Say, you have an Excel table and want to copy all column underneath each other so that you only have one column. For example, you have a table 2 rows by 4 columns like in the screenshot on the right-hand side. You want to copy and paste this table to one column. You often need such transformation for inserting PivotTables or to create database formats. This article provides 4 simple methods to transform a 2-dimensional table into one column in Excel.
Example
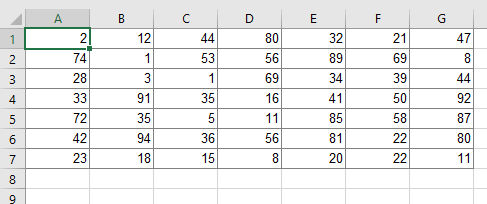
The following methods will be introduced with a simplified example as shown on the right-hand side. You have a table with numbers within the cell range A1 to G7. That means you have 7 rows and also 7 columns. In total 49 cells to be copied to one column.
Method 1: Copy table to one column manually
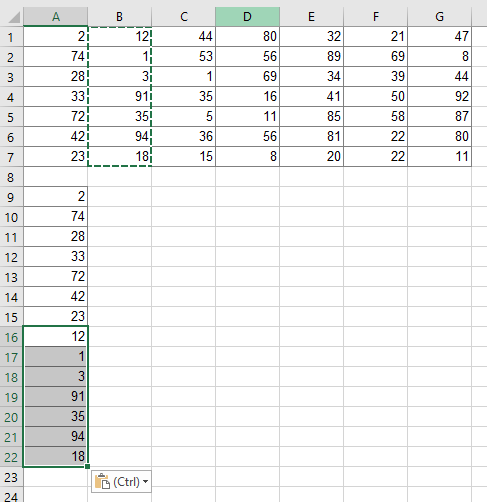
Like so often, copying and pasting the columns manually might be the fastest solution. Given that you are reading this article, this might not be the method you want to hear. But anyway, doing it manually is often the fastest way.
Maybe some advice to speed up the manual process might help. Try to use as many keyboard shortcuts as possible. That way you could save some time.
- Holding Ctrl and pressing one of the arrow keys makes you jump between tables and cells.
- Holding the Shift key, you can select cells and ranges.
- And – of course – with Ctrl + C and Ctrl + V you can copy and paste cells.
For more information about the keyboard shortcuts please refer to our big keyboard shortcut package.
Method 2: The INDEX formula
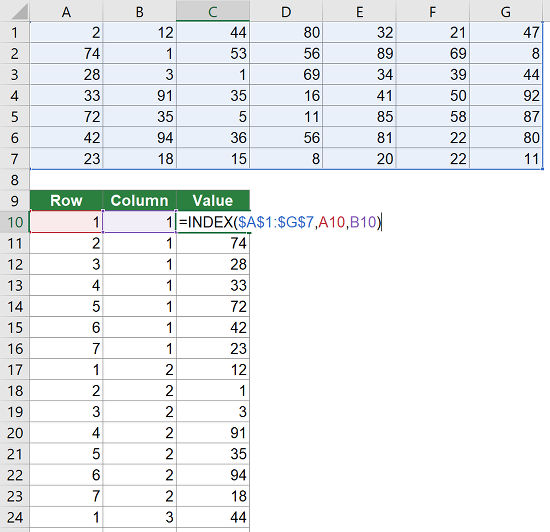
You can convert a two-dimensional table into just one column by using the INDEX formula. Unfortunately, it requires some preparations. But on the other hand, it’s one of the faster ways (compared to setting up the more complex OFFSET formula like in method 3 below or the INDIRECT formula).
Let’s see what you need to prepare. Basically you have to create the column and row number in additional helper columns. That way you can easily refer to the original table. The screenshot on the right-hand side shows the necessary preparations.
- You need one column containing the row number (here in column A). You always start with 1. So if you data start in row 3, the first number you write is still 1.
- You need one column containing the column number (here in column B). Also for the column number you always start with number one.
- The third column contains the actual values, pulled by the formula =INDEX($A$1:$G$7;A10;B10) . Example: In cell C10, the INDEX formula returns the value from the first row and first column of the range A1 to G7.
Please refer to this article for more information about the INDEX formula in Excel.
Method 3: OFFSET formula
The third method uses the OFFSET formula for copying several columns underneath each other to one column. If you need some introduction to the OFFSET formula, please refer to this article.
Because the formula is – in this universal case – very long, we don’t go much into detail here. It’s based on three cells.
- The top left cell of the table you want to convert (here: A1).
- The bottom left cell of the table you want to convert (here: A7).
- The heading cell of your single column, which is supposed to contain all the data from the table (here: A9)
Now you just have to replace the cell links in the following formula with your cells. Don’t forget to fix the references with the $-signs as shown in the formula below.
=OFFSET($A$1,(ROW()-ROW($A$9)-1)-(ROW($A$7)-ROW($A$1)+1)*ROUNDDOWN((ROW()-ROW($A$9)-1)/(ROW($A$7)-ROW($A$1)+1),0),ROUNDDOWN((ROW()-ROW($A$9)-1)/(ROW($A$7)-ROW($A$1)+1),0))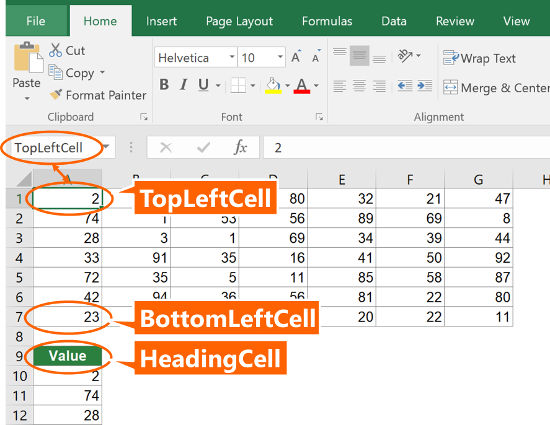
In order to make it easier for you to use the formula, you can use the version below. All you have to do is to give names to the three main cell as shown in the image on the right-hand side. In order to achieve this, select the top left cell of your original table (here: A1) and click into the name field. Type “TopLeftCell” and press Enter on the keyboard. Repeat this with the bottom left cell (name “BottomLeftCell”) as well as the heading cell of your new table (name “HeadingCell”).
Once done, copy and paste the following formula it the first cell (here: A10). Now just copy and paste this cell down until all columns from your original table are covered.
=OFFSET(TopLeftCell,(ROW()-ROW(HeadingCell)-1)-(ROW(BottomLeftCell)-ROW(TopLeftCell)+1)*ROUNDDOWN((ROW()-ROW(HeadingCell)-1)/(ROW(BottomLeftCell)-ROW(TopLeftCell)+1),0),ROUNDDOWN((ROW()-ROW(HeadingCell)-1)/(ROW(BottomLeftCell)-ROW(TopLeftCell)+1),0))Method 4: Professor Excel Tools
You want to use the most convenient way? Try the Excel add-in “Professor Excel Tools”. The steps are shown in the screenshot below.
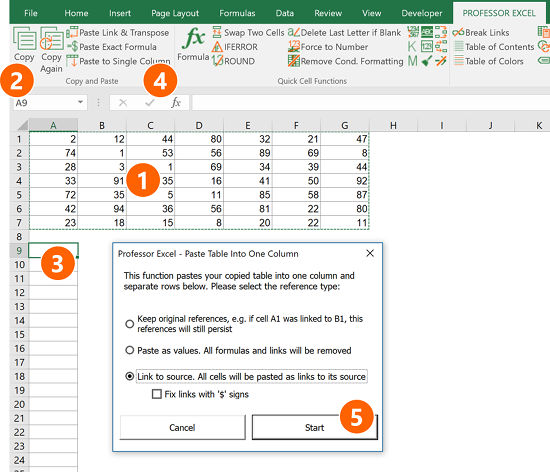
- Select the table you want to transform into a single column.
- Click on Copy on the left-hand side of the “Professor Excel”-ribbon.
- Select the first cell from which Professor Excel should paste the columns underneath.
- Click on “Paste to Single Column” on the “Professor Excel” ribbon.
- Now you can finetune the copy-and-paste-format. Do you which to copy the formulas without changing cell references, do you which to copy them as values or do you want to insert links to the original table? Then press Start.
That’s it. Do you want to try “Professor Excel” for free? Then just follow this link for more information or start the download right away.

