Содержание
- 1 Add where clause to the select statement
- 2 Creating a Select Query with ActiveX Data Objects
- 3 Executing a Select Query
- 4 Get DISTINCT records
- 5 Get DISTINCTROW
- 6 Get more than one column
- 7 Get only one column
- 8 Get the top 10 percent
- 9 Get the top 5 percent
- 10 Loop through the ResultSet after executing select statement
- 11 Modifying a Select Query
- 12 Order by two fields
- 13 Order record in a decscending order
- 14 Order the resultset with Order by clause
- 15 Select all columns
- 16 Use and to combine conditions
- 17 Use Between And
- 18 Use between and with number type column
- 19 Use Date function in where clause
- 20 Use IN and like in where clause
- 21 Use IN in select statement
- 22 Use «Is not null»
- 23 Use Is NULL to check if a column is null
- 24 Use Not In
- 25 Use «Select all»
- 26 use SUM in sql statement
- 27 Use where clause and order by clause together
- 28 Use wild card character in link
- 29 Using Date field type in select statement
- 30 You must use a pound symbol (#) when delimiting dates for Microsoft Access, like this:
Add where clause to the select statement
<source lang="vb">
Sub CreateRst_WithSQL()
Dim conn As ADODB.Connection
Dim myRecordset As ADODB.Recordset
Dim strConn As String
strConn = "Provider = Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;" & _
"Data Source=" & CurrentProject.Path & _
"mydb.mdb"
Set conn = New ADODB.Connection
conn.Open strConn
Set myRecordset = conn.Execute("SELECT txtCustFimyRecordsetName, txtCustLastName FROM tblCustomer WHERE txtState = "NJ"")
Do Until myRecordset.EOF
For Each fld In myRecordset.Fields
Debug.Print fld.Name & "=" & fld.Value
Next fld
myRecordset.MoveNext
Loop
myRecordset.Close
Set myRecordset = Nothing
conn.Close
Set conn = Nothing
End Sub
</source>
Creating a Select Query with ActiveX Data Objects
<source lang="vb">
Sub Create_SelectQuery()
Dim cat As ADOX.Catalog Dim cmd As ADODB.rumand Dim strPath As String Dim strSQL As String Dim strQryName As String On Error GoTo ErrorHandler strPath = CurrentProject.Path & "mydb.mdb" strSQL = "SELECT Employees.* FROM Employees WHERE Employees.City="London";" strQryName = "London Employees" Set cat = New ADOX.Catalog cat.ActiveConnection = "Provider=Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;Data Source=" & strPath Set cmd = New ADODB.rumand cmd.rumandText = strSQL cat.Views.Append strQryName, cmd
ExitHere:
Set cmd = Nothing
Set cat = Nothing
MsgBox "The procedure completed successfully.", _
vbInformation, "Create Select Query"
Exit Sub
ErrorHandler:
If InStr(Err.Description, "already exists") Then
cat.Views.Delete strQryName
Resume
Else
MsgBox Err.Number & ": " & Err.Description
Resume ExitHere
End If
End Sub
</source>
Executing a Select Query
<source lang="vb">
Sub Execute_SelectQuery()
Dim cmd As ADODB.rumand
Dim myRecordset As ADODB.Recordset
Dim strPath As String
strPath = CurrentProject.Path & "mydb.mdb"
Set cmd = New ADODB.rumand
With cmd
.ActiveConnection = "Provider=Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;Data Source=" & strPath
.rumandText = "[Products by Category]"
.rumandType = adCmdTable
End With
Set myRecordset = New ADODB.Recordset
Set myRecordset = cmd.Execute
Debug.Print myRecordset.GetString
myRecordset.Close
Set myRecordset = Nothing
Set cmd = Nothing
End Sub
</source>
Get DISTINCT records
<source lang="vb">
Sub CreateRst_WithSQL()
Dim conn As ADODB.Connection
Dim myRecordset As ADODB.Recordset
Dim strConn As String
strConn = "Provider = Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;" & _
"Data Source=" & CurrentProject.Path & _
"mydb.mdb"
Set conn = New ADODB.Connection
conn.Open strConn
Set myRecordset = conn.Execute("SELECT DISTINCT City FROM Employees ")
Do Until myRecordset.EOF
For Each fld In myRecordset.Fields
Debug.Print fld.Name & "=" & fld.Value
Next fld
myRecordset.MoveNext
Loop
myRecordset.Close
Set myRecordset = Nothing
conn.Close
Set conn = Nothing
End Sub
</source>
Get DISTINCTROW
<source lang="vb">
Sub CreateRst_WithSQL()
Dim conn As ADODB.Connection
Dim myRecordset As ADODB.Recordset
Dim strConn As String
strConn = "Provider = Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;" & _
"Data Source=" & CurrentProject.Path & _
"mydb.mdb"
Set conn = New ADODB.Connection
conn.Open strConn
Set myRecordset = conn.Execute("SELECT DISTINCTROW CompanyName FROM Customers, Orders WHERE Customers.CustomerID = Orders.CustomerID ORDER BY CompanyName;
«)
Do Until myRecordset.EOF
For Each fld In myRecordset.Fields
Debug.Print fld.Name & "=" & fld.Value
Next fld
myRecordset.MoveNext
Loop
myRecordset.Close
Set myRecordset = Nothing
conn.Close
Set conn = Nothing
End Sub
</source>
Get more than one column
<source lang="vb">
Sub CreateRst_WithSQL()
Dim conn As ADODB.Connection
Dim myRecordset As ADODB.Recordset
Dim strConn As String
strConn = "Provider = Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;" & _
"Data Source=" & CurrentProject.Path & _
"mydb.mdb"
Set conn = New ADODB.Connection
conn.Open strConn
Set myRecordset = conn.Execute("SELECT FirstName, LastName, PhoneNo FROM Employees")
Do Until myRecordset.EOF
For Each fld In myRecordset.Fields
Debug.Print fld.Name & "=" & fld.Value
Next fld
myRecordset.MoveNext
Loop
myRecordset.Close
Set myRecordset = Nothing
conn.Close
Set conn = Nothing
End Sub
</source>
Get only one column
