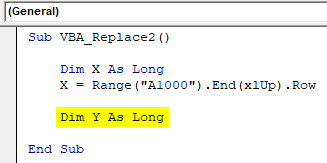Замена подстроки, содержащейся в текстовых значениях ячеек указанного диапазона, другой подстрокой с помощью метода Range.Replace из кода VBA Excel.
Range.Replace – это метод, который находит по шаблону подстроку в содержимом ячеек указанного диапазона, заменяет ее на другую подстроку и возвращает значение типа Boolean.
Метод имеет некоторые особенности, которые заключаются в следующем:
- при присвоении булева значения, возвращаемого методом Range.Replace, переменной, необходимо список параметров (аргументов) метода заключать в круглые скобки;
- если метод используется без присвоения возвращаемого значения переменной, параметры должны быть указаны без заключения их в круглые скобки.
Синтаксис и параметры метода
Синтаксис
Синтаксис при замене подстроки и присвоении переменной возвращаемого значения типа Boolean:
variable = expression.Replace(What, Replacement, [LookAt], [SearchOrder], [MatchCase], [MatchByte], [SearchFormat], [ReplaceFormat])
Синтаксис при замене подстроки без присвоения переменной возвращаемого значения:
expression.Replace What, Replacement, [LookAt], [SearchOrder], [MatchCase], [MatchByte], [SearchFormat], [ReplaceFormat]
- variable – переменная (тип данных — Boolean);
- expression – выражение, возвращающее объект Range.
Параметры
| Параметр | Описание |
|---|---|
| What | Искомая подстрока или шаблон*, по которому ищется подстрока в диапазоне ячеек. Обязательный параметр. |
| Replacement | Подстрока, заменяющая искомую подстроку. Обязательный параметр. |
| LookAt | Указывает правило поиска по полному или частичному вхождению искомой подстроки в текст ячейки: 1 (xlWhole) – поиск полного вхождения искомого текста; 2 (xlPart) – поиск частичного вхождения искомого текста. Необязательный параметр. |
| SearchOrder | Задает построчный или постолбцовый поиск: 1 (xlByRows) – построчный поиск; 2 (xlByColumns) – постолбцовый поиск. Необязательный параметр. |
| MatchCase | Поиск с учетом или без учета регистра: 0 (False) – поиск без учета регистра; 1 (True) – поиск с учетом регистра. Необязательный параметр. |
| MatchByte | Способы сравнения двухбайтовых символов: 0 (False) – двухбайтовые символы сопоставляются с однобайтовыми эквивалентами; 1 (True) – двухбайтовые символы сопоставляются только с двухбайтовым символами. Необязательный параметр. |
| SearchFormat | Формат поиска. Необязательный параметр. |
| ReplaceFormat | Формат замены. Необязательный параметр. |
* Смотрите знаки подстановки для шаблонов, которые можно использовать в параметре What.
Работа метода в VBA Excel
Исходная таблица для всех примеров:
Пример 1
Примеры записи строк кода с методом Range.Replace и поиском по частичному совпадению подстроки с содержимым ячейки:
|
Sub Primer1() ‘Запись 1: Range(«A1:C6»).Replace «Лиса», «Рысь», 2 ‘Запись 2: Range(«A1:C6»).Replace What:=«Лиса», Replacement:=«Рысь», LookAt:=2 ‘Запись 3: If Range(«A1:C6»).Replace(«Лиса», «Рысь», 2) Then End If ‘Запись 4: Dim a a = Range(«A1:C6»).Replace(«Лиса», «Рысь», 2) End Sub |
Результат выполнения любого из вариантов кода примера 1:
Пример 2
Поиск по шаблону с использованием знаков подстановки и по полному совпадению подстроки с содержимым ячейки:
|
Sub Primer2() Range(«A1:C6»).Replace «Ли??», «Рысь», 1 End Sub |
Обратите внимание, что слово «Лиса» заменено словом «Рысь» не во всех ячейках. Это произошло из-за того, что мы использовали параметр LookAt:=1 – поиск полного вхождения искомого текста в содержимое ячейки.
VBA Replace function in Excel is categorized as a Text/String function in VBA. It is a built-in function in MS Office Excel. It replaces a sub-string with another string in a given string. It has three required parameters and three optional parameters. If expression is Null, then the function returns an error. Expression contains length, then it returns an empty string.
This function use as a VBA function and a Excel Worksheet function(It has different syntax in Excel). The Replace function can be used in either procedure or function in a VBA editor window in Excel. We can use this VBA Replace function any number of times in any number of procedures or functions. In the following section we learn what is the syntax and parameters of the Replace function, where we can use this Replace function and real-time examples in VBA.
Table of Contents:
- Overview
- Syntax of VBA Replace Function
- Parameters or Arguments
- Where we can apply or use the VBA Replace Function?
- Ex 1: Replace all occurrences of substring “F1” with “Help”
- Ex 2: Replace all occurrences of substring “Help” with “F1”
- Ex 3: Replace all occurrences of substring “F1” with “Help” starting from position 13
- Ex 4: Replace all occurrences of substring “F1” with “Help” starting from position 13 and keep whole string
- Ex 5: Replace last occurrence of substring “F1” with “Help”
- Ex 6: Remove all occurrences of substring ‘F1’
- Instructions to Run VBA Macro Code
- Other Useful Resources
The syntax of the VBA Replace function is
Replace(Expression, Find, Replace, [Start], [Count], [Compare])
Note: This Replace function returns a string.
