Операторы сравнения чисел и строк, ссылок на объекты (Is) и строк по шаблону (Like), использующиеся в VBA Excel. Их особенности, примеры вычислений.
Операторы сравнения чисел и строк
Операторы сравнения чисел и строк представлены операторами, состоящими из одного или двух математических знаков равенства и неравенства:
- < – меньше;
- <= – меньше или равно;
- > – больше;
- >= – больше или равно;
- = – равно;
- <> – не равно.
Синтаксис:
|
Результат = Выражение1 Оператор Выражение2 |
- Результат – любая числовая переменная;
- Выражение – выражение, возвращающее число или строку;
- Оператор – любой оператор сравнения чисел и строк.
Если переменная Результат будет объявлена как Boolean (или Variant), она будет возвращать значения False и True. Числовые переменные других типов будут возвращать значения 0 (False) и -1 (True).
Операторы сравнения чисел и строк работают с двумя числами или двумя строками. При сравнении числа со строкой или строки с числом, VBA Excel сгенерирует ошибку Type Mismatch (несоответствие типов данных):
|
Sub Primer1() On Error GoTo Instr Dim myRes As Boolean ‘Сравниваем строку с числом myRes = «пять» > 3 Instr: If Err.Description <> «» Then MsgBox «Произошла ошибка: « & Err.Description End If End Sub |
Сравнение строк начинается с их первых символов. Если они оказываются равны, сравниваются следующие символы. И так до тех пор, пока символы не окажутся разными или одна или обе строки не закончатся.
Значения буквенных символов увеличиваются в алфавитном порядке, причем сначала идут все заглавные (прописные) буквы, затем строчные. Если необходимо сравнить длины строк, используйте функцию Len.
|
myRes = «семь» > «восемь» ‘myRes = True myRes = «Семь» > «восемь» ‘myRes = False myRes = Len(«семь») > Len(«восемь») ‘myRes = False |
Оператор Is – сравнение ссылок на объекты
Оператор Is предназначен для сравнения двух переменных со ссылками на объекты.
Синтаксис:
|
Результат = Объект1 Is Объект2 |
- Результат – любая числовая переменная;
- Объект – переменная со ссылкой на любой объект.
Если обе переменные Объект1 и Объект2 ссылаются на один и тот же объект, Результат примет значение True. В противном случае результатом будет False.
|
Set myObj1 = ThisWorkbook Set myObj2 = Sheets(1) Set myObj3 = myObj1 Set myObj4 = Sheets(1) myRes = myObj1 Is myObj2 ‘myRes = False myRes = myObj1 Is myObj3 ‘myRes = True myRes = myObj2 Is myObj4 ‘myRes = True |
По-другому ведут себя ссылки на диапазоны ячеек. При присвоении ссылок на один и тот же диапазон нескольким переменным, в памяти создаются уникальные записи для каждой переменной.
|
Set myObj1 = Range(«A1:D4») Set myObj2 = Range(«A1:D4») Set myObj3 = myObj1 myRes = myObj1 Is myObj2 ‘myRes = False myRes = myObj1 Is myObj3 ‘myRes = True |
Оператор Like – сравнение строк по шаблону
Оператор Like предназначен для сравнения одной строки с другой по шаблону.
Синтаксис:
|
Результат = Выражение Like Шаблон |
- Результат – любая числовая переменная;
- Выражение – любое выражение, возвращающее строку;
- Шаблон – любое строковое выражение, которое может содержать знаки подстановки.
Строка, возвращенная аргументом Выражение, сравнивается со строкой, возвращенной аргументом Шаблон. Если обе строки совпадают, переменной Результат присваивается значение True, иначе – False.
|
myRes = «восемь» Like «семь» ‘myRes = False myRes = «восемь» Like «*семь» ‘myRes = True myRes = «Куда идет король» Like «идет» ‘myRes = False myRes = «Куда идет король» Like «*идет*» ‘myRes = True |
Со знаками подстановки для оператора Like вы можете ознакомиться в статье Знаки подстановки для шаблонов.
