Return to VBA Code Examples
You may be required to convert numbers stored as text to actual numbers in your VBA code. In this tutorial, we are going to go over the functions that you need to use to convert a string to an integer, long, double, decimal or currency data type (Click here to learn about converting numbers to strings)
Convert String to Integer
You can use the CInt or CLng function to convert a string to an integer. If the fraction is less than .5 the function will round down, if the fraction is greater than or equal to .5 the function will round up. The following code will convert a string to an integer:
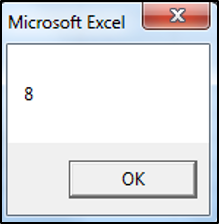
MsgBox CInt("7.55")The result is:
The following code uses the CLng function to convert a string to an integer:
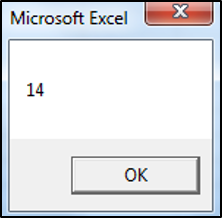
MsgBox CLng("13.5")The result is:
Note: You can use the CInt or CLng function to convert a string to an integer or long (respectively) data types. The Long Data type is the same as an integer data type except larger numbers are allowed. In the past, the distinction was required because of memory constraints. In modern programming, there’s no reason not to use the long data type since memory is no longer an issue. So it’s always better to use a long data type instead of an integer.
You can use the Immediate Window to see how the value would be processed if not converted to an integer:
Debug.Print "13.5" + "13.5"
Usually, the text will be stored as a variable and this variable will need to be converted to a number data type as shown in the code below:
Sub Using_Variables()
Dim valueOne As String
valueOne = 5
MsgBox CLng(valueOne) + CLng(valueOne)
End SubConvert String to Decimal
You can use the CDbl or CDec function to convert a string to a decimal. The following code would convert a string to a double data type:
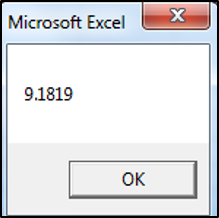
MsgBox CDbl("9.1819")The result is:
The following code would convert a string to a decimal data type:
MsgBox CDec("13.57") + CDec("13.4")The result is:
You can use the Immediate Window to see how the value would be processed if not converted to a double or decimal data type:
Debug.Print "13.57" + "13.4"The result is:
Note: The decimal data type can store larger numbers than the double data type, so it’s always advisable to use the decimal data type when you are uncertain.
Convert String to Currency
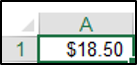
You can use the CCur function to convert a string to a currency. The following code would convert a string to a currency data type:
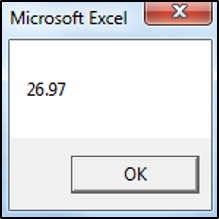
Range("A1").Value = CCur("18.5")The result is:
VBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro — A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Learn More!

This VBA Tutorial is accompanied by an Excel workbook containing the macros, data and formulas I use in the examples below. You can get immediate access to this example workbook by subscribing to the Power Spreadsheets Newsletter.
Use the following Table of Contents to navigate to the section that interests you.
Related VBA and Macro Tutorials
The following VBA and Macro Tutorials may help you better understand and implement the contents below:
- General VBA constructs and structures:
- Learn about essential VBA terms here.
- Learn how to work in the Visual Basic Editor here.
- Learn how to create Sub procedures here.
- Learn how to create Function procedures here.
- Learn how to work with variables here.
- Learn about VBA data types here.
- Learn about the Range object here.
- Tutorials about other useful topics:
- Learn how to work with the IFERROR worksheet function here.
You can find additional VBA and Macro Tutorials in the Archives.
#1: Convert String to Byte
VBA code to convert String to Byte
To convert a string to a number of the Byte data type, use the following statement:
CByte(String)
Process followed by VBA to convert String to Byte
To convert a string to a number of the Byte data type, use the CByte function to convert the String to a number of the Byte data type.
VBA statement explanation
- Item: CByte.
- VBA construct: CByte function.
- Description: The CByte function coerces String to the Byte data type.
CByte is usually able to carry out internationally-aware conversions from the String to the Byte data type. In other words, CByte generally recognizes between the different decimal/thousand separators and currency options that depend on your computer’s locale.
The Byte data type can hold numbers ranging from 0 to 255. If String is outside this range, an error occurs.
- Item: String.
- VBA construct: String expression and expression argument of the CByte function.
- Description: String is the string or numeric expression you convert to the Byte data type. If you explicitly declare a variable to represent String, use the Variant data type.
Macro example to convert String to Byte
The following macro example, a User-Defined Function, converts a string passed as argument (myString) to Byte.
Function stringToByte(myString As Variant)
'source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'converts String to Byte
'for further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/vba-string-to-number/
'convert String to Byte
stringToByte = CByte(myString)
End Function
Effects of executing macro example to convert String to Byte
The following image illustrates the results of using the macro example in a worksheet formula. For these purposes:
- Column A contains a numeric string.
- Column B contains a worksheet formula that uses the UDF example.
When String is outside the range of Byte, the worksheet formula returns the #VALUE! error.
- Column C displays the worksheet formula used in column B.
#2: Convert String to Integer
VBA code to convert String to Integer
To convert a string to a number of the Integer data type, use the following statement:
CInt(String)
Process followed by VBA to convert String to Integer
To convert a string to a number of the Integer data type, use the CInt function to convert the String to a number of the Integer data type.
