Замена подстроки, содержащейся в текстовых значениях ячеек указанного диапазона, другой подстрокой с помощью метода Range.Replace из кода VBA Excel.
Range.Replace – это метод, который находит по шаблону подстроку в содержимом ячеек указанного диапазона, заменяет ее на другую подстроку и возвращает значение типа Boolean.
Метод имеет некоторые особенности, которые заключаются в следующем:
- при присвоении булева значения, возвращаемого методом Range.Replace, переменной, необходимо список параметров (аргументов) метода заключать в круглые скобки;
- если метод используется без присвоения возвращаемого значения переменной, параметры должны быть указаны без заключения их в круглые скобки.
Синтаксис и параметры метода
Синтаксис
Синтаксис при замене подстроки и присвоении переменной возвращаемого значения типа Boolean:
variable = expression.Replace(What, Replacement, [LookAt], [SearchOrder], [MatchCase], [MatchByte], [SearchFormat], [ReplaceFormat])
Синтаксис при замене подстроки без присвоения переменной возвращаемого значения:
expression.Replace What, Replacement, [LookAt], [SearchOrder], [MatchCase], [MatchByte], [SearchFormat], [ReplaceFormat]
- variable – переменная (тип данных — Boolean);
- expression – выражение, возвращающее объект Range.
Параметры
| Параметр | Описание |
|---|---|
| What | Искомая подстрока или шаблон*, по которому ищется подстрока в диапазоне ячеек. Обязательный параметр. |
| Replacement | Подстрока, заменяющая искомую подстроку. Обязательный параметр. |
| LookAt | Указывает правило поиска по полному или частичному вхождению искомой подстроки в текст ячейки: 1 (xlWhole) – поиск полного вхождения искомого текста; 2 (xlPart) – поиск частичного вхождения искомого текста. Необязательный параметр. |
| SearchOrder | Задает построчный или постолбцовый поиск: 1 (xlByRows) – построчный поиск; 2 (xlByColumns) – постолбцовый поиск. Необязательный параметр. |
| MatchCase | Поиск с учетом или без учета регистра: 0 (False) – поиск без учета регистра; 1 (True) – поиск с учетом регистра. Необязательный параметр. |
| MatchByte | Способы сравнения двухбайтовых символов: 0 (False) – двухбайтовые символы сопоставляются с однобайтовыми эквивалентами; 1 (True) – двухбайтовые символы сопоставляются только с двухбайтовым символами. Необязательный параметр. |
| SearchFormat | Формат поиска. Необязательный параметр. |
| ReplaceFormat | Формат замены. Необязательный параметр. |
* Смотрите знаки подстановки для шаблонов, которые можно использовать в параметре What.
Работа метода в VBA Excel
Исходная таблица для всех примеров:
Пример 1
Примеры записи строк кода с методом Range.Replace и поиском по частичному совпадению подстроки с содержимым ячейки:
|
Sub Primer1() ‘Запись 1: Range(«A1:C6»).Replace «Лиса», «Рысь», 2 ‘Запись 2: Range(«A1:C6»).Replace What:=«Лиса», Replacement:=«Рысь», LookAt:=2 ‘Запись 3: If Range(«A1:C6»).Replace(«Лиса», «Рысь», 2) Then End If ‘Запись 4: Dim a a = Range(«A1:C6»).Replace(«Лиса», «Рысь», 2) End Sub |
Результат выполнения любого из вариантов кода примера 1:
Пример 2
Поиск по шаблону с использованием знаков подстановки и по полному совпадению подстроки с содержимым ячейки:
|
Sub Primer2() Range(«A1:C6»).Replace «Ли??», «Рысь», 1 End Sub |
Обратите внимание, что слово «Лиса» заменено словом «Рысь» не во всех ячейках. Это произошло из-за того, что мы использовали параметр LookAt:=1 – поиск полного вхождения искомого текста в содержимое ячейки.
|
The_Fog 0 / 0 / 2 Регистрация: 24.02.2016 Сообщений: 75 |
||||
|
1 |
||||
Поиска символов в ячейках и их замена02.02.2017, 14:48. Показов 9594. Ответов 14 Метки нет (Все метки)
Нужно найти определенное слово в ячейке и заменить без изменения остальных слов в этой ячейке.
но он не подходит, т.к. ищет значение всей ячейки а не только некоторых символов из нее.
0 |
|
KoGG 5590 / 1580 / 406 Регистрация: 23.12.2010 Сообщений: 2,366 Записей в блоге: 1 |
||||
|
02.02.2017, 15:53 |
2 |
|||
0 |
|
pashulka 4131 / 2235 / 940 Регистрация: 01.12.2010 Сообщений: 4,624 |
||||
|
02.02.2017, 16:22 |
3 |
|||
|
Заменить можно без цикла и поиска
1 |
|
The_Fog 0 / 0 / 2 Регистрация: 24.02.2016 Сообщений: 75 |
||||
|
03.02.2017, 08:54 [ТС] |
4 |
|||
|
Заменить можно без цикла и поиска
что значит xlPart ?
0 |
|
CyberHelp 6 / 6 / 1 Регистрация: 29.01.2017 Сообщений: 29 |
||||||||||
|
03.02.2017, 10:26 |
5 |
|||||||||
|
1)
2)
Смотрите вложенный файл. P.S. Вложения
1 |
|
The_Fog 0 / 0 / 2 Регистрация: 24.02.2016 Сообщений: 75 |
||||||||
|
03.02.2017, 13:19 [ТС] |
6 |
|||||||
|
А если у меня есть столбец 1 А мне нужно получить 2
Получаю весь столбец с 1. Т.е. мне надо чтобы если он заменил в одной ячейке 1 на 2, он переходил к другой и менял там 2 на 1, а не эту же ячейку заменял. Какое условие написать?
