Замена части строкового выражения в VBA Excel по указанному шаблону поиска и замены и возврат преобразованной строки с помощью функции Replace.
Replace – это функция, которая возвращает строку, полученную в результате замены одной подстроки в исходном строковом выражении другой подстрокой указанное количество раз.
Если замену подстроки необходимо осуществить в диапазоне ячеек, функцию Replace следует применить к значению каждой ячейки заданного диапазона. Проще замену в диапазоне ячеек произвести с помощью метода Range.Replace.
Синтаксис и параметры
Replace(expression, find, replace, [start], [count], [compare])
- expression – исходное строковое выражение, содержащее подстроку, которую необходимо заменить;
- find – искомая подстрока, подлежащая замене;
- replace – подстрока, заменяющая искомую подстроку;
- start – порядковый номер символа исходной строки, с которого необходимо начать поиск, часть строки до этого номера обрезается, по умолчанию равен 1 (необязательный параметр);
- count – количество замен подстроки, по умолчанию выполняется замена всех обнаруженных вхождений (необязательный параметр);
- compare – числовое значение, указывающее вид сравнения (необязательный параметр).
Сокращенный синтаксис функции Replace с необязательными параметрами по умолчанию:
Replace(expression, find, replace)
Параметр compare
| Константа | Значение | Описание |
|---|---|---|
| vbUseCompareOption | -1 | используется параметр, заданный оператором Option Compare |
| vbBinaryCompare | 0 | выполняется двоичное сравнение |
| vbTextCompare | 1 | применяется текстовое сравнение |
По умолчанию используется двоичное (бинарное) сравнение. При таком сравнении буквенные символы в нижнем и верхнем регистрах различаются. Если необходимо провести замену подстроки независимо от регистра букв, используйте значение параметра compare – vbTextCompare (1).
Примеры кода VBA Excel
Пример 1
Замена единственного вхождения искомой подстроки в строковое выражение:
|
Sub Primer1() Dim a a = «Сливочное масло» a = Replace(a, «Сливочное», «Рыжиковое») MsgBox a ‘Результат: «Рыжиковое масло» End Sub |
Пример 2
Замена нескольких вхождений искомой подстроки в строковое выражение:
|
Sub Primer2() Dim a a = «Идёт медведь, идёт лиса, идёт грач» ‘с параметром compare по умолчанию a = Replace(a, «идёт», «бежит») MsgBox a ‘Результат: ‘Идёт медведь, бежит лиса, бежит грач a = «Идёт медведь, идёт лиса, идёт грач» ‘с параметром compare=1(vbTextCompare) a = Replace(a, «идёт», «бежит», , , 1) MsgBox a ‘Результат: ‘бежит медведь, бежит лиса, бежит грач End Sub |
Пример 3
Замена одного вхождения искомой подстроки в строковое выражение из нескольких с обрезанием исходной строки до 15 символа:
|
Sub Primer3() Dim a a = «Идёт медведь, идёт лиса, идёт грач» a = Replace(a, «идёт», «бежит», 15, 1) MsgBox a ‘Результат: ‘бежит лиса, идёт грач End Sub |

This VBA Tutorial is accompanied by Excel workbooks containing the data and macros I use in the examples below. You can get immediate free access to these example workbooks by subscribing to the Power Spreadsheets Newsletter.
Use the following Table of Contents to navigate to the section you’re interested in.
Related VBA and Macro Tutorials
The following VBA and Macro Tutorials may help you better understand and implement the contents below:
- General VBA constructs and structures:
- Learn about commonly-used VBA terms here.
- Learn about the Excel Object Model here.
- Learn about working with variables here.
- Learn about data types here.
- Learn about working with arrays here.
- Practical VBA applications and macro examples:
- Learn about referring to cell ranges here.
- Learn about working with worksheet functions within VBA here.
You can find additional VBA and Macro Tutorials in the Archives.
#1: Replace String in Cell
VBA Code to Replace String in Cell
To replace a string in a cell with VBA, use a statement with the following structure:
Cell.Value = Replace(Expression:=Cell.Value, Find:=StringToReplace, Replace:=ReplacementString, Count:=NumberOfReplacements)
Process Followed by VBA Code to Replace String in Cell
VBA Statement Explanation
- Item: Cell.
- VBA Construct: Range object.
- Description: Range object representing the cell you work with.
You can usually return a Range object with constructs such as the Worksheet.Range, Worksheet.Cells (with the Range.Item) or Range.Offset properties.
- Item: Value.
- VBA Construct: Range.Value property.
- Description: The Range.Value property specifies the value (in this case string) within Cell.
- Item: =.
- VBA Construct: Assignment operator.
- Description: The = operator assigns the string returned by the Replace function to the Range.Value property of Cell.
- Item: Replace(…).
- VBA Construct: Replace function.
- Description: The Replace function returns a string where a specific substring (StringToReplace) is replaced by another substring (ReplacementString) a specific number of times (NumberOfReplacements).
- Item: Expression:=Cell.Value.
- VBA Construct: Expression parameter of the Replace function, Range object and Range.Value property.
- Description: The Expression parameter of the Replace function specifies the string expression containing the substring you want to replace (StringToReplace). Within this macro structure, Expression is the value (string) within Cell, as returned by the Range.Value property.
- Item: Find:=StringToReplace.
- VBA Construct: Find parameter of the Replace function.
- Description: The Find parameter of the Replace function specifies the substring you search for and replace.
If you explicitly declare a variable to represent StringToReplace, use the String data type.
- Item: Replace:=ReplacementString.
- VBA Construct: Replace parameter of the Replace function.
- Description: The Replace parameter of the Replace function specifies the substring you want to use as replacement for StringToReplace.
If you explicitly declare a variable to represent ReplacementString, use the String data type.
- Item: Count:=NumberOfReplacements.
- VBA Construct: Count parameter of the Replace function.
- Description: The Count parameter of the Replace function specifies the number of substitutions you want to carry out. In other words, the number of times you want to replace StringToReplace with ReplacementString.
If you want VBA to replace all occurrences of StringToReplace with ReplacementString, omit the Count parameter. In such case, Count defaults to -1 and VBA carries out all possible substitutions. Please refer to the appropriate section (Replace All Occurrences of String in Cell) below for further information about this scenario.
Macro Example to Replace String in Cell
The following macro replaces the string “replace” (myStringToReplace) with the string “substitute” (myReplacementString) one time (myNumberOfReplacements) within the string in cell A5 of the worksheet named “Excel VBA Replace” (myCell).
Sub replaceStringInCell()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-replace-substitute/
'declare object variable to hold reference to cell you work with
Dim myCell As Range
'declare variables to hold parameters for string replacement (string to replace, replacement string, and number of replacements)
Dim myStringToReplace As String
Dim myReplacementString As String
Dim myNumberOfReplacements As Long
'identify cell you work with
Set myCell = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Excel VBA Replace").Range("A5")
'specify parameters for string replacement (string to replace, replacement string, and number of replacements)
myStringToReplace = "replace"
myReplacementString = "substitute"
myNumberOfReplacements = 1
'replace string in cell you work with, and assign resulting string to Range.Value property of cell you work with
myCell.Value = Replace(Expression:=myCell.Value, Find:=myStringToReplace, Replace:=myReplacementString, Count:=myNumberOfReplacements)
End Sub
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Replace String in Cell
The following GIF illustrates the results of executing this macro example. As expected, the macro replaces the string “replace” with the string “substitute” one time within the string in cell A5.
#2: Replace String in Cell Specifying a Starting Position for Search
VBA Code to Replace String in Cell Specifying a Starting Position for Search
To replace a string in a cell and specify the starting position to search for the string with VBA, use a statement with the following structure:
Cell.Value = Left(String:=Cell.Value, Length:=StartPosition - 1) & Replace(Expression:=Cell.Value, Find:=StringToReplace, Replace:=ReplacementString, Start:=StartPosition, Count:=NumberOfReplacements)
Process Followed by VBA Code to Replace String in Cell Specifying a Starting Position for Search
VBA Statement Explanation
- Item: Cell.
- VBA Construct: Range object.
- Description: Range object representing the cell you work with.
You can usually return a Range object with constructs such as the Worksheet.Range, Worksheet.Cells (with the Range.Item) or Range.Offset properties.
- Item: Value.
- VBA Construct: Range.Value property.
- Description: The Range.Value property specifies the value (in this case string) within Cell.
- Item: =.
- VBA Construct: Assignment operator.
- Description: The = operator assigns the string returned by the Replace function to the Range.Value property of Cell.