VBA statement explanation
- Item: CInt.
- VBA construct: CInt function.
- Description: The CInt function coerces String to the Integer data type.
If String contains a fraction, CInt rounds it. If this fraction is precisely 0.5, CInt rounds to the nearest even number. For example:
- 0.5 is rounded to 0.
- Both 1.5 and 2.5 are rounded to 2.
- Both 3.5 and 4.5 are rounded to 4.
- CInt is usually able to carry out internationally-aware conversions from the String to the Integer data type. In other words, CInt generally recognizes between the different decimal/thousand separators and currency options that depend on your computer’s locale.
The Integer data type can hold numbers ranging from -32,768 to 32,767. If String is outside this range, an error occurs.
- Item: String.
- VBA construct: String expression and expression argument of the CInt function.
- Description: String is the string or numeric expression you convert to the Integer data type. If you explicitly declare a variable to represent String, use the Variant data type.
Macro example to convert String to Integer
The following macro example, a User-Defined Function, converts a string passed as argument (myString) to Integer.
Function stringToInteger(myString As Variant)
'source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'converts String to Integer
'for further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/vba-string-to-number/
'convert String to Integer
stringToInteger = CInt(myString)
End Function
Effects of executing macro example to convert String to Integer
The following image illustrates the results of using the macro example in a worksheet formula. For these purposes:
- Column A contains a numeric string.
- Column B contains a worksheet formula that uses the UDF example.
When String is outside the range of Integer, the worksheet formula returns the #VALUE! error. Additionally, if String contains a fraction that’s precisely 0.5, the UDF rounds to the nearest even number.
- Column C displays the worksheet formula used in column B.
#3: Convert String to Long
VBA code to convert String to Long
To convert a string to a number of the Long data type, use the following statement:
CLng(String)
Process followed by VBA to convert String to Long
To convert a string to a number of the Long data type, use the CLng function to convert the String to a number of the Integer data type.
VBA statement explanation
- Item: CLng.
- VBA construct: CLng function.
- Description: The CLng function coerces String to the Long data type.
If String contains a fraction, CLng rounds it. If this fraction is precisely 0.5, CLng rounds to the nearest even number. For example:
- 0.5 is rounded to 0.
- Both 1.5 and 2.5 are rounded to 2.
- Both 3.5 and 4.5 are rounded to 4.
CLng is usually able to carry out internationally-aware conversions from the String to the Long data type. In other words, CLng generally recognizes between the different decimal/thousand separators and currency options that depend on your computer’s locale.
The Long data type can hold numbers ranging from -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647. If String is outside this range, an error occurs.
- Item: String.
- VBA construct: String expression and expression argument of the CLng function.
- Description: String is the string or numeric expression you convert to the Long data type. If you explicitly declare a variable to represent String, use the Variant data type.
Macro example to convert String to Long
The following macro example, a User-Defined Function, converts a string passed as argument (myString) to Long.
Function stringToLong(myString As Variant)
'source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'converts String to Long
'for further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/vba-string-to-number/
'convert String to Long
stringToLong = CLng(myString)
End Function
Effects of executing macro example to convert String to Long
The following image illustrates the results of using the macro example in a worksheet formula. For these purposes:
- Column A contains a numeric string.
- Column B contains a worksheet formula that uses the UDF example.
When String is outside the range of Long, the worksheet formula returns the #VALUE! error. Additionally, if String contains a fraction that’s precisely 0.5, the UDF rounds to the nearest even number.
- Column C displays the worksheet formula used in column B.
#4: Convert String to Single
VBA code to convert String to Single
To convert a string to a number of the Single data type, use the following statement:
CSng(String)
Process followed by VBA to convert String to Single
To convert a string to a number of the Single data type, use the CSng function to convert the String to a number of the Single data type.
VBA statement explanation
- Item: CSng.
- VBA construct: CSng function.
- Description: The CSng function coerces String to the Single data type.
CSng is usually able to carry out internationally-aware conversions from the String to the Single data type. In other words, CSng generally recognizes between the different decimal/thousand separators and currency options that depend on your computer’s locale.
The Single data type can hold floating-point numbers ranging from:
- -3.402823E38 to -1.401298E-45 for negative values; and
- 1.401298E-45 to 3.402823E38 for positive values.
If String is outside the required range, an error occurs.
- Item: String.
- VBA construct: String expression and expression argument of the CSng function.
- Description: String is the string or numeric expression you convert to the Single data type. If you explicitly declare a variable to represent String, use the Variant data type.
Macro example to convert String to Single
The following macro example, a User-Defined Function, converts a string passed as argument (myString) to Single.
Function stringToSingle(myString As Variant)
'source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'converts String to Single
'for further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/vba-string-to-number/
'convert String to Single
stringToSingle = CSng(myString)
End Function
Effects of executing macro example to convert String to Single
The following image illustrates the results of using the macro example in a worksheet formula. For these purposes:
- Column A contains a numeric string.
- Column B contains a worksheet formula that uses the UDF example.
When String is outside the range of Single, the worksheet formula returns the #VALUE! error.
- Column C displays the worksheet formula used in column B.
#5: Convert String to Double
VBA code to convert String to Double
To convert a string to a number of the Double data type, use the following statement:
CDbl(String)
Process followed by VBA to convert String to Double
To convert a string to a number of the Double data type, use the CDbl to convert the String to a number of the Double data type.
VBA statement explanation
- Item: CDbl.
- VBA construct: CDbl function.
- Description: The CDbl function coerces String to the Double data type.
CDbl is usually able to carry out internationally-aware conversions from the String to the Double data type. In other words, CDbl generally recognizes between the different decimal/thousand separators and currency options that depend on your computer’s locale.
The Double data type can hold floating-point numbers ranging from:
- -1.79769313486231E308 to -4.94065645841247E-324 for negative values; and
- 4.94065645841247E-324 to 1.79769313486232E308 for positive values.
If String is outside the required range, an error occurs.
- Item: String.
- VBA construct: String expression and expression argument of the CDbl function.
- Description: String is the string or numeric expression you convert to the Double data type. If you explicitly declare a variable to represent String, use the Variant data type.
Macro example to convert String to Double
The following macro example, a User-Defined Function, converts a string passed as argument (myString) to Double.
Function stringToDouble(myString As Variant)
'source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'converts String to Double
'for further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/vba-string-to-number/
'convert String to Double
stringToDouble = CDbl(myString)
End Function
Effects of executing macro example to convert String to Double
The following image illustrates the results of using the macro example in a worksheet formula. For these purposes:
- Column A contains a numeric string.
- Column B contains a worksheet formula that uses the UDF example.
When String is outside the range of Double, the worksheet formula returns the #VALUE! error.
- Column C displays the worksheet formula used in column B.
#6: Convert String to Currency
VBA code to convert String to Currency
To convert a string to a number of the Currency data type, use the following statement:
CCur(String)
Process followed by VBA to convert String to Currency
To convert a string to a number of the Currency data type, use the CCur to convert the String to a number of the Currency data type.
VBA statement explanation
- Item: CCur.
- VBA construct: CCur function.
- Description: The CCur function coerces String to the Currency data type.
CCur is usually able to carry out internationally-aware conversions from the String to the Currency data type. In other words, CCur generally recognizes between the different decimal/thousand separators and currency options that depend on your computer’s locale.
The Currency data type holds integers scaled by 10,000. This results in Currency holding fixed-point numbers with 15 digits to the left of the decimal point and 4 digits to the right of the decimal point. Therefore, Currency can hold numbers ranging from -922,337,203,685,477.5808 to 922,337,203,685,477.5807. If String is outside this range, an error occurs.
- Item: String.
- VBA construct: String expression and expression argument of the CCur function.
- Description: String is the string or numeric expression you convert to the Currency data type. If you explicitly declare a variable to represent String, use the Variant data type.
Macro example to convert String to Currency
The following macro example, a User-Defined Function, converts a string passed as argument (myString) to Currency.
Function stringToCurrency(myString As Variant)
'source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'converts String to Currency
'for further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/vba-string-to-number/
'convert String to Currency
stringToCurrency = CCur(myString)
End Function
Effects of executing macro example to convert String to Currency
The following image illustrates the results of using the macro example in a worksheet formula. For these purposes:
- Column A contains a numeric string.
- Column B contains a worksheet formula that uses the UDF example.
When String is outside the range of Currency, the worksheet formula returns the #VALUE! error.
- Column C displays the worksheet formula used in column B.
#7: Convert String to Decimal
VBA code to convert String to Decimal
To convert a string to a number of the Decimal data type, use the following statement:
CDec(String)
Process followed by VBA to convert String to Decimal
To convert a string to a number of the Decimal data type, use the CDec function to convert the String to a number of the Decimal data type.
VBA statement explanation
- Item: CDec.
- VBA construct: CDec function.
- Description: From a broad perspective, the CDec function coerces String to the Decimal data subtype of the Variant data type. In other words, CDec doesn’t return a discrete data type, but rather a Variant converted to the Decimal subtype.
CDec is usually able to carry out internationally-aware conversions from the String to the Decimal data type. In other words, CDec generally recognizes between the different decimal/thousand separators and currency options that depend on your computer’s locale.
The Decimal data type holds integers scaled by a variable power of 10. This power of 10 specifies the number of digits to the right of the decimal point. Therefore, the value ranges Decimal can hold are as follows:
- When working with a scale of 0, which results in no decimal places: -79,228,162,514,264,337,593,543,950,335 to 79,228,162,514,264,337,593,543,950,335.
- When working with 28 decimal places:
- The largest and smallest values are +7.9228162514264337593543950335 and -7.9228162514264337593543950335.
- The smallest non-zero values are -0.0000000000000000000000000001 and 0.0000000000000000000000000001.
If String is outside the required range, an error occurs.
- Item: String.
- VBA construct: String expression and expression argument of the CDec function.
- Description: String is the string or numeric expression you convert to the CDec data type. If you explicitly declare a variable to represent String, use the Variant data type.
Macro example to convert String to Decimal
The following macro example, a User-Defined Function, converts a string passed as argument (myString) to Decimal.
Function stringToDecimal(myString As Variant)
'source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'converts String to Decimal
'for further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/vba-string-to-number/
'convert String to Decimal
stringToDecimal = CDec(myString)
End Function
Effects of executing macro example to convert String to Decimal
The following image illustrates the results of using the macro example in a worksheet formula. For these purposes:
- Column A contains a numeric string.
- Column B contains a worksheet formula that uses the UDF example.
When String is outside the range of Decimal, the worksheet formula returns the #VALUE! error.
- Column C displays the worksheet formula used in column B.
METHOD 1. Convert text to numbers with specific range using VBA
VBA
Sub Convert_Text_to_Numbers()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = Worksheets(«Analysis»)
With ws.Range(«B5»)
.NumberFormat = «General»
.Value = .Value
End With
End Sub
OBJECTS
Worksheets: The Worksheets object represents all of the worksheets in a workbook, excluding chart sheets.
Range: The Range object is a representation of a single cell or a range of cells in a worksheet.
PREREQUISITES
Worksheet Name: Have a worksheet named Analysis.
Range: In this example we are converting the text in cell («B5») to a number. Therefore, if using the exact VBA code, you need to capture the text that you want to convert to a number in cell («B5»).
ADJUSTABLE PARAMETERS
Range: Select the range that captures the text that you want to convert to a number by changing the cell reference («B5») in the VBA code to any range in the worksheet, that doesn’t conflict with the formula.
Worksheet Name: Select the worksheet where you are converting text to a number by changing the worksheet name («Analysis») in the VBA code to any existing worksheet in the workbook, that doesn’t conflict with the formula.
ADDITIONAL NOTES
Note 1: This VBA code will convert the text to a number in the same cell that the text is captured. In this example it will be cell («B5»).
METHOD 2. Convert text to numbers of selected range using VBA
VBA
Sub Convert_Text_to_Numbers()
With Selection
.NumberFormat = «General»
.Value = .Value
End With
End Sub
ADDITIONAL NOTES
Note 1: This VBA code will convert the text to a number in the selected cell.
METHOD 3. Convert text to numbers with specific range and different output range using VBA
VBA
Sub Convert_Text_to_Numbers()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = Worksheets(«Analysis»)
ws.Range(«D5») = ws.Range(«B5»)
With ws.Range(«D5»)
.NumberFormat = «General»
.Value = .Value
End With
End Sub
OBJECTS
Worksheets: The Worksheets object represents all of the worksheets in a workbook, excluding chart sheets.
Range: The Range object is a representation of a single cell or a range of cells in a worksheet.
PREREQUISITES
Worksheet Name: Have a worksheet named Analysis.
Range: In this example we are converting the text in cell («B5») to a number. Therefore, if using the exact VBA code, you need to capture the text that you want to convert to a number in cell («B5»).
ADJUSTABLE PARAMETERS
Range: Select the range that captures the text that you want to convert to a number by changing the cell reference («B5») in the VBA code to any range in the worksheet, that doesn’t conflict with the formula.
Range: Select the output range by changing the cell reference («D5») in the VBA code to any range in the worksheet, that doesn’t conflict with the formula.
Worksheet Name: Select the worksheet where you are converting text to a number by changing the worksheet name («Analysis») in the VBA code to any existing worksheet in the workbook, that doesn’t conflict with the formula.
METHOD 4. Convert text to numbers with specific range and different output range (with For Loop) using VBA
VBA
Sub Convert_Text_to_Numbers()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = Worksheets(«Analysis»)
For x = 5 To 10
ws.Range(«D» & x) = ws.Range(«B» & x)
With ws.Range(«D» & x)
.NumberFormat = «General»
.Value = .Value
End With
Next
End Sub
OBJECTS
Worksheets: The Worksheets object represents all of the worksheets in a workbook, excluding chart sheets.
Range: The Range object is a representation of a single cell or a range of cells in a worksheet.
PREREQUISITES
Worksheet Name: Have a worksheet named Analysis.
Range: In this example we are converting the text in range («B5:B10») to numbers. Therefore, if using the exact VBA code, you need to capture the text that you want to convert to numbers in range («B5:B10»).
ADJUSTABLE PARAMETERS
Output and Text Row Range: The text and output range in the same rows (row 5 to 10), which are represented by the x variable. You can select the output row range by changing the x For and To values in the VBA code.
Output and Text Column Range: Select the column text and output range by changing the column reference («B») and («D»), respectively, in the VBA code.
Worksheet Name: Select the worksheet where you are converting text to a number by changing the worksheet name («Analysis») in the VBA code to any existing worksheet in the workbook, that doesn’t conflict with the formula.
Numeric values are defined by data types like integer or byte. These data types are used for optimizing the processing and memory allocation in Excel. In this guide, we’re going to show you how to convert string into number in Excel VBA.
Download Workbook
Data types in VBA
Like in some other programming languages, VBA uses data types to identify what variables it can store and how they are stored. Most of the data types in VBA define numeric values. Here is a brief list of numeric data types:
| Data type | Storage | Range |
| Byte | 1 byte | 0 to 255 |
| Integer | 2 bytes | -32,768 to 32,767 |
| Long | 4 bytes | -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647 |
| Single | 4 bytes | -3.402823E38 to -1.401298E-45 for negative values; 1.401298E-45 to 3.402823E38 for positive values |
| Double | 8 bytes | -1.79769313486231E308 to-4.94065645841247E-324 for negative values; 4.94065645841247E-324 to 1.79769313486232E308 for positive values |
| LongLong | 8 bytes |
-9,223,372,036,854,775,808 to 9,223,372,036,854,775,807 Valid on 64-bit platforms only. |
| Currency | 8 bytes | -922,337,203,685,477.5808 to 922,337,203,685,477.5807 |
| Decimal | 14 bytes | +/-79,228,162,514,264,337,593,543,950,335 with no decimal point; +/-7.9228162514264337593543950335 with 28 places to the right of the decimal |
Since there are many numeric data types, there are many functions to convert a string into number in Excel VBA.
Functions to a convert string into number in Excel VBA
All conversion functions use the same syntax: Each requires a single string argument to convert into a number. For example:
Each function returns an error If the string argument either is not a numeric or is outside the range of the data type being converted.
CInt(«A») returns a type mismatch error, because the «A» is not a numeric value.
CByte(«1250») returns an overflow exception.
| Function | Return type | Example |
| CByte | Byte | CByte(«65.75») returns 66 |
| CCur | Currency | CCur(«$256,000.50») returns 256000.5 |
| CDbl | Double | CDbl(128.239856 * 4.8 * 0.04) returns 24.622052352 |
| CDec | Decimal | CDec(«15000000.5678») returns 15000000.5678 |
| CInt | Integer | CInt(«1234.56») returns 1235 |
| CLng | Long | CLng(«1,500,000.88») returns 15000001 |
| CLngLng | LongLong | CLngLng(«1,250,500,000.88») returns 1250500001 |
| CSng | Single | CSng(«5.67854») returns 5.67854 |
Bonus: Use IsNumeric function to verify value
To avoid type mismatch errors, you can use the IsNumeric function to check if the expression is numeric or not. The function returns Boolean value based on the expression. TRUE if the expression is numeric, FALSE otherwise.
Here is a sample function that can check the data first, and convert the it into an integer if it is numeric. If the argument is not a valid number, the function returns 0.
Function ConvertInt(arg As String) As Integer If IsNumeric(arg) Then ConvertInt = CInt(arg) End Function
Преобразование текста в число с помощью кода VBA Excel. Массовое преобразование чисел из текстового формата в числовой в заданном диапазоне.
Преобразование текста в число
Преобразование чисел, записанных как текст, в числовой формат осуществляется в VBA Excel с помощью функций преобразования типов данных. Числа в текстовом формате могут быть получены из:
- ячеек рабочего листа с текстовым форматом;
- элементов управления формы (TextBox, ListBox, ComboBox);
- строковых переменных;
- выражений, возвращающих число в виде текста;
- текстового поля функции InputBox.
В большинстве случаев VBA Excel сам распознает текст как число без всяких преобразований:
|
Sub Primer1() Debug.Print 23.1254 * 5.2 ‘Результат: 120,25208 Debug.Print «23,1254» * «5,2» ‘Результат: 120,25208 Debug.Print TypeName(«23,1254») ‘Результат: String Debug.Print TypeName(CDbl(«23,1254»)) ‘Результат: Double End Sub |
Обратите внимание на разделитель дробной части.
Преобразование смешанной строки
Преобразование в число строки, в начале которой имеются цифры, а далее идут другие символы, осуществляется в VBA Excel с помощью функции Val. Из других символов распознается только точка (.) в качестве разделителя дробной части.
|
Sub Primer2() Debug.Print Val(«021.36abcde») ‘Результат: 21,36 Debug.Print Format(Val(«021.36abcde»), «000.0») ‘Результат: 021,4 End Sub |
Массовое преобразование чисел
Иногда требуется массовое преобразование чисел из текстового формата в числовой в заданном диапазоне рабочего листа.
Пример преобразования диапазона ячеек с текстовым форматом в общий формат и значений ячеек из строки в число на примере объекта Selection:
|
Sub Primer3() Dim MyCell As Range Selection.NumberFormat = «General» For Each MyCell In Selection If IsNumeric(MyCell) Then MyCell = MyCell * 1 Next End Sub |
Сначала выбранному диапазону присваивается общий формат ("General"). Но текстовые значения в ячейках еще не преобразовались в числа. Обходим циклом все ячейки диапазона, и, если текстовое значение ячейки можно интерпретировать как число, умножаем это значение на единицу. После этого текст будет преобразован в число.
Sometimes you get a dataset that has numbers stored as text. This means you cannot work with the values as you would with actual numbers.
If you try to, they give unexpected results. For example, if you sum them, you get a 0 (zero) regardless of the values involved. This tutorial shows how to convert numbers stored as text to actual numbers using Excel VBA.
How to Identify Numbers Stored as Text
Sometimes Excel fails to convert numeric values to number format and stores them as text as in the example dataset below:
The values in the dataset are left-aligned meaning Excel treats them as text values.
When you select any cell in the dataset a yellow triangle with an exclamation point pops up beside it:
When you hover over the yellow triangle, you see the message “The number in this cell is formatted as text or preceded by an apostrophe.”
3 Methods to Convert Text to Number Using Excel VBA
There are several ways we can use to convert numbers stored as text to number format in Excel. This tutorial focuses on converting using Excel VBA. We shall use copies of the example dataset in our illustrations.
Method 1: Use the Excel VBA Range.NumberFormat Property
The Range.NumberFormat property returns or sets a Variant value that represents the format code for the object.
We use the following steps:
- In the active worksheet that contains the dataset, press Alt + F11 to open the Visual Basic Editor (VBE).
- Click Insert >> Module to insert a new module.
- Type the following procedure in the module and remember to change the range to your range:
|
Sub convertTextToNumber() With Range(«A2:A15») .NumberFormat = «General» .Value = .Value End With End Sub |
- Save the procedure and save the workbook as a macro-enabled workbook.
- Place the cursor anywhere in the procedure and press F5 to run the code.
- Press Alt + F11 to switch back to the active worksheet to see the results of the procedure.
The values in the data range are now right-aligned because they have been converted to number format.
- Close the Visual Basic Editor.
Explanation of the procedure
|
Sub convertTextToNumber() With Range(«A2:A15») .NumberFormat = «General» .Value = .Value End With End Sub |
- The With statement is used with the mentioned range to minimize the code.
- NumberFormat = “General”. The General number format is assigned to the values in the mentioned range.
- Value = Value. The values that have been converted to the General number format are assigned to the cells in the range.
Method 2: Use Excel VBA Loop and CSng function
In this method, the procedure loops through the dataset and converts the values to single-precision numbers using the CSng function.
We use the following steps:
- In the active worksheet that contains the dataset press Alt + F11 to open the Visual Basic Editor.
- Click Insert >> Module to insert a new module.
- Type the following procedure in the new module:
|
Sub convertTextToNumber2() Dim r As Variant For Each r In Sheets(«Method 2»).UsedRange.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeConstants) If IsNumeric(r) Then r.Value = CSng(r.Value) r.NumberFormat = «General» End If Next End Sub |
- Save the procedure and save the workbook as a macro-enabled workbook.
- Place the cursor anywhere in the procedure and press F5 to run the procedure.
- Press Alt + F11 to switch back to the active worksheet to see the results of the procedure.
The values in the data range are now right-aligned because they have been converted to number format.
- Close the Visual Basic Editor.
Explanation of the code
|
Sub convertTextToNumber2() Dim r As Variant For Each r In Sheets(«Method 2»).UsedRange.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeConstants) If IsNumeric(r) Then r.Value = CSng(r.Value) r.NumberFormat = «General» End If Next End Sub |
- The variable called r of type Variant is declared. The Variant data type can contain any type of data except the fixed-length String data. It is appropriate because the variable will first contain text values and then the converted numeric values.
- For Each Loop goes through each cell that contains a constant (a value that is directly inserted into a cell) in the used range of the mentioned worksheet and does the following:
- Checks if it is a number using the IsNumeric function. If it is a number, it turns it to single precision using the CSng function and assigns the General number format to it.
Method 3: Convert Text to Number in a Dynamic Range
In the previous methods, we worked with selected ranges.
In this method, we work with a dynamic range.
We use the following steps:
- In the active worksheet that contains the dataset press Alt + F11 to open the Visual Basic Editor.
- Click Insert >> Module to insert a new module.
- Type the following procedure in the new module:
|
Sub ConvertTextToNumber3() With Range(«A2:A» & Cells(Rows.Count, «A»).End(xlUp).Row) .NumberFormat = «General» .Value = .Value End With End Sub |
- Save the procedure and save the workbook as a macro-enabled workbook.
- Place the cursor anywhere in the procedure and press F5 to run the code.
- Press Alt + F11 to switch back to the active workbook to see the results of the procedure.
The values in the data range are now right-aligned because they have been converted to number format.
- Close the Visual Basic Editor.
Explanation of the procedure
|
Sub ConvertTextToNumber3() With Range(«A2:A» & Cells(Rows.Count, «A»).End(xlUp).Row) .NumberFormat = «General» .Value = .Value End With End Sub |
- The With statement is used with the mentioned range to minimize the code.
- “A2:A” & Cells(Rows.Count, “A”).End(xlUp).Row. The number of the last nonblank row in column A is dynamically identified by Cells(Rows.Count, “A”).End(xlUp).Row. That number is concatenated with “A2:A” to identify the range.
- NumberFormat = “General”. The number format of the range is set to General.
- Value = Value. The values that are now in General number format are assigned to the cells in the range.
Conclusion
If you get a dataset that has numbers that are stored as text, you cannot work with the values as you would with numbers. For example, if you try to sum them, you get a 0 (zero) regardless of the values involved. This tutorial explained how to convert such data range from text format to number format using Excel VBA.
Post Views: 553
In a recent task, I was doing filter through VBA on a number column. But that number column had numbers in text format. When I run the VBA script, it didn’t work of course, because the filter was a number and the column had numbers as text. In that case, I needed to convert the text into numbers manually and save it. Then the macro worked perfectly. But I wanted to convert these texts into numbers using the VBA script and I was able to do it. I wanted to share this as if anyone wanted to know how to convert text values into a number using VBA, they can have a look at it.
Convert text to number using Range.NumberFormat method
This first and easiest method. I prefer this method over other methods as it directly converts the selected excel range into number format.
So, if you have a fixed range that you want to convert to text then use this VBA snippet.
Sub ConvertTextToNumber()
Range("A3:A8").NumberFormat = "General"
Range("A3:A8").Value = Range("A3:A8").Value
End Sub
When you run the above code it converts the text of range A3:A8 into text.
This code can look more elegant if we write it like this.
Sub ConvertTextToNumber()
With Range("A3:A8")
.NumberFormat = "General"
.Value = .Value
End With
End Sub
How does it work?
Well, it is quite simple. We first change the number format of the range to General. Then we put the value of that range into the same range using VBA. This removes the text formatting completely. Simple, isn’t it?
Change the number of formatting of a dynamic range
In the above code, we changed the text to number in the above code of a fixed range but this will not be the case most of the time. To convert text to a number of dynamic ranges, we can evaluate the last used cell or select the range dynamically.
This is how it would look:
Sub ConvertTextToNumber()
With Range("A3:A" & Cells(Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row)
.NumberFormat = "General"
.Value = .Value
End With
Here, I know that the range starts from A3. But I don’t know where it may end.
So I dynamically identify last used excel row that has data in it using the VBA snippet Cells(Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row. It returns the last used row number that we are concatenating with «A3:A».
Note: This VBA snippet will work on the active workbook and active worksheet. If your code switches through multiple sheets, it would be better to set a range object of the intended worksheet. Like this
Sub ConvertTextToNumber()
Set Rng = ThisWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet1").Range("A3:A" & Cells(Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row)
With Rng
.NumberFormat = "General"
.Value = .Value
End With
End Sub
The above code will always change the text to the number of the sheet1 of the workbook that contains this code.
Loop and CSng to change the text to number
Another method is to loop through each cell and change the cell value to a number using CSng function. Here’s the code.
Sub ConvertTextToNumberLoop()
Set Rng = ThisWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet1").Range("A3:A" & Cells(Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row)
For Each cel In Rng.Cells
cel.Value = CSng(cel.Value)
Next cel
End Sub
In the above VBA snippet, we are using VBA For loop to iterate over each cell in the range and convert the value of each cell into a number using the CSng function of VBA.
So yeah guys, this is how you can change texts to numbers in Excel using VBA. You can use these snippets to ready your worksheet before you do any number operation on them. I hope I was explanatory enough. You can download the working file here.
Change Text to Number Using VBA.
If you have any doubts regarding this text to number conversion or any other excel/VBA related query, ask in the comments section below.
Related Articles:
How to get Text & Number in Reverse through VBA in Microsoft Excel | To reverse number and text we use loops and mid function in VBA. 1234 will be converted to 4321, «you» will be converted to «uoy». Here’s the snippet.
Format data with custom number formats using VBA in Microsoft Excel | To change the number format of specific columns in excel use this VBA snippet. It coverts the number format of specified to specified format in one click.
Popular Articles:
50 Excel Shortcuts to Increase Your Productivity | Get faster at your task. These 50 shortcuts will make you work even faster on Excel.
The VLOOKUP Function in Excel | This is one of the most used and popular functions of excel that is used to lookup value from different ranges and sheets.
COUNTIF in Excel 2016 | Count values with conditions using this amazing function. You don’t need filter your data to count specific value. Countif function is essential to prepare your dashboard.
How to Use SUMIF Function in Excel | This is another dashboard essential function. This helps you sum up values on specific conditions.

This article will discuss how we can convert a string to a number in VBA Excel. There is a step-by-step guide and many examples for our understanding.
Convert String to Number in VBA
In VBA code, converting numbers saved as text to real numbers is obligatory. We have many conversion options.
We can convert strings to numbers of the Byte, Integer, Long, Single, Double, Currency, and Decimal data types. We will discuss each conversion in detail with examples.
Convert String to Byte in VBA
We can easily transform a string into a number of the byte data type with the help of the following code.
# vba
byte = CByte(str)
We can use the CByte() function to achieve this conversion. The above statement has two items: CByte() and string.
CByte() function forces the string to change into a byte type. CByte() is often used to perform the internationally-aware string transformation to byte data type.
In simple terms, CByte() commonly distinguishes distinctive decimal/thousand separators and many currency options that hinge upon your computer’s location. The range that a byte data type can hold is 0 to 225. If your string does not fall in between this range, an error will occur.
Here is a macro example in which we have convertStr as an argument to convert a string to a byte.
# vba
Function convertStr(newStr As Variant)
MsgBox (CByte(newStr))
End Function
Sub newFunc()
convertStr ("12")
End Sub
Output:
Convert String to Integer in VBA
With the help of the following statement, you can easily convert a string to a number of the integer data type. The syntax of this function is shown below.
# vba
CInt(newStr)
It is recommended to use the Clnt() function to change a string to an integer data type. This function forces the string to change into the integer data type.
If a string holds a fraction, this function will convert it into an integer. If the fraction is precisely 0.4, this function will change it to the closest even number.
For example:
# vba
0.4 will become 0.
1.6 and 2.4 both will become 2.
3.7 and 4.3 will become 4
Clnt() is often used to perform the internationally-aware string transformation into the integer data type. In simple terms, Clnt() commonly distinguishes distinctive decimal/thousand separators and many currency options that hinge upon our computer’s location.
The range between which an integer data type can hold numbers is -32,768 to 32,767. If your string does not fall in between this range, an error will occur.
Let’s go through an example and use the CInt() function as shown below. This example sets newStr as an argument to change a string into an integer, as shown below.
# vba
Function convertToInteger(newStr As Variant)
MsgBox (CInt(newStr))
End Function
Sub newFunc()
convertToInteger ("12.5")
End Sub
Output:
Convert String to Long in VBA
We can use the CLng() function to achieve this conversion. The syntax of this function is shown below.
