Арифметические (математические) операторы, использующиеся в VBA Excel. Их предназначение, особенности вычислений, приоритет в выражениях.
Обзор арифметических операторов
| Операторы | Описание |
|---|---|
| Оператор «+» | Сложение двух чисел или объединение двух строк (для объединения строк предпочтительнее использовать оператор «&») |
| Оператор «-» | Вычитание (определение разности двух чисел) или отрицание (отражение отрицательного значения числового выражения: -15, -a) |
| Оператор «*» | Умножение двух чисел |
| Оператор «/» | Деление двух чисел (деление на 0 приводит к ошибке) |
| Оператор «^» | Возведение числа в степень |
| Оператор «» | Целочисленное деление |
| Оператор «Mod» | Возвращает остаток от деления двух чисел |
Особенности операторов «» и «Mod»
Перед вычислением целочисленного результата или остатка от деления двух чисел делимое и делитель округляются. Причем, используется бухгалтерское округление:
- -3.5 => -4
- -2.5 => -2
- -1.5 => -2
- -0.5 => 0
- 0.5 => 0
- 1.5 => 2
- 2.5 => 2
- 3.5 => 4
Следующие строки вызовут ошибку «Division by zero» («Деление на ноль»):
|
a = 3 Mod 0.5 a = 3 (2 — 2.5) |
Чтобы избежать ошибок, когда требуется общепринятое математическое округление, округляйте делитель и делимое с помощью оператора WorksheetFunction.Round.
Приоритет арифметических операторов
Приоритет определяет очередность выполнения математических операторов в одном выражении. Очередность выполнения арифметических операторов в VBA Excel следующая:
- «^» – возведение в степень;
- «—» – отрицание;
- «*» и «/» – умножение и деление;1
- «» – целочисленное деление;
- «Mod» – остаток от деления двух чисел;
- «+» и «—» – сложение и вычитание.2
1 Если умножение и деление выполняются в одном выражении, то каждая такая операция выполняется слева направо в порядке их следования.
2 Если сложение и вычитание выполняются в одном выражении, то каждая такая операция выполняется слева направо в порядке их следования.
Для переопределения приоритета выполнения математических операторов в VBA Excel используются круглые скобки. Сначала выполняются арифметические операторы внутри скобок, затем — операторы вне скобок. Внутри скобок приоритет операторов сохраняется.
|
a = 3 ^ 2 + 1 ‘a = 10 a = 3 ^ (2 + 1) ‘a = 27 a = 3 ^ (2 + 1 * —2) ‘a = 1 |
VBA MOD
VBA Mod is not a function, in fact, it is an operation which is used for calculating the remainder digit by dividing a number with divisor. In simple words, it gives us the remainder value, which is the remained left part of Number which could not get divided completely.
How to Use VBA MOD Function?
We will discuss how to use VBA MOD Function by using some examples.
You can download this VBA MOD Function Excel Template here – VBA MOD Function Excel Template
Example #1
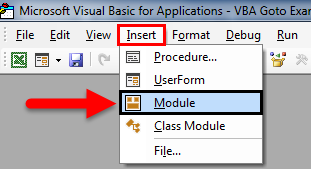
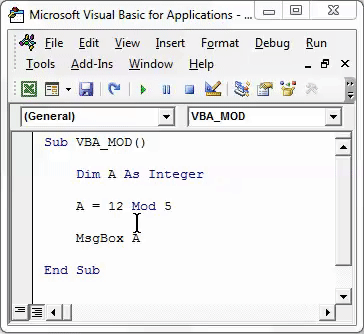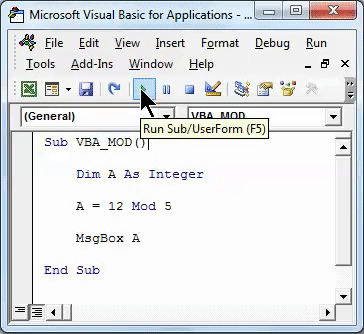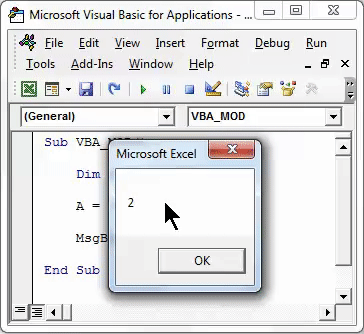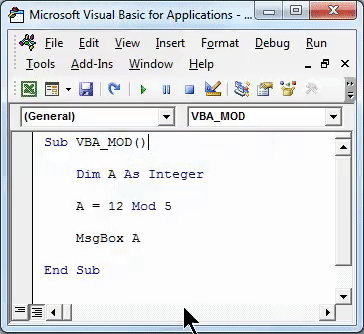
Press Alt + F11 to go in VBA coding mode. After that go to insert menu and select Module to open a new module.
