Import or export text (.txt or .csv) files
There are two ways to import data from a text file with Excel: you can open it in Excel, or you can import it as an external data range. To export data from Excel to a text file, use the Save As command and change the file type from the drop-down menu.
There are two commonly used text file formats:
-
Delimited text files (.txt), in which the TAB character (ASCII character code 009) typically separates each field of text.
-
Comma separated values text files (.csv), in which the comma character (,) typically separates each field of text.
You can change the separator character that is used in both delimited and .csv text files. This may be necessary to make sure that the import or export operation works the way that you want it to.
Note: You can import or export up to 1,048,576 rows and 16,384 columns.
Import a text file by opening it in Excel
You can open a text file that you created in another program as an Excel workbook by using the Open command. Opening a text file in Excel does not change the format of the file — you can see this in the Excel title bar, where the name of the file retains the text file name extension (for example, .txt or .csv).
-
Go to File > Open and browse to the location that contains the text file.
-
Select Text Files in the file type dropdown list in the Open dialog box.
-
Locate and double-click the text file that you want to open.
-
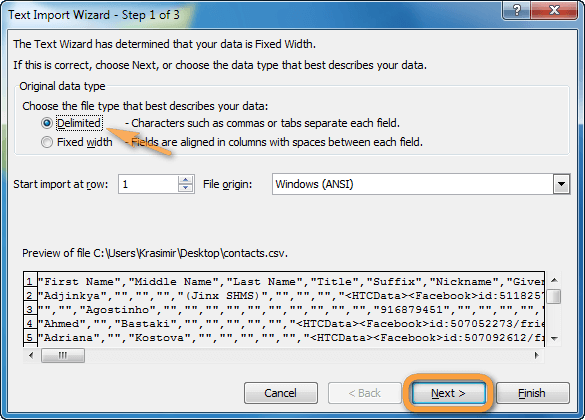
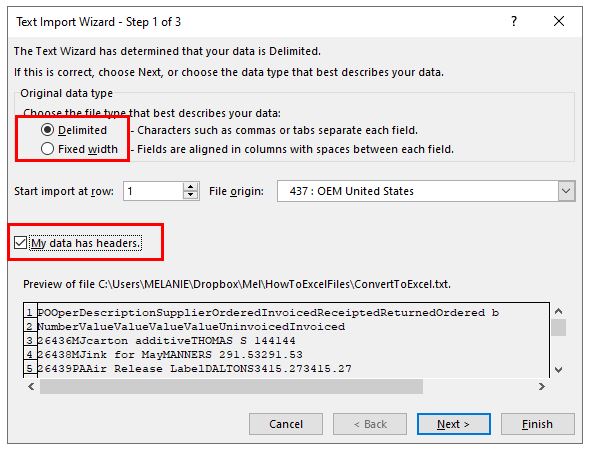
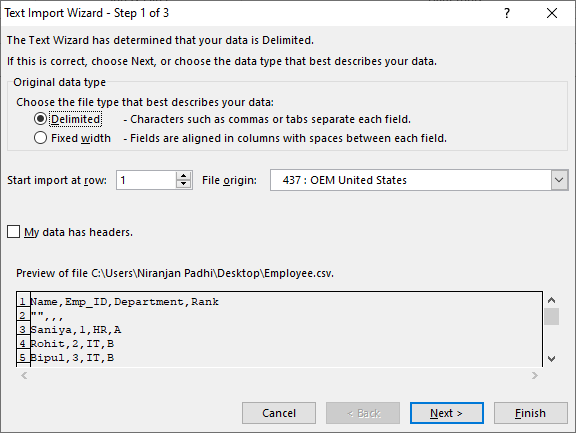
If the file is a text file (.txt), Excel starts the Import Text Wizard. When you are done with the steps, click Finish to complete the import operation. See Text Import Wizard for more information about delimiters and advanced options.
-
If the file is a .csv file, Excel automatically opens the text file and displays the data in a new workbook.
Note: When Excel opens a .csv file, it uses the current default data format settings to interpret how to import each column of data. If you want more flexibility in converting columns to different data formats, you can use the Import Text Wizard. For example, the format of a data column in the .csv file may be MDY, but Excel’s default data format is YMD, or you want to convert a column of numbers that contains leading zeros to text so you can preserve the leading zeros. To force Excel to run the Import Text Wizard, you can change the file name extension from .csv to .txt before you open it, or you can import a text file by connecting to it (for more information, see the following section).
-
Import a text file by connecting to it (Power Query)
You can import data from a text file into an existing worksheet.
-
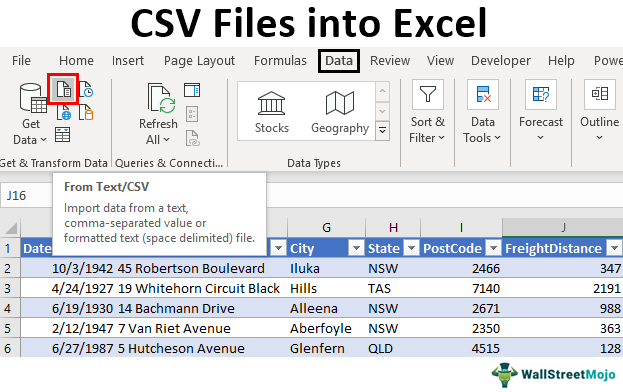
On the Data tab, in the Get & Transform Data group, click From Text/CSV.
-
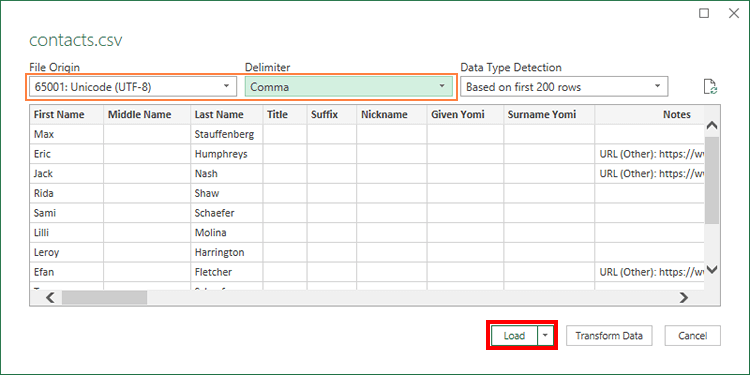
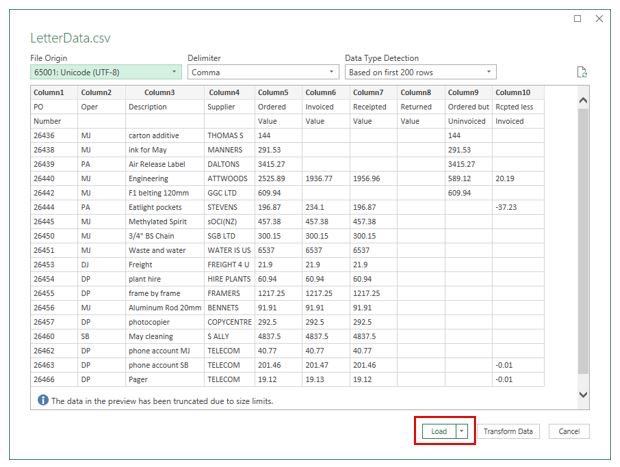
In the Import Data dialog box, locate and double-click the text file that you want to import, and click Import.
-
In the preview dialog box, you have several options:
-
Select Load if you want to load the data directly to a new worksheet.
-
Alternatively, select Load to if you want to load the data to a table, PivotTable/PivotChart, an existing/new Excel worksheet, or simply create a connection. You also have the choice of adding your data to the Data Model.
-
Select Transform Data if you want to load the data to Power Query, and edit it before bringing it to Excel.
-
If Excel doesn’t convert a particular column of data to the format that you want, then you can convert the data after you import it. For more information, see Convert numbers stored as text to numbers and Convert dates stored as text to dates.
Export data to a text file by saving it
You can convert an Excel worksheet to a text file by using the Save As command.
-
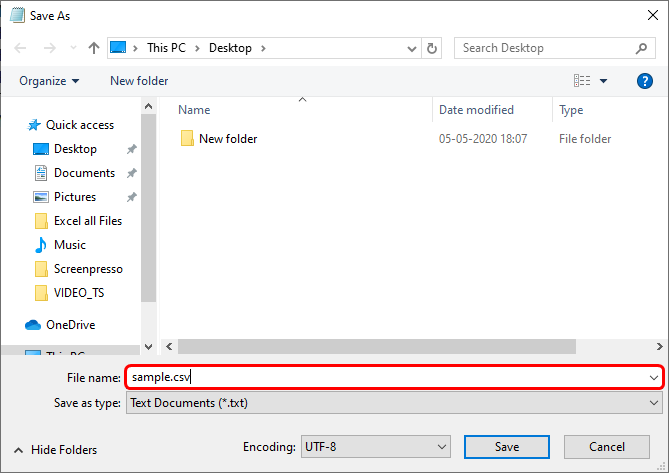
Go to File > Save As.
-
Click Browse.
-
In the Save As dialog box, under Save as type box, choose the text file format for the worksheet; for example, click Text (Tab delimited) or CSV (Comma delimited).
Note: The different formats support different feature sets. For more information about the feature sets that are supported by the different text file formats, see File formats that are supported in Excel.
-
Browse to the location where you want to save the new text file, and then click Save.
-
A dialog box appears, reminding you that only the current worksheet will be saved to the new file. If you are certain that the current worksheet is the one that you want to save as a text file, click OK. You can save other worksheets as separate text files by repeating this procedure for each worksheet.
You may also see an alert below the ribbon that some features might be lost if you save the workbook in a CSV format.
For more information about saving files in other formats, see Save a workbook in another file format.
Import a text file by connecting to it
You can import data from a text file into an existing worksheet.
-
Click the cell where you want to put the data from the text file.
-
On the Data tab, in the Get External Data group, click From Text.
-
In the Import Data dialog box, locate and double-click the text file that you want to import, and click Import.
Follow the instructions in the Text Import Wizard. Click Help
on any page of the Text Import Wizard for more information about using the wizard. When you are done with the steps in the wizard, click Finish to complete the import operation.
-
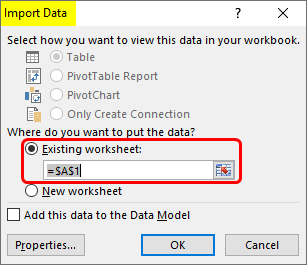
In the Import Data dialog box, do the following:
-
Under Where do you want to put the data?, do one of the following:
-
To return the data to the location that you selected, click Existing worksheet.
-
To return the data to the upper-left corner of a new worksheet, click New worksheet.
-
-
Optionally, click Properties to set refresh, formatting, and layout options for the imported data.
-
Click OK.
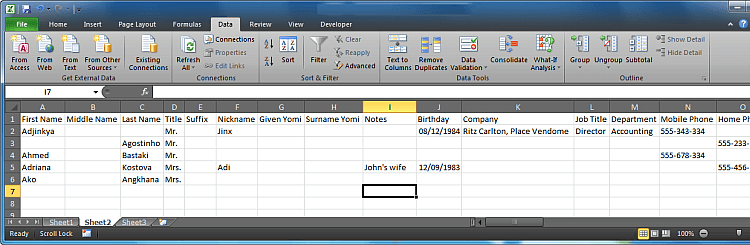
Excel puts the external data range in the location that you specify.
-
If Excel does not convert a column of data to the format that you want, you can convert the data after you import it. For more information, see Convert numbers stored as text to numbers and Convert dates stored as text to dates.
Export data to a text file by saving it
You can convert an Excel worksheet to a text file by using the Save As command.
-
Go to File > Save As.
-
The Save As dialog box appears.
-
In the Save as type box, choose the text file format for the worksheet.
-
For example, click Text (Tab delimited) or CSV (Comma delimited).
-
Note: The different formats support different feature sets. For more information about the feature sets that are supported by the different text file formats, see File formats that are supported in Excel.
-
-
Browse to the location where you want to save the new text file, and then click Save.
-
A dialog box appears, reminding you that only the current worksheet will be saved to the new file. If you are certain that the current worksheet is the one that you want to save as a text file, click OK. You can save other worksheets as separate text files by repeating this procedure for each worksheet.
-
A second dialog box appears, reminding you that your worksheet may contain features that are not supported by text file formats. If you are interested only in saving the worksheet data into the new text file, click Yes. If you are unsure and would like to know more about which Excel features are not supported by text file formats, click Help for more information.
For more information about saving files in other formats, see Save a workbook in another file format.
The way you change the delimiter when importing is different depending on how you import the text.
-
If you use Get & Transform Data > From Text/CSV, after you choose the text file and click Import, choose a character to use from the list under Delimiter. You can see the effect of your new choice immediately in the data preview, so you can be sure you make the choice you want before you proceed.
-
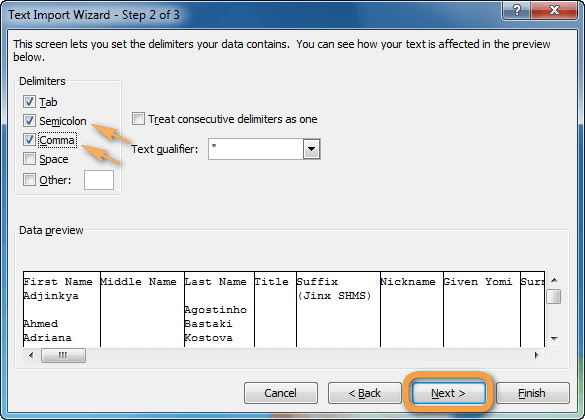
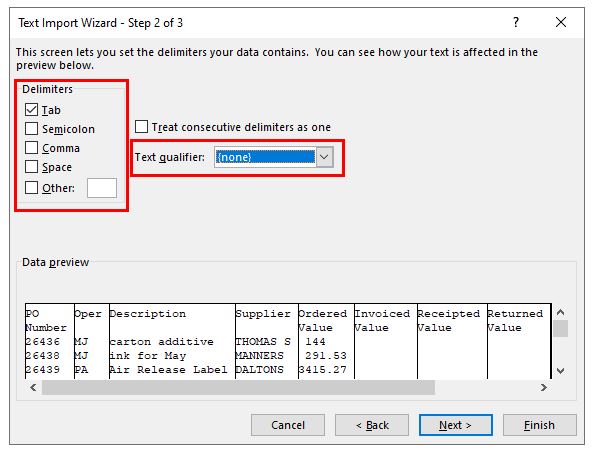
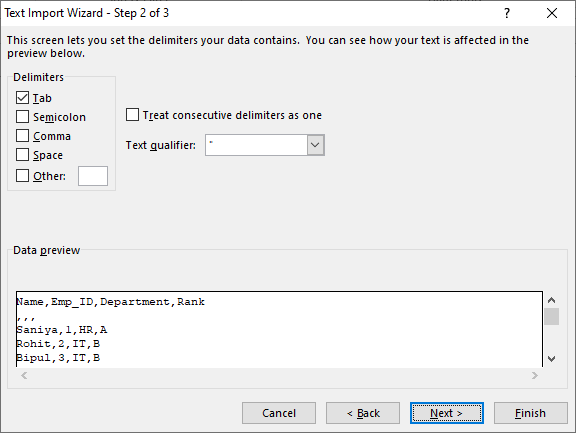
If you use the Text Import Wizard to import a text file, you can change the delimiter that is used for the import operation in Step 2 of the Text Import Wizard. In this step, you can also change the way that consecutive delimiters, such as consecutive quotation marks, are handled.
