In this VBA Tutorial, you learn how to check if a cell or range is empty.
This VBA Tutorial is accompanied by an Excel workbook containing the data and macros I use in the examples below. You can get immediate free access to this example workbook by subscribing to the Power Spreadsheets Newsletter.
Use the following Table of Contents to navigate to the section you’re interested in.
Related VBA and Macro Tutorials
The following VBA and Macro Tutorials may help you better understand and implement the contents below:
- Learn about commonly-used VBA terms here.
- Learn about the Excel Object Model and how to refer to objects here.
- Learn how to create references to cell ranges here.
- Learn how to declare and work with variables here.
- Learn about data types here.
- Learn how to work with worksheet functions within VBA here.
You can find additional VBA and Macro Tutorials in the Archives.
VBA Code to Check if Cell is Empty
To check if a cell is empty with VBA, use a macro with the following statement structure:
If IsEmpty(Cell) Then
StatementsIfCellIsEmpty
Else
StatementsIfCellIsNotEmpty
End If
Process Followed by VBA Code to Check if Cell is Empty
VBA Statement Explanation
Line #1: If IsEmpty(Cell) Then
- Item: If… Then.
- VBA Construct: Opening statement of If… Then… Else statement.
- Description: The If… Then… Else statement conditionally executes a group of statements depending on the value of an expression. For these purposes:
- The If… Then… Else statement tests the specified condition (IsEmpty(Cell)).
- If the condition is met and returns True: StatementsIfCellIsEmpty are executed.
- If the condition isn’t met and returns False: StatementsIfCellIsNotEmpty are executed.
- Item: IsEmpty(…).
- VBA Construct: IsEmpty function.
- Description: Generally, the IsEmpty function indicates whether a variable has been initialized. Nonetheless, you can also use IsEmpty to check if a cell is empty.
The IsEmpty function:
- Takes one parameter (expression) of the Variant data type. Within this macro structure, the parameter is a Range object (Cell).
- Returns True if the variable is uninitialized or explicitly set to Empty. Otherwise, IsEmpty returns False.
- Item: Cell.
- VBA Construct: Range object.
- Description: Range object representing the cell you work with.
You can usually return a Range object with constructs such as the Worksheet.Range, Worksheet.Cells (with the Range.Item) or Range.Offset properties. If you explicitly declare an object variable to represent Cell, use the Range object data type.
- Item: IsEmpty(Cell).
- VBA Construct: Condition of If… Then… Else statement.
- Description: This condition is an expression that evaluates to True or False. The IsEmpty function (IsEmpty(Cell)) returns True or False, as follows:
- True: Cell is empty.
- False: Cell is not empty.
Line #2: StatementsIfCellIsEmpty
- Item: StatementsIfCellIsEmpty.
- VBA Construct: Statements within If… Then… Else statement.
- Description: One or more VBA statements that are executed if the condition tested in the opening statement of the If… Then… Else statement (IsEmpty(Cell)) returns True. Within this macro structure, IsEmpty(Cell) returns True if Cell is empty.
Line #3: Else
- Item: Else.
- VBA Construct: Else clause of If… Then… Else statement.
- Description: The statements below the Else clause (StatementsIfCellIsNotEmpty) are executed if the condition tested in the opening statement of the If… Then… Else statement (IsEmpty(Cell)) returns False. Within this macro structure, IsEmpty(Cell) returns False if Cell is not empty.
Line #4: StatementsIfCellIsNotEmpty
- Item: StatementsIfCellIsNotEmpty.
- VBA Construct: Else Statements within If… Then… Else statement.
- Description: One or more VBA statements that are executed if the condition tested in the opening statement of the If… Then… Else statement (IsEmpty(Cell)) returns False. Within this macro structure, IsEmpty(Cell) returns False if Cell is not empty.
Line #5: End If
- Item: End If.
- VBA Construct: Closing statement of If… Then… Else statement.
- Description: The End If clause marks the end of the If… Then… Else block.
Macro Example to Check if Cell is Empty
The following macro example checks if cell A5 of the worksheet named “Check if Cell is Empty” (myCell) is empty and displays a message box confirming whether the cell is empty or not empty.
Sub checkIfCellIsEmpty()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-cell-empty/
'declare object variable to hold reference to cell you work with
Dim myCell As Range
'identify cell you work with
Set myCell = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Check if Cell is Empty").Range("A5")
'check if cell is empty. Depending on result, display message box indicating whether cell is empty (True) or not empty (False)
If IsEmpty(myCell) Then
MsgBox myCell.Address & " is empty"
Else
MsgBox myCell.Address & " is not empty"
End If
End Sub
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Check if Cell is Empty
The following GIF illustrates the results of executing the macro example. Cell A5 (This cell isn’t empty) is not empty and the message box displayed confirms that this is the case.
