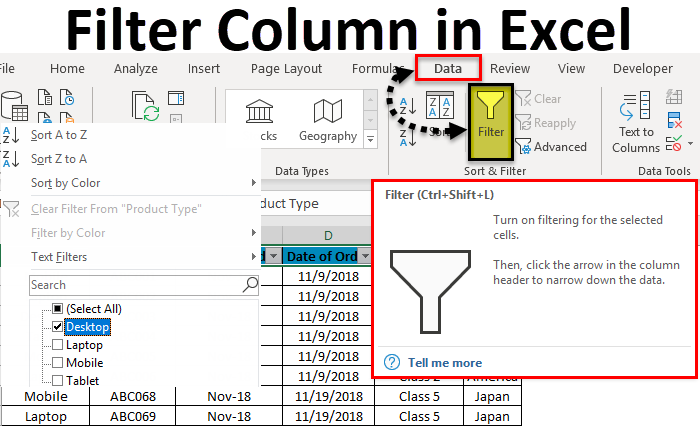
Use AutoFilter or built-in comparison operators like «greater than» and “top 10” in Excel to show the data you want and hide the rest. Once you filter data in a range of cells or table, you can either reapply a filter to get up-to-date results, or clear a filter to redisplay all of the data.
Use filters to temporarily hide some of the data in a table, so you can focus on the data you want to see.
Filter a range of data
-
Select any cell within the range.
-
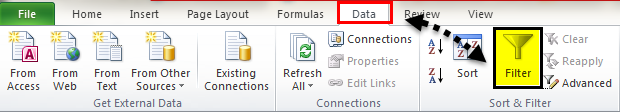
Select Data > Filter.
-
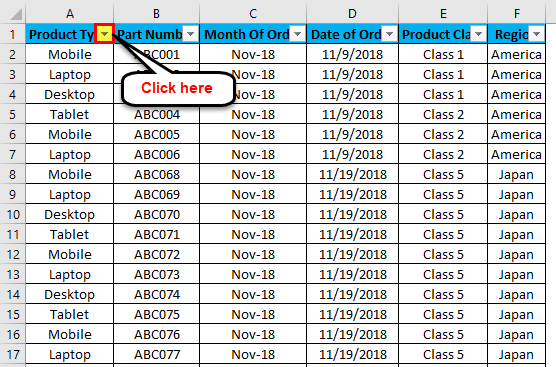
Select the column header arrow
.
-
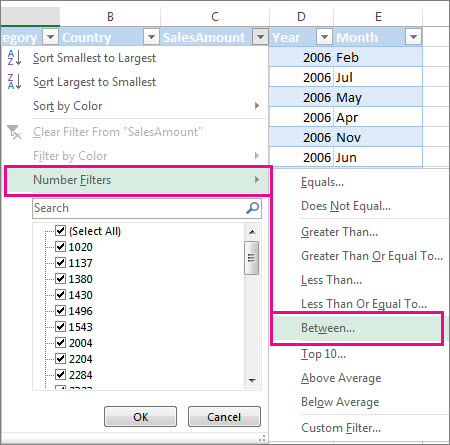
Select Text Filters or Number Filters, and then select a comparison, like Between.
-
Enter the filter criteria and select OK.
Filter data in a table
When you put your data in a table, filter controls are automatically added to the table headers.
-
Select the column header arrow
for the column you want to filter.
-
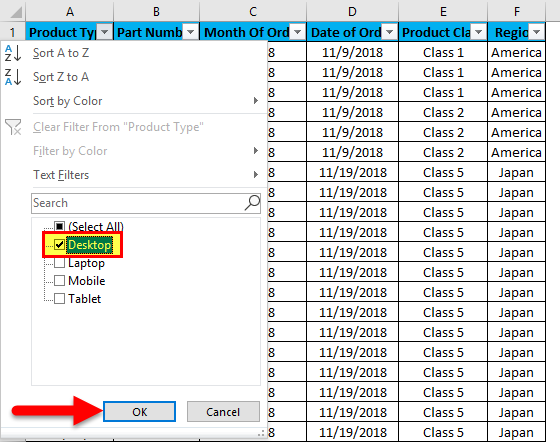
Uncheck (Select All) and select the boxes you want to show.
-
Click OK.
The column header arrow
changes to a
Filter icon. Select this icon to change or clear the filter.
Related Topics
Excel Training: Filter data in a table
Guidelines and examples for sorting and filtering data by color
Filter data in a PivotTable
Filter by using advanced criteria
Remove a filter
Filtered data displays only the rows that meet criteria that you specify and hides rows that you do not want displayed. After you filter data, you can copy, find, edit, format, chart, and print the subset of filtered data without rearranging or moving it.
You can also filter by more than one column. Filters are additive, which means that each additional filter is based on the current filter and further reduces the subset of data.
Note: When you use the Find dialog box to search filtered data, only the data that is displayed is searched; data that is not displayed is not searched. To search all the data, clear all filters.
The two types of filters
Using AutoFilter, you can create two types of filters: by a list value or by criteria. Each of these filter types is mutually exclusive for each range of cells or column table. For example, you can filter by a list of numbers, or a criteria, but not by both; you can filter by icon or by a custom filter, but not by both.
Reapplying a filter
To determine if a filter is applied, note the icon in the column heading:
-
A drop-down arrow
means that filtering is enabled but not applied.
When you hover over the heading of a column with filtering enabled but not applied, a screen tip displays «(Showing All)».
-
A Filter button
means that a filter is applied.
When you hover over the heading of a filtered column, a screen tip displays the filter applied to that column, such as «Equals a red cell color» or «Larger than 150».
When you reapply a filter, different results appear for the following reasons:
-
Data has been added, modified, or deleted to the range of cells or table column.
-
Values returned by a formula have changed and the worksheet has been recalculated.
Do not mix data types
For best results, do not mix data types, such as text and number, or number and date in the same column, because only one type of filter command is available for each column. If there is a mix of data types, the command that is displayed is the data type that occurs the most. For example, if the column contains three values stored as number and four as text, the Text Filters command is displayed .
Filter data in a table
When you put your data in a table, filtering controls are added to the table headers automatically.
-
Select the data you want to filter. On the Home tab, click Format as Table, and then pick Format as Table.
-
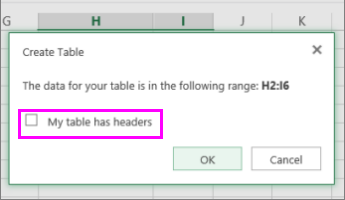
In the Create Table dialog box, you can choose whether your table has headers.
-
Select My table has headers to turn the top row of your data into table headers. The data in this row won’t be filtered.
-
Don’t select the check box if you want Excel for the web to add placeholder headers (that you can rename) above your table data.
-
-
Click OK.
-
To apply a filter, click the arrow in the column header, and pick a filter option.
Filter a range of data
If you don’t want to format your data as a table, you can also apply filters to a range of data.
-
Select the data you want to filter. For best results, the columns should have headings.
-
On the Data tab, choose Filter.
Filtering options for tables or ranges
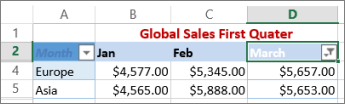
You can either apply a general Filter option or a custom filter specific to the data type. For example, when filtering numbers, you’ll see Number Filters, for dates you’ll see Date Filters, and for text you’ll see Text Filters. The general filter option lets you select the data you want to see from a list of existing data like this:
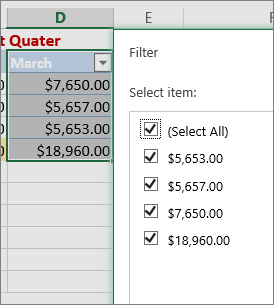
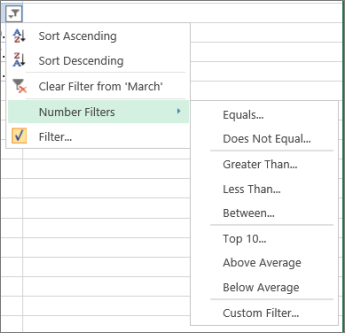
Number Filters lets you apply a custom filter:
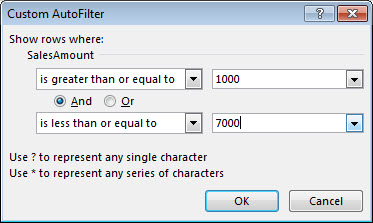
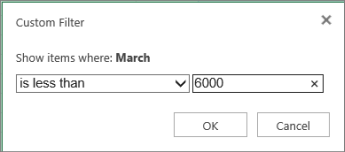
In this example, if you want to see the regions that had sales below $6,000 in March, you can apply a custom filter:
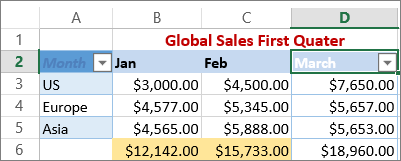
Here’s how:
-
Click the filter arrow next to March > Number Filters > Less Than and enter 6000.
-
Click OK.
Excel for the web applies the filter and shows only the regions with sales below $6000.
You can apply custom Date Filters and Text Filters in a similar manner.
To clear a filter from a column
-
Click the Filter
button next to the column heading, and then click Clear Filter from <«Column Name»>.
To remove all the filters from a table or range
-
Select any cell inside your table or range and, on the Data tab, click the Filter button.
This will remove the filters from all the columns in your table or range and show all your data.
-
Click a cell in the range or table that you want to filter.
-
On the Data tab, click Filter.
-
Click the arrow
in the column that contains the content that you want to filter.
-
Under Filter, click Choose One, and then enter your filter criteria.
Notes:
-
You can apply filters to only one range of cells on a sheet at a time.
-
When you apply a filter to a column, the only filters available for other columns are the values visible in the currently filtered range.
-
Only the first 10,000 unique entries in a list appear in the filter window.
-
Click a cell in the range or table that you want to filter.
-
On the Data tab, click Filter.
-
Click the arrow
in the column that contains the content that you want to filter.
-
Under Filter, click Choose One, and then enter your filter criteria.
-
In the box next to the pop-up menu, enter the number that you want to use.
-
Depending on your choice, you may be offered additional criteria to select:
Notes:
-
You can apply filters to only one range of cells on a sheet at a time.
-
When you apply a filter to a column, the only filters available for other columns are the values visible in the currently filtered range.
-
Only the first 10,000 unique entries in a list appear in the filter window.
-
Instead of filtering, you can use conditional formatting to make the top or bottom numbers stand out clearly in your data.
You can quickly filter data based on visual criteria, such as font color, cell color, or icon sets. And you can filter whether you have formatted cells, applied cell styles, or used conditional formatting.
