Return to VBA Code Examples
In this Article
- GoTo Examples
- GoTo Multiple Line Labels
- GoTo Error Handler End of Procedure
- GoTo Repeat Code
- VBA GoTo a Line Label in Access VBA
The GoTo Statement in VBA allows you to jump to a line of code.
First create a line label anywhere in your code:
Skip:Then add to “GoTo” statement to jump to the line label
GoTo SkipGoTo Examples
This example tests the year. If the year is 2019 or later it will GoTo the Skip line label. This allows you to skip over code if certain conditions are met.
Sub GoTo_Example()
Dim year As Integer
year = 2019
If year >= 2019 Then GoTo Skip
'Process Data for Years < 2019
MsgBox "Year is Prior to 2019"
Skip:
End SubGoTo Multiple Line Labels
You can also use GoTo statements to jump to relevant lines of code. Let’s adjust our previous example to go to different code locations based on which year it is:
Sub GoTo_Statement()
Dim year As Integer
year = 2019
If year = 2019 Then
GoTo year2019
ElseIf year = 2010 Then
GoTo year2020
Else
GoTo year2021
End If
year2019:
'Process 2019
MsgBox "Year is 2019"
GoTo EndProc
year2020:
'Process 2020
MsgBox "Year is 2020"
GoTo EndProc
year2021:
'Process 2021+
MsgBox "Year is 2021+"
EndProc:
End SubNotice the “GoTo EndProc” before each line label. We added this line of code so that those code sections are skipped unless they are accessed by the relevant “GoTo”.
GoTo Error Handler End of Procedure
Now let’s use Error Handling to go to the end of the procedure if there is an error.
Sub GoTo_OnError ()
Dim i As Integer
On Error GoTo EndProc
i = 5 / 0
MsgBox i
EndProc:
End SubGoTo Repeat Code
Our last example will use the GoTo Statement to repeat some code.
Below we’re using a Yes / No Messagebox (Click to learn more) to confirm that the user acknowledges the warning. If they click ‘No’, the message box will be displayed again until they click ‘Yes’ (see GIF below).
Sub GoTo_YesNoMsgBox()
RepeatMsg:
Dim answer As Integer
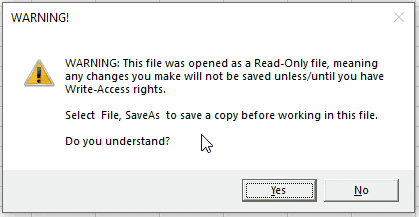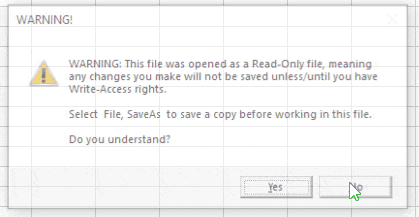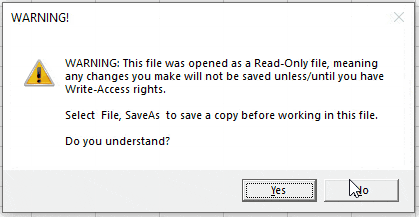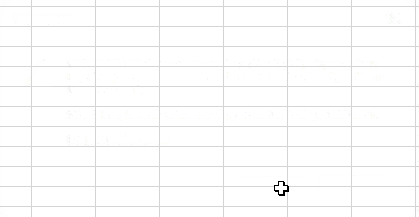
answer = MsgBox("WARNING: This file was opened as a Read-Only file, meaning any changes you make will not be saved unless/until you have Write-Access rights. " & _
Chr(13) & Chr(13) & "Select File, SaveAs to save a copy before working in this file." & vbNewLine & vbNewLine & "Do you understand?", vbExclamation + vbYesNo, "WARNING!")
If answer = vbNo Then GoTo RepeatMsg 'Repeat until user clicks "Yes"
End Sub
VBA GoTo a Line Label in Access VBA
All of the above examples work exactly the same in Access VBA as in Excel VBA.
