Null — это тип ошибки, которая возникает в Excel, когда две или более ссылки на ячейки, указанные в формулах, неверны или позиция, в которой они были размещены, неверна, если мы используем пробел в формулах между двумя ссылками на ячейки, мы столкнемся с нулевой ошибкой, там Есть две причины возникновения этой ошибки: одна — если мы использовали неправильную ссылку на диапазон, а другая — когда мы использовали оператор пересечения, который является символом пробела.
Нулевой в Excel
NULL — это не что иное, как ничего или пустое значение в excel. Обычно, когда мы работаем в excel, мы сталкиваемся с множеством NULL или пустых ячеек. Мы можем использовать формулу и выяснить, является ли конкретная ячейка пустой (NULL) или нет.
У нас есть несколько способов найти NULL-ячейки в Excel. В сегодняшней статье мы рассмотрим работу со значениями NULL в Excel.
Как определить, какая ячейка на самом деле пустая или пустая? Да, конечно, нам просто нужно посмотреть на конкретную ячейку и принять решение. Давайте откроем для себя множество методов поиска нулевых ячеек в Excel.
Функция ISBLANK для поиска значения NULL в Excel
В Excel у нас есть встроенная функция ISBLANK function, которая может находить пустые ячейки на листе. Давайте посмотрим на синтаксис функции ISBLANK.
Синтаксис прост и понятен. Значение — это не что иное, как ссылка на ячейку, которую мы проверяем, является ли она пустой или нет.
Поскольку ISBLANK — это логическая функция Excel, в результате она вернет TRUE или FALSE. Если ячейка ПУСТО (NULL), она вернет ИСТИНА, иначе она вернет ЛОЖЬ.
Примечание. ISBLANK будет рассматривать один пробел как один символ, и если в ячейке есть только пробел, он будет распознаваться как непустая или непустая ячейка.
# 1 — Как найти NULL ячейки в Excel?
Вы можете скачать этот шаблон Excel с нулевым значением здесь — Шаблон Excel с нулевым значением
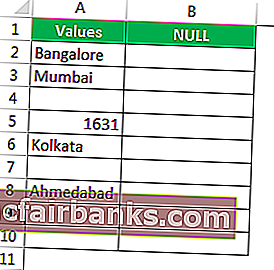
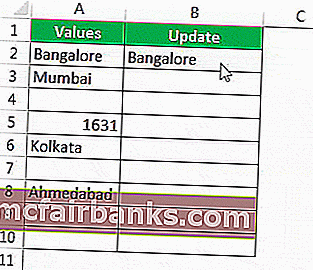
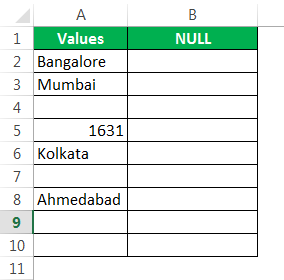
Предположим, у вас есть следующие значения в файле Excel, и вы хотите протестировать все пустые ячейки в диапазоне.
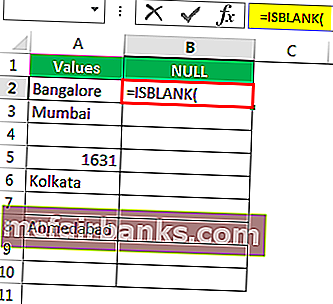
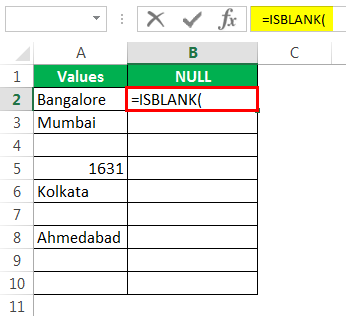
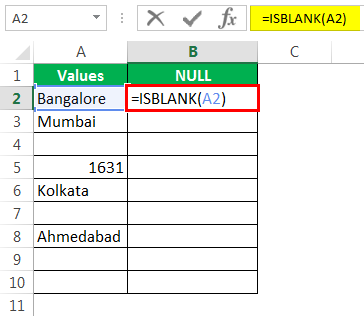
Откроем формулу ISBLANK в ячейке B2.
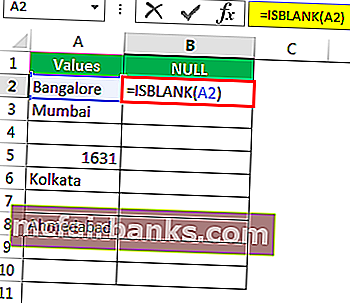
Выберите ячейку A2 в качестве аргумента. Поскольку есть только один аргумент, закройте скобку
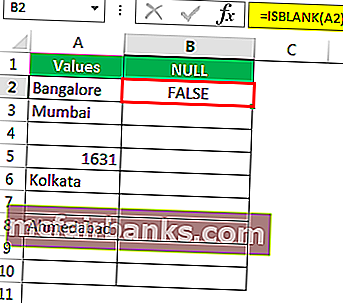
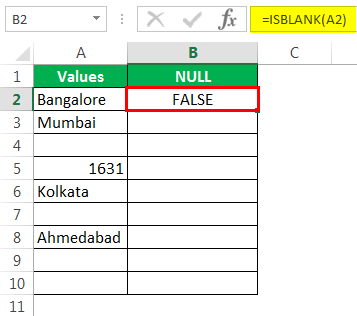
Мы получили результат, как показано ниже:
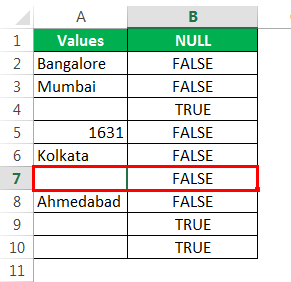
Перетащите формулу в другие оставшиеся ячейки.