Parameters or Arguments:
This function has three mandatory parameters and three optional parameters for the Replace Function.
Where
Expression: An Expression is a mandatory argument. It represents a string expression you want to replace sub-string in.
Find: Find is a mandatory argument. It represents a sub-string which we want to find or search within an expression.
Replace: Replace is a mandatory argument. It represents a sub-string which we want to replace within an expression.
Start: Start is an optional parameter. Default value is ‘1’. It represents the position in expression to start search.
Count: Count is an optional parameter. It represents the number of occurrences to replace sub-string within an expression. Default value is ‘-1’. If we ignore, it will replace all occurrences of sub-string with another specified sub-string.
Compare: Compare is an optional parameter. It represents a numeric value. It specifies the type of comparison to evaluate the sub-strings. This argument can have anyone of the following value. Default comparison is ‘vbBinaryCompare’.
| VBA Constant | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| vbUseCompareOption | -1 | Performs a comparison using the Option Compare statement. |
| vbBinaryCompare | 0 | performs a binary comparison |
| vbTextCompare | 1 | performs a text comparison |
| vbDatabaseCompare | 2 | performs a database comparison. It applies only in MS Access. |
Where we can apply or use the VBA Replace Function?
We can use this VBA Replace function in MS Office 365, MS Excel 2016, MS Excel 2013, 2011, Excel 2010, Excel 2007, Excel 2003, Excel 2016 for Mac, Excel 2011 for Mac, Excel Online, Excel for iPhone, Excel for iPad, Excel for Android tablets and Excel for Android Mobiles.
Example 1: Replace all occurrences of sub-string “F1” with “Help”
Here is a simple example of the VBA Replace function. This below example macro returns a string. The output of the below macro is ‘VBAHelp’.
'Replace all occurrences of sub-string "F1" with "Help".
Sub VBA_Replace_Function_Ex1()
Dim sString As String, sSubString As String
sString = "VBAF1"
sSubString = Replace(sString, "F1", "Help")
MsgBox "Replace F1 with Help :" & sSubString, vbInformation, "VBA Replace Function"
End Sub
Output: Here is the screen shot of the first example output.
Example 2: Replace all occurrences of substring “Help” with “F1”
Here is a simple example of the VBA Replace function. This below example macro returns a string. The output of the below macro is ‘VBAF1’.
'Replace all occurrences of sub-string "Help" with "F1".
Sub VBA_Replace_Function_Ex2()
Dim sString As String, sSubString As String
sString = "VBAF1"
sSubString = Replace(sString, "Help", "F1")
MsgBox "Replace Help with F1 :" & sSubString, vbInformation, "VBA Replace Function"
End Sub
Output: Here is the screen shot of the second example output.
Example 3: Replace all occurrences of sub-string “F1” with “Help” starting from position 13
Here is a simple example of the VBA Replace function. This below example macro returns a string. It ignores specified ‘N(start)’ characters, when we specify start position. The output of the below macro is ‘VBAHelp-VBAHelp-VBAHelp’.
'Replace all occurrences of sub-string "F1" with "Help" starting from position 13
Sub VBA_Replace_Function_Ex3()
Dim sString As String, sSubString As String
sString = "VBAF1-VBAF1-VBAF1-VBAF1-VBAF1"
sSubString = Replace(sString, "F1", "Help", 13)
MsgBox "Replace F1 with Help :" & sSubString, vbInformation, "VBA Replace Function"
End Sub
Output: Here is the screen shot of the third example output.
Example 4: Replace all occurrences of sub-string “F1” with “Help” starting from position 13 and keep whole string
Here is a simple example of the VBA Replace function. This below example macro returns a string. It ignores specified ’13(start)’ characters, when we specify start position. In this example we are using left function to extract left most characters from the given string. And adding the output to original output. Here is the final output of the below macro is ‘VBAF1-VBAF1-VBAHelp-VBAHelp-VBAHelp’.
'Replace all occurrences of sub-string "F1" with "Help" starting from position 13 and keep whole string
Sub VBA_Replace_Function_Ex4()
Dim sString As String, sSubString As String
sString = "VBAF1-VBAF1-VBAF1-VBAF1-VBAF1"
sSubString = Left(sString, 12) & Replace(sString, "F1", "Help", 13)
MsgBox "Replace F1 with Help :" & sSubString, vbInformation, "VBA Replace Function"
End Sub
Output: Here is the screen shot of the fourth example output.
Example 5: Replace last occurrence of sub-string “F1” with “Help”
Here is a simple example of the VBA Replace function. This below example macro returns a string. Here is the final output of the below macro is ‘VBAF1-VBAF1-VBAF1-VBAF1-VBAHelp’.
'Replace last occurrence of substring "F1" with "Help"
Sub VBA_Replace_Function_Ex5()
Dim sString As String, sSubString As String
sString = "VBAF1-VBAF1-VBAF1-VBAF1-VBAF1"
sString = StrReverse(sString)
sString = Replace(sString, StrReverse("F1"), StrReverse("Help"), , 1)
sSubString = StrReverse(sString)
MsgBox "Replace F1 with Help :" & sSubString, vbInformation, "VBA Replace Function"
End Sub
Output: Here is the screen shot of the fifth example output.
