Содержание
- Оператор между. и
- Синтаксис
- Замечания
- Пример
- См. также
- Поддержка и обратная связь
- Using «Between» in VBA? (1 Viewer)
- connexion
- ColinEssex
- connexion
- dcx693
- connexion
- Contact US
- Come Join Us!
- Posting Guidelines
- Is there a BETWEEN function?
- Is there a BETWEEN function?
- Is there a BETWEEN function?
- RE: Is there a BETWEEN function?
- RE: Is there a BETWEEN function?
- RE: Is there a BETWEEN function?
- RE: Is there a BETWEEN function?
- RE: Is there a BETWEEN function?
- RE: Is there a BETWEEN function?
- RE: Is there a BETWEEN function?
- RE: Is there a BETWEEN function?
- Quote:
- Red Flag Submitted
- Reply To This Thread
- Posting in the Tek-Tips forums is a member-only feature.
- Between…And operator
- Syntax
- Remarks
- Example
- See also
- Support and feedback
Оператор между. и
Применяется для: Access 2013 | Access 2016
Определяет, соответствует ли значение выражения указанному диапазону значений. Используйте этот оператор в инструкциях SQL.
Синтаксис
expr [ Not ] Междузначением1изначением2
Синтаксис оператора между. и состоит из следующих элементов:
| Часть | Описание |
|---|---|
| expr | Выражение, определяющее поле с данными, которые вы хотите оценить. |
| значение1, значение2 | Выражения, по которым требуется оценить expr. |
Замечания
Если значение expr находится между значениями value1 и value2 (включительно), значение Между. Оператор And возвращает значение True; В противном случае возвращается значение False. Вы можете включить логический оператор Not для оценки противоположных условий (т.е. находится ли значение expr вне диапазона, определяемого value1 и value2 ).
Вы можете использовать оператор между. и для определения того, находится ли значение поля в указанном числовом диапазоне. В примере ниже определяется, доставлен ли заказ до места в диапазоне указанных почтовых индексов. Если почтовый индекс находится в диапазоне между 98101 и 98199, функция IIf возвращает «Local» . В противном случае возвращается «Nonlocal» .
Если expr, value1 или value2 имеет значение Null, Между. Возвращает значение NULL .
Так как подстановочный знак, например, * , всегда рассматриваются как литералы, вы не сможете использовать их с оператором между. и. Например,вы не можете использовать 980* и 989* для поиска почтовых индексов, которые начинаются с 980-989.
Вместо этого, у вас есть две основные альтернативы для решения данной задачи. Вы можете добавить выражение к запросу, который оставляет три символа текстового поля и использовать оператор между. и для этих символов. Или вы можете использовать высокие и низкие значения с дополнительными символами, в этом случае от 98000 до 98999 или от 98000 до 98999-9999 при использовании расширенных почтовых индексов. (Необходимо опустить значение — 0000 из низких значений, так как в противном случае значение 98000 удаляется, если некоторые почтовые индексы имеют расширенные разделы, а другие — нет.)
Пример
В данном примере перечислены имена и контактные данные каждого клиента, разместившего заказ во втором квартале 1995 года.
В этом примере вызывает процедуре EnumFields, которую можно найти в приведенном примере инструкции SELECT.
См. также
Поддержка и обратная связь
Есть вопросы или отзывы, касающиеся Office VBA или этой статьи? Руководство по другим способам получения поддержки и отправки отзывов см. в статье Поддержка Office VBA и обратная связь.
Источник
Using «Between» in VBA? (1 Viewer)
connexion
Registered User.
Hi there,
this is just a quickie i’m sure.
I have used «Between» to indicate if a value is between two other values in queries for ages, and i know that i can use it with «WHERE» in an SQL string, BUT
When i just want to use it in an «If» statement Access doesn’t want to play?
If *** BETWEEN **** then
OR
If *** BETWEEN **** = true then
Anyone know the secret?
ColinEssex
Old registered user
Use the instead.
If Age >16 and Age
connexion
Registered User.
Thanks so far, but.
Hi Colin,
Thanks for that but i’m already doing that and just wanted to trim the code down by a few lines. It seems strange that you can’t use «BETWEEN» in VBA to find out if a value is between two others?
Here’s what i’m using so far.
Set rstSageData = CurrentDb.OpenRecordset(«SELECT * FROM tblSageData ORDER BY AccountRef ;»)
If rstSageData.RecordCount > 0 Then
With rstSageData
.MoveFirst
Do While Not .EOF
.Edit
If Val(!DaysOverdue) >= «0» Then
If Val(!DaysOverdue)
«The Shoe»
dcx693
Registered User.
«The Shoe»
connexion
Registered User.
So is «BETWEEN» possible then?
The table is being created specifically to pull together data from a whole load of places, including other Access tables, Sage Line 50 tables etc.
The table is created specifically to deal with aged debt and is renewed each time it is required.
Certain values are calculated and stored in the table so that as the table is built the data remains static, to be viewed and commited to print in word.
. so is «BETWEEN» a No-No then?
«The Shoe»
basically what we’re saying is to do this
UPDATE table set FIELDNAME=VALUE where DaysOverDue >=0
Источник
Thanks. We have received your request and will respond promptly.
Come Join Us!
- Talk With Other Members
- Be Notified Of Responses
To Your Posts - Keyword Search
- One-Click Access To Your
Favorite Forums - Automated Signatures
On Your Posts - Best Of All, It’s Free!
Posting Guidelines
Promoting, selling, recruiting, coursework and thesis posting is forbidden.
Is there a BETWEEN function?
Is there a BETWEEN function?
Is there a BETWEEN function?
Tried to find one, I know its simple enought to create, but I’m trying to get away from creating everything from scratch and dont want to use the IIf() function.
Looking to see if an equivalent function exists that mimics the keyword «Between» in queries.
If I have a number X, I want to know if it lies somewhere in the bounds of range A through B. For example:
Is 234 higher than 13 and less than 100? No
Is 55 higher than 13 and less than 100? Yes
The values Im using are calculated KEY_ID values that don’t exist in a table yet, and Im testing to prevent an overlap. This is the reason Im not using queries.
I don’t need to know HOW to write the code, just need to know if it already exists since I cant find one.
RE: Is there a BETWEEN function?
RE: Is there a BETWEEN function?
Seriously though, while indeed Select Case — in this case (pun intended) — does exactly what you are asking about (and seems to me the way to go). what is your problem with using IIf?
Option Explicit
Function CheckIt(TestMe As Long) As String
CheckIt = IIf(TestMe > 13 And TestMe RESULT? «No, it is not»
End Sub
Sub YaddaYadda2()
Dim j As Long
j = 55
MsgBox CheckIt(j) RESULT? «Yes, it is»
End Sub
Option Explicit
Function CheckIt(TestMe As Long, _
Bottom As Long, _
Top As Long) As String
CheckIt = IIf(TestMe > Bottom And TestMe RESULT? «No, it is not»
«A little piece of heaven
without that awkward dying part.»
advertisment for Reese’s Peanut Butter Cups (a chocolate/peanut butter confection)
RE: Is there a BETWEEN function?
Since no one has come right out and said «YES!» I’ll just assume it doesn’t exist.
PHV:
I’ll give you a star since the simplicity of a SELECT CASE statement never crossed my mind. thanks.
As I said I wasn’t looking for a solution, was just tired of making code when something already existed (my last fiasco was creating a function that mimics the RegExp class in Excel :P. never knew it was out there already)
For anyone looking for another solution to the problem, I put this together to use:
Function IsBetween(hTestValue As Long, hRngMIN As Long, hRngMAX As Long) As Boolean
If (hTestValue >= hRngMIN) And (hTestValue fumei:
To answer your question, code execution/optimization is the reason. Everything that I’ve read talks about using plain old IF over the IIf(). I never bothered with using it before, but my last few projects have been big enough that I’ve been trimming anywhere I can. Even fractional seconds add up. If you search for code optimization you can see what I mean. The explanation usually given is that if you use an IF/THEN/ELSE statement, the code only has to execute one path, the True or False (based on your logic test). Whereas IIf(), Choose() and Switch(), all paths have to be evaluated because they are functions.
Its along the same lines as assigning vbNullString over «» (empty string) X = vbNullString. something about when using «», the system has to evaluate the entire length of the data type (10 bytes + number of characters used)? before it can determine if the value is an empty string.
While using IIf() looks more elegant and conserves space, I’ll take optimization.
Thanks for the inputs!
RE: Is there a BETWEEN function?
Public defaultLowerLimit As Integer
Public defaultUpperLimit As Integer
Public Sub Main()
defaultLowerLimit = 13
defaultUpperLimit = 100
MsgBox IsBetween(234)
MsgBox IsBetween(55)
Public Function IsBetween(value As Integer, Optional lowerLimit As Variant, Optional upperLimit As Variant) As Boolean
If (IsMissing(lowerLimit)) Then lowerLimit = defaultLowerLimit
If (IsMissing(upperLimit)) Then upperLimit = defaultUpperLimit
IsBetween = (lowerLimit
RE: Is there a BETWEEN function?
>all paths have to be evaluated because they are functions
I’m guessing all paths have to be evaluated IF they are functions; if they are Constants (as in Gerry’s examples)they are already evaluated.
RE: Is there a BETWEEN function?
DaveInIowa:
Good point. I overlooked that direct assignment. Code already updated. Thanks.
HughLerwill:
Maybe someone knows more on the IIf() etc. (Im certainly not the expert), but everything I’ve read so far talks about dumping IIf for optimization (especially in queries).
RE: Is there a BETWEEN function?
Option Explicit
‘ if the paramters are NOT dynamic
Function IsBetween(num As Long) As Boolean
IsBetween = IIf(num > 13 And num ‘ if the paramters ARE dynamic
Function IsBetween2(num As Long, _
Bottom As Long, _
Top As Long) As Boolean
IsBetween2 = IIf(num > Bottom And num = hRngMIN) And _
(hTestValue Bottom And num both truepart (the -1), and falsepart (the 0).
So yeah, I can see why you are trying to avoid IIf if you are doing this a lot.
But, as was stated, PHV’s Select Case is probably the easiest way to do it.
«A little piece of heaven
without that awkward dying part.»
advertisment for Reese’s Peanut Butter Cups (a chocolate/peanut butter confection)
RE: Is there a BETWEEN function?
Quote:
Red Flag Submitted
Thank you for helping keep Tek-Tips Forums free from inappropriate posts.
The Tek-Tips staff will check this out and take appropriate action.
Reply To This Thread
Posting in the Tek-Tips forums is a member-only feature.
Click Here to join Tek-Tips and talk with other members! Already a Member? Login
Источник
Between…And operator
Applies to: Access 2013 | Access 2016
Determines whether the value of an expression falls within a specified range of values. Use this operator within SQL statements.
Syntax
expr [ Not ] Between value1 And value2
The Between…And operator syntax has these parts:
| Part | Description |
|---|---|
| expr | Expression identifying the field that contains the data you want to evaluate. |
| value1, value2 | Expressions against which you want to evaluate expr. |
If the value of expr is between value1 and value2 (inclusive), the Between…And operator returns True; otherwise, it returns False. You can include the Not logical operator to evaluate the opposite condition (that is, whether expr lies outside the range defined by value1 and value2 ).
You might use Between…And to determine whether the value of a field falls within a specified numeric range. The following example determines whether an order was shipped to a location within a range of postal codes. If the postal code is between 98101 and 98199, the IIf function returns «Local» . Otherwise, it returns «Nonlocal» .
If expr, value1, or value2 is Null, Between…And returns a Null value.
Because wildcard characters, such as * , are treated as literals, you cannot use them with the Between…And operator. For example, you cannot use 980* and 989* to find all postal codes that start with 980 to 989.
Instead, you have two alternatives for accomplishing this. You can add an expression to the query that takes the left three characters of the text field and use Between…And on those characters. Or you can pad the high and low values with extra characters—in this case, 98000 to 98999, or 98000 to 98999-9999 if using extended postal codes. (You must omit the — 0000 from the low values because otherwise 98000 is dropped if some postal codes have extended sections and others don’t.)
Example
This example lists the name and contact of every customer who placed an order in the second quarter of 1995.
This example calls the EnumFields procedure, which you can find in the SELECT statement example.
See also
Support and feedback
Have questions or feedback about Office VBA or this documentation? Please see Office VBA support and feedback for guidance about the ways you can receive support and provide feedback.
Источник
-
#1
Hi there,
this is just a quickie i’m sure.
I have used «Between» to indicate if a value is between two other values in queries for ages, and i know that i can use it with «WHERE» in an SQL string, BUT
When i just want to use it in an «If» statement Access doesn’t want to play?
If *** BETWEEN **** then
OR
If *** BETWEEN **** = true then
etc…etc…etc..
Anyone know the secret?
Vince
-
#2
Use the < or > instead.
If Age >16 and Age <32 Then
Do Something
Else
Don’t
End If
Col
-
#3
Thanks so far, but…
Hi Colin,
Thanks for that but i’m already doing that and just wanted to trim the code down by a few lines. It seems strange that you can’t use «BETWEEN» in VBA to find out if a value is between two others?
Here’s what i’m using so far…
Set rstSageData = CurrentDb.OpenRecordset(«SELECT * FROM tblSageData ORDER BY AccountRef ;»)
If rstSageData.RecordCount > 0 Then
With rstSageData
.MoveFirst
Do While Not .EOF
.Edit
If Val(!DaysOverdue) >= «0» Then
If Val(!DaysOverdue) < «10» Then
!ChaseLetter = «1»
End If
End If
etc…etc…etc…
finishing up with updating the table…
.Update
.MoveNext
Loop
End With
Else
End If
-
#4
why not peform that check in the where clause (criteria) of the query..
-
#5
Kodo said:
why not peform that check in the where clause (criteria) of the query..
In fact, why not just use an update query? But then again, I’d ask why you’re storing a calculated number in your table.
-
#6
dcx693 said:
In fact, why not just use an update query? But then again, I’d ask why you’re storing a calculated number in your table.
.
-
#7
So is «BETWEEN» possible then?
The table is being created specifically to pull together data from a whole load of places, including other Access tables, Sage Line 50 tables etc.
The table is created specifically to deal with aged debt and is renewed each time it is required.
Certain values are calculated and stored in the table so that as the table is built the data remains static, to be viewed and commited to print in word.
…so is «BETWEEN» a No-No then?
Vince
-
#8
basically what we’re saying is to do this
UPDATE table set FIELDNAME=VALUE where DaysOverDue >=0 <10
between is only valid in SQL for dates.
-
#9
Kodo said:
basically what we’re saying is to do this
UPDATE table set FIELDNAME=VALUE where DaysOverDue >=0 <10
between is only valid in SQL for dates.
Actually, you can use Between for non-dates. Use a syntax like this:
Code:
UPDATE tblSageData SET ChaseLetter = 1 WHERE (([DaysOverdue] Between 0 And 10));
-
#10
learn something new every day…
-
#11
Kodo said:
learn something new every day…
Happens to me everyday!
-
#12
I’ve attempted to use > x and < y in a select statement and it isn’t working? Suggestions? The code follows:
Select Case IsNumeric(CCValue)
Case Is = True
Select Case CCValue
Case Is = 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 24
cc = cc & «:00 am»
Case Is >= 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6
cc = cc & «:00 pm»
Case Is >= 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23
cc = (cc — 12) & «:00 pm»
-
#13
Wow, you’ve resurrected an 18-year-old thread.» Impressive!
Case Statements are a slightly special case… Try the following syntax
Code:
Case 7 to 11, 24
Case 1 to 6
Case 13 to 23
-
#14
Between is NOT limited to dates. But it is limited to SQL. It is not a VBA command.
Jon
Access World Site Owner
-
#15
Does this work….?
Code:
Select Case IsNumeric(CCValue)
Case Is = True
Select Case CCValue
Case 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 24
cc = cc & ":00 am"
Case 1 To 6
cc = cc & ":00 pm"
Case 13 To 23
cc = (cc - 12) & ":00 pm"
End Select
End Select
-
#16
Code:
? Eval("27 Between 10 AND 40")
-1Between would be usable in VBA, but surely that’s pretty bad style.
-
#17
Since I had a copy of the MS VBA Language Specification (v20140424, release date 30 Apr 2014), I did a simple search. At no time anywhere in that document is the word «BETWEEN» used in the context of a formal operator. All uses of «BETWEEN» (74 of them) are in discussions of the semantics of other syntax constructs. Therefore, I confirm Pat’s statement. BETWEEN is not a VBA operator unless it was added in a more recent release, and I have no evidence of such a change.
-
#18
Does this work….?
Code:
Select Case IsNumeric(CCValue) Case Is = True Select Case CCValue Case 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 24 cc = cc & ":00 am" Case 1 To 6 cc = cc & ":00 pm" Case 13 To 23 cc = (cc - 12) & ":00 pm" End Select End Select
Yes, the post of, Minty, AWF VIP, worked well: «Case 7 to 11, 24». It’s an honor to have your guidance. I have the ambition of being like all of you.
-
#19
Since I had a copy of the MS VBA Language Specification (v20140424, release date 30 Apr 2014), I did a simple search. At no time anywhere in that document is the word «BETWEEN» used in the context of a formal operator. All uses of «BETWEEN» (74 of them) are in discussions of the semantics of other syntax constructs. Therefore, I confirm Pat’s statement. BETWEEN is not a VBA operator unless it was added in a more recent release, and I have no evidence of such a change.
Thanks for the research. Forcing the use of ‘Between’ in the VBA context, when it is meant to dwell only in Query-SQL-land, is a bad idea.
-
#20
Code:
? Eval("27 Between 10 AND 40") -1Between would be usable in VBA, but surely that’s pretty bad style.
Creative. Square pegs do fit in round holes after all.


-
- #1
Dim Age, Milage, Radius, NCB As Integer
Age = ThisWorkbook.Sheets(«Sheet1»).Cells(9, 2).ValueIf Age = 45 Then ThisWorkbook.Sheets(«Sheet1»).Cells(9, 3).Value = 1
If Age = (46 <= 50) Then ThisWorkbook.Sheets(«Sheet1»).Cells(9, 3).Value = 0.95
If Age = (51 <= 54) Then ThisWorkbook.Sheets(«Sheet1»).Cells(9, 3).Value = 0.89
If Age = (55 <= 65) Then ThisWorkbook.Sheets(«Sheet1»).Cells(9, 3).Value = 0.87
If Age = (66 <= 69) Then ThisWorkbook.Sheets(«Sheet1»).Cells(9, 3).Value = 0.95This should be easy but I can’t seem to solve it, How do I get the Age ranges to work between 46 and 50, 51 and 54 etc. The one for 45 works fine but every other number I enter into Cell 9, 2 brings back 0.95 as its under 69.
Thanks
Em -
- #2
Re: VBA Code Between Two Values
Hi. Try:
If Age = > 46 And age <= 50 Then
an so on
-
- #3
Re: VBA Code Between Two Values
Select Case should do this.
Dim Age, Milage, Radius, NCB As Integer Age = ThisWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet1").Cells(9, 2).Value Select Case Age Case < 45 Case = 45 ThisWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet1").Cells(9, 3).Value = 1 Case <= 50 ThisWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet1").Cells(9, 3).Value = 0.95 Case <= 54 ThisWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet1").Cells(9, 3).Value = 0.89 Case <= 65 ThisWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet1").Cells(9, 3).Value = 0.87 Case <= 69 ThisWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet1").Cells(9, 3).Value = 0.95 End SelectDisplay More
-
- #4
Re: VBA Code Between Two Values
Thanks Omp65, I’ve only just started writing Vba code and finding it confusing. They should just have a between sign!
-
- #5
Re: VBA Code Between Two Values
There is a ‘between’…
Sub x() Dim i As Integer Randomize Timer i = Int(Rnd() * 10) Select Case i Case 1 To 5 MsgBox "1 to 5" Case Is < 7 MsgBox "< 7" Case 8, 10 MsgBox "8 or 10" Case Else MsgBox "something else" End Select End SubDisplay More
INTELLIGENT WORK FORUMS
FOR COMPUTER PROFESSIONALS
Contact US
Thanks. We have received your request and will respond promptly.
Log In
Come Join Us!
Are you a
Computer / IT professional?
Join Tek-Tips Forums!
- Talk With Other Members
- Be Notified Of Responses
To Your Posts - Keyword Search
- One-Click Access To Your
Favorite Forums - Automated Signatures
On Your Posts - Best Of All, It’s Free!
*Tek-Tips’s functionality depends on members receiving e-mail. By joining you are opting in to receive e-mail.
Posting Guidelines
Promoting, selling, recruiting, coursework and thesis posting is forbidden.
Students Click Here
Is there a BETWEEN function?Is there a BETWEEN function?(OP) 21 Jul 09 11:38 Tried to find one, I know its simple enought to create, but I’m trying to get away from creating everything from scratch and dont want to use the IIf() function. Looking to see if an equivalent function exists that mimics the keyword «Between» in queries. If I have a number X, I want to know if it lies somewhere in the bounds of range A through B. For example: Is 234 higher than 13 and less than 100? No The values Im using are calculated KEY_ID values that don’t exist in a table yet, and Im testing to prevent an overlap. This is the reason Im not using queries. I don’t need to know HOW to write the code, just need to know if it already exists since I cant find one. Red Flag SubmittedThank you for helping keep Tek-Tips Forums free from inappropriate posts. |
Join Tek-Tips® Today!
Join your peers on the Internet’s largest technical computer professional community.
It’s easy to join and it’s free.
Here’s Why Members Love Tek-Tips Forums:
Talk To Other Members
- Notification Of Responses To Questions
- Favorite Forums One Click Access
- Keyword Search Of All Posts, And More…
Register now while it’s still free!
Already a member? Close this window and log in.
Join Us Close
-
Excel Howtos
Between Formula in Excel [Quick Tips]
-
Last updated on June 24, 2010
Chandoo
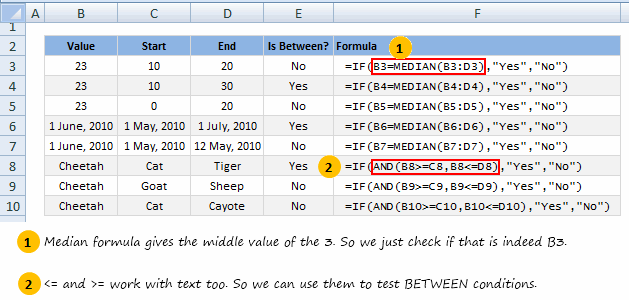
In today’s quick tip, lets find how to check for between conditions in Excel using formulas, like this:
Between Formula in Excel for Numbers:
Lets say you have 3 values in A1, A2 and A3. And you want to find out if A1 falls between A2 and A3.
Now, the simplest formula for such a thing would be test whether the conditions A1>=A2, A1<=A3 are both true. Hence, it would look like,
=if(AND(A1>=A2,A1<=A3),"Yes", "No")
However, there are 2 problems with a formula like above:
1. It assumes that A2 is smaller than A3.
2. It is just too big.
Shouldn’t there be a shorter and simpler formula?!?
Well, there is. Last week when chatting with Daniel Ferry, he mentioned a darned clever use of MEDIAN formula to test this. It goes like,
=if(A1=MEDIAN(A1:A3),"Yes","No")
Now, not only does the above formula look elegant and simple, it also works whether A2 is smaller or larger than A3.
Between Formula in Excel for Dates:
Well, dates are just numbers in Excel. So you can safely use the technique above to test if a given date in A1 falls between the two dates in A2 and A3, like this:
=if(A1=MEDIAN(A1:A3),"Yes","No")
Between Formula for Text Values:
Lets say you want to find-out if the text in A1 is between text in A2 and A3 when arranged alphabetically, a la in dictionary. You can do so in Excel using,
…
wait for it…
…
that is right, <= and >= operators, like this:
=if(AND(A1>=A2,A1<=A3),"Yes", "No")
Between Formulas in Excel – Summary and Examples:
Here is a list of examples and the corresponding Excel Formulas to test the between condition.
Do you check for Between Conditions in Excel?
Checking if a value falls between 2 other values is fairly common when you are working with data. I would love to know how you test for such conditions in excel? What kind of formulas do you use?
Share using comments.
Recommended Excel Formula Tutorials:
- Check for Either Or conditions in Excel
- Find out if 2 ranges of dates overlap using formulas
- Get my Excel Formulas e-Book, learn 75 most used formulas overnight
Share this tip with your colleagues

Get FREE Excel + Power BI Tips
Simple, fun and useful emails, once per week.
Learn & be awesome.
-
208 Comments -
Ask a question or say something… -
Tagged under
and(), between formula, Excel 101, if() excel formula, Learn Excel, logical operators in excel, median() formula, Microsoft Excel Formulas, quick tip, spreadsheets, using excel
-
Category:
Excel Howtos

Welcome to Chandoo.org
Thank you so much for visiting. My aim is to make you awesome in Excel & Power BI. I do this by sharing videos, tips, examples and downloads on this website. There are more than 1,000 pages with all things Excel, Power BI, Dashboards & VBA here. Go ahead and spend few minutes to be AWESOME.
Read my story • FREE Excel tips book



Excel School made me great at work.
5/5

From simple to complex, there is a formula for every occasion. Check out the list now.

