Excel for Microsoft 365 Excel for Microsoft 365 for Mac Excel 2021 Excel 2021 for Mac Excel 2019 Excel 2019 for Mac Excel 2016 Excel 2016 for Mac Excel 2013 Excel 2010 Excel 2007 Excel for Mac 2011 More…Less
Sometimes you need to check if a cell is blank, generally because you might not want a formula to display a result without input.
In this case we’re using IF with the ISBLANK function:
-
=IF(ISBLANK(D2),»Blank»,»Not Blank»)
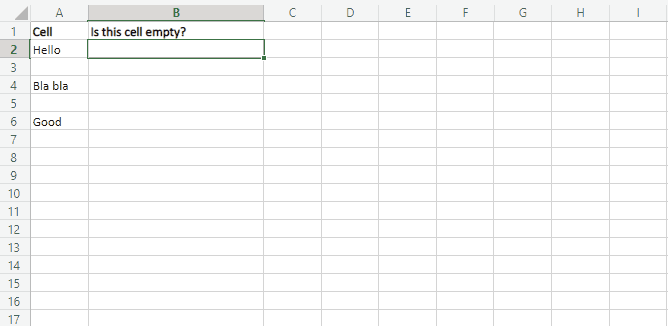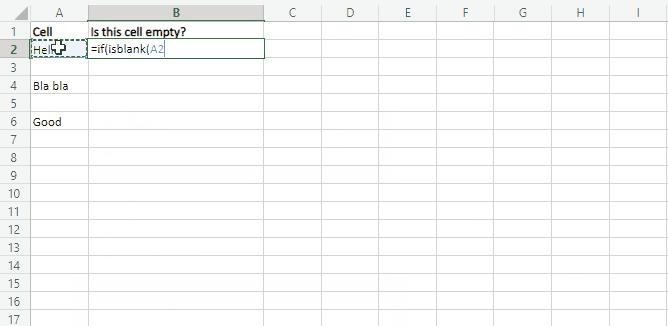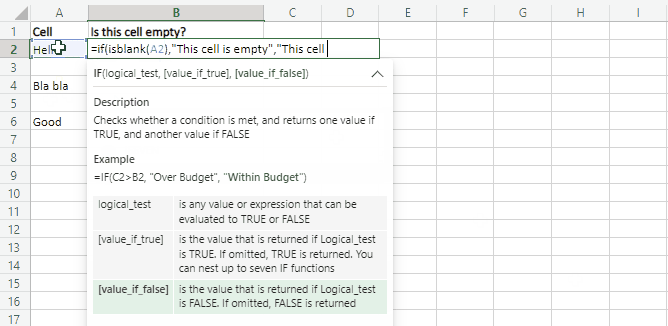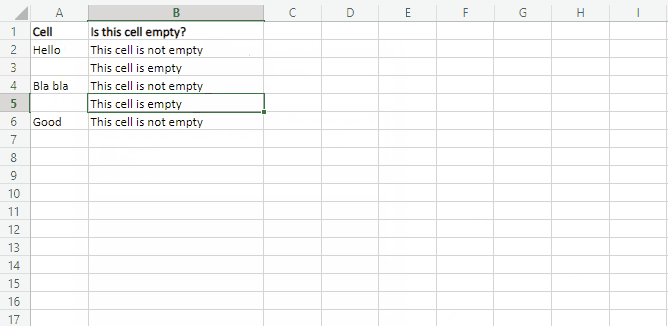
Which says IF(D2 is blank, then return «Blank», otherwise return «Not Blank»). You could just as easily use your own formula for the «Not Blank» condition as well. In the next example we’re using «» instead of ISBLANK. The «» essentially means «nothing».
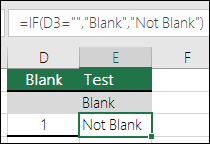
=IF(D3=»»,»Blank»,»Not Blank»)
This formula says IF(D3 is nothing, then return «Blank», otherwise «Not Blank»). Here is an example of a very common method of using «» to prevent a formula from calculating if a dependent cell is blank:
-
=IF(D3=»»,»»,YourFormula())
IF(D3 is nothing, then return nothing, otherwise calculate your formula).
Need more help?
Want more options?
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.
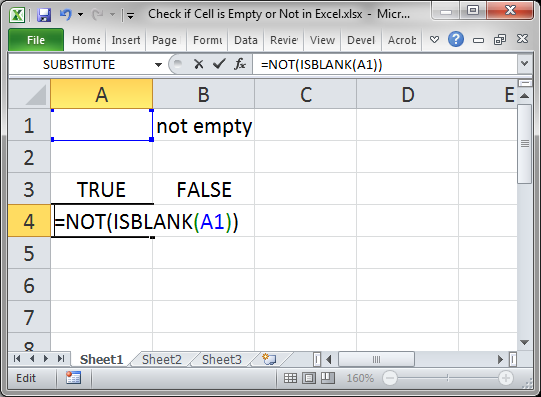
The ISBLANK function returns TRUE when a cell is empty, and FALSE when a cell is not empty. For example, if A1 contains «apple», ISBLANK(A1) returns FALSE. Use the ISBLANK function to test if a cell is empty or not. ISBLANK function takes one argument, value, which is a cell reference like A1.
The word «blank» is somewhat misleading in Excel, because a cell that contains only space will look blank but not be empty. In general, it is best to think of ISBLANK to mean «is empty» since it will return FALSE when a cell looks blank but is not empty.
Examples
If cell A1 contains nothing at all, the ISBLANK function will return TRUE:
=ISBLANK(A1) // returns TRUE
If cell A1 contains any value, or any formula, the ISBLANK function will return FALSE:
=ISBLANK(A1) // returns false
Is not blank
To test if a cell is not blank, nest ISBLANK inside the NOT function like this:
=NOT(ISBLANK(A1)) // test not blank
The above formula will return TRUE when a cell is not empty, and FALSE when a cell is empty.
Empty string syntax
Many formulas will use an abbreviated syntax to test for empty cells, instead of the ISBLANK function. This syntax uses an empty string («») with Excel’s math operators «=» or «<>». For example, to test if A1 is empty, you can use:
=A1="" // TRUE if A1 is empty
To test if A1 is not empty:
=A1<>"" // TRUE if A1 is not empty
This syntax can be used interchangeably with ISBLANK. For example, inside the IF function:
=IF(ISBLANK(A1),result1,result2) // if A1 is empty
is equivalent to:
=IF(A1="",result1,result2) // if A1 is empty
Likewise, the formula:
=IF(NOT(ISBLANK(A1)),result1,result2)
is the same, as:
=IF(A1<>"",result1,result2)
Both will return result1 when A1 is not empty, and result2 when A1 is empty.
Empty strings
If a cell contains any formula, the ISBLANK function and the alternatives above will return FALSE, even if the formula returns an empty string («»). This can cause problems when the goal is to count or process blank cells that include empty strings.
One workaround is to use the LEN function to test for a length of zero. For example, the formula below will return TRUE if A1 is empty or contains a formula that returns an empty string:
=LEN(A1)=0 // TRUE if empty
So, inside the IF function, you can use LEN like this:
=IF(LEN(A1)=0,result1,result2) // if A1 is empty
You can use this same approach to count cells that are not blank.
How to check if a cell is empty or is not empty in Excel; this tutorial shows you a couple different ways to do this.
Sections:
Check if a Cell is Empty or Not — Method 1
Check if a Cell is Empty or Not — Method 2
Notes
Check if a Cell is Empty or Not — Method 1
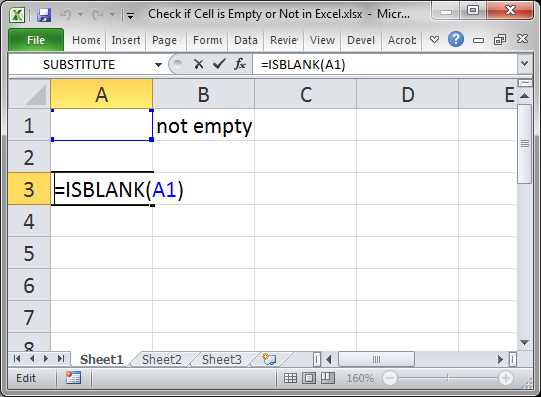
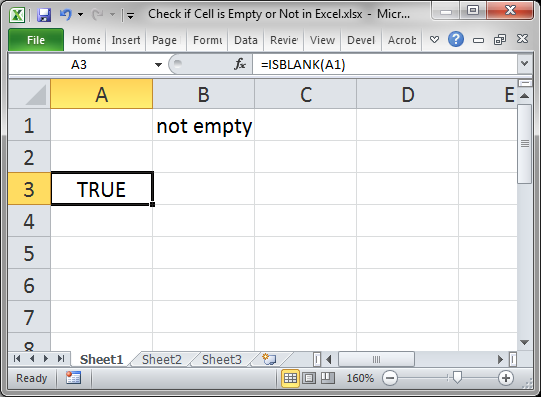
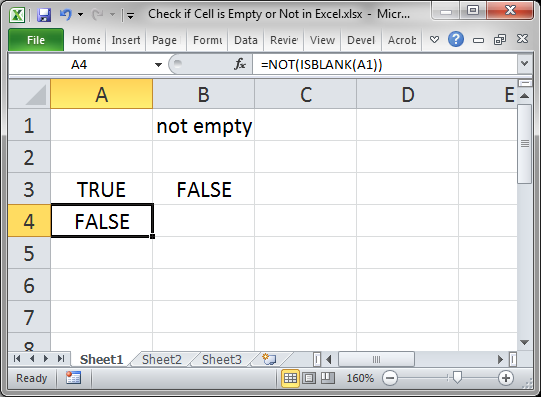
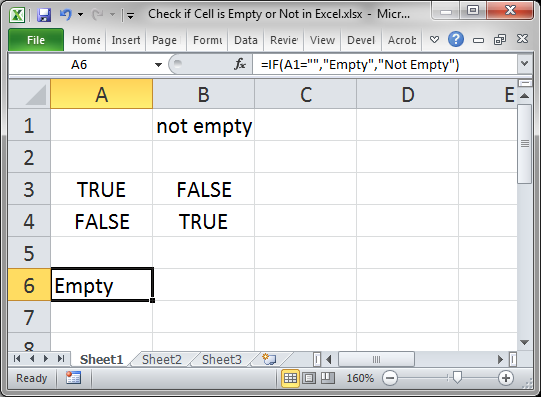
Use the ISBLANK() function.
This will return TRUE if the cell is empty or FALSE if the cell is not empty.
Here, cell A1 is being checked, which is empty.
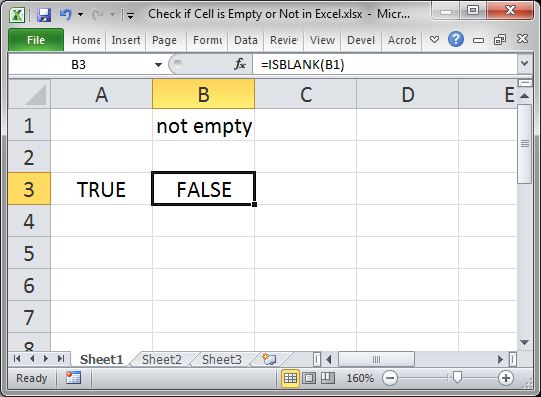
When the cell is not empty, it looks like this:
FALSE is output because cell B1 is not empty.
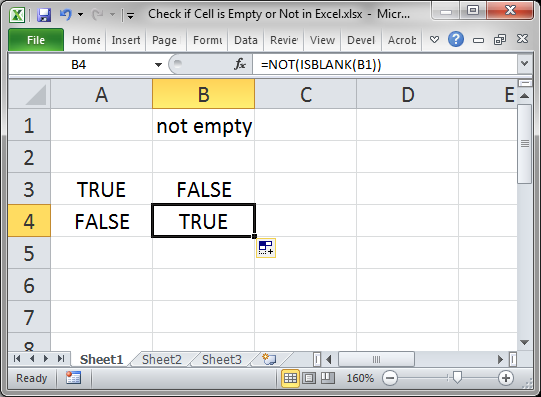
Reverse the True/False Output
Some formulas need to have TRUE or FALSE reversed in order to work correctly; to do this, use the NOT() function.
Result:
Whereas ISBLANK() output a TRUE for cell A1, the NOT() function reversed that and changed it to FALSE.
The same works for changing FALSE to TRUE.
Check if a Cell is Empty or Not — Method 2
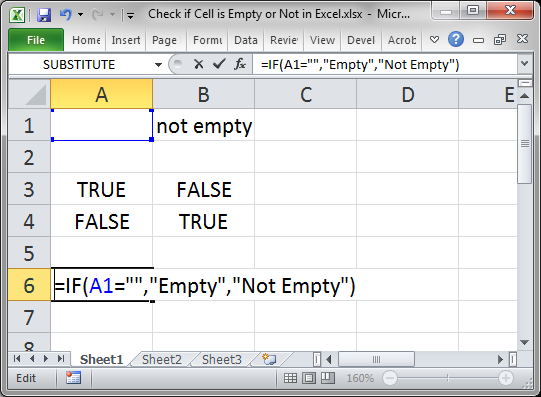
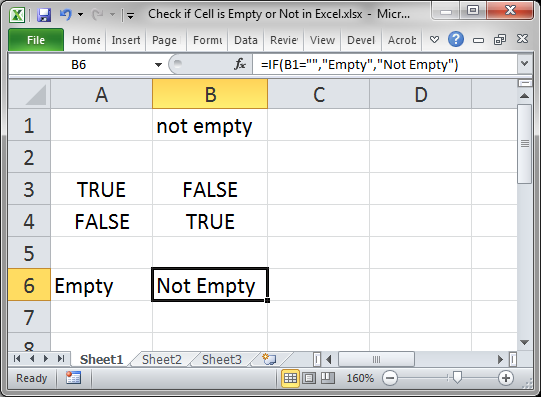
You can also use an IF statement to check if a cell is empty.
=IF(A1="","Empty","Not Empty")
Result:
The function checks if this part is true: A1=»» which checks if A1 is equal to nothing.
When there is something in the cell, it works like this:
Cell B1 is not empty so we get a Not Empty result.
In this example I set the IF statement to output «Empty» or «Not Empty» but you can change it to whatever you like.
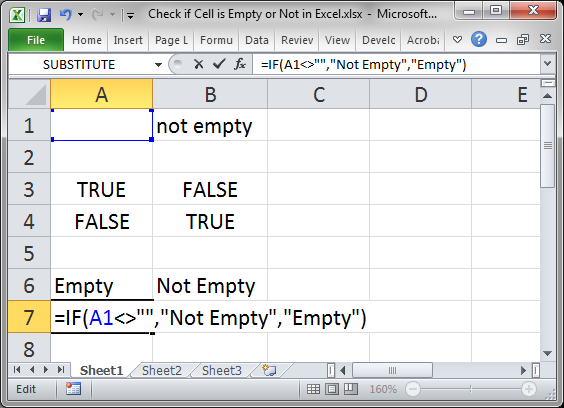
Reverse the Check
The example above checked if the cell was empty, but you can also check if the cell is not empty.
There are a few different ways to do this, but I will show you a simple and easy method here.