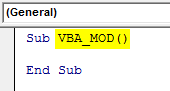
Now open the body of syntax as shown below. We have names the macro subcategory as VBA_MOD. By this, it will become easy for users to identify the code to run.
Code:
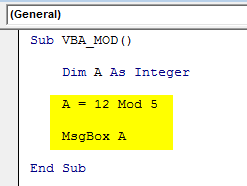
Sub VBA_MOD() End Sub
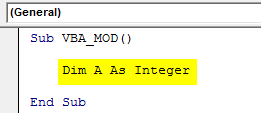
Now as we are calculating the Mod which includes numbers for that, define an Integer “A”. This can be any alphabet as shown in below screenshot.
Code:
Sub VBA_MOD() Dim A As Integer End Sub
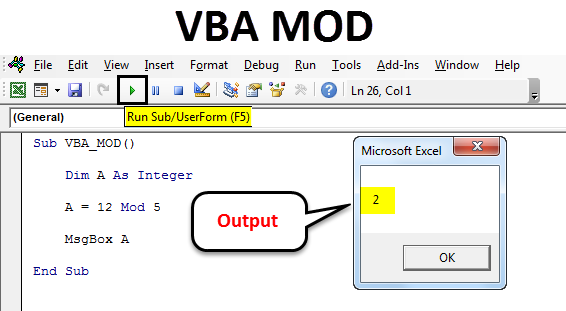
Now we will implement and test the same example which we have seen above. For this, in defined integer, we will write 12 Mod 5. This is a way to write the Mod operation in VBA and with the answer in the message box with msg function as shown below.
Code:
Sub VBA_MOD() Dim A As Integer A = 12 Mod 5 MsgBox A End Sub
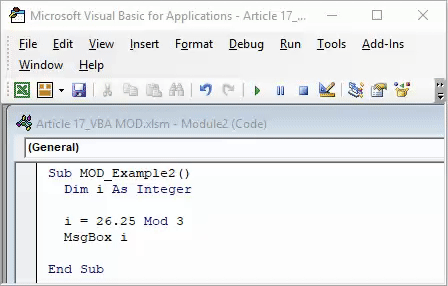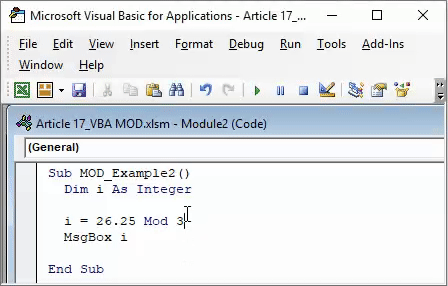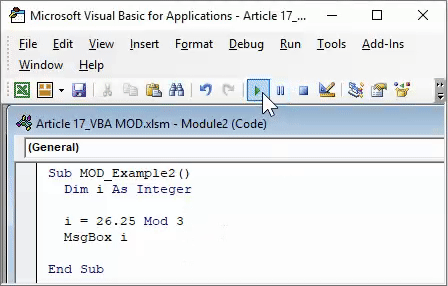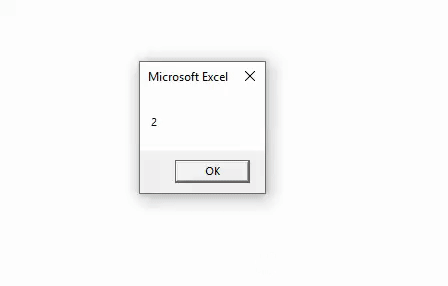
Once done, run the complete code by using F5 key or clicking on the play button as shown below. We will see the output of 12 Mod 5 as 2 which is the remainder obtained after dividing 12 by 5.
Example #2
There is another way to calculate the MOD in VBA. For this, we will see a decimal number and find how MOD.
Press Alt + F11 to go in VBA coding mode. After that go to insert menu and select Module to open a new module.
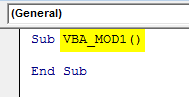
In opened new Module frame the syntax. Here we have named the macro subcategory as VBA_MOD1. By this, we will be able to differentiate the name of Marco sequence. Which we will see ahead.
Code:
Sub VBA_MOD1() End Sub
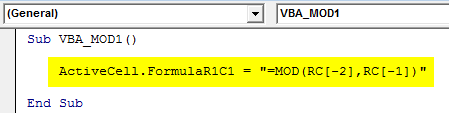
Now select an active cell where we need to see the result by ActiveCell.FormulaR1C1 as cell C1. Now Mod reference cell -2 and -1 are considered as cell A1 and cell B1 respectively as shown below.
Code:
Sub VBA_MOD1() ActiveCell.FormulaR1C1 = "=MOD(RC[-2],RC[-1])" End Sub
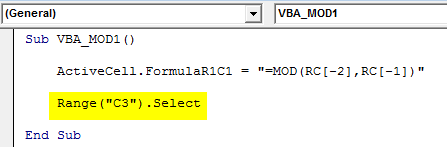
Now select the reference cell as Range where we will the output with Range(“C3”).Select. This will allow cell C3 to take the range of respective cells from -2 and -1 limit.