Calendars, invoices, trackers and much more. All free, fun and fantastic.

Power Query, Data model, DAX, Filters, Slicers, Conditional formats and beautiful charts. It’s all here.

Still on fence about Power BI? In this getting started guide, learn what is Power BI, how to get it and how to create your first report from scratch.
- Excel for beginners
- Advanced Excel Skills
- Excel Dashboards
- Complete guide to Pivot Tables
- Top 10 Excel Formulas
- Excel Shortcuts
- #Awesome Budget vs. Actual Chart
- 40+ VBA Examples
Related Tips
208 Responses to “Between Formula in Excel [Quick Tips]”
-
Clever use of MEDIAN, but it returns «Yes» if you use the upper or lower number. Whether you want to consider 20 as being «between» 10 and 20 is up to you.
Also, the examples made it harder to understand. In the first formula you use A1:A3 for the range, but the first picture looks like the formula is filled across rows, not columns.
-
@JP —
MEDIAN can be used regardless of your definition of «between.» To include the boundary points, I would write it like this:
.
=A1=MEDIAN(A1:A3)
.
To exclude them:
.
=A1=MEDIAN(A1,A2+1,A3-1)
.
Regards,
Daniel Ferry
excelhero.com-
Lucky says:
Hi I want to find out the difference in two numbers. But if the second number is minus it should not turn into plus in the results. Could you tell me the formula for it. Example (21.32)(-6.37) MY expectation to get the difference in between these two numbers. The answer should be 14.95. I do not hope the answer as 27.69. The actual mathematical answer that turn the second minus into plus and adds together. But excel always give me the second answer but please tell me the formula for the first answer. The deference between the numbers. Thanks
-
@Lucky
=21.32-abs(-6.37)
or
=Abs(A1)-Abs(A2)
-
-
-
Rob says:
Daniel —
your formula to exclude the boundary points would only work if you’re dealing strictly with integers. For example, if you test if 19.5 is between 10 and 20 using A1=MEDIAN(A1,A2+1,A3+1), it would fail.
Rob
-
Rob says:
I should clarify…I think it’s a very creative use of MEDIAN and if you’re testing numbers and want to include the end points, it’s a simpler method, but you need to use the other style using just instead of = to properly not include end points.
Rob -
Rob says:
darn…should have known my greater than and less than characters would be removed.
Meant to say you need to use the and() style test using just less than and greater than characters without the equal signs.
Rob -
cALi says:
I tried it using spanish MEDIANA(…) function, but it didn’t work. This is what I did, not such stylish, but it works fine: =IF(AND(A1=MIN(B1:C1)),»YES»,»NO»).
cALi
-
@Rob —
You bring up a good point that I should have clarified. When using the method I shared above to exclude the boundary points, the user is responsible for the precision. I have used this technique for years with operations scheduling and task management, often with a precision of days. However, I have used it with finer precision, hours, minutes, seconds. Again this is totally up to the user; he can use whatever value he wants instead of the integers of one:
.
=A1=MEDIAN(A1,A2+1/24,A3-1/24)
.
=A1=MEDIAN(A1,A2+1/24/60,A3-1/24/60)
.
=A1=MEDIAN(A1,A2+1/24/60/60,A3-1/24/60/60)
.
…of course those constants could/should be replaced by defined names.
.
Taking this to the extreme, one could easily define a constant that equals the smallest positive value that Excel can represent:
.
spv: =2.229E-308
.
We can then write the formula as:
.
=A1=MEDIAN(A1,A2+spv,A3-spv)
.
…which will work for any possible decimal value between the boundary points. It’s a robust and elegant solution, imo.Regards,
Daniel Ferry
excelhero.com -
cALi says:
Sorry, when copying and pasting, I should made some mistake, this is real one:
=IF(AND(A1=MIN(B1:C1)),»YES»,»NO»)A1: tested in Between Value
B1 and C1: limits -
cALi says:
I suppose HTML is in conflict with the code. Same code, different order of the arguments in the AND function:
=IF(AND(A1>=MIN(B1:C1),A1<=MAX(B1:C1)),»YES»,»NO») -
David says:
The formula =IF(A1=MEDIAN(B1:C1),»Yes»,»No») does not work when I tested it. It returns «No» for any value in A1, regardless if it falls between B1 and C1 or not.
-
@cALi —
I have no experience with the Spanish version of Excel, but I would be very surprised to learn that the worksheet functions differed in their outputs! Can you provide the exact formula (in Spanish) that did not work for you?
.
On a different note, here is an equivalent formula to yours, that does not use the AND() function, nor the IF() function:
.
=A1=MIN(MAX(A1:B1),MAX(B1:C1))
.
BTW, your formula (and hence my variation of it) has the characteristic where «between» includes the lower boundary point, but not the higher one. This can be altered in a similar fashion as my above example.
.
Regards,
Daniel Ferry
excelhero.com -
@Daniel —
We can also do both.For example, I created a data validation in cell H2 consisting of «True,False» values. (That is, True and False without quotes).
This formula would then allow you to toggle the output as exclusive or inclusive of the start and end numbers by changing the value in H2 (True means exclude, False means include):
=B3=MEDIAN(B3,C3+N(H2),D3-N(H2))
-
@JP —
That’s it!
Imagine the nested IF monster that you just avoided! Good job.
That is why I am always going on about better solutions to haplessly using IF(), when one understands the problem.
.
Regards,
Daniel Ferry
excelhero.com -
cALi says:
@Daniele
Thanks for your time, I made some mistake since testing both alternatives I received the same results:
=An=MIN(MAX(An:Bn),MAX(Bn:Cn))
=An=MEDIAN(An:Cn)Indeed, your solution is not just elegant but also practical, I could name it «minimalist».
Best regards,
cALi -
@David.. you have to include A1 as well to get it right. Like this,
=IF(A1=MEDIAN(A1,B1,C1),”Yes”,”No”)
-
sam says:
@ JP Instead of True/False use 1,0, we can then drop the N()
=B3=MEDIAN(B3,C3+H2,D3-H2)
-
Tim Buckingham says:
Turned into UDF for kicks
Function ISBETWEEN(Rng, num1, num2) As Boolean
‘ Checks if value between num1 and num2
Dim Low As Double, Hi As DoubleISBETWEEN = False
Low = Application.Min(num1, num2)
Hi = Application.Max(num1, num2)If Rng Is Nothing Then Exit Function
If Rng = Application.WorksheetFunction.Median(Rng, Low, Hi) Then ISBETWEEN = TrueEnd Function
I like how easy it is to read when wanting to count the values that fall between using
=COUNTIF(Rng,ISBETWEEN(Rng,Num1,Num2))
-
Gerald Higgins says:
I think the use of the MEDIAN function is very clever.
Nitpicking now.
If I understand correctly, Daniel’s suggestion for an amendment to exclude the =boundaries case as in
=A1=MEDIAN(A1,A2+1/24,A3-1/24)
assumes that all the numbers involved are positive.
If one or both of the boundary numbers are negative, I think this formula will produce wrong results for values of A1 just outside the true boundary range.Also, this formula
=A1=MIN(MAX(A1:B1),MAX(B1:C1))
works as long as the C1 value is higher than the B1 value, but not the other way round, which was described asa fault in the OP.
This formula solves that particular problem (it’s essentially the same as cALi’s)
=AND(A1MIN(B1:C1))
Replace < with <= as required. -
Gerald Higgins says:
Sorry, lost symbols in my last post.
I’ll try again.
The last formula should be
=AND(A1 (less than symbol) MAX(B1:C1),A1 (greater than symbol) MIN(B1:C1)) -
elad says:
CooL :)))) very elegant solution !
-
Guest says:
Great use of the function — I will be using this.
As always though, formulaic results are only as good as the data on which they’re based (it’s spelled «coyote» instead of «cayote,» so your last text example should actually read yes. 🙂
Not to nitpick….but to nitpick… 🙂 -
@sam —
«Instead of True/False use 1,0, we can then drop the N()»
That’s true, but who’s going to understand that? If your users can, they’re much smarter than mine.
-
[…] the problem is similar to between formula trick we discussed a few days back, yet very […]
-
[…] Between Formula in Excel, Chandoo presents some formulas for determining if a given value is in between two known […]
-
Daniel’s spv approach does not work because the spv addon never makes it into the mantissa of the floating point numbers.
Regards,
Bernd -
@Bernd —
With all due respect, you should double check that.
-
Daniel,
Excel 2010 (version 14.0.4760.1000 32 bit), spv set to 2.229E-308, A1 = 1, A2 = 1, A3 = 2, result A1=MEDIAN(A1,A2+spv,A3-spv) = True (should be False).
Again, if I am not mistaken, the very small value does not make it into the mantissa of the MEDIAN parameters which will then lead to MEDIAN(1,1,2) = True.
Regards,
Bernd -
Daniel,
I do like the spv idea. My suggestion to fix the mantissa issue would be something like this:
=A1=MEDIAN(A1,A2+POWER(10,INT(LOG10(A2))-14),A3-POWER(10,INT(LOG10(A3))-14))
But this is sort of a monster formula again. Maybe two functions InfInc and InfDec (for infinitesimal increase / decrease) should be introduced which return the smallest float greater than the input (resp. the greatest float which is smaller).
Regards,
Bernd -
@Bernd —
.
Touche.
.
While the formula logic is correct, Excel does not handle the very, very small number correctly in this instance. Good bug catch.
.
As I mentioned above, I have used the MEDIAN method countless times, but usually with dates, but also to the precision of hours, minutes, and seconds. I’ve never actually tried to use it with such fine precision before. I should have tested it before commenting, as Murphy’s Law always prevails.
.
After testing I discovered that 1E-14 is the finest precision where my idea does work. To be sure, this will work in virtually every situation, as this is a very small number:
.
0.00000000000001
.
In fact, this is exactly what your POWER/LOG formula results in. So there is no need to use the monster formula.
.
Instead of defining spv as the smallest possible value (in Excel) we can simply enter it’s definition as:
.
=1e-14
.
and now spv can stand for the smallest possible value (handled correctly). -
Daniel,
I am sorry, but — no, you cannot take an absolute 1e-14. Please note that my POWER/LOG formula flexibly adjust itself to the number in question:
For 1 it’s 1e-14, for 10 it’s 1e-13, for 100 it’s 1e-12, …
It will exactly impact on the lowest digit of the mantissa. Please note that it can be different for the two MEDIAN border parameters. Please see my example at
http://www.sulprobil.com/html/test_if_between_2_values.html
Regards,
Bernd -
Rick Rothstein (MVP — Excel) says:
There is always this purely mathematical method for determining if a value (A1) is between two limits (A2 and A3) excluding the end points…
=If(ABS(A1-((A2+A3)/2)).LT.ABS(A3-A2)/2,»Yes»,»No»)
To make it include the end points, change the less than to less than or equal….
=If(ABS(A1-((A2+A3)/2)).LE.ABS(A3-A2)/2,»Yes»,»No»)
Note that I used (with the surrounding dots) .LT. for the «less than» symbol and .LE. for the «less than or equal» symbol. Now, the only thing I am unsure of is how to adjust this for the spv that was brought up in the latter comments… anyone want to take a stab at it?
-
Rick,
Your ABS approach makes perfect sense for small numbers (ASCII code) or floats that are in the same ball park.
But test the values 0, 1, 2, 3, …, 9 on the border values 1e16 and 5 with .LT. and with .LE.
The ABS approach gets it horribly wrong here because the lower border value 5 gets off the mantissa when added or subtracted to or from 1e16.
Regards,
Bernd -
Rick Rothstein (MVP — Excel) says:
@Bernd,
While it is possible, of course, I would not normally expect a test for inclusion within a range to have such wildly divergent end points for the range.
-
Rick,
Why risk anything if you can only lose? If I deal with floating point numbers of unknown size and if I need to know whether a number is between two others I would use neither the MEDIAN approach nor the ABS approach.
I think it’s far more important to know the basics about floating point numbers than to know this MEDIAN «trick» or the ABS comparison:
http://docs.sun.com/source/806-3568/ncg_goldberg.html
Regards,
Bernd -
Debbie says:
Thanks for posting…! Worked perfectly for what I needed!!!
-
sanjeev khendi says:
i want to if function/ if total sales 200000 ,then com rate =5% give me information how to solve it with example
-
Hui… says:
@Sanjev
Assuming you are entering this in the cell representing Com Rate
=if(sum(sales range)>=200000,5%,10%)
10% is the value for Com Rate if sales -
cALi says:
@Sanjev
Using Daniel Ferry approach about IF function, which I have embraced as mine:C D E
Lower Limit Upper Limit Commission Rate
? -
cALi says:
@Sanjev
Using Daniel Ferry approach about IF function, which I have embraced as mine:C D E
Lower Limit Upper Limit Commission Rate
4 Range1 — 100,000.00 0%
5 Range2 100,000.00 200,000.00 2%
6 Range3 200,000.00 1,000,000.00 5%
7 Range4 1,000,000.00 1E+100 6%
8
9 Actual Sales 180,000.00
Comm. Rate 2% =SUMPRODUCT((C4:C7 -
cALi says:
@ Chandoo, really sorry for the mess, the text editor is definitely not my friend… this will be my last chance, I hope it works…
@ Sanjeev,
Using Daniel Ferry IF function approach, and using some dummy data:A B C D
Lower Limit Upper Limit Commission Rate
3 Range1 — 100,000.00 0%
4 Range2 100,000.00 200,000.00 2%
5 Range3 200,000.00 1,000,000.00 5%
6 Range4 1,000,000.00 1E+100 6%
7 Actual Sales 180,000.00
8 Comm. Rate 2% =SUMPRODUCT((B3:B6?$B$7)*($B$7?C3:C6)*D3:D6)Please replace ‘?’ with ‘less than or equal to’ and ‘?’ with ‘less than’ proper operators.
By the way, C6 is a dummy value, is ‘upper infinite’ to make this approach work.Regards,
cALi -
[…] Between Formula in Excel […]
-
KM says:
Sales Achievement
15,001 — 20,000 EL
20,001 — 50,000 E
50,001 — 100,000 D
100,001 — 160,000 C
160,001 — 240,000 B
240,001 & above AIf the sales achievement fall in between 50,001-100,000 is under Class D, can you help if i have many column of acheivement data which fall under different class. How can i set the formula in one time?
-
@KM
Are your Ranges in 1 Column or 3
ie: is 15,001 – 20,000 in 1 cell or 3 cells -
I want drop my serial no continuous automatically from the input value
e.g I have list of TV I given code for that
TV001
TV002
TV003
THEN I START ADDING BIKE
BIKE001
BIKE002
AGAIN I WANT ADD TV FROM PREVIOUS NUMBER CONTINUATION
LIKE
TV004
TV005
again i want add bike003 cotinuation from last number
IS THERE ANY FORMULAS FOR THAT?
PLEASE SEND THIS TO MY EMAIL ADDRESS sent to mani.n@govasool.com -
Antony says:
i have a problem: i have 2 rows, A1 and A2 are containing ID which are same. B1 has to be compared with B2 and B3, and if B1 falls between them then it should tell «YES» else «NO». How will I do this????
-
@Antony
Assuming B2 <= B3 then use:
=IF(AND(B1>=B2,B1<=B3),»Yes»,»No») -
@ Hui,
I have precisely the same situation as @KM has (in comment 40). I have the values in three colums («range begin», «range end», «category»). I need to find out in which range a given value lies and fetch the corresponding category. Help pls. -
Sid says:
How do I use to it see if a time value is between 2 values
Example if 09:18:24 is between 09:18:00 and 09:19:00 -
Sid,
.
Exactly the same way!
.
Assume your times are in these cells:
.
A1 = 09:18:24
A2 = 09:18:00
A3 = 09:19:00
.
The formula from any other cell will determine if 09:18:24 is between the other two values:
.
=A1=MEDIAN(A1:A3)-
Michael says:
How can I make it tell me if the current time and date is between two other times and dates.
I am working with the following:
Lets say that the time right now is Thursday at 4 PM. How would this work out?
Thursday: 11:00 AM — 2:00 AM (Friday)Then imagine that the current time is Friday at 1 AM.
Thanks!!!!
-
@Michael
=MEDIAN(DATE(2012,12,10)+TIME(11,0,0), DATE(2012,12,11)+TIME(16,0,0), DATE(2012,12,12)+TIME(18,0,0)) = DATE(2012,12,11)+TIME(16,0,0)
Adjust Dates/Times to suitor
=MEDIAN(A1, A2, A3)=A1
where A1 is the Date/Time now
A2 & A3 are the other dates/times-
Michael says:
Thanks for your help.
I’m a little unsure how to interpret your answer….
Also, where would I insert the following?
«DATE(2012,12,day(today()))+TIME(Hour(now()),minute(now()),second(now()))»
I think I would substitute this in at the end of your answer’s equation for the «= DATE(2012,12,11)+TIME(16,0,0)» part, so that my equation will always work… right? thanks again!!!
-
The Format is:
=Median(Start Date, End Date, Now)=Now
it doesn’t matter what order the components go
so:
=Median(Now, End Date, Start Date)=Now
is Just as valid
If you use the Now() function that already includes the date & time
So you can use
=Median(Start Date+Time, End Date+Time, Now())=Now()
=MEDIAN(DATE(2012,12,13)+TIME(11,0,0),DATE(2012,12,14)+TIME(2,0,0), Now())=Now()
or if you want to use Today
eg: 11am today until 2am tomorrow
=MEDIAN(Int(Now())+Time(11,0,0),Int(Now()+1)+TIME(2,0,0), Now())=Now()
-
-
-
-
-
msog says:
Daniel,
I’m quite confused by the results I’m receiving when trying this formula. I’m using it to try to validate if a date is between two other dates using the «short date» format. I receive «NO» all statements except for the exact middle date (which is what the median actually is, mathematically speaking). Is there something wrong with my formula that prevents me from getting any date between the two values?
Formula: =IF(A1=MEDIAN($E$1:$F$1),»YES», «NO»)
Thanks in advance
-
amal says:
Hi,
I need help:
A2 contains name of staff
C2 contains his weight
I need to fill D2 with Lean, Fit, Fat or Obese base on which range his weight fits in based on below grid:
50-60: Lean
60-70: Fit
70-80: fat
80-100: obese -
Jesus Rodriguez says:
Is there a list of the different symbols and what they represent, or what function they have when used in a formula? Example: = (equal to), < (greater than), etc.
Actually, what I’d like to know, it’s if there is a symbol that represents “between”. Let’s say I want a formula like this: =IF(A1betweenA2andA3,”Yes”,”No”).
Thank you in advance,
Jesus R -
Jesus R
There are only a few symbols useable in this context
X > Y, X Greater than Y
X < Y, X Less than Y
X = Y, X equal to YThey can be combined
X >= Y, X Greater than or equal to Y
X <= Y, X Less than or equal to YX <> Y, X not equal to Y
you can often use other Excel functions to make other logic
or(X=Y , Z=A), X=Y or Z=A will force this to be true
and(X=Y , Z=A), X=Y and Z=A both have to be True for this to be TrueThe above can be used in numerous ways to create quite complex logic
-
Shishir says:
There are a problem
I requered to the formula for example below
A1 B1 C1
A+++ A +++
A++ A ++
A+ A +
A AKindly suggest me the formula for that in write segment.
Thanks
-
@Shishir
.
Not sure but try the following
B1: =Left(A1,1)
C1: =Right(A1,Len(a1)-1)
Select B1 + C1
Copy down -
aa aa says:
Hello, nice topic.. It’s clear to use between value when there s just one.. how d you determine where the values in a range fall between in another range.. lets say I have a list goes like
1-5 100
6-13 200
14-32 300
what I want s to expand the list like
1- 100
2- 100
…
6- 200
…Guess first I need to find where the tax number fall between , then I ll reference to the cell just aside of that range.
Need help, thenks in edvance
-
neha says:
Dear All,
Plz help in formating the «if formula» in excel of the below condition
Less than 95% = 0
95.01% to 97.5% = 0.06
97.51% to 100% = 0.12
100.01% to 102.5% = 0.18
102.51% to 105% = 0.25 -
@Neha
Try this:
=IF(A1<=95%, 0, IF(A1<=97.5%, 0.06, IF(A1<=100%, 0.12, IF(A1<=102.5%, 0.18, 0.25))))
.
or this odd one
=CHOOSE( MIN( INT((( A1-95.001%)/2.5%)) + 2,5), 0, 0.06, 0.12, 0.18, 0.25) -
How about adding an else statement to this
=if(AND(A1>=A2,A1<=A3),»Yes», «No»)So if cell A1 is empty I the result will be a blank cell or an entry of my choosing.
-
Here is a better way of explaining what I’m looking for
Can you add an ELSE statement to this: =if(AND(A1>=A2,A1<=A3),»Yes», «No»)What I need is to be able to return a null value if cell A1 doesn’t have any data in it yet
-
@Jmichuck
=IF(A1<>"",IF(AND(A1>=A2,A1<=A3),"Yes", "No"),"Null")
Retype all » characters -
neha says:
Dear hui,
I have tried your suggested logic but it didn’t work.Err.502 come while putting it.Plz.help me out -
@Neha
Did you try:
=IF(A1<=0.95, 0, IF(A1<=0.975, 0.06, IF(A1<=1, 0.12, IF(A1<=1.025, 0.18, 0.25)))) -
neha says:
hai Hui Thanxxxxxxxxxx.a lot dear……….it works.With this i finally complited my report which need to submit by tomorrow.Thanks once again.
-
Thank you, but there seems to be an error in the formula.
By the way, thank you so much for your services. This will impress the boss for sure.
-
What do you mean by «Retype all ” characters»?
-
oK you literally mean they have to be re-typed. Strange but it worked. Thank you very much
-
Sometimes WordPress converts the » characters to something that looks like a » but isn’t
When you copy/paste to excel, excel doesn’t understand what those » look-like characters are
And returns an error
-
-
baum schausberger says:
problem. how to use ABS and IF here: (9-5)/2+9=11 but 11>9 so I need 11-9 = good. how to do this.
-
=if((9-5)/2+9<11,11-((9-5)/2+9),(9-5)/2+9) )
-
Pradhish says:
nice use of median. just what was i looking for, but i would appreciate if you could extend the number of rows it checks for inclusion. for eg in the sample data you posted,
http://chandoo.org/img/f/between-formula-in-excel.pngi wish to find out if «22» falls under range B2:C9. (Assuming «Value» is in cell A1). kindly help me with this since the only solution i can think of is using nested functions which makes it a monster formula..
-
thnks hui. now I got your formula =sqrt(A1^2+A2^)-1-IF(sqrt(A1^2+A2^2)-1>53,53,0) work good, now if it is possible, beside this I really need also in the same formula to use ABS value and ROUND, because I got negative numbers, and so many decimals, so to eliminate I need to use those functions, thank you.
-
neha says:
@ Dear Hui
there is a condition —
15001 — 20000 = Grade «C»
20001 — 50000 = Grade «B»
50001 — 100000 = Grade «A»
100001 & Abiove = Grade +A
I have used your earlier formula with some modification i.e.
=IF(A2<=20000,»c»,IF(A2<=50000,»b»,IF(A2<=100000,»a»,»a+»)))
it works but I also want with the change of grade colour of the cell is also changed for eg Grade A comes with green backgroung & grade C comes with Red background & like wise.
I tried conditional formatting but yet no appropriate result comes.
Plz help. -
@Neha
You will need to add 3 CF Rules and have them in the right order
Select your Range I am assuming B2:B10
Enter 3 CF Rules using formulas
CF1: =$A2<=20000 CF Color X, Stop If true Yes
CF2: =$A2<=50000 CF Color Y, Stop If true Yes
CF3: =$A2<=100000 CF Color Z, Stop If true Yes
Now apply this
Apply a Default Color which will be applicable if the score is Greater than 100000
That should be it
Make sure that the 3 CF’s are in the order above, you can shift them up/down once entered -
Shishir says:
Dear all
I want to
A B C
BP03/44/00/12FC BP03/44/00/12 FC
BP03/44/00/21SF BP03/44/00/21 SFKindly suggest me how i will do by using the formulas.
Thanks & Regards
Shishir-
B1: =Left(A1,Len(A1)-2)
C1: =Right(A1,2)
Copy both down
-
-
Sonal says:
Dear all
on dated 10/01/1012i make a excel sheet. If after the day like tomorrow or day after tommorow somebody modify any cell indicate in a seperate colour which cell somebody modity. which formula i use for that. Kindly suggest me.
ThanksSonal
-
walt says:
Vlookup is an excellent formula to find «between» values:
Table:
Value Multiplier
Column A Column B
0.00001 0.5
4.826369861 1
9.652739721 1.5
14.47910958 2
19.30547944 2.5
24.1318493 3
28.95821916 3.5
33.78458902 4
38.61095888 4.5
43.43732875 5
48.26369861 5.5
53.09006847 6Lookup value (cell A1) -> 3
vlookup(A1,$A$1:$B$12,2,TRUE) — will result in 0.5.Hope this helps.
-
Gaurav says:
Hi, can someone help me how to write this function in Excel.
There are 100 rows of 3 diferent numbers (so, 100 rows, 3 columns, C1, C2, C3).
I have to do the following:
If C1, C2 and C3 are equal to 2, 4, and 5 respectively, then answer should be 1
If C1 and C2, or C2 and C3, or C3 and C1 are able to match 2&4, or 4&5 or 5&2 respectively, [i.e, if two of the 3 entries match correctly] then answer should be 0.5
If none of C1, C2, C3 match 2,4,5 respectively, then answer should be 0.Thanks
-
Jessie says:
I’m a complete noob at Excel Formulas. I’ve been trying to increase my knowledge of excel but I can’t seem to find how to create this formula.
I have an employee that works from 6:00am to 2:30pm. She takes a 30 minute lunch and has two paid 15 minute breaks. At the end of the day she has 7.5 hours of productivity. The problem is some days she works in as many as 8 different queues. I have to record those times in each queue but at the end of the day her hours should not be more than 7.5. In a perfect world she’d work in one queue for 6-2:30pm and a simple formula would work to get 7.5 hours but that’s not the case. She may work 2 hours in one queue, 1 in another, 3 in another and 2 in another. How do I factor her breaks and her lunch in my formula. She goes to break at 8:30am, lunch at 12:00-12:30 and last break at 1:45.
Also some other factors, employees working 4-6 hours get on break. 7 hours a lunch and break, 8-12 hours is lunch and two breaks. employees can’t work more than 12 hours in a day. I hope someone can help. I’m lost. Here’s one formula I was using. but sometimes my hours go above 7.5. =IF(SUM(D23-C23),(24*MOD(D23-C23,1.25)-LOOKUP(24*MOD(D23-C23,1.25),{0,4,4.5,5,5.5,6,6.5,7,7.5,8,8.5,9-
Jessie says:
sorry, I left that formula incomplete.
=IF(SUM(D23-C23),(24*MOD(D23-C23,1.25)-LOOKUP(24*MOD(D23-C23,1.25),{0,4,4.5,5,5.5,6,6.5,7,7.5,8,8.5,9,9.5,10},{0,0.5,0.5,0.5,0.5,0.5,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1})),»»)
-
-
I am using this formula have a formula in cell E1 =IF(A1″»,IF(AND(A1>=C1,A1<=D1),»PASS»,»FAIL»),» «)
When I ener a value in cell A1, I get a pass/fail or null returned in cell E1.
I would like to also place a value into B1 but have that take priority over A1.
So If I was to only have an value in A1 the formula would work as stated above. If I was to place a value in Cell B1 it would then disregard cell A1 and return pass/fail based on input in B1.Hope that makes sense. Thank you
-
@Jmichuck
like:
=IF(B1<>"","B1 not empty" ,IF(A1 ="", IF(AND (A1>=C1, A1<=D1), "PASS", "FAIL"), ""))you will have to retype all the » marks
-
Hui,
Thank you but not quite correct. I would like the formula to take the value of A1 & B1 and evaluate if they fall between the values of C1 & D1. If so then I would get either a PASS/FAIL result. If there is a Value in B1 then it would disregard the value in A1. If both A1 and B1 are Empty then the cell with the formula would remain empty.
Thank you so much for looking into this. I really appreciate it.
-Chuck
-
-
jmichuck,
Here’s one way:
=CHOOSE(1+(INDEX(A1:B1,(LEN(B1)>0)+1)>=C1)*(INDEX(A1:B1,(LEN(B1)>0)+1)<=D1)+(LEN(A1&B1)=0)*2,"Fail","Pass","")
…or in the spirit of Chandoo’s article:
=CHOOSE(1+(INDEX(A1:B1,(LEN(B1)>0)+1)=MEDIAN(INDEX(A1:B1,(LEN(B1)>0)+1),C1,D1))+(LEN(A1&B1)=0)*2,"Fail","Pass","")
Regards,
Daniel Ferry
Excel MVP-
Daniel,
Thank you very much. That worked out perfectly
-
OK one thing. If cells A1 thru D1 have no values, I would like to see the cell with the formula to be null/empty. Currently with the formulas above I will get #VALUE or #REF!
Thanks again
-
Sorry the second formula returns #NUM! not #REF!
-
jmichuck,
To satisfy this further requirement is easy for the first formula (we just add another null at the end:
=CHOOSE(1+(INDEX(A1:B1,(LEN(B1)>0)+1)>=C1)*(INDEX(A1:B1,(LEN(B1)>0)+1)<=D1)+(LEN(A1&B1)=0)*2,"Fail","Pass","","")
You would need to trap the condition with an IF() or IFERROR() wrapper on the second formula, so for your requirements I’d go with this formula directly above, even though I made the MEDIAN() suggestion to Chandoo in the first place!
-
Looks like its working perfectly. Thank you!
-
-
-
-
Murray says:
Since Excel stores date/times as numbers, using median will only work if the times you are actually in the range.
This stumped me for a bit.
If I want to check that «01/12/1972 9:15AM», is between «9:00AM» and «10:00AM», the median formula won’t work. You need to check if its between «01/12/1972 9:00AM» and «01/12/1972 10:00AM»
Does anyone have an idea on how to quickly check if the date:time is between two times (with no date).
-
@Murray
Use median with the times
but instead of the date use
Date-Int(Date)-
Murray says:
@Hui
Can you give an example? The date:time is in one cell.
-
Murray says:
Oh, thanks Hui. I see what you mean now. Thanks again.
-
=MEDIAN(TIME(9,0,0),A1-INT(A1),TIME(10,0,0))
or
=IF(MEDIAN(TIME(9,0,0),A1-INT(A1),TIME(10,0,0))=A1-INT(A1),TRUE,FALSE)
the second will return True if it is between 9-10am
-
-
-
-
In excel 2010 I need a formula If a cell is blank > 21 days send an email.
Many thanks in advance!
-
Tara says:
I find this string very interesting and helpful. I am not sure I followed all of it, so if this has already been answered, I apologize.
Here is what I have:
Cell A1: =Today()
Column B: List of Dates by Week ending — Begins with 2/19/12
Column E: Percent completedI need a formula that will look at cell A1, determine which cell would apply in column B, and then populate the percentage from column E.
Any help would be greatly appreciated.
-
Tara says:
I realized that I can do this with a simple VLOOKUP. So, based on the information in my previous post:
=VLOOKUP(A1,B2:E52,4)