#2: Check if Active Cell is Empty
VBA Code to Check if Active Cell is Empty
To check if the active cell is empty with VBA, use a macro with the following statement structure:
If IsEmpty(ActiveCell) Then
StatementsIfActiveCellIsEmpty
Else
StatementsIfActiveCellIsNotEmpty
End If
Process Followed by VBA Code to Check if Active Cell is Empty
VBA Statement Explanation
Line #1: If IsEmpty(ActiveCell) Then
- Item: If… Then.
- VBA Construct: Opening statement of If… Then… Else statement.
- Description: The If… Then… Else statement conditionally executes a group of statements depending on the value of an expression. For these purposes:
- The If… Then… Else statement tests the specified condition (IsEmpty(ActiveCell)).
- If the condition is met and returns True: StatementsIfActiveCellIsEmpty are executed.
- If the condition isn’t met and returns False: StatementsIfActiveCellIsNotEmpty are executed.
- Item: IsEmpty(…).
- VBA Construct: IsEmpty function.
- Description: Generally, the IsEmpty function indicates whether a variable has been initialized. Nonetheless, you can also use IsEmpty to check if a cell is empty.
The IsEmpty function:
- Takes one parameter (expression) of the Variant data type. Within this macro structure, the parameter is a Range object (ActiveCell).
- Returns True if the variable is uninitialized or explicitly set to Empty. Otherwise, IsEmpty returns False.
- Item: ActiveCell.
- VBA Construct: Application.ActiveCell property.
- Description: The Application.ActiveCell property returns a Range object representing the active cell.
- Item: IsEmpty(ActiveCell).
- VBA Construct: Condition of If… Then… Else statement.
- Description: This condition is an expression that evaluates to True or False. The IsEmpty function (IsEmpty(ActiveCell)) returns True or False, as follows:
- True: Active cell is empty.
- False: Active cell is not empty.
Line #2: StatementsIfActiveCellIsEmpty
- Item: StatementsIfActiveCellIsEmpty.
- VBA Construct: Statements within If… Then… Else statement.
- Description: One or more VBA statements that are executed if the condition tested in the opening statement of the If… Then… Else statement (IsEmpty(ActiveCell)) returns True. Within this macro structure, IsEmpty(ActiveCell) returns True if the active cell is empty.
Line #3: Else
- Item: Else.
- VBA Construct: Else clause of If… Then… Else statement.
- Description: The statements below the Else clause (StatementsIfActiveCellIsNotEmpty) are executed if the condition tested in the opening statement of the If… Then… Else statement (IsEmpty(ActiveCell)) returns False. Within this macro structure, IsEmpty(ActiveCell) returns False if the active cell is not empty.
Line #4: StatementsIfActiveCellIsNotEmpty
- Item: StatementsIfActiveCellIsNotEmpty.
- VBA Construct: Else Statements within If… Then… Else statement.
- Description: One or more VBA statements that are executed if the condition tested in the opening statement of the If… Then… Else statement (IsEmpty(ActiveCell)) returns False. Within this macro structure, IsEmpty(ActiveCell) returns False if the active cell is not empty.
Line #5: End If
- Item: End If.
- VBA Construct: Closing statement of If… Then… Else statement.
- Description: The End If clause marks the end of the If… Then… Else block.
Macro Example to Check if Active Cell is Empty
The following macro example checks if the active cell is empty and displays a message box confirming whether the active cell is empty or not empty.
Sub checkIfActiveCellIsEmpty()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-cell-empty/
'check if active cell is empty. Depending on result, display message box indicating whether active cell is empty (True) or not empty (False)
If IsEmpty(ActiveCell) Then
MsgBox "The active cell is empty"
Else
MsgBox "The active cell is not empty"
End If
End Sub
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Check if Active Cell is Empty
The following GIF illustrates the results of executing the macro example. The active cell (A6) is empty and the message box displayed confirms that this is the case.
#3: Check if Range is Empty
VBA Code to Check if Range is Empty
To check if a range is empty with VBA, use a macro with the following statement structure:
If WorksheetFunction.CountA(CellRange) = 0 Then
StatementsIfRangeIsEmpty
Else
StatementsIfRangeIsNotEmpty
End If
Process Followed by VBA Code to Check if Range is Empty
VBA Statement Explanation
Line #1: If WorksheetFunction.CountA(CellRange) = 0 Then
- Item: If… Then.
- VBA Construct: Opening statement of If… Then… Else statement.
- Description: The If… Then… Else statement conditionally executes a group of statements depending on the value of an expression. For these purposes:
- The If… Then… Else statement tests the specified condition (WorksheetFunction.CountA(CellRange) = 0).
- If the condition is met and returns True: StatementsIfRangeIsEmpty are executed.
- If the condition isn’t met and returns False: StatementsIfRangeIsNotEmpty are executed.
- Item: WorksheetFunction.CountA(…).
- VBA Construct: WorksheetFunction.CountA method.
- Description: The WorksheetFunction.CountA method counts the number of cells that are not empty within the argument list (CellRange). For these purposes, a cell is deemed to not be empty if, for example, it contains an error value or empty text (“”).