Sub TestGoTo()
On Error GoTo ending
DoCmd.OpenForm "FrmClients"
Exit Sub
ending:
MsgBox "Cannot open form"
End SubVBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro — A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Learn More!
|
jfd Пользователь Сообщений: 302 |
Подскажите плиз, как по событию CommandButton1_Click() перейти к метке в коде? Изменено: jfd — 25.01.2016 13:58:33 |
|
The_Prist Пользователь Сообщений: 14181 Профессиональная разработка приложений для MS Office |
Создать отдельную функцию, в которую передать нужные параметры. Даже самый простой вопрос можно превратить в огромную проблему. Достаточно не уметь формулировать вопросы… |
|
jfd Пользователь Сообщений: 302 |
The_Prist,а можете поподробнее? Изменено: jfd — 25.01.2016 14:10:24 |
|
vikttur Пользователь Сообщений: 47199 |
Где метка? Где кнопка? В общем — пример вместо Вас рисовать?! 250 сообщений на форуме… |
|
китин Пользователь Сообщений: 931 |
#5 25.01.2016 14:18:44
ну дык не так много за 46 лет присутствия на форуме
Вполне такой нормальный кинжальчик. Процентов на 100 |
||||
|
jfd Пользователь Сообщений: 302 |
#6 25.01.2016 14:19:03 vikttur, мне не лень сделать пример, просто есть ли смысл грузит форум лишними файлами. Код модуля
Код userform
|
||||
|
The_Prist Пользователь Сообщений: 14181 Профессиональная разработка приложений для MS Office |
#7 25.01.2016 14:22:40 И на чем мне показывать? На пальцах? Плюс не очень корректно менять свое сообщение, удаляя из него то, чтобы было изначально и на что уже есть ответ.
саму функцию show_message можно вызвать из любой другой процедуры или функции. Это самый правильный подход.
Даже самый простой вопрос можно превратить в огромную проблему. Достаточно не уметь формулировать вопросы… |
||||
|
jfd Пользователь Сообщений: 302 |
#8 25.01.2016 14:27:59
извиняюсь, удалил до того как увидел ответ. |
||
|
Юрий М Модератор Сообщений: 60570 Контакты см. в профиле |
#9 25.01.2016 14:31:15
Возвращаясь к вопросу о том, оставить или убрать возможность редактирования своих сообщений: не раз сам попадал в глупую ситуацию — комментировал то, чего уже нет. |
||
|
Михаил Лебедев Пользователь Сообщений: 2855 |
#10 25.01.2016 14:31:32
есть. А так — вот ▼
Код userform
Всё сложное — не нужно. Всё нужное — просто /М. Т. Калашников/ |
||||||
Содержание
- Оператор GoTo
- Синтаксис
- Часть
- Remarks
- Ветвление и пробная конструкция
- Пример
- Application.Goto method (Excel)
- Syntax
- Parameters
- Remarks
- Example
- Support and feedback
- Метод Application.Goto (Excel)
- Синтаксис
- Параметры
- Замечания
- Пример
- Поддержка и обратная связь
- VBA Excel. Элемент управления Label (метка, надпись)
- Элемент управления Label
- Свойства элемента Метка
- Примеры кода VBA с Label
- VBA GoTo a Line Label
- GoTo Examples
- GoTo Multiple Line Labels
- GoTo Error Handler End of Procedure
- GoTo Repeat Code
- VBA GoTo a Line Label in Access VBA
- VBA Coding Made Easy
- VBA Code Examples Add-in
Оператор GoTo
Ветвления безоговорочно к указанной строке процедуры.
Синтаксис
Часть
line
Обязательный. Любая метка строки.
Оператор GoTo может ветвиться только к строкам в процедуре, в которой она отображается. Строка должна иметь метку строки, на которую GoTo можно ссылаться. Дополнительные сведения см. в разделе «Практическое руководство. Операторы меток».
GoTo операторы могут затруднить чтение и обслуживание кода. По возможности используйте вместо нее структуру управления. Дополнительные сведения см. в разделе Поток управления.
Оператор нельзя использовать GoTo для ветвления за пределами For . Next , For Each . Next , SyncLock . Try . End SyncLock Catch . Finally , With . End With , или Using . End Using конструкция на метку внутри.
Ветвление и пробная конструкция
Try Внутри . Catch . Finally Конструкции, следующие правила применяются к ветвлениям с помощью инструкции GoTo .
| Блокировка или регион | Ветвление извне | Ветвление изнутри |
|---|---|---|
| Блок Try | Только из Catch блока той же конструкции 1 | Только за пределами всей конструкции |
| Блок Catch | Никогда не допускается | Только за пределами всей конструкции, или к Try блоку того же строительства 1 |
| Блок Finally | Никогда не допускается | Никогда не допускается |
1 Если один Try . Catch . Finally Построение вложено в другой блок, Catch блок может ветвить в Try блок на собственном уровне вложения, но не в любой другой Try блок. Вложенный Try . Catch . Finally конструкция должна содержаться полностью в блоке Try Catch конструкции, в которой она вложена.