In the past, I had only used VLOOKUP to find exact matches, so I did not realize that for the range_lookup I could either use TRUE, or omit the criteria, and find the closest match.
Sometimes the simplest things elude us, so I just thought I would share this for anyone else who might be searching.
-
-
shishir says:
HI,
A B C D
1 ABC Y2 ACB Y Y ACB
3 CAB Y
4 CBA Y Y CBA
5 BCA Y Y BCA
I get THE VALUE OF COLUMN D BY USING IF, AND & INDEX FRMULA.THE PROBLEM IS I WANTED TO CONTINUE THE VALUE OF D LIKE WITHOUT ANY BLANK IN ROW (D1=ACB; D2=CBA; D3=BCA). KINDLY SUGGEST WHICH FUNCTION I USE.
-
Krystian says:
Hi
I wonder if someone could help me with this. How can I check if time beetween a and b fall in between the time c and d?
Thank you in advance
Krystian
-
Krystian says:
Following previous question: to be more specific, I need to check whether the time between 09:17:00 and 09:58:00 falls between the time 09:35:00 and 09:45:00?
Any help would be really appreciated
-
where here, and how, is possible to upload a vba code, I need to add some condition more to the code but I don’t know how to do it.
-
Syl says:
I have two excel documents I’m trying to use a look up formula to see compare the peoples names on both of the documents but I can’t seem to have any luck. I have used vlookups before and never had to dealed with text. any help will be appreciate it! and just I’m new on excel.
-
I’d like to use conditional formatting to highlight the rows where today’s date falls between various dates in a column but all those different dates need to be the range of plus 6 weeks.
Am I on the right tack with this?
CF1:=(today’s date=MEDIAN(DATEfirst cell/+DAY(42)CF color yello, stop IF true yes
-
sixseven says:
THis trick just saved me a ton of time. I used absolute references for two of the numbers instead of a range.
-
Rick January says:
I want to use a conditional formula as follows. If the result of a calculation produces a number less than -0.3 return a value. If the number is between -0.3 and +0.3 return a second value. If the number is greater than +0.3 return a third value. I tried this formula
=IF(E25<-0.3,»corrosive»,IF(E25>0.3,»scaling»,»balanced»)) and variationsHowever, it returns «corrosive» even if the calculated number is -0.3 and «scaling» when the number is +0.3.
-
Boppa says:
Hi All,
I am trying to find formula for the below scenario.
I have a object id and start date in spread sheet 1 and object id, 3 start date and 3 end dates for the same object in another spread sheet. I want to findout for which record in spread sheet 2 the start date of the spread sheet fall inbetween.
Sheet 1
53205649
8/3/2012Sheet 2
53205649
7/1/2012
12/31/999953205649
7/1/2011
6/30/201253205649
7/31/2010
6/30/2011Any help is much appreciated.
Boppa
-
Nitesh says:
Guys, I work in middle east & they have two calendars here.. one islamic calendar (lunar one) & second is Gregorian. I need to know if any specific date falls between two dates, then it automatically converts in islamic month/ date. I have already made a calendar which have first & last dates (gregorian dates) of any islamic month. Can anybody help me??
Thanks a lot in advance.
-
Alam says:
hi. it worked just like charm..
but applying it seems it works only with three columns….for example
column 1 (data)
column 2 data
column 3 (data)
column5 (value)If(column5=median(column1,2,3),»yes», ‘no’)
than this formula doesnt work…
do u think u can find anyothe way -
Juls says:
Hi there,
I have tried your formula for a project plan. Basically, if the date at the top of the row is equal to or inbetween a start or end date (located in the first two columns), I want it to write «YES» into the calendar — so I know a task is running on that date. Kind of like a Gantt chart.
However, this formula does not recognise that the 2nd of October is between the 1st and the 5th, and no formula I tried so far recognised the 1st is between the 1st and the 5th.
Any ideas?
-
[…] Click here for more Excel home works, quizzes & challenges. Clue: Click here for a clue. Got […]
-
Tan says:
The conditional formatting does not work along with the AND function in Office 2007. Is this only for 2010?
-
@Tan
I can confirm that both Conditional Formatting and And() functions work in Excel 2007, 2010 and 2013.
If you have a specific issue or problem post a question at the Chandoo.org Forums: http://chandoo.org/forums/?new=1
-
-
GatesIsAntichrist says:
Bravo! I simply could not make it to the end of all the posts above so forgive me if already covered:
Below I will show that
— the contiguous sequence A1,A2,A3 is not required, neither row-wise or column-wise.
— Furthermore, A1 can be a formula, not just a cell.
— So can A2 and A3!So you can hardcode 95% and 105% for A2 and A3; or Make A2 98% of something, etc.
Assuming notation X for one general cell address (or formula!) and Y and Z for the pair to go between where Y <= X <= Z,
=if(X=median(X,Y,Z),»yes»,»no») or minimally
X=median(X,Y,Z)Example: =if(C3-C2=median(C3-C2,$E$1,$F$1),»yes»,»no»)
where $E$1 is 95 and $F$1 is 105This capitalizes on the characteristic of ranges that you can build ranges noncontiguously with commas. You aren’t legally bound to that colon, you know, ha ha.
1. Correct me if I was imprecise about endpoint inclusion.
2. I saw some concern above about negative numbers. I have not tried to test that, much less an exhaustive bulletproofing.
3. floating point «epsilon» issues may still apply.
4. Tested only with XL2003 (because you’re crazy to use any later disastrous version, unless forced to do so) -
Mark R says:
Could somebody help me with the below formula?
I basically want it to sum column D but based on the criteria of column C……..i’m trying to ask the formula to look between codes 50000 and 60000……but this formula doesn’t work for me — what can I use instead of median to look between these codes?=SUMIFS(D8:D15,C8:C15,MEDIAN(50000:60000))
Many thanks in advance!
-
Clinton says:
Just wanted to say thanks so much for the tip on using Median. Saved me a lot of extra typing. Was working on a list of unit counts referencing a tiered pricing schedule. I utilized the following and it worked like a charm even though the counts and unit price schedule were in two different worksheets. Cheers!
=IF((B2+C2/5)=MEDIAN((B2+C2/5),Sheet3!$B$3:$C$3),Sheet3!$D$3,(IF((B2+C2/5)=MEDIAN((B2+C2/5),Sheet3!$B$4:$C$4),Sheet3!$D$4,(IF((B2+C2/5)=MEDIAN((B2+C2/5),Sheet3!$B$5:$C$5),Sheet3!$D$5,(IF((B2+C2/5)=MEDIAN((B2+C2/5),Sheet3!$B$6:$C$6),Sheet3!$D$6,(IF((B2+C2/5)=MEDIAN((B2+C2/5),Sheet3!$B$7:$C$7),Sheet3!$D$7,(IF((B2+C2/5)=MEDIAN((B2+C2/5),Sheet3!$B$8:$C$8),Sheet3!$D$8,(IF((B2+C2/5)=MEDIAN((B2+C2/5),Sheet3!$B$9:$C$9),Sheet3!$D$9,(IF((B2+C2/5)=MEDIAN((B2+C2/5),Sheet3!$B$10:$C$10),Sheet3!$D$10,(IF((B2+C2/5)=MEDIAN((B2+C2/5),Sheet3!$B$11:$C$11),Sheet3!$D$11,(IF((B2+C2/5)=MEDIAN((B2+C2/5),Sheet3!$B$12:$C$12),Sheet3!$D$12,IF((B2+C2/5)=MEDIAN((B2+C2/5),Sheet3!$B$13:$C$13),Sheet3!$D$13,(IF((B2+C2/5)=MEDIAN((B2+C2/5),Sheet3!$B$14:$C$14),Sheet3!$D$14,(IF((B2+C2/5)=MEDIAN((B2+C2/5),Sheet3!$B$15:$C$15),Sheet3!$D$15,0)))))))))))))))))))))))) -
Sumeet says:
Just a note of thanks. Due to this thread was able to solve a issue very quickly
-
JAYANT says:
=IF(A2=15, «OK», «Not OK»,IF(A2=15, «OK», «Not OK»,IF(A2=15, «OK», «Not OK»,IF(A2=15, «OK», «Not OK»,IF(A2=15, «OK», «Not OK»,IF(A2=15, «OK», «Not OK»,IF(A2=15, «OK», «Not OK»,IF(A2=15, «OK», «Not OK»,IF(A2=15, «OK», «Not OK»,IF(A2=15, «OK», «Not OK»,IF(A2=15, «OK», «Not OK»,)))))))))))
-
Not OK!
Hi Jayant.. is this supposed to be a question? If so, please note that the formula gives an error.
-
-
=(A1-A2)*(A1-A3)<=0
or
=(A1-A2)*(A1-A3)<0-
@Kirill.. good idea. Thanks for sharing.
-
-
Magda says:
Hi,
I need help.
I have 2 tables;
1) Dates Column A and prices column B
2) Date ranges column M and prices column QI need a formula which will do the following
— Identify if date in column A falls within the rangefrom column M
— If the answer is positive then I need a price from column Q to deduct a price from column BAny ideas?
Thanks
-
ericb says:
the median stuff saved my bacon. you rock!
-
lucyolsen says:
=(A3=MEDIAN(A1:A5))*(COUNTIF(A1:A5,A3)=1)
-
lucyolsen says:
Sorry, I mean
=A1=MEDIAN(A1:A3)*(COUNTIF(A1:A3,A1)=1)Also, if you put () around the first statement, it returns a 0 or 1 rather than true/false.
-
lucyolsen says:
…that doesn’t work for testing the number 0.
but these should work for an entire range of numbers, not just 2:
=MIN(A3:A16)=A1)
=MIN(A3:A16)A1)-
lucyolsen says:
try again…
[=(MIN(A3:A16)=A1)]
[=(MIN(A3:A16)A1)]-
lucyolsen says:
one more time (damn html tags)
{} are used in place of less/greater than
=MIN(A3:A16){=A1*(MAX(A3:A16)}=A1)
=MIN(A3:A16){A1*(MAX(A3:A16)}A1)
-
-
-
-
-
Richard K says:
This helped me figure out the basis to a formula to tell me if a number was between a set of numbers OR if it exceeded the top end of the numbers… Excel would not except the formula using the MEDIAN, probably since you are actually evaluating for three conditions.
=IF(AND($D17>5000,$D1710000), «Excessive», «No»))
Thanks for the assist on this =D
-
@Richard
Try: =IF(MEDIAN(5000,$D17,10000)=$D17,»No»,IF($D17>10000,»Excessive»,»Lower»))
-
-
Prasad TR says:
I have situation, where Find number in between A:A to B:B, if find the number then put the value of Cell column of «C»
Ex:-
what to find the number 24
Column A B i have numbers
A — B — C
1 — 5 — ram
8 — 10 — Ramesh
18 — 20 — David
23 — 31 — AbdulOut put / Answer = Abdul
Please suggest.-
@Prasad TR
=Vlookup(24,A2:C5,3)
-
-
Gigi says:
If number in cell M11 is between 500 and 1000 true value «DFG» but if the number is between 1001 and 1500,true value «ABC» but if the number is between 1501 and 5000, true value «ERT»
-
@Gigi
You could use something like:
=IF(B2<1000,»DFG»,IF(B2<1500,»ABC»,IF(B2<5000,»ERT»,»Other»)))
or
=IFERROR(CHOOSE(INT(B2/500),»DFG»,»ABC»,»ERT»,»ERT»,»ERT»,»ERT»,»ERT»,»ERT»,»ERT»,»Other»),»Other»)
-
-
Daniel S. Crisan says:
I have a relatively simple question (i assume) but due to the fact that I am an Excel newbie, it is relatively challenging for me.
Let us say that I am using 2 cells. Cell A1 & Cell A2
I want to be able to input any random number from 0-665 in cell A1
If the number in A1 is 15 but 20 but 30 but 50 but <66, I want cell A2 to show me 6.
So on and so forth….
I appreciate any help that i receive!
Sincerely,
Dan.
-
Helpseeker says:
Hi there, am looking to use a condition in conditional formatting and need to ABS and a formula fulfilling this condition. Please advise. Many
thanks in advance.
«if the values are between -0.25% and 0.25% then yellow» -
I need 3 date conditions met:
NOT STARTED, STARTED, COMPLETE for dates:
A2 no date, B2 no date, C2 no date = Not Started
A2 date, B2 date, C2 no date = Started
A2 date, B2 date, C2 date — CompleteCan you please help me? Thanks!
-
Robbee T says:
Thanks for the help. I’ve been looking for a way to do this formula.
-
HelpSeeker says:
if the value of school is 72 and class is 54, what will be the value of teacher?
-
razak says:
I have made in Excel sheet table of items location, some items are repeated in more than one location, how can i use lookup formula to find those items locatons?
-
razak says:
Item code Description LOC Bin Sys
Qty
T82133008 SOCKET WRENCH BI-HEX. DIN 3120 SQUARE DRIVE: 1/2″ SIZE: 8 MM. 108 D12-3 8
T82133010 SOCKET WRENCH BI-HEX. DIN 3120 SQUARE DRIVE: 1/2″ SIZE: 9 MM. 108 D12-3 8
82133013 SOCKET WRENCH BI-HEX. DIN 3120 SQUARE DRIVE: 1/2″ SIZE: 10 MM. 108 D12-3 8
82133013 SOCKET WRENCH BI-HEX. DIN 3120 SQUARE DRIVE: 1/2″ SIZE: 10 MM. 108 D12-3 2
82133025 SOCKET WRENCH BI-HEX. DIN 3120 SQUARE DRIVE: 1/2″ SIZE: 11 MM. 108 D12-7 9
82133025 SOCKET WRENCH BI-HEX. DIN 3120 SQUARE DRIVE: 1/2″ SIZE: 11 MM. 108 D12-7 3
82133037 SOCKET WRENCH BI-HEX. DIN 3120 SQUARE DRIVE: 1/2″ SIZE: 12 MM. 108 D12-3 13
82133037 SOCKET WRENCH BI-HEX. DIN 3120 SQUARE DRIVE: 1/2″ SIZE: 12 MM. 108 D12-3 2 -
Ahmed Fathy says:
i will give you a very quick example for what i want
i have a dead line date 20/2/2015 ( thats the date in cell )
if Today date is before it within 2 day ( 18/2/2015 )
i want cell to be fill with another color and font
if not then i need it to be the same as rest
-
Havanai says:
Why isn’t there a simple BETWEEN function like there is (or was) in FoxPro? To check to see if the value in field A3 is between .125 and .500 you’d write IF(BETWEEN(A3,.125,.500),»True»,»False»). Simple and straightforward.
I want to generate a random number and check to see if it is between two other numbers. Using Microsoft’s FoxPro syntax it would be IF(BETWEEN(RAND(),.125,.500),»True»,»False»). But despite it also being a Microsoft product, there seems to be no such BETWEEN() function in Excel. Crazy.
-
Feccc says:
A1=5
B1=3
C1=10=IF(AND(A1>B1,A1<C1),»YES»,»NO»)
-
Linda says:
Hello and thank you in advance for your help. I have a monthly bonus excel report which provides me a list of all employees who are subject to bonus changes. One column contains the date the bonus change was implemented as follows:
1. Mark Jones — bonus target % on 02/05/2015
2. Mary Freeze — Bonus type change on 02/15/2015
3. John Camden — Bonus target % on 02/27/2015
4. Freida Jones — Bonus type change on 03/03/2015
5. Sam Carrera — Bonus target % on 03/16/2015However, our Bonus plan rule states, any change on/or before the 15th of the month will default to the 1st of the applicable month.
Any change after the 15th, will default to the 1st of the following month. So, Mary Freeze bonus target change will take effect on 02/01/2015 and Sam’s will be effective 04/01/2015.
How can I create a formula that would auto populate the effective date based on these rules? Is it possible to create this under and IF/OR = X statement?
-
Hi and thank you in advance for your help. I have gone through all of the replies to see if my issue was answered but I can’t find anything. I have a time that I want to see if it falls between two other times. The formula =A1=MEDIAN(A1:A3) works for most of the times except for the following example… does 11:15 PM fall in between 8PM and 8AM. The answer the formula returns is NO, but it should be Yes. Any help would be appreciated!
Thanks.-
Hi Stephen,
In Excel there are no such thing as 8AM or 8PM. So, when you write 8AM in cell, it really is 8AM of January 0, year 1900.
So in your case, 11:15 PM check is failing because 8AM is before 11:15 PM.To overcome this, you can try below approach.
Assuming A1 is the time you want to check, A2 & A3 contain start & end times,
=A1 = median (A1, A2, A3 + AND(HOUR(A2)>12, HOUR(A3)<12))
-
-
Tolga says:
Hi,
This is what I am trying do
if value on A1 between
0-154 A2 0
155-462 A2 -1
463-770 A2 -2
771-1049 A3 -3 -
Adam says:
This isn’t working for me.
I’m trying to say whether a project that has a start and an end date is in progress in each week commencing.
E.g. start 14/08/15 end 25/08/15
The table has weeks commencing 03/08/15, 10/08/15, 17/08/15, 24/08/15, 31/08/15
What I want to return is «No», «Yes»,»Yes», «Yes», «No» (in cells in the row below)
-
Karlien says:
Hi,
I have a question:
I have amounts ranging from 10-45
I would like to make a rule that if it is between 10-24 it should show 7.5, if it is between 25-38 it should show 10 and if it between 39-45 it should show 13.
How do I do this, I tried the IF formula, but I’m struggling.
TIA
-
Joe says:
Hi,
I tried this in Excel 2010
=IF(1=MEDIAN(0,3),»Y»,»N»)
and the result is N.
Shouldn’t the correct result be Y
What did I do wrong?
Please advise.
Thank you.-
@Joe
Select the cell with the Formula =IF(1=MEDIAN(0,3),»Y»,»N»)
Edit the cell and select the part MEDIAN(0,3)
Now press F9
Excel displays 1.5 which is the median of the two values
So 1 NE 1.5 and so the If evaluates the False to be NNE = Not Equal
Median:
Returns the median of the given numbers.
The median is the number in the middle of a set of numbers.
-
-
joe says:
@Hui
Thank you for your quick reply.
I think I may have misunderstood about median and this part of the article — «Lets say you have 3 values in A1, A2 and A3. And you want to find out if A1 falls between A2 and A3.»
For example, if I want to find out if 1 is between 0 and 3,
then I tried =IF(1=MEDIAN(1,0,3),»Y»,»N»), the result is Y.
Is this the correct formula?
Thank you for you advice.
-
@Joe
I can only comment on the question posted and your example had 2 values not 3
To test if A1 is between A2 & A3
=IF(A1=MEDIAN(A1, A2, A3),»Y»,»N»)Using the formula =IF(A1=MEDIAN(A2, A3),»Y»,»N»)
will only work if A1 is exactly at the midpoint of A2 & A3
If
A1 = 3
A2 = 2
A3 = 10Median(2,10) =6
A1 NE 6Median(2,3,10) = 3
A1=3NE = Not equal
-
-
Sarita says:
Can you please help me with the below conditions using IF or Nested IF formula?
A1-67%, A2-120%, A3-157%
150%
Should i change it to 99.99% in place of 100%? or 149.99% for 150%??
So in B1 i want to the value using if formula that if A1 is less than 75% B1 should display <75%, if value in A1 is between 150%,»>150″,IF(A1<=150%,»100%-150%»,IF(A1<100%,»75%-100%»,IF(A1<75%,»<75%»,IF(A1=0%,»0″,IF(A1=»»,»»))))))I am not sure what am i missing here, its giving !00%-150% whereas the value in A1 is 96% so it should display 75%-100%
Can you please help at the earliest??-
Sarita says:
Please provide me the formula you think will work
-
@Saita
If(A1=»»,»»,if(A1 lt 75%,»lt 75%»,if(A1 lt 100%,»75%-100%»,if(A1 Lt 150%,»100%-150%»,»gt 150%»))))LT = Less Than sign
GT = Greater Than signIf you copy this from here change all the » to » signs
100% will show as 100%-150% as it is not less than 100% it is less than 150%
If you want it to show up as 75%-100% change the formula to:
If(A1=»»,»»,if(A1 Lt= 75%,»Lt 75%»,if(A1 Lt= 100%,»75%-100%»,if(A1 Lt= 150%,»100%-150%»,»Gt 150%»))))
-
-
Sarita says:
Hi Hui,
Thank you sooooooo much..it worked…. 🙂
-
Carrie says:
Need a formula that strings 2 formulas together:
A2 has a value of 0
A3 has a value of 5A1 has a value that falls between A2&A3 it will equal 40
B2 has a value of 4
B3 has a value of 13If B1 falls between B2&B3 it will have a value of 25
B1
-
Meghna says:
HI
i want to put an equation if A = (between 25 to 30) then this formula will apply, if not another formula
can u help me how can i do it?-
@Meghna
Lets assume that your talking about cell A2
In A3 or elsewhere: =If(And(A2>25, A2<30), «A», Other formula goes here)-
Meghna says:
Thank you so much
-
-
-
PK says:
Column A | Column B Column C | Column D
—————|————— —————-|————
0000000000001 000000000999 000000000001 032258064500
0300000000010 031000001999 032258064500 064516129030
0620000010010 080000010999 064516129031 096774193550I need a script or a formula to determine if the Range Between Column (A & B) falls between the Range of Column (C & D) to highlight them certain color.
If range overlaps multiple range to state the overlap.Thanks!
-
@PK
Sorry I was travelling when you posted this and missed itSelect the Range A1:B3
Conditional Format
New Rule
Use a Formula =AND($A1<=$D1,$B1>=$C1)
Apply a Format
-
-
Debbie says:
I’ve been searching for a formula that seems like it would be very simple, but have been unable to find. I want a certain cell to do this: if anything at all is typed into the cell, it will return «Yes.» If the cell is left blank, it would remain blank. So, no matter what is typed into the cell, it will simply say «Yes.» Is this possible?
-
@Debbie
Yes it isSelect the Cell/s
Ctrl 1 or Right click and Format Cells
Number, Custom
Apply a Custom Number Format of «Yes»;»Yes»;»Yes»;»Yes»
-
-
Debbie says:
Thank you! That did it.
-
Kurt Kramer says:
I want to generate a random number between 1 and 10000, maybe using this function: =RANDBETWEEN(1,10000)
Then, in that cell, if the randomly generated number is between 1 and 1500 I want to populate the cell with «Empty», and if it’s between 1501 and 7500, I want «Small», and if it’s between 7501 and 10000, I want «Large».
Can someone come up with a formula to do that?
Thanks.
-
@Kurt
In the cell enter =Randbetween(1,10000)
Then apply a Custom Number format of:
[<1501]»Empty»;[<7501]»Small»;»Large»If you really want a formula you can use:
=IF(RANDBETWEEN(1,10000)<=1500,»Empty»,IF(RANDBETWEEN(1501,10000)<=7500,»Small»,»Large»))But you should note that the second Randbetween will be using a different number than the first
-
Kurt Kramer says:
Hui, Thank you. That’s a good start. But I need more. Your response works for 3 options. I actually need 5 ranges/options. For example:
8000 then Tony
Your nested IF-statement won’t work because of the caveat you gave, that each nested RandBetween would be a different number.
Thanks again.
-
-
-
Kurt Kramer says:
Accch. Some of my text got deleted upon saving. I need something like this:
8000 then Tony.
-
Kurt Kramer says:
What the hell? I am listing five ranges and options in my text here, but when I post, the first four disappear! Maybe I cannot use the less than or greater than symbols. Try this:
Accch. Some of my text got deleted upon saving. I need something like this:
less than 1500 then Bill; between 1501 and 3500 then Nick; between 3501 and 4000 then Phil; between 4001 and 8000 then Fred; greater than 8000 then Tony.
-
ramkumar says:
=COUNTIF(H2:H7,LARGE(H2:H7,3))
it is correct or not -
ramkumar says:
can you please help me the below mentioned formula
i used this formula but wrongly shows the resultplease help me the formula
=COUNTIF(H2:H9,LARGE(H2:H9,3))
-
Craig says:
I have over 500,000 lines of data I need to determine the fiscal year the shipping date falls between. Here is a brief example of the data. What is the best formula to get this without a long nested if/then?
Ship Date Fiscal Year Fiscal Year Fiscal Beg. Fiscal End
1/8/2008 2016 1/3/2016 12/31/2016
12/30/2007 2015 1/4/2015 1/2/2016
1/2/2015 2014 12/29/2013 1/3/2015
1/2/2012 2013 12/30/2012 12/28/2013
1/1/2011 2012 1/1/2012 12/29/2012
2011 1/2/2011 12/31/2011
2010 12/27/2009 1/1/2011
2009 12/28/2008 12/26/2009
2008 12/30/2007 12/27/2008-
@Craig
It is hard to understand what data goes in which column, so I didn’t
But assuming the Fiscal year is July 1 to June 30, and it is Named the later year
eg: 1 July 15 to 30 June 16 is the 2016 Fiscal year
Then I would use:
=YEAR(EDATE(A1,6))If it is named after the preceding year use:
=YEAR(EDATE(A1,-6))-
Craig says:
The data I provided was supposed to be in columns. First column has all shipping dates that are random and I need to determine the Fiscal year for those dates which is not the calendar date (over 500,000 rows). The next set of columns would have the Fiscal Year, Beginning date, and then Ending Date for that year, in a small area to the right.
-
-
Craig says:
The data I provided was supposed to be in columns. First column has all shipping dates that are random and I need to determine the Fiscal year for those dates which is not the calendar date (over 500,000 rows). The next set of columns would have the Fiscal Year, Beginning date, and then Ending Date for that year, in a small area to the right. These are the reference point to determine the fiscal year for the shipping date.
Here is an attempt to put it in CSV format.
Ship Date,Fiscal Year,,Fiscal Year,Beg. Date,End Date
1/8/2008,,,2016,1/3/2016,12/31/2016
12/30/2007,,,2015,1/4/2015,1/2/2016
1/2/2015,,,2014,12/29/2013,1/3/2015
1/2/2012,,,2013,12/30/2012,12/28/2013
1/1/2011,,,2012,1/1/2012,12/29/2012
3/30/2015,,,2011,1/2/2011,12/31/2011
5/8/2008,,,2010,12/27/2009,1/1/2011
2/1/2010,,,2009,12/28/2008,12/26/2009
2/1/2009,,,2008,12/30/2007,12/27/2008
-
-
Shams Mahallati says:
I need a formula for this condition:
Consider the following table:
Col.T Col.U
3075 HDU2
4565 HDU4
5645 HDU5
6970 HDU8
9535 HDU11
14390 HDU14Now I have a value in Cell A1: 3568
This value (3568) sits between 3075 and 4565. So , I need a formula in cell, say, B1, to return «HDU4». For any value < 3075, I need a return of «HDU2».
Similarly, if my value in A1 is 6000, I need he formula go to the table above and returns: «HDU8» in cell B1. Because 6000 is 5645
If my value is 10000, I need cell B1 shows «HDU14».
If my value > 14390, I need a return of «HDU14».I have tried Vlookup and Index formulas, but it does not work.
thanks. ShamsIn cell A1 I have a value
-
Jaan says:
Hi Guys, I’m really stuck and desperately need help with this timesheet that I’m trying to build…
if worker works between 6am-9pm, the hourly rate is $50.
if worker works between 9pm-6am next day, the hourly rate is $75.
if where any hour of the job cuts across both rates, the higher rate of $75/hr will be used for that hour (e.g 8.10pm — 9.10pm = $75)
the above pro-rated by minutes as well.can any kind soul please help me with this formula?
-
KAILASH CHAVANKE says:
Dear sir
following formula is correct
=IF(28=MEDIAN(K2.B$4:B$140);»VLOOKUP(B6;K2.$C$4:$D$140;2;0)»;»0″)
Kailash Chavanke
-
Chriss says:
Hello,
Could you please help with formula for following.
In Formula cell I need to appear a number (price per person), which depend on interval it fits (e.g. between 1-6 person price would be 20 EUR per person, between 7-12 persons — 15 EUR/person, 12-16 persons — 10 EUR/person).
There is no problem for me to make between formula with one condition, but I do not know how to make it with 3 different intervals.
Many thanks! -
Usman says:
want to implement following logic in Excel
F2 = 1/22/2016 2:57:00 PM
H2 = 1/22/2016o If the day in column H is the same as the day in column F:
If the timestamp in column F is earlier than 8:00, then 8:00 AM on the day in column H
If the timestamp in column F is after 5:00 PM, then 5:00 PM on the day in column H
Else, the value from column F
o Else, 8:00 AM on the day in column H -
HarryS says:
Like the median trick for numbers =
a vba function that is within 5% of the speed but works for
strings Dates Numbers = but not
asFunction InLH(Vx, Va, Vb, Optional TestAsEq As Boolean = True) As Boolean
Dim LV, HV
If Va > Vb Then
HV = Va
LV = Vb
ElseIf Va = Vb Then
If Vx = Va Then GoTo IsIn Else GoTo IsBad
Else
LV = Va
HV = Vb
End If
If TestAsEq Then
If Vx HV Then GoTo IsBad
Else
If Vx = HV Then GoTo IsBad
End If
IsIn:
InLH = True
IsBad:End Function
-
HarryS says:
parte copied incorrectly
If TestAsEq Then
If Vx HV Then GoTo IsBad ‘GT
Else
If Vx = HV Then GoTo IsBad ‘ Gte
End If -
HarryS says:
It seems to remove «=»
-
Donovan says:
Hi Guys
Is it no possible to have the =if(and formula as a nested formula between a table of 10 different tiers.
Kindly advise
-
@Donovan
The answer is yes, but only in Excel versions 2007+
It is however not recomended
If you can post a question in the forums and attach a sample file we can probably provide a better, more efficent, solution
http://forum.chandoo.org/
-
-
Paramjeet says:
HOW IT WILL WORK FOR TEXT VALUES LIKE CHEETAH ,CAT,TIGER
-
I see you don’t monetize your blog, don’t
waste your traffic, you can earn extra bucks every month because you’ve got hi quality content.
If you want to know how to make extra money, search for:
Boorfe’s tips best adsense alternative -
Shuja Abbasi says:
i want can i check these two values falls (380225 380275 ) falls in bellow mentioned values
380000 380065
380065 380100
380100 380125
380125 380200
380200 380225
380225 380275
380275 380325
380325 380800
380800 380810
380810 380835
380910 381000
381000 381025
381025 381050
381050 381065
381065 381085
381085 381100
381100 381600-
@Shuja
Assuming your data is in A2:B18
In C2: =AND(A2<=380225,B2>=380275)
copy down
-
-
Shuja Abbasi says:
@Hui
sir i want to sort out the values from two column with the other to column values, that the values falls or overlap or not, just like i mentioned below. and i want value in return answer in one rang column formula, just look at 1st values of column C & D only from 38000 to 38035 is overlapping. please help me i am searching that kind of formula
(Values) (Values for checking)
A B C D
380000 380065 379000 380035
380065 380100 380225 380275
380100 380125 380525 380575
380125 380200 380575 380625
380200 380225 380625 380800
380225 380275 380910 381025
380275 380325 381050 381100
380325 380800 381100 381600
380800 380810 381600 381675
380810 380835 381675 383025
380910 381000 383025 383075
381000 381025 383090 383150
381025 381050 383175 383350
381050 381065 383350 383700
381065 381085 383700 383850
381085 381100 383850 383900
381100 381600 383900 383975
381600 381675 383975 384025
381675 382000 384025 384075-
@Shuja
Can you please ask the question in the Chandoo.org Forums
https://chandoo.org/forums/Please attach a sample file with an example of the output you expect
-
-
MOHAN k says:
581.17 581.66 148 48
581.67 582.46 148 49
582.47 583.33 149 49My lookup value is 581.91 from above data and I need an answer from right side mentioned value of (148 & 49) from column C & D
finally, I don’t want true or false statement instead of that i want answer of 148 & 49, please help me-
@Mohan K
assuming your data is in A2:D4
=VLOOKUP(581.91,A2:D4,3)
=VLOOKUP(581.91,A2:D4,4)
=VLOOKUP(581.91,A2:D4,3) &» & » & VLOOKUP(581.91,A2:D4,4)
-
-
Jei says:
Hi! Can someone help me with writing an Excel «if condition» the say «if cell H3 has «At Risk», then change cell fill to Red. I wrote the following: =If $H$3 ‘At Risk’ ($C$3, colour Red)
-
Hi Jei,
Welcome to Chandoo.org and thanks for your comment. You need to conditional formatting to do this. Follow below instructions.
- Select all cells you want to check.
- Go to Home > Conditional Formatting > Highlight Cell Rules > Equal to…
- Type «At Risk» as the condition and Click ok
Click here to learn more about conditional formatting.
-
Leave a Reply

