Операторы, использующиеся в VBA Excel для отрицания и сравнения логических выражений. Синтаксис, принимаемые значения, приоритет логических операторов.
Оператор «Not»
«Not» – это оператор логического отрицания (инверсия), который возвращает True, если условие является ложным, и, наоборот, возвращает False, если условие является истинным.
Синтаксис:
Таблица значений:
| Условие | Результат |
|---|---|
| True | False |
| False | True |
Оператор «And»
«And» – это оператор логического умножения (логическое И, конъюнкция), который возвращает значение True, если оба условия являются истинными.
Синтаксис:
|
Результат = Условие1 And Условие2 |
Таблица значений:
| Условие1 | Условие2 | Результат |
|---|---|---|
| True | True | True |
| True | False | False |
| False | True | False |
| False | False | False |
Оператор «Or»
«Or» – это оператор логического сложения (логическое ИЛИ, дизъюнкция), который возвращает значение True, если одно из двух условий является истинным, или оба условия являются истинными.
Синтаксис:
|
Результат = Условие1 Or Условие2 |
Таблица значений:
| Условие1 | Условие2 | Результат |
|---|---|---|
| True | True | True |
| True | False | True |
| False | True | True |
| False | False | False |
Оператор «Xor»
«Xor» – это оператор логического исключения (исключающая дизъюнкция), который возвращает значение True, если только одно из двух условий является истинным.
Синтаксис:
|
Результат = Условие1 Xor Условие2 |
Таблица значений:
| Условие1 | Условие2 | Результат |
|---|---|---|
| True | True | False |
| True | False | True |
| False | True | True |
| False | False | False |
Оператор «Eqv»
«Eqv» – это оператор логической эквивалентности (тождество, равенство), который возвращает True, если оба условия имеют одинаковое значение.
Синтаксис:
|
Результат = Условие1 Eqv Условие2 |
Таблица значений:
| Условие1 | Условие2 | Результат |
|---|---|---|
| True | True | True |
| True | False | False |
| False | True | False |
| False | False | True |
Оператор «Imp»
«Imp» – это оператор логической импликации, который возвращает значение False, если первое (левое) условие является истинным, а второе (правое) условие является ложным, в остальных случаях возвращает True.
Синтаксис:
|
Результат = Условие1 Imp Условие2 |
Таблица значений:
| Условие1 | Условие2 | Результат |
|---|---|---|
| True | True | True |
| True | False | False |
| False | True | True |
| False | False | True |
Приоритет логических операторов
Приоритет определяет очередность выполнения операторов в одном выражении. Очередность выполнения логических операторов в VBA Excel следующая:
- «Not» – логическое отрицание;
- «And» – логическое И;
- «Or» – логическое ИЛИ;
- «Xor» – логическое исключение;
- «Eqv» – логическая эквивалентность;
- «Imp» – логическая импликация.
Содержание
- VBA If – And, Or, Not
- IF…AND
- IF NOT…
- VBA Code Examples Add-in
- Логические операторы VBA
- Логический оператор AND
- Логический оператор OR
- Логический оператор NOT
- Логический оператор XOR
- Логический оператор EQV
- Логический оператор IMP
- VBA Logical Operators: AND, OR, NOT, IF NOT in Excel VBA
- Excel VBA Logical Operators
- VBA Logical Operators Example Source Code
- VBA Logical Operators – OR, AND, XOR, NOT, IS, & LIKE
- Using the And Logical Operator
- Using the Or Logical Operator
- Using the Not Logical Operator
- Using the Xor Logical Operator
- Is Operator
- Like Operator
- VBA Coding Made Easy
- VBA Code Examples Add-in
VBA If – And, Or, Not
In this Article
This article will demonstrate how to use the VBA If statement with And, Or and Not.
When we us an IF statement in Excel VBA, the statement will execute a line of code if the condition you are testing is true.
- We can use AND statement and OR statements in conjunction with IF statements to test for more than one condition and direct the code accordingly.
- We can also use a NOT statement with an IF statement to check if the condition is NOT true – it basically is the inverse of the IF statement when used alone.
