Home / VBA / VBA IF OR (Test Multiple Conditions)
You can use the OR operator with the VBA IF statement to test multiple conditions. When you use it, it allows you to test two or more conditions simultaneously and returns true if any of those conditions are true. But if all the conditions are false only then it returns false in the result.
Use OR with IF
- First, start the IF statement with the “IF” keyword.
- After that, specify the first condition that you want to test.
- Next, use the OR keyword to specify the second condition.
- In the end, specify the second condition that you want to test.

To have a better understanding let’s see an example.
Sub myMacro()
'two conditions to test using OR
If 1 = 1 Or 2 < 1 Then
MsgBox "One of the conditions is true."
Else
MsgBox "None of the conditions are true."
End If
End Sub
If you look at the above example, we have specified two conditions one if (1 = 1) and the second is (2 < 1), and here only the first condition is true, and even though it has executed the line of code that we have specified if the result is true.

Now let’s see if both conditions are false, let me use a different code here.
Sub myMacro()
'two conditions to test using OR
If 1 = 2 Or 2 < 1 Then
MsgBox "One of the conditions is true."
Else
MsgBox "None of the conditions are true."
End If
End Sub
In the above code, both conditions are false, and when you run this code, it executes the line of code that we have specified if the result is false.

In the same way, you can also test more than two conditions at the same time. Let’s continue the above example and add the third condition to it.
Sub myMacro()
'three conditions to test using OR
If 1 = 1 And 2 > 1 And 1 - 1 = 0 Then
MsgBox "one of the conditions is true."
Else
MsgBox "none of the conditions are true."
End If
End Sub
Now we have three conditions to test, and we have used the OR after the second condition to specify the third condition. As you learned above that when you use OR, any of the conditions need to be true to get true in the result. When you run this code, it executes the line of code that we have specified for the true.

And if all the conditions are false, just like you have in the following code, it returns false.
Sub myMacro()
'three conditions to test using OR
If 1 < 1 And 2 < 1 And 1 + 1 = 0 Then
MsgBox "one of the conditions is true."
Else
MsgBox "none of the conditions are true."
End If
End Sub
Return to VBA Code Examples
In this Article
- IF…AND
- IF…OR
- IF NOT…
This article will demonstrate how to use the VBA If statement with And, Or and Not.
When we us an IF statement in Excel VBA, the statement will execute a line of code if the condition you are testing is true.
- We can use AND statement and OR statements in conjunction with IF statements to test for more than one condition and direct the code accordingly.
- We can also use a NOT statement with an IF statement to check if the condition is NOT true – it basically is the inverse of the IF statement when used alone.
IF…AND
We can use the IF…AND combination of logical operators when we wish to test for more than one condition where all the conditions need to be true for the next line of code to execute.
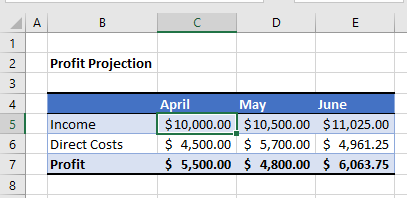
For example, consider the following sheet:
To check if the Profit is over $5,000, we can run the following macro:
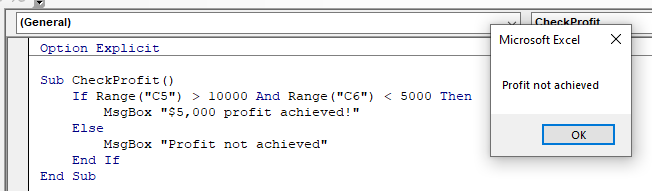
Sub CheckProfit()
If Range("C5") >= 10000 And Range("C6") < 5000 Then
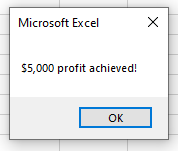
MsgBox "$5,000 profit achieved!"
Else
Msgbox "Profit not achieved!"
End If
End SubThis macro will check that the cell C5 is greater or equal to $10,000 AND check that the cell B6 is less than $5,000. If these conditions are BOTH true, it will show the message box.
If we amend the macro to check if C5 is just greater than $10,000, then the profit would not be achieved!
IF…OR
We can use the IF…OR combination of logical operators when we wish to test for more than one condition where only one of the conditions needs to be true for the next line of code to execute.
The format for this is almost identical to the IF…AND example above.
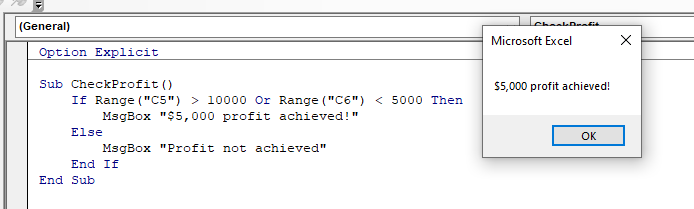
Sub CheckProfit()
If Range("C5") > 10000 Or Range("C6") < 5000 Then
MsgBox "$5,000 profit achieved!"
Else
Msgbox "Profit not achieved!"
End If
End SubHowever, with this macro, because we are using an IF …OR statement, only one of the conditions needs to be true.
IF NOT…
IF..NOT changes the IF statement around – it will check to see if the condition is NOT true rather than checking to see if the condition is true.
Sub CheckProfit()
If NOT Range("C5")< 10000 Or Range("C6") < 5000 Then
MsgBox "$5,000 profit achieved!"
Else
Msgbox "Profit not achieved!"
End If
End SubIn this example above, the IF statement is checking to see if the value in C5 is NOT smaller than 10000.
Therefore this line of code:
IF Range("C5") > 10000and this this line of code:
IF NOT Range("C5") < 10000are testing for the same thing!
|
christine Пользователь Сообщений: 91 |
Доброго времени суток, друзья как на vba прописать подобного рода процедуру: с учетом того, чтобы результат (‘f’ или последующие ‘g’, ‘h’) выгружали текст в ворд.. (п.с.говоря человеческим языком — имеются условия, с входящими «и» а также «или», которые в случае соблюдения заданых параметров, приводили бы к выводу в ворд определенного шаблонного текста (которому например, соответствует определенная буква, в противном случае искали бы другую «букву», для отображения в ворде другого шаблонного текста; vba только начинаю разбирать, поэтому низкий поклон и заранее благодарна вашему содействию и вниманию! Изменено: christine — 19.03.2013 20:53:48 |
|
ikki Пользователь Сообщений: 9709 |
#2 19.03.2013 22:30:05
да-да, уж пожалуйста. Изменено: ikki — 19.03.2013 22:30:21 фрилансер Excel, VBA — контакты в профиле |
||
|
christine Пользователь Сообщений: 91 |
1. хотелось бы понять логику функций если/и/или в vba — то бишь, как в данном случае прописываются эквивалентные обычным формулам конструкции — простым языком говоря… Изменено: christine — 20.03.2013 23:07:24 |
|
christine Пользователь Сообщений: 91 |
1. на первый вопрос частично получила ответ, логика описывается следующим выражением открытый вопрос — как в вба использовать более одного условия с «и»? как быть с «или»? Изменено: christine — 21.03.2013 22:04:55 |
|
christine Пользователь Сообщений: 91 |
ребят, ну помогите девчонке хотя бы частично ответить на вопросы Изменено: christine — 21.03.2013 22:08:18 |
|
k61 Пользователь Сообщений: 2441 |
#6 21.03.2013 22:15:57
или = Or |
||
|
Юрий М Модератор Сообщений: 60570 Контакты см. в профиле |
Можно в одной строке (как у Вас) перечислять несколько «И», но быстрее будет отсекать ненужные проверки: По поводу «ИЛИ» вопрос не понял |
|
christine Пользователь Сообщений: 91 |
[QUOTE]Юрий М пишет: дело в том что я описывала многофакторное условие, вроде f = если(2>x>3 и(4>y>3 или 5>z>3)), то e, иначе … (продолжение) |
|
Юрий М Модератор Сообщений: 60570 Контакты см. в профиле |
#9 21.03.2013 22:40:05 ElseIf — это не иначе. Иначе — Else. А ElseIf можно перевести, как ИЛИ-ЕСЛИ. |
IF OR is not a single statement. Rather, these are two logical functions used together in VBA when we have more than one criteria to check. When we use the IF statement, if any criteria meet, we get the TRUE result. OR statement is used between the two criteria of the IF statement.