VBA in Excel stands for Visual Basic for Applications which is Microsoft’s programming language. To optimize the performance and reduce the time in Excel we need Macros and VBA is the tool used in the backend.
Some helpful links to get more insights about Macros, VBA in Excel :
1. Record Macros in Excel.
2. How to Create a Macro in Excel?
In this article, we are going to discuss various comparison operators in Excel VBA.
Implementation :
In the Microsoft Excel tabs, select the Developer Tab. Initially, the Developer Tab may not be available.
The Developer Tab can be enabled easily by a two-step process :
- Right-click on any of the existing tabs in the top of the Excel window.
- Now select Customize the Ribbon from the pop-down menu.
- The Excel Options Box, check the box Developer to enable it and click on OK.
- Now, the Developer Tab is visible.
- Now click on the Visual Basic option in the Developer tab and make a new module to write the program.
Developer -> Visual Basic -> Tools -> Macros
Now create a Macro and give any suitable name.
This will open the Editor window where can write the code.
Comparison Operators in Excel:
| S.No. | Operators |
Definition |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | <> |
Not equal operator is used to compare two operands. If the two operands are not equal it returns TRUE else it returns FALSE. For example : A=10, B= 20 The condition will be TRUE for A <> B, since A and B are not equal. |
| 2 | = |
Equal operator is used to compare two operands. If the two operands are equal it returns TRUE else it returns FALSE. For example : A=20, B= 20 The condition will be TRUE for A = B, since A and B are equal. |
| 3 | > |
Greater than operator checks whether the operand on the left hand side is strictly greater than the operand on RHS. If greater then it returns TRUE else FALSE. For example : A=10, B= 5 The condition will be TRUE for A > B, since A is greater than B. |
| 4 | < |
Less than operator checks whether the operand on the left hand side is strictly less than the operand on RHS. If greater then it returns TRUE else FALSE. For example : A=10, B= 5 The condition will be FALSE for A < B, since A is greater than B. |
| 5 | >= |
Greater than equal to operator checks whether the operand on the left hand side is either greater or equal to the operand on RHS. If greater or equal then it returns TRUE else FALSE. For example : A=10, B=10 The condition will be TRUE for A >= B, since A is equal to B. |
| 6 | <= |
Less than equal to operator checks whether the operand on the left hand side is either lesser or equal to the operand on RHS. If lesser or equal then it returns TRUE else FALSE. For example : A=5, B=10 The condition will be TRUE for A <= B, since A is less than B. |
The comparison operators are mostly used with the If Else Then statement in Excel because comparison operators return TRUE if the condition is met and FALSE if not.
The syntax of If Else in Excel is :
If condition/expression Then
Code Block for True
Else
Code Block for False
End If
Let’s take an example where values of A=-1 and B=-5 and see the code in Excel VBA for all the comparison operators.
1. Equal To and Not Equal To
Sub Comparison_Operator_Demo()
'Entering the numbers
Dim A As Integer: A = -1
Dim B As Integer: B = -5
'Condition for Equal To
If A = B Then
MsgBox " A and B are equal"
Else
MsgBox " A and B are not equal"
End If
End Sub
In the above code, If the condition becomes FALSE since A and B values are not the same. So the code block inside Else will be executed.
Sub Comparison_Operator_Demo()
'Entering the numbers
Dim A As Integer: A = -1
Dim B As Integer: B = -5
'Condition for Not Equal To
If A <> B Then
MsgBox " True since A and B are not same"
Else
MsgBox " False since A and B are same"
End If
End Sub
In the above code If the condition becomes TRUE since A and B are not same. So the code block inside If will be executed.
2. Greater than or Less than operator :
Sub Comparison_Operator_Demo()
'Entering the numbers
Dim A As Integer: A = -1
Dim B As Integer: B = -5
'Condition for Greater Than
If A > B Then
MsgBox " A is greater than B"
Else
MsgBox " A is not greater than B"
End If
End Sub
In the above code If the condition becomes TRUE since A is greater than B. So the code block inside If will be executed.
