Excel for Microsoft 365 Excel for Microsoft 365 for Mac Excel for the web Excel 2021 Excel 2021 for Mac Excel 2019 Excel 2019 for Mac Excel 2016 Excel 2016 for Mac Excel 2013 Excel for Mac 2011 More…Less
This article describes the formula syntax and usage of the NUMBERVALUE function in Microsoft Excel.
Description
Converts text to a number, in a locale-independent way.
Syntax
NUMBERVALUE(Text, [Decimal_separator], [Group_separator ])
The NUMBERVALUE function syntax has the following arguments.
-
Text Required. The text to convert to a number.
-
Decimal_separator Optional. The character used to separate the integer and fractional part of the result.
-
Group_separator Optional. The character used to separate groupings of numbers, such as thousands from hundreds and millions from thousands.
Remarks
-
If the Decimal_separator and Group_separator arguments are not specified, separators from the current locale are used.
-
If multiple characters are used in the Decimal_separator or Group_separator arguments, only the first character is used.
-
If an empty string («») is specified as the Text argument, the result is 0.
-
Empty spaces in the Text argument are ignored, even in the middle of the argument. For example, » 3 000 » is returned as 3000.
-
If a decimal separator is used more than once in the Text argument, NUMBERVALUE returns the #VALUE! error value.
-
If the group separator occurs before the decimal separator in the Text argument , the group separator is ignored.
-
If the group separator occurs after the decimal separator in the Text argument, NUMBERVALUE returns the #VALUE! error value.
-
If any of the arguments are not valid, NUMBERVALUE returns the #VALUE! error value.
-
If the Text argument ends in one or more percent signs (%), they are used in the calculation of the result. Multiple percent signs are additive if they are used in the Text argument just as they are if they are used in a formula. For example, =NUMBERVALUE(«9%%») returns the same result (0.0009) as the formula =9%%.
Example
Copy the example data in the following table, and paste it in cell A1 of a new Excel worksheet. For formulas to show results, select them, press F2, and then press Enter. If you need to, you can adjust the column widths to see all the data.
|
Formula |
Description |
Result |
|---|---|---|
|
=NUMBERVALUE(«2.500,27″,»,»,».») |
Returns 2,500.27. The decimal separator of the text argument in the example is specified in the second argument as a comma, and the group separator is specified in the third argument as a period. |
2500.27 |
|
=NUMBERVALUE(«3.5%») |
Returns 0.035. Because no optional arguments are specified, the decimal and group separators of the current locale are used. The % symbol is not shown, although the percentage is calculated. |
0.035 |
Top of Page
Need more help?
Excel NUMBERVALUE функция
Иногда у вас может быть список чисел, которые импортируются на рабочий лист в текстовом формате, как показано на следующем снимке экрана. Excel не может распознать их как обычные числа. Как в таком случае преобразовать эти ячейки в нормальные числа? Фактически, функция ЧИСЛО в Excel может помочь вам быстро и легко преобразовать числа в текстовом формате в числовые значения.
Синтаксис:
Синтаксис функции ЧИСЛО в Excel:
=NUMBERVALUE (text, [decimal_separator], [group_separator])
Аргументы:
- text: Необходимые. Текст, который вы хотите преобразовать в обычное число.
- decimal_separator: Необязательный. Символ, используемый в качестве десятичного разделителя в текстовом значении.
- group_separator: Необязательный. Символ, используемый в качестве разделителя тысяч и миллионов в текстовом значении.
Заметки:
- 1. Если десятичный_разделитель и group_separator не указаны, функция ЧИСЛО будет использовать разделители из текущего языкового стандарта.
- 2. Если текстовая строка представляет собой пустую ячейку, результатом будет 0.
- 3. #VALUE! будет возвращено значение ошибки:
- 1). Если десятичный разделитель встречается в текстовой строке более одного раза;
- 2). Если разделитель групп стоит после десятичного разделителя в текстовой строке;
- 4. Если между текстовой строкой есть пустые пробелы, функция ЧИСЛО будет игнорировать их. Например, «1 0 0 0 0» возвращается как 10000.
- 5. Если в десятичном разделителе или разделителе групп несколько символов, используется только первый символ.
- 6. Функция ЧИСЛО применяется к Excel 2016, Excel 365 и более поздним версиям.
Вернуть:
Возврат реального числа из числа хранится в виде текста.
Примеры:
Пример 1. Базовое использование функции ЧИСЛО ЗНАЧ
Предположим, у меня есть список чисел, которые хранятся в текстовом формате, и я указываю десятичный разделитель и разделитель групп отдельно для каждого числа, как показано на следующем снимке экрана.
Чтобы преобразовать текст в формат действительных чисел, примените следующую формулу:
=NUMBERVALUE(A2, B2, C2)
Затем перетащите дескриптор заполнения вниз к ячейкам, к которым вы хотите применить эту формулу, и вы получите результат, как показано на скриншоте ниже:
Заметки:
1. В этой формуле A2 содержит ли ячейка текст, который вы хотите преобразовать, B2 является десятичным разделителем в тексте, а C2 содержит группу-разделитель.
2. Вы также можете использовать текстовые строки для замены ссылок на ячейки в приведенной выше формуле следующим образом:
=NUMBERVALUE(«12.432,56», «,», «.»)
Пример 2: функция NUMBERVALUE используется для работы с процентными значениями.
Если текст заканчивается одним или несколькими знаками процента (%), они будут использоваться при вычислении результата. Если имеется несколько знаков процента, функция ЧИСЛО будет рассматривать каждый знак и соответственно выдаст результаты. Смотрите скриншот:
Дополнительные функции:
- Функция Excel ВПРАВО
- Функция RIGHT используется для возврата текста справа от текстовой строки.
- Функция Excel PROPER
- Функция ПРОПИСН используется, чтобы сделать первую букву каждого слова в текстовой строке заглавной, а все остальные символы — в нижнем регистре.
- Функция ПОИСК в Excel
- Функция ПОИСК может помочь вам найти позицию определенного символа или подстроки в заданной текстовой строке.
Лучшие инструменты для работы в офисе
Kutools for Excel — Помогает вам выделиться из толпы
Хотите быстро и качественно выполнять свою повседневную работу? Kutools for Excel предлагает 300 мощных расширенных функций (объединение книг, суммирование по цвету, разделение содержимого ячеек, преобразование даты и т. д.) и экономит для вас 80 % времени.
- Разработан для 1500 рабочих сценариев, помогает решить 80% проблем с Excel.
- Уменьшите количество нажатий на клавиатуру и мышь каждый день, избавьтесь от усталости глаз и рук.
- Станьте экспертом по Excel за 3 минуты. Больше не нужно запоминать какие-либо болезненные формулы и коды VBA.
- 30-дневная неограниченная бесплатная пробная версия. 60-дневная гарантия возврата денег. Бесплатное обновление и поддержка 2 года.
Вкладка Office — включение чтения и редактирования с вкладками в Microsoft Office (включая Excel)
- Одна секунда для переключения между десятками открытых документов!
- Уменьшите количество щелчков мышью на сотни каждый день, попрощайтесь с рукой мыши.
- Повышает вашу продуктивность на 50% при просмотре и редактировании нескольких документов.
- Добавляет эффективные вкладки в Office (включая Excel), точно так же, как Chrome, Firefox и новый Internet Explorer.
Комментарии (0)
Оценок пока нет. Оцените первым!
The VALUE function in Excel gives the value of a text representing a number. For example, if we have a text as $5, this is a number format in a text. Therefore, using the VALUE formula on this data will give us 5. So, we can see how this function gives us the numerical value represented by a text in Excel.
Table of contents
- Excel VALUE Function
- Syntax
- Examples to use VALUE Function in Excel
- Example #1 – Convert TEXT into Number
- Example #2 – Convert TIME of the day into a number
- Example #3 – Mathematical Operations
- Example #4 – Convert DATE into Number
- Example #5 – Error in VALUE
- Example #6 – Error in NAME
- Example #7 – Text with NEGATIVE VALUE
- Example #8 – Text with FRACTIONAL VALUE
- Things to Remember
- Recommended Articles
Syntax
The Value formula is as follows:
The VALUE function has only one argument, which is the required one. The VALUE formula returns a numeric value.
Where,
- text = the text value that is to be converted into a number.
Examples to use VALUE Function in Excel
The VALUE function is a Worksheet (WS) function. As a WS function, it can be entered as a part of the formula in a worksheet cell. Refer to the examples given below to understand better.
You can download this VALUE Function Excel Template here – VALUE Function Excel Template
Example #1 – Convert TEXT into Number
In this example, cell C2 has a VALUE formula associated with it. So, C2 is a result cell. The argument of the VALUE function is “$1,000,” the text to be converted into the number. The result is 1,000.
Example #2 – Convert the TIME of the day into a number
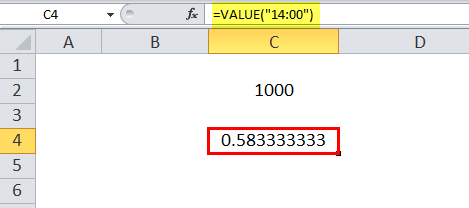
In this example, cell C4 has a VALUE formula associated with it. So, C4 is a result cell. The argument of the VALUE function is “14:00,” which is the time of the day. So, the result of converting it into a number is 0.58333.
Example #3 – Mathematical Operations
In this example, cell C6 has a VALUE formula associated with it. So, C6 is a result cell. The argument of the VALUE function is the difference between the two values. For example, the values are “1,000” and “500”. So, the difference is 500, and the function returns the same.
Example #4 – Convert DATE into Number
In this example, cell C8 has a VALUE formula associated with it. So, C8 is a result cell. The argument of the VALUE function is “01/12/2000,” which is the text in the date format. So, the result of converting it into the number is 36537.
Example #5 – Error in VALUE
In this example, cell C10 has a VALUE formula associated with it. So, C10 is a result cell. Unfortunately, the argument of the VALUE function is “abc,” which is the text in an inappropriate format. Hence, we cannot process the value. As a result, #VALUE! is returned, indicating the error in value.
Example #6 – Error in NAME
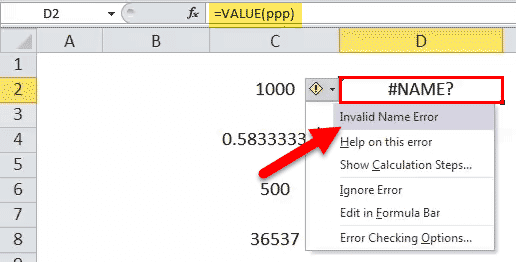
In this example, cell D2 has a VALUE formula in Excel associated with it. So, D2 is a result cell. Unfortunately, the argument of the VALUE function is ppp, which is the text in an inappropriate format, i.e., without double quotes (“). Hence, we cannot process the value.
As a result, #NAME! is returned, indicating the error is with the name provided. The same would be valid even if a valid text value is entered but not enclosed in the double quotes. E.g., VALUE (123) shall return #NAME! Error as a result.
Example #7 – Text with NEGATIVE VALUE
In this example, cell D4 has a VALUE formula associated with it. So, D4 is a result cell. The argument of the VALUE function is “-1,” which is the text containing a negative value. As a result, the corresponding value -1 is returned by the VALUE function Excel.
Example #8 – Text with FRACTIONAL VALUE
In this example, cell D6 has a VALUE formula in Excel associated with it. So, D6 is a result cell. The argument of the VALUE function in Excel is “0.89,” which is the text containing a fractional value. As a result, the corresponding value of 0.89 is returned by the VALUE function.
Things to Remember
- The VALUE function converts the text into a numeric value.
- It converts the formatted text such as date or time format into a numeric value.
- However, Excel normally takes care of the text-to-number conversion by default. So, the VALUE function is not explicitly required.
- It is more useful when the MS Excel data is to be made compatible with other similar spreadsheet applications.
- It processes any numeric value less or greater than or equal to zero.
- It processes any fractional values less or greater than or equal to zero.
- The text entered as a parameter to be converted into the number must be enclosed within double-quotes. The #NAME! Error is returned if not done, indicating the error with the NAME entered.
- Suppose a non-numeric text such as alphabets is entered as the parameter. In that case, the same cannot be processed by the VALUE function in Excel and returns #VALUE#VALUE! Error in Excel represents that the reference cell the user has either entered an incorrect formula or used a wrong data type (mostly numerical data). Sometimes, it is difficult to identify the kind of mistake behind this error.read more! as a result, indicating the error is with the VALUE generated.
Recommended Articles
This article has been a guide to VALUE Function in Excel. Here, we discuss the VALUE formula, how to use it, an Excel example, and a downloadable template. You may also look at these useful functions in Excel: –
- Value Property in VBAIn VBA, the value property is usually used alongside the range method to assign a value to a range. It’s a VBA built-in expression that we can use with other functions.read more
- Excel Shortcut Paste ValuePasting values is a common procedure that allows us to eliminate any formatting and formulas from the copied cell and paste them into the pasted cell. «Alt + E + S + V» is the shortcut key for pasting values.read more
- NETWORKDAYS FunctionThe NETWORKDAYS function is a date and time function that determines the number of working days between two given dates and is widely used in the fields of finance and accounting. When calculating the working days, NETWORKDAYS automatically excludes the weekend (Saturday and Sunday).read more
- PERCENTILE Excel FunctionThe PERCENTILE function is responsible for returning the nth percentile from a supplied set of values. read more
- Confidence Interval In ExcelConfidence Interval in excel is the range of population values that our true values lie in. read more
Функция ЗНАЧЕН преобразует текстовый аргумент в число.
Описание функции ЗНАЧЕН
Преобразует строку текста, отображающую число, в число.
Синтаксис
=ЗНАЧЕН(текст)Аргументы
текст
Обязательный. Текст в кавычках или ссылка на ячейку, содержащую текст, который нужно преобразовать.
Замечания
- Текст может быть в любом формате, допускаемом в Microsoft Excel для числа, даты или времени. Если текст не соответствует ни одному из этих форматов, то функция ЗНАЧЕН возвращает значение ошибки #ЗНАЧ!.
- Обычно функцию ЗНАЧЕН не требуется использовать в формулах, поскольку необходимые преобразования значений выполняются в Microsoft Excel автоматически. Эта функция предназначена для обеспечения совместимости с другими программами электронных таблиц.