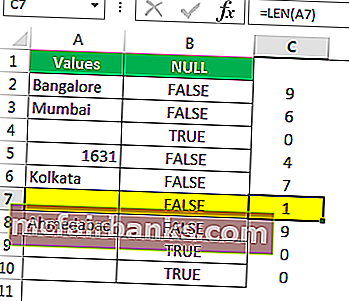
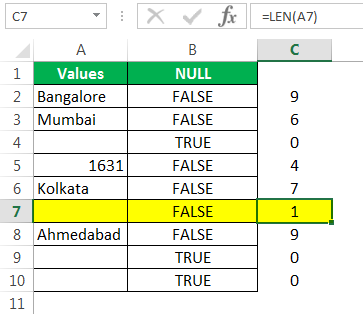
Мы получили результаты, но посмотрим на ячейку B7, хотя в ячейке A7 нет значения, формула все же вернула результат как False, т.е. ненулевую ячейку.
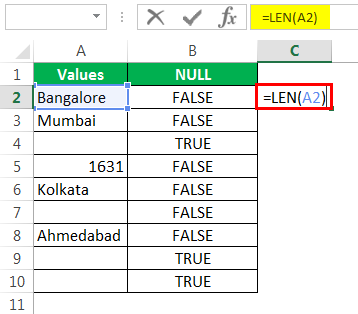
Давайте применим функцию LEN в Excel, чтобы найти номер. символов в ячейке.
Он считает нет. символов и дает результат.
Функция LEN вернула номер символа в ячейке A7 как 1. Итак, в нем должен быть символ.
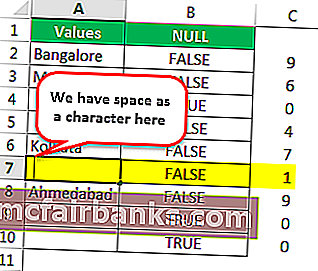
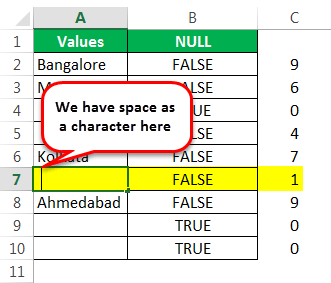
Теперь отредактируем ячейку. Итак, мы нашли здесь пробел, давайте удалим пробел, чтобы формула показывала точные результаты.
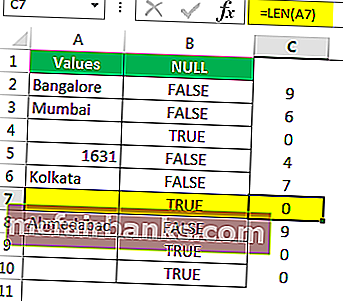
Я удалил пробел, и формула ISBLANK вернула результат как ИСТИНА, и даже функция LEN сообщает, что в ячейке A7 нет символов.
# 2 — Быстрый способ поиска NULL ячеек в Excel
Мы видели традиционный способ поиска пустых ячеек с помощью формулы. Без использования функции ISBLANK мы можем найти нулевые ячейки.
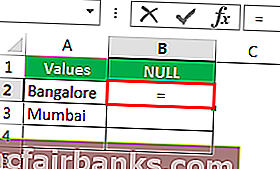
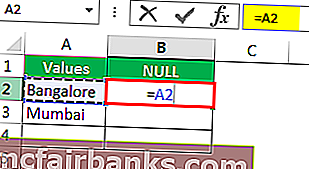
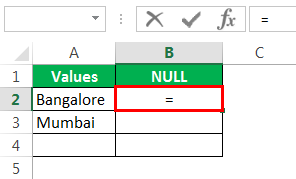
Откроем формулу со знаком равенства (=).
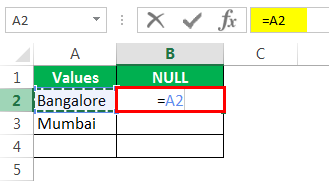
После равенства выбирает ячейку A2 в качестве ссылки.
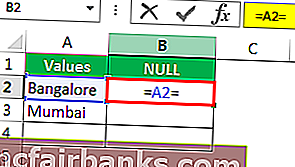
Теперь откройте еще один знак равенства после ссылки на ячейку.
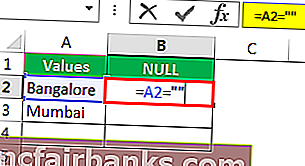
Теперь упомяните открытые двойные кавычки и закрытые двойные кавычки. («»)
Знаки, заключенные в двойные кавычки («»), указывают, является ли выбранная ячейка ПУСТОЙ или нет. Если выбранная ячейка — ПУСТО (NULL), мы получим ИСТИНА, иначе мы получим ЛОЖЬ.
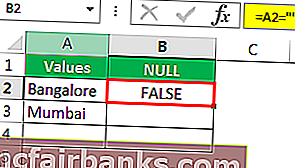
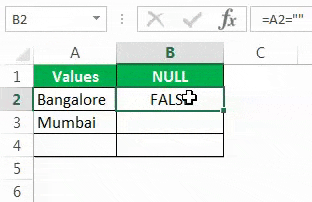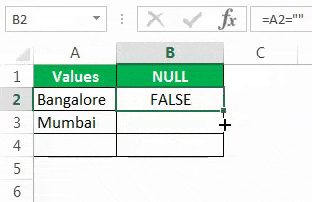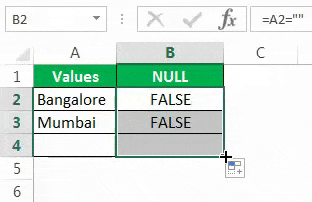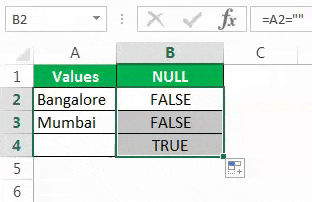
Перетащите формулу в оставшиеся ячейки.
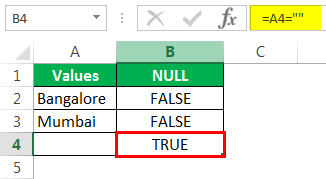
Мы видим, что в ячейке B7 мы получили результат «Истина». Это означает, что это пустая ячейка.
# 3 — Как заполнить наши собственные значения до NULL ячеек в Excel?
Мы видели, как найти NULL-ячейки на листе Excel. В нашей формуле в результате мы могли получить только ИСТИНА или ЛОЖЬ. Но мы также можем получить свои собственные значения для NULL ячеек.
Рассмотрим в качестве примера данные ниже.
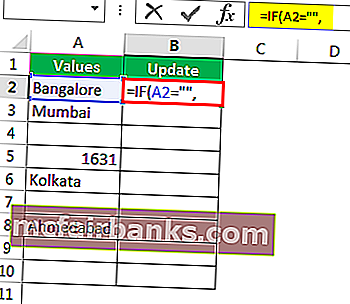
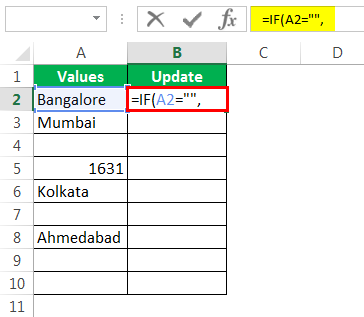
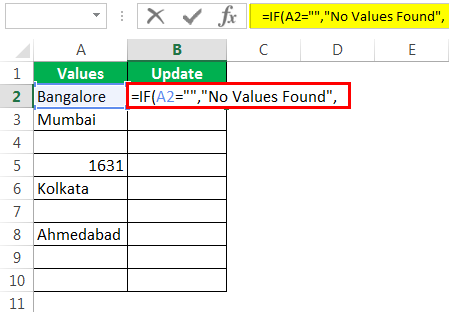
Шаг 1. Сначала откройте условие IF.
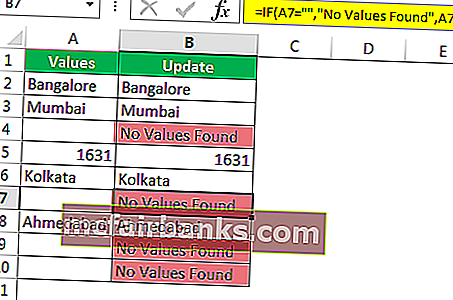
Шаг 2: Здесь нам нужно провести логический тест, т.е. нам нужно проверить, является ли ячейка NULL или нет. Так что примените A2 = ””.
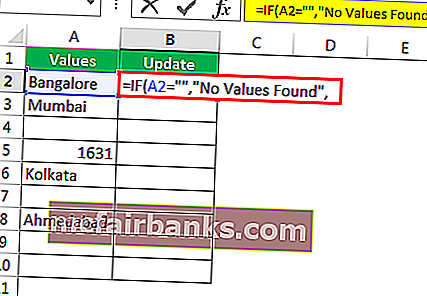
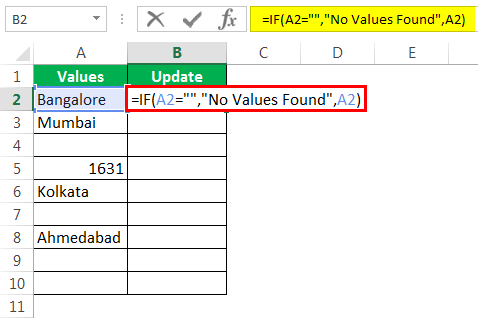
Шаг 3: Если логический тест — ИСТИНА (ИСТИНА означает, что ячейка НУЛЯ), нам нужен результат как «Значения не найдены».
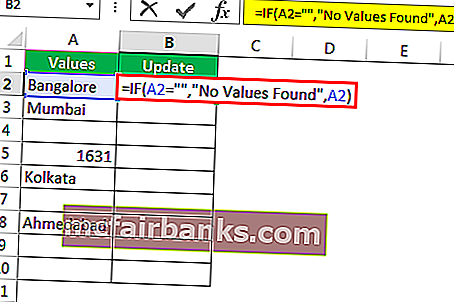
Шаг 4: Если логический тест — ЛОЖЬ (ЛОЖЬ означает, что ячейка содержит значения), то нам нужно то же значение ячейки.
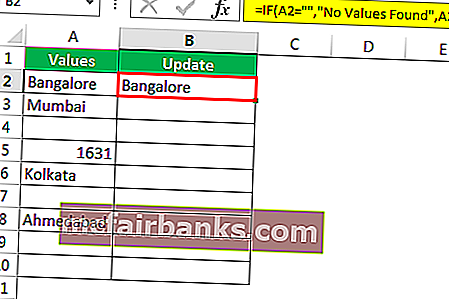
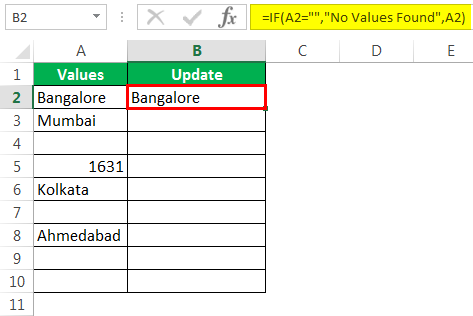
Мы получили результат как то же значение ячейки.
Шаг 5: Перетащите формулу в оставшиеся ячейки.
Итак, у нас есть собственное значение « Никаких значений не найдено» для всех ячеек NULL.
То, что нужно запомнить
- Даже пробел будет считаться символом и рассматриваться как непустая ячейка.
- Вместо ISBLANK мы также можем использовать двойные кавычки («») для проверки NULL ячеек.
- Если ячейка кажется пустой, а формула показывает ее как ненулевую ячейку, вам необходимо проверить количество символов с помощью функции LEN.
Проверка переменных и выражений с помощью встроенных функций VBA Excel: IsArray, IsDate, IsEmpty, IsError, IsMissing, IsNull, IsNumeric, IsObject.
Проверка переменных и выражений
Встроенные функции VBA Excel — IsArray, IsDate, IsEmpty, IsError, IsMissing, IsNull, IsNumeric, IsObject — проверяют значения переменных и выражений на соответствие определенному типу данных или специальному значению.
Синтаксис функций для проверки переменных и выражений:
Expression — выражение, переменная или необязательный аргумент для IsMissing.
Все функции VBA Excel для проверки переменных и выражений являются логическими и возвращают значение типа Boolean — True или False.
Функция IsArray
Описание функции
Функция IsArray возвращает значение типа Boolean, указывающее, является ли переменная массивом:
- True — переменная является массивом;
- False — переменная не является массивом.
Пример с IsArray
|
Sub Primer1() Dim arr1(), arr2(1 To 10), arr3 Debug.Print IsArray(arr1) ‘Результат: True Debug.Print IsArray(arr2) ‘Результат: True Debug.Print IsArray(arr3) ‘Результат: False arr3 = Array(1, 2, 3, 4, 5) Debug.Print IsArray(arr3) ‘Результат: True End Sub |
Как показывает пример, функция IsArray возвращает True и в том случае, если переменная только объявлена как массив, но еще не содержит значений.
Функция IsDate
Описание функции
Функция IsDate возвращает логическое значение, указывающее, содержит ли переменная значение, которое можно интерпретировать как дату:
- True — переменная содержит дату, выражение возвращает дату, переменная объявлена с типом As Date;
- False — в иных случаях.
Пример с IsDate
|
Sub Primer2() Dim d1 As String, d2 As Date Debug.Print IsDate(d1) ‘Результат: False Debug.Print IsDate(d2) ‘Результат: True d1 = «14.01.2023» Debug.Print IsDate(d1) ‘Результат: True Debug.Print IsDate(Now) ‘Результат: True End Sub |
Функция IsEmpty
Описание функции
Функция IsEmpty возвращает значение типа Boolean, указывающее, содержит ли переменная общего типа (As Variant) значение Empty:
- True — переменная содержит значение Empty;
- False — переменной присвоено значение, отличное от Empty.
Пример с IsEmpty
|
Sub Primer3() Dim s As String, v As Variant Debug.Print IsEmpty(s) ‘Результат: False Debug.Print IsEmpty(v) ‘Результат: True v = 125 Debug.Print IsEmpty(v) ‘Результат: False Range(«A1»).Clear Debug.Print IsEmpty(Range(«A1»)) ‘Результат: True Range(«A1») = 123 Debug.Print IsEmpty(Range(«A1»)) ‘Результат: False End Sub |
Как видно из примера, функцию IsEmpty можно использовать для проверки ячеек на содержание значения Empty (пустая ячейка общего формата).
Функция IsError
Описание функции
Функция IsError возвращает логическое значение, указывающее, является ли аргумент функции значением ошибки, определенной пользователем:
- True — аргумент функции является значением ошибки, определенной пользователем;
- False — в иных случаях.
Пользователь может определить одну или несколько ошибок для своей процедуры или функции с рекомендациями действий по ее (их) исправлению. Возвращается номер ошибки с помощью функции CVErr.
Пример с IsError
Допустим, пользователь определил, что ошибка №25 означает несоответствие аргумента функции Vkuba числовому формату:
|
Function Vkuba(x) If IsNumeric(x) Then Vkuba = x ^ 3 Else Vkuba = CVErr(25) End If End Function Sub Primer4() Debug.Print Vkuba(5) ‘Результат: 125 Debug.Print IsError(Vkuba(5)) ‘Результат: False Debug.Print Vkuba(«пять») ‘Результат: Error 25 Debug.Print IsError(Vkuba(«пять»)) ‘Результат: True End Sub |
Функция IsMissing
Описание функции
Функция IsMissing возвращает значение типа Boolean, указывающее, был ли необязательный аргумент типа данных Variant передан процедуре:
- True — если в процедуру не было передано значение для необязательного аргумента;
- False — значение для необязательного аргумента было передано в процедуру.
Пример с IsMissing
|
Function Scepka(x, Optional y) If Not IsMissing(y) Then Scepka = x & y Else Scepka = x & » (а необязательный аргумент не подставлен)» End If End Function Sub Primer5() Debug.Print Scepka(«Тропинка», » в лесу») ‘Результат: Тропинка в лесу Debug.Print Scepka(«Тропинка») ‘Результат: Тропинка (а необязательный аргумент не подставлен) End Sub |
Функция IsNull
Описание функции
Функция IsNull возвращает логическое значение, указывающее, является ли Null значением переменной или выражения:
- True — значением переменной или выражения является Null;
- False — в иных случаях.
Пример с IsNull
Функция IsNull особенно необходима из-за того, что любое условие с выражением, в которое входит ключевое слово Null, возвращает значение False:
|
Sub Primer6() Dim Var Var = Null If Var = Null Then Debug.Print Var ‘Результат: «» If Var <> Null Then Debug.Print Var ‘Результат: «» If IsNull(Var) Then Debug.Print Var ‘Результат: Null End Sub |
Функция IsNumeric
Описание функции
Функция IsNumeric возвращает значение типа Boolean, указывающее, можно ли значение выражения или переменной рассматривать как число:
- True — если аргумент функции может рассматриваться как число;
- False — в иных случаях.
Пример с IsNumeric
|
Sub Primer7() Debug.Print IsNumeric(«3,14») ‘Результат: True Debug.Print IsNumeric(«четыре») ‘Результат: False End Sub |
Функция IsObject
Описание функции
Функция IsObject возвращает логическое значение, указывающее, является ли переменная объектной:
- True — переменная содержит ссылку на объект или значение Nothing;
- False — в иных случаях.
Функция IsObject актуальна для переменных типа Variant, которые могут содержать как ссылки на объекты, так и значения других типов данных.
Пример с IsObject
|
Sub Primer8() Dim myObj As Object, myVar As Variant Debug.Print IsObject(myObj) ‘Результат: True Debug.Print IsObject(myVar) ‘Результат: False Set myVar = ActiveSheet Debug.Print IsObject(myVar) ‘Результат: True End Sub |
Содержание
- Функция IsNull
- Синтаксис
- Замечания
- Пример
- См. также
- Поддержка и обратная связь
- VBA Information Functions in Excel
- List of Information Functions in Excel VBA:
- Other Useful Resources:
- What is the different between IsNull, IsEmpty, =Empty, and an empty string ie «» and why might I use variants
- 2 Answers 2
- VBA Check if variable is empty
- 4 Answers 4
- Linked
- Related
- Hot Network Questions
- Subscribe to RSS
- VBA Excel. Проверка переменных и выражений
- Проверка переменных и выражений
- Функция IsArray
- Описание функции
- Пример с IsArray
- Функция IsDate
- Описание функции
- Пример с IsDate
- Функция IsEmpty
- Описание функции
- Пример с IsEmpty
- Функция IsError
- Описание функции
- Пример с IsError
Функция IsNull
Возвращает значение типа Boolean, которое указывает, не содержит ли выражение достоверных данных (Null).
Синтаксис
IsNull(выражение)
Замечания
IsNull возвращает значение True (Истина), если используется expression равное Null; в другом случае IsNull возвращает значение False (Ложь). Если expression состоит из нескольких переменных, значение Null, заданное для одной из них, приводит к возврату значения True для всего выражения.
Значение Null указывает, что Variant не содержит достоверных значений. Null не приравнивается к значению Empty (Пусто), которое указывает, что переменная не была инициализирована. Это также не то же самое, что строка нулевой длины («»), которую иногда называют пустой строкой.
Используйте функцию IsNull, чтобы определить, содержит ли выражение значение Null. Выражения, для которых может потребоваться значение True , в некоторых случаях, например If Var = Null и If Var <> Null , всегда имеют значение False. Это связано с тем, что любое выражение, содержащее значение NULL , само по себе имеет значение NULL и , следовательно, false.
Пример
В этом примере используется функция IsNull, чтобы определить, содержит ли переменная значение Null.
См. также
Поддержка и обратная связь
Есть вопросы или отзывы, касающиеся Office VBA или этой статьи? Руководство по другим способам получения поддержки и отправки отзывов см. в статье Поддержка Office VBA и обратная связь.
Источник
VBA Information Functions in Excel
VBA Information Functions can be use to convert numeric values or strings. These are ENVIRON, IsArray, IsDate, IsEmpty, IsError, IsMissing, IsNull, IsNumeric, IsObject etc. These functions are Built-In functions. We can use these VBA Information functions in either procedure or function. These functions we use in the VBA editor window in Excel. These Information functions you can use any number of times in VBA macro codes.
List of Information Functions in Excel VBA:
Here are the list of Information functions. And also find its description, syntax and return type. We can use these multiple Information functions in one statement.
| Function | Description | Syntax | Return Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| VBA ENVIRON | VBA ENVIRON function returns value of the current operating system environment variable. | Environ(Expression) | String |
| VBA IsArray | VBA IsArray function checks a specified variable is an array or not. | IsArray(VarName) | Boolean |
| VBA IsDate | VBA IsDate function checks specified Expression is date or not. It returns True if it is valid date. | IsDate(Expression) | Boolean |
| VBA IsEmpty | VBA IsEmpty function checks specified Expression is empty or not. | IsEmpty(Expression) | Boolean |
| VBA IsError | VBA IsError function checks specified Expression is error or not. | IsError(Expression) | Boolean |
| VBA IsMissing | VBA IsMissing function checks specified an optional argument is missing or not. | IsMissing(ArgName) | Boolean |
| VBA IsNull | VBA IsNull function checks specified Expression is Null or not. | IsNull(Expression) | Boolean |
| VBA IsNumeric | VBA IsNumeric function checks specified Expression is Numeric or not. | IsNumeric(Expression) | Boolean |
| VBA IsObject | VBA IsObject function checks specified variable is an object or not. | IsObject(Expression) | Boolean |
Other Useful Resources:
Click on the following links of the useful resources. These helps to learn and gain more knowledge.
Источник
What is the different between IsNull, IsEmpty, =Empty, and an empty string ie «» and why might I use variants
I’m trying to understand what a Null is and also what an Empty variable is. Are they the same? How do empty strings fit in?
When creating MS Access tables why do fields have an option of «Allow Zero Length String»?
I’ve been struggling with loading data from an Access database into variables (eg using DAO or ADO) and I find myself having to declare all the variables I use a Variant. This seems so wrong to me.
Does anyone have any good example code that demonstrates how these differ and can you explain why I might use a variant.
Can anyone advise.
(I have posted my own answer with lots of simple example code that has helped me. It shows how lots of functions work with variants, I hope people with similar difficulties find this useful)
2 Answers 2
A variant is the only type of variable that can store an empty value or a Null value, and is declared thus:
Immediately after declaration a variant stores no value and it is empty. Also you can assign empty to a variant using aVar = Empty and it will be empty again.
When a variant stores empty these are both true:
You can also set the value of a Variant variable to be Null
These would now be false
However, IsNull(aVar) would be true.
Null is particularly useful when you use VBA variables to store data that has come from a database table that allows NULL values to be stored in it’s fields. In this case it is generally advisable that all the variables need to accommodate storing NULL. So they all need to be variant as this is the only data type that stores NULL.
This is very unfortunate as it would be better to have more strongly typed variables in use.
A variant storing Null is not the same as a variant being Empty. Null indicates that a value was assigned to a variable and the value was Null.
This gets confusing as Null is used by databases to indicate no value has been stored in a field, and most databases allow fields with any datatype to be Null. When a database field stores Null, it is kind of the equivalent to a VBA variant variable having just been declared as “receptacle” for a value and not yet being given a value. The variable, just like the table field is an receptacle without anything in it.
However, if a VBA variant variable is given a Null value from a database table, then it stores the fact that it is Null, as this is different to it never having been given a value and is information your program might want to treat differently.
Also note that a variant storing and empty string «» is not the same as being empty.
ie «» does not equal Empty (and it is not the same as Null either!)
When using MS Access tables to store text, I would advise against setting the «Allow Zero Length» field property to true, which is the default setting, as this means your database field will be able to store «» (ie an empty string) as well as a Null value. Any code you write then has to work with the possibility that the field will store a «» or a Null. It’s easier just to work with a Null.
(It’s very rare to need to store an empty string in a database table).
Another useful technique is to use MyString = Nz(MyStringDatabaseField) to convert any nulls to be an empty string. At least then your code only has to test for empty strings and not for Nulls as well. This technique will also simplify code working with access tables that store empty strings. Sometimes it may be appropriate to use `MyInteger=Nz(MyIntegerDatabaseField) to convert any nulls to 0, but I am very uncomfortable with this as 0 has a more meaning than an empty string and really Null <> 0!
Note that SQL statements which use an OUTER JOIN between their tables, can result in the returned recordset containing NULL values in fields where the underlying table field is defined to prevent NULLs being stored.
Note that if you do not use a variant the data types then default values may be used unexpectedly. Eg
The code below helped me to understand the difference between the various functions that can be used to inspect variant variables
Adding to HarveyFrench’s answer.
The Variant of VBA gracefully handles NULL’s, and it also handles Empty’s. The concept of Empty is of debatable merit, and not represented in many database systems.
NULL means an unobtained or unobtainable value. It was a concept made essential to the proper handling of OUTER JOIN’s. An OUTER JOIN begins with a table (or subquery) that will have all of its rows selected. The condition of the JOIN is then used to link to another table (or subquery). In the case of an INNER JOIN, if the condition cannot be satisfied (i.e. resolved to TRUE) between the tables (or subqueries), then the rows of such situations do not get selected. However, in the case of an OUTER JOIN, the unsatisfied JOIN condition will still result in rows from the first table (or subquery) being selected alongside a set of NULL’s for each column of the other table (or subquery). These NULL’s would signal the failure of the JOIN; these would be the unobtainable values.
An «Empty» isn’t the same as a NULL. NULL means unobtained. «Empty» means «this field is intentionally blank.» It’s a subtle difference, but an «Empty» is somthing definitive, whereas a NULL is something left unknown. An intentional blank is deliberate, not a mistake, unambiguously there specifically to mean there is nothing to find in the first place.
Some folks may intentionally employ NULL to indicate an «Empty» for a column; or they may use NULL to indicate something else other than the unobtainable. There are some folks who would say using NULL in this way is bad practice. The reasoning to this is that now there isn’t a clear way to distinguish the intentionally blank from the unknown, and you may confuse yourself in complicated queries. I would say to that «just be careful, and are you sure that NULL is the best or only way to make it all work?»
As for the empty string, the «» , that is very much a value. As in something definitively known. It is also a specific datatype — namely that of a string (or text or varchar or whatever an array of characters may be taken as). Call it an «Empty» is you wish, although really it’s limited to where strings are expected. In practice it may amount to the same thing. But it’s not really «Empty», and it is most certainly not NULL.
Personally I regard NULL as more of a signal, like «not-a-number» conditions you may encounter in floating point numbers. In other words, NULL isn’t a particular value. It’s the signal of not having a value. When you look up three-valued logic (3VL), particularly where SQL and NULL get involved, you’ll better understand why the condition NULL=NULL simply isn’t TRUE.
«Empty» is also a signal, but a signal of «whatever amounts to the same as a blank.» Hence, the conditions EMPTY=»» and EMPTY=0 will both be TRUE — even though «»=0 probably won’t compute.
Источник
VBA Check if variable is empty
I have an object and within it I want to check if some properties are set to False , like:
But sometimes, objresult.EOF is Empty ; how can I check for this?
- IsEmpty function is for excel cells only
- objresult.EOF Is Nothing — returns Empty
- objresult.EOF <> null — returns Empty as well!
4 Answers 4
How you test depends on the Property’s DataType:
You can tell the DataType by pressing F2 to launch the Object Browser and looking up the Object. Another way would be to just use the TypeName function: MsgBox TypeName(obj.Property)
To check if a Variant is Null, you need to do it like:
For a number, it is tricky because if a numeric cell is empty VBA will assign a default value of 0 to it, so it is hard for your VBA code to tell the difference between an entered zero and a blank numeric cell.
The following check worked for me to see if there was an actual 0 entered into the cell:
I had a similar issue with an integer that could be legitimately assigned 0 in Access VBA. None of the above solutions worked for me.
At first I just used a boolean var and IF statement:
In my case, my integer variable assignment was within a for loop and another IF statement, so I ended up using «Exit For» instead as it was more concise.
Like so:
Linked
Hot Network Questions
To subscribe to this RSS feed, copy and paste this URL into your RSS reader.
Site design / logo © 2023 Stack Exchange Inc; user contributions licensed under CC BY-SA . rev 2023.3.17.43323
By clicking “Accept all cookies”, you agree Stack Exchange can store cookies on your device and disclose information in accordance with our Cookie Policy.
Источник
VBA Excel. Проверка переменных и выражений
Проверка переменных и выражений с помощью встроенных функций VBA Excel: IsArray, IsDate, IsEmpty, IsError, IsMissing, IsNull, IsNumeric, IsObject.
Проверка переменных и выражений
Встроенные функции VBA Excel — IsArray, IsDate, IsEmpty, IsError, IsMissing, IsNull, IsNumeric, IsObject — проверяют значения переменных и выражений на соответствие определенному типу данных или специальному значению.
Синтаксис функций для проверки переменных и выражений:
Expression — выражение, переменная или необязательный аргумент для IsMissing.
Все функции VBA Excel для проверки переменных и выражений являются логическими и возвращают значение типа Boolean — True или False.
Функция IsArray
Описание функции
Функция IsArray возвращает значение типа Boolean, указывающее, является ли переменная массивом:
- True — переменная является массивом;
- False — переменная не является массивом.
Пример с IsArray
Как показывает пример, функция IsArray возвращает True и в том случае, если переменная только объявлена как массив, но еще не содержит значений.
Функция IsDate
Описание функции
Функция IsDate возвращает логическое значение, указывающее, содержит ли переменная значение, которое можно интерпретировать как дату:
- True — переменная содержит дату, выражение возвращает дату, переменная объявлена с типом As Date;
- False — в иных случаях.
Пример с IsDate
Функция IsEmpty
Описание функции
Функция IsEmpty возвращает значение типа Boolean, указывающее, содержит ли переменная общего типа (As Variant) значение Empty:
- True — переменная содержит значение Empty;
- False — переменной присвоено значение, отличное от Empty.
Пример с IsEmpty
Как видно из примера, функцию IsEmpty можно использовать для проверки ячеек на содержание значения Empty (пустая ячейка общего формата).
Функция IsError
Описание функции
Функция IsError возвращает логическое значение, указывающее, является ли аргумент функции значением ошибки, определенной пользователем:
- True — аргумент функции является значением ошибки, определенной пользователем;
- False — в иных случаях.
Пользователь может определить одну или несколько ошибок для своей процедуры или функции с рекомендациями действий по ее (их) исправлению. Возвращается номер ошибки с помощью функции CVErr.
Пример с IsError
Допустим, пользователь определил, что ошибка №25 означает несоответствие аргумента функции Vkuba числовому формату:
Источник
This Excel tutorial explains how to use the Excel ISNULL function with syntax and examples.
Description
The Microsoft Excel ISNULL function returns TRUE if the expression is a null value. Otherwise, it returns FALSE.
The ISNULL function is a built-in function in Excel that is categorized as an Information Function. It can be used as a VBA function (VBA) in Excel. As a VBA function, you can use this function in macro code that is entered through the Microsoft Visual Basic Editor.
Syntax
The syntax for the ISNULL function in Microsoft Excel is:
IsNull( expression )
Parameters or Arguments
- expression
- A variant that contains a string or numeric value.
Returns
The ISNULL function returns TRUE if the expression is a NULL value.
The ISNULL function returns FALSE if the expression is not a NULL value.
Applies To
- Excel for Office 365, Excel 2019, Excel 2016, Excel 2013, Excel 2011 for Mac, Excel 2010, Excel 2007, Excel 2003, Excel XP, Excel 2000
Type of Function
- VBA function (VBA)
Example (as VBA Function)
The ISNULL function can only be used in VBA code in Microsoft Excel.
Let’s look at some Excel ISNULL function examples and explore how to use the ISNULL function in Excel VBA code:
IsNull(null)
Result: TRUE
IsNull("Tech on the Net")
Result: FALSE
For example:
Dim LValue As Boolean
LValue = IsNull("Tech on the Net")
In this example, the variable called LValue would contain FALSE as a value.
Null is an error that occurs in Excel when the two or more cell references provided in a formula are incorrect, or the position they have been placed in is erroneous. For example, suppose we use space in formulas between two cell references; we will encounter a null error. In that case, there are two reasons to meet this error, one if we used an incorrect range reference and another when we use the intersect operator, which is the space character.
NULL is nothing but nothing or blank in Excel. Usually, when working in Excel, we encounter many NULL or blank cells. We can use the formula and find out whether the particular cell is blank (NULL) or not.
We have several ways of finding the NULL cells in Excel. Today’s article will take a tour of dealing with NULL values in Excel.
How do you find which cell is blank or null? Yes, we must look at the particular cell and decide. Let us discover many methods of finding the null cells in Excel.
Table of contents
- Null in Excel
- ISBLANK Function to Find NULL Value in Excel
- #1 – How to Find NULL Cells in Excel?
- #2 – Shortcut Way of Finding NULL Cells in Excel
- #3 – How to Fill Our Own Values to NULL Cells in Excel?
- Things to Remember
- Recommended Articles
ISBLANK Function to Find NULL Value in Excel
In Excel, we have an ISBLANK function, which can find the blank cells in the worksheet. First, let us look at the syntax of the ISBLANK functionISBLANK in Excel is a logical function that checks if a target cell is blank or not. It returns the output “true” if the cell is empty (blank) or “false” if the cell is not empty. It is also known as referencing worksheet function and is grouped under the information function of Excel
read more.
The syntax is straightforward. Value is nothing but the cell reference; we are testing whether it is blank or not.
Since ISBLANK is a logical excel functionA logical test in Excel results in an analytical output, either true or false. The equals to operator, “=,” is the most commonly used logical test.read more, it will either return TRUE or FALSE. If the cell is NULL, it will return TRUE, or else it will return FALSE.
Note: ISBLANK will treat the single space as one character; if the cell has only space value, it will be recognized as a non-blank or non-null cell.
#1 – How to Find NULL Cells in Excel?
You can download this Null Value Excel Template here – Null Value Excel Template
Assume we have the values below in the Excel file and want to test all the null cells in the range.
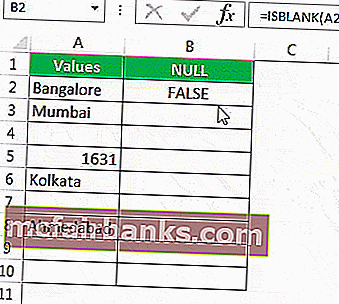
- Let us open the ISBLANK formula in cell B2 cell.
- Select cell A2 as the argument. Since there is only one argument, close the bracket.
- We got the result as given below:
- Then, drag and drop the formula to other remaining cells.
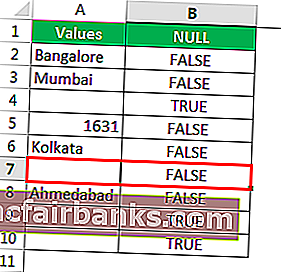
- We got the results. But look at cell B7. Even though there is still no value in cell A7, the formula returned the result as a FALSE, non-null cell.
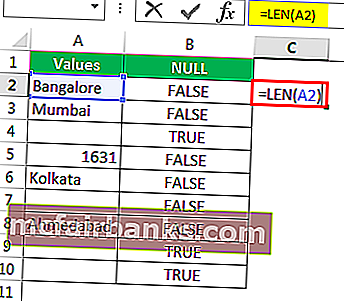
- Let us apply the LEN function in excelThe Len function returns the length of a given string. It calculates the number of characters in a given string as input. It is a text function in Excel as well as an inbuilt function that can be accessed by typing =LEN( and entering a string as input.read more to find the number of characters in the cell.
- It counts the no. of characters and gives the result.
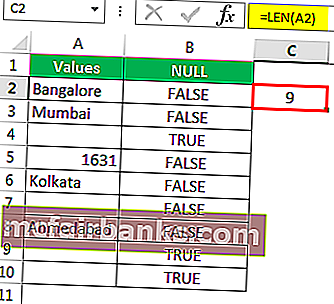
- The LEN function returned the no. of character in the A7 cell as 1. So, there should be a character in it.
- Let us edit the cell now. So, we found the space character here. Let us remove the space character to make the formula show accurate results.
- We have removed the space character, and the ISBLANK formula returned the result as TRUE. That is because even the LEN function says there are zero characters in cell A7.
#2 – Shortcut Way of Finding NULL Cells in Excel
We have seen the traditional formula way to find the null cells. Without using the ISBLANK function, we can find the null cells.
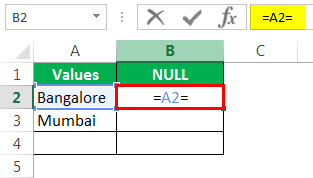
Let us open the formula with an equal sign (=).
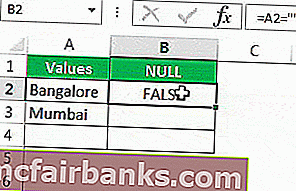
After the equal sign, select cell A2 as the reference.
Now open one more equal sign after the cell reference.
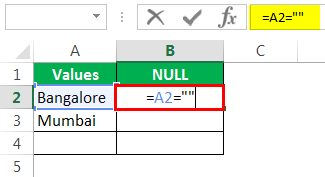
Now mention open double-quotes and close double-quotes. (“”)
The sign double quotes (“”) says the selected cell is NULL or not. If the selected cell is NULL, we will get TRUE. Else, we will get FALSE.
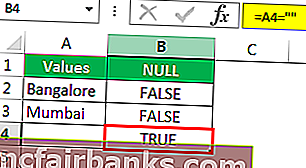
Drag the formula to the remaining cells.
We can see that in cell B7, we got the result as “TRUE.” So it means it is a null cell.
#3 – How to Fill Our Values to NULL Cells in Excel?
We have seen how to find the NULL cells in the Excel sheet. In our formula, we could only get TRUE or FALSE. But we can also receive our values for the NULL cells.
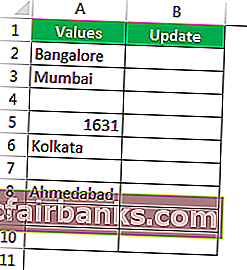
Consider the below data for an example.
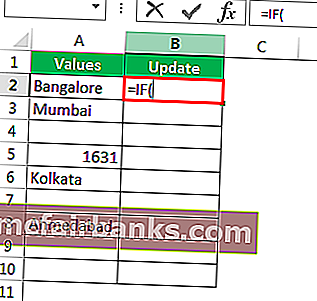
Step 1: Open the IF condition first.
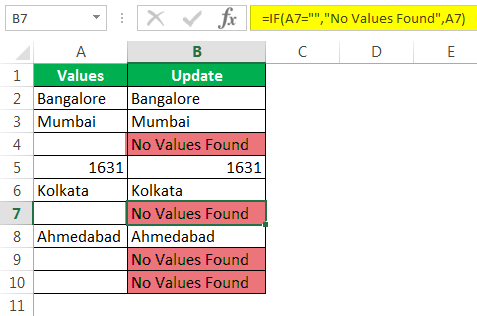
Step 2: Here, we need to do a logical test. We need to test whether the cell is NULL or not. So apply A2=”.”
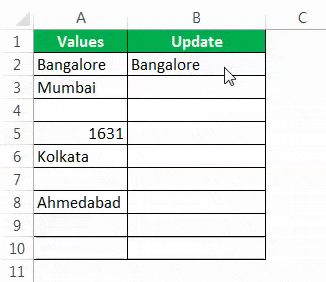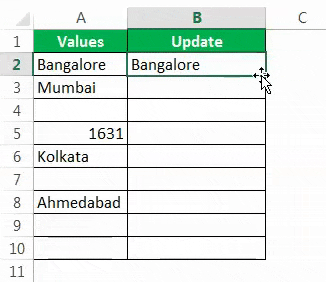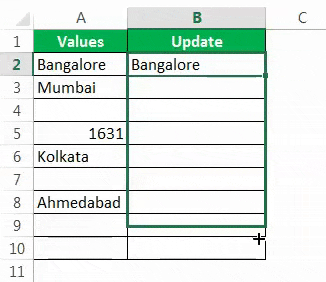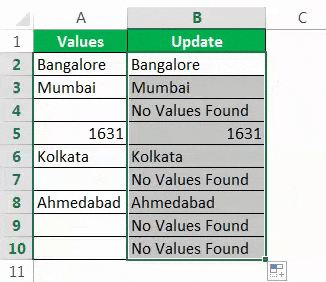
Step 3: If the logical test is TRUE (TRUE means cell is NULL), we need the result as “No Values Found.”
Step 4: If the logical test is FALSE (which means the cell contains values), then we need the same cell value.
We got the result as the same cell value.
Step 5: Drag the formula to the remaining cells.
So, we have got our value of No Values Found for all the NULL cells.
Things to Remember
- Even space will be considered a character and treated as a non-empty cell.
- Instead of ISBLANK, we can also use double quotes (“ ”) to test the NULL cells.
- If the cell seems blank and the formula shows it as a non-null cell, then you need to test the number of characters using the LEN function.
Recommended Articles
This article is a guide to Null in Excel. We discuss the top methods to find null values in Excel using ISBLANK and shortcuts to replace those null cells, along with practical examples and a downloadable template. You may learn more about Excel from the following articles: –
- Excel Count RowsThere are numerous ways to count rows in Excel using the appropriate formula, whether they are data rows, empty rows, or rows containing numerical/text values. Depending on the circumstance, you can use the COUNTA, COUNT, COUNTBLANK, or COUNTIF functions.read more
- VBA RangeRange is a property in VBA that helps specify a particular cell, a range of cells, a row, a column, or a three-dimensional range. In the context of the Excel worksheet, the VBA range object includes a single cell or multiple cells spread across various rows and columns.read more
- Countif not Blank in Excel
- Remove Blank Rows in ExcelThere are several methods for deleting blank rows from Excel: 1) Manually deleting blank rows if there are few blank rows 2) Use the formula delete 3) Use the filter to find and delete blank rows.read more