<source lang="vb">
Sub CreateRst_WithSQL()
Dim conn As ADODB.Connection
Dim myRecordset As ADODB.Recordset
Dim strConn As String
strConn = "Provider = Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;" & _
"Data Source=" & CurrentProject.Path & _
"mydb.mdb"
Set conn = New ADODB.Connection
conn.Open strConn
Set myRecordset = conn.Execute("SELECT LastName FROM Employees ")
Do Until myRecordset.EOF
For Each fld In myRecordset.Fields
Debug.Print fld.Name & "=" & fld.Value
Next fld
myRecordset.MoveNext
Loop
myRecordset.Close
Set myRecordset = Nothing
conn.Close
Set conn = Nothing
End Sub
</source>
Get the top 10 percent
<source lang="vb">
Sub CreateRst_WithSQL()
Dim conn As ADODB.Connection
Dim myRecordset As ADODB.Recordset
Dim strConn As String
strConn = "Provider = Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;" & _
"Data Source=" & CurrentProject.Path & _
"mydb.mdb"
Set conn = New ADODB.Connection
conn.Open strConn
Set myRecordset = conn.Execute("SELECT TOP 10 PERCENT * FROM Products ORDER BY UnitPrice ASC; ")
Do Until myRecordset.EOF
For Each fld In myRecordset.Fields
Debug.Print fld.Name & "=" & fld.Value
Next fld
myRecordset.MoveNext
Loop
myRecordset.Close
Set myRecordset = Nothing
conn.Close
Set conn = Nothing
End Sub
</source>
Get the top 5 percent
<source lang="vb">
Sub CreateRst_WithSQL()
Dim conn As ADODB.Connection
Dim myRecordset As ADODB.Recordset
Dim strConn As String
strConn = "Provider = Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;" & _
"Data Source=" & CurrentProject.Path & _
"mydb.mdb"
Set conn = New ADODB.Connection
conn.Open strConn
Set myRecordset = conn.Execute("SELECT TOP 5 * FROM Products ORDER BY UnitPrice DESC ")
Do Until myRecordset.EOF
For Each fld In myRecordset.Fields
Debug.Print fld.Name & "=" & fld.Value
Next fld
myRecordset.MoveNext
Loop
myRecordset.Close
Set myRecordset = Nothing
conn.Close
Set conn = Nothing
End Sub
</source>
Loop through the ResultSet after executing select statement
<source lang="vb">
Sub CreateRst_WithSQL()
Dim conn As ADODB.Connection
Dim myRecordset As ADODB.Recordset
Dim strConn As String
strConn = "Provider = Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;" & _
"Data Source=" & CurrentProject.Path & _
"mydb.mdb"
Set conn = New ADODB.Connection
conn.Open strConn
Set myRecordset = conn.Execute("select * from employees")
Do Until myRecordset.EOF
For Each fld In myRecordset.Fields
Debug.Print fld.Name & "=" & fld.Value
Next fld
myRecordset.MoveNext
Loop
myRecordset.Close
Set myRecordset = Nothing
conn.Close
Set conn = Nothing
End Sub
</source>
Modifying a Select Query
<source lang="vb">
Sub Modify_Query()
Dim cat As ADOX.Catalog
Dim cmd As ADODB.rumand
Dim strPath As String
Dim newStrSQL As String
Dim oldStrSQL As String
Dim strQryName As String
strPath = CurrentProject.Path & "mydb.mdb"
newStrSQL = "SELECT Employees.* FROM Employees" & _
" WHERE Employees.City="London"" & _
" ORDER BY BirthDate;"
strQryName = "London Employees"
Set cat = New ADOX.Catalog
cat.ActiveConnection = "Provider=Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;Data Source=" & strPath
Set cmd = New ADODB.rumand
Set cmd = cat.Views(strQryName).rumand
oldStrSQL = cmd.rumandText
Debug.Print oldStrSQL
cmd.rumandText = newStrSQL
Debug.Print newStrSQL
Set cat.Views(strQryName).rumand = cmd
Set cmd = Nothing
Set cat = Nothing
End Sub
</source>
Order by two fields
<source lang="vb">
Sub CreateRst_WithSQL()
Dim conn As ADODB.Connection
Dim myRecordset As ADODB.Recordset
Dim strConn As String
strConn = "Provider = Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;" & _
"Data Source=" & CurrentProject.Path & _
"mydb.mdb"
Set conn = New ADODB.Connection
conn.Open strConn
Set myRecordset = conn.Execute("SELECT txtCustFirstName, txtCustLastName FROM tblCustomer WHERE txtState = "NJ" ORDER BY txtCustLastName DESC, txtCustFirstName")
Do Until myRecordset.EOF
For Each fld In myRecordset.Fields
Debug.Print fld.Name & "=" & fld.Value
Next fld
myRecordset.MoveNext
Loop
myRecordset.Close
Set myRecordset = Nothing
conn.Close
Set conn = Nothing
End Sub
</source>
Order record in a decscending order
<source lang="vb">
Sub CreateRst_WithSQL()
Dim conn As ADODB.Connection
Dim myRecordset As ADODB.Recordset
Dim strConn As String
strConn = "Provider = Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;" & _
"Data Source=" & CurrentProject.Path & _
"mydb.mdb"
Set conn = New ADODB.Connection
conn.Open strConn
Set myRecordset = conn.Execute("SELECT * FROM Employees ORDER BY Country DESC")
Do Until myRecordset.EOF
For Each fld In myRecordset.Fields
Debug.Print fld.Name & "=" & fld.Value
Next fld
myRecordset.MoveNext
Loop
myRecordset.Close
Set myRecordset = Nothing
conn.Close
Set conn = Nothing
End Sub
</source>
Order the resultset with Order by clause
<source lang="vb">
Sub CreateRst_WithSQL()
Dim conn As ADODB.Connection
Dim myRecordset As ADODB.Recordset
Dim strConn As String
strConn = "Provider = Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;" & _
"Data Source=" & CurrentProject.Path & _
"mydb.mdb"
Set conn = New ADODB.Connection
conn.Open strConn
Set myRecordset = conn.Execute("SELECT * FROM Employees ORDER BY EmployeeID ")
Do Until myRecordset.EOF
For Each fld In myRecordset.Fields
Debug.Print fld.Name & "=" & fld.Value
Next fld
myRecordset.MoveNext
Loop
myRecordset.Close
Set myRecordset = Nothing
conn.Close
