We use UBound and LBound functions to get the length of an Array in Excel VBA. In this article, we will discuss them in detail.
Syntax: UBound() function
UBound (arrayname, [ dimension ])
Parameters:
- arrayname: required. Array variable name
- dimension: optional
Returns: Return upper limit of an array dimension.
Syntax: LBound() Function
LBound (arrayname, [ dimension ])
Parameters:
- arrayname : required. Array variable name
- dimension : optional
Returns: Return lower limit of an array dimension
Sample Data:
VBA Code to get the length of Array (one-dimensional array):
Declare Variables:
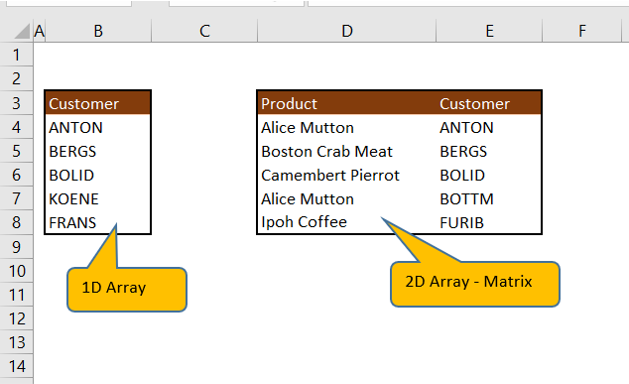
Declaring a customer array with the size of 10.
Sub oneDimArrayLength() ' Array variable Declaration Dim customer (1 To 10) As String
Assign values to array elements
customer(1) = "ANTON" customer(2) = "BERGS" customer(3) = "BOLID" customer(4) = "KOENE" customer(5) = "FRANS"
Use UBound function to get the size of an array and Message box to display the result
'Message box to popup length of 1D array MsgBox "Array has " & UBound(customer) & " element(s)." End Sub
To Run VBA Code
Press Alt+F8 to popup macro window. Select ” oneDimArrayLength” and Click Run button.
Output
VBA Code to get the length of Array (multi-dimensional array)
Declaring variables:
Declaring ProdAndCustomer multi-dimensional array size of 10 rows and 2 columns
Sub twoDimArrayLength() ' Array variable Declaration Dim ProdAndCustomer(1 To 10, 1 To 2) As String, noOfRow As Integer, noOfCol As Integer, noOfElements As Integer
Assign values to array elements
ProdAndCustomer(1, 1) = "Alice Mutton" ProdAndCustomer(2, 1) = "Boston Crab Meat" ProdAndCustomer(3, 1) = "Camembert Pierrot" ProdAndCustomer(4, 1) = "Alice Mutton" ProdAndCustomer(5, 1) = "Ipoh Coffee" ProdAndCustomer(1, 2) = "ANTON" ProdAndCustomer(2, 2) = "BERGS" ProdAndCustomer(3, 2) = "BOLID" ProdAndCustomer(4, 2) = "BOTTM" ProdAndCustomer(5, 2) = "FURIB"
Compute Number of Rows, Number of Columns using UBound and LBound function. Multiply by noOfRow and noOfCol variable to get Number of elements in multi-dimensional array.
noOfRow = UBound(ProdAndCustomer, 1) - LBound(ProdAndCustomer, 1) + 1 noOfCol = UBound(ProdAndCustomer, 2) - LBound(ProdAndCustomer, 2) + 1 noOfElements = noOfRow * noOfCol
Message box to popup result
'Message box to popup length of 1D array MsgBox "Array has " & noOfElements & " element(s)." End Sub
To Run VBA Code
Press Alt+F8 to popup macro window. Select ” twoDimArrayLength” and Click Run button.
Output:
Home / VBA / Arrays / VBA Array Length (Size)
In VBA, to get the length of an array means to count the number of elements you have in that array. For this, you need to know the lowest element and the highest element. So, to get this you can use the UBOUND and LBOUND functions that return the upper bound and lower bound, respectively.
Apart from that, you can also use the COUNTA which is a worksheet function. And in this tutorial, we will see both of the methods so you can use any of them at your convenience.
Steps to Get the Size of an Array
Here we have an array that contains a list of months and sales quantity for each month.

- Make sure to have an array declared properly with rows and columns.