-
In a range of cells or a table column, click a cell that contains the cell color, font color, or icon that you want to filter by.
-
On the Data tab, click Filter .
-
Click the arrow
in the column that contains the content that you want to filter.
-
Under Filter, in the By color pop-up menu, select Cell Color, Font Color, or Cell Icon, and then click a color.
This option is available only if the column that you want to filter contains a blank cell.
-
Click a cell in the range or table that you want to filter.
-
On the Data toolbar, click Filter.
-
Click the arrow
in the column that contains the content that you want to filter.
-
In the (Select All) area, scroll down and select the (Blanks) check box.
Notes:
-
You can apply filters to only one range of cells on a sheet at a time.
-
When you apply a filter to a column, the only filters available for other columns are the values visible in the currently filtered range.
-
Only the first 10,000 unique entries in a list appear in the filter window.
-
-
Click a cell in the range or table that you want to filter.
-
On the Data tab, click Filter .
-
Click the arrow
in the column that contains the content that you want to filter.
-
Under Filter, click Choose One, and then in the pop-up menu, do one of the following:
To filter the range for
Click
Rows that contain specific text
Contains or Equals.
Rows that do not contain specific text
Does Not Contain or Does Not Equal.
-
In the box next to the pop-up menu, enter the text that you want to use.
-
Depending on your choice, you may be offered additional criteria to select:
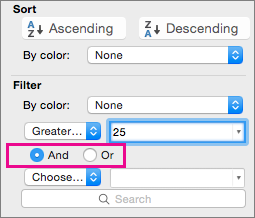
To
Click
Filter the table column or selection so that both criteria must be true
And.
Filter the table column or selection so that either or both criteria can be true
Or.
-
Click a cell in the range or table that you want to filter.
-
On the Data toolbar, click Filter .
-
Click the arrow
in the column that contains the content that you want to filter.
-
Under Filter, click Choose One, and then in the pop-up menu, do one of the following:
To filter for
Click
The beginning of a line of text
Begins With.
The end of a line of text
Ends With.
Cells that contain text but do not begin with letters
Does Not Begin With.
Cells that contain text but do not end with letters
Does Not End With.
-
In the box next to the pop-up menu, enter the text that you want to use.
-
Depending on your choice, you may be offered additional criteria to select:
To
Click
Filter the table column or selection so that both criteria must be true
And.
Filter the table column or selection so that either or both criteria can be true
Or.
Wildcard characters can be used to help you build criteria.
-
Click a cell in the range or table that you want to filter.
-
On the Data toolbar, click Filter.
-
Click the arrow
in the column that contains the content that you want to filter.
-
Under Filter, click Choose One, and select any option.
-
In the text box, type your criteria and include a wildcard character.
For example, if you wanted your filter to catch both the word «seat» and «seam», type sea?.
-
Do one of the following:
Use
To find
? (question mark)
Any single character
For example, sm?th finds «smith» and «smyth»
* (asterisk)
Any number of characters
For example, *east finds «Northeast» and «Southeast»
~ (tilde)
A question mark or an asterisk
For example, there~? finds «there?»
Do any of the following:
|
To |
Do this |
|---|---|
|
Remove specific filter criteria for a filter |
Click the arrow |
|
Remove all filters that are applied to a range or table |
Select the columns of the range or table that have filters applied, and then on the Data tab, click Filter. |
|
Remove filter arrows from or reapply filter arrows to a range or table |
Select the columns of the range or table that have filters applied, and then on the Data tab, click Filter. |
When you filter data, only the data that meets your criteria appears. The data that doesn’t meet that criteria is hidden. After you filter data, you can copy, find, edit, format, chart, and print the subset of filtered data.
Table with Top 4 Items filter applied
Filters are additive. This means that each additional filter is based on the current filter and further reduces the subset of data. You can make complex filters by filtering on more than one value, more than one format, or more than one criteria. For example, you can filter on all numbers greater than 5 that are also below average. But some filters (top and bottom ten, above and below average) are based on the original range of cells. For example, when you filter the top ten values, you’ll see the top ten values of the whole list, not the top ten values of the subset of the last filter.
In Excel, you can create three kinds of filters: by values, by a format, or by criteria. But each of these filter types is mutually exclusive. For example, you can filter by cell color or by a list of numbers, but not by both. You can filter by icon or by a custom filter, but not by both.
Filters hide extraneous data. In this manner, you can concentrate on just what you want to see. In contrast, when you sort data, the data is rearranged into some order. For more information about sorting, see Sort a list of data.
When you filter, consider the following guidelines:
-
Only the first 10,000 unique entries in a list appear in the filter window.
-
You can filter by more than one column. When you apply a filter to a column, the only filters available for other columns are the values visible in the currently filtered range.
-
You can apply filters to only one range of cells on a sheet at a time.
Note: When you use Find to search filtered data, only the data that is displayed is searched; data that is not displayed is not searched. To search all the data, clear all filters.
Need more help?
You can always ask an expert in the Excel Tech Community or get support in the Answers community.
Excel Column Filter (Table of Contents)
- Filter Column in Excel
- How to Filter a Column in Excel?
Filter Column in Excel
Filters in Excel are used for filtering the data by selecting the data type in the filter dropdown. By using a filter, we can make out the data that we want to see or on which we need to work.
To access/apply a filter in any column of excel, go to the Data menu tab; under Sort & Filter, we will find the Filter option.
How to Filter a Column in Excel?
To filter a column in excel is a very simple and easy task. Let’s understand the working of how to filter a column in Excel with an example.
You can download this Column Filter Excel Template here – Column Filter Excel Template
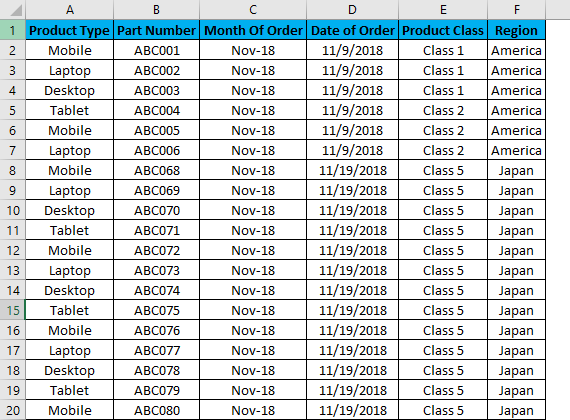
We have some sample data tables in excel, where we will apply the filter in columns. Below is the screenshot of a data set, which has multiple columns and multiple rows with various data sets.
For applying Excel Column Filter, select the top row first, and the filter will be applied to the selected row only, as shown below. Sometimes when we work for a large set of data and select the filter directly, the current look of the sheet can be applied.
As we can see in the above screenshot, row 1 is selected, and it is ready to apply the filters.
Now for applying filters, go to the Data menu, and under Sort & Filters, select Filters.
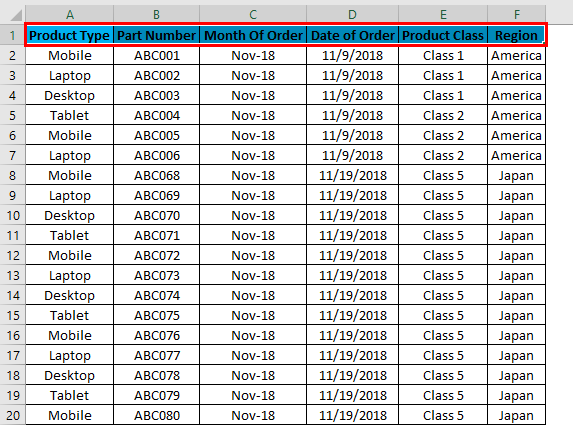
Once we click on Filters, we can see the filters will be applied in the selected row, as shown in the below screenshot.
The top row 1 now has the dropdown. This drop-down is those things by which we can filter the data as per our need.
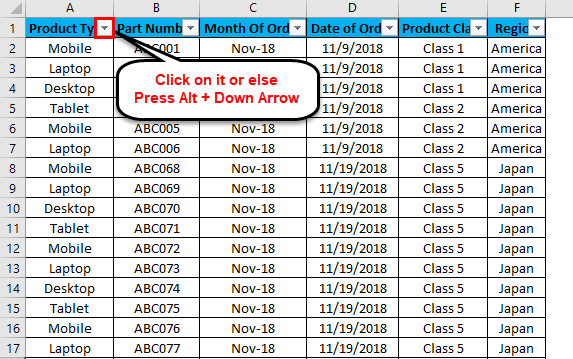
To open the drop-down option in an applied filter, click on the down arrow (as shown below) or go to any column top and press Alt + Down.
A drop-down menu will appear, as shown in the below screenshot.
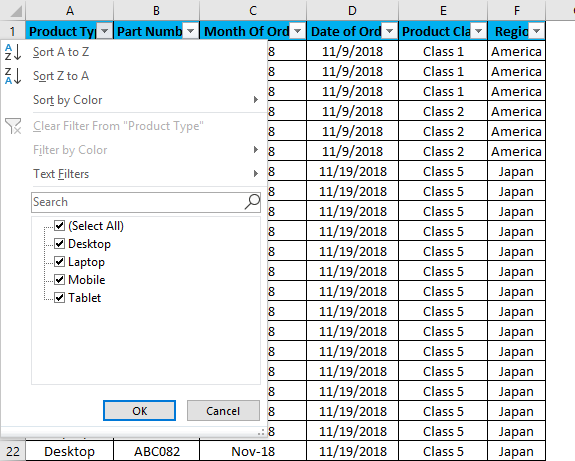
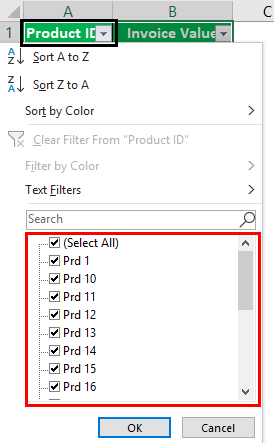
As we can see in the above screenshot, there are few filter options provided by Microsoft.
- Sort A to Z / Sort Oldest to Newest (for dates) / Sort Smallest to Largest (for numbers)
- Sort Z to A / Sort Newest to Oldest (for dates) / Sort Largest to Smallest (for numbers)
- Sort by Color
- Clear Filter From “Product Type” (This would entitle the name of columns where a filter is applied)
- Filter by Color
- Text Filters
- Search/Manual Filter
As we can see in the first screenshot, where data is in a randomly scattered format. Let us apply the filter and see what changes happen in the data. For that, go to column A and in the drop-down menu, select only Desktops, as shown in the below screenshot, and click on OK.