Set conn = Nothing
End Sub
</source>
Select all columns
<source lang="vb">
Sub CreateRst_WithSQL()
Dim conn As ADODB.Connection
Dim myRecordset As ADODB.Recordset
Dim strConn As String
strConn = "Provider = Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;" & _
"Data Source=" & CurrentProject.Path & _
"mydb.mdb"
Set conn = New ADODB.Connection
conn.Open strConn
Set myRecordset = conn.Execute("SELECT * FROM Employees")
Do Until myRecordset.EOF
For Each fld In myRecordset.Fields
Debug.Print fld.Name & "=" & fld.Value
Next fld
myRecordset.MoveNext
Loop
myRecordset.Close
Set myRecordset = Nothing
conn.Close
Set conn = Nothing
End Sub
</source>
Use and to combine conditions
<source lang="vb">
Sub CreateRst_WithSQL()
Dim conn As ADODB.Connection
Dim myRecordset As ADODB.Recordset
Dim strConn As String
strConn = "Provider = Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;" & _
"Data Source=" & CurrentProject.Path & _
"mydb.mdb"
Set conn = New ADODB.Connection
conn.Open strConn
Set myRecordset = conn.Execute("SELECT txtCustFimyRecordsetName, txtCustLastName FROM tblCustomer WHERE txtState = "NJ" AND txtCustLastName = "Miller"")
Do Until myRecordset.EOF
For Each fld In myRecordset.Fields
Debug.Print fld.Name & "=" & fld.Value
Next fld
myRecordset.MoveNext
Loop
myRecordset.Close
Set myRecordset = Nothing
conn.Close
Set conn = Nothing
End Sub
</source>
Use Between And
<source lang="vb">
Sub CreateRst_WithSQL()
Dim conn As ADODB.Connection
Dim myRecordset As ADODB.Recordset
Dim strConn As String
strConn = "Provider = Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;" & _
"Data Source=" & CurrentProject.Path & _
"mydb.mdb"
Set conn = New ADODB.Connection
conn.Open strConn
Set myRecordset = conn.Execute("Select * FROM Products WHERE UnitPrice NOT BETWEEN 10 and 25 ")
Do Until myRecordset.EOF
For Each fld In myRecordset.Fields
Debug.Print fld.Name & "=" & fld.Value
Next fld
myRecordset.MoveNext
Loop
myRecordset.Close
Set myRecordset = Nothing
conn.Close
Set conn = Nothing
End Sub
</source>
Use between and with number type column
<source lang="vb">
Sub CreateRst_WithSQL()
Dim conn As ADODB.Connection
Dim myRecordset As ADODB.Recordset
Dim strConn As String
strConn = "Provider = Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;" & _
"Data Source=" & CurrentProject.Path & _
"mydb.mdb"
Set conn = New ADODB.Connection
conn.Open strConn
Set myRecordset = conn.Execute("Select * FROM Products WHERE UnitPrice Between 10 and 25")
Do Until myRecordset.EOF
For Each fld In myRecordset.Fields
Debug.Print fld.Name & "=" & fld.Value
Next fld
myRecordset.MoveNext
Loop
myRecordset.Close
Set myRecordset = Nothing
conn.Close
Set conn = Nothing
End Sub
</source>
Use Date function in where clause
<source lang="vb">
Sub CreateRst_WithSQL()
Dim conn As ADODB.Connection
Dim myRecordset As ADODB.Recordset
Dim strConn As String
strConn = "Provider = Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;" & _
"Data Source=" & CurrentProject.Path & _
"mydb.mdb"
Set conn = New ADODB.Connection
conn.Open strConn
Set myRecordset = conn.Execute("SELECT * FROM Employees WHERE ((Year([HireDate])<1993) OR (City="Redmond")) ")
Do Until myRecordset.EOF
For Each fld In myRecordset.Fields
Debug.Print fld.Name & "=" & fld.Value
Next fld
myRecordset.MoveNext
Loop
myRecordset.Close
Set myRecordset = Nothing
conn.Close
Set conn = Nothing
End Sub
</source>
Use IN and like in where clause
<source lang="vb">
Sub CreateRst_WithSQL()
Dim conn As ADODB.Connection
Dim myRecordset As ADODB.Recordset
Dim strConn As String
strConn = "Provider = Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;" & _
"Data Source=" & CurrentProject.Path & _
"mydb.mdb"
Set conn = New ADODB.Connection
conn.Open strConn
Set myRecordset = conn.Execute("SELECT * FROM Employees WHERE City IN ("Redmond", "London") AND ReportsTo LIKE "Buchanan, Steven" ")
Do Until myRecordset.EOF
For Each fld In myRecordset.Fields
Debug.Print fld.Name & "=" & fld.Value
Next fld
myRecordset.MoveNext
Loop
myRecordset.Close
Set myRecordset = Nothing
conn.Close
Set conn = Nothing
End Sub
</source>
Use IN in select statement
<source lang="vb">
Sub CreateRst_WithSQL()
Dim conn As ADODB.Connection
Dim myRecordset As ADODB.Recordset
Dim strConn As String
strConn = "Provider = Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;" & _
"Data Source=" & CurrentProject.Path & _
"mydb.mdb"
Set conn = New ADODB.Connection
conn.Open strConn
Set myRecordset = conn.Execute("SELECT * FROM Employees WHERE City IN ("Redmond", "London")")
Do Until myRecordset.EOF
For Each fld In myRecordset.Fields
Debug.Print fld.Name & "=" & fld.Value
Next fld
myRecordset.MoveNext
Loop
myRecordset.Close
Set myRecordset = Nothing
conn.Close
Set conn = Nothing
End Sub
</source>
Use «Is not null»
<source lang="vb">
Sub CreateRst_WithSQL()
Dim conn As ADODB.Connection
Dim myRecordset As ADODB.Recordset
Dim strConn As String
strConn = "Provider = Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;" & _
"Data Source=" & CurrentProject.Path & _
"mydb.mdb"
Set conn = New ADODB.Connection
conn.Open strConn
Set myRecordset = conn.Execute("Select * from Employees WHERE ReportsTo IS NOT NULL ")
Do Until myRecordset.EOF
For Each fld In myRecordset.Fields
Debug.Print fld.Name & "=" & fld.Value
Next fld
myRecordset.MoveNext
Loop
myRecordset.Close
Set myRecordset = Nothing
conn.Close
Set conn = Nothing