это неправильно, но нужно что-то типа вот такого как это сделать? Добавлено через 11 минут 1 2
0 |
|
pashulka 4131 / 2235 / 940 Регистрация: 01.12.2010 Сообщений: 4,624 |
||||
|
03.02.2017, 20:23 |
7 |
|||
|
РешениеНа небольшом диапазоне можно и так :
1 |
|
The_Fog 0 / 0 / 2 Регистрация: 24.02.2016 Сообщений: 75 |
||||
|
06.02.2017, 11:33 [ТС] |
8 |
|||
а что значат эти звездочки около 1 =)
0 |
|
1024 / 227 / 21 Регистрация: 20.05.2016 Сообщений: 971 Записей в блоге: 19 |
|
|
06.02.2017, 13:19 |
9 |
|
0 |
|
4131 / 2235 / 940 Регистрация: 01.12.2010 Сообщений: 4,624 |
|
|
06.02.2017, 17:03 |
10 |
|
The_Fog, * это символ подстановки, обозначающий любое количество символов (в т.ч. 0), впрочем, если он Вас «пугает», то замените на If InStr(x, 1) > 0 Then
0 |
|
The_Fog 0 / 0 / 2 Регистрация: 24.02.2016 Сообщений: 75 |
||||
|
07.02.2017, 15:07 [ТС] |
11 |
|||
|
pashulka,
Вообще ничего не меняет =(
0 |
|
4131 / 2235 / 940 Регистрация: 01.12.2010 Сообщений: 4,624 |
|
|
07.02.2017, 18:42 |
12 |
|
The_Fog, А у меня меняет
1 |
|
0 / 0 / 2 Регистрация: 24.02.2016 Сообщений: 75 |
|
|
09.02.2017, 17:39 [ТС] |
13 |
|
pashulka, Спасибо все работает, просто у меня данные были на 3 листе =) Еще вопрос чтоб темы не плодить, а если ячейки объединенные DE и в символах есть пробелы как делать replace к какой ячейки обращаться?
0 |
|
4131 / 2235 / 940 Регистрация: 01.12.2010 Сообщений: 4,624 |
|
|
09.02.2017, 19:04 |
14 |
|
The_Fog, Если об’единены ячейки столбцов D и E, то просто перебирайте ячейки столбца D
1 |
|
0 / 0 / 2 Регистрация: 24.02.2016 Сообщений: 75 |
|
|
10.02.2017, 12:04 [ТС] |
15 |
|
pashulka, Спасибо вам за помощь ! =)
0 |

This VBA Tutorial is accompanied by Excel workbooks containing the data and macros I use in the examples below. You can get immediate free access to these example workbooks by subscribing to the Power Spreadsheets Newsletter.
Use the following Table of Contents to navigate to the section you’re interested in.
Related VBA and Macro Tutorials
The following VBA and Macro Tutorials may help you better understand and implement the contents below:
- General VBA constructs and structures:
- Learn about commonly-used VBA terms here.
- Learn about the Excel Object Model here.
- Learn about working with variables here.
- Learn about data types here.
- Learn about working with arrays here.
- Practical VBA applications and macro examples:
- Learn about referring to cell ranges here.
- Learn about working with worksheet functions within VBA here.
You can find additional VBA and Macro Tutorials in the Archives.
#1: Replace String in Cell
VBA Code to Replace String in Cell
To replace a string in a cell with VBA, use a statement with the following structure:
Cell.Value = Replace(Expression:=Cell.Value, Find:=StringToReplace, Replace:=ReplacementString, Count:=NumberOfReplacements)
Process Followed by VBA Code to Replace String in Cell
VBA Statement Explanation
- Item: Cell.
- VBA Construct: Range object.
- Description: Range object representing the cell you work with.
You can usually return a Range object with constructs such as the Worksheet.Range, Worksheet.Cells (with the Range.Item) or Range.Offset properties.
- Item: Value.
- VBA Construct: Range.Value property.
- Description: The Range.Value property specifies the value (in this case string) within Cell.
- Item: =.
- VBA Construct: Assignment operator.
- Description: The = operator assigns the string returned by the Replace function to the Range.Value property of Cell.
- Item: Replace(…).
- VBA Construct: Replace function.
- Description: The Replace function returns a string where a specific substring (StringToReplace) is replaced by another substring (ReplacementString) a specific number of times (NumberOfReplacements).
- Item: Expression:=Cell.Value.
- VBA Construct: Expression parameter of the Replace function, Range object and Range.Value property.
- Description: The Expression parameter of the Replace function specifies the string expression containing the substring you want to replace (StringToReplace). Within this macro structure, Expression is the value (string) within Cell, as returned by the Range.Value property.
- Item: Find:=StringToReplace.
- VBA Construct: Find parameter of the Replace function.
- Description: The Find parameter of the Replace function specifies the substring you search for and replace.
If you explicitly declare a variable to represent StringToReplace, use the String data type.
- Item: Replace:=ReplacementString.
- VBA Construct: Replace parameter of the Replace function.
- Description: The Replace parameter of the Replace function specifies the substring you want to use as replacement for StringToReplace.
If you explicitly declare a variable to represent ReplacementString, use the String data type.
- Item: Count:=NumberOfReplacements.
- VBA Construct: Count parameter of the Replace function.
- Description: The Count parameter of the Replace function specifies the number of substitutions you want to carry out. In other words, the number of times you want to replace StringToReplace with ReplacementString.
If you want VBA to replace all occurrences of StringToReplace with ReplacementString, omit the Count parameter. In such case, Count defaults to -1 and VBA carries out all possible substitutions. Please refer to the appropriate section (Replace All Occurrences of String in Cell) below for further information about this scenario.
Macro Example to Replace String in Cell
The following macro replaces the string “replace” (myStringToReplace) with the string “substitute” (myReplacementString) one time (myNumberOfReplacements) within the string in cell A5 of the worksheet named “Excel VBA Replace” (myCell).
Sub replaceStringInCell()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-replace-substitute/
'declare object variable to hold reference to cell you work with
Dim myCell As Range
'declare variables to hold parameters for string replacement (string to replace, replacement string, and number of replacements)
Dim myStringToReplace As String
Dim myReplacementString As String
Dim myNumberOfReplacements As Long
'identify cell you work with
Set myCell = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Excel VBA Replace").Range("A5")
'specify parameters for string replacement (string to replace, replacement string, and number of replacements)
myStringToReplace = "replace"
myReplacementString = "substitute"
myNumberOfReplacements = 1
'replace string in cell you work with, and assign resulting string to Range.Value property of cell you work with
myCell.Value = Replace(Expression:=myCell.Value, Find:=myStringToReplace, Replace:=myReplacementString, Count:=myNumberOfReplacements)
End Sub
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Replace String in Cell
The following GIF illustrates the results of executing this macro example. As expected, the macro replaces the string “replace” with the string “substitute” one time within the string in cell A5.
#2: Replace String in Cell Specifying a Starting Position for Search
VBA Code to Replace String in Cell Specifying a Starting Position for Search
To replace a string in a cell and specify the starting position to search for the string with VBA, use a statement with the following structure:
Cell.Value = Left(String:=Cell.Value, Length:=StartPosition - 1) & Replace(Expression:=Cell.Value, Find:=StringToReplace, Replace:=ReplacementString, Start:=StartPosition, Count:=NumberOfReplacements)
Process Followed by VBA Code to Replace String in Cell Specifying a Starting Position for Search
VBA Statement Explanation
- Item: Cell.