This function is included in our Excel Add-In ‘Professor Excel Tools’
(No sign-up, download starts directly)
Download
Please feel free to download all examples shown above in one comprehensive Excel file. Just click on this link and the download starts right away.
Are you having difficulty merging two or more Excel columns? Knowing how to combine multiple columns in Excel without losing data is a handy time-saver that allows you to consolidate your data and make your sheet look neater.
First and foremost, you should know that there are multiple ways you can merge data from two or more columns in Excel. Before we get started exploring these different ways, let’s start with a key step that helps the process — how to merge cells in Excel.
If you want to combine Google Sheets data, you can do that easily using Layer. Layer is a free add-on that allows you to share sheets or ranges of your main spreadsheet with different people. On top of that, you get to monitor and approve edits and changes made to the shared files before they’re merged back into your master file, giving you more control over your data.
Install the Layer Google Sheets Add-On today and Get Free Access to all the paid features, so you can start managing, automating, and scaling your processes on top of Google Sheets!
How to Combine Multiple Cells or Columns in Excel Without Losing Data?
Once you have merging cells under your belt, learning how to combine multiple Excel columns into one column becomes intuitive.
Whether you’re learning how to combine two cells in Excel, or ten, one of the main benefits of merging is that the formulae don’t change. Here are the following ways you can combine cells or merge columns within your Excel:
Use Ampersand (&) to merge two cells in Excel
If you want to know how to merge two cells in Excel, here’s the quickest and easiest way of doing so without losing any of your data.
- 1. Double-click the cell in which you want to put the combined data and type =
- 2. Click a cell you want to combine, type &, and click the other cell you wish to combine. If you want to include more cells, type &, and click on another cell you wish to merge, etc.
- 3. Press Enter when you have selected all the cells you want to combine

While this is useful for quickly merging data into a single cell, the merged data will not be formatted. This can make data untidy or challenging to read in some instances (e.g. full names or addresses).
If you want to add punctuation or spaces (delimiters), follow the below steps. For this example, let’s put a comma and a space between the first and last name as you would see on a registration list:
- 1. Double-click the cell in which you want to put the merged data and type =
- 2. Click a cell you want to merge
- 3. This time, type &”, ”& before you click the next cell you want to merge. If you want to include more cells, type &”, ”& before clicking the next cell you want to merge, etc.
- 4. Press Enter when you have selected all the cells you want to combine

As you can see, now your merged data comes out in a neater format, with each piece of data appropriately separated.
Use the CONCATENATE function to merge multiple columns in Excel
This method is similar to the ampersand method, and also allows you to format your merged data. First, you need to use the CONCATENATE function to merge a row of cells:
- 1. Insert the =CONCATENATE function as laid out in the instructions above
- 2. Type in the references of the cells you want to combine, separating each reference with ,», «, (e.g. B2,», «,C2,», «,D2). This will create spaces between each value.
- 3. Press Enter
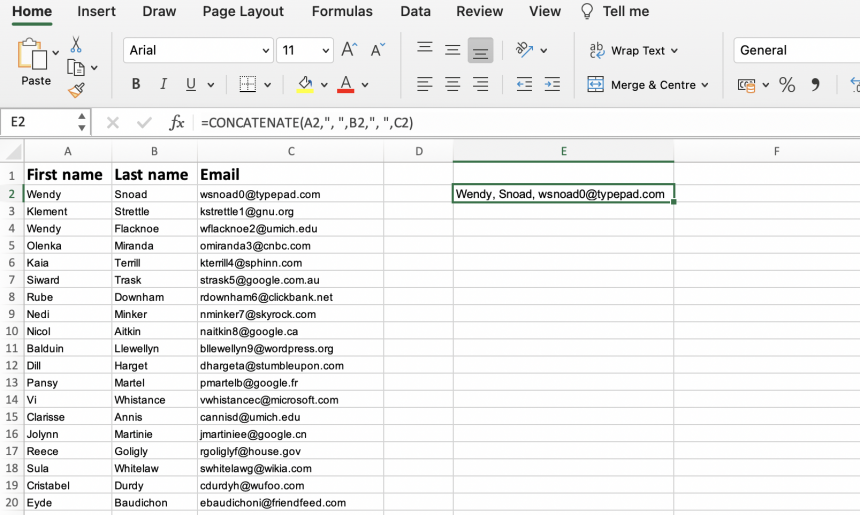
Now that you have successfully merged your cells, you can follow these simple steps to merge multiple columns:
- 1. Hover your mouse over the bottom-right corner of the merged cell you just created
- 2. When the cursor changes into a + symbol, drag your cursor as far down the column as you want and release it

Once you release the mouse, you should see that your merged cell has become a merged column, containing all of the data from your chosen columns.
*The CONCAT function is another formula used for combining data from different cells. However, it is limited to two references and does not allow you to include delimiters.
Use the TEXTJOIN function to merge multiple columns in Excel
This method works only with Excel 365, 2021, and 2019. As you can probably tell, this function is helpful when you want to combine two or more text cells in Excel.
The following steps will show you how to use the TEXTJOIN function, once again using the comma and space combination to create your first merged cell:
- 1. Double-click the cell in which you want to put the combined data
- 2. Type =TEXTJOIN to insert the function
- 3. Type “, ”,TRUE, followed by the references of the cells you want to combine, separating each reference with a comma (the role of TRUE is to disregard empty cells you may have input)
- 4. Press Enter

In order to create the rest of your combined column, use the drag-and-drop steps listed below:
- 1. Hover your mouse over the bottom-right corner of the merged cell you just created
- 2. When the cursor changes into a + symbol, drag your cursor as far down the column as you want and release it.