End Sub
</source>
Use Is NULL to check if a column is null
<source lang="vb">
Sub CreateRst_WithSQL()
Dim conn As ADODB.Connection
Dim myRecordset As ADODB.Recordset
Dim strConn As String
strConn = "Provider = Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;" & _
"Data Source=" & CurrentProject.Path & _
"mydb.mdb"
Set conn = New ADODB.Connection
conn.Open strConn
Set myRecordset = conn.Execute("Select * from Employees WHERE ReportsTo IS NULL")
Do Until myRecordset.EOF
For Each fld In myRecordset.Fields
Debug.Print fld.Name & "=" & fld.Value
Next fld
myRecordset.MoveNext
Loop
myRecordset.Close
Set myRecordset = Nothing
conn.Close
Set conn = Nothing
End Sub
</source>
Use Not In
<source lang="vb">
Sub CreateRst_WithSQL()
Dim conn As ADODB.Connection
Dim myRecordset As ADODB.Recordset
Dim strConn As String
strConn = "Provider = Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;" & _
"Data Source=" & CurrentProject.Path & _
"mydb.mdb"
Set conn = New ADODB.Connection
conn.Open strConn
Set myRecordset = conn.Execute("SELECT * FROM Employees WHERE City NOT IN ("Redmond", "London") ")
Do Until myRecordset.EOF
For Each fld In myRecordset.Fields
Debug.Print fld.Name & "=" & fld.Value
Next fld
myRecordset.MoveNext
Loop
myRecordset.Close
Set myRecordset = Nothing
conn.Close
Set conn = Nothing
End Sub
</source>
Use «Select all»
<source lang="vb">
Sub CreateRst_WithSQL()
Dim conn As ADODB.Connection
Dim myRecordset As ADODB.Recordset
Dim strConn As String
strConn = "Provider = Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;" & _
"Data Source=" & CurrentProject.Path & _
"mydb.mdb"
Set conn = New ADODB.Connection
conn.Open strConn
Set myRecordset = conn.Execute("SELECT ALL * FROM Employees ORDER BY EmployeeID; ")
Do Until myRecordset.EOF
For Each fld In myRecordset.Fields
Debug.Print fld.Name & "=" & fld.Value
Next fld
myRecordset.MoveNext
Loop
myRecordset.Close
Set myRecordset = Nothing
conn.Close
Set conn = Nothing
End Sub
</source>
use SUM in sql statement
<source lang="vb">
Private Sub RunningSumSQL()
Dim db As Database
Set db = CurrentDb
Dim qry As QueryDef
Dim sSQL As String
On Error Resume Next
db.QueryDefs.Delete "temp"
On Error GoTo 0
sSQL = "SELECT R1.Event,(SELECT SUM(R2.Duration) FROM Running As R2 WHERE R2.Event < R1.Event) AS StartTime FROM Running As R1"
Set qry = db.CreateQueryDef("temp", sSQL)
DoCmd.OpenQuery qry.Name
End Sub
</source>
Use where clause and order by clause together
<source lang="vb">
Sub CreateRst_WithSQL()
Dim conn As ADODB.Connection
Dim myRecordset As ADODB.Recordset
Dim strConn As String
strConn = "Provider = Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;" & _
"Data Source=" & CurrentProject.Path & _
"mydb.mdb"
Set conn = New ADODB.Connection
conn.Open strConn
Set myRecordset = conn.Execute("SELECT txtCustFirstName, txtCustLastName FROM tblCustomer WHERE txtState = "NJ" ORDER BY txtCustLastName, txtCustFirstName
«)
Do Until myRecordset.EOF
For Each fld In myRecordset.Fields
Debug.Print fld.Name & "=" & fld.Value
Next fld
myRecordset.MoveNext
Loop
myRecordset.Close
Set myRecordset = Nothing
conn.Close
Set conn = Nothing
End Sub
</source>
Use wild card character in link
<source lang="vb">
Sub CreateRst_WithSQL()
Dim conn As ADODB.Connection
Dim myRecordset As ADODB.Recordset
Dim strConn As String
strConn = "Provider = Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;" & _
"Data Source=" & CurrentProject.Path & _
"mydb.mdb"
Set conn = New ADODB.Connection
conn.Open strConn
Set myRecordset = conn.Execute("SELECT txtCustFimyRecordsetName, txtCustLastName FROM tblCustomer WHERE txtCustLastName Like "M*" ")
Do Until myRecordset.EOF
For Each fld In myRecordset.Fields
Debug.Print fld.Name & "=" & fld.Value
Next fld
myRecordset.MoveNext
Loop
myRecordset.Close
Set myRecordset = Nothing
conn.Close
Set conn = Nothing
End Sub
</source>
Using Date field type in select statement
<source lang="vb">
Sub FindProject()
Dim strSQL As String
Dim rst As ADODB.Recordset
Set rst = New ADODB.Recordset
rst.ActiveConnection = CurrentProject.Connection
rst.CursorType = adOpenStatic
rst.Open "Select * FROM Employees WHERE BirthDate = #12/31/2007#"
"Attempt to find a specific project
strSQL = "[EmployeeID] = " & 1
rst.Find strSQL
"Determine if the specified project was found
If rst.EOF Then
msgBox lngValue & " Not Found"
Else
msgBox lngValue & " Found"
End If
rst.Close
Set rst = Nothing
End Sub
</source>
You must use a pound symbol (#) when delimiting dates for Microsoft Access, like this:
<source lang="vb">
Sub FindProject()
Dim strSQL As String
Dim rst As ADODB.Recordset
Set rst = New ADODB.Recordset
rst.ActiveConnection = CurrentProject.Connection
rst.CursorType = adOpenStatic
rst.Open "Select * FROM Employees WHERE BirthDate = #12/31/2007#"
"Attempt to find a specific project
strSQL = "[EmployeeID] = " & 1
rst.Find strSQL
"Determine if the specified project was found
If rst.EOF Then
msgBox lngValue & " Not Found"
Else
msgBox lngValue & " Found"
End If
rst.Close
Set rst = Nothing
End Sub
</source>
UPDATE 21.10.15 Добавил «обратный» макрос — VBA в SQL и макрос для доступа к строке запроса SQL
Некоторое время назад я прошел несколько курсов по SQL. И мне было очень интересно — какую часть из мощного инструмента под названием T-SQL можно применять без использования SQL-Server (не дают мне сервачек под мои нужды, хнык-хнык).
