How to create autoshapes, lines and connectors in VBA macros
Part four of an eight-part series of blogs
You can use Visual Basic within Excel, PowerPoint or Word to draw shapes, format them and even assign macros to run — this long blog gives lots of ideas of how to proceed!
- Working with shapes in VBA
- Working with shapes — getting started
- Naming, referring to and positioning shapes
- Formatting shapes and adding text (this blog)
- Adding lines and connectors to join shapes together
- Working with multiple shapes
- Assigning macros to shapes
- Exercises on shapes
This is one small part of our free online Excel VBA tutorial. To find out how to learn in a more structured way, have a look at our training courses in VBA.
Posted by
Andy Brown
on 25 January 2014
You need a minimum screen resolution of about 700 pixels width to see our blogs. This is because they contain diagrams and tables which would not be viewable easily on a mobile phone or small laptop. Please use a larger tablet, notebook or desktop computer, or change your screen resolution settings.
Formatting shapes is easy provided that you understand that there are two
main properties that you can play about with:
| Property | What it allows you to change |
|---|---|
| Fill | The background colour or pattern for a shape |
| Line | The border line for a shape |
One other oddity: it’s the ForeColor of a shape’s fill that
you’ll usually want to change:
It’s the foreground colour of a shape’s fill pattern that’ll usually be of most interest.
An example of formatting a shape’s fill pattern
Here’s some code to create a pretty circle:
Set s = ws.Shapes.AddShape(9, 10, 10, 50, 50)
With s.Fill
.ForeColor.RGB = RGB(255, 240, 255)
.Transparency = 0.2
End With
This would create a circle which is 20% transparent and has a different
background colour:
The circle created by the above code.
An example of formatting a shape’s border
You could extend the macro above to change the border colour and style of the
shape:
With s.Line
.ForeColor.RGB = RGB(100, 0, 100)
.DashStyle = msoLineDashDot
.Weight = 5
End With
The circle is now beginning to look a bit silly:
Perhaps our choices weren’t so good after all …
To do detailed formatting of shapes, a good way forward is to record a macro
and then play about with the code generated.
Adding text to shapes
Any shape added has a TextFrame property, which gives you
access to the text within it. This in turn has a collection of
Characters!
CalloutBalloon.TextFrame.Characters.Text = «Wise Owl blog on shapes»
CalloutBalloon.TextFrame.Characters.Font.Color = 1
CalloutBalloon.TextFrame.Characters.Font.Size = 14
CalloutBalloon.TextFrame.HorizontalAlignment = xlHAlignCenter
CalloutBalloon.TextFrame.VerticalAlignment = xlVAlignCenter
Thus the code above sets the text in the relevant shape called
CalloutBalloon, then changes its font
and alignment. You can format only part of the text in a shape, as this example shows:
Here we’ve forwarded only the characters from 6 to 9.
Here’s some code to achieve the above:
Sub AddShapeToCell()
Dim s As Shape
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = ActiveSheet
Set s = ws.Shapes.AddShape(9, 10, 10, 140, 30)
s.Fill.ForeColor.RGB = RGB(245, 245, 255)
s.TextFrame.Characters.Text = «Wise Owl training»
s.TextFrame.Characters.Font.ColorIndex = 3
With s.TextFrame.Characters(6, 3)
.Font.Color = RGB(100, 200, 0)
End With
End Sub
This changes the colour of the 3 characters from position 6 onwards.
Note that this is one of those occasions when (to keep you on your toes) VBA
numbers things in a collection from 1, not 0.
A complete example — creating our Wise Owl call-out
Here’s the example from the beginning of this blog:
As promised, below is the code to create these two shapes!
