Home / VBA / VBA Check IF a Workbook is Open (Excel File)
To check if a workbook is open using a VBA code, you need to use FOR EACH loop that can loop through all the workbooks that are open at the moment and verify each workbook’s name with the name you have mentioned. You can use a message box to get the result of the loop. Or you can also make the code to enter the result in a cell.
- First, you need to declare variables to use in the code to create a loop.
- Use an input box to get the name of the workbook that you wish to search for.
- Start the loop to loop through all the open workbooks.
- Write code with IF STATEMENT to verify the name of the workbook with the name you have entered in the input box, and once the name matches, activates the workbook, show a message box that workbook is found, and exit the procedure.
- In the end, end the loop and use a message box to show a message box if nothing has been found.
Helpful Links: Run a Macro – Macro Recorder – Visual Basic Editor – Personal Macro Workbook
Here’s the full code.
Sub vba_check_workbook()
Dim WB As Workbook
Dim myWB As String
myWB = InputBox(Prompt:="Enter the workbook name.")
For Each WB In Workbooks
If WB.Name = myWB Then
WB.Activate
MsgBox "Workbook Found!"
Exit Sub
End If
Next WB
MsgBox "Not Found"
End SubMore on VBA Workbooks
VBA Save Workbook | VBA Close Workbook | VBA Delete Workbook | VBA ThisWorkbook | VBA Rename Workbook | VBA Activate Workbook | VBA Combine Workbook | VBA Protect Workbook (Unprotect) | VBA Open Workbook | VBA Check IF an Excel Workbook Exists in a Folder| VBA Create New Workbook (Excel File)
- VBA Workbook
This tutorial shows how to check if a specific workbook is open through the use of VBA
METHOD 1. Check if workbook is open in the same Excel session
VBA
Sub Check_if_workbook_is_open()
‘declare a variable
Dim wb As Workbook
For Each wb In Workbooks
If wb.Name = «Parameters.xlsx» Then
‘this message will appear if one of the open workbooks is Parameters.xlsx
MsgBox «File is Open»
End If
Next
End Sub
ADJUSTABLE PARAMETERS
File Name: Select the file name of a workbook that you want to check if it’s open by changing the file name «Parameters.xlsx» in the VBA code.
Message: Select the message that you want to be displayed if the workbook is open by changing the message «File is Open» in the VBA code.
ADDITIONAL NOTES
Note 1: This VBA code will check Excel workbooks in the same session as the workbook from which you are running this VBA code.
METHOD 2. Check if workbook is open across all Excel sessions
VBA
Sub Check_if_workbook_is_open()
‘declare a variable
Dim FilePath As String
FilePath = IsWBOpen(«C:ExcelParameters.xlsx»)
If FilePath = True Then
MsgBox «File is Open»
Else
MsgBox «File is Closed»
End If
End Sub
Function IsWBOpen(FileName As String)
‘declare variables
Dim FileNo As Long
Dim ErrorNo As Long
On Error Resume Next
FileNo = FreeFile()
Open FileName For Input Lock Read As #FileNo
Close FileNo
ErrorNo = Err
On Error GoTo 0
Select Case ErrorNo
Case 0
IsWBOpen = False
Case 70
IsWBOpen = True
Case Else
Error ErrorNo
End Select
End Function
ADJUSTABLE PARAMETERS
File Path and Name: Select the file path, including the name of the file, by changing «C:ExcelParameters.xlsx» in the VBA code.
Message if Workbook is Open: Select the message that you want to be displayed if the workbook is open by changing the message «File is Open» in the VBA code.
Message if Workbook is Closed: Select the message that you want to be displayed if the workbook is closed by changing the message «File is Closed» in the VBA code.
ADDITIONAL NOTES
Note 1: This VBA code will check workbooks in all Excel sessions.
Note 2: This method creates a User Defined Function called ‘IsWBOpen’ and then runs the VBA code.
Explanation about how to check if workbook is open
EXPLANATION
EXPLANATION
This tutorial shows how to check if a specific workbook is open in the same Excel session or across all Excel sessions, using VBA.