- Item: Left(…).
- VBA Construct: Left function.
- Description: The Left function returns a string containing the number of characters specified by the Length parameter (StartPosition – 1) from the left side of the string specified by the String parameter (Cell.Value).
Within this macro structure, you use the Left function to return the substring containing the first characters of the string within the cell you work with. This substring goes from the first character of the string to the character immediately before the position within the string where you start searching for the substring you want to replace (StringToReplace).
You need to do this because the Replace function doesn’t return a copy of the string (with substitutions) from start to finish. The string that Replace returns starts at the position within the string where you start searching for the substring you want to replace (StartPosition). Therefore, VBA truncates the string and the characters to the left of StartPosition aren’t part of the string returned by Replace.
- Item: String:=Cell.Value.
- VBA Construct: String parameter of the Left function, Range object and Range.Value property.
- Description: The String parameter of the Left function specifies the string expression containing the substring you want to replace (StringToReplace).
Within this macro structure, String is the value (string) within Cell, as returned by the Range.Value property. The value of the String parameter of the Left function is the same as the value of the Expression parameter of the Replace function.
- Item: Length:=StartPosition – 1.
- VBA Construct: Length parameter of the Left function.
- Description: The Length parameter of the Left function specifies the number of characters the Left function returns from the string you work with. StartPosition is the position within the string where you start searching for the substring you want to replace (StringToReplace). (StartPosition – 1) is the position of the character immediately before StartPosition. Therefore, the Left function returns the substring containing the first characters of the string within the cell you work with, up until the character located in position (StartPosition – 1).
If you explicitly declare a variable to represent StartPosition, use the Long data type. The value of StartPosition within the Length parameter of the Left function is the same as the value of the Start parameter of the Replace function.
- Item: &.
- VBA Construct: Concatenation operator.
- Description: The & operator concatenates the strings returned by the Left and Replace functions.
- Item: Replace(…).
- VBA Construct: Replace function.
- Description: The Replace function returns a string where a specific substring (StringToReplace) is replaced by another substring (ReplacementString) a specific number of times (NumberOfReplacements).
- Item: Expression:=Cell.Value.
- VBA Construct: Expression parameter of the Replace function, Range object and Range.Value property.
- Description: The Expression parameter of the Replace function specifies the string expression containing the substring you want to replace (StringToReplace). Within this macro structure, Expression is the value (string) within Cell, as returned by the Range.Value property.
- Item: Find:=StringToReplace.
- VBA Construct: Find parameter of the Replace function.
- Description: The Find parameter of the Replace function specifies the substring you search for and replace.
If you explicitly declare a variable to represent StringToReplace, use the String data type.
- Item: Replace:=ReplacementString.
- VBA Construct: Replace parameter of the Replace function.
- Description: The Replace parameter of the Replace function specifies the substring you want to use as replacement for StringToReplace.
If you explicitly declare a variable to represent ReplacementString, use the String data type.
- Item: Start:=StartPosition.
- VBA Construct: Start parameter of the Replace function.
- Description: The Start parameter of the Replace function specifies the position within the string you work with where you start searching for StringToReplace.
The default value of the Start parameter is 1. In such case, the Replace function doesn’t truncate the string. Therefore, you generally don’t have to work with the Left function and concatenation operator. Please refer to the appropriate section (Replace String in Cell) above for further information about this scenario.
- Item: Count:=NumberOfReplacements.
- VBA Construct: Count parameter of the Replace function.
- Description: The Count parameter of the Replace function specifies the number of substitutions you want to carry out. In other words, the number of times you want to replace StringToReplace with ReplacementString.
If you want VBA to replace all occurrences of StringToReplace after StartPosition with ReplacementString, omit the Count parameter. In such case, Count defaults to -1 and VBA carries out all possible substitutions. Please refer to the appropriate section (Replace All Occurrences of String in Cell) below for further information about this scenario.
Macro Example to Replace String in Cell Specifying a Starting Position for Search
The following macro replaces the string “replace” (myStringToReplace) with the string “substitute” (myReplacementString) one time (myNumberOfReplacements) within the string in cell A6 of the worksheet named “Excel VBA Replace” (myCell). The search for myStringToReplace begins in position 14 (myStartPosition) of the string in myCell.
Sub replaceStringInCellWithStartPosition()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-replace-substitute/
'declare object variable to hold reference to cell you work with
Dim myCell As Range
'declare variables to hold parameters for string replacement (string to replace, replacement string, start position for search of string to replace, and number of replacements)
Dim myStringToReplace As String
Dim myReplacementString As String
Dim myStartPosition As Long
Dim myNumberOfReplacements As Long
'identify cell you work with
Set myCell = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Excel VBA Replace").Range("A6")
'specify parameters for string replacement (string to replace, replacement string, start position for search of string to replace, and number of replacements)
myStringToReplace = "replace"
myReplacementString = "substitute"
myStartPosition = 14
myNumberOfReplacements = 1
'return and concatenate the following strings, and assign the resulting (concatenated) string to Range.Value property of cell you work with
'(i) string containing the first characters within the cell you work with (from first position up to the character before the start position for search of string to replace)
'(ii) string resulting from working with the Replace function and the parameter for string replacement you specify
myCell.Value = Left(String:=myCell.Value, Length:=myStartPosition - 1) & Replace(Expression:=myCell.Value, Find:=myStringToReplace, Replace:=myReplacementString, Start:=myStartPosition, Count:=myNumberOfReplacements)
End Sub
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Replace String in Cell Specifying a Starting Position for Search
The following GIF illustrates the results of executing this macro example. As expected, the macro replaces the string “replace” with the string “substitute” one time within the string in cell A6. The search for myStringToReplace begins in position 14 of the string in cell A6. This matches with the second occurrence of the “replace” string.
#3: Replace All Occurrences of String in Cell
VBA Code to Replace All Occurrences of String in Cell
To replace all occurrences of a string in a cell with VBA, use a statement with the following structure:
Cell.Value = Replace(Expression:=Cell.Value, Find:=StringToReplace, Replace:=ReplacementString)
Process Followed by VBA Code to Replace All Occurrences of String in Cell
VBA Statement Explanation
- Item: Cell.
- VBA Construct: Range object.
- Description: Range object representing the cell you work with.
You can usually return a Range object with constructs such as the Worksheet.Range, Worksheet.Cells (with the Range.Item) or Range.Offset properties.
- Item: Value.
- VBA Construct: Range.Value property.
- Description: The Range.Value property specifies the value (in this case string) within Cell.
- Item: =.
- VBA Construct: Assignment operator.
- Description: The = operator assigns the string returned by the Replace function to the Range.Value property of Cell.
- Item: Replace(…).
- VBA Construct: Replace function.
- Description: The Replace function returns a string where a specific substring (StringToReplace) is replaced by another substring (ReplacementString). Within this macro structure, Replace carries out all possible substitutions.
- Item: Expression:=Cell.Value.
- VBA Construct: Expression parameter of the Replace function, Range object and Range.Value property.
- Description: The Expression parameter of the Replace function specifies the string expression containing the substring you want to replace (StringToReplace). Within this macro structure, Expression is the value (string) within Cell, as returned by the Range.Value property.
- Item: Find:=StringToReplace.
- VBA Construct: Find parameter of the Replace function.
- Description: The Find parameter of the Replace function specifies the substring you search for and replace.
If you explicitly declare a variable to represent StringToReplace, use the String data type.
- Item: Replace:=ReplacementString.
- VBA Construct: Replace parameter of the Replace function.
- Description: The Replace parameter of the Replace function specifies the substring you want to use as replacement for StringToReplace.
If you explicitly declare a variable to represent ReplacementString, use the String data type.
Macro Example to Replace All Occurrences of String in Cell
The following macro replaces all occurrences of the string “replace” (myStringToReplace) with the string “substitute” (myReplacementString) within the string in cell A7 of the worksheet named “Excel VBA Replace” (myCell).
Sub replaceAll()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-replace-substitute/
'declare object variable to hold reference to cell you work with
Dim myCell As Range
'declare variables to hold parameters for string replacement (string to replace and replacement string)
Dim myStringToReplace As String
Dim myReplacementString As String
'identify cell you work with
Set myCell = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Excel VBA Replace").Range("A7")
'specify parameters for string replacement (string to replace and replacement string)
myStringToReplace = "replace"
myReplacementString = "substitute"
'replace all occurrences within string in cell you work with, and assign resulting string to Range.Value property of cell you work with
myCell.Value = Replace(Expression:=myCell.Value, Find:=myStringToReplace, Replace:=myReplacementString)
End Sub
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Replace All Occurrences of String in Cell
The following GIF illustrates the results of executing this macro example. As expected, the macro replaces all (2) occurrences of the string “replace” with the string “substitute” within the string in cell A7.