- Item: CellRange.
- VBA Construct: Range object.
- Description: Range object representing the cell range you work with.
You can usually return a Range object with constructs such as the Worksheet.Range property. If you explicitly declare an object variable to represent CellRange, use the Range object data type.
- Item: =.
- VBA Construct: = comparison operator.
- Description: The = comparison operator compares the 2 expressions to determine whether they’re equal:
- The expression to the left of the = comparison operator (WorksheetFunction.CountA(CellRange)).
- The expression to the right of the = comparison operator (0).
- Item: WorksheetFunction.CountA(CellRange) = 0.
- VBA Construct: Condition of If… Then… Else statement.
- Description: The condition is an expression that evaluates to True or False. The = comparison operator returns True or False as follows:
- True: If WorksheetFunction.CountA(CellRange) returns 0. This occurs when CellRange is empty.
- False: If WorksheetFunction.CountA(CellRange) returns a value other than 0. This occurs when CellRange isn’t empty.
Line #2: StatementsIfRangeIsEmpty
- Item: StatementsIfRangeIsEmpty.
- VBA Construct: Statements within If… Then… Else statement.
- Description: One or more VBA statements that are executed if the condition tested in the opening statement of the If… Then… Else statement (WorksheetFunction.CountA(CellRange) = 0) returns True. Within this macro structure, (WorksheetFunction.CountA(CellRange) = 0) returns True if CellRange is empty.
Line #3: Else
- Item: Else.
- VBA Construct: Else clause of If… Then… Else statement.
- Description: The statements below the Else clause (StatementsIfRangeIsNotEmpty) are executed if the condition tested in the opening statement of the If… Then… Else statement (WorksheetFunction.CountA(CellRange) = 0) returns False. Within this macro structure, (WorksheetFunction.CountA(CellRange) = 0) returns False if CellRange is not empty.
Line #4: StatementsIfRangeIsNotEmpty
- Item: StatementsIfRangeIsNotEmpty.
- VBA Construct: Else Statements within If… Then… Else statement.
- Description: One or more VBA statements that are executed if the condition tested in the opening statement of the If… Then… Else statement (WorksheetFunction.CountA(CellRange) = 0) returns False. Within this macro structure, (WorksheetFunction.CountA(CellRange) = 0) returns False if CellRange is not empty.
Line #5: End If
- Item: End If.
- VBA Construct: Closing statement of If… Then… Else statement.
- Description: The End If clause marks the end of the If… Then… Else block.
Macro Example to Check if Range is Empty
The following macro example checks if the range composed of cells A7 through A11 of the worksheet named “Check if Cell is Empty” (myCellRange) is empty and displays a message box confirming whether the range is empty or not empty.
Sub checkIfRangeIsEmpty()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-cell-empty/
'declare object variable to hold reference to cell range you work with
Dim myCellRange As Range
'identify cell range you work with
Set myCellRange = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Check if Cell is Empty").Range("A7:A11")
'check if number of non-empty cells in range is 0. Depending on result, display message box indicating whether cell range is empty (True) or not empty (False)
If WorksheetFunction.CountA(myCellRange) = 0 Then
MsgBox myCellRange.Address & " is empty"
Else
MsgBox myCellRange.Address & " is not empty"
End If
End Sub
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Check if Range is Empty
The following GIF illustrates the results of executing the macro example. Cells A7 through A11 (with fill) are empty and the message box displayed confirms that this is the case.
#4: Check if Any Cell in Range is Empty
VBA Code to Check if Any Cell in Range is Empty
To check if any cell in a range is empty with VBA, use a macro with the following statement structure:
If WorksheetFunction.CountA(CellRange) < CellRange.Count Then
StatementsIfAnyCellInRangeIsEmpty
Else
StatementsIfNoCellInRangeIsEmpty
End If
Process Followed by VBA Code to Check if Any Cell in Range is Empty
VBA Statement Explanation
Line #1: If WorksheetFunction.CountA(CellRange) < CellRange.Count Then
- Item: If… Then.
- VBA Construct: Opening statement of If… Then… Else statement.
- Description: The If… Then… Else statement conditionally executes a group of statements depending on the value of an expression. For these purposes:
- The If… Then… Else statement tests the specified condition (WorksheetFunction.CountA(CellRange) < CellRange.Count).
- If the condition is met and returns True: StatementsIfAnyCellInRangeIsEmpty are executed.
- If the condition isn’t met and returns False: StatementsIfNoCellInRangeIsEmpty are executed.
- Item: WorksheetFunction.CountA(…).
- VBA Construct: WorksheetFunction.CountA method.
- Description: The WorksheetFunction.CountA method counts the number of cells that are not empty within the argument list (CellRange). For these purposes, a cell is deemed to not be empty if, for example, it contains an error value or empty text (“”).
- Item: CellRange.
- VBA Construct: Range object.
- Description: Range object representing the cell range you work with.
