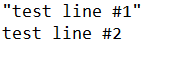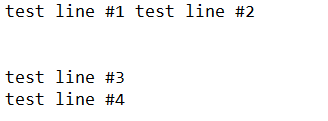Чтение и запись в файл, открытый с помощью оператора Open. Операторы Input, Line Input, Write и функция EOF. Примеры использования в VBA Excel.
Операторы чтения и записи в файл
Оператор Input #
Оператор Input # считывает данные из открытого файла с последовательным доступом и присваивает эти данные переменным.
Оператор Input # используется только с файлами, открытыми в режиме Input или Binary. При прочтении стандартные строковые или числовые значения присваиваются переменным без изменения.
Синтаксис оператора Input #:
|
Input #Номер_файла, Переменные |
Компоненты оператора Input #:
- Номер_файла – обязательный параметр, представляющий из себя номер, присвоенный файлу при открытии с помощью оператора Open.
- Переменные – обязательный параметр, представляющий из себя список переменных, разделенных запятой, которым присваиваются значения, считанные из файла.
Особенности применения оператора Input #:
- Элементы данных в файле должны быть указаны в том же порядке, что и переменные в списке Переменные, и соответствовать им по типу данных. Если переменная числовая, а данные текстовые, этой переменной будет присвоено нулевое значение.
- Если при чтении данных достигнут конец файла, чтение прерывается и возникает ошибка. Для ее предупреждения в коде VBA Excel используется функция EOF.
- Чтобы данные из файла могли быть правильно прочитаны и записаны в переменные с помощью оператора Input #, они должны быть записаны в файл с помощью оператора Write #. Он обеспечивает правильное разделение каждого из полей (элементов) данных.
Оператор Line Input #
Оператор Line Input # считывает одну строку из открытого файла с последовательным доступом и присваивает ее значение строковой переменной.
Оператор Line Input # считывает из файла по одному символу до тех пор, пока не встретится символ возврата каретки (Chr(13)) или последовательность символа возврата каретки и перевода строки (Chr (13) + Chr(10)).
Синтаксис оператора Line Input #:
|
Line Input #Номер_файла, Переменная |
Компоненты оператора Line Input #:
- Номер_файла – обязательный параметр, представляющий из себя номер, присвоенный файлу при открытии с помощью оператора Open.
- Переменная – обязательный параметр, представляющий из себя имя переменной, объявленной как String или Variant, которой присваивается строка, считанная из файла.
Оператор Write #
Оператор Write # записывает данные в файл с последовательным доступом.
Синтаксис оператора Write #:
|
Write #Номер_файла, [Данные] |
Компоненты оператора Write #:
- Номер_файла – обязательный параметр, представляющий из себя номер, присвоенный файлу при открытии с помощью оператора Open.
- Данные – необязательный параметр, представляющий из себя одно или несколько числовых или строковых выражений, разделенных запятой, которые нужно записать в файл.
Особенности применения оператора Write #:
- Данные, записанные с помощью оператора Write #, считываются из файла с помощью оператора Input #.
- Если опустить параметр Данные и добавить запятую после Номер_файла, в файл будет добавлена пустая строка.
- Несколько выражений в списке Данные могут быть разделены точкой с запятой или запятой.
- Числовые данные всегда записываются с точкой в качестве разделителя целой и дробной части.
- Оператор Write # вставляет запятые между элементами и прямые парные кавычки вокруг строк при их записи в файл.
- После записи в файл последнего символа из параметра Данные оператор Write # вставляет символы возврата каретки и перевода строки (Chr (13) + Chr(10)).
Функция EOF
Функция EOF возвращает логическое значение True, когда достигнут конец файла, открытого для последовательного (Input) или произвольного (Random) доступа.
Синтаксис функции EOF:
Номер_файла – это номер, присвоенный файлу при открытии с помощью оператора Open.
Функция EOF используется для предупреждения ошибок, вызываемых попытками выполнить чтение после конца файла. Она возвращает значение False, пока не будет достигнут конец файла.