Sub Comparison_Operator_Demo()
'Entering the numbers
Dim A As Integer: A = -1
Dim B As Integer: B = -5
'Condition for Less Than
If A < B Then
MsgBox "True because A is less than B"
Else
MsgBox "False because A is greater than B"
End If
End Sub
In the above code If the condition becomes FALSE since A is greater than B. So the code block inside Else will be executed.
Similarly, you can do for Greater than equal to and Less than equal to operators.
I would like to compare 2 cells’ value and see whether they are match or not.
I know how to do it on excel but I dont’ know how to put it vba code.
Input & output:
- The value of cell A1 is already in the excel.
- Manually enter a value in Cell B1.
- click on a button_click sub to see whether the value on 2 cells are the same or not.
- Show «Yes» or «No» on cell C1
Excel formula:
=IF(A1=B1,"yes","no")
asked Jan 21, 2015 at 15:55
Give this a try:
Sub CompareCells()
If [a1] = [b1] Then
[c1] = "yes"
Else
[c1] = "no"
End If
End Sub
Assign this code to the button.
answered Jan 21, 2015 at 15:58
Gary’s StudentGary’s Student
95.3k9 gold badges58 silver badges98 bronze badges
1
If (Range("A1").Value = Range("B1").Value) Then
Range("C1").Value = "Yes"
Else
Range("C1").Value = "No"
End If
Chrismas007
6,0654 gold badges23 silver badges47 bronze badges
answered Jan 21, 2015 at 16:03
EswinEswin
292 bronze badges
5
You can use the IIF function in VBA. It is similar to the Excel IF
[c1] = IIf([a1] = [b1], "Yes", "No")
answered Jan 21, 2015 at 16:47
Paul KellyPaul Kelly
9057 silver badges13 bronze badges
1
Here is an on change Sub (code MUST go in the sheet module). It will only activate if you change a cell in column B.
Private Sub Worksheet_Change(ByVal Target As Range)
If Target is Nothing Then Exit Sub
If Target.Cells.Count > 1 Then Exit Sub
If Target.Column <> 2 Then Exit Sub
If Cells(Target.Row, 1).Value = Cells(Target.Row, 2).Value Then
Cells(Target.Row, 3).Value = "Yes"
Else
Cells(Target.Row, 3).Value = "No"
End If
End Sub
For the record, this doesn’t use a button, but it accomplishes your goal of calculating if the two cells are equal any time you manually enter data into cells in Col B.
answered Jan 21, 2015 at 16:08
Chrismas007Chrismas007
6,0654 gold badges23 silver badges47 bronze badges
Sub CompareandHighlight()
Dim n As Integer
Dim sh As Worksheets
Dim r As Range
n = Worksheets("Indices").Range("E:E").Cells.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeConstants).Count
Application.ScreenUpdating = False
Dim match As Boolean
Dim valE As Double
Dim valI As Double
Dim i As Long, j As Long
For i = 2 To n
valE = Worksheets("Indices").Range("E" & i).Value
valI = Worksheets("Indices").Range("I" & i).Value
If valE = valI Then
Else:
Worksheets("Indices").Range("E" & i).Font.Color = RGB(255, 0, 0)
End If
Next i
Application.ScreenUpdating = True
End Sub
barbsan
3,39811 gold badges21 silver badges28 bronze badges
answered Nov 21, 2018 at 9:29
0
These are operators that are used to compare values. Comparison operators include equal to, less than, greater than and not equal to
Comparison operators are used to compare values for validation purposes. Let’s say you are developing a simple point of sale application. In this application, you want to validate the values entered before you post. In such cases, you can use comparison operators. This operator will check against the negative numbers or to ensure that the amount paid does not exceed the billed amount. Comparison operators come in handy in such situations.
The following table lists the comparison operators defined in VBA.