Example 6: Remove all occurrences of sub-string ‘F1’
Here is a simple example of the VBA Replace function. This below example macro returns a string. It removes all occurrences of sub-string within a string. Here is the final output of the below macro is ‘VBA-VBA-VBA-VBA-VBA’.
'Remove all occurrences of sub-string 'F1'
Sub VBA_Replace_Function_Ex6()
Dim sString As String, sSubString As String
sString = "VBAF1-VBAF1-VBAF1-VBAF1-VBAF1"
sSubString = Replace(sString, "F1", "")
MsgBox "Remove all occurences of F1 :" & sSubString, vbInformation, "VBA Replace Function"
End Sub
Output: Here is the screen shot of the sixth example output.
Instructions to Run VBA Macro Code or Procedure:
You can refer the following link for the step by step instructions.
Instructions to run VBA Macro Code
Other Useful Resources:
Click on the following links of the useful resources. These helps to learn and gain more knowledge.
VBA Tutorial VBA Functions List VBA Arrays in Excel Blog
VBA Editor Keyboard Shortcut Keys List VBA Interview Questions & Answers
In this Article
- Replace Function
- Starting Position
- Replace a Few Occurrences Only
- Case Sensitivity
- Double Quotes
- Replace Break Line in Cell
This tutorial will demonstrate how to use the VBA Replace Function to replace strings of text.
Replace Function
The VBA Replace function replaces a substring of text with another substring.
Sub ReplaceExample_1()
MsgBox Replace("ABCABCABC", "A", "!")
'Result is: "!BC!BC!BC"
MsgBox Replace("I like pink, red and black", "pink", "purple")
'Result is: "I like purple, red and black"
MsgBox Replace("A, B, C, A, B, C, A, B, C", ", ", ",")
'Result is: "ABCABCABC"
MsgBox Replace("ABCABCABC", "ABC", "!")
'Result is: "!!!"
MsgBox Replace("ABCABCABC", "ABc", "!")
'Result is: "ABCABCABC"
MsgBox Replace("ABCABCABC", "ZBC", "!")
'Result is: "ABCABCABC"
End Sub
Starting Position
By assigning a start position, you can indicate what character position to start with (default = 1).
Sub ReplaceExample_2()
MsgBox Replace("ABCABCABC", "A", "123") 'Result is: "123BC123BC123BC"
MsgBox Replace("ABCABCABC", "A", "123", 2) 'Result is: "BC123BC123BC"
MsgBox Replace("ABCABCABC", "A", "123", 7) 'Result is: "123BC"
MsgBox Replace("ABCABCABC", "A", "123", 8) 'Result is: "BC"
MsgBox Replace("ABCABCABC", "ABC", "!@") 'Result is: "!@!@!@"
MsgBox Replace("ABCABCABC", "ABC", "!@", 2) 'Result is: "BC!@!@"
MsgBox Replace("ABCABCABC", "ABC", "!@", 6) 'Result is: "C!@"
MsgBox Replace("ABCABCABC", "ABC", "!@", 7) 'Result is: "!@"
MsgBox Replace("ABCABCABC", "ABC", "!@", 8) 'Result is: "BC"
End Sub
Replace a Few Occurrences Only
You can also indicate how many instances of the substring to replace (default All)
Sub ReplaceExample_3()
MsgBox Replace("ABCABCABC", "A", "12") 'Result is: "12BC12BC12BC"
MsgBox Replace("ABCABCABC", "A", "12", , 1) 'Result is: "12BCABCABC"
MsgBox Replace("ABCABCABC", "A", "12", , 2) 'Result is: "12BC12BCABC"
MsgBox Replace("ABCABCABC", "A", "12", , 3) 'Result is: "12BC12BC12BC"
MsgBox Replace("ABCABCABC", "A", "12", , 5) 'Result is: "12BC12BC12BC"
MsgBox Replace("ABCABCABC", "A", "12", 3, 1)
'Result is: "C12BCABC"
'We replaced A with 12, 1 time starting from position 3 of the original string.
End Sub
Case Sensitivity
The Replace Function is case sensitive by default. You can switch to case insensitive by adding the optional parameter (vbTextCompare). Here, you must also define the starting position of the search.
Sub ReplaceExample_4()
MsgBox Replace("ABcABCABc", "ABc", "12")
'Result is: "12ABC12"
MsgBox Replace("ABcABCABc", "ABc", "12", , , vbTextCompare)
'Result is: "121212"
'When we use vbTextCompare we need to add the 2 other optional arguments:
'start and count
MsgBox Replace("ABcABCABcABc", "ABc", "12", 3, 1)
'Result is: "cABC12ABc"
'Started from position3 and replaced ABC only 1 time.
End Sub
You can also perform a case-insensitive Replace, by adding Option Compare Text to the top of your module:
Option Compare TextDouble Quotes
The Replace Function can replace the double quotes character used to delimit the start and end of a string.
VBA Chr function can return a character from its number in the character set.
MsgBox Chr(34) 'Result is: "Or
MsgBox Chr(64) 'Result is: @
Double quotes can be used inside the Replace Function using “””” or VBA Function Chr(34).