IF OR Function in VBA
Logical functions are the heart of any criteria-based calculations. The IF function is the most popular logical function, be it a worksheet function or a VBA function because it serves excellently for our needs. But one more logical function, OR in excel, is the most underrated. It is also important to master when it comes to solving complex calculations. This article will take you through the VBA IF OR function in detail. Read the full article to get the function in detail.
Table of contents
- IF OR Function in VBA
- How to Use IF with OR Function in VBA?
- IF OR VBA Function with Loops (Advanced)
- Recommended Articles
How to Use IF with OR Function in VBA?
We will show you a simple example of using the IF OR function in VBA.
You can download this VBA IF OR Excel Template here – VBA IF OR Excel Template
A combination of logical functions is the best pair in Excel. However, combining many logical formulas inside the other logical formula suggests that calculation requires many conditions to test.
Now, look at the syntax of the IF OR function in VBA.
[Test] OR [Test] OR [Test]
It is the same as we saw in the worksheet example. For a better understanding, look at the below example.
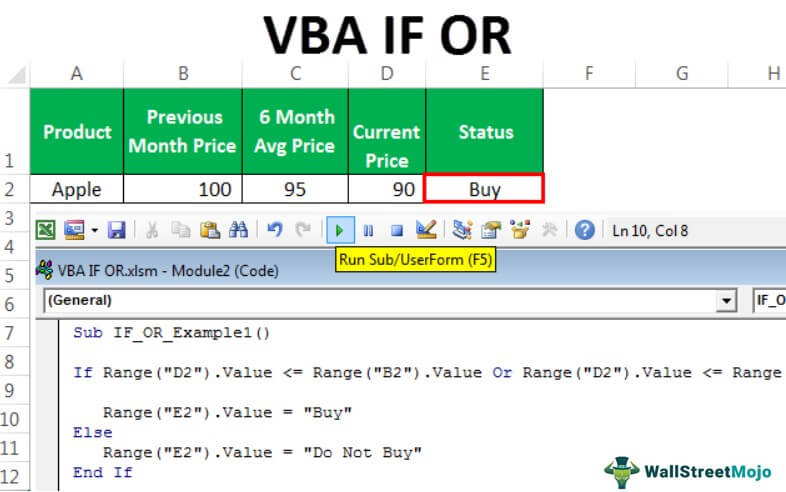
We have the previous month’s price, the last 6-month average price, and the current monthly price here.
To decide whether to buy the product, we need to do some tests here, and those tests are.
If the Current Price is less than or equal to any of the other two prices, we should get the result as “Buy” or else should get the result as “Do Not Buy.”
Step 1: Open the IF condition inside the Sub procedure.
Code:
Sub IF_OR_Example1() If End Sub
Step 2: Inside the IF condition, apply the first logical test as Range(“D2”).Value <= Range(“B2”).Value
Code:
Sub IF_OR_Example1() If Range(“D2”).Value <= Range(“B2”).Value End Sub
Step 3: The first logical condition completes. Now, open OR statement.
Code:
Sub IF_OR_Example1() If Range("D2").Value <= Range("B2").Value OR End Sub
Step 4: Now, apply the second logical condition as Range(“D2”).Value <= Range(“C2”).Value
Code:
Sub IF_OR_Example1() If Range("D2").Value <= Range("B2").Value OR Range("D2").Value <= Range("C2").Value End Sub
Step 5: We are done with the logical tests here. After the logical tests, put the word “Then.”
Code:
Sub IF_OR_Example1() If Range("D2").Value <= Range("B2").Value Or Range("D2").Value <= Range("C2").Value Then End Sub
Step 6: In the next line, write what the result should be if the logical testA logical test in Excel results in an analytical output, either true or false. The equals to operator, “=,” is the most commonly used logical test.read more is TRUE. If the condition is TRUE, we need the result as “Buy” in cell E2.
Code:
Sub IF_OR_Example1() If Range("D2").Value <= Range("B2").Value Or Range("D2").Value <= Range("C2").Value Then Range("E2").Value = "Buy" End Sub
Step 7: If the result is FALSE, we should get the result as “Do Not Buy.” So in the next line, put “Else” and write the code in the next line.
Code:
Sub IF_OR_Example1() If Range("D2").Value <= Range("B2").Value Or Range("D2").Value <= Range("C2").Value Then Range("E2").Value = "Buy" Else Range("E2").Value = "Do Not Buy" End Sub
Step 8: Close the IF statement with “End If.”
Code:
Sub IF_OR_Example1() If Range("D2").Value <= Range("B2").Value Or Range("D2").Value <= Range("C2").Value Then Range("E2").Value = "Buy" Else Range("E2").Value = "Do Not Buy" End If End Sub
We complete the coding part.
Let us run this code using F5 or manually through the run option and see the result in cell E2.
We got the result as “Buy” because the current monthly price of Apple is less than the price of both “Previous Month” as well as “6 Month Average Price”.
IF OR VBA Function with Loops (Advanced)
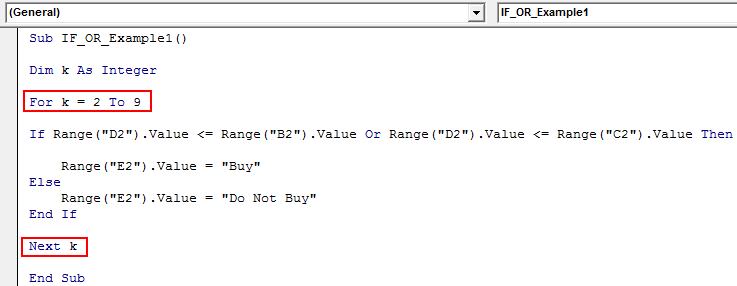
Once you understand the formula, try to use it with a larger number of cells. In the case of a larger number of cells, we cannot write any line of code, so we need to use VBA loopsA VBA loop in excel is an instruction to run a code or repeat an action multiple times.read more.
We have added a few more lines for the above data set.
We need to use the For Next Loop here.
Just keep the current code as it is.
Declare the variable as an Integer.
Now, open For Next Loop from 2 to 9.
Now, wherever we have cell referenceCell reference in excel is referring the other cells to a cell to use its values or properties. For instance, if we have data in cell A2 and want to use that in cell A1, use =A2 in cell A1, and this will copy the A2 value in A1.read more, change the current number, and concatenate the variable “k” with them.
For example, Range (“D2”).Value should be Range (“D” & k).Value
Now, run the code. First, we should get the status in all the cells.
You can copy the code below.
Code:
Sub IF_OR_Example1() Dim k As Integer For k = 2 To 9 If Range("D" & k).Value <= Range("B" & k).Value Or Range("D" & k).Value <= Range("C" & k).Value Then Range("E" & k).Value = "Buy" Else Range("E" & k).Value = "Do Not Buy" End If Next k End Sub
Recommended Articles
This article has been a guide to VBA IF OR. Here, we learn how to use IF Condition with OR function in Excel VBA, examples, and downloadable templates. Below are some useful articles related to VBA: –
- VBA INT
- VBA LEN
- VBA Integer
- VBA MID Function
На чтение 19 мин. Просмотров 24.3k.