На следующем рисунке показана одна Try конструкция, вложенная в другую. Различные ветви между блоками двух конструкций указываются как допустимые или недопустимые.
Пример
В следующем примере оператор используется GoTo для ветвления к подписям в процедуре.
Источник
Application.Goto method (Excel)
Selects any range or Visual Basic procedure in any workbook, and activates that workbook if it’s not already active.
Syntax
expression.Goto (Reference, Scroll)
expression A variable that represents an Application object.
Parameters
| Name | Required/Optional | Data type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reference | Optional | Variant | The destination. Can be a Range object, a string that contains a cell reference in R1C1-style notation, or a string that contains a Visual Basic procedure name. If this argument is omitted, the destination is the last range you used the Goto method to select. |
| Scroll | Optional | Variant | True to scroll through the window so that the upper-left corner of the range appears in the upper-left corner of the window. False to not scroll through the window. The default is False. |
This method differs from the Select method in the following ways:
If you specify a range on a sheet that’s not on top, Microsoft Excel will switch to that sheet before selecting. (If you use Select with a range on a sheet that’s not on top, the range will be selected but the sheet won’t be activated).
This method has a Scroll argument that lets you scroll through the destination window.
When you use the Goto method, the previous selection (before the Goto method runs) is added to the array of previous selections (for more information, see the PreviousSelections property). Use this feature to quickly jump between as many as four selections.
The Select method has a Replace argument; the Goto method doesn’t.
Example
This example selects cell A154 on Sheet1 and then scrolls through the worksheet to display the range.
Support and feedback
Have questions or feedback about Office VBA or this documentation? Please see Office VBA support and feedback for guidance about the ways you can receive support and provide feedback.
Источник
Метод Application.Goto (Excel)
Выбирает любой диапазон или процедуру Visual Basic в любой книге и активирует ее, если она еще не активна.
Синтаксис
expression. Goto (справочник, прокрутка)
выражение: переменная, представляющая объект Application.
Параметры
| Имя | Обязательный или необязательный | Тип данных | Описание |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reference | Необязательный | Variant | Назначение. Может быть объектом Range , строкой, содержащей ссылку на ячейку в нотации в стиле R1C1, или строкой, содержащей имя процедуры Visual Basic. Если этот аргумент опущен, назначение будет последним диапазоном, который использовался для выбора метода Goto . |
| Scroll | Необязательный | Variant | Значение true для прокрутки окна, чтобы верхний левый угол диапазона отображалось в левом верхнем углу окна. Значение false , чтобы не прокручивать окно. Значение по умолчанию — false. |
Замечания
Этот метод отличается от метода Select следующими способами:
Если вы укажете диапазон на листе, который не находится наверху, Microsoft Excel переключится на этот лист, прежде чем выбрать его. (Если вы используете Команду с диапазоном на листе, который не находится сверху, диапазон будет выбран, но лист не будет активирован).
Этот метод содержит аргумент Scroll , который позволяет прокручивать целевое окно.
При использовании метода Goto предыдущее выделение (перед выполнением метода Goto ) добавляется в массив предыдущих выделенных фрагментов (дополнительные сведения см. в свойстве PreviousSelections ). Используйте эту функцию для быстрого перехода между четырьмя выбранными вариантами.
Метод Select имеет аргумент Replace ; Метод Goto не поддерживает.
Пример
В этом примере выбирается ячейка A154 на листе Лист1, а затем прокручивается лист для отображения диапазона.
Поддержка и обратная связь
Есть вопросы или отзывы, касающиеся Office VBA или этой статьи? Руководство по другим способам получения поддержки и отправки отзывов см. в статье Поддержка Office VBA и обратная связь.
Источник
VBA Excel. Элемент управления Label (метка, надпись)
Элемент управления пользовательской формы Label, применяемый в VBA Excel для отображения надписей, меток, информационного текста. Свойства Label, примеры кода.
Элемент управления Label
Элемент управления Label, как и другие элементы управления, реагирует на нажатия мышью, то есть его можно использовать для запуска подпрограмм, изменения собственных свойств, свойств пользовательской формы и других элементов управления.