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| = | Equal: checks if two values are equal. It is also used as an assignment operator |
| < | Less than: This operator is used to subtract numbers |
| > | Greater than: This operator is used to multiply numbers |
| <> | Not equal to: This operator is used to divide numbers |
| <= | Less than or equal to: |
| >= | Greater than or equal to: |
VBA Comparison Operators with Example
The following table shows Excel VBA Comparison Operators with examples and output.
| S/N | Operator | Example | Output |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | = | If x = z Then | Returns true if they are equal, else it returns false |
| 2 | < | If x < z Then | Returns true if x is less than z, else it returns false |
| 3 | > | If x > z Then | Returns true if x is greater than z, else it returns false |
| 4 | <> | If x <> z Then | Returns true if they are not equal, else it returns false |
| 5 | <= | If x <= z Then | Returns true if x is less than or equal to z, else it returns false |
| 6 | >= | If x >= Then | Returns true if x is greater than or equal to z, else it returns false |
Example source code
Equal Comparison Operator
If 2 = 1 Then
MsgBox "True", vbOKOnly, "Equal Operator"
Else
MsgBox "False", vbOKOnly, "Equal Operator"
End If
HERE,
- “If 2 = 1 Then… Else… End If” uses the if statement to evaluate the condition “2 = 1”
- “MsgBox…” Is a built-in function that displays a message box.
- The first parameter “True” or “False” is what will be displayed in the message box. In our example, 2 is not equal to 1, therefore, it will show “false” in the msg box.
- The second parameter “vbOKOnly” is the button that is displayed in the message box
- The third parameter “Equal Operator” is the title of the message box.
Executing the above code gives the following results
Download the above Excel Code
Перейти к основному содержанию
Статья даёт ответы на следующие вопросы:
- Как сравнить две таблицы в Excel с помощью макросов VBA?
- Как обращаться к ячейкам таблицы Excel с помощью VBA?
- Как осуществлять перебор ячеек таблицы в цикле с помощью VBA?
В предыдущей статье Сравнение таблиц в Excel мы рассмотрели подход к сравнению сложных таблиц с использованием формул и без программирования.
В данной статье рассмотрим способ сравнения таблиц Excel с помощью VBA макросов на примере тех же исходных данных.
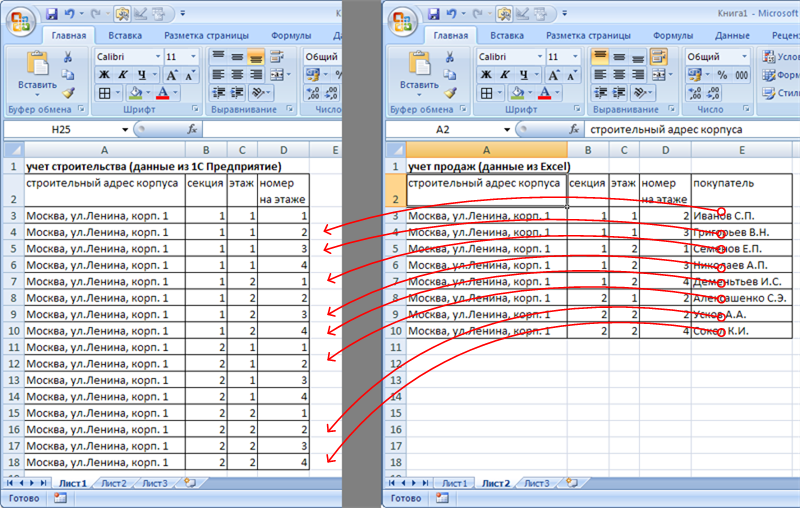
Проиллюстрируем задачу картинкой из первой статьи.
Для начала напишем алгоритм наших действий по сравнению таблиц.
- Определим диапазоны данных первой и второй таблицы, то есть найдем последние значимые строки и сохраним их номера в переменных (последняя строка таблицы 1 — last_i и последняя строка таблицы 2 — last_j).
- Начнем проходить по каждой строке таблицы 2 (внешний цикл), данные из которой нужно перенести в таблицу 1. С первой строки данных (в примере это строка 3) до последней строки таблицы 2.
- Для каждой строки таблицы 2 определим идентификатор строки, путем формирования строки, содержащей полный адрес квартиры (значения из нескольких колонок, разделенные дефисами).