Примеры чтения и записи в файл
Пример 1
Открытие (или создание, если он не существует) текстового файла для чтения и записи и запись в него одной строки, состоящей из двух текстовых и одного числового значений. Файл с именем myFile1.txt будет создан в той же папке, где расположен файл Excel с кодом VBA.
|
Sub Test1() Dim ff As Integer ‘Получаем свободный номер для открываемого файла ff = FreeFile ‘Открываем (или создаем) файл для чтения и записи Open ThisWorkbook.Path & «myFile1.txt» For Output As ff ‘Записываем в файл одну строку Write #ff, «Дает корова молоко!», _ «Куда идет король?», 25.35847 ‘Закрываем файл Close ff ‘Открываем файл для просмотра ThisWorkbook.FollowHyperlink (ThisWorkbook.Path & «myFile1.txt») End Sub |
Строки и число можно предварительно присвоить переменным, объявленным с соответствующими типами данных, и использовать их для записи данных в файл (в строках кода с оператором Write #, как в этом и следующем примерах).
Пример 2
Открытие (или создание, если он не существует) файла без расширения для чтения и записи и запись в него трех строк: двух текстовых и одной в числовом формате. Файл с именем myFile2 будет создан в той же папке, где расположен файл Excel с кодом VBA.
Так как у файла нет расширения, Windows выведет диалоговое окно для выбора открывающей его программы. Выберите любой текстовый редактор или интернет-браузер.
|
Sub Test2() Dim ff As Integer ‘Получаем свободный номер для открываемого файла ff = FreeFile ‘Открываем (или создаем) файл для чтения и записи Open ThisWorkbook.Path & «myFile2» For Output As ff ‘Записываем в файл три строки Write #ff, «Дает корова молоко!» Write #ff, «Куда идет король?» Write #ff, 25.35847 ‘Закрываем файл Close ff ‘Открываем файл для просмотра ThisWorkbook.FollowHyperlink (ThisWorkbook.Path & «myFile2») End Sub |
Пример 3
Считываем строку, разделенную на отдельные элементы, из файла myFile1.txt и записываем в три переменные, по типу данных соответствующие элементам.
|
Sub Test3() Dim ff As Integer, str1 As String, _ str2 As String, num1 As Single ‘Получаем свободный номер для открываемого файла ff = FreeFile ‘Открываем файл myFile1.txt для чтения Open ThisWorkbook.Path & «myFile1.txt» For Input As ff ‘Считываем строку из файла и записываем в переменные Input #ff, str1, str2, num1 Close ff ‘Смотрим, что записалось в переменные MsgBox «str1 = « & str1 & vbNewLine _ & «str2 = « & str2 & vbNewLine _ & «num1 = « & num1 End Sub |
Попробуйте заменить в этом примере строку Input #ff, str1, str2, num1 сначала на строку Input #ff, str1, затем на строку Line Input #ff, str1, чтобы наглядно увидеть разницу между операторами Input # и Line Input #.
В следующих примерах (4 и 5) замена оператора Input # на Line Input # не приведет ни к каким изменениям, так как данные в строках файла myFile2 не разделены на элементы (поля).
Пример 4
Считываем поочередно три строки из файла myFile2 и записываем в три элемента массива, объявленного как Variant, так как в этот файл ранее были записаны две строки с текстом и одна с числом.
|
Sub Test4() Dim ff As Integer, a(2) As Variant, i As Byte ‘Получаем свободный номер для открываемого файла ff = FreeFile ‘Открываем файл myFile2 для чтения Open ThisWorkbook.Path & «myFile2» For Input As ff ‘Считываем строки из файла и записываем в элементы массива For i = 0 To 2 Input #ff, a(i) Next Close ff ‘Смотрим, что записалось в элементы массива MsgBox «a(0) = « & a(0) & vbNewLine _ & «a(1) = « & a(1) & vbNewLine _ & «a(2) = « & a(2) End Sub |
Пример 5
Считываем с помощью цикла Do While… Loop все строки из файла myFile2 и записываем построчно в переменную, объявленную как String (число из третьей строки запишется как текст). Для остановки цикла при достижении конца файла используем функцию EOF.
|
Sub Test5() Dim ff As Integer, a As Variant, b As String ‘Получаем свободный номер для открываемого файла ff = FreeFile ‘Открываем файл myFile2 для чтения Open ThisWorkbook.Path & «myFile2» For Input As ff ‘Считываем строки из файла и записываем в элементы массива Do While Not EOF(ff) Input #ff, a b = b & a & vbNewLine Loop Close ff ‘Смотрим, что записалось в переменную MsgBox b End Sub |
Предыдущая часть темы об открытии файла для ввода и вывода информации опубликована в статье: Оператор Open (синтаксис, параметры). Смотрите также связанную статью: Функция FreeFile.
