Содержание
- VBA-Урок 3. Коллекция Sheets
- Как посчитать количество листов в книге
- Как добавить лист в книгу
- Как скрыть лист
- Объект Sheets (Excel)
- Замечания
- Пример
- Методы
- Свойства
- См. также
- Поддержка и обратная связь
- Count Sheets in Excel (using VBA)
- Count All Sheets in the Workbook
- VBA Code to Show Sheet Count in a Message Box
- Getting Sheet Count Result in Immediate Window
- Formula to Get Sheet Count in the Worksheet
- Count All Sheets in Another Workbook (Open or Closed)
- Sheet Count in Another Open Workbook
- Sheet Count from a Closed Workbook
- Count All Sheets that Have a Specific Word In It
- How to COUNT Sheets using VBA in Excel
- Count Sheets from the Active Workbook
- Count Sheets from a Different Workbook
- Count Sheets from All the Open Workbooks
- Count Sheets from a Closed Workbook
- VBA – Count the Sheets in a Workbook
- Application.Sheets.Count – Count Worksheets
- VBA Coding Made Easy
- VBA Code Examples Add-in
- VBA Code Generator
- AutoMacro: VBA Add-in with Hundreds of Ready-To-Use VBA Code Examples & much more!
- What is AutoMacro?
VBA-Урок 3. Коллекция Sheets
Данная коллекция представляет собой набор листов (Sheets) в книге (Workbooks). Давайте посмотрим, какие действия мы можем делать над листами.
Как посчитать количество листов в книге
Сначала попробуем узнать сколько листов имеет наша книга:
Данным кодом мы вызвали сообщения на экран (MsgBox), которое отобразило количество листов (Sheets.Count) в книге (Workbooks) » Test.xls«.
Под листом понимается не только ячейки, но и диаграммы. Также, как и лист для расчета, диаграмма будет включена в подсчет листов.
Как добавить лист в книгу
В коллекции листов также есть возможность добавлять свои листы, для этого существует метод Add. Этот метод имеет 4 параметра Add (Before, After, Count, Type). Все эти параметры необязательны. Первые два отвечают за место вставки листа. Далее, количество листов, вставляемых Count и тип листа Type . Типы могут быть, например, такие xlWorkSheet для расчетного листа и xlChart для диаграммы. Если местоположение не указывать, то лист будет вставляться относительно текущего листа.
Таким образом мы вставили 4 листа (Count: = 4) после листа «Лист3» .
Также можно вставить лист в самый конец книги:
Как скрыть лист
Если у Вас есть желание, то некоторые листы можно скрыть. Это бывает полезно, если у Вас есть константы или расчеты, которые Вы не хотите чтобы видели на экране в виде листов. Для этого можно использовать метод Visible. Устанавливая это свойство в TRUE или FALSE вы можете убрать или отобразить необходимый лист.
Источник
Объект Sheets (Excel)
Коллекция всех листов в указанной или активной книге.
Замечания
Коллекция Листов может содержать объекты Chart или Worksheet .
Коллекция Листов полезна, если требуется вернуть листы любого типа. Если вам нужно работать с листами только одного типа, см. раздел объекта для этого типа листа.
Пример
Используйте свойство Sheets объекта Workbook , чтобы вернуть коллекцию Sheets . В следующем примере печатаются все листы активной книги.
Используйте метод Add , чтобы создать новый лист и добавить его в коллекцию. В следующем примере два листа диаграммы добавляются в активную книгу, помещая их после двух листов в книге.
Используйте листы (индекс), где индекс — это имя листа или номер индекса, чтобы вернуть один объект Chart или Worksheet . В следующем примере активируется лист с именем Sheet1.
Используйте листы (массив), чтобы указать несколько листов. В следующем примере листы с именами Sheet4 и Sheet5 перемещаются в начало книги.
Методы
Свойства
См. также
Поддержка и обратная связь
Есть вопросы или отзывы, касающиеся Office VBA или этой статьи? Руководство по другим способам получения поддержки и отправки отзывов см. в статье Поддержка Office VBA и обратная связь.
Источник
Count Sheets in Excel (using VBA)
There are some simple things that are not possible for you to do with in-built functions and functionalities in Excel, but can easily be done using VBA.