Итак… Начнем с простого — подключение через Query Table в VBA. Можно записать через макрорекордер — для этого нужно создать подключение через Microsoft Query.
Выбираем Excel Files, указываем путь к файлу (пытаясь при этом не ругать разработчиков за интерфейс из 90х годов), фильтруем как-угодно поля. Нам сейчас это не важно — главное получить код, который дальше можно будет корректировать.
Должно получится что-то вроде этого:
Sub Макрос1()
With ActiveSheet.ListObjects.Add(SourceType:=0, Source:=Array(Array( _
"ODBC;DSN=Excel Files;DBQ=D:DropboxExcelтест excel_SQL-2015.xlsx;DefaultDir=D:DropboxExcel;DriverId=1046;MaxBufferSize=2048;Page" _
), Array("Timeout=5;")), Destination:=Range("$A$1")).QueryTable
.CommandType = 0
.CommandText = Array( _
"SELECT Продажи.F2, Продажи.F3" & Chr(13) & "FROM `D:DropboxExcelтест excel_SQL-2015.xlsx`.Продажи Продажи" _
)
.RowNumbers = False
.FillAdjacentFormulas = False
.PreserveFormatting = True
.RefreshOnFileOpen = False
.BackgroundQuery = True
.RefreshStyle = xlInsertDeleteCells
.SavePassword = False
.SaveData = True
.AdjustColumnWidth = True
.RefreshPeriod = 0
.PreserveColumnInfo = True
.ListObject.DisplayName = "Таблица_Запрос_из_Excel_Files"
.Refresh BackgroundQuery:=False
End With
End Sub
Строчка .CommandText = «SELECT…» — отвечает за SQL запрос. Если хотя бы немного почитать поисковую выдачу google по запросу QueryTable можно упростить код до следующего:
Sub CopyFromRecordset_To_Range()
DBPath = "C:InputData.xlsx"
sconnect = "Provider=MSDASQL.1;DSN=Excel Files;DBQ=" & DBPath & ";HDR=Yes';"
Conn.Open sconnect
sSQLSting = "SELECT * FROM [Sheet1$]"
rs.Open sSQLSting, Conn
Set QT1 = ActiveSheet.QueryTables.Add(rs, Range("A1"))
QT1.Refresh
rs.Close
Conn.Close
End Sub
Теперь начинаем копаться глубже — какого уровня запросы можно строить из VBA. Самые-самые базовые, основные конструкции — все работает, все ок.
Заполнение нового столбца одинаковым значением
SELECT 'YTikhonov', * FROM [Sheet1$]
Переименование столбцов
SELECT [Advertiser] AS 'Рекламодатель', [Quantity] AS 'Количество' FROM [Sheet1$]
Фильтрация записей
SELECT * FROM [Sheet1$] WHERE [Year] = 2014
Сортировка
SELECT * FROM [Sheet1$] ORDER BY [Advertiser] DESC
Агрегация записей
SELECT [Advertiser], Sum([Cost]) FROM [Sheet1$] GROUP BY [Advertiser]
Работа с датой
Дату можно впрямую через конструкцию
[SomeDateField] = {ts '2015-01-01 00:00:00'}
Но я люблю отталкиваться от текущей даты. За пару текущая дата-время отвечает функция SYSDATETIME() и она может вернуть в том числе текущий день. Для этого нужна еще одна функция — CONVERT(type,value)
SELECT CONVERT(date,SYSDATETIME())
С функцией DATEFROMPARTS строка запроса в Excel почему-то не дружит, поэтому придется использовать костыли функцию DATEADD:
DATEADD(minute, 59, DATEADD(hour, 23, DATEADD(month, MONTH(SYSDATETIME())+1, DATEADD(year, YEAR(SYSDATETIME()) - 1900, 0))))-1
Эта строчка в любой день октября 2015 вернет значение — 30.11.15 23:59
А теперь — немного best practice!
Объединение + Агрегация + Join + Подзапросы. И самое интересное — подключение к нескольким источникам:
SELECT [Year], O.Numbers, SCost, SVolume, SQuantity FROM
(
SELECT [Year], Month, SUM([Cost RUB]) AS SCost, SUM(Volume) AS SVolume, SUM(Quantity) AS SQuantity FROM
(
SELECT Advertiser, 2013 as [Year], Month, [Cost RUB], Quantity, Volume
FROM [N:GKRadioМаркетингСлужебный2013.xlsb].[Мониторинг$]
UNION
SELECT Advertiser, 2014 as [Year], Month, [Cost RUB], Quantity, Volume
FROM [N:GKRadioМаркетингСлужебный2014.xlsb].[Мониторинг$]
UNION
SELECT Advertiser, 2015 as [Year], Month, [Cost RUB], Quantity, Volume
FROM [N:GKRadioМаркетингСлужебный2015.xlsb].[Мониторинг$]
)
WHERE [Advertiser] = 'METRO GROUP'
GROUP BY [Year], Month
) as T INNER JOIN [C:testMonth.xlsb].[Test$] AS O
ON T.[Month] = O.[Month]
Одна проблема — если осуществлять такого вида запрос для соединения нескольких Excel-файлов, он будет выполняться достаточно медленно. У меня вышло порядка 2 минут. Но не стоит думать что это бесполезно — если подобные запросы выполнять при подключении к SQL-серверу, то время обработки будет 1-2 секунды (само собой, все зависит от сложности запроса, базы, и прочие прочие факторы).
Бонусы
Формировать более-менее сложный запрос SQL вручную в VBA мягко говоря неудобно. Поэтому я написал мини-макрос, который берет информацию из буфера обмена, и возвращает туда строчки для вставки в VBE.