Смотрите, как создавать и открывать текстовые файлы с помощью методов CreateTextFile и OpenTextFile. Чтение файла, запись и добавление информации с помощью объекта TextStream.
In this Article
- Write to a Text File
- Write to New Text File
- Write to Existing Text File
- Append to Text File
- WriteLine Method
- Write Method
- WriteBlankLines
- Data Range to Text File
- Array to Text File
This tutorial will demonstrate how to write to text files using VBA.
Write to a Text File
The below codes use the FileSystemObject (learn more). In order to use it, you will need to set a reference to the VB script run-time library.
Write to New Text File
With the CreateTextFile method of FileSystemObject you can create and then add content to a text file:
Sub FSOCreateAndWriteToTextFile()
Dim FSO As New FileSystemObject
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set FileToCreate = FSO.CreateTextFile("C:TestTestFile.txt")
FileToCreate.Write "test line"
FileToCreate.Close
End Sub
Please note that content will not be enclosed by quotes.
Write to Existing Text File
To write to an existing text file you can use the OpenTextFile method of FileSystemObject with ForWriting mode.
Sub FSOWriteToTextFile()
Dim FSO As New FileSystemObject
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set FileToWrite = FSO.OpenTextFile("C:TestTestFile.txt", ForWriting)
FileToWrite.Write "test line"
FileToWrite.Close
End Sub
Please note that you do not necessarily need FileSystemObject to write to an existing text file. The above example is shown in another way in this code below (see other example in the Data Range to Text File section):
Sub WriteToTextFile()
Dim FileName As String
FileName = "C:TestTestFile.txt"
Open FileName For Output As #1
Print #1, "test line"
Close #1
End SubPlease note that using Write command instead of Print will result in having the added content enclosed by quotes. Having both commands in your macro
Write #1, "test line #1"
Print #1, "test line #2"will result in a text file like this:
Append to Text File
By changing the mode in the above code to ForAppending, a line can be added to the end of the text file:
Set FileToWrite = FSO.OpenTextFile("C:TestTestFile.txt", ForAppending)WriteLine Method
This method appends the input string as a separate line to the existing content.
Write Method
The input string is appended on the same line as the existing content.
VBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro — A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Learn More
WriteBlankLines
This method takes the number of blank lines to be written to the text file as a parameter.
This code below illustrates the difference between the different write methods:
Sub WriteMethods()
Dim FSO As New FileSystemObject