This Excel VBA Select Case Tutorial is currently under development. Subscribe to the Power Spreadsheets Newsletter and get future updates to this Excel VBA Select Case Tutorial.
This Excel VBA Select Case Tutorial is accompanied by an Excel workbook with the data and VBA code I use in the examples below. Get this example workbook (for free) by clicking the button below.
The VBA code in the Excel workbook that accompanies this Excel VBA Select Case Tutorial is (always) stored in the Visual Basic Editor (VBE). If you don’t know how to work with the VBE, I suggest you read my Visual Basic Editor (VBE) Tutorial. I link to this Tutorial in the Related Excel Macro and VBA Training Materials and Resources Section below.
The following Excel Macro and VBA Tutorials may help you better understand and implement the contents below.
- Tutorials about general macro and VBA constructs and structures:
- Tutorials for Beginners:
- Excel Macros: Click here to open.
- Excel VBA: Click here to open.
- Enable macros in Excel: Click here to open.
- Work with the Visual Basic Editor (VBE): Click here to open.
- Create Sub procedures: Click here to open.
- Work with:
- Variables: Click here to open.
- Data types: Click here to open.
- Functions: Click here to open.
- Tutorials for Beginners:
- Tutorials with practical VBA applications and macro examples:
- Excel VBA Change Font Color Based on Cell Value: Click here to open.
- Create a message box: Click here to open.
- Create an input box: Click here to open.
This Excel VBA Select Case Tutorial is part of a more comprehensive series of Excel VBA Select Case Tutorials.
- Excel VBA Select Case Tutorial: Click here to open.
- Excel VBA Select Case Or: Click here to open.
- Excel VBA Select Case And Operator: Click here to open.
- Excel VBA Select Case Multiple Test Expressions: Click here to open.
- Excel VBA Select Case Like Wildcard: Click here to open.
- Excel VBA Select Case Inside For… Next Loop: Click here to open.
- Excel VBA Select Case Range of Cells: Click here to open.
You can find more Excel and VBA Tutorials in the organized Tutorials Archive: Click here to visit the Archives. The following are some of my most popular Excel Tutorials and Training Resources:
- Excel Keyboard Shortcuts Cheat Sheet: Click here to open.
- Work with the Excel XLOOKUP Function: Click here to open.
- Excel Power Query (Get & Transform) Tutorial for Beginners: Click here to open.
If you want to learn how to automate Excel (and save time) by working with macros and VBA, you may be interested in the following Premium Excel Macro and VBA Training Materials:
- Premium Courses at the Power Spreadsheets Academy: Click here to open.
- Books at the Power Spreadsheets Library: Click here to open.
- VBA Cheat Sheets: Click here to open.
If you want to save time when working with macros and VBA, you may be interested in AutoMacro: Click here to learn more about AutoMacro (affiliate link). AutoMacro is an add-in for VBA that installs directly into the VBE. Depending on the version, AutoMacro comes loaded with:
- Code generators.
- An extensive code library.
- The ability to create your own code library.
- Advanced coding tools.
If you need help with Excel tasks/projects, you may be interested in working with me: Click here to learn more about working with me.
(1) Excel VBA Select Case Without Case Else
In this Section, you learn how to create a basic Excel VBA Select Case statement (without the Case Else clause) to conditionally execute a set of statements based on an expression’s value.
Excel VBA Select Case Without Case Else Snippet Template/Structure
The following is the Excel VBA Select Case Without Case Else snippet template/structure I explain (step-by-step) in the Sections below.
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
Select Case TestExpression
Case CaseExpression1
CaseStatements1
Case CaseExpression2
CaseStatements2
'...
Case CaseExpression#
CaseStatements#
End Select
Step-by-Step Process to Set Up an Excel VBA Select Case Without Case Else Statement
Do the following to create an Excel VBA Select Case Without Case Else statement:
(1) Enter the opening and closing statements of the Select Case statement.
- Select Case.
- End Select.
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
Select Case '...
'...
End Select
(2) Specify the test expression VBA uses to identify the set of statements to execute: TestExpression.
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
Select Case TestExpression
'...
End Select
(3) Specify the case expressions used by VBA to identify the set of statements to execute:
- CaseExpression1.
- CaseExpression2.
- …
- CaseExpression#.
You can (as a general rule) include as many case expressions as required inside a single Select Case statement.
Each case expression is preceded by the Case keyword:
- Case CaseExpression1.
- Case CaseExpression2.
- …
- Case CaseExpression#.
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
Select Case TestExpression
Case CaseExpression1
'...
Case CaseExpression2
'...
'...
Case CaseExpression#
'...
End Select
The Case keyword plus associated case expression (Case CaseExpression#) form a Case clause.
When the test expression (you specified in step #2) matches an individual case expression, the Select Case statement:
- Executes the set of statements (you specify in step #4) associated to the applicable Case clause (whose case expression matched the test expression); and
- Exits the Select Case statement.
(4) Specify the set of statements to be executed when the applicable case expression (you specified in step #3) matches the test expression (you specified in step #2).
- CaseStatements1.
- CaseStatements2.
- …
- CaseStatements#.
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
Select Case TestExpression
Case CaseExpression1
CaseStatements1
Case CaseExpression2
CaseStatements2
'...
Case CaseExpression#
CaseStatements#
End Select
Additional Cues for Excel VBA Select Case Without Case Else
(1) The Select Case statement is an alternative to complex If… Then… Else statements (Select Case vs. If… Then… Else). Consider using the Select Case statement when dealing with (more) complex cases.
(2) Consider indenting the statements inside Select Case statements.
(3) Consider working with the separator character (:) to separate the Case clause (Case CaseExpression#) and the statements to be executed (CaseStatements#), when the following 2 conditions are met:
- The case results in a single statement (CaseStatement#) being executed; and
- The resulting line of VBA code is not excessively long.
(4) You have a significant degree of flexibility when specifying case expressions inside a Select Case statement.
Please refer to the Section on Excel VBA Select Case Multiple Conditions (in this Excel VBA Select Case Tutorial) for a more detailed explanation on how to create a Select Case statement to conditionally execute a set of statements based on multiple conditions (grouping several cases inside a single case expression).
(5) As a general rule: Organize case expressions:
- By decreasing order of probability.
- In such a way that any case expression excludes subsequent case expressions.
(6) The Select Case statement contains a set of catch-all statements executed if no case expression matches the test expression. These statements follow the Case Else keyword. The Case Else keyword (and clause) is optional.
Excel VBA Select Case Without Case Else Example Macro
This Excel VBA Select Case Tutorial is accompanied by an Excel workbook with the data and VBA code I use in the examples inside this Tutorial (including this Select Case Without Case Else example). Get this example workbook (for free) by clicking the button below.
I create the Excel VBA Select Case without Case Else example macro as follows:
(1) Declare a Sub procedure (SelectCaseWithoutCaseElse).
Sub SelectCaseWithoutCaseElse()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
'...
End Sub
(2) Declare a variable (MyWeekdayMessage) of the String data type.
Sub SelectCaseWithoutCaseElse()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
'Declare variable to represent message to be displayed in message box
Dim MyWeekdayMessage As String
'...
End Sub
(3) Enter the opening and closing statements of the Select Case statement.
Sub SelectCaseWithoutCaseElse()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
'Declare variable to represent message to be displayed in message box
Dim MyWeekdayMessage As String
Select Case '...
'...
End Select
'...
End Sub
(4) Specify the test expression VBA uses to identify the set of statements to execute.
The test expression I use (Weekday(Date:=Date, FirstDayOfWeek:=vbMonday)) returns an integer (1 to 7) representing the current day of the week.
Sub SelectCaseWithoutCaseElse()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
'Declare variable to represent message to be displayed in message box
Dim MyWeekdayMessage As String
Select Case Weekday(Date:=Date, FirstDayOfWeek:=vbMonday)
'...
End Select
'...
End Sub
(5) Specify the case expressions used by VBA to identify the set of statements to execute.
The test expression I specified in step #4 returns an integer between 1 and 7. The case expressions I specify are (therefore):
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
Sub SelectCaseWithoutCaseElse()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
'Declare variable to represent message to be displayed in message box
Dim MyWeekdayMessage As String
Select Case Weekday(Date:=Date, FirstDayOfWeek:=vbMonday)
Case 1: '...
Case 2: '...
Case 3: '...
Case 4: '...
Case 5: '...
Case 6: '...
Case 7: '...
End Select
'...
End Sub
(6) Specify the statement to be executed when the applicable case expression (I specified in step #5) matches the test expression (I specified in step #4).
The statements I use assign a string to the MyWeekdayMessage variable (I declared in step #2). The assigned string varies, depending on the applicable case expression (I specified in step #5):
- Case expression is 1: Assigned string is “It’s Monday”.
- Case expression is 2: Assigned string is “It’s Tuesday”.
- Case expression is 3: Assigned string is “It’s Wednesday”.
- Case expression is 4: Assigned string is “It’s Thursday”.
- Case expression is 5: Assigned string is “It’s Friday”.
- Case expression is 6: Assigned string is “It’s Saturday”.
- Case expression is 7: Assigned string is “It’s Sunday”.
Sub SelectCaseWithoutCaseElse()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
'Declare variable to represent message to be displayed in message box
Dim MyWeekdayMessage As String
'Assign a string to the MyWeekdayMessage variable, depending on the current day of the week
Select Case Weekday(Date:=Date, FirstDayOfWeek:=vbMonday)
Case 1: MyWeekdayMessage = "It's Monday"
Case 2: MyWeekdayMessage = "It's Tuesday"
Case 3: MyWeekdayMessage = "It's Wednesday"
Case 4: MyWeekdayMessage = "It's Thursday"
Case 5: MyWeekdayMessage = "It's Friday"
Case 6: MyWeekdayMessage = "It's Saturday"
Case 7: MyWeekdayMessage = "It's Sunday"
End Select
'...
End Sub
(6) Display a message box (MsgBox) with the value held by the MyWeekdayMessage variable.
Sub SelectCaseWithoutCaseElse()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
'Declare variable to represent message to be displayed in message box
Dim MyWeekdayMessage As String
'Assign a string to the MyWeekdayMessage variable, depending on the current day of the week
Select Case Weekday(Date:=Date, FirstDayOfWeek:=vbMonday)
Case 1: MyWeekdayMessage = "It's Monday"
Case 2: MyWeekdayMessage = "It's Tuesday"
Case 3: MyWeekdayMessage = "It's Wednesday"
Case 4: MyWeekdayMessage = "It's Thursday"
Case 5: MyWeekdayMessage = "It's Friday"
Case 6: MyWeekdayMessage = "It's Saturday"
Case 7: MyWeekdayMessage = "It's Sunday"
End Select
'Display message box with string held by the MyWeekdayMessage variable
MsgBox MyWeekdayMessage
End Sub
The image below displays the message box shown by Excel when I execute the Excel VBA Select Case without Case Else example macro. I execute the example macro (and create this screenshot) on a Sunday.