Code:
Sub VBA_MOD1() ActiveCell.FormulaR1C1 = "=MOD(RC[-2],RC[-1])" Range("C3").Select End Sub
Now, Run the code using F5 key or click on the play button which is located below the menu bar of VBA Application window as shown below.
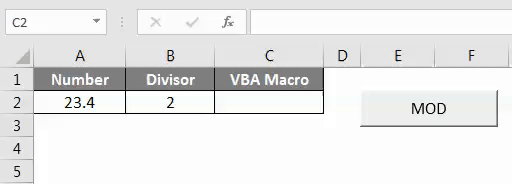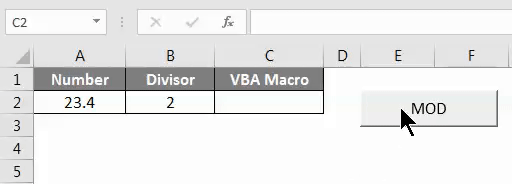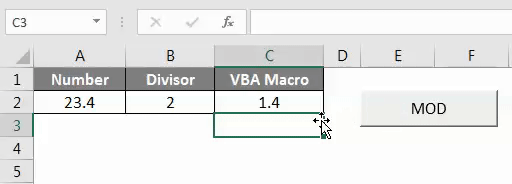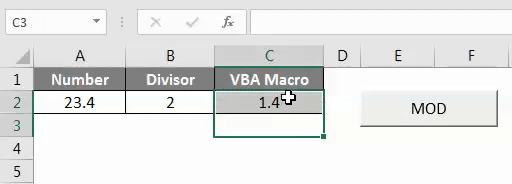
As we can see in the above screenshot, the output of VBA Coding is coming as 1.4.
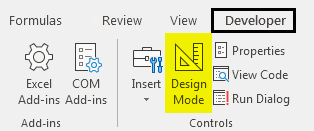
We can assign the written code to a button where can directly click and run the code instead of running the code in by select the macro. For this go to the Developer tab and click on Design Mode as shown below.
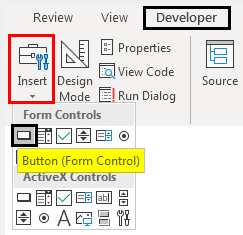
This will allow us to design different tabs without affecting the written code. Now go to Insert option under Developer tab which is just beside the Design Mode option. Then select a Button as shown below.
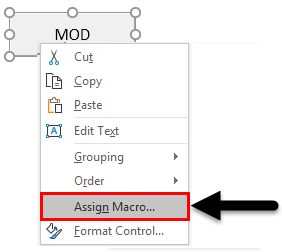
Now draw the selected button and name it as MOD with the name of operation which we will be going to perform.
Right click on created MOD Button and select Assign Marco from the right click list.
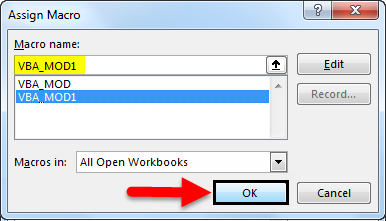
Now from the Assign Marco window, select the created macro. Once done, click on Ok as shown below.
Now to test the assigned macro in the created button, exit from Design Mode. Then put the cursor where we need to see the output as shown below.
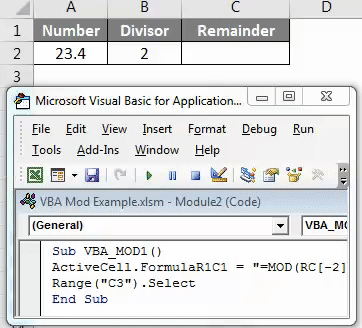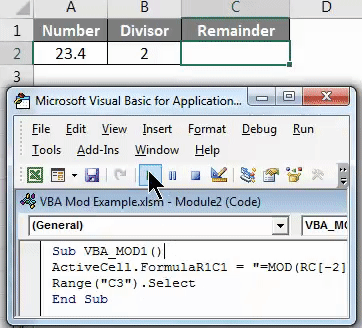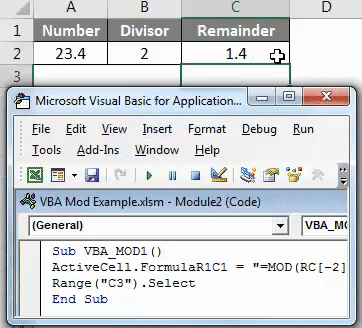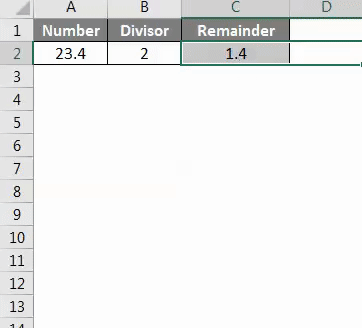
Now click on MOD Button to see the result as shown below.