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set FileToWrite = FSO.OpenTextFile("C:TestTestFile.txt", ForAppending)
FileToWrite.Write "test line #1 "
FileToWrite.Write "test line #2"
FileToWrite.WriteBlankLines (3)
FileToWrite.WriteLine "test line #3"
FileToWrite.WriteLine "test line #4"
FileToWrite.Close
End SubAnd the result:
Data Range to Text File
If you want to output a data range from your worksheet to a text file, you can use this code:
Sub OutputToTextFile()
Dim FileName As String, LineText As String
Dim MyRange As Range, i, j
FileName = "C:TestTestFile.txt" 'you can specify here the text file name you want to create
Open FileName For Output As #1
Set MyRange = Range("data") 'it assumes you have a data range named “data” on your worksheet
For i = 1 To MyRange.Rows.Count
For j = 1 To MyRange.Columns.Count
LineText = IIf(j = 1, "", LineText & ",") & MyRange.Cells(i, j) 'the text file creating will have a comma separator
Next j
Print #1, LineText 'using Write command instead of Print will result in having your data in quotes in the output text file
Next i
Close #1
End Sub
Array to Text File
You can also save your array of data into a text file like this:
Sub SaveArrayToTextFile()
Dim MyArray As Variant
Dim FSO As New FileSystemObject
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
MyArray = Array(Array("00", "01"), Array("10", "11"), Array("20", "21"))
Set FileToCreate = FSO.CreateTextFile("C:TestTestFile.txt")
For n = 0 To UBound(MyArray)
FileToCreate.WriteLine MyArray(n)(0) & "," & MyArray(n)(1)
Next
FileToCreate.Close
End SubThis VBA Program reads an Excel Range (Sales Data) and write to a Text file (Sales.txt)
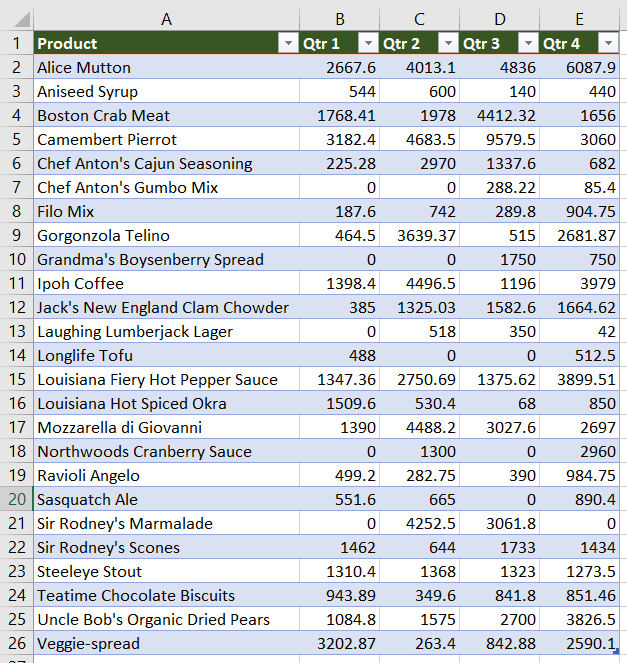
Excel VBA code to read data from an Excel file (Sales Data – Range “A1:E26”). Need two “For loop” for rows and columns. Write each value with a comma in the text file till the end of columns (write without comma only the last column value). Do the above step until reach the end of rows.
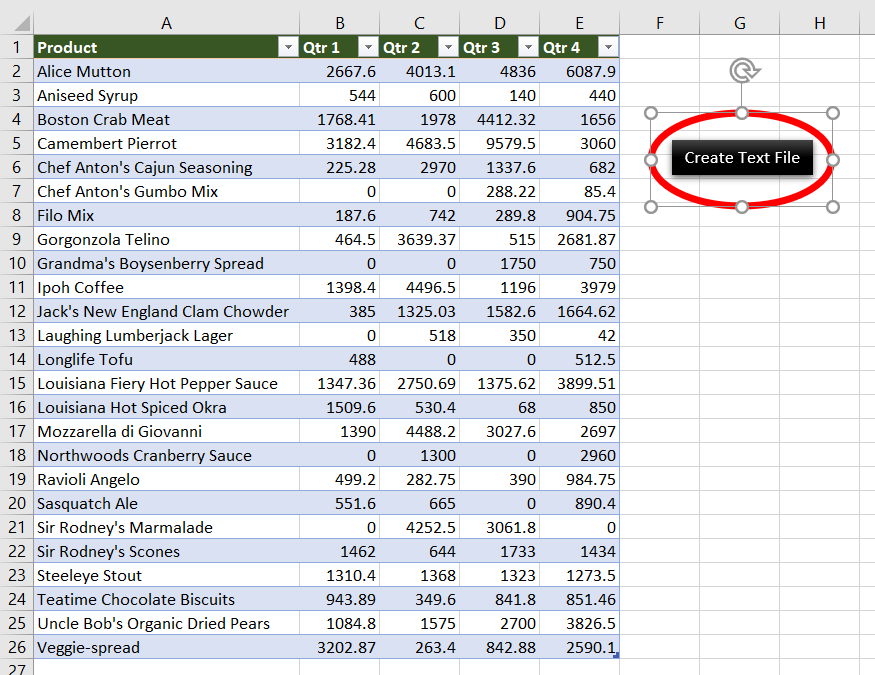
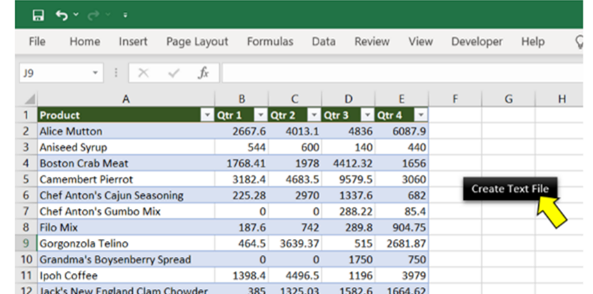
Sales Data in Excel: 5 columns and 25 rows
Sales Data
VBA code to create a text file as below
VBA Code:
- Declaring Variables :
| Variable | Data Type | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| myFileName | String | Output text file (Full path with file name) |
| rng | Range | Excel range to read |
| cellVal | Variant | Variable to assign each cell value |
| row | Integer | Iterate rows |
| col | Integer | Iterate columns |
'Variable declarations Dim myFileName As String, rng As Range, cellVal As Variant, row As Integer, col As Integer
- Initialize variables:
- myFileName: The file name with the full path of the output text file
- rng: Excel range to read data from an excel.
