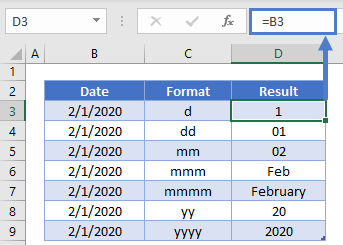
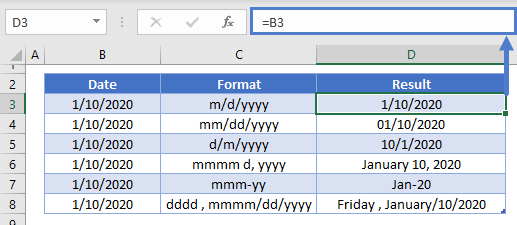
Format a date the way you want
Excel for Microsoft 365 Excel for Microsoft 365 for Mac Excel for the web Excel 2021 Excel 2021 for Mac Excel 2019 Excel 2019 for Mac Excel 2016 Excel 2016 for Mac Excel 2013 Excel 2010 Excel 2007 Excel for Mac 2011 More…Less
When you enter some text into a cell such as «2/2″, Excel assumes that this is a date and formats it according to the default date setting in Control Panel. Excel might format it as «2-Feb». If you change your date setting in Control Panel, the default date format in Excel will change accordingly. If you don’t like the default date format, you can choose another date format in Excel, such as «February 2, 2012″ or «2/2/12″. You can also create your own custom format in Excel desktop.
Follow these steps:
-
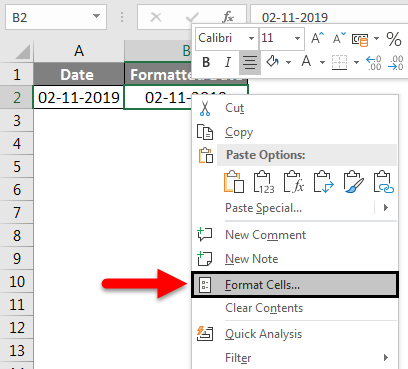
Select the cells you want to format.
-
Press CTRL+1.
-
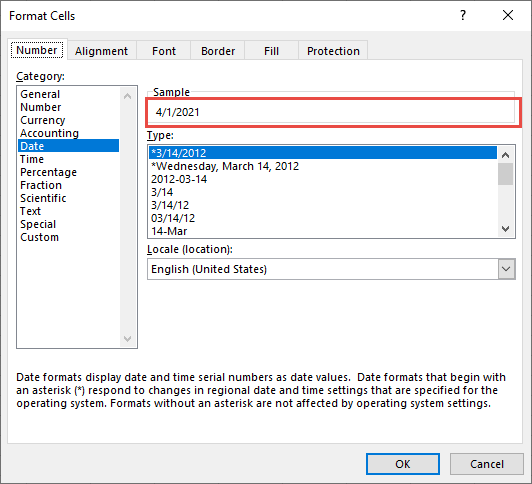
In the Format Cells box, click the Number tab.
-
In the Category list, click Date.
-
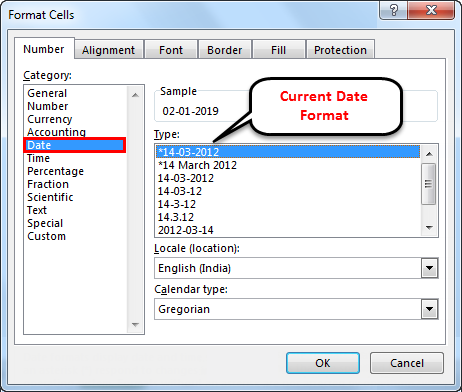
Under Type, pick a date format. Your format will preview in the Sample box with the first date in your data.
Note: Date formats that begin with an asterisk (*) will change if you change the regional date and time settings in Control Panel. Formats without an asterisk won’t change.
-
If you want to use a date format according to how another language displays dates, choose the language in Locale (location).
Tip: Do you have numbers showing up in your cells as #####? It’s likely that your cell isn’t wide enough to show the whole number. Try double-clicking the right border of the column that contains the cells with #####. This will resize the column to fit the number. You can also drag the right border of the column to make it any size you want.
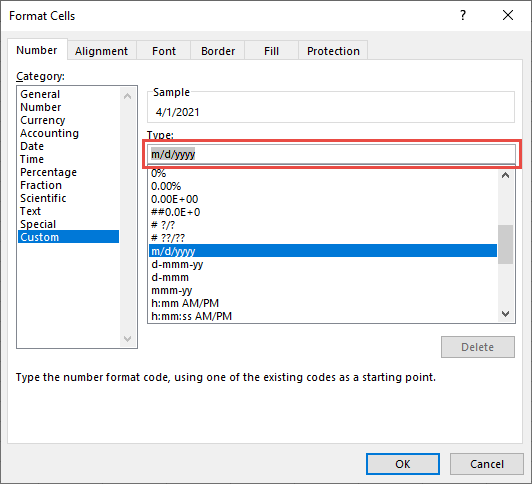
If you want to use a format that isn’t in the Type box, you can create your own. The easiest way to do this is to start from a format this is close to what you want.
-
Select the cells you want to format.
-
Press CTRL+1.
-
In the Format Cells box, click the Number tab.
-
In the Category list, click Date, and then choose a date format you want in Type. You can adjust this format in the last step below.
-
Go back to the Category list, and choose Custom. Under Type, you’ll see the format code for the date format you chose in the previous step. The built-in date format can’t be changed, so don’t worry about messing it up. The changes you make will only apply to the custom format you’re creating.
-
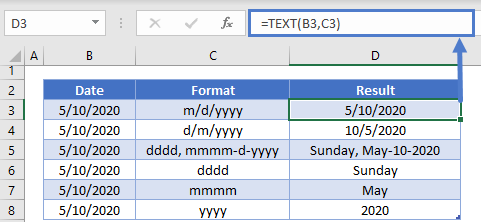
In the Type box, make the changes you want using code from the table below.
|
To display |
Use this code |
|---|---|
|
Months as 1–12 |
m |
|
Months as 01–12 |
mm |
|
Months as Jan–Dec |
mmm |
|
Months as January–December |
mmmm |
|
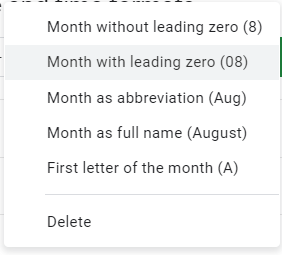
Months as the first letter of the month |
mmmmm |
|
Days as 1–31 |
d |
|
Days as 01–31 |
dd |
|
Days as Sun–Sat |
ddd |
|
Days as Sunday–Saturday |
dddd |
|
Years as 00–99 |
yy |
|
Years as 1900–9999 |
yyyy |
If you’re modifying a format that includes time values, and you use «m» immediately after the «h» or «hh» code or immediately before the «ss» code, Excel displays minutes instead of the month.
-
To quickly use the default date format, click the cell with the date, and then press CTRL+SHIFT+#.
-
If a cell displays ##### after you apply date formatting to it, the cell probably isn’t wide enough to show the whole number. Try double-clicking the right border of the column that contains the cells with #####. This will resize the column to fit the number. You can also drag the right border of the column to make it any size you want.
-
To quickly enter the current date in your worksheet, select any empty cell, press CTRL+; (semicolon), and then press ENTER, if necessary.
-
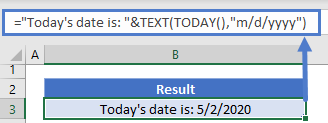
To enter a date that will update to the current date each time you reopen a worksheet or recalculate a formula, type =TODAY() in an empty cell, and then press ENTER.
When you enter some text into a cell such as «2/2″, Excel assumes that this is a date and formats it according to the default date setting in Control Panel. Excel might format it as «2-Feb». If you change your date setting in Control Panel, the default date format in Excel will change accordingly. If you don’t like the default date format, you can choose another date format in Excel, such as «February 2, 2012″ or «2/2/12″. You can also create your own custom format in Excel desktop.
Follow these steps:
-
Select the cells you want to format.
-
Press Control+1 or Command+1.
-
In the Format Cells box, click the Number tab.
-
In the Category list, click Date.
-
Under Type, pick a date format. Your format will preview in the Sample box with the first date in your data.
Note: Date formats that begin with an asterisk (*) will change if you change the regional date and time settings in Control Panel. Formats without an asterisk won’t change.
-
If you want to use a date format according to how another language displays dates, choose the language in Locale (location).
Tip: Do you have numbers showing up in your cells as #####? It’s likely that your cell isn’t wide enough to show the whole number. Try double-clicking the right border of the column that contains the cells with #####. This will resize the column to fit the number. You can also drag the right border of the column to make it any size you want.
If you want to use a format that isn’t in the Type box, you can create your own. The easiest way to do this is to start from a format this is close to what you want.
-
Select the cells you want to format.
-
Press Control+1 or Command+1.
-
In the Format Cells box, click the Number tab.
-
In the Category list, click Date, and then choose a date format you want in Type. You can adjust this format in the last step below.
-
Go back to the Category list, and choose Custom. Under Type, you’ll see the format code for the date format you chose in the previous step. The built-in date format can’t be changed, so don’t worry about messing it up. The changes you make will only apply to the custom format you’re creating.
-
In the Type box, make the changes you want using code from the table below.
|
To display |
Use this code |
|---|---|
|
Months as 1–12 |
m |
|
Months as 01–12 |
mm |
|
Months as Jan–Dec |
mmm |
|
Months as January–December |
mmmm |
|
Months as the first letter of the month |
mmmmm |
|
Days as 1–31 |
d |
|
Days as 01–31 |
dd |
|
Days as Sun–Sat |
ddd |
|
Days as Sunday–Saturday |
dddd |
|
Years as 00–99 |
yy |
|
Years as 1900–9999 |
yyyy |
If you’re modifying a format that includes time values, and you use «m» immediately after the «h» or «hh» code or immediately before the «ss» code, Excel displays minutes instead of the month.
-
To quickly use the default date format, click the cell with the date, and then press CTRL+SHIFT+#.
-
If a cell displays ##### after you apply date formatting to it, the cell probably isn’t wide enough to show the whole number. Try double-clicking the right border of the column that contains the cells with #####. This will resize the column to fit the number. You can also drag the right border of the column to make it any size you want.
-
To quickly enter the current date in your worksheet, select any empty cell, press CTRL+; (semicolon), and then press ENTER, if necessary.
-
To enter a date that will update to the current date each time you reopen a worksheet or recalculate a formula, type =TODAY() in an empty cell, and then press ENTER.
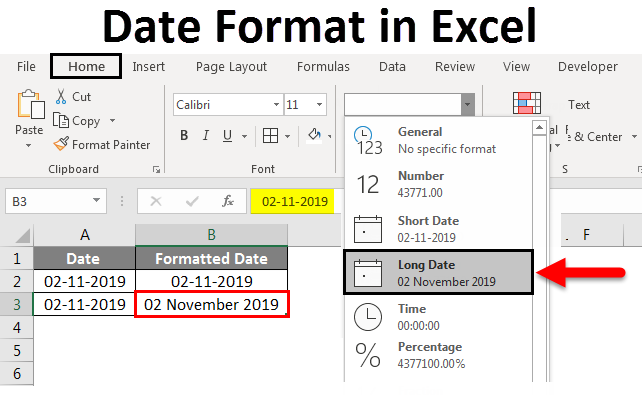
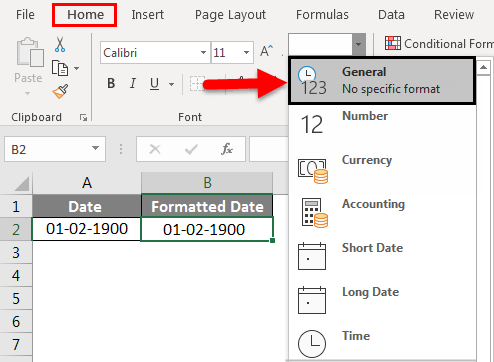
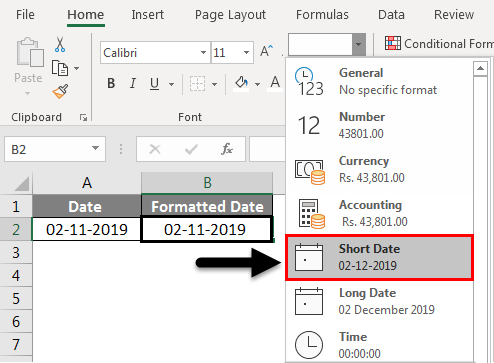
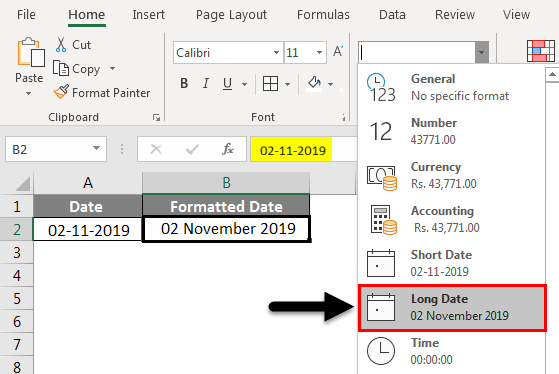
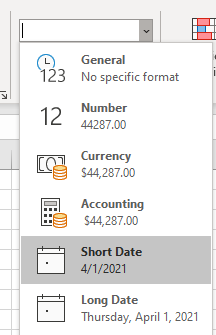
When you type something like 2/2 in a cell, Excel for the web thinks you’re typing a date and shows it as 2-Feb. But you can change the date to be shorter or longer.