Now your columns of data have successfully merged into your new column.
The Beginner’s Guide to Excel Version Control
Discover what Excel version control is, the version control features Excel has to offer, and how to use them to share, merge, and review Excel changes
READ MORE

Use the INDEX formula to stack multiple columns into one column in Excel
Let’s say you want to create a stack of data from your multiple columns, rather than create a single cell. You can easily do this across multiple cells and columns within your spreadsheet using the INDEX formula:
- 1. Select all of the cells containing your data
- 2. Type in a name for this group of data in the “Name Box” (box located to the left side of the formula bar). In this example, I’ve named the data “_my_data”
- 3. Select an empty cell in your Excel sheet where you want your stacked data to be located. Input the following INDEX formula (remember to substitute with your data name):
=INDEX(_my_data,1+INT((ROW(A1)-1)/COLUMNS(_my_data)),MOD(ROW(A1)-1+COLUMNS(_my_data),COLUMNS(_my_data))+1)
-
4. The first value from your data range should appear. Hover over the cell until the cursor changes into a + symbol, and drag your cursor as far down until you receive a #REF! value (this signals the end of your data set)
Other ways to combine multiple columns in Excel: Notepad and VBA script
There are two other ways you can combine multiple columns in Excel. These are often more time-consuming, and use other tools as part of the process. However, they may be more helpful for users who wish to avoid using Excel formulae.
Use Notepad to merge multiple columns in Excel
You can use Notepad to extract, format, and replace your data from multiple columns in your Excel. For this, you need to copy and paste each column from your Excel sheet into a Notepad file. Then, use the Replace function to add commas between each value. Once finished, you can copy and paste your formatted data back into your Excel.
Use VBA script to combine two or more columns in Excel
As an alternative to the INDEX function stacking method, you can use VBA script. Simply right-click and select “View code” within your Excel, and copy and paste the code in a new window. Press “F5” to run the code and create a Macro. You can then apply this to your Excel by selecting your data range and applying it to your destination column.
Want to Boost Your Team’s Productivity and Efficiency?
Transform the way your team collaborates with Confluence, a remote-friendly workspace designed to bring knowledge and collaboration together. Say goodbye to scattered information and disjointed communication, and embrace a platform that empowers your team to accomplish more, together.
Key Features and Benefits:
- Centralized Knowledge: Access your team’s collective wisdom with ease.
- Collaborative Workspace: Foster engagement with flexible project tools.
- Seamless Communication: Connect your entire organization effortlessly.
- Preserve Ideas: Capture insights without losing them in chats or notifications.
- Comprehensive Platform: Manage all content in one organized location.
- Open Teamwork: Empower employees to contribute, share, and grow.
- Superior Integrations: Sync with tools like Slack, Jira, Trello, and more.
Limited-Time Offer: Sign up for Confluence today and claim your forever-free plan, revolutionizing your team’s collaboration experience.
Conclusion
As you can see, combining multiple columns is easy in Excel. Whether you’re combing multiple Excel files, or columns and cells, there are a variety of ways that cater to different users, depending on their technical abilities or needs.
As a result, not only can you format your Excel into a cohesive and seamless spreadsheet, but also save time and optimize your productivity when evaluating, managing, or sharing important data. Once you know how to combine multiple columns in Excel into one column, combining or merging your data can become one quick and simple task.
Содержание
- How to Combine Multiple Excel Columns Into One?
- How to Combine Multiple Cells or Columns in Excel Without Losing Data?
- Use Ampersand (&) to merge two cells in Excel
- Use the CONCATENATE function to merge multiple columns in Excel
- Use the TEXTJOIN function to merge multiple columns in Excel
- The Beginner’s Guide to Excel Version Control
- Use the INDEX formula to stack multiple columns into one column in Excel
- Other ways to combine multiple columns in Excel: Notepad and VBA script
- Use Notepad to merge multiple columns in Excel
- Use VBA script to combine two or more columns in Excel
- How to combine Google Sheets files into one?
- Conclusion
- Related posts
- Accomplish more together!
- Convert Table to One Column in Excel: 4 Easy Methods to Copy All Columns underneath Each Other
- Example
- Method 1: Copy table to one column manually
- Method 2: The INDEX formula
- Method 3: OFFSET formula
- Method 4: Professor Excel Tools
- Download
How to Combine Multiple Excel Columns Into One?
Are you having difficulty merging two or more Excel columns? Knowing how to combine multiple columns in Excel without losing data is a handy time-saver that allows you to consolidate your data and make your sheet look neater.
First and foremost, you should know that there are multiple ways you can merge data from two or more columns in Excel. Before we get started exploring these different ways, let’s start with a key step that helps the process — how to merge cells in Excel.
If you want to combine Google Sheets data, you can do that easily using Layer. Layer is a free add-on that allows you to share sheets or ranges of your main spreadsheet with different people. On top of that, you get to monitor and approve edits and changes made to the shared files before they’re merged back into your master file, giving you more control over your data.
Install the Layer Google Sheets Add-On today and Get Free Access to all the paid features, so you can start managing, automating, and scaling your processes on top of Google Sheets!
Confluence is your remote-friendly team workspace where knowledge and collaboration meet.
How to Combine Multiple Cells or Columns in Excel Without Losing Data?
Once you have merging cells under your belt, learning how to combine multiple Excel columns into one column becomes intuitive.
Whether you’re learning how to combine two cells in Excel, or ten, one of the main benefits of merging is that the formulae don’t change. Here are the following ways you can combine cells or merge columns within your Excel:
Use Ampersand (&) to merge two cells in Excel
If you want to know how to merge two cells in Excel, here’s the quickest and easiest way of doing so without losing any of your data.
- 1. Double-click the cell in which you want to put the combined data and type =
- 2. Click a cell you want to combine, type &, and click the other cell you wish to combine. If you want to include more cells, type &, and click on another cell you wish to merge, etc.
- 3. Press Enter when you have selected all the cells you want to combine
While this is useful for quickly merging data into a single cell, the merged data will not be formatted. This can make data untidy or challenging to read in some instances (e.g. full names or addresses).
If you want to add punctuation or spaces (delimiters), follow the below steps. For this example, let’s put a comma and a space between the first and last name as you would see on a registration list:
- 1. Double-click the cell in which you want to put the merged data and type =
- 2. Click a cell you want to merge
- 3. This time, type &”, ”& before you click the next cell you want to merge. If you want to include more cells, type &”, ”& before clicking the next cell you want to merge, etc.
- 4. Press Enter when you have selected all the cells you want to combine
As you can see, now your merged data comes out in a neater format, with each piece of data appropriately separated.
Use the CONCATENATE function to merge multiple columns in Excel
This method is similar to the ampersand method, and also allows you to format your merged data. First, you need to use the CONCATENATE function to merge a row of cells:
- 1. Insert the =CONCATENATE function as laid out in the instructions above
- 2. Type in the references of the cells you want to combine, separating each reference with ,», «, (e.g. B2,», «,C2,», «,D2). This will create spaces between each value.
- 3. Press Enter
Now that you have successfully merged your cells, you can follow these simple steps to merge multiple columns:
- 1. Hover your mouse over the bottom-right corner of the merged cell you just created
- 2. When the cursor changes into a + symbol, drag your cursor as far down the column as you want and release it
Once you release the mouse, you should see that your merged cell has become a merged column, containing all of the data from your chosen columns.
*The CONCAT function is another formula used for combining data from different cells. However, it is limited to two references and does not allow you to include delimiters.
Discover the most popular methods used to manually or automatically combine multiple Excel spreadsheets and data inputs into one master file
Use the TEXTJOIN function to merge multiple columns in Excel
This method works only with Excel 365, 2021, and 2019. As you can probably tell, this function is helpful when you want to combine two or more text cells in Excel.
The following steps will show you how to use the TEXTJOIN function, once again using the comma and space combination to create your first merged cell:
- 1. Double-click the cell in which you want to put the combined data
- 2. Type =TEXTJOIN to insert the function