Counting the total number of sheets in the active workbook or any other workbook on your system is an example of such a task.
In this tutorial, I’ll show you some simple VBA code that you can use to count the total number of sheets in an Excel workbook.
This Tutorial Covers:
Count All Sheets in the Workbook
There are multiple ways I can use VBA to give me the total count of sheets in a workbook.
In the following sections, I will show you three different methods, and you can choose which one to use:
- Using the VBA code in a module (to get sheet count as a message box)
- Using Immediate window
- Using a Custom Formula (which will give you the sheet count in a cell in the worksheet)
VBA Code to Show Sheet Count in a Message Box
Below is the VBA code to get the total number of sheets in the current workbook shown in a message box:
In the above code, I have used Sheets, which will count all the sheets (be it worksheets or chart sheets). In case you only want to count the total number of worksheets, use Worksheets instead of Sheets. In most cases, people only use worksheets, using Sheets works fine. In layman terms, Sheets = Worksheets + Chart Sheets
Below are the steps to put this code in the VBA Backend:
- Click the Develope tab in the ribbon (don’t see the Developer tab – click here to know how to get it)
- In the Visual Basic Editor that opens, click on ‘Insert’ option in the menu
- Click on Module. This will insert a new module for the workbook
- Copy and Paste the above VBA code in the code window of the module
- Place the cursor anywhere in the code and press the F5 key (or click the green play button in the toolbar)
The above steps would run the code and you will see a message box that shows the total number of worksheets in the workbook.
Note: If you want to keep this code and reuse it in the future in the same workbook, you need to save the Excel file as a macro-enabled file (with a .XLSM extension). You will see this option when you try to save this file.
Getting Sheet Count Result in Immediate Window
The Immediate window gives you the result right there with a single line of code.
Below are the steps to get the count of sheets in the workbook using the immediate window:
- Click the Develope tab in the ribbon (don’t see the Developer tab – click here to know how to get it)
- Click on Visual Basic icon
- In the VB Editor that opens, you might see the Immediate Window already. If you don’t, click the ‘View’ option in the menu and then click on Immediate Window (or use the keyboard shortcut – Control + G)
- Copy and paste the following line of code: ? ThisWorkbook.Sheets.Count
- Place the cursor at the end of the code line and hit enter.
When you hit enter in Step 5, it executes the code and you get the result in the next line in the immediate window itself.
Formula to Get Sheet Count in the Worksheet
If you want to get the sheet count in a cell in any worksheet, using the formula method is the best way.
In this method, I will create a custom formula that will give me the total number of sheets in the workbook.
Below is the code that will do this:
You need to place this code in the module (just like the way I showed in the ” VBA Code to Show Sheet Count in a Message Box” section)
Once you have the code in the module, you can get the sheet count by using the below formula in any cell in the workbook:
Pro Tip: If you need to get the sheet count value often, I would recommend copying and pasting this formula VBA code in the Personal Macro Workbook. When you save a VBA code in the Personal Macro Workbook, it can be used on any Excel file on your system. In short, VBA codes in PMW are always available to you on your system.
Count All Sheets in Another Workbook (Open or Closed)
In the above example, I showed you how to count the number of sheets in the active workbook (the one where you’re working and where you added the VBA codes).
You can also tweak the code a little to get the sheet count in other workbooks (whether open or closed).
Sheet Count in Another Open Workbook
Suppose I want to know the sheet count of an already open workbook – Example.xlsx
The below VBA code with do this:
And in case you want to get the result in the immediate window, you can use the below code.
Sheet Count from a Closed Workbook
In case you need to get the sheet count of a file that’s closed, you either need to open it and then use the above codes, or you can use VBA to first open the file, then count the sheets in it, and then close it.
The first step would be to get the full file location of the Excel file. In this example, my file location is “C:UserssumitOneDriveDesktopTestExample File.xlsx”
You can get the full file path by right-clicking on the file and then clicking on the Copy Path option (or click on the Properties option).
Below are the VBA codes to get the sheet count from the closed workbook:
The above code first opens the workbook, then counts the total number of sheets in it, and then closes the workbook.
Since the code needs to do some additional tasks (apart from counting the sheets), it has some extra lines of code in it.
The Application.DisplayAlerts = False part of the code makes sure that the process of opening a file, counting the sheets, and then closing the file is not visible to the user. This line stops the alerts of the Excel application. And at the end of the code, we set it back to True, so things get back to normal and we see the alerts from thereon.
Count All Sheets that Have a Specific Word In It
One useful scenario of counting sheets would be when you have a lot of sheets in a workbook, and you only want to count the number of sheets that have a specific word in them.
For example, suppose you have a large workbook that has sheets for multiple departments in your company, and you only want to know the sheet count of the sales department sheets.
Below is the VBA code that will only give you the number of sheets that have the word ‘Sales’ in it
Note that the code is case-sensitive, so ‘Sales’ and ‘sales’ would be considered different words.
The above uses an IF condition to check the name of each sheet, and if the name of the sheet contains the specified word (which is checked using the INSTR function), it counts it, else it doesn’t.
So these are some simple VBA codes that you can use to quickly get a count of sheets in any workbook.
I hope you found this tutorial useful!
Other Excel tutorials you may also find useful:
Источник
How to COUNT Sheets using VBA in Excel
In Excel, if you have many sheets, you can use a VBA code to count them quickly instead of manually counting or using any formula. So, in the post, we will see different ways to do count sheets from a workbook.
Count Sheets from the Active Workbook
Following is the code that you need to use to count the sheet from the active workbook.
In this code, first, you have the referred to the active workbook using the “ThisWorkbook” and refer to all the sheet, in the end, use the count method to count all the sheets. And if you want to count the worksheets instead of sheets, then use the following code.
Count Sheets from a Different Workbook
You can use the name of the workbook to refer to and then count the sheets from it. Let’s say you want to count the sheets from the workbook “Book1”.
This code gives you the count of the sheets that you have in the workbook “sample-file.xlsx“. There is one thing that you need to take this workbook needs to be open.
Count Sheets from All the Open Workbooks
You might have more than one workbook that is open at the same time, and you can count all the sheets from all those workbooks.
Count Sheets from a Closed Workbook
Now here we have a code that refers to the workbook that is saved on my system’s desktop. When I run this code it opens that workbook at the backend and counts the sheets from it and then adds that count to cell A1.
We have turned OFF the display alerts to open and close the file at the backend.
Источник
VBA – Count the Sheets in a Workbook
Application.Sheets.Count – Count Worksheets
If you ever need to count the number of sheets in a workbook, use the VBA command: Application.Sheets.Count
Put this in a module:
VBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro – A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
VBA Code Examples Add-in
Easily access all of the code examples found on our site.
Simply navigate to the menu, click, and the code will be inserted directly into your module. .xlam add-in.
(No installation required!)
VBA Code Generator
AutoMacro: VBA Add-in with Hundreds of Ready-To-Use VBA Code Examples & much more!
What is AutoMacro?
AutoMacro is an add-in for VBA that installs directly into the Visual Basic Editor. It comes loaded with code generators, an extensive code library, the ability to create your own code library, and many other time-saving tools and utilities that add much needed functionality to the outdated VBA Editor.
Источник
Home / VBA / How to COUNT Sheets using VBA in Excel
In Excel, if you have many sheets, you can use a VBA code to count them quickly instead of manually counting or using any formula. So, in the post, we will see different ways to do count sheets from a workbook.
Count Sheets from the Active Workbook
Following is the code that you need to use to count the sheet from the active workbook.

ThisWorkbook.Sheets.CountIn this code, first, you have the referred to the active workbook using the “ThisWorkbook” and refer to all the sheet, in the end, use the count method to count all the sheets. And if you want to count the worksheets instead of sheets, then use the following code.
ThisWorkbook.Worksheets.CountHelpful Links: Run a Macro – Macro Recorder – Visual Basic Editor – Personal Macro Workbook
Count Sheets from a Different Workbook
You can use the name of the workbook to refer to and then count the sheets from it. Let’s say you want to count the sheets from the workbook “Book1”.
Here’s the code.
Workbooks("sample-file.xlsx").Sheets.CountThis code gives you the count of the sheets that you have in the workbook “sample-file.xlsx“. There is one thing that you need to take this workbook needs to be open.
Count Sheets from All the Open Workbooks
You might have more than one workbook that is open at the same time, and you can count all the sheets from all those workbooks.
Sub vba_loop_all_sheets()
Dim wb As Workbook
Dim i As Long
For Each wb In Application.Workbooks
If wb.Name <> "PERSONAL.XLSB" Then
i = i + wb.Sheets.Count
End If
Next wb
MsgBox "Total sheets in all the open workbooks: " & i
End SubCount Sheets from a Closed Workbook
Now here we have a code that refers to the workbook that is saved on my system’s desktop. When I run this code it opens that workbook at the backend and counts the sheets from it and then adds that count to cell A1.
Sub vba_count_sheets()
Dim wb As Workbook
Application.DisplayAlerts = False
Set wb = Workbooks.Open("C:UsersDellDesktopsample-file.xlsx")
ThisWorkbook.Sheets(1).Range("A1").Value _
= wb.Sheets.Count
wb.Close SaveChanges:=True
Application.DisplayAlerts = True
End SubWe have turned OFF the display alerts to open and close the file at the backend.
More Tutorials on VBA Worksheets
- Back to VBA Worksheet / VBA Tutorial
Создание, копирование, перемещение и удаление рабочих листов Excel с помощью кода VBA. Методы Sheets.Add, Worksheet.Copy, Worksheet.Move и Worksheet.Delete.
Создание новых листов
Создание новых рабочих листов осуществляется с помощью метода Sheets.Add.
Синтаксис метода Sheets.Add
expression.Add [Before, After, Count, Type]
где expression — переменная, представляющая собой объект Sheet.
Компоненты метода Sheets.Add
- Before* — необязательный параметр типа данных Variant, указывающий на лист, перед которым будет добавлен новый.
- After* — необязательный параметр типа данных Variant, указывающий на лист, после которого будет добавлен новый.
- Count — необязательный параметр типа данных Variant, указывающий, сколько листов будет добавлено (по умолчанию — 1).
- Type — необязательный параметр типа данных Variant, указывающий тип листа: xlWorksheet** (рабочий лист) или xlChart (диаграмма), по умолчанию — xlWorksheet.
*Если Before и After не указаны, новый лист, по умолчанию, будет добавлен перед активным листом.
**Для создания рабочего листа (xlWorksheet) можно использовать метод Worksheets.Add, который для создания диаграмм уже не подойдет.
Примеры создания листов
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
‘Создание рабочего листа: Sheets.Add Worksheets.Add ThisWorkbook.Sheets.Add After:=ActiveSheet, Count:=2 Workbooks(«Книга1.xlsm»).Sheets.Add After:=Лист1 Workbooks(«Книга1.xlsm»).Sheets.Add After:=Worksheets(1) Workbooks(«Книга1.xlsm»).Sheets.Add After:=Worksheets(«Лист1») ‘Создание нового листа с заданным именем: Workbooks(«Книга1.xlsm»).Sheets.Add.Name = «Мой новый лист» ‘Создание диаграммы: Sheets.Add Type:=xlChart ‘Добавление нового листа перед ‘последним листом рабочей книги Sheets.Add Before:=Sheets(Sheets.Count) ‘Добавление нового листа в конец Sheets.Add After:=Sheets(Sheets.Count) |
- Лист1 в After:=Лист1 — это уникальное имя листа, указанное в проводнике редактора VBA без скобок.
- Лист1 в After:=Worksheets(«Лист1») — это имя на ярлыке листа, указанное в проводнике редактора VBA в скобках.
Создаваемый лист можно присвоить объектной переменной:
|
Dim myList As Object ‘В активной книге Set myList = Worksheets.Add ‘В книге «Книга1.xlsm» Set myList = Workbooks(«Книга1.xlsm»).Worksheets.Add ‘Работаем с переменной myList.Name = «Listok1» myList.Cells(1, 1) = myList.Name ‘Очищаем переменную Set myList = Nothing |
Если создаваемый лист присваивается объектной переменной, он будет помещен перед активным листом. Указать дополнительные параметры невозможно.
Копирование листов
Копирование рабочих листов осуществляется с помощью метода Worksheet.Copy.
Синтаксис метода Worksheet.Copy
expression.Copy [Before, After]
где expression — переменная, представляющая собой объект Worksheet.
Компоненты метода Worksheet.Copy
- Before* — необязательный параметр типа данных Variant, указывающий на лист, перед которым будет добавлена копия.
- After* — необязательный параметр типа данных Variant, указывающий на лист, после которого будет добавлена копия.
*Если Before и After не указаны, Excel создаст новую книгу и поместит копию листа в нее. Если скопированный лист содержит код в проекте VBA (в модуле листа), он тоже будет перенесен в новую книгу.
Примеры копирования листов
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 |
‘В пределах активной книги ‘(уникальные имена листов) Лист1.Copy After:=Лист2 ‘В пределах активной книги ‘(имена листов на ярлычках) Worksheets(«Лист1»).Copy Before:=Worksheets(«Лист2») ‘Вставить копию в конец Лист1.Copy After:=Sheets(Sheets.Count) ‘Из одной книги в другую Workbooks(«Книга1.xlsm»).Worksheets(«Лист1»).Copy _ After:=Workbooks(«Книга2.xlsm»).Worksheets(«Лист1») ‘Один лист активной книги в новую книгу Лист1.Copy ‘Несколько листов активной книги в новую книгу* Sheets(Array(«Лист1», «Лист2», «Лист3»)).Copy ‘Все листы книги с кодом в новую книгу ThisWorkbook.Worksheets.Copy |
* Если при копировании в новую книгу нескольких листов хотя бы один лист содержит умную таблицу — копирование невозможно. Один лист, содержащий умную таблицу, копируется в новую книгу без проблем.
Если рабочие книги указаны как элементы коллекции Workbooks, в том числе ActiveWorkbook и ThisWorkbook, листы нужно указывать как элементы коллекции Worksheets, использование уникальных имен вызовет ошибку.
Перемещение листов
Перемещение рабочих листов осуществляется с помощью метода Worksheet.Move.
Синтаксис метода Worksheet.Move
expression.Move [Before, After]
где expression — переменная, представляющая собой объект Worksheet.
Компоненты метода Worksheet.Move
- Before* — необязательный параметр типа данных Variant, указывающий на лист, перед которым будет размещен перемещаемый лист.
- After* — необязательный параметр типа данных Variant, указывающий на лист, после которого будет размещен перемещаемый лист.
*Если Before и After не указаны, Excel создаст новую книгу и переместит лист в нее.
Примеры перемещения листов
Простые примеры перемещения листов:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
‘В пределах активной книги ‘(уникальные имена листов) Лист1.Move After:=Лист2 ‘В пределах активной книги ‘(имена листов на ярлычках) Worksheets(«Лист1»).Move Before:=Worksheets(«Лист2») ‘Размещение после последнего листа: Лист1.Move After:=Sheets(Sheets.Count) ‘Из одной книги в другую Workbooks(«Книга1.xlsm»).Worksheets(«Лист1»).Move _ After:=Workbooks(«Книга2.xlsm»).Worksheets(«Лист1») ‘В новую книгу Лист1.Move |
Если рабочие книги указаны как элементы коллекции Workbooks, в том числе ActiveWorkbook и ThisWorkbook, листы нужно указывать как элементы коллекции Worksheets, использование уникальных имен вызовет ошибку.
Перемещение листа «Лист4» в позицию перед листом, указанным как по порядковому номеру, так и по имени ярлыка:
|
Sub Peremeshcheniye() Dim x x = InputBox(«Введите имя или номер листа», «Перемещение листа «Лист4»») If IsNumeric(x) Then x = CLng(x) Sheets(«Лист4»).Move Before:=Sheets(x) End Sub |
Удаление листов
Удаление рабочих листов осуществляется с помощью метода Worksheet.Delete
Синтаксис метода Worksheet.Delete
expression.Delete
где expression — переменная, представляющая собой объект Worksheet.
Примеры удаления листов
|
‘По уникальному имени Лист1.Delete ‘По имени на ярлычке Worksheets(«Лист1»).Delete ‘По индексу листа Worksheets(1).Delete ‘В другой книге Workbooks(«Книга1.xlsm»).Worksheets(«Лист1»).Delete |
Если рабочие книги указаны как элементы коллекции Workbooks, в том числе ActiveWorkbook и ThisWorkbook, листы нужно указывать как элементы коллекции Worksheets, использование уникальных имен вызовет ошибку.
Как обратиться к рабочему листу, переименовать, скрыть или отобразить его с помощью кода VBA Excel, смотрите в этой статье.
There are some simple things that are not possible for you to do with in-built functions and functionalities in Excel, but can easily be done using VBA.
Counting the total number of sheets in the active workbook or any other workbook on your system is an example of such a task.
In this tutorial, I’ll show you some simple VBA code that you can use to count the total number of sheets in an Excel workbook.
Count All Sheets in the Workbook
There are multiple ways I can use VBA to give me the total count of sheets in a workbook.
In the following sections, I will show you three different methods, and you can choose which one to use:
- Using the VBA code in a module (to get sheet count as a message box)
- Using Immediate window
- Using a Custom Formula (which will give you the sheet count in a cell in the worksheet)
VBA Code to Show Sheet Count in a Message Box
Below is the VBA code to get the total number of sheets in the current workbook shown in a message box:
Sub SheetCount() MsgBox ThisWorkbook.Sheets.Count End Sub
In the above code, I have used Sheets, which will count all the sheets (be it worksheets or chart sheets). In case you only want to count the total number of worksheets, use Worksheets instead of Sheets. In most cases, people only use worksheets, using Sheets works fine. In layman terms, Sheets = Worksheets + Chart Sheets
Below are the steps to put this code in the VBA Backend:
- Click the Develope tab in the ribbon (don’t see the Developer tab – click here to know how to get it)

- Click on Visual Basic icon
- In the Visual Basic Editor that opens, click on ‘Insert’ option in the menu
- Click on Module. This will insert a new module for the workbook

- Copy and Paste the above VBA code in the code window of the module
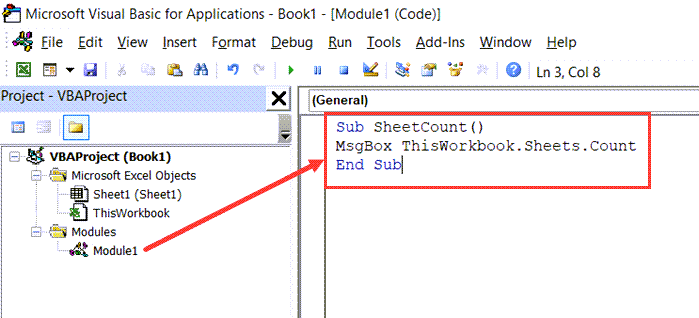
- Place the cursor anywhere in the code and press the F5 key (or click the green play button in the toolbar)

The above steps would run the code and you will see a message box that shows the total number of worksheets in the workbook.

Note: If you want to keep this code and reuse it in the future in the same workbook, you need to save the Excel file as a macro-enabled file (with a .XLSM extension). You will see this option when you try to save this file.
Getting Sheet Count Result in Immediate Window
The Immediate window gives you the result right there with a single line of code.
Below are the steps to get the count of sheets in the workbook using the immediate window:
- Click the Develope tab in the ribbon (don’t see the Developer tab – click here to know how to get it)
- Click on Visual Basic icon
- In the VB Editor that opens, you might see the Immediate Window already. If you don’t, click the ‘View’ option in the menu and then click on Immediate Window (or use the keyboard shortcut – Control + G)

- Copy and paste the following line of code: ? ThisWorkbook.Sheets.Count

- Place the cursor at the end of the code line and hit enter.
When you hit enter in Step 5, it executes the code and you get the result in the next line in the immediate window itself.

Formula to Get Sheet Count in the Worksheet
If you want to get the sheet count in a cell in any worksheet, using the formula method is the best way.
In this method, I will create a custom formula that will give me the total number of sheets in the workbook.
Below is the code that will do this:
Function SheetCount()
SheetCount = ThisWorkbook.Sheets.Count
End Function
You need to place this code in the module (just like the way I showed in the ” VBA Code to Show Sheet Count in a Message Box” section)
Once you have the code in the module, you can get the sheet count by using the below formula in any cell in the workbook:
=SheetCount()

Pro Tip: If you need to get the sheet count value often, I would recommend copying and pasting this formula VBA code in the Personal Macro Workbook. When you save a VBA code in the Personal Macro Workbook, it can be used on any Excel file on your system. In short, VBA codes in PMW are always available to you on your system.
Count All Sheets in Another Workbook (Open or Closed)
In the above example, I showed you how to count the number of sheets in the active workbook (the one where you’re working and where you added the VBA codes).
You can also tweak the code a little to get the sheet count in other workbooks (whether open or closed).
Sheet Count in Another Open Workbook
Suppose I want to know the sheet count of an already open workbook – Example.xlsx
The below VBA code with do this:
Sub SheetCount()
MsgBox Workbooks("Example.xlsx").Sheets.Count
End Sub
And in case you want to get the result in the immediate window, you can use the below code.
? Workbooks("Example.xlsx").Sheets.Count
Sheet Count from a Closed Workbook
In case you need to get the sheet count of a file that’s closed, you either need to open it and then use the above codes, or you can use VBA to first open the file, then count the sheets in it, and then close it.
The first step would be to get the full file location of the Excel file. In this example, my file location is “C:UserssumitOneDriveDesktopTestExample File.xlsx”
You can get the full file path by right-clicking on the file and then clicking on the Copy Path option (or click on the Properties option).
Below are the VBA codes to get the sheet count from the closed workbook:
Sub SheetCount()
Application.DisplayAlerts = False
Set wb = Workbooks.Open("C:UserssumitOneDriveDesktopTestExample File.xlsx")
ShCount = wb.Sheets.Count
wb.Close SaveChanges:=True
Application.DisplayAlerts = True
MsgBox ShCount
End Sub
The above code first opens the workbook, then counts the total number of sheets in it, and then closes the workbook.
Since the code needs to do some additional tasks (apart from counting the sheets), it has some extra lines of code in it.
The Application.DisplayAlerts = False part of the code makes sure that the process of opening a file, counting the sheets, and then closing the file is not visible to the user. This line stops the alerts of the Excel application. And at the end of the code, we set it back to True, so things get back to normal and we see the alerts from thereon.
Count All Sheets that Have a Specific Word In It
One useful scenario of counting sheets would be when you have a lot of sheets in a workbook, and you only want to count the number of sheets that have a specific word in them.
For example, suppose you have a large workbook that has sheets for multiple departments in your company, and you only want to know the sheet count of the sales department sheets.
Below is the VBA code that will only give you the number of sheets that have the word ‘Sales’ in it
Sub SheetCount()
Dim shCount As Long
For Each sh In ThisWorkbook.Worksheets
If InStr(1, sh.Name, "Sales", vbBinaryCompare) > 0 Then
shCount = shCount + 1
End If
Next sh
MsgBox shCount
End Sub
Note that the code is case-sensitive, so ‘Sales’ and ‘sales’ would be considered different words.
The above uses an IF condition to check the name of each sheet, and if the name of the sheet contains the specified word (which is checked using the INSTR function), it counts it, else it doesn’t.
So these are some simple VBA codes that you can use to quickly get a count of sheets in any workbook.
I hope you found this tutorial useful!
Other Excel tutorials you may also find useful:
- How to Insert New Worksheet in Excel (Easy Shortcuts)
- How to Group Worksheets in Excel
- How to Get the Sheet Name in Excel? Easy Formula
- How to Sort Worksheets in Excel using VBA (alphabetically)
- How to Delete Sheets in Excel (Shortcuts + VBA)
- How to Rename a Sheet in Excel (4 Easy Ways + Shortcut)
- Excel Tabs/Sheets Not Showing – How to Fix?
Return to VBA Code Examples
Application.Sheets.Count – Count Worksheets
If you ever need to count the number of sheets in a workbook, use the VBA command: Application.Sheets.Count
Put this in a module:
Public Sub CountMySheets()
MsgBox Application.Sheets.Count
End SubVBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro – A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Learn More!
<<Return to VBA Examples

VBA Code Examples Add-in
Easily access all of the code examples found on our site.
Simply navigate to the menu, click, and the code will be inserted directly into your module. .xlam add-in.
(No installation required!)
Free Download