'Full path of the text file
myFileName = "D:ExcelWriteTextsales.txt"
'Data range need to write on text file
Set rng = ActiveSheet.Range("A1:E26")
Open the output text file and assign a variable “#1”
'Open text file Open myFileName For Output As #1
‘Nested loop to iterate both rows and columns of a given range eg: “A1:E26” [5 columns and 26 rows]
'Number of Rows For row = 1 To rng.Rows.Count 'Number of Columns For col = 1 To rng.Columns.Count
Assign the value to variable cellVal
cellVal = rng.Cells(row, col).Value
Write cellVal with comma. If the col is equal to the last column of a row. write-only value without the comma.
'write cellVal on text file
If col = rng.Columns.Count Then
Write #1, cellVal
Else
Write #1, cellVal,
End If
Close both for loops
Next col Next row
Close the file
Close #1
Approach:
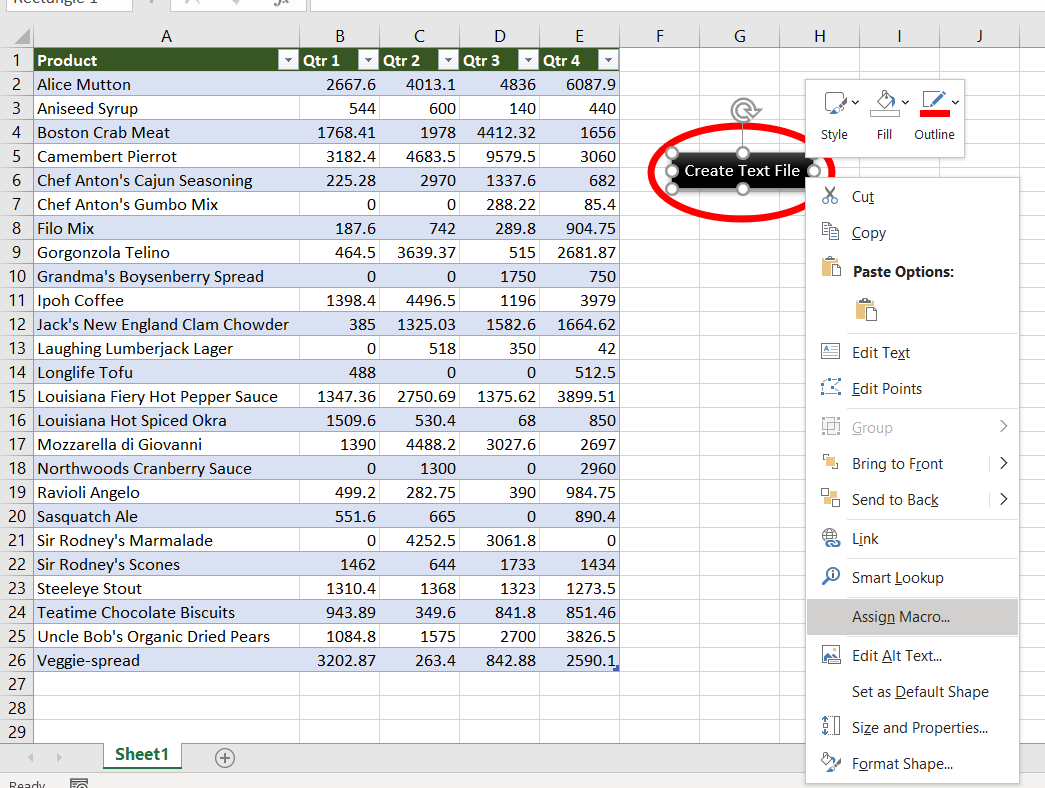
Step 1: Add a shape (Create Text File) to your worksheet
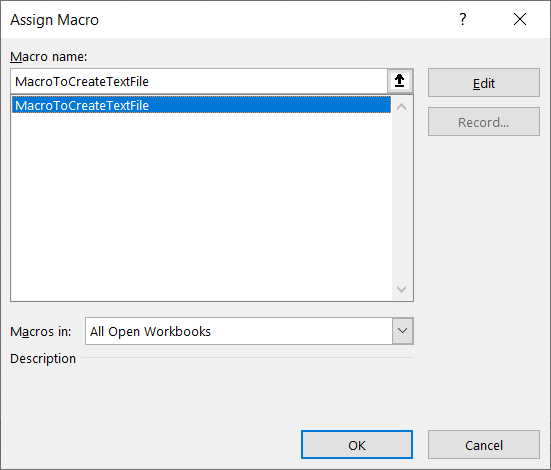
Step 2: Right-click on “Create a Text file” and “Assign Macro..”
Step 3: Select MacroToCreateTextFile
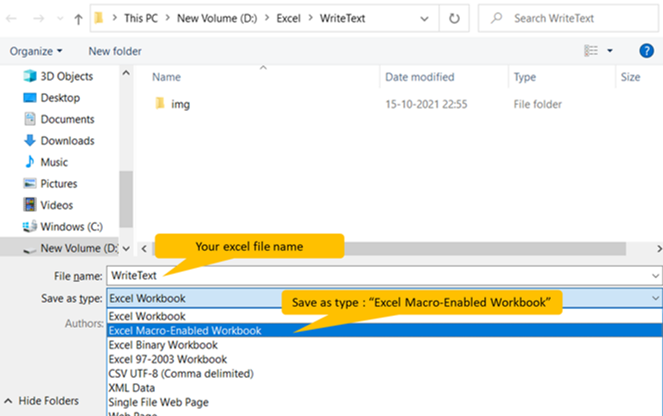
Step 4: Save your excel file as “Excel Macro-Enabled Workbook” *.xlsm
Step 5: Click “Create Text file”
Данные функции предназначены для работы с текстовыми файлами из VBA Excel.