=IF(A1<>"","Not Empty","Empty")
Notice the check this time is A1<>»» and that says «is cell A1 not equal to nothing.» It sounds confusing but just remember that <> is basically the reverse of =.
I also had to switch the «Empty» and «Not Empty» in order to get the correct result since we are now checking if the cell is not empty.
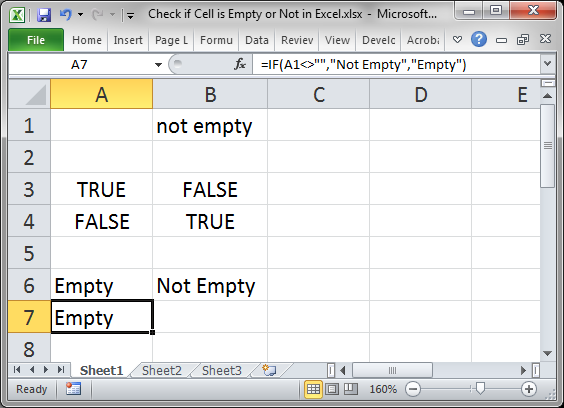
Result:
As you can see, it outputs the same result as the previous example, just like it should.
Using <> instead of = merely reverses it, making a TRUE become a FALSE and a FALSE become a TRUE, which is why «Empty» and «Not Empty» had to be reversed in order to still output the correct result.
Notes
It may seem useless to return TRUE or FALSE like in the first method, but remember that many functions in Excel, including IF(), AND(), and OR() all rely on results that are either TRUE or FALSE.
Checking for blanks and returning TRUE or FALSE is a simple concept but it can get a bit confusing in Excel, especially when you have complex formulas that rely on the result of the formulas in this tutorial. Save this tutorial and work with the attached sample file and you will have it down in no time.
Make sure to download the attached sample file to work with these examples in Excel.
Similar Content on TeachExcel
Excel VBA Check if a Cell is in a Range
Tutorial: VBA that checks if a cell is in a range, named range, or any kind of range, in Excel.
Sec…
Make Complex Formulas for Conditional Formatting in Excel
Tutorial: How to make complex formulas for conditional formatting rules in Excel. This will serve as…
Sort Data Alphabetically or Numerically in Excel 2007 and Later
Tutorial: This Excel tip shows you how to Sort Data Alphabetically and Numerically in Excel 2007. T…
Filter Data to Display the Results that Begin With Specified Text or Words in Excel — AutoFilter
Macro: This Excel macro automatically filters a set of data based on the words or text that are c…
Odd or Even Row Formulas in Excel
Tutorial: Formulas to determine if the current cell is odd or even; this allows you to perform speci…
Formula to Count Occurrences of a Word in a Cell or Range in Excel
Tutorial: Formula to count how many times a word appears in a single cell or an entire range in Exce…
Subscribe for Weekly Tutorials
BONUS: subscribe now to download our Top Tutorials Ebook!
Home / Excel Formulas / IF Cell is Blank (Empty) using IF + ISBLANK
In Excel, if you want to check if a cell is blank or not, you can use a combination formula of IF and ISBLANK. These two formulas work in a way where ISBLANK checks for the cell value and then IF returns a meaningful full message (specified by you) in return.
In the following example, you have a list of numbers where you have a few cells blank.