The first method shows how to check if a workbook, with a specific name, is open in the same Excel session in which the VBA code is run. The second method shows how to check if a specific workbook, including its location and name, is open in all Excel sessions. This is achieved by creating a User Defined Function and then applying this in a macro.
| Related Topic | Description | Related Topic and Description |
|---|---|---|
| Check if workbook is open, if closed open workbook | How to check if a specific workbook is open and if it’s closed then open the workbook using VBA | |
| Open an Excel workbook | How to open a single workbook using Excel, VBA and Shortcut | |
| Open an Excel workbook as Read-Only | How to open a single workbook as Read-Only using Excel and VBA |
This Excel tutorial explains how to use Workbooks Open Method to open a closed workbook and check if workbook is opened.
In worksheet automation, we may need to programmatically open another workbook to change data based on the active workbook. Workbooks Open Method is very straight forward to use, you just need to specify the file name to open, but there are many other optional parameters you may want to use.
Note that Workbooks Open Method is different from Workbook Open Event, the latter is to trigger VBA when a workbook is opened.
Example of Excel VBA Workbooks Open Method
Assume that you have two workbooks. One is called FileA.xlsm, another is called FileB.xlsx
Now you want to open FileB from FileA, so FileA should contain the Macro (therefore .xlsm) and FileB does not need any Macro.
In FileA, create a Sub in Module and insert the below code, which will open FileB.
Workbooks.Open ("C:UsersWYMANDesktopfolderFileB.xlsx")
After you open FileB, you may need to change the data. Therefore you need to give FileB a name in order to manipulate it.
The below code give FileB a name called masterWB.
Set masterWB = Workbooks.Open("C:UsersWYMANDesktopfolderFileB.xlsx")
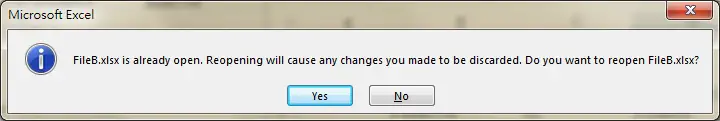
If the FileB is already opened, you will receive an alert.
Now you can manipulate FileA (using thisworkbook) and FileB(using masterWB) from FileA
masterWB.Sheets("Sheet1").Range("A1").Value = "FileB"
ThisWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet1").Range("A1").Value = "FileA"
Check if Workbook is opened already
You may already have FileB opened before the Macro is run, in that case you will receive an alert message if you use Workbooks.Open, this will prevent your Macro from further running.
There are some methods to test if a Workbook is already opened, below is my preferred method. This Function loop through all currently opened Workbook to see if there is a Workbook name same as the name provided in the Function argument.
Public Function wIfWbOpen(wbName As String) As Boolean Dim oWB As Excel.Workbook wIfWbOpen = False For Each oWB In Application.Workbooks If oWB.Name = wbName Then wIfWbOpen = True Exit For End If Next Set oWB = Nothing End Function
Finally use the Function in the Sub in which you want to run code in FileB.
Public Sub updateData()
If wIfWbOpen("FileB.xlsx") Then
Set masterWB = Workbooks("FileB.xlsx")
Else
Set masterWB = Workbooks.Open("C:UsersWYMANDesktopfolderFileB.xlsx")
End If
End Sub
Outbound References
http://www.ozgrid.com/forum/showthread.php?t=63350
Содержание
- Use Excel VBA to check if workbook is opened
- Excel VBA Workbooks Open Method
- Example of Excel VBA Workbooks Open Method
- Check if Workbook is opened already
- VBA Working with Workbooks (The Workbook Object)
- The Workbook Object
- Workbook Index Number
- Activate Workbook, ActiveWorkbook, and ThisWorkbook
- Activate Workbook
- ActiveWorkbook
- ThisWorkbook
- VBA Coding Made Easy
- Open Workbook
- Open and Assign to Variable
- Open File Dialog
- Create New (Add) Workbook
- Add New Workbook to Variable
- Close Workbook
- Close & Save
- Close without Save
- Workbook Save As
- Other Workbook VBA Examples
- Workbook Name
- Protect Workbook
- Loop Through all Open Workbooks
- Workbook Activate Event
- VBA Code Examples Add-in
- Opening
- Workbooks.Open
- Opening Workbooks
- Opening
- Running a macro automatically when it opens
- Checking if a workbook exists
- Checking if a workbook is currently open
- Running a macro automatically when it opens
- Excel VBA Workbooks.Open Method
- Excel VBA Workbooks.Open Method
- Syntax of Workbooks.Open Method
- Example 1 – Open a workbook
- Example 2 – Open a workbook with password
- Example 3 – Open a workbook without alert
Use Excel VBA to check if workbook is opened
This Excel tutorial explains how to use Workbooks Open Method to open a closed workbook and check if workbook is opened.