Используя эти функции, вы при помощи одной строки кода сможете записать текст из переменной в файл, или наоборот, загрузить содержимое текстового файла в переменную.
Подразумевается, что текстовые файлы имеют формат ANSI (он же ASCII, он же windows-1251)
Чтение текстового файла в переменную:
Function ReadTXTfile(ByVal filename As String) As String Set fso = CreateObject("scripting.filesystemobject") Set ts = fso.OpenTextFile(filename, 1, True): ReadTXTfile = ts.ReadAll: ts.Close Set ts = Nothing: Set fso = Nothing End Function
Запись в текстовый файл из переменной:
Function SaveTXTfile(ByVal filename As String, ByVal txt As String) As Boolean On Error Resume Next: Err.Clear Set fso = CreateObject("scripting.filesystemobject") Set ts = fso.CreateTextFile(filename, True) ts.Write txt: ts.Close SaveTXTfile = Err = 0 Set ts = Nothing: Set fso = Nothing End Function
Добавление в текстовый файл из переменной:
Function AddIntoTXTfile(ByVal filename As String, ByVal txt As String) As Boolean On Error Resume Next: Err.Clear Set fso = CreateObject("scripting.filesystemobject") Set ts = fso.OpenTextFile(filename, 8, True): ts.Write txt: ts.Close Set ts = Nothing: Set fso = Nothing AddIntoTXTfile = Err = 0 End Function
- 107060 просмотров
Не получается применить макрос? Не удаётся изменить код под свои нужды?