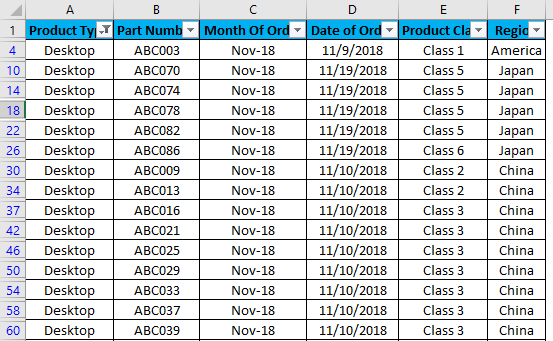
Once we do it, we will see, the data is now filtered with Desktop. And whatever the data is there in w.r.t. Desktop in the rest of the columns will also get filtered, as the screenshot below.
As we can see in the above screenshot, data is now filtered with Desktop, and all the columns are also sorted with data available for Desktop. Also, the line numbers, which are circled in the above screenshot, are also showing the random numbers. This means that the filter which we have applied was in a random format, so the line numbers have also been scattered when we applied the filter.
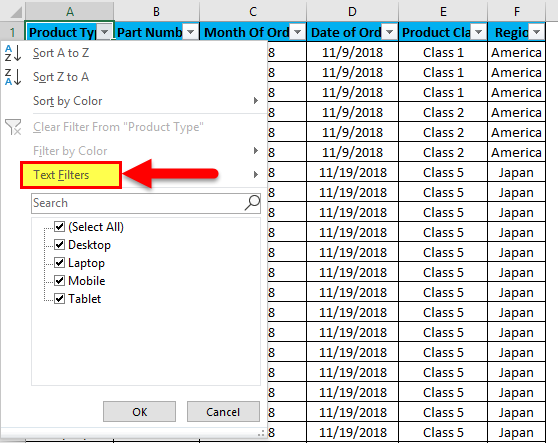
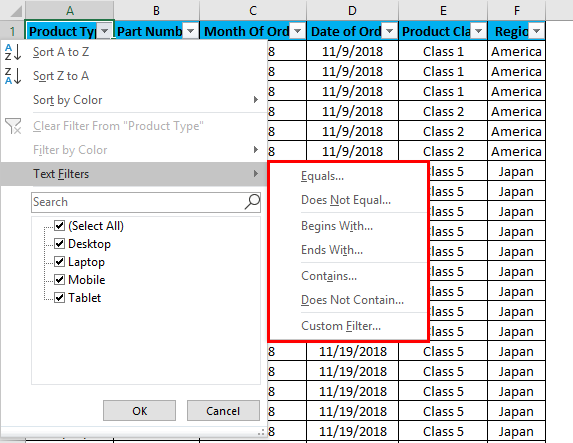
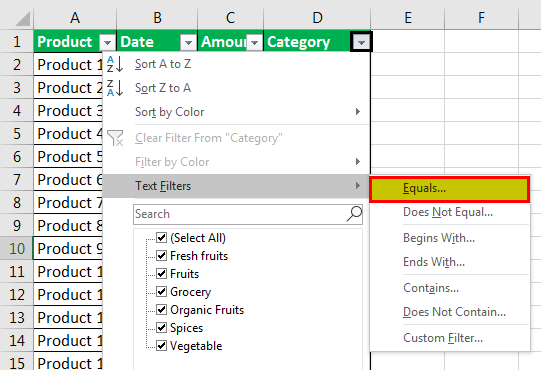
Now, let’s try to apply the text filter, which is a very interesting part of filtering the data. For that, go to any of the columns, and click on the drop-down button to see the filter options.
Now go to Text Filters.
We will find a few more options available for filtering the data, as shown in the below screenshot.
The highlighted portion of Text Filters in the box has Equals, Does Not Equal, Begins With, Ends With, Contains, Does Not Contain, and Custom Filter.
- Equal: With this, we can filter the data with an exact equal word available in the data.
- Does Not Equal: With this, we can filter the data with a word that does not match the available words in the data.
- Begins With: This filters the data, which begins with a specific word or letter, or character.
- Ends With – This filters the data, which ends with a specific word or letter, or character.
- Contains: With this, we can filter the data which contains any specific word or letter, or character.
- Does Not Contain: With this, we can filter the data which does not contain any specific word, letter, or character.
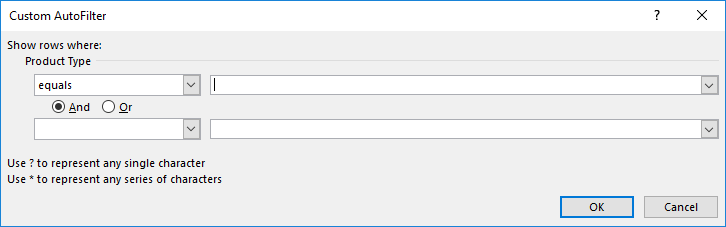
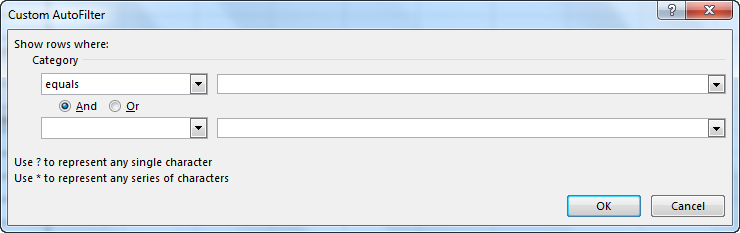
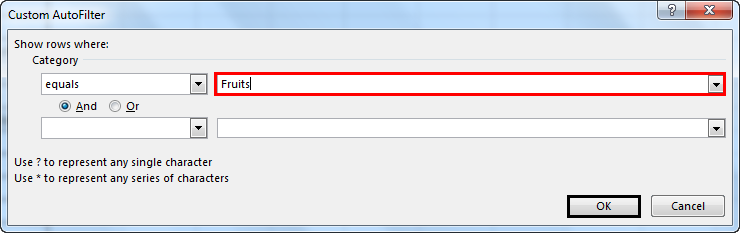
- Custom Filter: With this, we can apply any combination of the above-mentioned Text Filters in data together to get data filtered more deeply and specific to our requirement. Once we click on Custom Filter, we will get a box of Custom AutoFilter, as shown in the below screenshot.
As we can see in the above screenshot of Custom AutoFilter, it has to two filter options at the left sides, which And and Or check-in circles separate. And the other two boxes provided on the left side are for filling the criteria values. This can be called a smart filter.
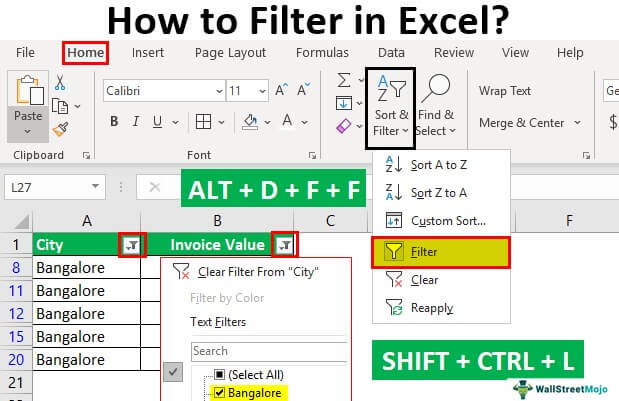
There are different ways of applying the Excel column filter.
- Data menu -> Filter
- By pressing Ctrl + Shift + L together.
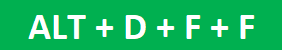
- By pressing Alt + D + F + F simultaneously.
Pros of Excel Column Filter
- By applying filters, we can sort the data as per our needs.
- By filters, performing the analysis or any work becomes easy.
- Filters sort the data with words, numbers, cell colors, font colors, or with any range. Also, multiple criteria can be used as well.
Cons of Excel Column Filter
- Filters can be applied to all kinds of range sizes, but it is not useful if the data size increases up to a certain limit. For some cases, if the data is going beyond 50,000 lines, then it becomes slow, and sometimes it does not show data available in any column.
Things to Remember
- If you are using filter and freeze panel together, then first apply the filter and then use freeze panel. By doing this, data will be frozen from the middle portion of the sheet.
- Avoid or be cautious while using a filter for huge sets of data (maybe for 50000 or more). It will take a lot more time to get applied, and sometimes the file also gets crashed.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Filter Column in Excel. Here we discuss how to filter a column in Excel along with practical examples and a downloadable excel template. You can also go through our other suggested articles –
- Excel AutoFilter
- Excel Data Filter
- Advanced Filter in Excel
- VBA Filter
What is Filter in Excel?
The filter in excel helps display relevant data by eliminating the irrelevant entries temporarily from the view. The data is filtered as per the given criteria. The purpose of filtering is to focus on the crucial areas of a dataset. For example, the city-wise sales data of an organization can be filtered by the location. Hence, the user can view the sales of selected cities at a given time.
A filter is necessarily required when working with a huge database. Being a widely used tool, the filter converts a comprehensive view into an easy-to-understand one. To apply filters, the dataset must contain a header row which specifies the name of every column.
Table of contents
- What is Filter in Excel?
- How to Filter in Excel?
- Method 1: With Filter Option Under the Home tab
- Method 2: With Filter Option Under the Data tab
- Method 3: With the Shortcut key
- How to Add Filters in Excel?
- Example #1–“Number Filters” Option
- Example #2–“Search Box” Option
- Option while you Drop Down the Filter Function
- The Techniques of Filtering in Excel
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Recommended Articles
- How to Filter in Excel?
How to Filter in Excel?
You can download this Filter Column Excel Template here – Filter Column Excel Template
It is good to work with filters because they fit our needs the way we want to. In order to filter data, select the entries to be visible and deselect the rest of the items.
The three methods to add filters in excel are listed as follows:
- With filter option under the Home tab
- With filter option under the Data tab
- With the shortcut key
Let us consider a dataset to go through the three methods of adding filters.
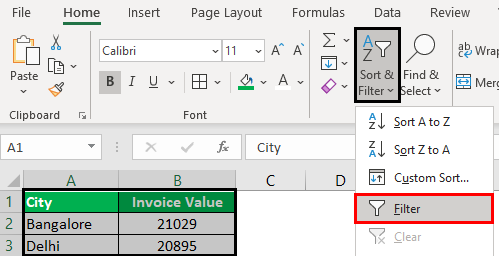
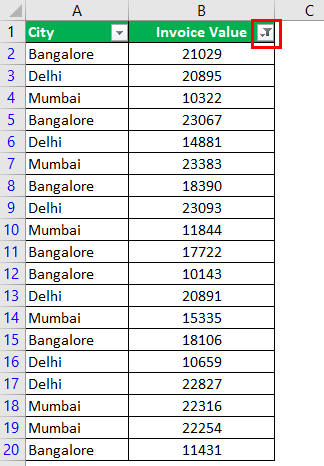
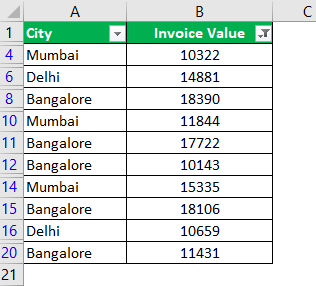
The following table shows the invoices issued to the buyers of different cities. We want to filter the data using different methods.