- After that, two more variables (as we have a two-dimensional array) to store the bounds of the array.
- Next, you need to use a formula where you have to use the Ubound function to get the upper bound and then Lbound to get the lower bound of the array.
- As you have a two-dimensional array you need to get bound for both of the dimensions and set that value to the variables.
- In the end, multiply lengths that you have got from the Ubound and Lbound as upper and lower bound.
Here’s the full code.
Dim yearSales(1 To 12, 1 To 2) As Integer
Dim iCount1 As Integer, iCount2 As Integer
iCount1 = UBound(yearSales, 1) - LBound(yearSales, 1) + 1
iCount2 = UBound(yearSales, 2) - LBound(yearSales, 2) + 1
MsgBox iCount1 * iCount2Note: You must be wondering that we have a total of 13 rows in the array that I shared with you at the start of the post.
But we have used an array with 13 rows because the first row was a heading. And here we have used an IF STATEMENT and ISEMPTY function to check if the declared array has zero elements.
Dim yearSales(1 To 12, 1 To 2) As Integer
Dim iCount1 As Integer, iCount2 As Integer
If IsEmpty(yearSales) = 0 Then
MsgBox "This array has zero elements."
Else
iCount1 = UBound(yearSales, 1) - LBound(yearSales, 1) + 1
iCount2 = UBound(yearSales, 2) - LBound(yearSales, 2) + 1
MsgBox "This array has " & iCount1 * iCount2 & " element(s)."Using COUNTA to get the Length of the Array
As you know that an array is a bunch of elements that are structured in a single or multi-dimensional way and you can use the COUNTA function (worksheet function) to count these elements in one go.
In the following code, you have used the same array that you have declared earlier and then used a variable to store the element count returned by the function.

And as you can see the result it has returned is 24 that’s the count of the total number of elements that we have in the array.
Dim yearSales(1 To 12, 1 To 2) As Integer
iCount = WorksheetFunction.CountA(yearSales)
MsgBox iCountThere’s one thing that you need to take care of that this method won’t be ideal to use in all situations, so it’s always good to use the method that we have discussed earlier.
You can also write a code to check first if the declared array is not blank.
Dim yearSales(1 To 12, 1 To 2) As Integer
If IsEmpty(yearSales) = 0 Then
MsgBox "This array has zero elements."
Else
iCount = WorksheetFunction.CountA(yearSales)
MsgBox "This array has " & iCount & " element(s)."Return to VBA Code Examples
In this Article
- Get Array Length
- LBound and UBound Functions
- Get Array Length Function
- Get 2D Array Size
This tutorial will teach you how to get the length (size) of an Array in VBA.
Get Array Length
In order to get the length of an Array, you need to know the array’s start and end positions. You can do this with the VBA’s UBound and LBound Functions.
LBound and UBound Functions
This procedure demonstrates how to use the UBound and LBound Functions on a a single dimension array:
Sub UBoundLBound()
Dim exArr(1 To 4) As String
MsgBox UBound(exArr)
MsgBox LBound(exArr)
End SubSubtracting the two will give you the array length (UBound – LBound +1).
Get Array Length Function
This function will calculate the size (length) of a single-dimensional Array:
Public Function GetArrLength(a As Variant) As Long
If IsEmpty(a) Then
GetArrLength = 0
Else
GetArrLength = UBound(a) - LBound(a) + 1
End If
End FunctionGet 2D Array Size
This function will calculate the number of positions in a two-dimensional array:
Sub testArrySize()
Dim arr2D(1 To 4, 1 To 4) As Long
MsgBox GetArrSize_2D(arr2D)
End Sub
Public Function GetArrSize_2D(a As Variant) As Long
Dim x As Long, y As Long
If IsEmpty(a) Then
GetArrSize_2D = 0
Else
x = UBound(a, 1) - LBound(a, 1) + 1
y = UBound(a, 2) - LBound(a, 2) + 1
GetArrSize_2D = x * y
End If
End FunctionVBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro — A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Learn More!
Introduction to VBA Array Length
Basically, an array is a set of elements that is in two dimensions. In excel we use arrays in our day to day lives. To calculate the length of an array in excel we either do it manually or use some functions to do so. But how do we get the length of an array in Excel VBA? We use two separate functions to do so. Lbound and Ubound functions are used to get an array length in excel VBA.