To see a short date like 2/2/2013, select the cell, and then click Home > Number Format > Short Date. For a longer date like Saturday, February 02, 2013, pick Long Date instead.
-
If a cell displays ##### after you apply date formatting to it, the cell probably isn’t wide enough to show the whole number. Try dragging the column that contains the cells with #####. This will resize the column to fit the number.
-
To enter a date that will update to the current date each time you reopen a worksheet or recalculate a formula, type =TODAY() in an empty cell, and then press ENTER.
Need more help?
You can always ask an expert in the Excel Tech Community or get support in the Answers community.
Need more help?
What is a date in Excel?
A date is a number! And like any number (currency, percentage, decimal, …), you can customize your date format 👍
Dates are whole numbers
Usually, when you insert a date in a cell it is displayed in the format dd/mm/yyyy or mm/dd/yyyy.
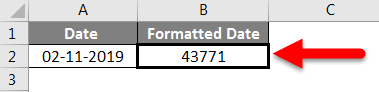
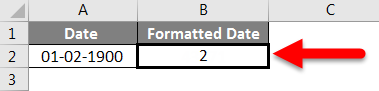
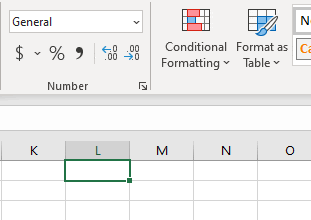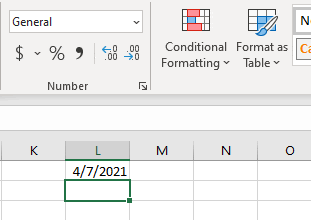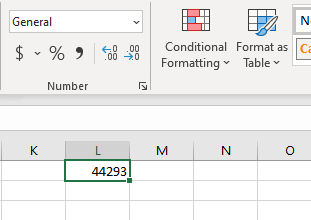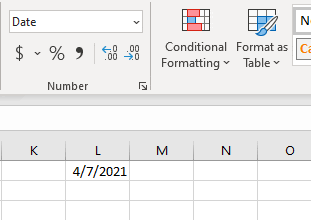
Let’s say you have the date 01/01/2016 in a cell. If you change the cell’s format to Standard, the cell displays 42370 😕🤔
Explanation of the numbering
In Excel, a date is the number of days since 01/01/1900 (the first date in Excel).
So 42370 is the number of days between 01/01/1900 and 01/01/2016.
Date format
Dates can be displayed in different ways using the following 2 options (available in the Number Format dropdown in the main menu):
- Short Date
- Long Date
How to customize a date?
To customize a date:
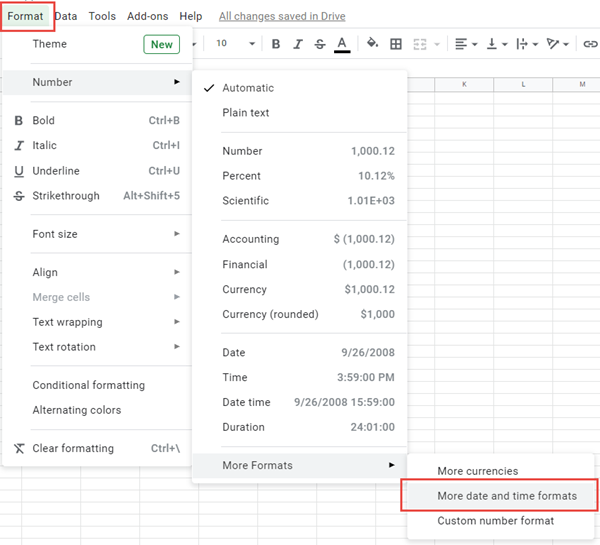
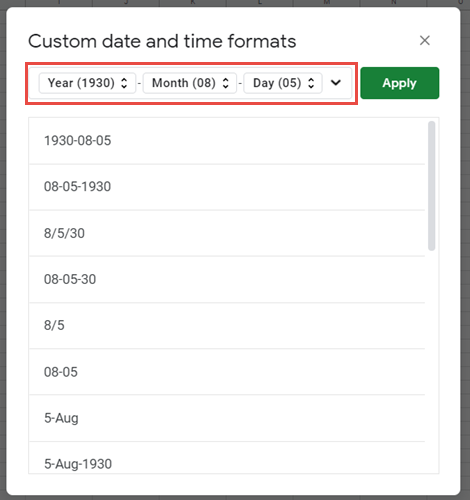
- Open the dialog box Custom Number (with the shortcut Ctrl + 1 or by clicking on the menu More number formats at the bottom of the number format dropdown)
- In this dialog box, you select ‘Custom‘ in the Category list and write the date format code in ‘Type‘.
To format a date, you just write the parameter d, m or y a different number of times. For example,
- dd/mm/yyyy will display 01/01/2016
- dd mmm yyyy => 01 Jan 2016
- mmmm yyyy => January 2016
- dddd dd => Friday 01
In function of your language , the letter could be different:
- t for «tag» (day) in German
- j for «jour» (day) in French
- a for «año» (year) in Spanish
Don’t write text in your cell !!!
With dates, one of the most common mistakes is to write text inside the format code (1 January 2016 for example). Never do this in Excel ⛔⛔⛔
If you do this, the contents of the cell will be Text and not a number
- In Excel, text is always displayed on the left of a cell.
- A number or a date is displayed on the right.
If you want to display the month in letters, just change the month format of your date.
Different examples of custom date
The following document shows you the same date but in different formats. The code for each date is in column A.
Different writing of dates according to the format code
In the following document, you can see the impact of each format on the same date.
In this guide, we’ll learn how to change date format in Excel. Date and Time data is an integral part of any statistical document or sheet. It is important to accurately track and analyze events, sales, figures, and others.
By convention, Excel uses a general data format that may be as per your need. But in most cases, that format may need to be customized.
Changing the format of Date in a particular cell or all the cells in your Excel sheet is an easy process and doesn’t require any complex methodologies. Excel provides a wide range of formatting options based on Location and Languages which helps in better date formatting in native language and style. Also, For some Languages there is also features to select from different Calendar types.
Follow the below step-by-step tutorial to change date format in Excel quickly and easily.
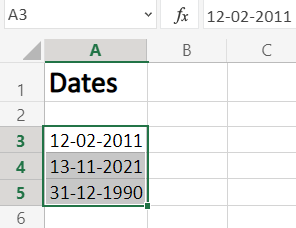
Step 1. Select the range of cells containing the date
To start with, select the cell values where want to change the date format, as shown in the image below.
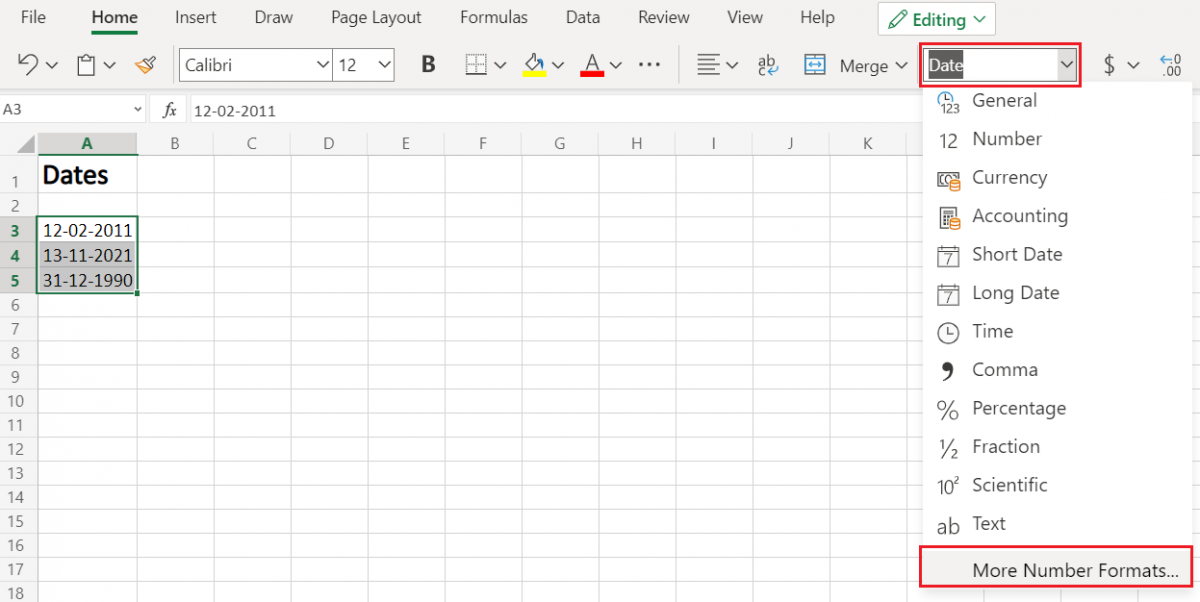
Step 2. Go to Number Format dropdown
- To select ‘Number Format’, go to ‘Home‘ in the option menu and look for Number Format, as shown below
- Then from the drop-down menu, select ‘More Number Formats‘ to reveal the ‘Number Format’ dialogue menu.
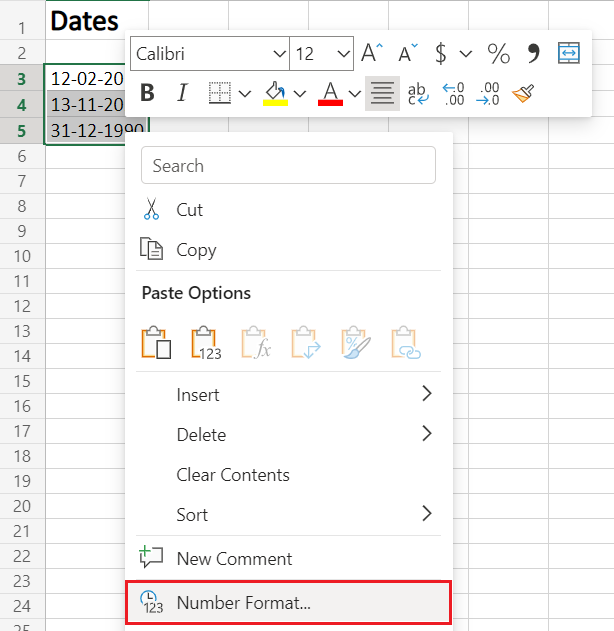
- Alternatively, you may directly go to Number Format, by right-clicking on the selected cell/s
- Click on ‘Number Format’.
Step 3. Choose Date
- From the Category menu on the right, choose ‘Date‘.
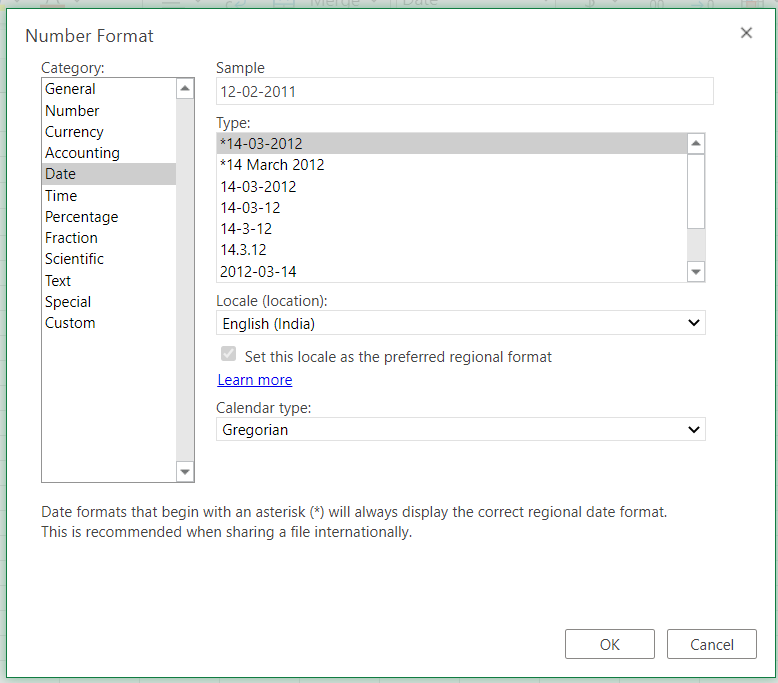
Now, to apply any date formatting type, select it from the right panel of the pop-up menu of Number Format. Click on ‘OK‘ to apply the formatting to the selected cell/s.