'работа с буфером обмена http://excelvba.ru/code/clipboard
Private Function ClipboardText() ' чтение из буфера обмена
With GetObject("New:{1C3B4210-F441-11CE-B9EA-00AA006B1A69}")
.GetFromClipboard
ClipboardText = .GetText
End With
End Function
Private Sub SetClipboardText(ByVal txt$) ' запись в буфер обмена
With GetObject("New:{1C3B4210-F441-11CE-B9EA-00AA006B1A69}")
.SetText txt$
.PutInClipboard
End With
End Sub
Public Sub SQL_String_To_VBA()
Dim sInput As String, sOut As String
Dim ArrInput, i As Integer
Dim cIdent As Integer: cIdent = 1 'Count of tabs
Dim sVar As String: sVar = "strSQL" 'Name of variable
sInput = ClipboardText()
ArrInput = Split(sInput, Chr(13))
For i = LBound(ArrInput) To UBound(ArrInput)
sOut = sOut & sVar & " = " & sVar & " & " & Chr(34)
sOut = sOut & String(cIdent, Chr(9))
sOut = sOut & Replace(ArrInput(i), Chr(10), "")
sOut = sOut & Chr(34) & "& chr(10)" & Chr(10)
Next i
SetClipboardText (sOut)
End Sub
Public Sub VBA_String_To_SQL()
Dim sInput As String, sOut As String
Dim ArrInput, i As Integer, sTemp
sInput = ClipboardText()
ArrInput = Split(sInput, Chr(10))
For i = LBound(ArrInput) To UBound(ArrInput)
sTemp = Replace(ArrInput(i), "& chr(10)", "")
If Right(sTemp, 1) = " " Then sTemp = Left(sTemp, Len(sTemp) - 1)
If Right(sTemp, 1) = Chr(34) Then sTemp = Left(sTemp, Len(sTemp) - 1)
If Len(sTemp) > 0 Then
sTemp = Right(sTemp, Len(sTemp) - InStr(1, sTemp, Chr(34)))
sOut = sOut & Chr(10) & sTemp
End If
Next i
SetClipboardText (sOut)
End Sub
Сами запросы просто и удобно создавать, например, используя Notepad++. Создали многострочный запрос SQL, копируете его в буфер обмена, запускаете макрос и вуаля — в буфере обмена строчки кода, готовые для вставки в ваши макросы. При желании вы можете настроить название переменной и количество табуляций.
И еще один небольшой бонус. Если у вас есть отчет по менеджерам/руководителям, построенный на запросах, то вам наверняка потребуется получать доступ к строке запроса через VBA. Сделать это можно через замечательную команду .CommandText — работает на чтение и запись. Мне для формирования отчета на 25 человек очень пригодился.
Public Sub ReplaceCommandText()
Dim con As WorkbookConnection
Dim sTemp As String
For Each con In ActiveWorkbook.Connections
sTemp = con.ODBCConnection.CommandText
con.ODBCConnection.CommandText = sTemp
con.Refresh
Next con
End Sub
PS Ссылка с ответом на вопрос — как вставить данные из Excel в SQL
https://www.simple-talk.com/sql/t-sql-programming/questions-about-using-tsql-to-import-excel-data-you-were-too-shy-to-ask/
Приятного использования!
The ‘Not In List Event’ occurs whenever a user tries to enter a value into a combobox that is not part of the existing list of choices. Below is a typical example of a ‘Not In List Event’ that will allow the user to add their new value to the existing list of choices for further use in the future, assuming you are using an underlying table as the list source.
Private Sub YourCboName_NotInList(NewData As String, Response As Integer)
'Requires that a reference to the Microsoft DAO 3.6 Object Library
On Error GoTo Error_Handler
Dim rst As DAO.Recordset
If MsgBox(NewData & "... not in list, add it?", vbOKCancel, "MessageBoxTitle") = vbOK Then
Set rst = CurrentDb.OpenRecordset("TableName") 'Table to add the new value to
With rst
.AddNew
.Fields("TableColumnName") = NewData 'Name of the table field to add the new value to
.Update
End With
Response = acDataErrAdded
Else
Response = acDataErrContinue
End If
Error_Handler_Exit:
On Error Resume Next
rst.Close
Set rst = Nothing
Exit Sub
Error_Handler:
MsgBox "MS Access has generated the following error" & vbCrLf & vbCrLf & "Error Number: " & _
Err.Number & vbCrLf & "Error Source: YourCboName_NotInList" & vbCrLf & "Error Description: " & _
Err.Description, vbCritical, "An Error has Occurred!"
Resume Error_Handler_Exit
End Sub
Many times I was irritated of the lack of some Excel functionality (or just I don’t know there is) to easily transform data w/o using pivot tables. SQL in VBA was the only thing that was missing for me.
Distinct, grouping rows of Excel data, running multiple selects etc. Some time agon when I had a moment of time to spare I did my homework on the topic only to discover that running SQL queries from Excel VBA is possible and easy…
Want to create SQL Queries directly from Excel instead? See my Excel SQL AddIn
Want to learn how to create a MS Query manually? See my MS Query Tutorial
Using SQL in VBA example
Sub RunSELECT()
Dim cn As Object, rs As Object, output As String, sql as String
'---Connecting to the Data Source---
Set cn = CreateObject("ADODB.Connection")
With cn
.Provider = "Microsoft.ACE.OLEDB.12.0"
.ConnectionString = "Data Source=" & ThisWorkbook.Path & "" & ThisWorkbook.Name & ";" & "Extended Properties=""Excel 12.0 Xml;HDR=YES"";"
.Open
End With
'---Run the SQL SELECT Query---
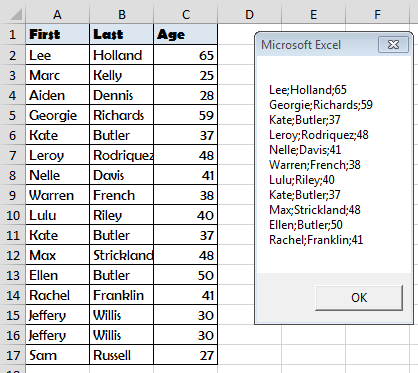
sql = "SELECT * FROM [Sheet1$]"
Set rs = cn.Execute(sql)
Do
output = output & rs(0) & ";" & rs(1) & ";" & rs(2) & vbNewLine
Debug.Print rs(0); ";" & rs(1) & ";" & rs(2)
rs.Movenext
Loop Until rs.EOF
MsgBox output
'---Clean up---
rs.Close
cn.Close
Set cn = Nothing
Set rs = Nothing
End Sub
Explaining the Code
So what is happening in the macro above? Let us break it down:
Connecting to the Data Source
First we need to connect via the ADODB Driver to our Excel Worksheet. This is the same Driver which runs SQL Queries on MS Access Databases:
'---Connect to the Workbook---
Set cn = CreateObject("ADODB.Connection")
With cn
.Provider = "Microsoft.ACE.OLEDB.12.0"
.ConnectionString = "Data Source=" & ThisWorkbook.Path & "" & ThisWorkbook.Name & ";" & _
"Extended Properties=""Excel 12.0 Xml;HDR=YES"";"
.Open
End With
The Provider is the Drive which is responsible for running the query.