- 3. Type “, ”,TRUE, followed by the references of the cells you want to combine, separating each reference with a comma (the role of TRUE is to disregard empty cells you may have input)
- 4. Press Enter
In order to create the rest of your combined column, use the drag-and-drop steps listed below:
- 1. Hover your mouse over the bottom-right corner of the merged cell you just created
- 2. When the cursor changes into a + symbol, drag your cursor as far down the column as you want and release it.
Now your columns of data have successfully merged into your new column.
The Beginner’s Guide to Excel Version Control
Discover what Excel version control is, the version control features Excel has to offer, and how to use them to share, merge, and review Excel changes
Use the INDEX formula to stack multiple columns into one column in Excel
Let’s say you want to create a stack of data from your multiple columns, rather than create a single cell. You can easily do this across multiple cells and columns within your spreadsheet using the INDEX formula:
- 1. Select all of the cells containing your data
- 2. Type in a name for this group of data in the “Name Box” (box located to the left side of the formula bar). In this example, I’ve named the data “_my_data”
- 3. Select an empty cell in your Excel sheet where you want your stacked data to be located. Input the following INDEX formula (remember to substitute with your data name):
- Share & Collaborate: Automate your data collection and validation through user controls.
- Automate & Schedule: Schedule recurring data collection and distribution tasks.
- Integrate & Sync: Connect to your tech stack and sync all your data in one place.
- Visualize & Report: Generate and share reports with real-time data and actionable decisions.
- Holding Ctrl and pressing one of the arrow keys makes you jump between tables and cells.
- Holding the Shift key, you can select cells and ranges.
- And – of course – with Ctrl + C and Ctrl + V you can copy and paste cells.
- You need one column containing the row number (here in column A). You always start with 1. So if you data start in row 3, the first number you write is still 1.
- You need one column containing the column number (here in column B). Also for the column number you always start with number one.
- The third column contains the actual values, pulled by the formula =INDEX($A$1:$G$7;A10;B10) . Example: In cell C10, the INDEX formula returns the value from the first row and first column of the range A1 to G7.
- The top left cell of the table you want to convert (here: A1).
- The bottom left cell of the table you want to convert (here: A7).
- The heading cell of your single column, which is supposed to contain all the data from the table (here: A9)
- Select the table you want to transform into a single column.
- Click on Copy on the left-hand side of the “Professor Excel”-ribbon.
- Select the first cell from which Professor Excel should paste the columns underneath.
- Click on “Paste to Single Column” on the “Professor Excel” ribbon.
- Now you can finetune the copy-and-paste-format. Do you which to copy the formulas without changing cell references, do you which to copy them as values or do you want to insert links to the original table? Then press Start.
4. The first value from your data range should appear. Hover over the cell until the cursor changes into a + symbol, and drag your cursor as far down until you receive a #REF! value (this signals the end of your data set)
Other ways to combine multiple columns in Excel: Notepad and VBA script
There are two other ways you can combine multiple columns in Excel. These are often more time-consuming, and use other tools as part of the process. However, they may be more helpful for users who wish to avoid using Excel formulae.
Use Notepad to merge multiple columns in Excel
You can use Notepad to extract, format, and replace your data from multiple columns in your Excel. For this, you need to copy and paste each column from your Excel sheet into a Notepad file. Then, use the Replace function to add commas between each value. Once finished, you can copy and paste your formatted data back into your Excel.
Use VBA script to combine two or more columns in Excel
As an alternative to the INDEX function stacking method, you can use VBA script. Simply right-click and select “View code” within your Excel, and copy and paste the code in a new window. Press “F5” to run the code and create a Macro. You can then apply this to your Excel by selecting your data range and applying it to your destination column.
How to combine Google Sheets files into one?
Layer is an add-on that equips you with the tools to increase efficiency and data quality in your processes on top of Google Sheets. Share parts of your Google Sheets, monitor, review and approve changes, and sync data from different sources – all within seconds. See how it works.
Using Layer, you can:
Limited Time Offer: Install the Layer Google Sheets Add-On today and Get Free Access to all the paid features, so you can start managing, automating, and scaling your processes on top of Google Sheets!
Conclusion
As you can see, combining multiple columns is easy in Excel. Whether you’re combing multiple Excel files, or columns and cells, there are a variety of ways that cater to different users, depending on their technical abilities or needs.
As a result, not only can you format your Excel into a cohesive and seamless spreadsheet, but also save time and optimize your productivity when evaluating, managing, or sharing important data. Once you know how to combine multiple columns in Excel into one column, combining or merging your data can become one quick and simple task.
Confluence is your remote-friendly team workspace where knowledge and collaboration meet.
Hady has a passion for tech, marketing, and spreadsheets. Besides his Computer Science degree, he has vast experience in developing, launching, and scaling content marketing processes at SaaS startups.
Originally published Jan 10 2022, Updated Feb 15 2023
Accomplish more together!
Confluence is your remote-friendly team workspace where knowledge and collaboration meet.
Источник
Convert Table to One Column in Excel: 4 Easy Methods to Copy All Columns underneath Each Other
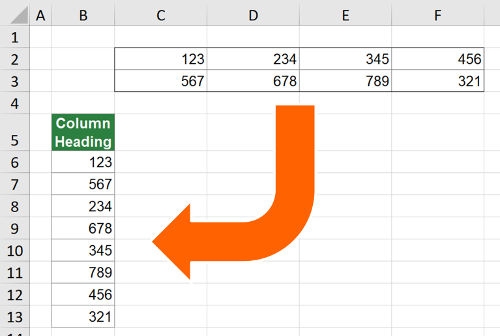
Say, you have an Excel table and want to copy all column underneath each other so that you only have one column. For example, you have a table 2 rows by 4 columns like in the screenshot on the right-hand side. You want to copy and paste this table to one column. You often need such transformation for inserting PivotTables or to create database formats. This article provides 4 simple methods to transform a 2-dimensional table into one column in Excel.
Example
The following methods will be introduced with a simplified example as shown on the right-hand side. You have a table with numbers within the cell range A1 to G7. That means you have 7 rows and also 7 columns. In total 49 cells to be copied to one column.
Method 1: Copy table to one column manually
Like so often, copying and pasting the columns manually might be the fastest solution. Given that you are reading this article, this might not be the method you want to hear. But anyway, doing it manually is often the fastest way.
Maybe some advice to speed up the manual process might help. Try to use as many keyboard shortcuts as possible. That way you could save some time.
For more information about the keyboard shortcuts please refer to our big keyboard shortcut package.
Method 2: The INDEX formula
You can convert a two-dimensional table into just one column by using the INDEX formula. Unfortunately, it requires some preparations. But on the other hand, it’s one of the faster ways (compared to setting up the more complex OFFSET formula like in method 3 below or the INDIRECT formula).
Let’s see what you need to prepare. Basically you have to create the column and row number in additional helper columns. That way you can easily refer to the original table. The screenshot on the right-hand side shows the necessary preparations.
Please refer to this article for more information about the INDEX formula in Excel.
Method 3: OFFSET formula
The third method uses the OFFSET formula for copying several columns underneath each other to one column. If you need some introduction to the OFFSET formula, please refer to this article.
Because the formula is – in this universal case – very long, we don’t go much into detail here. It’s based on three cells.
Now you just have to replace the cell links in the following formula with your cells. Don’t forget to fix the references with the $-signs as shown in the formula below.
In order to make it easier for you to use the formula, you can use the version below. All you have to do is to give names to the three main cell as shown in the image on the right-hand side. In order to achieve this, select the top left cell of your original table (here: A1) and click into the name field. Type “TopLeftCell” and press Enter on the keyboard. Repeat this with the bottom left cell (name “BottomLeftCell”) as well as the heading cell of your new table (name “HeadingCell”).
Once done, copy and paste the following formula it the first cell (here: A10). Now just copy and paste this cell down until all columns from your original table are covered.
You want to use the most convenient way? Try the Excel add-in “Professor Excel Tools”. The steps are shown in the screenshot below.
That’s it. Do you want to try “Professor Excel” for free? Then just follow this link for more information or start the download right away.
This function is included in our Excel Add-In ‘Professor Excel Tools’
(No sign-up, download starts directly)
More than 35,000 users can’t be wrong.
Download

