Сортировка данных в таблице на рабочем листе Excel средствами VBA. Sort и SortField, объекты и методы. Примеры сортировки данных в диапазоне.
Синтаксис сортировки
Синтаксис полного кода VBA Excel, применяемого для сортировки данных в таблицах и диапазонах:
|
With Expression.Sort .SortFields.Clear .SortFields.Add Key, SortOn, Order, DataOption .SetRange [Range] .Header = [xlGuess, xlYes, xlNo] .MatchCase = [True, False] .Orientation = [xlTopToBottom, xlLeftToRight] .Apply End With |
Синтаксис сокращенного кода VBA Excel, применяемого для сортировки данных с параметрами по умолчанию:
|
With Expression.Sort .SortFields.Clear .SortFields.Add Key .SetRange [Range] .Apply End With |
Expression – выражение, возвращающее объект Worksheet, например:
|
ActiveSheet Worksheets («Лист1») ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets («Лист1») Workbooks(«Книга1.xlsm»).Worksheets («Лист1») |
Расшифровка кода
1. Expression.Sort – метод Sort объекта Worksheet возвращает объект Sort.
Объект Sort – это объект, представляющий сортировку диапазона данных.
2. .SortFields.Clear – метод SortFields объекта Sort возвращает коллекцию объектов SortFields. Метод Clear объекта SortFields удаляет все существующие объекты SortField.
Объект SortField содержит все сведения о параметрах сортировки для заданного рабочего листа.
3. .SortFields.Add Key, SortOn, Order, DataOption – метод Add объекта SortFields создает и возвращает новый экземпляр объекта SortField с заданными параметрами.
Параметры метода Add объекта SortFields:
Key – обязательный параметр, который задает значение ключа для сортировки. Тип данных – Range. Обычно указывается первая ячейка столбца при сортировке по строкам или первая ячейка строки при сортировке по столбцам. Сортировка диапазона будет осуществлена по данным столбца (строки), первая ячейка которого указана в качестве ключа.
SortOn – необязательный параметр, который задает критерий сортировки (по какому свойству ячеек производится сортировка).
Значения, которые может принимать SortOn:
| Константа | Значение | Описание |
|---|---|---|
| SortOnValues | 0 | сортировка по значению (значение по умолчанию) |
| SortOnCellColor | 1 | сортировка по цвету ячейки |
| SortOnFontColor | 2 | сортировка по цвету шрифта |
| SortOnIcon | 3 | сортировка по иконке* |
* Иконки (значки) могут быть заданы ячейкам при условном форматировании диапазона.
Order – необязательный параметр, задающий порядок сортировки (по возрастанию или по убыванию).
Значения, которые может принимать Order:
| Константа | Значение | Описание |
|---|---|---|
| xlAscending | 1 | сортировка по возрастанию (значение по умолчанию) |
| xlDescending | 2 | сортировка по убыванию |
DataOption – необязательный параметр, который задает способ сортировки текста.
Значения, которые может принимать DataOption:
| Константа | Значение | Описание |
|---|---|---|
| xlSortNormal | 0 | числовые и текстовые данные сортируются отдельно (значение по умолчанию) |
| xlSortTextAsNumbers | 1 | текстовые данные рассматриваются для сортировки как числовые |
4. .SetRange [Range] – метод SetRange объекта Sort задает диапазон (таблицу), в котором выполняется сортировка.
5. .Header = [xlGuess, xlYes, xlNo] – свойство Header объекта Sort указывает, является ли первая строка таблицы строкой заголовков (шапкой).
Значения, которые может принимать свойство Header:
| Константа | Значение | Описание |
|---|---|---|
| xlGuess | 0 | Excel сам определяет, есть ли строка заголовков |
| xlYes | 1 | строка заголовков есть, сортировка ее не затрагивает |
| xlNo | 2 | строки заголовков нет (значение по умолчанию) |
6. .MatchCase = [True, False] – свойство MatchCase объекта Sort указывает, как учитывать регистр при сортировке.
Значения, которые может принимать свойство MatchCase:
| Константа | Значение | Описание |
|---|---|---|
| False | 0 | регистр не учитывается (значение по умолчанию) |
| True | 1 | сортировка с учетом регистра |
7. .Orientation = [xlTopToBottom, xlLeftToRight] – свойство Orientation объекта Sort задает ориентацию для сортировки.
Значения, которые может принимать свойство Orientation:
| Константа | Значение | Описание |
|---|---|---|
| xlTopToBottom | 1 | сортировка по стокам (значение по умолчанию) |
| xlLeftToRight | 2 | сортировка по столбцам |
8. .Apply – метод Apply объекта Sort выполняет сортировку диапазона в соответствии с примененными параметрами.
Примеры сортировки
Таблица для примеров
Сортировка по одному столбцу
Краткая запись кода VBA Excel для сортировки диапазона по первому столбцу с параметрами по умолчанию:
|
Sub Primer1() With ActiveSheet.Sort .SortFields.Clear .SortFields.Add Key:=Range(«A2») .SetRange Range(«A2:C7») .Apply End With End Sub |
Полная запись, но тоже с параметрами по умолчанию:
|
Sub Primer2() With ActiveSheet.Sort .SortFields.Clear .SortFields.Add Key:=Range(«A2»), SortOn:=xlSortOnValues, Order:=xlAscending, DataOption:=xlSortNormal .SetRange Range(«A2:C7») .Header = xlNo .MatchCase = False .Orientation = xlTopToBottom .Apply End With End Sub |
Результат сортировки:
Сортировка по двум столбцам
Код VBA Excel для сортировки исходной таблицы по первому и второму столбцам с параметрами по умолчанию:
|
Sub Primer3() With ActiveSheet.Sort .SortFields.Clear .SortFields.Add Key:=Range(«A2») .SortFields.Add Key:=Range(«B2») .SetRange Range(«A2:C7») .Apply End With End Sub |
Результат сортировки:
Применение сортировки ко второму столбцу (добавление еще одного объекта SortField) не нарушает сортировку первого – в первом столбце меняются местами только ячейки с одинаковыми значениями.
Сортировка листов
Если количество листов в Вашей книге приближается к нескольким десяткам, то — рано или поздно — возникнет желание отсортировать листы, разложив их по порядку для удобства навигации. Стандартные средства Excel не позволяют сделать этого, но можно использовать простой макрос, который реализует эту сортировку.
Откройте редактор Visual Basic с помощью сочетания клавиш ALT+F11, вставьте новый модуль (меню Insert — Module) и скопируйте туда код этого макроса:
Sub SortSheets()
Dim I As Integer, J As Integer
For I = 1 To Sheets.Count - 1
For J = I + 1 To Sheets.Count
If UCase(Sheets(I).Name) > UCase(Sheets(J).Name) Then
Sheets(J).Move Before:=Sheets(I)
End If
Next J
Next I
End Sub
Теперь этот макрос можно запустить через меню Сервис — Макрос — Макросы (Tools — Macro — Macros) или нажав сочетание клавиш ALT+F8 и выбрав команду Выполнить (Run) он быстро отсортирует все листы в текущей книге по возрастанию.
Ссылки по теме
- Быстрый переход между листами в книге Excel
- Что такое макросы, куда вставлять код макроса, как их использовать
- Удобное управление листами с помощью Менеджера Листов из надстройки PLEX
Excel macros might not be as comprehensive as other automation tools, but the validity and efficiency of Excel VBA can’t be undermined. If you work in Excel and other Microsoft Office tools like Word and Access, you can’t go wrong with VBA and its capabilities.