Excel VBA Workbooks Open Method
In worksheet automation, we may need to programmatically open another workbook to change data based on the active workbook. Workbooks Open Method is very straight forward to use, you just need to specify the file name to open, but there are many other optional parameters you may want to use.
Note that Workbooks Open Method is different from Workbook Open Event, the latter is to trigger VBA when a workbook is opened.
Example of Excel VBA Workbooks Open Method
Assume that you have two workbooks. One is called FileA.xlsm, another is called FileB.xlsx
Now you want to open FileB from FileA, so FileA should contain the Macro (therefore .xlsm) and FileB does not need any Macro.
In FileA, create a Sub in Module and insert the below code, which will open FileB.
After you open FileB, you may need to change the data. Therefore you need to give FileB a name in order to manipulate it.
The below code give FileB a name called masterWB.
If the FileB is already opened, you will receive an alert.
Now you can manipulate FileA (using thisworkbook) and FileB(using masterWB) from FileA
Check if Workbook is opened already
You may already have FileB opened before the Macro is run, in that case you will receive an alert message if you use Workbooks.Open, this will prevent your Macro from further running.
There are some methods to test if a Workbook is already opened, below is my preferred method. This Function loop through all currently opened Workbook to see if there is a Workbook name same as the name provided in the Function argument.
Finally use the Function in the Sub in which you want to run code in FileB.
Источник
VBA Working with Workbooks (The Workbook Object)
In this Article
This guide will introduce you working with the Workbook Object in VBA.
The Workbook Object
First, in order to interact with workbooks in VBA, you must understand the Workbook Object.
With the workbook object, you can reference workbooks by their name like this:
However, this code will only work if the workbook is open. If the workbook is closed, you will need to provide the full workbook path:
Instead of typing out the full path, if your desired workbook is in the same directory as the workbook where your code is stored, you could use this line code to open the workbook:
This makes use of the ThisWorkbook object that we will discuss in the next section.
Workbook Index Number
Last, you can reference workbooks by their “Index Number”. The index number of a workbook corresponds to the order that the workbook was opened (technically its the workbook’s position in the Workbooks Collection).
This is useful if you want to do something like close the first (or last) opened workbook.
Activate Workbook, ActiveWorkbook, and ThisWorkbook
If a workbook is NOT ACTIVE, you can access the Workbook’s objects like this:
However, if the workbook is Active, you can omit the workbook object:
And if you want to interact with the workbook’s active sheet, you can also ommit the sheets object:
Activate Workbook
To activate a workbook, use the Activate Method.
Now you can interact with Book2’s object’s without explicitly stating the workbook name.
ActiveWorkbook
The ActiveWorkbook object always refer to the active workbook. This is useful if you’d like to assign the ActiveWorkbook to a variable to use later.
ThisWorkbook
The ThisWorkbook object always refers to the workbook where the running code is stored. To activate ThisWorkbook, use this line of code:
VBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro — A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Open Workbook
To open a workbook, use the Open Method:
The newly opened workbook will always become the ActiveWorkbook, allowing you to easily interact with it.
The Open Method has several other arguments, allowing you to open read-only, open a password-protected workbook, and more. It’s covered here in our article about Opening / Closing Workbooks.
Open and Assign to Variable
You can also open a workbook and assign it to a variable at the same time:
Open File Dialog
You can also trigger the Open File Dialog Box like this:
Create New (Add) Workbook
This line of code will create a new workbook:
The new workbook now becomes the ActiveWorkbook, allowing you to interact with it (ex. save the new workbook).
Add New Workbook to Variable
You can also add a new workbook directly to a variable:
Close Workbook
Close & Save
To close a workbook with saving, use the Close Method with SaveChanges set to TRUE:
Close without Save
To close without saving, set SaveChanges equal to FALSE:
Workbook Save As
The SaveAs Method is used to save a workbook as.
To save a workbook with a new name, in the same directory, you can imply use this:
where “new” is the new file name.
To save a workbook in a new directory with a specific file extension, simply specify the new directory and file name:
Other Workbook VBA Examples
Workbook Name
Protect Workbook
To protect the workbook structure from editing, you can use the Protect Method (password optional):
To unprotect a workbook use the UnProtect Method:
Loop Through all Open Workbooks
To loop through all open workbooks:
Workbook Activate Event
You can run some code whenever a specific workbook is opened with the Workbook Open Event.