Method 1: With Filter Option Under the Home tab
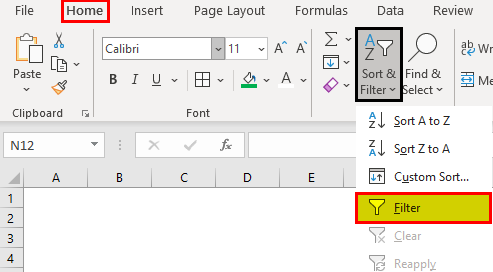
In the Home tab, there is a “filter” option under the “sort and filter” drop-down of the “editing” section, as shown in the following image.
Step 1: Select the data and click “filter” under the “sort and filter” drop-down.
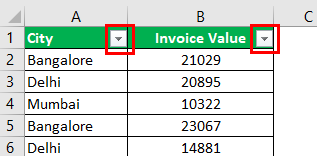
Step 2: The filters are added to the selected data range. The drop-down arrows, shown within the red boxes in the following image, are filters.
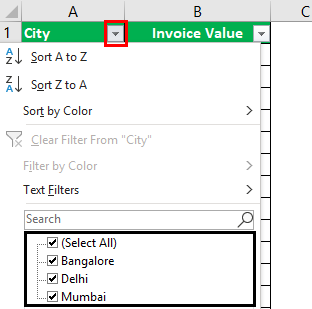
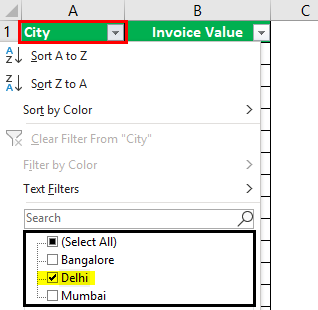
Step 3: Click the drop-down arrow of the column “city” to view the different names of the cities.
Step 4: To see the invoice values of “Delhi” only, select “Delhi” and uncheck all the remaining boxes.
Step 5: The data for the city “Delhi” is filtered and displayed in the following image.
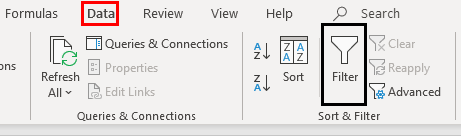
Method 2: With Filter Option Under the Data tab
In the Data tab, there is a “filter” option under the “sort and filter” section, as shown in the following image.
Method 3: With the Shortcut key
The keyboard shortcutsAn Excel shortcut is a technique of performing a manual task in a quicker way.read more are a good way to speed up the daily tasks. Select the data and add the filter using either of the following shortcuts:
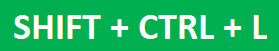
- Press the keys “Shift+Ctrl+L” together.
- Press the keys “Alt+D+F+F” together.
Note: The preceding shortcuts for adding filtersUsing sorting and filtering, we can see the data category wise. With filtering data quickly you can easily navigate through menus or clicking through a mouse in less time.read more are toggle keys. Repetitive pressing helps to turn on and turn off the filters.
How to Add Filters in Excel?
We can filter numbers using advanced techniques. Let us consider some examples to understand the working of filters in Excel.
Example #1–“Number Filters” Option
Working on the data under the preceding heading (methods of filtering in Excel), we want to apply the following filters:
a. To filter column B (invoice value) for numbers greater than 10000
b. To filter column B for numbers greater than 10000 but less than 20000
Let us go through the two cases one by one.
a. Filter numbers greater than 10000
Step 1: Open the filter in column B (invoice value) by clicking on the filter symbol.
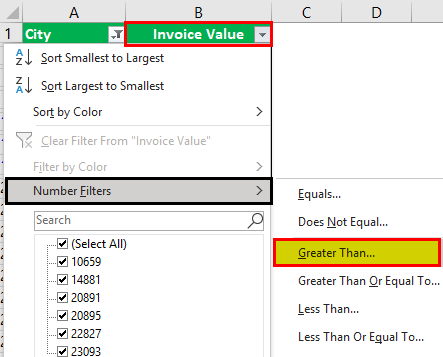
Step 2: In “number filters,” choose the “greater than” option, as shown in the following image.
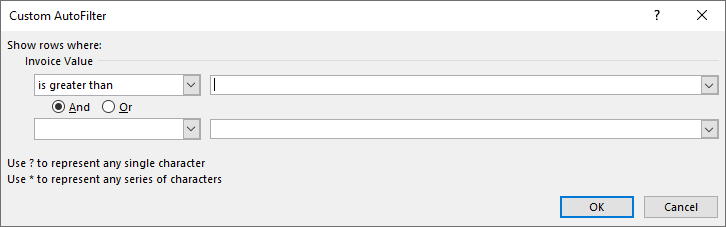
Step 3: The “custom autofilter” box appears.
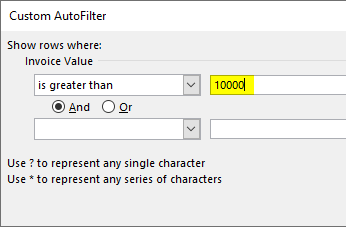
Step 4: Enter the number 10000 in the box to the right of “is greater than.”
Step 5: The output displays the invoice values greater than 10000. The symbol within the red box is the filter icon. It indicates that the filter has been applied to column B.
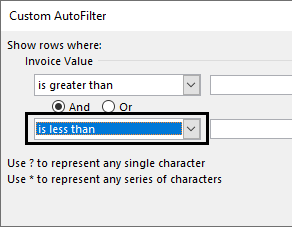
b. Filter numbers greater than 10000 but less than 20000
Step 1: In “number filters,” choose the “greater than” option.
Step 2: In the “custom autofilter” box, select “is less than” in the second box to the left-hand side. This is shown in the following image.
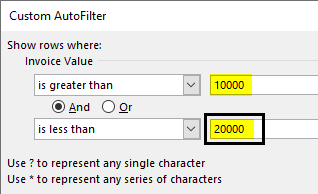
Step 3: Enter the number 10000 in the box to the right of “is greater than.” Enter the number 20000 in the box to the right of “is less than.”
Step 4: The output displays the invoice values greater than 10000 but less than 20000.
Example #2–“Search Box” Option
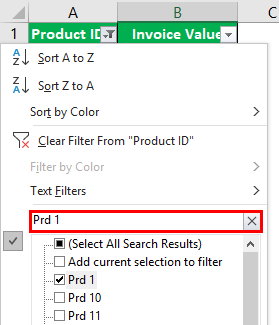
Working on the data under the preceding heading (methods of filtering in Excel), we have replaced the first column (city) with product IDs.
We want to filter the details of product ID “prd 1.”
The steps are listed as follows:
Step 1: Add filters to the columns “product ID” and “invoice value.”
Step 2: In the search boxA search box in Excel finds the needed data by typing into it, then filters the data and displays only that much info. When working with large datasheets, this simple tool may save a lot of time.read more, enter the value that is to be filtered. So, enter “prd 1.”
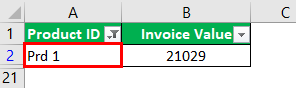
Step 3: The output displays only the filtered value from the list, as shown in the following image. Hence, we can see the invoice value of the product ID “prd 1.”
Option while you Drop Down the Filter Function
- Sort A to Z and Sort Z to A: If you wish to arrange your data ascending or descending order.
- Sort by Color: If you want to filter the data by color if a cell is filled by color.
- Text filter: When you want to filter a column with some exact text or number.
- Filter cells that begin with or end with an exact character or the text
- Filter cells that contain or do not contain a given character or word anywhere in the text.
- Filter cells that are exactly equal or not equal to a detailed character.
For example:
- Suppose you want to use the filter for a specific item. Click on to text filter and choose equals.
- It enables you the one dialogue, which includes a Custom Auto-Filter dialogue box.
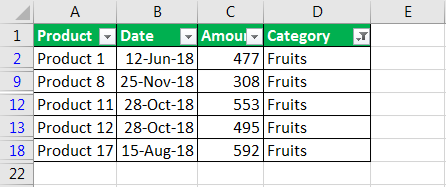
- Enter fruits under category and click Ok.
- Now you will get the data of fruits category only as shown below.
The Techniques of Filtering in Excel
The following techniques must be followed while filtering data:
- If the dataset is large, type the value to be filtered. This filters all the possible matches.
- If numerical data has to be filtered by specifying the greater than or the less than number, use the “number filters” option.
- If data has to be filtered by the color of specific rows, use the “filter by color” option.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are filters and how to add them in Excel?
Filtering is a technique which displays the required information and removes the unwanted data from the view. It helps the user focus on the relevant data at a given time.
The steps to add filters in Excel are listed as follows:
• Ensure that a header row appears on top of the data, specifying the column labels.
• Select the data on which filters are to be added.
• Add filters by any of the three given methods.
o Click the “filter” option under the “sort and filter” (editing section) drop-down of the Home tab.
o Click the “filter” option under the “sort and filter” section of the Data tab.
o Press the keys “Shift+Ctrl+L” or “Alt+D+F+F.”
Note: As soon as the filters are added, a drop-down arrow appears on the particular column header.
2. How to apply filters to one or more columns?
The steps to apply filters to one or more columns are listed as follows:
• Click the drop-down arrow of the column to be filtered.
• Uncheck the “select all” option which helps deselect all data.
• Select the boxes to be displayed.
• Click “Ok.”
The drop-down arrow changes to the filter icon as soon as a filter is applied. When filters are applied to multiple columns, the filter icon appears on each one of them. Hovering over the filter icon shows the filters that have been applied.
Note: The drop-down arrow on a column header indicates a filter is added. The filter icon indicates a filter has been applied.
3. How to use filters in Excel?
The filters can be applied to numbers, text values, and dates. These cases are discussed as follows:
Filter numbers
• Click on the “number filters.”
• Select any of the options like “equals,” “does not equals,” “greater than,” “less than,” “between,” “above average,” and so on.
• Specify the required fields in the dialog box that appears. This box may or may not be displayed.
For instance, in “equals,” enter the number against which the values should be compared. The filtered results show the matching numerical values.
Filter text and date values
• To filter text and date values, select “text filters” and “date filters” from the respective drop-down arrows.
• The “text filters” allow filtering text strings which contain specific characters or words. The “date filters” allow filtering dates for a particular year, month, week, and so on.
Note: The “plus” and the “minus” sign of the date filters are used for expanding and collapsing the various levels respectively.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Filter in Excel. Here we discuss how to use/add filters in excel along with step by step examples and a downloadable template. You may learn more about Excel from the following articles –
- VBA FilterThe VBA Filter tool is used to sort out or fetch the desired data. However, this function accepts optional arguments, and the only required argument is an expression that covers the range, such as worksheets(«Sheet1»). Range(“A1”).read more
- How to Filter Pivot Table?By right-clicking on the pivot table, we can access the pivot table filter option. Another approach is to use the filter options available in the pivot table fields.read more
- Advanced Filter in ExcelThe advanced filter is different from the auto filter in Excel. This feature is not like a button that one can use with a single click of the mouse. To use an advanced filter, we have to define criteria for the auto filter and then click on the “Data” tab. Then, in the advanced section for the advanced filter, we will fill our criteria for the data.read more
- Types of Filters in Power BIThe filter function in Power BI is more commonly used to read data or reports based on multiple criteria. Visual level filters, page-level filters, report-level filters, drill-through filters, and so on are all available filters in Power Bi.read more
The Excel Filter Feature is a great tool that proves to be a lifesaver at the time when you are working with huge data in Excel. In this blog, we would unlock this filter feature in Excel. We would learn how to filter huge data in excel. We would also get into answering the following common questions – how to filter values, or numbers, or dates and time in Excel, how to use filter using wildcard characters in excel, how to filter using the search box, how to filter by text or cell color.
Sample Data – Download Sample File
In this blog, we would be using the below data. Kindly download and practice along with using the Download button.
Table of Contents
- Sample Data – Download Sample File
- What is the Purpose of Filter Feature in Excel?
- Adding Filter Option on Header Rows
- Simple Ways to Filter Your Data Set in Excel
- Applying Filter on Single Column
- Applying Filter on Multiple Columns
- Filter Data Using Filter Search Box in Excel
- Clearing Filter on Columns in Excel
- How to Filter Values or Text in Excel?
- Filter Values based on Two Criteria
- How to Filter Numbers in Excel?
- How to Filter Dates in Excel?
- How to Filter By Color in Excel?
- Quick Way to Filter By A Specific Cell’s Value, Font Color, Cell Color or Icon
- A Solution To – AutoFilter Does Not Work After Changing Data
- Copy and Paste only Filtered Data in Excel
- Copy and Paste Filtered Data Including Header Row
- Copy and Paste Filtered Data Excluding Header Row
- Removing Filter From Headers in Excel
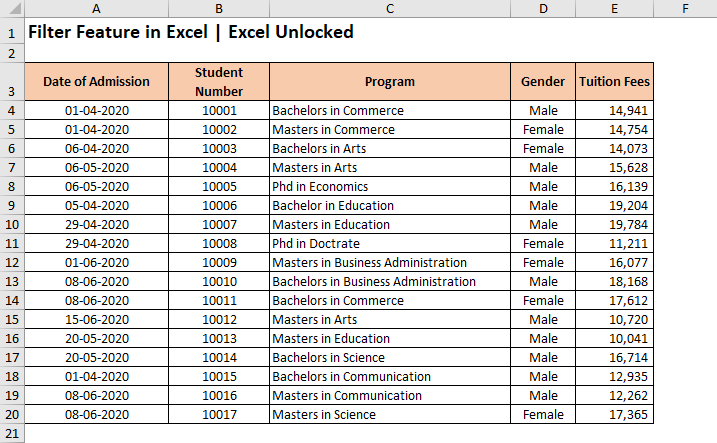
What is the Purpose of Filter Feature in Excel?
The Filter Feature (also known as AutoFilter) is a powerful tool provided by Excel that narrows down the excel data or data in excel tables to show only those data that you want to see by temporarily hiding all other data. In our sample data, for example, we can use this feature to condense the data such that it only shows the programs taken up by the ‘Female‘ applicants.
In a similar way, you can filter by dates, or values or by any other such criteria.
The filters are always added to the headers of the data set. Therefore, it is important that your excel data must contain a header row, with logical headings. In our example, row 3 is the header row with headings describing the column data.
Once your dataset has proper headers, you are now good to insert the AutoFilter on these headers. To add AutoFilter on the header row, click on any of the cells inside the excel data set (like C7) and use any of the below-mentioned ways:
- Go to ‘Home‘ tab > ‘Editing‘ Group > ‘Sort & Filter‘ Option > ‘Filter‘ button.
- Go to ‘Data‘ tab > ‘Sort & Filter‘ group > ‘Filter‘ Button.
- Keyboard Shortcut Method : Ctrl + Shift + L
As soon as you use any of the above methods, the excel would automatically detect the header row inside the table or data set and insert filter buttons on each of the header cells. These are the downward-facing arrows, like the way shown below:
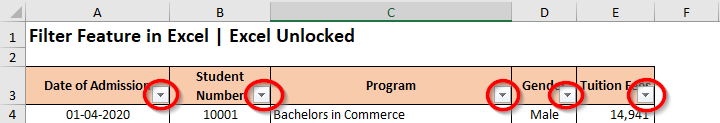
Simple Ways to Filter Your Data Set in Excel
Once the filter option added to the headers, you are good to start filtering your data set.
With this feature, you can filter your data by a single column or by multiple columns.
Applying Filter on Single Column
To apply the filter on a single column, simply click on the filter button (downward-facing arrow) of the respective column. (Let us firstly apply the filter on the column ‘Program Name’). As a result, you would notice that all the checkboxes are checked by default.
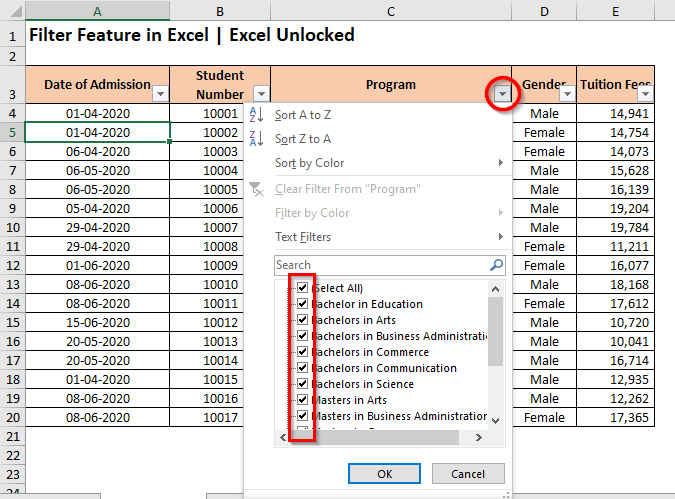
Uncheck the checkbox that says ‘Select All‘. This would remove the check boxes from all the values.
Now, start ticking the values that you wish to view and click on ‘OK’, like the way demonstrated in the below image.
Consequently, the excel would view or show only the selected values in the column, rest all are hidden. Don’t worry excel has not deleted them, they are still there in the backend.
Applying Filter on Multiple Columns
In a similar way, you can apply the filter on other columns in the Excel Data Table. There is no limitation on how many columns to which you can apply the filter.
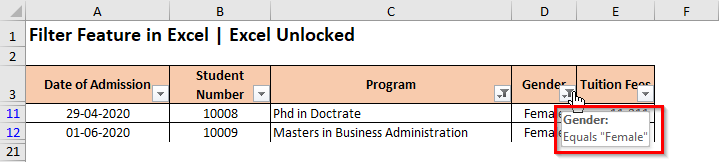
Let us now apply another filter on the column having header – ‘Gender‘.
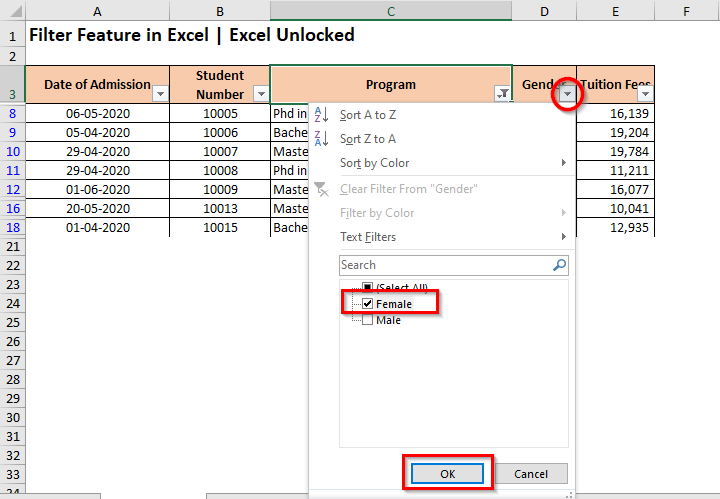
As a result, the excel would now only display the data set rows for selected ‘Program’ and for ‘Female’ candidates. All others are temporarily hidden (not removed).
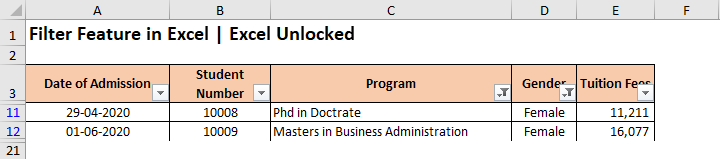
Some Useful Points and Tips
Once a filter is applied on the header row-
- The Downward-facing arrow on the filtered column changes its icon which denotes that there is a filter applied to this column.
- When you take your mouse cursor over the filter button, it shows the filter values.
- To increase or decrease the width of the filter window, take your mouse cursor on the bottom-right corner of the filter window. Once the mouse cursor changes to a two-side facing arrow, click and drag right (to increase) or left (to decrease). See the below demonstration for more clarity.
Filter Data Using Filter Search Box in Excel
In the earlier section, we learned about how to filter your data set by selecting the checkboxes in the Filter window. There is yet another way to filter out a specific text or value or numbers or dates/time in Excel which is by using the ‘Filter’ search box. The Filter search box is placed just above the list of values in the Filter window.
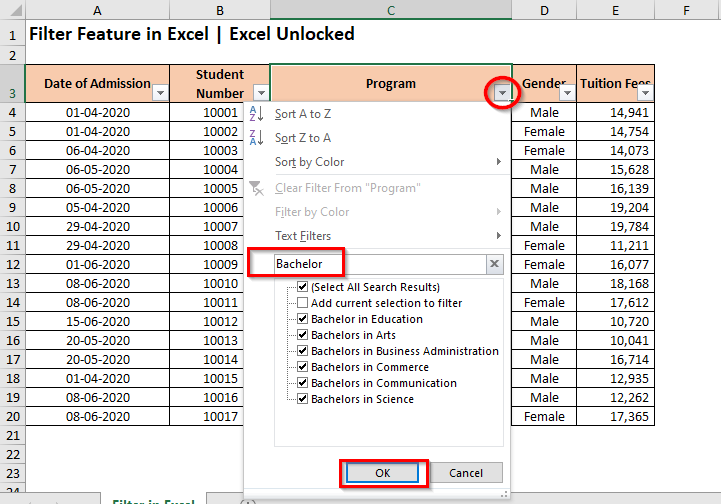
To filter your data set using the ‘Filter’ search box, simply click on the ‘Filter’ drop-down icon on the header and type the search value in the search box. As a result, the excel would narrow down the list to show only the specified values. Finally, click on the ‘OK’ button to apply the filter.
To illustrate with an example, let us filter out the ‘Program’ column with the Bachelor’s degree.
Not sure about the exact text to search, then use wildcard characters in the search box for a non-exact filter search in Excel. If you are unaware of what are wildcard characters in Excel and its usage, then please click here.
Clearing Filter on Columns in Excel
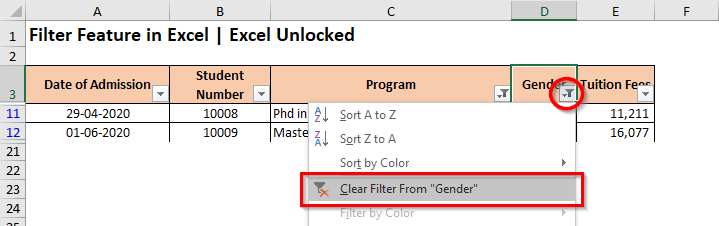
When you want to clear filter from selected or all the header columns in Excel, you can use any of the below-mentioned ways:
- Click on the ‘Filter‘ icon on the header of the column header, and click on the option that says – Clear Filter from <Column Header Name>
- Another way is to click on the ‘Filter‘ icon of the header, and check the checkbox – ‘Select All‘.
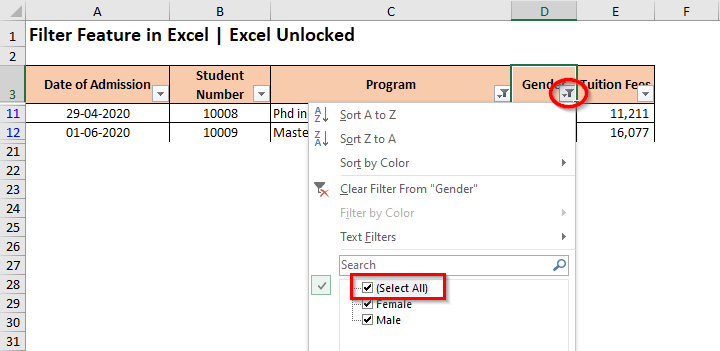
When you clear the filter from the column ‘Gender’, the data set would now only have a filter on the column header ‘Program’. It has only cleared filter from the row ‘Gender’ and has not touched any other filters.
To clear multiple filter from all the headers cells, use any of the following way:
- Click on any of the cells in the dataset and navigate to the path – Data tab > Sort & Filter Group and there click on the option that says – Clear.
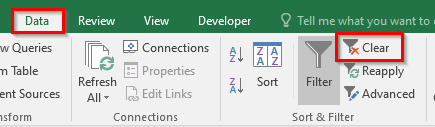
- Or you can even use this – Home Tab > Editing Group. Click the option Sort & Filter > Clear.
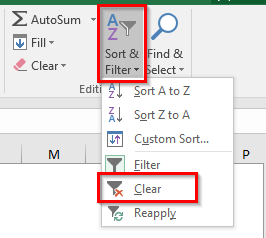
It is important to note that the above method only clears the filter from the header cell. It does not remove the filter icon from the header row. To learn how to remove the filter in Excel, wait until the end of this blog.
How to Filter Values or Text in Excel?
When you are working with text filters, there are many other text filter options available in addition to what we learned above. Below is the list of the same.
- You can filter the values or text which exactly Equals or which Does Not Equal to some text.
- Additionally, you can even filter for a non-exact match by using the Contains and Does Not Contain a text
- Or, you can even filter the values or text that starts or Begins With or Ends With a particular text.
These advanced filter options are available under the ‘Text Filter’ section of the Filter Window as shown in the image below:
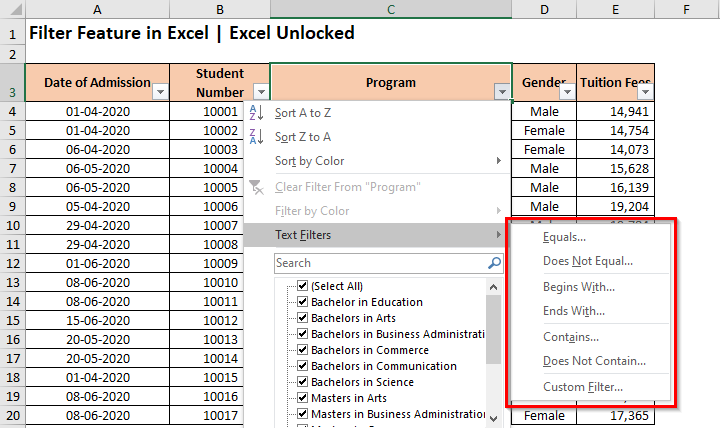
Let us understand this with the help of a small example: Let us, for example, get the program that contains the word ‘Business’ in it. To achieve it,
Click on the ‘Filter‘ icon on the column header – ‘Program’, and take your mouse cursor to the option – Text Filters.
In the list of options that come up, select the option that says – ‘Contains‘. As a result, the ‘Custom AutoFilter‘ dialog box would appear on your screen. In the input box besides the word ‘Contains’, write the text that you want to filter (in our case ‘Business’) and press OK.
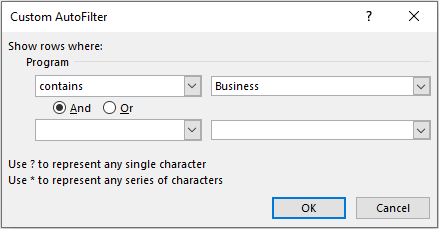
As soon as you press OK, excel would show all the values or text that contains the word ‘Business’ and will hide all other data rows.
Note that, just like Filter search box, this ‘Custom AutoFilter’ dialog box also accepts wildcard character search.
Filter Values based on Two Criteria
The Custom AutoFilter dialog box also allows us to filter out the data rows based on two criteria. Use the And and Or operator radio buttons based on how you wish to filter.
For example: Let us filter out all the programs for Commerce and Science. In this case, as we want both the values, we shall use Or operator, like this-
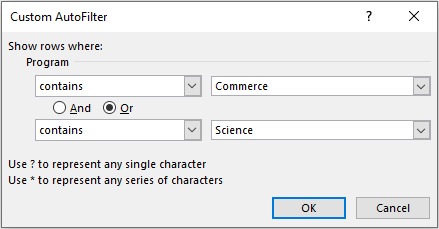
This would filter out those values which either contain the word ‘Commerce‘ or contain the word ‘Science‘.
How to Filter Numbers in Excel?
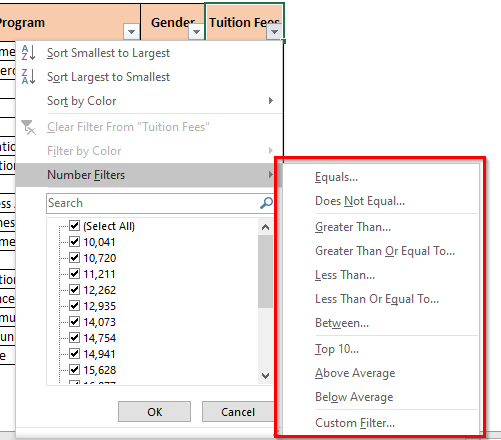
Similar to the text filter learned above, there are many additional filter options available carry Number Filters in Excel. Below is the list of the same:
- You can filter the exact number or amount by using Equals and Does Not Equal option under the ‘Number Filter’.
- Similarly, the Number Filter – Greater Than and Less Than allows us to get all values that are more or less than a specific value.
- Greater Than or Equal To and Less Than or Equal To works in a similar way.
- Between Number Filter allows you to filter out the values lies between two values (lower and upper values both inclusive)
- Other options are – Top 10, Above Average, Below Average
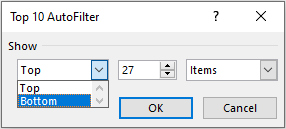
The filter option Top 10 does not exactly only mean Top 10 values. You can change it to any other value like Top 15, or Top 27 Values, and even Bottom 5 values and so on.
How to Filter Dates in Excel?
Unlike the Text and Number Filter, the Dates Filters option allows us with more advanced filtering options. The below image in itself is self-explanatory.
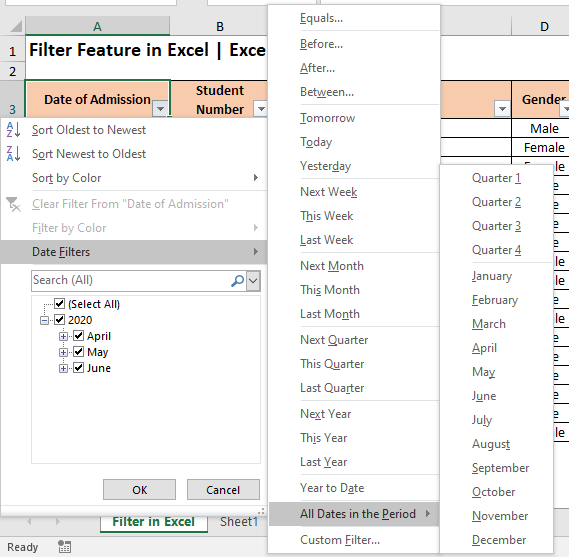
In a nutshell, below options are available for filtering dates in Excel –
- You can filter the dates which fall in the current month/week/quarter/year and even for previous and upcoming (i.e. next) month/week/quarter/year.
- Additionally, you can filter out by an exact date, or date that falls before or after a particular date, or between two dates.
- Excel provides with an option to filter all the dates in a particular month or quarter (regardless of the year in which it falls)
- You can create a custom date filter using the ‘Custom AutoFilter’ dialog box to which you are already aware of using.
Important to notice – Excel by default groups all the dates by year, months, and then the days. You can expand or collapse the groups (year, months, and days) to filter the dates and check/uncheck it to filter accordingly.
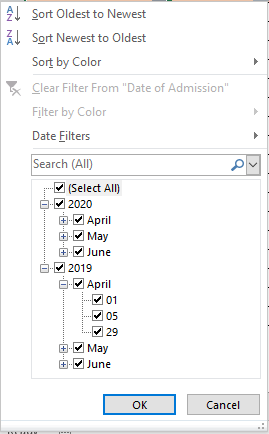
In the above image, you can see that all the dates are grouped by years first (2020 and 2019). Within the years there are months and then the days in the month. If you clear the checkbox for 2020, then the excel would only show the dates that lie in 2019.
How to Filter By Color in Excel?
When the data set contains any text with color or any cell with a background color, you can use the ‘Filter by Color‘ option in the ‘Filter’ Window to filter the dataset by a specific text or cell background color.
Let me explain this with a small example. I am changing the background color of different cells to yellow, orange, and green. Also, I have the font color in a few of the cells as ‘Red’.
To filter the values based on color, simply click on the ‘Filter’ drop-down arrow button on the header cell and take your mouse cursor over the option that says – ‘Filter by Color’.
As a result, you would see that excel lists all the cell and font color. You can choose the color that you want to filter with.

Let us, for example, filter the programs by Red font color. The result of the filter would be as below.
Quick Way to Filter By A Specific Cell’s Value, Font Color, Cell Color or Icon
Instead of using the ‘Filter’ drop-down icon to filter, you can even filter the dataset based on a specific cell’s value, icon, or font and cell color. To do so, follow the undermentioned steps:
- Right-click on the cell that contains the color by which you want to filter. Let us, in this case, filter by yellow color. Therefore, I have right-clicked on C4 (as it has a yellow cell color).
- Take your mouse cursor to the option that says – ‘Filter‘, and click on the option – ‘Filter by Selected Cell’s Color‘.
As a result, excel would filter the dataset based on the cell color – Yellow, as demonstrated in the below image:
A Solution To – AutoFilter Does Not Work After Changing Data
When you make any changes in the filtered data, you would notice that excel does not refresh the filter automatically. Yes, that is absolutely true. You need to reapply the filter in order to refresh the data and apply the filter on the changed data. There are a couple of ways to do the same, as listed below:
- Using Filter Window – After making changes in the filtered data, simply click on the ‘Filter’ drop-down arrow on the header cell and click ‘OK’ in there. However, there is are exceptions to this method. This would not work when you apply ‘filter by color’ or ‘Number Filter/Text Filter/Date Filter’. This technique only applies when you use the search box to filter out the data.
- Using Reapply Option – After making changes in the filtered data, simply navigate to the Data tab > Sort & Filter Group > Reapply Option. The keyboard shortcut key for the same is Ctrl + Alt + L.
This option is also available in the Home Tab > Editing Group > Sort & Filter Option > Reapply.
Copy and Paste only Filtered Data in Excel
There are two possibilities to copy and paste only filtered data in Excel.
Copy and Paste Filtered Data Including Header Row
Simply, click on any of the cell in the filtered area, and press Ctrl + A to select the entire excel table or data set. As a result, you would notice that excel selects the entire table including both data rows as well as the header row. Now, press Ctrl + C to copy the selection and use Ctrl + V at the destination location to paste the filtered data cells.
Copy and Paste Filtered Data Excluding Header Row
To copy and paste only filtered data (without header row), select the top-left cell of the data (which in our case it is C4). Press keyboard keys Ctrl + Shift + Down_Arrow and then press Ctrl + Shift + Right_Arrow (instead you can even use Ctrl + Shift + End). Any of these ways would select the entire data set (excluding headers). Now, use Ctrl + C to copy the selection and then Ctrl + V to paste the filtered data set at the destination cell.
Usually, when you copy the filtered dataset using the above methods, excel does not include the hidden rows in the copy area. The hidden rows are excluded and it only takes the visible rows while copying. However, sometimes when your data is huge, it may not work in expected behavior. In those cases, to play safe, you can use the GoTo (F5) > Special > Visible Cells Only feature to select only the visible rows. The keyboard shortcut for the same is Alt + ; (semi-colon).
Finally, let us now learn how to remove filters from the excel header row. There are multiple ways using which you can remove filters, as listed below-
- The easiest way is to use the keyboard shortcut – Ctrl + Shift + L.
- Another way is to use ribbon path – Data Tab > Sort & Filter Group > Filter option OR Home Tab > Editing Group > Sort & Filter Option > Filter Option.
RELATED POSTS
-
How to Make A Table In Excel – A Hidden Functionality
-
How to Sort a Table or Data in Excel
-
Text and Number Filter in Pivot Table in Excel
-
Group and Ungroup Rows in Excel
-
FILTER Function in Excel – Dynamic Filtered Range
-
Applications – FILTER Function in Excel
Advanced filter in Excel provides more opportunities for managing on data management spreadsheets. It is more complex in settings, but much more effective in action.
Using a standard filter, a Microsoft Excel user can solve not all of the tasks that are set. There is no visual display of the applied filtering conditions. It is not possible to apply more than two selection criteria. You can not filter the duplicate values to leave only unique records. And the criteria themselves are schematic and simple. The functionality of the extended filter is much richer. Let’s take a closer look at its possibilities.
How to make the advanced filter in Excel?
The advanced filter allows you to analysis data on an unlimited set of conditions. With this tool, the user can:
- to specify more than two selection criteria;
- to copy the result of filtering to another sheet;
- to set the condition of any complexity with the helping of formulas;
- to extract the unique values.
The algorithm for applying the extended filter is simple.
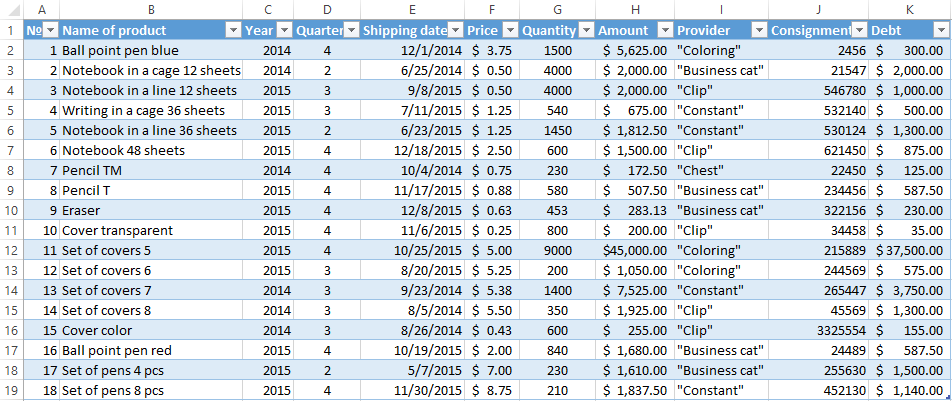
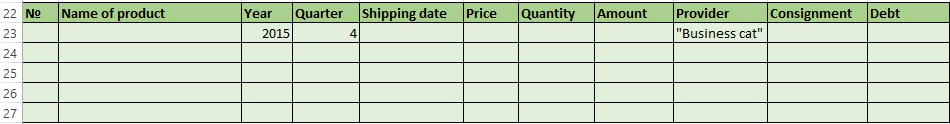
- To make the table with the original data or to open an existing one. Like so:
- To create the condition table. The features: the header line is the same with the «cap» of the filtered table. To avoid errors, need to copy the header line in the source table and paste it on the same sheet (side, top, underarm) or on another sheet. We enter the selection criteria into the condition table.
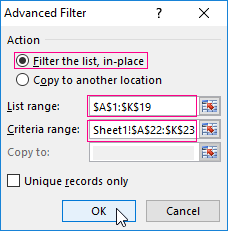
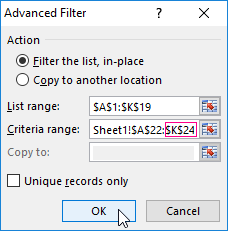
- Go to the «DATA» tab — «Sort and filter» — «Advanced». If the filtered information should be displayed on another sheet (NOT where the source table is), then you need to run the extended filter from another sheet.
- In the «Advanced Filter» window that opens, to select the method of processing information (on the same sheet or on the other one), set the initial range (the table 1, example) and the range of conditions (the table 2, conditions). The header lines must be included in the ranges.
- To close the «Advanced Filter» window, click OK. We see the result.
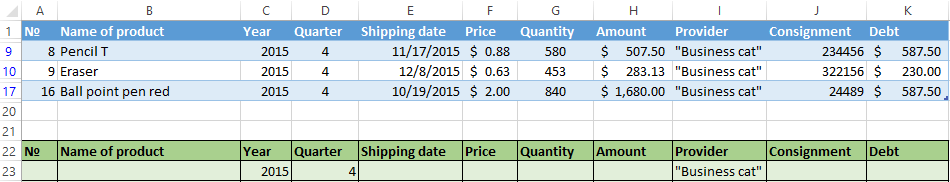
The top table is the result of the filtering. The lower nameplate with the conditions is given for clarity near.
How to use the advanced filter in Excel?
To cancel the action of the advanced filter, we place the cursor anywhere in the table and press Ctrl + Shift + L or «DATA» — «Sort and Filter» — «Clear».
We will find using the «Advanced Filter» tool information on the values that contain the word «Set».
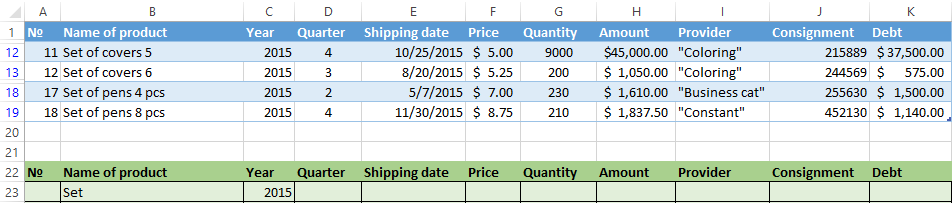
In the table of conditions we bring in the criteria. For example, these are:
The program in this case will search for all information on the goods, in the title of which there is the word «Set».
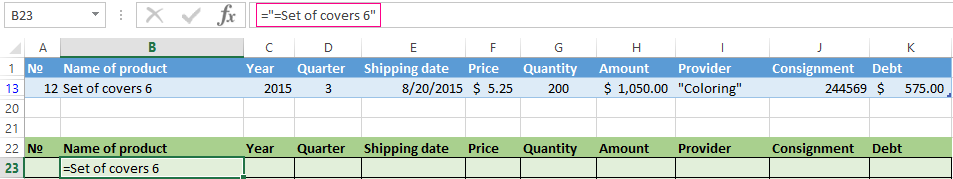
To search for the exact value, you can use the «=» sign. We enter the following criteria in the condition table:
Excel sees the «=» as a signal: the user will set the formula now. In order for the program to work correctly, the following should be written in the formula line: =»=Set of covers 6″.
After using the «Advanced Filter»:
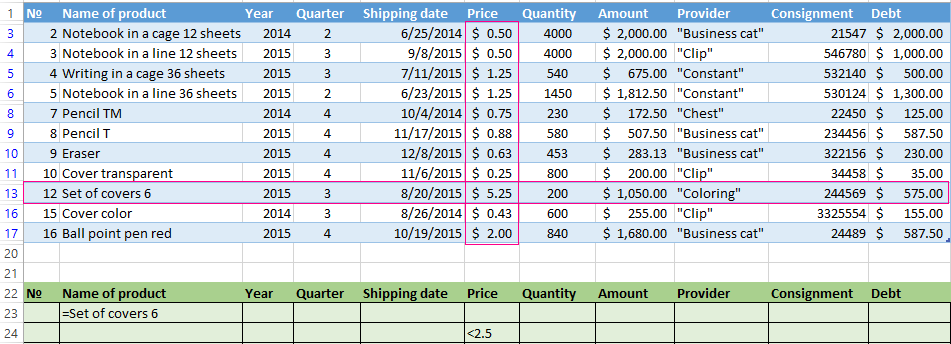
We filter the source table by the condition «OR» for different columns now. The operator «OR» is also in the tool «AutoFilter». But there it can be used within the single column.
In the condition label we introduce the selection criteria: =»=Set of covers 6″. (In the column «Name of product») and = «<2.5$» (in the column «Price»). That is, the program must select those values that contain the EXACTLY information about the good «Set of covers 6 ». OR to the information about the goods, which price is <2.5.
Please note: the criteria must be written under the corresponding headings in the DIFFERENT lines.
The result of selection:
The advanced filter allows you to use as a criterion of a formula. Let’s consider the example.
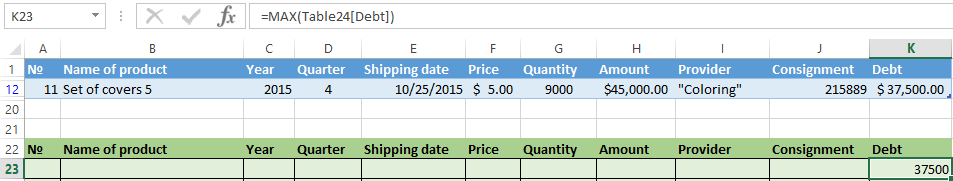
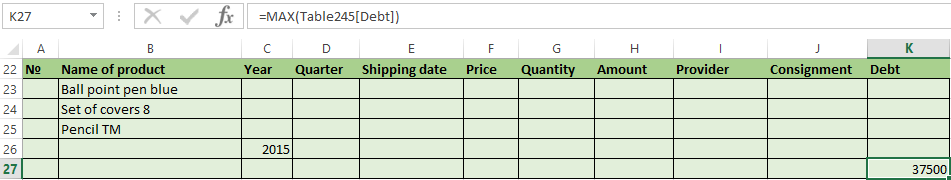
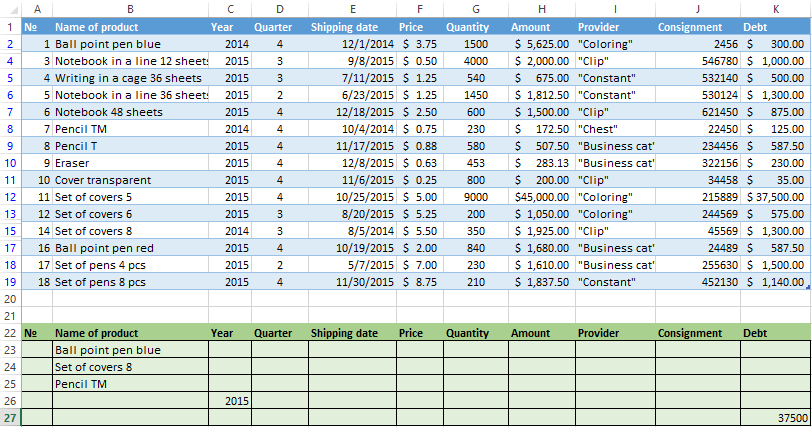
Selection of the line with the maximum indebtedness: =MAX(Table1[Debt]).
So we get the results as after running several filters on the one Excel sheet.
How to make few filters in Excel?
Let’s create the filter by several values. To do this, we enter in the table of conditions several criteria for selecting data:
Apply the tool «Advanced Filter»:
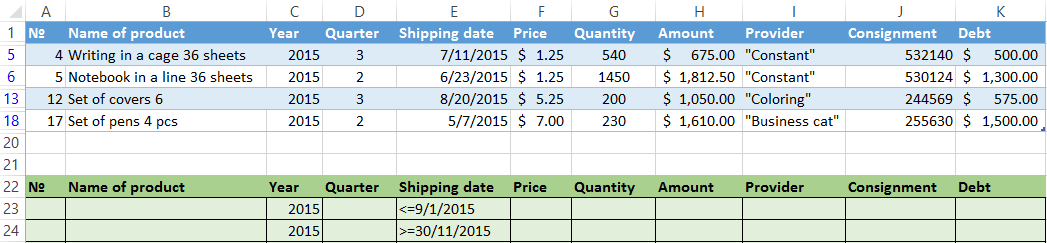
Now from the table with the selected data we will extract new information, which was selected according to other criteria. There are only shipping date for autumn 2015 (from September to November). Example:
We introduce a new criterion in the condition table and apply the filtering tool. The initial range — is the table with data selected according to the previous criterion. This is how the filter is performed across on several columns.
To use few filters, you can create several condition tables on the new sheets. The method of implementation depends from the task which was set by user.
How to make the filter in Excel by lines?
By standard methods — you may not do it by any ways. Microsoft Excel selects data only in columns. Therefore, we need to look for other solutions.
Here are some examples of string criteria for the extended filter in Excel:
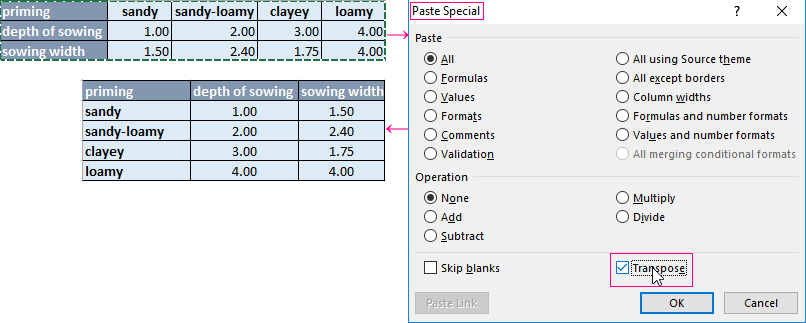
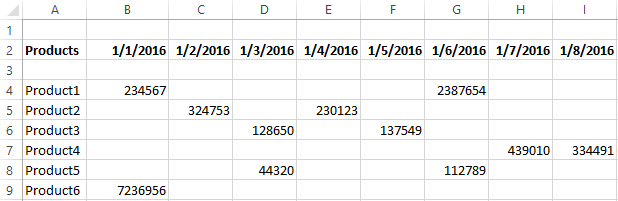
- Convert to the table. For example, from three rows make a list of three columns and apply the filtering to the transformed version.
- Use formulas to display exactly the data in the string that are needed. For example, make some indicator drop-down list. And in the next cell, enter the formula using the IF function. When a certain value is selected from the drop-down list, its parameter appears next to it.
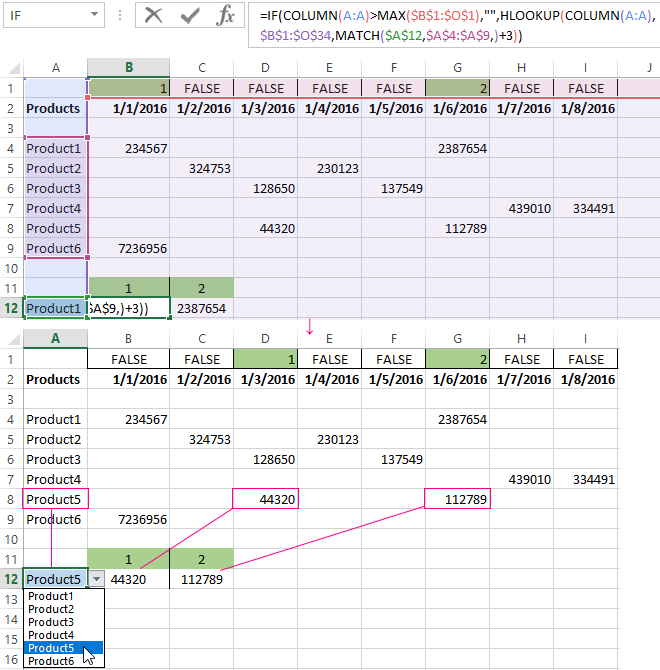
To give an example of how the filter works by rows in Excel, we are creating the label:
For the list of products, we create the drop-down list:
If necessary, learn how to create a drop-down list in Excel.
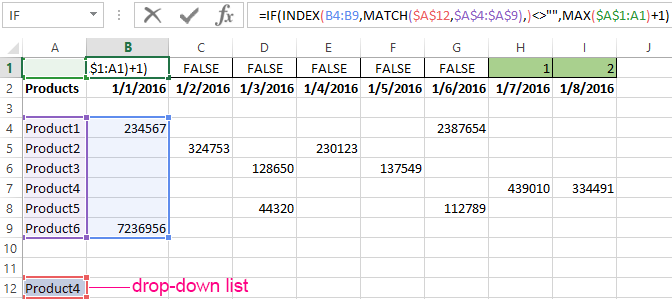
Above the table with the original data, we insert an empty line. In the cells, we introduce the formula that will show which columns the information is taken from.
Next to the drop-down list box, we enter the following formula:
Its task is select from the table those values, that correspond to a certain good.
Download examples of advanced filtering
Thus, using the tool «Drop-down list» and built-in functions Excel selects data in rows according to a certain criterion.


 .
.
 for the column you want to filter.
for the column you want to filter.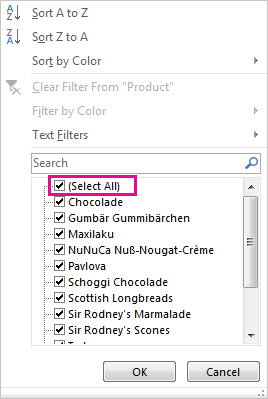
 Filter icon. Select this icon to change or clear the filter.
Filter icon. Select this icon to change or clear the filter.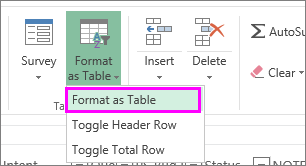

 in the column that contains the content that you want to filter.
in the column that contains the content that you want to filter.
 in the column that contains the content that you want to filter.
in the column that contains the content that you want to filter.