#4: Replace Character in String
VBA Code to Replace Character in String
To replace a character in a string within a cell with VBA, use a statement with the following structure:
Cell.Value = Replace(Expression:=Cell.Value, Find:=CharacterToReplace, Replace:=ReplacementCharacter)
Process Followed by VBA Code to Replace Character in String
VBA Statement Explanation
- Item: Cell.
- VBA Construct: Range object.
- Description: Range object representing the cell you work with.
You can usually return a Range object with constructs such as the Worksheet.Range, Worksheet.Cells (with the Range.Item) or Range.Offset properties.
- Item: Value.
- VBA Construct: Range.Value property.
- Description: The Range.Value property specifies the value (in this case string) within Cell.
- Item: =.
- VBA Construct: Assignment operator.
- Description: The = operator assigns the string returned by the Replace function to the Range.Value property of Cell.
- Item: Replace(…).
- VBA Construct: Replace function.
- Description: The Replace function returns a string where a specific character (CharacterToReplace) is replaced by another character (ReplacementCharacter). Within this macro structure, Replace carries out all possible substitutions.
- Item: Expression:=Cell.Value.
- VBA Construct: Expression parameter of the Replace function, Range object and Range.Value property.
- Description: The Expression parameter of the Replace function specifies the string expression containing the character you want to replace (CharacterToReplace). Within this macro structure, Expression is the value (string) within Cell, as returned by the Range.Value property.
- Item: Find:=CharacterToReplace.
- VBA Construct: Find parameter of the Replace function.
- Description: The Find parameter of the Replace function specifies the character you search for and replace.
If you explicitly declare a variable to represent CharacterToReplace, use the String data type.
- Item: Replace:=ReplacementCharacter.
- VBA Construct: Replace parameter of the Replace function.
- Description: The Replace parameter of the Replace function specifies the character you want to use as replacement for CharacterToReplace.
If you explicitly declare a variable to represent ReplacementCharacter, use the String data type.
Macro Example to Replace Character in String
The following macro replaces all occurrences of the character “a” (myCharacterToReplace) with the character “e” (myReplacementCharacter) within the string in cell A8 of the worksheet named “Excel VBA Replace” (myCell).
Sub replaceCharacterInString()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-replace-substitute/
'declare object variable to hold reference to cell you work with
Dim myCell As Range
'declare variables to hold parameters for character replacement (character to replace and replacement character)
Dim myCharacterToReplace As String
Dim myReplacementCharacter As String
'identify cell you work with
Set myCell = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Excel VBA Replace").Range("A8")
'specify parameters for string replacement (character to replace and replacement character)
myCharacterToReplace = "a"
myReplacementCharacter = "e"
'replace all occurrences of character within string in cell you work with, and assign resulting string to Range.Value property of cell you work with
myCell.Value = Replace(Expression:=myCell.Value, Find:=myCharacterToReplace, Replace:=myReplacementCharacter)
End Sub
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Replace Character in String
The following GIF illustrates the results of executing this macro example. As expected, the macro replaces all occurrences of the character “a” with the character “e” within the string in cell A8.
#5: Replace Multiple Characters in String
VBA Code to Replace Multiple Characters in String
To replace multiple characters in a string with VBA, use a macro with the following statement structure:
Dim StringReplace As String
StringReplace = Cell.Value
For Each Character In Array(CharactersList)
StringReplace = Replace(Expression:=StringReplace, Find:=Character, Replace:=ReplacementCharacter)
Next Character
Cell.Value = StringReplace
Process Followed by VBA Code to Replace Multiple Characters in String
VBA Statement Explanation
Line #1: Dim StringReplace As String
- Item: Dim StringReplace As String.
- VBA Construct: Dim statement.
- Description: The Dim statement declares the StringReplace variable as of the String data type.
StringReplace represents the string you work with. StringReplace is both (i) the string where you replace multiple characters (prior to working with the Replace function and the For Each… Next statement) and (ii) the new string after multiple characters have been replaced (after working with the Replace function and the For Each… Next statement).
Line #2: StringReplace = Cell.Value
- Item: StringReplace.
- VBA Construct: Variable of the string data type.
- Description: StringReplace represents the string you work with. StringReplace is both (i) the string where you replace multiple characters (prior to working with the Replace function and the For Each… Next statement) and (ii) the new string after multiple characters have been replaced (after working with the Replace function and the For Each… Next statement).
- Item: =.
- VBA Construct: Assignment operator.
- Description: The = operator assigns the string returned by the Range.Value property to the StringReplace variable.
- Item: Cell.
- VBA Construct: Range object.
- Description: Range object representing the cell you work with.
You can usually return a Range object with constructs such as the Worksheet.Range, Worksheet.Cells (with the Range.Item) or Range.Offset properties.
- Item: Value.
- VBA Construct: Range.Value property.
- Description: The Range.Value property returns the value (in this case string) within Cell.
Lines #3 and #5: For Each Character In Array(CharactersList) | Next Character
- Item: For Each… In… Next.
- VBA Construct: For Each… Next statement.
- Description: The For Each… Next statement repeats the statement within the loop (line #4) for each element (Character) in the array returned by the Array function (Array(CharactersList)).
- Item: Character.
- VBA Construct: Element of For Each… Next statement and variable of the Variant data type.
- Description: The Element of the For Each… Next statement is a variable used to iterate through the elements of the array returned by the Array function (Array(CharactersList)).
If you explicitly declare a variable to represent Character, use the Variant data type.
- Item: Array(CharactersList).
- VBA Construct: Array function.
- Description: The Array function returns a Variant containing an array. CharactersList is the comma-delimited list of characters (passed as strings) that you assign to each of the array elements
Line #4: StringReplace = Replace(Expression:=StringReplace, Find:=Character, Replace:=ReplacementCharacter)
- Item: StringReplace.
- VBA Construct: Variable of the String data type.
- Description: StringReplace represents the string you work with. StringReplace is both (i) the string where you replace multiple characters (prior to working with the Replace function and the For Each… Next statement) and (ii) the new string after multiple characters have been replaced (after working with the Replace function and the For Each… Next statement).
- Item: =.
- VBA Construct: Assignment operator.
- Description: The = operator assigns the string returned by the Replace function to StringReplace.
- Item: Replace(…).
- VBA Construct: Replace function.
- Description: The Replace function returns a string (starting with StringReplace) where a specific character (Character) is replaced by another character (ReplacementCharacter). Within this macro structure, Replace carries out all possible substitutions.
- Item: Expression:=StringReplace.
- VBA Construct: Expression parameter of the Replace function and variable of the String data type.
- Description: The Expression parameter of the Replace function specifies the string expression (StringReplace) containing the characters you want to replace (CharactersList).
- Item: Find:=Character.
- VBA Construct: Find parameter of the Replace function and variable of the Variant data type.
- Description: The Find parameter of the Replace function specifies the character you search for and replace.
Within this macro structure, Character is also the Element of the For Each… Next statement. This is the variable used to iterate through the elements of the array returned by the Array function (Array(CharactersList)).
If you explicitly declare a variable to represent Character, use the Variant data type.
- Item: Replace:=ReplacementCharacter.
- VBA Construct: Replace parameter of the Replace function.
- Description: The Replace parameter of the Replace function specifies the character you want to use as replacement for the characters you want to replace (CharactersList).
If you explicitly declare a variable to represent ReplacementCharacter, use the String data type.
Line #6: Cell.Value = StringReplace
- Item: Cell.
- VBA Construct: Range object.
- Description: Range object representing the cell you work with.
You can usually return a Range object with constructs such as the Worksheet.Range, Worksheet.Cells (with the Range.Item) or Range.Offset properties.
- Item: Value.
- VBA Construct: Range.Value property.
- Description: The Range.Value property specifies the value (in this case string) within Cell.
- Item: =.
- VBA Construct: Assignment operator.
- Description: The = operator assigns the string represented by the StringReplace variable to the Range.Value property of Cell.
- Item: StringReplace.
- VBA Construct: Variable of the String data type.
- Description: StringReplace represents the string you work with. StringReplace is both (i) the string where you replace multiple characters (prior to working with the Replace function and the For Each… Next statement) and (ii) the new string after multiple characters have been replaced (after working with the Replace function and the For Each… Next statement).
Macro Example to Replace Multiple Characters in String
The following macro replaces all occurrences of the characters “a”, “e” and “i” (myCharactersArray) with the character “o” (myReplacementCharacter) within the string in cell A9 of the worksheet named “Excel VBA Replace” (myCell).
Sub replaceMultipleCharactersInString()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-replace-substitute/
'declare object variable to hold reference to cell you work with
Dim myCell As Range
'declare variables to hold string you work with and replacement character
Dim myString As String
Dim myReplacementCharacter As String
'declare variable to hold Variant containing array whose elements are characters to replace, and variable used to iterate through the elements of the array
Dim myCharactersArray() As Variant
Dim iCharacter As Variant
'identify the cell you work with and the string within that cell
Set myCell = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Excel VBA Replace").Range("A9")
myString = myCell.Value
'specify elements of array (characters to replace) and replacement character
myCharactersArray = Array("a", "e", "i")
myReplacementCharacter = "o"
'loop through each element (iCharacter) of the array (myCharacterArray)
For Each iCharacter In myCharactersArray
'replace all occurrences of element (iCharacter) within current version of string you work with (myString), and assign resulting string to myString variable
myString = Replace(Expression:=myString, Find:=iCharacter, Replace:=myReplacementCharacter)
Next iCharacter
'assign string represented by myString variable to Range.Value property of cell you work with
myCell.Value = myString
End Sub
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Replace Multiple Characters in String
The following GIF illustrates the results of executing this macro example. As expected, the macro replaces all occurrences of the characters “a”, “e” and “i” with the character “o” within the string in cell A9.
#6: Replace Wildcard
VBA Code to Replace Wildcard
To replace characters in a string within a cell using a wildcard with VBA, use a statement with the following structure:
Cell.Replace What:=StringToReplace, Replacement:=ReplacementString, LookAt:=xlPart, SearchOrder:=xlByRows, MatchCase:=False, SearchFormat:=False, ReplaceFormat:=False
Process Followed by VBA Code to Replace Wildcard
VBA Statement Explanation
- Item: Cell.
- VBA Construct: Range object.
- Description: Range object representing the cell you work with.
You can usually return a Range object with constructs such as the Worksheet.Range, Worksheet.Cells (with the Range.Item) or Range.Offset properties.
- Item: Replace.
- VBA Construct: Range.Replace method.
- Description: The Range.Replace method replaces a specific substring (StringToReplace) by another substring (ReplacementString) within Cell.
- Item: What:=StringToReplace.
- VBA Construct: What parameter of the Range.Replace method.
- Description: The What parameter of the Range.Replace method specifies the string you want to replace (StringToReplace).
When specifying StringToReplace, use the following wildcards as required:
- Question mark (?): The question mark represents any single character. For example, “w?ldcard” represents a string (i) starting with a “w”, (ii) followed by any single character (including “i”), and (iii) ending with “lcard”.
- Asterisk (*): The asterisk represents any group of characters. For example, “w*card” represents a string (i) starting with a “w”, (ii) followed by any group of characters (including “ild”), and (iii) ending with “card”.
If you explicitly declare a variable to represent StringToReplace, use the String data type.
- Item: Replacement:=ReplacementString.
- VBA Construct: Replacement parameter of the Range.Replace method.
- Description: The Replacement parameter of the Range.Replace method specifies the substring you want to use as replacement for StringToReplace.
- Item: LookAt:=xlPart.
- VBA Construct: LookAt parameter of the Range.Replace method.
- Description: The LookAt parameter of the Range.Replace method specifies that Range.Replace looks at (and matches) a part (xlPart) of the search data.
- Item: SearchOrder:=xlByRows.
- VBA Construct: SearchOrder parameter of the Range.Replace method.
- Description: The SearchOrder parameter of the Range.Replace method specifies that Range.Replace searches by rows (xlByRows).
- Item: MatchCase:=False.
- VBA Construct: MatchCase parameter of the Range.Replace method.
- Description: The MatchCase parameter of the Range.Replace method specifies that the search isn’t case sensitive (False).
- Item: SearchFormat:=False.
- VBA Construct: SearchFormat parameter of the Range.Replace method.
- Description: The SearchFormat parameter of the Range.Replace method specifies that the search doesn’t consider formatting (False).
- Item: ReplaceFormat:=False.
- VBA Construct: ReplaceFormat parameter of the Range.Replace method.
- Description: The ReplaceFormat parameter of the Range.Replace method specifies that no replace format is set (False).
Macro Example to Replace Wildcard
The following macro replaces the string (i) starting with a “w”, (ii) followed by any group of characters (including “ild”), and (iii) ending with “card” (myStringToReplace), with the string “question mark” (myReplacementString) within the string in cell A10 of the worksheet named “Excel VBA Replace” (myCell).
Sub replaceWildcard()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-replace-substitute/
'declare object variable to hold reference to cell you work with
Dim myCell As Range
'declare variables to hold parameters for string replacement (string to replace and replacement string)
Dim myStringToReplace As String
Dim myReplacementString As String
'identify the cell you work with
Set myCell = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Excel VBA Replace").Range("A10")
'specify parameters for string replacement (string to replace and replacement string). Use wildcards (? or *) to specify string to replace
myStringToReplace = "w*card"
myReplacementString = "question mark"
'replace all occurrences within string in cell you work with, and assign resulting string to Range.Value property of cell you work with
myCell.Replace What:=myStringToReplace, Replacement:=myReplacementString, LookAt:=xlPart, SearchOrder:=xlByRows, MatchCase:=False, SearchFormat:=False, ReplaceFormat:=False
End Sub
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Replace Wildcard
The following GIF illustrates the results of executing this macro example. As expected, the macro replaces the string “wildcard” which (i) starts with a “w”, (ii) followed by a group of characters (“ild”), and (iii) ends with “card”, with the string “question mark” within the string in cell A10.
#7: Replace Character in String by Position
VBA Code to Replace Character in String by Position
To replace a character in a string within a cell according to its position with VBA, use a statement with the following structure:
Cell.Value = WorksheetFunction.Replace(Cell.Value, CharacterPosition, CharactersToReplace, ReplacementString)
Process Followed by VBA Code to Replace Character in String by Position
VBA Statement Explanation
- Item: Cell.
- VBA Construct: Range object.
- Description: Range object representing the cell you work with.
You can usually return a Range object with constructs such as the Worksheet.Range, Worksheet.Cells (with the Range.Item) or Range.Offset properties.
- Item: Value.
- VBA Construct: Range.Value property.
- Description: The Range.Value property specifies the value (in this case string) within Cell.
- Item: =.
- VBA Construct: Assignment operator.
- Description: The = operator assigns the string returned by the Replace function to the Range.Value property of Cell.
- Item: WorksheetFunction.Replace(…).
- VBA Construct: WorksheetFunction.Replace method.
- Description: The WorksheetFunction.Replace method replaces a substring with a different string (ReplacementString). The replaced substring is determined based on its position within the string you work with (CharacterPosition) and the number of characters to replace (CharactersToReplace).
- Item: Cell.Value.
- VBA Construct: Arg1 parameter of the WorksheetFunction.Replace method, Range object and Range.Value property.
- Description: The Arg1 parameter of the WorksheetFunction.Replace method specifies the string containing the substring you want to replace. Within this macro structure, Arg1 is the value (string) within Cell, as returned by the Range.Value property.
If you explicitly declare a variable to represent Arg1, use the String data type.
- Item: CharacterPosition.
- VBA Construct: Arg2 parameter of the WorksheetFunction.Replace method.
- Description: The Arg2 parameter of the WorksheetFunction.Replace method specifies the starting position within Arg1 (Cell.Value) of the substring you want to replace with Arg4 (ReplacementString).
If you explicitly declare a variable to represent Arg2 (CharacterPosition), use the Double data type.
- Item: CharactersToReplace.
- VBA Construct: Arg3 parameter of the WorksheetFunction.Replace method.
- Description: The Arg3 parameter of the WorksheetFunction.Replace method specifies the number of characters within Arg1 (Cell.Value) you want to replace with Arg4 (ReplacementString).
If you explicitly declare a variable to represent Arg3 (CharactersToReplace), use the Double data type.
- Item: ReplacementString.
- VBA Construct: Arg4 parameter of the WorksheetFunction.Replace method.
- Description: The Arg4 parameter of the WorksheetFunction.Replace method specifies the substring you want to use as replacement.
If you explicitly declare a variable to represent Arg4 (ReplacementString), use the String data type.
Macro Example to Replace Character in String by Position
The following macro replaces the string starting in position 10 (myCharacterPosition) with a length of 1 character (myCharactersToReplace) with the string “+” (myReplacementString) within the string in cell A11 of the worksheet named “Excel VBA Replace” (myCell).
Sub replaceCharacterByPosition()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-replace-substitute/
'declare object variable to hold reference to cell you work with
Dim myCell As Range
'declare variables to hold parameters for string replacement (starting position of string to replace, number of characters to replace, and replacement string)
Dim myCharacterPosition As Double
Dim myCharactersToReplace As Double
Dim myReplacementString As String
'identify the cell you work with
Set myCell = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Excel VBA Replace").Range("A11")
'specify parameters for string replacement (starting position of string to replace, number of characters to replace, and replacement string)
myCharacterPosition = 10
myCharactersToReplace = 1
myReplacementString = "+"
'replace string in cell you work with, and assign resulting string to Range.Value property of cell you work with
myCell.Value = WorksheetFunction.Replace(myCell.Value, myCharacterPosition, myCharactersToReplace, myReplacementString)
End Sub
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Replace Character in String by Position
The following GIF illustrates the results of executing this macro example. As expected, the macro replaces the string starting in position 10 with a length of 1 character with the string “+” within the string in cell A11.
References to VBA Constructs Used in this VBA Tutorial
Use the following links to visit the appropriate webpage in the Microsoft Developer Network:
- Identify the workbook and worksheet you work with:
- Workbook object.
- Application.ThisWorkbook property.
- Worksheet object.
- Workbook.Worksheets property.
- Identify the cell you work with:
- Range object.
- Worksheet.Range property.
- Worksheet.Cells property.
- Range.Item property.
- Range.Offset property.
- Obtain or set the string within the cell you work with:
- Range.Value property.
- Assign a new string to the cell you work with or to the variable representing the string you work with:
- = operator.
- Replace characters or strings:
- Replace function.
- Range.Replace method.
- WorksheetFunction.Replace method.
- Complete and concatenate truncated strings:
- Left function.
- & operator.
- Create an array containing characters and loop through its elements:
- For Each… Next statement.
- Array function.
- Work with variables and data types:
- Dim statement.
- Set statement.
- Data types:
- Double data type.
- Long data type.
- String data type.
- Variant data type.
In this Article
- Replace Function
- Starting Position
- Replace a Few Occurrences Only
- Case Sensitivity
- Double Quotes
- Replace Break Line in Cell
This tutorial will demonstrate how to use the VBA Replace Function to replace strings of text.
Replace Function
The VBA Replace function replaces a substring of text with another substring.
Sub ReplaceExample_1()
MsgBox Replace("ABCABCABC", "A", "!")
'Result is: "!BC!BC!BC"
MsgBox Replace("I like pink, red and black", "pink", "purple")
'Result is: "I like purple, red and black"
MsgBox Replace("A, B, C, A, B, C, A, B, C", ", ", ",")
'Result is: "ABCABCABC"
MsgBox Replace("ABCABCABC", "ABC", "!")
'Result is: "!!!"
MsgBox Replace("ABCABCABC", "ABc", "!")
'Result is: "ABCABCABC"
MsgBox Replace("ABCABCABC", "ZBC", "!")
'Result is: "ABCABCABC"
End Sub
Starting Position
By assigning a start position, you can indicate what character position to start with (default = 1).
Sub ReplaceExample_2()
MsgBox Replace("ABCABCABC", "A", "123") 'Result is: "123BC123BC123BC"
MsgBox Replace("ABCABCABC", "A", "123", 2) 'Result is: "BC123BC123BC"
MsgBox Replace("ABCABCABC", "A", "123", 7) 'Result is: "123BC"
MsgBox Replace("ABCABCABC", "A", "123", 8) 'Result is: "BC"
MsgBox Replace("ABCABCABC", "ABC", "!@") 'Result is: "!@!@!@"
MsgBox Replace("ABCABCABC", "ABC", "!@", 2) 'Result is: "BC!@!@"
MsgBox Replace("ABCABCABC", "ABC", "!@", 6) 'Result is: "C!@"
MsgBox Replace("ABCABCABC", "ABC", "!@", 7) 'Result is: "!@"
MsgBox Replace("ABCABCABC", "ABC", "!@", 8) 'Result is: "BC"
End Sub
Replace a Few Occurrences Only
You can also indicate how many instances of the substring to replace (default All)
Sub ReplaceExample_3()
MsgBox Replace("ABCABCABC", "A", "12") 'Result is: "12BC12BC12BC"
MsgBox Replace("ABCABCABC", "A", "12", , 1) 'Result is: "12BCABCABC"
MsgBox Replace("ABCABCABC", "A", "12", , 2) 'Result is: "12BC12BCABC"
MsgBox Replace("ABCABCABC", "A", "12", , 3) 'Result is: "12BC12BC12BC"
MsgBox Replace("ABCABCABC", "A", "12", , 5) 'Result is: "12BC12BC12BC"
MsgBox Replace("ABCABCABC", "A", "12", 3, 1)
'Result is: "C12BCABC"
'We replaced A with 12, 1 time starting from position 3 of the original string.
End Sub
Case Sensitivity
The Replace Function is case sensitive by default. You can switch to case insensitive by adding the optional parameter (vbTextCompare). Here, you must also define the starting position of the search.
Sub ReplaceExample_4()
MsgBox Replace("ABcABCABc", "ABc", "12")
'Result is: "12ABC12"
MsgBox Replace("ABcABCABc", "ABc", "12", , , vbTextCompare)
'Result is: "121212"
'When we use vbTextCompare we need to add the 2 other optional arguments:
'start and count
MsgBox Replace("ABcABCABcABc", "ABc", "12", 3, 1)
'Result is: "cABC12ABc"
'Started from position3 and replaced ABC only 1 time.
End Sub
You can also perform a case-insensitive Replace, by adding Option Compare Text to the top of your module:
Option Compare TextDouble Quotes
The Replace Function can replace the double quotes character used to delimit the start and end of a string.
VBA Chr function can return a character from its number in the character set.
MsgBox Chr(34) 'Result is: "Or
MsgBox Chr(64) 'Result is: @
Double quotes can be used inside the Replace Function using “””” or VBA Function Chr(34).
Sub ReplaceExample_5()
Dim StrEx As String
StrEx = "AB""AB"""
MsgBox StrEx 'Result is: AB"AB"
MsgBox Replace(StrEx, Chr(34), "12")
'Result is: AB12AB12
MsgBox Replace(StrEx, """", "DQ")
'Result is: "ABDQABDQ"
End Sub
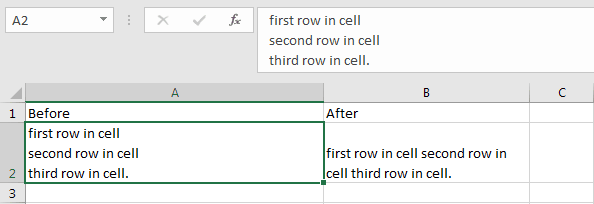
Replace Break Line in Cell
The Replace Function can find the break line special character in a cell and remove it or replace it with a space character. The break line special character can be entered in a cell using the keyboard shortcut Alt+Enter and can be used in VBA code with its Character set number using VBA function Chr(10).
Sub ReplaceExample_6()
Dim StrEx As String 'Define a string variable
'Read the value of cell A2 in worksheet Sheet1
StrEx = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Sheet1").Range("A2").Value
'The break line character entered with Alt+Enter is Chr(10) and is invisible.
'This code line replaces that character with space
StrEx = Replace(StrEx, Chr(10), " ")
'Write the replaced value in cell B2 in worksheet Sheet1
ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Sheet1").Range("B2").Value = StrEx
End Sub
VBA Replace function in Excel is categorized as a Text/String function in VBA. It is a built-in function in MS Office Excel. It replaces a sub-string with another string in a given string. It has three required parameters and three optional parameters. If expression is Null, then the function returns an error. Expression contains length, then it returns an empty string.
This function use as a VBA function and a Excel Worksheet function(It has different syntax in Excel). The Replace function can be used in either procedure or function in a VBA editor window in Excel. We can use this VBA Replace function any number of times in any number of procedures or functions. In the following section we learn what is the syntax and parameters of the Replace function, where we can use this Replace function and real-time examples in VBA.
Table of Contents:
- Overview
- Syntax of VBA Replace Function
- Parameters or Arguments
- Where we can apply or use the VBA Replace Function?