So we discussed above that we use Lbound and Ubound functions to get array length. But what are Lbound and Ubound functions. Lbound stands for lower bound and Ubound stands for Upper bound. Array length is also identified by function arr.length.
First, let us see how an array looks like. Look at the screenshot below for the same.
Above is an array with four rows and two columns. Now how will we find the length of this array or other sizes we will learn in this topic.
First, ensure we have the developer’s tab enabled so that we can use Excel VBA.
How to Use Excel VBA Array Length?
Now let us try on some examples on how to find array length in excel VBA.
You can download this VBA Array Length Excel Template here – VBA Array Length Excel Template
Example #1 – VBA Array Length
First, imagine we have an array size of four elements in each row and columns i.e. four rows and four columns. So the array size would be 16. Array length is the calculated product of a number of rows and columns. Let us do this in Excel VBA.
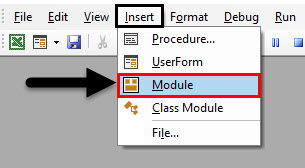
Step 1: Enter VB editor by going in the developer’s tab and then clicking on visual basic as follows.
Step 2: Once we are inside the VB editor let us insert a new module which will open code window for us.
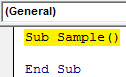
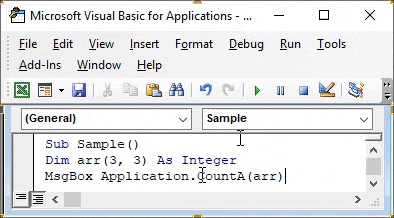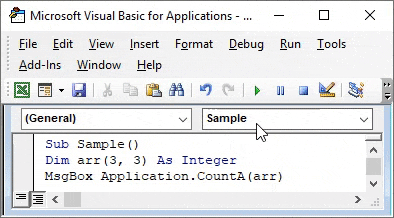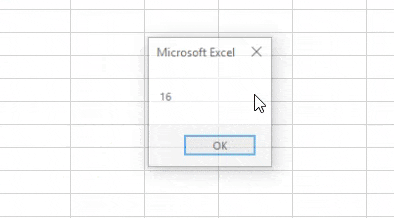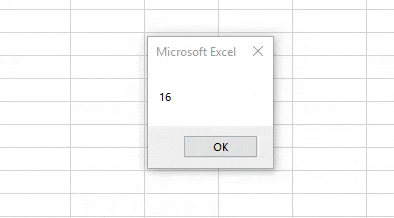
Step 3: Double click on the module we just inserted which will open code window for us. Now we can start writing the code by declaring a Sub Function.
Code:
Sub Sample() End Sub
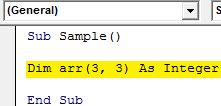
Step 4: Now declare an array as an integer as follows.
Code:
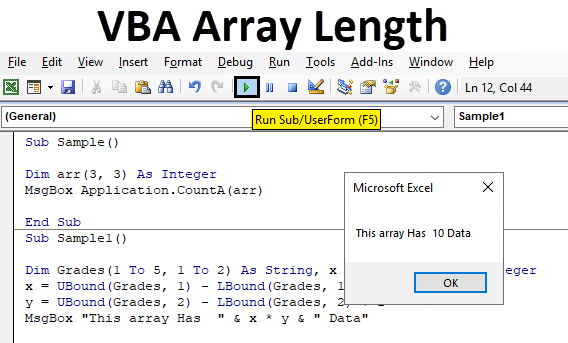
Sub Sample() Dim arr(3, 3) As Integer End Sub
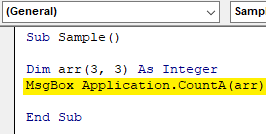
Step 5: Now use the console. writeline and arr.length function to find the array length as follows.
Code:
Sub Sample() Dim arr(3, 3) As Integer MsgBox Application.CountA(arr) End Sub
Step 6: When we run the above code we get 16 as output as 16 is the length of the integer.
Example #2 – VBA Array Length
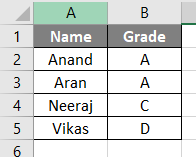
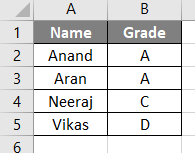
In the above method, we used arr.length method which is not ideal in many cases. We will use the traditional Lbound an Ubound method to find the array length. I have some data in sheet 1 as follows.
In the above screenshot, we have an array and we want to find the size of this array in VBA. We will follow similar steps from example 1 on how to enter the VB editor as follows.
Step 1: Enter VB editor by going in the developer’s tab and then clicking on visual basic as follows.
Step 2: Click on insert tab and add a new module.
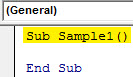
Step 3: Now we can start writing the code by declaring a sub-function.
Code:
Sub Sample1() End Sub
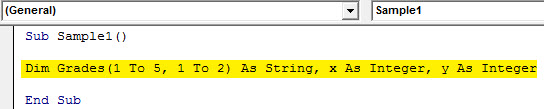
Step 4: Now first we need to declare an array for our data above and two another integers as follows.
Code:
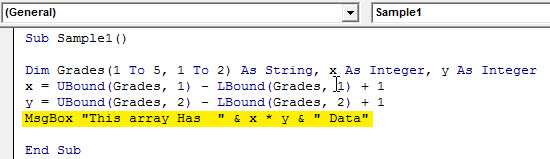
Sub Sample1() Dim Grades(1 To 5, 1 To 2) As String, x As Integer, y As Integer End Sub
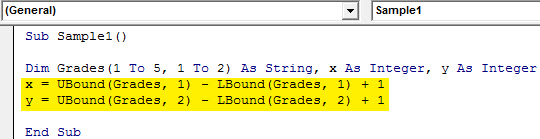
Step 5: Now as we have a size of the array we give an upper and lower limit to the dimension by the following code.
Code:
Sub Sample1() Dim Grades(1 To 5, 1 To 2) As String, x As Integer, y As Integer x = UBound(Grades, 1) - LBound(Grades, 1) + 1 y = UBound(Grades, 2) - LBound(Grades, 2) + 1 End Sub
Step 6: Now let’s use the Msgbox function to display the size of the array from the data above.
Code:
Sub Sample1() Dim Grades(1 To 5, 1 To 2) As String, x As Integer, y As Integer x = UBound(Grades, 1) - LBound(Grades, 1) + 1 y = UBound(Grades, 2) - LBound(Grades, 2) + 1 MsgBox "This array Has " & x * y & " Data" End Sub
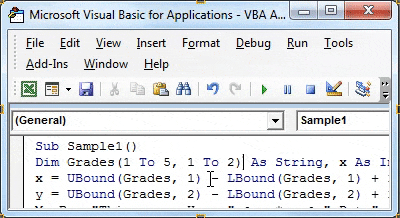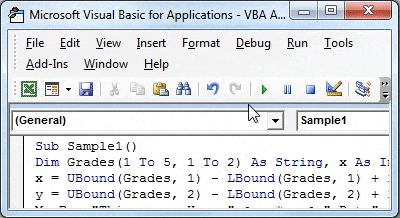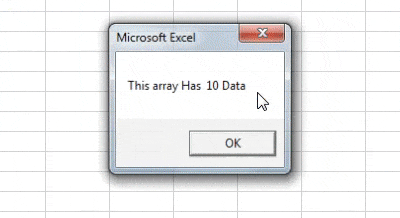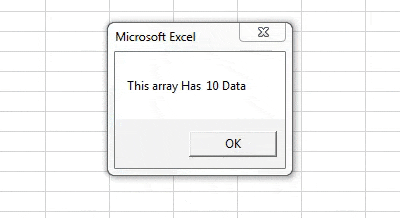
Step 7: Now run the code from the run button or press F5. When we run the code we see the following result,
Now we can check from the data it has 5 rows and two columns and each cell has one data so total there are 10 data.
Example #3 – VBA Array Length
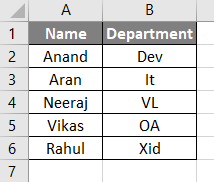
Now let us try to find the size of an array in another example. Now we have data in another sheet.
Now the data has one more rows from the above example 2. Let us try to find out the size of this array. Follow the following steps,
Step 1: Enter VB editor by going in the developer’s tab and then clicking on visual basic as follows,
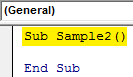
Step 2: Double click on the module we just inserted which will open code window for us. Now we can start writing the code by declaring a Sub Function.
Code:
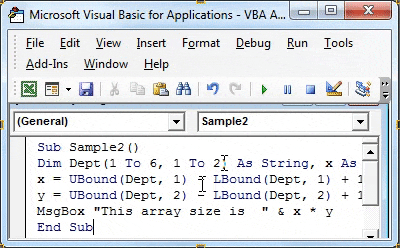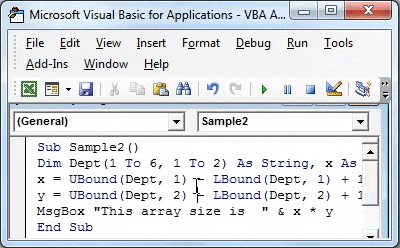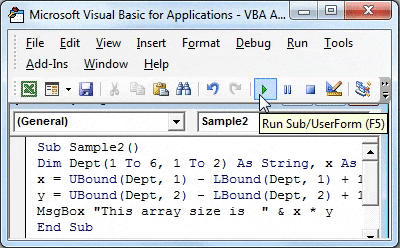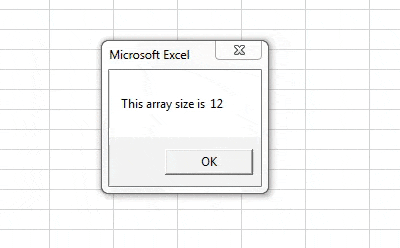
Sub Sample2() End Sub
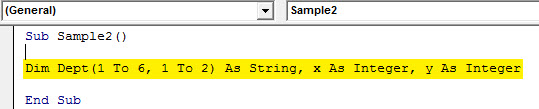
Step 3: Now similarly declare an array and two different variables as integers.
Code:
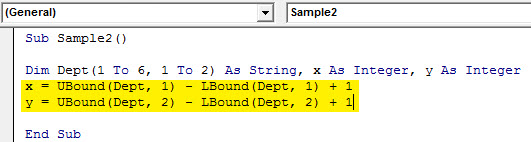
Sub Sample2() Dim Dept(1 To 6, 1 To 2) As String, x As Integer, y As Integer End Sub
Step 4: Now use Lbound and Ubound function to find the size of an array as follows.
Code:
Sub Sample2() Dim Dept(1 To 6, 1 To 2) As String, x As Integer, y As Integer x = UBound(Dept, 1) - LBound(Dept, 1) + 1 y = UBound(Dept, 2) - LBound(Dept, 2) + 1 End Sub
Step 5: Now use the Msgbox function to display the size of the array.
Code:
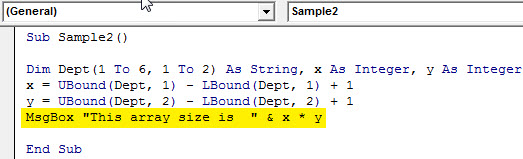
Sub Sample2() Dim Dept(1 To 6, 1 To 2) As String, x As Integer, y As Integer x = UBound(Dept, 1) - LBound(Dept, 1) + 1 y = UBound(Dept, 2) - LBound(Dept, 2) + 1 MsgBox "This array size is " & x * y End Sub
Step 6: When we run the code we get the following result,
Things to Remember
There are few things which we need to keep in mind for VBA Array length as follows:
- To find a length of an array we need to declare the array first.
- We use Lbound and Ubound function to find the length of an array.
- An array is a set of elements in two dimensions.
Conclusion
- Now as we discussed earlier what is an array. It is a set of elements in two dimensions. So in excel VBA, we can use Lbound and Ubound function to find the size of the array length.
- How do we calculate the array size. It is the product of a number of rows to the number of columns.
- How to use the VBA Array Length Function.
- In the above examples, we have learned how to use Ubound and Lbound function as follows.
- UBound(Array, 1) – LBound(Array, 1) + 1
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to VBA Array Length. Here we have discussed how to use Excel VBA Array Length along with practical examples and downloadable excel template. You can also go through our other suggested articles –
- VBA Active Cell
- VBA Delete Row
- VBA Transpose
- VBA LBound
Массивы в VBA Excel: одномерные, многомерные и динамические. Объявление и использование массивов. Операторы Public, Dim и ReDim. Функции Array, LBound, UBound.
Массивы – это множества однотипных элементов, имеющих одно имя и отличающиеся друг от друга индексами. Они могут быть одномерными (линейными), многомерными и динамическими. Массивы в VBA Excel, как и другие переменные, объявляются с помощью операторов Dim и Public. Для изменения размерности динамических массивов используется оператор ReDim. Массивы с заранее объявленной размерностью называют статическими.
Одномерные массивы
Объявление одномерных (линейных) статических массивов в VBA Excel:
|
Public Massiv1(9) As Integer Dim Massiv2(1 To 9) As String |
В первом случае публичный массив содержит 10 элементов от 0 до 9 (нижний индекс по умолчанию — 0, верхний индекс — 9), а во втором случае локальный массив содержит 9 элементов от 1 до 9.
По умолчанию VBA Excel считает в массивах нижним индексом нуль, но, при желании, можно сделать нижним индексом по умолчанию единицу, добавив в самом начале модуля объявление «Option Base 1».
Многомерные массивы
Объявление многомерных статических массивов в VBA Excel аналогично объявлению одномерных массивов, но с добавлением размерностей дополнительных измерений через запятую:
|
‘Массив двухмерный Public Massiv1(3, 6) As Integer ‘Массив трехмерный Dim Massiv2(1 To 6, 1 To 8, 1 To 5) As String ‘Массив четырехмерный Dim Massiv3(9, 9, 9, 9) As Date |
Третий массив состоит из 10000 элементов — 10×10×10×10.
Динамические массивы
Динамические массивы в VBA Excel, в отличие от статических, объявляются без указания размерности:
|
Public Massiv1() As Integer Dim Massiv2() As String |
Такие массивы используются, когда заранее неизвестна размерность, которая определяется в процессе выполнения программы. Когда нужная размерность массива становится известна, она в VBA Excel переопределяется с помощью оператора ReDim:
|
Public Massiv1() As Integer Dim Massiv2() As String ReDim Massiv1(1 To 20) ReDim Massiv2(3, 5, 4) |
При переопределении размерности массива вместо верхнего индекса можно использовать переменную:
|
Dim Massiv1() as Variant, x As Integer x = 20 ReDim Massiv1(1 To x) |
Переопределять размерность динамических массивов в процессе работы программы можно неоднократно, как по количеству измерений, так и по количеству элементов в измерении.
С помощью оператора ReDim невозможно изменить обычный массив, объявленный с заранее заданной размерностью. Попытка переопределить размерность такого массива вызовет ошибку компиляции с сообщением: Array already dimensioned (Массив уже измерен).
При переопределении размерности динамических массивов в VBA Excel теряются значения их элементов. Чтобы сохранить значения, используйте оператор Preserve:
|
Dim Massiv1() As String ——— операторы ——— ReDim Massiv1(5, 2, 3) ——— операторы ——— ReDim Preserve Massiv1(5, 2, 7) |
Обратите внимание!
Переопределить с оператором Preserve можно только последнюю размерность динамического массива. Это недоработка разработчиков, которая сохранилась и в VBA Excel 2016. Без оператора Preserve можно переопределить все размерности.
Максимальный размер
Размер массива – это произведение длин всех его измерений. Он представляет собой общее количество элементов, содержащихся в данный момент в массиве.
По информации с сайта разработчиков, максимальный размер массивов зависит от операционной системы и доступного объема памяти. Использование массивов, размер которых превышает объем доступной оперативной памяти компьютера, приводит к снижению скорости, поскольку системе необходимо выполнять запись данных и чтение с диска.
Использование массивов
Приведу два примера, где не обойтись без массивов.
1. Как известно, функция Split возвращает одномерный массив подстрок, извлеченных из первоначальной строки с разделителями. Эти данные присваиваются заранее объявленному строковому (As String) одномерному динамическому массиву. Размерность устанавливается автоматически в зависимости от количества подстрок.
2. Данные в массивах обрабатываются значительно быстрее, чем в ячейках рабочего листа. Построчную обработку информации в таблице Excel можно наблюдать визуально по мерцаниям экрана, если его обновление (Application.ScreenUpdating) не отключено. Чтобы ускорить работу кода, можно значения из диапазона ячеек предварительно загрузить в динамический массив с помощью оператора присваивания (=). Размерность массива установится автоматически. После обработки данных в массиве кодом VBA полученные результаты выгружаются обратно на рабочий лист Excel. Обратите внимание, что загрузить значения в диапазон ячеек рабочего листа через оператор присваивания (=) можно только из двумерного массива.
Функции Array, LBound, UBound
Функция Array
Функция Array возвращает массив элементов типа Variant из первоначального списка элементов, перечисленных через запятую. Нумерация элементов в массиве начинается с нуля. Обратиться к элементу массива можно, указав в скобках его номер (индекс).
|
Sub Test1() Dim a() As Variant a = Array(«text», 25, «solo», 35.62, «stop») MsgBox a(0) & vbNewLine & a(1) & vbNewLine _ & a(2) & vbNewLine & a(3) & vbNewLine & a(4) End Sub |
Скопируйте код в модуль VBA Excel и запустите его на выполнение. Информационное сообщение MsgBox покажет значения массива, извлеченные по индексу.
Функция LBound
Функция LBound возвращает значение типа Long, равное наименьшему (нижнему) доступному индексу в указанном измерении массива.
Синтаксис:
LBound (arrayname[, dimension])
- arrayname — это имя переменной массива, является обязательным аргументом;
- dimension — это номер измерения массива, необязательный аргумент, по умолчанию принимает значение 1.
Наименьший индекс по-умолчанию может быть равен 0 или 1 в зависимости от настроек оператора Option Base. Нижняя граница архива, полученного с помощью функции Array, всегда равна 0.
При объявлении переменных массивов или переопределении их размерности наименьшие индексы могут быть любыми целыми числами, в том числе отрицательными.
Функция UBound
Функция UBound возвращает значение типа Long, равное наибольшему (верхнему) доступному индексу в указанном измерении массива.
Синтаксис:
UBound( arrayname[, dimension])
- arrayname — это имя переменной массива, является обязательным аргументом;
- dimension — это номер измерения массива, необязательный аргумент, по умолчанию принимает значение 1.
Функция UBound используется вместе с функцией LBound для определения размера массива.
|
Sub Test2() Dim a(—2 To 53) As String MsgBox «Наименьший индекс = « & LBound(a) & _ vbNewLine & «Наибольший индекс = « & UBound(a) End Sub |
Скопируйте код в модуль VBA Excel и запустите его на выполнение. Информационное сообщение MsgBox покажет значения наименьшего и наибольшего индекса переменной массива a.
Обход массива циклом
Обход одномерного массива циклом For… Next, в котором для определения границ массива используются функции UBound и LBound:
|
Sub Test3() Dim a() As Variant, i As Long a = Array(«text», 25, «solo», 35.62, «stop») For i = LBound(a) To UBound(a) Debug.Print «a(« & i & «) = « & a(i) Next End Sub |
Результат работы цикла вы увидите в окне Immediate.
Очистка (обнуление) массивов
Первый способ
Очистить любой массив, статический или динамический, без использования цикла можно с помощью оператора Erase. Термин «обнуление» можно применить только к массиву числового типа.
|
Dim Massiv1(4, 3) As String, Massiv2() As Variant ——— операторы ——— ‘переопределяем динамический массив ReDim Massiv2(2, 5, 3) ——— операторы ——— ‘очищаем массивы Erase Massiv1 Erase Massiv2 |
Обратите внимание, что оба массива при таком способе очистки будут возвращены в исходное состояние, которое они имели сразу после объявления:
- статический Massiv1 сохранит размерность (4, 3);
- динамический Massiv2 не сохранит размерность ().
Второй способ
Динамический массив можно очистить (обнулить) без использования цикла с помощью оператора ReDim. Просто переопределите его с той же размерностью.
|
Dim Massiv() As Double ——— операторы ——— ‘переопределяем массив ReDim Massiv(5, 6, 8) ——— операторы ——— ‘очищаем массив ReDim Massiv(5, 6, 8) |