See Text Import Wizard for more information about delimiters and advanced options.
If you want to use a semi-colon as the default list separator when you Save As .csv, but need to limit the change to Excel, consider changing the default decimal separator to a comma — this forces Excel to use a semi-colon for the list separator. Obviously, this will also change the way decimal numbers are displayed, so also consider changing the Thousands separator to limit any confusion.
-
Clear Excel Options > Advanced > Editing options > Use system separators.
-
Set Decimal separator to , (a comma).
-
Set Thousands separator to . (a period).
When you save a workbook as a .csv file, the default list separator (delimiter) is a comma. You can change this to another separator character using Windows Region settings.
Caution: Changing the Windows setting will cause a global change on your computer, affecting all applications. To only change the delimiter for Excel, see Change the default list separator for saving files as text (.csv) in Excel.
-
In Microsoft Windows 10, right-click the Start button, and then click Settings.
-
Click Time & Language, and then click Region in the left panel.
-
In the main panel, under Regional settings, click Additional date, time, and regional settings.
-
Under Region, click Change date, time, or number formats.
-
In the Region dialog, on the Format tab, click Additional settings.
-
In the Customize Format dialog, on the Numbers tab, type a character to use as the new separator in the List separator box.
-
Click OK twice.
-
In Microsoft Windows, click the Start button, and then click Control Panel.
-
Under Clock, Language, and Region, click Change date, time, or number formats.
-
In the Region dialog, on the Format tab, click Additional settings.
-
In the Customize Format dialog, on the Numbers tab, type a character to use as the new separator in the List separator box.
-
Click OK twice.
Note: After you change the list separator character for your computer, all programs use the new character as a list separator. You can change the character back to the default character by following the same procedure.
Need more help?
You can always ask an expert in the Excel Tech Community or get support in the Answers community.
See Also
Import data from external data sources (Power Query)
Need more help?
Want more options?
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.
В этой статье Вы найдёте 2 простых способа преобразовать файл CSV в Excel. Кроме того, Вы узнаете, как импортировать в Excel несколько файлов CSV и как справиться с ситуациями, когда часть данных из файла CSV не отображается корректно на листе Excel.
Недавно мы начали изучать особенности формата CSV (Comma-Separated Values – значения, разделённые запятой) и различные способы преобразования файла Excel в CSV. Сегодня мы займёмся обратным процессом – импортом CSV в Excel.
Эта статья покажет Вам, как открывать CSV в Excel и как импортировать одновременно несколько файлов CSV. Мы также обозначим возможные подводные камни и предложим наиболее эффективные решения.
- Как преобразовать CSV в Excel
- Преобразование CSV в Excel: проблемы и решения
Содержание
- Как преобразовать CSV в Excel
- Как открыть файл CSV в Excel
- Как открыть файл CSV при помощи Проводника Windows
- Как импортировать CSV в Excel
- Преобразование CSV в Excel: проблемы и решения
- Файл CSV отображается в Excel неправильно
- Первые нули теряются при открытии файла CSV в Excel
- Excel преобразует некоторые значения в даты при открытии файла CSV
- Как импортировать в Excel несколько файлов CSV
Как преобразовать CSV в Excel
Если Вам нужно вытащить какую-то информацию на лист Excel из базы данных Вашей компании, то первая же идея, что приходит на ум, – экспортировать базу данных в файл CSV, а затем импортировать файл CSV в Excel.
Существует 3 способа преобразования CSV в Excel: Вы можете открыть файл с расширением .csv непосредственно в Excel, дважды кликнуть по файлу в Проводнике Windows либо импортировать CSV в Excel, как внешний источник данных. Далее я подробно расскажу об этих трёх способах и укажу преимущества и недостатки каждого из них.
- Способ 1: Открываем файл CSV в Excel
- Способ 2: Открываем файл CSV в Excel при помощи Проводника Windows
- Способ 3: Импортируем CSV в Excel
Как открыть файл CSV в Excel
Даже если файл CSV создан в другой программе, Вы всегда можете открыть его как книгу Excel при помощи команды Open (Открыть).
Замечание: Открытие файла CSV в Excel не изменяет формат файла. Другими словами, файл CSV при этом не будет преобразован в файл Excel (формат .xls или .xlsx), он сохранит свой изначальный тип (.csv или .txt).
- Запустите Microsoft Excel, на вкладке Home (Главная) нажмите Open (Открыть).
- Появится диалоговое окно Open (Открытие документа), в выпадающем списке в нижнем правом углу выберите Text Files (Текстовые файлы).
- Найдите в Проводнике Windows файл CSV и откройте его, дважды кликнув по нему.
Если Вы открываете файл CSV, то Excel откроет его сразу же вставив данные в новую книгу Excel. Если Вы открываете текстовый файл (.txt), то Excel запустит Мастер импорта текстов. Подробнее об этом читайте в разделе Импортируем CSV в Excel.
Замечание: Когда Microsoft Excel открывает файл CSV, то для того, чтобы понять, как именно импортировать каждый столбец данных, он использует настройки форматирования, заданные по умолчанию.
Если данные соответствуют хотя бы одному из следующих пунктов, то воспользуйтесь Мастером импорта текстов:
- В файле CSV использованы различные разделители;
- В файле CSV использованы различные форматы даты;
- Вы преобразуете данные, среди которых есть числа с нулём в начале, и Вы хотите сохранить этот ноль;
- Вы хотите предварительно просмотреть, как будут импортированы данные из файла CSV в Excel;
- Вам хочется большей гибкости в работе.
Чтобы заставить Excel запустить Мастер импорта текстов, Вы можете либо изменить расширение фала с .csv на .txt (прежде чем открывать файл), либо импортировать CSV в Excel так, как это будет описано далее.
Как открыть файл CSV при помощи Проводника Windows
Это самый быстрый способ открыть CSV в Excel. В Проводнике Windows дважды кликните по файлу .csv, и он откроется как новая книга Excel.
Однако, этот способ сработает только в том случае, если приложение Microsoft Excel установлено как программа, заданная по умолчанию, для открытия файлов .csv. Если это так, то Вы будете видеть знакомую иконку в Проводнике Windows рядом с именем файла.
Если Excel не является программой по умолчанию, вот как Вы можете это исправить:
- Кликните правой кнопкой мыши по любому файлу .csv в Проводнике Windows и в открывшемся контекстном меню нажмите Open with (Открыть с помощью) > Choose default program (Выбрать программу).
- Выберите Excel в списке рекомендованных программ, убедитесь, что стоит галочка для параметра Always use the selected program to open this kind of file (Всегда использовать выбранное приложение для такого типа файлов) и нажмите ОК.
Как импортировать CSV в Excel
Этим способом Вы можете импортировать данные из файла .csv в существующий или в новый лист Excel. В отличие от предыдущих двух способов, он не просто открывает CSV в Excel, а именно конвертирует формат .csv в .xlsx (если Вы используете Excel 2007, 2010 или 2013) или .xls (в версиях Excel 2003 и более ранних).
- Откройте нужный лист Excel и кликните по ячейке, куда нужно импортировать данные из файла .csv или .txt.
- На вкладке Data (Данные) в разделе Get External Data (Получение внешних данных) кликните From Text (Из текста).
- Найдите файл .csv, который требуется импортировать, выберите его и нажмите кнопку Import (Импорт), или просто дважды кликните по нужному CSV файлу.
- Откроется Мастер импорта текстов, Вам нужно просто выполнить его шаги.
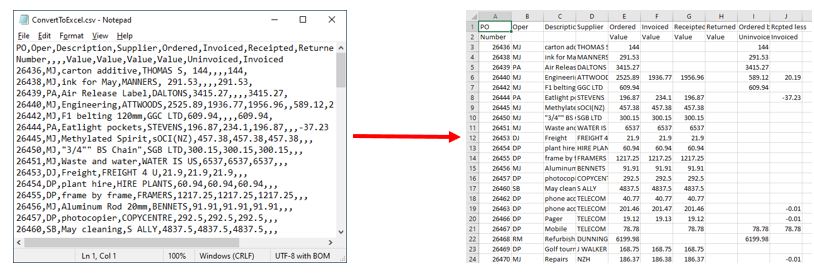
Прежде, чем мы двинемся дальше, пожалуйста, посмотрите на снимок экрана ниже, на нем показан исходный файл CSV и желаемый результат в Excel. Надеюсь, это поможет Вам лучше понять, почему мы выбираем те или иные параметры настроек в последующем примере.
- Шаг 1. Выберите формат данных и номер строки, с которой нужно начинать импорт. Чаще всего выбирают Delimited (С разделителями) и со строки 1. Область предварительного просмотра в нижней части диалогового окна мастера показывает первые несколько записей импортируемого файла CSV.
- Шаг 2. На этом шаге нужно выбрать разделители и ограничитель строк. Delimiter (Разделитель) – это символ, который разделяет значения в файле CSV. Если в Вашем файле CSV использован какой-то символ, которого нет в предложенном списке, то поставьте галочку в варианте Other (Другой) и введите нужный символ. В нашем примере мы указали Tab (Знак табуляции) и Comma (Запятая), чтобы каждый товар (они разделены табуляцией) начинался с новой строки, а информация о товаре, например, ID и данные о продажах (они разделены запятыми), были помещены в разные ячейки.Text qualifier (Ограничитель строк) – это символ, в который заключены отдельные значения. Весь текст, заключённый между такими символами, например, «текст1, текст2», будет импортирован как одно значение, даже если в этом тексте содержится символ, указанный Вами как разделитель.В этом примере мы указали запятую как разделитель, и кавычки как ограничитель строк. В результате, все числа с разделителем десятичных разрядов (которым тоже в нашем случае служит запятая!) будут импортированы в одну ячейку, как это видно в области предпросмотра на рисунке ниже. Если мы не укажем кавычки как ограничитель строк, то все числа будут импортированы в разные ячейки.
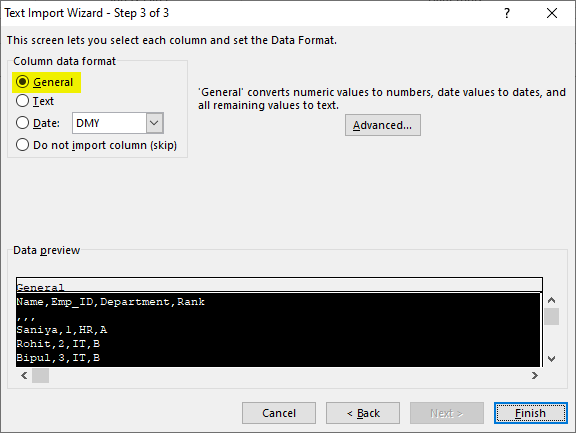
- Шаг 3. Посмотрите в область Data preview (Образец разбора данных). Если Вы довольны тем, как выглядят Ваши данные, тогда жмите кнопку Finish (Готово).
- Шаг 1. Выберите формат данных и номер строки, с которой нужно начинать импорт. Чаще всего выбирают Delimited (С разделителями) и со строки 1. Область предварительного просмотра в нижней части диалогового окна мастера показывает первые несколько записей импортируемого файла CSV.
Совет: Если в Вашем файле CSV используется последовательно более одной запятой или другого символа-разделителя, то поставьте галочку для параметра Treat consecutive delimiters as one (Считать последовательные разделители одним), чтобы избежать появления пустых ячеек.
- Выберите, куда вставлять импортированные данные, на существующий или на новый лист, и нажмите ОК, чтобы завершить импорт файла CSV в Excel.
Совет: Вы можете нажать кнопку Properties (Свойства), чтобы настроить дополнительные параметры, такие как обновление, разметка и форматирование для импортированных данных.
Замечание: Если Ваш файл CSV содержит численные данные или даты, Excel может преобразовать их с ошибками. Чтобы изменить формат импортированных данных, выберите столбец (столбцы), в которых возникли ошибки, кликните по ним правой кнопкой мыши и в контекстном меню выберите Format cells (Формат ячеек).
Преобразование CSV в Excel: проблемы и решения
Формат CSV используется уже более 30 лет, но несмотря на его длительную историю, он никогда не был официально задокументирован. Название CSV (Comma-Separated Values) возникло из-за использования запятых для разделения полей данных. Но это в теории. На самом деле, множество так называемых CSV-файлов используют другие символы для разделения данных, например:
- Табуляция – TSV-файлы (tab-separated values)
- Точка с запятой – SCSV-файлы (semicolon separated values)
Некоторые вариации файлов CSV разделяют поля данных одинарными или двойными кавычками, другие требуют маркер последовательности байтов из Юникода (BOM), например, UTF-8, для корректной интерпретации Юникода.
Это отсутствие стандартов порождает разнообразные проблемы, с которыми Вы можете столкнуться, пытаясь преобразовать файл Excel в CSV, и особенно, когда импортируете файл CSV в Excel. Давайте разберёмся с известными проблемами, начиная с самой распространённой.
- Файл CSV отображается в Excel неправильно (все данные помещены в первый столбец)
- Первые нули потеряны при открытии файла CSV в Excel
- Значения преобразованы в даты при импорте файла CSV в Excel
Файл CSV отображается в Excel неправильно
Признаки: Вы пытаетесь открыть файл CSV в Excel, и все данные попадают в первый столбец.
Причина: Корень проблемы кроется в том, что в Ваших региональных и языковых настройках Windows и в Вашем файле CSV установлены различные разделители. В Северной Америке и некоторых других странах разделителем полей списка по умолчанию является запятая. В то время как в Европейских странах запятая используется как разделитель десятичных разрядов, а разделителем полей списка является точка с запятой.
Решение: Есть несколько возможных решений этой проблемы. Вы можете быстро просмотреть приведённые ниже рекомендации и выбрать наиболее подходящие для конкретно Вашей задачи.
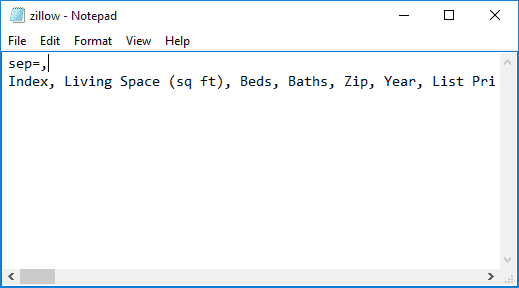
- Укажите правильный разделитель непосредственно в файле CSV. Откройте файл CSV в любом текстовом редакторе (подойдёт даже обычный блокнот) и в первой строке вставьте следующий текст. Обратите внимание, что это должна быть отдельная строка перед любыми другими данными:
- Чтобы установить разделитель запятую: sep=,
- Чтобы установить разделитель точку с запятой: sep=;
Как Вы уже догадались, таким образом можно установить в качестве разделителя любой другой символ, просто указав его сразу после знака равенства.
- Выберите нужный разделитель в Excel. В Excel 2013 или 2010 на вкладке Data (Данные) в разделе Data Tools (Работа с данными) нажмите Text To Columns (Текст по столбцам).
Когда запустится Мастер распределения текста по столбцам, на первом шаге выберите формат данных Delimited (С разделителями) и нажмите Next (Далее). На втором шаге выберите нужный разделитель и нажмите Finish (Готово).
- Измените расширение с .csv на .txt. Открытие файла .txt в Excel приведёт к запуску Мастера импорта текстов, и Вы сможете выбрать нужный разделитель, как это было описано в разделе Как импортировать CSV в Excel.
- Откройте файл CSV с точкой с запятой в качестве разделителя при помощи VBA. Вот пример кода VBA, который открывает в Excel файл CSV, где в качестве разделителя используется точка с запятой. Код был написан несколько лет назад для более ранних версий Excel (2000 и 2003), но если Вы достаточно хорошо знакомы с VBA, то у Вас не должно возникнуть проблем с его обновлением или изменением для работы с файлами CSV с запятой в качестве разделителя.
Замечание: Все показанные решения изменяют разделитель только для данного файла CSV. Если Вы хотите раз и навсегда изменить разделитель, заданный по умолчанию, то Вам подойдёт следующее решение.
- Изменяем разделители в настройках региональных стандартов. Нажмите кнопку Start (Пуск) и запустите Control Panel (Панель управления), кликните пункт Region and Language (Региональные стандарты) > Additional Settings (Дополнительные параметры). Откроется диалоговое окно Customize Format (Настройка формата), в котором Вам нужно выбрать точку (.) для параметра Decimal symbol (Разделитель целой и дробной части), и установить запятую (,) для параметра List separator (Разделитель элементов списка).
Примечание переводчика: Данные настройки приведены для английской локализации Excel (и ряда других стран). Для русской локализации привычнее будет использовать запятую в качестве разделителя целой и дробной части и точку с запятой для разделения элементов списка.
Дважды нажмите ОК, чтобы закрыть диалоговые окна – всё готово! С этого момента Microsoft Excel будет открывать и отображать все файлы CSV (с разделителем запятой) корректно.
Замечание: Установка в Панели управления Windows символов-разделителей целой и дробной части и элементов списка изменит настройки символов, заданные по умолчанию, для всех программ на Вашем компьютере, а не только в Microsoft Excel.
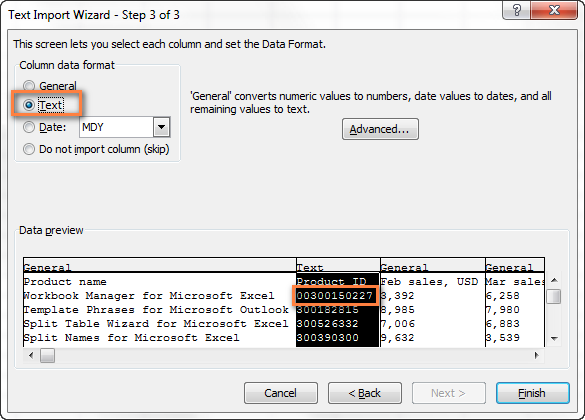
Первые нули теряются при открытии файла CSV в Excel
Признаки: Ваш файл CSV содержит значения с первыми нулями, и эти нули теряются при открытии файла CSV в Excel.
Причина: По умолчанию, Microsoft Excel отображает файл CSV в формате General (Общий), в котором первые нули отсекаются.
Решение: Вместо того, чтобы открывать файл .csv в Excel, запустите, как мы это делали ранее, Мастер импорта текстов, чтобы конвертировать файл CSV в Excel.
На шаге 3 мастера выберите столбцы, содержащие значения с первыми нулями и измените формат этих столбцов на текстовый. Так Вы конвертируете Ваш файл CSV в Excel, сохранив нули на своих местах.
Excel преобразует некоторые значения в даты при открытии файла CSV
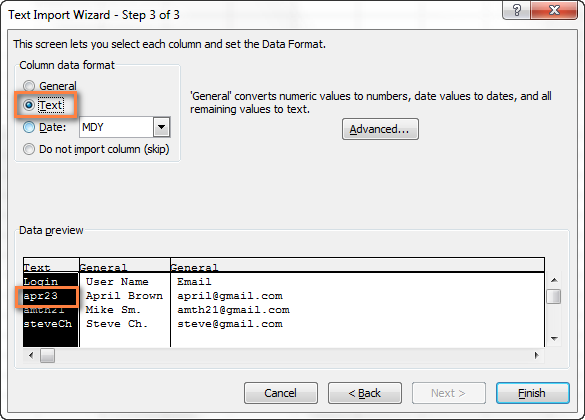
Признаки: Некоторые значения в Вашем файле CSV похожи на даты, и Excel автоматически преобразует такие значения из текстового формата в формат даты.
Причина: Как упоминалось выше, Excel открывает файл CSV в формате General (Общий), при этом значения, похожие на даты, преобразует из текстового формата в формат даты. Например, если Вы открываете файл CSV, содержащий логины пользователей, то запись «апр23» будет преобразована в дату.
Решение: Преобразуйте файл CSV в Excel при помощи Мастера импорта текстов. На шаге 3 мастера выберите столбцы с записями, похожими на даты, и измените формат столбца на текстовый.
Если Вам нужно достичь противоположного результата, то есть в определённом столбце преобразовать значения в даты, тогда установите формат Date (Дата) и выберите подходящий формат даты в выпадающем списке.
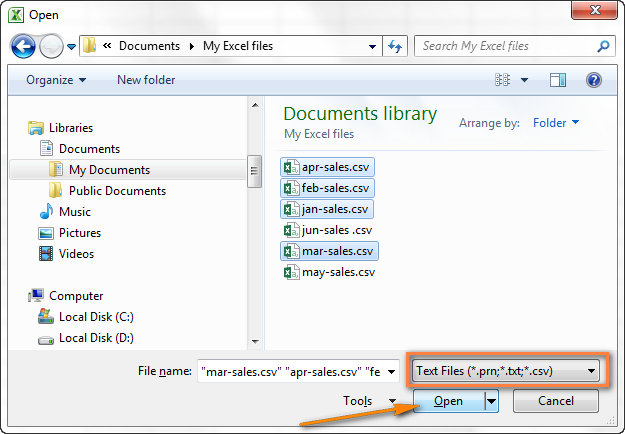
Как импортировать в Excel несколько файлов CSV
Думаю, Вы знаете, что Microsoft Excel позволяет открывать несколько файлов CSV при помощи команды Open (Открыть).
- На вкладке File (Файл) нажмите Open (Открыть) и в выпадающем списке в нижней правой части диалогового окна выберите Text Files (Текстовые файлы).
- Чтобы выделить несколько файлов подряд, кликните по первому файлу, затем нажав и удерживая клавишу Shift, кликните по крайнему файл. Оба эти файла, а также все, что находятся между ними, будут выделены.Чтобы выделить файлы, расположенные не подряд, удерживайте клавишу Ctrl и щелкайте по каждому файлу .csv, который хотите открыть.
- Когда выделены все нужные файлы CSV, нажмите кнопку Open (Открыть).
Этот способ простой и быстрый, и мы могли бы назвать его отличным, если бы не одно обстоятельство – каждый файл CSV открывается таким образом как отдельная книга Excel. На практике переключение туда-сюда между несколькими открытыми файлами Excel может быть крайне неудобным и обременительным.
Надеюсь, теперь Вы легко сможете преобразовать любой файл CSV в Excel. Если у Вас возникают какие-либо вопросы или сложности, смело пишите мне в комментариях. И благодарю за терпение каждого, кто осилил чтение этой длинной статьи до самого конца! 🙂
Оцените качество статьи. Нам важно ваше мнение:
CSV files offer a simple and reliable way to record and share database information in a tabular format. They hold plain text as a series of values (cells) in a series of rows.
The great thing about CSV files is that they’re quick and compact, using less memory than spreadsheets. As a result, they provide a quick and easy way to handle, store, and parse data. They’re versatile too: most applications can open CSV files. So why import CSV to Excel?
Although CSV is good for storing large amounts of data, once you need to start manipulating, analyzing, and reporting your data, you’ll probably want to move it to a spreadsheet.
Spreadsheet tools like Excel offer incredible functionalities to effectively organize and optimize your raw data into actionable insights, which you can then use to make important business decisions.
If you’ve ever converted a CSV to Excel manually, you’ll know that it can be a cumbersome task. Luckily there’s now a way to do it automatically. Without further ado, let’s explore how to convert CSV to Excel automatically in a few simple steps.
Import CSV to Excel automatically
- Converting CSV files to Excel format manually
- Automated method: Why sync CSV to Excel?
- How to import CSV to Excel automatically
- How to import multiple CSV files into Excel
- How to filter CSV data to Excel
Converting CSV files to Excel format manually
Excel can read CSV files but when you open a CSV directly inside Excel, your data may be imported incorrectly.
CSV stands for comma-separated values and those commas can prove problematic when Excel tries to read them.
To solve data loss problems, you may need to manually adjust the settings when saving CSV as Excel. If you’re working with an older version of Excel (Office 2010-2016), use the Text Import Wizard feature. Those working with a newer version of Excel can import CSV data into Excel using Power Query.
This is a good choice if you want to pull CSV data into specific tables, charts, and visual reports inside Excel. To manipulate imported CSV data at an advanced level with Power Query’s M formula language, note that you’ll need a basic knowledge of coding and familiarity with writing queries.
Manually import CSV data into Excel with Power Query
To import CSV data into Excel with Power Query, you need to:
1. Download the CSV file to your computer.
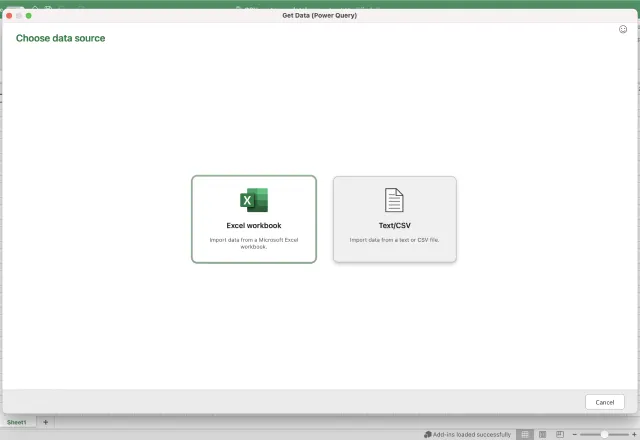
2. Open a blank workbook in Excel and go to Get Data. Choose the data source Text/CSV
3. Browse for your CSV file. Once selected, click Get data.
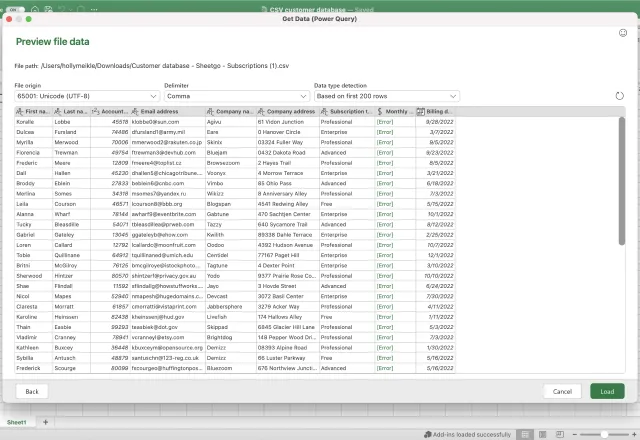
4. Click Next. A preview of your CSV data should load in Excel and look something like this:
5. At the bottom of the preview window, select Load to add it to your worksheet.
If you find that some of the columns are still displaying data incorrectly, you can convert them manually. Check Microsoft’s tutorials for details on how to adjust dates and numbers imported from text files.
Automated method: Why sync CSV to Excel?
For one-off data transfers, the manual import method works perfectly well. But if you regularly need to import a bunch of CSVs to Excel, this is extremely time-consuming. You’ll need to repeat the process for each CSV file you want to import. And when the data in the CSV file changes, you’ll need to create a new file version — again.
The best option is to use an automation tool like Sheetgo to import your CSV files to Excel for you.
Why use Sheetgo to connect CSV to Excel?
Sheetgo is a no-code tool that allows you to link CSV to Excel and import CSV data into spreadsheets automatically. You can import one single file or import CSV files in bulk. Once the connection is created, the system will run automatically. This enables you to pull dynamic CSV data directly into Excel.
It’s far easier and more efficient to set up an automated workflow to connect CSV to Excel. With Sheetgo, you can:
- Convert CSV to Excel format automatically: Create a workflow where you can automate the transfer process from start to finish. What’s more, when you update your original CSV file, Sheetgo will automatically update your Excel file for you.
- Import CSV data to Excel without manual adjustments: Simply upload your CSV to an online storage folder like OneDrive or Dropbox, and directly import your data to Excel.
- Sync CSV to Excel with regular updates: Create a custom automation schedule for your needs; automate from once an hour to once a month.
- Merge multiple CSV files into one Excel file: Combine multiple CSV files into tabs within a single workbook for easy access to all of your data.
- Pull data from colleagues’ CSV files into Excel: Create connections between various CSV files and your Excel file to receive CSV data from various locations at the same time.
Now that you understand the benefits of automatically syncing CSV to Excel with Sheetgo, let’s go through a simple step-by-step on how to import your CSV to Excel using the Sheetgo web app.
How to import CSV to Excel automatically
Step 1: Sign up to Sheetgo
Signing up to Sheetgo is easy – simply log in with your Google, Microsoft, or Dropbox account. Click on the button below to sign up for free.
Sheetgo
Step 2: Sync files to an online storage folder
In order to automate data transfer between your CSV and Excel files, you need to make sure you have activated the synching between your files and an online storage folder.
This way, any changes made to your source file (CSV) will automatically be transferred to your new destination file (Excel). It also keeps your files secure and allows you to access them from anywhere. Learn more here.
Step 3: Create a new workflow
Now it’s time to start connecting! Head to My workspace in the Sheetgo web app, and click +New workflow. Under Create a custom workflow section, click Create connection.
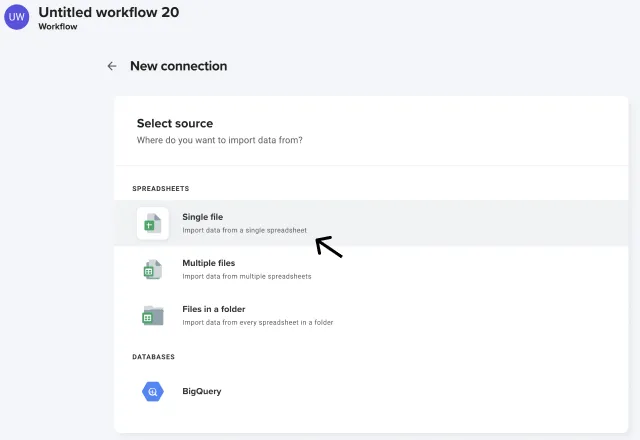
Step 4: Select source file
Select your source file. If you’re importing multiple CSV files, click the Multiple files option. In this example, I am only importing one CSV, so I will click Single file.
Please note: Don’t forget to name your workflow at the top of the screen!
Now it’s time to upload your file. Click +Select file and browse to find your CSV. You can change the online storage file on the left-hand side of the pop-up. Double-click to select your file.
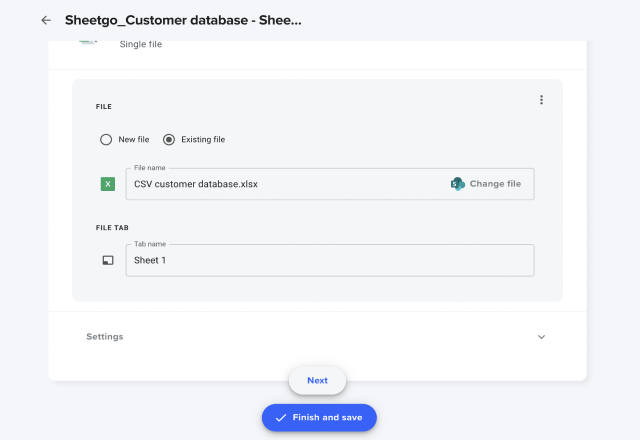
In this example, I’m showing you how to import data CSV from one CSV file to Excel. To import data from multiple CSVs into one Excel worksheet, click +Add another source file. Jump to: how to merge multiple CSVs into one Excel sheet.
Step 5: Connect to your Excel file
Scroll down to the Send to section. As I am connecting to a single Excel file, I will choose Single file.
Here, you can choose whether to import the CSV to a new or an existing spreadsheet.
Import CSV to an existing Excel file
Select the Existing file option, then click +Select file to upload your Excel. Sheetgo will automatically create a new tab for your imported data – simply rename the tab if needed.
Import CSV to a new Excel file
If you choose to import the CSV data to a new Excel workbook, Sheetgo will create it for you automatically.
Select the New file option. By default, the file will be saved to your main (root) folder in the same cloud storage folder as your CSV file. If you want to save the new Excel file to a specific folder or a different cloud storage platform, click Change destination folder.
In the File name box, enter a name for your new spreadsheet. Sheetgo will create a new tab (worksheet) in the Excel file containing the imported CSV data. If you want to rename the tab, type a name in the New file tab box.
Step 6: Complete the connection
To save your connection between your CSV and Excel file, click Finish and Save.
If you open your Excel file, you will see that your CSV file data has successfully been imported.
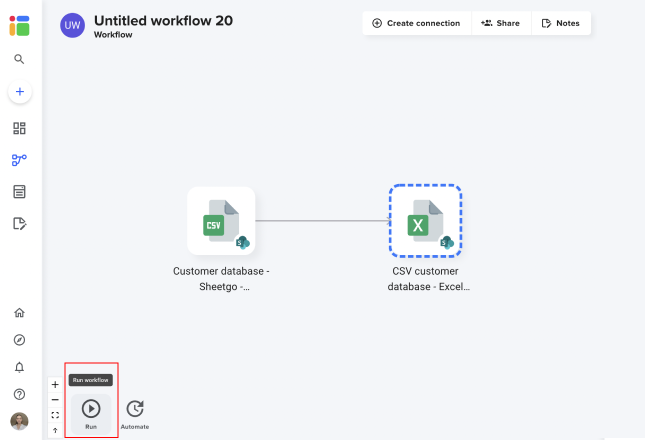
To get a visual representation of how your files are connected, click on Workflow.
Step 7: Sync your files
Your CSV file is now linked to the Excel file via a Sheetgo connection. This means that you can sync changes in the CSV file to the Excel file, whenever you like. You can either manually or automatically sync your files.
Option 1: Manually sync files
In Workflow, click on the Run button to update your connections and sync your files.
When you run the connection, data in the destination Excel tab will be refreshed with the latest data from the CSV file. For this reason, it’s best not to edit or analyze your data inside the Sheetgo tab because changes will be removed when the connection is updated.
To work on the imported data, transfer it to another tab using formulas.
Option 2: Automatically sync files
In Workflow, click on the Automate button. Activate the Run automatically button and create your own automation schedule. You can choose what days to automate your workflow, up to every hour. Once you’ve created your schedule, click Save.
And there you have it! Your workflow is complete and ready to use! To start importing your CSV to Excel automatically, you can sign up for free to Sheetgo by pressing the blue button below!
Sheetgo
How to import multiple CSV files into Excel
If you have a bunch of CSVs that you want to combine – or merge – into one Excel file, you can simply add more files to the Sheetgo connection. You can even import an entire folder of CSV files into one Excel worksheet.
First, let’s see how to add an extra file to the connection you already made.
Add another CSV to a connection
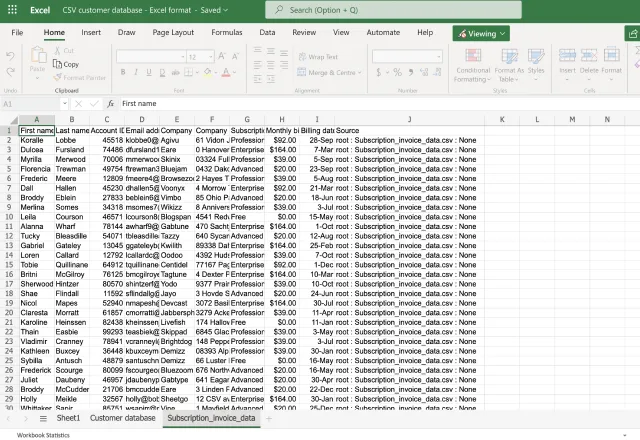
Let’s say I want to import data from a second CSV file into the Excel workbook I just created – subscription invoice data.
1. Open the Sheetgo web app and select your workflow within the My workspace area.
2. Select Workflow and expand the sidebar on the right-hand side. In the Connections tab, click the more options button (⋮).
3. Select Edit.
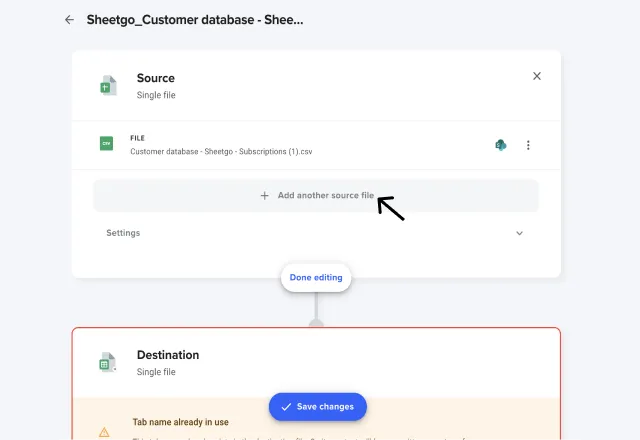
4. Under the Source section, click +Add another source file.
5. Click +Select file, then browse and select your additional CSV file from your cloud storage.
Data merging tip: to consolidate (combine) data from multiple CSVs into one Excel file correctly, you must check that your source files all have the same column layout and headers.
6. Repeat this step until you’ve added all the additional CSV files you want to merge. Click Done editing.
Optional: Identify source
When you merge multiple CSV files into one Excel sheet, it’s sometimes useful to know where the data originated from.
To add an identifying code to your destination file, enable Sheetgo’s Identify data feature.
- Click on Settings underneath your source files.
- Enable Identify data by switching on the button.
- Choose an identifier: Source file location (cloud storage folder), Source file name, Source file creation date, Source file update date, Source tab name, or Destination file update date and time.
Sheetgo will add an additional column to the destination sheet. Values in this column will indicate which CSV file the imported data originated from.
Once you’ve added your additional CSV file and made changes to the settings, click Save changes.
Sheetgo will now add the additional CSV file(s) to the workflow. To transfer the data, update the workflow by clicking Run.
Open your Excel workbook and you will see that data from multiple CSVs has been imported into the destination sheet, along with an extra column identifying your data source.
Merge multiple CSVs into one Excel file: folder option
If you want to combine a large number of CSV files into one Excel file, it’s more efficient to consolidate from a folder. Sheetgo lets you consolidate up to 80 files in one. It’s a time-saving option as there’s no need to select each source file individually.
On top of that, it automates another stage of your workflow. Whenever you drop a new CSV file into the folder, it will be included in the next update automatically.
1. Open the Sheetgo web app and create a new workflow.
2. This time, under the Source section, select Files in a folder.
3. Select the folder from your cloud storage.
4. Continue with the usual steps listed in the how to import CSV to Excel automatically section.
Want to filter CSV data to Excel?
By default, Sheetgo will import data from the entire CSV source file into the destination tab (sheet). What if you only want to pull specific data from your CSV into Excel? No problem — just apply a filter.
Note that you can currently only apply a filter to files stored in Google Drive. If you’ve already signed into Sheetgo using your Microsoft details, just log out of Sheetgo and sign in again using your Google account.
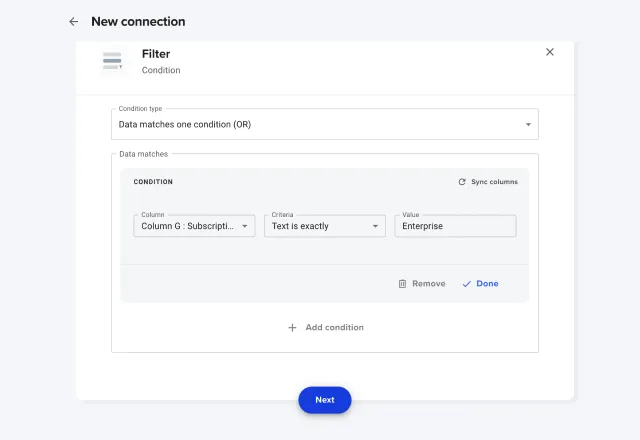
How to apply a filter
1. Create a new workflow and connect your source file.
2. Scroll down to the Process section and select Filter. Here, you can select whether to filter your data by Condition, or Query.
3. In this example, let’s filter my data by condition. Adjust the settings to create a condition, specifying the criteria and value.
4. Once finished with your filters, click Next.
5. Choose your destination file and save the workflow.
Once you’ve set up the workflow, you can update it at any time by clicking Run. Or click Automate to schedule automatic updates. Each time the connection is updated, the latest data will be filtered from the CSV file to Excel. You can also adjust the filter, or add new connections to the workflow to build a larger system that manages all your dynamic data.
You can start connecting and synching your CSV and Excel files automatically if you sign up for a free trial to Sheetgo’s paid plans! Click on the blue button below to get started today.
Sheetgo
Automated CSV to Excel imports
And there you have it! That’s a complete guide on how to convert CSV files to Excel automatically! Once you’ve set up your workflow it’s easy to add more files and build a bigger data management system. Head to Sheetgo for more inspiration.
Looking for more time-saving CSV automation tips? Check out our guide on How to merge and combine multiple CSV files into one or How to import CSV to Google Sheets automatically.
Editor’s note: This is a revised version of a previous post that has been updated for accuracy and comprehensiveness.
Whether you’re generating financial reports, processing your accounts for month end, or simply moving information between data sources to analyze it for valuable insights, chances are you’ll need to get external data (e.g., access a text-based flat file format like a comma separated values (CSV) document). And when you do, it’s also probable you’ll do so by importing it from a text file into one of the most common applications for handling CSV files: Microsoft Excel.
The actual process for creating an excel workbook from text files like the CSV format is fairly straightforward. But it’s important to follow the process exactly to avoid potential pitfalls and make sure your data makes the transition smoothly and completely.
Why Knowing How to Open CSV Files in Excel Matters
Native Microsoft Excel files (.xlsx files) are designed for that application and provide support for macros, separate data tabs, and other advanced features. They’re meant to be used both as part of the larger Microsoft Office suite and as a data manipulation and management tool that can import and process data for exporting to other applications.
CSV files (their file extension mirrors their name: .csv) are rarely accessed directly. Instead, they’re used for storing and transferring information that’s been broken into manageable chunks, such as calendar appointments, statistics, customer databases, contact information, etc. They don’t support macros or plug-ins or more advanced features, but that’s intentional, as once the data’s in Excel, it can be manipulated, connected to other workbooks, analyzed using pivot tables, etc.
NOTE: Despite the name of the format, data values may be separated by commas, semicolons, or other punctuation, depending on how the original was created.
They’re text-based (and can even be created in very simple text editor applications such as Notepad, and can be saved directly to, and created from, the .txt format), easy to create and use, and let you handle large amounts of information without worrying about being locked into a specific application.
CSV files come in four types:
- CSV UTF-8 (Eight-bit Unicode Transformation Format) (Comma delimited)
- CSV (Comma delimited)
- CSV (Macintosh)
- CSV (MS-DOS)
Each format has its distinct uses, but all four are supported by Microsoft Excel. That’s important, because it gives you more flexibility in managing your data; you can easily import from any of the formats and export copies to any of the four CSV formats (using the Save As…dialogue) for use in other applications as needed.
That said, while all four formats are supported natively, simply opening a CSV file rather than importing it into an excel worksheet will often result in a screen full of gibberish. Importing to an Excel sheet from the CSV file preserves the data’s utility and accessibility (It saves you the headache of trying to pick through an improperly formatted document, too!).
Given Excel’s large market share and the near ubiquity it shares with CSV files in the modern office environment, understanding how to import data from the CSV format to Excel is a critical skill for financial and other professionals who need to access, create, collect, and manage data across different platforms, in various file types, on a regular basis.
Importing to an Excel sheet from the CSV file preserves the data’s utility and accessibility (It saves you the headache of trying to pick through an improperly formatted document, too!).
Open CSV Files in Microsoft Excel the Right Way
Generally, you’ll rely on Excel’s built-in Import Text Wizard to help you get data from your CSV file into your existing Excel workbook (or a new worksheet). You can also try opening it directly from Excel’s File menu or with a double-click on the file in Explorer, but that can be an exercise in frustration if your settings aren’t properly configured.
Depending on your location and the version of Excel you’re using, Excel will rely on its localized Region and Language settings to make certain assumptions about files you use, and how files will most likely be formatted. This includes the “default” file separator; different regions have different delimiters. In the United States, for example, commas are most often used, but in Germany, it’s the semicolon that gets the heaviest usage.
Naturally, things can get even more complicated if you’re working with files created in other locations with different regional settings.
The more data you’re working with, and the more diverse your data sources, the higher the chances simply double-clicking to open a .csv file (or using the Open command) will end in woe rather than work-friendly data.
Another important caveat: while .txt files and .csv files are essentially the same in many ways, always save any .txt file you plan to import into Excel as a .csv file before trying to import it. You can do this very easily in Notepad by simply changing the extension to “.csv” in the “Save As…” dialogue.
To use the more complicated, but also much more reliable, Text Import Wizard:
- Open a New Excel Document, or open a new worksheet in your existing Excel workbook.
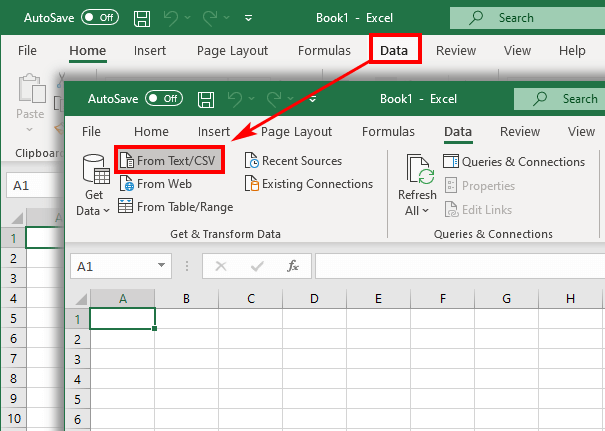
- Navigate to the “Data” tab.
- Click on the “From Text” button.
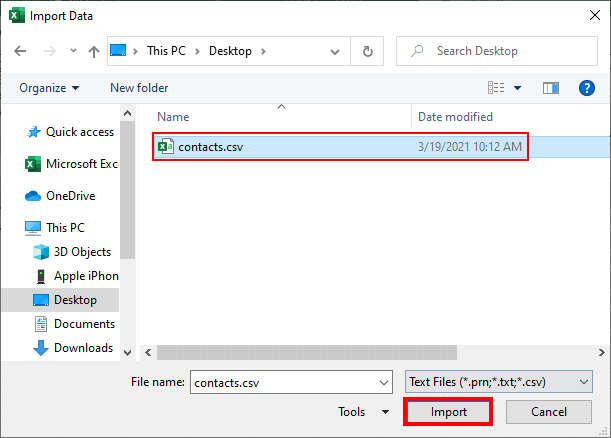
- Navigate to the folder holding the .csv file you want to open and click on the correct file name.
- Click “Import.”
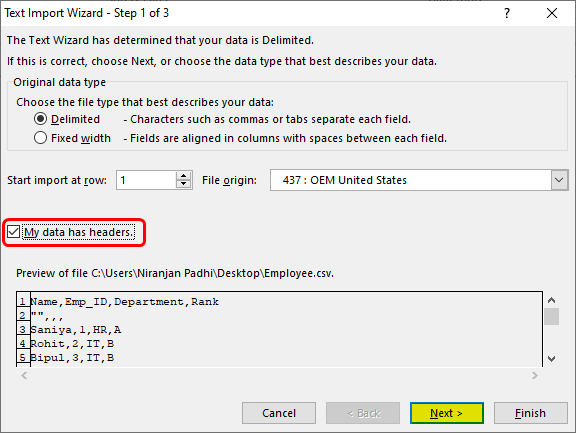
- The Text Import Wizard will open. Make sure you choose the “Delimited” radio button/checkbox under “Original Data Type” in the open dialog box. If your data has headers, don’t forget to select the “My data has headers” checkbox as well.
- Click “Next.”
- Select the checkbox corresponding to the correct delimiter used in the original .csv document. This will usually be a comma or a semicolon, but could be a tab, a space, or even a special character. It’s important to choose the correct delimiter to ensure the data fields can be properly parsed during the import.
- Choose the correct text qualifier (usually double quotes) from the drop-down list.
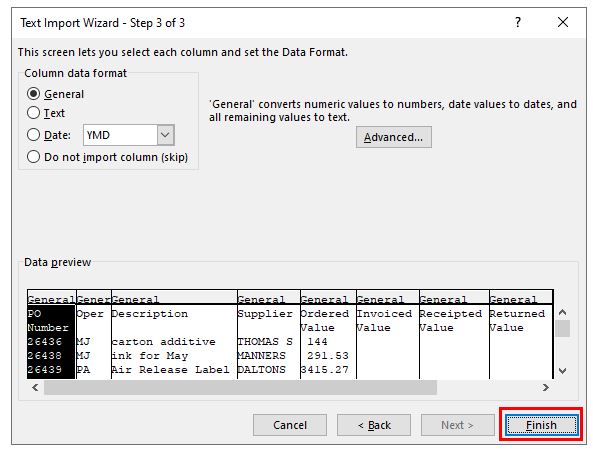
- Click “Next.”
- In the Data Preview field, only the first column of data will be highlighted. Drag the horizontal window control all the way to the right.
- While holding down the Shift key, click on the final column heading. This should select and highlight every column in the Data Preview pane.
- Choose “Text” as your Column Data Format. Every column should now be labeled “Text” in the Data Preview pane.
- Review the Data Preview window to ensure your data looks the way it should.
- Click “Finish.”
- If prompted to select a location for your data (e.g., “Where do you want to put the data?”), click on whichever cell in the worksheet (or new workbook, or new worksheet in your existing workbook) you want to receive the first item in the .csv file and then click “OK.”
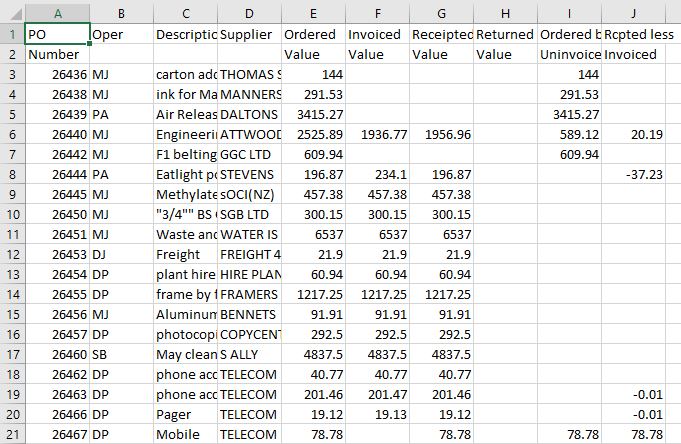
Your data should appear in your spreadsheet, organized in columns and, where relevant, with their original headers. If your data contained fields with leading zeros, double-check to make sure they made the transition through the Import Text Wizard.
Bringing CSV Data into Microsoft Excel Doesn’t Have to Be Difficult
When it comes to your data, it pays to be cautious, even when dealing with a relatively simple task like importing CSV data into Excel. By taking the time to practice proper protocols when you either open or import data from CSV files, you can save time and frustration, and make sure your information is complete and accurate for optimal reporting, analysis, and strategic planning.
CSV, or comma-separated values, is a common format for storing and transmitting content, such as contacts, calendars, databases, and spreadsheets. CSV files are used to move data between programs that aren’t ordinarily able to exchange data.
Excel is supposed to read CSV files, but in most cases, when you open CSV file in Excel, you see scrambled data that’s impossible to read. This article demonstrates how to convert CSV to excel.
How to open CSV file in Excel:
- Open CSV files in Excel 2016 and later
- Open CSV files in Excel 2003
BONUS: Find out how to export iPhone contacts to Excel.
Open a CSV file in Excel
Excel 2016 and later
- Create a new Excel file and click Data ➔ From Text/CSV.
- Find the CSV file on your PC and click Import.
- Preview the resulting table in the pop-up window and click Load.
- All done.
Change the delimiter and encoding type if needed.
Excel 2003
- Open a new Excel document and navigate to the Data tab.
- Click From Text.
- Navigate to the CSV file you wish to open and click Import.
- In the newly-opened window, choose Delimited. Then click Next.
- Check the box next to the type of delimiter: in most cases, this is either a semicolon or a comma. Then click Next.
- Click Finish.
That’s it! you have just imported a CSV file to Excel!
Many software programs offer data output in the form of a downloadable CSV file.
Owing to their simplicity and versatility, CSV files take up less space and are easily transferable. As such, CSV is often the go-to extension for a lot of database programs.
In fact, CSV and spreadsheets go hand in hand.
That is why Excel provides multiple ways to convert a CSV file to Excel. In this tutorial we will look at three such ways:
- By opening the file from Windows Explorer
- By opening the file directly in Excel
- By importing the file
We will also look at a few issues you are likely to face when you convert a CSV file to Excel and how to address and resolve these issues.
What is a CSV File?
A CSV file is a very commonly used file extension.
It is a plaintext format file in which values are separated by commas, hence the name Comma Separated Values (CSV).
However, it is not uncommon to find CSV files where the values are separated by other symbols like semicolons or tabs.
These files can be opened using any spreadsheet program like Excel, Google Sheets, Open Office, etc.
You can also open them in a simple text editor like Notepad.
The files contain simply the data in text form, without any formatting or formulas.
Owing to their ease of storage and their compatibility, the CSV format is a popular file format.
The data in CSV files do not contain any kind of formatting.
So, if you want to use it in Excel, you will need to first get Excel to format the data into a form that can be displayed in cells.
Let us look at three ways in which we can convert a CSV file to Excel.
Method 1: Directly Opening a CSV File in Excel from Windows Explorer
You can directly open a CSV file that is in any folder from Windows Explorer or your file browser.
To open the file in Excel, simply double-click the file.
Most of the time computers are set up to open CSV, TSV and other similar files directly in Excel, if it is present on your computer.
You can tell if Excel is the default program to open the file from the familiar green Excel icon as shown below:

However, if your computer has not been set up to open CSV files directly in Excel, you can set it up as follows:
- Right-click on the CSV file.
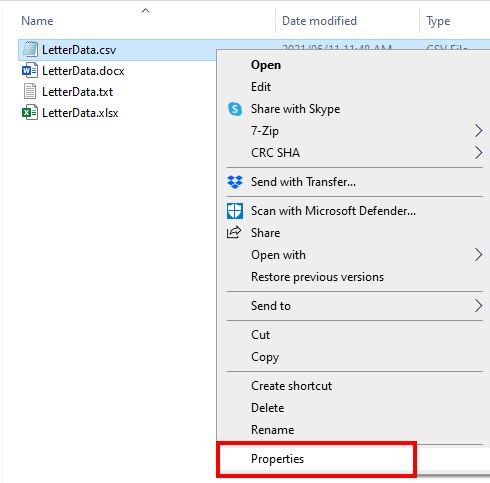
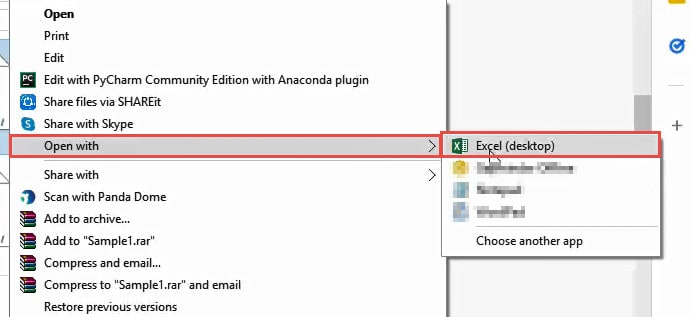
- Select ‘Open With’ from the context menu that appears.
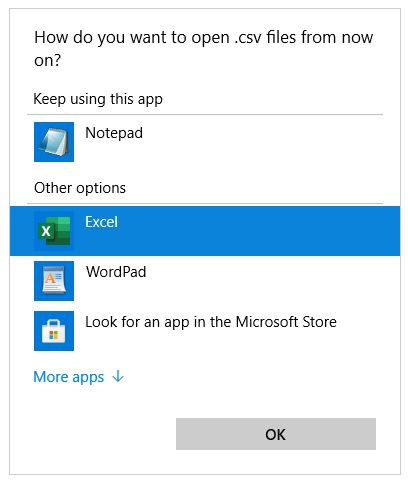
- You should now see a submenu with a list of applications. If you see ‘Excel’ as one of the options, go ahead and select it.
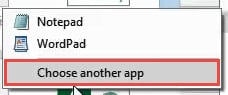
- If you don’t see Excel as one of the options, then click on ‘Choose another app’.
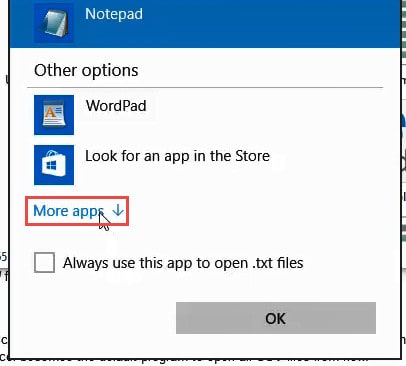
- Select Excel from the app options (Click ‘More Apps’ for more app options).
- Click on the checkmark next to ‘Always use this app to open .csv files’. This will make sure that Excel becomes the default program to open all CSV files from now.
Also read: How to Open XML Files in Excel?
Method 2: Opening a CSV File Directly in Excel
You can also open a CSV file directly in Excel as follows:
- Open Microsoft Excel.
- Click on the File tab.
- Click on Open.
- Browse and select the CSV file that you want to open.
That’s it! Your CSV file should automatically open in Excel.
Once the file opens, you might find some data items looking out of place.
You might also find some of the data formatted differently from what you had expected.
This is because Excel uses your default data format settings to convert each column of the original file to Excel.
However, there is no need to worry. You can always format the data according to your requirements either in the original CSV file or within Excel.
We will discuss more on how to do that towards the end of this tutorial.
Note that the first two methods discussed so far do not change the format of the CSV file to XLS or XLSX.
If you save the file, it will still get saved as a CSV file.
Also read: How to Open an MPP file in Excel?
Method 3: Importing a CSV File to Excel
This method lets you import and converts data from a CSV file into an existing Excel worksheet.
The steps to import a CSV file to Excel is as follows:
- Select the cell from where you want to start displaying the imported data.
- From the Data tab, select ‘From Text’ under the ‘Get External Data’ group.
- This will open a dialog box, from where you can select the CSV file that you want to import.
- Either double click on the file name or select the file and press Open.
- This will open the ‘Text Import Wizard’.
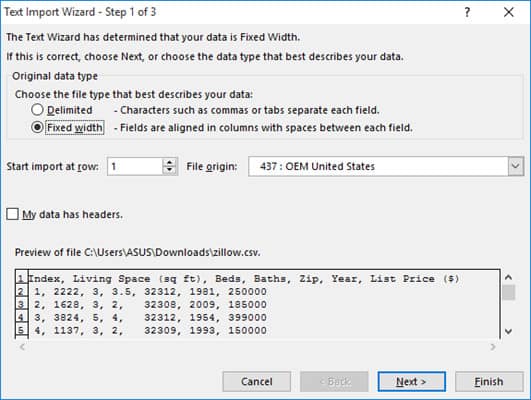
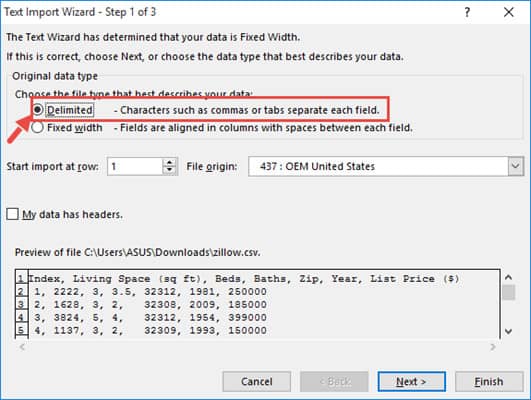
- The first step of the wizard lets you choose the file type that best describes your data. Make sure the ‘Delimited’ option is selected.
- Click Next.
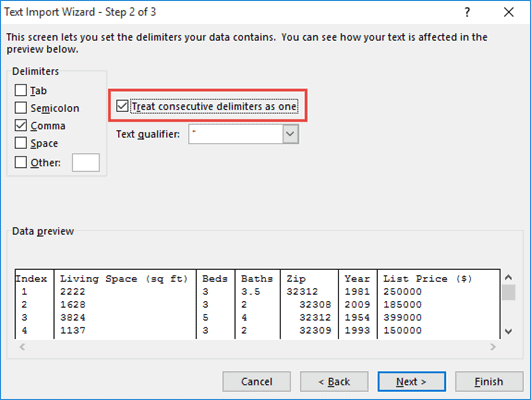
- The second step lets you set the delimiter by which you want to separate the data. Since the data items in our CSV file are separated by commas, make sure the ‘Comma’ option is checked.
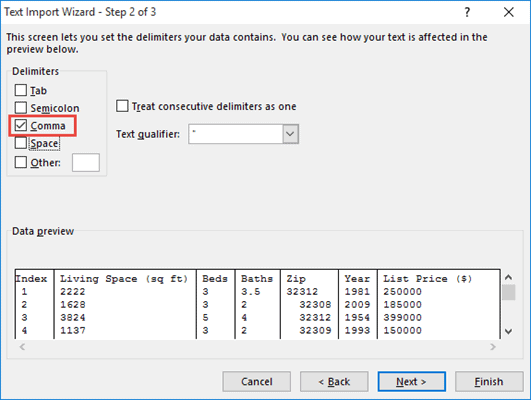
- You can also make sure the checkbox next to ‘Treat consecutive delimiters as one’ is checked. This ensures you don’t get unnecessary blank cells due to the presence of repeated consecutive commas (that were probably there by mistake).
- Click Next.
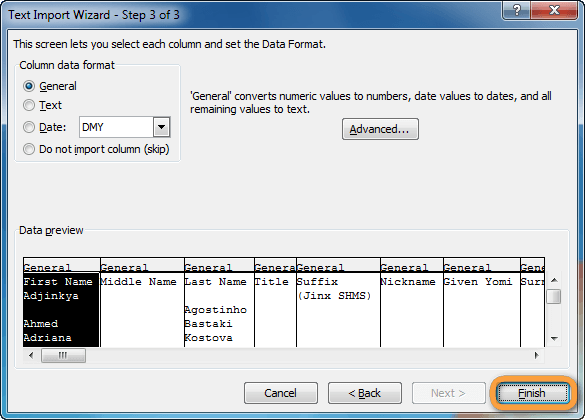
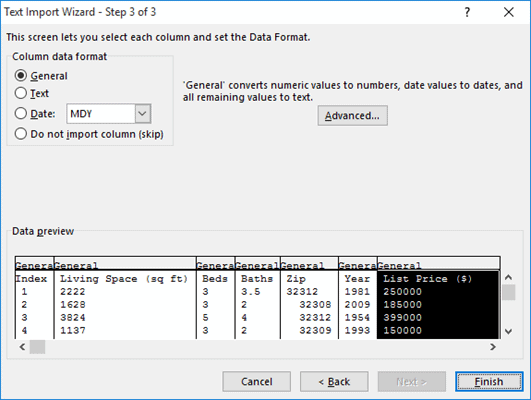
- The third step lets you set the format for each column. At the bottom of the wizard window, you can see a preview of how your data is going to look after splitting the column. If you want to change the format for any of the columns, simply select the column you need to format from the preview and select the radio button corresponding to the format you want for that column. If you don’t want the column to show at all, then you can select the ‘Do not import column (skip)’ option.
- Click Finish.
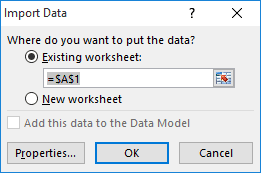
- Finally you will get asked to confirm where you want to start displaying your imported data. If importing to the same sheet, check if the starting cell is correctly mentioned in the input box below ‘Existing worksheet’. If you want to display the imported data in a new worksheet, check the radio button next to ‘New worksheet’.
- Click OK.
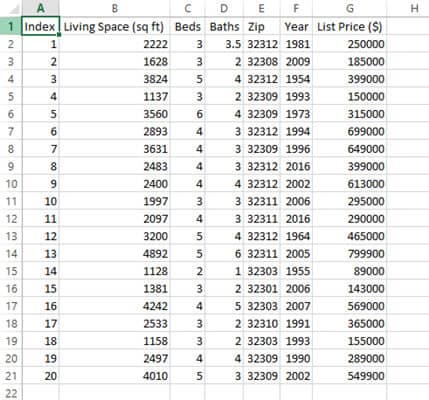
You should now see your CSV data imported into the cells starting from your selected cell.
Also read: How to Open VCF File in Excel?
Handling Problems that Arise After Converting a CSV File to Excel
Now let us take a look at some issues that are likely to arise when you convert a CSV file to Excel and how to address and handle these issues.
Some of the problems you might see after conversion include:
- Data displayed in a single column
- Values not separated as expected
- Lost leading zeros in numerical values
- Numerical or Text values converted to dates
- Dates converted to text
Let’s address each of these issues and see how to resolve them.
Data Displayed in a Single Column
After converting your CSV file to Excel you might find each record of data displayed in a single Excel column as shown below:
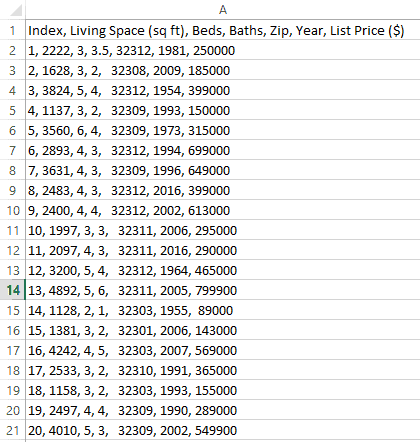
To break them up into separate columns, you can use the Text to Columns feature of Excel as follows:
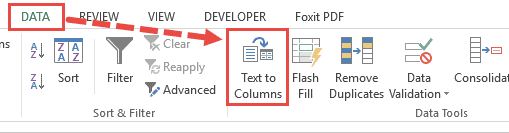
- Select the range of cells containing your copied data
- From the Data tab, select the ‘Text to Columns’ button (in the ‘Data Tools’ group).
- This will open the Convert Text to Columns wizard.
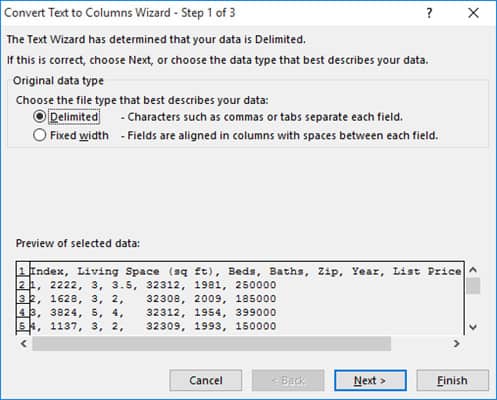
- You will notice that the steps in this wizard are exactly like the ‘Text Import Wizard’ discussed in method 3 of this tutorial (importing a CSV file to Excel). So you can follow steps 6 to 12 from method 3.
- At the end of 12, when you click the Finish button, you should see your CSV data imported into the cells starting from your selected cell.
Your data should now be split into separate columns for each field, based on the comma delimiter in the CSV file.
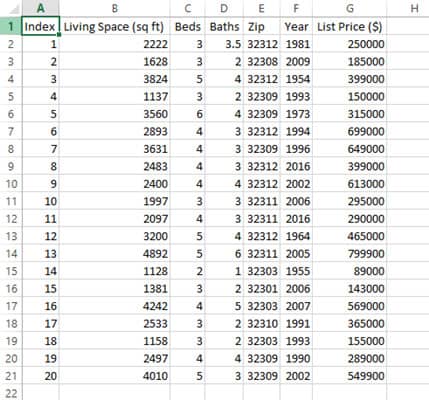
You can now go ahead and further clean up / format the data as required.
Values not Separated as Expected After Converting CSV to Excel
In some cases, you might find the entire structure of the table gone awry.
This could be because you have different separators set in your computer’s regional and language settings from the separators set in the CSV file.
For example, in some countries, the default separator is the comma, while in certain others, it is the semicolon.
To solve this issue, you can do one of the following:
- Change the Separator in your Computer’s Regional Settings
- Import the File instead of Opening Directly
Change the Separator in your Computer’s Regional Settings
Specify the separator for your region directly in the CSV file, by typing “sep=,” or “sep=;” in the first line.
You can add this in any text editor, for example, Notepad.
Import the File instead of Opening Directly
Instead of directly opening the file, you can try importing the file (as shown in method 3 – importing a CSV file to Excel), and provide the right delimiter in Step 2 of 3 in the Text Import Wizard.
Note: Sometimes you might find more than one value put into a single cell. This might be because of the absence of a delimiter separating the two values in the original CSV file. To solve this problem, you can either open the CSV file in a text editor, add the separators in the right place, or you could split the cell using the Text to Columns feature. Make sure the cells to the right are empty before splitting the cell. You don’t want the existing values to get overwritten by the split values.
Lost Leading zeros in numerical values after Converting CSV to Excel
If your original CSV file contains numerical values with leading zeros, you might find them absent after converting the file to Excel.
This is because your Excel cells are automatically set to display numerical values in the General format.
This format removes leading zeros from numbers. If you want to retain the leading zeros, you can try changing the format of the column cells to Text.
Numerical or Text Values Converted to Dates after Importing CSV to Excel
You might find certain text values from the original CSV file mysteriously converted to dates after importing to Excel.
This could be because the original values in your CSV file happen to resemble date values. For example, you might have a user name as jan19, which Excel might interpret as a date.
The solution to this problem is simple. Simply change the format of the cell to Text.
Dates Converted to Text after Importing CSV to Excel
Finally, you might find certain dates from the original CSV file converted to text.
This might be because Excel did not recognize the date format, so it assumed it to be a Text value.
The solution to this problem is to simply convert the format of the cell to Date and set the date to your required format.
In this tutorial, we showed you three different ways to convert a CSV file to Excel.
We also pointed out certain issues you are likely to face after converting the file, and suggested solutions to overcome the issues.
We tried to make this tutorial informative enough so you know exactly what to do when using CSV files in Excel. Hope we did not miss any points.
Other Excel tutorials you may also find useful:
- How to Convert a Text File to Excel?
- How to Open Excel File [xls, xlsx] Online (for FREE)
- Why does Excel Open on Startup (and How to Stop it)
- How to Make Excel File Read Only
- How to Insert an Excel file into MS Word
- How to Save Selection in Excel as PDF (3 Easy Methods)
- How to Merge Two Excel Files?
- How to Convert PDF to Excel without Software?
- How to Open DAT Files in Excel?
It is easy to read the data presented in comma-separated values format by opening with Excel but scrambled data makes it hard to read. There are also a few problems associated, like unexpected data changes, by changing the format when the CSV file is opened directly. This article shows different ways to convert the CSV files into Excel by covering the following topics.
Excel has a handling feature for various data presented in different formats, including Comma Separated Values (CSV). In addition, it contains various useful functions that help import these files and easily convert them into Excel sheet tables. As a result, it is the most commonly used for transmitting and storing data related to contacts, statistical information, and calendar appointments.
This section facilitates examples of ways to convert the Comma Separated Values files into excel.
Table of contents
- What Is Converting CSV Files In Excel?
- Explanation
- How To Open, Import & Convert CSV File Into Excel?
- How to Use CSV Files in Excel?
- Important Things To Note
- Recommended Articles
- Converting CSV files in excel is an easy process. CSV stands for Comma separated Values. It indicates that the values will be separated by a comma.
- We can have CSV files in Excel in two different ways. One is by importing the file, and the other one is by opening the file.
- We should remember that the format of the CSV file inserted using the open method will be in .csv format and will not change into .xlsx or .xls formats.
- For CSV files, excel allows a maximum of 1,048,576 rows and 16,384 columns.
Explanation
We have been using the data available in CSV format for several years. It indicates that data is separated by a comma using the common fields. Different ways are available to convert the CSV files into Excel. Those include:
- Direct opening of CSV files with Excel.
- Double-clicking and opening the file through the windows explorer option.
- Importing CSV files into worksheets.
The main intention behind the conversion of CSV data into Excel is that supportability. Each comma-separated value is placed into each cell to separate easily with the conversion. The data presented in the CSV format limits the capabilities of a user in generating insights from the data in performing the data analysis.
How To Open, Import & Convert CSV File Into Excel?
Let us discuss some examples of the comma-separated values file in Excel to understand how to open, import and convert CSV files into Excel.
You can download this CSV Files into Excel Template here – CSV Files into Excel Template
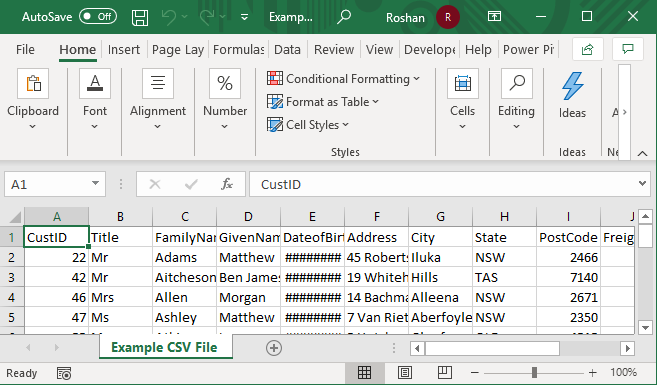
Example #1 – Open CSV File In WorkSheet
Step 1: We must open the Excel worksheet and go to the File menu.
It shows the Open dialog box, as shown in the figure.
Step 2: Then, we need to go to the CSV file’s directory. Select All Files on the right of the File name field.
Select the name of the CSV file. Then, click on Open to open the file with Excel.
Step 3: It directly displays the data in the new workbook, as shown in the figure.
Data separated by a comma is placed into each cell in the Excel sheet.
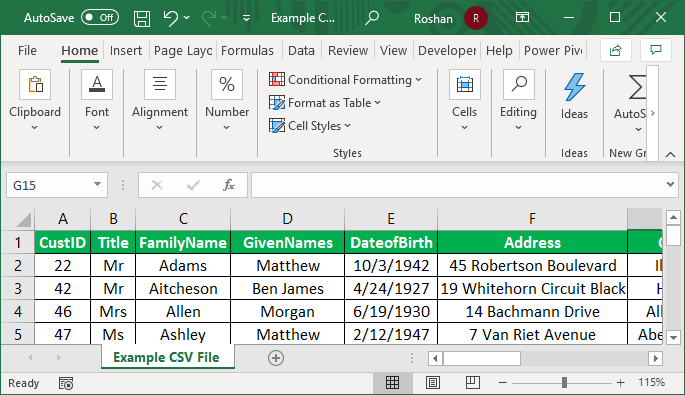
Step 4: We need to apply the formatting to the title fields to differentiate the headers of columns.
Step 5: Use the data for required purposes by applying the excel functions and formula.
Note: In this Excel, if we open a .txt file instead of a .csv file, Import Text Wizard is used to import the data into Excel.
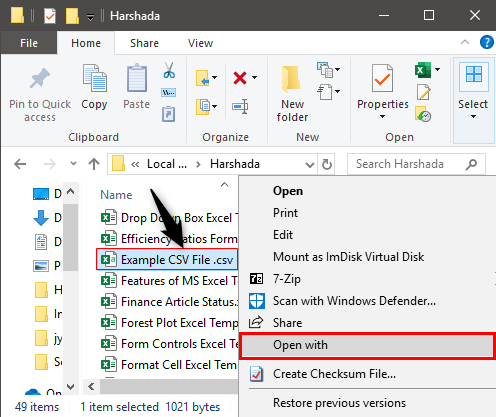
Example #2 – Using Windows Explorer
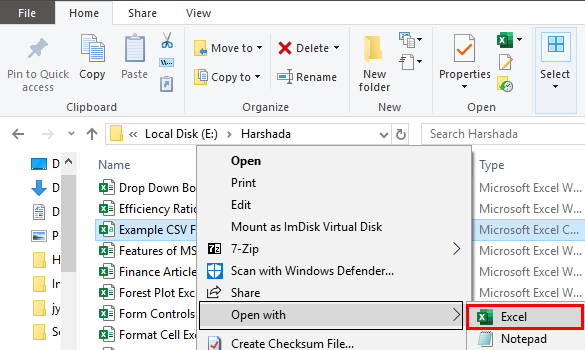
Step 1: We must go to the CSV file’s directory. Right-click on the file and choose Open with.
Step 2: Select the choose default program option on the right side of the Open with command, as shown in the figure. Then, choose Excel (desktop) among the recommended programs.
Step 3: As a result, now, the file is opened, and data is displayed, as shown in the figure.
Example #3 – Import CSV File Through External Data
This method requires a lot of steps to import data compared to the other two techniques. However, it helps in importing the data into the current worksheet.
The steps to import CSV files through external data are as follows:
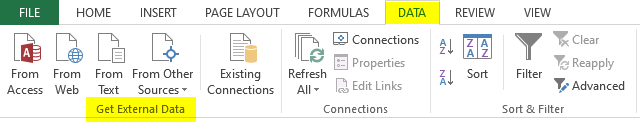
- First, we must open an Excel worksheet and place the cursor into a cell where we want to locate the data by importing from a .txt file or .csv file.
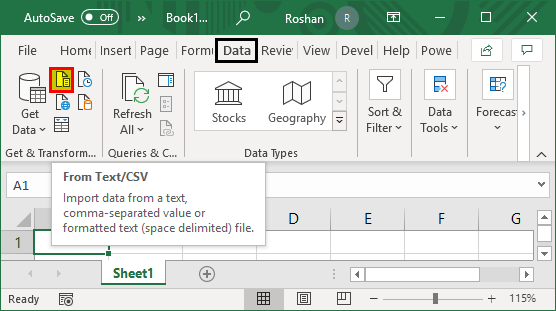
- Then, we need to go to the Data tab on the ribbon and click From Text/CSV under the Get External Data group, as shown in the screenshot.
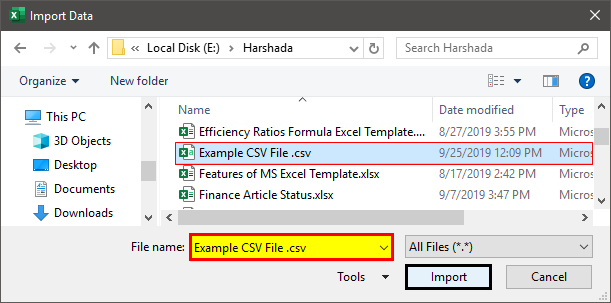
- Browse to the location of the CSV or txt file to import the data. Then, select the .csv file and click on the Import button.
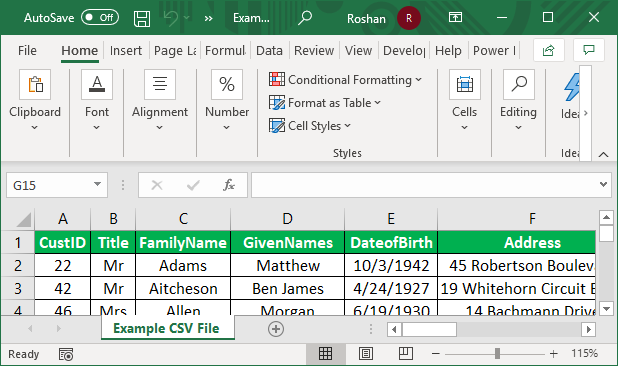
- The Example CSV File wizard will open when clicking on Import.
- Then we need to set the delimiter as Comma and click on ‘Load to’ to move to the next step.
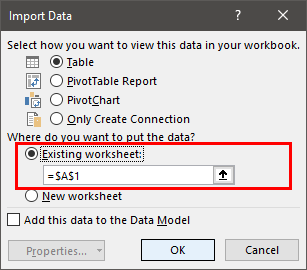
- It opens the ‘Import data’ dialog box. Here, we must choose the existing worksheet, place the cell address, and click OK.
- Consequently, the data will be imported into the Excel sheet, as shown in the screenshot.
We can use the data for various purposes in Excel.
How to Use CSV Files in Excel?
- Storing data and performing the required calculations on the data.
- Improving the security of the files as Excel files are not opened by any other software.
- Possible to save the data in tabular format with the extension of .xls and .xlsx.
- Display of data in rows and columns to represent the fields.
- Using the required format for the data of different types.
- Development of graphs and charts on the numerical data if presented.
- Using the statistical analysis of the data.
- Using the programming and macros and developing the data in developer mode.
- Improving the flexibility in reading large data by using sorting and filtering.
Important Things To Note
- Opening the CSV files is an easy way to convert the CSV data into Excel, and it does not change the file format to .xls or .xlsx
- Default settings are provided for when the .csv file is opened with Excel.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is CSV file in excel?
CSV (Comma separated Values) are the values separated by commas in Excel. This feature is available in any version, from 365 to 2007 version.
2. What are the two ways to insert CSV files into Excel?
In Excel, we have 2 ways to insert CSV files. One is by importing and another, by opening. The shortcut to open a CSV file in Excel is Ctrl +O.
3. Which is better? Opening or importing a CSV file into Excel?
Though both methods are used commonly to insert CSV files into Excel, opening a file uses default data formatting settings. We cannot decide how to display the data.
If the data has other values (such as data formats), it is better to import the CSV file into Excel to control how to display the data.
Recommended Articles
This article is a guide to CSV files into Excel. Here, we discuss how to open, import, and convert CSV files into Excel, practical examples, and a downloadable Excel template. You may learn more about Excel from the following articles: –
- Excel CSV UTF8
- CSV vs. Excel
- What is OneDrive Excel?
- Power Query Excel
This tutorial will demonstrate how to convert a .csv file to Excel or Google Sheets.
Excel has the ability to open or import both .csv and .txt files.
Opening a .txt or .csv File in Excel
1. In the Ribbon, select File > Open > Browse, and then select the text or .csv file to be opened.
The Text Import Wizard will open to the first of three steps.
2. Depending on the data contained in the file selected, you can either choose Delimited or Fixed Width as the file type. If the data is separated with a character like a comma, semicolon, space, or tab, select Delimited. If the first row of data contains column headings, check My data has headers.
3. Click Next to go to the next step.
4. In Step 2, select the type of delimiter contained in your text file – in this case, tab delimiter.
Then select the text qualifier. In some cases, the data may be enclosed in quote marks but for this example, (none) is selected as the text qualifier.
5. Click Next to go to the next step.
6. The final step of the Text Import Wizard allows us to specify the data type contained in each column. Most of the time, Excel will be able to determine the data type automatically, and you can leave the selected Column data format on General.
7. Click Finish to import the data into Excel.
Opening a .csv File in Excel From Windows Explorer
A .csv file is similar to a text file, but due to the fact it has the .csv extension, it is typically shown in Windows Explorer as associated with Excel.
This means if you double-click on the file in Windows Explorer, the file will automatically open in Excel. As it is a comma delimited file, Excel will automatically separate the data into columns without the need to use the Text Import Wizard.
If a .csv file does not show the Excel icon, then it is not associated and will not open automatically in Excel, but that can be changed.
1. To associate a .csv file with Excel, right-click on the file in the Windows Explorer and then select Properties.
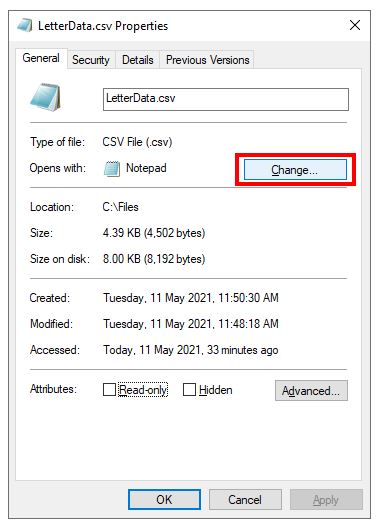
2. To the right of Opens with, select the Change button.
3. Select Excel and then click OK.
4. All .csv files will now be associated to open with Excel. Double-click on the .csv file from the Windows Explorer to open the file in Excel.
5. The delimiter in the file (in this case, comma) will automatically be selected, as will the file origin. The columns will be divided based on the data contained in the file as determined by Excel. Click Load to load the data into Excel.
Importing a Text file into Excel using Get Data
An alternative way of importing data into Excel from a text or .csv file is to use the Get and Transform Data function.
1. In the Ribbon, select Data > Get and Transform Data > From Text/CSV.
2. Select the file to be imported, and then click Import.
3. The file will appear in a dialog box with the delimiter already automatically selected, and the text divided by Excel according to the data stored in the .csv file. Click Load to load the data into Excel.
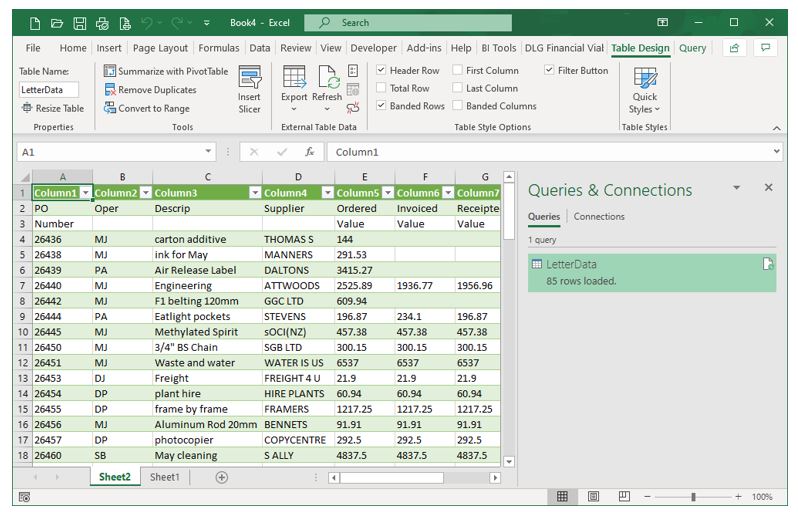
The data now appears in a new sheet in Excel. There are now two new tabs on the ribbon: Table Design and Query. A Queries & Connections pane appearing on the right-hand side of the screen. This shows us that the data is linked to the .csv file and if any data in the .csv file changes (external to Excel), then the data displayed in Excel would change too. This is especially useful when the data in Excel is linked to an external file such as a database.
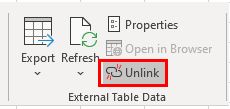
4. To unlink the imported data from the external .csv file, in the Ribbon, select Table Design, External Table Data > Unlink.
5. The data is imported into Excel as a table. To convert it to a standard Excel range, in the Ribbon, select Table Design > Tools > Convert to Range.
Both the Table Design and Query tabs on the Ribbon will then disappear.
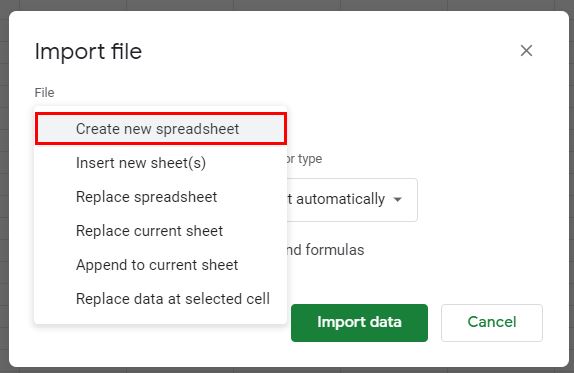
How to Convert a .csv File to Google Sheets
1. From the File menu, select Import.
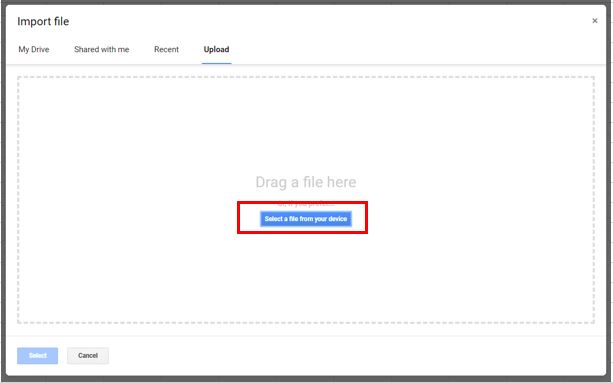
2. Click Upload, and then click on the blue “Select a file from your device” button to select the required file.
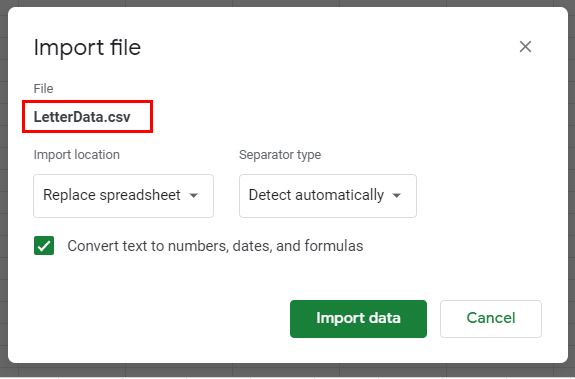
3. The name of the file to be imported will be displayed under File with the default options available for importing automatically selected.
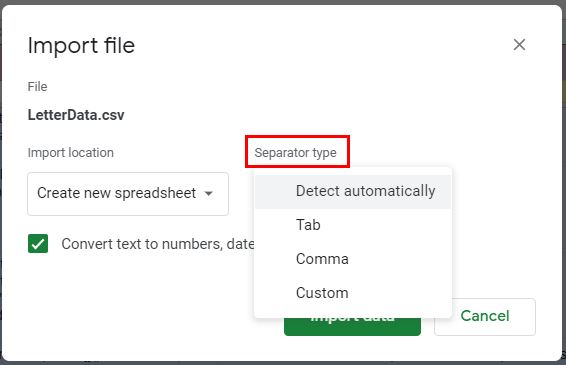
4. To change the Import Location, click the drop down list under Import Location and select the option required.
5. To change the Separator type, click the drop down list under Separator type and select the separator required.
6. Keep “Convert text to numbers, dates and formulas” checked and then click Import Data to import the file into Google Sheets.
CSV Files into Excel (Table of Contents)
- Introduction to CSV Files into Excel
- Methods to Open CSV Files in Excel
Introduction to CSV Files into Excel
MS Excel is an interesting tool when it comes to handling data. Excel data can be imported in many software, and even Excel can import data from different sources. Most of the time, we have unstructured data or data in different formats. For that, the solution is Excel. It converts data into a tabular structure. CSV or Comma Separated Values file is a commonly used format to store important data related to statistics, contacts, etc. Importing data makes it easier to read CSV files, but sometimes there are unexpected data changes with change in format and data looks scrambled. CSV files can be imported further to many software like SAS, Tableau, etc., for Data analysis and visualization.
There are different techniques for CSV data to look better and organized in Excel. Below are some examples and methods to import and read data in Comma Separated Values format.
Example
Let us suppose we have a text file that has data separated by commas.
- This file is saved as CSV file with .csv extension.
- Now, the CSV file is ready for use. Next, we’ll go to Excel > File > Open > Browse. Then select the saved CSV file as shown below.
- We can see that the CSV file is imported now.
- But the data is not clear. We can apply formatting to the data and see the change as shown below.
Finally, the CSV file is converted into an Excel file and is organized now.
Explanation
CSV files have data separated by commas. These files can be created in Notepad, Excel, etc. CSV files are used in organizations for transmitting and storing data. There are multiple ways for converting CSV files into Excel, as given below:
- Directly open CSV files with Excel.
- Opening CSV files through the windows explorer option.
- Importing CSV file data into Excel.
CSV files are converted into Excel for supportability as it is hard for Data analysts to draw insights from the data. After conversion, each value separated by commas is placed into each cell separately, which makes the data clear. There are multiple advantages of converting CSV files into Excel, including
- Better storing of data and calculations as per need.
- Any other software cannot open improved data security as Excel files.
- Saving CSV file in tabular manner with .xlsx extension.
- Data display in a perfect manner with each value in each cell.
- The formatting of data becomes easier and convenient.
- Analysis, Graph plotting, and Visualization of numerical data after conversion of CSV file into Excel.
- Programming and macros using VBA for data development.
Methods to Open CSV Files in Excel
There are various methods of opening CSV files in Excel, as mentioned above. We’ll see in detail how these methods work.
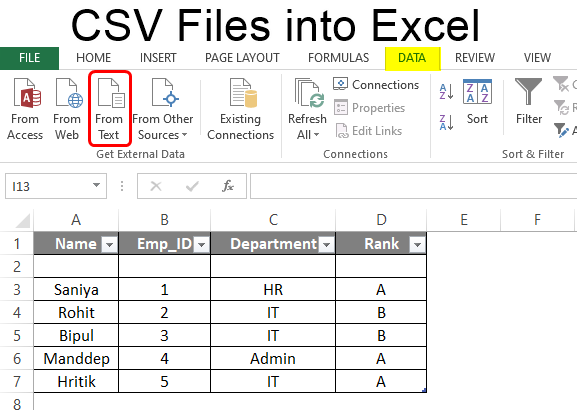
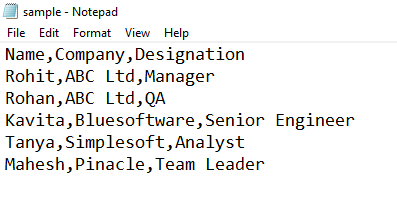
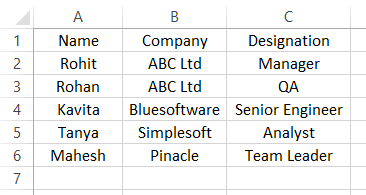
1. Opening CSV file in Excel
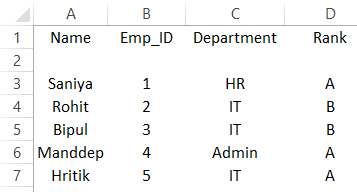
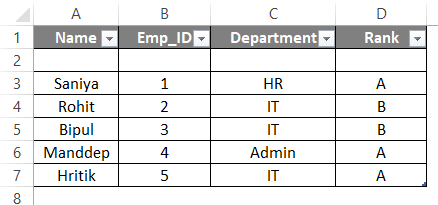
- CSV files can be opened in Excel, and it becomes a new file in Excel later. Suppose we have a CSV file with data separated with commas, as shown below. This file is a text file saved with a .csv extension.
- Here the first row is the header, and below are the data about employees of the company. A comma separates each value. We’ll import the file in Excel by going to Excel now.
- We can Go to File at the top left corner and then Open > Browse, as shown below.
- Then we’ll select the file from the location. If we can’t see the file, then at file type “All Excel files” can be changed to “All files” and then select the CSV file as shown below.
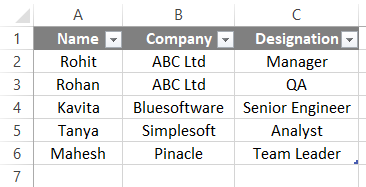
- Now, our CSV file is ready in Excel.
- To make the data clear and organized, we can apply some formatting to differentiate the headers from other fields, and finally, the file is ready for further use.
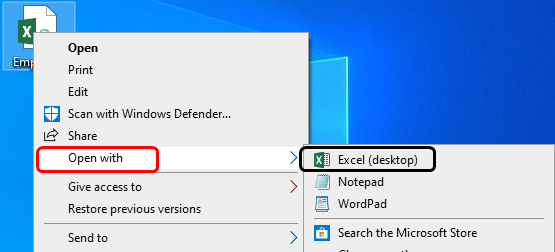
2. Using Windows Explorer if we’re using Windows OS
- We’ll have to go to the directory where the CSV file is located and right-click on it. Here our file is located on the desktop. Then go to Open with > Excel, and the file will be opened in Excel.
- After selecting Excel, it becomes the default program from then onwards; when we click on it, it will be opened in Excel by default. Here is the CSV file open in Excel.
After a bit of formatting, the file is ready to use.
3. Importing CSV File by Importing Data Externally
- This method helps in importing data in the current worksheet but is a bit longer process than the above two processes. First, we need to open MS Excel and select a blank workbook from it. A new workbook is now ready. we’ll place the cursor where we want to import the data.
- Next, we’ll have to go to the “Data” tab then go to “Get External Data”, as shown below.
- Then we’ll select “From Text” from the option as the CSV file was created in “Notepad”.
- We have to browse to the location where the file is stored. As we have imported the file earlier, it is showing as a CSV file. If we are using it for the first time also, the process is the same.
- Now, we can see a window that has some options, as shown below.
- Then, we have to click on “My data has headers” and choose the file type as “Delimited”, and click “Next”, as shown below.
- A new window comes as shown below.
Now, untick the “Tab” and select “Comma”, and click “Next”.
Then we’ll click on the “Finish” button, and a new window is displayed where we need to select the “Existing worksheet”.
- Finally, the CSV file will be imported, and the data is displayed below.
- With little formatting, the data can be organized and used further for analysis.
Things to Remember
- Opening a CSV file is easy, and it doesn’t change the format of the file to .xlsx or any other file.
- By default, the file is not organized. After importing it, we need to apply formatting to make the data look better.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to CSV Files into Excel. Here we discuss How to open CSV Files in Excel along with practical examples and a downloadable excel template. You can also go through our other suggested articles –
- Formatting Text in Excel
- HLOOKUP Formula in Excel
- Excel Export to PDF
- Autofit Row Height in Excel

 on any page of the Text Import Wizard for more information about using the wizard. When you are done with the steps in the wizard, click Finish to complete the import operation.
on any page of the Text Import Wizard for more information about using the wizard. When you are done with the steps in the wizard, click Finish to complete the import operation.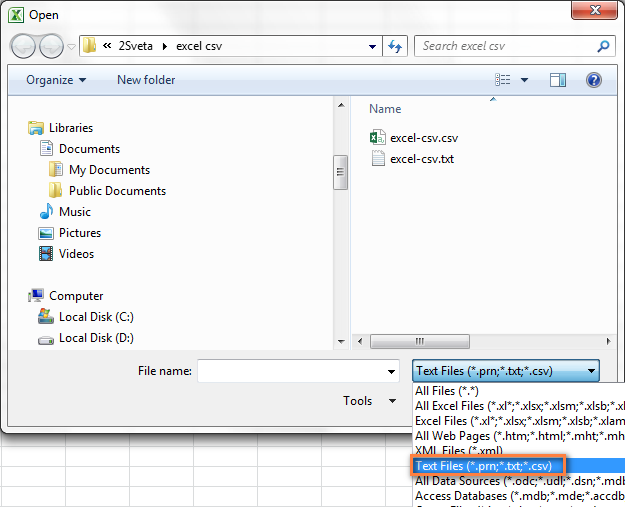
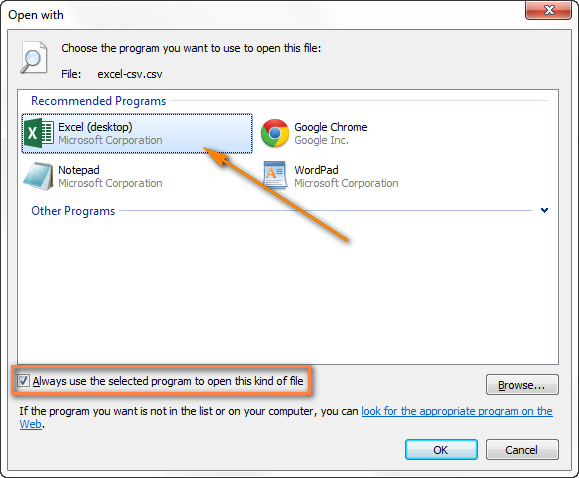
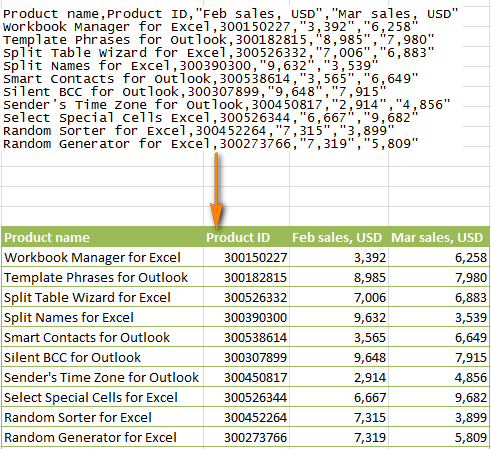
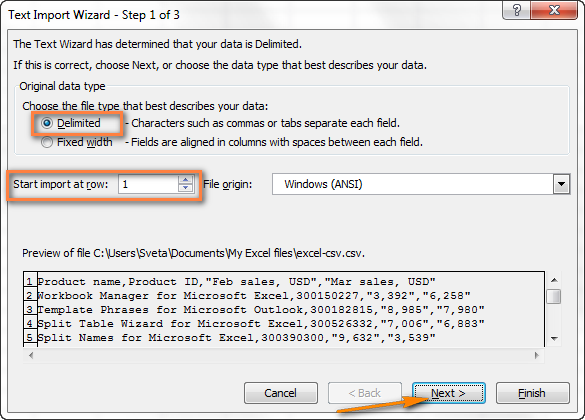
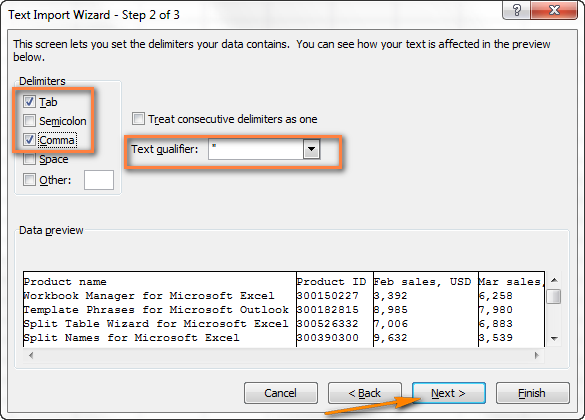
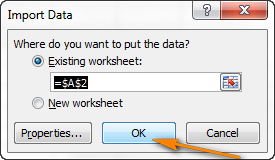
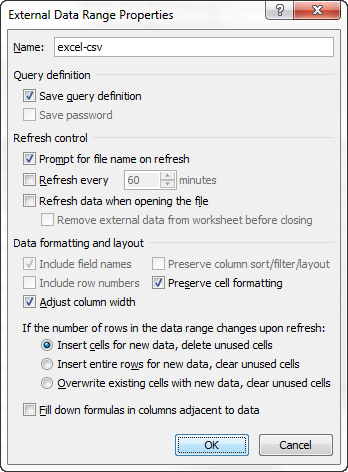
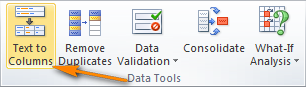 Когда запустится Мастер распределения текста по столбцам, на первом шаге выберите формат данных Delimited (С разделителями) и нажмите Next (Далее). На втором шаге выберите нужный разделитель и нажмите Finish (Готово).
Когда запустится Мастер распределения текста по столбцам, на первом шаге выберите формат данных Delimited (С разделителями) и нажмите Next (Далее). На втором шаге выберите нужный разделитель и нажмите Finish (Готово).
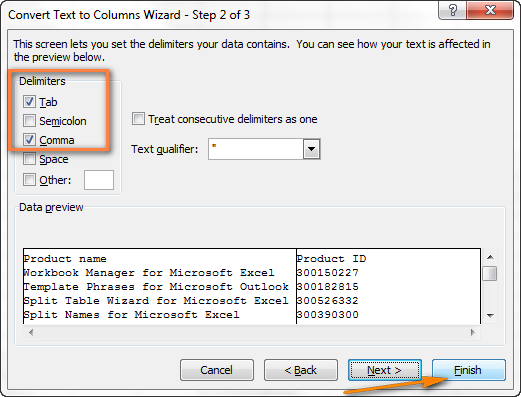
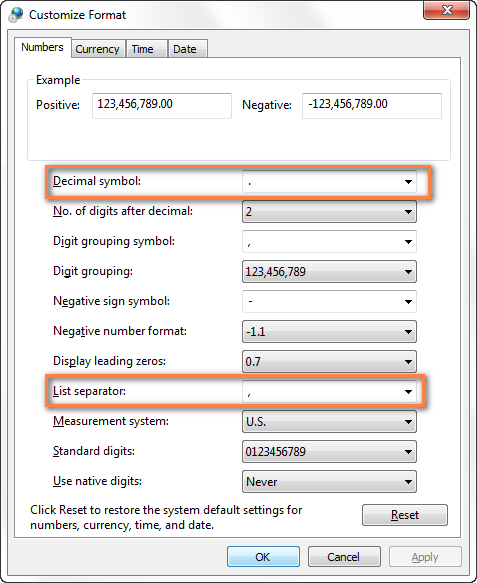 Дважды нажмите ОК, чтобы закрыть диалоговые окна – всё готово! С этого момента Microsoft Excel будет открывать и отображать все файлы CSV (с разделителем запятой) корректно.
Дважды нажмите ОК, чтобы закрыть диалоговые окна – всё готово! С этого момента Microsoft Excel будет открывать и отображать все файлы CSV (с разделителем запятой) корректно.