- Начнем проходить по каждой строке таблицы 1 (внутренний цикл) с первой строки данных (в примере это строка 3) до последней строки таблицы 1, определяя при этом идентификатор строки.
- Сравним значения идентификаторов строк таблицы 1 и таблицы 2.
- Если идентификаторы равны, перепишем ФИО покупателя из ячейки таблицы 2 в соответствующую ячейку таблицы 1; прервем внутренний цикл по таблице 1 и перейдем к следующей строке таблицы 2 (переход к п.2).
Теперь остается реализовать алгоритм в виде программного кода макроса.
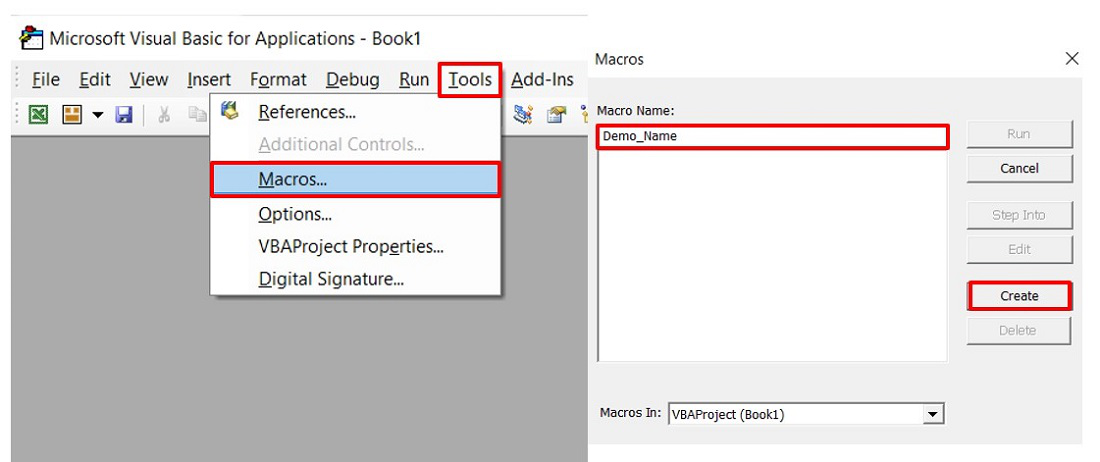
Для этого откроем вкладку Вид ленты функций Excel. Щелкнем на нижнюю часть со стрелкой кнопки Макросы. В открывшемся подменю выберем Запись макроса. В результате начнется запись нового макроса. Поскольку код мы будем формировать вручную, то еще раз зайдем в подменю макросов и выберем Остановить запись. Далее еще раз войдем в подменю макросов и выберем Макросы.
В появившемся диалоге выделим наш макрос и нажмем Изменить.
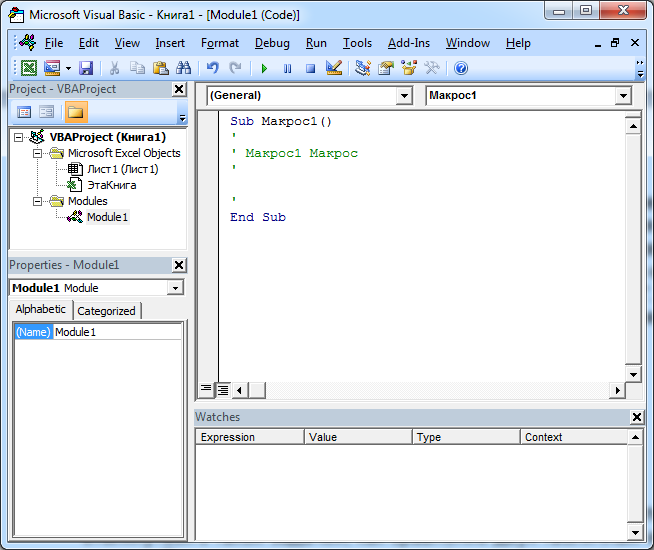
На экране откроется окно редактора макросов Visual Basic for Applications. В области кода (правая верхняя область) отображается код только что созданного пустого макроса.