- Ex 1: Replace all occurrences of substring “F1” with “Help”
- Ex 2: Replace all occurrences of substring “Help” with “F1”
- Ex 3: Replace all occurrences of substring “F1” with “Help” starting from position 13
- Ex 4: Replace all occurrences of substring “F1” with “Help” starting from position 13 and keep whole string
- Ex 5: Replace last occurrence of substring “F1” with “Help”
- Ex 6: Remove all occurrences of substring ‘F1’
- Instructions to Run VBA Macro Code
- Other Useful Resources
The syntax of the VBA Replace function is
Replace(Expression, Find, Replace, [Start], [Count], [Compare])
Note: This Replace function returns a string.
Parameters or Arguments:
This function has three mandatory parameters and three optional parameters for the Replace Function.
Where
Expression: An Expression is a mandatory argument. It represents a string expression you want to replace sub-string in.
Find: Find is a mandatory argument. It represents a sub-string which we want to find or search within an expression.
Replace: Replace is a mandatory argument. It represents a sub-string which we want to replace within an expression.
Start: Start is an optional parameter. Default value is ‘1’. It represents the position in expression to start search.
Count: Count is an optional parameter. It represents the number of occurrences to replace sub-string within an expression. Default value is ‘-1’. If we ignore, it will replace all occurrences of sub-string with another specified sub-string.
Compare: Compare is an optional parameter. It represents a numeric value. It specifies the type of comparison to evaluate the sub-strings. This argument can have anyone of the following value. Default comparison is ‘vbBinaryCompare’.
| VBA Constant | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| vbUseCompareOption | -1 | Performs a comparison using the Option Compare statement. |
| vbBinaryCompare | 0 | performs a binary comparison |
| vbTextCompare | 1 | performs a text comparison |
| vbDatabaseCompare | 2 | performs a database comparison. It applies only in MS Access. |
Where we can apply or use the VBA Replace Function?
We can use this VBA Replace function in MS Office 365, MS Excel 2016, MS Excel 2013, 2011, Excel 2010, Excel 2007, Excel 2003, Excel 2016 for Mac, Excel 2011 for Mac, Excel Online, Excel for iPhone, Excel for iPad, Excel for Android tablets and Excel for Android Mobiles.
Example 1: Replace all occurrences of sub-string “F1” with “Help”
Here is a simple example of the VBA Replace function. This below example macro returns a string. The output of the below macro is ‘VBAHelp’.
'Replace all occurrences of sub-string "F1" with "Help".
Sub VBA_Replace_Function_Ex1()
Dim sString As String, sSubString As String
sString = "VBAF1"
sSubString = Replace(sString, "F1", "Help")
MsgBox "Replace F1 with Help :" & sSubString, vbInformation, "VBA Replace Function"
End Sub
Output: Here is the screen shot of the first example output.
Example 2: Replace all occurrences of substring “Help” with “F1”
Here is a simple example of the VBA Replace function. This below example macro returns a string. The output of the below macro is ‘VBAF1’.
'Replace all occurrences of sub-string "Help" with "F1".
Sub VBA_Replace_Function_Ex2()
Dim sString As String, sSubString As String
sString = "VBAF1"
sSubString = Replace(sString, "Help", "F1")
MsgBox "Replace Help with F1 :" & sSubString, vbInformation, "VBA Replace Function"
End Sub
Output: Here is the screen shot of the second example output.
Example 3: Replace all occurrences of sub-string “F1” with “Help” starting from position 13
Here is a simple example of the VBA Replace function. This below example macro returns a string. It ignores specified ‘N(start)’ characters, when we specify start position. The output of the below macro is ‘VBAHelp-VBAHelp-VBAHelp’.
'Replace all occurrences of sub-string "F1" with "Help" starting from position 13
Sub VBA_Replace_Function_Ex3()
Dim sString As String, sSubString As String
sString = "VBAF1-VBAF1-VBAF1-VBAF1-VBAF1"
sSubString = Replace(sString, "F1", "Help", 13)
MsgBox "Replace F1 with Help :" & sSubString, vbInformation, "VBA Replace Function"
End Sub
Output: Here is the screen shot of the third example output.
Example 4: Replace all occurrences of sub-string “F1” with “Help” starting from position 13 and keep whole string
Here is a simple example of the VBA Replace function. This below example macro returns a string. It ignores specified ’13(start)’ characters, when we specify start position. In this example we are using left function to extract left most characters from the given string. And adding the output to original output. Here is the final output of the below macro is ‘VBAF1-VBAF1-VBAHelp-VBAHelp-VBAHelp’.
'Replace all occurrences of sub-string "F1" with "Help" starting from position 13 and keep whole string
Sub VBA_Replace_Function_Ex4()
Dim sString As String, sSubString As String
sString = "VBAF1-VBAF1-VBAF1-VBAF1-VBAF1"
sSubString = Left(sString, 12) & Replace(sString, "F1", "Help", 13)
MsgBox "Replace F1 with Help :" & sSubString, vbInformation, "VBA Replace Function"
End Sub
Output: Here is the screen shot of the fourth example output.
Example 5: Replace last occurrence of sub-string “F1” with “Help”
Here is a simple example of the VBA Replace function. This below example macro returns a string. Here is the final output of the below macro is ‘VBAF1-VBAF1-VBAF1-VBAF1-VBAHelp’.
'Replace last occurrence of substring "F1" with "Help"
Sub VBA_Replace_Function_Ex5()
Dim sString As String, sSubString As String
sString = "VBAF1-VBAF1-VBAF1-VBAF1-VBAF1"
sString = StrReverse(sString)
sString = Replace(sString, StrReverse("F1"), StrReverse("Help"), , 1)
sSubString = StrReverse(sString)
MsgBox "Replace F1 with Help :" & sSubString, vbInformation, "VBA Replace Function"
End Sub
Output: Here is the screen shot of the fifth example output.
Example 6: Remove all occurrences of sub-string ‘F1’
Here is a simple example of the VBA Replace function. This below example macro returns a string. It removes all occurrences of sub-string within a string. Here is the final output of the below macro is ‘VBA-VBA-VBA-VBA-VBA’.
'Remove all occurrences of sub-string 'F1'
Sub VBA_Replace_Function_Ex6()
Dim sString As String, sSubString As String
sString = "VBAF1-VBAF1-VBAF1-VBAF1-VBAF1"
sSubString = Replace(sString, "F1", "")
MsgBox "Remove all occurences of F1 :" & sSubString, vbInformation, "VBA Replace Function"
End Sub
Output: Here is the screen shot of the sixth example output.
Instructions to Run VBA Macro Code or Procedure:
You can refer the following link for the step by step instructions.
Instructions to run VBA Macro Code
Other Useful Resources:
Click on the following links of the useful resources. These helps to learn and gain more knowledge.
VBA Tutorial VBA Functions List VBA Arrays in Excel Blog
VBA Editor Keyboard Shortcut Keys List VBA Interview Questions & Answers
Excel VBA Replace String
Excel VBA Replace looks for a substring within a list and replaces the substring with a second substring. When we use Excel VBA Replace Strings in Data there are some situations when we need to replace some character or a string from a sentence. If we have a large set of data that we want to replace it can be a tedious task to do it manually but with this function, it is very easy to provide the arguments and replace the string.
Syntax:
The syntax for Replace String function:
Replace ( Expression as String, Old String, New String, Start, Count, Compare)
Now the expression is the main string from where we want to remove the old string and new string which will replace the old string. The other arguments are optional. If we compare this function to excel worksheet substitute function we will find that Replace in VBA is the replacement of the substitute function in excel.
How to Replace Text in String Using VBA?
We will learn how to Replace Text in String using the VBA Code in Excel.
You can download this VBA Replace String Excel Template here – VBA Replace String Excel Template
Example #1
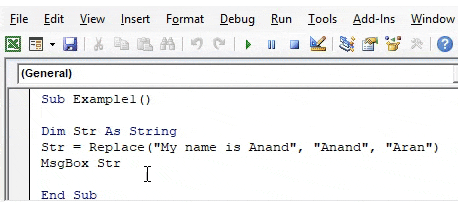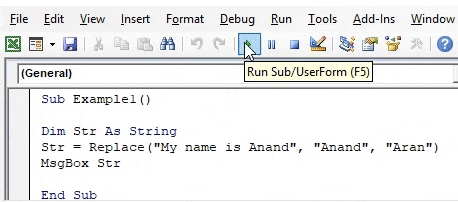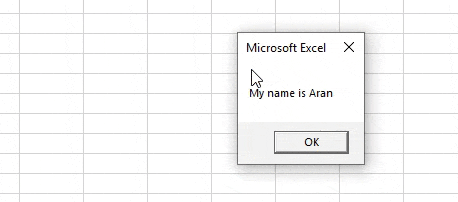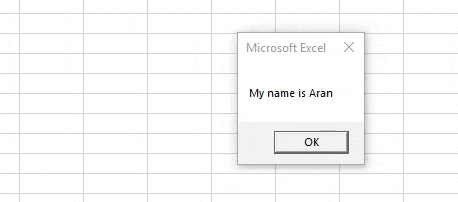
Let us start with a basic example of using the replace function where we will replace a simple word name from the sentence “My name is Anand”. Here we will replace Anand to Aran. For this, follow the below steps:
Step 1: Insert a new module inside Visual Basic Editor (VBE). Click on Insert tab > select Module.
Step 2: Insert a new subprocedure for example 1.
Code:
Sub Example1() End Sub
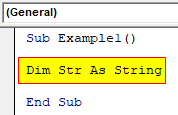
Step 3: Declare a variable as a string.
Code:
Sub Example1() Dim Str As String End Sub
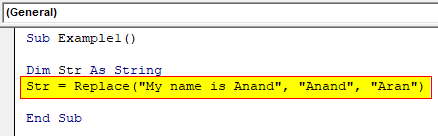
Step 4: Now let us use replace function while providing a string as the expression to the variable.
Code:
Sub Example1() Dim Str As String Str = Replace("My name is Anand", "Anand", "Aran") End Sub
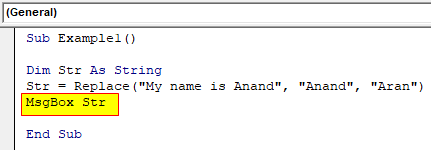
Step 5: Let us use the Msgbox function to display the value we have in this variable.
Code:
Sub Example1() Dim Str As String Str = Replace("My name is Anand", "Anand", "Aran") MsgBox Str End Sub
Step 6: When we execute the code.
Example #2
Let us begin with the second example where we can use the arguments used in the replace function as the variables. We will use a different statement for this example. For this, follow the below steps:
Step 1: In the same module let us start another subprocedure.
Code:
Sub Example2() End Sub
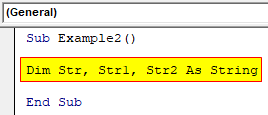
Step 2: Now let us declare three different variables as a string.
Code:
Sub Example2() Dim Str, Str1, Str2 As String End Sub
Step 3: In the first variable we can provide any string statement.
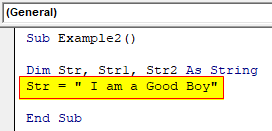
Code:
Sub Example2() Dim Str, Str1, Str2 As String Str = " I am a Good Boy" End Sub
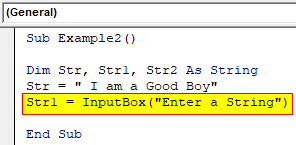
Step 4: Now in the second variable we can use the Input Box function to get input from the user.
Code:
Sub Example2() Dim Str, Str1, Str2 As String Str = " I am a Good Boy" Str1 = InputBox("Enter a String") End Sub
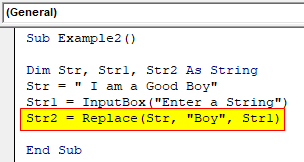
Step 5: Now in the third variable we can use the replace function to replace the second string to the desired string.
Code:
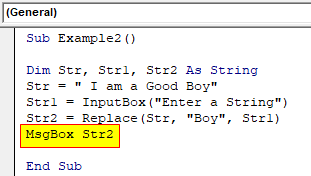
Sub Example2() Dim Str, Str1, Str2 As String Str = " I am a Good Boy" Str1 = InputBox("Enter a String") Str2 = Replace(Str, "Boy", Str1) End Sub
Step 6: We will use the Msgbox function to display the result in the third string.
Code:
Sub Example2() Dim Str, Str1, Str2 As String Str = " I am a Good Boy" Str1 = InputBox("Enter a String") Str2 = Replace(Str, "Boy", Str1) MsgBox Str2 End Sub
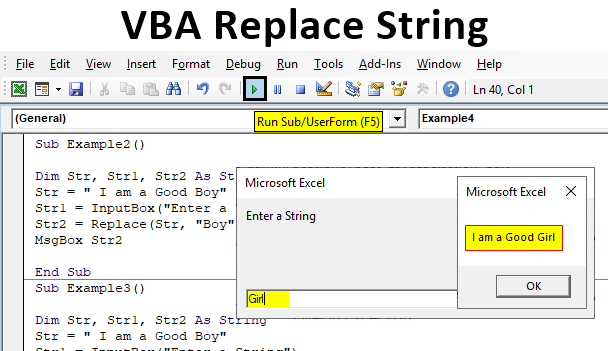
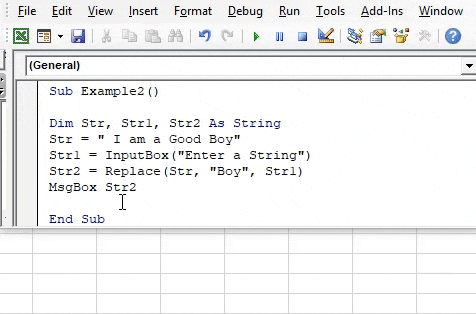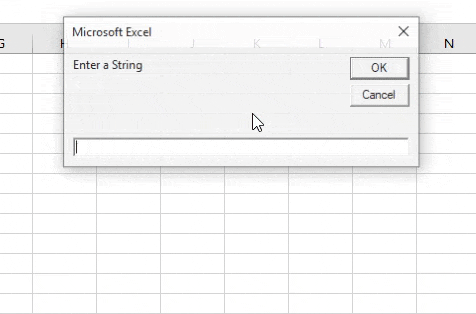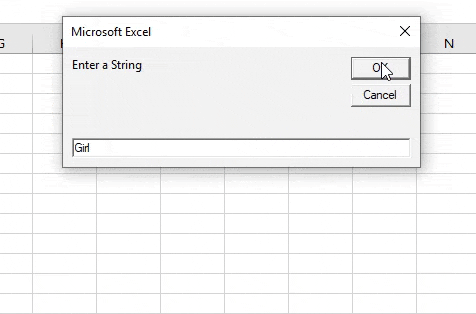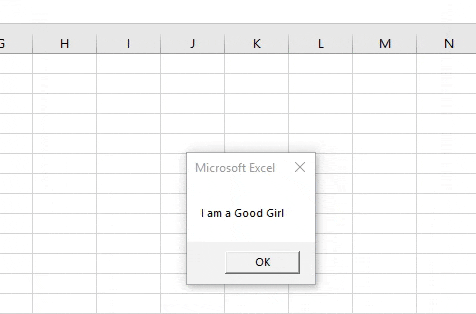
Step 7: When we execute the code above and give input as “girl”.
Example #3
Now we will discuss one of the optional arguments in the function which is the start option where we can define from which position we want. For this, follow the below steps:
Step 1: In the same module let us start another subprocedure.
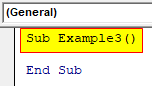
Code:
Sub Example3() End Sub
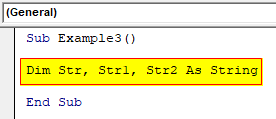
Step 2: Now let us declare three different variables as a string.
Code:
Sub Example3() Dim Str, Str1, Str2 As String End Sub
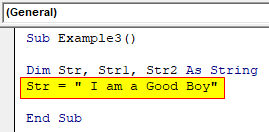
Step 3: In the first variable we can provide any string statement.
Code:
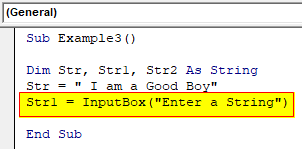
Sub Example3() Dim Str, Str1, Str2 As String Str = " I am a Good Boy" End Sub
Step 4: Now in the second variable we can use the Input Box function to get input from the user.
Code:
Sub Example3() Dim Str, Str1, Str2 As String Str = " I am a Good Boy" Str1 = InputBox("Enter a String") End Sub
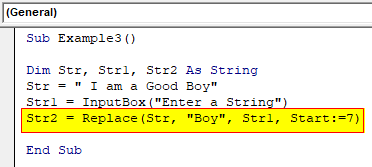
Step 5: Now in the third variable we can use the replace function to replace the second string to the desired string and give start position as 7.
Code:
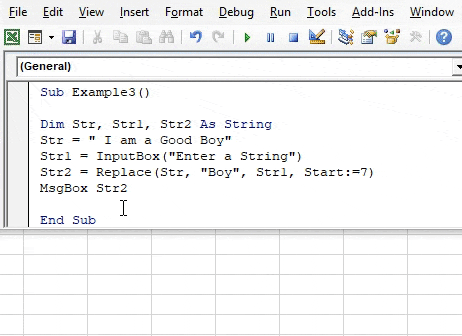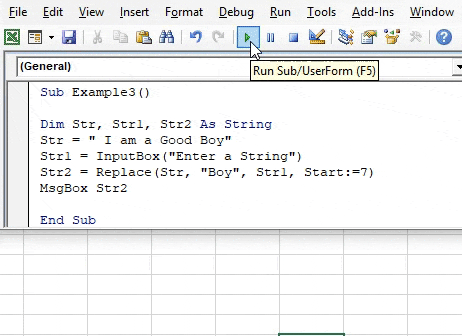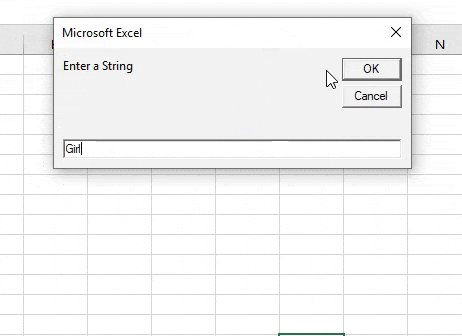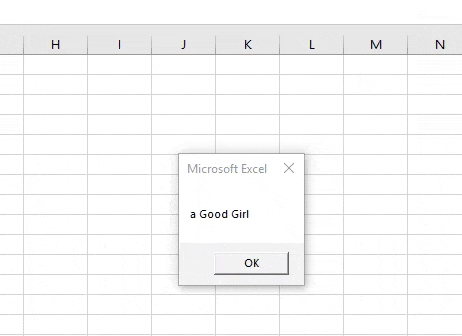
Sub Example3() Dim Str, Str1, Str2 As String Str = " I am a Good Boy" Str1 = InputBox("Enter a String") Str2 = Replace(Str, "Boy", Str1, Start:=7) End Sub
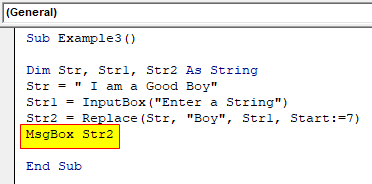
Step 6: We can use the Msgbox function to show the result and when we execute the code which will ask us for a string.
Code:
Sub Example3() Dim Str, Str1, Str2 As String Str = " I am a Good Boy" Str1 = InputBox("Enter a String") Str2 = Replace(Str, "Boy", Str1, Start:=7) MsgBox Str2 End Sub
Step 7: When we press Ok we will see the final result.
Example #4
Now there is another optional argument which is the number of times we want to replace a string. For this, follow the below steps:
Step 1: In the same module let us start another subprocedure.
Code:
Sub Example4() End Sub
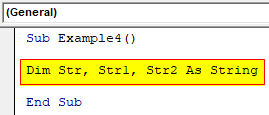
Step 2: Now let us declare three different variables as a string.
Code:
Sub Example4() Dim Str, Str1, Str2 As String End Sub
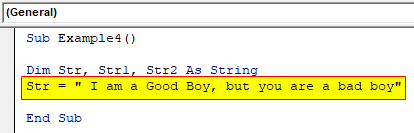
Step 3: In the first variable we can provide any string statement.
Code:
Sub Example4() Dim Str, Str1, Str2 As String Str = " I am a Good Boy, but you are a bad boy" End Sub
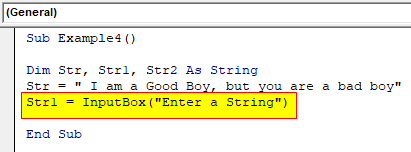
Step 4: Now in the second variable we can use the Input Box function to get an Input from the user.
Code:
Sub Example4() Dim Str, Str1, Str2 As String Str = " I am a Good Boy, but you are a bad boy" Str1 = InputBox("Enter a String") End Sub
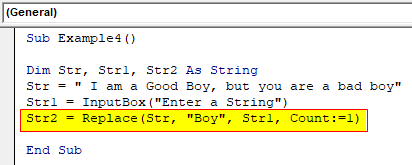
Step 5: Now in the third variable we can use the replace function to replace the second string to the desired string as shown in the below screenshot and use the number of instances we want to replace the string as follows and then use msgbox function to display the result.
Code:
Sub Example4() Dim Str, Str1, Str2 As String Str = " I am a Good Boy, but you are a bad boy" Str1 = InputBox("Enter a String") Str2 = Replace(Str, "Boy", Str1, Count:=1) End Sub
Step 6: Use the number of instances we want to replace the string as follows and then use the Msgbox function to display the result.
Code:
Sub Example4() Dim Str, Str1, Str2 As String Str = " I am a Good Boy, but you are a bad boy" Str1 = InputBox("Enter a String") Str2 = Replace(Str, "Boy", Str1, Count:=1) MsgBox Str2 End Sub
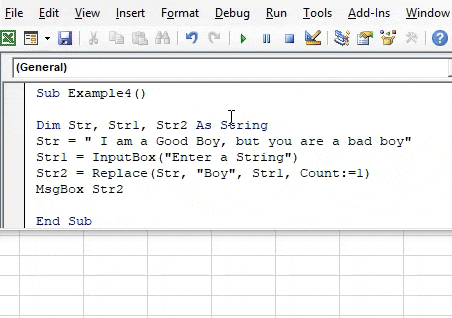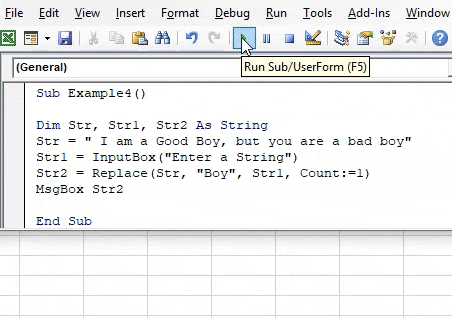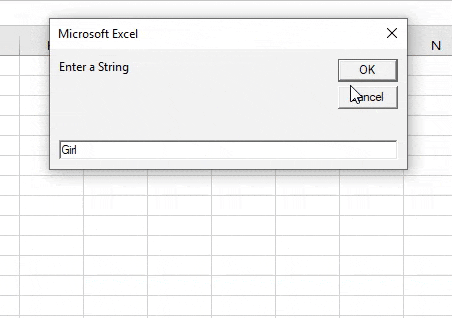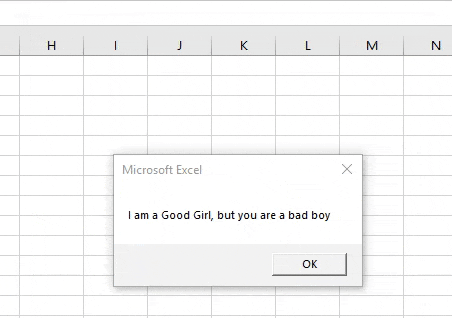
Step 7: Once we execute the code and provide a second string as “girl” we will see the following result.
Explanation of VBA Replace String:
We have seen from the above examples that the Replace function is the replacement of the substitute function of excel. It has three mandatory arguments and other arguments are optional. We can use the optional arguments together or one at a time. Start refers to the position of the string whereas count refers to the number of times we want to replace the old string with the new string.
How to Use VBA Replace String?
The method to use this function is very simple and similar to excel worksheet function. This function needs three mandatory arguments:
- First is the expression or the main string.
- Then we have to provide a target string which needs to replaced.
- And the final argument is the string which is the new string that needs to be replaced.
Things to Remember
There are few things which we need to remember about Replace string in VBA such as follows:
- There are three arguments in the Replace function of excel and there are two optional arguments.
- The two optional arguments are either for the number of times we want to replace or the position where we want to replace.
- This function is similar to a substitute function in excel.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the VBA Replace String. Here we discuss How to Replace Text in String in Excel VBA along with practical examples and downloadable excel template. You can also go through our other suggested articles –
- VBA RGB
- VBA CDEC
- VBA XML
- VBA IsError