The ConnectionStrings defines the Connection properties, like the path to the Queries File (example above is for ThisWorkbook) or if the first row contains a header (HDR).
The Open command executes the connection.
You can find more information on the ADODB.Connection Object on MSDN.
Running the SQL Select Query
Having connected to our Data Source Excel Worksheet we can now run a SQL SELECT Query:
'---Running the SQL Select Query--- Sql = "SELECT * FROM [Sheet1$]" Set rs = cn.Execute(Sql) Do output = output & rs(0) & ";" & rs(1) & ";" & rs(2) & vbNewLine Debug.Print rs(0); ";" & rs(1) & ";" & rs(2) rs.Movenext Loop Until rs.EOF MsgBox output
So what happens here? First we run the Execute command with our SELECT query:
SELECT * FROM [Sheet1$]
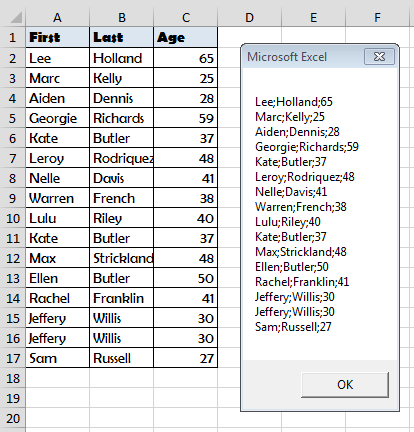
What does it do? It indicates that our records are in Sheet1. We can obviously extend this query just to filter people above the age of 30:
SELECT * FROM [Sheet1$] WHERE Age > 30
This would be the result:
The Execute command returns a ADODB RecordSet. We need to loop through the recordset to get each record:
Do
'...
'Loop through records - rs(0) - first column, rs(1) - second column etc.
'...
rs.Movenext 'Move to next record
Loop Until rs.EOF 'Have we reached End of RecordSet
Clean up
Lastly we need to Clean up our Objects to free memory. This is actually quite an important step as if you VBA code is runs a lot of queries or computations you might see a slow-down soon enough!
rs.Close cn.Close Set cn = Nothing Set rs = Nothing
What Else Can I Do?
You can do tons of great things with ADODB / MS Queries / SQL in Excel. Here are some additional ideas:
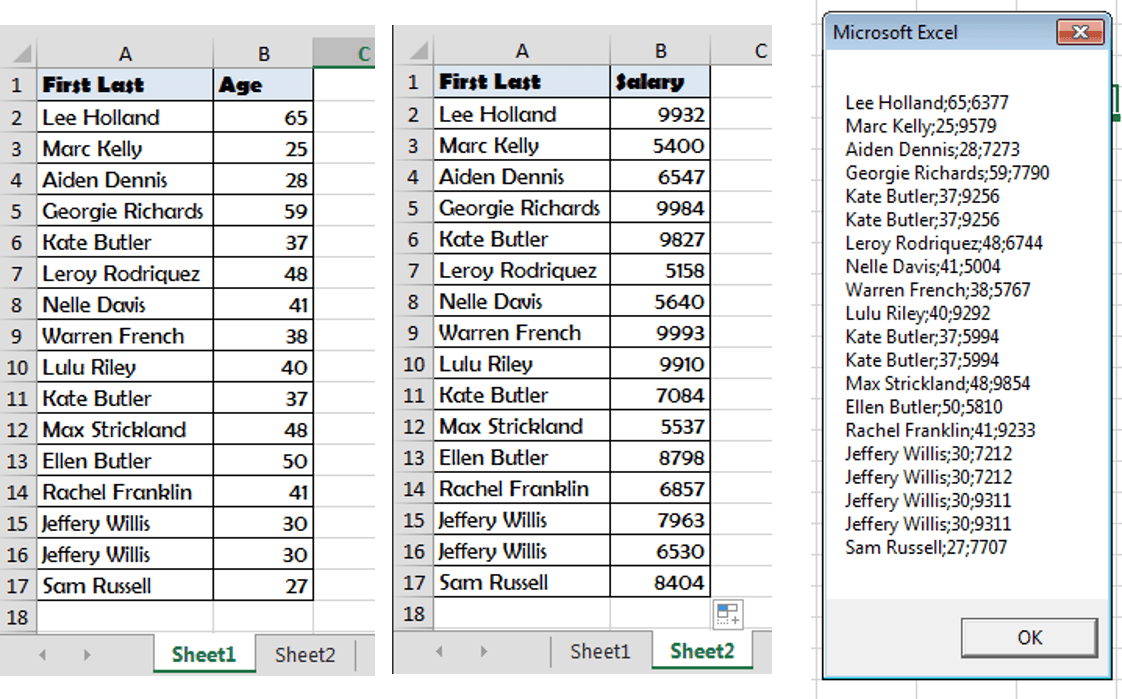
- Run Queries Across Worksheets – you can run JOIN queries on multiple Excel Worksheets. E.g.