- VBA Construct: Range object.
- Description: Range object representing the cell you work with.
You can usually return a Range object with constructs such as the Worksheet.Range, Worksheet.Cells (with the Range.Item) or Range.Offset properties.
- Item: Value.
- VBA Construct: Range.Value property.
- Description: The Range.Value property specifies the value (in this case string) within Cell.
- Item: =.
- VBA Construct: Assignment operator.
- Description: The = operator assigns the string returned by the Replace function to the Range.Value property of Cell.
- Item: Left(…).
- VBA Construct: Left function.
- Description: The Left function returns a string containing the number of characters specified by the Length parameter (StartPosition – 1) from the left side of the string specified by the String parameter (Cell.Value).
Within this macro structure, you use the Left function to return the substring containing the first characters of the string within the cell you work with. This substring goes from the first character of the string to the character immediately before the position within the string where you start searching for the substring you want to replace (StringToReplace).
You need to do this because the Replace function doesn’t return a copy of the string (with substitutions) from start to finish. The string that Replace returns starts at the position within the string where you start searching for the substring you want to replace (StartPosition). Therefore, VBA truncates the string and the characters to the left of StartPosition aren’t part of the string returned by Replace.
- Item: String:=Cell.Value.
- VBA Construct: String parameter of the Left function, Range object and Range.Value property.
- Description: The String parameter of the Left function specifies the string expression containing the substring you want to replace (StringToReplace).
Within this macro structure, String is the value (string) within Cell, as returned by the Range.Value property. The value of the String parameter of the Left function is the same as the value of the Expression parameter of the Replace function.
- Item: Length:=StartPosition – 1.
- VBA Construct: Length parameter of the Left function.
- Description: The Length parameter of the Left function specifies the number of characters the Left function returns from the string you work with. StartPosition is the position within the string where you start searching for the substring you want to replace (StringToReplace). (StartPosition – 1) is the position of the character immediately before StartPosition. Therefore, the Left function returns the substring containing the first characters of the string within the cell you work with, up until the character located in position (StartPosition – 1).
If you explicitly declare a variable to represent StartPosition, use the Long data type. The value of StartPosition within the Length parameter of the Left function is the same as the value of the Start parameter of the Replace function.
- Item: &.
- VBA Construct: Concatenation operator.
- Description: The & operator concatenates the strings returned by the Left and Replace functions.
- Item: Replace(…).
- VBA Construct: Replace function.
- Description: The Replace function returns a string where a specific substring (StringToReplace) is replaced by another substring (ReplacementString) a specific number of times (NumberOfReplacements).
- Item: Expression:=Cell.Value.
- VBA Construct: Expression parameter of the Replace function, Range object and Range.Value property.
- Description: The Expression parameter of the Replace function specifies the string expression containing the substring you want to replace (StringToReplace). Within this macro structure, Expression is the value (string) within Cell, as returned by the Range.Value property.
- Item: Find:=StringToReplace.
- VBA Construct: Find parameter of the Replace function.
- Description: The Find parameter of the Replace function specifies the substring you search for and replace.
If you explicitly declare a variable to represent StringToReplace, use the String data type.
- Item: Replace:=ReplacementString.
- VBA Construct: Replace parameter of the Replace function.
- Description: The Replace parameter of the Replace function specifies the substring you want to use as replacement for StringToReplace.
If you explicitly declare a variable to represent ReplacementString, use the String data type.
- Item: Start:=StartPosition.
- VBA Construct: Start parameter of the Replace function.
- Description: The Start parameter of the Replace function specifies the position within the string you work with where you start searching for StringToReplace.
The default value of the Start parameter is 1. In such case, the Replace function doesn’t truncate the string. Therefore, you generally don’t have to work with the Left function and concatenation operator. Please refer to the appropriate section (Replace String in Cell) above for further information about this scenario.
- Item: Count:=NumberOfReplacements.
- VBA Construct: Count parameter of the Replace function.
- Description: The Count parameter of the Replace function specifies the number of substitutions you want to carry out. In other words, the number of times you want to replace StringToReplace with ReplacementString.
If you want VBA to replace all occurrences of StringToReplace after StartPosition with ReplacementString, omit the Count parameter. In such case, Count defaults to -1 and VBA carries out all possible substitutions. Please refer to the appropriate section (Replace All Occurrences of String in Cell) below for further information about this scenario.
Macro Example to Replace String in Cell Specifying a Starting Position for Search
The following macro replaces the string “replace” (myStringToReplace) with the string “substitute” (myReplacementString) one time (myNumberOfReplacements) within the string in cell A6 of the worksheet named “Excel VBA Replace” (myCell). The search for myStringToReplace begins in position 14 (myStartPosition) of the string in myCell.
Sub replaceStringInCellWithStartPosition()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-replace-substitute/
'declare object variable to hold reference to cell you work with
Dim myCell As Range
'declare variables to hold parameters for string replacement (string to replace, replacement string, start position for search of string to replace, and number of replacements)
Dim myStringToReplace As String
Dim myReplacementString As String
Dim myStartPosition As Long
Dim myNumberOfReplacements As Long
'identify cell you work with
Set myCell = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Excel VBA Replace").Range("A6")
'specify parameters for string replacement (string to replace, replacement string, start position for search of string to replace, and number of replacements)
myStringToReplace = "replace"
myReplacementString = "substitute"
myStartPosition = 14
myNumberOfReplacements = 1
'return and concatenate the following strings, and assign the resulting (concatenated) string to Range.Value property of cell you work with
'(i) string containing the first characters within the cell you work with (from first position up to the character before the start position for search of string to replace)
'(ii) string resulting from working with the Replace function and the parameter for string replacement you specify
myCell.Value = Left(String:=myCell.Value, Length:=myStartPosition - 1) & Replace(Expression:=myCell.Value, Find:=myStringToReplace, Replace:=myReplacementString, Start:=myStartPosition, Count:=myNumberOfReplacements)
End Sub
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Replace String in Cell Specifying a Starting Position for Search
The following GIF illustrates the results of executing this macro example. As expected, the macro replaces the string “replace” with the string “substitute” one time within the string in cell A6. The search for myStringToReplace begins in position 14 of the string in cell A6. This matches with the second occurrence of the “replace” string.