As we can see in the above screenshot, we have got the output as 1.4 which is Mod of number 23.4 with by divisor 2.
Pros of VBA MOD
- We can calculate Mod of multiple criteria with the help of VBA Mod in quick time.
- An obtained result from the Excel function and VBA Code will be the same.
Things to Remember
- Don’t forget the save the file in Macro Enable Worksheet. This will allow us to use that file multiple time without losing the written code.
- Always compile the code before running. This will detect the error instead of getting error while actual run.
- It is recommended to assign the written code to a Button. This process saves time.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Excel VBA MOD. Here we discussed how to use VBA MOD Function to remove spaces along with some practical examples and downloadable excel template. You can also go through our other suggested articles-
- VBA TRIM
- VBA Arrays
- VBA Select Case
- VBA Find
Home / VBA / How to use MOD in VBA
In VBA, MOD is an operator, not a function and this operator helps you to divide two numbers and returns the remainder value in the result.
It’s equivalent to the mod function in Excel.
You can use the mod in so many ways and, in this tutorial, we will see some examples. Use the below steps to use the mod operator in VBA:
Range("A1") = 10 Mod 3- Specify the first number which you want to get divided.
- After that, enter the “mod” operator.
- Now, enter a number that you want to divide by.
- In the end, use a message box or a cell to get the remainder from the division.

In the same way, you can also get the remainder using a message box.
And in the following code, we have used a message box and then used the mod operator to get the remainder after dividing.
MsgBox 9 Mod 3And when you run this code, it returns zero in the result in the message box as when you divide 9 by 3 there’s no remainder left, so as in the result of this code.

Note: As I said, there’s also a function in Excel to get the remainder from the division of two numbers and there are a few situations where you will find that the result you get from Excel will be different from the result you got in VBA.
Error in MOD
If you try to divide a number with zero it always returns a division by zero error.
Debug.Print 10 Mod 0And the above code returns that error.
Excel VBA MOD Operator
In VBA, MOD is the same as the application in mathematics. For example, when we divide a number by its divisor, we get a reminder from that division. This function one may use to give us that remainder from the division. It is not a function in VBA. Rather, it is an operator.
MOD is nothing but MODULO, a mathematical operation. It is the same as the division, but the result is slightly different where division takes the divided amount. But, MOD takes the remainder of the division. For example: If you divide 21 by 2 divisions, the result is 10.50 by MOD is the remainder of the division, i.e., 1. (Number 2 can divide only 20, not 21, so the remainder is 1).
In normal Excel, it is a function. But in VBA, it is not a function. Instead, it is just a mathematical operator. In this article, we will look into this operator in detail.
Table of contents
- Excel VBA MOD Operator
- Syntax
- How to use MOD in VBA?
- Example #1
- Example #2
- Excel MOD Function vs. VBA MOD Operator
- Things to Remember
- Recommended Articles
Syntax
To remind you, this is not a function to have syntax. But, for our reader’s understanding, let me put it in the word.
Number 1 MOD Number 2 (Divisor)
Number 1 is nothing, but what is the number we are trying to divide?
Number 2 is the divisor, i.e., we will divide Number 1 by this divisor.
MOD is the result given by Number 1 / Number 2.
How to use MOD in VBA?
You can download this VBA MOD Function Template here – VBA MOD Function Template
Example #1
Follow the below steps to write the code.
Step 1: Create a macro name.
Code:
Sub MOD_Example1() End Sub
Step 2: Define one of the variables as “Integer.”
Code:
Sub MOD_Example1() Dim i As Integer End Sub
Step 3: Now perform the calculation as “i = 20 MOD 2.”
As we said in the beginning, MOD is an operator, not a function. So, we have used the word MOD like how we enter a plus (+).