Select Case Without Case Else vs. If… Then… ElseIf… Example Macro
The following If… Then… ElseIf… example macro is an equivalent example macro (to the Select Case without Case Else example macro I explain above) working with the If… Then… Else statement (vs. the Select Case statement).
Sub SelectCaseWithoutCaseElseVsIfThenElseIf()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
'Declare variables to represent:
'(1) Number representing day of the week
'(2) Message to be displayed in message box
Dim MyWeekday As Integer
Dim MyWeekdayMessage As String
'Assign number representing day of the week to the MyWeekday variable
MyWeekday = Weekday(Date:=Date, FirstDayOfWeek:=vbMonday)
'Assign a string to the MyWeekdayMessage variable, depending on the current day of the week
If MyWeekday = 1 Then
MyWeekdayMessage = "It's Monday"
ElseIf MyWeekday = 2 Then
MyWeekdayMessage = "It's Tuesday"
ElseIf MyWeekday = 3 Then
MyWeekdayMessage = "It's Wednesday"
ElseIf MyWeekday = 4 Then
MyWeekdayMessage = "It's Thursday"
ElseIf MyWeekday = 5 Then
MyWeekdayMessage = "It's Friday"
ElseIf MyWeekday = 6 Then
MyWeekdayMessage = "It's Saturday"
ElseIf MyWeekday = 7 Then
MyWeekdayMessage = "It's Sunday"
End If
'Display message box with string held by the MyWeekdayMessage variable
MsgBox MyWeekdayMessage
End Sub
Notice how the Select Case statement results in more efficient VBA code that’s easier to:
- Read;
- Follow;
- Understand; and
- Work with.
The image below displays the message box shown by Excel when I execute the Excel VBA If… Then… ElseIf… example macro. I execute the example macro (and create this screenshot) on a Sunday.

In this Section, you learn how to create a basic Excel VBA Select Case statement (with the Case Else clause) to:
- Conditionally execute a set of statements based on an expression’s value; and
- Specify a set of catch-all statements that are executed when none of the conditions you (originally) expected is met.
Excel VBA Select Case Else Snippet Template/Structure
The following is the Excel VBA Select Case Else snippet template/structure I explain (step-by-step) in the Sections below.
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
Select Case TestExpression
Case CaseExpression1
CaseStatements1
Case CaseExpression2
CaseStatements2
'...
Case CaseExpression#
CaseStatements#
Case Else
ElseStatements
End Select
Step-by-Step Process to Set Up an Excel VBA Select Case Else Statement
Do the following to create an Excel VBA Select Case Else statement:
(1) Enter the opening and closing statements of the Select Case statement.
- Select Case.
- End Select.
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
Select Case '...
'...
End Select
(2) Specify the test expression VBA uses to identify the set of statements to execute: TestExpression.
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
Select Case TestExpression
'...
End Select
(3) Specify the case expressions used by VBA to identify the set of statements to execute:
- CaseExpression1.
- CaseExpression2.
- …
- CaseExpression#.
You can (as a general rule) include as many case expressions as required inside a single Select Case statement.
Each case expression is preceded by the Case keyword:
- Case CaseExpression1.
- Case CaseExpression2.
- …
- Case CaseExpression#.
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
Select Case TestExpression
Case CaseExpression1
'...
Case CaseExpression2
'...
'...
Case CaseExpression#
'...
'...
End Select
The Case keyword plus associated case expression (Case CaseExpression#) form a Case clause.
When the test expression (you specified in step #2) matches an individual case expression, the Select Case statement:
- Executes the set of statements (you specify in step #4) associated to the applicable Case clause (whose case expression matched the test expression); and
- Exits the Select Case statement.
(4) Specify the set of statements to be executed when the applicable case expression (you specified in step #3) matches the test expression (you specified in step #2).
- CaseStatements1.
- CaseStatements2.
- …
- CaseStatements#.
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
Select Case TestExpression
Case CaseExpression1
CaseStatements1
Case CaseExpression2
CaseStatements2
'...
Case CaseExpression#
CaseStatements#
'...
End Select
(5) Specify the set of statements to be executed if no case expression (you specified in step #3) matches the test expression (you specified in step #2). These catch-all statements follow the Case Else keyword.
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
Select Case TestExpression
Case CaseExpression1
CaseStatements1
Case CaseExpression2
CaseStatements2
'...
Case CaseExpression#
CaseStatements#
Case Else
ElseStatements
End Select
Additional Cues for Excel VBA Select Case Else
(1) The Select Case statement is an alternative to complex If… Then… Else statements (Select Case vs. If… Then… Else). Consider using the Select Case statement when dealing with (more) complex cases.
(2) Consider indenting the statements inside Select Case statements.
(3) Consider working with the separator character (:) to separate:
- The Case clause (Case CaseExpression#) and the statements to be executed (CaseStatements#); or
- The Case Else keyword (Case Else) and the catch-all statements (ElseStatements);
When the following 2 conditions are met:
- The case results in a single statement (CaseStatement#) being executed or there’s (only) a single catch-all statement (ElseStatement); and
- The resulting line of VBA code is not excessively long.
(3) You have a significant degree of flexibility when specifying case expressions inside a Select Case statement.
Please refer to the Section on Excel VBA Select Case Multiple Conditions (in this Excel VBA Select Case Tutorial) for a more detailed explanation on how to create a Select Case statement to conditionally execute a set of statements based on multiple conditions (grouping several cases inside a single case expression).
(4) As a general rule: Organize case expressions:
- By decreasing order of probability.
- In such a way that any case expression excludes subsequent case expressions.
(5) The Case Else keyword/clause (Case Else: ElseStatements) is optional.
Work with the Case Else clause to specify a set of catch-all statements that are executed when none of the conditions you (originally) expected is met (no case expression matches the test expression).
(6) If:
- You omit the Case Else clause; and
- No case expression matches the test expression;
Procedure execution continues with the first statement after the end of the Select Case statement (after “End Select”).
Excel VBA Select Case Else Example Macro
This Excel VBA Select Case Tutorial is accompanied by an Excel workbook with the data and VBA code I use in the examples inside this Tutorial (including this Select Case Else example). Get this example workbook (for free) by clicking the button below.
I create the Excel VBA Select Case Else example macro as follows:
(1) Declare a Sub procedure (SelectCaseElse).
Sub SelectCaseElse()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
'…
End Sub
(2) Declare a variable (MyMonthPartMessage) of the String data type.
Sub SelectCaseElse()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
'Declare variable to represent message to be displayed in message box
Dim MyMonthPartMessage As String
'…
End Sub
(3) Enter the opening and closing statements of the Select Case statement.
Sub SelectCaseElse()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
'Declare variable to represent message to be displayed in message box
Dim MyMonthPartMessage As String
Select Case '…
'…
End Select
'…
End Sub
(4) Specify the test expression VBA uses to identify the set of statements to execute.
The test expression I use (Day(Date:=Date)) returns an integer (1 to 31) representing the current day of the month.
Sub SelectCaseElse()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
'Declare variable to represent message to be displayed in message box
Dim MyMonthPartMessage As String
Select Case Day(Date:=Date)
'…
End Select
'…
End Sub
(5) Specify the case expressions used by VBA to identify the set of statements to execute.
The test expression I specified in step #4 returns an integer between 1 and 31. The case expressions I specify are (therefore):
- 1 To 5.
- 6 To 10.
- 11 To 15.
- 16 To 20.
- 21 To 25.
Sub SelectCaseElse()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
'Declare variable to represent message to be displayed in message box
Dim MyMonthPartMessage As String
Select Case Day(Date:=Date)
Case 1 To 5: '…
Case 6 To 10: '…
Case 11 To 15: '…
Case 16 To 20: '…
Case 21 To 25: '…
'…
End Select
'…
End Sub
(6) Specify the statement to be executed when the applicable case expression (I specified in step #5) matches the test expression (I specified in step #4).
The statements I use assign a string to the MyMonthPartMessage variable (I declared in step #2). The assigned string varies, depending on the applicable case expression (I specified in step #5):
- Case expression is 1 to 5 (both inclusive): Assigned string is “We’re between the first and the fifth of the month”.
- Case expression is 6 to 10 (both inclusive): Assigned string is “We’re between the sixth and the tenth of the month”.
- Case expression is 11 to 15 (both inclusive): Assigned string is “We’re between the eleventh and the fifteenth of the month”.
- Case expression is 16 to 20 (both inclusive): Assigned string is “We’re between the sixteenth and the twentieth of the month”.
- Case expression is 21 to 25 (both inclusive): Assigned string is “We’re between the twenty-first and the twenty-fifth of the month”.
Sub SelectCaseElse()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
'Declare variable to represent message to be displayed in message box
Dim MyMonthPartMessage As String
'Assign a string to the MyMonthPartMessage variable, depending on the current day of the month
Select Case Day(Date:=Date)
Case 1 To 5: MyMonthPartMessage = "We're between the first and the fifth of the month"
Case 6 To 10: MyMonthPartMessage = "We're between the sixth and the tenth of the month"
Case 11 To 15: MyMonthPartMessage = "We're between the eleventh and the fifteenth of the month"
Case 16 To 20: MyMonthPartMessage = "We're between the sixteenth and the twentieth of the month"
Case 21 To 25: MyMonthPartMessage = "We're between the twenty-first and the twenty-fifth of the month"
'…
End Select
'…
End Sub
(7) Specify the catch-all statement to be executed if no case expression (from the case expressions I specified in step #5) matches the test expression (I specified in step #4).
The statement I use assigns a string to the MyMonthPartMessage variable (I declared in step #2): “We’re past the twenty-fifth of the month”.
Sub SelectCaseElse()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
'Declare variable to represent message to be displayed in message box
Dim MyMonthPartMessage As String
'Assign a string to the MyMonthPartMessage variable, depending on the current day of the month
Select Case Day(Date:=Date)
Case 1 To 5: MyMonthPartMessage = "We're between the first and the fifth of the month"
Case 6 To 10: MyMonthPartMessage = "We're between the sixth and the tenth of the month"
Case 11 To 15: MyMonthPartMessage = "We're between the eleventh and the fifteenth of the month"
Case 16 To 20: MyMonthPartMessage = "We're between the sixteenth and the twentieth of the month"
Case 21 To 25: MyMonthPartMessage = "We're between the twenty-first and the twenty-fifth of the month"
Case Else: MyMonthPartMessage = "We're past the twenty-fifth of the month"
End Select
'…
End Sub
(8) Display a message box (MsgBox) with the value held by the MyMonthPartMessage variable.
Sub SelectCaseElse()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
'Declare variable to represent message to be displayed in message box
Dim MyMonthPartMessage As String
'Assign a string to the MyMonthPartMessage variable, depending on the current day of the month
Select Case Day(Date:=Date)
Case 1 To 5: MyMonthPartMessage = "We're between the first and the fifth of the month"
Case 6 To 10: MyMonthPartMessage = "We're between the sixth and the tenth of the month"
Case 11 To 15: MyMonthPartMessage = "We're between the eleventh and the fifteenth of the month"
Case 16 To 20: MyMonthPartMessage = "We're between the sixteenth and the twentieth of the month"
Case 21 To 25: MyMonthPartMessage = "We're between the twenty-first and the twenty-fifth of the month"
Case Else: MyMonthPartMessage = "We're past the twenty-fifth of the month"
End Select
'Display message box with string held by the MyMonthPartMessage variable
MsgBox MyMonthPartMessage
End Sub
The image below displays the message box shown by Excel when I execute the Excel VBA Select Case Else example macro. I execute the example macro (and create this screenshot) on day 13 of the month.

Select Case Else vs. If… Then… ElseIf… Else Example Macro
The following If… Then… ElseIf… Else example macro is an equivalent example macro (to the Select Case Else example macro I explain above) working with the If… Then… Else statement (vs. the Select Case statement).
Sub SelectCaseElseVsIfThenElseIfElse()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
'Declare variables to represent:
'(1) Number representing day of the month
'(2) Message to be displayed in message box
Dim MyMonthDay As Integer
Dim MyMonthPartMessage As String
'Assign number representing day of the month to the MyMonthDay variable
MyMonthDay = Day(Date:=Date)
'Assign a string to the MyMonthPartMessage variable, depending on the current day of the month
If MyMonthDay <= 5 Then
MyMonthPartMessage = "We're between the first and the fifth of the month"
ElseIf (MyMonthDay >= 6) And (MyMonthDay <= 10) Then
MyMonthPartMessage = "We're between the sixth and the tenth of the month"
ElseIf (MyMonthDay >= 11) And (MyMonthDay <= 15) Then
MyMonthPartMessage = "We're between the eleventh and the fifteenth of the month"
ElseIf (MyMonthDay >= 16) And (MyMonthDay <= 20) Then
MyMonthPartMessage = "We're between the sixteenth and the twentieth of the month"
ElseIf (MyMonthDay >= 21) And (MyMonthDay <= 25) Then
MyMonthPartMessage = "We're between the twenty-first and the twenty-fifth of the month"
Else
MyMonthPartMessage = "We're past the twenty-fifth of the month"
End If
'Display message box with string held by the MyMonthPartMessage variable
MsgBox MyMonthPartMessage
End Sub
Notice how the Select Case statement results in more efficient VBA code that’s easier to:
- Read;
- Follow;
- Understand; and
- Work with.
The image below displays the message box shown by Excel when I execute the Excel VBA If… Then… ElseIf… Else example macro. I execute the example macro (and create this screenshot) on day 13 of the month.

