I’ve received a large number of questions on how to command other programs with VBA through Excel. In this post, we will walk through how to copy a specified cell range and paste it into a brand new PowerPoint presentation. This might seem like a task that would be much more efficient to carry out manually. However, when you need to put together a presentation with 50+ Excel images, having a VBA macro do all the heavy lifting is much faster! Let me first show you the VBA code and then I will highlight some of the main sections that are most important.
Sub ExcelRangeToPowerPoint()
‘PURPOSE: Copy/Paste An Excel Range Into a New PowerPoint Presentation
‘SOURCE: www.TheSpreadsheetGuru.com
Dim rng As Range
Dim PowerPointApp As Object
Dim myPresentation As Object
Dim mySlide As Object
Dim myShape As Object
‘Copy Range from Excel
Set rng = ThisWorkbook.ActiveSheet.Range(«A1:C12»)
‘Create an Instance of PowerPoint
On Error Resume Next
‘Is PowerPoint already opened?
Set PowerPointApp = GetObject(class:=»PowerPoint.Application»)
‘Clear the error between errors
Err.Clear
‘If PowerPoint is not already open then open PowerPoint
If PowerPointApp Is Nothing Then Set PowerPointApp = CreateObject(class:=»PowerPoint.Application»)
‘Handle if the PowerPoint Application is not found
If Err.Number = 429 Then
MsgBox «PowerPoint could not be found, aborting.»
Exit Sub
End If
On Error GoTo 0
‘Optimize Code
Application.ScreenUpdating = False
‘Create a New Presentation
Set myPresentation = PowerPointApp.Presentations.Add
‘Add a slide to the Presentation
Set mySlide = myPresentation.Slides.Add(1, 11) ’11 = ppLayoutTitleOnly
‘Copy Excel Range
rng.Copy
‘Paste to PowerPoint and position
mySlide.Shapes.PasteSpecial DataType:=2 ‘2 = ppPasteEnhancedMetafile
Set myShape = mySlide.Shapes(mySlide.Shapes.Count)
‘Set position:
myShape.Left = 66
myShape.Top = 152
‘Make PowerPoint Visible and Active
PowerPointApp.Visible = True
PowerPointApp.Activate
‘Clear The Clipboard
Application.CutCopyMode = False
End Sub
Teaching Excel The PowerPoint Language
In order to control PowerPoint from inside Excel’s Visual Basic Editor, we need to teach Excel how to speak in PowerPoint’s terms. PowerPoint uses a vocabulary containing terms such as «Slide» and «Presentation» that simply do not exist in Excel’s own code language. You can learn more about this topic by reading my post Teaching Excel To Speak PowerPoint. In order to activate PowerPoint’s object library, simply click the Tools menu in the Visual Basic Editor and select Reference. Then make sure the reference Microsoft Office PowerPoint 12.0 Object Library is checked (the version number may verify, for example in Office 2016 the reference would be Office PowerPoint 16.0 Object Library). In the below image, I show you exactly how to do this and prove afterward that Excel now knows PowerPoint lingo!
UPDATE: I have updated the code in this article so you do not need to do this step, however IntelliSense for any PowerPoint objects in the Visual Basic Editor will not work. This is not that big of a deal unless you need coding direction when adding additional PowerPoint automation to your VBA macro.
In this part of the code, we are determining if Microsoft PowerPoint is open or not. If PowerPoint is already open, we can set a variable equal to the entire program by using GetObject. If PowerPoint is not currently running we can use CreateObject to run an instance of PowerPoint and then set a variable equal to that specific instance of PowerPoint.
When using CreateObject, the target application will start running but it is not visible on the screen. Therefore we need to turn the Visible setting on (equal to true). Also, VBA with PowerPoint is a little bit different than with Excel in that it is much more dependent on its window showing on the screen. Therefore a second command must be written to Activate PowerPoint.
Copy From Excel, Paste Onto Slide
Now that you have a new presentation and a new slide, you can command Excel to paste your range into PowerPoint. Near the beginning of the code, there was a line that allowed you to specify the exact range you wanted to copy. The variable rng was used to remember this range and to allow you to reference the range later on in the code.
Guru Tip: It is a good idea to place code that may need to be manually changed at some point in the future near the beginning of the subroutine. This prevents you from having to scroll through your code and pinpoint the exact place where you spelled out which range you wanted to copy or which worksheet you wanted to pull data from. This can save you a bunch of time and prevent confusion!
Notice how we set a variable equal to the newly pasted item. This is important because it allows you to modify the picture after it has been placed into PowerPoint. In the example code, I chose to change the picture position by setting the Left and Top dimensions. You could also choose to resize the image, add a shadow, or apply any other modification you would typically do manually inside of PowerPoint.
You have now reached the end of the macro and successfully pasted in a range from Excel into a PowerPoint presentation!
Learn What VBA Can Do With PowerPoint
For the longest time, I had no idea I could use VBA with PowerPoint. I thought VBA was strictly an Excel thing. It was actually through an online VBA course that I was shown how to control PowerPoint & Word with VBA commands. It’s unfortunate that there is very little documentation out on the web concerning VBA outside of Excel. It is one of the major contributors in personally deciding to create this site and I hope to compile a bunch of resources for you in these areas. The best place to get your feet wet with VBA for PowerPoint is to hop on over to the PowerPoint Code Vault. This is where I post pre-written code and it serves as a great guide on how to write VBA for PowerPoint.
About The Author
Hey there! I’m Chris and I run TheSpreadsheetGuru website in my spare time. By day, I’m actually a finance professional who relies on Microsoft Excel quite heavily in the corporate world. I love taking the things I learn in the “real world” and sharing them with everyone here on this site so that you too can become a spreadsheet guru at your company.
Through my years in the corporate world, I’ve been able to pick up on opportunities to make working with Excel better and have built a variety of Excel add-ins, from inserting tickmark symbols to automating copy/pasting from Excel to PowerPoint. If you’d like to keep up to date with the latest Excel news and directly get emailed the most meaningful Excel tips I’ve learned over the years, you can sign up for my free newsletters. I hope I was able to provide you with some value today and I hope to see you back here soon!
— Chris
Excel VBA PowerPoint
Using VBA, we can automate the work we do for PowerPoint. But first, to use VBA code or snippets to work in PowerPoint, first work through the security options in PowerPoint to enable all Macros. Then, we can use PowerPoint VBA reference for Macros in MS PowerPoint.
The beauty of VBA is that we can reference other Microsoft products like “Microsoft Word” and “Microsoft PowerPoint.” We usually create reports in Excel and then create PowerPoint presentations. All Excel users usually spend a considerable amount of time preparing the presentation from Excel data and reports. If you spend considerable time preparing PowerPoint presentations, this tutorial will show you how to create a PowerPoint presentation from Excel using VBA CodingVBA code refers to a set of instructions written by the user in the Visual Basic Applications programming language on a Visual Basic Editor (VBE) to perform a specific task.read more.
Table of contents
- Excel VBA PowerPoint
- Enable Powerpoint Object Model
- VBA Tutorial to Create PowerPoint Presentation
- Recommended Articles
Enable Powerpoint Object Model
Let us follow the below steps..
- Open “VBA Editor.” Then, go to “Tools” and “References.”
- Now, you will see all the references to the “VBA Project.” Scroll down and select “Microsoft PowerPoint 15.0 Object Library”.
- Click on “OK.” Now, we can access PowerPoint from Excel.
VBA Tutorial to Create PowerPoint Presentation
We can create PPT in “Early Binding” and “Late Binding.” Finally, we will show you how to create a PowerPoint presentationThe full form of PPT is PowerPoint Presentation. They are generally used in corporate meetings for educational purposes such as training, induction, etc. and are even used by students for creating their high school/ college projects and assignments. Such presentations are prepared by sourcing and combining individual slides together into one with the help of MS PowerPoint Software.read more using the “Early Binding” technique.
You can download this VBA PowerPoint Excel Template here – VBA PowerPoint Excel Template
Usually, from Excel, we prepare presentations based on charts and interpretation of the charts. So, for this purpose, we have created some simple excel chartsIn Excel, a graph or chart lets us visualize information we’ve gathered from our data. It allows us to visualize data in easy-to-understand pictorial ways. The following components are required to create charts or graphs in Excel: 1 — Numerical Data, 2 — Data Headings, and 3 — Data in Proper Order.read more and interpretations in the same worksheet.
Step 1: Start the subroutine in VBASUB in VBA is a procedure which contains all the code which automatically gives the statement of end sub and the middle portion is used for coding. Sub statement can be both public and private and the name of the subprocedure is mandatory in VBA.read more. We have already enabled the PowerPoint object model in the earlier steps to access PowerPoint. To access this, we need to declare the variable as PowerPoint.Application.
Code:
Sub PPT_Example() Dim PPApp As PowerPoint.Application End Sub
Step 2: To add the presentation to PowerPoint, we need to declare a variable as PowerPoint.Presentation.
Code:
Dim PPPresentation As PowerPoint.Presentation
Step 3: After adding the presentation to the PowerPoint, we need to add a Slide to declare the variable as PowerPoint.Slide.
Code:
Dim PPSlide As PowerPoint.Slide
Step 4: Once we add the slide to the PowerPoint, we need to use shapes in the PowerPoint, i.e., text boxes, to declare a variable as PowerPoint.Shape.
Code:
Dim PPShape As PowerPoint.Shape
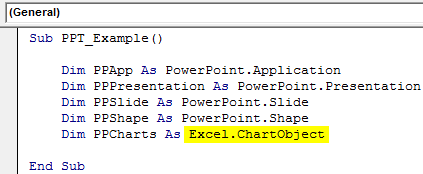
Step 5: Now, we need to declare the variable as Excel to access all the charts in the worksheet.ChartObjects.
Code:
Dim PPCharts As Excel.ChartObject
These variables are enough to start the proceedings.
Step 6: Now, we need to launch the PowerPoint from Excel. Since it is an external object, we need to set this as a new PowerPoint.
Code:
Set PPApp = New PowerPoint.Application
It will launch the new PowerPoint from Excel.
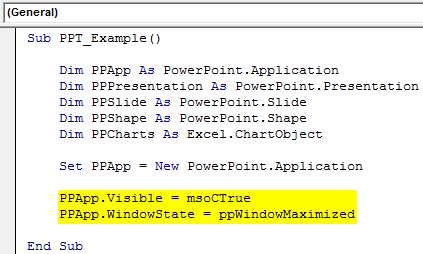
Step 7: The variable PPApp is equal to the PowerPoint we launched. Now, make this PowerPoint visible and maximize the window.
Code:
PPApp.Visible = msoCTrue PPApp.WindowState = ppWindowMaximized
Now, just run the code using the F5 key or manually. You should see the PowerPoint app launched like the one below.
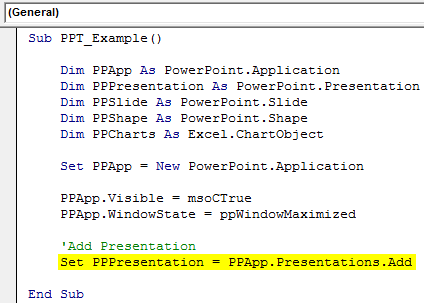
Step 8: We need to add a presentation to the PowerPoint app we have launched.
Code:
Set PPPresentation = PPApp.Presentations.Add
Now, we should see the PowerPoint presentation like this.
Step 9: We need to add a slide after adding the presentation
Code:
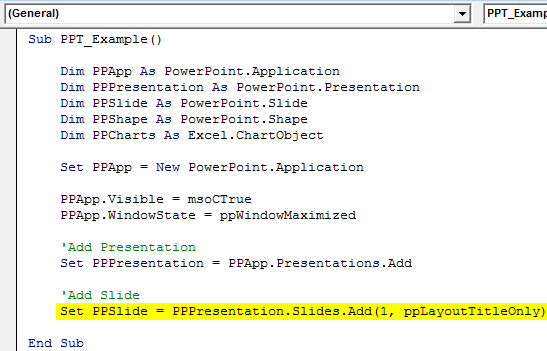
Set PPSlide = PPPresentation.Slides.Add(1, ppLayoutTitleOnly)
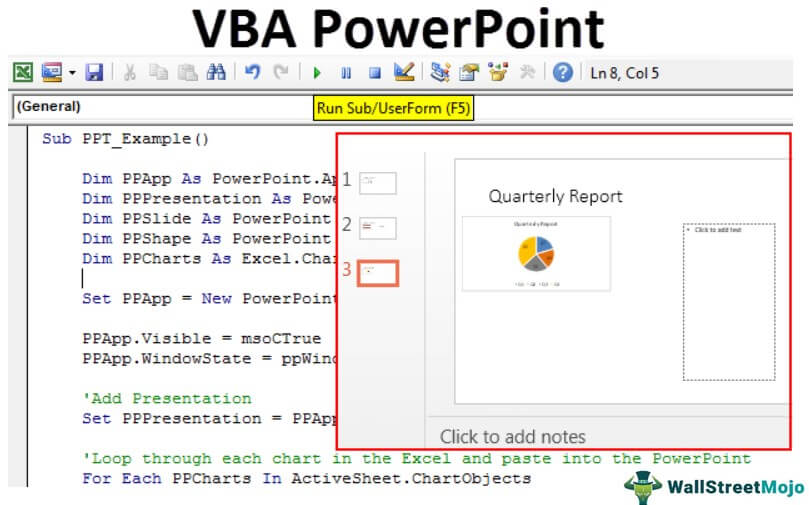
Now, this will add the title slide like the below.
Step 10: Now that we have more than one chart in the worksheet, we need to loop through each chart and paste it into the presentation. Below is the code to copy and paste the chart and interpretation.
Below is the complete code for you.
Sub PPT_Example() Dim PPApp As PowerPoint.Application Dim PPPresentation As PowerPoint.Presentation Dim PPSlide As PowerPoint.Slide Dim PPShape As PowerPoint.Shape Dim PPCharts As Excel.ChartObject Set PPApp = New PowerPoint.Application PPApp.Visible = msoCTrue PPApp.WindowState = ppWindowMaximized 'Add Presentation Set PPPresentation = PPApp.Presentations.Add 'Loop through each chart in the Excel and paste into the PowerPoint For Each PPCharts In ActiveSheet.ChartObjects PPApp.ActivePresentation.Slides.Add PPApp.ActivePresentation.Slides.Count + 1, ppLayoutText PPApp.ActiveWindow.View.GotoSlide PPApp.ActivePresentation.Slides.Count Set PPSlide = PPApp.ActivePresentation.Slides(PPApp.ActivePresentation.Slides.Count) 'Copy the chart and paste in Powerpoint PPCharts.Select ActiveChart.ChartArea.Copy PPSlide.Shapes.PasteSpecial(DataType:=ppPasteMetafilePicture).Select 'Add heading to the slide PPSlide.Shapes(1).TextFrame.TextRange.Text = PPCharts.Chart.ChartTitle.Text 'Allignment of the chart PPApp.ActiveWindow.Selection.ShapeRange.Left = 15 PPApp.ActiveWindow.Selection.ShapeRange.Top = 125 PPSlide.Shapes(2).Width = 200 PPSlide.Shapes(2).Left = 505 'Add interpretation If InStr(PPSlide.Shapes(1).TextFrame.TextRange.Text, "Region") Then PPSlide.Shapes(2).TextFrame.TextRange.Text = Range("K2").Value & vbNewLine PPSlide.Shapes(2).TextFrame.TextRange.InsertAfter (Range("K3").Value & vbNewLine) 'Else if the chart is the "Renewable" consumption chart, then enter the appropriate comments ElseIf InStr(PPSlide.Shapes(1).TextFrame.TextRange.Text, "Month") Then PPSlide.Shapes(2).TextFrame.TextRange.Text = Range("K20").Value & vbNewLine PPSlide.Shapes(2).TextFrame.TextRange.InsertAfter (Range("K21").Value & vbNewLine) PPSlide.Shapes(2).TextFrame.TextRange.InsertAfter (Range("K22").Value & vbNewLine) End If 'Now let's change the font size of the callouts box PPSlide.Shapes(2).TextFrame.TextRange.Font.Size = 16 Next PPCharts End Sub
Recommended Articles
This article is a guide to VBA PowerPoint Tutorial. Here, we learn how to create a PowerPoint presentation using the “Early Binding” technique in VBA code, examples, and a downloadable template. Below are some useful Excel articles related to VBA: –
- VBA ByRef Function
- Excel VBA Charts
- VBA Val Function
- Create VBA Pivot Table
In this Article
- VBA PDF (Free Downloads)
- PowerPoint VBA (Macros) Tutorial
- Save As Macro-Enabled Presentation
- Enable ‘Developer’ Tab in the Ribbon
- Create PowerPoint Macro
- PowerPoint Application
- Open a New Presentation
- Open an Existing Presentation
- Open and Assign to a Variable
- Refer to Active Presentation
- Save Current Presentation
- Close Current Presentation
- Useful References
- Assign Existing Presentation (by name) to Variable
- Assign Active Slide to Variable
- Assign slide by Index to Variable
- Count Number of Slides
- Get Slide Index Number of Current Slide
- Add a Blank Slide to End of Slide Show
- Add a slide after current slide
- Delete a Slide
- Go to a Specific Slide
- Move Slide
- Loop Through All Slides
- Loop through All Shapes of Active Slide
- Loop through All shapes in All Slides
- Loop through All TextBoxes of Active Slide
- Loop through All TextBoxes in All Slides
- Copy Selected slides to new PPT Presentation
- Copy Active Slide to End of Active Presentation
- Useful PowerPoint Macro Examples
- Change Slide During Slide Show
- Change Font on All Slides in All TextBoxes
- Change Case From Upper to Normal in All TextBoxes
- Toggle Case between Upper and Normal in All TextBoxes
- Remove Underline from Descenders
- Remove Animations From All Slides
- Save Presentation As PDF
- Find and Replace Text
- Export Slide As Image
- Resize Image To Cover Full Slide
- Exit All Running Slide Shows
- Automating PowerPoint from Excel
- Open PowerPoint – Early Binding
- Open PowerPoint – Late Binding
- Make Application Visible
- Maniplulate PowerPoint
- Close the Application
- Copy From Excel to PowerPoint
- PowerPoint VBA FAQs
This is a complete guide to automating PowerPoint using VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) Macros. Below you will find many useful examples.
VBA PDF (Free Downloads)
Download our free Microsoft PowerPoint VBA Tutorial! Or VBA Tutorials for other Office Programs!
Download
PowerPoint VBA (Macros) Tutorial
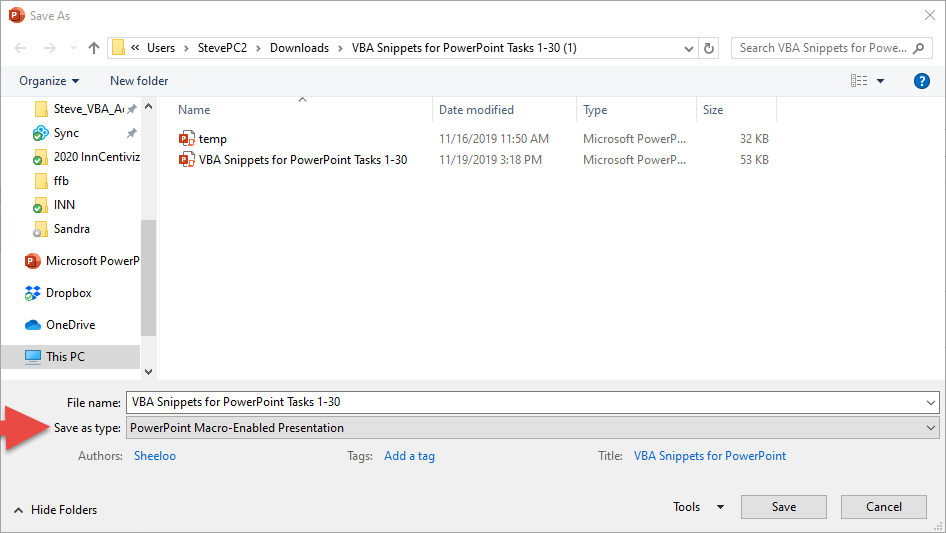
Save As Macro-Enabled Presentation
The Presentation with VBA code should be ‘Saved As’ PowerPoint Macro-Enabled Presentation (*.pptm)
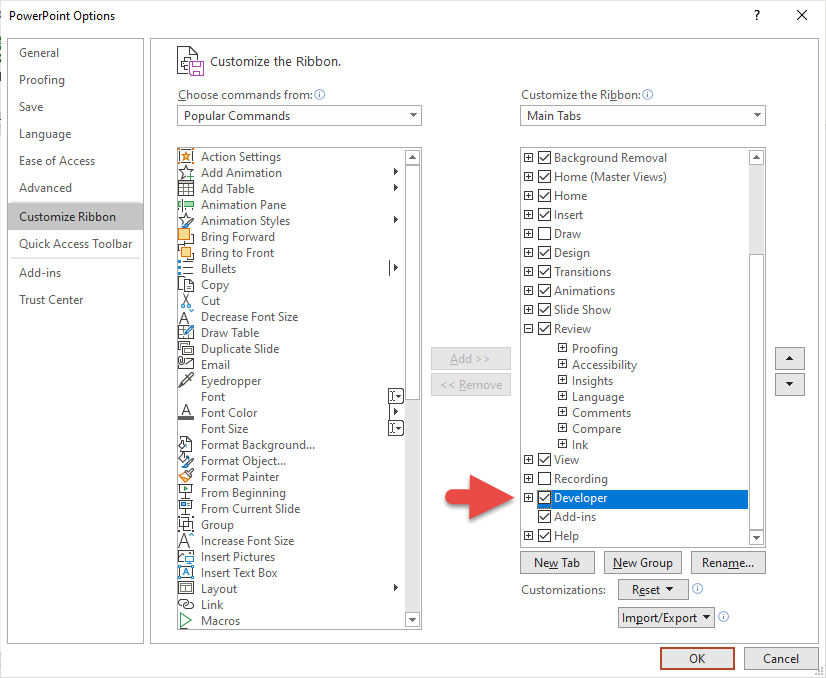
Enable ‘Developer’ Tab in the Ribbon
You should to enable the Developer tab on the Ribbon before creating VBA code. To do so choose File -> Options then click on ‘Customize Ribbon’ and check the box next to ‘Developer’ tab in the right pane.
Create PowerPoint Macro
This is a simple example of a PowerPoint VBA Macro:
Sub SavePresentationAsPDF()
Dim pptName As String
Dim PDFName As String
' Save PowerPoint as PDF
pptName = ActivePresentation.FullName
' Replace PowerPoint file extension in the name to PDF
PDFName = Left(pptName, InStr(pptName, ".")) & "pdf"
ActivePresentation.ExportAsFixedFormat PDFName, 2 ' ppFixedFormatTypePDF = 2
End SubIt saves the active presentation as a PDF. Each line of code does the following:
- Creates variables for the PowerPoint name and PDF name
- Assigns the active presentation name to pptName variable
- Creates the full PDF name
- Saves the presentation as a PDF
PowerPoint Application
When VBA code is running within a PowerPoint Presentation, PowerPoint Application is the default application and it can be manipulated without explicitly reference. Create a New Presentation
To create a presentation, use the Add method of PowerPoint application.
Application.Presentations.Add
' or without explicit reference
Presentations.Add
VBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro — A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Learn More
Open a New Presentation
To open a new and blank presentation use the Add method of Application.Presentations collection
Presentations.AddOpen an Existing Presentation
To open a presentation which you have already created, use the Open method of Application.Presentations collection
Presentations.Open ("My Presentation.pptx")The code above assumes that the presentation is in the same directory as the PowerPoint Presentation containing the code.
Open and Assign to a Variable
You should assign the presentation you open to a variable so that you can manipulate it as per your requirements.
Dim ppt As Presentation
Set ppt = Presentations.Open("My Presentation.pptx")VBA Programming | Code Generator does work for you!
Refer to Active Presentation
Use the reference ActivePresentation to manipulate the Presentation active in the GUI when the VBA code is executed.
' Print the name of the ActivePresentation to the Immediate Window
Debug.Print ActivePresentation.NameSave Current Presentation
The statement below will save the Active Presentation if it was saved before. It it has not been saved then you will be prompted with the ‘Save As’ dialog.
ActivePresentation.SaveClose Current Presentation
The statement below will close the Active Presentation even if it was not saved after the last edit.
ActivePresentation.CloseUseful References
Assign Existing Presentation (by name) to Variable
Dim myPresentationByName As Presentation
Set myPresentationByName = Application.Presentations("My Presentation")AutoMacro | Ultimate VBA Add-in | Click for Free Trial!
Assign Active Slide to Variable
Dim currentSlide As Slide
Set currentSlide = Application.ActiveWindow.View.SlideAssign slide by Index to Variable
Dim mySlide As Slide
Set mySlide = ActivePresentation.Slides(11)Count Number of Slides
Dim slideCount As Long
slideCount = ActivePresentation.Slides.CountGet Slide Index Number of Current Slide
Dim currentSlideIndex As Integer
currentSlideIndex = Application.ActiveWindow.View.Slide.SlideIndexAutoMacro | Ultimate VBA Add-in | Click for Free Trial!
Add a Blank Slide to End of Slide Show
Dim slideCount As Long
Dim newSlide as Slide
slideCount = ActivePresentation.Slides.Count
Set newSlide = ActivePresentation.Slides.Add(slideCount + 1, 12)
' or as ppLayoutBlank = 12
Set newSlide = ActivePresentation.Slides.Add(slideCount + 1, ppLayoutBlank)Add a slide after current slide
Dim newSlide As Slide
Dim currentSlideIndex as Integer
currentSlideIndex = Application.ActiveWindow.View.Slide.SlideIndex
Set newSlide = ActivePresentation.Slides.Add(currentSlideIndex, ppLayoutBlank)Delete a Slide
Dim currentSlideIndex as Integer
currentSlideIndex = Application.ActiveWindow.View.Slide.SlideIndex
ActivePresentation.Slides(currentSlideIndex).DeleteGo to a Specific Slide
' This will take you to slide number 4
Application.ActiveWindow.View.GotoSlide (4)AutoMacro | Ultimate VBA Add-in | Click for Free Trial!
Move Slide
You can move a slide from its old position to the new position
' Move from slide 3 to first slide
Dim oldPosition as integer, dim newPosition as integer
oldPosition = 3
newPosition = 1
ActivePresentation.Slides(oldPosition).MoveTo toPos:=newPositionLoop Through All Slides
You can do something with each slide or go through all slides to find a few slides and do something about with using the code;
Dim mySlide as Slide
For Each mySlide In ActivePresentation.Slides
' Do something with the current slide referred to in variable 'mySlide'
' Debug.Print mySlide.Name
Next SlideLoop through All Shapes of Active Slide
The power of PowerPoint can be realized by using ‘Shapes.’ The code below loops through all the shapes on the current slide so that you can manipulate them as you want;
Dim currentSlide as Slide
Dim shp as Shape
Set currentSlide = Application.ActiveWindow.View.Slide
For Each shp In currentSlide.Shapes
' Do something with the current shape referred to in variable 'shp'
' For example print the name of the shape in the Immediate Window
Debug.Print shp.Name
Next shpLoop through All shapes in All Slides
You can loop through all the shapes in the presentation by adding a loop to go through all slides.
Dim currentSlide as Slide
Dim shp as Shape
For Each currentSlide In ActivePresentation.Slides
For Each shp In currentSlide.Shapes
' Do something with the current shape referred to in variable 'shp'
Debug.Print shp.Name
Next shp
Next currentSlideAutoMacro | Ultimate VBA Add-in | Click for Free Trial!
Loop through All TextBoxes of Active Slide
TextBoxes are the most often used Shape in PowerPoint presentations. You can loop through all the Text Boxes by adding a check for ‘Shape Type.’ TexBoxes have the shape type defined as the VBA constant msoTextBox (the numerical value of the constant is 17)
Dim currentSlide as Slide
Dim shp as Shape
Set currentSlide = Application.ActiveWindow.View.Slide
For Each shp In currentSlide.Shapes
' Check if the shape type is msoTextBox
If shp.Type = 17 Then ' msoTextBox = 17
'Print the text in the TextBox
Debug.Print shp.TextFrame2.TextRange.Text
End If
Next shpLoop through All TextBoxes in All Slides
Again, you can loop through all the textboxes in the presentation by adding a loop to go through all slides.
Dim currentSlide as Slide Dim shp as Shape
For Each currentSlide In ActivePresentation.Slides
For Each shp In currentSlide.Shapes
' Check if the shape type is msoTextBox
If shp.Type = 17 Then ' msoTextBox = 17
' Do something with the TextBox referred to in variable 'shp'
Debug.Print shp.TextFrame2.TextRange.Text
End If
Next shp
Next currentSlideCopy Selected slides to new PPT Presentation
To copy certain slides to a new presentations, first select the desired slides in the existing presentation and then run the code below;
Dim currentPresentation as Presentation
Dim currentSlide as Slide
Dim newPresentation as Presentation
' Save reference to current presentation
Set currentPresentation = Application.ActivePresentation
' Save reference to current slide
Set currentSlide = Application.ActiveWindow.View.Slide
' Add new Presentation and save to a reference
Set NewPresentation = Application.Presentations.Add
' Copy selected slides
Selection.Copy
' Paste it in new Presentation
NewPresentation.Slides.PasteCopy Active Slide to End of Active Presentation
' Copy current slide
Application.ActiveWindow.View.Slide.Copy
' Paste at the end
ActivePresentation.Slides.PasteAutoMacro | Ultimate VBA Add-in | Click for Free Trial!
Useful PowerPoint Macro Examples
Here are some useful macro examples showing how to do tasks. These will also demonstrate the concepts described above.
Change Slide During Slide Show
Sub ChangeSlideDuringSlideShow()
Dim SlideIndex As Integer
Dim SlideIndexPrevious As Integer
' Change Current slide to selected slide 4 during during slide show
SlideIndex = 4
' Index of the current slide show window is 1 in the SlideShowWindows collection
SlideIndexPrevious = SlideShowWindows(1).View.CurrentShowPosition
SlideShowWindows(1).View.GotoSlide SlideIndex
End SubChange Font on All Slides in All TextBoxes
Sub ChangeFontOnAllSlides()
Dim mySlide As slide
Dim shp As Shape
' Change Font Size on all Slides
For Each mySlide In ActivePresentation.Slides
For Each shp In mySlide.Shapes
If shp.Type = 17 Then ' msoTextBox = 17
' Change Fontsize to 24
shp.TextFrame.TextRange.Font.Size = 24
End If
Next shp
Next mySlide
End SubChange Case From Upper to Normal in All TextBoxes
Sub ChangeCaseFromUppertoNormal()
Dim mySlide As slide
Dim shp As Shape
' Change From Upper Case to Normal Case for all slides
For Each mySlide In ActivePresentation.Slides
For Each shp In mySlide.Shapes
If shp.Type = 17 Then ' msoTextBox = 17
' Change Upper Case to Normal Case
shp.TextFrame2.TextRange.Font.Allcaps = False
End If
Next shp
Next mySlide
End SubAutoMacro | Ultimate VBA Add-in | Click for Free Trial!
Toggle Case between Upper and Normal in All TextBoxes
Sub ToggleCaseBetweenUpperAndNormal()
Dim mySlide As slide
Dim shp As Shape
' Toggle between Upper Case and Normal Case for all slides
For Each mySlide In ActivePresentation.Slides
For Each shp In mySlide.Shapes
If shp.Type = 17 Then ' msoTextBox = 17
' Toggle between Upper Case and Normal Case
shp.TextFrame2.TextRange.Font.Allcaps = _
Not shp.TextFrame2.TextRange.Font.Allcaps
End If
Next shp
Next mySlide
End SubRemove Underline from Descenders
In typography, a descender is the portion of a letter that extends below the baseline of a font. In most fonts, descenders are reserved for lowercase characters such as g, j, q, p, y, and sometimes f.
When you underline text, it does not look nice under descenders. Here is the code to remove underline from all such characters g, j, p, q, and y in the whole Presentation.
Sub RemoveUnderlineFromDescenders()
Dim mySlide As slide
Dim shp As Shape
Dim descenders_list As String
Dim phrase As String
Dim x As Long
' Remove underlines from Descenders
descenders_list = "gjpqy"
For Each mySlide In ActivePresentation.Slides
For Each shp In mySlide.Shapes
If shp.Type = 17 Then ' msoTextBox = 17
' Remove underline from letters "gjpqy"
With shp.TextFrame.TextRange
phrase = .Text
For x = 1 To Len(.Text)
If InStr(descenders_list, Mid$(phrase, x, 1)) > 0 Then
.Characters(x, 1).Font.Underline = False
End If
Next x
End With
End If
Next shp
Next mySlide
End SubRemove Animations From All Slides
Use the code below to remove all animations set in a Presentation.
Sub RemoveAnimationsFromAllSlides()
Dim mySlide As slide
Dim i As Long
For Each mySlide In ActivePresentation.Slides
For i = mySlide.TimeLine.MainSequence.Count To 1 Step -1
'Remove Each Animation
mySlide.TimeLine.MainSequence.Item(i).Delete
Next i
Next mySlide
End SubSave Presentation As PDF
You can easily save Active Presentation in PDF format.
Sub SavePresentationAsPDF()
Dim pptName As String
Dim PDFName As String
' Save PowerPoint as PDF
pptName = ActivePresentation.FullName
' Replace PowerPoint file extension in the name to PDF
PDFName = Left(pptName, InStr(pptName, ".")) & "pdf"
ActivePresentation.ExportAsFixedFormat PDFName, 2 ' ppFixedFormatTypePDF = 2
End SubAutoMacro | Ultimate VBA Add-in | Click for Free Trial!
Find and Replace Text
You can find and replace text in All TextBoxes of All Slides. After the fist instance of the text you want to find (defined by findWhat) you need to loop through the Find command to find other instances, if any.
Sub FindAndReplaceText()
Dim mySlide As slide
Dim shp As Shape
Dim findWhat As String
Dim replaceWith As String
Dim ShpTxt As TextRange
Dim TmpTxt As TextRange
findWhat = "jackal"
replaceWith = "fox"
' Find and Find and Replace
For Each mySlide In ActivePresentation.Slides
For Each shp In mySlide.Shapes
If shp.Type = 17 Then ' msoTextBox = 17
Set ShpTxt = shp.TextFrame.TextRange
'Find First Instance of "Find" word (if exists)
Set TmpTxt = ShpTxt.Replace(findWhat, _
Replacewhat:=replaceWith, _
WholeWords:=True)
'Find Any Additional instances of "Find" word (if exists)
Do While Not TmpTxt Is Nothing
Set ShpTxt = ShpTxt.Characters(TmpTxt.Start + TmpTxt.Length, ShpTxt.Length)
Set TmpTxt = ShpTxt.Replace(findWhat, _
Replacewhat:=replaceWith, _
WholeWords:=True)
Loop
End If
Next shp
Next mySlide
End SubExport Slide As Image
You can export Current SLide (or any other slide) as a PNG or JPG (JPEG) or BMP image.
Sub ExportSlideAsImage()
Dim imageType As String
Dim pptName As String
Dim imageName As String
Dim mySlide As slide
' Export current Slide to Image
imageType = "png" ' or jpg or bmp
pptName = ActivePresentation.FullName
imageName = Left(pptName, InStr(pptName, ".")) & imageType
Set mySlide = Application.ActiveWindow.View.slide
mySlide.Export imageName, imageType
End SubResize Image To Cover Full Slide
Sub ResizeImageToCoverFullSlide()
Dim mySlide As slide
Dim shp As Shape
' Resize Image to full slide size
' Change height and width of the first shape on the current slide
' to fit the slide dimensions
Set mySlide = Application.ActiveWindow.View.slide
Set shp = mySlide.Shapes(1)
''
'' Replace two statemetns above with
'' the following statement if you want to
'' expand the currently selected shape
'' will give error if nothing is selected
'Set shp = ActiveWindow.Selection.ShapeRange(1)
With shp
.LockAspectRatio = False
.Height = ActivePresentation.PageSetup.SlideHeight
.Width = ActivePresentation.PageSetup.SlideWidth
.Left = 0
.Top = 0
End With
End SubExit All Running Slide Shows
If you have multiple Slide Shows open at the same time then you can close all of them using the macro below.
Sub ExitAllRunningSlideShows()
Do While SlideShowWindows.Count > 0
SlideShowWindows(1).View.Exit
Loop
End SubAutoMacro | Ultimate VBA Add-in | Click for Free Trial!
Automating PowerPoint from Excel
You can also connect to PowerPoint though other applications (like Excel and Word). As as first step, you must refer to an instance of PowerPoint.
There are two ways of doing it – early binding and late binding .
Open PowerPoint – Early Binding
In ‘Early Binding’ you must explicitly set a reference to ‘Microsoft PowerPoint 16 Object Library’ (for MS Office 2019) in the VBE (Visual Basic Editor) using the option Tools->References.
' Early Binding
Dim pptApp As Application
Set pptApp = New PowerPoint.ApplicationOpen PowerPoint – Late Binding
In ‘Late Binding’ application variable is declared as an object and VBA engine connects to the correct application at run time.
' Late Binding
Dim pptApp As Object
Set pptApp = CreateObject("PowerPoint.Application")Make Application Visible
After setting the reference to PowperPoint application, you may need to make it visible.
pptApp.Visible = TrueAutoMacro | Ultimate VBA Add-in | Click for Free Trial!
Maniplulate PowerPoint
You can use all the methods to manipulate presentations, from within PowerPoint, described above from Excel by just adding the reference to PowerPoint created by you above.
For example
Presentations.Open ("My Presentation.pptx")has to be used liked this
pptApp .Presentations.Open ("My Presentation.pptx")Close the Application
Once you have completed what you wanted to do with the PowerPoint application you must close it and should release the reference.
pptApp.Quit
Set pptApp = NothingCopy From Excel to PowerPoint
This code will copy a range from Excel to PowerPoint:
Note: It has been kept as simple as possible to show how a range from Excel can be copied to PowerPoint using VBA.
Sub copyRangeToPresentation()
' Open New PowerPoint Instance
Set pptApp = CreateObject("PowerPoint.Application")
With pptApp
' Create A New Presentation
Set ppt = .Presentations.Add
' Add A Blank Slide
Set newSlide = ppt.Slides.Add(1, 12) ' ppLayoutBlank = 12
' Copy Range from Active Sheet in Excel
ActiveSheet.Range("A1:E10").Copy
' Paste to Powerpoint as an Image
newSlide.Shapes.PasteSpecial DataType:=2 '2 = ppPasteEnhancedMetafile
' Switch to PowerPoint
.Activate
End With
End SubPowerPoint VBA FAQs
What are macros in PPT?
A Macro is a general term that refers to a set of programming instructions that automates tasks. PowerPoint (PPT) Macros automate tasks in PowerPoint using the VBA programming language.
How do I use VBA in PowerPoint?
To use VBA in PowerPoint, open the VBA Editor (ALT + F11 or Developer > Visual Basic).
How do I create a Macro in PowerPoint?
1. Open the VBA Editor (ALT + F11 or Developer > Visual Basic)
2. Go to Insert > Module to create a Code Module
3. Type ‘Sub HelloWorld’ and press Enter
4. In between the lines ‘Sub HelloWorld’ and ‘End Sub’, type ‘MsgBox “Hello World!’
5. You’ve created a Macro!
6. Now press ‘F5’ to run the Macro
Written by: Vinamra Chandra
Excel VBA PowerPoint Tutorial
VBA is a powerful tool which can be used within any area of Microsoft integrated tools. Like MS Excel, Powerpoint also has a provision for creating a macro and automating the presentation. The automation can be of any form. You have seen presentations where the slides are so big and detailed, which sometimes end up having 50+ slides just to cover a training topic or a report. So instead of adding the charts in PowerPoint from Excel, we can create a code which will directly copy the charts from Excel and paste that into PowerPoint slide.
How to Create a PowerPoint Presentation From Excel VBA?
Below is the example to create a powerpoint presentation Using VBA Code in Excel:
You can download this VBA PowerPoint Excel Template here – VBA PowerPoint Excel Template
VBA PowerPoint Example
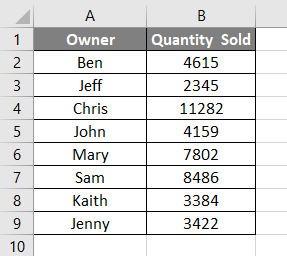
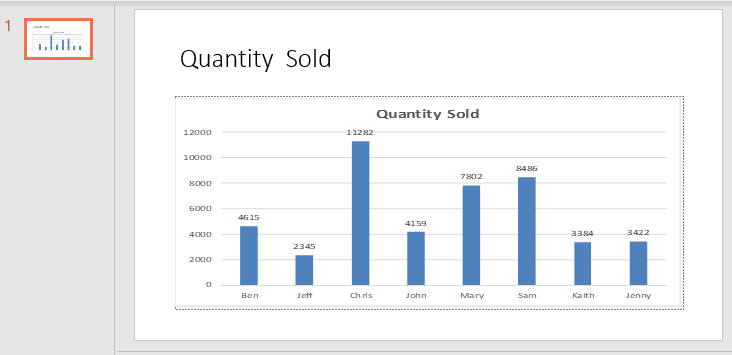
Let’s create a chart first in excel. For that, we need data. Below we have some sales data of 8 salespersons.
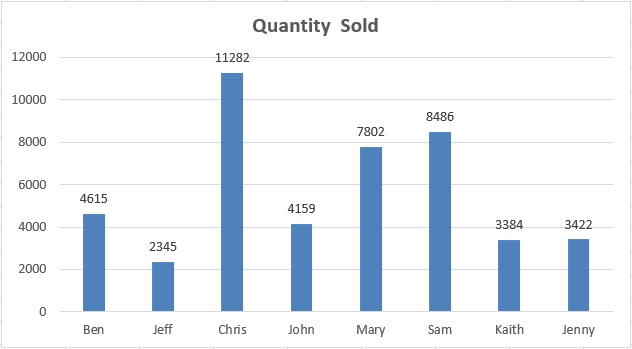
Now let’s create a Column Chart or Graph with the help of the above data. We will see below, we have now a column chart with the title Quantity Sold and all labels inserted.
Now our task is to get this graph in PowerPoint slide as it is showing here with the title of the chart as the title of PowerPoint slide. For this, we need to enable the PowerPoint in VBA.
Follow the below steps:
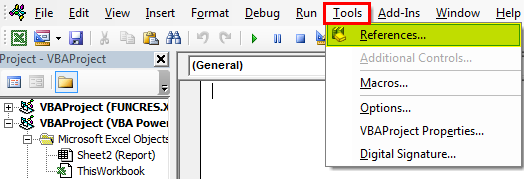
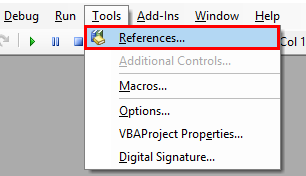
Step 1: Go to VBA Tool menu as shown below and select References… option as shown below.
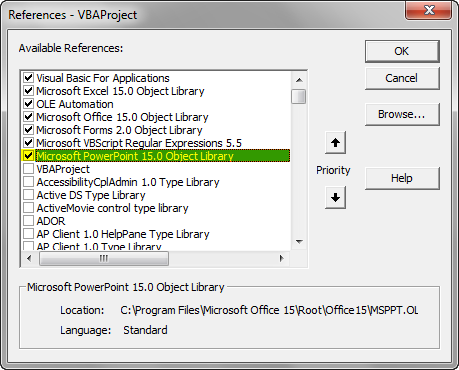
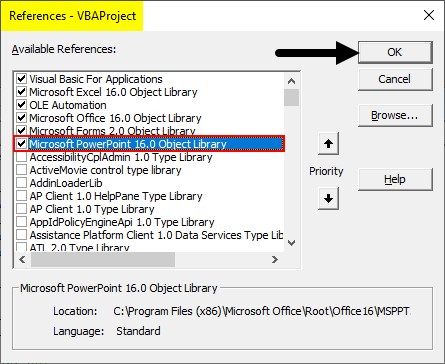
Step 2: Once we do that we will get a References VBA Project windows. From that list select MS PowerPoint 15.0 Object Library as shown below. This will activate all the commands related to MS PowerPoint in VBA. Without this, we cannot run VBA in PowerPoint. Check the box of mentioned Library and click on Ok.
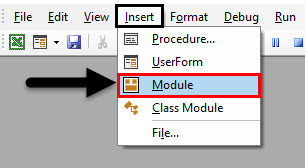
Step 3: Now for writing the code for VBA PowerPoint, we need a module. To get a new module, go to Insert menu and select a Module option as shown below.
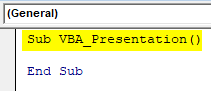
Step 4: In that module write the subcategory of VBA PowerPoint or in any other name as per your need as shown below.
Code:
Sub VBA_Presentation() End Sub
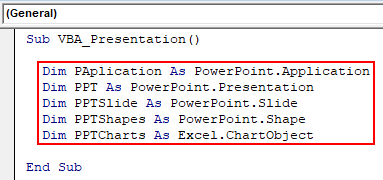
Step 5: Now for creating a presentation with the help of Chart in excel, we need few Variables. Let’s consider 5 variables as:
- PApplication for PowerPoint Application.
- PPT for PowerPoint Presentation,
- PPTSlide for PowerPoint Slide,
- PPTShapes for PowerPoints,
- PPTCharts for Excel Chart Object.
Code:
Sub VBA_Presentation() Dim PAplication As PowerPoint.Application Dim PPT As PowerPoint.Presentation Dim PPTSlide As PowerPoint.Slide Dim PPTShapes As PowerPoint.Shape Dim PPTCharts As Excel.ChartObject End Sub
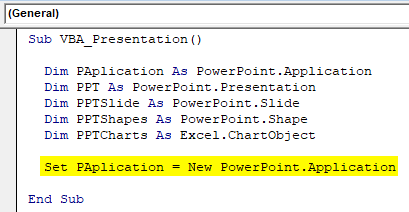
Step 6: Now use Set command to add New PowerPoint Application as shown below.
Code:
Sub VBA_Presentation() Dim PAplication As PowerPoint.Application Dim PPT As PowerPoint.Presentation Dim PPTSlide As PowerPoint.Slide Dim PPTShapes As PowerPoint.Shape Dim PPTCharts As Excel.ChartObject Set PAplication = New PowerPoint.Application End Sub
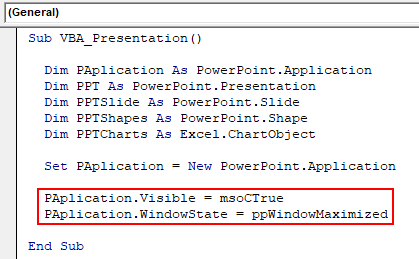
Step 7: In a line of code, make PowerPoint Application visible and use msoCTrue for mysteriously evaluating the incorrect way. And after that, the same application will get be used as Maximized in PowerPoint to get the full view.
Code:
Sub VBA_Presentation() Dim PAplication As PowerPoint.Application Dim PPT As PowerPoint.Presentation Dim PPTSlide As PowerPoint.Slide Dim PPTShapes As PowerPoint.Shape Dim PPTCharts As Excel.ChartObject Set PAplication = New PowerPoint.Application PAplication.Visible = msoCTrue PAplication.WindowState = ppWindowMaximized End Sub
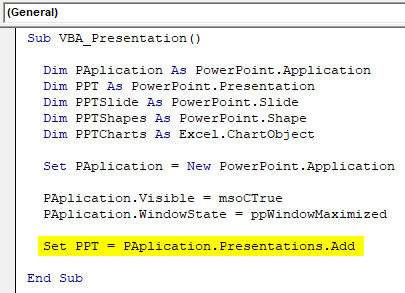
Step 8: Now set the PPT which is our presentation to add in MS PowerPoint Application,
Code:
Sub VBA_Presentation() Dim PAplication As PowerPoint.Application Dim PPT As PowerPoint.Presentation Dim PPTSlide As PowerPoint.Slide Dim PPTShapes As PowerPoint.Shape Dim PPTCharts As Excel.ChartObject Set PAplication = New PowerPoint.Application PAplication.Visible = msoCTrue PAplication.WindowState = ppWindowMaximized Set PPT = PAplication.Presentations.Add End Sub
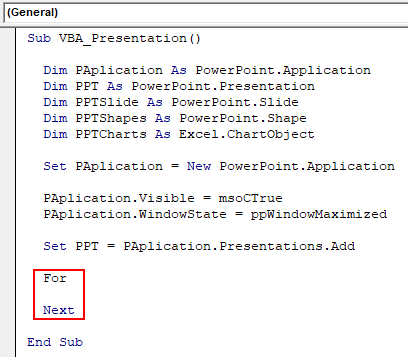
Step 9: Now we will use a combination of For-Next and If-Else loop. Starting with For-Next Loop.
Code:
Sub VBA_Presentation() Dim PAplication As PowerPoint.Application Dim PPT As PowerPoint.Presentation Dim PPTSlide As PowerPoint.Slide Dim PPTShapes As PowerPoint.Shape Dim PPTCharts As Excel.ChartObject Set PAplication = New PowerPoint.Application PAplication.Visible = msoCTrue PAplication.WindowState = ppWindowMaximized Set PPT = PAplication.Presentations.Add For Next End Sub
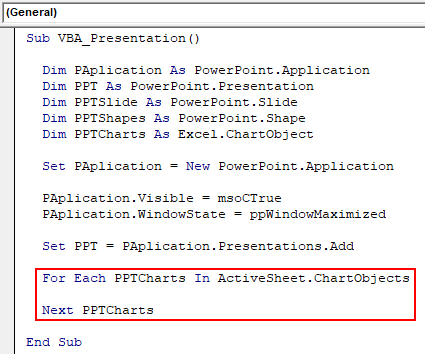
Step 10: In For loop of PPTCharts, first active charts in excel.
Code:
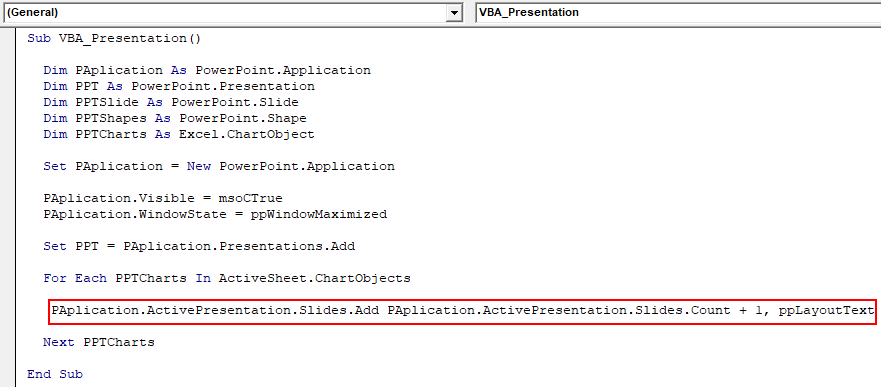
Sub VBA_Presentation() Dim PAplication As PowerPoint.Application Dim PPT As PowerPoint.Presentation Dim PPTSlide As PowerPoint.Slide Dim PPTShapes As PowerPoint.Shape Dim PPTCharts As Excel.ChartObject Set PAplication = New PowerPoint.Application PAplication.Visible = msoCTrue PAplication.WindowState = ppWindowMaximized Set PPT = PAplication.Presentations.Add For Each PPTCharts In ActiveSheet.ChartObjects Next PPTCharts End Sub
Step 11: Below is the code for pasting the chart from excel to PowerPoint slide. Use code to add a slide into defined PAplication adding +1 slide each time we run the code.
Code:
Sub VBA_Presentation() Dim PAplication As PowerPoint.Application Dim PPT As PowerPoint.Presentation Dim PPTSlide As PowerPoint.Slide Dim PPTShapes As PowerPoint.Shape Dim PPTCharts As Excel.ChartObject Set PAplication = New PowerPoint.Application PAplication.Visible = msoCTrue PAplication.WindowState = ppWindowMaximized Set PPT = PAplication.Presentations.Add For Each PPTCharts In ActiveSheet.ChartObjects PAplication.ActivePresentation.Slides.Add PAplication.ActivePresentation.Slides.Count + 1, ppLayoutText Next PPTCharts End Sub
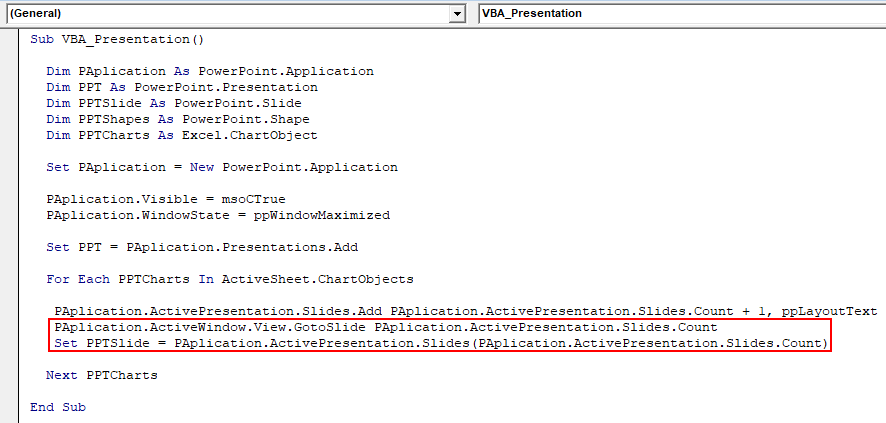
Step 12: Now on the continuation to the next line of code, use the below set of code to set an active window view. This will take use to slide after Chart gets pasted in PowerPoint presentation.
Code:
Sub VBA_Presentation() Dim PAplication As PowerPoint.Application Dim PPT As PowerPoint.Presentation Dim PPTSlide As PowerPoint.Slide Dim PPTShapes As PowerPoint.Shape Dim PPTCharts As Excel.ChartObject Set PAplication = New PowerPoint.Application PAplication.Visible = msoCTrue PAplication.WindowState = ppWindowMaximized Set PPT = PAplication.Presentations.Add For Each PPTCharts In ActiveSheet.ChartObjects PAplication.ActivePresentation.Slides.Add PAplication.ActivePresentation.Slides.Count + 1, ppLayoutText PAplication.ActiveWindow.View.GotoSlide PAplication.ActivePresentation.Slides.Count Set PPTSlide = PAplication.ActivePresentation.Slides(PAplication.ActivePresentation.Slides.Count) Next PPTCharts End Sub
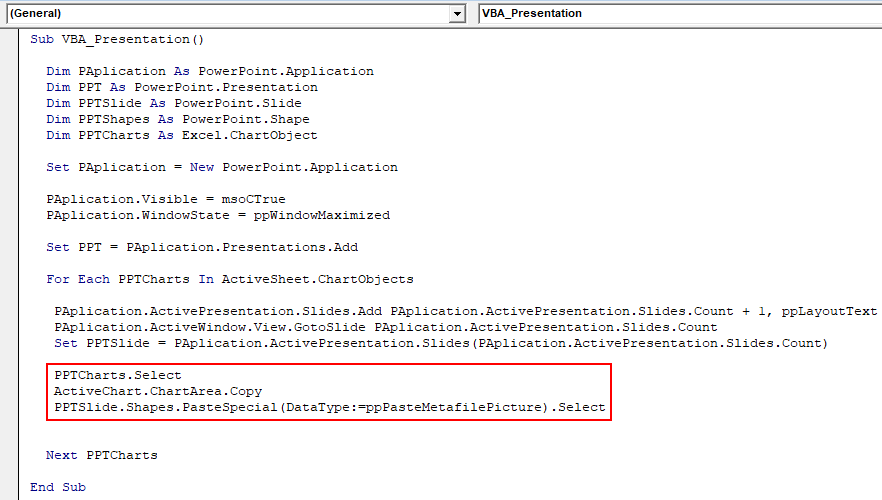
Step 13: Once done, select the PPTChart variable which we defined earlier. After that copy the selected active chart into the chart area where it will be placed. And use Paste Special command to paste the chart with pictures.
Code:
Sub VBA_Presentation() Dim PAplication As PowerPoint.Application Dim PPT As PowerPoint.Presentation Dim PPTSlide As PowerPoint.Slide Dim PPTShapes As PowerPoint.Shape Dim PPTCharts As Excel.ChartObject Set PAplication = New PowerPoint.Application PAplication.Visible = msoCTrue PAplication.WindowState = ppWindowMaximized Set PPT = PAplication.Presentations.Add For Each PPTCharts In ActiveSheet.ChartObjects PAplication.ActivePresentation.Slides.Add PAplication.ActivePresentation.Slides.Count + 1, ppLayoutText PAplication.ActiveWindow.View.GotoSlide PAplication.ActivePresentation.Slides.Count Set PPTSlide = PAplication.ActivePresentation.Slides(PAplication.ActivePresentation.Slides.Count) PPTCharts.Select ActiveChart.ChartArea.Copy PPTSlide.Shapes.PasteSpecial(DataType:=ppPasteMetafilePicture).Select Next PPTCharts End Sub
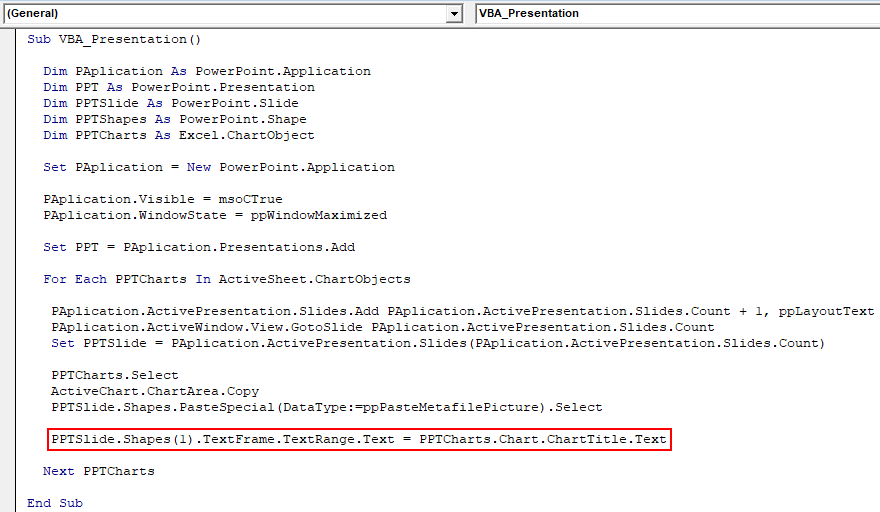
Step 14: Now select the shape of the Chart which is at first position as text range. And carry the same title which is “Quantity Sold” into the PowerPoint Presentation.
Code:
Sub VBA_Presentation() Dim PAplication As PowerPoint.Application Dim PPT As PowerPoint.Presentation Dim PPTSlide As PowerPoint.Slide Dim PPTShapes As PowerPoint.Shape Dim PPTCharts As Excel.ChartObject Set PAplication = New PowerPoint.Application PAplication.Visible = msoCTrue PAplication.WindowState = ppWindowMaximized Set PPT = PAplication.Presentations.Add For Each PPTCharts In ActiveSheet.ChartObjects PAplication.ActivePresentation.Slides.Add PAplication.ActivePresentation.Slides.Count + 1, ppLayoutText PAplication.ActiveWindow.View.GotoSlide PAplication.ActivePresentation.Slides.Count Set PPTSlide = PAplication.ActivePresentation.Slides(PAplication.ActivePresentation.Slides.Count) PPTCharts.Select ActiveChart.ChartArea.Copy PPTSlide.Shapes.PasteSpecial(DataType:=ppPasteMetafilePicture).Select PPTSlide.Shapes(1).TextFrame.TextRange.Text = PPTCharts.Chart.ChartTitle.Text Next PPTCharts End Sub
This completes the code for VBA PowerPoint.
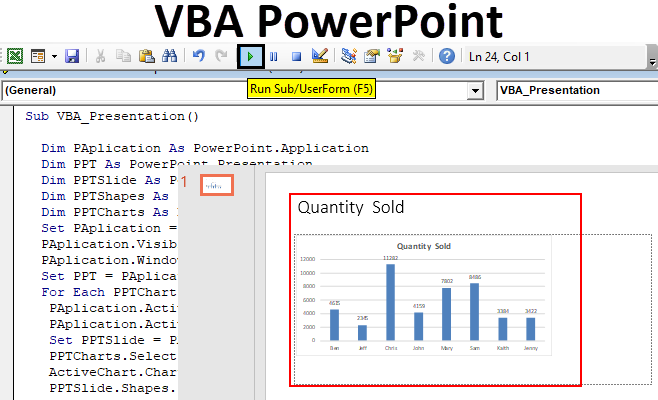
Step 15: Now compile the code step by step to know if any line of code has an error by pressing function key F8. And after that run the code by clicking on the Play button which is below the menu bar as shown below.
We will get the chart posted in PowerPoint file in the first slide of it as shown below.
As the code is big, so the complete code can be seen in the text box below.
Pros of Excel VBA PowerPoint
- Using VBA in Powerpoint makes easy to handle if a ppt file has so many slides with huge content.
- VBA with Powerpoint gives a touch of automation even with limited functions available.
Cons of Excel VBA PowerPoint
- We need to select the Microsoft PowerPoint 15.0 Object Library from the Reference option located in Tool menu option, which we need in the start of example-1, every time we run the code for PowerPoint.
Things to Remember
- Save the file in the Macro-Enable Presentation format after writing the code. This will help us to avoid losing the code and using the same multiple time in the future.
- Recoding feature will not work here as we need to jump from Excel to PowerPoint changing the interface between the pages.
- Always compile the code before running. This will help you to find the error in the code. This is quite helpful when we write big lines of code.
- To run and implement the code we need to open the excel sheet with Chart that we want to paste it in PowerPoint slide.
- We can align the chart in PowerPoint as per our needs.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to VBA PowerPoint. Here we discuss how to create PowerPoint Presentation From Excel Using VBA Code along with a practical example and downloadable excel template. You can also go through our other suggested articles –
- VBA Delete Column
- Status Bar in Excel
- VBA Remove Duplicates
- Create Spreadsheet in Excel
In this post we will explore how VBA paste from Excel to PowerPoint objects such as a Range, Chart or other element. Below you will find working code snippets. We will learn also to modify this routine to address different VBA Copy Paste from Excel to PowerPoint.
We will start with an example of VBA Paste Excel Range into PowerPoint as Picture as this is the most typical scenario. For this I created a custom function called CopyFromExcelToPPT:
Function CopyFromExcelToPPT(excelFilePath As String, sheetName As String, rngCopy As String, dstSlide As Long, Optional shapeTop As Long, Optional shapeLeft As Long)
On Error GoTo ErrorHandl 'Handle Errors
'Set Variables and Open Excel
Dim eApp As Excel.Application, wb As Excel.Workbook, ppt As PowerPoint.Presentation
Set eApp = New Excel.Application
eApp.Visible = False
Set wb = eApp.Workbooks.Open(excelFilePath)
Set ppt = ActivePresentation
'Copy cells in Excel
wb.Sheets(sheetName).Range(rngCopy).Copy
'Paste into first slide in active PowerPoint presentation
ppt.Slides(dstSlide).Shapes.PasteSpecial ppPasteBitmap
'Close and clean-up Excel
wb.Close SaveChanges:=False
eApp.Quit
Set wb = Nothing: Set eApp = Nothing
'Move the new shape if left/top provided
If Not (IsMissing(shapeTop)) Then
With ppt.Slides(dstSlide).Shapes(ppt.Slides(dstSlide).Shapes.Count)
.Left = shapeLeft
.Top = shapeTop
End With
End If
CopyFromExcelToPPT = True
Exit Function
ErrorHandl:
'Make sure to close the workbook and Excel and return False
On Error Resume Next
If Not (eApp Is Nothing) Then
wb.Close SaveChanges:=False
eApp.Quit
End If
CopyFromExcelToPPT = False
End Function
What does the VBA Function do? In short you need to provide the following parameters:
- excelFilePath – full file path to the Excel from which you want to copy a VBA Range
- sheetName – the Sheet name from which you want to copy
- rngCopy – the VBA Range you want to copy
- dstSlide – the number of the slide (starting at 1) to which you want to copy the Range
- shapeTop – Optional. The Top position in pixels of the new pasted Shape
- shapeLeft – Optional. The Left position in pixels of the new pasted Shape
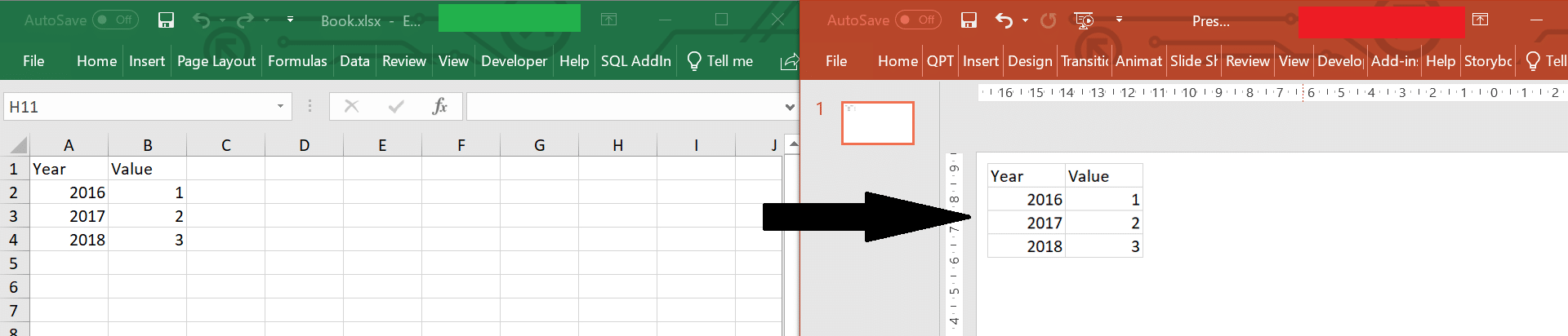
Let us use this function in the following scenario. We want to copy range A1:B4.
Let us use our function above for this scenario
Sub Test()
'Copy from Excel worksheet named Sheet1 the A1:B4 range
If CopyFromExcelToPPT("C:Book.xlsx", "Sheet1", "A1:B4", 1) Then
Debug.Print "Success"
Else
Debug.Print "Failure"
End If
End Sub
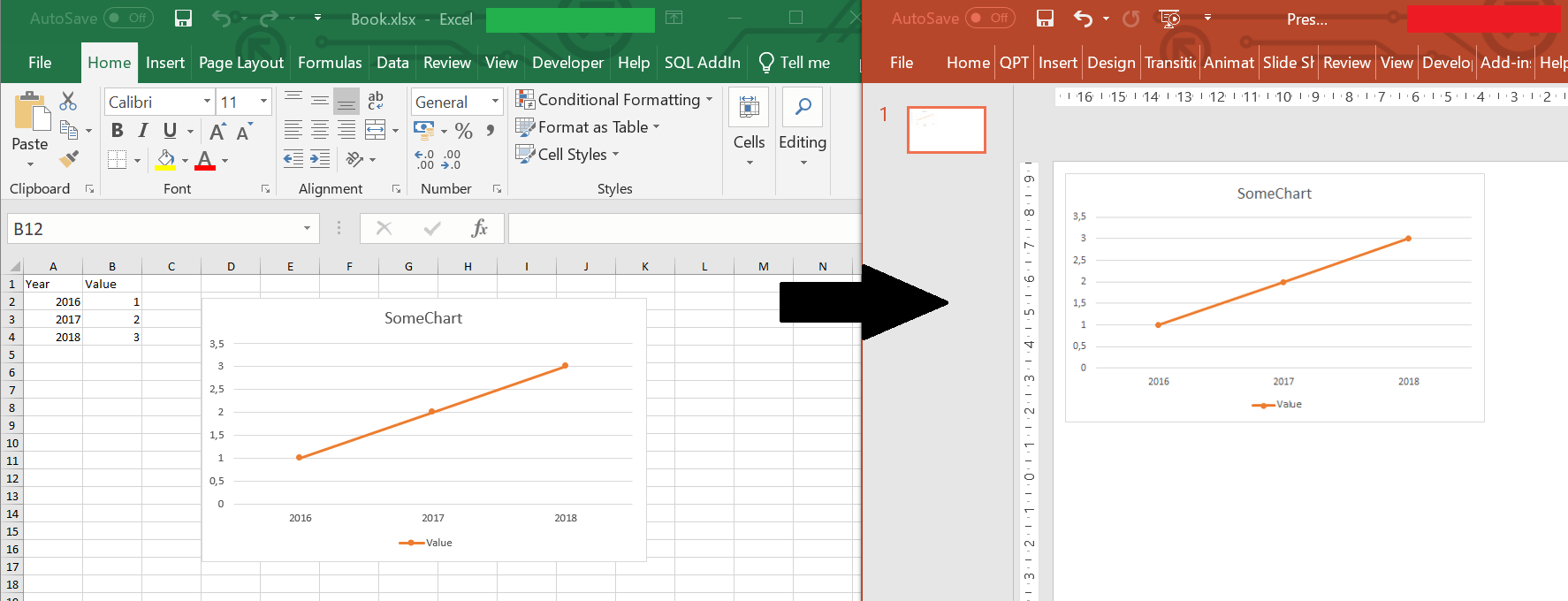
VBA Paste Chart from Excel to PowerPoint
Now an example of VBA Paste Excel Graph into PowerPoint as Picture as this is also a useful case. For this I created a custom function called CopyChartFromExcelToPPT:
Function CopyChartFromExcelToPPT(excelFilePath As String, sheetName As String, chartName As String, dstSlide As Long, Optional shapeTop As Long, Optional shapeLeft As Long)
On Error GoTo ErrorHandl 'Handle Errors
'Set Variables and Open Excel
Dim eApp As Excel.Application, wb As Excel.Workbook, ppt As PowerPoint.Presentation, ws As Excel.Worksheet
Set eApp = New Excel.Application
eApp.Visible = False
Set wb = eApp.Workbooks.Open(excelFilePath)
Set ppt = ActivePresentation
'Copy Chart in Excel
wb.Sheets(sheetName).ChartObjects(chartName).Copy
'Paste into first slide in active PowerPoint presentation
ppt.Slides(dstSlide).Shapes.PasteSpecial ppPasteBitmap
'Close and clean-up Excel
wb.Close SaveChanges:=False
eApp.Quit
Set wb = Nothing: Set eApp = Nothing
'Move the new shape if left/top provided
If Not (IsMissing(shapeTop)) Then
With ppt.Slides(dstSlide).Shapes(ppt.Slides(dstSlide).Shapes.Count)
.Left = shapeLeft
.Top = shapeTop
End With
End If
CopyChartFromExcelToPPT = True
Exit Function
ErrorHandl:
'Make sure to close the workbook and Excel and return False
On Error Resume Next
If Not (eApp Is Nothing) Then
wb.Close SaveChanges:=False
eApp.Quit
End If
CopyChartFromExcelToPPT = False
End Function
Again let us use it on the example below where we want to copy a Chart from a Excel Workbook to PowerPoint:
Example execution of the VBA Function below:
Sub Test()
If CopyChartFromExcelToPPT("C:Book.xlsx", "Sheet1", "Chart 1", 1) Then
Debug.Print "Success"
Else
Debug.Print "Failure"
End If
End Sub
If you want to place the Chart at a specific place use the shapeTop and shapeLeft arguments. The below will place the chart at 10 pixels from the Top and 100 pixels from the Left.
Sub Test()
If CopyChartFromExcelToPPT("C:Book.xlsx", "Sheet1", "Chart 1", 1, 10, 100) Then
Debug.Print "Success"
Else
Debug.Print "Failure"
End If
End Sub
Changing Height / Width of pasted elements
In the examples above we didn’t change the Width and Height of the pasted Range or Chart. To do this use the adjusted functions below:
Function CopyFromExcelToPPT(excelFilePath As String, sheetName As String, rngCopy As String, dstSlide As Long, Optional shapeTop As Long, Optional shapeLeft As Long, Optional shapeHeight As Long, Optional shapeWidth As Long)
On Error GoTo ErrorHandl 'Handle Errors
'Set Variables and Open Excel
Dim eApp As Excel.Application, wb As Excel.Workbook, ppt As PowerPoint.Presentation
Set eApp = New Excel.Application
eApp.Visible = False
Set wb = eApp.Workbooks.Open(excelFilePath)
Set ppt = ActivePresentation
'Copy cells in Excel
wb.Sheets(sheetName).Range(rngCopy).Copy
'Paste into first slide in active PowerPoint presentation
ppt.Slides(1).Shapes.PasteSpecial ppPasteBitmap
'Close and clean-up Excel
wb.Close SaveChanges:=False
eApp.Quit
Set wb = Nothing: Set eApp = Nothing
'Move the new shape if left/top provided
If Not (IsMissing(shapeTop)) Then
With ppt.Slides(1).Shapes(ppt.Slides(1).Shapes.Count)
.Left = shapeLeft
.Top = shapeTop
End With
End If
'Resize the shape if height/width provided
If Not (IsMissing(shapeHeight)) Then
With ppt.Slides(dstSlide).Shapes(ppt.Slides(1).Shapes.Count)
.Height = shapeHeight
.Width = shapeWidth
End With
End If
CopyFromExcelToPPT = True
Exit Function
ErrorHandl:
'Make sure to close the workbook and Excel and return False
On Error Resume Next
If Not (eApp Is Nothing) Then
wb.Close SaveChanges:=False
eApp.Quit
End If
CopyFromExcelToPPT = False
End Function
Function CopyChartFromExcelToPPT(excelFilePath As String, sheetName As String, chartName As String, dstSlide As Long, Optional shapeTop As Long, Optional shapeLeft As Long, Optional shapeHeight As Long, Optional shapeWidth As Long)
On Error GoTo ErrorHandl 'Handle Errors
'Set Variables and Open Excel
Dim eApp As Excel.Application, wb As Excel.Workbook, ppt As PowerPoint.Presentation, ws As Excel.Worksheet
Set eApp = New Excel.Application
eApp.Visible = False
Set wb = eApp.Workbooks.Open(excelFilePath)
Set ppt = ActivePresentation
'Copy Chart in Excel
wb.Sheets(sheetName).ChartObjects(chartName).Copy
'Paste into first slide in active PowerPoint presentation
ppt.Slides(dstSlide).Shapes.PasteSpecial ppPasteBitmap
'Close and clean-up Excel
wb.Close SaveChanges:=False
eApp.Quit
Set wb = Nothing: Set eApp = Nothing
'Move the new shape if left/top provided
If Not (IsMissing(shapeTop)) Then
With ppt.Slides(dstSlide).Shapes(ppt.Slides(1).Shapes.Count)
.Height = shapeHeight
.Width = shapeWidth
End With
End If
'Resize the shape if height/width provided
If Not (IsMissing(shapeHeight)) Then
With ppt.Slides(dstSlide).Shapes(ppt.Slides(1).Shapes.Count)
.Height = shapeHeight
.Width = shapeWidth
End With
End If
CopyChartFromExcelToPPT = True
Exit Function
ErrorHandl:
'Make sure to close the workbook and Excel and return False
On Error Resume Next
If Not (eApp Is Nothing) Then
wb.Close SaveChanges:=False
eApp.Quit
End If
CopyChartFromExcelToPPT = False
End Function