#3: Replace All Occurrences of String in Cell
VBA Code to Replace All Occurrences of String in Cell
To replace all occurrences of a string in a cell with VBA, use a statement with the following structure:
Cell.Value = Replace(Expression:=Cell.Value, Find:=StringToReplace, Replace:=ReplacementString)
Process Followed by VBA Code to Replace All Occurrences of String in Cell
VBA Statement Explanation
- Item: Cell.
- VBA Construct: Range object.
- Description: Range object representing the cell you work with.
You can usually return a Range object with constructs such as the Worksheet.Range, Worksheet.Cells (with the Range.Item) or Range.Offset properties.
- Item: Value.
- VBA Construct: Range.Value property.
- Description: The Range.Value property specifies the value (in this case string) within Cell.
- Item: =.
- VBA Construct: Assignment operator.
- Description: The = operator assigns the string returned by the Replace function to the Range.Value property of Cell.
- Item: Replace(…).
- VBA Construct: Replace function.
- Description: The Replace function returns a string where a specific substring (StringToReplace) is replaced by another substring (ReplacementString). Within this macro structure, Replace carries out all possible substitutions.
- Item: Expression:=Cell.Value.
- VBA Construct: Expression parameter of the Replace function, Range object and Range.Value property.
- Description: The Expression parameter of the Replace function specifies the string expression containing the substring you want to replace (StringToReplace). Within this macro structure, Expression is the value (string) within Cell, as returned by the Range.Value property.
- Item: Find:=StringToReplace.
- VBA Construct: Find parameter of the Replace function.
- Description: The Find parameter of the Replace function specifies the substring you search for and replace.
If you explicitly declare a variable to represent StringToReplace, use the String data type.
- Item: Replace:=ReplacementString.
- VBA Construct: Replace parameter of the Replace function.
- Description: The Replace parameter of the Replace function specifies the substring you want to use as replacement for StringToReplace.
If you explicitly declare a variable to represent ReplacementString, use the String data type.
Macro Example to Replace All Occurrences of String in Cell
The following macro replaces all occurrences of the string “replace” (myStringToReplace) with the string “substitute” (myReplacementString) within the string in cell A7 of the worksheet named “Excel VBA Replace” (myCell).
Sub replaceAll()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-replace-substitute/
'declare object variable to hold reference to cell you work with
Dim myCell As Range
'declare variables to hold parameters for string replacement (string to replace and replacement string)
Dim myStringToReplace As String
Dim myReplacementString As String
'identify cell you work with
Set myCell = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Excel VBA Replace").Range("A7")
'specify parameters for string replacement (string to replace and replacement string)
myStringToReplace = "replace"
myReplacementString = "substitute"
'replace all occurrences within string in cell you work with, and assign resulting string to Range.Value property of cell you work with
myCell.Value = Replace(Expression:=myCell.Value, Find:=myStringToReplace, Replace:=myReplacementString)
End Sub
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Replace All Occurrences of String in Cell
The following GIF illustrates the results of executing this macro example. As expected, the macro replaces all (2) occurrences of the string “replace” with the string “substitute” within the string in cell A7.
#4: Replace Character in String
VBA Code to Replace Character in String
To replace a character in a string within a cell with VBA, use a statement with the following structure:
Cell.Value = Replace(Expression:=Cell.Value, Find:=CharacterToReplace, Replace:=ReplacementCharacter)
Process Followed by VBA Code to Replace Character in String
VBA Statement Explanation
- Item: Cell.
- VBA Construct: Range object.
- Description: Range object representing the cell you work with.
You can usually return a Range object with constructs such as the Worksheet.Range, Worksheet.Cells (with the Range.Item) or Range.Offset properties.
- Item: Value.
- VBA Construct: Range.Value property.
- Description: The Range.Value property specifies the value (in this case string) within Cell.
- Item: =.
- VBA Construct: Assignment operator.
- Description: The = operator assigns the string returned by the Replace function to the Range.Value property of Cell.
- Item: Replace(…).
- VBA Construct: Replace function.
- Description: The Replace function returns a string where a specific character (CharacterToReplace) is replaced by another character (ReplacementCharacter). Within this macro structure, Replace carries out all possible substitutions.
- Item: Expression:=Cell.Value.
- VBA Construct: Expression parameter of the Replace function, Range object and Range.Value property.
- Description: The Expression parameter of the Replace function specifies the string expression containing the character you want to replace (CharacterToReplace). Within this macro structure, Expression is the value (string) within Cell, as returned by the Range.Value property.
- Item: Find:=CharacterToReplace.
- VBA Construct: Find parameter of the Replace function.
- Description: The Find parameter of the Replace function specifies the character you search for and replace.
If you explicitly declare a variable to represent CharacterToReplace, use the String data type.
- Item: Replace:=ReplacementCharacter.
- VBA Construct: Replace parameter of the Replace function.
- Description: The Replace parameter of the Replace function specifies the character you want to use as replacement for CharacterToReplace.
If you explicitly declare a variable to represent ReplacementCharacter, use the String data type.
Macro Example to Replace Character in String
The following macro replaces all occurrences of the character “a” (myCharacterToReplace) with the character “e” (myReplacementCharacter) within the string in cell A8 of the worksheet named “Excel VBA Replace” (myCell).
Sub replaceCharacterInString()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-replace-substitute/
'declare object variable to hold reference to cell you work with
Dim myCell As Range
'declare variables to hold parameters for character replacement (character to replace and replacement character)
Dim myCharacterToReplace As String
Dim myReplacementCharacter As String
'identify cell you work with
Set myCell = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Excel VBA Replace").Range("A8")
'specify parameters for string replacement (character to replace and replacement character)
myCharacterToReplace = "a"
myReplacementCharacter = "e"
'replace all occurrences of character within string in cell you work with, and assign resulting string to Range.Value property of cell you work with
myCell.Value = Replace(Expression:=myCell.Value, Find:=myCharacterToReplace, Replace:=myReplacementCharacter)
End Sub
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Replace Character in String
The following GIF illustrates the results of executing this macro example. As expected, the macro replaces all occurrences of the character “a” with the character “e” within the string in cell A8.
#5: Replace Multiple Characters in String
VBA Code to Replace Multiple Characters in String
To replace multiple characters in a string with VBA, use a macro with the following statement structure:
Dim StringReplace As String
StringReplace = Cell.Value
For Each Character In Array(CharactersList)
StringReplace = Replace(Expression:=StringReplace, Find:=Character, Replace:=ReplacementCharacter)
Next Character
Cell.Value = StringReplace
Process Followed by VBA Code to Replace Multiple Characters in String
VBA Statement Explanation
Line #1: Dim StringReplace As String
- Item: Dim StringReplace As String.
- VBA Construct: Dim statement.