# vba
CLng(Str)
We can use the CLng() function when our goal is to change a string into several long data types. The items in this statement are CLng() and string.
This function forces a string to change into the long data type.
If a string holds a fraction, this function will round it. If the fraction is precisely 0.4, this function will change it to the closest even number, as shown below.
# vba
0.4 will become 0.
1.6 and 2.4 both will become 2.
3.7 and 4.3 will become 4
CLng() is often used to perform the internationally-aware string transformation to long data types. In simple terms, CLng() commonly distinguishes distinctive decimal/thousand separators and many currency options that hinge upon your computer’s location.
The range between which an integer data type can hold numbers is -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647. If your string does not fall in between this range, an error will occur.
Let’s go through an example and use the CLng() function. In this example, we have set newStr as an argument to change a string into long, as shown below.
# vba
Function convertToLong(newStr As Variant)
MsgBox (CLng(newStr))
End Function
Sub newFunc()
convertToLong ("15.7")
End Sub
Output:
Long data type differs from integer data type by only one thing. Larger numbers are acceptable in long data types.
But there wasn’t enough memory in the old days, and it was not recommended to use long data types.
In modern times, memory is no longer a problem. We can use the long data type instead of an integer.
Convert String to Single in VBA
We can easily transform a string into a number of a single data type with the help of the following syntax, as shown below.
# vba
CSng(str)
We can use the CSng() function to achieve this conversion. There are two items in the above statement, CSng() and string.
This function forces a string to change into a single data type.
CSng() is often used to perform the internationally-aware string transformation to a single data type. CSng() commonly distinguishes distinctive decimal/thousand separators and currency options that hinge upon your computer’s location.
The range between which a single data type can hold floating-point numbers is
- 3.402823E38 to -1.401298E-45 when values are negative
- 1.401298E-45 to 3.402823E38 when values are positive
An error will appear if your string does not fall between this range. As shown below, let’s go through an example in which we set newStr as an argument to change a string into a single.
# vba
Function convertToSingle(newStr As Variant)
MsgBox (CSng(newStr))
End Function
Sub newFunc()
convertToSingle ("1.3")
End Sub
Output:
Convert String to Double in VBA
With the help of the following statement, we can easily convert a string to several double data types. The syntax of this function is as shown below.
# vba
CDbl(str)
It is recommended to use the CDbl() function to change a string to a double data type. This function forces a string to change into the double data type.
CDbl() is often used to perform the internationally-aware string transformation to a double data type.
In simple words, CDbl() commonly distinguishes distinctive decimal/thousand separators and many currency options that hinge upon your computer’s location.
The range between which a double data type can hold floating-point numbers is below.
- -1.79769313486231E308 to -4.94065645841247E-324 when values are negative.
- 4.94065645841247E-324 to 1.79769313486232E308 when values are positive.
An error will appear if our string does not fall between this range. As shown below, let’s go through an example in which we set newStr as an argument to change a string into a double.
# vba
Function convertToDouble(newStr As Variant)
MsgBox (CDbl(newStr))
End Function
Sub newFunc()
convertToDouble ("1.345")
End Sub
Output:
Convert String to Currency in VBA
With the help of the following statement, you can easily convert a string to several currency data types. The syntax of the function is shown below.
# vba
CCur(newStr)
It is recommended to use the CCur() function to change a string to a currency data type. This function forces a string to change into the currency data type.
CCur() is often used to perform the internationally-aware string transformation to a currency data type.
It means CCur() commonly distinguishes distinctive decimal/thousand separators and many currency options that hinge upon your computer’s location. The currency data type can hold integers by 10,000.
As a result, a currency can hold 15 numbers to the left of the decimal point and four numbers to the right of the decimal point. So the range between which a currency can hold numbers is:
-922,337,203,685,477.5808 to 922,337,203,685,477.5807.
An error will appear if your string does not fall between this range.
As shown below, let’s go through an example in which we set newStr as an argument to change a string into a currency.
# vba
Function convertToCurrency(newStr As Variant)
msgBox(CCur(newStr))
End Function
Convert String to Decimal in VBA
We can use the following statement to achieve this conversion.
# vba
CDec(newStr)
We can use the CDec() function when our goal is to change a string into several decimal data types. This function forces a string to change into the decimal data subtype of the Variant data type.
In simple words, CDec() will return a variant changed to the Decimal subtype.
CDec() is often used to perform the internationally-aware transformation of a string to a decimal data type. It means CDec() commonly distinguishes distinctive decimal/thousand separators and many currency options that hinge upon your computer’s location.
The decimal data type can carry integers having variable power of 10. The power denotes the number of digits that can be present to the right of the decimal point.
The range in which decimals can hold values is shown below.
- When the scale is 0, that is no decimal present the range is from 79,228,162,514,264,337,593,543,950,335 to 79,228,162,514,264,337,593,543,950,335.
- When there are 28 decimal places, the biggest and smallest values are +7.9228162514264337593543950335 and -7.9228162514264337593543950335.
- The smallest values containing no zero values are -0.0000000000000000000000000001 and 0.0000000000000000000000000001.
As shown below, let’s go through an example in which we set newStr as an argument to change a string into a decimal.
# vba
Function convertToDecimal(newStr As Variant)
msgBox(CDec(newStr))
End Function