Excel for Microsoft 365 Excel for Microsoft 365 for Mac Excel 2021 Excel 2021 for Mac Excel 2019 Excel 2019 for Mac Excel 2016 Excel 2016 for Mac Excel 2013 Excel 2010 Excel 2007 Excel for Mac 2011 More…Less
Sometimes you need to check if a cell is blank, generally because you might not want a formula to display a result without input.
In this case we’re using IF with the ISBLANK function:
-
=IF(ISBLANK(D2),»Blank»,»Not Blank»)
Which says IF(D2 is blank, then return «Blank», otherwise return «Not Blank»). You could just as easily use your own formula for the «Not Blank» condition as well. In the next example we’re using «» instead of ISBLANK. The «» essentially means «nothing».
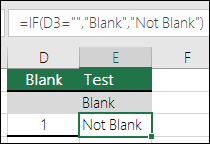
=IF(D3=»»,»Blank»,»Not Blank»)
This formula says IF(D3 is nothing, then return «Blank», otherwise «Not Blank»). Here is an example of a very common method of using «» to prevent a formula from calculating if a dependent cell is blank:
-
=IF(D3=»»,»»,YourFormula())
IF(D3 is nothing, then return nothing, otherwise calculate your formula).
Need more help?
Home / Excel Formulas / IF Cell is Blank (Empty) using IF + ISBLANK
In Excel, if you want to check if a cell is blank or not, you can use a combination formula of IF and ISBLANK. These two formulas work in a way where ISBLANK checks for the cell value and then IF returns a meaningful full message (specified by you) in return.
In the following example, you have a list of numbers where you have a few cells blank.

Formula to Check IF a Cell is Blank or Not (Empty)
- First, in cell B1, enter IF in the cell.
- Now, in the first argument, enter the ISBLANK and refer to cell A1 and enter the closing parentheses.
- Next, in the second argument, use the “Blank” value.
- After that, in the third argument, use “Non-Blank”.
- In the end, close the function, hit enter, and drag the formula up to the last value that you have in the list.

As you can see, we have the value “Blank” for the cell where the cell is empty in column A.
=IF(ISBLANK(A1),"Blank","Non-Blank")Now let’s understand this formula. In the first part where we have the ISBLANK which checks if the cells are blank or not.

And, after that, if the value returned by the ISBLANK is TRUE, IF will return “Blank”, and if the value returned by the ISBLANK is FALSE IF will return “Non_Blank”.

Alternate Formula
You can also use an alternate formula where you just need to use the IF function. Now in the function, you just need to specify the cell where you want to test the condition and then use an equal operator with the blank value to create a condition to test.
And you just need to specify two values that you want to get the condition TRUE or FALSE.

Download Sample File
- Ready
And, if you want to Get Smarter than Your Colleagues check out these FREE COURSES to Learn Excel, Excel Skills, and Excel Tips and Tricks.
Explanation
In this example, the goal is to create a formula that will return «Done» in column E when a cell in column D contains a value. In other words, if the cell in column D is «not blank», then the formula should return «Done». In the worksheet shown, column D is is used to record the date a task was completed. Therefore, if the column contains a date (i.e. is not blank), we can assume the task is complete. This problem can be solved with the IF function alone or with the IF function and the ISBLANK function. It can also be solved with the LEN function. All three approaches are explained below.
IF function
The IF function runs a logical test and returns one value for a TRUE result, and another value for a FALSE result. You can use IF to test for a blank cell like this:
=IF(A1="",TRUE) // IF A1 is blank
=IF(A1<>"",TRUE) // IF A1 is not blankIn the first example, we test if A1 is empty with =»». In the second example, the <> symbol is a logical operator that means «not equal to», so the expression A1<>»» means A1 is «not empty». In the worksheet shown, we use the second idea in cell E5 like this:
=IF(D5<>"","Done","")
If D5 is «not empty», the result is «Done». If D5 is empty, IF returns an empty string («») which displays as nothing. As the formula is copied down, it returns «Done» only when a cell in column D contains a value. To display both «Done» and «Not done», you can adjust the formula like this:
=IF(D5<>"","Done","Not done")
ISBLANK function
Another way to solve this problem is with the ISBLANK function. The ISBLANK function returns TRUE when a cell is empty and FALSE if not. To use ISBLANK directly, you can rewrite the formula like this:
=IF(ISBLANK(D5),"","Done")
Notice the TRUE and FALSE results have been swapped. The logic now is if cell D5 is blank. To maintain the original logic, you can nest ISBLANK inside the NOT function like this:
=IF(NOT(ISBLANK(D5)),"Done","")
The NOT function simply reverses the result returned by ISBLANK.