Пьер Корнель
Угадай, если сможешь, и выбери, если посмеешь
Содержание
- Краткое руководство по VBA If Statement
- Что такое IF и зачем оно тебе?
- Тестовые данные
- Формат операторов VBA If Then
- Простой пример If Then
- Условия IF
- Использование If ElseIf
- Использование If Else
- Используя If And/If Or
- Функция IIF
- Использование Select Case
- Попробуйте это упражнение
Краткое руководство по VBA If Statement
| Описание | Формат | Пример |
| If Then | If [условие верно] Then [действие] End If |
If score = 100 Then Debug.Print «Отлично» End If |
| If Else | If [условие верно] Then [действие] Else [действие] End If |
If score = 100 Then Debug.Print «Отлично» Else Debug.Print «Попробуй снова» End If |
| If ElseIf | If [1 условие верно] Then [действие] ElseIf [2 условие верно] Then [действие] End If |
If score = 100 Then Debug.Print «Отлично» ElseIf score > 50 Then Debug.Print «Пройдено» ElseIf score <= 50 Then Debug.Print «Попробуй снова» End If |
| Else и ElseIf (Else должно идти после ElseIf’s) |
If [1 условие верно] Then [действие] ElseIf [2 условие верно] Then [действие] Else [действие] End If |
If score = 100 Then Debug.Print «Отлично» ElseIf score > 50 Then Debug.Print «Пройдено» ElseIf score > 30 Then Debug.Print «Попробуй снова» Else Debug.Print «Ой» End If |
| If без Endif (Только одна строка) |
If [условие верно] Then [действие] |
If value <= 0 Then value = 0 |
В следующем коде показан простой пример использования
оператора VBA If
If Sheet1.Range("A1").Value > 5 Then
Debug.Print "Значение больше 5."
ElseIf Sheet1.Range("A1").Value < 5 Then
Debug.Print "Значение меньше 5."
Else
Debug.Print "Значение равно 5."
End If
Что такое IF и зачем оно тебе?
Оператор VBA If используется, чтобы позволить вашему коду
делать выбор, когда он выполняется.
Вам часто захочется сделать выбор на основе данных, которые
читает ваш макрос.
Например, вы можете захотеть читать только тех учеников, у
которых оценки выше 70. Когда вы читаете каждого учащегося, вы можете
использовать инструкцию If для проверки отметок каждого учащегося.
Важным словом в последнем предложении является проверка. Оператор
If используется для проверки значения, а затем для выполнения задачи на основе
результатов этой проверки.
Тестовые данные
Мы собираемся использовать следующие тестовые данные для
примеров кода в этом посте.
Формат операторов VBA If Then
Формат оператора If Then следующий
За ключевым словом If следуют условие и ключевое слово Then
Каждый раз, когда вы используете оператор If Then, вы должны использовать соответствующий оператор End If.
Когда условие оценивается как истинное, обрабатываются все
строки между If Then и End If.
If [условие верно] Then
[строки кода]
[строки кода]
[строки кода]
End If
Чтобы сделать ваш код более читабельным, рекомендуется
делать отступы между операторами If Then и End If.
Отступ между If и End If
Отступ означает просто переместить строку кода на одну вкладку вправо. Правило большого пальца состоит в том, чтобы сделать отступ между начальным и конечным операторами, такими как:
Sub … End Sub
If Then … End If
If Then… ElseIf … Else … Endif
For … Next
Do While … Loop
Select Case … End Case
Для отступа в коде вы можете выделить строки для отступа и нажать клавишу Tab. Нажатие клавиш Shift + Tab сделает отступ кода, т.е. переместит его на одну вкладку влево.
Вы также можете использовать значки на панели инструментов Visual Basic для отступа кода.
Если вы посмотрите на примеры кода на этом сайте, вы увидите, что код имеет отступ.
Простой пример If Then
Следующий код выводит имена всех студентов с баллами более 50.
Sub ChitatOcenki()
Dim i As Long
' Пройдите столбцы отметок
For i = 2 To 11
' Проверьте, больше ли баллов,чем 50
If Sheet1.Range("C" & i).Value > 50 Then
' Напечатайте имя студента в «Immediate Window» (Ctrl + G)
Debug.Print Sheet1.Range("A" & i).Value & " " & Sheet1.Range("B" & i).Value
End If
Next
End Sub
Результаты:
- Василий Кочин
- Максим Бородин
- Дмитрий Маренин
- Олеся Клюева
- Евгений Яшин
Поэкспериментируйте с этим примером и проверьте значение или знак > и посмотрите, как изменились результаты.
Условия IF
Часть кода между ключевыми словами If и Then называется условием. Условие — это утверждение, которое оценивается как истинное или ложное. Они в основном используются с операторами Loops и If. При создании условия вы используете такие знаки, как «>, <, <>,> =, <=, =».
Ниже приведены примеры условий:
| Условие | Это верно, когда |
| x < 5 | x меньше,чем 5 |
| x <= 5 | x меньше, либо равен 5 |
| x > 5 | x больше, чем 5 |
| x >= 5 | x больше, либо равен 5 |
| x = 5 | x равен 5 |
| x <> 5 | x не равен 5 |
| x > 5 And x < 10 | x больше, чем 5 И x меньше, чем 10 |
| x = 2 Or x >10 | x равен 2 ИЛИ x больше,чем 10 |
| Range(«A1») = «Иван» | Ячейка A1 содержит текст «Иван» |
| Range(«A1») <> «Иван» | Ячейка A1 не содержит текст «Иван» |
Вы могли заметить x = 5, как условие. Не стоит путать с х = 5, при использовании в качестве назначения.
Когда в условии используется «=», это означает, что «левая сторона равна правой стороне».
В следующей таблице показано, как знак равенства используется
в условиях и присваиваниях.
| Использование «=» | Тип | Значение |
| Loop Until x = 5 | Условие | Равен ли x пяти |
| Do While x = 5 | Условие | Равен ли x пяти |
| If x = 5 Then | Условие | Равен ли x пяти |
| For x = 1 To 5 | Присваивание | Установите значение х = 1, потом = 2 и т.д. |
| x = 5 | Присваивание | Установите х до 5 |
| b = 6 = 5 | Присваивание и условие |
Присвойте b результату условия 6 = 5 |
| x = MyFunc(5,6) | Присваивание | Присвойте х значение, возвращаемое функцией |
Последняя запись в приведенной выше таблице показывает
оператор с двумя равными. Первый знак равенства — это присвоение, а любые
последующие знаки равенства — это условия.
Поначалу это может показаться странным, но подумайте об этом
так. Любое утверждение, начинающееся с переменной и равно, имеет следующий
формат
[переменная] [=] [оценить эту часть]
Поэтому все, что находится справа от знака равенства, оценивается и результат помещается в переменную. Посмотрите на последние три строки таблицы, как:
[x] [=] [5]
[b] [=] [6 = 5]
[x] [=] [MyFunc (5,6)]
Использование If ElseIf
Инструкция ElseIf позволяет вам выбирать из нескольких вариантов. В следующем примере мы печатаем баллы, которые находятся в диапазоне.
Sub IspElseIf()
If Marks >= 85 Then
Debug.Print "Высший балл"
ElseIf Marks >= 75 Then
Debug.Print "Отлично"
End If
End Sub
Важно понимать, что порядок важен. Условие If проверяется
первым.
Если это правда, то печатается «Высший балл», и оператор If заканчивается.
Если оно ложно, то код переходит к следующему ElseIf и
проверяет его состояние.
