Printing values instead of the formulas themselves can help protect your IP or prevent users from changing them. In this article, we’re going to show you how to have Excel convert formula to value using VBA.
How to have Excel convert formula to value
We can check each cell using a For Each…Next loop. Below you will find 3 examples using the loop that check cells in a selected area, in the entire worksheet, and all worksheets in a workbook.
After identifying the cells, we can check whether they contain formulas using the HasFormula property. This returns a Boolean value. If the HasFormula returns TRUE, then our code overwrites the formula by setting the cell value into the Formula property of the cell.
rng.Formula = rng.Value
First, you need to add the module into the workbook or the add-in file. Copy and paste the code into the module to run it. The main advantage of the module method is that it allows saving the code in the file, so that it can be used again later. Furthermore, the subroutines in modules can be used by icons in the menu ribbons or keyboard shortcuts. Remember to save your file in either XLSM or XLAM format to save your VBA code.
Convert formulas to values in a selected range
Sub ConvertFormulasToValuesInSelection() Dim rng As Range For Each rng In Selection If rng.HasFormula Then rng.Formula = rng.Value End If Next rng End Sub
Convert formulas to values in active worksheet
Sub ConvertFormulasToValuesInActiveWorksheet() Dim rng As Range For Each rng In ActiveSheet.UsedRange If rng.HasFormula Then rng.Formula = rng.Value End If Next rng End Sub
Convert formulas to values in all worksheets
Sub ConvertFormulasToValuesAllWorksheets() Dim ws As Worksheet, rng As Range For Each ws In ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets For Each rng In ws.UsedRange If rng.HasFormula Then rng.Formula = rng.Value End If Next rng Next ws End Sub
In this Article
- Formulas in VBA
- Macro Recorder and Cell Formulas
- VBA FormulaR1C1 Property
- Absolute References
- Relative References
- Mixed References
- VBA Formula Property
- VBA Formula Tips
- Formula With Variable
- Formula Quotations
- Assign Cell Formula to String Variable
- Different Ways to Add Formulas to a Cell
- Refresh Formulas
This tutorial will teach you how to create cell formulas using VBA.
Formulas in VBA
Using VBA, you can write formulas directly to Ranges or Cells in Excel. It looks like this:
Sub Formula_Example()
'Assign a hard-coded formula to a single cell
Range("b3").Formula = "=b1+b2"
'Assign a flexible formula to a range of cells
Range("d1:d100").FormulaR1C1 = "=RC2+RC3"
End SubThere are two Range properties you will need to know:
- .Formula – Creates an exact formula (hard-coded cell references). Good for adding a formula to a single cell.
- .FormulaR1C1 – Creates a flexible formula. Good for adding formulas to a range of cells where cell references should change.
For simple formulas, it’s fine to use the .Formula Property. However, for everything else, we recommend using the Macro Recorder…
Macro Recorder and Cell Formulas
The Macro Recorder is our go-to tool for writing cell formulas with VBA. You can simply:
- Start recording
- Type the formula (with relative / absolute references as needed) into the cell & press enter
- Stop recording
- Open VBA and review the formula, adapting as needed and copying+pasting the code where needed.
I find it’s much easier to enter a formula into a cell than to type the corresponding formula in VBA.
Notice a couple of things:
- The Macro Recorder will always use the .FormulaR1C1 property
- The Macro Recorder recognizes Absolute vs. Relative Cell References
VBA FormulaR1C1 Property
The FormulaR1C1 property uses R1C1-style cell referencing (as opposed to the standard A1-style you are accustomed to seeing in Excel).
Here are some examples:
Sub FormulaR1C1_Examples()
'Reference D5 (Absolute)
'=$D$5
Range("a1").FormulaR1C1 = "=R5C4"
'Reference D5 (Relative) from cell A1
'=D5
Range("a1").FormulaR1C1 = "=R[4]C[3]"
'Reference D5 (Absolute Row, Relative Column) from cell A1
'=D$5
Range("a1").FormulaR1C1 = "=R5C[3]"
'Reference D5 (Relative Row, Absolute Column) from cell A1
'=$D5
Range("a1").FormulaR1C1 = "=R[4]C4"
End SubNotice that the R1C1-style cell referencing allows you to set absolute or relative references.
Absolute References
In standard A1 notation an absolute reference looks like this: “=$C$2”. In R1C1 notation it looks like this: “=R2C3”.
To create an Absolute cell reference using R1C1-style type:
- R + Row number
- C + Column number
Example: R2C3 would represent cell $C$2 (C is the 3rd column).
'Reference D5 (Absolute)
'=$D$5
Range("a1").FormulaR1C1 = "=R5C4"Relative References
Relative cell references are cell references that “move” when the formula is moved.
In standard A1 notation they look like this: “=C2”. In R1C1 notation, you use brackets [] to offset the cell reference from the current cell.
Example: Entering formula “=R[1]C[1]” in cell B3 would reference cell D4 (the cell 1 row below and 1 column to the right of the formula cell).
Use negative numbers to reference cells above or to the left of the current cell.
'Reference D5 (Relative) from cell A1
'=D5
Range("a1").FormulaR1C1 = "=R[4]C[3]"Mixed References
Cell references can be partially relative and partially absolute. Example:
'Reference D5 (Relative Row, Absolute Column) from cell A1
'=$D5
Range("a1").FormulaR1C1 = "=R[4]C4"VBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro — A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Learn More
VBA Formula Property
When setting formulas with the .Formula Property you will always use A1-style notation. You enter the formula just like you would in an Excel cell, except surrounded by quotations:
'Assign a hard-coded formula to a single cell
Range("b3").Formula = "=b1+b2"VBA Formula Tips
Formula With Variable
When working with Formulas in VBA, it’s very common to want to use variables within the cell formulas. To use variables, you use & to combine the variables with the rest of the formula string. Example:
Sub Formula_Variable()
Dim colNum As Long
colNum = 4
Range("a1").FormulaR1C1 = "=R1C" & colNum & "+R2C" & colNum
End SubVBA Programming | Code Generator does work for you!
Formula Quotations
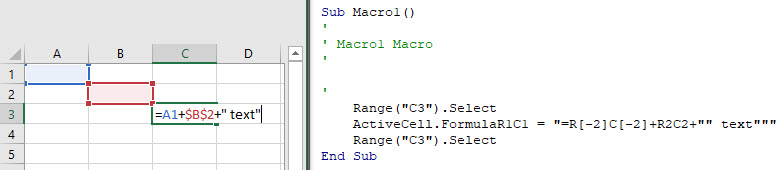
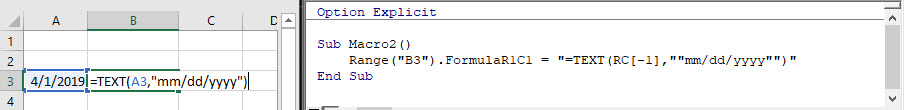
If you need to add a quotation (“) within a formula, enter the quotation twice (“”):
Sub Macro2()
Range("B3").FormulaR1C1 = "=TEXT(RC[-1],""mm/dd/yyyy"")"
End SubA single quotation (“) signifies to VBA the end of a string of text. Whereas a double quotation (“”) is treated like a quotation within the string of text.
Similarly, use 3 quotation marks (“””) to surround a string with a quotation mark (“)
MsgBox """Use 3 to surround a string with quotes"""
' This will print <"Use 3 to surround a string with quotes"> immediate windowAssign Cell Formula to String Variable
We can read the formula in a given cell or range and assign it to a string variable:
'Assign Cell Formula to Variable
Dim strFormula as String
strFormula = Range("B1").FormulaDifferent Ways to Add Formulas to a Cell
Here are a few more examples for how to assign a formula to a cell:
- Directly Assign Formula
- Define a String Variable Containing the Formula
- Use Variables to Create Formula
Sub MoreFormulaExamples ()
' Alternate ways to add SUM formula
' to cell B1
'
Dim strFormula as String
Dim cell as Range
dim fromRow as long, toRow as long
Set cell = Range("B1")
' Directly assigning a String
cell.Formula = "=SUM(A1:A10)"
' Storing string to a variable
' and assigning to "Formula" property
strFormula = "=SUM(A1:A10)"
cell.Formula = strFormula
' Using variables to build a string
' and assigning it to "Formula" property
fromRow = 1
toRow = 10
strFormula = "=SUM(A" & fromValue & ":A" & toValue & ")
cell.Formula = strFormula
End SubRefresh Formulas
As a reminder, to refresh formulas, you can use the Calculate command:
CalculateTo refresh single formula, range, or entire worksheet use .Calculate instead:
Sheets("Sheet1").Range("a1:a10").CalculateВставка формулы со ссылками в стиле A1 и R1C1 в ячейку (диапазон) из кода VBA Excel. Свойства Range.FormulaLocal и Range.FormulaR1C1Local.