IF…AND
We can use the IF…AND combination of logical operators when we wish to test for more than one condition where all the conditions need to be true for the next line of code to execute.
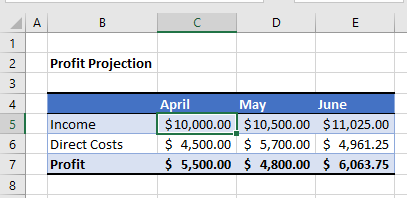
For example, consider the following sheet:
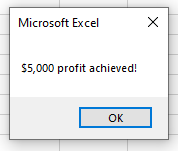
To check if the Profit is over $5,000, we can run the following macro:
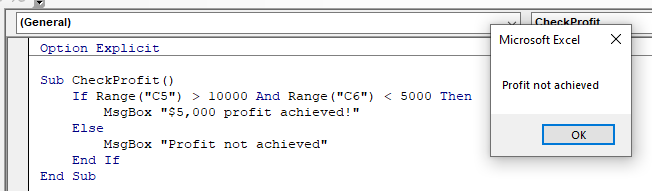
This macro will check that the cell C5 is greater or equal to $10,000 AND check that the cell B6 is less than $5,000. If these conditions are BOTH true, it will show the message box.
If we amend the macro to check if C5 is just greater than $10,000, then the profit would not be achieved!
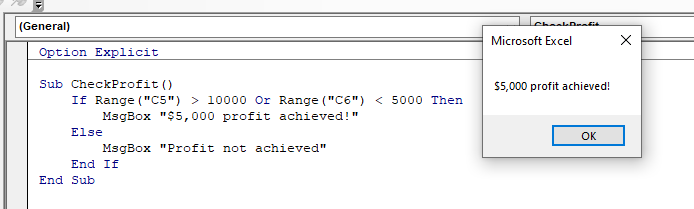
We can use the IF…OR combination of logical operators when we wish to test for more than one condition where only one of the conditions needs to be true for the next line of code to execute.
The format for this is almost identical to the IF…AND example above.
However, with this macro, because we are using an IF …OR statement, only one of the conditions needs to be true.
IF NOT…
IF..NOT changes the IF statement around – it will check to see if the condition is NOT true rather than checking to see if the condition is true.
In this example above, the IF statement is checking to see if the value in C5 is NOT smaller than 10000.
Therefore this line of code:
and this this line of code:
are testing for the same thing!
VBA Code Examples Add-in
Easily access all of the code examples found on our site.
Simply navigate to the menu, click, and the code will be inserted directly into your module. .xlam add-in.
Источник
Логические операторы VBA
| Оператор | Синтаксис | Описание |
| AND | A AND B | Конъюнкция: Если А и В имеют значение True, то — True. Иначе — False |
| OR | A OR B | Дизъюнкция: Если любой из операндов имеет значение True, то — True. Иначе — False |
| NOT | NOT A | Отрицание: Если А имеет значение False, то — True. Иначе — False |
| XOR | A XOR B | Исключение: Если А имеет значение True или В имеет значение True, то — True. Иначе — False |
| EQV | A EQV B | Эквивалентность: Если А имеет такое же значение что и В, то — True. Иначе — False |
| IMP | A IMP B | Импликация: Если А имеет значение True и В имеет значение False, то — False. Иначе — True |
В качестве операнда для логического оператора можно использовать любое действительное выражение, имеющее результат типа Boolean, а также число, которое может быть преобразовано в значение типа Boolean.
Результатом логической операции является значение типа Boolean (или Null, если хотя бы один из операндов имеет значение Null).
Логический оператор AND
Синтаксис:
Операнд_1 AND Операнд_2
Оператор AND выполняет логическую конъюнкцию.
Результатом данной операции является значение True, только когда оба операнда имеют значение True, иначе — False.
| Операнд_1 | Операнд_2 | Результат |
| True | True | True |
| True | False | False |
| False | True | False |
| False | False | False |
Оператор AND можно использовать для нескольких операндов:
(5 3) AND (5=6) результатом будет False
Независимо от количества операндов результатом логической операции AND будет True только в том случае, когда все операнды выражения будут иметь значение True. В любом другом случае результатом будет False. Обратите внимание, что операнды заключаются в круглые скобки. VBA сначала вычисляет значение каждого операнда внутри скобок, а затем уже все выражение полностью.