Давайте поменяемся местами If и ElseIf из последнего
примера. Код теперь выглядит так
Sub IspElseIfNeverno()
' Этот код неверен, так как ElseIf никогда не будет верным
If Marks >= 75 Then
Debug.Print "Отлично"
ElseIf Marks >= 85 Then
' код никогда не достигнет здесь
Debug.Print "Высший балл"
End If
End Sub
В этом случае мы сначала проверяем значение более 75. Мы никогда не будем печатать «Высший балл», потому что, если значение больше 85, это вызовет первый оператор if.
Чтобы избежать подобных проблем, мы должны использовать два
условия. Они помогают точно указать, что вы ищете, чтобы избежать путаницы.
Пример ниже показывает, как их использовать. Мы рассмотрим более многочисленные
условия в разделе ниже.
If marks >= 75 And marks < 85 Then
Debug.Print "Отлично"
ElseIf marks >= 85 And marks <= 100 Then
Debug.Print "Высший балл"
End If
Давайте расширим оригинальный код. Вы можете использовать столько операторов ElseIf, сколько захотите. Мы добавим еще несколько, чтобы учесть все наши классификации баллов.
Использование If Else
Утверждение Else используется, как ловушка для всех. Это в основном означает «если бы не было условий» или «все остальное». В предыдущем примере кода мы не включили оператор печати для метки сбоя. Мы можем добавить это, используя Else.
Sub IspElse()
If Marks >= 85 Then
Debug.Print "Высший балл"
ElseIf Marks >= 75 Then
Debug.Print "Отлично"
ElseIf Marks >= 55 Then
Debug.Print "Хорошо"
ElseIf Marks >= 40 Then
Debug.Print "Удовлетворительно"
Else
' Для всех других оценок
Debug.Print "Незачет"
End If
End Sub
Так что, если это не один из других типов, то это провал.
Давайте напишем некоторый код с помощью наших примеров
данных и распечатаем студента и его классификацию.
Sub DobClass()
' получить последнюю строку
Dim startRow As Long, lastRow As Long
startRow = 2
lastRow = Sheet1.Cells(Sheet1.Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row
Dim i As Long, Marks As Long
Dim sClass As String
' Пройдите столбцы отметок
For i = startRow To lastRow
Marks = Sheet1.Range("C" & i).Value
' Проверьте отметки и классифицируйте соответственно
If Marks >= 85 Then
sClass = "Высший балл"
ElseIf Marks >= 75 Then
sClass = "Отлично"
ElseIf Marks >= 55 Then
sClass = "Хорошо"
ElseIf Marks >= 40 Then
sClass = "Удовлетворительно"
Else
' Для всех других оценок
sClass = "Незачет"
End If
' Запишите класс в столбец E
Sheet1.Range("E" & i).Value = sClass
Next
End Sub
Результаты выглядят так: в столбце E — классификация баллов
Используя If And/If Or
В выражении If может быть несколько условий. Ключевые слова VBA And и Or позволяют использовать несколько условий.
Эти слова работают так же, как вы используете их на
английском языке.
Давайте снова посмотрим на наши примеры данных. Теперь мы
хотим напечатать всех студентов, которые набрали от 50 до 80 баллов.
Мы используем Аnd, чтобы добавить дополнительное условие. Код гласит: если оценка больше или равна 50 и меньше 75, напечатайте имя студента.
Sub ProverkaStrokiOcenok()
Dim i As Long, marks As Long
For i = 2 To 11
' Хранить оценки для текущего студента
marks = Sheet1.Range("C" & i).Value
' Проверьте, если отметки больше 50 и меньше 75
If marks >= 50 And marks < 80 Then
' Напечатайте имя и фамилию в Immediate window (Ctrl+G)
Debug.Print Sheet1.Range("A" & i).Value & Sheet1.Range("B" & i).Value
End If
Next
End Sub
Вывести имя и фамилию в результаты:
- Дмитрий Маренин
- Олеся Клюева
- Евгений Яшин
В нашем следующем примере мы хотим знать, кто из студентов сдавал историю или геометрию. Таким образом, в данном случае мы говорим, изучал ли студент «История» ИЛИ изучал ли он «Геометрия» (Ctrl+G).
Sub ChitatObektOcenki()
Dim i As Long, marks As Long
' Пройдите столбцы отметок
For i = 2 To 11
marks = Sheet1.Range("D" & i).Value
' Проверьте, если отметки больше 50 и меньше 80
If marks = "История" Or marks = "Геометрия" Then
' Напечатайте имя и фамилию в Immediate window (Ctrl+G)
Debug.Print Sheet1.Range("A" & i).Value & " " & Sheet1.Range("B" & i).Value
End If
Next
End Sub
Результаты:
- Василий Кочин
- Александр Грохотов
- Дмитрий Маренин
- Николай Куликов
- Олеся Клюева
- Наталия Теплых
- Дмитрий Андреев
Использование нескольких таких условий часто является
источником ошибок. Эмпирическое правило, которое нужно помнить, должно быть
максимально простым.
Использование IF AND
And работает следующим образом:
| Условие 1 | Условие 2 | Результат |
| ИСТИНА | ИСТИНА | ИСТИНА |
| ИСТИНА | ЛОЖЬ | ЛОЖЬ |
| ЛОЖЬ | ИСТИНА | ЛОЖЬ |
| ЛОЖЬ | ЛОЖЬ | ЛОЖЬ |
Что вы заметите, так это то, что And верно только тогда, когда все условия выполняются.
Использование IF OR
Ключевое слово OR работает следующим образом
| Условие 1 | Условие 2 | Результат |
| ИСТИНА | ИСТИНА | ИСТИНА |
| ИСТИНА | ЛОЖЬ | ИСТИНА |
| ЛОЖЬ | ИСТИНА | ИСТИНА |
| ЛОЖЬ | ЛОЖЬ | ЛОЖЬ |
Что вы заметите, так это то, что OR ложно, только когда все условия ложны.
Смешивание And и Or может затруднить чтение кода и привести к ошибкам. Использование скобок может сделать условия более понятными.
Sub OrSAnd()
Dim subject As String, marks As Long
subject = "История"
marks = 5
If (subject = "Геометрия" Or subject = "История") And marks >= 6 Then
Debug.Print "ИСТИНА"
Else
Debug.Print "ЛОЖЬ"
End If
End Sub
Использование IF NOT
Также есть оператор NOT. Он возвращает противоположный результат условия.
| Условие | Результат |
| ИСТИНА | ЛОЖЬ |
| ЛОЖЬ | ИСТИНА |
Следующие две строки кода эквивалентны.
If marks < 40 Then If Not marks >= 40 Then
так же, как и
If True Then If Not False Then
и
If False Then If Not True Then
Помещение условия в круглые скобки облегчает чтение кода
If Not (marks >= 40) Then
Распространенное использование Not — при проверке, был ли установлен объект. Возьмите Worksheet для примера. Здесь мы объявляем рабочий лист.
Dim mySheet As Worksheet ' Некоторый код здесь
Мы хотим проверить действительность mySheet перед его использованием. Мы можем проверить, если это Nothing.
If mySheet Is Nothing Then
Нет способа проверить, является ли это чем-то, поскольку есть много разных способов, которым это может быть что-то. Поэтому мы используем NOT с Nothing.
If Not mySheet Is Nothing Then
Если вы находите это немного запутанным, вы можете использовать круглые скобки, как здесь
If Not (mySheet Is Nothing) Then
Функция IIF
VBA имеет функцию, аналогичную функции Excel If. В Excel вы часто используете функцию If следующим образом:
= ЕСЛИ (F2 =»»,»», F1 / F2)
Формат
= If (условие, действие, если ИСТИНА, действие, если ЛОЖЬ).