Источник
When you move or copy rows and columns, by default Excel moves or copies all data that they contain, including formulas and their resulting values, comments, cell formats, and hidden cells.
When you copy cells that contain a formula, the relative cell references are not adjusted. Therefore, the contents of cells and of any cells that point to them might display the #REF! error value. If that happens, you can adjust the references manually. For more information, see Detect errors in formulas.
You can use the Cut command or Copy command to move or copy selected cells, rows, and columns, but you can also move or copy them by using the mouse.
By default, Excel displays the Paste Options button. If you need to redisplay it, go to Advanced in Excel Options. For more information, see Advanced options.
-
Select the cell, row, or column that you want to move or copy.
-
Do one of the following:
-
To move rows or columns, on the Home tab, in the Clipboard group, click Cut
or press CTRL+X.
-
To copy rows or columns, on the Home tab, in the Clipboard group, click Copy
or press CTRL+C.
-
-
Right-click a row or column below or to the right of where you want to move or copy your selection, and then do one of the following:
-
When you are moving rows or columns, click Insert Cut Cells.
-
When you are copying rows or columns, click Insert Copied Cells.
Tip: To move or copy a selection to a different worksheet or workbook, click another worksheet tab or switch to another workbook, and then select the upper-left cell of the paste area.
-
Note: Excel displays an animated moving border around cells that were cut or copied. To cancel a moving border, press Esc.
By default, drag-and-drop editing is turned on so that you can use the mouse to move and copy cells.
-
Select the row or column that you want to move or copy.
-
Do one of the following:
-
Cut and replace
Point to the border of the selection. When the pointer becomes a move pointer, drag the rows or columns to another location. Excel warns you if you are going to replace a column. Press Cancel to avoid replacing.
-
Copy and replace Hold down CTRL while you point to the border of the selection. When the pointer becomes a copy pointer
, drag the rows or columns to another location. Excel doesn’t warn you if you are going to replace a column. Press CTRL+Z if you don’t want to replace a row or column.
-
Cut and insert Hold down SHIFT while you point to the border of the selection. When the pointer becomes a move pointer
, drag the rows or columns to another location.
-
Copy and insert Hold down SHIFT and CTRL while you point to the border of the selection. When the pointer becomes a move pointer
, drag the rows or columns to another location.
Note: Make sure that you hold down CTRL or SHIFT during the drag-and-drop operation. If you release CTRL or SHIFT before you release the mouse button, you will move the rows or columns instead of copying them.
-
Note: You cannot move or copy nonadjacent rows and columns by using the mouse.
If some cells, rows, or columns on the worksheet are not displayed, you have the option of copying all cells or only the visible cells. For example, you can choose to copy only the displayed summary data on an outlined worksheet.
-
Select the row or column that you want to move or copy.
-
On the Home tab, in the Editing group, click Find & Select, and then click Go To Special.
-
Under Select, click Visible cells only, and then click OK.
-
On the Home tab, in the Clipboard group, click Copy
or press Ctrl+C. .
-
Select the upper-left cell of the paste area.
Tip: To move or copy a selection to a different worksheet or workbook, click another worksheet tab or switch to another workbook, and then select the upper-left cell of the paste area.
-
On the Home tab, in the Clipboard group, click Paste
or press Ctrl+V.
If you click the arrow below Paste
, you can choose from several paste options to apply to your selection.
Excel pastes the copied data into consecutive rows or columns. If the paste area contains hidden rows or columns, you might have to unhide the paste area to see all of the copied cells.
When you copy or paste hidden or filtered data to another application or another instance of Excel, only visible cells are copied.
-
Select the row or column that you want to move or copy.
-
On the Home tab, in the Clipboard group, click Copy
or press Ctrl+C.
-
Select the upper-left cell of the paste area.
-
On the Home tab, in the Clipboard group, click the arrow below Paste
, and then click Paste Special.
-
Select the Skip blanks check box.
-
Double-click the cell that contains the data that you want to move or copy. You can also edit and select cell data in the formula bar.
-
Select the row or column that you want to move or copy.
-
On the Home tab, in the Clipboard group, do one of the following:
-
To move the selection, click Cut
or press Ctrl+X.
-
To copy the selection, click Copy
or press Ctrl+C.
-
-
In the cell, click where you want to paste the characters, or double-click another cell to move or copy the data.
-
On the Home tab, in the Clipboard group, click Paste
or press Ctrl+V.
-
Press ENTER.
Note: When you double-click a cell or press F2 to edit the active cell, the arrow keys work only within that cell. To use the arrow keys to move to another cell, first press Enter to complete your editing changes to the active cell.
When you paste copied data, you can do any of the following:
-
Paste only the cell formatting, such as font color or fill color (and not the contents of the cells).
-
Convert any formulas in the cell to the calculated values without overwriting the existing formatting.
-
Paste only the formulas (and not the calculated values).
Procedure
-
Select the row or column that you want to move or copy.
-
On the Home tab, in the Clipboard group, click Copy
or press Ctrl+C.
-
Select the upper-left cell of the paste area or the cell where you want to paste the value, cell format, or formula.
-
On the Home tab, in the Clipboard group, click the arrow below Paste
, and then do one of the following:
-
To paste values only, click Values.
-
To paste cell formats only, click Formatting.
-
To paste formulas only, click Formulas.
-
When you paste copied data, the pasted data uses the column width settings of the target cells. To correct the column widths so that they match the source cells, follow these steps.
-
Select the row or column that you want to move or copy.
-
On the Home tab, in the Clipboard group, do one of the following:
-
To move cells, click Cut
or press Ctrl+X.
-
To copy cells, click Copy
or press Ctrl+C.
-
-
Select the upper-left cell of the paste area.
Tip: To move or copy a selection to a different worksheet or workbook, click another worksheet tab or switch to another workbook, and then select the upper-left cell of the paste area.
-
On the Home tab, in the Clipboard group, click the arrow under Paste
, and then click Keep Source Column Widths.
You can use the Cut command or Copy command to move or copy selected cells, rows, and columns, but you can also move or copy them by using the mouse.
-
Select the cell, row, or column that you want to move or copy.
-
Do one of the following:
-
To move rows or columns, on the Home tab, in the Clipboard group, click Cut
or press CTRL+X.
-
To copy rows or columns, on the Home tab, in the Clipboard group, click Copy
or press CTRL+C.
-
-
Right-click a row or column below or to the right of where you want to move or copy your selection, and then do one of the following:
-
When you are moving rows or columns, click Insert Cut Cells.
-
When you are copying rows or columns, click Insert Copied Cells.
Tip: To move or copy a selection to a different worksheet or workbook, click another worksheet tab or switch to another workbook, and then select the upper-left cell of the paste area.
-
Note: Excel displays an animated moving border around cells that were cut or copied. To cancel a moving border, press Esc.
-
Select the row or column that you want to move or copy.
-
Do one of the following:
-
Cut and insert
Point to the border of the selection. When the pointer becomes a hand pointer, drag the row or column to another location
-
Cut and replace Hold down SHIFT while you point to the border of the selection. When the pointer becomes a move pointer
, drag the row or column to another location. Excel warns you if you are going to replace a row or column. Press Cancel to avoid replacing.
-
Copy and insert Hold down CTRL while you point to the border of the selection. When the pointer becomes a move pointer
, drag the row or column to another location.
-
Copy and replace Hold down SHIFT and CTRL while you point to the border of the selection. When the pointer becomes a move pointer
, drag the row or column to another location. Excel warns you if you are going to replace a row or column. Press Cancel to avoid replacing.