LEN function
One problem with testing for blank cells in Excel is that ISBLANK(A1) or A1=»» will both return FALSE if A1 contains a formula that returns an empty string. In other words, if a formula returns an empty string in a cell, Excel interprets the cell as «not empty». To work around this problem, you can use the LEN function to test for characters in a cell like this:
=IF(LEN(A1)>0,TRUE)This is a much more literal formula. We are not asking Excel if A1 is blank, we are literally counting the characters in A1. The LEN function will return a positive number only when a cell contains actual characters.
17 авг. 2022 г.
читать 2 мин
Вы можете использовать следующую формулу в Excel для выполнения какой-либо задачи, если ячейка не пуста:
=IF( A1 <> "" , Value_If_Not_Empty, Value_If_Empty)
Эта конкретная формула проверяет, пуста ли ячейка A1 .
Если он не пустой, то возвращается Value_If_Not_Empty .
Если он пуст, возвращается значение Value_If_Empty .
В следующем примере показано, как использовать эту формулу на практике.
Пример: используйте формулу «Если не пусто» в Excel
Предположим, у нас есть следующий набор данных в Excel, который содержит информацию о различных баскетбольных командах:
Мы можем использовать следующую формулу, чтобы вернуть значение «Команда существует», если ячейка в столбце A не пуста.
В противном случае мы вернем значение «Не существует»:
=IF( A2 <> "" , "Team Exists", "Does Not Exist")
На следующем снимке экрана показано, как использовать эту формулу на практике:
Если имя команды не пусто в столбце А, возвращается «Команда существует».
В противном случае возвращается «Не существует».
Если бы мы хотели, мы могли бы также возвращать числовые значения вместо символьных значений.
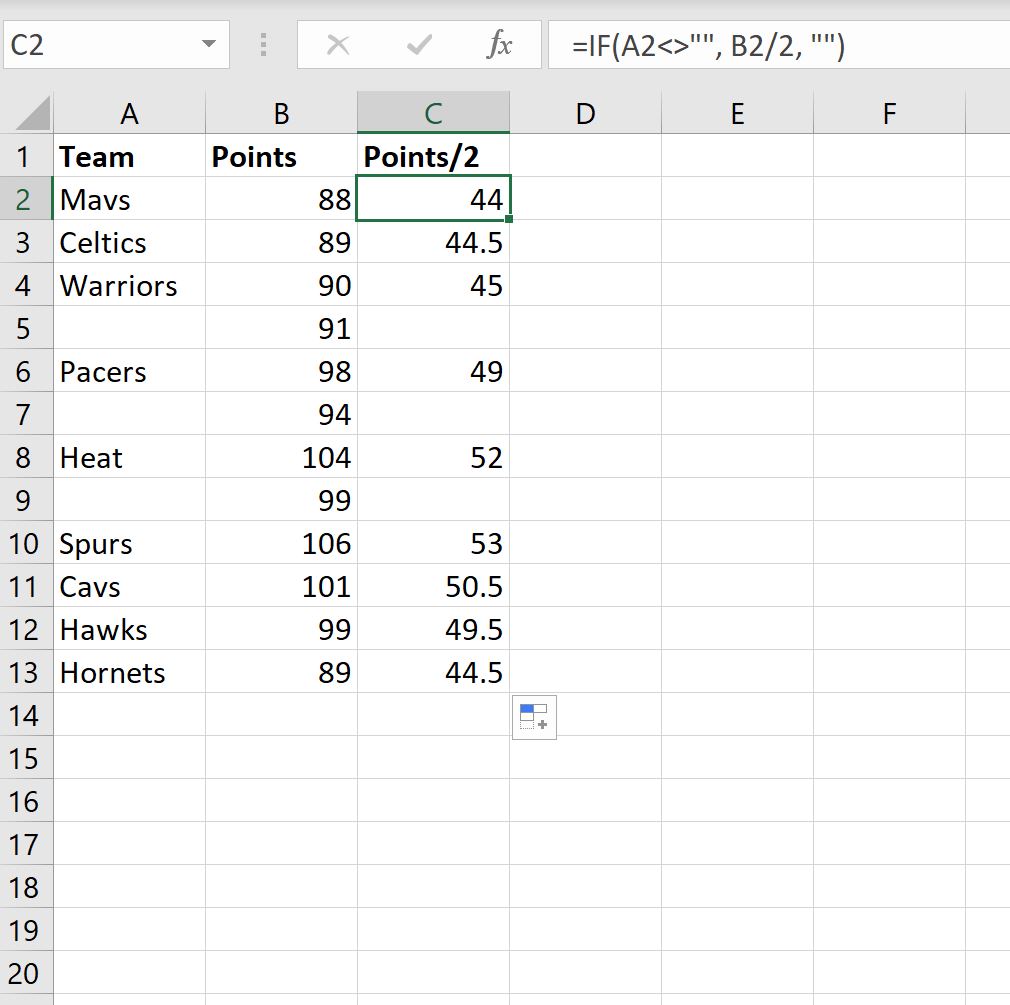
Например, мы могли бы использовать следующую формулу, чтобы вернуть значение столбца очков, разделенное на два, если ячейка в столбце A не пуста.
В противном случае мы вернем пустое значение:
=IF( A2 <> "" , B2 / 2 , "" )
На следующем снимке экрана показано, как использовать эту формулу на практике:
Если название команды не пусто в столбце A, то мы возвращаем значение в столбце очков, умноженное на два.
В противном случае мы возвращаем пустое значение.
Дополнительные ресурсы
В следующих руководствах объясняется, как выполнять другие распространенные задачи в Google Таблицах:
Как отфильтровать ячейки, содержащие текст, в Google Sheets
Как извлечь подстроку в Google Sheets
Как извлечь числа из строки в Google Sheets
EXCEL FORMULA 1. If a cell is not blank using the IF function
EXCEL
Hard coded formula

Cell reference formula

|
GENERIC FORMULA =IF(cell_ref<>»», value_if_true, value_if_false) ARGUMENTS GENERIC FORMULA =IF(cell_ref<>»», value_if_true, value_if_false) ARGUMENTS EXPLANATION This formula uses the IF function with a test criteria of two double quotation marks («»), without any value inserted between them and ‘does not equal to’ sign (<>) in front of them, to assess if a cell is not empty and return a specific value. The expression <>»» means «not empty». If a cell is not blank the formula will return a value that has been assigned as the true value, alternatively if a cell is blank the formula will return a value assigned as the false value. With this formula you can enter the values, that will be returned if the cell is empty or not, directly into the formula or reference them to specific cells that capture these values. Click on either the Hard Coded or Cell Reference button to view the formula that has the return values directly entered into the formula or referenced to specific cells that capture these values, respectively. In this example the formula tests if a specific cell is not blank. If the cell is not blank the formula will return a value of «Yes» (hard coded example) or value in cell C5 (cell reference example). If the cell is empty the formula will return a value of «No» (hard coded example) or value in cell C6 (cell reference example). If you are using the formula with values entered directly in the formula and want to return a numerical value, instead of a text value, you do not need to apply the double quotation marks around the values that are to be returned e.g. (=IF(C5<>»»,1,0)). |
EXCEL FORMULA 2. If a cell is not blank using the IF, NOT and ISBLANK functions
EXCEL
Hard coded formula

Cell reference formula

|
GENERIC FORMULA =IF(NOT(ISBLANK(cell_ref)), value_if_true, value_if_false) ARGUMENTS GENERIC FORMULA =IF(NOT(ISBLANK(cell_ref)), value_if_true, value_if_false) ARGUMENTS EXPLANATION This formula uses a combination of the IF, NOT and ISBLANK functions to assess if a cell is not blank and return a specific value. Unlike the first formula, which uses the double quotation marks («») to test if the selected cell is not blank, this formula uses the NOT and ISBLANK functions. If the cell is not blank the ISBLANK function will return FALSE, alternatively it will return TRUE. The NOT function will then return the opposite to what the ISBLANK function has returned. Therefore, if the cell is not blank the combination of the NOT and ISBLANK function will return a TRUE value. The formula will then return a value that has been assigned as the true value, alternatively if the cell is blank the formula will return a value assigned as the false value. With this formula you can enter the values, that will be returned if the cell is empty or not, directly into the formula or reference them to specific cells that capture these values. Click on either the Hard Coded or Cell Reference button to view the formula that has the return values directly entered into the formula or referenced to specific cells that capture these values, respectively. In this example the formula tests if a specific cell is not blank. If the cell is not blank the formula will return a value of «Yes» (hard coded example) or value in cell C5 (cell reference example). If the cell is empty the formula will return a value of «No» (hard coded example) or value in cell C6 (cell reference example). If you are using the formula with values entered directly in the formula and want to return a numerical value, instead of a text value, you do not need to apply the double quotation marks around the values that are to be returned e.g. (=IF(NOT(ISBLANK(C5)),1,0)). |
VBA CODE 1. If a cell is not blank using the If Statement
VBA
Hard coded against single cell
Sub If_a_cell_is_not_blank()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = Worksheets(«Analysis»)
If ws.Range(«C5») <> «» Then
ws.Range(«D5») = «Yes»
Else
ws.Range(«D5») = «No»
End If
End Sub
Cell reference against single cell
Sub If_a_cell_is_not_blank()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = Worksheets(«Analysis»)
If ws.Range(«C9») <> «» Then
ws.Range(«D9») = ws.Range(«C5»)
Else
ws.Range(«D9») = ws.Range(«C6»)
End If
End Sub
Hard coded against range of cells
Sub If_a_cell_is_not_blank()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = Worksheets(«Analysis»)
For x = 5 To 11
If ws.Cells(x, 3) <> «» Then
ws.Cells(x, 4) = «Yes»
Else
ws.Cells(x, 4) = «No»
End If
Next x
End Sub
Cell reference against range of cells
Sub If_a_cell_is_not_blank()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = Worksheets(«Analysis»)
For x = 9 To 15
If ws.Cells(x, 3) <> «» Then
ws.Cells(x, 4) = ws.Range(«C5»)
Else
ws.Cells(x, 4) = ws.Range(«C6»)
End If
Next x
End Sub
KEY PARAMETERS
Output Range: Select the output range by changing the cell reference («D5») in the VBA code.
Cell to Test: Select the cell that you want to check if it’s not blank by changing the cell reference («C5») in the VBA code.
Worksheet Selection: Select the worksheet which captures the cells that you want to test if they are not blank and return a specific value by changing the Analysis worksheet name in the VBA code. You can also change the name of this object variable, by changing the name ‘ws’ in the VBA code.
True and False Results: In this example if a cell is not blank the VBA code will return a value of «Yes». If a cell is blank the VBA code will return a value of «No». Both of these values can be changed to whatever value you desire by directly changing them in the VBA code.
NOTES
Note 1: If the cell that is being tested is returning a value of («») this VBA code will identify the cell as blank.
Note 2: If your True or False result is a text value it will need to be captured within quotation marks («»). However, if the result is a numeric value, you can enter it without the use of quotation marks.
KEY PARAMETERS
Output Range: Select the output range by changing the cell reference («D9») in the VBA code.
Cell to Test: Select the cell that you want to check if it’s not blank by changing the cell reference («C9») in the VBA code.
Worksheet Selection: Select the worksheet which captures the cells that you want to test if they are not blank and return a specific value by changing the Analysis worksheet name in the VBA code. You can also change the name of this object variable, by changing the name ‘ws’ in the VBA code.
True and False Results: In this example if a cell is not blank the VBA code will return a value stored in cell C5. If a cell is blank the VBA code will return a value stored in cell C6. Both of these values can be changed to whatever value you desire by either referencing to a different cell that captures the value that you want to return or change the values in those cells.
NOTES
Note 1: If the cell that is being tested is returning a value of («») this VBA code will identify the cell as blank.
KEY PARAMETERS
Output and Test Range: Select the output rows and the rows that captures the cells that are to be tested by changing the x values (5 to 11). This example assumes that both the output and the associated test cell will be in the same row.
Test Column: Select the column that captures the cells that are to be tested by changing number 3, in ws.Cells(x, 3).
Output Column: Select the output column by changing number 4, in ws.Cells(x, 4).
Worksheet Selection: Select the worksheet which captures the cells that you want to test if they are not blank and return a specific value by changing the Analysis worksheet name in the VBA code. You can also change the name of this object variable, by changing the name ‘ws’ in the VBA code.
True and False Results: In this example if a cell is not blank the VBA code will return a value of «Yes». If a cell is blank the VBA code will return a value of «No». Both of these values can be changed to whatever value you desire by directly changing them in the VBA code.
NOTES
Note 1: If the cell that is being tested is returning a value of («») this VBA code will identify the cell as blank.
Note 2: If your True or False result is a text value it will need to be captured within quotation marks («»). However, if the result is a numeric value, you can enter it without the use of quotation marks.
KEY PARAMETERS
Output and Test Range: Select the output rows and the rows that captures the cells that are to be tested by changing the x values (9 to 15). This example assumes that both the output and the associated test cell will be in the same row.
Test Column: Select the column that captures the cells that are to be tested by changing number 3, in ws.Cells(x, 3).
Output Column: Select the output column by changing number 4, in ws.Cells(x, 4).
Worksheet Selection: Select the worksheet which captures the cells that you want to test if they are not blank and return a specific value by changing the Analysis worksheet name in the VBA code. You can also change the name of this object variable, by changing the name ‘ws’ in the VBA code.
True and False Results: In this example if a cell is not blank the VBA code will return a value stored in cell C5. If a cell is blank the VBA code will return a value stored in cell C6. Both of these values can be changed to whatever value you desire by either referencing to a different cell that captures the value that you want to return or change the values in those cells.
NOTES
Note 1: If the cell that is being tested is returning a value of («») this VBA code will identify the cell as blank.
VBA CODE 2. If a cell is not blank using Not and IsEmpty
VBA
Hard coded against single cell
Sub If_a_cell_is_not_blank_using_Not_and_IsEmpty()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = Worksheets(«Analysis»)
If Not (IsEmpty(ws.Range(«C5»)))Then
ws.Range(«D5») = «Yes»
Else
ws.Range(«D5») = «No»
End If
End Sub
Cell reference against single cell
Sub If_a_cell_is_not_blank_using_Not_and_IsEmpty()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = Worksheets(«Analysis»)
If Not (IsEmpty(ws.Range(«C9»)))Then
ws.Range(«D9») = ws.Range(«C5»)
Else
ws.Range(«D9») = ws.Range(«C6»)
End If
End Sub
Hard coded against range of cells
Sub If_a_cell_is_not_blank_using_Not_and_IsEmpty()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = Worksheets(«Analysis»)
For x = 5 To 11
If Not (IsEmpty(ws.Cells(x, 3))) Then
ws.Cells(x, 4) = «Yes»
Else
ws.Cells(x, 4) = «No»
End If
Next x
End Sub
Cell reference against range of cells
Sub If_a_cell_is_not_blank_using_Not_and_IsEmpty()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = Worksheets(«Analysis»)
For x = 9 To 15
If Not (IsEmpty(ws.Cells(x, 3))) Then
ws.Cells(x, 4) = ws.Range(«C5»)
Else
ws.Cells(x, 4) = ws.Range(«C6»)
End If
Next x
End Sub
KEY PARAMETERS
Output Range: Select the output range by changing the cell reference («D5») in the VBA code.
Cell to Test: Select the cell that you want to check if it’s not blank by changing the cell reference («C5») in the VBA code.
Worksheet Selection: Select the worksheet which captures the cells that you want to test if they are not blank and return a specific value by changing the Analysis worksheet name in the VBA code. You can also change the name of this object variable, by changing the name ‘ws’ in the VBA code.
True and False Results: In this example if a cell is not blank the VBA code will return a value of «Yes». If a cell is blank the VBA code will return a value of «No». Both of these values can be changed to whatever value you desire by directly changing them in the VBA code.
NOTES
Note 1: If the cell that is being tested is returning a value of («») this VBA code will identify the cell as not blank.
Note 2: If your True or False result is a text value it will need to be captured within quotation marks («»). However, if the result is a numeric value, you can enter it without the use of quotation marks.
KEY PARAMETERS
Output Range: Select the output range by changing the cell reference («D9») in the VBA code.
Cell to Test: Select the cell that you want to check if it’s not blank by changing the cell reference («C9») in the VBA code.
Worksheet Selection: Select the worksheet which captures the cells that you want to test if they are not blank and return a specific value by changing the Analysis worksheet name in the VBA code. You can also change the name of this object variable, by changing the name ‘ws’ in the VBA code.
True and False Results: In this example if a cell is not blank the VBA code will return a value stored in cell C5. If a cell is blank the VBA code will return a value stored in cell C6. Both of these values can be changed to whatever value you desire by either referencing to a different cell that captures the value that you want to return or change the values in those cells.
NOTES
Note 1: If the cell that is being tested is returning a value of («») this VBA code will identify the cell as not blank.
KEY PARAMETERS
Output and Test Range: Select the output rows and the rows that captures the cells that are to be tested by changing the x values (5 to 11). This example assumes that both the output and the associated test cell will be in the same row.
Test Column: Select the column that captures the cells that are to be tested by changing number 3, in ws.Cells(x, 3).
Output Column: Select the output column by changing number 4, in ws.Cells(x, 4).
Worksheet Selection: Select the worksheet which captures the cells that you want to test if they are not blank and return a specific value by changing the Analysis worksheet name in the VBA code. You can also change the name of this object variable, by changing the name ‘ws’ in the VBA code.
True and False Results: In this example if a cell is not blank the VBA code will return a value of «Yes». If a cell is blank the VBA code will return a value of «No». Both of these values can be changed to whatever value you desire by directly changing them in the VBA code.
NOTES
Note 1: If the cell that is being tested is returning a value of («») this VBA code will identify the cell as blank.
Note 2: If your True or False result is a text value it will need to be captured within quotation marks («»). However, if the result is a numeric value, you can enter it without the use of quotation marks.
KEY PARAMETERS
Output and Test Range: Select the output rows and the rows that captures the cells that are to be tested by changing the x values (9 to 15). This example assumes that both the output and the associated test cell will be in the same row.
Test Column: Select the column that captures the cells that are to be tested by changing number 3, in ws.Cells(x, 3).
Output Column: Select the output column by changing number 4, in ws.Cells(x, 4).
Worksheet Selection: Select the worksheet which captures the cells that you want to test if they are not blank and return a specific value by changing the Analysis worksheet name in the VBA code. You can also change the name of this object variable, by changing the name ‘ws’ in the VBA code.
True and False Results: In this example if a cell is not blank the VBA code will return a value stored in cell C5. If a cell is blank the VBA code will return a value stored in cell C6. Both of these values can be changed to whatever value you desire by either referencing to a different cell that captures the value that you want to return or change the values in those cells.
NOTES
Note 1: If the cell that is being tested is returning a value of («») this VBA code will identify the cell as blank.
VBA CODE 3. If a cell is not blank using vbNullString
VBA
Hard coded against single cell
Sub If_a_cell_is_not_blank_using_vbNullString()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = Worksheets(«Analysis»)
If ws.Range(«C5») <> vbNullString Then
ws.Range(«D5») = «Yes»
Else
ws.Range(«D5») = «No»
End If
End Sub
Cell reference against single cell
Sub If_a_cell_is_not_blank_using_vbNullString()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = Worksheets(«Analysis»)
If ws.Range(«C9») <> vbNullString Then
ws.Range(«D9») = ws.Range(«C5»)
Else
ws.Range(«D9») = ws.Range(«C6»)
End If
End Sub
Hard coded against range of cells
Sub If_a_cell_is_not_blank_using_vbNullString()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = Worksheets(«Analysis»)
For x = 5 To 11
If ws.Cells(x, 3) <> vbNullString Then
ws.Cells(x, 4) = «Yes»
Else
ws.Cells(x, 4) = «No»
End If
Next x
End Sub
Cell reference against range of cells
Sub If_a_cell_is_not_blank_using_vbNullString()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = Worksheets(«Analysis»)
For x = 9 To 15
If ws.Cells(x, 3) <> vbNullString Then
ws.Cells(x, 4) = ws.Range(«C5»)
Else
ws.Cells(x, 4) = ws.Range(«C6»)
End If
Next x
End Sub
KEY PARAMETERS
Output Range: Select the output range by changing the cell reference («D5») in the VBA code.
Cell to Test: Select the cell that you want to check if it’s not blank by changing the cell reference («C5») in the VBA code.
Worksheet Selection: Select the worksheet which captures the cells that you want to test if they are not blank and return a specific value by changing the Analysis worksheet name in the VBA code. You can also change the name of this object variable, by changing the name ‘ws’ in the VBA code.
True and False Results: In this example if a cell is not blank the VBA code will return a value of «Yes». If a cell is blank the VBA code will return a value of «No». Both of these values can be changed to whatever value you desire by directly changing them in the VBA code.
NOTES
Note 1: If the cell that is being tested is returning a value of («») this VBA code will identify the cell as blank.
Note 2: If your True or False result is a text value it will need to be captured within quotation marks («»). However, if the result is a numeric value, you can enter it without the use of quotation marks.
KEY PARAMETERS
Output Range: Select the output range by changing the cell reference («D9») in the VBA code.
Cell to Test: Select the cell that you want to check if it’s not blank by changing the cell reference («C9») in the VBA code.
Worksheet Selection: Select the worksheet which captures the cells that you want to test if they are not blank and return a specific value by changing the Analysis worksheet name in the VBA code. You can also change the name of this object variable, by changing the name ‘ws’ in the VBA code.
True and False Results: In this example if a cell is not blank the VBA code will return a value stored in cell C5. If a cell is blank the VBA code will return a value stored in cell C6. Both of these values can be changed to whatever value you desire by either referencing to a different cell that captures the value that you want to return or change the values in those cells.
NOTES
Note 1: If the cell that is being tested is returning a value of («») this VBA code will identify the cell as blank.
KEY PARAMETERS
Output and Test Rows: Select the output rows and the rows that captures the cells that are to be tested by changing the x values (5 to 11). This example assumes that both the output and the associated test cell will be in the same row.
Test Column: Select the column that captures the cells that are to be tested by changing number 3, in ws.Cells(x, 3).
Output Column: Select the output column by changing number 4, in ws.Cells(x, 4).
Worksheet Selection: Select the worksheet which captures the cells that you want to test if they are not blank and return a specific value by changing the Analysis worksheet name in the VBA code. You can also change the name of this object variable, by changing the name ‘ws’ in the VBA code.
True and False Results: In this example if a cell is not blank the VBA code will return a value of «Yes». If a cell is blank the VBA code will return a value of «No». Both of these values can be changed to whatever value you desire by directly changing them in the VBA code.
NOTES
Note 1: If the cell that is being tested is returning a value of («») this VBA code will identify the cell as blank.
Note 2: If your True or False result is a text value it will need to be captured within quotation marks («»). However, if the result is a numeric value, you can enter it without the use of quotation marks.
KEY PARAMETERS
Output and Test Rows: Select the output rows and the rows that captures the cells that are to be tested by changing the x values (9 to 15). This example assumes that both the output and the associated test cell will be in the same row.
Test Column: Select the column that captures the cells that are to be tested by changing number 3, in ws.Cells(x, 3).
Output Column: Select the output column by changing number 4, in ws.Cells(x, 4).
Worksheet Selection: Select the worksheet which captures the cells that you want to test if they are not blank and return a specific value by changing the Analysis worksheet name in the VBA code. You can also change the name of this object variable, by changing the name ‘ws’ in the VBA code.
True and False Results: In this example if a cell is not blank the VBA code will return a value stored in cell C5. If a cell is blank the VBA code will return a value stored in cell C6. Both of these values can be changed to whatever value you desire by either referencing to a different cell that captures the value that you want to return or change the values in those cells.
NOTES
Note 1: If the cell that is being tested is returning a value of («») this VBA code will identify the cell as blank.