The code to produce it could be as follows:
Dim w As Worksheet
Sub DeleteShapesOnSheet()
Dim w As Worksheet
Dim s As Shape
Set w = ActiveSheet
For Each s In w.Shapes
s.Delete
Next s
End Sub
Sub CreateWiseOwlBalloon()
Dim CalloutBalloon As Shape
Dim Logo As Shape
Set w = ActiveSheet
DeleteShapesOnSheet
Set CalloutBalloon = w.Shapes.AddShape(108, 50, 10, 150, 120)
CalloutBalloon.Fill.ForeColor.RGB = RGB(227, 214, 213)
CalloutBalloon.Line.ForeColor.RGB = RGB(0, 0, 0)
CalloutBalloon.TextFrame.Characters.Text = «Wise Owl blog on shapes»
CalloutBalloon.TextFrame.Characters.Font.Color = 1
CalloutBalloon.TextFrame.Characters.Font.Size = 14
CalloutBalloon.TextFrame.HorizontalAlignment = xlHAlignCenter
CalloutBalloon.TextFrame.VerticalAlignment = xlVAlignCenter
Set Logo = w.Shapes.AddShape(1, 30, 160, 80, 80)
Logo.Fill.UserPicture «C:ajb fileswise-owl-logo.jpg»
Logo.Line.Visible = msoFalse
End Sub
Running the CreateWiseOwlBalloon routine should create the
two shapes shown (although you’ll need to substitute your own picture file path
to get it to work).
Time now to look at some specialist shapes: lines and connectors.
This blog has 0 threads
Add post
Работа с фигурами в VBA Excel: создание фигур методом Shapes.AddShape, типы фигур (MsoAutoShapeType), обращение к фигурам и изменение их свойств. Примеры.
Объекты для работы с фигурами
Фигуры в VBA Excel представлены тремя объектами:
| Объект | Описание |
|---|---|
| Shapes | Коллекция всех фигур на рабочем листе. Используется для создания новых фигур, для обращения к одной фигуре по имени и для перебора фигур циклом. |
| ShapeRange | Коллекция нескольких фигур, аргументом которой является массив имен выбранных объектов. Используется для редактирования сразу всех фигур, входящих в эту коллекцию. |
| Shape | Объект, представляющий одну фигуру. Используется для редактирования одной этой фигуры. |
Фигуры в VBA Excel создаются методом Shapes.AddShape.
Синтаксис метода AddShape
|
Shapes.AddShape (Type, Left, Top, Width, Height) |
Shapes — выражение, возвращающее коллекцию фигур на рабочем листе, например: ActiveSheet.Shapes.
Параметры метода AddShape
| Параметр | Описание |
|---|---|
| Type | Константа из коллекции MsoAutoShapeType, определяющая тип создаваемой фигуры. |
| Left | Расстояние от левой границы фигуры до левой границы табличной части рабочего листа в пунктах.. Тип данных — Single. |
| Top | Расстояние от верхней границы фигуры до верхней границы табличной части рабочего листа в пунктах.. Тип данных — Single. |
| Width | Ширина фигуры по внешним границам в пунктах. |
| Height | Высота фигуры по внешним границам в пунктах. |
Все параметры метода Shapes.AddShape являются обязательными.
Константы MsoAutoShapeType
Константы коллекции MsoAutoShapeType, определяющие основные типы создаваемых фигур:
| Константа | Значение | Тип фигуры |
|---|---|---|
| msoShapeRectangle | 1 | Прямоугольник |
| msoShapeParallelogram | 2 | Параллелограмм |
| msoShapeTrapezoid | 3 | Трапеция |
| msoShapeDiamond | 4 | Ромб |
| msoShapeRoundedRectangle | 5 | Прямоугольник: скругленные углы |
| msoShapeOctagon | 6 | Восьмиугольник (октаэдр) |
| msoShapeIsoscelesTriangle | 7 | Равнобедренный треугольник |
| msoShapeRightTriangle | 8 | Прямоугольный треугольник |
| msoShapeOval | 9 | Овал |
| msoShapeHexagon | 10 | Шестиугольник (гексаэдр) |
| msoShapeCross | 11 | Крест |
| msoShapeRegularPentagon | 12 | Пятиугольник (пентаэдр) |
| msoShapeCan | 13 | Цилиндр |
| msoShapeCube | 14 | Куб |
| msoShapeDonut | 18 | Круг: прозрачная заливка (кольцо) |
| msoShapeLightningBolt | 22 | Молния |
| msoShapeSun | 23 | Солнце |
| msoShapeMoon | 24 | Месяц (луна) |
| msoShape5pointStar | 92 | Звезда: 5 точек (пятиконечная) |
| msoShapeCloud | 179 | Облако |
Все доступные константы из коллекции MsoAutoShapeType смотрите на сайте разработчиков.
Создание объекта ShapeRange
Создание коллекции ShapeRange из выбранных фигур:
|
Dim myShapeRange As ShapeRange Set myShapeRange = ActiveSheet.Shapes.Range(Array(«Пятиугольник 140», «Солнце 141», «Облако 144»)) |
Объектная переменная myShapeRange не обязательна, можно обратиться непосредственно к возвращенной коллекции, например, присвоив всем ее элементам синий цвет:
|
ActiveSheet.Shapes.Range(Array(«Пятиугольник 140», «Солнце 141», «Облако 144»)).Fill.ForeColor.RGB = vbBlue |
Примеры работы с фигурами
Пример 1
Создание пяти разных фигур из кода VBA Excel методом Shapes.AddShape:
|
Sub Primer1() With ActiveSheet.Shapes ‘При создании фигуры без присвоения ее переменной скобки не нужны .AddShape msoShapeCube, 30, 40, 72, 72 .AddShape msoShapeIsoscelesTriangle, 130, 40, 72, 72 .AddShape msoShapeSun, 230, 40, 72, 72 .AddShape msoShapeLightningBolt, 330, 40, 72, 72 ‘Чтобы выбрать фигуру, параметры необходимо заключить в скобки .AddShape(msoShapeCloud, 430, 40, 72, 72).Select End With End Sub |
Результат работы кода:
Пример 2
Работа с одной фигурой:
|
Sub Primer2() Dim myShape As Shape ‘Создаем фигуру «Месяц» и присваивает ссылку на нее переменной myShape Set myShape = ActiveSheet.Shapes.AddShape(msoShapeMoon, 50, 50, 80, 80) With myShape ‘Меняем высоту и ширину фигуры .Height = 150 .Width = 100 ‘Меняем цвет фигуры .Fill.ForeColor.RGB = vbYellow ‘Поворачиваем фигуру влево на 40 градусов .Rotation = —40 End With End Sub |
Пример 3
Редактирование одновременно нескольких фигур с помощью коллекции ShapeRange:
|
Sub Primer3() With ActiveSheet.Shapes.Range(Array(«Овал 1», «Овал 2», «Овал 3»)) ‘Меняем цвет всех фигур из коллекции ShapeRange .Fill.ForeColor.RGB = vbBlue ‘Задаем высоту и ширину овалов .Height = 150 .Width = 50 ‘Поворачиваем фигуры вправо на 45 градусов .Rotation = 45 End With End Sub |
Пример 4
Редактирование одновременно всех фигур на рабочем листе с помощью коллекции ShapeRange:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
Sub Primer4() Dim myShapeRange As ShapeRange, i As Integer, _ myShape As Shape, myArray() As String ‘Задаем массиву размерность от 1 до количества фигур на листе ReDim myArray(1 To ActiveSheet.Shapes.Count) ‘Проходим циклом по всем фигурам коллекции и записываем их имена в массив For Each myShape In ActiveSheet.Shapes i = i + 1 myArray(i) = myShape.Name Next ‘Создаем коллекцию ShapeRange и присваиваем ссылку на нее переменной myShapeRange Set myShapeRange = ActiveSheet.Shapes.Range(myArray) With myShapeRange ‘Изменяем цвет всех фигур на рабочем листе .Fill.ForeColor.RGB = RGB(100, 150, 200) ‘Поворачиваем все фигуры вокруг вертикальной оси .Flip msoFlipVertical End With End Sub |
Пример 5
Добавление надписи (текста) на фигуру:
|
Sub Primer5() Dim myShape As Shape Set myShape = ActiveSheet.Shapes.AddShape(msoShapeCloud, 50, 30, 300, 300) With myShape.TextFrame2 ‘Добавление текста на фигуру .TextRange.Characters.Text = «Объект TextFrame представляет текстовую рамку в объекте Shape. Содержит текст в текстовом кадре, а также свойства и методы, которые контролируют выравнивание и закрепление текстового кадра.» ‘Задаем курсивное начертание .TextRange.Characters.Font.Italic = True ‘Указываем размер шрифта .TextRange.Characters.Font.Size = 13 ‘Отступ левой границы текстового поля от левой внутренней границы фигуры .MarginLeft = 30 ‘Отступ верхней границы текстового поля от верхней внутренней границы фигуры .MarginTop = 20 End With End Sub |
Результат работы кода:
Изменить цвет текста, например на черный, можно двумя способами:
|
‘С помощью константы MsoThemeColorIndex myShape.TextFrame2.TextRange.Characters.Font.Fill.ForeColor.ObjectThemeColor = msoThemeColorDark1 ‘С помощью цветовой модели RGB myShape.TextFrame2.TextRange.Characters.Font.Fill.ForeColor.RGB = RGB(0, 0, 0) |
С константами из коллекции MsoThemeColorIndex вы можете ознакомиться на сайте разработчиков.
Пример 6
Удаление фигур с рабочего листа из кода VBA Excel с помощью метода Delete.
Удаление одной фигуры:
|
ActiveSheet.Shapes(«Ромб 5»).Delete |
Удаление нескольких фигур:
|
ActiveSheet.Shapes.Range(Array(«Овал 1», «Овал 2», «Овал 3»)).Delete |
Удаление всех фигур с рабочего листа с помощью цикла:
|
Sub Primer6() Dim myShape As Shape For Each myShape In ActiveSheet.Shapes myShape.Delete Next End Sub |
В 7 примере рассмотрено удаление всех фигур без цикла.
Пример 7
Выделение всех фигур на рабочем листе:
|
ActiveSheet.Shapes.SelectAll |
Выбор всех фигур и удаление выбранного (всех фигур):
|
Sub Primer7() ActiveSheet.Shapes.SelectAll Selection.Delete End Sub |
Продолжение темы в статье VBA Excel. Копирование, перемещение и поворот фигур.
VBA Coding With Shape Objects
In this comprehensive guide, you will be learning all the ways you can create and manipulate shapes with VBA macros.
Shapes are objects you can insert into your spreadsheet through the Insert Tab via the Shapes gallery button. These objects can add visualizations to your dashboards, store text, or even serve as buttons to launch macro code.
Here is an outline of the topics covered in this guide:
Creating A New Shape With AddShape()
To create a shape object in Excel using VBA, you must call the AddShape function.
The AddShape function has 4 required inputs in order to generate a new shape:
-
Type — Name of the type of shape you wish to generate
-
Left — Where on the spreadsheet the left side of the shape should be located
-
Top — Where on the spreadsheet the top of the shape should be located
-
Width — How wide your shape should be
-
Height — How tall your shape should be
Here is a snippet of VBA code showing how to create 2 shapes and store the newly created shape to a variable for easy reference later on in your code.
Sub CreateShape()
Dim shp1 As Shape
Dim shp2 As Shape
‘Create & Store New Shape to Variable
Set shp1 = ActiveSheet.Shapes.AddShape(msoShape16pointStar, _
ActiveCell.Left, ActiveCell.Top, 80, 27)
‘Create & Store New Shape to Variable (use Enum Code)
Set shp2 = ActiveSheet.Shapes.AddShape(94, _
ActiveCell.Left, ActiveCell.Top, 80, 27)
End Sub
Continue reading through the next few sections to learn how to determine the type, size, and position values you should be using to create your desired shape.
Choosing A Shape Type
There are a TON of shape types available to you through VBA. There are so many in fact, that I have painstakenly gone through and visually cataloged them for your ease in the below slide show.
Once you have determined which shape you would like to create, grab either the shape textual name or the enumeration number. You will use this MSOAutoShapeType reference to code the exact shape you want.
If you have a shape already created on your spreadsheet, you can use the following code to figure out its enumeration code that you can reference in your VBA code.
Sub DetermineShapeType()
‘PURPOSE: Display The Shape Type of Selected Shape
‘SOURCE: www.TheSpreadsheetGuru.com
Dim ActiveShape As Shape
Dim UserSelection As Variant
‘Pull-in what is selected on screen
Set UserSelection = ActiveWindow.Selection
‘Determine if selection is a shape
On Error GoTo NoShapeSelected
Set ActiveShape = ActiveSheet.Shapes(UserSelection.Name)
On Error Resume Next
‘Tell User the Shape Type Enumeration Number
MsgBox «The Select Shape Type = » & ActiveShape.AutoShapeType
Exit Sub
‘Error Handler
NoShapeSelected:
MsgBox «You do not have a shape selected!»
End Sub
Determining Shape Position
There are two properties you can modify to change the location of a shape on the spreadsheet with VBA. These two properties are the Left and Top values of the shape.
If you are unsure what the size of your shape should be, there are two popular ways you can size your shape:
Method 1: You can base it on the left and top positions of a cell on your spreadsheet.
The following VBA code shows you how to use the Left value of Cell B1 and the Top value of Cell B10 to reposition the rectangle shape that is created.
Sub ShapePositionFromCell()
Dim shp As Shape
‘Create Shape
Set shp = ActiveSheet.Shapes.AddShape(msoShapeRectangle, _
Range(«B1»).Left, Range(«B10»).Top, 100, 50)
End Sub
Method 2: You can position the shape to your liking manually on the spreadsheet and read the left and top positions using VBA.
The following VBA code will output a message box that displays the Left and Top positions of a currently selected shape (ActiveShape).
Sub DetermineShapePosition()
‘PURPOSE: Display Selected Shape’s Position
‘SOURCE: www.TheSpreadsheetGuru.com
Dim ActiveShape As Shape
Dim UserSelection As Variant
‘Pull-in what is selected on screen
Set UserSelection = ActiveWindow.Selection
‘Determine if selection is a shape
On Error GoTo NoShapeSelected
Set ActiveShape = ActiveSheet.Shapes(UserSelection.Name)
On Error Resume Next
‘Tell User the Shape Position Values
MsgBox «Left Position = » & ActiveShape.Left & vbNewLine & _
«Top Position = » & ActiveShape.Top
Exit Sub
‘Error Handler
NoShapeSelected:
MsgBox «You do not have a shape selected!»
End Sub
Determining Shape Size
There are two properties you can modify to change the size of a shape with VBA. These two properties are the Width and Height values of the shape.
If you are unsure what the size of your shape should be, there are two popular ways you can size your shape:
Method 1: You can base it on the size of a range of cells
Sub ShapeSizeFromRange()
Dim shp As Shape
Dim rng As Range
‘Provide Range for Shape Size
Set rng = Range(«A1:C4»)
‘Create Shape
Set shp = ActiveSheet.Shapes.AddShape(msoShapeRectangle, _
ActiveCell.Left, ActiveCell.Top, rng.Width, rng.Height)
End Sub
Method 2: You can create the shape to your liking manually and read the width and height using VBA
Sub DetermineShapeSize()
‘PURPOSE: Display Selected Shape’s Size
‘SOURCE: www.TheSpreadsheetGuru.com
Dim ActiveShape As Shape
Dim UserSelection As Variant
‘Pull-in what is selected on screen
Set UserSelection = ActiveWindow.Selection
‘Determine if selection is a shape
On Error GoTo NoShapeSelected
Set ActiveShape = ActiveSheet.Shapes(UserSelection.Name)
On Error Resume Next
‘Tell User the Shape Position Values
MsgBox «Width = » & ActiveShape.Width & vbNewLine & _
«Height = » & ActiveShape.Height
Exit Sub
‘Error Handler
NoShapeSelected:
MsgBox «You do not have a shape selected!»
End Sub
Text Formatting
Sub CreateShapeWithText()
Dim shp As Shape
‘Create & Store New Shape to Variable
Set shp = ActiveSheet.Shapes.AddShape(msoShape16pointStar, _
ActiveCell.Left, ActiveCell.Top, 80, 27)
‘Add Text To Shape
shp.TextFrame2.TextRange.Text = «My Awesome Shape!»
‘Bold/Italicize/Underline Text
shp.TextFrame2.TextRange.Font.Bold = True
shp.TextFrame2.TextRange.Font.Italic = True
shp.TextFrame2.TextRange.Font.UnderlineStyle = msoUnderlineDottedLine
‘Change Text Color
shp.TextFrame2.TextRange.Font.Fill.ForeColor.RGB = RGB(225, 140, 71)
‘Change Text Size
shp.TextFrame2.TextRange.Font.Size = 14
‘Center Align Text
shp.TextFrame.HorizontalAlignment = xlHAlignCenter
shp.TextFrame.VerticalAlignment = xlVAlignCenter
End Sub
Fill Color & Borders
Sub CreateShapeWithBorder()
Dim shp As Shape
‘Create & Store New Shape to Variable
Set shp = ActiveSheet.Shapes.AddShape(msoShapeRoundedRectangle, _
ActiveCell.Left, ActiveCell.Top, 80, 27)
‘Light Orange Fill
shp.Fill.ForeColor.RGB = RGB(253, 234, 218)
‘Add Dotted Border
shp.Line.DashStyle = msoLineDashDotDot
‘Dark Orange Border
shp.Line.ForeColor.RGB = RGB(252, 213, 181)
‘Adjust Border Thickness
shp.Line.Weight = 2
‘Remove Border
shp.Line.Visible = False
End Sub
Change Shape Type
If you are looking to change the shape type of an existing type, you can do so by setting the AutoShapeType to a different shape type value.
Sub ChangeShapeType()
Dim shp As Shape
‘Store specific shape on spreadsheet to a variable
Set shp = ActiveSheet.Shapes(«Shape1»)
‘Change shape type to oval
shp.AutoShapeType = msoShapeOval
End Sub
Create Your Own Macro Button With VBA Code
I personally cannot stand the native Excel form control button. It looks so outdated and really makes your spreadsheets look unprofessional. That is why I prefer to use VBA code to create a shape that looks like a button.
I thought this would be a great example to show you a real-world coding example where I need to create and format a shape to have a specific appearance. The following VBA macro code puts everything we have covered in this guide together and provides you with some sample code that comprises of a true shape-building solution.
Sub Create_Button()
‘PURPOSE: Creates a SpreadsheetGuru macro button shape
‘SOURCE: www.TheSpreadsheetGuru.com
Dim bttn As Shape
‘Create & Position Macro Button
Set bttn = ActiveSheet.Shapes.AddShape(msoShapeRoundedRectangle, _
ActiveCell.Left, ActiveCell.Top, 80, 27)
‘Modify Text Formatting
With bttn.TextFrame2.TextRange
.Text = «Macro»
.Font.Bold = msoTrue
.Font.Fill.ForeColor.RGB = RGB(0, 0, 0)
.Font.Size = 14
End With
‘Center Alignment
bttn.TextFrame.HorizontalAlignment = xlHAlignCenter
bttn.TextFrame.VerticalAlignment = xlVAlignCenter
‘Light Gray Fill
bttn.Fill.ForeColor.RGB = RGB(217, 217, 217)
‘No Border
bttn.Line.Visible = msoFalse
End Sub
Loop Through All Shapes Of Specific Type
If you need to target a specific shape type on your spreadsheet, you can create a loop that tests the AutoShapeType value to filter your results.
The following VBA code example loops through all shape objects in the currently selected spreadsheet and only changes the fill color of the rectangle shapes.
Sub ChangeRectangleShapes()
Dim shp As Shape
‘Loop through each shape on ActiveSheet
For Each shp In ActiveSheet.Shapes
‘Only modify rectangle shapes
If shp.AutoShapeType = msoShapeRectangle Then
shp.Fill.ForeColor.RGB = RGB(253, 234, 218)
End If
Next shp
End Sub
I Hope This Microsoft Excel Article Helped!
Hopefully, I was able to explain how you use VBA code to create and format shapes on your Excel spreadsheets. If you have any questions about these techniques or suggestions on how to improve them, please let me know in the comments section below.
About The Author
Hey there! I’m Chris and I run TheSpreadsheetGuru website in my spare time. By day, I’m actually a finance professional who relies on Microsoft Excel quite heavily in the corporate world. I love taking the things I learn in the “real world” and sharing them with everyone here on this site so that you too can become a spreadsheet guru at your company.
Through my years in the corporate world, I’ve been able to pick up on opportunities to make working with Excel better and have built a variety of Excel add-ins, from inserting tickmark symbols to automating copy/pasting from Excel to PowerPoint. If you’d like to keep up to date with the latest Excel news and directly get emailed the most meaningful Excel tips I’ve learned over the years, you can sign up for my free newsletters. I hope I was able to provide you with some value today and I hope to see you back here soon!
— Chris
A TextFrame object is used to manipulate various elements of the text frame –basically a box of text — related to shape objects.
When we have a shape object (ex. rectangle, circle, etc.), we can control the text associated with the shape through the TextFrame object. This object includes one method and 15 properties.
The only method in the TextFrame object is the Characters method. It takes two optional parameters; start and length, given that we set the text property of the Characters method.
| Name | Required | Data Type | Description |
| Start | Optional | Variant | Determines the starting character. If set to 1 or omitted then all of the text will be returned. |
| Length | Optional | Variant | The number of characters to be returned. |
The Characters method can have its text value set and the various text properties as well such as the font bold, font, etc. The following code sets the text of the characters method to “Hello World”. Then, it sets the First letter (H) and the seventh letter (W) to bold.
'assume we already have a shape on the active sheet, and we set its text to Hello World. ActiveSheet.Shapes(1).TextFrame.Characters.Text = “Hello World” 'bold the first letter (H) ActiveSheet.Shapes(1).TextFrame.Characters(1,1).Font.Bold = True 'bold the 7th letter (W) ActiveSheet.Shapes(1).TextFrame.Characters(7,1).Font.Bold = True
The result of the above code is shown as follows.
TextFrame has many properties that can be manipulated to present it in a desirable format.
| Property | Description | Value |
| Application | The application that created the shape object | Ex. “Microsoft Excel” |
| AutoMargins | If True, then the values of the other margin properties (MarginBottom, MarginLeft, MarginRight, MarginTop) will be ignored | True or False |
| AutoSize | If True, then the size of the text frame on the shape will be adjusted to fit its text | True or False |
| Creator | The application that created the shape object (similar to the Application property) | Ex. “XCEL” |
| HorizontalAlignment | Sets the horizontal alignment value | xlHAlignCenter, xlHAlignCenterAcrossSelection, xlHAlignDistributed, xlHAlignFill, xlHAlignGeneral, xlHAlignJustify, xlHAlignLeft, xlHAlignRight |
| VerticalAlignment | Sets the vertical alignment value | xlVAlignCenter, xlVAlignJustify, xlVAlignBottom, xlVAlignDistributed, xlVAlignTop |
| HorizontalOverflow | Enables or disables horizontal overflow | 0 (for no overflow), 1 ( for allowing overflow) |
| VerticalOverflow | Enables or disables horizontal overflow | 0 (for no overflow), 1 ( for allowing overflow) |
| MarginBottom, MarginLeft, MarginRight, MarginTop | Sets the margin for the text frame. | Integer value greater than 0. |
| Orientation | Sets the value of the orientation. | 3 (downward), 1(horizontal), 6 (horizontal and rotated as required for Asian language support), 2 (upward), 5 (vertical), 4 (vertical as required for Asian language support). |
| Parent | Represents the parent of the textframe object | Shape object |
| ReadingOrder | Sets the reading order of the text. | xlContext (according to context), xlLTR (left-to-right), xlRTL (right-to-left) |
We start first by creating the shapes. The following code provides an example on how to create shapes.
Sub createShapes() Set starShape = Sheets(1).Shapes.AddShape(msoShape10pointStar, 150, 20, 100, 30) Set rectangleShape = Sheets(1).Shapes.AddShape(msoShapeRectangle, 406.8, 29.4, 67.8, 36) End Sub
This results in the creation of a star shape and a rectangle shape that we set reference variables for.
Example 1: Characters.Text
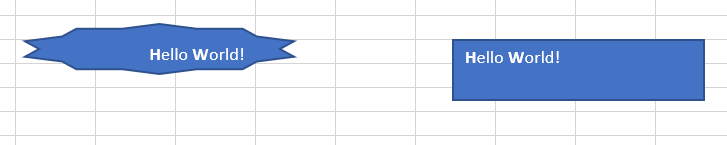
One of the most common and useful properties that TextFrame objects allow us to manipulate is the text that we can place in shapes. The below code sets the text of the shapes we just created to “Hello World!”
Sub CreateShapes() Set starShape = Sheets(1).Shapes.AddShape(msoShape10pointStar, 150, 20, 100, 30) Set rectangleShape = Sheets(1).Shapes.AddShape(msoShapeRectangle, 406.8, 29.4, 67.8, 36) starShape.TextFrame.Characters.Text = "Hello World!" rectangleShape.TextFrame.Characters.Text = "Hello World!" End Sub
Example 2: Alignment
Here you can see the text being left-aligned in the rectangle and right-aligned in the star:
Sub createShapes_align() Set starShape = Sheets(1).Shapes.AddShape(msoShape10pointStar, 150, 20, 100, 30) Set rectangleShape = Sheets(1).Shapes.AddShape(msoShapeRectangle, 406.8, 29.4, 67.8, 36) With rectangleShape.TextFrame .Characters.Text = "Hello World!" .Characters(1, 1).Font.Bold = True .Characters(7, 1).Font.Bold = True .HorizontalAlignment = xlHAlignLeft End With With starShape.TextFrame .Characters.Text = "Hello World!" .Characters(1, 1).Font.Bold = True .Characters(7, 1).Font.Bold = True .HorizontalAlignment = xlHAlignRight End With End Sub
Example 3: Margin
And finally, we can add margin around the characters too.
Sub createShapes_Margin() Set rectangle2Shape = Sheets(1).Shapes.AddShape(msoShapeRectangle, 150, 20, 100, 30) With rectangle1Shape.TextFrame .Characters.Text = "Hello World" .MarginLeft = 15 End With With rectangle2Shape.TextFrame .Characters.Text = "Hello World!" .MarginLeft = 40 End With End Sub
These are some examples that should help you gain insight into how to use the methods and properties of the TextFrame object. Whenever you’re using a shape in any of the office applications while programming in VBA, you’re likely to work with Textframe. These examples are a great starting point for getting introduced to this object.
drom
Active Member
- Joined
- Mar 20, 2005
- Messages
- 494
- Office Version
-
- 2019
- 2016
- 2013
- 2011
- 2010
- 2007
-
#1
Hi and Thanks in advance!
I have inserted a shapes as follows:
InsertShapesbasic shapes and I have inserted the «Bevel 1» shape.
I have added a text to this Shape, say eg: «HELLO»
how can I get or modify this text by vba?
Happy new year!
Excel Facts
Highlight Duplicates
Home, Conditional Formatting, Highlight Cells, Duplicate records, OK to add pink formatting to any duplicates in selected range.
VoG
Legend
- Joined
- Jun 19, 2002
- Messages
- 63,650
-
#2
Try like this
Code:
Sub bevel()
ActiveSheet.Shapes("Bevel 1").TextFrame.Characters.Text = "Hello World!"
End Sub
mjrofra
Board Regular
- Joined
- May 18, 2009
- Messages
- 180
-
#3
Hi,
Maybe
Code:
Sheets("Sheet1").Shapes("Shape name").TextFrame.Characters.Text = "Hello"EDIT: Sorry, did no see VoG response went I sent mine.
Last edited by a moderator: Jul 5, 2021
drom
Active Member
- Joined
- Mar 20, 2005
- Messages
- 494
- Office Version
-
- 2019
- 2016
- 2013
- 2011
- 2010
- 2007
-
#4
Re: [Solved] change a shape’s text by vba
Solved
Thanks to both!
astrodon
New Member
- Joined
- Dec 29, 2019
- Messages
- 13
- Office Version
-
- 365
- 2010
- 2007
- Platform
-
- Windows
-
#5
I realize many years and versions have passed since this post but, neither one of those work (Excel 365)
Fluff
MrExcel MVP, Moderator
- Joined
- Jun 12, 2014
- Messages
- 83,774
- Office Version
-
- 365
- Platform
-
- Windows
-
#6
Actually they both work.
astrodon
New Member
- Joined
- Dec 29, 2019
- Messages
- 13
- Office Version
-
- 365
- 2010
- 2007
- Platform
-
- Windows
-
#7
Actually they both work.
![Wink ;) ;)]()
Tell that to my version.
Similar threads