Открытие книги Excel из кода VBA. Проверка существования книги. Создание новой книги, обращение к открытой книге и ее закрытие. Методы Open, Add и Close.
Открытие существующей книги
Существующая книга открывается из кода VBA Excel с помощью метода Open:
|
Workbooks.Open Filename:=«D:test1.xls» |
или
|
Workbooks.Open («D:test1.xls») |
В кавычках указывается полный путь к открываемому файлу Excel. Если такой файл не существует, произойдет ошибка.
Проверка существования файла
Проверить существование файла можно с помощью функции Dir. Проверка существования книги Excel:
|
If Dir(«D:test1.xls») = «» Then MsgBox «Файл не существует» Else MsgBox «Файл существует» End If |
Или, если файл (книга Excel) существует, можно сразу его открыть:
|
If Dir(«D:test1.xls») = «» Then MsgBox «Файл не существует» Else Workbooks.Open Filename:=«D:test1.xls» End If |
Создание новой книги
Новая рабочая книга Excel создается в VBA с помощью метода Add:
Созданную книгу, если она не будет использоваться как временная, лучше сразу сохранить:
|
Workbooks.Add ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:=«D:test2.xls» |
В кавычках указывается полный путь сохраняемого файла Excel, включая присваиваемое имя, в примере — это «test2.xls».
Обращение к открытой книге
Обращение к активной книге:
Обращение к книге с выполняемым кодом:
Обращение к книге по имени:
|
Workbooks(«test1.xls») Workbooks(«test2.xls») |
Обратиться по имени можно только к уже открытой книге, а чтобы из кода VBA Excel книгу открыть, необходимо указать полный путь к файлу.
Открытая рабочая книга закрывается из кода VBA Excel с помощью метода Close:
|
Workbooks(«test1.xlsx»).Close |
Если закрываемая книга редактировалась, а внесенные изменения не были сохранены, тогда при ее закрытии Excel отобразит диалоговое окно с вопросом: Вы хотите сохранить изменения в файле test1.xlsx? Чтобы файл был закрыт без сохранения изменений и вывода диалогового окна, можно воспользоваться параметром метода Close — SaveChanges:
|
Workbooks(«test1.xlsx»).Close SaveChanges:=False |
или
|
Workbooks(«test1.xlsx»).Close (False) |
Закрыть книгу Excel из кода VBA с сохранением внесенных изменений можно также с помощью параметра SaveChanges:
|
Workbooks(«test1.xlsx»).Close SaveChanges:=True |
или
|
Workbooks(«test1.xlsx»).Close (True) |
Фразы для контекстного поиска: открыть книгу, открытие книги, создать книгу, создание книги, закрыть книгу, закрытие книги, открыть файл Excel, открытие файла Excel, существование книги, обратиться к открытой книге.
Содержание
- Работа с внешним Excel файлом из VBA
- Открытие файла Excel
- Альтернативный вариант открытия файла
- Записать книгу и закрыть
- VBA Open / Close Workbook
- Open a Workbook in VBA
- Open Workbook From Path
- Open Workbook – ActiveWorkbook
- Open Workbook and Assign to a Variable
- Workbook Open File Dialog
- Open New Workbook
- VBA Coding Made Easy
- Open New Workbook To Variable
- Open Workbook Syntax
- Open Workbook Read-Only
- Open Password Protected Workbook
- Open Workbook Syntax Notes
- Close a Workbook in VBA
- Close Specific Workbook
- Close Active Workbook
- Close All Open Workbooks
- Close First Opened Workbook
- Close Without Saving
- Save and Close Without Prompt
- Other Workbook Open Examples
- Open Multiple New Workbooks
- Open All Excel Workbooks in a Folder
- Check if a Workbook is Open
- Workbook_Open Event
- Open Other Types of Files in VBA
- Open a Text file and Read its Contents
- Open a Text File and Append to it
- Opening a Word File and Writing to it
- VBA Code Examples Add-in
- Метод Workbooks.Open (Excel)
- Синтаксис
- Параметры
- Возвращаемое значение
- Замечания
- Пример
- Поддержка и обратная связь
Работа с внешним Excel файлом из VBA
Задача по объединению данных из нескольких Excel-файлов, или подгрузка доп.данных из внешнего файла решается достаточно просто: создается объект Excel, который можно скрыть визуально, затем открывается необходимый файл и выполняются нужные действия. Просто приведу несколько примеров.
Открытие файла Excel
В первой строке запускаем новый Excel, затем делаем его невидимым, в 3-й строке открываем файл fname. В последней строке получаем первый лист открытого excel-кого файла.
Альтернативный вариант открытия файла
При открытии файла можно использовать доп.параметры (приведу некоторые):
UpdateLinks — обновлять или нет внешние ссылки при открытии файла;
ReadOnly — открытие в режиме только для чтения;
Format — используемый при открытии разделитель (1 — символ tab, 2 — запятые, 3 — пробелы, 4 — точка с запятой, 5 — без разделителя, 6 — пользовательский разделитель, заданный в Delimiter);
Delimiter — пользовательский разделитель (в случае, если Format = 6);
Origin — тип операционной системы (xlMacintosh, xlWindows или xlMSDOS);
Local — использование в Excel языка такого же, как в открываемом файле.
Теперь можно выполнять какие-то действия с открытым файлом, просто обращаясь через wb и ws.
Записать книгу и закрыть
Для записи текущей книги (где находится макрос), можно использовать:
Чтобы сохранить или перезаписать книгу Excel без вопросов, можно применить такой вариант:
У метода SaveAs есть несколько параметров сохранения, с ними можно ознакомиться на сайте Microsoft.
Если нужно, можно закрыть книгу Excel без сохранения изменений таким образом:
Источник
VBA Open / Close Workbook
In this Article
In this tutorial, you will learn how to use VBA to open and close Excel Workbooks and other types of Files in several ways.
VBA allows you to open or close files using the standard methods .Open and .Close.
If you want to learn how to check if a file exists before attempting to open the file, you can click on this link: VBA File Exists
Open a Workbook in VBA
Open Workbook From Path
If you know which file you want to open, you can specify its full path name in the function. Here is the code:
This line of the code opens “Sample file 1” file from the “VBA Folder”.