Note: You may check the date format implementation in the ‘Sample‘ at the top of the menu option
Choose the Date Type
The general option type to choose from a variety of Date Formatting options. Scroll down in this section to reveal a plethora of options for formatting, ranging from date, text (month name), year, and others.
This option can be perceived as the display menu, as the formatting options in this will keep on changing as per the selection in Locale(Location) and Calendar type.
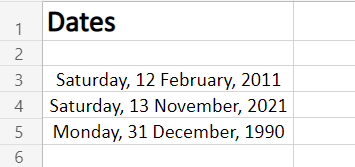
Choose the Locale (location)
This option features the Location or Language options to help format the date accordingly. This option is probably the most used option as users require to format the date according to their or audience preference as per the native formatting style, based on language and location.
Choose any language or Location from this options menu. After selecting, all the supported date format options available for that particular locale will be available for selecting in the above Type menu.
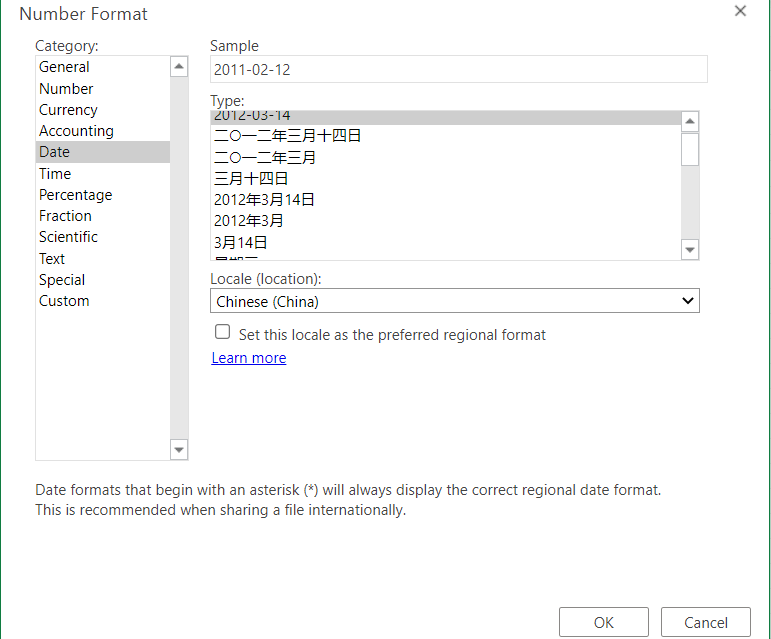
Choose the type of calendar
This option reveals different calendar types available based on the Locale(Location) selected from the above option menu. This formatting option is only available for certain Locale and not all.
As shown in our example below, the variety of calendar types available for selection are only available for the Locale (location) selected (here, Arabia), for other locales the calendar type might be different or not at all present.
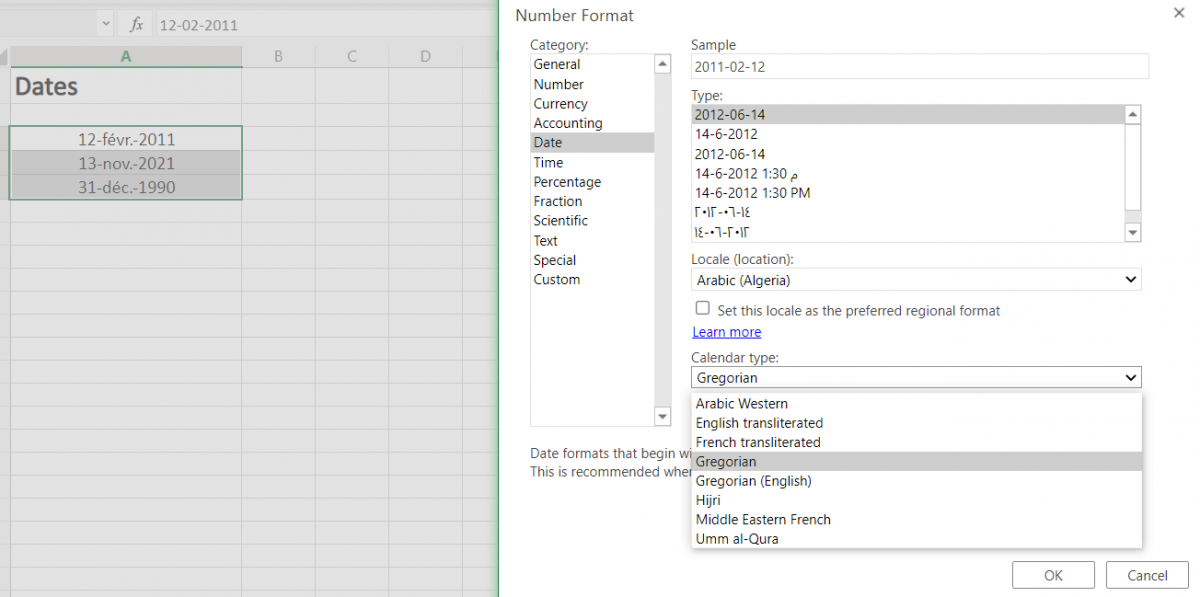
To apply selected formatting, you will need to click ‘OK‘ after selection to apply to your dates.
Conclusion
That’s It! You can now easily convert your dates to your desired format style easily.
We hope you learned and enjoyed this lesson and we’ll be back soon with another awesome Excel tutorial at QuickExcel!
What is the Date Format in Excel?
In Excel, a date is displayed according to the format selected by the user. One can choose from the different formats available or create a customized format according to the requirement. The default date format is specified in the “Control Panel” of the system. However, it is possible to change these default settings.
For example, the date 01/01/2021 corresponds to the format dd/mm/yyyy. If the format is changed to d-mmm-yyyy, the date becomes 1-Jan-2021.
We can change the date format in Excel either from the “Number Format” of the “Home” tab or the “Format Cells” option of the context menu.
In Excel for Windows, 1900 is the default date system. Whereas, in Excel for Mac, 1904 is the default date system. Both these systems store the dates as consecutive numbers having a difference of 1. These numbers are known as serial values or serial numbers. The reason dates are stored as serial numbers is to facilitate calculations.
In the 1900 date system, the first date that Excel recognizes is January 1, 1900. This date is stored as the number 1 in Excel. Consequently, the number 2 represents January 2, 1900. The last date recognized by Excel is December 31, 9999. It is represented by the serial number 2958465. Date before 1900 or after 9999 is identified as a text value by Excel.
Dates are stored only as positive integers in the 1900 date system. However, to display negative numbers as negative dates, one needs to switch to the 1904 date system.
In the 1904 date system, 0 represents January 1, 1904, and -1 means January -2, 1904. The number 1 represents January 2, 1904. The last date recognized by Excel (in the 1904 date system) is December 31, 9999, represented by the serial number 2957003.
In this article, we follow the 1900 date system.
Table of contents
- What is theDate Format in Excel?
- Code of Date Format in Excel
- How to Change Date Format in Excel?
- Example #1–Apply Default Format of Long Date in Excel
- Example #2–Change the Date Excel Format Using “Custom” Option
- Example #3–Apply Different Types of Customized Date Formats in Excel
- Example #4–Convert Text Values Representing Dates to Actual Dates
- Example #5–Change the Date Format Using “Find and Replace” Box
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Recommended Articles
Code of Date Format in Excel
A code (like dd-mm-yyyy) is a representation of a day (d), month (m), and year (y). We can change the appearance of the date by changing the specified code.
The different codes, their explanation, and output (for days, months, and years) have been presented in the following images.
Notations for a Day
Notations for a Month
Notations for a Year
How to Change Date Format in Excel?
Here we look at some of the date format examples in Excel and how to change them.
Example #1–Apply Default Format of Long Date in Excel
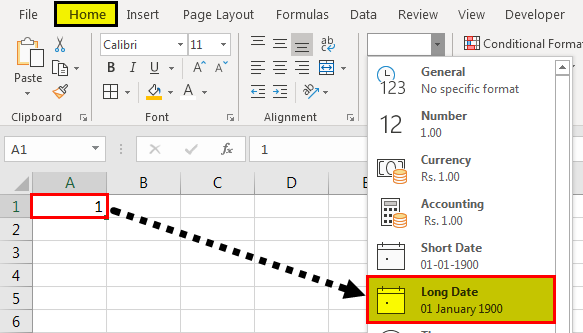
The following image shows a number in cell A1. We want to know the date represented by this number. The output should be in the long date format of Excel.
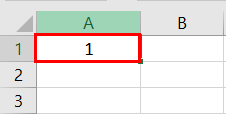
The steps to know the date represented by the number in cell A1 are listed as follows:
- We must first select cell A1. Then, from the “Home” tab, click the “Number Format” drop-down appearing in the “Number” section. Next, select “Long Date,” shown in the following image.
- The output is shown in the following image. The long date format displayed is dd mmmm yyyy. Hence, the number 1 represents the date 01 January 1900 in the long date format.
Note: The short and long dates appear as set in the “Control Panel.” Click “Clock, Language, and Region” in the “Control Panel” to change these default date formats. After that, click “Change date, time, or number formats.” Make the desired changes and click “OK.”Likewise, had there been 2 in cell A1, the long date format would have been 02 January 1900. The number 3 would have been displayed as 03 January 1900 in the long date format.
Note: To switch to the 1904 date system, we must select “Advanced” from the “Options” of the “File” tab. Under “When calculating this workbook,” select “use 1904 date system” and click “OK.”
You can download this Change Date Format Excel Template here – Change Date Format Excel Template
Example #2–Change the Date Excel Format Using “Custom” Option
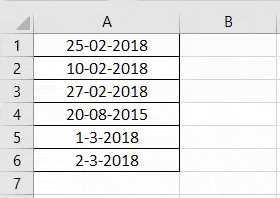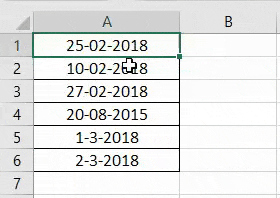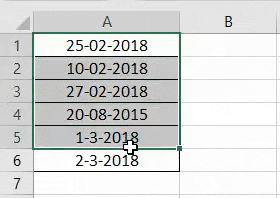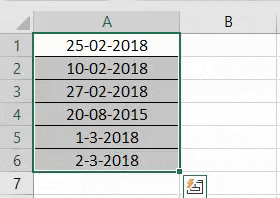
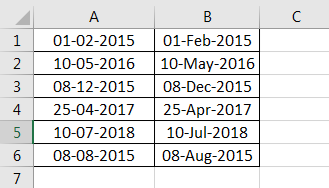
The following image shows some dates in the range A1:A6. These dates are in the format dd-mm-yyyy. We want to change their format to dd-mmmm-yyyy.
For instance, the date in cell A1 should appear as 25-February-2018. We may use the “Custom” option of the “Format Cells” dialog box.
The steps to change the date format in Excel are listed as follows:
Step 1: We need to select all the dates of the range A1:A6. The same is shown in the following image.
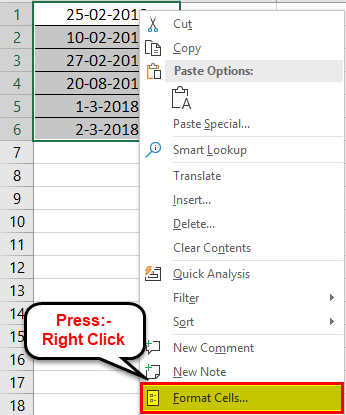
Step 2: We must right-click the selection and choose “Format Cells” from the context menu. Alternatively, we may also press the keys “Ctrl+1” together.