VBA имеет функцию IIf, которая работает так же. Давайте посмотрим на примере. В следующем коде мы используем IIf для проверки значения переменной val. Если значение больше 10, мы печатаем ИСТИНА, в противном случае мы печатаем ЛОЖЬ.
Sub ProveritVal()
Dim result As Boolean
Dim val As Long
' Печатает ИСТИНА
val = 11
result = IIf(val > 10, ИСТИНА, ЛОЖЬ)
Debug.Print result
' печатает ЛОЖЬ
val = 5
result = IIf(val > 10, ИСТИНА, ЛОЖЬ)
Debug.Print result
End Sub
В нашем следующем примере мы хотим распечатать «Удовлетворитеьно» или «Незачет» рядом с каждым студентом в зависимости от их баллов. В первом фрагменте кода мы будем использовать обычный оператор VBA If, чтобы сделать это.
Sub ProveritDiapazonOcenok()
Dim i As Long, marks As Long
For i = 2 To 11
' Хранить оценки для текущего студента
marks = Sheet1.Range("C" & i).Value
' Проверьте, прошел ли студент или нет
If marks >= 40 Then
' Запишите имена для столбца F
Sheet1.Range("E" & i) = "Удовлетворительно"
Else
Sheet1.Range("E" & i) = "Незачет"
End If
Next
End Sub
В следующем фрагменте кода мы будем использовать функцию IIf. Код здесь намного аккуратнее.
Sub ProveritDiapazonOcenok ()
Dim i As Long, marks As Long
For i = 2 To 11
' Хранить оценки для текущего студента
marks = Sheet1.Range("C" & i)
' Проверьте, прошел ли студент или нет
Sheet1.Range("E" & i).Value = IIf(marks >= 40,"Удовлетворительно","Незачет")
Next
End Sub
Функция IIf очень полезна для простых случаев, когда вы имеете дело с двумя возможными вариантами.
Использование Nested IIf
Вы также можете вкладывать IIf-операторы, как в Excel. Это означает использование результата одного IIf с другим. Давайте добавим еще один тип результата в наши предыдущие примеры. Теперь мы хотим напечатать «Отлично», «Удовлетворительно» или «Незачетт» для каждого студента.
Используя обычный VBA, мы сделали бы это так
Sub ProveritRezultatiTip2()
Dim i As Long, marks As Long
For i = 2 To 11
' Хранить оценки для текущего студента
marks = Sheet1.Range("C" & i).Value
If marks >= 75 Then
Sheet1.Range("E" & i).Value = "Отлично"
ElseIf marks >= 40 Then
' Запишите имена для столбца F
Sheet1.Range("E" & i).Value = "Удовлетворительно"
Else
Sheet1.Range("E" & i).Value = "Незачет"
End If
Next
End Sub
Используя вложенные IIfs, мы могли бы сделать это так
Sub IspNestedIIF()
Dim i As Long, marks As Long, result As String
For i = 2 To 11
marks = Sheet1.Range("C" & i).Value
result = IIf(marks >= 55,"Хорошо",IIf(marks >= 40,"Удовлетворительно","Незачет"))
Sheet1.Range("E" & i).Value = result
Next
End Sub
Использование вложенного IIf хорошо в простых случаях, подобных этому. Код прост для чтения и, следовательно, вряд ли вызовет ошибки.
Чего нужно остерегаться
Важно понимать, что функция IIf всегда оценивает как
Истинную, так и Ложную части выражения независимо от условия.
В следующем примере мы хотим разделить по баллам, когда он не равен нулю. Если он равен нулю, мы хотим вернуть ноль.
marks = 0 total = IIf(marks = 0, 0, 60 / marks)
Однако, когда отметки равны нулю, код выдаст ошибку «Делить на ноль». Это потому, что он оценивает как Истинные, так и Ложные утверждения. Здесь ложное утверждение, т.е. (60 / Marks), оценивается как ошибка, потому что отметки равны нулю.
Если мы используем нормальный оператор IF, он будет
запускать только соответствующую строку.
marks = 0
If marks = 0 Then
'Выполняет эту строку только когда отметки равны нулю
total = 0
Else
'Выполняет только эту строку, когда отметки не равны нулю
total = 60 / marks
End If
Это также означает, что если у вас есть функции для ИСТИНА и ЛОЖЬ, то обе будут выполнены. Таким образом, IIF будет запускать обе функции, даже если он использует только одно возвращаемое значение. Например:
' Обе функции будут выполняться каждый раз total = IIf(marks = 0, Func1, Func2)
IF против IIf
Так что лучше?
В этом случае вы можете видеть, что IIf короче для написания и аккуратнее. Однако если условия усложняются, вам лучше использовать обычное выражение If. Недостатком IIf является то, что он недостаточно известен, поэтому другие пользователи могут не понимать его так же, как и код, написанный с помощью обычного оператора if.
Кроме того, как мы обсуждали в последнем разделе, IIF всегда оценивает части ИСТИНА и ЛОЖЬ, поэтому, если вы имеете дело с большим количеством данных, оператор IF будет быстрее.
Мое эмпирическое правило заключается в том, чтобы
использовать IIf, когда
он будет прост для чтения и не требует вызовов функций. Для более сложных
случаев используйте обычный оператор If.
Использование Select Case
Оператор Select Case
— это альтернативный способ написания статистики If с большим количеством ElseIf. Этот тип операторов
вы найдете в большинстве популярных языков программирования, где он называется
оператором Switch. Например,
Java, C #, C ++ и Javascript
имеют оператор switch.
Формат
Select Case [переменная]
Case [условие 1]
Case [условие 2]
Case [условие n]
Case Else
End Select
Давайте возьмем наш пример DobClass сверху и перепишем его с помощью оператора Select Case.
Sub DobavitClass()
' получить последнюю строку
Dim startRow As Long, lastRow As Long
startRow = 2
lastRow = Sheet1.Cells(Sheet1.Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row
Dim i As Long, Marks As Long
Dim sClass As String
' Пройдите столбцы отметок
For i = startRow To lastRow
Marks = Sheet1.Range("C" & i).Value
' Проверьте отметки и классифицируйте соответственно
If Marks >= 85 Then
sClass = "Высший балл"
ElseIf Marks >= 75 Then
sClass = "Отлично"
ElseIf Marks >= 55 Then
sClass = "Хорошо"
ElseIf Marks >= 40 Then
sClass = "Удовлетворительно"
Else
' Для всех других оценок
sClass = "Незачет"
End If
' Запишите класс в столбец E
Sheet1.Range("E" & i).Value = sClass
Next
End Sub
Ниже приведен тот же код с использованием оператора Select Case. Главное, что вы заметите, это то, что мы используем “Case 85 to 100” rather than “marks >=85 And marks <=100”. , а не “marks >=85 And marks <=100”.
Sub DobavitClassSSelect()
' получить первую и последнюю строки
Dim firstRow As Long, lastRow As Long
firstRow = 2
lastRow = Cells(Cells.Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row
Dim i As Long, marks As Long
Dim sClass As String
' Пройдите столбцы отметок
For i = firstRow To lastRow
marks = Sheet1.Range("C" & i).Value
' Проверьте отметки и классифицируйте соответственно
Select Case marks
Case 85 To 100
sClass = "Высший балл"
Case 75 To 84
sClass = "Отлично"
Case 55 To 74
sClass = "Хорошо"
Case 40 To 54
sClass = "Удовлетворительно"
Case Else
' Для всех других оценок
sClass = "Незачет"
End Select
' Запишите класс в столбец E
Sheet1.Range("E" & i).Value = sClass
Next
End Sub
Использование Case Is
Вы можете переписать оператор select в том же формате, что и оригинальный ElseIf. Вы можете использовать Is с Case.
Select Case marks
Case Is >= 85
sClass = "Высший балл"
Case Is >= 75
sClass = "Отлично"
Case Is >= 55
sClass = "Хорошо"
Case Is >= 40
sClass = "Удовлетворительно"
Case Else
' Для всех других оценок
sClass = "Незачет"
End Select
Вы можете использовать Is для проверки нескольких значений.
В следующем коде мы проверяем, равны ли оценки 5, 7 или 9.
Sub TestNeskZnach()
Dim marks As Long
marks = 7
Select Case marks
Case Is = 5, 7, 9
Debug.Print True
Case Else
Debug.Print False
End Select
End Sub
Попробуйте это упражнение
В этой статье много рассказывали о выражении If. Хороший способ помочь вам понять — это попытаться написать код, используя темы, которые мы рассмотрели. В следующем упражнении используются тестовые данные из этой статьи. Ответ на упражнение ниже.
Мы будем использовать ячейку G1, чтобы написать имя
субъекта.
В колонках от H до L запишите всех студентов, которые имеют оценки по этому предмету. Мы хотим классифицировать их результат как успешный или неудачный. Оценка ниже 40 — неудача, оценка 40 или выше — Зачет.
Колонка H: Имя
Колонка I: Фамилия
Колонка J: Баллы
Колонка H: Предмет
Столбец I: Тип результата — Зачет или Незачет
Если ячейка G1 содержит «Геометрия», то ваш результат должен выглядеть следующим образом:
Ответ на упражнение
Следующий код показывает, как выполнить вышеупомянутое упражнение.
Примечание: есть много способов выполнить задачу, поэтому не расстраивайтесь, если ваш код отличается.
Sub ZapisatRezultat()
' Получить тему
Dim subject As String
subject = Sheet1.Range("G1").Value
If subject = "" Then
Exit Sub
End If
' Получить первый и последний ряд
Dim firstRow As Long, lastRow As Long
firstRow = 2
lastRow = Cells(Cells.Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row
' Очистить любой существующий вывод
Sheet1.Range("H:L").ClearContents
' Отслеживать выходной ряд
Dim outRow As Long
outRow = 1
Dim i As Long, marks As Long, rowSubject As String
' Прочитать данные
For i = firstRow To lastRow
marks = Sheet1.Range("C" & i).Value
rowSubject = Sheet1.Range("D" & i).Value
If rowSubject = subject Then
' Запишите данные студента, если предмет Геометрия
Sheet1.Range("A" & i & ":" & "D" & i).Copy
Sheet1.Range("H" & outRow).PasteSpecial xlPasteValues
' Запишите Зачет или Незачет
If marks < 40 Then
Sheet1.Range("L" & outRow).Value = "Незачет"
ElseIf marks >= 40 Then
Sheet1.Range("L" & outRow).Value = "Зачет"
End If
' Переместить вывод в следующую строку
outRow = outRow + 1
End If
Next i
End Sub
Операторы, использующиеся в VBA Excel для отрицания и сравнения логических выражений. Синтаксис, принимаемые значения, приоритет логических операторов.
Оператор «Not»
«Not» – это оператор логического отрицания (инверсия), который возвращает True, если условие является ложным, и, наоборот, возвращает False, если условие является истинным.
Синтаксис:
Таблица значений:
| Условие | Результат |
|---|---|
| True | False |
| False | True |
Оператор «And»
«And» – это оператор логического умножения (логическое И, конъюнкция), который возвращает значение True, если оба условия являются истинными.
Синтаксис:
|
Результат = Условие1 And Условие2 |
Таблица значений:
| Условие1 | Условие2 | Результат |
|---|---|---|
| True | True | True |
| True | False | False |
| False | True | False |
| False | False | False |
Оператор «Or»
«Or» – это оператор логического сложения (логическое ИЛИ, дизъюнкция), который возвращает значение True, если одно из двух условий является истинным, или оба условия являются истинными.
Синтаксис:
|
Результат = Условие1 Or Условие2 |
Таблица значений:
| Условие1 | Условие2 | Результат |
|---|---|---|
| True | True | True |
| True | False | True |
| False | True | True |
| False | False | False |
Оператор «Xor»
«Xor» – это оператор логического исключения (исключающая дизъюнкция), который возвращает значение True, если только одно из двух условий является истинным.
Синтаксис:
|
Результат = Условие1 Xor Условие2 |
Таблица значений:
| Условие1 | Условие2 | Результат |
|---|---|---|
| True | True | False |
| True | False | True |
| False | True | True |
| False | False | False |
Оператор «Eqv»
«Eqv» – это оператор логической эквивалентности (тождество, равенство), который возвращает True, если оба условия имеют одинаковое значение.
Синтаксис:
|
Результат = Условие1 Eqv Условие2 |
Таблица значений:
| Условие1 | Условие2 | Результат |
|---|---|---|
| True | True | True |
| True | False | False |
| False | True | False |
| False | False | True |
Оператор «Imp»
«Imp» – это оператор логической импликации, который возвращает значение False, если первое (левое) условие является истинным, а второе (правое) условие является ложным, в остальных случаях возвращает True.
Синтаксис:
|
Результат = Условие1 Imp Условие2 |
Таблица значений:
| Условие1 | Условие2 | Результат |
|---|---|---|
| True | True | True |
| True | False | False |
| False | True | True |
| False | False | True |
Приоритет логических операторов
Приоритет определяет очередность выполнения операторов в одном выражении. Очередность выполнения логических операторов в VBA Excel следующая:
- «Not» – логическое отрицание;
- «And» – логическое И;
- «Or» – логическое ИЛИ;
- «Xor» – логическое исключение;
- «Eqv» – логическая эквивалентность;
- «Imp» – логическая импликация.
Содержание
- VBA Logical Operators – OR, AND, XOR, NOT, IS, & LIKE
- Using the And Logical Operator
- Using the Or Logical Operator
- Using the Not Logical Operator
- Using the Xor Logical Operator
- Is Operator
- Like Operator
- VBA Coding Made Easy
- VBA Code Examples Add-in
- VBA Logical Operators: AND, OR, NOT, IF NOT in Excel VBA
- Excel VBA Logical Operators
- VBA Logical Operators Example Source Code
- VBA If – And, Or, Not
- IF…AND
- IF NOT…
- VBA Code Examples Add-in
- VBA IF OR (Test Multiple Conditions)
- Use OR with IF
- Multiple Conditions with IF OR
- VBA OR Function
- What is OR Function in VBA?
- The formula of VBA OR Function
- Examples of Using OR Function in VBA
- VBA OR Function With IF Condition is Powerful
- Case Study to Solve
- Recommended Articles
VBA Logical Operators – OR, AND, XOR, NOT, IS, & LIKE
In this Article
VBA allows you to use the logical operators And, Or, Not, Xor to compare values. The operators are considered “Boolean”, which means they return True or False as a result.
If you want to learn how to compare strings, click here: VBA Compare Strings – StrComp
If you want to learn how to use comparison operators, click here: VBA Comparison Operators – Not Equal to & More
Using the And Logical Operator
The And logical operator compares two or more conditions. If all the conditions are true, the operator will return True. If at least one of the conditions is not true, the operator will return False. Here is an example:
In this example, we want to check if both intA and intB are equal to 5. If this is true, the value of Boolean blnResult will be True, otherwise, it will be False.
First, we set values of intA and intB to 5:
After that, we use the And operator in the If statement to check if the values are equal to 5:
As both variables are equal to 5, the blnResult returns True:
Image 1. Using the And logical operator in VBA
Using the Or Logical Operator
The Or logical operator compares two or more conditions. If at least one of the conditions is true, it will return True. If none of the conditions are true, the operator will return False. Here is the code for the example:
In this example, we want to check if both intA is equal to 5. or intB is equal to 10. If any of these conditions is true, the value of Boolean blnResult will be True, otherwise, it will be False.
First, we set the value of intA to 5 and intB to 10:
After that, we use the Or operator in the If statement to check if any of the values is equal to 5:
As intA value is 5, the blnResult returns True:
Image 2. Using the Or logical operator in VBA
Using the Not Logical Operator
The Not logical operator checks one or more conditions. If the conditions are true, the operator returns False. Otherwise, it returns True. Here is the code for the example:
In this example, we want to check if the value of intA is not equal to 6. If intA is different than 6, the value of Boolean blnResult will be True, otherwise, it will be False.
First, we set the value of intA to 5:
After that, we use the Not operator in the If statement to check if the value of intA is different than 6:
As intA value is 5, the blnResult returns True:
Image 3. Using the Not logical operator in VBA
Using the Xor Logical Operator
The Xor logical operator compares two or more conditions. If exactly one of the conditions is true, it will return True. If none of the conditions are true, or more than one are true, it will return False. Here is the code for the example:
In this example, we want to check if exactly one of the values (intA or IntB) are equal to 5. If only one condition is true, the value of Boolean blnResult will be True, otherwise, it will be False.
First, we set the value of intA to 5 and intB to 10:
After that, we use the Or operator in the If statement to check if any of the values is equal to 5:
As intA value is 5 and intB is 10, the blnResult returns True:
Image 4. Using the Xor logical operator in VBA
Is Operator
The Is Operator tests if two object variables store the same object.
Let’s look at an example. Here we will assign two worksheets to worksheet objects rng1 and rng2, testing if the two worksheet objects store the same worksheet:
Of course the worksheet objects are not the same, so “Different WSs” is returned.
Like Operator
The Like Operator can compare two strings for inexact matches. This example will test if a string starts with “Mr.”
VBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro — A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users! 
VBA Code Examples Add-in
Easily access all of the code examples found on our site.
Simply navigate to the menu, click, and the code will be inserted directly into your module. .xlam add-in.
Источник
VBA Logical Operators: AND, OR, NOT, IF NOT in Excel VBA
Updated January 20, 2023
Excel VBA Logical Operators
Let’s say you want to process a customer order. For that, you want to first check to see if the ordered product exists or not. If it does, you also want to check if the quantity on hand is enough. Logical operators come in handy in such cases. Logical operators are used to evaluate more than one condition.
The main Excel VBA logical operators AND, OR, NOT are listed in the table below:
| S/N | Operator | Description | Example | Output |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | AND | AND: This is used to combine more than one condition. If all the conditions are true, AND evaluates to true. If any of the condition is false, AND evaluates to false | If true = true AND false = true THEN | false |
| 2 | OR | OR: This is used to combine more than one condition. If any of the conditions evaluate to true, OR returns true. If all of them are false, OR returns false | If true = true OR true = false THEN | true |
| 3 | NOT | NOT: This one works like an inverse function. If the condition is true, it returns false, and if a condition is false, it returns true. | If NOT (true) Then | false |
VBA Logical Operators Example Source Code
For the sake of simplicity, we will be comparing hard coded numbers.
Add ActiveX buttons to the sheet from the “Insert option.”
Set the properties as shown in the image below

The following table shows the properties that you need to change and the values that you need to update too.
Источник
VBA If – And, Or, Not
In this Article
This article will demonstrate how to use the VBA If statement with And, Or and Not.
When we us an IF statement in Excel VBA, the statement will execute a line of code if the condition you are testing is true.
- We can use AND statement and OR statements in conjunction with IF statements to test for more than one condition and direct the code accordingly.
- We can also use a NOT statement with an IF statement to check if the condition is NOT true – it basically is the inverse of the IF statement when used alone.
IF…AND
We can use the IF…AND combination of logical operators when we wish to test for more than one condition where all the conditions need to be true for the next line of code to execute.
For example, consider the following sheet:
To check if the Profit is over $5,000, we can run the following macro:
This macro will check that the cell C5 is greater or equal to $10,000 AND check that the cell B6 is less than $5,000. If these conditions are BOTH true, it will show the message box.
If we amend the macro to check if C5 is just greater than $10,000, then the profit would not be achieved!
We can use the IF…OR combination of logical operators when we wish to test for more than one condition where only one of the conditions needs to be true for the next line of code to execute.
The format for this is almost identical to the IF…AND example above.
However, with this macro, because we are using an IF …OR statement, only one of the conditions needs to be true.
IF NOT…
IF..NOT changes the IF statement around – it will check to see if the condition is NOT true rather than checking to see if the condition is true.
In this example above, the IF statement is checking to see if the value in C5 is NOT smaller than 10000.
Therefore this line of code:
and this this line of code:
are testing for the same thing!
VBA Code Examples Add-in
Easily access all of the code examples found on our site.
Simply navigate to the menu, click, and the code will be inserted directly into your module. .xlam add-in.
Источник
VBA IF OR (Test Multiple Conditions)
You can use the OR operator with the VBA IF statement to test multiple conditions. When you use it, it allows you to test two or more conditions simultaneously and returns true if any of those conditions are true. But if all the conditions are false only then it returns false in the result.
Use OR with IF
- First, start the IF statement with the “IF” keyword.
- After that, specify the first condition that you want to test.
- Next, use the OR keyword to specify the second condition.
- In the end, specify the second condition that you want to test.
To have a better understanding let’s see an example.
If you look at the above example, we have specified two conditions one if (1 = 1) and the second is (2
Now let’s see if both conditions are false, let me use a different code here.
In the above code, both conditions are false, and when you run this code, it executes the line of code that we have specified if the result is false.
Multiple Conditions with IF OR
In the same way, you can also test more than two conditions at the same time. Let’s continue the above example and add the third condition to it.
Now we have three conditions to test, and we have used the OR after the second condition to specify the third condition. As you learned above that when you use OR, any of the conditions need to be true to get true in the result. When you run this code, it executes the line of code that we have specified for the true.
And if all the conditions are false, just like you have in the following code, it returns false.
Источник
VBA OR Function
The OR function is a logical function in any of the programming languages. Similar to VBA, we have an OR function, as it is a logical function. The result given by this function is either “True” or “False.” This function is used for two or many conditions together. It gives us a “True” result when either of the conditions returns “True.”
What is OR Function in VBA?
We hope you have used them quite often as a worksheet function. In VBA, too, we can use all of them, and in this article, we will explain the ways of using the “VBA OR” function.
What is the first thing that comes to mind when you think of the word “OR”?
In simple terms, “OR” means “either this or that.”
With the same idea, OR is a logical function that gives the result as TRUE if any of the logical tests is TRUE and gives FALSE if none of the logical tests are TRUE.
It works exactly the opposite of the VBA AND function. The AND function returns TRUE only if all the logical conditions are TRUE. If any of the conditions are not satisfied, we will get FALSE.
Table of contents
You are free to use this image on your website, templates, etc., Please provide us with an attribution link How to Provide Attribution? Article Link to be Hyperlinked
For eg:
Source: VBA OR Function (wallstreetmojo.com)
The formula of VBA OR Function
Let me frame a syntax for you to understand the function.
First, we need to mention the logical test, then mention the word “OR,” and then mention the second logical test. If you wish to conduct a more logical test, mention the word OR after a logical test.
Of all the logical tests you do, if any of the tests are satisfied or true, then we will get the result as TRUE if none or satisfied, then the result is FALSE.
Examples of Using OR Function in VBA
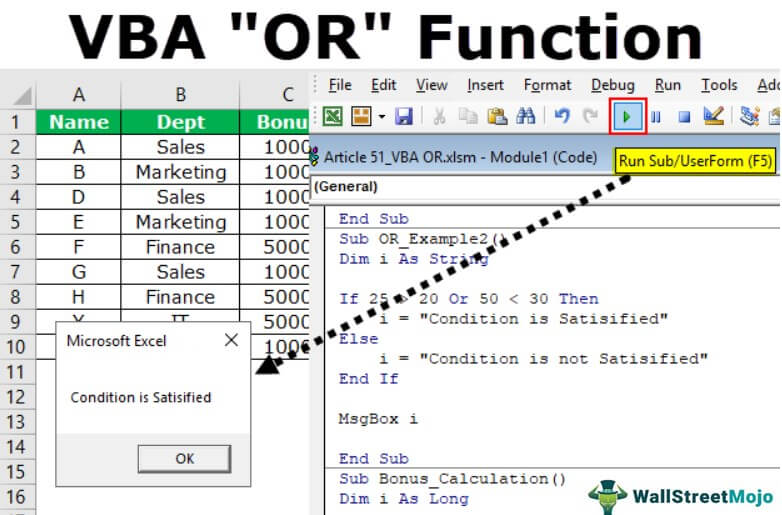
We will show you a simple example of using the OR function in VBA.
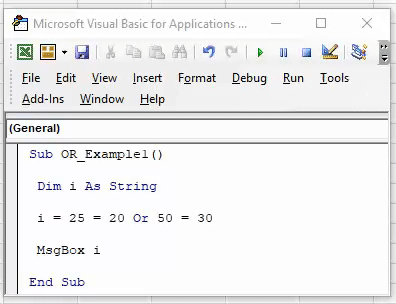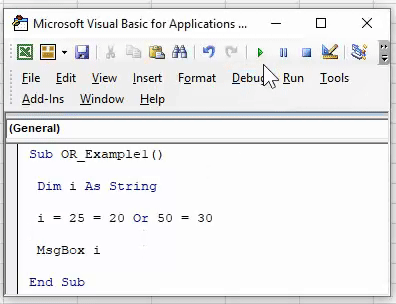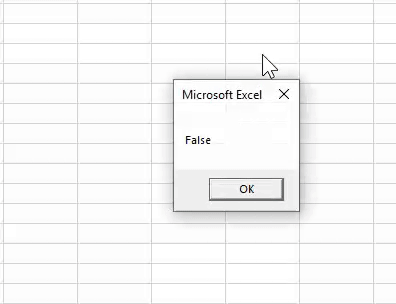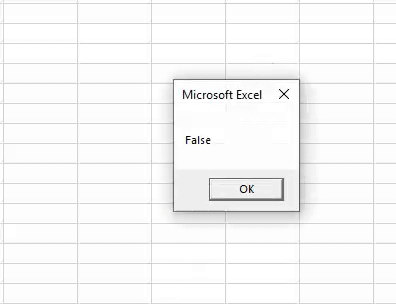
To understand the logical VBA function OR let us give you an example. Let us say we want to conduct the logical test of whether the number 25 is greater than 20 or the number 50 is less than 30.
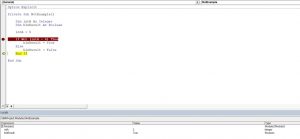
Step 1: Create a macro name.
Step 2: Define the variable as a string.
Code:
Step 3: Now, we will assign the value through the OR logical test for this variable.
Code:
Step 4: Our first logical test is 25 >20.
Code:
Step 5: Now, after the first logical test, mention the word OR and enter the second logical test.
Code:
Step 6: Now, VBA OR function tests whether the logical tests are TRUE or FALSE. Now assign the result of the variable to the VBA message box.
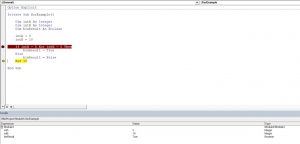
Code:
Step 7: Run the Macro and what the result is.
25 is greater than 20, and 50 is not less than 30. In this case, the first logical test is TRUE, but the second is FALSE. Because we have applied the VBA OR function, it needs any one of the conditions to be TRUE to get the result as TRUE.
Now, look at the code below.
Code:
We have changed the logical test equations from > and
VBA OR Function With IF Condition is Powerful
As we said, the OR function can return either TRUE or FALSE as a result, but with the other logical function, “IF,” we can manipulate results as per our needs.
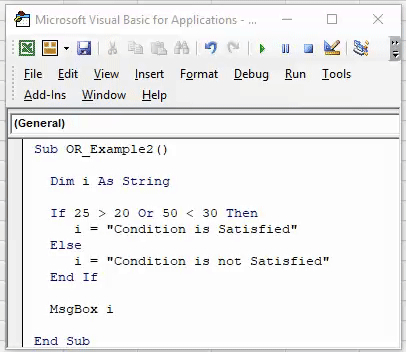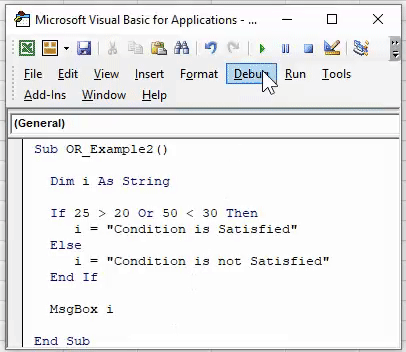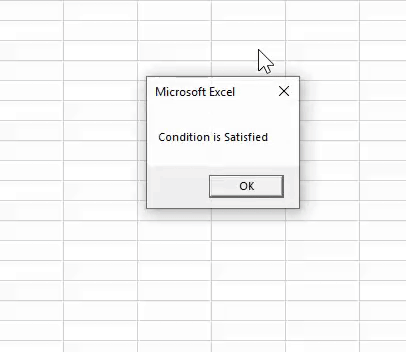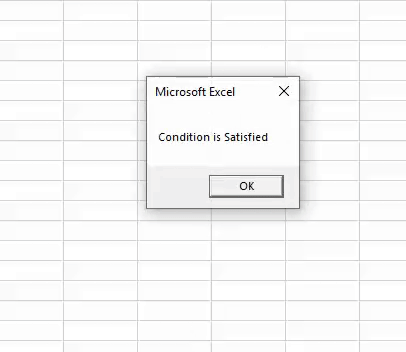
Take the same logical tests from above. Again, the OR function has returned only TRUE or FALSE, but let us combine this OR with IF.
Step 1: Before conducting any test, open the function IF.
Code:
Step 2: Now, conduct tests using the OR function.
Code:
Step 3: Put the word “Then” and write the result. If the condition is TRUE, assign the value to the variable as “Condition is Satisfied.”
Code:
Step 4: If the condition is FALSE, then we need a different result, so put the word “ELSE” and, in the next line, assign the value to the variable “what should be the result if the condition or logical test is FALSE.”
Code:
Step 5: End the IF function with “End If.”
Code:
Step 6: Assign the value of the variable result to the message box.
Code:
Run the Macro. If the logical test is TRUE, we will get the result as “Condition is Satisfied,” or else we will get “Condition is not Satisfied.”
We got the result “Condition is not Satisfied” because both the logical tests are FALSE.
Now, we will change the logical tests.
Code:
We will run the macro and see what the result is.
Like this, we can use one logical function with other logical functions to arrive at the results.
Solve the below case study to get used to logical functions.
Case Study to Solve
We have employee names and their respective departments.
If you have tried and not found the result, then you can refer below code to understand the logic.
Code:
If the employee is from “Finance” or “IT,” then they should get the bonus of “5000.” For other department employees, the bonus is “1000.”
Conduct the logical test and arrive at the results.
Recommended Articles
This article has been a guide to VBA OR Function. Here, we learn how to use OR Logical Operator in VBA along with some practical examples and a downloadable Excel template. Below are some useful Excel articles related to VBA: –
Источник