Code:
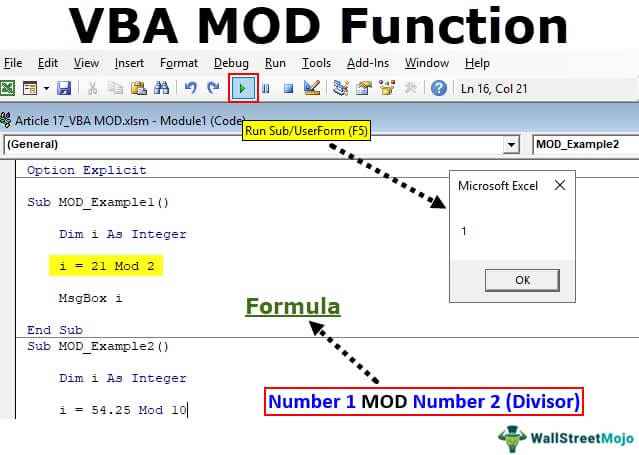
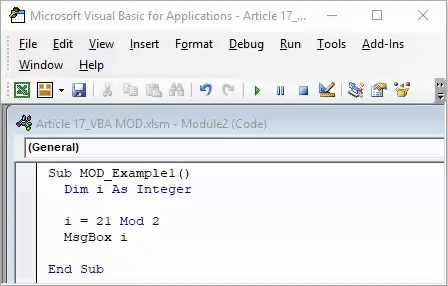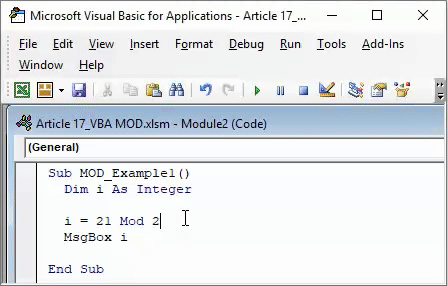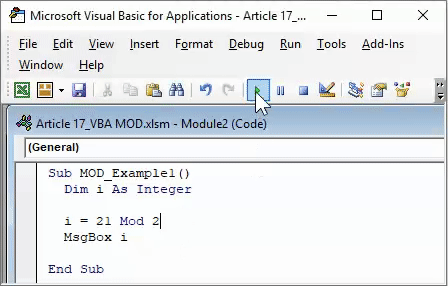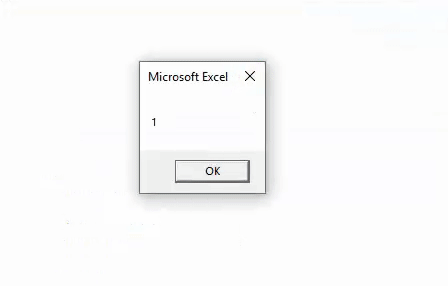
Sub MOD_Example1() Dim i As Integer i = 21 Mod 2 End Sub
Step 4: Now, assign the value of “I” to the message box.
Code:
Sub MOD_Example1() Dim i As Integer i = 21 Mod 2 MsgBox i End Sub
Step 5: Run the code message box that will show the value of “I.”
Example #2
The MOD function in VBA always returns an integer value, i.e., without decimals if you supply the number in decimals. For example, look at the below code.
Code:
Sub MOD_Example2() Dim i As Integer i = 26.25 Mod 3 MsgBox i End Sub
Divisor 3 can divide 24, so the remainder here is 2.25. But the MOD operator returns the integer value, i.e., 2, not 2.25.
Now, we will modify the number to 26.51 and see the difference.
Code:
Sub MOD_Example2() Dim i As Integer i = 26.51 Mod 3 MsgBox i End Sub
We will run this code and see what the result is.
We have got zero as the answer. We got zero because VBA roundsRound function in VBA is a mathematical function that rounds up or down the given number to the specific set of decimal places specified by the user to ease calculation.read more the numbers like our bankers do, i.e., it will round up any decimal point greater than 0.5 to the next integer value. So, in this case, 26.51 is rounded up to 27.
Since 3 can divide the 27 by 9, we will not get any remainder values, so the value of i equals zero.
Now, we will supply the divisor value also in decimal points.
Code:
Sub MOD_Example2() Dim i As Integer i = 26.51 Mod 3.51 MsgBox i End Sub
Step 6: Run this code and see what the result is.
We got 3 as the answer because 26.51 rounded up to 27, and the divisor value 3.51 will be rounded up to 4.
So, if you divide 27 by 4, the remainder is 3.
Excel MOD Function vs. VBA MOD Operator
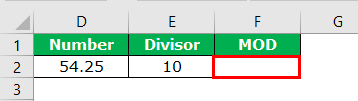
Step 1: Now, look at the difference between excel and VBA MOD operator. We have a value of 54.24. The divisor value is 10.
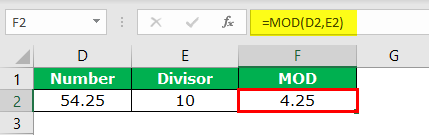
Step 2: If we apply the MOD function, we will get the result of 4.25.
Step 3: But if you do the same operation with VBA, we will get 4 as the remainder, not 4.25.
Code:
Sub MOD_Example2() Dim i As Integer i = 54.25 Mod 10 MsgBox i End Sub
Step 4: Run this code and see what the result is.
Things to Remember
- It is not a function, but it is an arithmetic operator.
- It is roundup and rounddown decimal values, unlike our MOD function in the worksheet function.
Recommended Articles
This article has been a guide to VBA MOD Function. Here, we learned how to use the modulo, practical examples, and a downloadable Excel template. Below you can find some useful Excel VBA articles: –
- VBA Return Statement
- VBA RoundUp
- VBA Cell References
- What is VBA Range?