Оформите заказ у нас на сайте, не забыв прикрепить примеры файлов, и описать, что и как должно работать.

Looking at various resources I missed a single resource which would demonstrate the various methods for PROPERLY writing files in VBA. It is important to remember that you shouldn’t write all fills using the same approach. Be aware of the structure of the file. If you want performance – always select the right approach.
Approach #1: The Write function (strings in quotes)
Writing strings of data to text files with quotes:
Dim fileName As String, textData As String, textRow As String, fileNo As Integer fileName = "C:test.txt" fileNo = FreeFile 'Get first free file number textData ="Hello World!" Open fileName For Output As #fileNo 'Open file for overwriting! Replace Output with Append to append Write #fileNo, textData Close #fileNo
This approach will result in the following output:
"Hello, World!"
Notice the “” quotes. Writing further strings will result in appending further strings wrapped in double quotes which might not be a satisfactory approach. Look down to the Print function to avoid these quotes.
To Append to the text file instead of overwriting replace For Output with For Append in the Open fileName For Output As #fileNo
Approach #2: The Print function (dumping strings without quotes)
Writing strings of data to text files without quotes:
Dim fileName As String, textData As String, textRow As String, fileNo As Integer
fileName = "C:test.txt"
fileNo = FreeFile 'Get first free file number
Open fileName For Output As #fileNo 'Open file for overwriting! Replace Output with Append to append
Print #fileNo, textData
Close #fileNo
This approach will result in the following output:
Hello, World!
This time there are no quotes in the file. In most case you will want to use the Print function instead of the Write function
Writing binary files in VBA
Dim fileName As String, fileNo As Integer, testVar As Integer fileName = "C:test.bin" testVar = 4 fileNo = FreeFile Open fileName For Binary Lock Read Write As #fileNo Put #fileNo, , testVar Close #fileNo
With Binary files often you will be using objects which are not of fixed byte length like Integers. For example you would want to save Strings. In such cases use the VBA Type object data type.
Below a simple example using the Type data type to save an object with an Integer and String.
Type TestType
intVar As Integer
strVar As String
End Type
Sub WriteBinary()
Dim fileName As String, fileNo As Integer, testVar As TestType
fileName = "C:test.bin"
testVar.intVar = 4
testVar.strVar = "Hello!"
fileNo = FreeFile
Open fileName For Binary Lock Read Write As #fileNo
Put #fileNo, , testVar
Close #fileNo
End Sub
Writing CSV files in VBA
If you want to save your worksheet as CSV you can always resort to the Text file section. However, this is an ineffective approach. If you want to save your current worksheet as a semicolon delimited file (‘;’) you can use the Workbook.SaveAs function like below.
PathName = "C:test.csv" 'Assuming you want to export your current Worksheet ActiveSheet.Move 'Move the Worksheet to a new Workbook ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:=PathName, FileFormat:=xlCSV, CreateBackup:=False
In case you want to instead copy your worksheet simply replace Move for Copy:
PathName = "C:test.csv" 'Assuming you want to export your current Worksheet ActiveSheet.Copy 'Copy the Worksheet to a new Workbook ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:=PathName, FileFormat:=xlCSV, CreateBackup:=False
Functions needed to write files in VBA
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| FreeFile | Get next free file number available for the Open statement / FileOpen function. Using this function is important especially when operating on multiple files simultaneously. More info here. |
| BOF(fileNumber) | Returns true if you are at the beginning of the file described by the file number. More info here. |
| EOF(fileNumber) | Returns true if you have reached the end of the file described by the file number. More info here. |
| Loc(fileNumber) | Returns the current read/write position within an open file. More info here. |
| LOF(fileNumber) | Returns the size in bytes of the file represented by the file number. More info here. |
Write file VBA summary
Writing files in VBA is not hard and usually takes just a couple of lines of code. It makes sense however to do it write and be aware of certain traps like not omitting the use of the FreeFile function or knowing the difference between Print and Write.