Свойства элемента Метка
| Свойство | Описание |
|---|---|
| AutoSize | Автоподбор размера надписи. True – размер автоматически подстраивается под длину набираемой строки. False – размер элемента управления определяется свойствами Width и Height. |
| Caption | Текст надписи (заголовок). |
| ControlTipText | Текст всплывающей подсказки при наведении курсора на метку. |
| Enabled | Возможность взаимодействия пользователя с элементом управления Label. True – взаимодействие включено, False – отключено (цвет текста становится серым). |
| Font | Шрифт, начертание и размер текста надписи. |
| Height | Высота элемента управления. |
| Left | Расстояние от левого края внутренней границы пользовательской формы до левого края элемента управления. |
| Picture | Добавление изображения вместо текста метки или дополнительно к нему. |
| PicturePosition | Выравнивание изображения и текста в поле надписи. |
| TabIndex | Определяет позицию элемента управления в очереди на получение фокуса при табуляции, вызываемой нажатием клавиш «Tab», «Enter». Отсчет начинается с 0. |
| TextAlign* | Выравнивание текста надписи: 1 (fmTextAlignLeft) – по левому краю, 2 (fmTextAlignCenter) – по центру, 3 (fmTextAlignRight) – по правому краю. |
| Top | Расстояние от верхнего края внутренней границы пользовательской формы до верхнего края элемента управления. |
| Visible | Видимость элемента управления Label. True – элемент отображается на пользовательской форме, False – скрыт. |
| Width | Ширина элемента управления. |
| WordWrap | Перенос текста надписи на новую строку при достижении ее границы. True – перенос включен, False – перенос выключен. |
* При загруженной в надпись картинке свойство TextAlign не работает, следует использовать свойство PicturePosition.
Свойство по умолчанию для элемента Label – Caption, основное событие – Click.
В таблице перечислены только основные, часто используемые свойства надписи. Все доступные свойства отображены в окне Properties элемента управления Label.
Примеры кода VBA с Label
Пример 1
Загрузка элемента управления Label на пользовательскую форму с параметрами, заданными в коде VBA Excel:
Источник
VBA GoTo a Line Label
In this Article
The GoTo Statement in VBA allows you to jump to a line of code.
First create a line label anywhere in your code:
Then add to “GoTo” statement to jump to the line label
GoTo Examples
This example tests the year. If the year is 2019 or later it will GoTo the Skip line label. This allows you to skip over code if certain conditions are met.
GoTo Multiple Line Labels
You can also use GoTo statements to jump to relevant lines of code. Let’s adjust our previous example to go to different code locations based on which year it is:
Notice the “GoTo EndProc” before each line label. We added this line of code so that those code sections are skipped unless they are accessed by the relevant “GoTo”.
GoTo Error Handler End of Procedure
Now let’s use Error Handling to go to the end of the procedure if there is an error.
GoTo Repeat Code
Our last example will use the GoTo Statement to repeat some code.
Below we’re using a Yes / No Messagebox (Click to learn more) to confirm that the user acknowledges the warning. If they click ‘No’, the message box will be displayed again until they click ‘Yes’ (see GIF below).
VBA GoTo a Line Label in Access VBA
All of the above examples work exactly the same in Access VBA as in Excel VBA.
VBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro — A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users! 
VBA Code Examples Add-in
Easily access all of the code examples found on our site.
Simply navigate to the menu, click, and the code will be inserted directly into your module. .xlam add-in.
Источник
The need for a branching statement in code
In a procedure, the program code or the application in which the code is running may encounter unexpected issues or may not work like you expect. To be on the safe side, we can transfer the program’s control to any specific line, thereby skipping the error prone block of code.
This kind of branching helps us skip any block of code or even re-run a block of code from any previous line if the expected action has not happened and the program steps need to be repeated.
The Goto branching statement
Goto is a popular branching statement available for use in most programming languages. In VBA, we can use this statement to move the program control to any line (forward or backward) within the same sub-procedure.
Syntax of the Goto statement
Goto <line>
The parameter line can either be a label or a line number.
A label is a any word with a colon in front of any line of code. When a label is used in the Goto statement, the control is transferred to the line which starts with that label.
Sample Programs
Validate age to see if it is realistic
This is a sample program that validates age. If the age is not realistic , the control is transferred to the line that has the label “Line_no1”.
Sub Goto_demo()
Dim age
Line_no1:
age = InputBox("Enter your age")
If age > 110 Then
MsgBox "It is impossible. Try again"
Goto Line_no1
End If
'Rest of the code can go here
End Sub
Error display using Goto label
Sub Goto_demo1()
' handling error at any line in the code using this label
On Error Goto I_handle_error
' declare variables
Dim a, b
' initialize variables
a = "Hello World"
b = Split(a, " ")
' Try to display a value out of the array's upperbound
MsgBox b(2)
' label and content
I_handle_error:
Debug.Print "There is an error " & Err.Number & vbCrLf & Err.Description
End Sub
Output is available in the screenshot below. As you can see a “Subscript out of range” error is caught.