Place this procedure your workbook’s ThisWorkbook Module:
This procedure will activate Sheet1 every time the workbook is opened.
VBA Code Examples Add-in
Easily access all of the code examples found on our site.
Simply navigate to the menu, click, and the code will be inserted directly into your module. .xlam add-in.
Источник
Opening
Workbooks.Open
FileName — The filename of the workbook to open
UpdateLinks — Specifies how links in the file are updated. 1 user specifies how links will be updated. 2 never update the links. 3 always update the links. If this argument is omitted, the user is (meant to be) prompted to make a choice.
ReadOnly — Opens the file as read-only
Format — If you are opening a text file this specifies the delimiter character. 1 tabs. 2 commas. 3 spaces. 4 semi-colons. 5 nothing. 6 custom character.
Password — The password required to open the workbook.
WriteResPassword — The password required to write to a write-reserved workbook
IgnoreReadOnlyRecommended — Lets you supress the read-only recommended prompt (assuming the workbook was saved with a Read-Only recommendation).
Origin — If you are opening a text file this indicates where is originated.
Delimiter — If you are opening a text file and the ‘Format’ argument is 6 then this is the custom delimiter character.
Editable — If the file is an Excel template, then true opens the specific template for editing. False opens a new workbook based on this template.
Notify — If the file cannot be opened in read/write mode, true will add the file to the file notification list.
Converter — The index of the first file converter to try when opening the file.
AddToMru — Adds the workbook to the list of recently used files.
Local — Saves the file either against the language of VBA or against the language of Excel. True is Excel language, false is VBA language.
CorruptLoad — The first attempt is normal. If Excel stops operating while opening the file, the second attempt is safe load. If Excel stops operating on the second attempt then the next attempt is data recovery.
Opening Workbooks
When a workbook is opened it automatically becomes the active workbook.
Opening
Running a macro automatically when it opens
In the (Microsoft Excel Objects > ThisWorkbook) folder, select Workbook in the top left drop-down and select Open from the top right drop-down.
This event is the default event used when you select «Workbook»
Checking if a workbook exists
Checking if a workbook is currently open
This function returns true if the workbook is currently open
Tries to assign a object variable to the workbook
If the assignment was successful then the workbook must be open
Running a macro automatically when it opens
In the (Microsoft Excel Objects > ThisWorkbook) folder, select Workbook in the top left drop-down and select Open from the top right drop-down.
This event is the default event used when you select «Workbook»
Источник
Excel VBA Workbooks.Open Method
This Excel VBA tutorial explains how to use Workbooks.Open Method to open another workbook.
Excel VBA Workbooks.Open Method
Workbooks.Open Method is useful when you try to open another Workbook using VBA. For example, you can open a workbook > format the spreadsheet > close the workbook automatically. There are a lot of rarely used arguments for Workbooks.Open Method. As most of them are self explanatory, I will demonstrate some common uses of the Method.
Syntax of Workbooks.Open Method
| Name | Required/Optional | Data Type | Description |
| FileName | Optional | Variant | String. The file name of the workbook to be opened. |
| UpdateLinks | Optional | Variant | Specifies the way external references (links) in the file, such as the reference to a range in the Budget.xls workbook in the following formula =SUM([Budget.xls]Annual!C10:C25), are updated. If this argument is omitted, the user is prompted to specify how links will be updated. For more information about the values used by this parameter, see the Remarks section. If Microsoft Excel is opening a file in the WKS, WK1, or WK3 format and the UpdateLinks argument is 0, no charts are created; otherwise Microsoft Excel generates charts from the graphs attached to the file. |
| ReadOnly | Optional | Variant | True to open the workbook in read-only mode. |
| Format | Optional | Variant | If Microsoft Excel opens a text file, this argument specifies the delimiter character. If this argument is omitted, the current delimiter is used. For more information about the values used by this parameter, see the Remarks section. |
| Password | Optional | Variant | A string that contains the password required to open a protected workbook. If this argument is omitted and the workbook requires a password, the user is prompted for the password. |
| WriteResPassword | Optional | Variant | A string that contains the password required to write to a write-reserved workbook. If this argument is omitted and the workbook requires a password, the user will be prompted for the password. |
| IgnoreReadOnlyRecommended | Optional | Variant | True to have Microsoft Excel not display the read-only recommended message (if the workbook was saved with the Read-Only Recommended option). |
| Origin | Optional | Variant | If the file is a text file, this argument indicates where it originated, so that code pages and Carriage Return/Line Feed (CR/LF) can be mapped correctly. Can be one of the following XlPlatform constants: xlMacintosh, xlWindows, or xlMSDOS. If this argument is omitted, the current operating system is used. |
| Delimiter | Optional | Variant | If the file is a text file and the Format argument is 6, this argument is a string that specifies the character to be used as the delimiter. For example, use Chr(9) for tabs, use “,” for commas, use “;” for semicolons, or use a custom character. Only the first character of the string is used. |
| Editable | Optional | Variant | If the file is a Microsoft Excel 4.0 add-in, this argument is True to open the add-in so that it is a visible window. If this argument is False or omitted, the add-in is opened as hidden, and it cannot be unhidden. This option does not apply to add-ins created in Microsoft Excel 5.0 or later. If the file is an Excel template, True to open the specified template for editing. False to open a new workbook based on the specified template. The default value is False. |
| Notify | Optional | Variant | If the file cannot be opened in read/write mode, this argument is True to add the file to the file notification list. Microsoft Excel will open the file as read-only, poll the file notification list, and then notify the user when the file becomes available. If this argument is False or omitted, no notification is requested, and any attempts to open an unavailable file will fail. |
| Converter | Optional | Variant | The index of the first file converter to try when opening the file. The specified file converter is tried first; if this converter does not recognize the file, all other converters are tried. The converter index consists of the row numbers of the converters returned by the FileConverters property. |
| AddToMru | Optional | Variant | True to add this workbook to the list of recently used files. The default value is False. |
| Local | Optional | Variant | True saves files against the language of Microsoft Excel (including control panel settings). False (default) saves files against the language of Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) (which is typically United States English unless the VBA project where Workbooks.Open is run from is an old internationalized XL5/95 VBA project). |
| CorruptLoad | Optional | XlCorruptLoad | Can be one of the following constants: xlNormalLoad, xlRepairFile and xlExtractData. The default behavior if no value is specified is xlNormalLoad and does not attempt recovery when initiated through the OM. |
Example 1 – Open a workbook
The below code opens workbook 1.xls and set the workbook as “wb” so that you can use wb to access other workbook Methods.
Example 2 – Open a workbook with password
There are two kinds of password protection – password to open the workbook, and password to modify the workbook.
In either case, if a workbook is password protected, opening the file will pop up a password box.
You can add the password argument to open the file with password automatically. If you open a non-password protected workbook but you add the password argument, you can still open the workbook.
Lets say you have a workbook 3.xlsx which is non-password protected, using the below code will still be able to open the workbook.
Example 3 – Open a workbook without alert
There are many kinds of alerts that may pop up when you open a workbook, preventing you from running the subsequent procedures. Turn off all alerts ensures you to run all the procedures successfully.
Источник
- Remove From My Forums
-
Question
-
Hello Developers
I am using following code in workbook A to open workbook B and than run some code. Issue happens when workbook B is already open. I want to check if workbook B is open than do something and if it is close than do something
dim wbdata as workbook
Set wbDATA = Workbooks.Open(ThisWorkbook.Path & «filename.xlsx»)
»»’some code that make changes to wbDATA
Thanks.
-
Edited by
Monday, May 5, 2014 6:14 PM
-
Edited by
Answers
-
Adapt the following
Sub test() Dim bWasOpen As Boolean Dim path As String, file As String Dim wb As Workbook path = ThisWorkbook.path & "" file = "filename.xlsx" If GetOrOpenWB(wb, path, file, bWasOpen) Then 'do stuff, 'when done If bWasOpen Then ' does the user want to keep it open ? Else wb.Close savechanges:=True ' or false End If 'problem to open the file, read only? End If End Sub Function GetOrOpenWB(wb As Workbook, path As String, file As String, bWasOpen As Boolean) As Boolean On Error Resume Next Set wb = Workbooks(file) On Error GoTo errH: If Not wb Is Nothing Then bWasOpen = True Else Set wb = Workbooks.Open(path & file) End If GetOrOpenWB = Not wb Is Nothing Exit Function errH: MsgBox Err.Description End Function-
Marked as answer by
zaveri cc
Friday, May 9, 2014 7:15 PM
-
Marked as answer by
EdE
Board Regular
-
#2
Hi Jill —
I am doing something similar. Here is how I do it:
Workbooks.Open FileName:= _
«file.xls», _
updatelinks:=3, WriteResPassword:=»password»
‘check to see if read only
If ActiveWorkbook.ReadOnly Then
ActiveWorkbook.Saved = True
ActiveWorkbook.Close
This assumes you have passwords on your files. The VBA should open the file and if someone else has it open, it will open as read only. It will see that, then skip save, then close. Let me know if it works for you.
EdE
-
#3
Try:
Sub Check_If_Workbook_Open()
Dim wbk As Workbook
For Each wbk In Workbooks
If wbk.Name = «Your Workbook.xls» Then
MsgBox «workbook is open»
End If
Next
End Sub
-
#4
The code I’m writing to manipulate the Excel spreadsheet is in MSAccess, so I tried…
If xl.Application.Workbooks.Name = MyFileName Then
xl.Application.Workbooks(FileName).Close
End If
But I got an error saying «Object doesn’t support this property or method.»
Any ideas?
Jill
-
#5
Good idea, but when I tried…
If xl.Application.Workbooks(FileName).ReadOnly = True Then
xl.Application.Workbooks(FileName).Close End If
But got the error «Subscript out of range» if the file was already closed.
Jill
Legacy 103420
Guest
-
#6
Try:
Sub Check_If_Workbook_Open()
Dim wbk As Workbook
For Each wbk In Workbooks
If wbk.Name = «Your Workbook.xls» Then
MsgBox «workbook is open»
End If
Next
End Sub
Thanks! This one helped me.
#littleBIGthings
-
#7
I’ve had this same issue and been working it out for days. FYI to anyone else out there, here is how I solved it:
Code:
TargetWb = "Your Workbook.xls"
For Each Workbook In Workbooks
If Workbook.FullName = TargetWb Then Workbook.Close (False)
Next Workbook
Workbooks.Open(TargetWb).ActivateHope this saves somebody the hours of aggravation I spent trying to work out an elegant solution to this.
-
#8
just for completeness, you need not to loop through workbooks to check if it is open
Code:
Sub WBG()
Dim WB As Workbook
On Error Resume Next
Set WB = Workbooks("Your Workbook.xls")
If Err Then MsgBox "The workbook is not open"
On Error GoTo 0
End Sub
-
#9
Sometimes I actually have a workbook open in the background while running a macro fetching data from it.
When the workbook is already open, I don’t want to close it. So here’s what I do:
Code:
Sub Fetch_data()
Dim WbOpen As Boolean
Dim Wb2 As Workbook, Sh2 As Worksheet
' Check if workbook is open
On Error Resume Next
Set Wb2 = Workbooks("MyWorkbook.xls")
On Error GoTo 0
If Wb2 Is Nothing Then
' If workbook was NOT open, we'll open it
' We'll use the parameter WbOpen to remember whether the workbook was open or not
Set Wb2 = Workbooks.Open("C:ExcelMyWorkbook.xls", ReadOnly:=True) ' I prefer readonly when fetching data
Set Sh2 = Wb2.Sheets("MySheet")
WbOpen = False
Else
' If the workbook was open, we'll just assign the sheet and WbOpen
Set Sh2 = Wb2.Sheets("MySheet")
WbOpen = True
End If
' Code here...
' ............
' Code ended..
' If the workbook was NOT open, we'll close it
If WbOpen = False Then Wb2.Close SaveChanges:=False
End Sub
-
#10
Jill this just work fine for me… the error handler is see if it is open it will set work workbook but if not only it is going to go to the workbook is not open
Sub Sample()
Dim BA As Workbook
On Error GoTo Handler
Set BA = Workbooks(«BA.xlsm»)
If BA.Name = «BA.xlsm» Then
MsgBox «Workook is open»
Else
Handler:
MsgBox «Workbook is closed»
End If
End Sub
I’m using Excel 97.
I wrote some VBA code that loops through all of the workbooks in a specified subdirectory and popolates each of them with data from a MS Access 97 database. It works well, but I’m stuck on one thing….
How can I check to see if a specific workbook is currently open (or closed)?
Any help would be greatly appreciated.
Thanks,
Jill
Хитрости »
4 Май 2011 93376 просмотров
Как проверить открыта ли книга?
Собственно суть темы отражена в названии. Как при выполнении кода из VBA узнать перед обращением к книге открыта она или нет? Ведь если книга закрыта, то обращение к ней вызовет ошибку, а если открывать без проверки — то это может повлечь за собой утерю данных, если предварительно эта книга не была сохранена. Ни один ни второй вариант, естественно, не устраивают. Я покажу два способа проверки через функции. Если функция вернет True — книга открыта, если False — закрыта. Для проверки функций используем проверочную процедуру Check_Open_Book:
Sub Check_Open_Book() If IsBookOpen("Книга1.xls") Then MsgBox "Книга открыта", vbInformation, "Сообщение" Else MsgBox "Книга закрыта", vbInformation, "Сообщение" 'открываем книгу Workbooks.Open "C:Книга1.xls" End If End Sub
Данная процедура вызывает функцию IsBookOpen, передавая ей в качестве параметра имя книги, «открытость» которой мы хотим проверить. Я приведу несколько вариантов самой функции IsBookOpen. Во всех вариантах действует один и тот же принцип: код любого из вариантов функции IsBookOpen необходимо скопировать и вставить в стандартный модуль. Модуль должен быть внутри той книги, в кодах которой планируется проверять открыта ли книга. Только тогда IsBookOpen будет доступна для вызова из любого кода этой же книги.
Если вдруг в момент выполнения на строке If IsBookOpen(«Книга1.xls») Then появится ошибка «Sub or function not defined» — значит функция IsBookOpen либо не была скопирована в стандартный модуль, либо она вообще не в стандартном модуле, а в модуле листа, формы или книги.
Вариант 1:
Function IsBookOpen(wbName As String) As Boolean Dim wbBook As Workbook For Each wbBook In Workbooks If wbBook.Name <> ThisWorkbook.Name Then If Windows(wbBook.Name).Visible Then If wbBook.Name = wbName Then IsBookOpen = True: Exit For End If End If Next wbBook End Function
Функция просматривает все открытые книги и если находит среди них книгу с указанным именем, то функция возвращает True. Есть небольшая особенность — функция исключает скрытые книги(это либо надстройки, либо PERSONAL.XLS). Так же из просмотра исключена та книга, в которой расположен сам код. Если Вам нужно проверить наличие книги независимо от её видимости, то необходимо просто заменить блок
If Windows(wbBook.Name).Visible Then If wbBook.Name = wbName Then IsBookOpen = True: Exit For End If
на одну строку(просто убрать лишнее условие проверки)
If wbBook.Name = wbName Then IsBookOpen = True: Exit For
Либо можно использовать
Вариант 2:
Function IsBookOpen(wbName As String) As Boolean Dim wbBook As Workbook: On Error Resume Next Set wbBook = Workbooks(wbName) IsBookOpen = Not wbBook Is Nothing End Function
Данный способ обращается к любой открытой книге, даже если она скрыта как PERSONAL.XLS или надстройка. Однако у данной функции есть недостаток — используется оператор On Error и если в настройках VBA(Tools —Options -вкладка General) установлено Break on All Errors — то этот код не сработает, если книга не открыта — получим ошибку. В то время как Вариант1 с циклом по всем открытым книгам сработает без ошибок.
Вариант 3:
По просьбам читателей решил добавить код, который проверяет открыта ли книга независимо от её месторасположения и используемого приложения Excel. Книга может быть открыта другим пользователем (если книга на сервере), в другом экземпляре Excel или в этом же экземпляре Excel.
Function IsBookOpen(wbFullName As String) As Boolean Dim iFF As Integer, retval As Boolean iFF = FreeFile On Error Resume Next Open wbFullName For Random Access Read Write Lock Read Write As #iFF retval = (Err.Number <> 0) Close #iFF IsBookOpen = retval End Function
Функция несколько отличается от приведенных выше — передается в неё не только имя книги, а полный путь к книге, включая имя и расширение:
Sub Test() MsgBox "Файл 'Книга1'" & IIf(IsBookOpen("C:Книга1.xls"), " уже открыт", " не занят") End Sub
Или более близкий к жизненной ситуации вариант: надо открыть книгу, внести в книгу изменения, сохранить и закрыть. Если книга кем-то уже открыта — получим ошибку на этапе сохранения или запрос на этапе открытия. Поэтому сначала проверяем доступность книги и если она доступна — вносим изменения и сохраняем.
Sub Test() Dim sWBFullName As String Dim wb As Workbook 'полный путь к проверяемой книге sWBFullName = "C:DocumentsКнига1.xls" 'если книга кем-то открыта - пропускаем обработку этой книги 'книга закрыта - вносим изменения, сохраняем, закрываем If IsBookOpen(sWBFullName) = False Then Set wb = Application.Workbooks.Open(sWBFullName) 'изменяем значение ячейки "A1" на первом листе книги wb.Sheets(1).Range("A1").Value = "www.excel-vba.ru" ws.Close True End If End Sub
При использовании функции IsBookOpen так же надо учитывать, что она может посчитать книгу открытой не только если она реально кем-то открыта, а если к ней просто нет доступа(например, заблокирован доступ со стороны администратора и т.п.).
Также см.:
Как получить данные из закрытой книги?
Как узнать существует ли лист в книге?
Как узнать существует ли модуль в книге
Статья помогла? Поделись ссылкой с друзьями!
Видеоуроки
Поиск по меткам
Access
apple watch
Multex
Power Query и Power BI
VBA управление кодами
Бесплатные надстройки
Дата и время
Записки
ИП
Надстройки
Печать
Политика Конфиденциальности
Почта
Программы
Работа с приложениями
Разработка приложений
Росстат
Тренинги и вебинары
Финансовые
Форматирование
Функции Excel
акции MulTEx
ссылки
статистика
Открыта или закрыта книга Excel? Проверяем с помощью кода VBA по краткому или полному имени файла, используя объектную переменную, цикл или оператор Open.
Проверка по краткому имени
Способ проверки по краткому имени, открыта ли рабочая книга, позволяет определить состояние проверяемой книги в том же экземпляре приложения Excel, в котором открыта книга с проверяющим кодом.
Использование объектной переменной
Вариант пользовательской функция VBA Excel, предназначенной для проверки, открыта или закрыта рабочая книга, путем определения результата присвоения ссылки на нее объектной переменной. Присвоение состоялось (BookOpenClosed = True) – книга открыта, произошла ошибка и присвоение не состоялось (BookOpenClosed = False) – книга закрыта.
|
Function BookOpenClosed(wbName As String) As Boolean Dim myBook As Workbook On Error Resume Next Set myBook = Workbooks(wbName) BookOpenClosed = Not myBook Is Nothing End Function |
Аргумент функции:
- wbName – краткое имя проверяемой рабочей книги.
Перебор открытых книг циклом
Этот вариант функции BookOpenClosed перебирает с помощью цикла все открытые книги Excel и проверяет их краткие имена на совпадение с кратким именем проверяемой книги. Совпадение найдено (BookOpenClosed = True) – книга открыта, совпадение не найдено (BookOpenClosed = False) – книга закрыта.
|
Function BookOpenClosed(wbName As String) As Boolean Dim myBook As Workbook For Each myBook In Workbooks If myBook.Name = wbName Then BookOpenClosed = True Exit For End If Next End Function |
В коллекцию Workbooks входят и скрытые книги, в том числе Личная книга макросов, и книга с функцией.
Проверка по полному имени
Проверка по полному имени с помощью оператора Open позволяет узнать, открыта ли рабочая книга каким-либо другим процессом: текущим экземпляром Excel, в котором открыта книга с проверяющим кодом, другим экземпляром Excel или сторонним приложением.
|
Function BookOpenClosed(wbFullName As String) As Boolean Dim ff As Integer ff = FreeFile On Error Resume Next Open wbFullName For Random Access Read Write Lock Read Write As #ff Close #ff BookOpenClosed = (Err.Number <> 0) End Function |
Аргумент функции:
- wbFullName – полное имя проверяемой рабочей книги.
Эта функция открывает с помощью оператора Open файл проверяемой книги с разрешением чтения и записи (параметр access) и запретом чтения и записи, если этот файл уже открыт другим процессом (параметр lock).
Если файл уже открыт другим процессом, а указанный тип доступа (параметр access) не разрешен (параметр lock), операция открытия завершится с ошибкой, а выражение (Err.Number <> 0) возвратит значение True.
Примеры проверки состояния книги
По краткому имени
|
Sub Primer1() If BookOpenClosed(«Книга1.xlsx») Then MsgBox «Книга открыта» Else MsgBox «Книга закрыта» End If End Sub |
По полному имени
|
Sub Primer2() If BookOpenClosed(«C:Папка1Папка2Папка3Книга1.xlsx») Then MsgBox «Книга открыта» Else MsgBox «Книга закрыта» End If End Sub |