Open Workbook – ActiveWorkbook
When you open a workbook, it automatically becomes the ActiveWorkbook. You can reference the newly opened workbook like so:
When you reference a sheet or range and omit the workbook name, VBA will assume you are referring to the ActiveWorkbook:
Open Workbook and Assign to a Variable
You can also open a workbook and assign it directly to an object variable. This procedure will open a workbook to the wb variable and then save the workbook.
Assigning workbooks to variables when they open is the best way to keep track of your workbooks
Workbook Open File Dialog
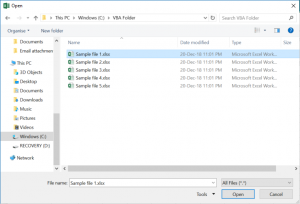
You can also trigger the workbook Open File Dialog box. This allows the user to navigate to a file and open it:
As you can see in Image 1, with this approach users can choose which file to open. The Open File Dialog Box can be heavily customized. You can default to a certain folder, choose which types of files are visible (ex. .xlsx only), and more. Read our tutorial on the Open File Dialog Box for detailed examples.
Open New Workbook
This line of code will open a new workbook:
VBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro — A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Open New Workbook To Variable
This procedure will open a new workbook, assigning it to variable wb:
Open Workbook Syntax
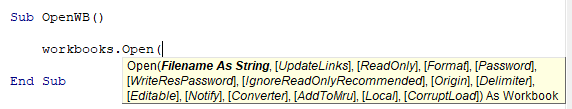
When you use Workbooks.Open you might notice that there are many options available when opening the workbook:
The Filename is required. All other arguments are optional – and you probably won’t need to know most of the other arguments. Here are the two most common:
Open Workbook Read-Only
When workbook is opened read-only, you can’t save over the original file. This prevents the file from being edited by the user.
Open Password Protected Workbook
A workbook might be password-protected. Use this code to open the password-protected workbook:
Open Workbook Syntax Notes
Notice that in the image above, we included a parenthesis “(” to show the syntax. If you use parenthesis when working with Workbooks.Open, you must assign the workbook to a variable:
Close a Workbook in VBA
Close Specific Workbook
Similarly to opening a workbook, there are several ways to close a file. If you know which file you want to close, you can use the following code:
This line of code closes the file “Sample file 1” if it’s opened. If not, it will return an error, so you should take care of error handling.
Close Active Workbook
If you want to close the Workbook which is currently active, this line of code will enable you to do that:
Close All Open Workbooks
To close all open Workbooks, you can simply use this code:
Close First Opened Workbook
This will close the first opened/created workbook:
Replace 1 with 2 to close the second opened / created workbook and so on.
Close Without Saving
This will close a Workbook without saving and without showing the save prompt:
Save and Close Without Prompt
Similarly this will save and close a Workbook without showing the save prompt:
Note: There are several other ways to indicate whether to save or not save a Workbook and also whether to show prompts or not. This is discussed in more detail here.
Other Workbook Open Examples
Open Multiple New Workbooks
This procedure will open multiple new workbooks, assigning the new workbooks to an array:
Open All Excel Workbooks in a Folder
This procedure will open all Excel Workbooks in a folder, using the Open File Dialog picker.
Check if a Workbook is Open
Workbook_Open Event
VBA Events are “triggers” that tell VBA to run certain code. You can set up workbook events for open, close, before save, after save and more.
Read our Workbook_Open Event tutorial to learn more about automatically running macros when a workbook is opened.
Open Other Types of Files in VBA
You can use the VBA to open other types of files with VBA – such as txt or Word files.
Open a Text file and Read its Contents
The VBA open method allows you to read or write to the file once you have opened it. To read the contents of a file, we can open the file for INPUT.
The code above will open the text file “test.txt” and then it will read the entire contents of the file to the strBody variable. Once you have extracted the file data into the strBody variable, you can use it for what you require. Using the Debug.Print command above enables us to see the contents of the strBody variable in the Immediate window in the VBE.
Open a Text File and Append to it
We can also open a text file in VBA, and then append to the bottom of the file using the Append method.
The above code will open the text file and then append 2 lines of text to the bottom of the file using the #intFile variable (the # sign is the key!). The code then closes the file.
Opening a Word File and Writing to it
We can also use VBA in Excel to open a Word file.
This code will open a copy of Word, and then open the document test.docx.
VBA Code Examples Add-in
Easily access all of the code examples found on our site.
Simply navigate to the menu, click, and the code will be inserted directly into your module. .xlam add-in.
Источник
Метод Workbooks.Open (Excel)
Хотите создавать решения, которые расширяют возможности Office на разнообразных платформах? Ознакомьтесь с новой моделью надстроек Office. Надстройки Office занимают меньше места по сравнению с надстройками и решениями VSTO, и вы можете создавать их, используя практически любую технологию веб-программирования, например HTML5, JavaScript, CSS3 и XML.
Синтаксис
expression. Открыть (FileName, UpdateLinks, ReadOnly, Format, Password, WriteResPassword, IgnoreReadOnlyRecommended, Origin, Разделитель, Editable, Notify, Converter, AddToMru, Local, CorruptLoad)
Выражение Переменная, представляющая объект Workbooks .
Параметры
| Имя | Обязательный или необязательный | Тип данных | Описание |
|---|---|---|---|
| FileName | Необязательный | Variant | Строка. Имя файла открываемой книги. |
| UpdateLinks | Необязательный | Variant | Указывает способ обновления внешних ссылок (ссылок) в файле, например ссылки на диапазон в книге Budget.xls в следующей формуле =SUM([Budget.xls]Annual!C10:C25) . Если этот аргумент опущен, пользователю будет предложено указать, как будут обновляться ссылки. Дополнительные сведения о значениях, используемых этим параметром, см. в разделе Примечания. |
Если Microsoft Excel открывает файл в формате WKS, WK1 или WK3 и аргумент UpdateLinks имеет значение 0, диаграммы не создаются; В противном случае Microsoft Excel создает диаграммы из диаграмм, присоединенных к файлу. ReadOnly Необязательно устанавливать. Variant Значение true, чтобы открыть книгу в режиме только для чтения. Format Необязательный Variant Если Microsoft Excel открывает текстовый файл, этот аргумент задает символ разделителя. Если этот аргумент опущен, используется текущий разделитель. Дополнительные сведения о значениях, используемых этим параметром, см. в разделе Примечания. Password Необязательный Variant Строка, содержащая пароль, необходимый для открытия защищенной книги. Если этот аргумент опущен, а для книги требуется пароль, пользователю будет предложено ввести пароль. WriteResPassword Необязательный Variant Строка, содержащая пароль, необходимый для записи в книгу, зарезервированную для записи. Если этот аргумент опущен, а книге требуется пароль, пользователю будет предложено ввести пароль. IgnoreReadOnlyRecommended Необязательный Variant Значение true , чтобы Microsoft Excel не отображал рекомендуемое сообщение только для чтения (если книга была сохранена с параметром «Только для чтения рекомендуется «). Происхождения Необязательный Variant Если файл является текстовым файлом, этот аргумент указывает, где он возник, чтобы кодовые страницы и возврат/строка каретки (CR/LF) можно было правильно сопоставить. Может быть одной из следующих констант XlPlatform : xlMacintosh, xlWindows или xlMSDOS. Если этот аргумент опущен, используется текущая операционная система. Разделитель Необязательный Variant Если файл является текстовым файлом, а аргумент Format равен 6, этот аргумент представляет собой строку, указывающую символ, который будет использоваться в качестве разделителя. Например, используйте Chr(9) для вкладок, «,» для запятых, «;» для точки с запятой или используйте пользовательский символ. Используется только первый символ строки. Изменяемость Необязательный Variant Если файл является надстройкой Microsoft Excel 4.0, этот аргумент имеет значение True , чтобы открыть надстройку, чтобы она была видимым окном. Если этот аргумент имеет значение False или опущен, надстройка открывается как скрытая и не может быть раскрыта. Этот параметр не применяется к надстройкам, созданным в Microsoft Excel 5.0 или более поздней версии.
Если файл является шаблоном Excel, значение True , чтобы открыть указанный шаблон для редактирования. Значение false , чтобы открыть новую книгу на основе указанного шаблона. Значение по умолчанию — False. Уведомить Необязательный Variant Если файл не удается открыть в режиме чтения и записи, этот аргумент имеет значение True , чтобы добавить файл в список уведомлений о файлах. Microsoft Excel откроет файл как доступный только для чтения, опрашивает список уведомлений о файлах, а затем уведомляет пользователя, когда файл станет доступен. Если этот аргумент имеет значение False или опущен, уведомление не запрашивается, и любые попытки открыть недоступный файл завершатся ошибкой. Конвертер Необязательный Variant Индекс первого преобразователя файлов, который следует попробовать при открытии файла. Сначала выполняется попытка указанного преобразователя файлов; Если этот преобразователь не распознает файл, все остальные преобразователи будут испытаны. Индекс преобразователя состоит из номеров строк преобразователей, возвращаемых свойством FileConverters . AddToMru Необязательный Variant Значение true , чтобы добавить эту книгу в список недавно использовавшихся файлов. Значение по умолчанию — False. Local Необязательный Variant Значение True сохраняет файлы на языке Microsoft Excel (включая параметры панели управления). Значение False (по умолчанию) сохраняет файлы на языке Visual Basic для приложений (VBA) (который обычно США английском языке, если проект VBA, из которого выполняется Workbooks.Open, не является старым проектом VBA с международной версией XL5/95). Поврежденная загрузка Необязательный XlCorruptLoad Может быть одной из следующих констант: xlNormalLoad, xlRepairFile и xlExtractData. Поведение по умолчанию, если значение не указано, — xlNormalLoad и не пытается выполнить восстановление при инициировании с помощью OM.
Возвращаемое значение
Объект Workbook , представляющий открытую книгу.
Замечания
По умолчанию макросы включены при открытии файлов программным способом. Используйте свойство AutomationSecurity , чтобы задать режим безопасности макросов, используемый при программном открытии файлов.
Можно указать одно из следующих значений в параметре UpdateLinks , чтобы определить, обновляются ли внешние ссылки (ссылки) при открытии книги.
| Значение | Описание |
|---|---|
| 0 | Внешние ссылки (ссылки) не будут обновляться при открытии книги. |
| 3 | Внешние ссылки (ссылки) будут обновлены при открытии книги. |
Можно указать одно из следующих значений в параметре Format , чтобы определить символ разделителя для файла.
| Значение | Разделитель |
|---|---|
| 1 | Вкладки |
| 2 | Запятыми |
| 3 | Пробелы |
| 4 | Точка с запятой |
| 5 | Отсутствует |
| 6 | Пользовательский символ (см. аргумент Разделитель ) |
Пример
В следующем примере кода открывается книга Analysis.xls, а затем выполняется ее макрос Auto_Open.
Следующий пример кода импортирует лист из другой книги на новый лист в текущей книге. Лист 1 в текущей книге должен содержать имя пути к книге для импорта в ячейку D3, имя файла в ячейке D4 и имя листа в ячейке D5. Импортированный лист вставляется после Листа1 в текущую книгу.
Поддержка и обратная связь
Есть вопросы или отзывы, касающиеся Office VBA или этой статьи? Руководство по другим способам получения поддержки и отправки отзывов см. в статье Поддержка Office VBA и обратная связь.
Источник
| title | keywords | f1_keywords | ms.prod | api_name | ms.assetid | ms.date | ms.localizationpriority |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Workbooks.Open method (Excel) |
vbaxl10.chm203082 |
vbaxl10.chm203082 |
excel |
Excel.Workbooks.Open |
1d1c3fca-ae1a-0a91-65a2-6f3f0fb308a0 |
08/14/2019 |
medium |
Workbooks.Open method (Excel)
Opens a workbook.
[!includeAdd-ins note]
Syntax
expression.Open (FileName, UpdateLinks, ReadOnly, Format, Password, WriteResPassword, IgnoreReadOnlyRecommended, Origin, Delimiter, Editable, Notify, Converter, AddToMru, Local, CorruptLoad)
expression A variable that represents a Workbooks object.
Parameters
| Name | Required/Optional | Data type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| FileName | Optional | Variant | String. The file name of the workbook to be opened. |
| UpdateLinks | Optional | Variant | Specifies the way external references (links) in the file, such as the reference to a range in the Budget.xls workbook in the following formula =SUM([Budget.xls]Annual!C10:C25), are updated. If this argument is omitted, the user is prompted to specify how links will be updated. For more information about the values used by this parameter, see the Remarks section.
If Microsoft Excel is opening a file in the WKS, WK1, or WK3 format and the UpdateLinks argument is 0, no charts are created; otherwise, Microsoft Excel generates charts from the graphs attached to the file. |
| ReadOnly | Optional | Variant | True to open the workbook in read-only mode. |
| Format | Optional | Variant | If Microsoft Excel opens a text file, this argument specifies the delimiter character. If this argument is omitted, the current delimiter is used. For more information about the values used by this parameter, see the Remarks section. |
| Password | Optional | Variant | A string that contains the password required to open a protected workbook. If this argument is omitted and the workbook requires a password, the user is prompted for the password. |
| WriteResPassword | Optional | Variant | A string that contains the password required to write to a write-reserved workbook. If this argument is omitted and the workbook requires a password, the user will be prompted for the password. |
| IgnoreReadOnlyRecommended | Optional | Variant | True to have Microsoft Excel not display the read-only recommended message (if the workbook was saved with the Read-Only Recommended option). |
| Origin | Optional | Variant | If the file is a text file, this argument indicates where it originated, so that code pages and Carriage Return/Line Feed (CR/LF) can be mapped correctly. Can be one of the following XlPlatform constants: xlMacintosh, xlWindows, or xlMSDOS. If this argument is omitted, the current operating system is used. |
| Delimiter | Optional | Variant | If the file is a text file and the Format argument is 6, this argument is a string that specifies the character to be used as the delimiter. For example, use Chr(9) for tabs, use «,» for commas, use «;» for semicolons, or use a custom character. Only the first character of the string is used. |
| Editable | Optional | Variant | If the file is a Microsoft Excel 4.0 add-in, this argument is True to open the add-in so that it is a visible window. If this argument is False or omitted, the add-in is opened as hidden, and it cannot be unhidden. This option does not apply to add-ins created in Microsoft Excel 5.0 or later.
If the file is an Excel template, True to open the specified template for editing. False to open a new workbook based on the specified template. The default value is False. |
| Notify | Optional | Variant | If the file cannot be opened in read/write mode, this argument is True to add the file to the file notification list. Microsoft Excel will open the file as read-only, poll the file notification list, and then notify the user when the file becomes available. If this argument is False or omitted, no notification is requested, and any attempts to open an unavailable file will fail. |
| Converter | Optional | Variant | The index of the first file converter to try when opening the file. The specified file converter is tried first; if this converter does not recognize the file, all other converters are tried. The converter index consists of the row numbers of the converters returned by the FileConverters property. |
| AddToMru | Optional | Variant | True to add this workbook to the list of recently used files. The default value is False. |
| Local | Optional | Variant | True saves files against the language of Microsoft Excel (including control panel settings). False (default) saves files against the language of Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) (which is typically United States English unless the VBA project where Workbooks.Open is run from is an old internationalized XL5/95 VBA project). |
| CorruptLoad | Optional | XlCorruptLoad | Can be one of the following constants: xlNormalLoad, xlRepairFile and xlExtractData. The default behavior if no value is specified is xlNormalLoad, and does not attempt recovery when initiated through the OM. |
Return value
A Workbook object that represents the opened workbook.
Remarks
By default, macros are enabled when opening files programmatically. Use the AutomationSecurity property to set the macro security mode used when opening files programmatically.
You can specify one of the following values in the UpdateLinks parameter to determine whether external references (links) are updated when the workbook is opened.
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| 0 | External references (links) will not be updated when the workbook is opened. |
| 3 | External references (links) will be updated when the workbook is opened. |
You can specify one of the following values in the Format parameter to determine the delimiter character for the file.
| Value | Delimiter |
|---|---|
| 1 | Tabs |
| 2 | Commas |
| 3 | Spaces |
| 4 | Semicolons |
| 5 | Nothing |
| 6 | Custom character (see the Delimiter argument) |
Example
The following code example opens the workbook Analysis.xls and then runs its Auto_Open macro.
Workbooks.Open "ANALYSIS.XLS" ActiveWorkbook.RunAutoMacros xlAutoOpen
The following code example imports a sheet from another workbook onto a new sheet in the current workbook. Sheet1 in the current workbook must contain the path name of the workbook to import in cell D3, the file name in cell D4, and the worksheet name in cell D5. The imported worksheet is inserted after Sheet1 in the current workbook.
Sub ImportWorksheet() ' This macro will import a file into this workbook Sheets("Sheet1").Select PathName = Range("D3").Value Filename = Range("D4").Value TabName = Range("D5").Value ControlFile = ActiveWorkbook.Name Workbooks.Open Filename:=PathName & Filename ActiveSheet.Name = TabName Sheets(TabName).Copy After:=Workbooks(ControlFile).Sheets(1) Windows(Filename).Activate ActiveWorkbook.Close SaveChanges:=False Windows(ControlFile).Activate End Sub
[!includeSupport and feedback]
Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) is a frequently used utility for Microsoft applications — including Microsoft Excel, Office, PowerPoint, Word, and Publisher. As VBA is a fairly complicated language to learn, much has been written about it and its capabilities (and if you want to learn more about VBA and Excel, you can read about it here).
One of the most basic tasks you can use VBA for is to open and manipulate files, such as an Excel file. VBA open files will open the Excel file — from there you can control how it is read and written. Commonly, you would use VBA code to open the file, and then use Excel VBA macros to write to the file.
Let’s take a deeper look into how VBA open files can be used with an Excel Workbook.
What is VBA Open Files and how does it work?
VBA is extremely similar to Visual Basic, a programming language used within the Microsoft ecosystem. It is used to create “macros.” A macro is a sequence of automated events which can fine-tune, optimize, automate, and improve your operations. The Excel VBA implementation can open files and run macros on them.
In Excel, you use VBA by inserting the code in the Visual Basic Editor. You can also choose the “Macro” button on the Developer Tab. From there, you will enter in code as though programming.
Before you start digging into VBA, you should have some understanding of programming. Programming means directing a computer to perform a certain sequence of events. Keep a few things in mind:
- You should always test your programming thoroughly to make sure it does what you want it to do.
- You should never implement your programming in a “live” environment with important data rather than test data.
- You should save your work frequently and you should be prepared to restore both your programming and your data if needed.

Running the macros you program
When macros are created, they’re assigned to given keypresses. Sometimes this is a combination of keys, and sometimes it’s an extra mouse button. Regardless, they’re intended to set off an automated chain of events whenever you do the given action (whether it’s pressing a key on your keyboard, or a button on your mouse). You can also run a macro manually by selecting it.
So, when you run a macro, you have Microsoft Excel already open. The macro runs within Excel, and you will do all your VBA programming inside of that program. Likewise, you will do your Microsoft Word VBA programming inside of Microsoft Word.
Opening an Excel file with VBA
The first step to updating, modifying, and saving Excel files is to be able to open them. To open an Excel file with VBA you would program as follows:
Sub openworksheet()
Workbooks.Open filename:= _ “filepath”
End subThe “sub” above is a lot like a function. It creates a small amount of code that is intended to take action. It begins with “Sub” and ends with “End Sub.”
In the above code, note that the italicized “filepath” references the full path of the workbook. Without the appropriate Workbooks.Open filename, you won’t be able to open the given file. You will also need the appropriate file type (Microsoft Excel, which is either XLS or XLSX) or the open method will fail.
Of course, the above assumes that you are always going to be opening the Workbook at the “filepath.” You might also want to open any file at all. You can create a macro that opens a dialog, through which you can select any file.
Sub openworksheet()
Dim Flocation as Variant
Flocation = Application.GetOpenFileName()
If Flocation <> false then
Workbooks.Open Filename:= Flocation
End If
End SubThe above code prompts the user to give a file name. If the user does give a file name (the variable, Flocation is no longer false), then the program will open that file.
Also note that Flocation is just the name of the variable that’s being used. You could call it something else; in fact, you could even call it just “f.” All that’s important is that you don’t use a word that the code already uses, such as “Variant” or “Filename.”
You might also be wondering why this code is so important. After all, you can open your own files at any time. But you can bind it to a specific keypress, making it a macro. So, now, typing something like “F8” will automatically open the “open a file” dialog.
But once you’ve automatically opened a file, what’s next? Generally, opening the file is only the first step. Once you’ve opened the Excel file, you still need to be able to read and write to it.
Reading the Excel file
You’ve opened your Excel file. But what’s inside of it? Luckily for you, it’s pretty easy to start reading an Excel file once you’ve opened it with VBA.
First, you should know that when you open a file, it becomes the ActiveWorkbook, which can be referenced in code as “ActiveWorkbook.”
Let’s say you want to read the first cell of the book.
Dim contents As Integer
contents = ActiveWorkbook.Range(“A1”).valueNow, that does assume that the cell is an Integer. You would need to change it to a String if you were reading a string, or a Date if you were reading a Date. Consequently, you need to be really familiar with the type of data you’re reading before you go any further.
Now, note that this is reading the contents of the cell into just a variable. That’s not displaying it. That’s not doing anything with it at all. If you wanted to see, perhaps, what the contents were, you would then type:
MsgBox contentsAlternatively, you could:
MsgBox ActiveWorkbook.Range(“A1”).valueEither of these options should display the value. But, of course, it’s a static value; it’s always going to display A1. So, you might need to code things a little more expressively if you’re trying to read the entirety of a document, or if you’re trying to transition one document to another.
Writing to the file
So, you have your workbook open through the power of VBA. But now you want to write to the file. Writing can be used in tandem with reading; once the Workbook is open you could do both.
As an example, you could write a macro that would open a Workbook and copy one column to another column, by reading the data in the first column and then writing that data to the second column.
Similarly, you could write a macro that would open two Workbooks and copy data from one to another, and then save both Workbooks, and then close both Workbooks.
As mentioned, once you open a workbook with VBA, the workbook that you opened becomes the ActiveWorkbook. This also happens if you have created a new workbook within VBA.
You can then access its data through:
ActiveWorkbook.Sheets
ActiveWorbook.CellsAs an example, if you wanted to edit the cell at column 1, row 1, on Sheet 1, you would write as follows:
ActiveWorkbook.Sheets(“Sheet 1”).Cells(1,1).Value= “1”If this is confusing, you can also use the “Range” field.
ActiveWorkbook.Sheets(“Sheet 1”).Range(“A1”).Value= “1”The above would have the same result.
Writing to a sheet can become very complex. Consider that, when you’re writing the macro system, you don’t know what data is in those cells. You only know their positions. You’re essentially writing to that position blindly.
Macros are frequently used to do things such as read CSV files and import that CSV information into a brand new Microsoft Excel workbook. But it takes a lot of time and a lot of testing to ensure that the data is going through correctly.
In the above case, you’re only altering range A1. But you could iterate through all the rows and columns of a workbook one by one if you were trying to fill it out line by line. As you learn more about Excel and VBA, you will learn more advanced methods of both reading and writing data.
Saving the Excel workbook file
Just like when you’re using Excel regularly, you still need to save your changes. If you have opened and changed a Workbook, save it before you close it.
ActiveWorkbook.SaveYou could even write a Macro that would save all your workbooks and close them, as follows:
For each workbook in Application.Workbooks
workbook.Save
Next workbook
Application.QuitThe above code iterates through each Workbook saving it until it cannot find a Workbook anymore. Once it can no longer find a Workbook, it quits the application. This is very useful for those who want to shut down fast and have a lot of workbooks left to save.
Closing the selected file
Closing the file is just as easy as opening a workbook. In fact, it’s actually easier, because you don’t need to know the file name. VBA already knows which file it has opened.
To close the Excel file you would type:
ActiveWorkbook.CloseOn the other hand, perhaps you wanted to close a specific Workbook. In that case, you would use the following:
Workbooks(“book.xlsx”).CloseThis is under the assumption the book was called “book.xlsx”; you would replace the given name for your sheet. Once you have closed the Workbook, you will not be able to make any further modifications to it until you open it again.
Opening a Microsoft Excel workbook that is password protected
Sometimes you may have password-protected your workbooks. That goes into more complicated territory. Understandably, it’s not going to open if you just try to directly open it.
But you can still open it with VBA.
Workbooks.Open(filename:= “filename”, Password:= “password”)As you can see above, you just added the password directly into the macro. Now the file is going to open just fine.
But there’s a problem with the above, which (if you’re good with security) you already know. You just saved your password as plain text!
Now, anyone with access to your computer could potentially open that file without knowing the password. And if you’ve been using that password for multiple files (a big no-no), they could be compromised, too.
So, VBA does provide a method of opening files that have a password. But it’s not a good method because of the above reasons. It means that your system could be compromised. If you just have a password to prevent outside intrusion (the file being sent somewhere else and opened by an outsider), this may not be a problem. But if you’re trying to protect your file internally as well as externally, it can be a major issue.
The alternative is to use the previous method of opening a file with a dialogue box. When you press a button (or otherwise launch your macro), you’ll be given a dialogue box, and you’ll be able to open whatever file you want. Your macro can then continue actions on the file after you have manually entered your password.
Opening a read-only file
Some Microsoft Excel files don’t have a password when you open them. Instead, they are set to read-only. If they’re set to read-only, you’ll be able to open and read from them. But you won’t be able to actually write to them without a secondary password.
ActiveWorkbook.Password = “password”Above is the method that you would call after you’ve opened the book so that you can start to write to it. You wouldn’t include the password when opening the file, because you wouldn’t have been prompted for it then.
The benefits of using Excel VBA Open
VBA is used to automate routine, mundane tasks, such as copying large volumes of data from one book to another. Any time you’re finding yourself spending hours just copying and pasting data, or running fairly mundane calculations, a macro can help.
You can also use VBA to automate smaller tasks that you find use a lot of keypresses. If you find yourself frequently needing to open the same 10 Excel Workbooks at once, for instance, you can create a macro that will open all of them on a single keypress, and close them all, too.
While it may only save you a few minutes of time, those minutes of time add up.
Potential issues with Excel VBA Open
It’s possible to run into issues with VBA open. If you have a protected workbook, you won’t be able to open it without the password (as noted). If you don’t have the password, you aren’t going to be able to open the file.
If the selected file is read-only, you aren’t going to be able to write to it without the right permissions. If you don’t realize that the file is read-only, you could try writing to it only for the action to fail.
And because you can’t always see what the macro is doing until you run it, you can potentially overwrite data or delete it altogether. This is why it’s always important to test your macros with test data before trying to implement it with live data.
But even so, Excel VBA open is a robust language. Most common activities with Workbooks (such as opening, closing, reading, writing, and saving) can be completed quite intuitively and often with a single line of code.
Learning more about Excel VBA
In the right hands, VBA is very powerful. If you have any automated, routine tasks in Excel, consider automating them with Excel VBA. Even better, once you learn the basics of VBA, you can also use it in other Microsoft applications such as Microsoft Word.
Still, powerful also means that mistakes can be made. Because VBA can open files and write to them, it’s also possible that it can overwrite data. This is why testing your programming is so important.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Can a macro open a file?
The Excel Macro can be used to prompt a user to open a file or to open a specific file (given the entire filename).
How do I open a text file in Excel VBA?
The VBA OpenTextFile method can be used to open a text file, just as the VBA Workbooks.Open method is used to open an Excel file.
How do I open a new workbook in VBA?
To open a new workbook in VBA, you would use the Workbooks.Add() VBA function. This function both creates a new workbook and prioritizes it as the active workbook.
Задача по объединению данных из нескольких Excel-файлов, или подгрузка доп.данных из внешнего файла решается достаточно просто: создается объект Excel, который можно скрыть визуально, затем открывается необходимый файл и выполняются нужные действия. Просто приведу несколько примеров.
Открытие файла Excel
Set objExcel = New Excel.Application objExcel.Visible = False Set wb = objExcel.Workbooks.Open(fname) Set ws = wb.Sheets(1)
В первой строке запускаем новый Excel, затем делаем его невидимым, в 3-й строке открываем файл fname. В последней строке получаем первый лист открытого excel-кого файла.
Альтернативный вариант открытия файла
Set objExcel = New Excel.Application Set wb = objExcel.Workbooks wb.Open fname, local:=True Set ws = wb.Item(1).ActiveSheet
При открытии файла можно использовать доп.параметры (приведу некоторые):
UpdateLinks — обновлять или нет внешние ссылки при открытии файла;
ReadOnly — открытие в режиме только для чтения;
Format — используемый при открытии разделитель (1 — символ tab, 2 — запятые, 3 — пробелы, 4 — точка с запятой, 5 — без разделителя, 6 — пользовательский разделитель, заданный в Delimiter);
Delimiter — пользовательский разделитель (в случае, если Format = 6);
Origin — тип операционной системы (xlMacintosh, xlWindows или xlMSDOS);
Local — использование в Excel языка такого же, как в открываемом файле.
Теперь можно выполнять какие-то действия с открытым файлом, просто обращаясь через wb и ws.
ws.Cells(1, 1).Value = "Test" ws.Cells(1, 1).Font.Size = 18 ' Поменять размер шрифта ws.Cells(1, 1).HorizontalAlignment = xlCenter '
Записать книгу и закрыть
wb.Save ' Записать с тем же именем wb.SaveAs Filename:="имя_нового_файла", FileFormat:=xlOpenXMLWorkbookMacroEnabled ' Записать в новый файл wb.Close ' Закрыть книгу
Для записи текущей книги (где находится макрос), можно использовать:
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs
Чтобы сохранить или перезаписать книгу Excel без вопросов, можно применить такой вариант:
Application.DisplayAlerts = False ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:="c:Temp001.xlsm", FileFormat:=xlOpenXMLWorkbookMacroEnabled Application.DisplayAlerts = True
У метода SaveAs есть несколько параметров сохранения, с ними можно ознакомиться на сайте Microsoft.
Если нужно, можно закрыть книгу Excel без сохранения изменений таким образом:
wb.Close False
In this Article
- Open a Workbook in VBA
- Open Workbook From Path
- Open Workbook – ActiveWorkbook
- Open Workbook and Assign to a Variable
- Workbook Open File Dialog
- Open New Workbook
- Open New Workbook To Variable
- Open Workbook Syntax
- Open Workbook Read-Only
- Open Password Protected Workbook
- Open Workbook Syntax Notes
- Close a Workbook in VBA
- Close Specific Workbook
- Close Active Workbook
- Close All Open Workbooks
- Close First Opened Workbook
- Close Without Saving
- Save and Close Without Prompt
- Other Workbook Open Examples
- Open Multiple New Workbooks
- Open All Excel Workbooks in a Folder
- Check if a Workbook is Open
- Workbook_Open Event
- Open Other Types of Files in VBA
- Open a Text file and Read its Contents
- Open a Text File and Append to it
- Opening a Word File and Writing to it
In this tutorial, you will learn how to use VBA to open and close Excel Workbooks and other types of Files in several ways.
VBA allows you to open or close files using the standard methods .Open and .Close.
If you want to learn how to check if a file exists before attempting to open the file, you can click on this link: VBA File Exists
Open a Workbook in VBA
Open Workbook From Path
If you know which file you want to open, you can specify its full path name in the function. Here is the code:
Workbooks.Open "C:VBA FolderSample file 1.xlsx"This line of the code opens “Sample file 1” file from the “VBA Folder”.
Open Workbook – ActiveWorkbook
When you open a workbook, it automatically becomes the ActiveWorkbook. You can reference the newly opened workbook like so:
ActiveWorkbook.SaveWhen you reference a sheet or range and omit the workbook name, VBA will assume you are referring to the ActiveWorkbook:
Sheets("Sheet1").Name = "Input"Open Workbook and Assign to a Variable
You can also open a workbook and assign it directly to an object variable. This procedure will open a workbook to the wb variable and then save the workbook.
Sub OpenWorkbookToVariable()
Dim wb As Workbook
Set wb = Workbooks.Open("C:VBA FolderSample file 1.xlsx")
wb.Save
End Sub
Assigning workbooks to variables when they open is the best way to keep track of your workbooks
Workbook Open File Dialog
You can also trigger the workbook Open File Dialog box. This allows the user to navigate to a file and open it:
Sub OpenWorkbook ()
Dim strFile As String
strFile = Application.GetOpenFilename()
Workbooks.Open (strFile)
End SubAs you can see in Image 1, with this approach users can choose which file to open. The Open File Dialog Box can be heavily customized. You can default to a certain folder, choose which types of files are visible (ex. .xlsx only), and more. Read our tutorial on the Open File Dialog Box for detailed examples.
Open New Workbook
This line of code will open a new workbook:
Workbooks.AddVBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro — A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Learn More
Open New Workbook To Variable
This procedure will open a new workbook, assigning it to variable wb:
Sub OpenNewWorkbook()
Dim wb As Workbook
Set wb = Workbooks.Add
End SubOpen Workbook Syntax
When you use Workbooks.Open you might notice that there are many options available when opening the workbook:
The Filename is required. All other arguments are optional – and you probably won’t need to know most of the other arguments. Here are the two most common:
Open Workbook Read-Only
When workbook is opened read-only, you can’t save over the original file. This prevents the file from being edited by the user.
Workbooks.Open "C:VBA FolderSample file 1.xlsx", , TrueVBA Programming | Code Generator does work for you!
Open Password Protected Workbook
A workbook might be password-protected. Use this code to open the password-protected workbook:
Workbooks.Open "C:VBA FolderSample file 1.xlsx", , , "password"Open Workbook Syntax Notes
Notice that in the image above, we included a parenthesis “(” to show the syntax. If you use parenthesis when working with Workbooks.Open, you must assign the workbook to a variable:
Sub OpenWB()
Dim wb As Workbook
Set wb = Workbooks.Open("C:VBA FolderSample file 1.xlsx", True, True)
End SubClose a Workbook in VBA
Close Specific Workbook
Similarly to opening a workbook, there are several ways to close a file. If you know which file you want to close, you can use the following code:
Workbooks.Close ("C:VBA FolderSample file 1.xlsx")This line of code closes the file “Sample file 1” if it’s opened. If not, it will return an error, so you should take care of error handling.
Close Active Workbook
If you want to close the Workbook which is currently active, this line of code will enable you to do that:
ActiveWorkbook.CloseAutoMacro | Ultimate VBA Add-in | Click for Free Trial!
Close All Open Workbooks
To close all open Workbooks, you can simply use this code:
Workbooks.CloseClose First Opened Workbook
This will close the first opened/created workbook:
Workbooks(1).CloseReplace 1 with 2 to close the second opened / created workbook and so on.
Close Without Saving
This will close a Workbook without saving and without showing the save prompt:
ActiveWorkbook.Close savechanges:=FalseSave and Close Without Prompt
Similarly this will save and close a Workbook without showing the save prompt:
ActiveWorkbook.Close savechanges:=TrueNote: There are several other ways to indicate whether to save or not save a Workbook and also whether to show prompts or not. This is discussed in more detail here.
AutoMacro | Ultimate VBA Add-in | Click for Free Trial!
Other Workbook Open Examples
Open Multiple New Workbooks
This procedure will open multiple new workbooks, assigning the new workbooks to an array:
Sub OpenMultipleNewWorkbooks()
Dim arrWb(3) As Workbook
Dim i As Integer
For i = 1 To 3
Set arrWb(i) = Workbooks.Add
Next i
End SubOpen All Excel Workbooks in a Folder
This procedure will open all Excel Workbooks in a folder, using the Open File Dialog picker.
Sub OpenMultipleWorkbooksInFolder()
Dim wb As Workbook
Dim dlgFD As FileDialog
Dim strFolder As String
Dim strFileName As String
Set dlgFD = Application.FileDialog(msoFileDialogFolderPicker)
If dlgFD.Show = -1 Then
strFolder = dlgFD.SelectedItems(1) & Application.PathSeparator
strFileName = Dir(strFolder & "*.xls*")
Do While strFileName <> ""
Set wb = Workbooks.Open(strFolder & strFileName)
strFileName = Dir
Loop
End If
End Sub
Check if a Workbook is Open
This procedure will test if a workbook is open:
Sub TestByWorkbookName()
Dim wb As Workbook
For Each wb In Workbooks
If wb.Name = "New Microsoft Excel Worksheet.xls" Then
MsgBox "Found it"
Exit Sub 'call code here, we'll just exit for now
End If
Next
End SubAutoMacro | Ultimate VBA Add-in | Click for Free Trial!
Workbook_Open Event
VBA Events are “triggers” that tell VBA to run certain code. You can set up workbook events for open, close, before save, after save and more.
Read our Workbook_Open Event tutorial to learn more about automatically running macros when a workbook is opened.
Open Other Types of Files in VBA
You can use the VBA to open other types of files with VBA – such as txt or Word files.
Open a Text file and Read its Contents
The VBA open method allows you to read or write to the file once you have opened it. To read the contents of a file, we can open the file for INPUT.
Sub OpenTextFile()
Dim strFile As String
Dim strBody As String
Dim intFile As Integer
strFile = "C:datatest.txt"
intFile = FreeFile
Open strFile For Input As intFile
strBody = Input(LOF(intFile), intFile)
'loop here through your text body and extract what you need
''some vba code here
Debug.Print strBody
Close intFile
End SubThe code above will open the text file “test.txt” and then it will read the entire contents of the file to the strBody variable. Once you have extracted the file data into the strBody variable, you can use it for what you require. Using the Debug.Print command above enables us to see the contents of the strBody variable in the Immediate window in the VBE.
Open a Text File and Append to it
We can also open a text file in VBA, and then append to the bottom of the file using the Append method.
Sub AppendToTextFile()
Dim strFile As String
Dim strBody As String
Dim intFile As Integer
strFile = "C:datatest.txt"
intFile = FreeFile
Open strFile For Append As intFile
'add two lines to the bottom
Print #intFile, "This is an extra line of text at the bottom"
Print #intFile, "and this is another one"
'close the file
Close intFile
End SubThe above code will open the text file and then append 2 lines of text to the bottom of the file using the #intFile variable (the # sign is the key!). The code then closes the file.
Opening a Word File and Writing to it
We can also use VBA in Excel to open a Word file.
Sub OpenWordFile()
Dim wApp As Object
Dim wDoc As Object
Set wApp = CreateObject("Word.Application")
Set wd = wApp.documents.Open("c:datatest.docx")
wApp.Visible = True
End SubThis code will open a copy of Word, and then open the document test.docx.
VBA Open Excel File – Explained with Examples!
VBA code to open Excel File will help you to open Excel Workbook using VBA. VBA open excel file Examples to show you use of Workbook.Open method in Excel VBA 2003, 2007, 2010, 2013.
VBA Code to Open an Excel File using Workbooks.Open Method
We can open Excel Workbook using Workbooks.Open Method. Following are the VBA Examples and syntax of VBA Code to Open an Excel File.
VBA Code to Open an Excel File using Workbooks.Open Method: Syntax
Here is the syntax to Open an Excel File using VBA. Here we need to pass the Workbook path to open.
Workbooks.Open("C:temptest.xlsx")
VBA Code to Open an Excel File using Workbooks.Open Method: Examples
The following Excel VBA example will open the test.xlsx file in the C:temp folder. Here we are opening the workbook and setting to an object. This will help us to re use the open workbook in the program.
Sub sbVBA_To_Open_Workbook()
Dim wb As Workbook
Set wb = Workbooks.Open("C:temptest.xlsx")
End Sub
VBA Code to Open an Excel File Explained:
‘Starting procedure to write VBA code to open excel file
Sub sbVBA_To_Open_Workbook()
‘Declaring the wb variable as workbook
Dim wb As Workbook
‘Opening a workbook and setting to the wb object for further use
Set wb = Workbooks.Open(“C:temptest.xlsx”)
‘Ending the sub procedure
End Sub
VBAopen excel file: Why we are using an Object
This is is the best approach to opening and assigning workbook to an object. This will help us to re use the Opened workbook and deal with its worksheets, ranges and other objects. The following example will show you how to access the different examples of opened workbook by setting and assigning to an object.
The below VBA Code example will get the Name of the Opened Workbook
We are using the Workbook.Name property to get the workbook name of the opened workbook.
Sub sbVBA_To_Open_WorkbookName()
Dim wb As Workbook
Set wb = Workbooks.Open("C:temptest.xlsx")
'This will return the workbook name
MsgBox wb.Name
End sub
The below VBA Code will get the count of worksheets in the Opened Workbook
We are using the Worksheets.Count property of workbook to get the number of worksheets in the opened workbook.
Sub sbVBA_To_Open_Workbook_Worksheets_Count()
Dim wb As Workbook
Set wb = Workbooks.Open("C:temptest.xlsx")
'This will return number of worksheets in the workbook
MsgBox wb.Worksheets.Count
End sub
The below VBA Code example will get the first worksheet Name of the Opened Workbook
We are using the Worksheet.Name property of workbook to get the name of the of worksheets in the opened workbook.
Sub sbVBA_To_Open_Workbook_Worksheets_Count()
Dim wb As Workbook
Set wb = Workbooks.Open("C:temptest.xlsx")
'This will return the first sheet name of the workbook
MsgBox wb.Sheets(1).Name
End sub
The below VBA Code example will get the Range C2 value of the Worksheet “Main” of the Opened Workbook
We are using the Worksheet.Range object of workbook to get the Range value of the worksheets in the opened workbook.
Sub sbVBA_To_Open_Workbook_Worksheets_Count()
Dim wb As Workbook
Set wb = Workbooks.Open("C:temptest.xlsx")
'This will return the Range C2 value of the worksheet "Main"
MsgBox wb.Sheets("Main").Range("C2")
End sub
A Powerful & Multi-purpose Templates for project management. Now seamlessly manage your projects, tasks, meetings, presentations, teams, customers, stakeholders and time. This page describes all the amazing new features and options that come with our premium templates.
Save Up to 85% LIMITED TIME OFFER

All-in-One Pack
120+ Project Management Templates
Essential Pack
50+ Project Management Templates
Excel Pack
50+ Excel PM Templates
PowerPoint Pack
50+ Excel PM Templates
MS Word Pack
25+ Word PM Templates
Ultimate Project Management Template
Ultimate Resource Management Template
Project Portfolio Management Templates
Related Posts
- VBA Code to Open an Excel File using Workbooks.Open Method
- VBA Code to Open an Excel File using Workbooks.Open Method: Syntax
- VBA Code to Open an Excel File using Workbooks.Open Method: Examples
- VBAopen excel file: Why we are using an Object
VBA Reference
Effortlessly
Manage Your Projects
120+ Project Management Templates
Seamlessly manage your projects with our powerful & multi-purpose templates for project management.
120+ PM Templates Includes:
One Comment
-
Sunil
March 14, 2016 at 12:04 PM — Reply
Effectively Manage Your
Projects and Resources
ANALYSISTABS.COM provides free and premium project management tools, templates and dashboards for effectively managing the projects and analyzing the data.
We’re a crew of professionals expertise in Excel VBA, Business Analysis, Project Management. We’re Sharing our map to Project success with innovative tools, templates, tutorials and tips.
Project Management
Excel VBA
Download Free Excel 2007, 2010, 2013 Add-in for Creating Innovative Dashboards, Tools for Data Mining, Analysis, Visualization. Learn VBA for MS Excel, Word, PowerPoint, Access, Outlook to develop applications for retail, insurance, banking, finance, telecom, healthcare domains.
Page load link
Go to Top