You can usually return a Range object with constructs such as the Worksheet.Range property. If you explicitly declare an object variable to represent CellRange, use the Range object data type.
- Item: <.
- VBA Construct: < comparison operator.
- Description: The < comparison operator compares 2 expressions to determine whether (i) the expression to its left (WorksheetFunction.CountA(CellRange)), (ii) is less than (iii) the expression to its right (CellRange.Count).
- Item: CellRange.Count.
- VBA Construct: Range.Count property.
- Description: The Range.Count property returns the number of objects in the collection (CellRange). Within this macro structure, the Count property returns the number of individual cells within CellRange.
- Item: WorksheetFunction.CountA(CellRange) < CellRange.Count.
- VBA Construct: Condition of If… Then… Else statement.
- Description: The condition is an expression that evaluates to True or False. The < comparison operator returns True or False as follows:
- True: If WorksheetFunction.CountA(CellRange) returns a value smaller than the value returned by CellRange.Count. Within this macro structure, this occurs when (i) the number of non-empty cells in CellRange (returned by WorksheetFunction.CountA(CellRange)) (ii) is less than (iii) the number of cells in CellRange (returned by CellRange.Count). This occurs when CellRange contains at least 1 empty cell.
- False: If WorksheetFunction.CountA(CellRange) returns a value equal to the value returned by CellRange.Count. Within this macro structure, this occurs when (i) the number of non-empty cells in CellRange (returned by WorksheetFunction.CountA(CellRange)) (ii) is equal to (iii) the number of cells in CellRange (returned by CellRange.Count). This occurs when CellRange contains no empty cells.
Line #2: StatementsIfAnyCellInRangeIsEmpty
- Item: StatementsIfAnyCellInRangeIsEmpty.
- VBA Construct: Statements within If… Then… Else statement.
- Description: One or more VBA statements that are executed if the condition tested in the opening statement of the If… Then… Else statement (WorksheetFunction.CountA(CellRange) < CellRange.Count) returns True. Within this macro structure, (WorksheetFunction.CountA(CellRange) < CellRange.Count) returns True if CellRange contains at least 1 empty cell.
Line #3: Else
- Item: Else.
- VBA Construct: Else clause of If… Then… Else statement.
- Description: The statements below the Else clause (StatementsIfNoCellInRangeIsEmpty) are executed if the condition tested in the opening statement of the If… Then… Else statement (WorksheetFunction.CountA(CellRange) < CellRange.Count) returns False. Within this macro structure, (WorksheetFunction.CountA(CellRange) < CellRange.Count) returns False if CellRange doesn’t contain any empty cells.
Line #4: StatementsIfNoCellInRangeIsEmpty
- Item: StatementsIfNoCellInRangeIsEmpty.
- VBA Construct: Else Statements within If… Then… Else statement.
- Description: One or more VBA statements that are executed if the condition tested in the opening statement of the If… Then… Else statement (WorksheetFunction.CountA(CellRange) < CellRange.Count) returns False. Within this macro structure, (WorksheetFunction.CountA(CellRange) < CellRange.Count) returns False if CellRange doesn’t contain any empty cells.
Line #5: End If
- Item: End If.
- VBA Construct: Closing statement of If… Then… Else statement.
- Description: The End If clause marks the end of the If… Then… Else block.
Macro Example to Check if Any Cell in Range is Empty
The following macro example checks if the range composed of cells A13 through A17 of the worksheet named “Check if Cell is Empty” (myCellRange) contains any empty cells and displays a message box confirming whether the range contains or not any empty cells.
Sub checkIfAnyCellInRangeIsEmpty()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-cell-empty/
'declare object variable to hold reference to cell range you work with
Dim myCellRange As Range
'identify cell range you work with
Set myCellRange = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Check if Cell is Empty").Range("A13:A17")
'check if number of non-empty cells in range is less than total number of cells in range. Depending on result, display message box indicating whether cell range contains any empty cell (True) or not (False)
If WorksheetFunction.CountA(myCellRange) < myCellRange.Count Then
MsgBox myCellRange.Address & " contains at least 1 empty cell"
Else
MsgBox myCellRange.Address & " doesn't contain empty cells"
End If
End Sub
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Check if Any Cell in Range is Empty
The following GIF illustrates the results of executing the macro example. Cell A15 is empty. The message box displayed confirms that the cell range containing cells A13 to A17 (with fill) contains at least one empty cell (A15).
References to VBA Constructs Used in this VBA Tutorial
Use the following links to visit the appropriate webpage within the Microsoft Developer Network:
- Identify the cell or cell range you work with:
- Workbook object.
- Application.ThisWorkbook property.
- Worksheet object.
- Workbook.Worksheets property.
- Range object.
- Worksheet.Range property.
- Worksheet.Cells property.
- Range.Item property.
- Range.Offset property.
- Application.ActiveCell property.
- Test if a cell or cell range is empty:
- If… Then… Else statement.
- IsEmpty function.