(3) Excel VBA Select Case String
In this Section, you learn how to create an Excel VBA Select Case string statement, to conditionally execute a set of statements based on a string.
Excel VBA Select Case String Formula/Snippet Template/Structure
The following is the Excel VBA Select Case string snippet template/structure I explain (step-by-step) in the Sections below.
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
Select Case StringTestExpression
Case StringCaseExpression1
CaseStatements1
Case StringCaseExpression2
CaseStatements2
'...
Case StringCaseExpression#
CaseStatements#
Case Else
ElseStatements
End Select
Step-by-Step Process to Set Up an Excel VBA Select Case String Statement
Do the following to create an Excel VBA Select Case string statement:
(1) Enter the opening and closing statements of the Select Case statement.
- Select Case.
- End Select.
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
Select Case '...
'...
End Select
(2) Specify the string test expression VBA uses to identify the set of statements to execute: StringTestExpression.
To create an Excel VBA Select Case string statement, specify this string test expression as:
- A string; or
- A string expression.
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
Select Case StringTestExpression
'...
End Select
(3) Specify the string case expressions used by VBA to identify the set of statements to execute:
- StringCaseExpression1.
- StringCaseExpression2.
- …
- StringCaseExpression#.
You can (as a general rule) include as many string case expressions as required inside a single Select Case statement.
Each string case expression is preceded by the Case keyword:
- Case StringCaseExpression1.
- Case StringCaseExpression2.
- …
- Case StringCaseExpression#.
To create an Excel VBA Select Case string statement, specify case expressions as:
- A string; or
- A string expression.
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
Select Case StringTestExpression
Case StringCaseExpression1
'...
Case StringCaseExpression2
'...
'...
Case StringCaseExpression#
'...
'...
End Select
The Case keyword plus associated string case expression (Case StringCaseExpression#) form a Case clause.
When the string test expression (you specified in step #2) matches an individual string case expression, the Select Case statement:
- Executes the set of statements (you specify in step #4) associated to the applicable Case clause (whose string case expression matched the string test expression); and
- Exits the Select Case statement.
(4) Specify the set of statements to be executed when the applicable string case expression (you specified in step #3) matches the string test expression (you specified in step #2).
- CaseStatements1.
- CaseStatements2.
- …
- CaseStatements#.
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
Select Case StringTestExpression
Case StringCaseExpression1
CaseStatements1
Case StringCaseExpression2
CaseStatements2
'...
Case StringCaseExpression#
CaseStatements#
'...
End Select
(5) Specify the set of statements to be executed if no string case expression (you specified in step #3) matches the string test expression (you specified in step #2). These catch-all statements:
- Follow the Case Else keyword; and
- Are optional.
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
Select Case StringTestExpression
Case StringCaseExpression1
CaseStatements1
Case StringCaseExpression2
CaseStatements2
'...
Case StringCaseExpression#
CaseStatements#
Case Else
ElseStatements
End Select
Additional Cues for Excel VBA Select Case String
(1) The Select Case statement is an alternative to complex If… Then… Else statements (Select Case vs. If… Then… Else). Consider using the Select Case statement when dealing with (more) complex cases.
(2) Consider indenting the statements inside Select Case statements.
(3) Consider working with the separator character (:) to separate:
- The Case clause (Case StringCaseExpression#) and the statements to be executed (CaseStatements#); or
- The Case Else keyword (Case Else) and the catch-all statements (ElseStatements);
When the following 2 conditions are met:
- The case results in a single statement (CaseStatement#) being executed or there’s (only) a single catch-all statement (ElseStatement); and
- The resulting line of VBA code is not excessively long.
(3) You have a significant degree of flexibility when specifying case expressions inside a Select Case statement. This flexibility includes the possibility to group several cases inside a single case expression.
Please refer to the Section on Excel VBA Select Case Multiple Conditions (in this Excel VBA Select Case Tutorial) for a more detailed explanation on how to create a Select Case statement to conditionally execute a set of statements based on multiple conditions (grouping several cases inside a single case expression).
(5) Use the Option Compare statement (at the module level) to specify the default comparison method VBA uses when comparing strings:
- Option Compare Binary; or
- Option Compare Text.
Option Compare Binary results in a case sensitive comparison. Option Compare Text results in a case insensitive comparison.
The default string comparison method is binary.
(6) As a general rule: Organize case expressions:
- By decreasing order of probability.
- In such a way that any case expression excludes subsequent case expressions.
(7) The Case Else keyword/clause (Case Else: ElseStatements) is optional.
Work with the Case Else clause to specify a set of catch-all statements that are executed when none of the conditions you (originally) expected is met (no string case expression matches the string test expression).
(8) If:
- You omit the Case Else clause; and
- No string case expression matches the string test expression;
Procedure execution continues with the first statement after the end of the Select Case statement (after “End Select”).
Excel VBA Select Case String Example Macro
This Excel VBA Select Case Tutorial is accompanied by an Excel workbook with the data and VBA code I use in the examples inside this Tutorial (including this example). Get this example workbook (for free) by clicking the button below.
I create the Excel VBA Select Case string example macro as follows:
(1) Declare a Sub procedure (SelectCaseString).
Sub SelectCaseString()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
'...
End Sub
(2) Declare a variable (MyQuarterMessage) of the String data type.
Sub SelectCaseString()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
'Declare variable to represent message to be displayed in message box
Dim MyQuarterMessage As String
'...
End Sub
(3) Enter the opening and closing statements of the Select Case statement.
Sub SelectCaseString()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
'Declare variable to represent message to be displayed in message box
Dim MyQuarterMessage As String
Select Case '...
'...
End Select
'...
End Sub
(4) Specify the string test expression VBA uses to identify the set of statements to execute.
The test expression I use (MonthName(Month(Date:=Date))) returns the current month’s name.
Sub SelectCaseString()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
'Declare variable to represent message to be displayed in message box
Dim MyQuarterMessage As String
Select Case MonthName(Month(Date:=Date))
'...
End Select
'...
End Sub
(5) Specify the string case expressions used by VBA to identify the set of statements to execute.
The string test expression I specified in step #4 returns a month’s name (“January” to “December”). Additionally, I use commas to separate multiple strings inside a single string case expression.
The string case expressions I specify are (therefore):
- “January”, “February”, “March”.
- “April”, “May”, “June”.
- “July”, “August”, “September”.
- “October”, “November”, “December”.
Sub SelectCaseString()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
'Declare variable to represent message to be displayed in message box
Dim MyQuarterMessage As String
Select Case MonthName(Month(Date:=Date))
Case "January", "February", "March" '...
Case "April", "May", "June" '...
Case "July", "August", "September" '...
Case "October", "November", "December" '...
End Select
'...
End Sub
(6) Specify the statement to be executed when the applicable string case expression (I specified in step #5) matches the string test expression (I specified in step #4).
The statements I use assign a string to the MyQuarterMessage variable (I declared in step #2). The assigned string varies, depending on the applicable string case expression (I specified in step #5):
- String case expression is “January”, “February”, “March”: Assigned string is “It’s Q1”.
- String case expression is “April”, “May”, “June”: Assigned string is “It’s Q2”.
- String case expression is “July”, “August”, “September”: Assigned string is “It’s Q3”.
- String case expression is “October”, “November”, “December”: Assigned string is “It’s Q4”.
Sub SelectCaseString()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
'Declare variable to represent message to be displayed in message box
Dim MyQuarterMessage As String
'Assign a string to the MyQuarterMessage variable, depending on the current month
Select Case MonthName(Month(Date:=Date))
Case "January", "February", "March": MyQuarterMessage = "It's Q1"
Case "April", "May", "June": MyQuarterMessage = "It's Q2"
Case "July", "August", "September": MyQuarterMessage = "It's Q3"
Case "October", "November", "December": MyQuarterMessage = "It's Q4"
End Select
'...
End Sub
(7) Display a message box (MsgBox) with the value held by the MyQuarterMessage variable.
Sub SelectCaseString()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
'Declare variable to represent message to be displayed in message box
Dim MyQuarterMessage As String
'Assign a string to the MyQuarterMessage variable, depending on the current month
Select Case MonthName(Month(Date:=Date))
Case "January", "February", "March": MyQuarterMessage = "It's Q1"
Case "April", "May", "June": MyQuarterMessage = "It's Q2"
Case "July", "August", "September": MyQuarterMessage = "It's Q3"
Case "October", "November", "December": MyQuarterMessage = "It's Q4"
End Select
'Display message box with string held by the MyQuarterMessage variable
MsgBox MyQuarterMessage
End Sub
The image below displays the message box shown by Excel when I execute the Excel VBA Select Case string example macro. I execute the example macro (and create this screenshot) during April.

Select Case String vs. If… Then… Else String Example Macro
The following If… Then… Else string example macro is an equivalent example macro (to the Select Case string example macro I explain above) working with the If… Then… Else statement (vs. the Select Case statement).
Sub SelectCaseStringVsIfThenElseIfString()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
'Declare variables to represent:
'(1) Month name
'(2) Message to be displayed in message box
Dim MyMonth As String
Dim MyQuarterMessage As String
'Assign current month's name to the MyMonth variable
MyMonth = MonthName(Month(Date:=Date))
'Assign a string to the MyQuarterMessage variable, depending on the current month
If (MyMonth = "January") Or (MyMonth = "February") Or (MyMonth = "March") Then
MyQuarterMessage = "It's Q1"
ElseIf (MyMonth = "April") Or (MyMonth = "May") Or (MyMonth = "June") Then
MyQuarterMessage = "It's Q2"
ElseIf (MyMonth = "July") Or (MyMonth = "August") Or (MyMonth = "September") Then
MyQuarterMessage = "It's Q3"
ElseIf (MyMonth = "October") Or (MyMonth = "November") Or (MyMonth = "December") Then
MyQuarterMessage = "It's Q4"
End If
'Display message box with string held by the MyQuarterMessage variable
MsgBox MyQuarterMessage
End Sub
Notice how the Select Case statement results in more efficient VBA code that’s easier to:
- Read;
- Follow;
- Understand; and
- Work with.
The image below displays the message box shown by Excel when I execute the Excel VBA If… Then… Else string example macro. I execute the example macro (and create this screenshot) during April.

(4) Excel VBA Select Case Between 2 Values
In this Section, you learn how to create an Excel VBA Select Case between 2 values statement to conditionally execute a set of statements based on whether an expression returns a value between 2 (other) values.
Excel VBA Select Case Between 2 Values Snippet Template/Structure
The following is the Excel VBA Select Case between 2 values snippet template/structure I explain (step-by-step) in the Sections below.
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
Select Case NumericTestExpression
Case LowerBoundCase1 To UpperBoundCase1
CaseStatements1
Case LowerBoundCase2 To UpperBoundCase2
CaseStatements2
'...
Case LowerBoundCase# To UpperBoundCase#
CaseStatements#
Case Else
ElseStatements
End Select
Step-by-Step Process to Set Up an Excel VBA Select Case Between 2 Values Statement
Do the following to create an Excel VBA Select Case between 2 values statement:
(1) Enter the opening and closing statements of the Select Case statement.
- Select Case.
- End Select.
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
Select Case '...
'...
End Select
(2) Specify the test expression VBA uses to identify the set of statements to execute, as a numeric expression (an expression that can be evaluated as a number): NumericTestExpression.
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
Select Case NumericTestExpression
'...
End Select
(3) Specify the numeric case expressions used by VBA to identify the set of statements to execute. Use the To keyword to specify a range of values for each single case expression.
- LowerBoundCase1 To UpperBoundCase1.
- LowerBoundCase2 To UpperBoundCase2.
- …
- LowerBoundCase# To UpperBoundCase#.
For these purposes:
- LowerBoundCase# is the smaller value in the specified range of values; and
- UpperBoundCase# is the larger value in the specified range of values.
You can (as a general rule) include as many case expressions as required inside a single Select Case statement.
Each case expression is preceded by the Case keyword:
- Case LowerBoundCase1 To UpperBoundCase1.
- Case LowerBoundCase2 To UpperBoundCase2.
- …
- Case LowerBoundCase# To UpperBoundCase#.
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
Select Case NumericTestExpression
Case LowerBoundCase1 To UpperBoundCase1
'...
Case LowerBoundCase2 To UpperBoundCase2
'...
'...
Case LowerBoundCase# To UpperBoundCase#
'...
'...
End Select
The Case keyword plus associated case expression (Case LowerBoundCase# To UpperBoundCase#) form a Case clause.
When the value returned by the numeric test expression (you specified in step #2) is between a case expression’s 2 values, the Select Case statement:
- Executes the set of statements (you specify in step #4) associated to the applicable Case clause (whose case expression matched the test expression); and
- Exits the Select Case statement.
(4) Specify the set of statements to be executed when the value returned by the numeric test expression (you specified in step #2) is between a case expression’s 2 values (you specified in step #3).
- CaseStatements1.
- CaseStatements2.
- …
- CaseStatements#.
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
Select Case NumericTestExpression
Case LowerBoundCase1 To UpperBoundCase1
CaseStatements1
Case LowerBoundCase2 To UpperBoundCase2
CaseStatements2
'...
Case LowerBoundCase# To UpperBoundCase#
CaseStatements#
'...
End Select
(5) Specify the set of statements to be executed if the value returned by the numeric test expression (you specified in step #2) isn’t between any case expression’s 2 values (you specified in step #3). These catch-all statements follow the Case Else keyword.
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
Select Case NumericTestExpression
Case LowerBoundCase1 To UpperBoundCase1
CaseStatements1
Case LowerBoundCase2 To UpperBoundCase2
CaseStatements2
'...
Case LowerBoundCase# To UpperBoundCase#
CaseStatements#
Case Else
ElseStatements
End Select
Additional Cues for Excel VBA Select Case Between 2 Values
(1) The Select Case statement is an alternative to complex If… Then… Else statements (Select Case vs. If… Then… Else). Consider using the Select Case statement when dealing with (more) complex cases.
(2) Consider indenting the statements inside Select Case statements.
(3) Consider working with the separator character (:) to separate:
- The Case clause (Case LowerBoundCase# To UpperBoundCase#) and the statements to be executed (CaseStatements#); or
- The Case Else keyword (Case Else) and the catch-all statements (ElseStatements);
When the following 2 conditions are met:
- The case results in a single statement (CaseStatement#) being executed or there’s (only) a single catch-all statement (ElseStatement); and
- The resulting line of VBA code is not excessively long.
(3) You have a significant degree of flexibility when specifying case expressions inside a Select Case statement. This flexibility includes the possibility to specify a range of values for a single case expression (as you learned in this Section).
Please refer to the Section on Excel VBA Select Case Multiple Conditions (in this Excel VBA Select Case Tutorial) for a more detailed explanation on how to create a Select Case statement to conditionally execute a set of statements based on multiple conditions (grouping several cases inside a single case expression).
(4) As a general rule: Organize case expressions:
- By decreasing order of probability.
- In such a way that any case expression excludes subsequent case expressions.
(5) The Case Else keyword/clause (Case Else: ElseStatements) is optional.
Work with the Case Else clause to specify a set of catch-all statements that are executed when none of the conditions you (originally) expected is met (no case expression matches the test expression).
(6) If:
- You omit the Case Else clause; and
- No case expression matches the test expression;
Procedure execution continues with the first statement after the end of the Select Case statement (after “End Select”).
Excel VBA Select Case Between 2 Values Example Macro
This Excel VBA Select Case Tutorial is accompanied by an Excel workbook with the data and VBA code I use in the examples inside this Tutorial (including this example). Get this example workbook (for free) by clicking the button below.
I create the Excel VBA Select Case between 2 values example macro as follows:
(1) Declare a Sub procedure (SelectCaseBetween2Values).
Sub SelectCaseBetween2Values()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
'...
End Sub
(2) Declare a variable (MyQuarterMessage) of the String data type.
Sub SelectCaseBetween2Values()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
'Declare variable to represent message to be displayed in message box
Dim MyQuarterMessage As String
'...
End Sub
(3) Enter the opening and closing statements of the Select Case statement.
Sub SelectCaseBetween2Values()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
'Declare variable to represent message to be displayed in message box
Dim MyQuarterMessage As String
Select Case '...
'...
End Select
'...
End Sub
(4) Specify the numeric test expression VBA uses to identify the set of statements to execute, as a numeric expression.
The test expression I use (Month(Date:=Date)) returns an integer (1 to 12) representing the current month of the year.
Sub SelectCaseBetween2Values()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
'Declare variable to represent message to be displayed in message box
Dim MyQuarterMessage As String
Select Case Month(Date:=Date)
'...
End Select
'...
End Sub
(5) Specify the numeric case expressions used by VBA to identify the set of statements to execute. I use the To keyword to specify a range of values for each single case expression.
The test expression I specified in step #4 returns an integer between 1 and 12.
The case expressions I specify (considering the above) are:
- 1 To 3.
- 4 To 6.
- 7 To 9.
- 10 To 12.
Sub SelectCaseBetween2Values()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
'Declare variable to represent message to be displayed in message box
Dim MyQuarterMessage As String
Select Case Month(Date:=Date)
Case 1 To 3: '...
Case 4 To 6: '...
Case 7 To 9: '...
Case 10 To 12: '...
End Select
'...
End Sub
(6) Specify the statement to be executed when the value returned by the numeric test expression (I specified in step #4) is between a case expression’s 2 values (I specified in step #5).
The statements I use assign a string to the MyQuarterMessage variable (I declared in step #2). The assigned string varies, depending on the applicable numeric case expression (I specified in step #5):
- 1 To 3: Assigned string is “It’s Q1”.
- 4 To 6: Assigned string is “It’s Q2”.
- 7 To 9: Assigned string is “It’s Q3”.
- 10 To 12: Assigned string is “It’s Q4”.
Sub SelectCaseBetween2Values()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
'Declare variable to represent message to be displayed in message box
Dim MyQuarterMessage As String
'Assign a string to the MyQuarterMessage variable, depending on the current month
Select Case Month(Date:=Date)
Case 1 To 3: MyQuarterMessage = "It's Q1"
Case 4 To 6: MyQuarterMessage = "It's Q2"
Case 7 To 9: MyQuarterMessage = "It's Q3"
Case 10 To 12: MyQuarterMessage = "It's Q4"
End Select
'...
End Sub
(7) Display a message box (MsgBox) with the value held by the MyQuarterMessage variable.
Sub SelectCaseBetween2Values()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
'Declare variable to represent message to be displayed in message box
Dim MyQuarterMessage As String
'Assign a string to the MyQuarterMessage variable, depending on the current month
Select Case Month(Date:=Date)
Case 1 To 3: MyQuarterMessage = "It's Q1"
Case 4 To 6: MyQuarterMessage = "It's Q2"
Case 7 To 9: MyQuarterMessage = "It's Q3"
Case 10 To 12: MyQuarterMessage = "It's Q4"
End Select
'Display message box with string held by the MyQuarterMessage variable
MsgBox MyQuarterMessage
End Sub
The image below displays the message box shown by Excel when I execute the Excel VBA Select Case between 2 values example macro. I execute the example macro (and create this screenshot) during April.

Select Case Between 2 Values vs. If… Then… ElseIf… Between 2 Values Example Macro
The following If… Then… ElseIf… between 2 values example macro is an equivalent example macro (to the Select Case between 2 values example macro I explain above) working with the If… Then… Else statement (vs. the Select Case statement).
Sub SelectCaseBetween2ValuesVsIfThenElseIfBetween2Values()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
'Declare variables to represent:
'(1) Number representing month
'(2) Message to be displayed in message box
Dim MyCurrentMonth As Integer
Dim MyQuarterMessage As String
'Assign number representing month to the MyCurrentMonth variable
MyCurrentMonth = Month(Date:=Date)
'Assign a string to the MyQuarterMessage variable, depending on the current month
If (MyCurrentMonth >= 1) And (MyCurrentMonth <= 3) Then
MyQuarterMessage = "It's Q1"
ElseIf (MyCurrentMonth >= 4) And (MyCurrentMonth <= 6) Then
MyQuarterMessage = "It's Q2"
ElseIf (MyCurrentMonth >= 7) And (MyCurrentMonth <= 9) Then
MyQuarterMessage = "It's Q3"
ElseIf (MyCurrentMonth >= 10) And (MyCurrentMonth <= 12) Then
MyQuarterMessage = "It's Q4"
End If
'Display message box with string held by the MyQuarterMessage variable
MsgBox MyQuarterMessage
End Sub
Notice how the Select Case statement results in more efficient VBA code that’s easier to:
- Read;
- Follow;
- Understand; and
- Work with.
The image below displays the message box shown by Excel when I execute the Excel VBA If… Then… ElseIf… between 2 values example macro. I execute the example macro (and create this screenshot) during April.

(5) Excel VBA Select Case Multiple Values
In this Section, you learn how to create a VBA Select Case multiple values statement to conditionally execute a set of statements based on whether an expression returns one of multiple (other) values.
Excel VBA Select Case Multiple Values Snippet Template/Structure
The following is the Excel VBA Select Case multiple values snippet template/structure I explain (step-by-step) in the Sections below.
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
Select Case NumericTestExpression
Case Value1Case1, Value2Case1, ..., Value#Case1
CaseStatements1
Case Value1Case2, Value2Case2, ..., Value#Case2
CaseStatements2
'...
Case Value1Case#, Value2Case#, ..., Value#Case#
CaseStatements#
Case Else
ElseStatements
End Select
Step-by-Step Process to Set Up an Excel VBA Select Case Multiple Values Statement
Do the following to create an Excel VBA Select Case multiple values statement:
(1) Enter the opening and closing statements of the Select Case statement.
- Select Case.
- End Select.
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
Select Case '...
'...
End Select
(2) Specify the test expression VBA uses to identify the set of statements to execute, as a numeric expression (an expression that can be evaluated as a number): NumericTestExpression.
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
Select Case NumericTestExpression
'...
End Select
(3) Specify the numeric case expressions used by VBA to identify the set of statements to execute. Use commas to separate multiple values inside a single numeric case expression.
- Value1Case1, Value2Case1, …, Value#Case1.
- Value1Case2, Value2Case2, …, Value#Case2.
- …
- Value1Case#, Value2Case#, …, Value#Case#.
You can (as a general rule) include as many case expressions as required inside a single Select Case statement.
Each case expression is preceded by the Case keyword:
- Case Value1Case1, Value2Case1, …, Value#Case1.
- Case Value1Case2, Value2Case2, …, Value#Case2.
- …
- Case Value1Case#, Value2Case#, …, Value#Case#.
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
Select Case NumericTestExpression
Case Value1Case1, Value2Case1, ..., Value#Case1
'...
Case Value1Case2, Value2Case2, ..., Value#Case2
'...
'...
Case Value1Case#, Value2Case#, ..., Value#Case#
'...
'...
End Select
The Case keyword plus associated case expression (Case Value1Case#, Value2Case#, …, Value#Case#) form a Case clause.
When the value returned by the numeric test expression (you specified in step #2) is equal to one of the multiple values inside a case expression, the Select Case statement:
- Executes the set of statements (you specify in step #4) associated to the applicable Case clause (whose case expression matched the test expression); and
- Exits the Select Case statement.
(4) Specify the set of statements to be executed when the value returned by the numeric test expression (you specified in step #2) is equal to one of the multiple values (you specified in step #3) inside a case expression.
- CaseStatements1.
- CaseStatements2.
- …
- CaseStatements#.
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
Select Case NumericTestExpression
Case Value1Case1, Value2Case1, ..., Value#Case1
CaseStatements1
Case Value1Case2, Value2Case2, ..., Value#Case2
CaseStatements2
'...
Case Value1Case#, Value2Case#, ..., Value#Case#
CaseStatements#
'...
End Select
(5) Specify the set of statements to be executed if the value returned by the numeric test expression (you specified in step #2) isn’t equal to any of the multiple values inside any of the case expressions (you specified in step #3). These catch-all statements follow the Case Else keyword.
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
Select Case NumericTestExpression
Case Value1Case1, Value2Case1, ..., Value#Case1
CaseStatements1
Case Value1Case2, Value2Case2, ..., Value#Case2
CaseStatements2
'...
Case Value1Case#, Value2Case#, ..., Value#Case#
CaseStatements#
Case Else
ElseStatements
End Select
Additional Cues for Excel VBA Select Case Multiple Values
(1) The Select Case statement is an alternative to complex If… Then… Else statements (Select Case vs. If… Then… Else). Consider using the Select Case statement when dealing with (more) complex cases.
(2) Consider indenting the statements inside Select Case statements.
(3) Consider working with the separator character (:) to separate:
- The Case clause (Case Value1Case#, Value2Case#, …, Value#Case#) and the statements to be executed (CaseStatements#); or
- The Case Else keyword (Case Else) and the catch-all statements (ElseStatements);
When the following 2 conditions are met:
- The case results in a single statement (CaseStatement#) being executed or there’s (only) a single catch-all statement (ElseStatement); and
- The resulting line of VBA code is not excessively long.
(3) You have a significant degree of flexibility when specifying case expressions inside a Select Case statement. This flexibility includes the possibility to specify multiple values for a single case expression (as you learned in this Section).
Please refer to the Section on Excel VBA Select Case Multiple Conditions (in this Excel VBA Select Case Tutorial) for a more detailed explanation on how to create a Select Case statement to conditionally execute a set of statements based on multiple conditions (grouping several cases inside a single case expression).
(4) As a general rule: Organize case expressions:
- By decreasing order of probability.
- In such a way that any case expression excludes subsequent case expressions.
(5) The Case Else keyword/clause (Case Else: ElseStatements) is optional.
Work with the Case Else clause to specify a set of catch-all statements that are executed when none of the conditions you (originally) expected is met (no case expression matches the test expression).
(6) If:
- You omit the Case Else clause; and
- No case expression matches the test expression;
Procedure execution continues with the first statement after the end of the Select Case statement (after “End Select”).
Excel VBA Select Case Multiple Values Example Macro
This Excel VBA Select Case Tutorial is accompanied by an Excel workbook with the data and VBA code I use in the examples inside this Tutorial (including this example). Get this example workbook (for free) by clicking the button below.
I create the VBA Select Case multiple values example macro as follows:
(1) Declare a Sub procedure (SelectCaseMultipleValues).
Sub SelectCaseMultipleValues()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
'...
End Sub
(2) Declare a variable (MyMonthMessage) of the String data type.
Sub SelectCaseMultipleValues()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
'Declare variable to represent message to be displayed in message box
Dim MyMonthMessage As String
'...
End Sub
(3) Enter the opening and closing statements of the Select Case statement.
Sub SelectCaseMultipleValues()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
'Declare variable to represent message to be displayed in message box
Dim MyMonthMessage As String
Select Case '...
'...
End Select
'...
End Sub
(4) Specify the numeric test expression VBA uses to identify the set of statements to execute, as a numeric expression.
The test expression I use (Month(Date:=Date)) returns an integer (1 to 12) representing the current month of the year.
Sub SelectCaseMultipleValues()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
'Declare variable to represent message to be displayed in message box
Dim MyMonthMessage As String
Select Case Month(Date:=Date)
'...
End Select
'...
End Sub
(5) Specify the numeric case expressions used by VBA to identify the set of statements to execute. I use commas to separate multiple values inside a single numeric case expression.
The test expression I specified in step #4 returns an integer between 1 and 12.
The case expressions I specify (considering the above) are:
- 1, 4, 7, 10.
- 2, 5, 8, 11.
- 3, 6, 9, 12.
Sub SelectCaseMultipleValues()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
'Declare variable to represent message to be displayed in message box
Dim MyMonthMessage As String
Select Case Month(Date:=Date)
Case 1, 4, 7, 10: '...
Case 2, 5, 8, 11: '...
Case 3, 6, 9, 12: '...
End Select
'...
End Sub
(6) Specify the statement to be executed when the value returned by the numeric test expression (I specified in step #4) is equal to one of the multiple values (I specified in step #5) inside a case expression.
The statements I use assign a string to the MyMonthMessage variable (I declared in step #2). The assigned string varies, depending on the applicable numeric case expression (I specified in step #5):
- 1, 4, 7, 10: Assigned string is “It’s January, April, July, or October”.
- 2, 5, 8, 11: Assigned string is “It’s February, May, August, or November”.
- 3, 6, 9, 12: Assigned string is “It’s March, June, September, or December”.
Sub SelectCaseMultipleValues()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
'Declare variable to represent message to be displayed in message box
Dim MyMonthMessage As String
'Assign a string to the MyMonthMessage variable, depending on the current month
Select Case Month(Date:=Date)
Case 1, 4, 7, 10: MyMonthMessage = "It's January, April, July, or October"
Case 2, 5, 8, 11: MyMonthMessage = "It's February, May, August, or November"
Case 3, 6, 9, 12: MyMonthMessage = "It's March, June, September, or December"
End Select
'...
End Sub
(7) Display a message box (MsgBox) with the value held by the MyMonthMessage variable.
Sub SelectCaseMultipleValues()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
'Declare variable to represent message to be displayed in message box
Dim MyMonthMessage As String
'Assign a string to the MyMonthMessage variable, depending on the current month
Select Case Month(Date:=Date)
Case 1, 4, 7, 10: MyMonthMessage = "It's January, April, July, or October"
Case 2, 5, 8, 11: MyMonthMessage = "It's February, May, August, or November"
Case 3, 6, 9, 12: MyMonthMessage = "It's March, June, September, or December"
End Select
'Display message box with string held by the MyMonthMessage variable
MsgBox MyMonthMessage
End Sub
The image below displays the message box shown by Excel when I execute the Excel VBA Select Case multiple values example macro. I execute the example macro (and create this screenshot) during May.

Select Case Multiple Values vs. If… Then… ElseIf… Multiple Values Example Macro
The following If… Then… ElseIf… multiple values example macro is an equivalent example macro (to the Select Case multiple values example macro I explain above) working with the If… Then… Else statement (vs. the Select Case statement).
Sub SelectCaseMultipleValuesVsIfThenElseIfMultipleValues()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
'Declare variables to represent:
'(1) Number representing month
'(2) Message to be displayed in message box
Dim MyCurrentMonth As Integer
Dim MyMonthMessage As String
'Assign number representing month to the MyCurrentMonth variable
MyCurrentMonth = Month(Date:=Date)
'Assign a string to the MyMonthMessage variable, depending on the current month
If (MyCurrentMonth = 1) Or (MyCurrentMonth = 4) Or (MyCurrentMonth = 7) Or (MyCurrentMonth = 10) Then
MyMonthMessage = "It's January, April, July, or October"
ElseIf (MyCurrentMonth = 2) Or (MyCurrentMonth = 5) Or (MyCurrentMonth = 8) Or (MyCurrentMonth = 11) Then
MyMonthMessage = "It's February, May, August, or November"
ElseIf (MyCurrentMonth = 3) Or (MyCurrentMonth = 6) Or (MyCurrentMonth = 9) Or (MyCurrentMonth = 12) Then
MyMonthMessage = "It's March, June, September, or December"
End If
'Display message box with string held by the MyMonthMessage variable
MsgBox MyMonthMessage
End Sub
Notice how the Select Case statement results in more efficient VBA code that’s easier to:
- Read;
- Follow;
- Understand; and
- Work with.
The image below displays the message box shown by Excel when I execute the Excel VBA If… Then… ElseIf… multiple values example macro. I execute the example macro (and create this screenshot) during May.

(6) Excel VBA Select Case Multiple Conditions
In this Section, you learn how to create an Excel VBA Select Case statement to conditionally execute a set of statements based on:
- An expression’s value; and
- Multiple conditions (grouping several cases inside a single case expression).
Excel VBA Select Case Multiple Conditions Snippet Template/Structure
The following is the Excel VBA Select Case multiple conditions snippet template/structure I explain (step-by-step) in the Sections below.
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
Select Case TestExpression
Case CaseExpression1
CaseStatements1
Case CaseExpression2
CaseStatements2
'...
Case CaseExpression#
CaseStatements#
Case Else
ElseStatements
End Select
When creating a Select Case multiple conditions statement, each CaseExpression# can follow (as appropriate) one of the following templates/structures:
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/ 'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/ LowerBoundCase To UpperBoundCase Is ComparisonOperator ComparisonCase Case1, Case2, Case3, …, Case# CaseRange1, CaseRange2, CaseRange3, …, CaseRange#
Step-by-Step Process to Set Up an Excel VBA Select Case Multiple Conditions Statement
Do the following to create an Excel VBA Select Case multiple conditions statement:
(1) Enter the opening and closing statements of the Select Case statement.
- Select Case.
- End Select.
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
Select Case '...
'...
End Select
(2) Specify the test expression VBA uses to identify the set of statements to execute: TestExpression.
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
Select Case TestExpression
'...
End Select
(3) Specify the case expressions used by VBA to identify the set of statements to execute:
- CaseExpression1.
- CaseExpression2.
- …
- CaseExpression#.
You can (as a general rule) include as many case expressions as required inside a single Select Case statement.
Each case expression is preceded by the Case keyword:
- Case CaseExpression1.
- Case CaseExpression2.
- …
- Case CaseExpression#.
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
Select Case TestExpression
Case CaseExpression1
'...
Case CaseExpression2
'...
'...
Case CaseExpression#
'...
End Select
When creating a Select Case multiple conditions statement, use the following constructs and structures to group several cases inside a single case expression:
(3.1.) Use the To and Is keywords to specify a range of values or strings for a single case expression.
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/ 'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/ 'To keyword LowerBoundCase To UpperBoundCase 'Is keyword Is ComparisonOperator ComparisonCase
(3.2.) Use commas to separate multiple:
- Values or strings; or
- Value or string ranges (usually created by working with the To or Is keywords I explain above);
Inside a single case expression.
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/ 'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/ 'Values or strings Case1, Case2, Case3, …, Case# 'Value or string ranges CaseRange1, CaseRange2, CaseRange3, …, CaseRange#
The Case keyword plus associated case expression (Case CaseExpression#) form a Case clause.
When the test expression (you specified in step #2) matches an individual case expression, the Select Case statement:
- Executes the set of statements (you specify in step #4) associated to the applicable Case clause (whose case expression matched the test expression); and
- Exits the Select Case statement.
(4) Specify the set of statements to be executed when the applicable case expression (you specified in step #3) matches the test expression (you specified in step #2).
- CaseStatements1.
- CaseStatements2.
- …
- CaseStatements#.
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
Select Case TestExpression
Case CaseExpression1
CaseStatements1
Case CaseExpression2
CaseStatements2
'...
Case CaseExpression#
CaseStatements#
'...
End Select
(5) Specify the set of statements to be executed if no case expression (you specified in step #3) matches the test expression (you specified in step #2). These catch-all statements follow the Case Else keyword.
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
Select Case TestExpression
Case CaseExpression1
CaseStatements1
Case CaseExpression2
CaseStatements2
'...
Case CaseExpression#
CaseStatements#
Case Else
ElseStatements
End Select
Additional Cues for Excel VBA Select Case Multiple Conditions
(1) The Select Case statement is an alternative to complex If… Then… Else statements (Select Case vs. If… Then… Else). Consider using the Select Case statement when dealing with (more) complex cases.
(2) Consider indenting the statements inside Select Case statements.
(3) Consider working with the separator character (:) to separate:
- The Case clause (Case CaseExpression#) and the statements to be executed (CaseStatements#); or
- The Case Else keyword (Case Else) and the catch-all statements (ElseStatements);
When the following 2 conditions are met:
- The case results in a single statement (CaseStatement#) being executed or there’s (only) a single catch-all statement (ElseStatement); and
- The resulting line of VBA code is not excessively long.
(3) You have a significant degree of flexibility when specifying case expressions inside a Select Case statement. This flexibility includes the possibility to group several cases inside a single case expression (as you learned in this Section).
(4) When using the Is keyword to specify a range of values or strings for a single case expression (Is ComparisonOperator ComparisonCase), ComparisonOperator is a comparison operator, excluding the following operators:
- Is.
- Like.
(5) As a general rule: Organize case expressions:
- By decreasing order of probability.
- In such a way that any case expression excludes subsequent case expressions.
(6) The Case Else keyword/clause (Case Else: ElseStatements) is optional.
Work with the Case Else clause to specify a set of catch-all statements that are executed when none of the conditions you (originally) expected is met (no case expression matches the test expression).
(7) If:
- You omit the Case Else clause; and
- No case expression matches the test expression;
Procedure execution continues with the first statement after the end of the Select Case statement (after “End Select”).
Excel VBA Select Case Multiple Conditions Example Macro
This Excel VBA Select Case Tutorial is accompanied by an Excel workbook with the data and VBA code I use in the examples inside this Tutorial (including this example). Get this example workbook (for free) by clicking the button below.
I create the Excel VBA Select Case multiple conditions example macro as follows:
(1) Declare a Sub procedure (SelectCaseMultipleConditions).
Sub SelectCaseMultipleConditions()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
'...
End Sub
(2) Declare a variable (MyMonthMessage) of the String data type.
Sub SelectCaseMultipleConditions()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
'Declare variable to represent message to be displayed in message box
Dim MyMonthMessage As String
'...
End Sub
(3) Enter the opening and closing statements of the Select Case statement.
Sub SelectCaseMultipleConditions()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
'Declare variable to represent message to be displayed in message box
Dim MyMonthMessage As String
Select Case '...
'...
End Select
'...
End Sub
(4) Specify the test expression VBA uses to identify the set of statements to execute.
The test expression I use (Month(Date:=Date)) returns an integer (1 to 12) representing the current month of the year.
Sub SelectCaseMultipleConditions()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
'Declare variable to represent message to be displayed in message box
Dim MyMonthMessage As String
Select Case Month(Date:=Date)
'...
End Select
'...
End Sub
(5) Specify the case expressions used by VBA to identify the set of statements to execute.
I use the following constructs and structures to group several cases inside a single case expression:
- The To and Is keywords to specify a range of values or strings for a single case expression.
- Commas to separate multiple values or strings.
The test expression I specified in step #4 returns an integer between 1 and 12.
The case expressions I specify (considering the above) are:
- Is < 7.
- 7 To 9.
- 10, 11.
Sub SelectCaseMultipleConditions()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
'Declare variable to represent message to be displayed in message box
Dim MyMonthMessage As String
Select Case Month(Date:=Date)
Case Is < 7: '...
Case 7 To 9: '...
Case 10, 11: '...
Case Else: '...
End Select
'...
End Sub
(6) Specify the statement to be executed when the applicable case expression (I specified in step #5) matches the test expression (I specified in step #4).
The statements I use assign a string to the MyMonthMessage variable (I declared in step #2). The assigned string varies, depending on the applicable case expression (I specified in step #5):
- Is < 7: Assigned string is “It’s H1”.
- 7 To 9: Assigned string is “It’s Q3”.
- 10, 11: Assigned string is “It’s Q4, but not yet December”.
Sub SelectCaseMultipleConditions()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
'Declare variable to represent message to be displayed in message box
Dim MyMonthMessage As String
'Assign a string to the MyMonthMessage variable, depending on the current month
Select Case Month(Date:=Date)
'If the current month is less than 7, message is "It's H1"
Case Is < 7: MyMonthMessage = "It's H1"
'If the current month is from 7 to 9, message is "It's Q3"
Case 7 To 9: MyMonthMessage = "It's Q3"
'If the current month is 10 or 11, message is "It's Q4, but not yet December"
Case 10, 11: MyMonthMessage = "It's Q4, but not yet December"
'...
End Select
'...
End Sub
(7) Specify the catch-all statement to be executed if no case expression (from the case expressions I specified in step #5) matches the test expression (I specified in step #4).
The statement I use assigns a string to the MyMonthMessage variable (I declared in step #2): “It’s December”.
Sub SelectCaseMultipleConditions()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
'Declare variable to represent message to be displayed in message box
Dim MyMonthMessage As String
'Assign a string to the MyMonthMessage variable, depending on the current month
Select Case Month(Date:=Date)
'If the current month is less than 7, message is "It's H1"
Case Is < 7: MyMonthMessage = "It's H1"
'If the current month is from 7 to 9, message is "It's Q3"
Case 7 To 9: MyMonthMessage = "It's Q3"
'If the current month is 10 or 11, message is "It's Q4, but not yet December"
Case 10, 11: MyMonthMessage = "It's Q4, but not yet December"
'If the current month doesn't match any of the previous case expressions, message is "It's December"
Case Else: MyMonthMessage = "It's December"
End Select
'...
End Sub
(8) Display a message box (MsgBox) with the value held by the MyMonthMessage variable.
Sub SelectCaseMultipleConditions()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
'Declare variable to represent message to be displayed in message box
Dim MyMonthMessage As String
'Assign a string to the MyMonthMessage variable, depending on the current month
Select Case Month(Date:=Date)
'If the current month is less than 7, message is "It's H1"
Case Is < 7: MyMonthMessage = "It's H1"
'If the current month is from 7 to 9, message is "It's Q3"
Case 7 To 9: MyMonthMessage = "It's Q3"
'If the current month is 10 or 11, message is "It's Q4, but not yet December"
Case 10, 11: MyMonthMessage = "It's Q4, but not yet December"
'If the current month doesn't match any of the previous case expressions, message is "It's December"
Case Else: MyMonthMessage = "It's December"
End Select
'Display message box with string held by the MyMonthMessage variable
MsgBox MyMonthMessage
End Sub
The image below displays the message box shown by Excel when I execute the Excel VBA Select Case multiple conditions example macro. I execute the example macro (and create this screenshot) during March.

Select Case Multiple Conditions vs. If… Then… ElseIf… Else Multiple Conditions Example Macro
The following If… Then… ElseIf… Else multiple conditions example macro is an equivalent example macro (to the Select Case multiple conditions example macro I explain above) working with the If… Then… Else statement (vs. the Select Case statement).
Sub SelectCaseMultipleConditionsVsIfThenElseIfElseMultipleConditions()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'More information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-select-case/
'Declare variables to represent:
'(1) Number representing month
'(2) Message to be displayed in message box
Dim MyCurrentMonth As Integer
Dim MyMonthMessage As String
'Assign number representing month to the MyCurrentMonth variable
MyCurrentMonth = Month(Date:=Date)
'Assign a string to the MyMonthMessage variable, depending on the current month
If MyCurrentMonth < 7 Then
MyMonthMessage = "It's H1"
ElseIf (MyCurrentMonth >= 7) And (MyCurrentMonth <= 9) Then
MyMonthMessage = "It's Q3"
ElseIf (MyCurrentMonth = 10) Or (MyCurrentMonth = 11) Then
MyMonthMessage = "It's Q4, but not yet December"
Else
MyMonthMessage = "It's December"
End If
'Display message box with string held by the MyMonthMessage variable
MsgBox MyMonthMessage
End Sub
Notice how the Select Case statement results in more efficient VBA code that’s easier to:
- Read;
- Follow;
- Understand; and
- Work with.
The image below displays the message box shown by Excel when I execute the Excel VBA If… Then… ElseIf… Else multiple conditions example macro. I execute the example macro (and create this screenshot) during March.

Download the Excel VBA Select Case Example Workbook
This Excel VBA Select Case Tutorial is accompanied by an Excel workbook with the data and VBA code I use in the examples above. Get this example workbook (for free) by clicking the button below.
The following Excel Macro and VBA Tutorials may help you better understand and implement the contents above.
- Tutorials about general macro and VBA constructs and structures:
- Tutorials for Beginners:
- Excel Macros: Click here to open.
- Excel VBA: Click here to open.
- Enable macros in Excel: Click here to open.
- Work with the Visual Basic Editor (VBE): Click here to open.
- Create Sub procedures: Click here to open.
- Work with:
- Variables: Click here to open.
- Data types: Click here to open.
- Functions: Click here to open.
- Tutorials for Beginners:
- Tutorials with practical VBA applications and macro examples:
- Excel VBA Change Font Color Based on Cell Value: Click here to open.
- Create a message box: Click here to open.
- Create an input box: Click here to open.
This Excel VBA Select Case Tutorial is part of a more comprehensive series of Excel VBA Select Case Tutorials.
- Excel VBA Select Case Tutorial: Click here to open.
- Excel VBA Select Case Or: Click here to open.
- Excel VBA Select Case And Operator: Click here to open.
- Excel VBA Select Case Multiple Test Expressions: Click here to open.
- Excel VBA Select Case Like Wildcard: Click here to open.
- Excel VBA Select Case Inside For… Next Loop: Click here to open.
- Excel VBA Select Case Range of Cells: Click here to open.
You can find more Excel and VBA Tutorials in the organized Tutorials Archive: Click here to visit the Archives. The following are some of my most popular Excel Tutorials and Training Resources:
- Excel Keyboard Shortcuts Cheat Sheet: Click here to open.
- Work with the Excel XLOOKUP Function: Click here to open.
- Excel Power Query (Get & Transform) Tutorial for Beginners: Click here to open.
If you want to learn how to automate Excel (and save time) by working with macros and VBA, you may be interested in the following Premium Excel Macro and VBA Training Materials:
- Premium Courses at the Power Spreadsheets Academy: Click here to open.
- Books at the Power Spreadsheets Library: Click here to open.
- VBA Cheat Sheets: Click here to open.
If you want to save time when working with macros and VBA, you may be interested in AutoMacro: Click here to learn more about AutoMacro (affiliate link). AutoMacro is an add-in for VBA that installs directly into the VBE. Depending on the version, AutoMacro comes loaded with:
- Code generators.
- An extensive code library.
- The ability to create your own code library.
- Advanced coding tools.
If you need help with Excel tasks/projects, you may be interested in working with me: Click here to learn more about working with me.
This post provides a complete guide to the VBA If Statement in VBA. If you are looking for the syntax then check out the quick guide in the first section which includes some examples.
The table of contents below provides an overview of what is included in the post. You use this to navigate to the section you want or you can read the post from start to finish.
“Guess, if you can, and choose, if you dare.” – Pierre Corneille
Quick Guide to the VBA If Statement
| Description | Format | Example |
|---|---|---|
| If Then | If [condition is true] Then [do something] End If |
If score = 100 Then Debug.Print «Perfect» End If |
| If Else | If [condition is true] Then [do something] Else [do something] End If |
If score = 100 Then Debug.Print «Perfect» Else Debug.Print «Try again» End If |
| If ElseIf | If [condition 1 is true] Then [do something] ElseIf [condition 2 is true] Then [do something] End If |
If score = 100 Then Debug.Print «Perfect» ElseIf score > 50 Then Debug.Print «Passed» ElseIf score <= 50 Then Debug.Print «Try again» End If |
| Else and ElseIf (Else must come after ElseIf’s) |
If [condition 1 is true] Then [do something] ElseIf [condition 2 is true] Then [do something] Else [do something] End If |
If score = 100 Then Debug.Print «Perfect» ElseIf score > 50 Then Debug.Print «Passed» ElseIf score > 30 Then Debug.Print «Try again» Else Debug.Print «Yikes» End If |
| If without Endif (One line only) |
If [condition is true] Then [do something] | If value <= 0 Then value = 0 |
The following code shows a simple example of using the VBA If statement
If Sheet1.Range("A1").Value > 5 Then Debug.Print "Value is greater than five." ElseIf Sheet1.Range("A1").Value < 5 Then Debug.Print "value is less than five." Else Debug.Print "value is equal to five." End If
The Webinar
Members of the Webinar Archives can access the webinar for this article by clicking on the image below.
(Note: Website members have access to the full webinar archive.)
What is the VBA If Statement
The VBA If statement is used to allow your code to make choices when it is running.
You will often want to make choices based on the data your macros reads.
For example, you may want to read only the students who have marks greater than 70. As you read through each student you would use the If Statement to check the marks of each student.
The important word in the last sentence is check. The If statement is used to check a value and then to perform a task based on the results of that check.
The Test Data and Source Code
We’re going to use the following test data for the code examples in this post:
You can download the test data with all the source code for post plus the solution to the exercise at the end:
Format of the VBA If-Then Statement
The format of the If Then statement is as follows
If [condition is true] Then
The If keyword is followed by a Condition and the keyword Then
Every time you use an If Then statement you must use a matching End If statement.
When the condition evaluates to true, all the lines between If Then and End If are processed.
If [condition is true] Then [lines of code] [lines of code] [lines of code] End If
To make your code more readable it is good practice to indent the lines between the If Then and End If statements.
Indenting Between If and End If
Indenting simply means to move a line of code one tab to the right. The rule of thumb is to indent between start and end statements like
Sub … End Sub
If Then … End If
If Then… ElseIf … Else … Endif
For … Next
Do While … Loop
Select Case … End Case
To indent the code you can highlight the lines to indent and press the Tab key. Pressing Shift + Tab will Outdent the code i.e. move it one tab to the left.
You can also use the icons from the Visual Basic Toolbar to indent/outdent the code
Select code and click icons to indent/outdent
If you look at any code examples on this website you will see that the code is indented.
A Simple If Then Example
The following code prints out the names of all students with marks greater than 50 in French.
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub ReadMarks() Dim i As Long ' Go through the marks columns For i = 2 To 11 ' Check if marks greater than 50 If Sheet1.Range("C" & i).Value > 50 Then ' Print student name to the Immediate Window(Ctrl + G) Debug.Print Sheet1.Range("A" & i).Value & " " & Sheet1.Range("B" & i).Value End If Next End Sub
Results
Bryan Snyder
Juanita Moody
Douglas Blair
Leah Frank
Monica Banks
Play around with this example and check the value or the > sign and see how the results change.
Using Conditions with the VBA If Statement
The piece of code between the If and the Then keywords is called the condition. A condition is a statement that evaluates to true or false. They are mostly used with Loops and If statements. When you create a condition you use signs like >,<,<>,>=,<=,=.
The following are examples of conditions
| Condition | This is true when |
|---|---|
| x < 5 | x is less than 5 |
| x <= 5 | x is less than or equal to 5 |
| x > 5 | x is greater than 5 |
| x >= 5 | x is greater than or equal to 5 |
| x = 5 | x is equal to 5 |
| x <> 5 | x does not equal 5 |
| x > 5 And x < 10 | x is greater than 5 AND x is less than 10 |
| x = 2 Or x >10 | x is equal to 2 OR x is greater than 10 |
| Range(«A1») = «John» | Cell A1 contains text «John» |
| Range(«A1») <> «John» | Cell A1 does not contain text «John» |
You may have noticed x=5 as a condition. This should not be confused with x=5 when used as an assignment.
When equals is used in a condition it means “is the left side equal to the right side”.
The following table demonstrates how the equals sign is used in conditions and assignments
| Using Equals | Statement Type | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| Loop Until x = 5 | Condition | Is x equal to 5 |
| Do While x = 5 | Condition | Is x equal to 5 |
| If x = 5 Then | Condition | Is x equal to 5 |
| For x = 1 To 5 | Assignment | Set the value of x to 1, then to 2 etc. |
| x = 5 | Assignment | Set the value of x to 5 |
| b = 6 = 5 | Assignment and Condition | Assign b to the result of condition 6 = 5 |
| x = MyFunc(5,6) | Assignment | Assign x to the value returned from the function |
The last entry in the above table shows a statement with two equals. The first equals sign is the assignment and any following equals signs are conditions.
This might seem confusing at first but think of it like this. Any statement that starts with a variable and an equals is in the following format
[variable] [=] [evaluate this part]
So whatever is on the right of the equals sign is evaluated and the result is placed in the variable. Taking the last three assignments again, you could look at them like this
[x] [=] [5]
[b] [=] [6 = 5]
[x] [=] [MyFunc(5,6)]
Using ElseIf with the VBA If Statement
The ElseIf statement allows you to choose from more than one option. In the following example we print for marks that are in the Distinction or High Distinction range.
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub UseElseIf() If Marks >= 85 Then Debug.Print "High Destinction" ElseIf Marks >= 75 Then Debug.Print "Destinction" End If End Sub
The important thing to understand is that order is important. The If condition is checked first.
If it is true then “High Distinction” is printed and the If statement ends.
If it is false then the code moves to the next ElseIf and checks it condition.
Let’s swap around the If and ElseIf from the last example. The code now look like this
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub UseElseIfWrong() ' This code is incorrect as the ElseIf will never be true If Marks >= 75 Then Debug.Print "Destinction" ElseIf Marks >= 85 Then ' code will never reach here Debug.Print "High Destinction" End If End Sub
In this case we check for a value being over 75 first. We will never print “High Distinction” because if a value is over 85 is will trigger the first if statement.
To avoid these kind of problems we should use two conditions. These help state exactly what you are looking for a remove any confusion. The example below shows how to use these. We will look at more multiple conditions in the section below.
If marks >= 75 And marks < 85 Then Debug.Print "Destinction" ElseIf marks >= 85 And marks <= 100 Then Debug.Print "High Destinction" End If
Let’s expand the original code. You can use as many ElseIf statements as you like. We will add some more to take into account all our mark classifications.
If you want to try out these examples you can download the code from the top of this post.
Using Else With the VBA If Statement
The VBA Else statement is used as a catch all. It basically means “if no conditions were true” or “everything else”. In the previous code example, we didn’t include a print statement for a fail mark. We can add this using Else.
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub UseElse() If Marks >= 85 Then Debug.Print "High Destinction" ElseIf Marks >= 75 Then Debug.Print "Destinction" ElseIf Marks >= 55 Then Debug.Print "Credit" ElseIf Marks >= 40 Then Debug.Print "Pass" Else ' For all other marks Debug.Print "Fail" End If End Sub
So if it is not one of the other types then it is a fail.
Let’s write some code to go through our sample data and print the student and their classification:
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub AddClass() ' get the last row Dim startRow As Long, lastRow As Long startRow = 2 lastRow = Sheet1.Cells(Sheet1.Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row Dim i As Long, Marks As Long Dim sClass As String ' Go through the marks columns For i = startRow To lastRow Marks = Sheet1.Range("C" & i).Value ' Check marks and classify accordingly If Marks >= 85 Then sClass = "High Destinction" ElseIf Marks >= 75 Then sClass = "Destinction" ElseIf Marks >= 55 Then sClass = "Credit" ElseIf Marks >= 40 Then sClass = "Pass" Else ' For all other marks sClass = "Fail" End If ' Write out the class to column E Sheet1.Range("E" & i).Value = sClass Next End Sub
The results look like this with column E containing the classification of the marks
Results
Remember that you can try these examples for yourself with the code download from the top of this post.
Using Logical Operators with the VBA If Statement
You can have more than one condition in an If Statement. The VBA keywords And and Or allow use of multiple conditions.
These words work in a similar way to how you would use them in English.
Let’s look at our sample data again. We now want to print all the students that got over between 50 and 80 marks.
We use And to add an extra condition. The code is saying: if the mark is greater than or equal 50 and less than 75 then print the student name.
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub CheckMarkRange() Dim i As Long, marks As Long For i = 2 To 11 ' Store marks for current student marks = Sheet1.Range("C" & i).Value ' Check if marks greater than 50 and less than 75 If marks >= 50 And marks < 80 Then ' Print first and last name to Immediate window(Ctrl G) Debug.Print Sheet1.Range("A" & i).Value & Sheet1.Range("B" & i).Value End If Next End Sub
Results
Douglas Blair
Leah Frank
Monica Banks
In our next example we want the students who did History or French. So in this case we are saying if the student did History OR if the student did French:
' Description: Uses OR to check the study took History or French. ' Worksheet: Marks ' Output: Result are printed to the Immediate Windows(Ctrl + G) ' https://excelmacromastery.com/vba-if Sub UseOr() ' Get the data range Dim rg As Range Set rg = shMarks.Range("A1").CurrentRegion Dim i As Long, subject As String ' Read through the data For i = 2 To rg.Rows.Count ' Get the subject subject = rg.Cells(i, 4).Value ' Check if subject greater than 50 and less than 80 If subject = "History" Or subject = "French" Then ' Print first name and subject to Immediate window(Ctrl G) Debug.Print rg.Cells(i, 1).Value & " " & rg.Cells(i, 4).Value End If Next End Sub
Results
Bryan History
Bradford French
Douglas History
Ken French
Leah French
Rosalie History
Jackie History
Using Multiple conditions like this is often a source of errors. The rule of thumb to remember is to keep them as simple as possible.
Using If And
The AND works as follows
| Condition 1 | Condition 2 | Result |
| TRUE | TRUE | TRUE |
| TRUE | FALSE | FALSE |
| FALSE | TRUE | FALSE |
| FALSE | FALSE | FALSE |
What you will notice is that AND is only true when all conditions are true
Using If Or
The OR keyword works as follows
| Condition 1 | Condition 2 | Result |
| TRUE | TRUE | TRUE |
| TRUE | FALSE | TRUE |
| FALSE | TRUE | TRUE |
| FALSE | FALSE | FALSE |
What you will notice is that OR is only false when all the conditions are false.
Mixing AND and OR together can make the code difficult to read and lead to errors. Using parenthesis can make the conditions clearer.
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub OrWithAnd() Dim subject As String, marks As Long subject = "History" marks = 5 If (subject = "French" Or subject = "History") And marks >= 6 Then Debug.Print "True" Else Debug.Print "False" End If End Sub
Using If Not
There is also a NOT operator. This returns the opposite result of the condition.
| Condition | Result |
| TRUE | FALSE |
| FALSE | TRUE |
The following two lines of code are equivalent.
If marks < 40 Then If Not marks >= 40 Then
as are
If True Then If Not False Then
and
If False Then If Not True Then
Putting the condition in parenthesis makes the code easier to read
If Not (marks >= 40) Then
A common usage of Not when checking if an object has been set. Take a worksheet for example. Here we declare the worksheet
Dim mySheet As Worksheet ' Some code here
We want to check mySheet is valid before we use it. We can check if it is nothing.
If mySheet Is Nothing Then
There is no way to check if it is something as there is many different ways it could be something. Therefore we use Not with Nothing
If Not mySheet Is Nothing Then
If you find this a bit confusing you can use parenthesis like this
If Not (mySheet Is Nothing) Then
The IIF function
Note that you can download the IIF examples below and all source code from the top of this post.
VBA has an fuction similar to the Excel If function. In Excel you will often use the If function as follows:
=IF(F2=””,””,F1/F2)
The format is
=If(condition, action if true, action if false).
VBA has the IIf statement which works the same way. Let’s look at an example. In the following code we use IIf to check the value of the variable val. If the value is greater than 10 we print true otherwise we print false:
' Description: Using the IIF function to check a number. ' Worksheet: Marks ' Output: Result are printed to the Immediate Windows(Ctrl + G) ' https://excelmacromastery.com/vba-if Sub CheckNumberIIF() Dim result As Boolean Dim number As Long ' Prints True number = 11 result = IIf(number > 10, True, False) Debug.Print "Number " & number & " greater than 10 is " & result ' Prints false number = 5 result = IIf(number > 10, True, False) Debug.Print "Number " & number & " greater than 10 is " & result End Sub
In our next example we want to print out Pass or Fail beside each student depending on their marks. In the first piece of code we will use the normal VBA If statement to do this:
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub CheckMarkRange() Dim i As Long, marks As Long For i = 2 To 11 ' Store marks for current student marks = Sheet1.Range("C" & i).Value ' Check if student passes or fails If marks >= 40 Then ' Write out names to to Column F Sheet1.Range("E" & i) = "Pass" Else Sheet1.Range("E" & i) = "Fail" End If Next End Sub
In the next piece of code we will use the IIf function. You can see that the code is much neater here:
' Description: Using the IIF function to check marks. ' Worksheet: Marks ' Output: Result are printed to the Immediate Windows(Ctrl + G) ' https://excelmacromastery.com/vba-if Sub CheckMarkRange() ' Get the data range Dim rg As Range Set rg = shMarks.Range("A1").CurrentRegion Dim i As Long, marks As Long, result As String ' Go through the marks columns For i = 2 To rg.Rows.Count ' Store marks for current student marks = rg.Cells(i, 3).Value ' Check if student passes or fails result = IIf(marks >= 40, "Pass", "Fail") ' Print the name and result Debug.Print rg.Cells(i, 1).Value, result Next End Sub
You can see the IIf function is very useful for simple cases where you are dealing with two possible options.
Using Nested IIf
You can also nest IIf statements like in Excel. This means using the result of one IIf with another. Let’s add another result type to our previous examples. Now we want to print Distinction, Pass or Fail for each student.
Using the normal VBA we would do it like this
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub CheckResultType2() Dim i As Long, marks As Long For i = 2 To 11 ' Store marks for current student marks = Sheet1.Range("C" & i).Value If marks >= 75 Then Sheet1.Range("E" & i).Value = "Distinction" ElseIf marks >= 40 Then ' Write out names to to Column F Sheet1.Range("E" & i).Value = "Pass" Else Sheet1.Range("E" & i).Value = "Fail" End If Next End Sub
Using nested IIfs we could do it like this:
' Description: Using a nested IIF function to check marks. ' Worksheet: Marks ' Output: Result are printed to the Immediate Windows(Ctrl + G) ' https://excelmacromastery.com/vba-if Sub UsingNestedIIF() ' Get the data range Dim rg As Range Set rg = shMarks.Range("A1").CurrentRegion Dim i As Long, marks As Long, result As String ' Go through the marks columns For i = 2 To rg.Rows.Count marks = rg.Cells(i, 3).Value result = IIf(marks >= 55, "Credit", IIf(marks >= 40, "Pass", "Fail")) Debug.Print marks, result Next i End Sub
Using nested IIf is fine in simple cases like this. The code is simple to read and therefore not likely to have errors.
What to Watch Out For
It is important to understand that the IIf function always evaluates both the True and False parts of the statement regardless of the condition.
In the following example we want to divide by marks when it does not equal zero. If it equals zero we want to return zero.
marks = 0 total = IIf(marks = 0, 0, 60 / marks)
However, when marks is zero the code will give a “Divide by zero” error. This is because it evaluates both the True and False statements. The False statement here i.e. (60 / Marks) evaluates to an error because marks is zero.
If we use a normal IF statement it will only run the appropriate line.
marks = 0 If marks = 0 Then 'Only executes this line when marks is zero total = 0 Else 'Only executes this line when marks is Not zero total = 60 / marks End If
What this also means is that if you have Functions for True and False then both will be executed. So IIF will run both Functions even though it only uses one return value. For example
'Both Functions will be executed every time total = IIf(marks = 0, Func1, Func2)
(Thanks to David for pointing out this behaviour in the comments)
If Versus IIf
So which is better?
You can see for this case that IIf is shorter to write and neater. However if the conditions get complicated you are better off using the normal If statement. A disadvantage of IIf is that it is not well known so other users may not understand it as well as code written with a normal if statement.
Also as we discussed in the last section IIF always evaluates the True and False parts so if you are dealing with a lot of data the IF statement would be faster.
My rule of thumb is to use IIf when it will be simple to read and doesn’t require function calls. For more complex cases use the normal If statement.
Using Select Case
The Select Case statement is an alternative way to write an If statment with lots of ElseIf’s. You will find this type of statement in most popular programming languages where it is called the Switch statement. For example Java, C#, C++ and Javascript all have a switch statement.
The format is
Select Case [variable] Case [condition 1] Case [condition 2] Case [condition n] Case Else End Select
Let’s take our AddClass example from above and rewrite it using a Select Case statement.
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub AddClass() ' get the last row Dim startRow As Long, lastRow As Long startRow = 2 lastRow = Sheet1.Cells(Sheet1.Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row Dim i As Long, Marks As Long Dim sClass As String ' Go through the marks columns For i = startRow To lastRow Marks = Sheet1.Range("C" & i).Value ' Check marks and classify accordingly If Marks >= 85 Then sClass = "High Destinction" ElseIf Marks >= 75 Then sClass = "Destinction" ElseIf Marks >= 55 Then sClass = "Credit" ElseIf Marks >= 40 Then sClass = "Pass" Else ' For all other marks sClass = "Fail" End If ' Write out the class to column E Sheet1.Range("E" & i).Value = sClass Next End Sub
The following is the same code using a Select Case statement. The main thing you will notice is that we use “Case 85 to 100” rather than “marks >=85 And marks <=100”.
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub AddClassWithSelect() ' get the first and last row Dim firstRow As Long, lastRow As Long firstRow = 2 lastRow = Cells(Cells.Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row Dim i As Long, marks As Long Dim sClass As String ' Go through the marks columns For i = firstRow To lastRow marks = Sheet1.Range("C" & i).Value ' Check marks and classify accordingly Select Case marks Case 85 To 100 sClass = "High Destinction" Case 75 To 84 sClass = "Destinction" Case 55 To 74 sClass = "Credit" Case 40 To 54 sClass = "Pass" Case Else ' For all other marks sClass = "Fail" End Select ' Write out the class to column E Sheet1.Range("E" & i).Value = sClass Next End Sub
Using Case Is
You could rewrite the select statement in the same format as the original ElseIf. You can use Is with Case.
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Select Case marks Case Is >= 85 sClass = "High Destinction" Case Is >= 75 sClass = "Destinction" Case Is >= 55 sClass = "Credit" Case Is >= 40 sClass = "Pass" Case Else ' For all other marks sClass = "Fail" End Select
You can use Is to check for multiple values. In the following code we are checking if marks equals 5, 7 or 9.
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub TestMultiValues() Dim marks As Long marks = 7 Select Case marks Case Is = 5, 7, 9 Debug.Print True Case Else Debug.Print False End Select End Sub
What’s Next?
Free VBA Tutorial If you are new to VBA or you want to sharpen your existing VBA skills then why not try out the The Ultimate VBA Tutorial.
Related Training: Get full access to the Excel VBA training webinars and all the tutorials.
(NOTE: Planning to build or manage a VBA Application? Learn how to build 10 Excel VBA applications from scratch.)
There is no explicit Between formula in Excel, however, we can come up with creative ways to create this functionality. Our goal is to evaluate if a given value is between a range, for example, is 6 between 1 and 10?
We have three possible scenarios:
- Between formula in Excel for Numbers
- Between formula in Excel for Dates
- Between formula in Excel for Text
You can download this Excel Workbook and follow along:
DOWNLOAD EXCEL WORKBOOK
Between formula in Excel for Numbers
OPTION 1:Using a combination of MIN, MAX & AND function
In the example below, you have the start of the range in Column A, end of the range in Column B and the value to be evaluated in Column C.
You need to check whether the number entered in Column C is in between the numbers in Column A & Column B using a creatively formulated BETWEEN formula in Excel.
The function that can be used to determine if the value in cell D7 is in-between values in cell A7 & B7 is
=IF(AND(C7>=MIN(A7,B7),C7<=MAX(A7,B7)), “Yes”, “No”)
Let’s break this formula into parts to understand it better:
- C7 >= MIN(A7, B7) – This expression checks whether the value in cell C7 is greater than (or equal to) the smaller of the two numbers in cell A7 and B7.
- C7 <= MAX(A7, B7) – This expression checks whether the value in cell C7 is smaller than (or equal to) the larger of the two numbers in cell A7 and B7.
- AND( C7 >= MIN(A7, B7), C7 <= MAX(A7, B7)) – AND function simply checks whether the above two conditions are met or not i.e. whether the value in cell C7 is greater than (or equal to) the smaller number and less than (or equal to) the larger number.
OPTION 2:Using a MEDIAN function
You can use a simpler version of this complicated function by creatively using the Median formula:
=IF(C7=MEDIAN(A7:C7), “Yes”, “No”)
In our first example above, the range is 20-60, upon checking the value 50, it is in between this range.
The median formula will return the value in the middle of these 3 values when arranged in increasing order: 20, 50, 60. The median value is 50.
Since it matches the value we are evaluating, then the answer we get is a Yes, this value (50) is in between the range.
Now that you have learned how to use Excel if between two numbers, let’s move forward to dates and text.
Between formula in Excel for Dates
Irrespective of how you format a cell to display a date, Excel always stores it as a number. The number stored for each date actually represents the number of days since 0-Jan-1990.
1st Jan 1990 is stored as 1 (representing 1 day since 0-Jan-1990) and 23rd June 2020 is stored as 44,005 (representing 44005 days since 0-Jan-1990).
So, to check whether a date is in between two mentioned dates, we have the same application as the median formula.
Below is an example of how to use the median function to check dates.
=IF(C10=MEDIAN(A10:C10), “Yes”, “No”)
In our first example above, the range is May 1 – July 1, upon checking the date June 1, it is in between this range.
The median formula will return the value in the middle of these 3 dates when arranged in increasing order: May 1, June 1, July 1. The median value is June 1.
Since it matches the value we are evaluating, then the answer we get is a Yes, this value (June 1) is in between the range.
Between formula in Excel for Text
For text, we are checking if the value is alphabetically in the middle. We will be using the and formula:
=IF(AND(C12>=A12, C12<=B12, “Yes”, “No”)
Interestingly enough, you can compare texts using the >= and <= operators. Excel is able to compare them which goes alphabetically first or last.
In our first example above, the range is Cat – Dog, upon checking the text Cow, it is in between this range. As when arranged alphabetically, it would be: Cat, Cow, Dog.
The And formula checks if Cow >= Cat, and Cow <= Dog. You will see that both of these are true, as Cow is alphabetically later than Cat, while Cow is alphabetically ahead of Dog. Which is why we get a Yes result.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, you have learned how to use Between formula in Excel even when there is no explicit formula available to do this. You can use a combination of various other available function to create Excel if between range functionality.
You can use MIN, MAX, MEDIAN & AND functions to create a creative Between function in Excel for numbers, dates and text.
HELPFUL RESOURCE:
Make sure to download our FREE PDF on the 333 Excel keyboard Shortcuts here:


 Talk To Other Members
Talk To Other Members