- Description: The Dim statement declares the StringReplace variable as of the String data type.
StringReplace represents the string you work with. StringReplace is both (i) the string where you replace multiple characters (prior to working with the Replace function and the For Each… Next statement) and (ii) the new string after multiple characters have been replaced (after working with the Replace function and the For Each… Next statement).
Line #2: StringReplace = Cell.Value
- Item: StringReplace.
- VBA Construct: Variable of the string data type.
- Description: StringReplace represents the string you work with. StringReplace is both (i) the string where you replace multiple characters (prior to working with the Replace function and the For Each… Next statement) and (ii) the new string after multiple characters have been replaced (after working with the Replace function and the For Each… Next statement).
- Item: =.
- VBA Construct: Assignment operator.
- Description: The = operator assigns the string returned by the Range.Value property to the StringReplace variable.
- Item: Cell.
- VBA Construct: Range object.
- Description: Range object representing the cell you work with.
You can usually return a Range object with constructs such as the Worksheet.Range, Worksheet.Cells (with the Range.Item) or Range.Offset properties.
- Item: Value.
- VBA Construct: Range.Value property.
- Description: The Range.Value property returns the value (in this case string) within Cell.
Lines #3 and #5: For Each Character In Array(CharactersList) | Next Character
- Item: For Each… In… Next.
- VBA Construct: For Each… Next statement.
- Description: The For Each… Next statement repeats the statement within the loop (line #4) for each element (Character) in the array returned by the Array function (Array(CharactersList)).
- Item: Character.
- VBA Construct: Element of For Each… Next statement and variable of the Variant data type.
- Description: The Element of the For Each… Next statement is a variable used to iterate through the elements of the array returned by the Array function (Array(CharactersList)).
If you explicitly declare a variable to represent Character, use the Variant data type.
- Item: Array(CharactersList).
- VBA Construct: Array function.
- Description: The Array function returns a Variant containing an array. CharactersList is the comma-delimited list of characters (passed as strings) that you assign to each of the array elements
Line #4: StringReplace = Replace(Expression:=StringReplace, Find:=Character, Replace:=ReplacementCharacter)
- Item: StringReplace.
- VBA Construct: Variable of the String data type.
- Description: StringReplace represents the string you work with. StringReplace is both (i) the string where you replace multiple characters (prior to working with the Replace function and the For Each… Next statement) and (ii) the new string after multiple characters have been replaced (after working with the Replace function and the For Each… Next statement).
- Item: =.
- VBA Construct: Assignment operator.
- Description: The = operator assigns the string returned by the Replace function to StringReplace.
- Item: Replace(…).
- VBA Construct: Replace function.
- Description: The Replace function returns a string (starting with StringReplace) where a specific character (Character) is replaced by another character (ReplacementCharacter). Within this macro structure, Replace carries out all possible substitutions.
- Item: Expression:=StringReplace.
- VBA Construct: Expression parameter of the Replace function and variable of the String data type.
- Description: The Expression parameter of the Replace function specifies the string expression (StringReplace) containing the characters you want to replace (CharactersList).
- Item: Find:=Character.
- VBA Construct: Find parameter of the Replace function and variable of the Variant data type.
- Description: The Find parameter of the Replace function specifies the character you search for and replace.
Within this macro structure, Character is also the Element of the For Each… Next statement. This is the variable used to iterate through the elements of the array returned by the Array function (Array(CharactersList)).
If you explicitly declare a variable to represent Character, use the Variant data type.
- Item: Replace:=ReplacementCharacter.
- VBA Construct: Replace parameter of the Replace function.
- Description: The Replace parameter of the Replace function specifies the character you want to use as replacement for the characters you want to replace (CharactersList).
If you explicitly declare a variable to represent ReplacementCharacter, use the String data type.
Line #6: Cell.Value = StringReplace
- Item: Cell.
- VBA Construct: Range object.
- Description: Range object representing the cell you work with.
You can usually return a Range object with constructs such as the Worksheet.Range, Worksheet.Cells (with the Range.Item) or Range.Offset properties.
- Item: Value.
- VBA Construct: Range.Value property.
- Description: The Range.Value property specifies the value (in this case string) within Cell.
- Item: =.
- VBA Construct: Assignment operator.
- Description: The = operator assigns the string represented by the StringReplace variable to the Range.Value property of Cell.
- Item: StringReplace.
- VBA Construct: Variable of the String data type.
- Description: StringReplace represents the string you work with. StringReplace is both (i) the string where you replace multiple characters (prior to working with the Replace function and the For Each… Next statement) and (ii) the new string after multiple characters have been replaced (after working with the Replace function and the For Each… Next statement).
Macro Example to Replace Multiple Characters in String
The following macro replaces all occurrences of the characters “a”, “e” and “i” (myCharactersArray) with the character “o” (myReplacementCharacter) within the string in cell A9 of the worksheet named “Excel VBA Replace” (myCell).
Sub replaceMultipleCharactersInString()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-replace-substitute/
'declare object variable to hold reference to cell you work with
Dim myCell As Range
'declare variables to hold string you work with and replacement character
Dim myString As String
Dim myReplacementCharacter As String
'declare variable to hold Variant containing array whose elements are characters to replace, and variable used to iterate through the elements of the array
Dim myCharactersArray() As Variant
Dim iCharacter As Variant
'identify the cell you work with and the string within that cell
Set myCell = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Excel VBA Replace").Range("A9")
myString = myCell.Value
'specify elements of array (characters to replace) and replacement character
myCharactersArray = Array("a", "e", "i")
myReplacementCharacter = "o"
'loop through each element (iCharacter) of the array (myCharacterArray)
For Each iCharacter In myCharactersArray
'replace all occurrences of element (iCharacter) within current version of string you work with (myString), and assign resulting string to myString variable
myString = Replace(Expression:=myString, Find:=iCharacter, Replace:=myReplacementCharacter)
Next iCharacter
'assign string represented by myString variable to Range.Value property of cell you work with
myCell.Value = myString
End Sub
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Replace Multiple Characters in String
The following GIF illustrates the results of executing this macro example. As expected, the macro replaces all occurrences of the characters “a”, “e” and “i” with the character “o” within the string in cell A9.
#6: Replace Wildcard
VBA Code to Replace Wildcard
To replace characters in a string within a cell using a wildcard with VBA, use a statement with the following structure:
Cell.Replace What:=StringToReplace, Replacement:=ReplacementString, LookAt:=xlPart, SearchOrder:=xlByRows, MatchCase:=False, SearchFormat:=False, ReplaceFormat:=False
Process Followed by VBA Code to Replace Wildcard
VBA Statement Explanation
- Item: Cell.