- WorksheetFunction.CountA method.
- Range.Count property.
- Comparison operators.
- Display a message box including, among others, the address of a cell or cell range:
- MsgBox function.
- Range.Address property.
- & operator.
- Work with variables and data types:
- Dim statement.
- Set statement.
- = operator.
- Data types:
- Boolean data type.
- String data type.
- Variant data type.
Home / VBA / VBA Check IF a Cell is Empty + Multiple Cells
To check if a cell is empty you can use VBA’s ISEMPTY function. In this function, you need to use the range object to specify the cell that you want to check, and it returns true if that cell is empty, otherwise false. You can use a message box or use a cell to get the result.
- Start with the function name “IsEmpty”.
- Specify the cell that you want to check.
- Use a message box or a cell to get the result value.
- In the end, run the code.
MsgBox IsEmpty(Range("A1"))
Check IF Multiple Cells Empty
If you want to check and count the empty cells from a range when you need to loop through each cell in the range.
Sub vba_check_empty_cells()
Dim i As Long
Dim c As Long
Dim myRange As Range
Dim myCell As Range
Set myRange = Range("A1:A10")
For Each myCell In myRange
c = c + 1
If IsEmpty(myCell) Then
i = i + 1
End If
Next myCell
MsgBox _
"There are total " & i & " empty cell(s) out of " & c & "."
End SubThe above code loops through each cell in the range A1:A10 and check each cell one by one using the ISEMPTY function if it’s empty or not.
And for each empty cell it takes a count, and in the end, shows a message box with the total number of cells and empty cells out of that.
Use the following code if you want to highlight empty cells as well.
Dim i As Long
Dim c As Long
Dim myRange As Range
Dim myCell As Range
Set myRange = Range("A1:A10")
For Each myCell In myRange '
c = c + 1
If IsEmpty(myCell) Then
myCell.Interior.Color = RGB(255, 87, 87)
i = i + 1
End If
Next myCell
MsgBox _
"There are total " & i & " empty cell(s) out of " & c & "."More Tutorials
- Count Rows using VBA in Excel
- Excel VBA Font (Color, Size, Type, and Bold)
- Excel VBA Hide and Unhide a Column or a Row
- Excel VBA Range – Working with Range and Cells in VBA
- Apply Borders on a Cell using VBA in Excel
- Find Last Row, Column, and Cell using VBA in Excel
- Insert a Row using VBA in Excel
- Merge Cells in Excel using a VBA Code
- Select a Range/Cell using VBA in Excel
- SELECT ALL the Cells in a Worksheet using a VBA Code
- ActiveCell in VBA in Excel
- Special Cells Method in VBA in Excel
- UsedRange Property in VBA in Excel
- VBA AutoFit (Rows, Column, or the Entire Worksheet)
- VBA ClearContents (from a Cell, Range, or Entire Worksheet)
- VBA Copy Range to Another Sheet + Workbook
- VBA Enter Value in a Cell (Set, Get and Change)
- VBA Insert Column (Single and Multiple)
- VBA Named Range | (Static + from Selection + Dynamic)
- VBA Range Offset
- VBA Sort Range | (Descending, Multiple Columns, Sort Orientation
- VBA Wrap Text (Cell, Range, and Entire Worksheet)
⇠ Back to What is VBA in Excel
Helpful Links – Developer Tab – Visual Basic Editor – Run a Macro – Personal Macro Workbook – Excel Macro Recorder – VBA Interview Questions – VBA Codes
Introduction to Cells
In Microsoft Excel, a cell is nothing but an intersection of a column and a row. This cell is referenced by its row number and column letter. A cell can hold a formula/data directly. It can be formatted with font styles and colors or background colors too.
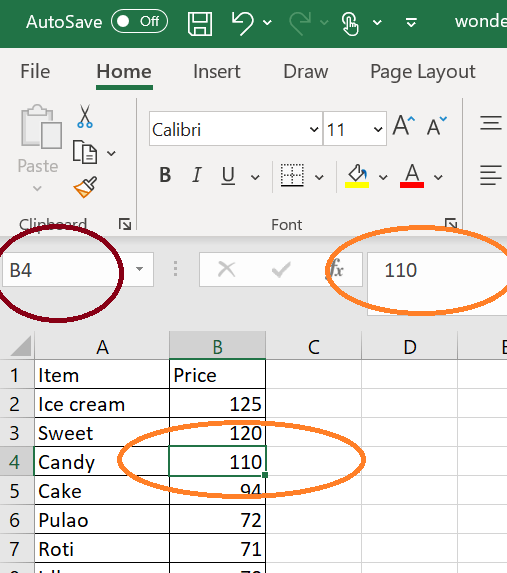
In the image above, cell B4 is selected. It is the intersection of row number “4” and column letter “B.” Since the value of the cell does not start with an “=”, it means that the cell is holding some data directly. Here the data held is “110.”