- VBA Randomize
Арифметические сдвиги не являются циклическими. Это означает, что биты, сдвинутые с одного конца результата, не возвращаются на другом конце. Битовые позиции, освобожденные при смещении, задаются следующим образом:
0 для арифметического сдвига влево
0 для арифметического сдвига вправо положительного числа
0 для арифметического сдвига вправо типа данных без знака ( Byte , , UShort UInteger , ULong )
1 для арифметического сдвига вправо отрицательного числа ( SByte , Short , Integer или Long )
В следующем примере значение смещается влево Integer и вправо.
Арифметические сдвиги никогда не создают исключения переполнения.
Битовые операции
Помимо логических операторов, Not , Or , And и Xor выполняют побитовую арифметику при использовании числовых значений. Дополнительные сведения см. в разделе «Побитовые операции» статьи Логические и побитовые операторы в Visual Basic.
Безопасность типов
Операнды обычно должны иметь один и тот же тип. Например, если вы выполняете сложение с переменной Integer , следует добавить ее в другую Integer переменную и присвоить результат переменной типа Integer .
Одним из способов обеспечения правильного типобезопасного кодирования является использование оператора Option Strict. Если задано Option Strict On значение , Visual Basic автоматически выполняет типобезопасные преобразования. Например, при попытке добавить переменную Integer в переменную Double и присвоить ей Double значение, операция будет выполняться обычным образом, так как Integer значение можно преобразовать Double в без потери данных. С другой стороны, небезопасные преобразования типа вызывают ошибку компилятора с Option Strict On . Например, если попытаться добавить переменную в переменную Double и присвоить значение переменной Integer , компилятор выдает ошибку, так как переменная Double не может быть неявно преобразована в тип Integer . Integer
Однако если задано Option Strict Off значение , Visual Basic позволяет выполнять неявные сужающие преобразования, хотя они могут привести к непредвиденной потере данных или точности. По этой причине рекомендуется использовать Option Strict On при написании рабочего кода. Для получения дополнительной информации см. Widening and Narrowing Conversions.
Источник
Оператор Mod (Visual Basic)
Делит два числа и возвращает только остаток.
Синтаксис
Компоненты
result
Обязательный. Любая числовая переменная или свойство.
number1
Обязательный. Произвольное числовое выражение.
number2
Обязательный. Произвольное числовое выражение.
Поддерживаемые типы
все числовые типы. Сюда входят неподписанные типы и типы с плавающей запятой и Decimal .
Результат
Результатом будет остаток после number1 деления на number2 . Например, выражение 14 Mod 4 принимает значение 2.
В математике существует разница между остатками и модулями с разными результатами для отрицательных чисел. Оператор Mod в Visual Basic, оператор платформа .NET Framework op_Modulus и базовая инструкция rem IL выполняют операцию остатка.
Результат Mod операции сохраняет знак дивиденда, number1 и поэтому он может быть положительным или отрицательным. Результат всегда находится в диапазоне (- number2 , number2 ), монопольно. Пример:
Remarks
Если или number1 number2 является значением с плавающей запятой, возвращается остаток деления с плавающей запятой. Тип данных результата — это наименьший тип данных, который может содержать все возможные значения, полученные в результате деления на типы number1 данных и number2 .
Если number1 значение или number2 имеет значение Nothing, оно обрабатывается как ноль.
К связанным операторам относятся следующие:
Оператор (Visual Basic) возвращает целочисленное частное деление. Например, выражение 14 4 принимает значение 3.
Оператор / (Visual Basic) возвращает полное частное, включая остаток, в виде числа с плавающей запятой. Например, выражение 14 / 4 принимает значение 3,5.
Попытка деления на ноль
Если number2 значение равно нулю, поведение Mod оператора зависит от типа данных операндов:
- Целочисленное деление создает DivideByZeroException исключение, если number2 не удается определить во время компиляции, и создает ошибку BC30542 Division by zero occurred while evaluating this expression во время компиляции, если number2 вычисляется как нулевое во время компиляции.
- Деление с плавающей запятой возвращает Double.NaN.
Эквивалентная формула
Выражение a Mod b эквивалентно любой из следующих формул:
Неточным числом с плавающей запятой
При работе с числами с плавающей запятой помните, что они не всегда имеют точное десятичное представление в памяти. Это может привести к непредвиденным результатам определенных операций, таких как сравнение значений Mod и оператор . Дополнительные сведения см. в разделе Устранение неполадок с типами данных.
Перегрузка
Оператор Mod может быть перегружен, что означает, что класс или структура могут переопределить свое поведение. Если код применяется к Mod экземпляру класса или структуры, которая включает в себя такую перегрузку, убедитесь, что вы понимаете его переопределенное поведение. Для получения дополнительной информации см. Operator Procedures.