- VBA Construct: Range object.
- Description: Range object representing the cell you work with.
You can usually return a Range object with constructs such as the Worksheet.Range, Worksheet.Cells (with the Range.Item) or Range.Offset properties.
- Item: Replace.
- VBA Construct: Range.Replace method.
- Description: The Range.Replace method replaces a specific substring (StringToReplace) by another substring (ReplacementString) within Cell.
- Item: What:=StringToReplace.
- VBA Construct: What parameter of the Range.Replace method.
- Description: The What parameter of the Range.Replace method specifies the string you want to replace (StringToReplace).
When specifying StringToReplace, use the following wildcards as required:
- Question mark (?): The question mark represents any single character. For example, “w?ldcard” represents a string (i) starting with a “w”, (ii) followed by any single character (including “i”), and (iii) ending with “lcard”.
- Asterisk (*): The asterisk represents any group of characters. For example, “w*card” represents a string (i) starting with a “w”, (ii) followed by any group of characters (including “ild”), and (iii) ending with “card”.
If you explicitly declare a variable to represent StringToReplace, use the String data type.
- Item: Replacement:=ReplacementString.
- VBA Construct: Replacement parameter of the Range.Replace method.
- Description: The Replacement parameter of the Range.Replace method specifies the substring you want to use as replacement for StringToReplace.
- Item: LookAt:=xlPart.
- VBA Construct: LookAt parameter of the Range.Replace method.
- Description: The LookAt parameter of the Range.Replace method specifies that Range.Replace looks at (and matches) a part (xlPart) of the search data.
- Item: SearchOrder:=xlByRows.
- VBA Construct: SearchOrder parameter of the Range.Replace method.
- Description: The SearchOrder parameter of the Range.Replace method specifies that Range.Replace searches by rows (xlByRows).
- Item: MatchCase:=False.
- VBA Construct: MatchCase parameter of the Range.Replace method.
- Description: The MatchCase parameter of the Range.Replace method specifies that the search isn’t case sensitive (False).
- Item: SearchFormat:=False.
- VBA Construct: SearchFormat parameter of the Range.Replace method.
- Description: The SearchFormat parameter of the Range.Replace method specifies that the search doesn’t consider formatting (False).
- Item: ReplaceFormat:=False.
- VBA Construct: ReplaceFormat parameter of the Range.Replace method.
- Description: The ReplaceFormat parameter of the Range.Replace method specifies that no replace format is set (False).
Macro Example to Replace Wildcard
The following macro replaces the string (i) starting with a “w”, (ii) followed by any group of characters (including “ild”), and (iii) ending with “card” (myStringToReplace), with the string “question mark” (myReplacementString) within the string in cell A10 of the worksheet named “Excel VBA Replace” (myCell).
Sub replaceWildcard()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-replace-substitute/
'declare object variable to hold reference to cell you work with
Dim myCell As Range
'declare variables to hold parameters for string replacement (string to replace and replacement string)
Dim myStringToReplace As String
Dim myReplacementString As String
'identify the cell you work with
Set myCell = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Excel VBA Replace").Range("A10")
'specify parameters for string replacement (string to replace and replacement string). Use wildcards (? or *) to specify string to replace
myStringToReplace = "w*card"
myReplacementString = "question mark"
'replace all occurrences within string in cell you work with, and assign resulting string to Range.Value property of cell you work with
myCell.Replace What:=myStringToReplace, Replacement:=myReplacementString, LookAt:=xlPart, SearchOrder:=xlByRows, MatchCase:=False, SearchFormat:=False, ReplaceFormat:=False
End Sub
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Replace Wildcard
The following GIF illustrates the results of executing this macro example. As expected, the macro replaces the string “wildcard” which (i) starts with a “w”, (ii) followed by a group of characters (“ild”), and (iii) ends with “card”, with the string “question mark” within the string in cell A10.
#7: Replace Character in String by Position
VBA Code to Replace Character in String by Position
To replace a character in a string within a cell according to its position with VBA, use a statement with the following structure:
Cell.Value = WorksheetFunction.Replace(Cell.Value, CharacterPosition, CharactersToReplace, ReplacementString)
Process Followed by VBA Code to Replace Character in String by Position
VBA Statement Explanation
- Item: Cell.
- VBA Construct: Range object.
- Description: Range object representing the cell you work with.
You can usually return a Range object with constructs such as the Worksheet.Range, Worksheet.Cells (with the Range.Item) or Range.Offset properties.
- Item: Value.
- VBA Construct: Range.Value property.
- Description: The Range.Value property specifies the value (in this case string) within Cell.
- Item: =.
- VBA Construct: Assignment operator.
- Description: The = operator assigns the string returned by the Replace function to the Range.Value property of Cell.
- Item: WorksheetFunction.Replace(…).
- VBA Construct: WorksheetFunction.Replace method.
- Description: The WorksheetFunction.Replace method replaces a substring with a different string (ReplacementString). The replaced substring is determined based on its position within the string you work with (CharacterPosition) and the number of characters to replace (CharactersToReplace).
- Item: Cell.Value.
- VBA Construct: Arg1 parameter of the WorksheetFunction.Replace method, Range object and Range.Value property.
- Description: The Arg1 parameter of the WorksheetFunction.Replace method specifies the string containing the substring you want to replace. Within this macro structure, Arg1 is the value (string) within Cell, as returned by the Range.Value property.
If you explicitly declare a variable to represent Arg1, use the String data type.
- Item: CharacterPosition.
- VBA Construct: Arg2 parameter of the WorksheetFunction.Replace method.
- Description: The Arg2 parameter of the WorksheetFunction.Replace method specifies the starting position within Arg1 (Cell.Value) of the substring you want to replace with Arg4 (ReplacementString).
If you explicitly declare a variable to represent Arg2 (CharacterPosition), use the Double data type.
- Item: CharactersToReplace.
- VBA Construct: Arg3 parameter of the WorksheetFunction.Replace method.
- Description: The Arg3 parameter of the WorksheetFunction.Replace method specifies the number of characters within Arg1 (Cell.Value) you want to replace with Arg4 (ReplacementString).
If you explicitly declare a variable to represent Arg3 (CharactersToReplace), use the Double data type.
- Item: ReplacementString.
- VBA Construct: Arg4 parameter of the WorksheetFunction.Replace method.
- Description: The Arg4 parameter of the WorksheetFunction.Replace method specifies the substring you want to use as replacement.
If you explicitly declare a variable to represent Arg4 (ReplacementString), use the String data type.
Macro Example to Replace Character in String by Position
The following macro replaces the string starting in position 10 (myCharacterPosition) with a length of 1 character (myCharactersToReplace) with the string “+” (myReplacementString) within the string in cell A11 of the worksheet named “Excel VBA Replace” (myCell).
Sub replaceCharacterByPosition()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-replace-substitute/
'declare object variable to hold reference to cell you work with
Dim myCell As Range
'declare variables to hold parameters for string replacement (starting position of string to replace, number of characters to replace, and replacement string)
Dim myCharacterPosition As Double
Dim myCharactersToReplace As Double
Dim myReplacementString As String
'identify the cell you work with
Set myCell = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Excel VBA Replace").Range("A11")
'specify parameters for string replacement (starting position of string to replace, number of characters to replace, and replacement string)
myCharacterPosition = 10
myCharactersToReplace = 1
myReplacementString = "+"
'replace string in cell you work with, and assign resulting string to Range.Value property of cell you work with
myCell.Value = WorksheetFunction.Replace(myCell.Value, myCharacterPosition, myCharactersToReplace, myReplacementString)
End Sub
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Replace Character in String by Position
The following GIF illustrates the results of executing this macro example. As expected, the macro replaces the string starting in position 10 with a length of 1 character with the string “+” within the string in cell A11.
References to VBA Constructs Used in this VBA Tutorial
Use the following links to visit the appropriate webpage in the Microsoft Developer Network:
- Identify the workbook and worksheet you work with:
- Workbook object.
- Application.ThisWorkbook property.
- Worksheet object.
- Workbook.Worksheets property.
- Identify the cell you work with:
- Range object.
- Worksheet.Range property.
- Worksheet.Cells property.
- Range.Item property.
- Range.Offset property.
- Obtain or set the string within the cell you work with:
- Range.Value property.
- Assign a new string to the cell you work with or to the variable representing the string you work with:
- = operator.
- Replace characters or strings:
- Replace function.
- Range.Replace method.
- WorksheetFunction.Replace method.
- Complete and concatenate truncated strings:
- Left function.
- & operator.
- Create an array containing characters and loop through its elements:
- For Each… Next statement.
- Array function.
- Work with variables and data types:
- Dim statement.
- Set statement.
- Data types:
- Double data type.
- Long data type.
- String data type.
- Variant data type.
In this Article
- Replace Function
- Starting Position
- Replace a Few Occurrences Only
- Case Sensitivity
- Double Quotes
- Replace Break Line in Cell
This tutorial will demonstrate how to use the VBA Replace Function to replace strings of text.
Replace Function
The VBA Replace function replaces a substring of text with another substring.
Sub ReplaceExample_1()
MsgBox Replace("ABCABCABC", "A", "!")
'Result is: "!BC!BC!BC"
MsgBox Replace("I like pink, red and black", "pink", "purple")
'Result is: "I like purple, red and black"
MsgBox Replace("A, B, C, A, B, C, A, B, C", ", ", ",")
'Result is: "ABCABCABC"
MsgBox Replace("ABCABCABC", "ABC", "!")
'Result is: "!!!"
MsgBox Replace("ABCABCABC", "ABc", "!")
'Result is: "ABCABCABC"
MsgBox Replace("ABCABCABC", "ZBC", "!")
'Result is: "ABCABCABC"
End Sub
Starting Position
By assigning a start position, you can indicate what character position to start with (default = 1).
Sub ReplaceExample_2()
MsgBox Replace("ABCABCABC", "A", "123") 'Result is: "123BC123BC123BC"
MsgBox Replace("ABCABCABC", "A", "123", 2) 'Result is: "BC123BC123BC"
MsgBox Replace("ABCABCABC", "A", "123", 7) 'Result is: "123BC"
MsgBox Replace("ABCABCABC", "A", "123", 8) 'Result is: "BC"
MsgBox Replace("ABCABCABC", "ABC", "!@") 'Result is: "!@!@!@"
MsgBox Replace("ABCABCABC", "ABC", "!@", 2) 'Result is: "BC!@!@"
MsgBox Replace("ABCABCABC", "ABC", "!@", 6) 'Result is: "C!@"
MsgBox Replace("ABCABCABC", "ABC", "!@", 7) 'Result is: "!@"
MsgBox Replace("ABCABCABC", "ABC", "!@", 8) 'Result is: "BC"
End Sub
Replace a Few Occurrences Only
You can also indicate how many instances of the substring to replace (default All)
Sub ReplaceExample_3()
MsgBox Replace("ABCABCABC", "A", "12") 'Result is: "12BC12BC12BC"
MsgBox Replace("ABCABCABC", "A", "12", , 1) 'Result is: "12BCABCABC"
MsgBox Replace("ABCABCABC", "A", "12", , 2) 'Result is: "12BC12BCABC"
MsgBox Replace("ABCABCABC", "A", "12", , 3) 'Result is: "12BC12BC12BC"
MsgBox Replace("ABCABCABC", "A", "12", , 5) 'Result is: "12BC12BC12BC"
MsgBox Replace("ABCABCABC", "A", "12", 3, 1)
'Result is: "C12BCABC"
'We replaced A with 12, 1 time starting from position 3 of the original string.
End Sub
Case Sensitivity
The Replace Function is case sensitive by default. You can switch to case insensitive by adding the optional parameter (vbTextCompare). Here, you must also define the starting position of the search.
Sub ReplaceExample_4()
MsgBox Replace("ABcABCABc", "ABc", "12")
'Result is: "12ABC12"
MsgBox Replace("ABcABCABc", "ABc", "12", , , vbTextCompare)
'Result is: "121212"
'When we use vbTextCompare we need to add the 2 other optional arguments:
'start and count
MsgBox Replace("ABcABCABcABc", "ABc", "12", 3, 1)
'Result is: "cABC12ABc"
'Started from position3 and replaced ABC only 1 time.
End Sub
You can also perform a case-insensitive Replace, by adding Option Compare Text to the top of your module:
Option Compare TextDouble Quotes
The Replace Function can replace the double quotes character used to delimit the start and end of a string.
VBA Chr function can return a character from its number in the character set.
MsgBox Chr(34) 'Result is: "Or
MsgBox Chr(64) 'Result is: @
Double quotes can be used inside the Replace Function using “””” or VBA Function Chr(34).
Sub ReplaceExample_5()
Dim StrEx As String
StrEx = "AB""AB"""
MsgBox StrEx 'Result is: AB"AB"
MsgBox Replace(StrEx, Chr(34), "12")
'Result is: AB12AB12
MsgBox Replace(StrEx, """", "DQ")
'Result is: "ABDQABDQ"
End Sub
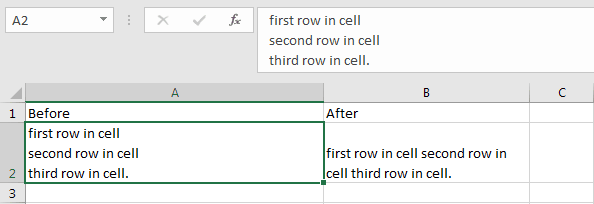
Replace Break Line in Cell
The Replace Function can find the break line special character in a cell and remove it or replace it with a space character. The break line special character can be entered in a cell using the keyboard shortcut Alt+Enter and can be used in VBA code with its Character set number using VBA function Chr(10).
Sub ReplaceExample_6()
Dim StrEx As String 'Define a string variable
'Read the value of cell A2 in worksheet Sheet1
StrEx = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Sheet1").Range("A2").Value
'The break line character entered with Alt+Enter is Chr(10) and is invisible.
'This code line replaces that character with space
StrEx = Replace(StrEx, Chr(10), " ")
'Write the replaced value in cell B2 in worksheet Sheet1
ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Sheet1").Range("B2").Value = StrEx
End Sub
Dim numberColumn, phraseColumn, titleColumn, nFirstRow, nLastRow As Integer
Dim currentPosition As Long
Dim currentRow As Integer
Sub DoEverything()
Call DoInit
'x = Application.CountA(Rows("35:35"))
'x = Application.WorksheetFunction.CountA(ActiveWorksheet.Columns("A"))
Worksheets(1).Copy After:=Worksheets(Worksheets.Count)
Set currentWorksheet = Worksheets(Worksheets.Count)
currentWorksheet.Activate
currentWorksheet.Name = "Технические данные"
currentColumns = Application.WorksheetFunction.CountA(currentWorksheet.Rows("1"))
currentColumns = currentColumns + 1
currentWorksheet.Cells(1, currentColumns - 1).Copy currentWorksheet.Cells(1, currentColumns)
currentWorksheet.Cells(1, currentColumns).Value = "Список фраз"
'fusion
outText = ""
completedRow = nFirstRow
counter = CStr(currentWorksheet.Cells(completedRow, numberColumn))
For currentRow = completedRow To nLastRow
If CStr(currentWorksheet.Cells(currentRow, numberColumn)) = CStr(counter) Then
If outText = "" Then
outText = currentWorksheet.Cells(currentRow, phraseColumn).Value
Else
outText = outText & ", " & currentWorksheet.Cells(currentRow, phraseColumn).Value
End If
Else
'counter = counter + 1
counter = CStr(currentWorksheet.Cells(currentRow, numberColumn))
currentWorksheet.Cells(completedRow, currentColumns).Value = outText
completedRow = currentRow
outText = currentWorksheet.Cells(currentRow, phraseColumn).Value
End If
If currentRow = nLastRow Then
If outText = "" Then
outText = currentWorksheet.Cells(currentRow, phraseColumn).Value
Else
outText = outText & ", " & currentWorksheet.Cells(currentRow, phraseColumn).Value
End If
currentWorksheet.Cells(completedRow, currentColumns).Value = outText
End If
Next currentRow
'removal
completedRow = nFirstRow
counter = CStr(currentWorksheet.Cells(completedRow, numberColumn))
For currentRow = completedRow To nLastRow
If CStr(currentWorksheet.Cells(currentRow, numberColumn)) <> CStr(counter) Then
counter = CStr(currentWorksheet.Cells(currentRow, numberColumn))
completedRow = completedRow + 1
nLastRow = nLastRow - (currentRow - 1 - completedRow)
If currentRow > completedRow Then
currentWorksheet.Range(Rows(completedRow).EntireRow, Rows(currentRow - 1).EntireRow).Delete
End If
' For j = currentRow - 1 To completedRow Step -1
' currentWorksheet.Rows(j).EntireRow.Delete
' Next j
currentRow = completedRow
End If
Next currentRow
'New column Заголовок ТЗ
nLastRow = currentWorksheet.Cells(Rows.Count, numberColumn).End(xlUp).Row
currentWorksheet.Columns(1).Insert Shift:=xlToLeft
currentWorksheet.Cells(1, 2).Copy currentWorksheet.Cells(1, 1)
currentWorksheet.Cells(1, 1).Value = "Заголовок ТЗ"
currentWorksheet.Columns(1).ColumnWidth = 62
currentWorksheet.Range(currentWorksheet.Cells(1, 1), currentWorksheet.Cells(nLastRow, 1)).Interior.Color = 11910834
currentColumns = currentColumns + 1
titleColumn = 3
For currentColumn = 3 To currentColumns
If currentWorksheet.Cells(1, currentColumn).Value = "Название" Then
titleColumn = currentColumn
End If
Next currentColumn
For currentRow = nFirstRow To nLastRow
'currentWorksheet.Cells(currentRow, 2).Copy currentWorksheet.Cells(currentRow, 1)
currentWorksheet.Cells(currentRow, 1).Value = "ТЗ №" & CStr(currentWorksheet.Cells(currentRow, 2).Value) & " для страницы - " & CStr(currentWorksheet.Cells(currentRow, titleColumn).Value)
Next currentRow
End Sub
Sub DoInit()
numberColumn = 1
phraseColumn = 2
titleColumn = 3
nFirstRow = 2
nLastRow = ActiveSheet.Cells(Rows.Count, numberColumn).End(xlUp).Row
End Sub
Sub macrzamena()
'Замена символов
Columns("A:A").Select
Selection.Replace What:=",", Replacement:="ггггг", LookAt:=xlPart, _
SearchOrder:=xlByRows, MatchCase:=False, SearchFormat:=False, _
ReplaceFormat:=False
Selection.Replace What:=":", Replacement:="ааа", LookAt:=xlPart, _
SearchOrder:=xlByRows, MatchCase:=False, SearchFormat:=False, _
ReplaceFormat:=False
Selection.Replace What:="~?", Replacement:="ааа", LookAt:=xlPart, _
SearchOrder:=xlByRows, MatchCase:=False, SearchFormat:=False, _
ReplaceFormat:=False
Selection.Cells(1).Select
ExecuteExcel4Macro ("SOUND.PLAY(,""C:WindowsMediattt.wav"")")
'Замена символов
End Sub





 Сообщение было отмечено The_Fog как решение
Сообщение было отмечено The_Fog как решение