Логический оператор OR
Синтаксис:
Операнд_1 OR Операнд_2
Оператор OR выполняет логическую дизъюнкцию.
Результатом данной операции является значение True, если хотя бы один из операндов имеет значение True, иначе — False.
| Операнд_1 | Операнд_2 | Результат |
| True | True | True |
| True | False | True |
| False | True | True |
| False | False | False |
Оператор OR можно использовать для нескольких операндов:
(5 3) OR (5=6) результатом будет True
Независимо от количества операндов результатом логической операции OR будет всегда True в том случае, если хотя бы один из операндов выражения будет иметь значение True. Иначе результатом будет False.
Операторы AND и OR можно комбинировать:
((5 3)) OR (5=6) результатом будет True
Логический оператор NOT
Синтаксис:
NOT Операнд
Оператор NOT выполняет логическое отрицание.
Оператор NOT использует только один операнд.
| Операнд | Результат |
| True | False |
| False | True |
Операторы AND OR NOT можно комбинировать:
((5 3)) OR NOT (5=6) результатом будет True
Логический оператор XOR
Синтаксис:
Операнд_1 XOR Операнд_2
Оператор XOR выполняет логическое исключение.
Результатом данной операции является значение True, если операнды имеют разные значения, иначе — False.
| Операнд_1 | Операнд_2 | Результат |
| True | True | False |
| True | False | True |
| False | True | True |
| False | False | False |
((5 3)) OR NOT (5=6) XOR (5=5) результатом будет False
Логический оператор EQV
Синтаксис:
Операнд_1 EQV Операнд_2
Оператор EQV — это оператор логической эквивалентности.
Результатом данной операции является значение True, если операнды имеют одинаковые значения, иначе — False.
| Операнд_1 | Операнд_2 | Результат |
| True | True | True |
| True | False | False |
| False | True | False |
| False | False | True |
((5 3)) OR NOT (5=6) EQV (5=5) результатом будет True
Логический оператор IMP
Синтаксис:
Операнд_1 IMP Операнд_2
Оператор IMP выполняет логическую операцию импликации.
| Операнд_1 | Операнд_2 | Результат |
| True | True | True |
| True | False | False |
| False | True | True |
| False | False | True |
((5 3)) OR NOT (5=6) IMP (5=5) результатом будет True
Логический оператор IMP наименее интуитивно понятный из всех логических операторов. К счастью, необходимость в его применении возникает довольно редко.
Источник
VBA Logical Operators: AND, OR, NOT, IF NOT in Excel VBA
Updated January 20, 2023
Excel VBA Logical Operators
Let’s say you want to process a customer order. For that, you want to first check to see if the ordered product exists or not. If it does, you also want to check if the quantity on hand is enough. Logical operators come in handy in such cases. Logical operators are used to evaluate more than one condition.
The main Excel VBA logical operators AND, OR, NOT are listed in the table below:
| S/N | Operator | Description | Example | Output |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | AND | AND: This is used to combine more than one condition. If all the conditions are true, AND evaluates to true. If any of the condition is false, AND evaluates to false | If true = true AND false = true THEN | false |
| 2 | OR | OR: This is used to combine more than one condition. If any of the conditions evaluate to true, OR returns true. If all of them are false, OR returns false | If true = true OR true = false THEN | true |
| 3 | NOT | NOT: This one works like an inverse function. If the condition is true, it returns false, and if a condition is false, it returns true. | If NOT (true) Then | false |
VBA Logical Operators Example Source Code
For the sake of simplicity, we will be comparing hard coded numbers.
Add ActiveX buttons to the sheet from the “Insert option.”
Set the properties as shown in the image below

The following table shows the properties that you need to change and the values that you need to update too.
