sSh arr = Array("Отчет", "База", "Бланк") For Each sSh in arr Protect_for_User_Non_for_VBA Me.Sheets(sSh) Next End Sub Sub Protect_for_User_Non_for_VBA(wsSh As Worksheet) wsSh.Protect Password:="1111", AllowFiltering:=True, UserInterfaceOnly:=True End Sub
Для применения в своих задачах в данном коде необходимо лишь изменить(добавить, удалить, вписать другие имена) имена листов в этой строке: Array(«Отчет», «База», «Бланк»)
Примечание: Метод защиты через UsefInterface всем хорош, но есть одно ограничение: метод невозможно использовать в книге с общим доступом(Рецензирование -Доступ к книге), т.к. при общем доступе существуют ограничения, среди которых и такое, которое запрещает изменять параметры защиты для книги в общем доступе.
Также см.:
Как разрешить изменять только выбранные ячейки?
Защита листов/снятие защиты
Как оставить возможность работать со структурой на защищенном листе?
Статья помогла? Поделись ссылкой с друзьями!
Видеоуроки
Поиск по меткам
Access
apple watch
Multex
Power Query и Power BI
VBA управление кодами
Бесплатные надстройки
Дата и время
Записки
ИП
Надстройки
Печать
Политика Конфиденциальности
Почта
Программы
Работа с приложениями
Разработка приложений
Росстат
Тренинги и вебинары
Финансовые
Форматирование
Функции Excel
акции MulTEx
ссылки
статистика
Protecting and unprotecting sheets is a common action for an Excel user. There is nothing worse than when somebody, who doesn’t know what they’re doing, overtypes essential formulas and cell values. It’s even worse when that person happens to be us; all it takes is one accidental keypress, and suddenly the entire worksheet is filled with errors. In this post, we explore using VBA to protect and unprotect sheets.
Protection is not foolproof but prevents accidental alteration by an unknowing user.
Sheet protection is particularly frustrating as it has to be applied one sheet at a time. If we only need to protect a single sheet, that’s fine. But if we have more than 5 sheets, it is going to take a while. This is why so many people turn to a VBA solution.
The VBA Code Snippets below show how to do most activities related to protecting and unprotecting sheets.
Download the example file: Click the link below to download the example file used for this post:
Adapting the code for your purposes
Unless stated otherwise, every example below is based on one specific worksheet. Each code includes Sheets(“Sheet1”)., this means the action will be applied to that specific sheet. For example, the following protects Sheet1.
Sheets("Sheet1").ProtectBut there are lots of ways to reference sheets for protecting or unprotecting. Therefore we can change the syntax to use one of the methods shown below.
Using the active sheet
The active sheet is whichever sheet is currently being used within the Excel window.
ActiveSheet.ProtectApplying a sheet to a variable
If we want to apply protection to a sheet stored as a variable, we could use the following.
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = Sheets("Sheet1")
ws.ProtectLater in the post, we look at code examples to loop through each sheet and apply protection quickly.
Let’s begin with some simple examples to protect and unprotect sheets in Excel.
Protect a sheet without a password
Sub ProtectSheet()
'Protect a worksheet
Sheets("Sheet1").Protect
End SubUnprotect a sheet (no password)
Sub UnProtectSheet()
'Unprotect a worksheet
Sheets("Sheet1").Unprotect
End SubProtecting and unprotecting with a password
Adding a password to give an extra layer of protection is easy enough with VBA. The password in these examples is hardcoded into the macro; this may not be the best for your scenario. It may be better to apply using a string variable, or capturing user passwords with an InputBox.
VBA Protect sheet with password
Sub ProtectSheetWithPassword()
'Protect worksheet with a password
Sheets("Sheet1").Protect Password:="myPassword"
End SubVBA Unprotect sheet with a password
Sub UnProtectSheetWithPassword()
'Unprotect a worksheet with a password
Sheets("Sheet1").Unprotect Password:="myPassword"
End SubNOTE – It is not necessary to unprotect, then re-protect a sheet to change the settings. Instead, just protect again with the new settings.
Using a password based on user input
Using a password that is included in the code may partly defeat the benefit of having a password. Therefore, the codes in this section provide examples of using VBA to protect and unprotect based on user input. In both scenarios, clicking Cancel is equivalent to entering no password.
Protect with a user-input password
Sub ProtectSheetWithPasswordFromUser()
'Protect worksheet with a password
Sheets("Sheet1").Protect Password:=InputBox("Enter a protection password:")
End SubUnprotect with a user-input password
Sub UnProtectSheetWithPasswordFromUser()
'Protect worksheet with a password
Sheets("Sheet1").Unprotect _
Password:=InputBox("Enter a protection password:")
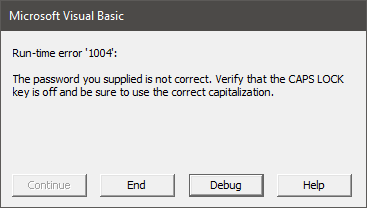
End SubCatching errors when incorrect password entered
If an incorrect password is provided, the following error message displays.
The code below catches the error and provides a custom message.
Sub CatchErrorForWrongPassword()
'Keep going even if error found
On Error Resume Next
'Apply the wrong password
Sheets("Sheet1").Unprotect Password:="incorrectPassword"
'Check if an error has occured
If Err.Number <> 0 Then
MsgBox "The Password Provided is incorrect"
Exit Sub
End If
'Reset to show normal error messages
On Error GoTo 0
End SubIf you forget a password, don’t worry, the protection is easy to remove.
Applying protection to different parts of the worksheet
VBA provides the ability to protect 3 aspects of the worksheet:
- Contents – what you see on the grid
- Objects – the shapes and charts which are on the face of the grid
- Scenarios – the scenarios contained in the What If Analysis section of the Ribbon
By default, the standard protect feature will apply all three types of protection at the same time. However, we can be specific about which elements of the worksheet are protected.
Protect contents
Sub ProtectSheetContents()
'Apply worksheet contents protection only
Sheets("Sheet1").Protect Password:="myPassword", _
DrawingObjects:=False, _
Contents:=True, _
Scenarios:=False
End SubProtect objects
Sub ProtectSheetObjects()
'Apply worksheet objects protection only
Sheets("Sheet1").Protect Password:="myPassword", _
DrawingObjects:=True, _
Contents:=False, _
Scenarios:=False
End SubProtect scenarios
Sub ProtectSheetScenarios()
'Apply worksheet scenario protection only
Sheets("Sheet1").Protect Password:="myPassword", _
DrawingObjects:=False, _
Contents:=False, _
Scenarios:=True
End SubProtect contents, objects and scenarios
Sub ProtectSheetAll()
'Apply worksheet protection to contents, objects and scenarios
Sheets("Sheet1").Protect Password:="myPassword", _
DrawingObjects:=True, _
Contents:=True, _
Scenarios:=True
End SubApplying protection to multiple sheets
As we have seen, protection is applied one sheet at a time. Therefore, looping is an excellent way to apply settings to a lot of sheets quickly. The examples in this section don’t just apply to Sheet1, as the previous examples have, but include all worksheets or all selected worksheets.
Protect all worksheets in the active workbook
Sub ProtectAllWorksheets()
'Create a variable to hold worksheets
Dim ws As Worksheet
'Loop through each worksheet in the active workbook
For Each ws In ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets
'Protect each worksheet
ws.Protect Password:="myPassword"
Next ws
End SubProtect the selected sheets in the active workbook
Sub ProtectSelectedWorksheets()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim sheetArray As Variant
'Capture the selected sheets
Set sheetArray = ActiveWindow.SelectedSheets
'Loop through each worksheet in the active workbook
For Each ws In sheetArray
On Error Resume Next
'Select the worksheet
ws.Select
'Protect each worksheet
ws.Protect Password:="myPassword"
On Error GoTo 0
Next ws
sheetArray.Select
End SubUnprotect all sheets in active workbook
Sub UnprotectAllWorksheets()
'Create a variable to hold worksheets
Dim ws As Worksheet
'Loop through each worksheet in the active workbook
For Each ws In ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets
'Unprotect each worksheet
ws.Unprotect Password:="myPassword"
Next ws
End SubChecking if a worksheet is protected
The codes in this section check if each type of protection has been applied.
Check if Sheet contents is protected
Sub CheckIfSheetContentsProtected()
'Check if worksheets contents is protected
If Sheets("Sheet1").ProtectContents Then MsgBox "Protected Contents"
End SubCheck if Sheet objects are protected
Sub CheckIfSheetObjectsProtected()
'Check if worksheet objects are protected
If Sheets("Sheet1").ProtectDrawingObjects Then MsgBox "Protected Objects"
End SubCheck if Sheet scenarios are protected
Sub CheckIfSheetScenariosProtected()
'Check if worksheet scenarios are protected
If Sheets("Sheet1").ProtectScenarios Then MsgBox "Protected Scenarios"
End SubChanging the locked or unlocked status of cells, objects and scenarios
When a sheet is protected, unlocked items can still be edited. The following codes demonstrate how to lock and unlock ranges, cells, charts, shapes and scenarios.
When the sheet is unprotected, the lock setting has no impact. Each object becomes locked on protection.
All the examples in this section set each object/item to lock when protected. To set as unlocked, change the value to False.
Lock a cell
Sub LockACell()
'Changing the options to lock or unlock cells
Sheets("Sheet1").Range("A1").Locked = True
End SubLock all cells
Sub LockAllCells()
'Changing the options to lock or unlock cells all cells
Sheets("Sheet1").Cells.Locked = True
End SubLock a chart
Sub LockAChart()
'Changing the options to lock or unlock charts
Sheets("Sheet1").ChartObjects("Chart 1").Locked = True
End SubLock a shape
Sub LockAShape()
'Changing the option to lock or unlock shapes
Sheets("Sheet1").Shapes("Rectangle 1").Locked = True
End SubLock a Scenario
Sub LockAScenario()
'Changing the option to lock or unlock a scenario
Sheets("Sheet1").Scenarios("scenarioName").Locked = True
End SubAllowing actions to be performed even when protected
Even when protected, we can allow specific operations, such as inserting rows, formatting cells, sorting, etc. These are the same options as found when manually protecting the sheet.
Allow sheet actions when protected
Sub AllowSheetActionsWhenProtected()
'Allowing certain actions even if the worksheet is protected
Sheets("Sheet1").Protect Password:="myPassword", _
DrawingObjects:=False, _
Contents:=True, _
Scenarios:=False, _
AllowFormattingCells:=True, _
AllowFormattingColumns:=True, _
AllowFormattingRows:=True, _
AllowInsertingColumns:=False, _
AllowInsertingRows:=False, _
AllowInsertingHyperlinks:=False, _
AllowDeletingColumns:=True, _
AllowDeletingRows:=True, _
AllowSorting:=False, _
AllowFiltering:=False, _
AllowUsingPivotTables:=False
End SubAllow selection of any cells
Sub AllowSelectionAnyCells()
'Allowing selection of locked or unlocked cells
Sheets("Sheet1").EnableSelection = xlNoRestrictions
End SubAllow selection of unlocked cells
Sub AllowSelectionUnlockedCells()
'Allowing selection of unlocked cells only
Sheets("Sheet1").EnableSelection = xlUnlockedCells
End SubDon’t allow selection of any cells
Sub NoSelectionAllowed()
'Do not allow selection of any cells
Sheets("Sheet1").EnableSelection = xlNoSelection
End SubAllowing VBA code to make changes, even when protected
Even when protected, we still want our macros to make changes to the sheet. The following VBA code changes the setting to allow macros to make changes to a protected sheet.
Sub AllowVBAChangesOnProtectedSheet()
'Enable changes to worksheet by VBA code, even if protected
Sheets("Sheet1").Protect Password:="myPassword", _
UserInterfaceOnly:=True
End SubUnfortunately, this setting is not saved within the workbook. It needs to be run every time the workbook opens. Therefore, calling the code in the Workbook_Open event of the Workbook module is probably the best option.
Allowing the use of the Group and Ungroup feature
To enable users to make use of the Group and Ungroup feature of protected sheets, we need to allow changes to the user interface and enable outlining.
Sub AllowGroupingAndUngroupOnProtectedSheet()
'Allow user to group and ungroup whilst protected
Sheets("Sheet1").Protect Password:="myPassword", _
UserInterfaceOnly:=True
Sheets("Sheets1").EnableOutlining = True
End SubAs noted above the UserInterfaceOnly setting is not stored in the workbook; therefore, it needs to be run every time the workbook opens.
Conclusion
Wow! That was a lot of code examples; hopefully, this covers everything you would ever need for using VBA to protect and unprotect sheets.
Related posts:
- Office Scripts – Workbook & worksheet protection
- VBA Code to Password Protect an Excel file
- VBA code to Protect and Unprotect Workbooks
About the author
Hey, I’m Mark, and I run Excel Off The Grid.
My parents tell me that at the age of 7 I declared I was going to become a qualified accountant. I was either psychic or had no imagination, as that is exactly what happened. However, it wasn’t until I was 35 that my journey really began.
In 2015, I started a new job, for which I was regularly working after 10pm. As a result, I rarely saw my children during the week. So, I started searching for the secrets to automating Excel. I discovered that by building a small number of simple tools, I could combine them together in different ways to automate nearly all my regular tasks. This meant I could work less hours (and I got pay raises!). Today, I teach these techniques to other professionals in our training program so they too can spend less time at work (and more time with their children and doing the things they love).
Do you need help adapting this post to your needs?
I’m guessing the examples in this post don’t exactly match your situation. We all use Excel differently, so it’s impossible to write a post that will meet everybody’s needs. By taking the time to understand the techniques and principles in this post (and elsewhere on this site), you should be able to adapt it to your needs.
But, if you’re still struggling you should:
- Read other blogs, or watch YouTube videos on the same topic. You will benefit much more by discovering your own solutions.
- Ask the ‘Excel Ninja’ in your office. It’s amazing what things other people know.
- Ask a question in a forum like Mr Excel, or the Microsoft Answers Community. Remember, the people on these forums are generally giving their time for free. So take care to craft your question, make sure it’s clear and concise. List all the things you’ve tried, and provide screenshots, code segments and example workbooks.
- Use Excel Rescue, who are my consultancy partner. They help by providing solutions to smaller Excel problems.
What next?
Don’t go yet, there is plenty more to learn on Excel Off The Grid. Check out the latest posts:
In this Article
- Unprotect Excel Worksheet Without Password
- Unprotect Excel Worksheet With Password
- Unprotect Sheet – Lost Password
- Protect Worksheets
- Protect Worksheet – Without Password
- Protect Worksheet – Password Protect
- Protect Worksheet Settings
- Protect Sheet – Allow VBA to Make Changes
- Unprotect All Sheets Macro
- Protect All Sheets Macro
This tutorial will teach you everything about Excel Worksheet protection in VBA – How to Protect or Unprotect Worksheets in Excel.
Unprotect Excel Worksheet Without Password
To unprotect a Worksheet that isn’t password-protected use this simple line of code:
Worksheets("Sheet1").UnprotectUnprotect Excel Worksheet With Password
To unprotect a Worksheet that’s password-protected, you must also enter the password:
Worksheets("Sheet1").Unprotect "Password"Unprotect Sheet – Lost Password
To unprotect a Worksheet without knowing the password, you must use a password recovery add-in.
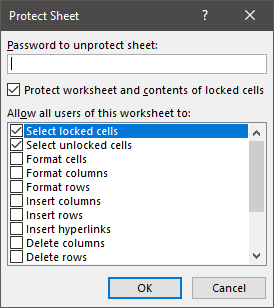
Protect Worksheets
Worksheet Protection allows you to lock certain aspects of the sheet from editing.
This menu is found in Home > Format > Protect sheet or by right-clicking on the Sheet tab name:
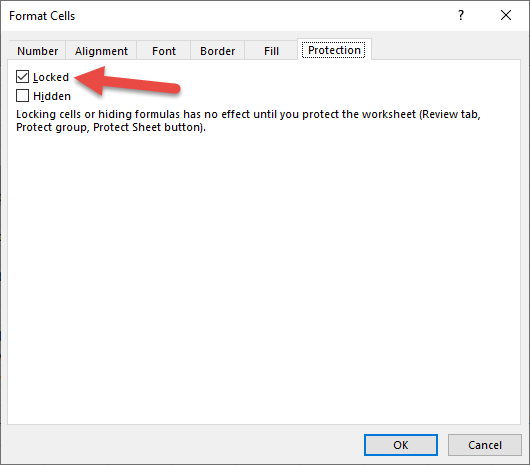
Most commonly this is used to protect “Locked” cells from editing, only allowing the end-user to edit certain cells.
You can lock cells by selecting them, and opening the Protection tab of the Cell Formatting Menu (CTRL + 1).
You can also prevent the user from changing the worksheet structure (inserting, deleting, or resizing Rows & Columns), or from interacting with AutoFilters, and much more.
Protect Worksheet – Without Password
You might want to protect a Worksheet without entering a password. This will prevent accidental changes to the worksheet, while giving the user access to make changes if desired.
Worksheets("Sheet1").ProtectProtect Worksheet – Password Protect
Worksheets("Sheet1").Protect "Password"VBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro — A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Learn More
Protect Worksheet Settings
The above examples will protect Worksheets with the standard protection settings. Instead you might want to customize what is protected:
Worksheets("Sheet1").Protect Password:=strPassword, DrawingObjects:=True, Contents:=True, Scenarios:=True, _
UserInterfaceOnly:=True, AllowFormattingCells:=False, AllowFormattingColumns:=False, _
AllowFormattingRows:=False, AllowInsertingColumns:=False, AllowInsertingRows:=False, _
AllowInsertingHyperlinks:=False, AllowDeletingColumns:=False, AllowDeletingRows:=False, _
AllowSorting:=False, AllowFiltering:=False, AllowUsingPivotTables:=FalseInstead of using the syntax above, I recommend recording a Macro with your desired settings (chosen with the Worksheet Protection menu above) and copying + pasting the recorded code into your procedure.
Protect Sheet – Allow VBA to Make Changes
By default, when you protect a sheet, the protection applies to VBA operations in addition to user actions. If VBA attempts to modify a locked cell, you will see a runtime error 1004. To avoid this, you could unprotect and re-protect your worksheets whenever VBA needs to interact with them:
Sub Edit_Sheet1()
'Unprotect Sheet1
Worksheets("Sheet1").Unprotect
'Do Something to Sheet1
'Reprotect Sheet1
Worksheets("Sheet1").Protect
End SubHowever, it’s easy to forget to unprotect and/or re-protect your worksheets. This can can increase the probability of a coding error.
Instead, you can use the UserInterFaceOnly setting. When TRUE, worksheets will ONLY be protected from users, NOT from VBA. Your VBA code will be free to edit the worksheet just like if it was unlocked.
Two important points about UserInterFaceOnly:
- This setting is not available from the Worksheet Protection menu (shown above). It’s a setting that must be defined in VBA.
- The setting is not saved when you close a workbook. It must be re-defined each time a workbook is opened.
So in order to set the UserInterFaceOnly property, you should place the following Workbook_Open event procedure in ThisWorkbook module:
Private Sub Workbook_Open()
Dim ws As Worksheet
For Each ws In ThisWorkbook.Worksheets
ws.Protect UserInterfaceOnly:=True
Next ws
End SubWorkbook_Open is a special event procedure that will run each time the workbook is open. It must be placed in the ThisWorkbook module. Alternatively, you could use the Auto_Open event procedure (not covered here).
Unprotect All Sheets Macro
This Macro will unprotect all Sheets in a workbook:
' UnProtect All Worksheets
Sub UnProtectAllSheets()
Dim ws As Worksheet
For Each ws In Worksheets
ws.Unprotect "password"
Next ws
End SubVBA Programming | Code Generator does work for you!
Protect All Sheets Macro
This Macro will protect all Sheets in a Workbook:
' Protect All Worksheets
Sub ProtectAllSheets()
Dim ws As Worksheet
For Each ws In Worksheets
ws.Protect "password"
Next ws
End SubExcel VBA Protecting Sheet
We can protect the Excel sheet using VBA code which does not allow the user to make any changes to the worksheet data. All they can do is just read the report. For this, we have a built-in VBA method called “Protect.”
Like we protect our worksheets in Excel; similarly, we can use VBA to protect our worksheets. There are two methods to protect the sheet using a .protect statement. One is with a password, and another is without a password. The syntax to protect a worksheet is as follows Worksheets().Protect Password.
We usually share the end report with the user or reader. When we share the end report with the user, we wish the user would not make any modifications or manipulate the end report. It is all about trust in such a scenario.
Table of contents
- Excel VBA Protecting Sheet
- Syntax
- How to Protect Sheet using VBA Code?
- Step 1: Select Sheet which needs to be protected
- Step 2: Define Worksheet Variable
- Step 3: Give Worksheet Reference
- Step 4: Select Protect Method
- Step 5: Enter Password
- Step 6: Run the Code
- Recommended Articles
Syntax
The protecting sheet involves various parameters to supply. It is unlike Unprotecting the sheet. Let us look at the syntax of the Protect method with a password.
Don’t get intimidated by looking at the syntax. Instead, have a look at the explanation of each argument below.
- Worksheet Name: First, we must mention which worksheet we will protect.
- Password: We need to enter the password we are using to protect. If we ignore this parameter, Excel will lock the sheet without a password. While unprotecting it, it will unprotect without asking for any password.
- Note: Remember the password you are giving, because if you forget, you must go through various hard ways.
- Drawing Object: If you wish to protect objects in the worksheet, you can pass the argument as TRUE or else FALSE. The default value is TRUE.
- Contents: To protect the contents of the worksheet, set the parameter as TRUE or else FALSE. The default value is FALSE. So, it will protect only locked cells. And the default value is TRUE.
- Scenarios: If there are any what-if analysis in excelWhat-If Analysis in Excel is a tool for creating various models, scenarios, and data tables. It enables one to examine how a change in values influences the outcomes in the sheet. The three components of What-If analysis are Scenario Manager, Goal Seek in Excel, and Data Table in Excel.read more scenarios, we can also protect them. To protect TRUE or else FALSE. The default value is TRUE.
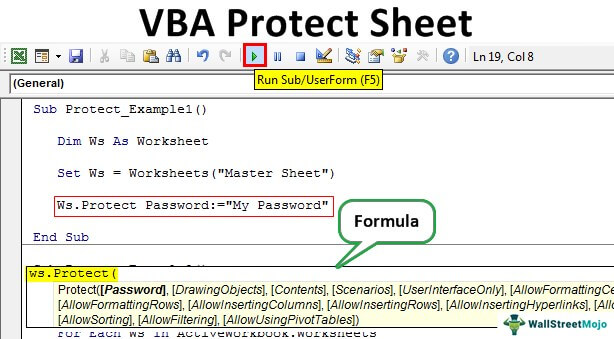
- User Interface Only: If you want to protect the user interface other than Macro, it should be TRUE. If this argument is omitted, it will protect Macros and the user interface. If you set the argument to TRUE, it will only protect the user interface. The default value is FALSE.
- Allow Formatting Cells: If you want to allow the user to format the cell, then you can set the parameter to TRUE or else FALSE. The default value is FALSE.
- Allow Formatting Columns: If you want to allow the user to format any column in the protected sheet, then you can set the parameter to TRUE or else FALSE. The default value is FALSE.
- Allow Formatting Rows: If you want to allow the user to format any row in the protected sheet, then you can set the parameter to TRUE or else FALSE. The default value is FALSE.
- Allow Insert Columns in VBA: If you wish to allow the user to insert new columns, then you need to set this to TRUE. The default value is FALSE.
- Allow Insert Rows: If you wish to allow the user to insert new rowsTo insert rows we use worksheet method with the insert command to insert a row, we also provide a row reference where we want to insert another row similar to the columns.read more, you must set this to TRUE. The default value is FALSE.
- Allow Insert Hyperlinks: If you wish to allow the user to insert hyperlinks, then you need to set this to TRUE. The default value is FALSE.
- Allow Deleting Columns: If you wish to allow the user to delete columns in VBAIn VBA, deleting columns is simple. To select the column, we must first use the COLUMNS property, and then construct the syntax for the column delete method in VBA as follows: Columns (Column Reference). Deleteread more, then you need to set this to TRUE. The default value is FALSE.
- Allow Deleting Rows: If you wish to allow the user to delete rows, you need to set this to TRUE. The default value is FALSE.
- Allow Sorting: If you wish to allow the user to sort the data, you need to set this to TRUE. The default value is FALSE.
- Allow Filtering: If you wish to allow the user to filter the data, then you need to set this to TRUE. The default value is FALSE.
- Allow Using Pivot Tables: If you wish to allow the user to use pivot tablesA Pivot Table is an Excel tool that allows you to extract data in a preferred format (dashboard/reports) from large data sets contained within a worksheet. It can summarize, sort, group, and reorganize data, as well as execute other complex calculations on it.read more, then you need to set this to TRUE. The default value is FALSE.
How to Protect Sheet using VBA Code?
You can download this VBA Protect Sheet Excel Template here – VBA Protect Sheet Excel Template
Step 1: Select the Sheet which needs to be protected
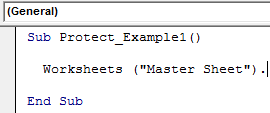
The first step is to decide which sheet we need to protect using a password to protect the sheet. Next, we need to call the sheet by name using the VBA Worksheet Object.
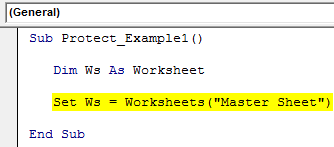
For example, assume you want to protect the “Master Sheet” sheet, then you need to mention the worksheet name below.
Step 2: Define Worksheet Variable
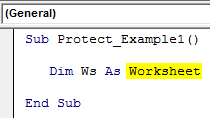
After mentioning the worksheet name, put a dot, but we don’t see any IntelliSense list to work with. So, it makes the job difficult. To access the IntelliSense list, define the variable as a worksheet.
Code:
Sub Protect_Example1() Dim Ws As Worksheet End Sub
Step 3: Give Worksheet Reference
Now, set the worksheet reference to the variable as Worksheets(“Master Sheet”).
Code:
Sub Protect_Example1() Dim Ws As Worksheet Set Ws = Worksheets("Master Sheet") End Sub
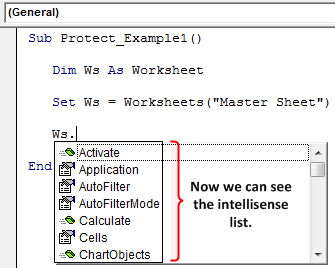
Now, the variable “Ws” holds the reference of the worksheet named “Master Sheet.” By using this variable, we can access the IntelliSense list.
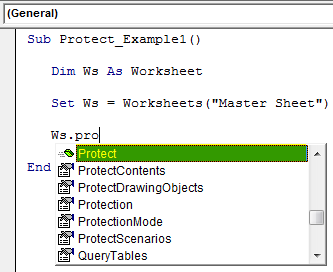
Step 4: Select Protect Method
Select the “Protect” method from the IntelliSense list.
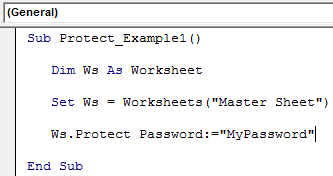
Step 5: Enter Password
Specify the password in double-quotes.
Code:
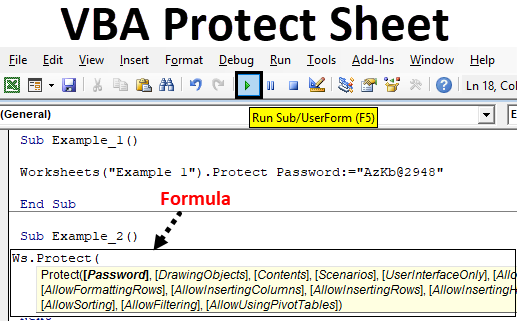
Sub Protect_Example1() Dim Ws As Worksheet Set Ws = Worksheets("Master Sheet") Ws.Protect Password:="MyPassword" End Sub
Step 6: Run the Code
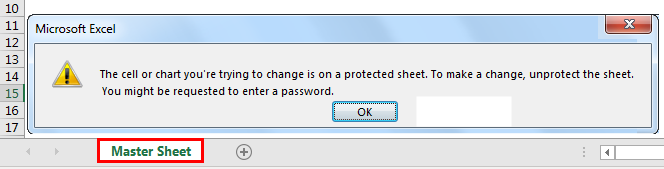
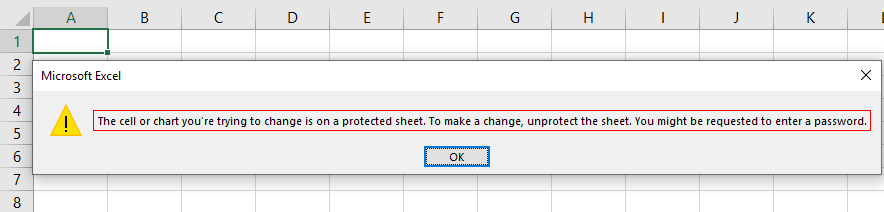
Run the code manually or use the shortcut key F5. Then, it will protect the sheet named “Master Sheet.”
When the sheet is protected, if we want to modify it, it shows an error message, as shown below.
We need to use loops if you wish to protect more than one sheet. Below is the example code to protect the sheet.
Sub Protect_Example2() Dim Ws As Worksheet For Each Ws In ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets Ws.Protect Password:="My Passw0rd" Next Ws End Sub
Note: Use other parameters to experiment.
Recommended Articles
This article is a guide to VBA Protect Sheets. Here, we learn how to use Protect methods in VBA to protect or lock an Excel sheet using a password, along with a practical example and a downloadable template. Below you can find some useful Excel VBA articles: –
- VBA Do Loop
- Rename Sheet in VBA
- Activate a Sheet with VBA Code
- Use WorksheetFunction in VBA
Excel VBA Protect Sheet
Protecting a worksheet is an important task for those who work on Microsoft Excel very frequently. It is a task you need to protect your sheet from being edited by some other user. Suppose you are sending a report to management and then the management knowingly or by mistake changes the parameters or values through the report. It becomes hectic to identify the bug as well as at the same time the rework is something that consumes your time. In order to overcome this issue, it is always a good practice to protect a sheet/s for being edited using a password. This option helps you by not allowing a user to make any changes within the sheet/s. You also can share the password with the person who is intended as well as authorized to make the changes. Though Excel has Protect Worksheet option within it through the Review tab present at the Excel ribbon, it becomes hectic when you have more than one-sheets to protect. It will consume ample of your time protecting each sheet one by one. Instead, it is a good practice to write a VBA code which can protect either single or multiple sheets from your workbook for being edited.
Syntax of VBA Protect Sheet
This built-in VBA function associated with Worksheet, allows you to protect the sheet with the help of password. The syntax for VBA Protect Sheet function is as below:
All the parameters are optional in this function which you can guess through the squared brackets mentioned for each of them.
- Password: Specifies password for the sheet. If not provided, sheet will be protected without a password and the user can edit it without being asked for a password.
- DrawingObjects: Optional arguments which allow you to protect different shapes of the worksheet. Takes Boolean values. By default set to FALSE.
- Contents: Optional argument. Protects all objects. By default values is set to TRUE.
- Scenarios: Protects all different scenarios. Default value is set to TRUE.
- UserInterfaceOnly: It protects the user interface but not the macros. The default value is TRUE if the macro is ignored, as well as the user interface will be protected.
- AllowFormattingCells: Default value is set to FALSE due to which user can’t format the cells of the sheet. If set TRUE, the user can format the cells from the sheet.
- AllowInsertingColumns: Default value set to FALSE. If set TRUE, user can insert a column into the sheet.
- AllowInsertingRows: Default value is set to FALSE. If set TRUE, user can insert rows into the sheet.
- AllowInsertingHyperlinks: Default value is set to FALSE. If set TRUE, user can insert hyperlinks in the sheet.
- AllowDeletingColumns: Default value is set to FALSE. If set TRUE, user can delete any column from the sheet.
- AllowDeletingRows: Default value is set to FALSE. If set TRUE, user can delete any number of rows from the sheet.
- AllowSorting: Default value is set to FALSE. If set TRUE, the user can sort the data present in the sheet.
- AllowFiltering: Default value is set to FALSE. If set TRUE, the user can filter the data present in the sheet.
- AllowUsingPivotTables: Default value is set to FALSE. If set TRUE, user can use and modify the pivot tables.
How to Protect Sheet in Excel VBA?
Below are the different examples to protect sheet in Excel using VBA Protect.
You can download this VBA Protect Sheet Excel Template here – VBA Protect Sheet Excel Template
VBA Protect Sheet – Example #1
Suppose we have a sheet named as “Example 1” in a workbook named “VBA Protect Sheet”. We want this sheet to be protected with a password. For this, follow the below steps:
Step 1: Insert a new module in Visual Basic Editor (VBE). Click on Insert > select Module.
Step 2: Define a new sub-procedure within the module.
Code:
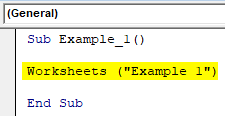
Sub Example_1() End Sub
Step 3: Now we have to use the Protect function which can be applied on an object called Worksheet. Start the code with Worksheets object and type the name of a worksheet within parentheses which you want to be protected.
Code:
Sub Example_1() Worksheets("Example 1") End Sub
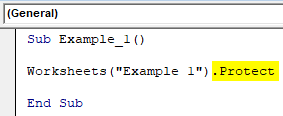
Step 4: Now, put a dot after the closing parentheses and use Protect keyword which initiates the process of protecting the sheet named “Example 1”.
Code:
Sub Example_1() Worksheets("Example 1").Protect End Sub
You can stop here while protecting a sheet. As all the arguments are optional, your sheet still will be protected but will not ask the user to input the password before editing and will be same as an unprotected sheet. You surely would not want it this way. Therefore add a strong password to protect this sheet in the next step.
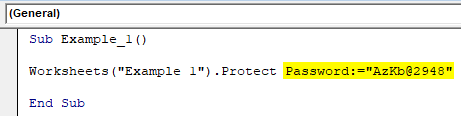
Step 5: Enter Password keyword and use a strong password to protect this sheet.
Code:
Sub Example_1() Worksheets("Example 1").Protect Password:="[email protected]" End Sub
We will only use the first argument of the function which is called as Password and for rest all arguments we will go with the default values.
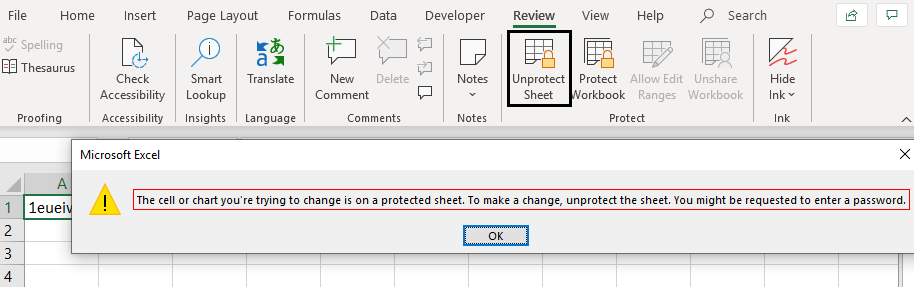
Step 6: This is it, you can run this code by hitting F5 or Run button and can see that the file is now protected and will ask user the password as soon as he/she tries to edit any of the cells.
This is how we protect a sheet using VBA Protect function.
VBA Protect Sheet – Example #2
Now, we want to protect all the sheets present in a workbook. For this, follow the below steps:
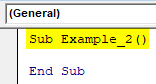
Step 1: Define a sub-procedure in the module.
Code:
Sub Example_2() End Sub
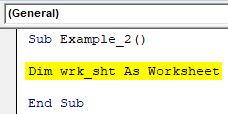
Step 2: Define a new variable as worksheet using Dim.
Code:
Sub Example_2() Dim wrk_sht As Worksheet End Sub
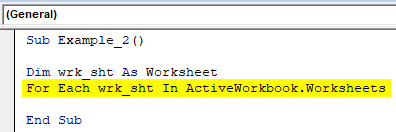
Step 3: Start a For loop. This loop should run until the last Worksheet of Active Workbook.
Code:
Sub Example_2() Dim wrk_sht As Worksheet For Each wrk_sht In ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets End Sub
This line of code selects each worksheet of the active workbook and stores it under variable wrk_sht for each iteration of the loop. Loop ends as soon as the last sheet of the workbook is selected and stored in the variable wrk_sht. We need to define an operation for this loop. It surely will be protecting the sheet using a password.
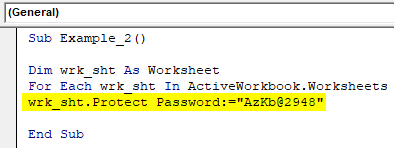
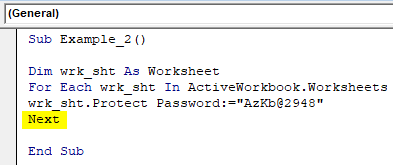
Step 4: Now, use Protect function to protect the sheets getting stored under wrk_sht variable for every iteration of For loop.
Code:
Sub Example_2() Dim wrk_sht As Worksheet For Each wrk_sht In ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets wrk_sht.Protect Password:="[email protected]" End Sub
Step 5: Use the Next statement, it allows the loop to run till each worksheet gets protected.
Code:
Sub Example_2() Dim wrk_sht As Worksheet For Each wrk_sht In ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets wrk_sht.Protect Password:="[email protected]" Next End Sub
If you run this code, each worksheet of the active workbook will be protected by password and you need to input it every time you want to edit the sheets.
Things to Remember
- It is recommended to use a password while you protect a sheet. Otherwise, the user will not be prompted to input a password and can directly edit the file though you have protected it.
- It is recommended to remember the password. Otherwise forgetting of the same will never ever allow you to edit the file. You may have to go through the various methods if you lose the password and those methods are beyond the scope of this article.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to VBA Protect Sheet. Here we discuss how to protect or lock sheets using VBA Protect function in Excel along with practical examples and downloadable excel template. You can also go through our other suggested articles –
- VBA Rename Sheet
- Unprotect Sheet in Excel
- VBA Activate Sheet
- Copy Excel Sheet