Sub ReplaceExample_5()
Dim StrEx As String
StrEx = "AB""AB"""
MsgBox StrEx 'Result is: AB"AB"
MsgBox Replace(StrEx, Chr(34), "12")
'Result is: AB12AB12
MsgBox Replace(StrEx, """", "DQ")
'Result is: "ABDQABDQ"
End Sub
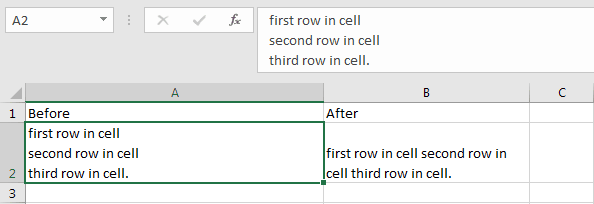
Replace Break Line in Cell
The Replace Function can find the break line special character in a cell and remove it or replace it with a space character. The break line special character can be entered in a cell using the keyboard shortcut Alt+Enter and can be used in VBA code with its Character set number using VBA function Chr(10).
Sub ReplaceExample_6()
Dim StrEx As String 'Define a string variable
'Read the value of cell A2 in worksheet Sheet1
StrEx = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Sheet1").Range("A2").Value
'The break line character entered with Alt+Enter is Chr(10) and is invisible.
'This code line replaces that character with space
StrEx = Replace(StrEx, Chr(10), " ")
'Write the replaced value in cell B2 in worksheet Sheet1
ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Sheet1").Range("B2").Value = StrEx
End Sub
Excel VBA Replace Function
As in Excel, we have a function where we can find and replace any word or character or sentence with any letter. But by that process, we can only replace one kind of sentence or letter at a time. With the help of the VBA Replace Function, we can replace as many words or letters or sentences in a single shot. This saves huge time and effort doing single activity multiple times. For this, we will use the Replace function, which is in the built-in VBA function list.
Below the syntax and argument of Replace function in VBA.
How to Use Excel VBA Replace Function?
We will learn how to use a VBA Replace Excel function with few examples.
You can download this VBA Replace Excel Template here – VBA Replace Excel Template
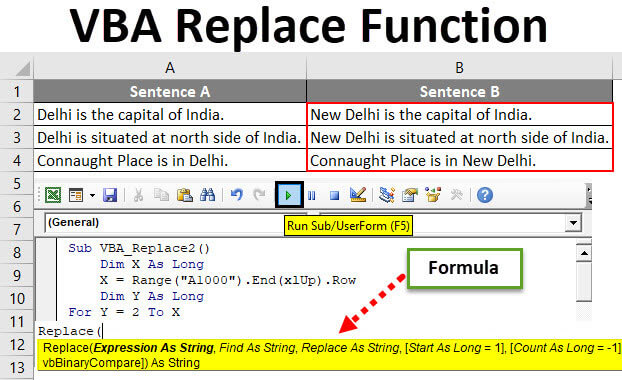
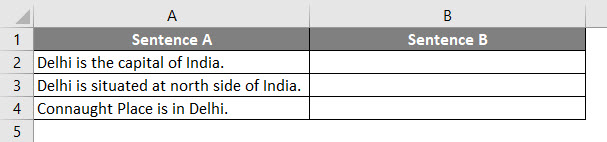
VBA Replace Function – Example #1
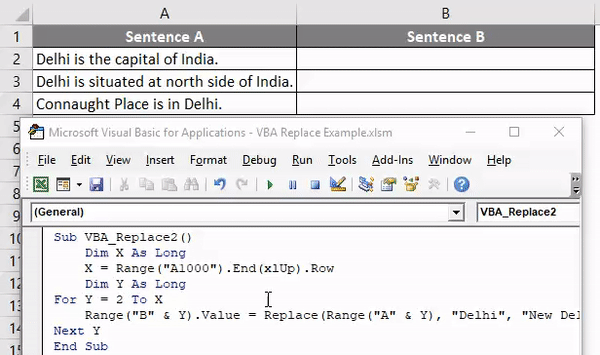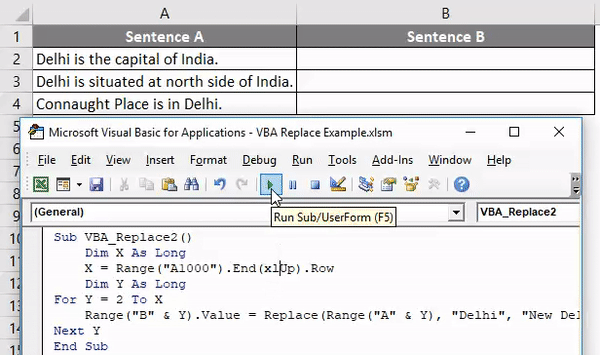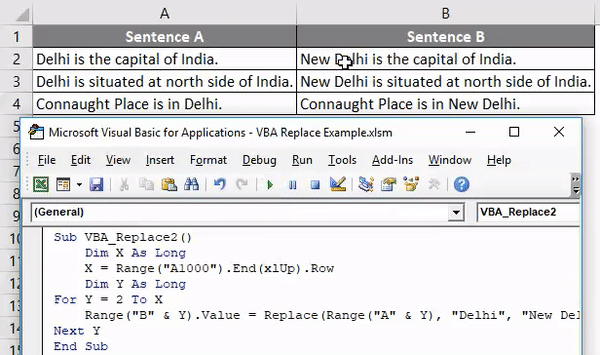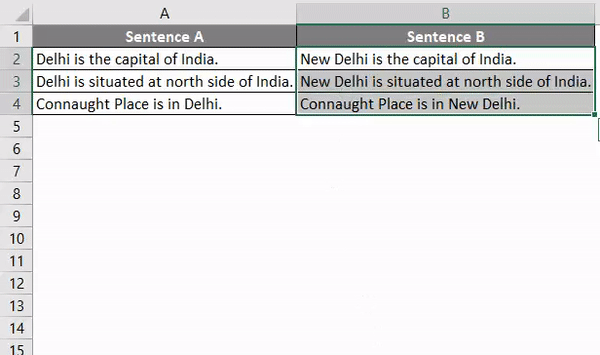
We have a sample data of some sentences where we will replace one word and paste that updated sentence in Sentence B Column.