Пример 1
В следующем примере оператор используется для Mod деления двух чисел и возврата только оставшейся части. Если любое из чисел является числом с плавающей запятой, результатом будет число с плавающей запятой, представляющее остаток.
Пример 2
В следующем примере показано потенциальное отсутствие операндов с плавающей запятой. В первом операторе операнды — , а 0,2 — бесконечно повторяющаяся Double двоичная дробь с сохраненным значением 0,20000000000000001. Во втором операторе символ D литерального типа приводит оба операнда к Decimal , а 0,2 имеет точное представление.
Источник
Функции VBA для работы с числовыми значениями
- ABS() — эта функция возвращает абсолютное значение переданного ей числа (то же число, но без знака). Например, ABS(3) и ABS(-3) вернут одно и то же значение 3.
- Int() , Fix() и Round() позволяют по разному округлять числа:
- Int() возвращает ближайшее меньшее целое;
- Fix() отбрасывает дробную часть;
- Round() округляет до указанного количества знаков после запятой.
Однако Round может вернуть не совсем ожидаемый результат, т.к. функция применяет финансовое округление. По правилам данного округления если за последней к округлению цифрой стоит 5, то округляемую цифру увеличивают в том случае, если она нечетная и уменьшают, если четная.
Математическое же округление всегда округляет цифру в большую сторону, если за ней идет цифра 5 и выше, и отбрасывает остаток если 4 и меньше.
Т.е. если мы выполним такую строку кодаMsgBox Round(2.505, 2)
то результатом будет 2,5 , хотя предполагалось получить 2,51 . Поэтому порой для округления лучше использовать Format :
MsgBox Format(2.505, «#,##0.00»)
но в этом случае мы получим не число в чистом виде, а текст. И если нужно именно число, то придется производить дополнительные преобразования:
MsgBox CDbl(Format(2.505, «#,##0.00»))
Так же, для математического округления, можно использовать и такой вариант:
MsgBox Application.Round(2.505, 2)
Но здесь стоит учитывать, что это не чистый VB и этот метод сработает только в Excel, т.к. по сути мы обращаемся к встроенной в Excel функции округления ОКРУГЛ (ROUND) , которая применяет именно математическое округление.
Rnd и команда Randomize используются для получения случайных значений (очень удобно для генерации имен файлов и в других ситуациях). Перед вызовом функции Rnd() необходимо выполнить команду Randomize для инициализации генератора случайных чисел.Dim lRundNum As Long, lMinNum As Long, lMaxNum As Long lMinNum = 1: lMaxNum = 100 Randomize lRundNum = Int(lMinNum + (Rnd() * lMaxNum)) MsgBox lRundNum
Источник
VBA Excel. Арифметические операторы
Арифметические (математические) операторы, использующиеся в VBA Excel. Их предназначение, особенности вычислений, приоритет в выражениях.
Обзор арифметических операторов
Операторы Описание Оператор «+» Сложение двух чисел или объединение двух строк (для объединения строк предпочтительнее использовать оператор «&») Оператор «-» Вычитание (определение разности двух чисел) или отрицание (отражение отрицательного значения числового выражения: -15, -a) Оператор «*» Умножение двух чисел Оператор «/» Деление двух чисел (деление на 0 приводит к ошибке) Оператор «^» Возведение числа в степень Оператор «» Целочисленное деление Оператор «Mod» Возвращает остаток от деления двух чисел Особенности операторов «» и «Mod»
Перед вычислением целочисленного результата или остатка от деления двух чисел делимое и делитель округляются. Причем, используется бухгалтерское округление:
- -3.5 => -4
- -2.5 => -2
- -1.5 => -2
- -0.5 => 0
- 0.5 => 0
- 1.5 => 2
- 2.5 => 2
- 3.5 => 4
Следующие строки вызовут ошибку «Division by zero» («Деление на ноль»):
Чтобы избежать ошибок, когда требуется общепринятое математическое округление, округляйте делитель и делимое с помощью оператора WorksheetFunction.Round.
Приоритет арифметических операторов
Приоритет определяет очередность выполнения математических операторов в одном выражении. Очередность выполнения арифметических операторов в VBA Excel следующая:
- «^» – возведение в степень;
- «—» – отрицание;
- «*» и «/» – умножение и деление; 1
- «» – целочисленное деление;
- «Mod» – остаток от деления двух чисел;
- «+» и «—» – сложение и вычитание. 2
1 Если умножение и деление выполняются в одном выражении, то каждая такая операция выполняется слева направо в порядке их следования.
2 Если сложение и вычитание выполняются в одном выражении, то каждая такая операция выполняется слева направо в порядке их следования.Для переопределения приоритета выполнения математических операторов в VBA Excel используются круглые скобки. Сначала выполняются арифметические операторы внутри скобок, затем — операторы вне скобок. Внутри скобок приоритет операторов сохраняется.