Источник
VBA Logical Operators – OR, AND, XOR, NOT, IS, & LIKE
In this Article
VBA allows you to use the logical operators And, Or, Not, Xor to compare values. The operators are considered “Boolean”, which means they return True or False as a result.
If you want to learn how to compare strings, click here: VBA Compare Strings – StrComp
If you want to learn how to use comparison operators, click here: VBA Comparison Operators – Not Equal to & More
Using the And Logical Operator
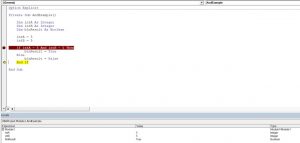
The And logical operator compares two or more conditions. If all the conditions are true, the operator will return True. If at least one of the conditions is not true, the operator will return False. Here is an example:
In this example, we want to check if both intA and intB are equal to 5. If this is true, the value of Boolean blnResult will be True, otherwise, it will be False.
First, we set values of intA and intB to 5:
After that, we use the And operator in the If statement to check if the values are equal to 5:
As both variables are equal to 5, the blnResult returns True:
Image 1. Using the And logical operator in VBA
Using the Or Logical Operator
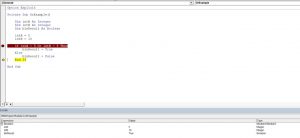
The Or logical operator compares two or more conditions. If at least one of the conditions is true, it will return True. If none of the conditions are true, the operator will return False. Here is the code for the example:
In this example, we want to check if both intA is equal to 5. or intB is equal to 10. If any of these conditions is true, the value of Boolean blnResult will be True, otherwise, it will be False.
First, we set the value of intA to 5 and intB to 10:
After that, we use the Or operator in the If statement to check if any of the values is equal to 5:
As intA value is 5, the blnResult returns True:
Image 2. Using the Or logical operator in VBA
Using the Not Logical Operator
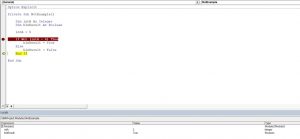
The Not logical operator checks one or more conditions. If the conditions are true, the operator returns False. Otherwise, it returns True. Here is the code for the example:
In this example, we want to check if the value of intA is not equal to 6. If intA is different than 6, the value of Boolean blnResult will be True, otherwise, it will be False.
First, we set the value of intA to 5:
After that, we use the Not operator in the If statement to check if the value of intA is different than 6:
As intA value is 5, the blnResult returns True:
Image 3. Using the Not logical operator in VBA
Using the Xor Logical Operator
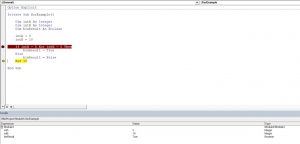
The Xor logical operator compares two or more conditions. If exactly one of the conditions is true, it will return True. If none of the conditions are true, or more than one are true, it will return False. Here is the code for the example:
In this example, we want to check if exactly one of the values (intA or IntB) are equal to 5. If only one condition is true, the value of Boolean blnResult will be True, otherwise, it will be False.
First, we set the value of intA to 5 and intB to 10:
After that, we use the Or operator in the If statement to check if any of the values is equal to 5:
As intA value is 5 and intB is 10, the blnResult returns True:
Image 4. Using the Xor logical operator in VBA
Is Operator
The Is Operator tests if two object variables store the same object.
Let’s look at an example. Here we will assign two worksheets to worksheet objects rng1 and rng2, testing if the two worksheet objects store the same worksheet:
Of course the worksheet objects are not the same, so “Different WSs” is returned.
Like Operator
The Like Operator can compare two strings for inexact matches. This example will test if a string starts with “Mr.”
VBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro — A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users! 
VBA Code Examples Add-in
Easily access all of the code examples found on our site.
Simply navigate to the menu, click, and the code will be inserted directly into your module. .xlam add-in.
Источник
Logical operators in VBA allow you to make decisions when certain conditions are met.
They allow you to check if something equals this OR that; this AND that; NOT this; and combinations of all three. When used in conjunction with IF statements, they allows you to make more complex choices in your macros and VBA.
Logical Operators
| Operator | Meaning |
|---|---|
| AND |
A < B AND B < 10 — Checks if both conditions are true. |
| OR |
A < B OR B < 10 — Checks if one of the conditions is true. |
|
NOT |
Not A < B — This reverses the check, which means this will evaluate to true if A is greater than B and NOT if it is less than B. |
| Xor |
Rarely used. Click here for more info on it. |
These are easier to understand when you see them in the examples below.
Logical Operator Examples
These examples assume that you are familiar with the IF statement in VBA/Macros.
AND
Check if all of the conditions evaluate to true.
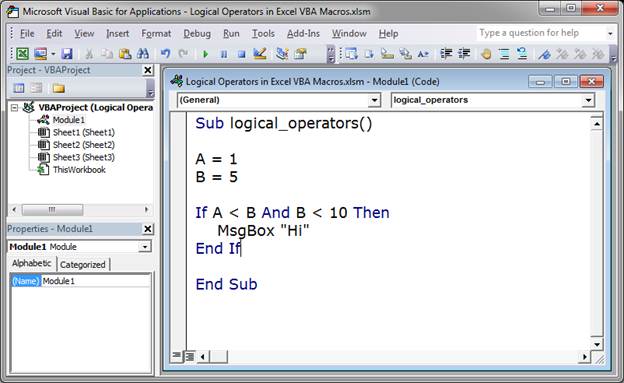
Check if A is less than B AND B is less than 10:
If A < B And B < 10 Then
MsgBox "Hi"
End If
The important part of the code is: A < B And B < 10
You do not need parentheses around this here and you can have as many conditions as you need.
Here is the full example:
This says that if A is less than B AND B is less than 10, a message box that says «Hi» will appear.
This evaluates to True because A is less than B (A is set to 1 and B to 5) and B is less than 10.
Or
Check if ANY of the conditions evaluate to true.
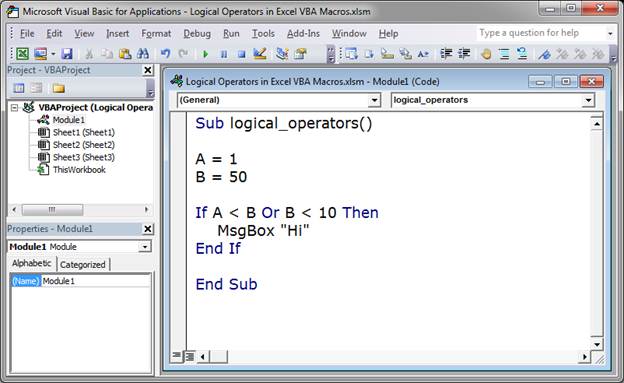
Check if A is less than B OR B is less than 10.
If A < B Or B < 10 Then
MsgBox "Hi"
End If
The important part of the code is: A < B Or B < 10
You do not need parentheses around this here and you can have as many conditions as you need.
Here is the full example:
This time I set B equal to 50, but the IF statement still evaluates to True because A, which is 1, is less than B. As such, the message box will appear and say «Hi».
When using Or only 1 condition has to be true for the statement to evaluate to true.
Not
Not literally reverses whatever condition it precedes.
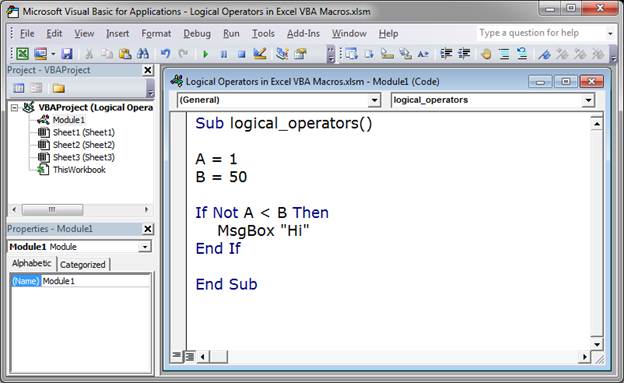
Here, let’s check if A is less than B, BUT let’s put a Not in front of it.
If Not A < B Then
MsgBox "Hi"
End If
The important part of the code is: Not A < B
Here is the full example:
Normally, this would evaluate to True because A is less than B, but, since there is a Not in front of the check, this evaluates to False.
If this is confusing, just mentally remove the Not and perform the comparison in your head, in this case you will get a True, then just return the opposite when a Not is present.
In this example, the message box will not appear.
More Complex Examples
Let’s kick things up a notch.
When you have more complex checks in your IF statement, you will need to use parenthesis.
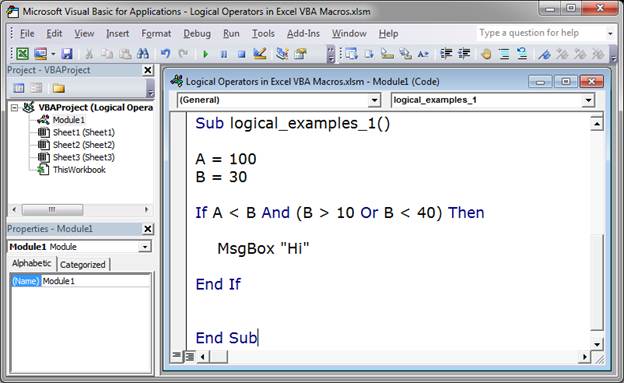
Example 1
Check if A is less than B AND B is greater than 10 OR it is less than 40.
Sub logical_examples_1()
A = 100
B = 30
If A < B And (B > 10 Or B < 40) Then
MsgBox "Hi"
End If
End Sub
This evaluates to False; however, without the parentheses after the And, this would evaluate to True.
Parentheses force a part of the check to be evaluated first or simply just together. In this example, the part before the And is evaluated and then everything within the parentheses is evaluated together; after that the part on the left of the And is compare to the part on the right.
This is kind of confusing; you really need to download the sample file for this tutorial and play around with this until you understand it; that is the best way to learn this concept.
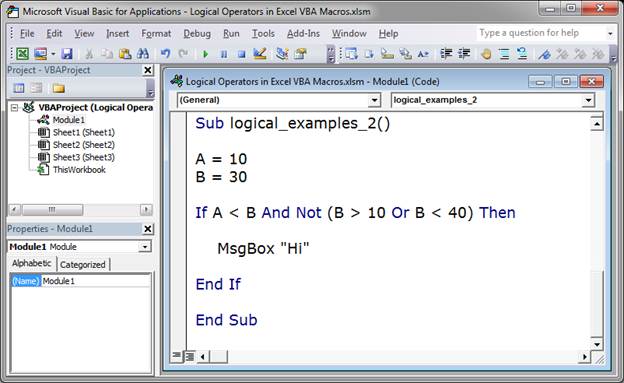
Example 2 (Not)
Let’s use the same example, except A now equals 10 and we will put a Not after the And.
Sub logical_examples_2()
A = 10
B = 30
If A < B And Not (B > 10 Or B < 40) Then
MsgBox "Hi"
End If
End Sub
If there was no Not after the And in this example, it would evaluate to True and the message box would appear.
However, the Not reverses the result. In this case, the Not reverses the result of the checks within the parenthesis.
Look to each comparison, evaluate it, and then compare them using the logical operators. This is the best way to understand how all of this works. This may sound confusing, but it will help if you download the sample file attached to this tutorial and play around with this example.
Notes
The And, Or, and Not logical operators are extremely useful in VBA and Macros. You must learn how to use them if you want to build more useful macros in Excel.
When it comes to parentheses, people tend to over-use them; however, I say that you should use them to the point that everything becomes clear and easy-to-understand for you! If you need a lot of parentheses, add them; if you are really good with the order of precedence, which controls what parts of the condition will be evaluated first, use fewer parentheses.
To help learn how to use these operators and parentheses, download the sample file attached to this tutorial and play around with the examples in there; compare them with this tutorial and edit them and see what happens. If you do this, you will have these concepts memorized in no time.
Subscribe for Weekly Tutorials
BONUS: subscribe now to download our Top Tutorials Ebook!
In this Article
- Using the And Logical Operator
- Using the Or Logical Operator
- Using the Not Logical Operator
- Using the Xor Logical Operator
- Is Operator
- Like Operator
VBA allows you to use the logical operators And, Or, Not, Xor to compare values. The operators are considered “Boolean”, which means they return True or False as a result.
If you want to learn how to compare strings, click here: VBA Compare Strings – StrComp
If you want to learn how to use comparison operators, click here: VBA Comparison Operators – Not Equal to & More
Using the And Logical Operator
The And logical operator compares two or more conditions. If all the conditions are true, the operator will return True. If at least one of the conditions is not true, the operator will return False. Here is an example:
Dim intA As Integer
Dim intB As Integer
Dim blnResult As Boolean
intA = 5
intB = 5
If intA = 5 And intB = 5 Then
blnResult = True
Else
blnResult = False
End IfIn this example, we want to check if both intA and intB are equal to 5. If this is true, the value of Boolean blnResult will be True, otherwise, it will be False.
First, we set values of intA and intB to 5:
intA = 5
intB = 5After that, we use the And operator in the If statement to check if the values are equal to 5:
If intA = 5 And intB = 5 Then
blnResult = True
Else
blnResult = False
End IfAs both variables are equal to 5, the blnResult returns True:
Image 1. Using the And logical operator in VBA
Using the Or Logical Operator
The Or logical operator compares two or more conditions. If at least one of the conditions is true, it will return True. If none of the conditions are true, the operator will return False. Here is the code for the example:
Dim intA As Integer
Dim intB As Integer
Dim blnResult As Boolean
intA = 5
intB = 10
If intA = 5 Or intB = 5 Then
blnResult = True
Else
blnResult = False
End IfIn this example, we want to check if both intA is equal to 5. or intB is equal to 10. If any of these conditions is true, the value of Boolean blnResult will be True, otherwise, it will be False.
First, we set the value of intA to 5 and intB to 10:
intA = 5
intB = 10After that, we use the Or operator in the If statement to check if any of the values is equal to 5:
If intA = 5 Or intB = 5 Then
blnResult = True
Else
blnResult = False
End IfAs intA value is 5, the blnResult returns True:
Image 2. Using the Or logical operator in VBA
Using the Not Logical Operator
The Not logical operator checks one or more conditions. If the conditions are true, the operator returns False. Otherwise, it returns True. Here is the code for the example:
Dim intA As Integer
Dim blnResult As Boolean
intA = 5
If Not (intA = 6) Then
blnResult = True
Else
blnResult = False
End IfIn this example, we want to check if the value of intA is not equal to 6. If intA is different than 6, the value of Boolean blnResult will be True, otherwise, it will be False.
First, we set the value of intA to 5:
intA = 5After that, we use the Not operator in the If statement to check if the value of intA is different than 6:
If Not (intA = 6) Then
blnResult = True
Else
blnResult = False
End IfAs intA value is 5, the blnResult returns True:
Image 3. Using the Not logical operator in VBA
Using the Xor Logical Operator
The Xor logical operator compares two or more conditions. If exactly one of the conditions is true, it will return True. If none of the conditions are true, or more than one are true, it will return False. Here is the code for the example:
Dim intA As Integer
Dim intB As Integer
Dim blnResult As Boolean
intA = 5
intB = 10
If intA = 5 Xor intB = 5 Then
blnResult = True
Else
blnResult = False
End IfIn this example, we want to check if exactly one of the values (intA or IntB) are equal to 5. If only one condition is true, the value of Boolean blnResult will be True, otherwise, it will be False.
First, we set the value of intA to 5 and intB to 10:
intA = 5
intB = 10After that, we use the Or operator in the If statement to check if any of the values is equal to 5:
If intA = 5 Xor intB = 5 Then
blnResult = True
Else
blnResult = False
End IfAs intA value is 5 and intB is 10, the blnResult returns True:
Image 4. Using the Xor logical operator in VBA
Is Operator
The Is Operator tests if two object variables store the same object.
Let’s look at an example. Here we will assign two worksheets to worksheet objects rng1 and rng2, testing if the two worksheet objects store the same worksheet:
Sub CompareObjects()
Dim ws1 As Worksheet, ws2 As Worksheet
Set ws1 = Sheets("Sheet1")
Set ws2 = Sheets("Sheet2")
If ws1 Is ws2 Then
MsgBox "Same WS"
Else
MsgBox "Different WSs"
End If
End SubOf course the worksheet objects are not the same, so “Different WSs” is returned.
Like Operator
The Like Operator can compare two strings for inexact matches. This example will test if a string starts with “Mr.”
Sub LikeDemo()
Dim strName As String
Dim blnResult As Boolean
strName = "Mr. Michael James"
If strName Like "Mr*" Then
blnResult = True
Else
blnResult = False
End If
End SubVBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro — A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Learn More!
VBA Logical Operators: AND, OR, NOT
Let’s say you want to process a customer order. For that, you want to first check to see if the ordered product exists or not. If it does, you also want to check if the quantity on hand is enough. Logical operators come in handy in such cases. Logical operators are used to evaluate more than one condition.
The main Excel VBA logical operators AND, OR, NOT are listed in the table below:
| S/N | Operator | Description | Example | Output |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | AND | AND: This is used to combine more than one condition. If all the conditions are true, AND evaluates to true. If any of the condition is false, AND evaluates to false | If true = true AND false = true THEN | false |
| 2 | OR | OR: This is used to combine more than one condition. If any of the conditions evaluate to true, OR returns true. If all of them are false, OR returns false | If true = true OR true = false THEN | true |
| 3 | NOT | NOT: This one works like an inverse function. If the condition is true, it returns false, and if a condition is false, it returns true. | If NOT (true) Then | false |
VBA Logical Operators Example Source Code
For the sake of simplicity, we will be comparing hard coded numbers.
Add ActiveX buttons to the sheet from the “Insert option.”
Set the properties as shown in the image below
The following table shows the properties that you need to change and the values that you need to update too.
| S/N | Control | Property | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CommandButton1 | Name | btnAND |
| Caption | AND Operator (0 = 0) | ||
| 2 | CommandButton2 | Name | btnOR |
| Caption | OR Operator (1 = 1) Or (5 = 0) | ||
| 3 | CommandButton3 | Name | btnNOT |
| Caption | NOT Operator Not (0 = ) |
Add the following code to btnAND_Click
Private Sub btnAND_Click()
If (1 = 1) And (0 = 0) Then
MsgBox "AND evaluated to TRUE", vbOKOnly, "AND operator"
Else
MsgBox "AND evaluated to FALSE", vbOKOnly, "AND operator"
End If
End Sub
VBA If AND Operator
- “If (1 = 1) And (0 = 0) Then” the if statement uses the AND logical operator to combine two conditions (1 = 1) And (0 = 0). If both conditions are true, the code above ‘Else’ keyword is executed. If both conditions are not true, the code below ‘Else’ keyword is executed.
Add the following code to btnOR_Click
Private Sub btnOR_Click()
If (1 = 1) Or (5 = 0) Then
MsgBox "OR evaluated to TRUE", vbOKOnly, "OR operator"
Else
MsgBox "OR evaluated to FALSE", vbOKOnly, "OR operator"
End If
End Sub
VBA If OR Operator
- “If (1 = 1) Or (5 = 0) Then” the if statement uses the OR logical operator to combine two conditions (1 = 1) And (5 = 0). If any of the conditions is true, the code above Else keyword is executed. If both conditions are false, the code below Else keyword is executed.
Add the following code to btnNOT_Click
Private Sub btnNOT_Click()
If Not (0 = 0) Then
MsgBox "NOT evaluated to TRUE", vbOKOnly, "NOT operator"
Else
MsgBox "NOT evaluated to FALSE", vbOKOnly, "NOT operator"
End If
End Sub
VBA If NOT Operator
- “If Not (0 = 0) Then” the VBA If Not function uses the NOT logical operator to negate the result of the if statement condition. If the conditions is true, the code below ‘Else’ keyword is executed. If the condition is true, the code above Else keyword is executed.
Download Excel containing above code