Empty Cells in Excel
If the cell does not have any value, it is said to be empty. There’s a chance that a cell has the same font color and background color, but with some data. In that case, it may look empty but actually isn’t. So, to find this, we have to select the cell and check the formula bar.

Here the selected cell D9 looks blank but has a value “India.” It is not visible on the cell because the color of the font in that cell is white, which is equal to its background color.
ISBLANK Formula
Microsoft Excel offers a formula named ISBLANK which returns/provides a Boolean result stating whether the value of that cells is blank or not.
Syntax:
ISBLANK( <value> )
Where <value> can be a reference to a cell.


In the above images, the selected cells hold the formula as in the formula bar referring to the cells B7 (first image) and C8 (second image) respectively. The false and true values are returned depending on the values in the cells referred as parameters.
The selected cells hold the formula seen in the formula bar referring to the cells B7 (first image) and C8 (second image) respectively. The false and true values are returned depending on the values in the cells referred as parameters.
Range of Cells in Excel
In Excel a range is a set of continuous cells which can be a part of one or more columns or one or more rows or both. For example, in this image above Range(“A1:B12”) can be termed as a range.
Empty Cells in a Range
If there is a need to find the empty cells in a huge range of cells, it might be time consuming and tiring to select each cell and find this manually.
VBA to Find Empty Cells
VBA offers an inbuilt function called “IsEmpty” to do this for us.
Syntax
<Var> = IsEmpty ( <expression> )
Where <var> is any Boolean variable that can hold the end result value (return value) of the function and <expression> is any value that needs to be checked if empty.
For Example:
Select a Cell and Display if it is Empty
Sub empty_demo() ' select an empty cell Cells(1, 5).Select ' display a msg to cross check if the selected cell is empty MsgBox IsEmpty(Cells(1, 5).Value) End Sub
The same with a non-empty cell:
Sub empty_demo() ' select a non-empty cell Cells(1, 1).Select ' display a msg to cross check if the selected cell is empty MsgBox IsEmpty(Cells(1, 1).Value) End Sub
Another Simple Program to Check if a Cell is Empty
Sub demo2()
' check if the value of a particular cell is nothing or ""
' if there is a value, the value is displayed . If not, a statement is displayed
If Cells(3, 4).Value = "" Then
MsgBox "The cell in 3rd row and 4th col is empty"
Else
MsgBox Cells(3, 4).Value
End If
End Sub
This program looks if the value of a specific cell is empty using just the “”. The same can also be done on several cells using a loop/range.
VBA – Find Empty Cells in a Range
It is possible to find the cells that are empty in a range of cells. Once a range is defined, we can loop through each cell in the range. As we loop, we can check if the cell is empty.
Program to Count the Number of Empty Cells in a Range of Cells
In this program:
- We declare a count variable and initialize it to “0.” This will help us count the number of empty cells in a range.
- We define a range in an Excel worksheet.
- Then we loop through the cells in it using a “for each” loop. Inside the loop, we check if the cell is empty/blank using the inbuilt VBA function “ISEMPTY()”.
- If so, the value of the “cnt” variable is incremented by “1.” Once we come out of the loop, we display the value of “cnt” as the number of empty cells in the declared range.
Sub empty_demo()
' declare a range
Dim myrange
'declare a variable to store count
Dim cnt
' define the range and initialize count
myrange = Range("A1:A20")
cnt = 0
'loop through each cell of the range
For Each cell In myrange
' if the cell is empty , we increment the value of cnt variable by 1
If IsEmpty(cell) Then
cnt = cnt + 1
End If
Next cell
' display the number of empty cells
MsgBox "There are " &amp; cnt &amp; " empty cells in the mentioned range. "
End Sub
Color the Empty Cells in a Range of Cells Without Defining Any Range
In this program, instead of using a range, we use a nested “for loop” to iterate through every row in every column. The outer loop iterates through the columns while the inner loop iterates through the rows. The upper and lower bounds of the desired range/table are already provided in the “for loop” definition. Inside the inner loop, as in the previous example, we check if the cell is empty and add a number to the “cnt” variable’s value if so. Here, in addition, we also color those empty cells that are identified within the inner loop’s condition.
Sub empty_demo_1() ' declare variables to indicate, row, col and counter Dim r, c, cnt ' intialize the variables r = 1 c = 1 cnt = 0 ' loop through each col in the worksheet till we reach col no "2" For c = 1 To 2 ' loop through each row in the worksheet till we reach row no "20" For r = 1 To 20 ' if the cell ( intersection of the row and col) is empty , we increment the value of cnt variable by 1 If IsEmpty(Cells(r, c).Value) = True Then cnt = cnt + 1 ' Color the cells in yellow just to identify Cells(r, c).Interior.Color = 65535 End If Next r Next c ' display the number of empty cells MsgBox "There are " &amp;amp; cnt &amp;amp; " empty cells in the mentioned range. " End Sub
Using IsEmpty() for Variable Values
This program checks if a variable is empty and displays the result.
Sub demo3() ' declare a variable and do not initialize Dim var1 ' check if variable has value If IsEmpty(var1) = True Then ' statement if empty Debug.Print "Var1 is Empty" Else ' statement if not empty Debug.Print "Var1 has a value " &amp;amp; var1 End If End Sub
Output would be:
“Var1 is Empty”
Sub demo3() ' declare a variable and initialize it Dim var1 var1 = "This is a good day" ' check if variable has value If IsEmpty(var1) = True Then ' statement if empty Debug.Print "Var1 is Empty" Else ' statement if not empty Debug.Print "Var1 has a value. " &amp;amp; var1 End If
Output would be:
“Var1 has a value. This is a good day”
Conclusion
Apart from cells and variables, the IsEmpty() function offered by VBA can be used for arrays and many such objects. However, these are not elaborated here as the focus of this article is on checking if a cell is empty. The “” ( empty double quotes) can also be used to check if the cell(s) are empty. This is just a replacement for the IsEmpty() function and straightforward too. At times, we get stuck into a situation where nothing works out to validate if a cell is empty. In that case we can also try the len() function. The length of the cell value is “0” if it is actually empty.
Check out our other articles on the specific functions to know much about their usage.
Tagged with: Cells and Ranges, empty cells, Excel, Formulas, Functions and Formulas, isempty, Loop, Microsoft Excel, Range, VBA, VBA Boolean, VBA For Excel
Return to VBA Code Examples
In this article, you will learn how to use the IsEmpty function in VBA to check if a cell is empty. If you want to do the same in Excel, a similar function is the IsBlank function. In this step-by-step tutorial, for all levels of Excel and VBA users, you will see how to use both functions.
Using the IsEmpty function in VBA
As we already mentioned in the introduction, the IsEmpty is the simple function in VBA which checks if a cell is empty. If the selected does not contain any value, the function will return Boolean TRUE. On the other side, if the cell contains a value, the function returns FALSE. Here is the code:
If IsEmpty(Sheet1.Range("A1").Value) = True Then
Sheet1.Range("B1").Value = "The cell A1 is empty"
Else
Sheet1.Range("B1").Value = "The value in A1 is " & Sheet1.Range("A1").Value
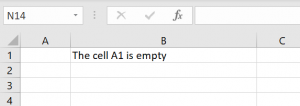
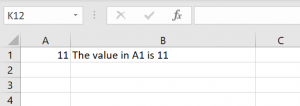
End IfIn the example, we want to check if the cell A1 in the Sheet1 contains any value. Therefore, if the cell is empty, we will return “The cell A1 is empty” in the cell B1. If the cell contains a value, we will return the value of the cell A1 in the cell B1. Let’s run the code first with empty A1 and then with A1 containing some value:
Image 1. Using the IsEmpty in VBA with the empty cell
Image 2. Using the IsEmpty in VBA with populated cell
Using the IsBlank function in Excel
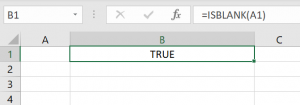
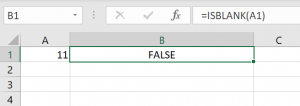
The IsBlank function also checks if the value of the cell is blank, but this function does not exist in VBA. We’ll see on similar examples how to check if the cell is blank in Excel, using this formula:
=ISBLANK(A1)Image 3. Using the IsBlank in Excel with blank A1 cell
Image 4. Using the IsBlank in Excel with populated A1 cell
As you can see, we check if the cell A1 is blank and return the result of the function in the cell B1. In Image 3, the result of the function is Boolean TRUE. On the other side, in Image 4, the result of the function is FALSE, as the cell A1 is “11” and is not blank.
VBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro — A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Learn More!
- Ways to Check if a Cell Is Empty
- Method 1: The
IsEmptyFunction - Method 2: Compare With
vbNullString - Method 3: Compare With an Empty String
- Method 4: The
LenFunction - Method 5: The
CountandCountaFunctions - Method 6: The
IsNullFunction - Conclusion
VBA is a programming language for Microsoft Excel applications that provides users with various functions and features. In this article, we will be learning about how to check if a cell is empty.
Ways to Check if a Cell Is Empty
In MS Excel, a cell is a block identified as the intersection of a row and a column, having the row number and column letter as the identifier. These cells can hold various types of data.
However, we can also have an empty cell, which refers to one that holds no data.
In MS Excel, there can be many situations where we have to check if the cell contains any data or not. To assist us in doing this, MS Excel VBA provides multiple methods to check if a cell is empty.
These methods are explained in detail below, along with VBA code examples to help you understand them better.
Method 1: The IsEmpty Function
The IsEmpty function in Excel VBA is a built-in function that returns a Boolean value. This function can also be used along with cells to check if a variable is uninitialized.
It has the following syntax:
IsEmpty(value)
Here, value is the cell or variable you want to check.
If the cell is empty or the variable is uninitialized, this function returns True. Otherwise, it returns False.