Formula to Check IF a Cell is Blank or Not (Empty)
- First, in cell B1, enter IF in the cell.
- Now, in the first argument, enter the ISBLANK and refer to cell A1 and enter the closing parentheses.
- Next, in the second argument, use the “Blank” value.
- After that, in the third argument, use “Non-Blank”.
- In the end, close the function, hit enter, and drag the formula up to the last value that you have in the list.

As you can see, we have the value “Blank” for the cell where the cell is empty in column A.
=IF(ISBLANK(A1),"Blank","Non-Blank")Now let’s understand this formula. In the first part where we have the ISBLANK which checks if the cells are blank or not.

And, after that, if the value returned by the ISBLANK is TRUE, IF will return “Blank”, and if the value returned by the ISBLANK is FALSE IF will return “Non_Blank”.

Alternate Formula
You can also use an alternate formula where you just need to use the IF function. Now in the function, you just need to specify the cell where you want to test the condition and then use an equal operator with the blank value to create a condition to test.
And you just need to specify two values that you want to get the condition TRUE or FALSE.

Download Sample File
- Ready
And, if you want to Get Smarter than Your Colleagues check out these FREE COURSES to Learn Excel, Excel Skills, and Excel Tips and Tricks.
EXCEL FORMULA 1. If a cell is not blank using the IF function
EXCEL
Hard coded formula

Cell reference formula

|
GENERIC FORMULA =IF(cell_ref<>»», value_if_true, value_if_false) ARGUMENTS GENERIC FORMULA =IF(cell_ref<>»», value_if_true, value_if_false) ARGUMENTS EXPLANATION This formula uses the IF function with a test criteria of two double quotation marks («»), without any value inserted between them and ‘does not equal to’ sign (<>) in front of them, to assess if a cell is not empty and return a specific value. The expression <>»» means «not empty». If a cell is not blank the formula will return a value that has been assigned as the true value, alternatively if a cell is blank the formula will return a value assigned as the false value. With this formula you can enter the values, that will be returned if the cell is empty or not, directly into the formula or reference them to specific cells that capture these values. Click on either the Hard Coded or Cell Reference button to view the formula that has the return values directly entered into the formula or referenced to specific cells that capture these values, respectively. In this example the formula tests if a specific cell is not blank. If the cell is not blank the formula will return a value of «Yes» (hard coded example) or value in cell C5 (cell reference example). If the cell is empty the formula will return a value of «No» (hard coded example) or value in cell C6 (cell reference example). If you are using the formula with values entered directly in the formula and want to return a numerical value, instead of a text value, you do not need to apply the double quotation marks around the values that are to be returned e.g. (=IF(C5<>»»,1,0)). |
EXCEL FORMULA 2. If a cell is not blank using the IF, NOT and ISBLANK functions
EXCEL
Hard coded formula

Cell reference formula

|
GENERIC FORMULA =IF(NOT(ISBLANK(cell_ref)), value_if_true, value_if_false) ARGUMENTS GENERIC FORMULA =IF(NOT(ISBLANK(cell_ref)), value_if_true, value_if_false) ARGUMENTS EXPLANATION This formula uses a combination of the IF, NOT and ISBLANK functions to assess if a cell is not blank and return a specific value. Unlike the first formula, which uses the double quotation marks («») to test if the selected cell is not blank, this formula uses the NOT and ISBLANK functions. If the cell is not blank the ISBLANK function will return FALSE, alternatively it will return TRUE. The NOT function will then return the opposite to what the ISBLANK function has returned. Therefore, if the cell is not blank the combination of the NOT and ISBLANK function will return a TRUE value. The formula will then return a value that has been assigned as the true value, alternatively if the cell is blank the formula will return a value assigned as the false value. With this formula you can enter the values, that will be returned if the cell is empty or not, directly into the formula or reference them to specific cells that capture these values. Click on either the Hard Coded or Cell Reference button to view the formula that has the return values directly entered into the formula or referenced to specific cells that capture these values, respectively. In this example the formula tests if a specific cell is not blank. If the cell is not blank the formula will return a value of «Yes» (hard coded example) or value in cell C5 (cell reference example). If the cell is empty the formula will return a value of «No» (hard coded example) or value in cell C6 (cell reference example). If you are using the formula with values entered directly in the formula and want to return a numerical value, instead of a text value, you do not need to apply the double quotation marks around the values that are to be returned e.g. (=IF(NOT(ISBLANK(C5)),1,0)). |
VBA CODE 1. If a cell is not blank using the If Statement
VBA
Hard coded against single cell
Sub If_a_cell_is_not_blank()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = Worksheets(«Analysis»)
If ws.Range(«C5») <> «» Then
ws.Range(«D5») = «Yes»
Else
ws.Range(«D5») = «No»
End If
End Sub
Cell reference against single cell
Sub If_a_cell_is_not_blank()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = Worksheets(«Analysis»)
If ws.Range(«C9») <> «» Then
ws.Range(«D9») = ws.Range(«C5»)
Else
ws.Range(«D9») = ws.Range(«C6»)
End If
End Sub
Hard coded against range of cells
Sub If_a_cell_is_not_blank()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = Worksheets(«Analysis»)
For x = 5 To 11
If ws.Cells(x, 3) <> «» Then
ws.Cells(x, 4) = «Yes»
Else
ws.Cells(x, 4) = «No»
End If
Next x
End Sub
Cell reference against range of cells
Sub If_a_cell_is_not_blank()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = Worksheets(«Analysis»)
For x = 9 To 15
If ws.Cells(x, 3) <> «» Then
ws.Cells(x, 4) = ws.Range(«C5»)
Else
ws.Cells(x, 4) = ws.Range(«C6»)
End If
Next x
End Sub
KEY PARAMETERS
Output Range: Select the output range by changing the cell reference («D5») in the VBA code.
Cell to Test: Select the cell that you want to check if it’s not blank by changing the cell reference («C5») in the VBA code.
Worksheet Selection: Select the worksheet which captures the cells that you want to test if they are not blank and return a specific value by changing the Analysis worksheet name in the VBA code. You can also change the name of this object variable, by changing the name ‘ws’ in the VBA code.
True and False Results: In this example if a cell is not blank the VBA code will return a value of «Yes». If a cell is blank the VBA code will return a value of «No». Both of these values can be changed to whatever value you desire by directly changing them in the VBA code.
NOTES
Note 1: If the cell that is being tested is returning a value of («») this VBA code will identify the cell as blank.
Note 2: If your True or False result is a text value it will need to be captured within quotation marks («»). However, if the result is a numeric value, you can enter it without the use of quotation marks.
KEY PARAMETERS
Output Range: Select the output range by changing the cell reference («D9») in the VBA code.
Cell to Test: Select the cell that you want to check if it’s not blank by changing the cell reference («C9») in the VBA code.
Worksheet Selection: Select the worksheet which captures the cells that you want to test if they are not blank and return a specific value by changing the Analysis worksheet name in the VBA code. You can also change the name of this object variable, by changing the name ‘ws’ in the VBA code.
True and False Results: In this example if a cell is not blank the VBA code will return a value stored in cell C5. If a cell is blank the VBA code will return a value stored in cell C6. Both of these values can be changed to whatever value you desire by either referencing to a different cell that captures the value that you want to return or change the values in those cells.
NOTES
Note 1: If the cell that is being tested is returning a value of («») this VBA code will identify the cell as blank.
KEY PARAMETERS
Output and Test Range: Select the output rows and the rows that captures the cells that are to be tested by changing the x values (5 to 11). This example assumes that both the output and the associated test cell will be in the same row.
Test Column: Select the column that captures the cells that are to be tested by changing number 3, in ws.Cells(x, 3).
Output Column: Select the output column by changing number 4, in ws.Cells(x, 4).
Worksheet Selection: Select the worksheet which captures the cells that you want to test if they are not blank and return a specific value by changing the Analysis worksheet name in the VBA code. You can also change the name of this object variable, by changing the name ‘ws’ in the VBA code.
True and False Results: In this example if a cell is not blank the VBA code will return a value of «Yes». If a cell is blank the VBA code will return a value of «No». Both of these values can be changed to whatever value you desire by directly changing them in the VBA code.
NOTES
Note 1: If the cell that is being tested is returning a value of («») this VBA code will identify the cell as blank.
Note 2: If your True or False result is a text value it will need to be captured within quotation marks («»). However, if the result is a numeric value, you can enter it without the use of quotation marks.
KEY PARAMETERS
Output and Test Range: Select the output rows and the rows that captures the cells that are to be tested by changing the x values (9 to 15). This example assumes that both the output and the associated test cell will be in the same row.
Test Column: Select the column that captures the cells that are to be tested by changing number 3, in ws.Cells(x, 3).
Output Column: Select the output column by changing number 4, in ws.Cells(x, 4).
Worksheet Selection: Select the worksheet which captures the cells that you want to test if they are not blank and return a specific value by changing the Analysis worksheet name in the VBA code. You can also change the name of this object variable, by changing the name ‘ws’ in the VBA code.
True and False Results: In this example if a cell is not blank the VBA code will return a value stored in cell C5. If a cell is blank the VBA code will return a value stored in cell C6. Both of these values can be changed to whatever value you desire by either referencing to a different cell that captures the value that you want to return or change the values in those cells.
NOTES
Note 1: If the cell that is being tested is returning a value of («») this VBA code will identify the cell as blank.
VBA CODE 2. If a cell is not blank using Not and IsEmpty
VBA
Hard coded against single cell
Sub If_a_cell_is_not_blank_using_Not_and_IsEmpty()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = Worksheets(«Analysis»)
If Not (IsEmpty(ws.Range(«C5»)))Then
ws.Range(«D5») = «Yes»
Else
ws.Range(«D5») = «No»
End If
End Sub
Cell reference against single cell
Sub If_a_cell_is_not_blank_using_Not_and_IsEmpty()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = Worksheets(«Analysis»)
If Not (IsEmpty(ws.Range(«C9»)))Then
ws.Range(«D9») = ws.Range(«C5»)
Else
ws.Range(«D9») = ws.Range(«C6»)
End If
End Sub
Hard coded against range of cells
Sub If_a_cell_is_not_blank_using_Not_and_IsEmpty()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = Worksheets(«Analysis»)
For x = 5 To 11
If Not (IsEmpty(ws.Cells(x, 3))) Then
ws.Cells(x, 4) = «Yes»
Else
ws.Cells(x, 4) = «No»
End If
Next x
End Sub
Cell reference against range of cells
Sub If_a_cell_is_not_blank_using_Not_and_IsEmpty()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = Worksheets(«Analysis»)
For x = 9 To 15
If Not (IsEmpty(ws.Cells(x, 3))) Then
ws.Cells(x, 4) = ws.Range(«C5»)
Else
ws.Cells(x, 4) = ws.Range(«C6»)
End If
Next x
End Sub
KEY PARAMETERS
Output Range: Select the output range by changing the cell reference («D5») in the VBA code.
Cell to Test: Select the cell that you want to check if it’s not blank by changing the cell reference («C5») in the VBA code.
Worksheet Selection: Select the worksheet which captures the cells that you want to test if they are not blank and return a specific value by changing the Analysis worksheet name in the VBA code. You can also change the name of this object variable, by changing the name ‘ws’ in the VBA code.
True and False Results: In this example if a cell is not blank the VBA code will return a value of «Yes». If a cell is blank the VBA code will return a value of «No». Both of these values can be changed to whatever value you desire by directly changing them in the VBA code.
NOTES
Note 1: If the cell that is being tested is returning a value of («») this VBA code will identify the cell as not blank.
Note 2: If your True or False result is a text value it will need to be captured within quotation marks («»). However, if the result is a numeric value, you can enter it without the use of quotation marks.
KEY PARAMETERS
Output Range: Select the output range by changing the cell reference («D9») in the VBA code.
Cell to Test: Select the cell that you want to check if it’s not blank by changing the cell reference («C9») in the VBA code.
Worksheet Selection: Select the worksheet which captures the cells that you want to test if they are not blank and return a specific value by changing the Analysis worksheet name in the VBA code. You can also change the name of this object variable, by changing the name ‘ws’ in the VBA code.
True and False Results: In this example if a cell is not blank the VBA code will return a value stored in cell C5. If a cell is blank the VBA code will return a value stored in cell C6. Both of these values can be changed to whatever value you desire by either referencing to a different cell that captures the value that you want to return or change the values in those cells.
NOTES
Note 1: If the cell that is being tested is returning a value of («») this VBA code will identify the cell as not blank.
KEY PARAMETERS
Output and Test Range: Select the output rows and the rows that captures the cells that are to be tested by changing the x values (5 to 11). This example assumes that both the output and the associated test cell will be in the same row.
Test Column: Select the column that captures the cells that are to be tested by changing number 3, in ws.Cells(x, 3).
Output Column: Select the output column by changing number 4, in ws.Cells(x, 4).
Worksheet Selection: Select the worksheet which captures the cells that you want to test if they are not blank and return a specific value by changing the Analysis worksheet name in the VBA code. You can also change the name of this object variable, by changing the name ‘ws’ in the VBA code.
True and False Results: In this example if a cell is not blank the VBA code will return a value of «Yes». If a cell is blank the VBA code will return a value of «No». Both of these values can be changed to whatever value you desire by directly changing them in the VBA code.
NOTES
Note 1: If the cell that is being tested is returning a value of («») this VBA code will identify the cell as blank.
Note 2: If your True or False result is a text value it will need to be captured within quotation marks («»). However, if the result is a numeric value, you can enter it without the use of quotation marks.
KEY PARAMETERS
Output and Test Range: Select the output rows and the rows that captures the cells that are to be tested by changing the x values (9 to 15). This example assumes that both the output and the associated test cell will be in the same row.
Test Column: Select the column that captures the cells that are to be tested by changing number 3, in ws.Cells(x, 3).
Output Column: Select the output column by changing number 4, in ws.Cells(x, 4).
Worksheet Selection: Select the worksheet which captures the cells that you want to test if they are not blank and return a specific value by changing the Analysis worksheet name in the VBA code. You can also change the name of this object variable, by changing the name ‘ws’ in the VBA code.
True and False Results: In this example if a cell is not blank the VBA code will return a value stored in cell C5. If a cell is blank the VBA code will return a value stored in cell C6. Both of these values can be changed to whatever value you desire by either referencing to a different cell that captures the value that you want to return or change the values in those cells.
NOTES
Note 1: If the cell that is being tested is returning a value of («») this VBA code will identify the cell as blank.
VBA CODE 3. If a cell is not blank using vbNullString
VBA
Hard coded against single cell
Sub If_a_cell_is_not_blank_using_vbNullString()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = Worksheets(«Analysis»)
If ws.Range(«C5») <> vbNullString Then
ws.Range(«D5») = «Yes»
Else
ws.Range(«D5») = «No»
End If
End Sub
Cell reference against single cell
Sub If_a_cell_is_not_blank_using_vbNullString()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = Worksheets(«Analysis»)
If ws.Range(«C9») <> vbNullString Then
ws.Range(«D9») = ws.Range(«C5»)
Else
ws.Range(«D9») = ws.Range(«C6»)
End If
End Sub
Hard coded against range of cells
Sub If_a_cell_is_not_blank_using_vbNullString()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = Worksheets(«Analysis»)
For x = 5 To 11
If ws.Cells(x, 3) <> vbNullString Then
ws.Cells(x, 4) = «Yes»
Else
ws.Cells(x, 4) = «No»
End If
Next x
End Sub
Cell reference against range of cells
Sub If_a_cell_is_not_blank_using_vbNullString()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = Worksheets(«Analysis»)
For x = 9 To 15
If ws.Cells(x, 3) <> vbNullString Then
ws.Cells(x, 4) = ws.Range(«C5»)
Else
ws.Cells(x, 4) = ws.Range(«C6»)
End If
Next x
End Sub
KEY PARAMETERS
Output Range: Select the output range by changing the cell reference («D5») in the VBA code.
Cell to Test: Select the cell that you want to check if it’s not blank by changing the cell reference («C5») in the VBA code.
Worksheet Selection: Select the worksheet which captures the cells that you want to test if they are not blank and return a specific value by changing the Analysis worksheet name in the VBA code. You can also change the name of this object variable, by changing the name ‘ws’ in the VBA code.
True and False Results: In this example if a cell is not blank the VBA code will return a value of «Yes». If a cell is blank the VBA code will return a value of «No». Both of these values can be changed to whatever value you desire by directly changing them in the VBA code.
NOTES
Note 1: If the cell that is being tested is returning a value of («») this VBA code will identify the cell as blank.
Note 2: If your True or False result is a text value it will need to be captured within quotation marks («»). However, if the result is a numeric value, you can enter it without the use of quotation marks.
KEY PARAMETERS
Output Range: Select the output range by changing the cell reference («D9») in the VBA code.
Cell to Test: Select the cell that you want to check if it’s not blank by changing the cell reference («C9») in the VBA code.
Worksheet Selection: Select the worksheet which captures the cells that you want to test if they are not blank and return a specific value by changing the Analysis worksheet name in the VBA code. You can also change the name of this object variable, by changing the name ‘ws’ in the VBA code.
True and False Results: In this example if a cell is not blank the VBA code will return a value stored in cell C5. If a cell is blank the VBA code will return a value stored in cell C6. Both of these values can be changed to whatever value you desire by either referencing to a different cell that captures the value that you want to return or change the values in those cells.
NOTES
Note 1: If the cell that is being tested is returning a value of («») this VBA code will identify the cell as blank.
KEY PARAMETERS
Output and Test Rows: Select the output rows and the rows that captures the cells that are to be tested by changing the x values (5 to 11). This example assumes that both the output and the associated test cell will be in the same row.
Test Column: Select the column that captures the cells that are to be tested by changing number 3, in ws.Cells(x, 3).
Output Column: Select the output column by changing number 4, in ws.Cells(x, 4).
Worksheet Selection: Select the worksheet which captures the cells that you want to test if they are not blank and return a specific value by changing the Analysis worksheet name in the VBA code. You can also change the name of this object variable, by changing the name ‘ws’ in the VBA code.
True and False Results: In this example if a cell is not blank the VBA code will return a value of «Yes». If a cell is blank the VBA code will return a value of «No». Both of these values can be changed to whatever value you desire by directly changing them in the VBA code.
NOTES
Note 1: If the cell that is being tested is returning a value of («») this VBA code will identify the cell as blank.
Note 2: If your True or False result is a text value it will need to be captured within quotation marks («»). However, if the result is a numeric value, you can enter it without the use of quotation marks.
KEY PARAMETERS
Output and Test Rows: Select the output rows and the rows that captures the cells that are to be tested by changing the x values (9 to 15). This example assumes that both the output and the associated test cell will be in the same row.
Test Column: Select the column that captures the cells that are to be tested by changing number 3, in ws.Cells(x, 3).
Output Column: Select the output column by changing number 4, in ws.Cells(x, 4).
Worksheet Selection: Select the worksheet which captures the cells that you want to test if they are not blank and return a specific value by changing the Analysis worksheet name in the VBA code. You can also change the name of this object variable, by changing the name ‘ws’ in the VBA code.
True and False Results: In this example if a cell is not blank the VBA code will return a value stored in cell C5. If a cell is blank the VBA code will return a value stored in cell C6. Both of these values can be changed to whatever value you desire by either referencing to a different cell that captures the value that you want to return or change the values in those cells.
NOTES
Note 1: If the cell that is being tested is returning a value of («») this VBA code will identify the cell as blank.
Looking for coding that checks if cell is empty or not. If it is not empty then move to the next cell group. But I need to check if the next cell group is empty or not. If not, then move to the next and so on.
My Current coding below.
If IsEmpty(ActiveSheet.Range("h3")) Then
Do
Checkbox1.Value = True
Range("H3") = 17002
Sheets("Sheet1").Range("I3") = Printerformat2.Text
Else
Checkbox1.Value = True
Range("l3") = 17002
Sheets("Sheet1").Range("m3") = Printerformat2.Text
End If
asked Aug 12, 2011 at 15:37
2
You need to use a for loop to iterate through the specified range in «H»
Dim i As Long
With ActiveSheet
For i = 1 to 500
If IsEmpty(.Range("h" & CStr(i)).Value) Then
'Do 'Not sure where you're going with this one? This is not really needed from what I can tell.
Checkbox1.Value = True
.Range("H" & CStr(i)).Value = 17002
Sheets("Sheet1").Range("I" & CStr(i)).Value = Printerformat2.Text
Else
Checkbox1.Value = True
.Range("l" & CStr(i)) = 17002
Sheets("Sheet1").Range("m" & CStr(i)).value = Printerformat2.Text
End If
Next
End With
Hope that helps?
answered Aug 13, 2011 at 1:23
2
I think you should have a look at Range("your range").specialcells(xlCellTypeBlanks). This is the fastest way to loop through empty cells.
If you need to loop on non blank cells, you can check if your cell Intersect the empty cells range.
answered Aug 13, 2011 at 18:15
iDevlopiDevlop
24.6k11 gold badges89 silver badges147 bronze badges
The most optimized way to make sure a cell is not empty is «If Len(cell) <> 0».
You can use .offset to access another cell in relation to it’s position from the current cell, or reference it directly, so you can check if it’s empty or not.
answered Aug 13, 2011 at 13:46
GaijinhunterGaijinhunter
14.5k4 gold badges50 silver badges57 bronze badges
Use
Application.WorksheetFunction.isblank(ActiveSheet.range("h3"))
instead of
IsEmpty(ActiveSheet.Range("h3"))
Cordially
answered Aug 3, 2012 at 9:43
MUY BelgiumMUY Belgium
2,2624 gold badges30 silver badges44 bronze badges
0
Explanation
ISBLANK function checks if a cell is empty. If it is blank, it returns TRUE, otherwise, it returns FALSE.
The ISBLANK function is usually combined with an IF function, in order to check if a certain cell is blank, and perform a different calculation accordingly.
For example, let’s ask Excel to check if a certain cell is empty, and in case it is – returns “The cell is empty”. Otherwise, returns “This cell is not empty”:
Note that we don’t need to type “=TRUE” after the ISBLANK formula, as it’s the default condition that is checked.
Please remember that if there’s even one whitespace in the cell – it will not be considered blank!
Syntax
The syntax of ISBLANK is:
=ISBLANK(value)
value – The cell that we want to check if blank or not. If it’s blank, the result will be TRUE, if it’s not blank the result will be FALSE.
Practice ISBLANK
Okay, now let’s practice the ISBLANK function!
We can determine if a cell is not blank in Excel by either using the IF function or by using the IF and ISBLANK function combined. This tutorial will assist all levels of Excel users in both methods to identify non-blank cells

IF Function in Excel
IF function evaluates a given logical test and returns a TRUE or a FALSE
Syntax
=IF(logical_test, [value_if_true], [value_if_false])
- The arguments “value_if_true” and “value_if_false” are optional. If left blank, the function will return TRUE if the logical test is met, and FALSE if otherwise.
ISBLANK Function in Excel
ISBLANK function is more straightforward. It tests whether a value or a cell is blank or not.
Syntax
=ISBLANK(value)
- The function returns TRUE if the value is blank; FALSE if otherwise
Setting up the Data
Below is a list of Projects and a column for Date Completed. We want to know if column C for the “Date Completed” is blank or not.

Determine If a Cell is Not Blank
Using the IF function
In cell D3, enter the formula:
=IF(C3<>"","Not blank","Blank")
- The symbol <> in Excel means “not equal to”
- “” in Excel means empty string, or blank
- C3<>”” means C3 is not equal to blank, or C3 is not blank
This formula returns “Not blank” because cell C3 is not blank. It has the value “July 26, 2018”.

In cell D4, enter the formula:
=IF(C4<>"","Not blank","Blank")
The result is “Blank” because cell D4 is empty.

Using the IF and ISBLANK function
In cell D5, enter the formula:
=IF(ISBLANK(C5),"Blank","Not Blank")
- ISBLANK evaluates whether cell C5 is blank or not
- If the ISBLANK function returns TRUE, the formula will return “Blank”; otherwise, it returns “Not Blank”
- The result is “Blank” because C5 is empty

Note
We can customize the action that the IF function will return depending on the logical test results.
Example
We want to return the status “Completed” if the cell in column C is not blank, and “In Progress” if otherwise.
Enter the following formula:
In cell D3: =IF(C3<>"","Completed","In Progress")
In cell D4: =IF(C4<>"","Completed","In Progress")
In cell D5: =IF(ISBLANK(C5),"In Progress","Completed")
In cell D6: =IF(ISBLANK(C6),"In Progress","Completed")

Most of the time, the problem you will need to solve will be more complex than a simple application of a formula or function. If you want to save hours of research and frustration, try our live Excelchat service! Our Excel Experts are available 24/7 to answer any Excel question you may have. We guarantee a connection within 30 seconds and a customized solution within 20 minutes.
Are you still looking for help with the IF function? View our comprehensive round-up of IF function tutorials here.
You can use the following formula in Excel to perform some task if a cell is not empty:
=IF(A1<>"", Value_If_Not_Empty, Value_If_Empty)
This particular formula checks if cell A1 is empty.
If it is not empty, then Value_If_Not_Empty is returned.
If it is empty, then Value_If_Empty is returned.
The following example shows how to use this formula in practice.
Example: Use “If Not Empty” Formula in Excel
Suppose we have the following dataset in Excel that contains information about various basketball teams:
We can use the following formula to return a value of “Team Exists” if the cell in column A is not empty.
Otherwise, we’ll return a value of “Does Not Exist”:
=IF(A2<>"", "Team Exists", "Does Not Exist")
The following screenshot shows how to use this formula in practice:
If the team name is not empty in column A, then “Team Exists” is returned.
Otherwise, “Does Not Exist” is returned.
If we’d like, we could also return numeric values instead of character values.
For example, we could use the following formula to return the value of the points column divided by two if the cell in column A is not empty.
Otherwise, we’ll return an empty value:
=IF(A2<>"", B2/2, "")
The following screenshot shows how to use this formula in practice:
If the team name is not empty in column A, then we return the value in the points column multiplied by two.
Otherwise, we return an empty value.
Additional Resources
The following tutorials explain how to perform other common tasks in Excel:
How to Replace Blank Cells with Zero in Excel
How to Replace #N/A Values in Excel
How to Ignore #VALUE! Error in Excel