В процедуру Макрос1 (между объявлениями начала и конца процедуры: Sub и End Sub) необходимо вставить код, решающий поставленную задачу.
Образец кода представлен ниже.
Sub Макрос1()
'
' Макрос1 сравнение двух таблиц с использованием макроса VBA
'
' ссылка на первый лист книги
Dim sheet1 As Worksheet
Set sheet1 = ActiveWorkbook.Sheets(1)
' ссылка на второй лист книги
Dim sheet2 As Worksheet
Set sheet2 = ActiveWorkbook.Sheets(2)
' строка для хранения идентификатора строки первой таблицы
Dim str1 As String
' строка для хранения идентификатора строки второй таблицы
Dim str2 As String
' позиция курсора (номер строки) в первой таблице
Dim i As Integer
i = 3
Dim last_i As Integer
last_i = 3
' позиция курсора (номер строки) во второй таблице
Dim j As Integer
j = 3
Dim last_j As Integer
last_j = 3
' определяем последнюю значимую строку первой таблицы (последняя строка, в первой колонке которой есть значение)
For Each Cell In sheet1.Range("A:A")
If Cell.Row > 2 Then
If Cell.Value > "" Then
last_i = Cell.Row
Else
Exit For
End If
End If
Next Cell
' определяем последнюю значимую строку второй таблицы (последняя строка, в первой колонке которой есть значение)
For Each Cell In sheet2.Range("A:A")
If Cell.Row > 2 Then
If Cell.Value > "" Then
last_j = Cell.Row
Else
Exit For
End If
End If
Next Cell
' пробегаем по строкам второй таблицы (внешний цикл)
For j = 3 To last_j
' определяем идентификатор текущей строки
str2 = sheet2.Cells(j, 1).Value & "-" & sheet2.Cells(j, 2).Value & "-" & sheet2.Cells(j, 3).Value & "-" & sheet2.Cells(j, 4).Value
' пробегаем по строкам первой таблицы (внутренний цикл)
For i = 3 To last_i
' определяем идентификатор текущей строки
str1 = sheet1.Cells(i, 1).Value & "-" & sheet1.Cells(i, 2).Value & "-" & sheet1.Cells(i, 3).Value & "-" & sheet1.Cells(i, 4).Value
' сравниваем идентификаторы строк первой и второй таблицы
If str2 = str1 Then
' если совпадение найдено, то записываем покупателя из второй таблицы в первую в строку с соответствующей ему квартирой
sheet1.Cells(i, 5).Value = sheet2.Cells(j, 5).Value
' прекращаем внутренний цикл, переходим к следующей итерации внешнего цикла
' (к следующей записи второй таблицы)
Exit For
End If
Next i
Next j
End Sub
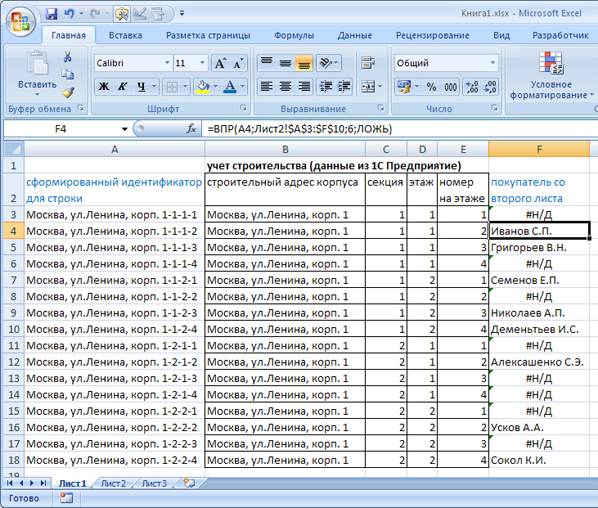
Результат решения задачи:
Другие интересные статьи
- Как сравнить две таблицы в Excel с использованием формул?
- Горячие клавиши Excel
Тэги:
- Статьи
- Excel
- сравнение таблиц
- VBA
- макросы