Свойство Range.FormulaLocal
FormulaLocal — это свойство объекта Range, которое возвращает или задает формулу на языке пользователя, используя ссылки в стиле A1.
В качестве примера будем использовать диапазон A1:E10, заполненный числами, которые необходимо сложить построчно и результат отобразить в столбце F:
Примеры вставки формул суммирования в ячейку F1:
|
Range(«F1»).FormulaLocal = «=СУММ(A1:E1)» Range(«F1»).FormulaLocal = «=СУММ(A1;B1;C1;D1;E1)» |
Пример вставки формул суммирования со ссылками в стиле A1 в диапазон F1:F10:
|
Sub Primer1() Dim i As Byte For i = 1 To 10 Range(«F» & i).FormulaLocal = «=СУММ(A» & i & «:E» & i & «)» Next End Sub |
В этой статье я не рассматриваю свойство Range.Formula, но если вы решите его применить для вставки формулы в ячейку, используйте англоязычные функции, а в качестве разделителей аргументов — запятые (,) вместо точек с запятой (;):
|
Range(«F1»).Formula = «=SUM(A1,B1,C1,D1,E1)» |
После вставки формула автоматически преобразуется в локальную (на языке пользователя).
Свойство Range.FormulaR1C1Local
FormulaR1C1Local — это свойство объекта Range, которое возвращает или задает формулу на языке пользователя, используя ссылки в стиле R1C1.
Формулы со ссылками в стиле R1C1 можно вставлять в ячейки рабочей книги Excel, в которой по умолчанию установлены ссылки в стиле A1. Вставленные ссылки в стиле R1C1 будут автоматически преобразованы в ссылки в стиле A1.
Примеры вставки формул суммирования со ссылками в стиле R1C1 в ячейку F1 (для той же таблицы):
|
‘Абсолютные ссылки в стиле R1C1: Range(«F1»).FormulaR1C1Local = «=СУММ(R1C1:R1C5)» Range(«F1»).FormulaR1C1Local = «=СУММ(R1C1;R1C2;R1C3;R1C4;R1C5)» ‘Ссылки в стиле R1C1, абсолютные по столбцам и относительные по строкам: Range(«F1»).FormulaR1C1Local = «=СУММ(RC1:RC5)» Range(«F1»).FormulaR1C1Local = «=СУММ(RC1;RC2;RC3;RC4;RC5)» ‘Относительные ссылки в стиле R1C1: Range(«F1»).FormulaR1C1Local = «=СУММ(RC[-5]:RC[-1])» Range(«F2»).FormulaR1C1Local = «=СУММ(RC[-5];RC[-4];RC[-3];RC[-2];RC[-1])» |
Пример вставки формул суммирования со ссылками в стиле R1C1 в диапазон F1:F10:
|
‘Ссылки в стиле R1C1, абсолютные по столбцам и относительные по строкам: Range(«F1:F10»).FormulaR1C1Local = «=СУММ(RC1:RC5)» ‘Относительные ссылки в стиле R1C1: Range(«F1:F10»).FormulaR1C1Local = «=СУММ(RC[-5]:RC[-1])» |
Так как формулы с относительными ссылками и относительными по строкам ссылками в стиле R1C1 для всех ячеек столбца F одинаковы, их можно вставить сразу, без использования цикла, во весь диапазон.
Bottom line: Learn 3 tips for writing and creating formulas in your VBA macros with this article and video.
Skill level: Intermediate
Video Tutorial
Download the File
Download the Excel file to follow along with the video.
Automate Formula Writing
Writing formulas can be one of the most time consuming parts of your weekly or monthly Excel task. If you’re working on automating that process with a macro, then you can have VBA write the formula and input it into the cells for you.