Follow the below steps to use the Replace function in Excel VBA.
Step 1: Go to VBA, and in the Insert menu tab, select Module.
Step 2: Now, write a sub-category in the name of a performed function or in any name as per your choice, as shown below.
Code:
Sub VBA_Replace2() End Sub
Step 3: Now define a dimension as Long as we will be selecting a complete sentence. Here we have taken it as X.
Code:
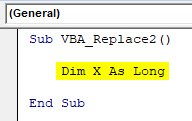
Sub VBA_Replace2() Dim X As Long End Sub
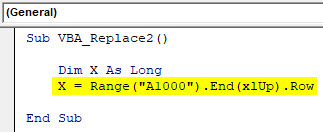
Step 4: Now, in that Long X, select the maximum range till where our data could go up. Here we have taken as A1000 cell range, and for going up till our data starts, use End(xlUp) followed by a dot(.)Row. Which means we will be moving up in the same column till that row which has the data. This process in life Ctrl + Up arrow key in excel.
Code:
Sub VBA_Replace2() Dim X As Long X = Range("A1000").End(xlUp).Row End Sub
Note: We can select from End(xlDown), but it may not add any break or blank cell in between the data if data has.
Step 5: Now again, define one more dimension, Y, as Long as shown below.
Code:
Sub VBA_Replace2() Dim X As Long X = Range("A1000").End(xlUp).Row Dim Y As Long End Sub
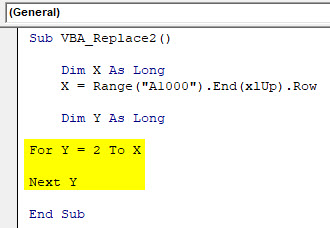
Step 6: Now start a For Next loop for second defined dimension Y from cell position 2 to till X range (last filled cell)
Note: Selecting cell 2 means that we are not considering the header here for replace.
Code:
Sub VBA_Replace2() Dim X As Long X = Range("A1000").End(xlUp).Row Dim Y As Long For Y = 2 To X Next Y End Sub
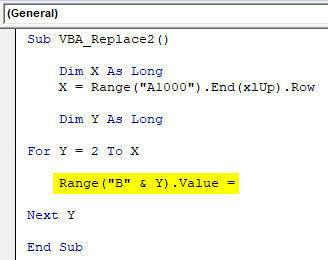
Step 7: Now select the Value of Column B as Range as Y followed by a dot(.); this is like inserting a function in excel.
Code:
Sub VBA_Replace2() Dim X As Long X = Range("A1000").End(xlUp).Row Dim Y As Long For Y = 2 To X Range("B" & Y).Value = Next Y End Sub
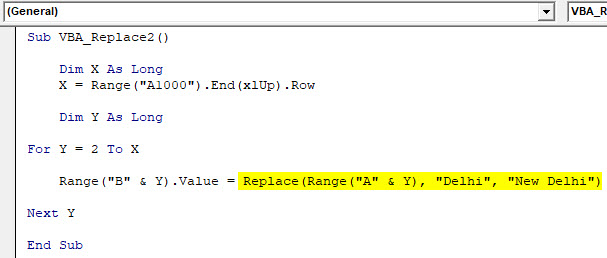
Step 8: Now, as we have seen in the VBA syntax of Replace function above now type Replace and select Column A and Y as the first expression of string followed by the words which we need to replace from the table.
Code:
Sub VBA_Replace2() Dim X As Long X = Range("A1000").End(xlUp).Row Dim Y As Long For Y = 2 To X Range("B" & Y).Value = Replace(Range("A" & Y), "Delhi", "New Delhi") Next Y End Sub
Step 9: Now, compile the complete code and run. Once we do that, we will the word “Delhi” from Sentence A is now replaced with work “New Delhi”, and the whole sentence is copied to Sentence B.
We can select a string of words or a sentence and replace that with any required letters or sentence.
VBA Replace Function – Example #2
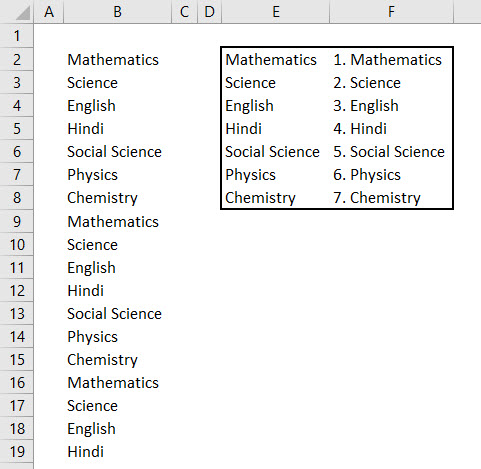
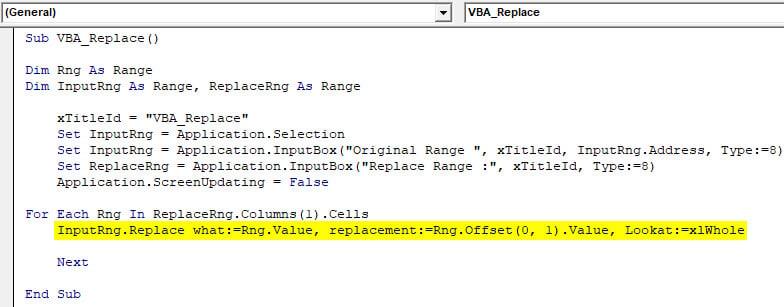
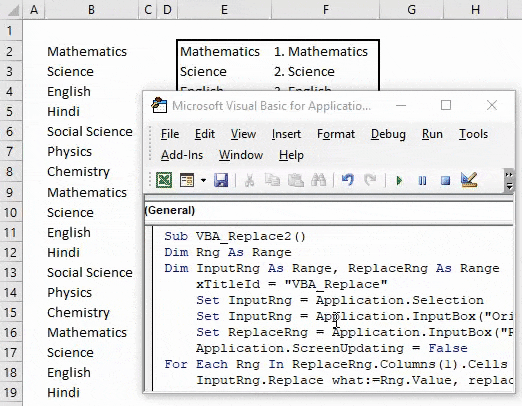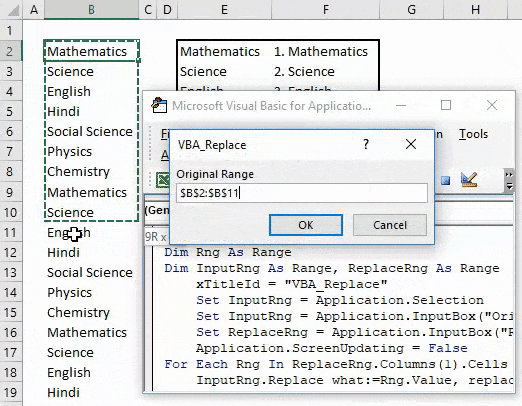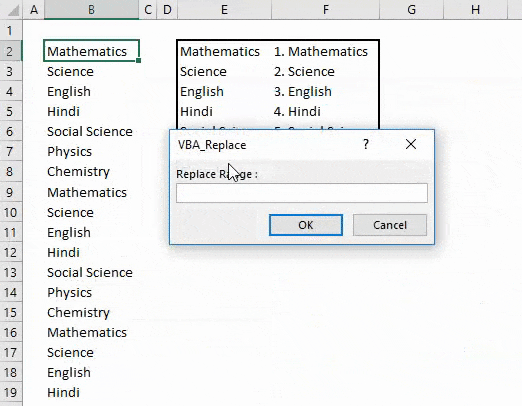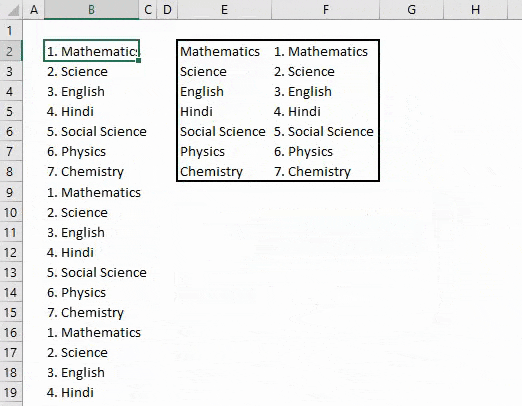
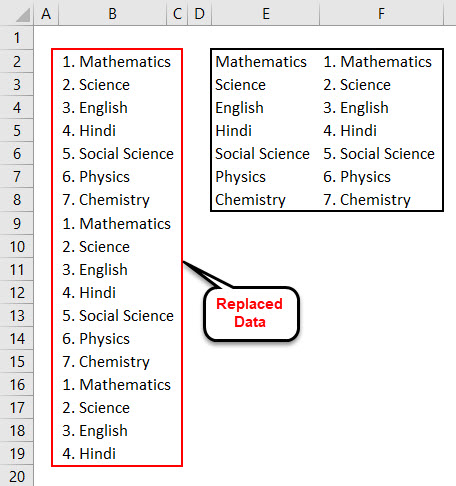
There is another way to replace words or sentences with the help of VBA coding. For this, we have a list of 7 subjects which are getting repeated. And we need to replace those subject names with adding serial numbers before each subject name, as shown below.
As we can see in the above screenshot, column E has unique names of those subjects which are there in column B, and column F has the subject names with a serial number at the start of it.
Follow the below steps to use Replace function in VBA.
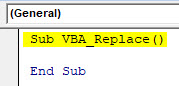
Step 1: Now, go to VBA and from the Insert menu, add a new Module. Once we get it, start writing the Sub-category in the name of a function which is being performed, as shown below.
Code:
Sub VBA_Replace() End Sub
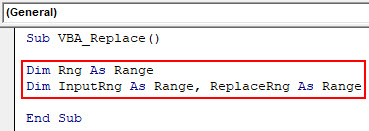
Step 2: Now consider a dimension Rng as Range, InputRng as Range and ReplaceRng as Range. You can choose any other letters or words for defining ranges.
Code:
Sub VBA_Replace() Dim Rng As Range Dim InputRng As Range, ReplaceRng As Range End Sub
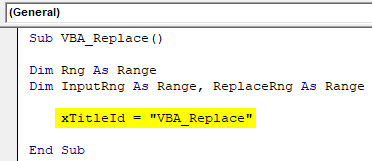
Step 3: Now, use xTitleId as dialog box and give it a name. Here we have named it “VBA_Replace“.
Code:
Sub VBA_Replace() Dim Rng As Range Dim InputRng As Range, ReplaceRng As Range xTitleId = "VBA_Replace" End Sub
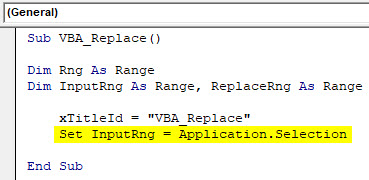
Step 4: Now assign the Application.Selection with InputRng, this will enable the selected application to be used in VBA.
Code:
Sub VBA_Replace() Dim Rng As Range Dim InputRng As Range, ReplaceRng As Range xTitleId = "VBA_Replace" Set InputRng = Application.Selection End Sub
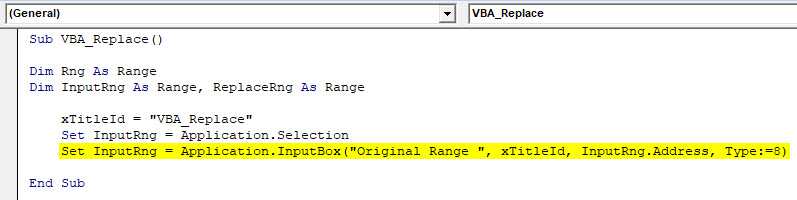
Step 5: Now, in the next line, insert an InputBox of 3 types, Original range, xTitleId, and InputRng. Original Range is a list of those subject which are needed to get replaced, listed in column B. xTitledId is the dialog box names in the performed function. And InputRng is a range of data table in column E and F.
Code:
Sub VBA_Replace() Dim Rng As Range Dim InputRng As Range, ReplaceRng As Range xTitleId = "VBA_Replace" Set InputRng = Application.Selection Set InputRng = Application.InputBox("Original Range ", xTitleId, InputRng.Address, Type:=8) End Sub
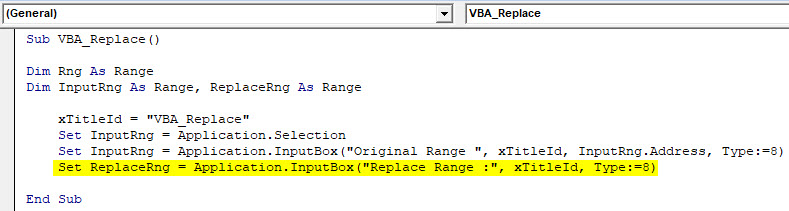
Step 6: Now, in the next line, assign an Input for ReplaceRng and for this, select Replace Range column. The rest of it is the same.
Code:
Sub VBA_Replace() Dim Rng As Range Dim InputRng As Range, ReplaceRng As Range xTitleId = "VBA_Replace" Set InputRng = Application.Selection Set InputRng = Application.InputBox("Original Range ", xTitleId, InputRng.Address, Type:=8) Set ReplaceRng = Application.InputBox("Replace Range :", xTitleId, Type:=8) End Sub
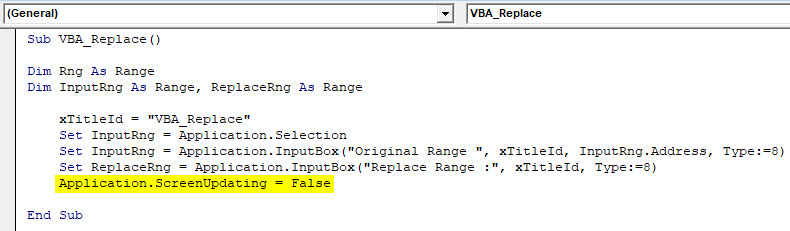
Step 7: Now, we will use the Application.screenupdating function, as the name says it is used for updating if it is FALSE.
Code:
Sub VBA_Replace() Dim Rng As Range Dim InputRng As Range, ReplaceRng As Range xTitleId = "VBA_Replace" Set InputRng = Application.Selection Set InputRng = Application.InputBox("Original Range ", xTitleId, InputRng.Address, Type:=8) Set ReplaceRng = Application.InputBox("Replace Range :", xTitleId, Type:=8) Application.ScreenUpdating = False End Sub
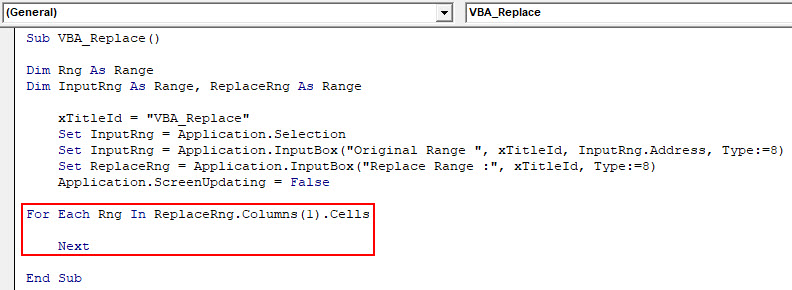
Step 8: Now insert a For-Next loop. And for each Rng range, replace the values from ReplaceRng column.
Code:
Sub VBA_Replace() Dim Rng As Range Dim InputRng As Range, ReplaceRng As Range xTitleId = "VBA_Replace" Set InputRng = Application.Selection Set InputRng = Application.InputBox("Original Range ", xTitleId, InputRng.Address, Type:=8) Set ReplaceRng = Application.InputBox("Replace Range :", xTitleId, Type:=8) Application.ScreenUpdating = False For Each Rng In ReplaceRng.Columns(1).Cells Next End Sub
Step 9: At last, replace InputRng with the values present in Rng from the whole sheet.
Code:
Sub VBA_Replace() Dim Rng As Range Dim InputRng As Range, ReplaceRng As Range xTitleId = "VBA_Replace" Set InputRng = Application.Selection Set InputRng = Application.InputBox("Original Range ", xTitleId, InputRng.Address, Type:=8) Set ReplaceRng = Application.InputBox("Replace Range :", xTitleId, Type:=8) Application.ScreenUpdating = False For Each Rng In ReplaceRng.Columns(1).Cells InputRng.Replace what:=Rng.Value, replacement:=Rng.Offset(0, 1).Value, Lookat:=xlWhole Next End Sub
Step 10: Once done, now compile and run the code. We will get and dialog box in the name of VBA_Replace. From here, select the list of subjects which we need to replace as Original Range and click on OK. Then we will get another box; from there, select the Replace range from E2 to F8. This table has the data which need to get replaced, and click on OK.
We will get Data in column B, which will get replaced from the data in column F with a serial number.
To an overview, column E has unique subject names. And column F has subject names with serial numbers. So by this, data in column B is replaced with data in column F.
Pros of VBA Replace Function
- We can replace multiple words or sentences in a single shot.
- There is no limit of words or text what we cannot replace with.
- Syntax of Replace in VBA is as easy as using the SumIf function in excel.
- VBA Replace, as shown in example-1, is the easiest way to apply.
Things to Remember
- Save as Marco Enabled Excel to avoid losing written code in VBA.
- Always consider the dimensions in such a way that it will create a value-added while we select those in code.
- Make sure you select the whole range of the sheet as shown in example-2 if it is limited to get the result. Or else you can define and select a limited cell range which would be used under Replace function.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to VBA Replace Function. Here we discussed VBA Replace and how to use Excel VBA Replace Function along with practical examples and a downloadable excel template. You can also go through our other suggested articles –
- VBA Loops
- VBA Do While Loop
- VBA Number Format
- VBA MsgBox
| title | keywords | f1_keywords | ms.prod | api_name | ms.assetid | ms.date | ms.localizationpriority |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Range.Replace method (Excel) |
vbaxl10.chm144186 |
vbaxl10.chm144186 |
excel |
Excel.Range.Replace |
12647334-f911-69e4-de31-b4df2722eff3 |
05/11/2019 |
medium |
Range.Replace method (Excel)
Returns a Boolean indicating characters in cells within the specified range. Using this method doesn’t change either the selection or the active cell.
Syntax
expression.Replace (What, Replacement, LookAt, SearchOrder, MatchCase, MatchByte, SearchFormat, ReplaceFormat)
expression A variable that represents a Range object.
Parameters
| Name | Required/Optional | Data type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| What | Required | Variant | The string that you want Microsoft Excel to search for. |
| Replacement | Required | Variant | The replacement string. |
| LookAt | Optional | Variant | Can be one of the following XlLookAt constants: xlWhole or xlPart. |
| SearchOrder | Optional | Variant | Can be one of the following XlSearchOrder constants: xlByRows or xlByColumns. |
| MatchCase | Optional | Variant | True to make the search case-sensitive. |
| MatchByte | Optional | Variant | Use this argument only if you have selected or installed double-byte language support in Microsoft Excel. True to have double-byte characters match only double-byte characters. False to have double-byte characters match their single-byte equivalents. |
| SearchFormat | Optional | Variant | The search format for the method. |
| ReplaceFormat | Optional | Variant | The replace format for the method. |
Return value
Boolean
Remarks
The settings for LookAt, SearchOrder, MatchCase, and MatchByte are saved each time you use this method. If you don’t specify values for these arguments the next time you call the method, the saved values are used. Setting these arguments changes the settings in the Find dialog box, and changing the settings in the Find dialog box changes the saved values that are used if you omit the arguments. To avoid problems, set these arguments explicitly each time that you use this method.
Example
This example replaces every occurrence of the trigonometric function SIN with the function COS. The replacement range is column A on Sheet1.
Worksheets("Sheet1").Columns("A").Replace _ What:="SIN", Replacement:="COS", _ SearchOrder:=xlByColumns, MatchCase:=True
[!includeSupport and feedback]