Using Goto 0 instead of the actual line number or a label
Goto 0 enables the normal debugging process.
You might wonder what difference this statement makes and why it’s even useful.
Imagine a scenario where “On Error Resume Next” is used at the beginning of the program to skip known errors that need to be ignored. But later after the 100th line of code, we suspect there might be some errors that need to be debugged.
So, in this case, we can use this “On error Goto 0” statement before that 100th line to enable the normal error handling and to prevent the compiler from ignoring the upcoming errors.
This statement essentially disables or reverses the effect of “on error resume next.”
Another example using Goto 0
As in the previous example, we first use “On error resume next” to ignore errors. The program ignores all errors until it encounters the “On Error Goto 0” statement. After this line, error are displayed as usual during runtime.
Sub Goto_demo2() ' skip the normal error handling process On Error Resume Next ' declare variables Dim a, b ' initialize variables a = "Hello World" b = Split(a, " ") ' Try to display a value out of the array's upperbound - error will be skipped Debug.Print b(2) ' Display a proper value Debug.Print b(0) ' enable the normal error handling On Error Goto 0 ' Try running the below error prone code. Debug.Print b(10) End Sub
Goto statement that re-runs a block of code
Sub chk_weight()
' declare variables
Dim allwed_wt, current_wt, flag
' assign values in kg
allwed_wt = 10
flag = 0
'set a label to start again if weight is not within limits
' CInt is used to convert the string to a number
checkagain:
current_wt = CInt(InputBox(" Please enter the weight of your baggage"))
' check if the weight is within limits
' display appropriate message to the passenger
If current_wt <= allwed_wt Then
MsgBox "The weight of your baggage is within the permitted limit. No further action is required."
Else
MsgBox "The weight of your baggage is more than the permitted limit. Please remove some baggage now as the current weight will be asked again."
'Goto the block of code that gets input and validates the weight of baggage
Goto checkagain
End If
End Sub
Goto statement using a line number
Considering the example above, the label “Checkagain” can be replaced with the respective line number 89 as show in the image below. But as we keep maintaining code by adding and removing lines of code in our modules or procedures, the line numbers are subject to change.
Hence, it is not a good practice to use line numbers in your Goto statements. It is always advisable to create and use labels instead.
Conclusion
Goto is a very popular branching statement which is used in many programming languages in combination with conditions. If used wisely, this statement can help you save time, prevent unnecessary errors, capture or debug unknown errors, and keep your code organized.
Home / VBA / VBA GoTo Statement
VBA GoTo statement helps code execution to jump to a specific line within the procedure. In simple words, with the goto statement, VBA jumps to a particular line that is specified by you. For example, if you have specified to jump to the second line go will jump to that line.
How to use VBA GoTo Statement in a Code
- First, you need to use the goto statement.
- After that, you need to define the place where you want to VBA to jump from goto.
- Next, create the tag to create that place in the procedure.
- In the end, add the line(s) of code that you want to get executed.

Sub vba_goto()
GoTo Last Range("A1").Select Last:
Range("A12").Select
End SubGoTo to Repeat a Code
You can also use the go to statement to repeat a code using a set of condition.
Sub goto_repeat()
Dim iMessage As String
Question:
iMessage = InputBox("what's the day today?")
If iMessage <> "tuesday" Then
MsgBox ("wrong answer, try again.")
GoTo Question
Else
MsgBox ("that's the right answer.")
End If
End SubWhen you run the above code it asks you for the day name and if you enter anything other than “Tuesday” it will repeat the question. If you look at the code, you can see we have to use the goto statement and the if statement.
Now when the user enters anything other than the right answer, the goto statement makes VBA repeat the code. (but whenever you are using these sorts of codes you need to be extra cautious as it can create an endless loop.
VBA GoTo End
You can also exit a sub using the goto statement.

In the above code, we have used the “last” tag just before the end statement and when VBA reaches the GoTo statement, it makes VBA jump to the “Last” at the end of the procedure.
GoTo Statement to go to a Line in Another Sub Routine
Well, go to statement as quite handy to make VBA jump from one place to another, but it’s not possible to make it go to another procedure in the module.