Home / VBA / How to SELECT ALL the Cells in a Worksheet using a VBA Code
In VBA, there is a property called CELLS that you can use to select all the cells that you have in a worksheet.
Cells.Select- First, type the CELLS property to refer to all the cells in the worksheet.
- After that, enter a (.) dot.
- At this point, you’ll have a list of methods and properties.
- From that list select “Select” or type “Select”.
Once you select the entire worksheet you can change the font, clear contents from it, or do other things.
Notes
- The CELLS property works just like the way you use the keyboard shortcut Control + A to select all the cells.
- When you run this VBA code, it will select all the cells even if the sheet is protected and some of the cells are locked.
- It will select cells that are hidden as well.
The sheet Must Be Activated
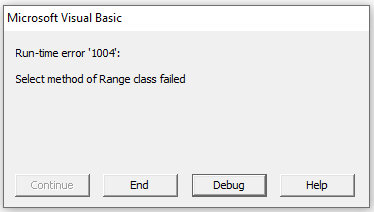
Now you need to understand one thing here when you select all the cells from a sheet that sheet needs to be activated. In short, you can’t select cells from a sheet that is not activated.
Let’s say you want to select all the cells from “Sheet1”. If you use the type below code, you’ll get an error. You need to activate the “Sheet1” first and then use the “Cells” property to select all the cells.
Worksheets("Sheet1").Activate
Cells.SelectNow when you run this it will first activate the “Sheet1” and then select all the cells. This thing gives you a little limitation that you can’t select the entire sheet if that sheet is not activated.
Here’s another thing that you can do: You can add a new sheet and then select all the cells.
Sheets.Add.Name = "mySheet"
Cells.SelectMore Tutorials
- Count Rows using VBA in Excel
- Excel VBA Font (Color, Size, Type, and Bold)
- Excel VBA Hide and Unhide a Column or a Row
- Excel VBA Range – Working with Range and Cells in VBA
- Apply Borders on a Cell using VBA in Excel
- Find Last Row, Column, and Cell using VBA in Excel
- Insert a Row using VBA in Excel
- Merge Cells in Excel using a VBA Code
- Select a Range/Cell using VBA in Excel
- ActiveCell in VBA in Excel
- Special Cells Method in VBA in Excel
- UsedRange Property in VBA in Excel
- VBA AutoFit (Rows, Column, or the Entire Worksheet)
- VBA ClearContents (from a Cell, Range, or Entire Worksheet)
- VBA Copy Range to Another Sheet + Workbook
- VBA Enter Value in a Cell (Set, Get and Change)
- VBA Insert Column (Single and Multiple)
- VBA Named Range | (Static + from Selection + Dynamic)
- VBA Range Offset
- VBA Sort Range | (Descending, Multiple Columns, Sort Orientation
- VBA Wrap Text (Cell, Range, and Entire Worksheet)
- VBA Check IF a Cell is Empty + Multiple Cells
⇠ Back to What is VBA in Excel
Helpful Links – Developer Tab – Visual Basic Editor – Run a Macro – Personal Macro Workbook – Excel Macro Recorder – VBA Interview Questions – VBA Codes
Return to VBA Code Examples
In this Article
- Select All Cells In Worksheet with .Cells
- An example of selecting all cells on Sheet1 using the code name Sheet1:
- An example of selecting all cells on Sheet1 using it’s tabname. You can replace “PlaceTabNameHere” with the name of your tab
- VBA Coding Made Easy
Select All Cells In Worksheet with .Cells
To select all the cells on a sheet using VBA you can use the .cells property of the worksheet, without specifying a specific cell.
An example of selecting all cells on Sheet1 using the code name Sheet1:
Sub MySelectAll()
Sheet1.Activate
Sheet1.Cells.Select
End Sub
An example of selecting all cells on Sheet1 using it’s tabname. You can replace “PlaceTabNameHere” with the name of your tab
Sub MySelectAll2()
Sheets("PlaceTabNameHere").Activate
Sheets("PlaceTabNameHere").Cells.Select
End Sub
VBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro – A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Learn More!
Did you find this VBA tutorial useful? Then share it with your friends and colleagues using the share buttons at the side or the bottom.
I found a similar solution to this question in c# How to Select all the cells in a worksheet in Excel.Range object of c#?
What is the process to do this in VBA?
I select data normally by using «ctrl+shift over arrow, down arrow» to select an entire range of cells. When I run this in a macro it codes out A1:Q398247930, for example. I need it to just be
.SetRange Range("A1:whenever I run out of rows and columns")
I could easily do it myself without a macro, but I’m trying to make the entire process a macro, and this is just a piece of it.
Sub sort()
'sort Macro
Range("B2").Select
ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets("Master").sort.SortFields.Clear
ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets("Master").sort.SortFields.Add Key:=Range("B2"), _
SortOn:=xlSortOnValues, Order:=xlAscending, DataOption:=xlSortNormal
With ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets("Master").sort
.SetRange Range("A1:whenever I run out of rows and columns")
.Header = xlNo
.MatchCase = False
.Orientation = xlTopToBottom
.SortMethod = xlPinYin
.Apply
End With
End Sub
edit:
There are other parts where I might want to use the same code but the range is say «C3:End of rows & columns». Is there a way in VBA to get the location of the last cell in the document?
asked Jul 30, 2013 at 18:50
C. TewaltC. Tewalt
2,2612 gold badges29 silver badges47 bronze badges
I believe you want to find the current region of A1 and surrounding cells — not necessarily all cells on the sheet.
If so — simply use…
Range(«A1»).CurrentRegion
answered Jul 30, 2013 at 19:17
ExcelExpertExcelExpert
3522 silver badges4 bronze badges
1
You can simply use cells.select to select all cells in the worksheet. You can get a valid address by saying Range(Cells.Address).
If you want to find the last Used Range where you have made some formatting change or entered a value into you can call ActiveSheet.UsedRange and select it from there. Hope that helps.
June7
19.5k8 gold badges24 silver badges33 bronze badges
answered Jul 30, 2013 at 19:11
chanceachancea
5,8083 gold badges28 silver badges39 bronze badges
2
you can use all cells as a object like this :
Dim x as Range
Set x = Worksheets("Sheet name").Cells
X is now a range object that contains the entire worksheet
answered Apr 15, 2015 at 11:47
you have a few options here:
- Using the UsedRange property
- find the last row and column used
- use a mimic of shift down and shift right
I personally use the Used Range and find last row and column method most of the time.
Here’s how you would do it using the UsedRange property:
Sheets("Sheet_Name").UsedRange.Select
This statement will select all used ranges in the worksheet, note that sometimes this doesn’t work very well when you delete columns and rows.
The alternative is to find the very last cell used in the worksheet
Dim rngTemp As Range
Set rngTemp = Cells.Find("*", SearchOrder:=xlByRows, SearchDirection:=xlPrevious)
If Not rngTemp Is Nothing Then
Range(Cells(1, 1), rngTemp).Select
End If
What this code is doing:
- Find the last cell containing any value
- select cell(1,1) all the way to the last cell
answered Jul 30, 2013 at 20:32
Derek ChengDerek Cheng
5353 silver badges8 bronze badges
3
Another way to select all cells within a range, as long as the data is contiguous, is to use Range("A1", Range("A1").End(xlDown).End(xlToRight)).Select.
answered Mar 29, 2019 at 19:38
I would recommend recording a macro, like found in this post;
Excel VBA macro to filter records
But if you are looking to find the end of your data and not the end of the workbook necessary, if there are not empty cells between the beginning and end of your data, I often use something like this;
R = 1
Do While Not IsEmpty(Sheets("Sheet1").Cells(R, 1))
R = R + 1
Loop
Range("A5:A" & R).Select 'This will give you a specific selection
You are left with R = to the number of the row after your data ends. This could be used for the column as well, and then you could use something like Cells(C , R).Select, if you made C the column representation.
answered Jul 30, 2013 at 19:25
MakeCentsMakeCents
7321 gold badge5 silver badges15 bronze badges
2
Sub SelectAllCellsInSheet(SheetName As String)
lastCol = Sheets(SheetName).Range("a1").End(xlToRight).Column
Lastrow = Sheets(SheetName).Cells(1, 1).End(xlDown).Row
Sheets(SheetName).Range("A1", Sheets(SheetName).Cells(Lastrow, lastCol)).Select
End Sub
To use with ActiveSheet:
Call SelectAllCellsInSheet(ActiveSheet.Name)
answered Mar 14, 2017 at 20:57
Yehia AmerYehia Amer
5985 silver badges11 bronze badges
Here is what I used, I know it could use some perfecting, but I think it will help others…
''STYLING''
Dim sheet As Range
' Find Number of rows used
Dim Final As Variant
Final = Range("A1").End(xlDown).Row
' Find Last Column
Dim lCol As Long
lCol = Cells(1, Columns.Count).End(xlToLeft).Column
Set sheet = ActiveWorkbook.ActiveSheet.Range("A" & Final & "", Cells(1, lCol ))
With sheet
.Interior.ColorIndex = 1
End With
answered Mar 16, 2019 at 4:29
I have found that the Worksheet «.UsedRange» method is superior in many instances to solve this problem.
I struggled with a truncation issue that is a normal behaviour of the «.CurrentRegion» method. Using [ Worksheets(«Sheet1»).Range(«A1»).CurrentRegion ] does not yield the results I desired when the worksheet consists of one column with blanks in the rows (and the blanks are wanted). In this case, the «.CurrentRegion» will truncate at the first record. I implemented a work around but recently found an even better one; see code below that allows copying the whole set to another sheet or to identify the actual address (or just rows and columns):
Sub mytest_GetAllUsedCells_in_Worksheet()
Dim myRange
Set myRange = Worksheets("Sheet1").UsedRange
'Alternative code: set myRange = activesheet.UsedRange
'use msgbox or debug.print to show the address range and counts
MsgBox myRange.Address
MsgBox myRange.Columns.Count
MsgBox myRange.Rows.Count
'Copy the Range of data to another sheet
'Note: contains all the cells with that are non-empty
myRange.Copy (Worksheets("Sheet2").Range("A1"))
'Note: transfers all cells starting at "A1" location.
' You can transfer to another area of the 2nd sheet
' by using an alternate starting location like "C5".
End Sub
answered May 2, 2019 at 19:38
Maybe this might work:
Sh.Range(«A1», Sh.Range(«A» & Rows.Count).End(xlUp))
answered Oct 31, 2014 at 18:38
Refering to the very first question, I am looking into the same.
The result I get, recording a macro, is, starting by selecting cell A76:
Sub find_last_row()
Range("A76").Select
Range(Selection, Selection.End(xlDown)).Select
End Sub
answered Aug 7, 2015 at 12:40
In this post you will learn about different ways to select all cells of a worksheet using VBA. When developing VBA macros you may need the VBA program to select all cells of a worksheet. For an example you might need to select all cells before printing the Excel sheet. There are many ways to select all cells of an Excel worksheet using VBA. In this lesson you will learn four different ways to select all cells of an Excel sheet.
Table of contents
Select all cells using Cells.Select Method
Select all cells using UsedRange property
Select all cells using last row and column numbers
Select all cells using CurrentRegion property
Cells.Select Method
This is the simplest way to select all the cells of an Excel worksheet using VBA. If you want to select all the cells of the activesheet then you can use the below code to do that.
Sub SelectAllCells_Method1_A()
ActiveSheet.Cells.Select
End Sub
However keep in mind that this method will select all cells of the worksheet including the empty cells.
Sometimes you may need to select all cells of a specific sheet of a workbook which contains multiple worksheets. Then you can refer to that specific sheet by its name. If the name of the sheet is “Data” then you can modify the above VBA macro as follows.
Sub SelectAllCells_Method1_B()
Dim WS As Worksheet
Set WS = Worksheets(«Data»)
WS.Activate
WS.Cells.Select
End Sub
Note that it is important to use the Worksheet.Activate method before selecting all cells. Because the VBA program can’t select cells of a worksheet which is not active. Program will throw an error if you try to select cells of a worksheet which is not active.
UsedRange Method
Above macros select all the cells of the worksheet. So VBA programs select cells even beyond the last row and column having data. But what if you want to select all the cells only inside the range you have used? For that you can use Worksheet.UsedRange property.
Sub SelectAllCells_Method2()
Dim WS As Worksheet
Set WS = Worksheets(«Data»)
WS.Activate
WS.UsedRange.Select
End Sub
Above VBA code will select all the cells inside the range you have used.
Select all cells using last row and column numbers
Also there is an alternative way to do this using VBA. First we can find the row number of the bottom most cell having data. Next we can find the column number of the rightmost cell having data. Then we can select the complete range from cell A1 to cell with those last row and column numbers using VBA. Here is how we can do it.
Sub SelectAllCells_Method3()
Dim WS As Worksheet
Dim WS_LastRow As Long
Dim WS_LastColumn As Long
Dim MyRange As Range
Set WS = Worksheets(«Data»)
WS_LastRow = WS.Cells.Find(«*», [A1], , , xlByRows, xlPrevious).Row
WS_LastColumn = WS.Cells.Find(«*», [A1], , , xlByColumns, xlPrevious).Column
Set MyRange = WS.Range(Cells(1, 1), Cells(WS_LastRow, WS_LastColumn))
WS.Activate
MyRange.Select
End Sub
There is one difference between those last two methods. If you use the last row and column numbers method, the range will be selected from cell A1. But if you use the UsedRange property then the range will be started from the first cell with the data. However you can also modify the last row and column numbers macro to get the same result as the Worksheet.UsedRange property method. But it will be a little more complicated.
Using CurrentRegion Property
We can also use the Range.CurrentRegion property to select all cells of an Excel worksheet. We can easily do that by making a slight change to the UsedRange method. Here is how we can select all cells using the CurrentRegion property.
Sub SelectAllCells_Method4()
Dim WS As Worksheet
Set WS = Worksheets(«Data»)
WS.Activate
WS.Range(«A1»).CurrentRegion.Select
End Sub
However there is one limitation in this method. If you have empty rows in your worksheet, then the VBA program will select cells only upto that row.
One of the easiest way to select all cells from the current worksheet using Excel VBA is using the cells property of the Worksheet and the calling the Select function without specifying the index or name of the cell.
How to Select All Cells using Excel VBA?
For example, below is a code snippet that selects all the cells from the worksheet “TestWorkSheet”.
Sub DP_SelectAllCells()
TestWorkSheet.Activate
TestWorkSheet.Cells.Select
End Sub