Источник
Mod operator (Visual Basic)
Divides two numbers and returns only the remainder.
Syntax
Parts
result
Required. Any numeric variable or property.number1
Required. Any numeric expression.number2
Required. Any numeric expression.Supported types
All numeric types. This includes the unsigned and floating-point types and Decimal .
Result
The result is the remainder after number1 is divided by number2 . For example, the expression 14 Mod 4 evaluates to 2.
There is a difference between remainder and modulus in mathematics, with different results for negative numbers. The Mod operator in Visual Basic, the .NET Framework op_Modulus operator, and the underlying rem IL instruction all perform a remainder operation.
The result of a Mod operation retains the sign of the dividend, number1 , and so it may be positive or negative. The result is always in the range (- number2 , number2 ), exclusive. For example:
If either number1 or number2 is a floating-point value, the floating-point remainder of the division is returned. The data type of the result is the smallest data type that can hold all possible values that result from division with the data types of number1 and number2 .
If number1 or number2 evaluates to Nothing, it is treated as zero.
Related operators include the following:
The Operator (Visual Basic) returns the integer quotient of a division. For example, the expression 14 4 evaluates to 3.
The / Operator (Visual Basic) returns the full quotient, including the remainder, as a floating-point number. For example, the expression 14 / 4 evaluates to 3.5.
Attempted division by zero
If number2 evaluates to zero, the behavior of the Mod operator depends on the data type of the operands:
- An integral division throws a DivideByZeroException exception if number2 cannot be determined in compile-time and generates a compile-time error BC30542 Division by zero occurred while evaluating this expression if number2 is evaluated to zero at compile-time.
- A floating-point division returns Double.NaN.
Equivalent formula
The expression a Mod b is equivalent to either of the following formulas:
Floating-point imprecision
When you work with floating-point numbers, remember that they do not always have a precise decimal representation in memory. This can lead to unexpected results from certain operations, such as value comparison and the Mod operator. For more information, see Troubleshooting Data Types.
Overloading
The Mod operator can be overloaded, which means that a class or structure can redefine its behavior. If your code applies Mod to an instance of a class or structure that includes such an overload, be sure you understand its redefined behavior. For more information, see Operator Procedures.
Example 1
The following example uses the Mod operator to divide two numbers and return only the remainder. If either number is a floating-point number, the result is a floating-point number that represents the remainder.
Example 2
The following example demonstrates the potential imprecision of floating-point operands. In the first statement, the operands are Double , and 0.2 is an infinitely repeating binary fraction with a stored value of 0.20000000000000001. In the second statement, the literal type character D forces both operands to Decimal , and 0.2 has a precise representation.
Источник
Adblock
detector
Mod 101 | Even or Odd | Divisible by Another Number
The Mod operator in Excel VBA gives the remainder of a division. This page starts with some simple examples.
Mod 101
Place a command button on your worksheet and add the following code line:
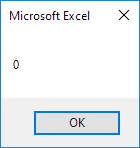
MsgBox 7 Mod 2
Result when you click the command button on the sheet:
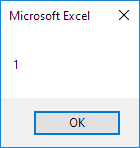
Explanation: 7 divided by 2 equals 3 with a remainder of 1.
Code line:
MsgBox 8 Mod 2
Result:
Explanation: 8 divided by 2 equals 4 with a remainder of 0.
Even or Odd
Let’s create a program that uses the Mod operator to check if a number is even or odd.
Code lines:
Dim x As Integer
x = Range(«A1»).Value
If x Mod 2 = 0 Then
Range(«B1»).Value = «Even»
Else
Range(«B1»).Value = «Odd»
End If
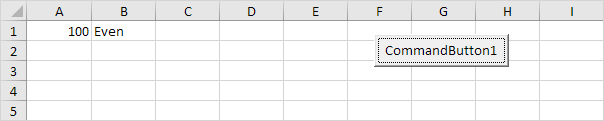
For example, enter the value 100 into cell A1 and click the command button on the sheet.
Result:
Explanation: a number is even if it is divisible by 2 without a remainder.
Divisible by Another Number
Let’s create a program that uses the Mod operator to check if a number is divisible by another number.
Code lines:
Dim x As Integer
x = Range(«A1»).Value
If x Mod 4 = 0 Then
Range(«B1»).Value = «Divisible by 4»
Else
Range(«B1»).Value = «Not divisible by 4»
End If
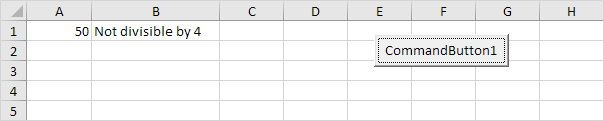
For example, enter the value 50 into cell A1 and click the command button on the sheet.
Result:
Explanation: 50 divided by 4 equals 12 with a remainder of 2. In other words, 50 is not divisible by 4.