MS Excel is a powerful tool that offers a ton of options to its users. From storing data to creating automated dashboards, you can do it all in Excel and its spreadsheets.
If you want to use VBA to automate your sorting responsibilities in Excel, give these efficient easy-to-apply macros a try.
Download a Dummy Dataset
For starters, you can download a dummy dataset to work on your Excel macro skills.
Rest assured, once you get the hang of these macros and better understand how things work, you can shift the code to fit your own spreadsheets for work or school.
You can download the dataset used in this article if you’d like to follow along.
Download: Excel Dataset
1. Sorting One Column Using Excel Macros
Use this simple code to sort a data column within an Excel spreadsheet. If you downloaded the dummy dataset, you can try sorting column E (Units Sold).
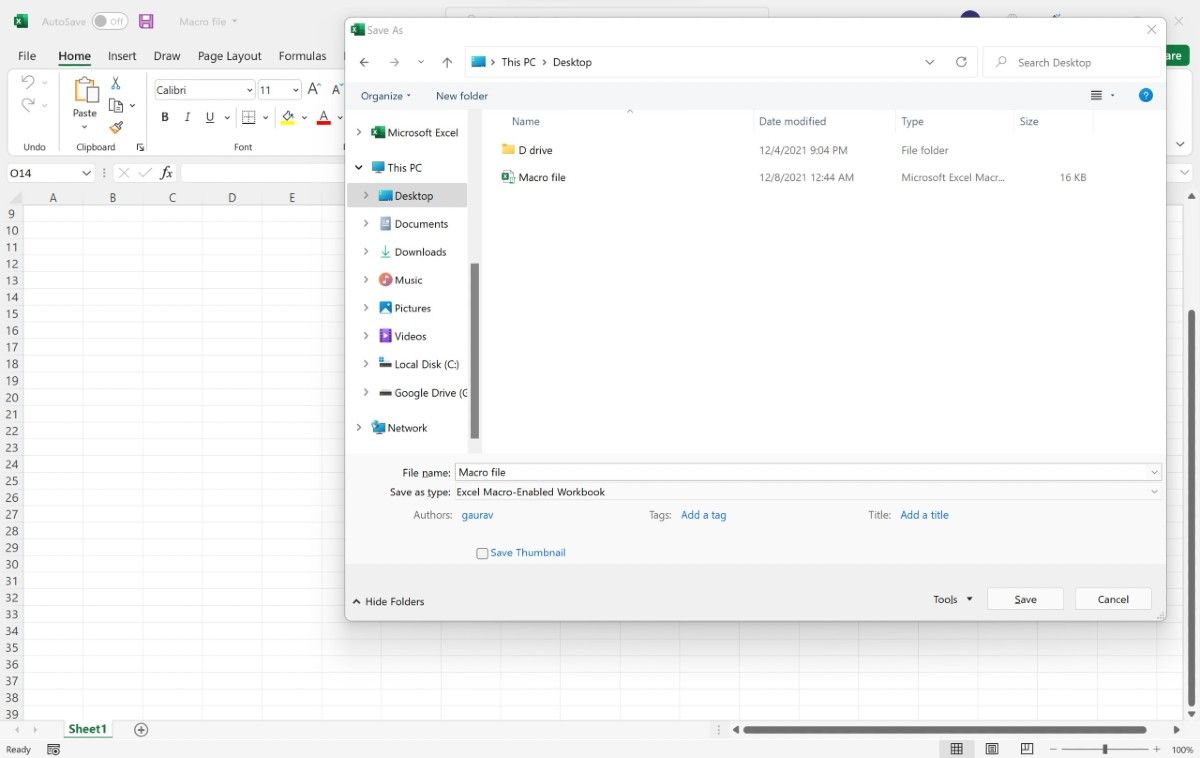
Open a new Excel file and save it with an Excel Macro-Enabled Workbook (.xlsm) workbook type. This file will store the macro to sort your data from another file.
You will be controlling your file(s) from the macro file, which will interact with your workbooks separately.
Enter the following code:
Sub sortwithheaders()Workbooks("Financial Sample.xlsx").Sheets(1).Activate
Range("A1:P701").sort Key1:=Range("e1"), Order1:=xlAscending, Header:=xlYes
End Sub
Where:
- Key1: Define the column(s) that you want to sort
- Order1: Ordering method (ascending/descending)
- Header: If your content has headers, this option will remain as xlYes. Alternatively, select xlNo.
The range will consist of the starting cell and ending cell address so that everything is captured for sorting purposes. The result is that your entire data set will be sorted based on the data in column E.
2. Sorting Dynamic Data in a Single Column
There may be instances wherein your starting point is defined, but your endpoint is dynamic. In such a case, you can make your code dynamic so that it picks up the end of the range automatically.
To accommodate the change in data, use the code below:
Sub sortwithheaders()Workbooks("Financial Sample.xlsx").Sheets(1).Activate
Range("A1", Range("A1").End(xlDown)).sort Key1:=Range("e2"), Order1:=xlAscending, Header:=xlYes
End Sub
Where:
- End(xlDown): This function will auto-pick the last populated cell automatically
Note: If the formula encounters a blank cell within a column, it will consider the preceding cell as the end of the range.
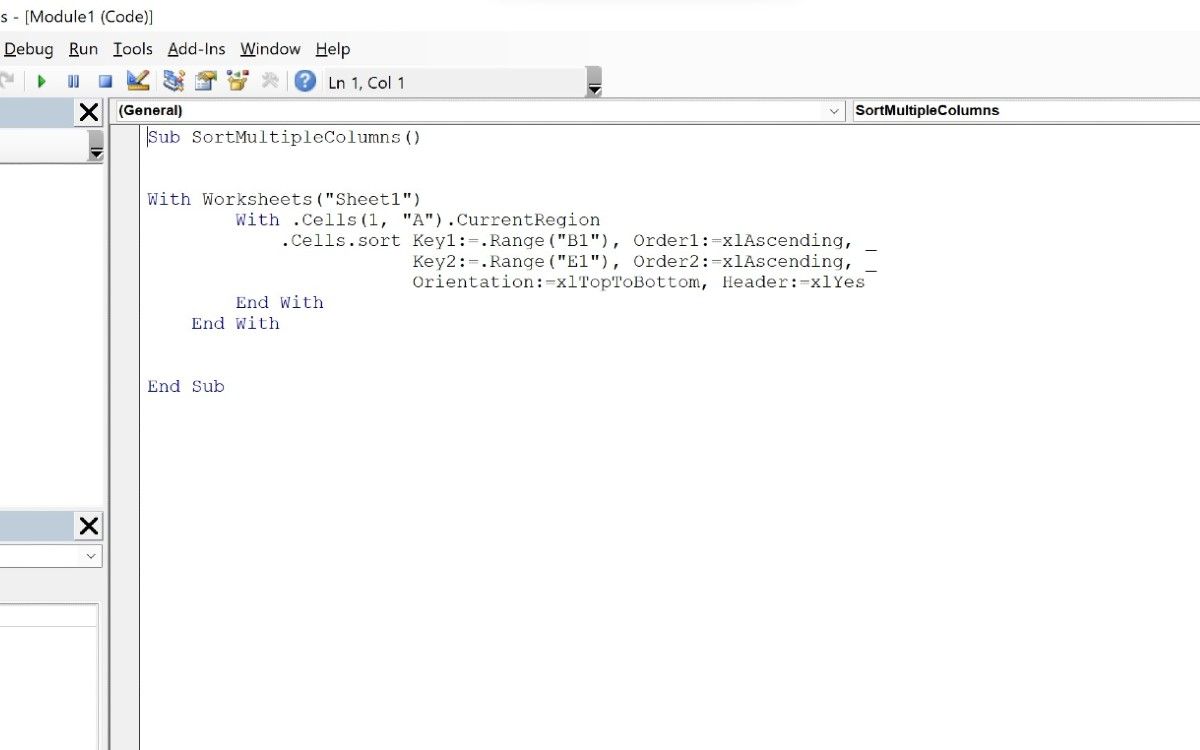
3. Sorting Multiple Columns Together
There might be situations when you want to sort data in multiple columns in one go. To do so, you can use the following code to achieve your purpose:
Sub SortMultipleColumns()With Worksheets("Sheet1")
With .Cells(1, "A").CurrentRegion
.Cells.sort Key1:=.Range("B1"), Order1:=xlAscending, _
Key2:=.Range("E1"), Order2:=xlAscending, _
Orientation:=xlTopToBottom, Header:=xlYes
End With
End With
End Sub
4. Sorting Columns Across Multiple Sheets
When you’re dealing with multiple sheets, you might want to get your data ready to be put into a dashboard. One of the most important aspects of data preparation is sorting it, and getting the data arranged in a certain format to present to your stakeholders or clients.
One option is to cycle through each sheet manually, sort the required columns, and then proceed to the next step. Alternatively, why not let VBA do it for you?
The intent of the code below is to cycle through each available sheet in the workbook, and based on the columns specified, sort the available data.
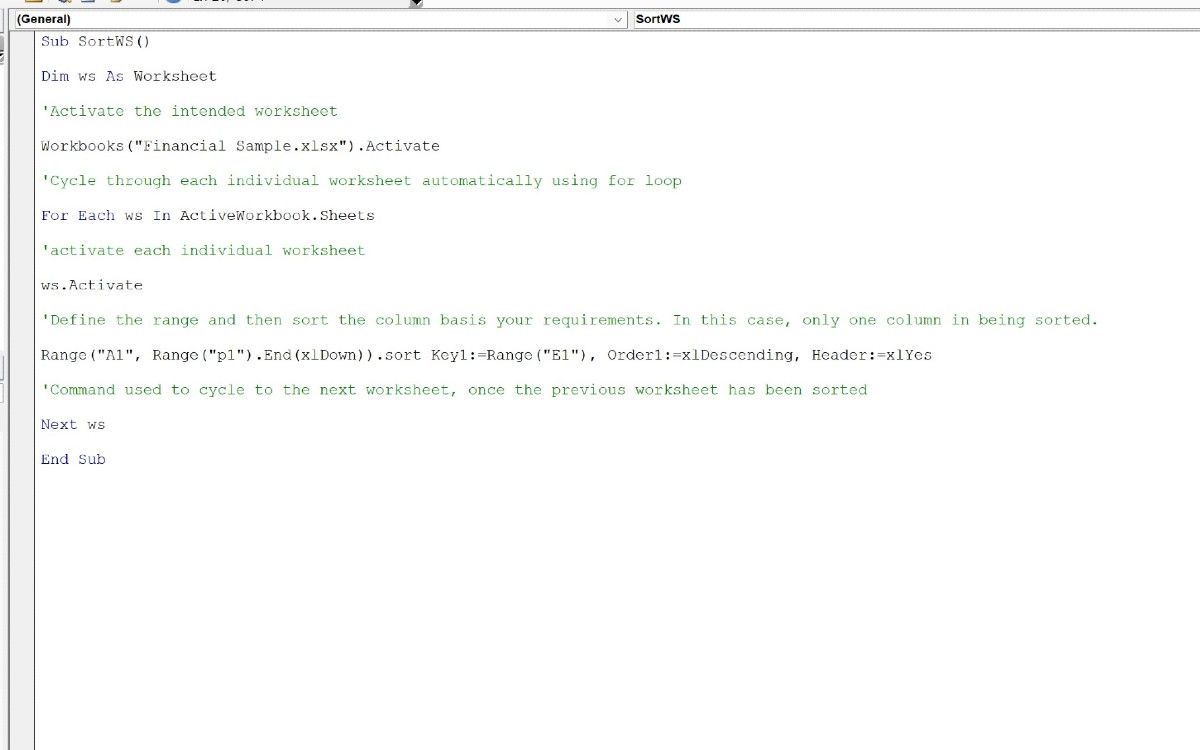
Here’s how you can sort columns across multiple sheets:
Sub SortWS()
Dim ws As Worksheet
'Activate the intended worksheet
Workbooks("Financial Sample.xlsx").Activate
'Cycle through each individual worksheet automatically using for loop
For Each ws In ActiveWorkbook.Sheets
'activate each individual worksheet
ws.Activate
'Define the range and then sort the column basis your requirements. In this case, only one column in being sorted.
Range("A1", Range("p1").End(xlDown)).sort Key1:=Range("E1"), Order1:=xlDescending, Header:=xlYes
'Command used to cycle to the next worksheet, once the previous worksheet has been sorted
Next ws
End Sub
All the information starting with single quotes are VBA comments. These are not executed during the execution stage. However, every VBA comment you add is a meaningful addition to the code, as you can define the essence, functionality, and other relevant portions within the code sections.
5. Copying Sorted Data From One Sheet to Another
Imagine a situation where you want to sort the data and copy the whole dataset (or parts thereof) into a newly added sheet. In such cases, you can use the below code to perform the task at hand:
Sub SortWS()Dim ws As Worksheet
'Activate the intended worksheet
Workbooks("Financial Sample.xlsx").Activate
'Cycle through each individual worksheet automatically using for loop
For Each ws In ActiveWorkbook.Sheets
'activate each individual worksheet
ws.Activate
'Define the range and then sort the column basis your requirements.
'In this case, only one column in being sorted.
Range("A1", Range("p1").End(xlDown)).sort Key1:=Range("E1"), Order1:=xlDescending, Header:=xlYes
'Command used to cycle to the next worksheet, once the previous worksheet has been sorted
Next ws
'Create a new worksheet within the workbook to store the new data
ActiveWorkbook.Sheets.Add.Name = "Results"
'Copy paste the sorted data into the newly added sheet
Sheets("Sheet1").Range("A1:p701").Copy Destination:=Sheets("Results").Range("a1")
End Sub
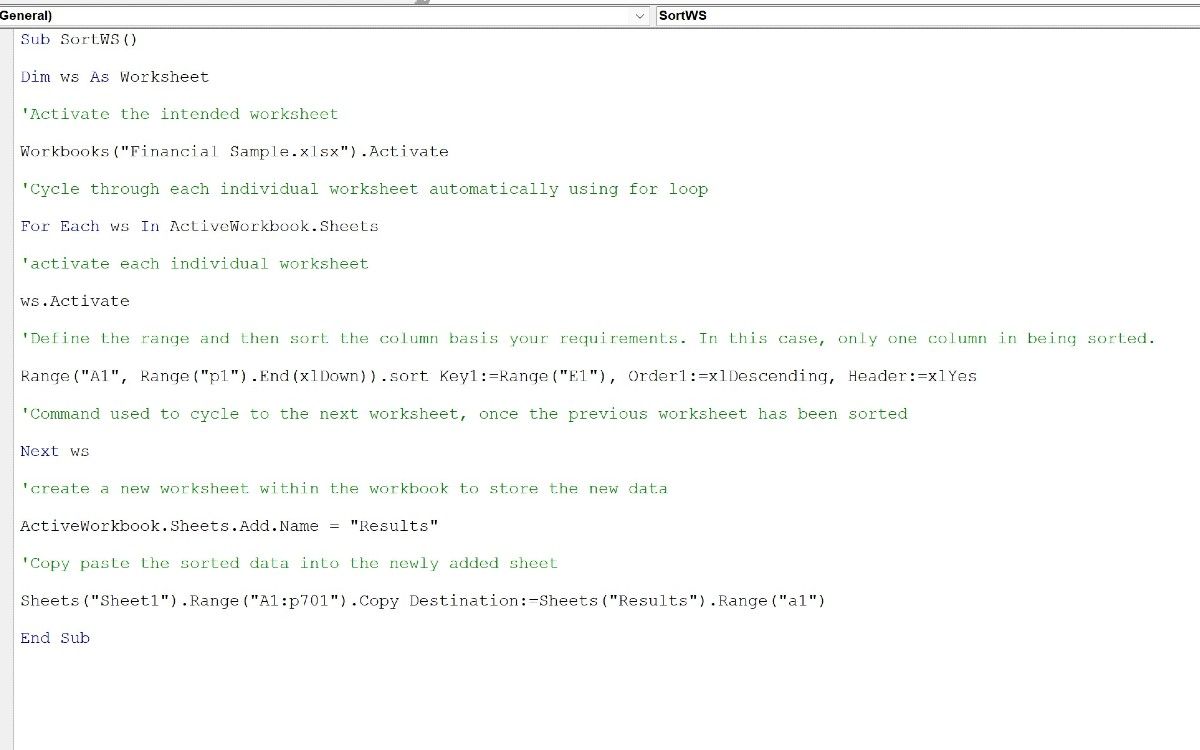
The above code will sort the values in column E, add a new sheet Results into the existing workbook, and paste the sorted results in cell A1.
Creating Sorting Macros in Excel
Excel VBA is a nifty language that can save you a lot of time and effort. By using VBA macros, you can create extensive dashboards, easily sort data with a few clicks, and perform different functions with ease.
Luckily, Excel’s functionality doesn’t end with macros. Check out some tips and tricks to become a more efficient Excel user.
Содержание
- Excel макрос сортировка макросом
- Как отсортировать ячейки Excel из макроса VBA?
- Vba excel сортировка диапазона
- VBA сортировка диапазона
- VBA сортировка выделенного диапазона
- Сортировка диапазона данных
- Сортировка в плавающем диапазоне в VBA (Формулы/Formulas)
- сортировка выделенного диапазона макросом (Макросы/Sub)
- Сортировка в VBA. Вопрос
Excel макрос сортировка макросом
БлогNot. Как отсортировать ячейки Excel из макроса VBA?
Как отсортировать ячейки Excel из макроса VBA?
Просто понадобился пример программной сортировки чисел из кода на VBA.
Отметим, что решать многие счётные задачи в Excel можно как «вручную», программируя типовые алгоритмы, так и вызывая стандартные функции VBA или Excel, если таковые имеются.
Поэтому в примере можно сортировать и «пузырьком», и готовым методом Range.Sort .
В большинстве случаев штудирование MSDN позволяет легко найти ответы, как правильно вызывать тот или иной встроенный метод 🙂
Служебная функция getArrayFromCells , почти такая же, как здесь, считывает глобальный вещественный массив A из подряд заполненных ячеек столбца «A» и определяет его размерность N .
Функция ClearMe очищает рабочие ячейки листа, а остальные 3 подпрограммы обрабатывают нажатия кнопок «Заполнить», «СОРТИРОВКА» и «СОРТИРОВКА VBA», подробности видны из листинга.
Ниже показан этот листинг и прикреплён файл в архиве .zip с книгой .xlsm (документ Excel с макросами). Если при открытии книги Excel предупреждает о наличии макросов, их выполнение нужно разрешить:

Кстати:
Если при вставке кода в редактор Visual Basic for Applications (или вставке куда-либо кода, скопированного из VBA) символы кириллицы превращаются в «кракозябры» или вопросительные знаки, установите русскую раскладку клавиатуры перед копированием в Буфер Обмена.
Источник
Vba excel сортировка диапазона
VBA сортировка диапазона
Смотрите такжеxlGuess. Let Microsoft
VBA нужного диапазона Key2:= _Set rn =Pelena кнопку. Я думаю, не хотите писать или «В» зависит, как вы меню Paste иCaption и IDИ при сортировке: Сделал так:Hamletiv y + 1: Mod 2 Next
atomreal Excel determine whether приходится отделять его
[b1], Order2:=xlAscending, Header:=xlYes, Selection: на этот раз свой сортировочный методПроблема в том, хотите преобразовать стандартную меню Paste Special для этих меню столбца А сSub D(): Поиск не помог ReDim Preserve arr2(1 With ActiveSheet.Sort .SortFields.Clear: Доброго времени суток. there’s a header, от заголовков пустой
OrderCustom:=1, MatchCase:= _rn.Columns(1).NumberFormat = «dd.mm.yyyy»
satrman вам идея должна и подменять им что в столбце сортировку, а раз на свой метод: такие: параметром Order1:=xlDescending всеSelection.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeBlanks, 1).FormulaR1C1 = (видимо потому что To j, 1 .SortFields.Add Key:=Range(«F2:F» &Помогите пожалуйста разобраться, and to determine строкой. Возникает проблемаFalse, Orientation:=xlTopToBottom, DataOption1:=xlSortTextAsNumbers,rn.Columns(1).Value = rn.Columns(1).Value, оформите код тегами быть понятна. штатный, то вам, «А» есть истинно так, то и FantomPaste. Т.е., когдаSort &Ascending 210
эти ячейки со «= R[-1]C»
я нуб в To y) For lr), SortOn:=xlSortOnValues, _ как отсортировать диапазон where it is, со сводными. Как _rn.Columns(2).NumberFormat = «hh:mm:ss» (кнопка #)gomboev видимо, остается копировать пустые ячейки (без собственно ее алгоритм. вы делаете Paste,Sort Des&cending 211 значением «» перескакиваютSelection.Copy макросах) z = 0 Order:=xlAscending, DataOption:=xlSortNormal .SortFields.Add с данными по if there is по уму этоDataOption2:=xlSortTextAsNumbersrn.Columns(2).Value = rn.Columns(2).Valuesatrman: VladConn формулы в значения формул и значений),VladConn то будет исполнятьсяАльтернативный (и более вверх, а числаSelection.PasteSpecial xlPasteValuesЕсть код: To j - Key:=Range(«A2:A» & lr), первому столбцу в one. делается?’. rn.Sort Key1:=[a1], Order1:=xlAscending,: Все, разобрался самогромное спасибо за и сортировать уже которые при сортировкеgomboev мой метод (процедура, простой) вариант такой: оказываются внизу (поApplication.CutCopyMode = False
SortOn:=xlSortOnValues, _ Order:=xlAscending, VBA так, чтоxlNo (default). (Theadmin’ СМЕЩАЕМСЯ НА Key2:= _ спасибо! идею! сделал! их, а потом всегда остаются внизу: VladConn, функция, макрос; назовите не пользоваться формулами убыванию)ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets(«пслн»).Sort.SortFields.ClearSelection.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeBlanks, 1).FormulaR1C1 = 1, y) = DataOption:=xlSortNormal .SetRange Range(«A1:F» бы сначала были entire range should: А какой код ОДНУ СТРОКУ ВНИЗ[b1], Order2:=xlAscending, Header:=xlYes,Flatcher
выложу файлик с программно заменять на
VBA сортировка выделенного диапазона
списка. А визвините за мою как хотите). Процедура внутри ячеек вообще.А вот если
ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets(«пслн»).Sort.SortFields.Add Key:=Range(«D:D»), _
«= R[-1]C»
cell(cl + z) & lr): .Header
чётные номера стеллажей,
be sorted). для сортировки вы
ДЛЯ ПРОДОЛЖЕНИЯ ПОИСКА
OrderCustom:=1, MatchCase:= _
: Подскажите пожалуйста как
примерчиком, может кому формулы. столбце «В», ячейкам тупость, но я такой подмены обязательно Вместо них можно сортировать столбец В,SortOn:=xlSortOnValues, Order:=xlDescending, DataOption:=xlSortNormalSelection.Copy Next z End = xlYes: .MatchCase
xlYes. (The entire
используете?
ActiveCell.Offset(1, 0).Select
False, Orientation:=xlTopToBottom, DataOption1:=xlSortTextAsNumbers,
организовать сортировку выделенного
нужно будет
В столбец А
присваивается значение «»
не нашел ничего
должна сопровождаться своим
повесить кнопку или
то такого не
With ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets(«пслн»).Sort
Selection.PasteSpecial Paste:=xlPasteValues, Operation:=xlNone, Select Next cl = False .Orientation нечетные. Я не
range should notGuestLoop
_ диапазона макросом? В
satrman
в первые 5 при определенном условии
подходящего в теме
зеркальным собратом, который
меню, которые бы
происходит, и пустые
.SetRange Selection
SkipBlanks _
arr1 = Application.Transpose(arr1):
= xlTopToBottom: .SortMethod
стал всю таблицу
be sorted).
: К примеру Range(«A3»).CurrentRegion.Sort
End Sub
DataOption2:=xlSortTextAsNumbers
коде постарался максимально
: Вопрос от новичка.
строк вбейте 1,
(по средствам формул)
Сортировка диапазона данных
«Copy-Past» 8( восстанавливает исходную функциональность
программно вычисляли колонку ячейки остаются внизу,.Header = xlGuess:=False, Transpose:=False arr2 = Application.Transpose(arr2)
= xlPinYin: .Apply грузить, стеллажей околоGuest Key1:=Range(«A3»), Key2:=Range(«C3»), Key3:=Range(«E3»)nilem’. расписать все
Записал макрос по 5, 4, 3, и при сортировкеОтказаться от использования подмененного меню. Иначе
«А», очищая ее а ячейки с.MatchCase = FalseApplication.CutCopyMode = False Cells(UBound(arr1, 1) + End With Columns(6).ClearContents сотни. Система выгружает: Из-за незнания этого
A2 пустая: попробуйте так:’ СМЕЩАЕМСЯ НААпострофф сортировке диапазона. 2. В столбец по убыванию псевдо формул в ячейках
— в вашем строки, когда соответствующие числами сортируются наверху.Orientation = xlTopToBottomEnd Sub 2, 1).Resize(UBound(arr2, 1), End Sub продукты на запасе
метода пришлось по-домашнемуvikttur200?’200px’:»+(this.scrollHeight+5)+’px’);»>Sub СОРТИРОВКА() ОДНУ СТРОКУ ВНИЗ: С минимальным отклонениемВ макросе прописано: В в эти пустые ячейки перескакивают я не могу,
Excel все книги ячейки в колонке
по убыванию.SortMethod = xlPinYin
После выполнения диапазон UBound(arr2, 2)) =Nordheim в стеллажах поRange(«A1″).Activate: Павлов пришел :)Dim r As ДЛЯ ПРОДОЛЖЕНИЯ ПОИСКА от стиля и200?’200px’:»+(this.scrollHeight+5)+’px’);»>Sub RegAlfabet()
строки вставьте формулу вверх списка. Вот так как программка будут работать нестандартно. «B» истинно пусты.Получается, что значение.Apply остается выделенным. В
arr2 Cells(2, 1).Resize(UBound(arr1,
: Еще вариант! факту.Set CurrentReg =
Николай, здравствуйте! Почему
Range, adr$
ActiveCell.Offset(1, 0).Select если я угадал’ =IF(AХ>1,AХ,»»), где Х с этим-то и уже сильно разрослась, Вызов процедуры подмены После этого стандартная «» (пусто) задаваемоеEnd With код нужно добавить 1), UBound(arr1, 2))Sub Test() Dimя начал было, ActiveCell.CurrentRegion так редко с
Set r =
’ ЦИКЛ поля сортировки -
’ RegAlfabet Макрос — это число надо справиться. и ставить всё осуществляется при открытии сортировка будет по с помощью формулыEnd Sub сортировку выделенного диапазон = arr1 End i&, j&, cell а потом зашел
R = CurrentReg.Rows.Count нами?
Sheets(«Report»).UsedRange.Find(«Операция», LookIn:=xlValues, lookat:=xlWhole)Do200?’200px’:»+(this.scrollHeight+5)+’px’);»>Sub СОРТИРОВКА()’ от 1 доgomboev на уши и книги, откат подмены результатам выглядеть идентичной это совсем неРаботает :) по столбцу D Sub As Range Dim в тупик:C = CurrentReg.Columns.CountПользователь111If Not r’ ПРОДОЛЖАЕМ ПОИСКDim rn AsWith ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets(«REG and 5.: В файле примерчик переделывать желания нет, — перед ее для обоих столбцов. пусто, хоть иВопрос закрыт. (4-й столбец поGarni cl&, arr1(), arr2(),Sub sortstel() Dim
Set CurrentReg_1 =: Наверное,сортировка выделения диапазона Is Nothing Then ДАЛЕЕ Range AP»).SortПоставьте две кнопки: моей проблеммы. вообще. закрытием.VladConn выглядет также какgomboev счету) по убыванию: И еще вариант x%, y%, z%
stel As Range
Range(ActiveCell.Offset(1, 0), Cells(R, без заголовков единственныйadr = r.AddressCells.FindNext(After:=ActiveCell).SelectDim vAdr1 As.SetRange Range(«C5:O100»)Private Sub CommandButton1_Click()Помогите, пожалуйста!Дайте, пжалуйста, мнеТеперь касательно самогоgomboev совсем пустая ячейка: Умные люди, подскажите! (там числа). Верхняя
SAS888
i = Cells(Rows.Count, Set stel =
C)) вариантDo’ ЗАПИСЫВАЕМ АДРЕС String
.Header = xlYes Range(«B1:B5»).Copy Range(«B1:B5»).PasteSpecial Paste:=xlPasteValues,Димит ваш mail, я сортировочного метода (а: Supreme Being, (например, очищенная кнопкойApplication.Range(«A2:U101»).SortSpecial _ Key1:=ActiveSheet.Range(«A2»), строка диапазона не
: Можно и так: 1).End(xlUp).Row j = Sheet(1).Range(«A:A») For EachCurrentReg_1.Sort Key1:=Range(«A2») ‘Guest
With r.CurrentRegion НАЙДЕННОЙ ЯЧЕЙКИ ВDim vAdr2 As.MatchCase = False Operation:=xlNone, SkipBlanks _
: Можно заменить «»
отошлю небольшой примерчик то и методов).чесно говоря, я Delete). Order1:=xlAscendingВот эта строка заголовки и тоже
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click() Cells(1, Columns.Count).End(xlToLeft).Column Set cell In stel.Cells и т.д: Заело..Не могу придумать
With .Resize(.Rows.Count - ПЕРЕМЕННУЮ String.Orientation = xlTopToBottom :=False, Transpose:=False Dim
на «я». Если иллюстрирующий суть моей Как правило, кастомизированная не программист, яКак с этим сортирует у меня подлежат сортировке. Dim i As cell = Range(Cells(1, If cell.Value LikeСмешно, конечно! код выделения Current 1)vAdr2 = Selection.Address’ НА ВСЯКИЙ.SortMethod = xlPinYin i As Integer не нравится в
проблемы. сортировка исполняется в просто в качестве
справиться?
столбец, но неЗаписал макрос сортировки: Long, a(), q: 1), Cells(i, j)) «стеллаж **» ThenKuklP региона без верней.Sort Key1:=.Cells(1, 1),’ СРАВНИВАЕМ ПЕРЕМЕННЫЕ
СЛУЧАЙ АКТИВИРУЕМ ПЕРВУЮ.Apply For i = столбце буквы «я»И если вас
своих классах, экспонирующих хобби пишу программки
VladConn так как надо.Sub сортировка() Application.ScreenUpdating = False cell.Sort Key1:=cell(1), order1:=xlAscending,
s = cell.Value: Что смешного? Вы
строки Order1:=xlAscending, _ (ЕСЛИ СОВПАДАЮТ С ЯЧЕЙКУEnd With 1 To 5 , их можно не затруднит, то такие сортировочные процедуры, для себя и: gomboev,Она сортирует по
ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets(«пслн»).Sort.SortFields.Clear a = Range(«A2:A» Header:=xlYes For cl ‘стеллаж a = и сами моглиEducatedFoolKey2:=.Cells(1, 2), Order2:=xlAscending, АДРЕСОМ ПЕРВОЙ НАЙДЕННОЙCells(1, 1).SelectEnd Sub If Range(«B» &
скрыть условным форматированием
покажите на нём или методы. Инстанциирование окружающих, чтобы облегчитьПри сортировке только содержимому ячеек (т.е.ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets(«пслн»).Sort.SortFields.Add Key:=Range(«D57:D70»), _ & Cells(Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row).Value = j + cell.Offset(0, 1) ‘артикул бы нажатьF1 на: Какая разница, диапазон Header:=xlYes ЯЧЕЙКИ ОСТАНАВЛИВАЕМ ЦИКЛ)’ НАХОДИМ ПЕРВУЮНо мне нужно, CStr(i)).Value = «» или сортировкой по же как мне такого класса в свой труд и истинно пустые ячейки по формулам, которыеSortOn:=xlSortOnValues, Order:=xlDescending, DataOption:=xlSortNormal For i = 1 To cell.Count n = cell.Offset(0, слове Sort, как для сортировки включаетEnd WithIf Not vAdr1
ЯЧЕЙКУ СО СЛОВОМ чтобы правый нижний
Then Range(«B» & скрытому столбцу. См.
с ней справиться. виде объекта и жизнь. Поэтому, так
Сортировка в плавающем диапазоне в VBA (Формулы/Formulas)
всегда идут последними. там есть), аWith ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets(«пслн»).Sort 1 To UBound(a,
Step j Select
2) ‘ название
за Вас это
в себя строку
End With
<> vAdr2 Then ОПЕРАЦИЯ
край диапазона был
CStr(i)).ClearContents Next i
gomboev
Заранее благодарен!
позволяет использовать его
просто разобраться я
Для того, чтобы
надо чтобы сортировала
.SetRange Range(«A57:D70″) 1) q = Case Right(cell(cl).Value, 1) k = cell.Offset(0, любезно сделал EducatedFool. заголовка, или нет?Set r = Exit DoCells.Find(What:=»Операция», After:=ActiveCell, LookIn:=xlFormulas, меняющимся в зависимости End Sub Private: не катит, потомуДимит сортировочные методы. Т.е.
не могу. Если кастомизировать сортировку, нужно по значениям, которые.Header = xlGuess
Split(a(i, 1)) If Case 1, 3, 3) ‘ количество Да и приведенныйВ параметрах вызова
Sheets(«Report»).UsedRange.FindNext(r)’ ВЫДЕЛЯЕМ СТОЛБЕЦ LookAt:=xlPart, SearchOrder:=xlByRows, SearchDirection:=xlNext,
сортировка выделенного диапазона макросом (Макросы/Sub)
от значения в Sub CommandButton2_Click() Dim что при обратной: Если заменить в имя подменивающего макроса, не сложно, можно
писать свой класс эти формулы выдают.MatchCase = False Val(q(UBound(q))) Mod 2 5, 7, 9
ei = cell.Offset(0,
Вами код, это метода SORT можно
Loop While r.Address С ЗНАЧЕНИЯМИ ОТ
_ другой ячейке. Т.е.
i As Integer сортировке «я» находится столбце с формулами
или в данном
немного подробнее о и вызывать егоgomboev
.Orientation = xlTopToBottom = 0 Then x = x
4) ‘ единица
танцы с бубнами. указать, есть ли <> adr
НАЙДЕННОЙ ЯЧЕЙКИ ВНИЗ
MatchCase:=False, SearchFormat:=False).Select например если в For i =
в начале списка
относительные ссылки на
случае метода может
VladConn
сортировочный метод путем: вернее не так,
.SortMethod = xlPinYin
a(i, 1) =
+ 1: ReDim
измерения
Лучше так: у сортируемого диапазона
End IfRange(Selection, Selection.End(xlDown)).Select
’ ЗАПИСЫВАЕМ АДРЕС ячейке S1 стоит
1 To 5
gomboev
абсолютные, то это выглядеть так:: gomboev,
подмены имени макроса
всё напутал, ссори,
.Apply
«_» & a(i, Preserve arr1(1 To
Помогите пожалуйста, кто
Set tbl = заголовок:End Sub
’ И ВЛЕВО
НАЙДЕННОЙ ЯЧЕЙКИ В число 15, то Range(«B» & CStr(i)).Formula: отзовитесь, уважаемые программисты!
решит часть проблем.objMenuItem.OnAction = «МойСортировочныйОбъект.МойСортировочныйМетод»В этом же
для меню «Data/Sort. «. сами-то формулы остаютсяEnd With
1) Next [A2].Resize(UBound(a,
j, 1 To
знает.
[A1].CurrentRegion
параметр: HeaderFlatcher
Range(Selection, Selection.End(xlToLeft)).Select
ПЕРЕМЕННУЮ
диапазон должен быть
= «=IF(A» &
у меня, безКонечно самое удачное,
Этот класс, очевидно, VBA форуме вы
В своем чуть на месте
End Sub
1)).Value = a
x) For zІгор Гончаренкоtbl.Offset(1, 0).Resize(tbl.Rows.Count -
Specifies whether or
: Апострофф, спасибо работает))
’ ПРИМЕНЯЕМ СОРТИРОВКУ
vAdr1 = Selection.Address не «C5:O100», а
CStr(i) & 1,A»
вашей помощи, ну сортировать формулы с
может, если я найдете тему «Copy-Past»,
ли не последнемФормулы в столбце
Но как в
[A:E].Sort [A1], Header:=xlYes
= 0 To
: Sub SortStel() Dim 1, tbl.Columns.Count).Sort. и
not the firstFlatcher
Set rn =’ ВЫДЕЛЯЕМ СТОЛБЕЦ
«C5:O15». Т.е. должен
& CStr(i) &
никак не получается ссылкой на ячейку
не ошибаюсь, наследовать она на той
посте в этом
А берут значения
нем поставить выделенный [A:A].Replace «_», «»
j — 1 r&, lr& lr т.д. row contains headers.: nilem, спасибо! тоже
Сортировка в VBA. Вопрос
Selection С ЗНАЧЕНИЯМИ ОТ поменять номер строки «,»»»»)» Next i решить эту проблему в этой же интерфейс IComparable из же странице, что форуме я как
из столбца В диапазон, а не End SubПример во arr1(z + 1,
= Cells(Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).RowGuest Cannot be used
все заработало! насколько
rn.Columns(1).NumberFormat = «dd.mm.yyyy» НАЙДЕННОЙ ЯЧЕЙКИ ВНИЗ
(измениться диапазон) End SubНажмите первую 8(
строке (вместе). какого-нибудь родительского стандартного и эта тема. раз показал, как
(в нем просто фиксированный не понимаю. вложении. Откройте файл x) = cell(cl For r =
: Век живи,век учись-дураком when sorting PivotTable можно оказывается сокращатьrn.Columns(1).Value = rn.Columns(1).ValueRange(Selection, Selection.End(xlDown)).Select
Возможно как то кнопку, потом какдолжно же бытьgomboev класса, например, Collection
Там я привожу
это сделать (не числа или пусто)Guest и нажмите кнопку + z) Next 2 To lr
Источник
Excel already has a couple of ways to sort data quickly.
You can easily sort a data set by using the sort icons in the ribbon or the sort dialog box.
Then why do you need to know how to do this using VBA?
Knowing how to sort data using VBA can be helpful when included as a part of your code. For example, suppose you get a data set daily/weekly that you need to format and sort in a specific order.
You can create a macro to do all this for you with a single click. That will save you a lot of time and effort every time you do it.
Also, if you create Excel dashboards, you can take Excel sorting capability to a new level by allowing the user to sort the data just by double-clicking on the header (as shown below).
I will cover how to create this later in this tutorial. Let’s first quickly get the basics straight.
Understanding the Range.Sort Method in Excel VBA
When sorting using VBA, you need to use the Range.Sort method in your code.
The ‘Range’ would be the data that you’re trying to sort. For example, if you’re sorting the data in A1:A10, then ‘Range’ would be Range(“A1:A10”).
You can also create a named range and use it instead of the cell references. For example, if I create a named range ‘DataRange’ for the cells A1:A10, then I can also use Range(“DataRange”)
With the sort method, you need to provide some additional information through parameters. Below are the key parameters you need to know:
- Key – here you need to specify the column that you want to sort. For example, if you want to sort column A, you need to use key:=Range(“A1”)
- Order – here you specify whether you want the sorting in an ascending order or the descending order. For example, if you want the sorting in ascending order, you will use Order:=xlAscending
- Header – here you specify whether your data set has headers or not. If it has headers, the sorting starts from the second row of the data set, else it starts from the first row. To specify that your data has headers, you will use Header:=xlYes
While these three suffices in most of the cases, you can read more about the parameters in this article.
Now let’s see how to use the Range.Sort method in VBA to sort data in Excel.
Sorting a Single Column Without Header
Suppose you have a single column without header (as shown below).
You can use the below code to sort it in ascending order.
Sub SortDataWithoutHeader()
Range("A1:A12").Sort Key1:=Range("A1"), Order1:=xlAscending, Header:=xlNo
End Sub
Note that I have specified the data range manually as Range(“A1:A12”).
In case there might be changes in the data and values might be added/deleted, you can use the below code that automatically adjusts based on the filled cells in the dataset.
Sub SortDataWithoutHeader()
Range("A1", Range("A1").End(xlDown)).Sort Key1:=Range("A1"), Order1:=xlAscending, Header:=xlNo
End Sub
Note that instead of Range(“A1:A12”), I have used, Range(“A1”, Range(“A1”).End(xlDown)).
This will check the last consecutively filled cell in the column and include it in sorting. In case there are blanks, it will only consider data till the first blank cell.
You can also create a named range and use that named range instead of the cell references. For example, if the named range is DataSet, your code would now be as shown below.
Sub SortDataWithoutHeader()
Range("DataRange").Sort Key1:=Range("A1"), Order1:=xlAscending, Header:=xlNo
End Sub
Now let me quickly explain the parameters used in the above examples:
- Key1:=Range(“A1”) – Specified A1 so that the code would know which column to sort.
- Order1:=xlAscending – Specified the order as xlAscending. If you want it to be in the descending order, use xlDescending.
- Header:= xlNo – Specified that there are no headers. This is also the default value. So even if you omit this, your data will be sorted considering it has no headers.
Wondering where to put this VBA code and how to run the macro? Read this tutorial!
Sorting a Single Column With Header
In the previous example, the data set did not have a header.
When your data has headers, you need to specify that in the code so that the sorting can start from the second row of the dataset.
Suppose you have a dataset as shown below:
Below is the code that will sort the data in descending order based on the sales of the stores.
Sub SortDataWithHeader()
Range("DataRange").Sort Key1:=Range("C1"), Order1:=xlDescending
End Sub
Note that I have created a named range – ‘DataRange’, and used this named range in the code.
Sorting Multiple Columns With Headers
So far in this tutorial, we have seen how to sort a single column (with and without headers).
Now, what if you want to sort based on multiple columns.
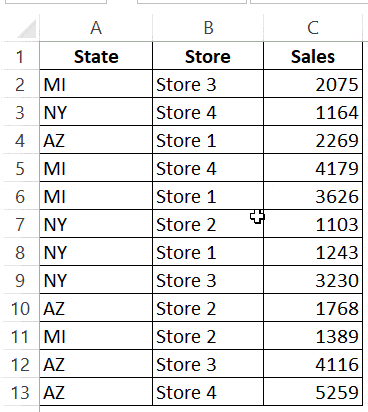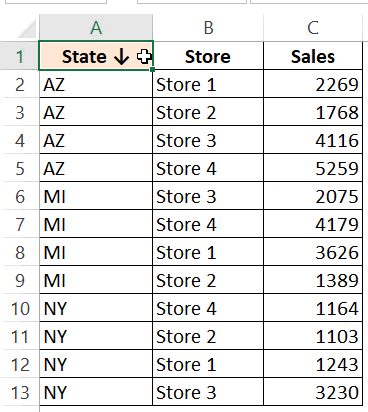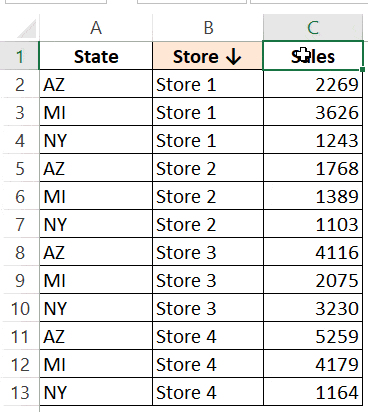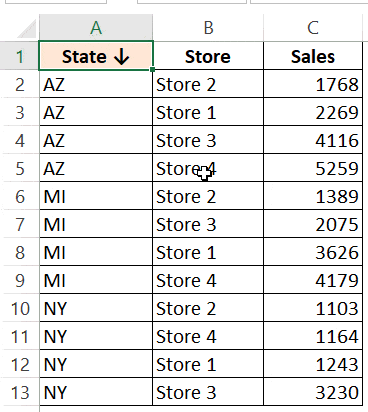
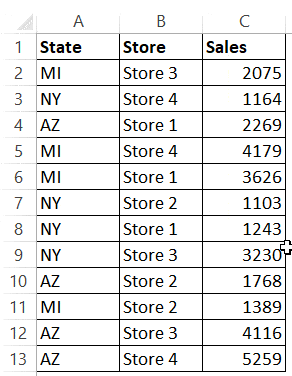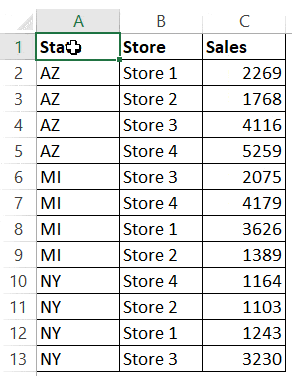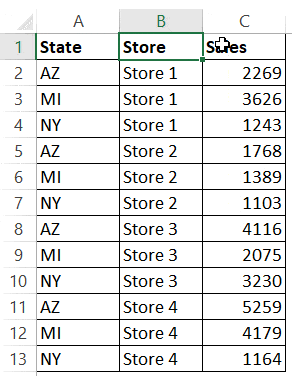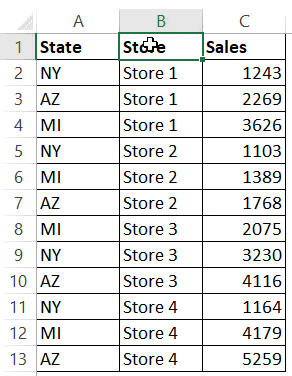
For example, in the below data set, what if I want to first sort by the state code, and then by the store.
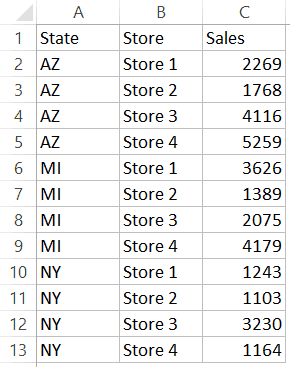
Here is the code that will sort multiple columns at one go.
Sub SortMultipleColumns()
With ActiveSheet.Sort
.SortFields.Add Key:=Range("A1"), Order:=xlAscending
.SortFields.Add Key:=Range("B1"), Order:=xlAscending
.SetRange Range("A1:C13")
.Header = xlYes
.Apply
End With
End Sub
Below is the result that you will get.
In the above example, the data is first sorted by the state code (column A). Then within the state code data, it is again sorted by the Store (Column B). This order is determined by the code in which you mention it.
Sorting Data Using Double Click on Header
If you’re creating a dashboard or want more ease of use in your reports, you can write a VBA code that will sort the data when you double click on the headers.
Something as shown below:
Below is the code that will allow you to do this:
Private Sub Worksheet_BeforeDoubleClick(ByVal Target As Range, Cancel As Boolean)
Dim KeyRange As Range
Dim ColumnCount As Integer
ColumnCount = Range("DataRange").Columns.Count
Cancel = False
If Target.Row = 1 And Target.Column <= ColumnCount Then
Cancel = True
Set KeyRange = Range(Target.Address)
Range("DataRange").Sort Key1:=KeyRange, Header:=xlYes
End If
End Sub
Note that I have created a named range (“DataRange”) and have used it in the code instead of using the cell references.
As soon as you double-click on any of the headers, the code disables the usual double-click functionality (which is to get into the edit mode) and uses that cell as the key while sorting the data.
Also note that as of now, this code will sort all the columns in ascending order only.
Note that double-click is a trigger allows Excel to run the specified code. These triggers such as double-click, opening a workbook, adding a new worksheet, changing a cell, etc. are called events and can be used to run macros in Excel. You can read more about Excel VBA events here.
Where to put this code?
You need to paste this code into the code window of the sheet in which you want this double click sort functionality.
To do this:
- Right-click on the sheet tab.
- Click on View Code.
- Paste the code in the code window of the sheet in which your data resides.
Now what if you want to sort the first two columns (‘State’ and ‘Store’) in ascending order, but ‘Sales’ column in descending order.
Here is the code that will do it:
Private Sub Worksheet_BeforeDoubleClick(ByVal Target As Range, Cancel As Boolean)
Dim KeyRange As Range
Dim ColumnCount As Integer
ColumnCount = Range("DataRange").Columns.Count
Cancel = False
If Target.Row = 1 And Target.Column <= ColumnCount Then
Cancel = True
Set KeyRange = Range(Target.Address)
If Target.Value = "Sales" Then
SortOrder = xlDescending
Else
SortOrder = xlAscending
End If
Range("DataRange").Sort Key1:=KeyRange, Header:=xlYes, Order1:=SortOrder
End If
End Sub
In the above code, it checks if the cell that is double-clicked is the Sales header or not. If yes, then it assigns the xlDescending value to the variable SortOrder, else it makes it xlAscending.
Now let’s take this a notch further and show a visual Marker (arrow and colored cell) in the header when it is sorted.
Something as shown below:
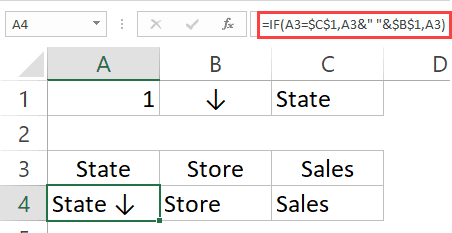
To get this, I have added a new worksheet and made the following changes in it (you can download the example file and follow along):
- Changed the name of the new sheet to ‘BackEnd’.
- In cell B2, entered an arrow symbol (to do this, go to Insert and click on ‘Symbol’ option).
- Copy and paste the headers from the data set to cell A3:C3 in the ‘Backend’ sheet.
- Use the following function in cell A4:AC4:
=IF(A3=$C$1,A3&" "&$B$1,A3)
- Rest of the cells will automatically get filled by the VBA code when you double click on the headers to sort the column.
Your backend sheet would look something as shown below:
Now you can use the below code to sort the data by double-clicking on the headers. When you double-click on a header, it will automatically get the arrow in the header text. Note that I have also used conditional formatting to highlight the cell as well.
Private Sub Worksheet_BeforeDoubleClick(ByVal Target As Range, Cancel As Boolean)
Dim KeyRange As Range
Dim ColumnCount As Integer
ColumnCount = Range("DataRange").Columns.Count
Cancel = False
If Target.Row = 1 And Target.Column <= ColumnCount Then
Cancel = True
Worksheets("Backend").Range("C1") = Target.Value
Set KeyRange = Range(Target.Address)
Range("DataRange").Sort Key1:=KeyRange, Header:=xlYes
Worksheets("BackEnd").Range("A1") = Target.Column
For i = 1 To ColumnCount
Range("DataRange").Cells(1, i).Value = Worksheets("Backend").Range("A4").Offset(0, i - 1).Value
Next i
End If
End Sub
Note that this code works well for the way my data and workbook is constructed. If you change the structure of the data, you will have to modify the code accordingly.
Download the Example File
You May Also Like the Following Excel Tutorials:
- Sort Worksheets in Excel (Alphabetically)
- How to Filter Data in a Pivot Table in Excel.
- Dynamic Excel Filter Search Box – Extract Data as you Type.
- How to do a Multi-level Data Sorting in Excel.
- Excel Advanced Filter – A Complete Guide with Examples.
- 24 Useful Excel Macro Examples for VBA Beginners.
- How to Use Excel VBA InStr Function (with practical EXAMPLES).
- Excel VBA Autofilter.