Note: Make sure that you hold down CTRL or SHIFT during the drag-and-drop operation. If you release CTRL or SHIFT before you release the mouse button, you will move the rows or columns instead of copying them.
-
Note: You cannot move or copy nonadjacent rows and columns by using the mouse.
-
Double-click the cell that contains the data that you want to move or copy. You can also edit and select cell data in the formula bar.
-
Select the row or column that you want to move or copy.
-
On the Home tab, in the Clipboard group, do one of the following:
-
To move the selection, click Cut
or press Ctrl+X.
-
To copy the selection, click Copy
or press Ctrl+C.
-
-
In the cell, click where you want to paste the characters, or double-click another cell to move or copy the data.
-
On the Home tab, in the Clipboard group, click Paste
or press Ctrl+V.
-
Press ENTER.
Note: When you double-click a cell or press F2 to edit the active cell, the arrow keys work only within that cell. To use the arrow keys to move to another cell, first press Enter to complete your editing changes to the active cell.
When you paste copied data, you can do any of the following:
-
Paste only the cell formatting, such as font color or fill color (and not the contents of the cells).
-
Convert any formulas in the cell to the calculated values without overwriting the existing formatting.
-
Paste only the formulas (and not the calculated values).
Procedure
-
Select the row or column that you want to move or copy.
-
On the Home tab, in the Clipboard group, click Copy
or press Ctrl+C.
-
Select the upper-left cell of the paste area or the cell where you want to paste the value, cell format, or formula.
-
On the Home tab, in the Clipboard group, click the arrow below Paste
, and then do one of the following:
-
To paste values only, click Paste Values.
-
To paste cell formats only, click Paste Formatting.
-
To paste formulas only, click Paste Formulas.
-
You can move or copy selected cells, rows, and columns by using the mouse and Transpose.
-
Select the cells or range of cells that you want to move or copy.
-
Point to the border of the cell or range that you selected.
-
When the pointer becomes a
, do one of the following:
|
To |
Do this |
|---|---|
|
Move cells |
Drag the cells to another location. |
|
Copy cells |
Hold down OPTION and drag the cells to another location. |
Note: When you drag or paste cells to a new location, if there is pre-existing data in that location, Excel will overwrite the original data.
-
Select the rows or columns that you want to move or copy.
-
Point to the border of the cell or range that you selected.
-
When the pointer becomes a
, do one of the following:
|
To |
Do this |
|---|---|
|
Move rows or columns |
Drag the rows or columns to another location. |
|
Copy rows or columns |
Hold down OPTION and drag the rows or columns to another location. |
|
Move or copy data between existing rows or columns |
Hold down SHIFT and drag your row or column between existing rows or columns. Excel makes space for the new row or column. |
-
Copy the rows or columns that you want to transpose.
-
Select the destination cell (the first cell of the row or column into which you want to paste your data) for the rows or columns that you are transposing.
-
On the Home tab, under Edit, click the arrow next to Paste, and then click Transpose.
Note: Columns and rows cannot overlap. For example, if you select values in Column C, and try to paste them into a row that overlaps Column C, Excel displays an error message. The destination area of a pasted column or row must be outside the original values.
See also
Insert or delete cells, rows, columns
This post will guide you how to transpose multiple columns into a single columns with multiple rows in Excel. How do I put data from multiple columns into one column with Excel formula; How to transpose columns into single column with VBA macro in excel.
Assuming that you have a data list in range B1:D4 contain 3 columns and you want to transpose them into a single column F. just following the below two ways.
Table of Contents
- Transpose Multiple Columns into One Column with Formula
- Transpose Multiple Columns into One Column with VBA Macro
- Related Functions
You can use the following excel formula to transpose multiple columns that contain a range of data into a single column F:
#1 type the following formula in the formula box of cell F1, then press enter key.
=INDEX($B$1:$D$4,1+INT((ROW(B1)-1)/COLUMNS($B$1:$D$4)),MOD(ROW(B1)-1+COLUMNS($B$1:$D$4),COLUMNS($B$1:$D4))+1)
#2 select cell F1, then drag the Auto Fill Handler over other cells until all values in range B1:D4 are displayed.
#3 you will see that all the data in range B1:D4 has been transposed into single column F.
Transpose Multiple Columns into One Column with VBA Macro
You can also write an Excel VBA Macro to transpose the data of range in B1:D4 into single column F quickly. Just do the following steps:
#1 click on “Visual Basic” command under DEVELOPER Tab.
#2 then the “Visual Basic Editor” window will appear.
#3 click “Insert” ->”Module” to create a new module.
#4 paste the below VBA code into the code window. Then clicking “Save” button.
Sub transposeColumns()
Dim R1 As Range
Dim R2 As Range
Dim R3 As Range
Dim RowN As Integer
wTitle = "transpose multiple Columns"
Set R1 = Application.Selection
Set R1 = Application.InputBox("please select the Source data of Ranges:", wTitle, R1.Address, Type:=8)
Set R2 = Application.InputBox("Select one destination single Cell or column:", wTitle, Type:=8)
RowN = 0
Application.ScreenUpdating = False
For Each R3 In R1.Rows
R3.Copy
R2.Offset(RowN, 0).PasteSpecial Paste:=xlPasteAll, Transpose:=True
RowN = RowN + R3.Columns.Count
Next
Application.CutCopyMode = False
Application.ScreenUpdating = True
End Sub
#5 back to the current worksheet, then run the above excel macro. Click Run button.
#6 select the source data of ranges, such as: B1:D4
#7 select one single cell in the destination Column, such as: F1
#8 let’s see the last result.
- Excel INDEX function
The Excel INDEX function returns a value from a table based on the index (row number and column number)The INDEX function is a build-in function in Microsoft Excel and it is categorized as a Lookup and Reference Function.The syntax of the INDEX function is as below:= INDEX (array, row_num,[column_num])… - Excel INT function
The Excel INT function returns the integer portion of a given number. And it will rounds a given number down to the nearest integer. And the INT function rounds down, so if you provide a negative number, the returned value will become more negative.The syntax of the INT function is as below:= INT (number)… - Excel ROW function
The Excel ROW function returns the row number of a cell reference.The ROW function is a build-in function in Microsoft Excel and it is categorized as a Lookup and Reference Function.The syntax of the ROW function is as below:= ROW ([reference])…. - Excel Columns function
The Excel COLUMNS function returns the number of columns in an Array or a reference.The syntax of the COLUMNS function is as below:=COLUMNS (array)…. - Excel MOD function
he Excel MOD function returns the remainder of two numbers after division. So you can use the MOD function to get the remainder after a number is divided by a divisor in Excel. The syntax of the MOD function is as below:=MOD (number, divisor)….
You can write a simple formula in your cell (B9 in your example) which uses INDIRECT(ADDRESS(x,y)) where x and y are the positions of the data you need to get. In your case, it would start at (1,1).
(As noted by Scott Craner in a comment, you probably want to use INDEX() instead of INDIRECT()).
The x position is going to increment from 1 to n and then repeat. So you can use the MOD() function to do that. In our case the ROW() is the number we need to use. Since MOD() is zero based, you have to do a little bit of math, nothing major:
MOD(ROW() - 9, 1000) + 1
- The ‘-9’ is because we start on row 9. In your case, if you have 2,000 rows, it will be closer to 2,000, of course. The number must become 0 in the very first entry.
- The 1,000 is the number of columns you have in your spreadsheet.
For the y position, you use an integer division (i.e. a FLOOR()). Again, the ROW() starts at 1, so we need to take that in account.
FLOOR((ROW() - 9) / 1000) + 1
- The ‘-9’ and 1,000 are like above.
Now we have a complete formula:
=INDIRECT(ADDRESS(MOD(ROW() - 9, 1000) + 1, FLOOR((ROW() - 9) / 1000) + 1))
First verify that this works as expected for the first cell (i.e. B9) then try again for the next few cells (B10, B11) by copying the line (i.e. select B9 and N number of lines after that and then hit Ctrl-D). You should test enough cells so you start seeing the second line appearing in your new column.
Now select B9 and all the rows to copy the entire set of values vertically (so if you have 1,000 columns × 2,000 rows, you need 2,000,000 rows in that column, not too sure Excel goes that far, though)
This will copy the data vertically. If necessary, you could do that in a separate sheet instead of below the existing data. Up to you. When referencing rows, it needs to include the name of the sheet. I’m not too sure how to do that with ADDRESS but you can probably find the info in the docs. At this point, though, this is formulae and not just plain data. If you want to convert that column to plain data, save it in a CSV file where formulae do not get saved. Then reload the CSV and copy that column where you want it.
Done without VBA. (although formulae are kind of VBA expressions…)
I have multiple lists that are in separate columns in excel. What I need to do is combine these columns of data into one big column. I do not care if there are duplicate entries, however I want it to skip row 1 of each column.
Also what about if ROW1 has headers from January to December, and the length of the columns are different and needs to be combine into one big column?
ROW1| 1 2 3
ROW2| A D G
ROW3| B E H
ROW4| C F I
should combine into
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
The first row of each column needs to be skipped.
asked Jun 4, 2010 at 20:40
Try this. Click anywhere in your range of data and then use this macro:
Sub CombineColumns()
Dim rng As Range
Dim iCol As Integer
Dim lastCell As Integer
Set rng = ActiveCell.CurrentRegion
lastCell = rng.Columns(1).Rows.Count + 1
For iCol = 2 To rng.Columns.Count
Range(Cells(1, iCol), Cells(rng.Columns(iCol).Rows.Count, iCol)).Cut
ActiveSheet.Paste Destination:=Cells(lastCell, 1)
lastCell = lastCell + rng.Columns(iCol).Rows.Count
Next iCol
End Sub
answered Jun 5, 2010 at 13:15
Alex PAlex P
12.2k5 gold badges51 silver badges69 bronze badges
3
You can combine the columns without using macros. Type the following function in the formula bar:
=IF(ROW()<=COUNTA(A:A),INDEX(A:A,ROW()),IF(ROW()<=COUNTA(A:B),INDEX(B:B,ROW()-COUNTA(A:A)),IF(ROW()>COUNTA(A:C),"",INDEX(C:C,ROW()-COUNTA(A:B)))))
The statement uses 3 IF functions, because it needs to combine 3 columns:
- For column A, the function compares the row number of a cell with the total number of cells in A column that are not empty. If the result is true, the function returns the value of the cell from column A that is at row(). If the result is false, the function moves on to the next IF statement.
- For column B, the function compares the row number of a cell with the total number of cells in A:B range that are not empty. If the result is true, the function returns the value of the first cell that is not empty in column B. If false, the function moves on to the next IF statement.
- For column C, the function compares the row number of a cell with the total number of cells in A:C range that are not empty. If the result is true, the function returns a blank cell and doesn’t do any more calculation. If false, the function returns the value of the first cell that is not empty in column C.
TylerH
20.6k64 gold badges76 silver badges97 bronze badges
answered Dec 3, 2014 at 8:25
CristinaPCristinaP
3063 silver badges6 bronze badges
0
Not sure if this completely helps, but I had an issue where I needed a «smart» merge. I had two columns, A & B. I wanted to move B over only if A was blank. See below. It is based on a selection Range, which you could use to offset the first row, perhaps.
Private Sub MergeProjectNameColumns()
Dim rngRowCount As Integer
Dim i As Integer
'Loop through column C and simply copy the text over to B if it is not blank
rngRowCount = Range(dataRange).Rows.Count
ActiveCell.Offset(0, 0).Select
ActiveCell.Offset(0, 2).Select
For i = 1 To rngRowCount
If (Len(RTrim(ActiveCell.Value)) > 0) Then
Dim currentValue As String
currentValue = ActiveCell.Value
ActiveCell.Offset(0, -1) = currentValue
End If
ActiveCell.Offset(1, 0).Select
Next i
'Now delete the unused column
Columns("C").Select
selection.Delete Shift:=xlToLeft
End Sub
answered Jun 4, 2010 at 20:49
Function Concat(myRange As Range, Optional myDelimiter As String) As String
Dim r As Range
Application.Volatile
For Each r In myRange
If Len(r.Text) Then
Concat = Concat & IIf(Concat <> "", myDelimiter, "") & r.Text
End If
Next
End Function
answered Jun 4, 2010 at 21:01
Mark BakerMark Baker
208k31 gold badges340 silver badges383 bronze badges
Home / Excel Basics / How to Copy and Paste a Column in Excel
Copying the data is a very frequent task in our day-to-day lives while working in Excel or any other word processing software. Usually, we have to copy a single cell from one place to another or even sometimes in a different worksheet also. It is very easy to do.
But when it comes to copying multiple continuous cells as well as non-adjacent cells then we all find ourselves in very big trouble.
In this tutorial, we will learn methods to copy the single or multiple (continuous, and non-continuous) columns. Now, let’s go through it step-by-step.
- First, select the entire column from its Column Header Letter on the top of it that you want to copy.
- Then, press the right-click button on the mouse and select the “Copy” option from the pop-up box.
- After this, select the range of cells of that particular column where you wish to “Paste” your data.
- Once you are selecting the range, click on the right key of the mouse and choose the paste option from it.
Copying the Column by using a Keyboard Shortcut
Here’s an easier way to copy and paste the data by using the keyboard shortcut instead of doing it manually.
- First of all, click on any cell of the column that you want to copy.
- From here, select the entire column by holding the shortcut key that is (Control + Spacebar).
- Next, you can copy the selected column by pressing the Control + C button on the keyboard.
- Now, you’ll see that column is highlighted, and then paste it by using the Control + V.
Related ➜ Keyboard Shortcuts for Excel (PDF Cheatsheet)
Copy and Paste Multiple Adjacent Columns
If you want to copy multiple columns of the spreadsheet at the same time, you can do this. Here, below are the steps.
- Select the multiple columns in a sequence with the left key of your mouse by the column header.
- Next, right-click on the selected columns.
- Click on the “Copy” option from the dialog box to select the entire data.
- Now, you’ll see that column is highlighted, and then paste it by using the Control + V.
Important Note: Make sure that you have enough blank columns where you would like to paste your data or in case you already have something in that range of cells, then it would be overwritten.
Copy Multiple Non-Adjacent Columns
The simplest way to copy multiple non-adjacent columns is by using the CTRL key. Let’s do it stepwise.
- In your worksheet, select the first column by clicking on its header.
- After that, click on the next columns one by one that you want to highlight by holding down the Control key.
- Following this, right-click on any of the selected columns and choose “Copy” from the dialog box.
- Now, you’ll see all the selected columns have been highlighted on the sheet.
- In the end, select the destination cell where you would like to paste your data and by pressing Control + V you can paste it.
Copy and Paste the column is from the Ribbon
It is an interesting thing to know that you can also copy and paste the values from the ribbon. Let’s do it by the following steps:
- First, select all the columns that you wish to copy.
- Then, go to the Home tab and from the Clipboard> choose Copy or either use (Ctrl + C) from the keyboard to copy the columns.
- Select the particular cell where you wish to paste your data.
- And then, click on the paste from the Ribbon or you can use the shortcut that is (Ctrl + V).
So, these are the ways by which you can copy and paste columns in excel.
Moreover, if you want to copy multiple non-adjacent columns then you can use the third method for this.
Along with this, the above-given shortcut of copy and paste will help you to compile your data as soon as possible.
When working with Excel spreadsheets, copying and pasting data is a frequent task.
And many times, you will need to copy and paste an entire column (or multiple columns) in Excel. It could be a copy-paste in the same worksheet, or in any other worksheet or workbook.
In this tutorial, I will cover everything that you need to know about copy-pasting columns in Excel.
There there are multiple ways to do it. You can choose to copy and paste an entire column or multiple columns as is, or only copy the values or formatting, or formulas from a column.
Let’s see how to do all this.
Copying a Column As-Is Using a Keyboard Shortcut
Suppose you have a dataset as shown below and you want to copy column A and paste it as Column D.
For the purpose of illustration, I have also highlighted Column A in yellow color.

If all you want is to copy a column and paste it, below are the steps to get this done:
- Select the column that you want to copy. To do this, click on the column header letter (which is at the top of the column)
- With the entire column selected, use the keyboard shortcut – Control + C (or Command + C if using Mac). This will copy the entire selected column (you will see dancing ants at the borders)
- Select the destination column where you want to paste the copied column
- Paste it using the keyboard shortcut – Control + V (or Command + V if using a Mac)

The above steps would copy the selected column and paste it into the destination.
Note that this would copy everything from the source column to the destination column (including values, formatting, and formulas).
In case there is conditional formatting applied in the column, it would also be copied.
For this to work, you will have to select an entire destination column. If you only select a cell or a range in the destination column (as not the whole column), you will get an error.
Note: In this example, I have used the keyboard shortcuts Control + C and Control + V. You can also get the same thing by right-clicking on the selection and then clicking on Copy or Paste options.
Copying a Column As-Is Using a Keyboard+ Mouse Trick
Another really quick way to copy a column and paste it into the destination is by using a simple keyboard and mouse combo.
Suppose you have a dataset as shown below and you want to copy column A and paste it over Column D.

Below are the steps to do this:
- Select the column that you want to copy

- Hold the Control key (or Command key in Mac)
- Place the mouse cursor at the edge of the selected column. You will notice that it changes to pointed arrow with a plus sign

- With the Control/Command key pressed, press the left mouse key and drag the column to the position where you want it copied

The above steps would copy and then paste the columns that you dragged to the destination location.
Note that this technique will also work with multiple contiguous columns, but it won’t work with non-contiguous columns. For example, if you select columns A and D, then you won’t be able to use this, but you can use this if you select columns A and B.
Copy Paste a Column using Paste Special (Copy Value or Formatting or Formula Only)
Many times, you don’t need to copy the entire column with all the data and the formatting and formulas.
You may only need to copy the formatting or only copy the values without the formatting.
This can easily be done using the paste special feature in Excel.
Paste Special allows to copy and then paste specific elements from the copied data (such as values or formulas or formatting)
Suppose you have a dataset as shown below, and you want to copy and paste only values from column A to column D.

Below are the steps to do this using Paste Special:
- Select the column that you want to copy (column A in this example)
- Copy the column (or the range in the column). You can do this using Control + C (or Command + C) or right-click on the selection and then click on Copy
- Right-clcik on the destination cell (D1 in this example)
- Click on Paste Special option. This will open the Paste Special dialog box

- Select Values

- Click Ok
The above steps copy the entire column A, but only paste the values and not the formatting.
If you only want to paste the formatting, you can select the ‘Formats’ option in the Paste Special dialog box.
In case you want to copy values as well as formatting (but nothing else such as formulas), you can repeat the process twice. So copy Column A, then first paste values and then paste formatting.
Shortcut to Open Paste Special dialog box: ALT + E + S
Some other options that you get when using Paste Special:
- Column width
- Formulas
- Formulas and Number formats
- Values and Number formats
- Everything except the borders
- Comments and Notes
- Data validation (drop down lists)
So these are some of the ways you can use to copy and paste columns in Excel.
If you want to copy the entire column, you can use the first two methods, and in case you want to selectively copy something from the column, then you can use the Paste Special technique.
I hope you found this tutorial useful!
Other Excel tutorials you may also find useful:
- How to Copy Conditional Formatting to Another Cell in Excel
- How to Copy Excel Table to MS Word (4 Easy Ways)
- How to Copy and Paste Formulas in Excel without Changing Cell References
- How to Quickly Copy Chart (Graph) Format in Excel
- How to Multiply in Excel Using Paste Special
- Copy and Paste Multiple Cells in Excel (Adjacent & Non-Adjacent)
- How to Cut a Cell Value in Excel (Keyboard Shortcuts)










 or press CTRL+X.
or press CTRL+X. or press CTRL+C.
or press CTRL+C. , drag the rows or columns to another location. Excel warns you if you are going to replace a column. Press Cancel to avoid replacing.
, drag the rows or columns to another location. Excel warns you if you are going to replace a column. Press Cancel to avoid replacing. , drag the rows or columns to another location. Excel doesn’t warn you if you are going to replace a column. Press CTRL+Z if you don’t want to replace a row or column.
, drag the rows or columns to another location. Excel doesn’t warn you if you are going to replace a column. Press CTRL+Z if you don’t want to replace a row or column.
 or press Ctrl+V.
or press Ctrl+V. , drag the row or column to another location
, drag the row or column to another location , do one of the following:
, do one of the following: