Excel for Microsoft 365 Excel 2021 Excel 2019 Excel 2016 Excel 2013 Excel 2010 Excel 2007 More…Less
You can use Excel to create and edit connections to external data sources that are stored in a workbook or in a connection file. You can easily manage these connections, including creating, editing, and deleting them using the current Queries & Connections pane or the Workbook Connections dialog box (available in previous versions).
Data in an Excel workbook can come from two different locations. The data may be stored directly in the workbook, or it may be stored in an external data source, such as a text file, a database, or an Online Analytical Processing (OLAP) cube. The external data source is connected to the workbook through a data connection, which is a set of information that describes how to locate, log in, query, and access the external data source.
When you are connected to an external data source, you can also perform a refresh operation to retrieve the updated data. Each time that you refresh data, you see the most recent version of the data, including any changes that were made to the data since it was last refreshed.
Connection information can either be stored in the workbook or in a connection file, such as an Office Data Connection (ODC) file (.odc) or a Universal Data Connection (UDC) file (.udcx). Connection files are particularly useful for sharing connections on a consistent basis and for facilitating data source administration.
If you use a connection file to connect to a data source, Excel copies the connection information from the connection file into the Excel workbook. When you make changes by using the Connection Properties dialog box, you are editing the data connection information that is stored in the current Excel workbook, and not the original data connection file that may have been used to create the connection, indicated by the file name that is displayed in the Connection File property. Once you edit the connection information (with the exception of the Connection Name and Connection Description properties), the link to the connection file is removed and the Connection File property is cleared.
By using the Connection Properties dialog box or the Data Connection Wizard, you can use Excel to create an Office Data Connection (ODC) file (.odc). For more information, see Connection properties and Share data with ODC.
-
Do one of the following:
-
Create a new connection to the data source. For more information, see Move data from Excel to Access, Import or export text files, or Connect to SQL Server Analysis Services Database (Import).
-
Use an existing connection. For more information, see Connect to (Import) external data.
-
-
Save the connection information to a connection file by clicking Export Connection File on the Definition tab of the Connection Properties dialog box to display the File Save dialog box, and then save the current connection information to an ODC file.
Note The Queries & Connections pane is available in Microsoft Office 365 for Excel and Excel stand-alone version 2019 or later. It replaced the Workbook Connections dialog box which is available in Excel stand-alone versions 2010, 2013, and 2016.
The Queries & Connections pane (Select Data > Queries & Connections) In one location, you can get to all the information and commands you need to work with your external data. This pane has two tabs:
-
Queries Displays all the queries in the workbook. Right click a query to see available commands. For more information, see Manage queries.
-
Connections
Displays all the connections in the workbook. Right click a connection to see available commands. For more information, see Connection properties.
Note The Workbook Connections dialog box is available in Excel stand-alone versions 2010, 2013, and 2016, but was replaced in Microsoft Office 365 for Excel and Excel stand-alone version 2019 with the Queries & Connections pane.
The Workbook Connections dialog box (Select Data > Connections) helps you manage one or more connections to external data sources in your workbook.
You can use this dialog box to do the following:
-
Create, edit, refresh, and delete connections that are in use in the workbook.
-
Verify where external data is coming from, because, for example, the connection was defined by another user.
-
Show where each connection is used in the current workbook.
-
Diagnose an error message about connections to external data.
-
Redirect a connection to a different server or data source, or replace the connection file for an existing connection.
-
Display the Existing Connections dialog box to create new connections. For more information, see Connect to (Import) external data.
-
Display the Connection Properties dialog box to modify data connection properties, edit queries, and change parameters. For more information, see Connection properties.
-
Make it easy to create and share connection files with users.
To manage the connections in the current workbook, do one or more of the following:
Identify a connection
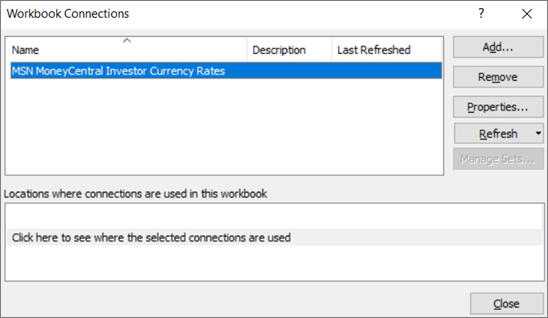
In the top portion of the dialog box, all connections in the workbook are displayed automatically with the following information:
|
Column |
Comment |
|---|---|
|
Name |
The name of the connection, defined in the Connection Properties dialog box. |
|
Description |
An optional description of the connection, defined in the Connection Properties dialog box. |
|
Last refreshed |
The date and time that the connection was last successfully refreshed. If blank, then the connection has never been refreshed. |
Add a connection
-
Click Add to display the Existing Connections dialog box. For more information, see Connect to (Import) external data.
Display connection information
-
Select a connection, and then click Properties to display the Connection Properties dialog box. For more information, see Connection properties.
Refresh the external data
-
Click the arrow next to Refresh, and then do one of the following:
-
To refresh specific connections, select one or more connections, and then click Refresh.
-
To refresh all connections in the workbook, clear all connections, and then click Refresh All.
-
To get status information about a refresh operation, select one or more connections, and then click Refresh Status.
-
To stop the current refresh operation, click Cancel Refresh.
-
For more information, see Refresh an external data connection in Excel.
Remove one or more connections
-
Select one or more connections to be removed from the workbook, and then click Remove.
Notes:
-
This button is disabled when the workbook is protected or an object, such as a PivotTable report, that uses the connection is protected.
-
Removing a connection only removes the connection and does not remove any object or data from the workbook.
-
Important: Removing a connection breaks the connection to the data source and may cause unintended consequences, such as different formula results and possible problems with other Excel features.
Display the locations of one or more connections in the workbook
-
Select one or more connections, and then under Locations where connections are used in this workbook, click the link Click here to see where the selected connections are used.
The following information is displayed.
|
Column |
Comment |
|---|---|
|
Sheet |
The worksheet where the connection is used. |
|
Name |
The Excel query name. |
|
Location |
The reference to a cell, range, or object. |
|
Value |
The value of a cell, or blank for a range of cells. |
|
Formula |
The formula of a cell, or for a range of cells. |
Selecting another connection at the top of the dialog box clears the display of the current information.
See Also
Power Query for Excel Help
Need more help?
Want more options?
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.
You all must have heard of Excel Workbook Connections but do know how to manage workbook connection in Excel? Well if you are not having any idea of enabling data connection in Excel workbook.
In that case our, this Excel workbook connections tutorial will help in grabbing every pinch of information reading this. So, that any Excel user can easily perform and manage external data connections in Excel.
What Is Data Connection In Excel?
Data of any Excel workbook can only be bring from different locations. Firstly, either the data is directly stored in your Excel workbook. Or secondly it may be saved in the external data source, like a database, an OLAP (Online Analytical Processing cube) or text file.
Using the data connection in Excel, external data sources are well connected with Excel workbook. Basically this data connection in Excel contains set of information about how to log in, query, locate, and perfectly access the external data source.
After connecting your excel workbook with external data source. One can easily use the refresh option to extract the updated data from their workbook. Using this way, user can get the most updated version of their data including the changes made in the data since it was last refreshed.
Well the Connection information can be stored in a connection file or in the workbook like Universal Data Connection (UDC) file (.udcx) or Office Data Connection (ODC) file (.odc)
These connection files are very useful to share connections on regular basis also to facilitate data source administration.
If you are using the connection file for connecting with the data source. Then in that case Excel will copies down the connection details from the connection file into your Excel workbook.
Different Ways To Perform Excel Workbook Connections
In this Excel workbook connections tutorial we will learn 3 different ways to use Data Connection In Excel 2010/2013/2016/2019:
- Workbook Connections dialog box
- Creating an Office Data Connection (ODC) file (.odc)
- Refresh external data connection
Method 1: Excel Workbook Connections Using Workbook Connections Dialog Box
Excel Workbook Connections dialog box option helps in easy managing of single or multiple connections with the external data sources of your workbook. Apart from this the Workbook Connections dialog box is helpful to perform the following tasks:
- It helps to edit, refresh, create and delete connections which are used in Excel workbook.
- Show the location of each connection that is already been used in the current Excel workbook.
- Easy diagnosis of error message regarding external data connections.
- With this option, user can either redirect connection to different data or to the different server. Or alternatively user can easily replace the connection file with the existing connection.
- It becomes too easy to make & share connection files.
Steps To Manage Excel Workbook Connection Using Workbook Connections Dialog Box
Here is how to manage connections in your current using Excel workbook i.e by using Workbook Connections dialog box:
Identify a connection
In the top portion of the dialog box, all connections in the workbook are displayed automatically with the following information:
| Column | Comment |
| Name | connection name is, defined within Connection Properties dialog box. |
| Description | A short description about connection, is mentioned in Connection Properties dialog box. |
| Last refreshed | when was the connection was last refreshed such as it’s date and time appears in this section. If it is blank, then it means that the connection has not refreshed yet. |
Add a connection
- Tap to the Add option to get the dialog box of Existing Connections.
Display Connection Information
- For this you need to choose a connection from the opened Existing Connections dialog box.
- Now hit the Properties option and this will open the dialog box of Connection Properties.
Refresh The External Data.
- Hit the arrow option present next to the Refresh option. After then perform anyone of the following:
- If you want to refresh any specific connections only, then make selections of those connections. After then tap to the Refresh option.
- For refreshing all connections of your workbook, just clear off all the connections. After that tap to the Refresh All option.
- If you want to get the status information about refresh operation then choose the connections about which you want to extract information. After then hit on the Refresh Status option.
- For stopping down the current running refresh operation just tap to the Cancel Refresh option.
Remove One Or More Connections
- Choose the connections which you wants to remove from your Excel workbook. After then tap to the Remove option.
Notes:
- Well this option appears disabled to you if your workbook is protected one or if it is an object, like PivotTable report, which uses the protected connection.
- Removing connection will only deletes off the connection. It will not remove any data or any object from your Excel workbook.
Important: By removing connection you are actually breaking the connection with the data source which may leads to cause unintentional consequences, Like different formula results or you may face difficulty in accessing Excel features.
Method 2: Excel Workbook Connections Using Refresh External Data Connection Option
User can connect their Excel workbook with an external data source, like to another Excel workbook, SQL Server database or an OLAP cube.
Well this connection information gets displayed on your workbook as PivotTable report, PivotChart, table.
For keeping the data of your Excel workbook updated you can make use of “Refresh” option to link the data with its source.
So whenever you will refresh your connection, you will only get the most current updated data.
Step To Use Refresh External Data Connection Option
For connections just tap to any cell of your Excel table which uses the connection. After then perform any of the following operation:
- Automatically refresh data when excel workbook is opened
- Automatically refresh data at regular interval
Step To Automatically Refresh Data When Excel Workbook Is Opened
- Tap to the cell present within the external data range.
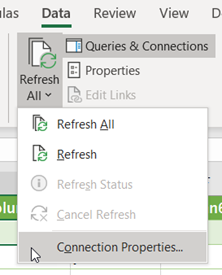
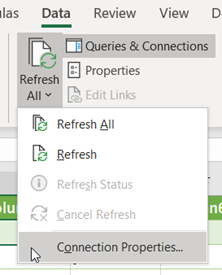
- Now on the Data tab, go to the Queries & Connections Hit the arrow key present within the Refresh All option, and from this tap to the Connection Properties.
- From the opened dialog box of Connection Properties dialog tap to the Usage tab, within Refresh control. After then choose the check box “Refresh data when opening the file”.
- In order to save your workbook with the complete query definition excluding external data. You need to choose the check box “Remove data from the external data range before saving the workbook”.
Step To Automatically refresh data at regular interval:
- Tap to the cell present within the external data range.
- Now on the Data tab, go to the Queries & Connections Hit the arrow key present within the Refresh All option, and from this tap to the Connection Properties.
- In the opened Connection Properties dialog box. Hit Usage tab option.
- Choose the check box Refresh every. After then set the minute interval that will automatically refresh your data after certain period of time.
Method 3: Excel Workbook Connections By Creating An Office Data Connection (ODC) File
By making use of the Data Connection Wizard or Connection Properties dialog box one can easily use their Excel worksheet to create an Office Data Connection (ODC) file (.odc).
- You can perform any of the following task:
- Make new connection with data source. To catch more information, have a look at following topics :
- Connect to SQL Server Analysis Services Database (Import)
- Import or export text files
- Move data from Excel to Access
- Make new connection with data source. To catch more information, have a look at following topics :
- Or you can just make use of the existing connection. For more information, see Connect to (Import) external data.
- After then save the connection detail into the connection file. For this, just make a tap to the Export Connection File option present on the Definition tab of Connection Properties dialog box. This will open the File Save dialog box, so save your current connection information into the ODC file.
Wrap Up:
Hopefully, all the above mentioned fixes to setup Excel Workbook Connections will help you in easy using of data connection in your respective Excel 2010/2013/2016/2019 application. Apart from this if you you have any other query to ask then, ask it in our comment section.
Priyanka is an entrepreneur & content marketing expert. She writes tech blogs and has expertise in MS Office, Excel, and other tech subjects. Her distinctive art of presenting tech information in the easy-to-understand language is very impressive. When not writing, she loves unplanned travels.
Working with Excel, a day will come when you’ll need to reference data from one workbook in another one. It’s a common use case and pretty easy to pull off. Join us as we explain how to link two Excel files and discuss many possible scenarios.
How to link Excel files – what are the available options?
Just as there are many different versions of Excel, the ways to link data also differ. It’s a lot easier if you share your Excel files in OneDrive rather than locally but we’ll discuss both scenarios.
Choosing how to link data depends also on the sheer volume of what you wish to link. If we’re talking here about particular cells or a column from your workbook, the default methods will do just fine. If you’re after linking entire Excel files, using tools such as Coupler.io with its Excel integrations may prove to be more efficient. But we’ll get to that!
You can link two or more Excel files stored on your hard drive. When the data changes in a Source file, the change will be quickly reflected in the Destination file.
The drawback of this approach is that it will only work on your local machine. Even if you share both files with another user, the link will cease to exist and they’ll be forced to re-add it. What’s more, the data will be only updated if both files are open at the same time.
So if you have a choice, it’s better to add both files to your OneDrive. If they’re already in there, you may as well jump to the How to link between Cloud-based Excel files section.
To link 2 Excel files stored locally, you have two options:
- Type in a formula referencing the exact location in a Source file
- Copy the desired cells and paste them as a link
How to link between files in desktop Excel?
To reference a single cell in another local file, you’ll use the following formula:
=[SourceWorkbook.xlsx]Sheet1!$A$1
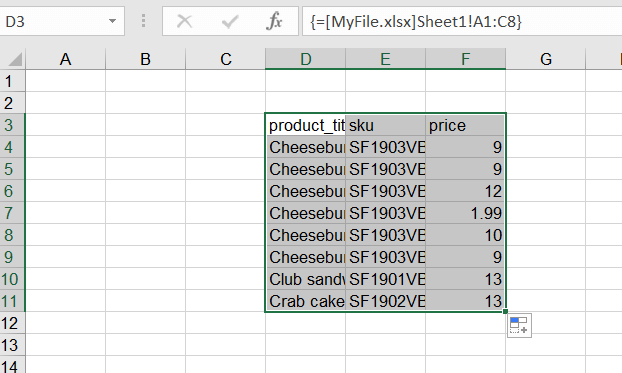
Replace SourceWorkbook.xlsx with the name of the file stored on your machine. Then, point to an exact sheet and a cell. A reference to a range of cells could like this:
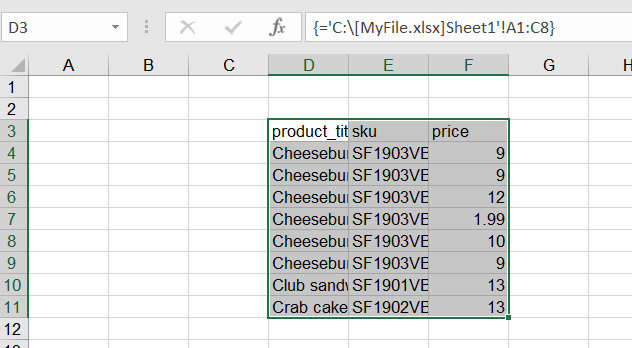
=[MyFile.xlsx]Sheet1!A1:C8
Press ENTER to save the formula and pull the data. If you’re on an older version of Excel, you may need to press CTRL+SHIFT+ENTER instead.
When you close the Source file, the formulas will change to include the entire path of the file – for example:
='C:[MyFile.xlsx]Sheet1'!A1:C8
As an alternative, you can:
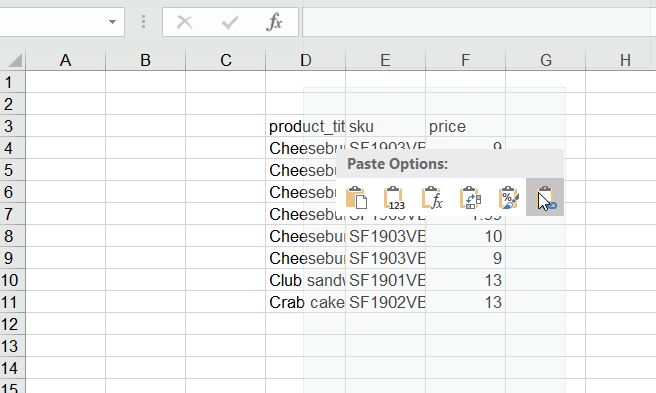
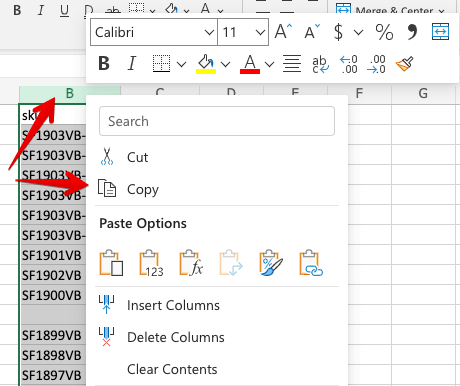
- Open a Source file, select the desired cells, and copy them.
- Head back to the Destination file, right-click on a desired cell or cells and choose to paste as a link.
- Here is the result:
Note that if the Source file is closed, and you reference it with a formula, no data will be pulled until you open a file.
How to link between cloud-based files in Excel?
When you wish to link Excel Online files or use those stored in OneDrive, things become easier. You can freely share files among coworkers and any interlinking won’t be affected. Links in files also refresh in near real time, giving you peace of mind that you’re working with the latest data.
The feature that enables it is called Workbook Links. We’ll explain how it works in the following chapters.
Workbook Links are suitable for individual cells or ranges of them. You may also link individual columns but the more data is involved, the slower your calculations will be. If you’re going to be linking entire worksheets or workbooks, it’s far better to focus on importing, rather than linking them. This is best done with dedicated tools.
There is more on that in the How to link a wide range of cells to Excel or another service chapter.
How to link two Excel files?
Let’s start with a most basic use case – you’re running some operations in your Excel workbook. In one of the fields, you wish to use the value(s) from another workbook and have it update automatically.
The flow is simple:
- In workbook 1 (source), highlight the data you want to link and copy it.
- In workbook 2 (destination), right-click on the first row and select the Link icon.
The latest data will be imported. A yellow bar will, however, appear now as well as every time you open a destination workbook.
To enable the data sync, select Enable Content.
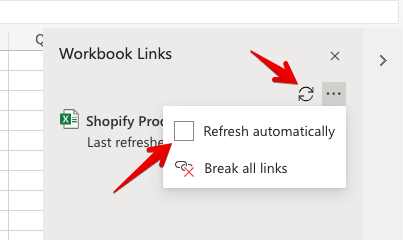
For some more advanced settings, you can choose the Manage Workbook Links button to look up the list of connected workbooks and a status for each – most likely it will be Connection Blocked.
To sync, press the Enable Content button from the yellow bar.
If any errors occur, you’ll see them in the menu to the right. For each of the connected files, you can press the Refresh button to manually pull the latest data. You can also use the button above to refresh data for all your links.
Of course, the whole idea of creating links between workbooks is not to keep refreshing the data manually. Once the data has been refreshed, an option to set automatic updates will be enabled.
If you tick Refresh automatically, the data will start to refresh periodically.
How to link a wide range of cells to Excel or another service?
The more data you link, the more computing your Excel needs to perform to pull the data and refresh it. It’s not an issue if you have a few or a few dozens of links spread across files.
However, if you wish to regularly pull thousands of cells into your workbooks, it will significantly slow down your workbooks. It may delay the data refresh and may leave you wondering whether the data has already been refreshed or not.
To avoid that, for larger operations it’s better to use tools dedicated to importing data such as Coupler.io. With Coupler.io, you can pull the desired ranges of cells directly into another Excel workbook or worksheet. You can then refresh the data automatically at a chosen schedule.
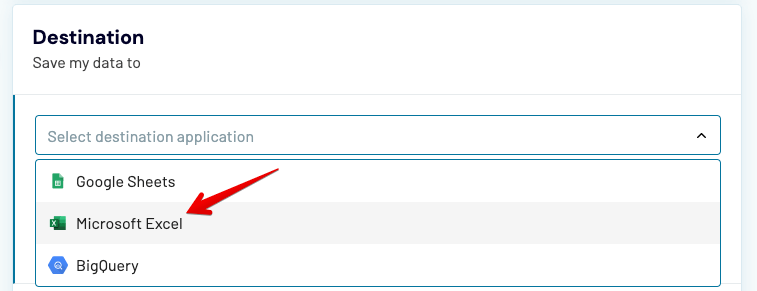
If you wish to, you can also import the Excel data to other services, such as Google Sheets or Google BigQuery, or bring it to Excel from Airtable, Pipedrive, Hubspot, and many others.
To get started with Coupler.io, create an account, log in, and click the Add an importer button.
From the list of source applications, choose Excel.
Next, click the Connect button. Log in with your Microsoft account and allow for Coupler.io to connect.
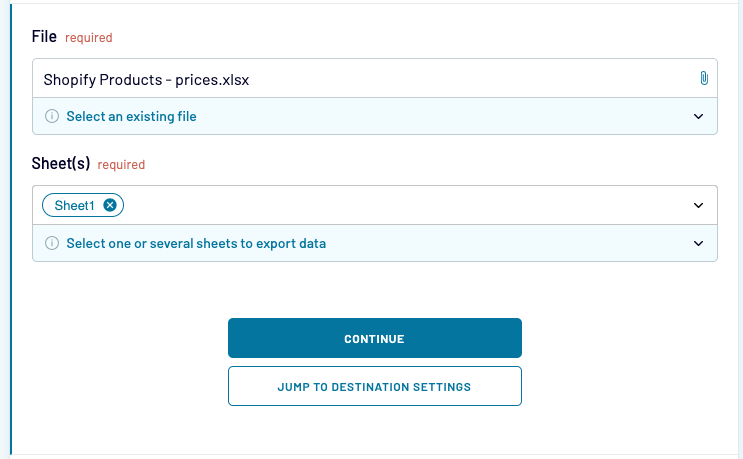
Once connected, you’ll need to choose the workbook from your OneDrive that we’ll be importing from. Also select the worksheet in this file.
Although it’s optional, most often you’ll want to specify the range of cells to import. If you don’t, all data from a given sheet will be fetched.
You may use the standard Excel formatting and pull, for example, cells C1:D8. You may also pull an entire column by typing, for example, C1:C.
Jumping to the Destination settings, choose where to import the data to. We’ll go with Excel as we just want to move the data from one workbook to another but there are other options available too.
If you’re importing from Excel to Excel, there’s no need to connect your account again, unless you’re importing to someone else’s account. Select it, and specify the exact destination.
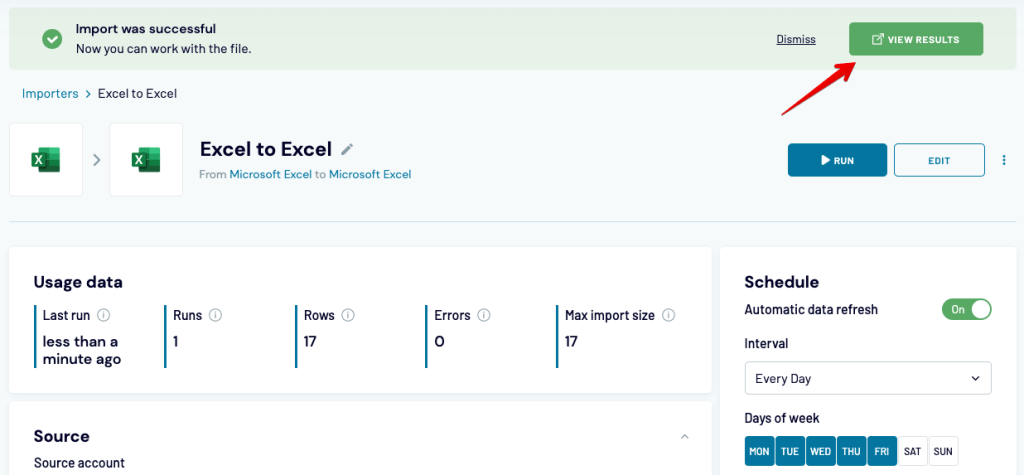
Finally, you can create a schedule for when the data should be imported. Choose what works best for you and run the importer.
Give it a little while to load, and then open the destination worksheet to see the results.
How to link Excel files and sync in real-time?
One of the advantages of using Excel files stored on OneDrive is their ability to sync data between one another. Microsoft advertises it as real-time sync but after some tests, we would call it a near real time.
If you’re used to the refresh rate of Google Sheets, for example, you may be disappointed. However, in most situations, a slight delay won’t cause any trouble.
To link files in Excel, follow the steps we outlined in the How to link Excel files chapter.
When data is changed in the destination file, most likely you won’t see an update visible right away in the source file. If you do nothing about it and just move on to the next task, you should see a refreshed number in a cell in a few minutes’ time. It will then continue refreshing at regular intervals.
If you want to speed things up, you can run an instant refresh by clicking Data -> Workbook Links in the menu and then the icon to refresh the data from a particular workbook.
This will often work, but only if the data in the source workbook has already been saved. Once again, it doesn’t happen instantly but only at regular (quite frequent) intervals.
If you’re anxious to have the data refreshed presently, you may consider refreshing the source file after making a change. This will prompt an automatic save. After that, manually force a data refresh in the destination file and it will fetch the latest saved data.
As a reminder, if you use Coupler.io to import data from one Excel workbook to another, you decide on the refresh schedule. For some, morning sync from Monday to Friday will do just fine. Others will prefer more frequent syncs – with Coupler.io you can even do it every 15 minutes.
FAQ: How to link Excel files
Let’s now discuss some specific use cases for how to link files in Excel. The tips below apply for files stored in OneDrive. If you only use Excel locally, jump back to the How to link local files in Excel section.
How to link cells in different Excel files?
For linking individual cells across files, the procedure is very much the same as we discussed earlier:
- Highlight the cell you want to reuse elsewhere and copy it.
- Right-click on the desired destination and select the Link icon from the Paste Options section.
If you’re importing to the same workbook as before, you won’t need to Enable Content again. If you reloaded it in the meantime, or are just linking the data to a new workbook, choose Manage Workbook Links and then Enable Content from the same bar.
Note that if you link multiple sets of cells or data ranges from the same workbook serving as a Source, they will all appear as a single position on your list of Workbook Links.
In the example below, you can see the data we imported from our sample Shopify store using Coupler.io.
We have a range of prices to the left linked from the respective workbook. Below there’s also a name of one of our products linked from another place in the same workbook. To the right, we can refresh data for all linked fields or, for example, enable automatic data refreshes.
How to link two Excel files without opening the source file?
You can link files in Excel without actually opening the source file. Of course, you’ll need to know the exact location of the cell or range of cells you wish to link. What’s more, to link Excel Online files or anything else stored on your OneDrive, you’ll need to fetch your unique ID.
To do so, set up a link in the traditional way we described above. Then, click on any linked cell in the Destination file and check its formula. It will look something like this:
='https://d.docs.live.net/18644c626caae38c/[myworkbook1.xlsx]Sheet1'!$C$2
The ID will follow right after the live.net link:
To insert a link from any given workbook, copy the formula with your ID and swap the file name and the cell range with the right values. Press ENTER and the latest data will be fetched.
How to link Excel columns between files?
Choosing a range of cells limits you to only the values currently present in the Source workbook. If anything new appears, it won’t be linked and, as such, won’t appear in the Destination workbook.
The solution is often to link an entire column and reference it in another file. To do so, click on any column in the Source file and copy it.
Then, select the first row of a column you want to add a link to and choose the Link icon. All the rows from the chosen column will be imported.
Rather than click, you can also enter the formulas directly. To link an entire column, it’s best to link to the first cell and then stretch the formula to the other rows.
When you insert the formula for the first row, be sure to remove the second $ (dollar) sign pointing to the specific cell. So, instead of the reference:
(...)Sheet1'!$C$2
Make it:
(...)Sheet1'!$C2
How to link fields between multiple files in Excel?
Advanced calculations may require referencing data from multiple spreadsheets at the same time. In the same way, the calculated data can then be referenced in other workbooks, creating a complex network of interconnected links.
As you recall from the earlier chapters, the formulas for linking cells between Excel Online files look somewhat like this:
='https://d.docs.live.net/18373e637ca3e48c/[Shopify Products - prices.xlsx]Sheet1'!$C$8
For the purpose of running any calculations or just adjusting the formulas as we go, the link is far too complex. It’s much better to link the desired fields into the destination workbook and then reference them from another worksheet in the same workbook.
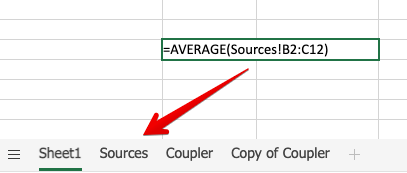
To do so, create a separate worksheet in your destination file where you’ll link all the external data. Name it accordingly – for example, “Sources”. Link the desired data by copying it from the source file and then pasting it as links (just as we did before).
Then, jump to the worksheet in the destination file. To reference the data from another sheet, use the following pattern:
Sheet_name!$A$1
For example, for calculating the average value of a range of cells present now in another worksheet, we would use:
=AVERAGE(Sources!B2:B12)
You can also type in the “=” sign (plus optionally a function name) and then jump to another worksheet and highlight the arguments. Press ENTER and the formula will be resolved.
In the standard version of Excel, the approach is pretty much the same, just with some small changes in the syntax of the links, as we mentioned earlier.
How to link Excel files – summing up
Linking Excel files can save you plenty of time and help you automate many dull processes.
It can also make things harder if you begin to link from one file to another, then to another, and another. The more interconnected workbooks become, the more complex it will be to troubleshoot the entire flow.
Find the right balance and use the right methods for linking your data.
When moving individual cells or ranges of them, Workbook Links work perfectly and are very easy to set up.
For moving large sets of data between workbooks or linking entire files, it’s a lot better to use tools such as Coupler.io. You’ll be able to set up your own schedule for imports, and all data transfers will happen outside of Excel. As a result, no Excel resources will be used, and you’ll be able to work much more smoothly while the information is synced in the background.
Thanks for reading!
-
Technical Content Writer on Coupler.io who loves working with data, writing about it, and even producing videos about it. I’ve worked at startups and product companies, writing content for technical audiences of all sorts. You’ll often see me cycling🚴🏼♂️, backpacking around the world🌎, and playing heavy board games.
Back to Blog
Focus on your business
goals while we take care of your data!
Try Coupler.io
Although Excel does a great job at saving data in a nice table structure, some projects require data to be stored or exported elsewhere. Text files, other excel files, databases, or even web pages can be used as a means to consume or store data. If you need to periodically update your data, moving or copying to an Excel spreadsheet can be time consuming and prone to errors. Data connection features of Excel can help establish permanent links with other data sources and automate this process.
Excel can pull data from an external data source into your spreadsheet with the help of data connection features. Excel can connect external data sources when you provide certain information about the external data and allows you to refresh them manually, automatically in specified intervals, or in a more customized fashion using VBA. In this article, we’re going to be using an equipment rental data and connect it with data from a Microsoft Access database. You can download the workbook and the Access file below.
Data connection features can be found under the DATA tab and consists of two categories:
- Get External Data
- Connections
Features under the Get External Data section help create a connection with sources like other workbooks, databases, text files, or websites. Connections section contains features for managing existing connections. To begin creating a new link, click Connections. You will be taken to the Workbook Connections window.
When you connect an external data in Excel, data will be first saved in the workbook. This data can then be exported in other formats, such as Office Data Connection (ODC) (.odc), or a Universal Data Connection (UDC) file (.udcx), to save or share the information.
Creating a data connection
Follow the steps below to connect an external data source to your workbook.
- Begin by going to the Data tab and selecting the connection type that corresponds to your data source. In this example, we are using a Microsoft Access database. Please note that the exact steps will be different if you choose another data type. For example, while you need to select a file for an Access or a text file, you will need to enter the server address for a SQL database. Click the From Access icon to connect to an Access file.
- Select your file and click Open.
- Select Table window will appear. Select the table you’d like to use and click OK to continue.
- In the Import Data window, you can choose how and where to display your data, and you can access advanced settings by pressing the Properties You don’t have to this now as you can open the Properties window at any time after creating connection.
In our example, we choose the Table option. Here is brief summary of all options.
- Table: Data is displayed in a tabular form
- PivotTable Report: You can use the columns to create a PivotTable
- PivotChart: You can use the columns to create a PivotChart
- Only Create Connection: Data will not be displayed, but the connection can be used by other features or VBA, and can be exported.
- Add this data to Data Model: Data is added to the Power Pivot Data Model. This option is independent from the display option above. However, it is advisable to use it with Only Create Connection option, because you can manage your data better in the Data Model.
You can choose to pull certain columns, instead of the entire table, if necessary. Try the PivotTable and Only Create Connection options to create connections without displaying the data in your spreadsheet.
Refreshing and managing data connections
There are several ways to refresh existing connections. The first method is by using the icons under both DATA and TABLE TOOLS — DESIGN tabs in the ribbon. These icons can be used to refresh data connection manually.
Both options essentially do the same thing. However, the default actions are different for the Refresh buttons in the DATA and TABLE TOOLS – DESIGN tabs. While Refresh All action is the default action in DATA tab. Refresh action is the default in the TABLE TOOLS – DESIGN tab. The Refresh button only refreshes the active table’s connection.
Power Pivot and Power Query windows also contain refresh buttons.
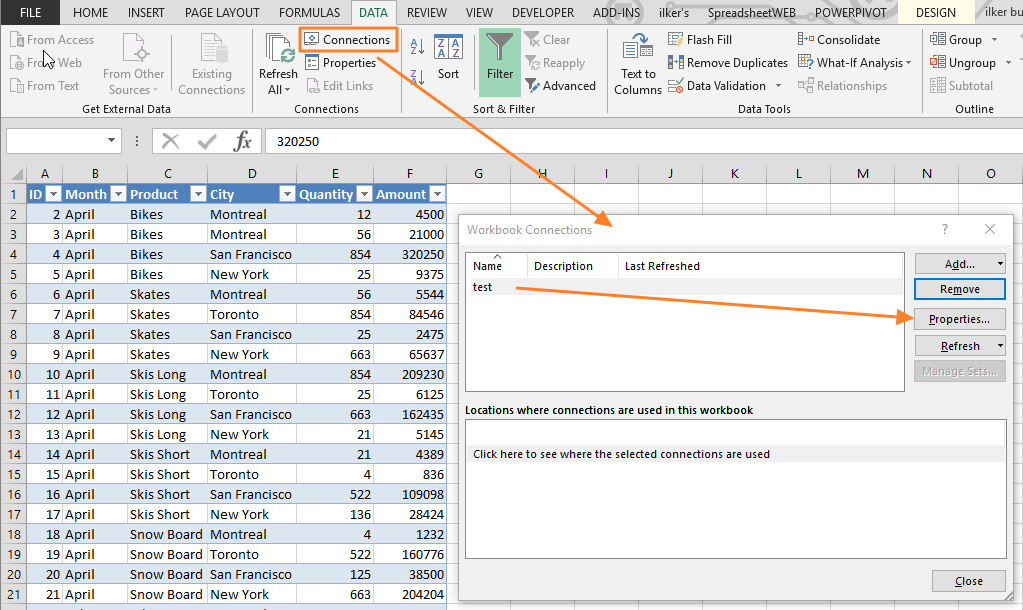
To automate this process, you can set a time interval to refresh data connections. To set a refresh interval, and manage the connections (including advanced Properties), use the Connections button to open the Workbook Connections window. You can add new connections, or refresh existing ones in this menu. Select the existing connection and click the Properties button to open Connection Properties window.
Enable the Refresh every option and modify the number that represents minutes. When you click OK, your data connection will be updated in selected intervals.
An alternative way to automatically refresh data is using VBA. This allows combining data connection features with your own custom code. Below is sample codes that can refresh data connections.
ActiveWorkbook.Connections("test").Refresh 'Refresh only the connection named "test"
ActiveWorkbook.RefreshAll 'Refresh all connections
You might have to use data from various sources for analysis. In Excel, you can import data from different data sources. Some of the data sources are as follows −
- Microsoft Access Database
- Web Page
- Text File
- SQL Server Table
- SQL Server Analysis Cube
- XML File
You can import any number of tables simultaneously from a database.
Importing Data from Microsoft Access Database
We will learn how to import data from MS Access database. Follow the steps given below −
Step 1 − Open a new blank workbook in Excel.
Step 2 − Click the DATA tab on the Ribbon.
Step 3 − Click From Access in the Get External Data group. The Select Data Source dialog box appears.
Step 4 − Select the Access database file that you want to import. Access database files will have the extension .accdb.
The Select Table dialog box appears displaying the tables found in the Access database. You can either import all the tables in the database at once or import only the selected tables based on your data analysis needs.
Step 5 − Select the Enable selection of multiple tables box and select all the tables.
Step 6 − Click OK. The Import Data dialog box appears.
As you observe, you have the following options to view the data you are importing in your workbook −
- Table
- PivotTable Report
- PivotChart
- Power View Report
You also have an option — only create connection. Further, PivotTable Report is selected by default.
Excel also gives you the options to put the data in your workbook −
- Existing worksheet
- New worksheet
You will find another check box that is selected and disabled – Add this data to the Data Model. Whenever you import data tables into your workbook, they are automatically added to the Data Model in your workbook. You will learn more about the Data Model in later chapters.
You can try each one of the options to view the data you are importing, and check how the data appears in your workbook −
-
If you select Table, Existing worksheet option gets disabled, New worksheet option gets selected and Excel creates as many worksheets as the number of tables you are importing from the database. The Excel tables appear in these worksheets.
-
If you select PivotTable Report, Excel imports the tables into the workbook and creates an empty PivotTable for analyzing the data in the imported tables. You have an option to create the PivotTable in an existing worksheet or a new worksheet.
Excel tables for the imported data tables will not appear in the workbook. However, you will find all the data tables in the PivotTable fields list, along with the fields in each table.
-
If you select PivotChart, Excel imports the tables into the workbook and creates an empty PivotChart for displaying the data in the imported tables. You have an option to create the PivotChart in an existing worksheet or a new worksheet.
Excel tables for the imported data tables will not appear in the workbook. However, you will find all the data tables in the PivotChart fields list, along with the fields in each table.
-
If you select Power View Report, Excel imports the tables into the workbook and creates a Power View Report in a new worksheet. You will learn how to use Power View Reports for analyzing data in later chapters.
Excel tables for the imported data tables will not appear in the workbook. However, you will find all the data tables in the Power View Report fields list, along with the fields in each table.
-
If you select the option — Only Create Connection, a data connection will be established between the database and your workbook. No tables or reports appear in the workbook. However, the imported tables are added to the Data Model in your workbook by default.
You need to choose any of these options, based on your intent of importing data for data analysis. As you observed above, irrespective of the option you have chosen, the data is imported and added to the Data Model in your workbook.
Importing Data from a Web Page
Sometimes, you might have to use the data that is refreshed on a web site. You can import data from a table on a website into Excel.
Step 1 − Open a new blank workbook in Excel.
Step 2 − Click the DATA tab on the Ribbon.
Step 3 − Click From Web in the Get External Data group. The New Web Query dialog box appears.
Step 4 − Enter the URL of the web site from where you want to import data, in the box next to Address and click Go.
Step 5 − The data on the website appears. There will be yellow arrow icons next to the table data that can be imported.
Step 6 − Click the yellow icons to select the data you want to import. This turns the yellow icons to green boxes with a checkmark as shown in the following screen shot.
Step 7 − Click the Import button after you have selected what you want.
The Import Data dialog box appears.
Step 8 − Specify where you want to put the data and click Ok.
Step 9 − Arrange the data for further analysis and/or presentation.
Copy-pasting data from web
Another way of getting data from a web page is by copying and pasting the required data.
Step 1 − Insert a new worksheet.
Step 2 − Copy the data from the web page and paste it on the worksheet.
Step 3 − Create a table with the pasted data.
Importing Data from a Text File
If you have data in .txt or .csv or .prn files, you can import data from those files treating them as text files. Follow the steps given below −
Step 1 − Open a new worksheet in Excel.
Step 2 − Click the DATA tab on the Ribbon.
Step 3 − Click From Text in the Get External Data group. The Import Text File dialog box appears.
You can see that .prn, .txt and .csv extension text files are accepted.
Step 4 − Select the file. The selected file name appears in the File name box. The Open button changes to Import button.
Step 5 − Click the Import button. Text Import Wizard – Step 1 of 3 dialog box appears.
Step 6 − Click the option Delimited to choose the file type and click Next.
The Text Import Wizard – Step 2 of 3 dialog box appears.
Step 7 − Under Delimiters, select Other.
Step 8 − In the box next to Other, type | (That is the delimiter in the text file you are importing).
Step 9 − Click Next.
The Text Import Wizard – Step 3 of 3 dialog box appears.
Step 10 − In this dialog box, you can set column data format for each of the columns.
Step 11 − After you complete the data formatting of columns, click Finish. The Import Data dialog box appears.
You will observe the following −
-
Table is selected for view and is grayed. Table is the only view option you have in this case.
-
You can put the data either in an existing worksheet or a New worksheet.
-
You can select or not select the check box Add this data to the Data Model.
-
Click OK after you have made the choices.
Data appears on the worksheet you specified. You have imported data from Text file into Excel workbook.
Importing Data from another Workbook
You might have to use data from another Excel workbook for your data analysis, but someone else might maintain the other workbook.
To get up to date data from another workbook, establish a data connection with that workbook.
Step 1 − Click DATA > Connections in the Connections group on the Ribbon.
The Workbook Connections dialog box appears.
Step 2 − Click the Add button in the Workbook Connections dialog box. The Existing Connections dialog box appears.
Step 3 − Click Browse for More… button. The Select Data Source dialog box appears.
Step 4 − Click the New Source button. The Data Connection Wizard dialog box appears.
Step 5 − Select Other/Advanced in the data source list and click Next. The Data Link Properties dialog box appears.
Step 6 − Set the data link properties as follows −
-
Click the Connection tab.
-
Click Use data source name.
-
Click the down-arrow and select Excel Files from the drop-down list.
-
Click OK.
The Select Workbook dialog box appears.
Step 7 − Browse to the location where you have the workbook to be imported is located. Click OK.
The Data Connection Wizard dialog box appears with Select Database and Table.
Note − In this case, Excel treats each worksheet that is getting imported as a table. The table name will be the worksheet name. So, to have meaningful table names, name / rename the worksheets as appropriate.
Step 8 − Click Next. The Data Connection Wizard dialog box appears with Save Data Connection File and Finish.
Step 9 − Click the Finish button. The Select Table dialog box appears.
As you observe, Name is the worksheet name that is imported as type TABLE. Click OK.
The Data connection with the workbook you have chosen will be established.
Importing Data from Other Sources
Excel provides you options to choose various other data sources. You can import data from these in few steps.
Step 1 − Open a new blank workbook in Excel.
Step 2 − Click the DATA tab on the Ribbon.
Step 3 − Click From Other Sources in the Get External Data group.
Dropdown with various data sources appears.
You can import data from any of these data sources into Excel.
Importing Data using an Existing Connection
In an earlier section, you have established a data connection with a workbook.
Now, you can import data using that existing connection.
Step 1 − Click the DATA tab on the Ribbon.
Step 2 − Click Existing Connections in the Get External Data group. The Existing Connections dialog box appears.
Step 3 − Select the connection from where you want to import data and click Open.
Renaming the Data Connections
It will be useful if the data connections you have in your workbook have meaningful names for the ease of understanding and locating.
Step 1 − Go to DATA > Connections on the Ribbon. The Workbook Connections dialog box appears.
Step 2 − Select the connection that you want to rename and click Properties.
The Connection Properties dialog box appears. The present name appears in the Connection name box −
Step 3 − Edit the Connection name and click OK. The data connection will have the new name that you have given.
Refreshing an External Data Connection
When you connect your Excel workbook to an external data source, as you have seen in the above sections, you would like to keep the data in your workbook up to date reflecting the changes made to the external data source time to time.
You can do this by refreshing the data connections you have made to those data sources. Whenever you refresh the data connection, you see the most recent data changes from that data source, including anything that is new or that is modified or that has been deleted.
You can either refresh only the selected data or all the data connections in the workbook at once.
Step 1 − Click the DATA tab on the Ribbon.
Step 2 − Click Refresh All in the Connections group.
As you observe, there are two commands in the dropdown list – Refresh and Refresh All.
-
If you click Refresh, the selected data in your workbook is updated.
-
If you click Refresh All, all the data connections to your workbook are updated.
Updating all the Data Connections in the Workbook
You might have several data connections to your workbook. You need to update them from time to time so that your workbook will have access to the most recent data.
Step 1 − Click any cell in the table that contains the link to the imported data file.
Step 2 − Click the Data tab on the Ribbon.
Step 3 − Click Refresh All in the Connections group.
Step 4 − Select Refresh All from the dropdown list. All the data connections in the workbook will be updated.
Automatically Refresh Data when a Workbook is opened
You might want to have access to the recent data from the data connections to your workbook whenever your workbook is opened.
Step 1 − Click any cell in the table that contains the link to the imported data file.
Step 2 − Click the Data tab.
Step 3 − Click Connections in the Connections group.
The Workbook Connections dialog box appears.
Step 4 − Click the Properties button. The Connection Properties dialog box appears.
Step 5 − Click the Usage tab.
Step 6 − Check the option — Refresh data when opening the file.
You have another option also — Remove data from the external data range before saving the workbook. You can use this option to save the workbook with the query definition but without the external data.
Step 7 − Click OK. Whenever you open your workbook, the up to date data will be loaded into your workbook.
Automatically Refresh Data at regular Intervals
You might be using your workbook keeping it open for longer durations. In such a case, you might want to have the data refreshed periodically without any intervention from you.
Step 1 − Click any cell in the table that contains the link to the imported data file.
Step 2 − Click the Data tab on the Ribbon.
Step 3 − Click Connections in the Connections group.
The Workbook Connections dialog box appears.
Step 4 − Click the Properties button.
The Connection Properties dialog box appears. Set the properties as follows −
-
Click the Usage tab.
-
Check the option Refresh every.
-
Enter 60 as the number of minutes between each refresh operation and click Ok.
Your Data will be automatically refreshed every 60 min. (i.e. every one hour).
Enabling Background Refresh
For very large data sets, consider running a background refresh. This returns control of Excel to you instead of making you wait several minutes or more for the refresh to finish. You can use this option when you are running a query in the background. However, during this time, you cannot run a query for any connection type that retrieves data for the Data Model.
-
Click in any cell in the table that contains the link to the imported data file.
-
Click the Data tab.
-
Click Connections in the Connections group. The Workbook Connections dialog box appears.
Click the Properties button.
The Connection Properties dialog box appears. Click the Usage tab. The Refresh Control options appear.
- Click Enable background refresh.
- Click OK. The Background refresh is enabled for your workbook.