Note: If you want to check if a value is blank in a worksheet cell, you can also use the
IsBlank(value)worksheet function in the formula bar. However, you cannot use theIsBlankfunction in VBA as an alternative to theIsEmptyfunction.
Using the code below, let us test the IsEmpty function on some simple cells. We will also use the same two cells in the subsequent examples.
Sub ExampleIsEmpty()
If IsEmpty(Range("A1")) = True Then
MsgBox "Cell A1 is empty"
Else
MsgBox "Cell A1 is not empty"
End If
If IsEmpty(Range("A2").Value) = True Then
MsgBox "Cell A2 is empty"
Else
MsgBox "Cell A2 is not empty"
End If
End Sub
Running this code will give the following output in message boxes:
Note how we have used both
IsEmpty(Range("A1"))andIsEmpty(Range("A2").Value). Both will work fine.
Method 2: Compare With vbNullString
If we want to check if a cell does not contain any value, we can also compare it with vbNullString. vbNullString is a constant which holds the Null value for strings.
If the comparison shows that the value in the cell is equal to vbNullString, we can conclude that the cell is empty.
The following code demonstrates how we can use the vbNullString constant to check for empty cells.
Sub ExamplevbNullString()
If Range("A1").Value = vbNullString Then
MsgBox "Cell A1 is empty"
Else
MsgBox "Cell A1 is not empty"
End If
If Range("A2").Value = vbNullString Then
MsgBox "Cell A2 is empty"
Else
MsgBox "Cell A2 is not empty"
End If
End Sub
Again, we can see that the output prompts the following message boxes:
Note: This method will not work when the cell does not have a value but contains an error like
#N/A!. Therefore, it is safer to use theIsEmptyfunction.
Method 3: Compare With an Empty String
A similar method is to compare the value present in the cell with an empty string, which is defined in code as "". If the comparison returns True, the cell is empty and non-empty otherwise.
Here is an example of that which uses comparison with "" to determine if the cell is empty.
Sub ExampleEmptyString()
If Range("A1").Value = "" Then
MsgBox "Cell A1 is empty"
Else
MsgBox "Cell A1 is not empty"
End If
If Range("A2").Value = "" Then
MsgBox "Cell A2 is empty"
Else
MsgBox "Cell A2 is not empty"
End If
End Sub
The output will be as follows:
Method 4: The Len Function
To check if a cell is empty, we can also compute the length of the data in there and compare if it is equal to zero.
If the length is equal to zero, we can say that the cell is empty, implying that it contains no data. Otherwise, we say that the cell is not empty.
We use the VBA built-in Len function to compute the length of the data. It has the following syntax:
Len(value)
Here, value is the value of the cell you want to check.
Let us look at an example code that uses the Len function to determine if a cell is empty.
Sub ExampleLen()
If Len(Range("A1").Value) = 0 Then
MsgBox "Cell A1 is empty"
Else
MsgBox "Cell A1 is not empty"
End If
If Len(Range("A2").Value) = 0 Then
MsgBox "Cell A2 is empty"
Else
MsgBox "Cell A2 is not empty"
End If
End Sub
As expected, we get the following output:
Method 5: The Count and Counta Functions
The Count and Counta functions are worksheet functions in VBA that return the number of non-empty cells in the given range. The difference between them is that the Count function only counts numeric values, whereas the Counta function can work on any data.
We can utilize these functions to check if a given cell is empty. If the count is returned as 0, the cell is empty since the function counts only non-empty cells.
It is better to use the Counta function instead of the Count function because the Count function will consider textual or string-type data as blank.
The following code demonstrates the usage of the Counta function to check for empty cells.
Sub ExampleCounta()
If Application.WorksheetFunction.CountA(Range("A1")) = 0 Then
MsgBox "Cell A1 is empty"
Else
MsgBox "Cell A1 is not empty"
End If
If Application.WorksheetFunction.CountA(Range("A2")) = 0 Then
MsgBox "Cell A2 is empty"
Else
MsgBox "Cell A2 is not empty"
End If
End Sub
The output is as expected.
Method 6: The IsNull Function
Another method to check if a cell contains a Null value is to use the IsNull function. This is also a built-in function in VBA that returns a Boolean value: True if the value is equal to Null and False otherwise.
If this function returns True for the value of a cell, we can conclude that the cell is empty.
The syntax for the IsNull function is as follows:
IsNull(value)
Here, value is the value of the cell you want to check.
However, a point to be noted is that the Null value is not inherently allocated to a cell. Therefore, in many cases, this method will not work and will say that a cell is not empty even when it is blank because its value is not equal to NULL.
Conclusion
In this article, we have explained six methods to check if a cell is empty in Excel VBA:
- The
IsEmptyfunction - Comparison with
vbNullString - Comparison with an empty string
- The
Lenfunction - The
CountandCountafunctions - The
IsNullfunction
We hope you were able to grasp these concepts. Keep learning!