Writing formulas in VBA can be a bit tricky at first, so here are 3 tips to help save time and make the process easier.
Tip #1: The Formula Property
The Formula property is a member of the Range object in VBA. We can use it to set/create a formula for a single cell or range of cells.
There are a few requirements for the value of the formula that we set with the Formula property:
- The formula is a string of text that is wrapped in quotation marks. The value of the formula must start and end in quotation marks.
- The formula string must start with an equal sign = after the first quotation mark.
Here is a simple example of a formula in a macro.
Sub Formula_Property()
'Formula is a string of text wrapped in quotation marks
'Starts with an = sign
Range("B10").Formula = "=SUM(B4:B9)"
End Sub
The Formula property can also be used to read an existing formula in a cell.
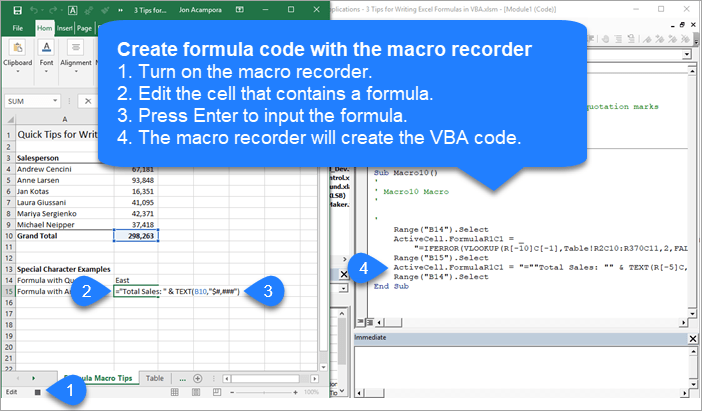
Tip #2: Use the Macro Recorder
When your formulas are more complex or contain special characters, they can be more challenging to write in VBA. Fortunately we can use the macro recorder to create the code for us.
Here are the steps to creating the formula property code with the macro recorder.
- Turn on the macro recorder (Developer tab > Record Macro)
- Type your formula or edit an existing formula.
- Press Enter to enter the formula.
- The code is created in the macro.
If your formula contains quotation marks or ampersand symbols, the macro recorder will account for this. It creates all the sub-strings and wraps everything in quotes properly. Here is an example.
Sub Macro10()
'Use the macro recorder to create code for complex formulas with
'special characters and relative references
ActiveCell.FormulaR1C1 = "=""Total Sales: "" & TEXT(R[-5]C,""$#,###"")"
End Sub
Tip #3: R1C1 Style Formula Notation
If you use the macro recorder for formulas, you will notices that it creates code with the FormulaR1C1 property.
R1C1 style notation allows us to create both relative (A1), absolute ($A$1), and mixed ($A1, A$1) references in our macro code.
R1C1 stands for Rows and Columns.
Relative References
For relative references we specify the number of rows and columns we want to offset from the cell that the formula is in. The number of rows and columns are referenced in square brackets.
The following would create a reference to a cell that is 3 rows above and 2 rows to the right of the cell that contains the formula.
R[-3]C[2]
Negative numbers go up rows and columns to the left.
Positive numbers go down rows and columns to the right.
Absolute References
We can also use R1C1 notation for absolute references. This would typically look like $A$2.
For absolute references we do NOT use the square brackets. The following would create a direct reference to cell $A$2, row 2 column 1
R2C1
Mixed References
with mixed references we add the square brackets for either the row or column reference, and no brackets for the other reference. The following formula in cell B2 would create this reference to A$2, where the row is absolute and the column is relative.
R2C[-1]
When creating mixed references, the relative row or column number will depend on what cell the formula is in.
It’s easiest to just use the macro recorder to figure these out.
FormulaR1C1 Property versus Formula Property
The FormulaR1C1 property reads the R1C1 notation and creates the proper references in the cells. If you use the regular Formula property with R1C1 notation, then VBA will attempt to put those letters in the formula, and it will likely result in a formula error.
Therefore, use the Formula property when your code contains cell references ($A$1), the FormulaR1C1 property when you need relative references that are applied to multiple cells or dependent on where the formula is entered.
If your spreadsheet changes based on conditions outside your control, like new columns or rows of data are imported from the data source, then relative references and R1C1 style notation will probably be best.
I hope those tips help. Please leave a comment below with questions or suggestions.
It is possible to use Excel’s ready-to-use formulas through VBA programming. These are properties that can be used with Range or Cells.
VBA Formula
Formula adds predefined Excel formulas to the worksheet. These formulas should be written in English even if you have a language pack installed.
Range("F2").Formula = "=SUM(B2:C7)"
Range("F3").Formula = "=SUM($B$2:$C$7)"

Do not worry if the language of your Excel is not English because, as in the example, it will do the translation to the spreadsheet automatically.
Multiple formulas
You can insert multiple formulas at the same time using the Formula property. To do this, simply define a Range object that is larger than a single cell, and the predefined formula will be «dragged» across the range.
«Dragging» manually:

«Dragging» by VBA:
Range("D2:D7").Formula = "=SUM(B2:C2)"

Another way to perform the same action would be using FillDown method.
Range("D2").Formula = "=SUM(B2:C2)"
Range("D2:D7").FillDown
VBA FormulaLocal
FormulaLocal adds predefined Excel formulas to the worksheet. These formulas, however, should be written in the local language of Excel (in the case of Brazil, in Portuguese).
Range("F2").FormulaLocal = "=SOMA(B2:C7)"
Just as the Formula property, FormulaLocal can be used to make multiple formulas.
VBA FormulaR1C1
FormulaR1C1, as well as Formula and FormulaLocal, also adds pre-defined Excel formulas to the spreadsheet; however, the use of relative and absolute notations have different rules. The formula used must be written in English.
FormulaR1C1 is the way to use Excel’s ready-to-use formulas in VBA by easily integrating them into loops and counting variables.
In the notations:
- R refers to rows, in the case of vertical displacement
- C refers to columns, in the case of horizontal displacement
- N symbolizes an integer that indicates how much must be shifted in number of rows and/or columns
- Relative notation: Use as reference the Range that called it
The format of the relative formula is: R[N]C[N]:R[N]C[N].
Range("F2").FormulaR1C1 = "=SUM(R[0]C[-4]:R[5]C[-3])" 'Equals the bottom row
Range("F2").FormulaR1C1 = "=SUM(RC[-4]:R[5]C[-3])"
When N is omitted, the value 0 is assumed.
In the example, RC[-4]:R[5]C[-3] results in «B2: C7». These cells are obtained by: receding 4 columns to the left RC[-4] from Range(«F2») to obtain «B2»; and 5 lines down and 3 columns to the left R[5]C[-3] from Range(«F2») to obtain «C7».
- Absolute notation: Use the start of the spreadsheet as a reference
The format of the relative formula is: RNCN:RNCN.
Range("F2").FormulaR1C1 = "=SUM(R2C2:R7C3)" 'Results in "$B$2:$C$7"
N negative can only be used in relative notation.
The two notations (relative and absolute) can be merged.
Range("F2").FormulaR1C1 = "=SUM(RC[-4]:R7C3)" 'Results in "B2:$C$7"
VBA WorksheetFunction
Excel formulas can also be accessed by object WorksheetFunction methods.
Range("F2") = WorksheetFunction.Sum(Range("B2:C7"))
Excel formulas can also be accessed similarly to functions created in VBA.
The formulas present in the WorksheetFunction object are all in English.
One of the great advantages of accessing Excel formulas this way is to be able to use them more easily in the VBA environment.
MsgBox (WorksheetFunction.Sum(3, 4, 5))
Expense=4
MsgBox (WorksheetFunction.Sum(3, 4, 5,-Expense))
To list the available Excel formulas in this format, simply type WorksheetFunction. that automatically an option menu with all formulas will appear:

Consolidating Your Learning
Suggested Exercise
SuperExcelVBA.com is learning website. Examples might be simplified to improve reading and basic understanding. Tutorials, references, and examples are constantly reviewed to avoid errors, but we cannot warrant full correctness of all content. All Rights Reserved.
Excel ® is a registered trademark of the Microsoft Corporation.
© 2023 SuperExcelVBA | ABOUT