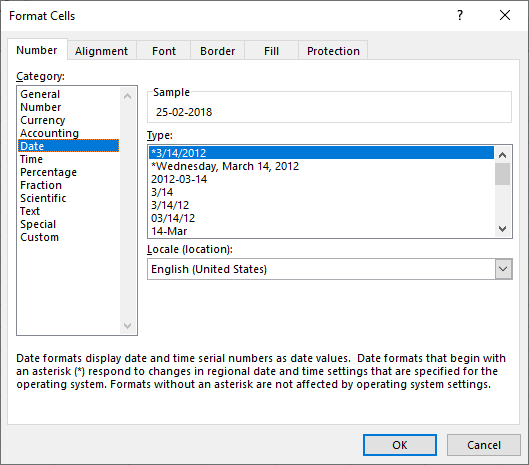
Step 3: The “Format Cells” window opens, as shown in the following image.
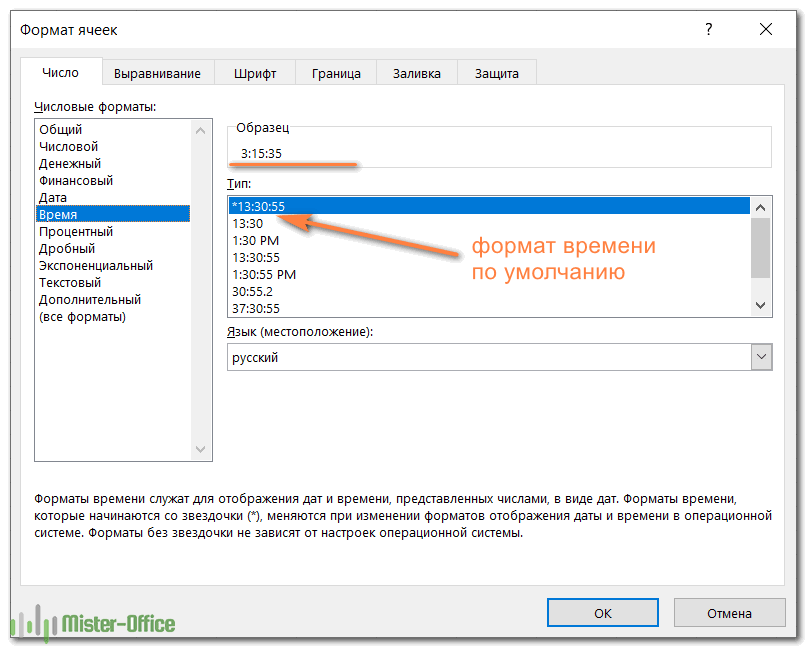
Note: The default short date and long date formats are marked with an asterisk (*) in the box under “type.” The short date is 3/14/2012 (m/dd/yyyy), and the long date is Wednesday, March 14, 2012 (dddd, mmmm dd, yyyy).
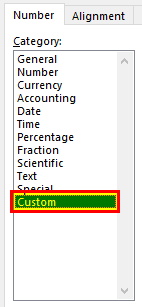
Step 4: From the “Number” tab, we need to select “Custom” under “Category.” The categories are shown on the left side of the “Format Cells” window.
Step 5: Under “Type,” we must insert the required date format. Either type the format (dd-mmmm-yyyy) or select it from the various options displayed in the box below “Type.”
Once the format has been entered, check the preview of the first date (of the range A1:A6) under “Sample.” The same is shown in the following image. Click “OK” in the “Format Cells” window if the date preview looks good.
Note 1: The date under “Sample” is displayed according to the format specified under “Type.”
Note 2: While creating custom date formats, we can use a forward slash (/), hyphen (-), comma (,), space ( ), etc.
Step 6: The output is shown in the following image. All dates of the range A1:A6 have been converted to the format dd-mmmm-yyyy. However, the Excel formula bar can still see the default date format. This default format corresponds with the short date set in the “Control Panel.”
Example #3–Apply Different Types of Customized Date Formats in Excel
The next image shows certain dates in the range A1:A6. At present, the date format is dd-mm-yyyy.
We want to apply four different formats to these dates. For using each format, the common steps to be performed are given as follows:
- First, we must select the range A1:A6.
- Then, right-click the selection and choose “Format Cells.”
- After that, from the “Number” tab, select “Custom” under “Category.”
Further, under each format, the additional steps to be performed followed by two images are given.
Format 1: dd-mmm-yyyy
- In the “Custom” option of the “Number” tab, select the format “dd-mmm-yyyy” under “Type.”
- Click “Ok.”
The output is given in the following image. All dates are displayed according to the format dd-mmm-yyyy. The hyphen is the separator between the day, month, and year in this format.
Format 2: dd mmm yyyy
- We must select the format “dd mmm yyyy” under “Type” of the “custom” option.
- Click “Ok.”
The output is given in the following image. All dates are converted to the format dd mmm yyyy. The space is the only separator between the day, month, and year in this format.
Format 3: ddd mmm yyyy
- In the “Custom” option, select the format “ddd mmm yyyy” under “Type.”
- Click “Ok.”
The output is given in the following image. The dates are shown in the format ddd mmm yyyy. The day and the month are displayed in their short notations in this format.
Format 4: dddd mmmm yyyy
- From the “Custom” option of the “Number” tab, select “dddd mmmm yyyy” under “Type.”
- Click “Ok.”
The output is given in the following image. All dates have been converted to the format dddd mmmm yyyy. The date, month, and year are displayed in their respective full forms in this format.
It must be observed that the date format changes as per the style set by the user. Therefore, the user can select a date format according to their convenience.
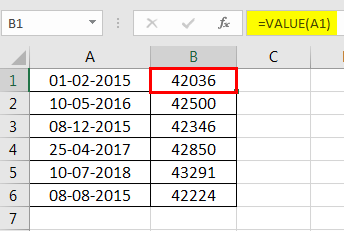
Example #4–Convert Text Values Representing Dates to Actual Dates
The following image shows a list of dates in the range A1:A6. At present, these dates are appearing as text values. We want to convert these text values to dates having the format dd-mmm-yyyy.
The steps to convert text values to dates having the given format are listed as follows:
Step 1: First, enter the following formula in cell B1.
“=VALUE(A1)”
Then, press the “Enter” key.
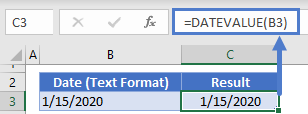
Note 1: The VALUE functionIn Excel, the value function returns the value of a text representing a number. So, if we have a text with the value $5, we can use the value formula to get 5 as a result, so this function gives us the numerical value represented by a text.read more returns the numeric form of a text string that represents a number. In other words, it converts a number looking like the text into an actual number.
Note 2: Instead of the VALUE function, one can also use the DATEVALUE functionThe DATEVALUE function in Excel shows any given date in absolute format. This function takes an argument in the form of date text normally not represented by Excel as a date and converts it into a format that Excel can recognize as a date.read more of Excel. The latter converts a date stored as text to a serial number. This serial number is recognized as a date by Excel.
Step 2: We must select cell B1 and drag the fill handle until cell B6. The output is shown in the following image. All text values (A1:A6) have been converted to numbers (in the range B1:B6).
Ideally, the text string in Excel is left-aligned while the number string is right-aligned. However, we have centrally aligned both the ranges (A1:A6 and B1:B6).
Note: When text strings representing dates have been converted to serial values (or dates), we can use them for performing different calculations like addition, subtraction, and so on.
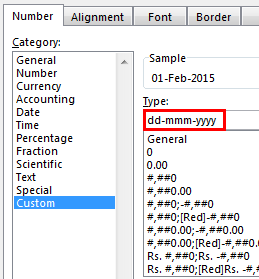
Step 3: To view the obtained serial numbers (in column B) as dates, apply the required format. We must select the range B1:B6, right-click and choose “Format Cells.”
In the “Number” tab, select the option “Custom.” Then, under “Type,” enter or choose the format “dd-mmm-yyyy.” The same is shown in the following image.
If the sample date looks alright, click “OK.”
Step 4: The output is shown in the following image. Hence, all text values (of column A) have been converted to valid dates (in column B) having the format dd-mmm-yyyy.
Note: To ensure that a value is recognized as a date by Excel, check for the following signs:
- The dates are right-aligned as they are numerical values.
- If two or more dates are selected, the status bar (at the bottom of the worksheet) shows the count, average, numerical count, and sum. In addition, it may display one or more options according to the Excel version.
If a value is a text string, it would be left-aligned, and the status bar will show only the count.
Often, the Excel date format needs to be changed (from text to dates) when data is downloaded (or copied and pasted) from the web. That is because, in such instances, the dates may not be displayed as numbers.
Example #5–Change the Date Format Using “Find and Replace” Box
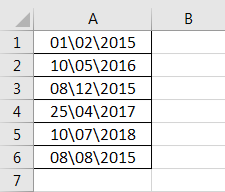
The following image shows some text values representing dates in the range A1:A6. The days, months, and numbers have been separated with a backslash. That is because we want to perform the following tasks:
- Replace all the backslashes () with forwarding slashes (/) by using the “Find and Replace” dialog box.
- Convert text values representing dates to actual dates.
The steps to perform the given tasks are listed as follows:
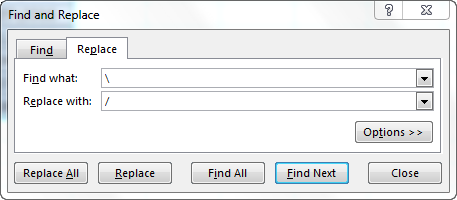
Step 1: We must press the keys “Ctrl+H” together. Then, the “find and replace” dialog box opens, as shown in the following image.
Step 2: Type a backslash in the “Find what” box (). In the “Replace with” box, type a forward slash (/).
Step 3: Next, we must click “Replace All.” Excel shows a message stating the number of replacements it has made. Click “OK” to proceed. The final output is shown in the following image.
Hence, all backslashes have been replaced with forwarding slashes. With this replacement, the text values representing dates have automatically been converted to actual dates by Excel.
Since column A was aligned centrally from the beginning, this alignment is retained even after the values are converted to dates.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How can the date format in Excel be changed?
The steps to change the date format in Excel are listed as follows:
The steps to change the date format in Excel are listed as follows:
a. Select the cell containing the date. If the date format of a range needs to be changed, select the entire range.
b. Right-click the selection and choose “Format Cells” from the context menu. Alternatively, press the keys “Ctrl+1” together.
c. IIn the “Number” tab, select the option “Date.” Next, select the required date format under “Type.”
d. Check the preview (of the first date of the selected range) under “Sample.” If the preview is good, click “OK.”
The date format of the selected cell or cells (selected in step a) is changed.
Note 1: The required date format may not be available under the “Date” option’s “Type.” If it is not available, select “Custom” as the “category” from the “Number” tab. Then, type the required date format under “Type” and click “OK.”
Note 2: If the selected cell (selected in step a) contains a text string representing a date, convert this string to date first. Then change the format to the desired date format.
2. How to change the date format permanently in Excel?
To change a date format permanently, one needs to make changes to the date formats of the “Control Panel.” That is because the short and long date formats of Excel reflect the date settings of the “Control Panel.”
The steps to change the date settings of the “Control Panel” are listed as follows:
We must open the “Control Panel” first from the “Start” menu.
b. In the “Clock, Language, and Region” category, click “Change date, time, or number format.” It is available under the “Region and Language” option.
c. The “Region and Language” or “Region” dialog box opens. Under “Format,” we must select the region.
d. Enter the required short and long date formats under “Date and Time Formats.” To enter customized short and long date formats, click “Additional Settings.” The “Customize Format” dialog box opens. Make the changes in the “Date” tab and click “OK.”
e. Check the preview under “Examples” at the bottom of the “Region and Language” box. If the preview is alright, click “OK.”
The default date settings have been changed. Now, we should enter a date in any format in Excel. Then select the short or the long date format from the “Number Format” (in the “Number” section) of the “Home” tab.
The dates will appear in the format set in the “Control Panel.” So, the user need not change the format of each date manually.
3. How to change a date to a text string in Excel?
Let us change the date 22/1/2019 in cell A1 to a text string in Excel. The text string should be in the format yyyy-mm-dd.
The steps to change a date to a text string are listed as follows:
a. First, we must enter the formula =TEXT(A1, “yyyy-mm-dd”) in cell B1.
b. Then, press the “Enter” key.
The date in cell A1 (22/1/2019) is converted to 2019-01-22 in cell B1. We must note that the date in cell A1 is right-aligned, being a number. In contrast, the text in cell B1 is left-aligned.