SELECT [Sheet1$].[First Last], [Age], [Salary] FROM [Sheet1$] INNER JOIN [Sheet2$] ON [Sheet1$].[First Last]=[Sheet2$].[First Last]
On the below tables:
- Extracting Data from External Data Sources – use different connection strings to connect to Access Databases, CSV files or text files
- Do more efficient LOOKUPs – read my post on VLOOKUP vs SQL to learn more
When it comes to big amount of data, Excel application is not the best solution to work with, in case of storage. Much better fit would be a database like Access or MSSM. In this article I’m going to show You how to connect to Microsoft SQL Server using VBA.

Database & server
In my case I got AdventureWorks2016 database installed on my PC. I connected to that base and the view of Object Explorer in Managament Studio looks like this.
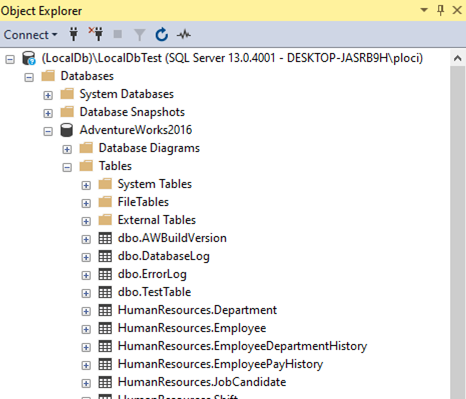
Here You can see the server name, database name and tables name in Tables folder, which all will be necessary in further steps.
References
To be able to create connection and then operate on pulled data from database, You need to check in the Tools/References 2 checkboxes: Microsoft ActiveX Data Objects Library and Microsoft ActiveX Data Objects Recordset Library.

It doesn’t have to be the version 2.8, just like in the screen above. You have much more possibilities.

When choosing the references try to think about the future users (ot their Office version) of this code You create.
ADODB Connection
After setting up the references You can declare connection of ADODB library.
Dim connection As ADODB.connection
Set connection = New ADODB.connectionConnection String
This is the main thing of ADODB connection, to be able to connect to the database. You need to know at least the provider, server name, database name and authentication method.
For MS SQL use SQLOLEDB.1 as provider. That should always work, unless You know that the provider for your database is different.
The server name You can see at the top of the object explorer.

So in my case it is (LocalDb)LocalDbTest.
Let server_name = "(LocalDb)LocalDbTest"The database name is the name under the Databases folder tree in Object Explorer.

In my case this is AdventureWorks2016.
Let database_name = "AdventureWorks2016"The authentication method depends on that if You pass the credentials in the connection string or use windows authentication and on provider. You can choose from the values: true , false, yes, no and sspi.
So putting all together it can look like this.
.ConnectionString = "Provider=SQLOLEDB.1;Server=" & server_name & _
";database=" & database_name & ";Integrated Security=SSPI;"Solution to connect local database
In case of MS SQL use SQLOLEDB.1 as provider, but if You got your database locally, as I have, go with SQLNCLI11. This is something I was fighting with and looking for hours to connect.
.ConnectionString = "Provider=SQLNCLI11;Server=" & server_name & _
";database=" & database_name & ";Integrated Security=SSPI;"Open connection & state check
After completing the connection string, You can also set other properties like timeout. In the end open the connection using .Open.
With connection
.ConnectionString = "Provider=SQLNCLI11;Server=" & server_name & _
";database=" & database_name & ";Integrated Security=SSPI;"
.ConnectionTimeout = 10
.Open
End WithIf there was no error check the state of database You connected.
If connection.State = 1 Then
Debug.Print "Connected!"
End IfSQL query
Having opened database connection You need to ask for data, I mean to build SQL query. In my case I just want to take all (*) data from TestTable table. The database name in this query is not really needed, because it is already in the connection string.
Dim sqlQuery As String
sqlQuery = "Select * from [AdventureWorks2016].[dbo].[TestTable]"If You are not familiar with SQL I can say that the basics are even easier than VBA. As I said, basics of SQL.
Recordset – copy paste data from database
If You want to get the data from the query, You need to create Recordset of ADODB library. There are 2 main things – sqlQuery and connection. About the rest of properties You can read here.
Dim rsSql As New ADODB.Recordset
rsSql.CursorLocation = adUseClient
rsSql.Open sqlQuery, connection, adOpenStaticAfter You .Open the recordset – get the data from database with SQL query using created connection, You can paste everything in chosen location.
ThisWorkbook.Sheets(1).Range("A1").CopyFromRecordset rsSql
And just like that all the data from the specified table is in the chosen range of your Workbook.

And remember that this method is not pasting headers, only the values of the columns below headline!
Connect to MS SQL code
Option Explicit
Sub connect2mssql()
Dim connection As ADODB.connection
Set connection = New ADODB.connection
Dim server_name As String, database_name As String
Let server_name = "(LocalDb)LocalDbTest"
Let database_name = "AdventureWorks2016"
With connection
.ConnectionString = "Provider=SQLNCLI11;Server=" & server_name & _
";database=" & database_name & ";Integrated Security=SSPI;"
'SQLOLEDB.1
.ConnectionTimeout = 10
.Open
End With
If connection.State = 1 Then
Debug.Print "Connected!"
End If
Dim sqlQuery As String
sqlQuery = "Select * from [AdventureWorks2016].[dbo].[TestTable]"
Dim rsSql As New ADODB.Recordset
rsSql.CursorLocation = adUseClient
rsSql.Open sqlQuery, connection, adOpenStatic
ThisWorkbook.Sheets(1).Range("A1").CopyFromRecordset rsSql
End SubSo, this is how You connect to Microsoft SQL Server using Excel VBA!
At first sight it seems like complex stuff, but in the end it is not that hard and it opens wide range of possibilities to automate data from other sources than only Excel workbooks. Combining the VBA knowledge with some more complex SQL queries can lead to really big tools dealing with tons of data. It is much easier to connect to the source than converting the data to Excel format and then start the macro. Also it speeds up the whole work a lot.
I’m very advanced in VBA, Excel, also easily linking VBA with other Office applications (e.g. PowerPoint) and external applications (e.g. SAP). I take part also in RPA processes (WebQuery, DataCache, IBM Access Client Solutions) where I can also use my SQL basic skillset. I’m trying now to widen my knowledge into TypeScript/JavaScript direction.
View all posts by Tomasz Płociński