Note: The TEXT function helps convert numbers to text strings. It is used to display values in a specific format. The syntax is TEXT(value,format_text). “Value” is the number to be converted to text. “Format_text” is the format in which the number should be displayed.
Recommended Articles
This article has been a guide to the Date Format in Excel. We discuss changing and customizing date formats in Excel, practical examples, and a downloadable Excel template. You may also look at these useful functions in Excel: –
- Concatenate Columns in Excel
- Convert Date to Text in Excel
- Insert Date in Excel
- Concatenate Date in Excel
Skip to content
Это руководство посвящено форматированию даты в Excel и объясняет, как установить вид даты и времени по умолчанию, как изменить их формат и создать собственный.
Помимо чисел, наиболее распространенными типами данных, которые используются в Excel, являются дата и время. Однако работать с ними может быть довольно сложно:
- Одна и та же дата может отображаться различными способами,
- Excel всегда хранит дату в одном и том же виде, независимо от того, как вы оформили её представление.
Более глубокое знание форматов временных показателей поможет вам сэкономить массу времени. И это как раз цель нашего подробного руководства. Мы сосредоточимся на следующих моментах:
- Что такое формат даты
- Формат даты по умолчанию
- Как поменять формат даты
- Как изменить язык даты
- Создание собственного формата отображения даты
- Дата в числовом формате
- Формат времени
- Время в числовом формате
- Создание пользовательского формата времени
- Формат Дата — Время
- Почему не работает? Проблемы и их решение.
Формат даты в Excel
Прежде всего нужно чётко уяснить, как Microsoft Excel хранит дату и время. Часто это – основной источник путаницы. Хотя вы ожидаете, что он запоминает день, месяц и год, но это работает не так …
Excel хранит даты как последовательные числа, и только форматирование ячейки приводит к тому, что число отображается как дата, как время или и то, и другое вместе.
Дата в Excel
Все даты хранятся в виде целых чисел, обозначающих количество дней с 1 января 1900 г. (записывается как 1) до 31 декабря 9999 г. (сохраняется как 2958465).
В этой системе:
- 2 — 2 января 1900 г.
- 44197 — 1 января 2021 г. (потому что это 44 197 дней после 1 января 1900 г.)
Время в Excel
Время хранится в виде десятичных дробей от 0,0 до 0,99999, которые представляют собой долю дня, где 0,0 — 00:00:00, а 0,99999 — 23:59:59.
Например:
- 0.25 — 06:00
- 0.5 — 12:00.
- 0.541655093 это 12:59:59.
Дата и время в Excel
Дата и время хранятся в виде десятичных чисел, состоящих из целого числа, представляющего день, месяц и год, и десятичной части, представляющей время.
Например: 44197.5 — 1 января 2021 г., 12:00.
Формат даты по умолчанию в Excel и как его быстро изменить
Краткий и длинный форматы даты, которые как раз и установлены по умолчанию как основные, извлекаются из региональных настроек Windows. Они отмечены звездочкой (*) в диалоговом окне:
Они изменяются, как только вы меняете настройки даты и времени в панели управления Windows.
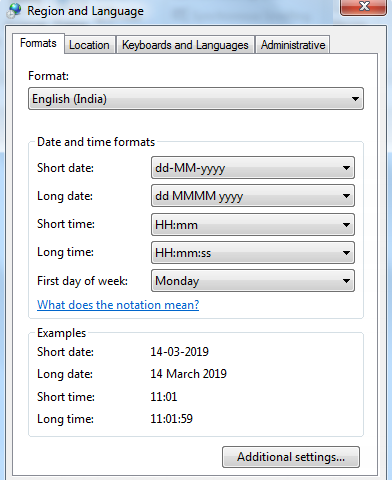
Если вы хотите установить другое представление даты и/или времени по умолчанию на своем компьютере, например, изменить их с американского на русское, перейдите в Панель управления и нажмите “Региональные стандарты» > «Изменение форматов даты, времени и чисел» .
На вкладке Форматы выберите регион, а затем установите желаемое отображение, щелкнув стрелку рядом с пунктом, который вы хотите изменить, и выбрав затем наиболее подходящий из раскрывающегося списка:
Если вас не устраивают варианты, предложенные на этой вкладке, нажмите кнопку “Дополнительные параметры» в нижней правой части диалогового окна. Откроется новое окно “Настройка …”, в котором вы переключаетесь на вкладку “Дата” и вводите собственный краткий или длинный формат в соответствующее поле.
Как быстро применить форматирование даты и времени по умолчанию
Как мы уже уяснили, в Microsoft Excel есть два формата даты и времени по умолчанию — короткий и длинный.
Чтобы быстро изменить один из них, сделайте следующее:
- Выберите даты, которые хотите отформатировать.
- На вкладке «Главная» в группе «Число» щелкните маленькую стрелку рядом с полем “Формат числа» и выберите нужный пункт — краткую дату, длинную или же время.
Если вам нужны дополнительные параметры форматирования, либо выберите “Другие числовые форматы» из раскрывающегося списка, либо нажмите кнопку запуска диалогового окна рядом с “Число».
Откроется знакомое диалоговое окно “Формат ячеек”, в котором вы сможете изменить любые нужные вам параметры. Об этом и пойдёт речь далее.
Как изменить формат даты в Excel
Даты могут отображаться разными способами. Когда дело доходит до изменения их вида для данной ячейки или диапазона, самый простой способ — открыть диалоговое окно ”Формат ячеек” и выбрать один из имеющихся там стандартных вариантов.
- Выберите данные, которые вы хотите изменить, или пустые ячейки, в которые вы хотите вставить даты.
- Нажмите
Ctrl + 1, чтобы открыть диалоговое окно «Формат ячеек». Кроме того, вы можете кликнуть выделенные ячейки правой кнопкой мыши и выбрать этот пункт в контекстном меню. - В окне “Формат ячеек» перейдите на вкладку “Число” и выберите “Дата» в списке числовых форматов.
- В разделе “Тип» выберите наиболее подходящий для вас вариант. После этого в поле “Образец» отобразится предварительный просмотр в выбранном варианте оформления.
- Если вас устраивает то, что вы увидели, нажмите кнопку ОК, чтобы сохранить изменение и закрыть окно.
Если, несмотря на ваши усилия, отображение числа, месяца и года в вашей таблице не меняется, скорее всего, ваши данные записаны как текст, и вам сначала нужно преобразовать их в формат даты.
Как сменить язык даты.
Если у вас есть файл, полный иностранных дат, вы, скорее всего, захотите изменить их те, которые используются в вашей стране. Допустим, вы хотите преобразовать американский формат (месяц/день/год) в европейский стиль (день/месяц/год).
Самый простой способ сделать это заключается в следующем:
- Выберите столбец, который вы хотите преобразовать в другой язык.
- Используйте комбинацию
Ctrl + 1, чтобы открыть знакомые нам настройки. - Выберите нужный язык в выпадающем списке «Язык (местоположение)» и нажмите «ОК», чтобы сохранить изменения.
Создание пользовательского формата даты.
Если вам не подходит ни один из стандартных вариантов, вы можете создать свой собственный.
- На листе выделите нужные ячейки.
- Нажмите
Ctrl + 1. - На вкладке Число выберите Все форматы в списке и запишите нужный формат даты в поле Тип. Это показано на скриншоте ниже.
- Щелкните ОК, чтобы сохранить изменения.
При настройке пользовательского формата даты вы можете использовать следующие коды.
| Код | Описание | Пример |
| м | Номер месяца без нуля в начале | 1 |
| мм | Номер месяца с нулем в начале | 01 |
| ммм | Название месяца, краткая форма | Янв |
| мммм | Название месяца, полная форма | Январь |
| ммммм | Первая буква месяца | М (обозначает март и май) |
| д | Номер дня без нуля в начале | 1 |
| дд | Номер дня с нулем в начале | 01 |
| ддд | День недели, краткая форма | Пн |
| дддд | День недели, полная форма | понедельник |
| гг | Год (последние 2 цифры) | 05 |
| гггг | Год (4 цифры) | 2020 |
Можно также использовать дополнительные коды, которые обязательно нужно заключать в квадратные скобки [].
| Код | Пояснение |
| x-sysdate | Системный длинный формат. Месяц в родительном падеже. |
| x-systime | Системное время. |
| x-genlower | Используется родительный падеж в нижнем регистре для любых полных названий месяцев (только для русского языка). Рекомендуется использовать вместе с кодом языка [ru-RU-x-genlower]. |
| x-genupper | Используется родительный падеж в верхнем регистре для любых полных названий месяцев (только на русском языке). Например, [ru-RU-x-genupper]. |
| x-nomlower | Для любых полных названий месяцев применяется именительный падеж в нижнем регистре (только на русском языке): [ru-RU-x-nomlower]. |
Вот как это может выглядеть на примерах:
При создании пользовательского формата в Excel вы можете использовать запятую (,), тире (-), косую черту (/), двоеточие (:) и другие символы.
Как создать собственный формат даты для другого языка
Если вы хотите отображать даты на другом языке, не меняя региональные настройки своего Windows, придётся создать собственный формат и использовать специальный префикс с соответствующим кодом языкового стандарта.
Код языка должен быть заключен в [квадратные скобки] и предваряться знаком доллара ($) и тире (-). Вот несколько примеров:
- [$-419] — Россия
- [$-409] – английский (США)
- [$-422] — Украина
- [$-423] — Беларусь
- [$-407] — Германия
Вы можете найти полный список кодов языков в этом блоге.
Например, вот как это можно настроить для белорусского языка в формате времени -день-месяц-год (день недели) :
Как показать число вместо даты.
Если вы хотите узнать, какое число представляет определенную дату или время, отображаемые в ячейке, вы можете сделать это двумя способами.
1. Диалоговое окно «Форматирование ячеек»
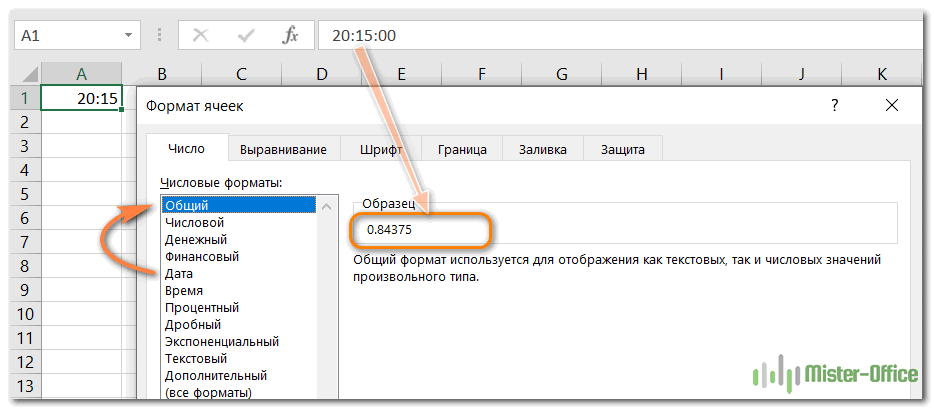
Выделите эту ячейку, нажмите Ctrl + 1, чтобы открыть знакомое нам окно настроек и переключиться на вкладку «Общие».
Если вы просто хотите узнать число, стоящее за датой, ничего не меняя в вашей таблице, то запишите число, которое вы видите в поле «Образец», и нажмите “Отмена», чтобы закрыть окно. Если вы хотите заменить дату числом в текущей ячейке, нажмите ОК.
Вы также можете выбрать формат «Общий» на ленте в разделе «Число». Дата будет тут же заменена соответствующим ей числом.
2. Функции ДАТАЗНАЧ и ВРЕМЗНАЧ
Можно также использовать функцию ДАТАЗНАЧ(), для преобразования даты в соответствующее ей число
=ДАТАЗНАЧ(«20/1/2021»)
Используйте функцию ВРЕМЗНАЧ(), чтобы получить десятичную дробь, представляющую время
=ВРЕМЗНАЧ(«16:30»)
Чтобы узнать дату и время, объедините эти две функции следующим образом:
= ДАТАЗНАЧ(«20/1/2021») & ВРЕМЗНАЧ(«16:30»)
Получится записанное в виде текста число, соответствующее дате-времени.
А если применить операцию сложения –
= ДАТАЗНАЧ(«20/1/2021») + ВРЕМЗНАЧ(«16:30»)
То получим число, которое можно отформатировать в виде даты-времени и с которым можно производить математические операции (найти разность дат и т.п.)
Если вы запишете, скажем, 31.12.1812, то это будет текстовое значение, а не дата. Это означает, что вы не сможете выполнять обычные арифметические операции с ней. Чтобы убедиться в этом, можете ввести формулу =ДАТАЗНАЧ(«31/12/1812») в какую-нибудь ячейку, и вы получите ожидаемый результат — ошибку #ЗНАЧ!.
Формат времени в Excel
Если помните, выше мы уже говорили, что Excel обрабатывает время как часть дня, и время сохраняется как десятичная часть.
Например:
- 00:00:00 сохраняется как 0,0
- 23:59:59 сохраняется как 0,99999
- 06:00 — 0,25
- 12:00 — 0,5
Когда в ячейку вводятся и дата, и время, они сохраняются как десятичное число, состоящее из целой части, представляющего дату, и десятичной части, представляющей время.
Формат времени по умолчанию.
При изменении формата времени в диалоговом окне ”Формат ячеек” вы могли заметить, что один из пунктов начинается со звездочки (*). Это формат времени по умолчанию в вашем Excel. Как и в случае с датой, он определяется региональными настройками Windows.
Чтобы быстро применить формат времени по умолчанию к выбранной ячейке или диапазону ячеек, щелкните стрелку раскрывающегося списка в группе Число на вкладке Главная и выберите Время.
Изменить формат времени по умолчанию, перейдите в Панель управления и перейдите “Региональные стандарты» > «Изменение форматов даты, времени и чисел». Подробно мы этот процесс описали выше, когда рассматривали установки параметров даты по умолчанию.
Десятичное представление времени.
Быстрый способ выбрать десятичное число, представляющее определенное время, — использовать диалоговое окно ”Формат ячеек”.
Просто выберите ячейку, содержащую время, и нажмите Ctrl + 1, чтобы открыть окно настроек. На вкладке “Число” выберите “Общие» в разделе “Категория», и вы увидите десятичную дробь в поле “Образец».
Теперь вы можете записать это число и нажать “Отмена», чтобы закрыть окно. Или же нажмите OK и замените время соответствующим десятичным числом в ячейке.
Фактически это самый быстрый, простой и не требующий формул способ преобразования времени в десятичное число.
Как применить или изменить формат времени.
Microsoft Excel достаточно умен, чтобы распознавать время при вводе и соответствующем форматировании ячейки. Например, если вы наберете 10:30 или 18:40, программа будет воспринимать и отображать это как время в зависимости от установленного по умолчанию формата времени.
Если вы хотите отформатировать некоторые числа как время или применить другой формат времени к существующим значениям, вы можете сделать это с помощью диалогового окна ”Формат ячеек”, как описано ниже.
- На листе Excel выберите ячейки, в которых вы хотите применить или изменить формат времени.
2. Откройте диалоговое окно Формат ячеек , нажав Ctrl + 1или щелкнув значок “Панель запуска диалогового окна» рядом с полем ”Число» на вкладке “Главная”.
3. На вкладке “Число” выберите “Время» в списке и укажите подходящий образец в окне “Тип» .
4. Нажмите OK, чтобы применить выбранное.
Создание пользовательского формата времени.
Хотя Microsoft Excel предоставляет несколько различных форматов времени, вы можете создать свой собственный, который лучше всего подходит для конкретной задачи. Для этого откройте знакомое нам окно настроек, выберите “Все форматы» и введите подходящее время в поле “Тип» .
Созданный вами пользовательский формат времени останется в списке Тип в следующий раз, когда он вам понадобится.
Совет. Самый простой способ создать собственный формат времени – использовать один из существующих в качестве отправной точки. Для этого щелкните “Время» в списке «Категория» и выберите один из предустановленных форматов. После этого внесите в него изменения.
При этом вы можете использовать следующие коды.
| Код | Описание | Отображается как |
| ч | Часы без нуля в начале | 0:35:00 |
| чч | Часы с нулем в начале | 03:35:00 |
| м | Минуты без нуля в начале | 0:0:59 |
| мм | Минуты с нулем в начале | 00:00:59 |
| c | Секунды без нуля в начале | 00:00:9 |
| сс | Секунды с нулем в начале | 00:00:09 |
Когда вы рассчитываете, к примеру, табель рабочего времени, то сумма может превысить 24 часа. Чтобы Microsoft Excel правильно отображал время, выходящее за пределы суток, примените один из следующих настраиваемых форматов времени. На скриншоте ниже – отображение одного и того же времени разными способами.
Пользовательские форматы для отрицательных значений времени
Пользовательские форматы времени, описанные выше, работают только для положительных значений. Если результат ваших вычислений представляет собой отрицательное число, отформатированное как время (например, когда вы вычитаете большее количество времени из меньшего), результат будет отображаться как #####. И увеличение ширины столбца не поможет избавиться от этих решёток.
Если вы хотите обозначить отрицательные значения времени, вам доступны следующие параметры:
- Отобразите пустую ячейку для отрицательных значений времени. Для этого введите точку с запятой в конце формата времени, например [ч]: мм;
- Вывести сообщение об ошибке. Введите точку с запятой в конце формата времени, а затем напишите сообщение в кавычках, например
[ч]: мм; «Отрицательное время»
Если вы хотите отображать отрицательные значения времени именно как отрицательные значения, например -11:15, самый простой способ — изменить систему дат Excel на систему 1904 года. Для этого щелкните Файл> Параметры> Дополнительно, прокрутите вниз до раздела Вычисления и установите флажок Использовать систему дат 1904.
Формат «Дата – Время».
Если нужно показать и дату, и время, вы можете просто объединить в единое целое те форматы, о которых мы говорили выше.
На скриншоте ниже вы видите несколько вариантов, как могут выглядеть ваши значения:
Ничего сложного: сначала описываем дату, затем – время.
Формат даты Excel не работает – как исправить?
Обычно Microsoft Excel очень хорошо понимает даты, и вы вряд ли столкнетесь с какими-либо серьёзными проблемами при работе с ними.
Но если всё же у вас возникла проблема с отображением дня, месяца и года, ознакомьтесь со следующими советами по устранению неполадок.
Ячейка недостаточно широка, чтобы вместить всю информацию.
Если вы видите на листе несколько знаков решетки (#####) вместо даты, то скорее всего, ваши ячейки недостаточно широки, чтобы вместить её целиком.
Решение. Дважды кликните по правой границе столбца, чтобы изменить его размер в соответствии с содержимым. Кроме того, вы можете просто перетащить мышкой правую границу, чтобы установить нужную ширину столбца.
Отрицательные числа форматируются как даты
Во всех современных версиях Excel 2013, 2010 и 2007 решетка (#####) также отображается, когда ячейка, отформатированная как дата или время, содержит отрицательное значение. Обычно это результат, возвращаемый какой-либо формулой. Но это также может произойти, когда вы вводите отрицательное значение в ячейку, а затем представляете эту ячейку как дату.
Если вы хотите отображать отрицательные числа как отрицательные даты, вам доступны два варианта:
Решение 1. Переключитесь на систему 1904.
Перейдите в Файл > Параметры > Дополнительно , прокрутите вниз до раздела При вычислении этой книги , установите флажок Использовать систему дат 1904 и нажмите ОК .
В этой системе 0 – это 1 января 1904 года; 1 – 2 января 1904 г .; а -1 отображается как: -2-янв-1904.
Конечно, такое представление очень необычно и требуется время, чтобы к нему привыкнуть.
Решение 2. Используйте функцию ТЕКСТ.
Другой возможный способ отображения отрицательных дат в Excel – использование функции ТЕКСТ. Например, если вы вычитаете C1 из B1, а значение в C1 больше, чем в B1, вы можете использовать следующую формулу для вывода результата в нужном вам виде:
=ТЕКСТ(ABS(B1-C1);»-ДД ММ ГГГГ»)
Получим результат «-01 01 1900».
Вы можете в формуле ТЕКСТ использовать любые другие настраиваемые форматы даты.
Замечание. В отличие от предыдущего решения, функция ТЕКСТ возвращает текстовое значение, поэтому вы не сможете использовать результат в других вычислениях.
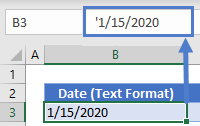
Даты импортированы в Excel как текст
Когда вы импортируете данные из файла .csv или какой-либо другой внешней базы данных, даты часто импортируются как текстовые значения. Они могут выглядеть для вас как обычно, но Excel воспринимает их как текст и обрабатывает соответственно.
Решение. Вы можете преобразовать «текстовые даты» в надлежащий для них вид с помощью функции ДАТАЗНАЧ или функции Текст по столбцам. Подробную информацию см. в следующей статье: Как преобразовать текст в дату.
Мы рассмотрели возможные способы представления даты и времени в Excel. Спасибо за чтение!
 Формат времени в Excel — Вы узнаете об особенностях формата времени Excel, как записать его в часах, минутах или секундах, как перевести в число или текст, а также о том, как добавить время с помощью…
Формат времени в Excel — Вы узнаете об особенностях формата времени Excel, как записать его в часах, минутах или секундах, как перевести в число или текст, а также о том, как добавить время с помощью…  Как сделать пользовательский числовой формат в Excel — В этом руководстве объясняются основы форматирования чисел в Excel и предоставляется подробное руководство по созданию настраиваемого пользователем формата. Вы узнаете, как отображать нужное количество десятичных знаков, изменять выравнивание или цвет шрифта,…
Как сделать пользовательский числовой формат в Excel — В этом руководстве объясняются основы форматирования чисел в Excel и предоставляется подробное руководство по созданию настраиваемого пользователем формата. Вы узнаете, как отображать нужное количество десятичных знаков, изменять выравнивание или цвет шрифта,…  7 способов поменять формат ячеек в Excel — Мы рассмотрим, какие форматы данных используются в Excel. Кроме того, расскажем, как можно быстро изменять внешний вид ячеек самыми различными способами. Когда дело доходит до форматирования ячеек в Excel, большинство…
7 способов поменять формат ячеек в Excel — Мы рассмотрим, какие форматы данных используются в Excel. Кроме того, расскажем, как можно быстро изменять внешний вид ячеек самыми различными способами. Когда дело доходит до форматирования ячеек в Excel, большинство…  Как удалить формат ячеек в Excel — В этом коротком руководстве показано несколько быстрых способов очистки форматирования в Excel и объясняется, как удалить форматы в выбранных ячейках. Самый очевидный способ сделать часть информации более заметной — это…
Как удалить формат ячеек в Excel — В этом коротком руководстве показано несколько быстрых способов очистки форматирования в Excel и объясняется, как удалить форматы в выбранных ячейках. Самый очевидный способ сделать часть информации более заметной — это…  8 способов разделить ячейку Excel на две или несколько — Как разделить ячейку в Excel? С помощью функции «Текст по столбцам», мгновенного заполнения, формул или вставив в нее фигуру. В этом руководстве описаны все варианты, которые помогут вам выбрать технику, наиболее подходящую…
8 способов разделить ячейку Excel на две или несколько — Как разделить ячейку в Excel? С помощью функции «Текст по столбцам», мгновенного заполнения, формул или вставив в нее фигуру. В этом руководстве описаны все варианты, которые помогут вам выбрать технику, наиболее подходящую…
When you enter a date into Microsoft Excel, the program will format it according to the default date settings. For example, if you want to enter the date February 6, 2020, the date could appear as 6-Feb, February 6, 2020, 6 February, or 02/06/2020, all depending on your settings. You may find that if you change a cell’s formatting to “Standard,” your date becomes stored as integers. For example, February 6, 2020 would become 43865, because Excel bases date formatting off of January 1, 1900. Each of these options are ways to format dates in Excel. To help with organizing data in Excel, learn about how to change the date format in Excel.
Choosing from the Date Format List
Formatting dates in Excel is easiest with the date formats list. Most date formats you may want to use can be found in this menu.
How to Change The Excel Date Format
- Select the cells you want to format
- Click Ctrl+1 or Command+1
- Select the “Numbers” tab
- From the categories, choose “Date”
- From the “Type” menu, select the date format you want
Creating a Custom Excel Date Format Option
To customize the date format, follow the steps for choosing an option from the date format list. Once you’ve selected the closest date format to what you want, you can customize it and change it.
- In the “Category” menu, select “Custom”
- The type you chose earlier will appear. The changes you make will only apply to your customized setting, not to the default
- In the “Type” box, enter the correct code to alter the date
- If you are trying to change the date display to DD/MM/YYYY, simply go to Format Cells > Custom
- Next, Enter DD/MM/YYYY in the available space given.
Converting Date Formats to Other Locales
If you are using dates for several different locations, you might need to convert to a different locale:
- Select the right cell or cells
- Hit Ctrl+1 or Command+1
- From the “Numbers” menu, select “Date”
- Underneath the “Type” menu, there’s a drop-down menu for “Locale”
- Select the right “Locale”
You can also customize the locale settings:
- Follow the steps for customizing a date
- Once you’ve created the right date format, you need to add the locale code to the front of the customized date format
- Choose the right locale codes. All locale codes are formatted as [$-###]. Some examples include:
- [$-409]—English, United States
- [$-804]—Chinese, China
- [$-807]—German, Switzerland
- Find more locale codes
Tips for Displaying Dates in Excel
Once you have the right date format, there are additional tips to help you figure out how to organize data in Excel for your datasets.
- Make sure the cell is wide enough to fit the entire date. If the cell isn’t wide enough, it will display #####. Double click on the right border of the column to make your column expand enough to display the date correctly.
- Change the date system if negative numbers appear as dates. Sometimes Excel will format any negative numbers as a date because of the hyphens. To fix this, select the cells, open the options menu, and select “Advanced.” On that menu, select “Use 1904 date system.”
- Use functions to work with today’s date. If you want a cell to always display the current date, use the formula =TODAY() and press ENTER.
- Convert imported text to dates. If you import from an external database, Excel will automatically register the dates as text. The display may look the same as if they were formatted as dates, but Excel will treat the two differently. You can use the DATEVALUE function to convert.
Why Your Date Format May Not Be Having Issues Changing
There are many reasons why you might be experiencing issues changing the date format in Excel. Listed are a few common difficulties.
- There could be text in the column, not dates (which are actually numbers).
- Dates are left-aligned
- An apostrophe could be included in the date
- A cell may be too wide.
- Negative numbers are formatted as dates
- Excel TEXT function is not being utilized.
Even with correctly formatted dates and displays, organizing data in Excel can only work as well as the data does. Messy data won’t lead to insights during analysis, however, it’s formatted.
Data Preparation with Excel
Formatting data, by doing things like formatting dates, is part of a larger process known as “data preparation,” or all of the steps required to clean, standardize, and prepare data for analytic use.
While data preparation is certainly possible in Excel, it becomes exponentially more difficult as analysts work with larger and more complex datasets. Instead, many of today’s analysts are investing in modern data preparation platforms like Designer Cloud to accelerate the overall data preparation process for data big or small.
Schedule a demo of Designer Cloud to see how it can improve your data preparation process, or try the platform for yourself by getting started with Designer Cloud today.
Excel Date Format (Table of Contents)
- Date Format in Excel
- How Excel stores Dates?
- How to Change Date Format in Excel?
Date Format in Excel
A date is one of the data types that are available in excel, which we use mostly in our day to day excel data works. A date can be displayed in several ways in excel as per requirement. A date has multiple numbers of formats based on geographical regions. Because different geographical regions use a date in different ways, Excel comes with multiple numbers of formats to display dates.
How Excel Stores Dates?
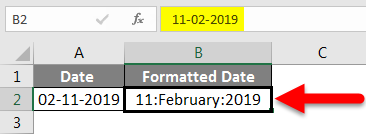
Before getting into the data formats, try to understand how Excel stores dates. Excel stores the date in an integer format. To make you understand better, we will look at the following example. Consider today’s date, 11 Feb 2019.
If we observe the above date, it is in the format of Month-Day-Year. Select this date and convert this to general or number format, then we will find a number. Let’s see how to convert. Select the date and choose the drop-down list from the Number segment under the Home tab. From the drop-down, select the option General and observe how the date will be converted.
Once you convert, it will change as an integer value, as shown in the below picture.
Now we will understand what that number is and what calculation is used by Excel to convert the data into an integer. Excel gives the number series for the dates starting from 1 Jan 1900 to 31 Dec 9999, which means 1 Jan 1900 will store as 1, and 2 Jan 1900 will store as 2. Now just try to check for the date 2 Jan 1900.
When we select the general option, it converted to 2, as shown below.
I hope you understand how Excel stores the date.
How to Change Date Format in Excel?
Let’s understand how to change the date format in Excel by using some examples.
You can download this Date Format in Excel Template here – Date Format in Excel Template
Example #1
First, we will see a short date and a Long date. Then, we will find the formats Short date and Long date from the same drop list of numbers.
Short date: As the name itself speaks, how it looks like. It will display a date in a simple way that is 2/11/2019. We can observe in the drop-down itself how it will display.
Long date: It will display a date in the long format. We can observe in the below image how it will display.
Example #2
A system has one default format to display the date whenever the user inputs the date. We will see how to check the default format in excel. Then, select the date and right-click.
The above pop up will appear; from that pop-up menu, select the Format Cells. Then, another screen will appear, which is the “Format cells” screen in which we can apply different kinds of formats like Number, Alignment, Font, Border, fill and protection.
Select Number and select the Date from the Category box. When we select the “Date”, the right side box will show the different formats available for the different locations.
If we observe, the first two date formats, which are highlighted in the red box, have a * (asterisk) mark, which shows that those are default date formats.
If we want to change the default date settings, we should go to the control panel and select Region and Language, then select Formats and change the date format as per your requirement.
Example #3
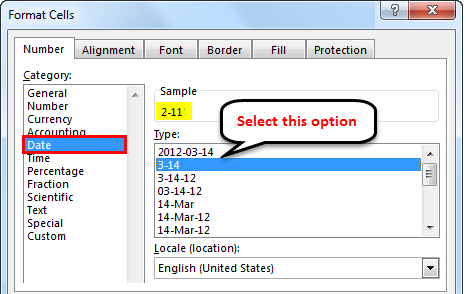
If we observe the below screenshot and the dates with ‘ * ‘, there are also different formats. We can select the required date format to change the current date format.
When we select the required format, we can observe a preview of how it will display in excel under the Sample box. There are different formats available like M/D, M/D/Y, MM/DD/YY etc.
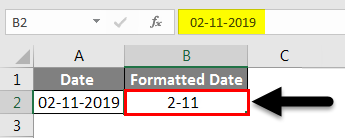
Select the M-D format, as shown below.
Then the date will look like 2-11 if we observe in the formula bar, which is highlighted. The formula bar shows as 2-11-2019; however, in Excel, it is displaying as 2-11.
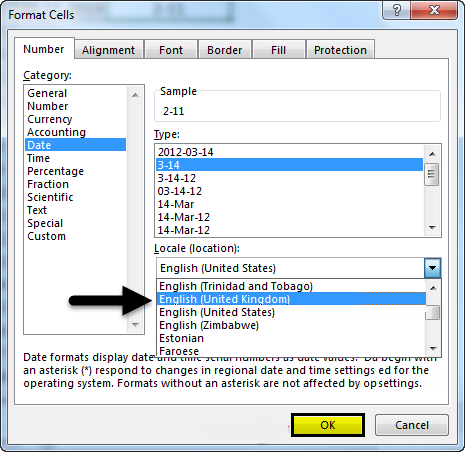
We can also change the location by selecting the required location from the selected dropdown. Observe the below image how the drop-down looks like.
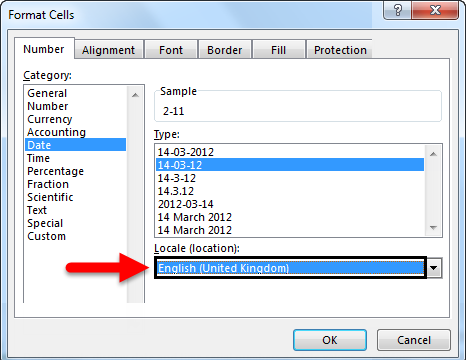
When we select a particular location from the drop-down, then different data formats will appear in the box “Type”. Currently, it is English (United States), now select the English (United Kingdom). Click OK. Then the date formats in the Type will change. Observe the below screenshot.
Observe the formats in the location United Kingdom are different from the United States. Still, if you are not happy with the date formats, we can create our customized format.
Example #4
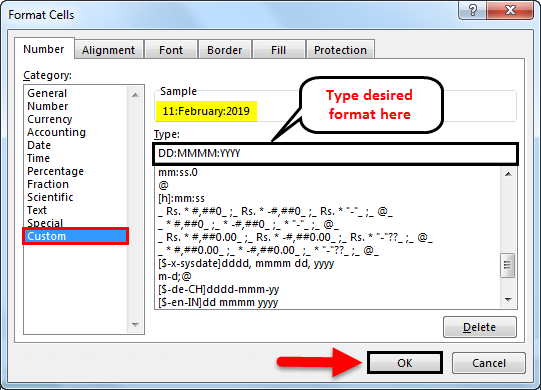
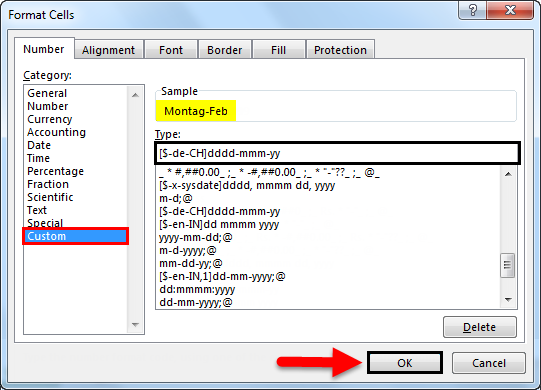
To create a customized format, select the Custom option from the Category box.
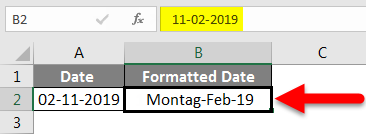
Once we select the Custom category, we can input the required format in Type. To make it more clear, suppose we want the format like DD:MMMM: YYYY, then type this format in the “Type” box.
Observe the above image; whatever input is in Type, the same format is showing in Sample. If we click OK, then it will apply to the date in excel.
Example #5
Date format in Other languages
We can display dates in other languages too. We will be able to do this using the “custom” format under the category. For doing this, we should know that particular language code; once we know that code, we just need to add the country code before our date format.
The language code should be in square brackets preceded with $ followed by a “- “in the format of [$-xxx].
In the below example, we created the date format of the German language similarly; we can give date formats for Chinese, Spanish, Japanese, French, Italian, Greek, etc. Use Google for language codes as per your requirement.
Things to Remember
- Dates before 1 Jan 1900 cannot convert to text in excel as it will not read negative numbers; hence it remains in the same format.
- Dates can display in short and long formats from the drop-down number under the “Home” tab.
- To convert the data into number format with the formula “Date value”.
- Default date represents with “*” symbol, to change the default selection, need to go to “Control panel”.
- CTRL + 1 is the shortcut for the “Format cell”. CTRL + ; is used to display the current date.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Date Format in Excel. Here we discussed How to change the Date Format in Excel along with practical examples and a downloadable excel template. You can also go through our other suggested articles –
- Excel DATEDIF Function
- VBA Date Format
- Excel Date Function
- Date Formula in Excel
You are not limited to using Excel’s built-in date formats. You can create your desired custom date formats in more than one way. You can even display your dates in a different language, change the appearance and order in which your dates are shown, add display color, and much more. In this article, you can learn how to format dates using a built-in format and how to format dates with use of the TEXT() function.
Using the DATE function available in Microsoft Excel is pretty simple as the function itself is very intuitive and self-explanatory. This function requires several variables to work, such as year, month and day, which can be inserted directly or entered as references to other cells with these variables. The Date function has the following syntax: DATE( year, month, day ). I have used the DATE function in many of my Calendars Templates, Project Gantt Chart, etc.
The DATE function can be used as a part of other functions or custom formulas and can also use other functions within for entering required variables. For example, one of the commonly used together with DATE functions is TODAY(), which returns the current date and can be used inside the DATE function and make it more dynamic.
The question that I have often been asked is how to format dates in the cell to display dates in alphanumerical format? Another issue is how to format dates using the TEXT() function? Additionally, why the date that is shown is either partly correct or displaying error when the spreadsheet is used in the non-English version of Microsoft Excel?
Examples
To follow along and see the examples described on this page in action, download the Excel file below.
Download the Example File (custom-date-formats.xlsx)
Change the Date Appearance with Format Cells Option
There a few methods in which you can approach these problems. The first method applies to scenarios where the content of the cell has to be displayed in some specific way, or you want to enter custom formatting. You can easily format the cell to show the date the way you need by following these steps:
- Select the cell (or multiple cells) you want to format
- Right-click on a cell (or cells) and select “Format Cells…” or use Ctrl+1 shortcut
- In the Format Cells dialog box choose the Date from the categories on the left
- Using the Locale drop-down list, choose a country or region of the date format you want to use
- Choose the desired format type in the Type section, then click OK to apply the format
The steps to apply custom formatting to the date entered into a cell or multiple cells are very similar.
- Select the cell (or multiple cells) you want to format
- Right-click on a cell (or cells) and select “Format Cells…” or use Ctrl+1 shortcut
- In the Format Cells window choose Custom from the categories on the left
- Select the desired formatting from the list in the Type section or enter your custom format type
I won’t go through all custom formatting types that can be entered here as there are quite a few of them and it is quite frankly outside the scope of this article, but I will briefly touch upon the few of them. If you want to learn about all possible formatting types that you can create in Excel, please let me know in the comments below.
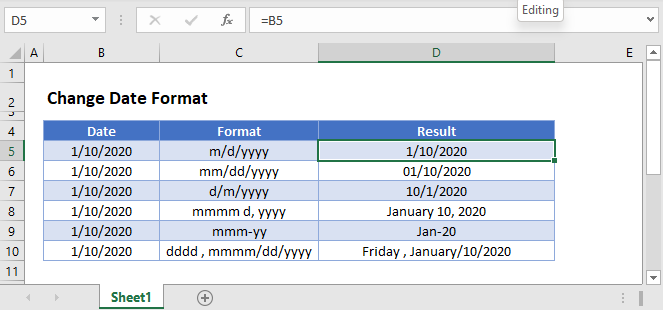
Here are some Date Format examples:
| Format Code | Cell Value | Cell Appearance |
|---|---|---|
| dd/mm/yyyy | 16/11/2018 | 16/11/2018 |
| mm/dd/yyyy | 16/11/2018 | 11/16/2018 |
| mm-dd-yy | 16/11/2018 | 11-16-18 |
| mmmm d, yyyy | 16/11/2018 | November 16, 2018 |
| d mmmm yyyy | 16/11/2018 | 16 November 2018 |
| d mmmm yyyy (dddd) | 16/11/2018 | 16 November 2018 (Friday) |
| mm•dd•yyyy | 16/11/2018 | 11•16•2018 |
| “Date:” d mmmm yyyy | 16/11/2018 | Date: 16 November 2018 |
You can enter your custom format type by clicking in the area as shown on the image above. For example, if you want to display the date as November 16, 2018, you would enter the following: mmmm dd, yyyy. Check the table below for more date format options.
| Format Code | Description |
|---|---|
| dddd | Full day of week names displayed as Monday-Sunday |
| ddd | Abbreviated day of week names displayed as Mon-Sun |
| dd | Days displayed with leading 0 as 01-31 |
| d | Days displayed as 1-31 |
| mmmmm | First letter of the month J-D |
| mmmm | Month Names displayed in full as January-December |
| mmm | Abbreviated month name displayed as Jan-Dec |
| mm | Month number displayed with leading 0 as 01-12 |
| m | Month number displayed as 1-12 |
| yyyy | Year displayed in four digit format: 2018, 2019, etc. |
| y or yy | Year displayed in two digit format: 18, 19, etc. |
In this table, you can view some examples that you can apply to change the appearance of the date in the cell.
| Format Code | Date Appearance |
|---|---|
| d mmm ddd | 6 Sep Thu |
| d mmm dddd | 6 Sep Thursday |
| d mmm yyyy (dddd) | 6 Sep 2018 (Thursday) |
| d mmm | 6 Sep |
| d mmmm | 6 September |
| dd/mm/yyyy | 06/09/2018 |
| dd-mm-yyyy | 06-09-2018 |
| d/m/yy | 6/9/18 |
| m/d/y | 9/6/18 |
| d mmm yy | 6 Sep 18 |
| mmm d, yy | Sep 6, 18 |
| d mmmm yyyy | 6 September 2018 |
| mmmm d, yyyy | September 6, 2018 |
| [$-C0A]mmmm d, yyyy | febrero 6, 2018 (Spanish) |
Additionally, the date can also appear in a different language by applying the language code to your formatting. For example, if you use the following language code [$-413] for Dutch, your date will appear in the Dutch language despite the system language settings of your computer. Language format can come in very handy, especially for use in spreadsheets where you want to display dates in various languages. I have posted the table with all applicable language codes at the bottom of this article.
All custom formatting applied via Excel built-in cell format option can be overwritten by conditional formatting or by accidental changes.
Format Dates with TEXT Function in Excel
If you are using the TEXT() function in your spreadsheet as a part of a formula or on its own, for applying a custom format to the date output, you can set the desired format right within the TEXT() function. To instruct the TEXT() function, you can use the same code that I have provided in the table above.
=TEXT(A1,"mmmm d, yyyy")
The formula above assumes that the date is in A1 (9/10/2018). The TEXT() function will apply the specified format to its output regardless of the initial format of the A1. So you should end up with the following output: September 9, 2018.
The output of the TEXT() function with a specified format cannot be changed with conditional formatting, which could sometimes be very useful. For example, you may not want to allow any system changes to override the format of your spreadsheet, such as system language changes. TEXT() function provides the ability to lock your set formats and can, to some extent prevent changes in the output.
One of many pros of using TEXT() function for setting a format of the date is the ability to set the different language for the output. You do this by including the language code with brackets to the format string, as shown in the example below
=TEXT(A1,"[$-C0A]mmmm d, yyyy")
Besides, you can make the TEXT() function even more dynamic by taking format string out of the worksheet function and placing it into any cell, then reference that cell in the format portion of the TEXT() function. Now you can change the format of the date by modifying the format string in the cell, without altering the TEXT() function.
=TEXT(A1,C2)
The formula in the example above assumes that A1 contains date and C2 includes the desired format string. The output of the TEXT() function will change every time you modify the format string in C2.
Custom Date Formats for Chart Labels and Axes
As with almost everything else in Excel, few different methods can be used to apply a custom format to the dates in the chart axes and labels. The first method is to add the custom date format from the Format Axis pane. You should notice that the Linked to source box is unchecked.
You can also follow the other methods to add a custom format to the date. For example, you can modify the format of the data source first then apply this format to your chart axis by checking the Link to source box in Format Axis pane.
Any formats applied with TEXT() function to the data source whether in cells or chart axes, cannot be overridden.
Custom Location Codes for Dates
The table below includes all custom location codes for dates. You can use these location codes at the beginning of the format code string in square brackets for displaying month names and weekday names in other languages. The location/language code contains either three or four digits and/or letters, but if the leading digit is a zero, you do not need to include it.
| Format Code | Language/Location |
|---|---|
| 0436 | Afrikaans |
| 041C | Albanian |
| 045E | Amharic |
| 0401 | Arabic |
| 042B | Armenian |
| 044D | Assamese |
| 082C | Azeri (Cyrillic) |
| 042C | Azeri (Latin) |
| 042D | Basque |
| 0423 | Belarusian |
| 0445 | Bengali |
| 0402 | Bulgarian |
| 0403 | Catalan |
| 045C | Cherokee |
| 0804 | Chinese (Simplified) |
| 0404 | Chinese (Traditional) |
| 041A | Croatian |
| 0405 | Czech |
| 0406 | Danish |
| 0465 | Dhivehi |
| 0413 | Dutch |
| 0466 | Edo |
| 0C09 | English (Australian) |
| 1009 | English (Canadian) |
| 0809 | English (U.K.) |
| 0409 | English (U.S.) |
| 0425 | Estonian |
| 0438 | Faeroese |
| 0464 | Filipino |
| 040B | Finnish |
| 040C | French |
| 0C0C | French (Canadian) |
| 0462 | Frisian |
| 0467 | Fulfulde |
| 0456 | Galician |
| 0437 | Georgian |
| 0407 | German |
| 0C07 | German (Austrian) |
| 0807 | German (Swiss) |
| 0408 | Greek |
| 0447 | Gujarati |
| 0468 | Hausa |
| 0475 | Hawaiian |
| 040D | Hebrew |
| 0439 | Hindi |
| 040E | Hungarian |
| 0469 | Ibibio |
| 040F | Icelandic |
| 0470 | Igbo |
| 0421 | Indonesian |
| 045D | Inuktitut |
| 0410 | Italian |
| 0411 | Japanese |
| 044B | Kannada |
| 0471 | Kanuri |
| 0460 | Kashmiri (Arabic) |
| 043F | Kazakh |
| 0457 | Konkani |
| 0412 | Korean |
| 0440 | Kyrgyz |
| 0476 | Latin |
| 0426 | Latvian |
| 0427 | Lithuanian |
| 042F | Macedonian FYROM |
| 043E | Malay |
| 044C | Malayalam |
| 043A | Maltese |
| 0458 | Manipuri |
| 044E | Marathi |
| 0450 | Mongolian |
| 0461 | Nepali |
| 0414 | Norwegian Bokmal |
| 0814 | Norwegian Nynorsk |
| 0448 | Oriya |
| 0472 | Oromo |
| 0463 | Pashto |
| 0429 | Persian |
| 0415 | Polish |
| 0416 | Portuguese (Brazil) |
| 0816 | Portuguese (Portugal) |
| 0446 | Punjabi |
| 0418 | Romanian |
| 0419 | Russian |
| 044F | Sanskrit |
| 0C1A | Serbian (Cyrillic) |
| 081A | Serbian (Latin) |
| 0459 | Sindhi |
| 045B | Sinhalese |
| 041B | Slovak |
| 0424 | Slovenian |
| 0477 | Somali |
| 0C0A | Spanish |
| 0441 | Swahili |
| 041D | Swedish |
| 045A | Syriac |
| 0428 | Tajik |
| 045F | Tamazight (Arabic) |
| 085F | Tamazight (Latin) |
| 0449 | Tamil |
| 0444 | Tatar |
| 044A | Telugu |
| 041E | Thai |
| 0873 | Tigrigna (Eritrea) |
| 0473 | Tigrigna (Ethiopia) |
| 041F | Turkish |
| 0442 | Turkmen |
| 0422 | Ukrainian |
| 0420 | Urdu |
| 0843 | Uzbek (Cyrillic) |
| 0443 | Uzbek (Latin) |
| 042A | Vietnamese |
| 0478 | Yi |
| 043D | Yiddish |
| 046A | Yoruba |
Other Notes about Custom Date Formats
You can quickly delete any custom formats created with built-in Format Cells option. To do so, open the Format Cells dialog box, select Custom from the categories on the left, select the custom format from the list then click Delete then click OK. All values that use the custom format which you want to delete will revert to the General format.
All custom date formats that you create belong to the workbook in which they were created. You will have to recreate the custom formats again in the new workbook or copy/paste the formatting from the file where you have initially created them. You can achieve this by copying and pasting the formatted cell, by copying the format code and pasting this code into the Format Cells dialog box or by using the Format Painter tool.
References
- Excel Custom Number Format by Mynda Treacy, Excel MVP (MyOnlineTrainingHub.com)
- Excel TEXT Function by Dave and Lisa Bruns (ExcelJet.net)
Return to Excel Formulas List
Download Example Workbook
Download the example workbook
This tutorial will demonstrate how to change date formats in Excel and Google Sheets.
Excel Date Format
In spreadsheets, dates are stored as serial numbers, each whole number represents an unique day. When you type a date into a cell, the date is converted to it’s corresponding serial number and the number format is changed to date.
After a date is entered in Excel as a date, there are several ways to change the formatting:
Change Date Formats
Short Date / Long Date
The Ribbon Home > Number menu allows you to change between Short Dates (default) and Long Dates:
Format Cells Menu – Date
The Format Cells Menu gives you numerous preset formats:
Notice that in the ‘Sample’ area you can see the impact the new number format will have on the active cell.
The Format Cells Menu can be accessed with the shortcut CTRL + 1 or by clicking this button:
Custom Number Formatting
The Custom section of the Format Cells Menu allows you the ability to create your own number formats:
To set custom number formatting for dates, you’ll need to specify how to display days, months, and / or years. Use this table as guide:
You can use the above examples to only display a day, month, or year. Or you can combine them:
Dates Stored as Text
Date as Text
To store a date as text, type an apostrophe (‘) in front of the date as you’re typing the date:
However, as long as the date is stored as text you’ll be unable to change the formatting like a normal date.
You can convert the date stored as text, back to a date using the DATEVALUE or VALUE Functions:
=DATEVALUE(B3)Text Function
The TEXT Function is a great way to display a date as text. The TEXT Function allows you to display dates in formats just like the Custom Number Formatting discussed previously.
=TEXT(B3,C3)You can combine the TEXT Function with a string of text like this:
="Today's date is: "&TEXT(TODAY(),"m/d/yyyy")Google Sheets Date Formatting
Google Sheets makes formatting dates slightly easier. With Google Sheets, you simply need to navigate to the ‘More date and time formats:
The menu looks like this:
You’ll be able to select from a wide range of presets. Or you can utilize the drop-downs on top to select your desired format: