Содержание
- VBA Calculate – Now, Workbook, Worksheet, or Range
- Calculate Now
- Calculate Sheet Only
- Calculate Range
- Calculate Individual Formula
- Calculate Workbook
- Calculate Workbook – Methods That Don’t Work
- VBA Coding Made Easy
- VBA Code Examples Add-in
- Calculate Method of Worksheet Object VBA
- VBA Reference
- 120+ Project Management Templates
- Why we use Calculate Worksheet Method in VBA?
- VBA Calculate Worksheet Method- Syntax
- VBA Calculate Worksheet Method: All Open Workbooks
- VBA Calculate Worksheet Method: In Specific Sheet
- VBA Calculate Worksheet Method: In Specified Range
- VBA Calculate Worksheet Method: Instructions
- VBA Range Calculate — Explained with Examples
- VBA Reference
- 120+ Project Management Templates
- VBA Range Calculate – Syntax
- VBA Range Calculate – Examples
- VBA Range Calculate – Instructions
- Calculate the Columns using VBA
- Calculate the Rows using VBA
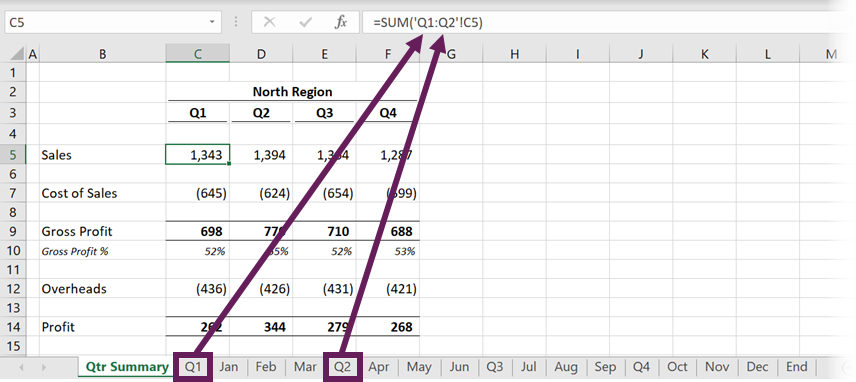
- VBA, Calculation for multiple worksheets/workbook
- 1 Answer 1
- Related
- Hot Network Questions
- Subscribe to RSS
- Calculate Method of Application Object VBA
- VBA Reference
- 120+ Project Management Templates
- VBA Calculate Application Method – Syntax
- VBA Calculate Application Method: Example 1
- VBA Calculate Application Method: Example 2
- VBA Calculate Application Method: Example 3
- VBA Calculate Application Method – Instructions
VBA Calculate – Now, Workbook, Worksheet, or Range
In this Article
This tutorial will teach you all of the different Calculate options in VBA.
By default Excel calculates all open workbooks every time a workbook change is made. It does this by following a calculation tree where if cell A1 is changed, it updates all cells that rely on cell A1 and so on. However, this can cause your VBA code to run extremely slowly, as every time a cell changes, Excel must re-calculate.
To increase your VBA speed, you will often want to disable automatic calculations at the beginning of your procedures:
and re-enable it at the end:
However, what if you want to calculate all (or part) of your workbooks within your procedure? The rest of this tutorial will teach you what to do.
Calculate Now
You can use the Calculate command to re-calculate everything (in all open workbooks):
This is usually the best method to use. However, you can also perform more narrow calculations for improved speed.
Calculate Sheet Only
You can also tell VBA to calculate only a specific sheet.
This code will recalculate the active sheet:
This code will recalculate Sheet1:
Calculate Range
If you require a more narrow calculation, you can tell VBA to calculate only a range of cells:
Calculate Individual Formula
This code will calculate only an individual cell formula:
Calculate Workbook
There is no VBA option to calculate only an entire workbook. If you need to calculate an entire workbook, the best option is to use the Calculate command:
This will calculate all open workbooks. If you’re really concerned about speed, and want to calculate an entire workbook, you might be able to be more selective about which workbooks are open at one time.
Calculate Workbook – Methods That Don’t Work
There are a couple of methods that you might be tempted to use to force VBA to calculate just a workbook, however none of them will work properly.
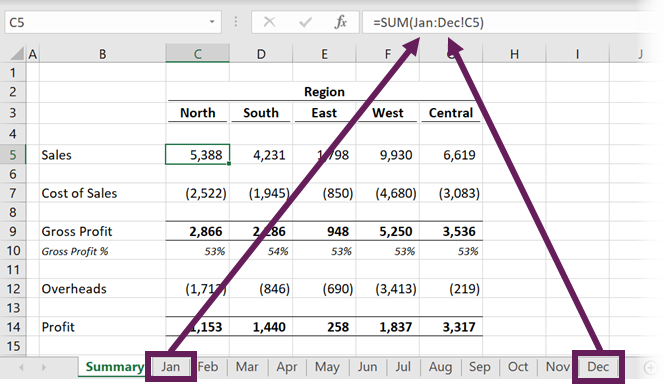
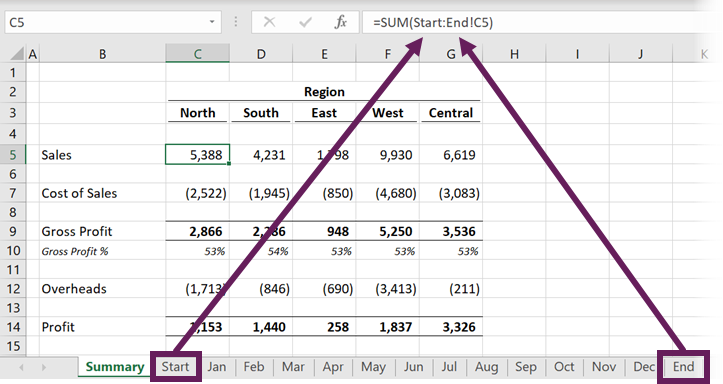
This code will loop through each worksheet in the workbook and recalculate the sheets one at a time:
This code will work fine if all of your worksheets are “self-contained”, meaning none of your sheets contain calculations that refer to other sheets.
However, if your worksheets refer to other sheets, your calculations might not update properly. For example, if you calculate Sheet1 before Sheet2, but Sheet1’s formulas rely on calculations done in Sheet2 then your formulas will not contain the most up-to-date values.
You might also try selecting all sheets at once and calculating the activesheet:
However, this will cause the same issue.
VBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro — A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users! 
VBA Code Examples Add-in
Easily access all of the code examples found on our site.
Simply navigate to the menu, click, and the code will be inserted directly into your module. .xlam add-in.
Источник
Calculate Method of Worksheet Object VBA
VBA Reference
Effortlessly
Manage Your Projects
120+ Project Management Templates
Seamlessly manage your projects with our powerful & multi-purpose templates for project management.
120+ PM Templates Includes:
50+ Excel Templates
50+ PowerPoint Templates
25+ Word Templates
A Powerful & Multi-purpose Templates for project management. Now seamlessly manage your projects, tasks, meetings, presentations, teams, customers, stakeholders and time. This page describes all the amazing new features and options that come with our premium templates.
Save Up to 85% LIMITED TIME OFFER
All-in-One Pack
120+ Project Management Templates
Essential Pack
50+ Project Management Templates
Excel Pack
50+ Excel PM Templates
PowerPoint Pack
50+ Excel PM Templates
MS Word Pack
25+ Word PM Templates
Ultimate Project Management Template
Ultimate Resource Management Template
Project Portfolio Management Templates
Calculate Worksheet Method in VBA is used to calculate all open workbooks or a specific worksheet in a workbook or a specified range in a worksheet.
Why we use Calculate Worksheet Method in VBA?
If a workbook or a worksheet or a specific range has formulas we need to refresh each time when the values are changing. In that time we can use Calculate Worksheet Method in VBA.
VBA Calculate Worksheet Method- Syntax
Here is the example syntax to Calculate Worksheet method in Excel VBA.
Where Worksheet represents the object and Calculate is the method of worksheet object.
VBA Calculate Worksheet Method: All Open Workbooks
Please see the below VBA code to Calculate all open Workbooks. In this example we are using calculate method of application object.
VBA Calculate Worksheet Method: In Specific Sheet
Please see the below VBA code to Calculate in specified Worksheet named “Sheet1”.
VBA Calculate Worksheet Method: In Specified Range
Please see the below VBA code to Calculate in specified range (“A1:E10”) in a specified worksheet named “Sheet1”.
VBA Calculate Worksheet Method: Instructions
Please follow the below step by step instructions to execute the above mentioned VBA macros or codes:
- Open an Excel Worksheet
- Press Alt+F11 to Open VBA Editor
- Insert a Module from Insert Menu
- Copy the above code for activating worksheet and Paste in the code window(VBA Editor)
- Save the file as macro enabled Worksheet
- Press ‘F5’ to run it or Keep Pressing ‘F8’ to debug the code line by line and observe the calculations in the Worksheet.
Источник
VBA Range Calculate — Explained with Examples
VBA Reference
Effortlessly
Manage Your Projects
120+ Project Management Templates
Seamlessly manage your projects with our powerful & multi-purpose templates for project management.
120+ PM Templates Includes:
50+ Excel Templates
50+ PowerPoint Templates
25+ Word Templates
A Powerful & Multi-purpose Templates for project management. Now seamlessly manage your projects, tasks, meetings, presentations, teams, customers, stakeholders and time. This page describes all the amazing new features and options that come with our premium templates.
Save Up to 85% LIMITED TIME OFFER
All-in-One Pack
120+ Project Management Templates
Essential Pack
50+ Project Management Templates
Excel Pack
50+ Excel PM Templates
PowerPoint Pack
50+ Excel PM Templates
MS Word Pack
25+ Word PM Templates
Ultimate Project Management Template
Ultimate Resource Management Template
Project Portfolio Management Templates
We calculate the particular range using VBA. Calculate method in Excel help us to calculate all opened workbooks, specific workbooks, specific worksheets, Ranges, columns or rows. This method will be useful when your Excel Calculation method is set to manual mode. or if you have many formulas in the workbook and want to refresh or recalculate a particular range you can use Range.Calculate method.
VBA Range Calculate – Syntax
You can use the calculate method of the range to calculate any range.
VBA Range Calculate – Examples
Here is the simple example to calculate a specific Range. This example will calculate Range “A2:D10” using VBA.
VBA Range Calculate – Instructions
Please follow the below step by step instructions to execute the above mentioned VBA macros or codes:
- Open an Excel Workbook from your start menu or type Excel in your run command
- Enter some formula at B2 as “=D2” and enter some value at D2. Now you can see the D2 value at B2.
- Set the caluclation mode to manual to test this macro
- Change the value at D2, now you can see that B2 value is not change even you have made changes at D2
- Press Alt+F11 to Open VBA Editor or you can goto Developer Table from Excel Ribbon and click on the Visual Basic Command to launch the VBA Editor
- Insert a Module from Insert Menu of VBA
- Copy the above code (for Calculating a Range using VBA) and Paste in the code window(VBA Editor)
- Save the file as Macro Enabled Workbook (i.e; .xlsm file format)
- Press ‘F5′ to run it or Keep Pressing ‘F8′ to debug the code line by line.
Now you can observe that the value at B2 is changed as per D2.
Calculate the Columns using VBA
Here is the simple example to calculate a specific Columns. This example will calculate the columns “A to D” using VBA.
Calculate the Rows using VBA
Here is the simple example to calculate a specific rows using VBA. This example will calculate the Rows”1 to 20″ using VBA.
Источник
VBA, Calculation for multiple worksheets/workbook
I have the following Macro:
How can I apply this across multiple worksheets in a workbook? Or multiple workbooks with multiple worksheets? I have a macro to open all Excel files in my directory. Even better if I could bypass opening all Excel files.
Pretty much want to automate this macro within a large amount of files/sheets.
1 Answer 1
You can’t calculate without opening all the workbooks, but there is a simple command for what you are looking for: Application.CalculateFull . It re-calculates all sheets in all open workbooks. Be aware that this may take a long time and may make Excel seem like it is not responding until it finishes. In addition, if the open sheets are in a different instance of Excel from your macro above, they will not calculate.
So I would imagine your process to look like this:
- Run your macro to open all the files
- Run your macro above, with .CalculateFull just after .Calculation = xlCalculationAutomatic and just before End With , End Sub
Hot Network Questions
To subscribe to this RSS feed, copy and paste this URL into your RSS reader.
Site design / logo © 2023 Stack Exchange Inc; user contributions licensed under CC BY-SA . rev 2023.3.20.43331
By clicking “Accept all cookies”, you agree Stack Exchange can store cookies on your device and disclose information in accordance with our Cookie Policy.
Источник
Calculate Method of Application Object VBA
VBA Reference
Effortlessly
Manage Your Projects
120+ Project Management Templates
Seamlessly manage your projects with our powerful & multi-purpose templates for project management.
120+ PM Templates Includes:
50+ Excel Templates
50+ PowerPoint Templates
25+ Word Templates
A Powerful & Multi-purpose Templates for project management. Now seamlessly manage your projects, tasks, meetings, presentations, teams, customers, stakeholders and time. This page describes all the amazing new features and options that come with our premium templates.
Save Up to 85% LIMITED TIME OFFER
All-in-One Pack
120+ Project Management Templates
Essential Pack
50+ Project Management Templates
Excel Pack
50+ Excel PM Templates
PowerPoint Pack
50+ Excel PM Templates
MS Word Pack
25+ Word PM Templates
Ultimate Project Management Template
Ultimate Resource Management Template
Project Portfolio Management Templates
Calculate Application Method in VBA is used to calculate the all open Workbooks or a specific Worksheet or a specified range on a worksheet. Please find the syntax and examples of Calculate Application Method in VBA.
VBA Calculate Application Method – Syntax
Here is the syntax for the Calculate method of application object in VBA.
In the above syntax Application represents object and Calculate is the method of Application object.
VBA Calculate Application Method: Example 1
Please find the below example for calculate method of application object in excel VBA.
‘The below macro is used to calculates in all open workbooks
VBA Calculate Application Method: Example 2
Please find the below example for calculate method of application object in excel VBA.
‘The below macro is used to calculates in a specific Worksheet
VBA Calculate Application Method: Example 3
Please find the below example for calculate method of application object in excel VBA.
‘The below macro is used to calculates in a specified range
The example is used to calculate the formulas in column A, B, …, and E in the Worksheet names Sheet1.
VBA Calculate Application Method – Instructions
Please follow the below steps to execute the VBA code to save the excel file.
Step 1: Open any existing Excel Application.
Step 2: Press Alt+F11 – This will open the VBA Editor or Open it from Developer Tab..
Step 3: Insert a code module from then insert menu.
Step 4: Copy the above code and paste in the code module which have inserted in the above step.
Step 5: Calculate any Application.
Step 6: Now press F5 to execute the code and check the calculations in the Worksheet.
Источник
Many users find that using an external keyboard with keyboard shortcuts for Excel helps them work more efficiently. For users with mobility or vision disabilities, keyboard shortcuts can be easier than using the touchscreen and are an essential alternative to using a mouse.
Notes:
-
The shortcuts in this topic refer to the US keyboard layout. Keys for other layouts might not correspond exactly to the keys on a US keyboard.
-
A plus sign (+) in a shortcut means that you need to press multiple keys at the same time.
-
A comma sign (,) in a shortcut means that you need to press multiple keys in order.
This article describes the keyboard shortcuts, function keys, and some other common shortcut keys in Excel for Windows.
Notes:
-
To quickly find a shortcut in this article, you can use the Search. Press Ctrl+F, and then type your search words.
-
If an action that you use often does not have a shortcut key, you can record a macro to create one. For instructions, go to Automate tasks with the Macro Recorder.
-
Download our 50 time-saving Excel shortcuts quick tips guide.
-
Get the Excel 2016 keyboard shortcuts in a Word document: Excel keyboard shortcuts and function keys.
In this topic
-
Frequently used shortcuts
-
Ribbon keyboard shortcuts
-
Use the Access keys for ribbon tabs
-
Work in the ribbon with the keyboard
-
-
Keyboard shortcuts for navigating in cells
-
Keyboard shortcuts for formatting cells
-
Keyboard shortcuts in the Paste Special dialog box in Excel 2013
-
-
Keyboard shortcuts for making selections and performing actions
-
Keyboard shortcuts for working with data, functions, and the formula bar
-
Keyboard shortcuts for refreshing external data
-
Power Pivot keyboard shortcuts
-
Function keys
-
Other useful shortcut keys
Frequently used shortcuts
This table lists the most frequently used shortcuts in Excel.
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Close a workbook. |
Ctrl+W |
|
Open a workbook. |
Ctrl+O |
|
Go to the Home tab. |
Alt+H |
|
Save a workbook. |
Ctrl+S |
|
Copy selection. |
Ctrl+C |
|
Paste selection. |
Ctrl+V |
|
Undo recent action. |
Ctrl+Z |
|
Remove cell contents. |
Delete |
|
Choose a fill color. |
Alt+H, H |
|
Cut selection. |
Ctrl+X |
|
Go to the Insert tab. |
Alt+N |
|
Apply bold formatting. |
Ctrl+B |
|
Center align cell contents. |
Alt+H, A, C |
|
Go to the Page Layout tab. |
Alt+P |
|
Go to the Data tab. |
Alt+A |
|
Go to the View tab. |
Alt+W |
|
Open the context menu. |
Shift+F10 or Windows Menu key |
|
Add borders. |
Alt+H, B |
|
Delete column. |
Alt+H, D, C |
|
Go to the Formula tab. |
Alt+M |
|
Hide the selected rows. |
Ctrl+9 |
|
Hide the selected columns. |
Ctrl+0 |
Top of Page
Ribbon keyboard shortcuts
The ribbon groups related options on tabs. For example, on the Home tab, the Number group includes the Number Format option. Press the Alt key to display the ribbon shortcuts, called Key Tips, as letters in small images next to the tabs and options as shown in the image below.
You can combine the Key Tips letters with the Alt key to make shortcuts called Access Keys for the ribbon options. For example, press Alt+H to open the Home tab, and Alt+Q to move to the Tell me or Search field. Press Alt again to see KeyTips for the options for the selected tab.
Depending on the version of Microsoft 365 you are using, the Search text field at the top of the app window might be called Tell Me instead. Both offer a largely similar experience, but some options and search results can vary.
In Office 2013 and Office 2010, most of the old Alt key menu shortcuts still work, too. However, you need to know the full shortcut. For example, press Alt, and then press one of the old menu keys, for example, E (Edit), V (View), I (Insert), and so on. A notification pops up saying you’re using an access key from an earlier version of Microsoft 365. If you know the entire key sequence, go ahead, and use it. If you don’t know the sequence, press Esc and use Key Tips instead.
Use the Access keys for ribbon tabs
To go directly to a tab on the ribbon, press one of the following access keys. Additional tabs might appear depending on your selection in the worksheet.
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Move to the Tell me or Search field on the ribbon and type a search term for assistance or Help content. |
Alt+Q, then enter the search term. |
|
Open the File menu. |
Alt+F |
|
Open the Home tab and format text and numbers and use the Find tool. |
Alt+H |
|
Open the Insert tab and insert PivotTables, charts, add-ins, Sparklines, pictures, shapes, headers, or text boxes. |
Alt+N |
|
Open the Page Layout tab and work with themes, page setup, scale, and alignment. |
Alt+P |
|
Open the Formulas tab and insert, trace, and customize functions and calculations. |
Alt+M |
|
Open the Data tab and connect to, sort, filter, analyze, and work with data. |
Alt+A |
|
Open the Review tab and check spelling, add notes and threaded comments, and protect sheets and workbooks. |
Alt+R |
|
Open the View tab and preview page breaks and layouts, show and hide gridlines and headings, set zoom magnification, manage windows and panes, and view macros. |
Alt+W |
Top of Page
Work in the ribbon with the keyboard
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Select the active tab on the ribbon and activate the access keys. |
Alt or F10. To move to a different tab, use access keys or the arrow keys. |
|
Move the focus to commands on the ribbon. |
Tab key or Shift+Tab |
|
Move down, up, left, or right, respectively, among the items on the ribbon. |
Arrow keys |
|
Show the tooltip for the ribbon element currently in focus. |
Ctrl+Shift+F10 |
|
Activate a selected button. |
Spacebar or Enter |
|
Open the list for a selected command. |
Down arrow key |
|
Open the menu for a selected button. |
Alt+Down arrow key |
|
When a menu or submenu is open, move to the next command. |
Down arrow key |
|
Expand or collapse the ribbon. |
Ctrl+F1 |
|
Open a context menu. |
Shift+F10 Or, on a Windows keyboard, the Windows Menu key (usually between the Alt Gr and right Ctrl keys) |
|
Move to the submenu when a main menu is open or selected. |
Left arrow key |
|
Move from one group of controls to another. |
Ctrl+Left or Right arrow key |
Top of Page
Keyboard shortcuts for navigating in cells
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Move to the previous cell in a worksheet or the previous option in a dialog box. |
Shift+Tab |
|
Move one cell up in a worksheet. |
Up arrow key |
|
Move one cell down in a worksheet. |
Down arrow key |
|
Move one cell left in a worksheet. |
Left arrow key |
|
Move one cell right in a worksheet. |
Right arrow key |
|
Move to the edge of the current data region in a worksheet. |
Ctrl+Arrow key |
|
Enter the End mode, move to the next nonblank cell in the same column or row as the active cell, and turn off End mode. If the cells are blank, move to the last cell in the row or column. |
End, Arrow key |
|
Move to the last cell on a worksheet, to the lowest used row of the rightmost used column. |
Ctrl+End |
|
Extend the selection of cells to the last used cell on the worksheet (lower-right corner). |
Ctrl+Shift+End |
|
Move to the cell in the upper-left corner of the window when Scroll lock is turned on. |
Home+Scroll lock |
|
Move to the beginning of a worksheet. |
Ctrl+Home |
|
Move one screen down in a worksheet. |
Page down |
|
Move to the next sheet in a workbook. |
Ctrl+Page down |
|
Move one screen to the right in a worksheet. |
Alt+Page down |
|
Move one screen up in a worksheet. |
Page up |
|
Move one screen to the left in a worksheet. |
Alt+Page up |
|
Move to the previous sheet in a workbook. |
Ctrl+Page up |
|
Move one cell to the right in a worksheet. Or, in a protected worksheet, move between unlocked cells. |
Tab key |
|
Open the list of validation choices on a cell that has data validation option applied to it. |
Alt+Down arrow key |
|
Cycle through floating shapes, such as text boxes or images. |
Ctrl+Alt+5, then the Tab key repeatedly |
|
Exit the floating shape navigation and return to the normal navigation. |
Esc |
|
Scroll horizontally. |
Ctrl+Shift, then scroll your mouse wheel up to go left, down to go right |
|
Zoom in. |
Ctrl+Alt+Equal sign ( = ) |
|
Zoom out. |
Ctrl+Alt+Minus sign (-) |
Top of Page
Keyboard shortcuts for formatting cells
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Open the Format Cells dialog box. |
Ctrl+1 |
|
Format fonts in the Format Cells dialog box. |
Ctrl+Shift+F or Ctrl+Shift+P |
|
Edit the active cell and put the insertion point at the end of its contents. Or, if editing is turned off for the cell, move the insertion point into the formula bar. If editing a formula, toggle Point mode off or on so you can use the arrow keys to create a reference. |
F2 |
|
Insert a note. Open and edit a cell note. |
Shift+F2 Shift+F2 |
|
Insert a threaded comment. Open and reply to a threaded comment. |
Ctrl+Shift+F2 Ctrl+Shift+F2 |
|
Open the Insert dialog box to insert blank cells. |
Ctrl+Shift+Plus sign (+) |
|
Open the Delete dialog box to delete selected cells. |
Ctrl+Minus sign (-) |
|
Enter the current time. |
Ctrl+Shift+Colon (:) |
|
Enter the current date. |
Ctrl+Semicolon (;) |
|
Switch between displaying cell values or formulas in the worksheet. |
Ctrl+Grave accent (`) |
|
Copy a formula from the cell above the active cell into the cell or the formula bar. |
Ctrl+Apostrophe (‘) |
|
Move the selected cells. |
Ctrl+X |
|
Copy the selected cells. |
Ctrl+C |
|
Paste content at the insertion point, replacing any selection. |
Ctrl+V |
|
Open the Paste Special dialog box. |
Ctrl+Alt+V |
|
Italicize text or remove italic formatting. |
Ctrl+I or Ctrl+3 |
|
Bold text or remove bold formatting. |
Ctrl+B or Ctrl+2 |
|
Underline text or remove underline. |
Ctrl+U or Ctrl+4 |
|
Apply or remove strikethrough formatting. |
Ctrl+5 |
|
Switch between hiding objects, displaying objects, and displaying placeholders for objects. |
Ctrl+6 |
|
Apply an outline border to the selected cells. |
Ctrl+Shift+Ampersand sign (&) |
|
Remove the outline border from the selected cells. |
Ctrl+Shift+Underscore (_) |
|
Display or hide the outline symbols. |
Ctrl+8 |
|
Use the Fill Down command to copy the contents and format of the topmost cell of a selected range into the cells below. |
Ctrl+D |
|
Apply the General number format. |
Ctrl+Shift+Tilde sign (~) |
|
Apply the Currency format with two decimal places (negative numbers in parentheses). |
Ctrl+Shift+Dollar sign ($) |
|
Apply the Percentage format with no decimal places. |
Ctrl+Shift+Percent sign (%) |
|
Apply the Scientific number format with two decimal places. |
Ctrl+Shift+Caret sign (^) |
|
Apply the Date format with the day, month, and year. |
Ctrl+Shift+Number sign (#) |
|
Apply the Time format with the hour and minute, and AM or PM. |
Ctrl+Shift+At sign (@) |
|
Apply the Number format with two decimal places, thousands separator, and minus sign (-) for negative values. |
Ctrl+Shift+Exclamation point (!) |
|
Open the Insert hyperlink dialog box. |
Ctrl+K |
|
Check spelling in the active worksheet or selected range. |
F7 |
|
Display the Quick Analysis options for selected cells that contain data. |
Ctrl+Q |
|
Display the Create Table dialog box. |
Ctrl+L or Ctrl+T |
|
Open the Workbook Statistics dialog box. |
Ctrl+Shift+G |
Top of Page
Keyboard shortcuts in the Paste Special dialog box in Excel 2013
In Excel 2013, you can paste a specific aspect of the copied data like its formatting or value using the Paste Special options. After you’ve copied the data, press Ctrl+Alt+V, or Alt+E+S to open the Paste Special dialog box.
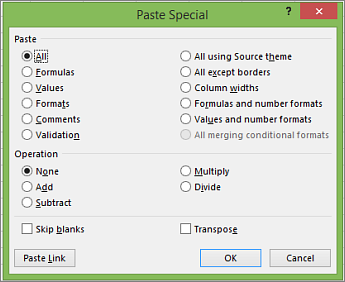
Tip: You can also select Home > Paste > Paste Special.
To pick an option in the dialog box, press the underlined letter for that option. For example, press the letter C to pick the Comments option.
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Paste all cell contents and formatting. |
A |
|
Paste only the formulas as entered in the formula bar. |
F |
|
Paste only the values (not the formulas). |
V |
|
Paste only the copied formatting. |
T |
|
Paste only comments and notes attached to the cell. |
C |
|
Paste only the data validation settings from copied cells. |
N |
|
Paste all cell contents and formatting from copied cells. |
H |
|
Paste all cell contents without borders. |
X |
|
Paste only column widths from copied cells. |
W |
|
Paste only formulas and number formats from copied cells. |
R |
|
Paste only the values (not formulas) and number formats from copied cells. |
U |
Top of Page
Keyboard shortcuts for making selections and performing actions
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Select the entire worksheet. |
Ctrl+A or Ctrl+Shift+Spacebar |
|
Select the current and next sheet in a workbook. |
Ctrl+Shift+Page down |
|
Select the current and previous sheet in a workbook. |
Ctrl+Shift+Page up |
|
Extend the selection of cells by one cell. |
Shift+Arrow key |
|
Extend the selection of cells to the last nonblank cell in the same column or row as the active cell, or if the next cell is blank, to the next nonblank cell. |
Ctrl+Shift+Arrow key |
|
Turn extend mode on and use the arrow keys to extend a selection. Press again to turn off. |
F8 |
|
Add a non-adjacent cell or range to a selection of cells by using the arrow keys. |
Shift+F8 |
|
Start a new line in the same cell. |
Alt+Enter |
|
Fill the selected cell range with the current entry. |
Ctrl+Enter |
|
Complete a cell entry and select the cell above. |
Shift+Enter |
|
Select an entire column in a worksheet. |
Ctrl+Spacebar |
|
Select an entire row in a worksheet. |
Shift+Spacebar |
|
Select all objects on a worksheet when an object is selected. |
Ctrl+Shift+Spacebar |
|
Extend the selection of cells to the beginning of the worksheet. |
Ctrl+Shift+Home |
|
Select the current region if the worksheet contains data. Press a second time to select the current region and its summary rows. Press a third time to select the entire worksheet. |
Ctrl+A or Ctrl+Shift+Spacebar |
|
Select the current region around the active cell. |
Ctrl+Shift+Asterisk sign (*) |
|
Select the first command on the menu when a menu or submenu is visible. |
Home |
|
Repeat the last command or action, if possible. |
Ctrl+Y |
|
Undo the last action. |
Ctrl+Z |
|
Expand grouped rows or columns. |
While hovering over the collapsed items, press and hold the Shift key and scroll down. |
|
Collapse grouped rows or columns. |
While hovering over the expanded items, press and hold the Shift key and scroll up. |
Top of Page
Keyboard shortcuts for working with data, functions, and the formula bar
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Turn on or off tooltips for checking formulas directly in the formula bar or in the cell you’re editing. |
Ctrl+Alt+P |
|
Edit the active cell and put the insertion point at the end of its contents. Or, if editing is turned off for the cell, move the insertion point into the formula bar. If editing a formula, toggle Point mode off or on so you can use the arrow keys to create a reference. |
F2 |
|
Expand or collapse the formula bar. |
Ctrl+Shift+U |
|
Cancel an entry in the cell or formula bar. |
Esc |
|
Complete an entry in the formula bar and select the cell below. |
Enter |
|
Move the cursor to the end of the text when in the formula bar. |
Ctrl+End |
|
Select all text in the formula bar from the cursor position to the end. |
Ctrl+Shift+End |
|
Calculate all worksheets in all open workbooks. |
F9 |
|
Calculate the active worksheet. |
Shift+F9 |
|
Calculate all worksheets in all open workbooks, regardless of whether they have changed since the last calculation. |
Ctrl+Alt+F9 |
|
Check dependent formulas, and then calculate all cells in all open workbooks, including cells not marked as needing to be calculated. |
Ctrl+Alt+Shift+F9 |
|
Display the menu or message for an Error Checking button. |
Alt+Shift+F10 |
|
Display the Function Arguments dialog box when the insertion point is to the right of a function name in a formula. |
Ctrl+A |
|
Insert argument names and parentheses when the insertion point is to the right of a function name in a formula. |
Ctrl+Shift+A |
|
Insert the AutoSum formula |
Alt+Equal sign ( = ) |
|
Invoke Flash Fill to automatically recognize patterns in adjacent columns and fill the current column |
Ctrl+E |
|
Cycle through all combinations of absolute and relative references in a formula if a cell reference or range is selected. |
F4 |
|
Insert a function. |
Shift+F3 |
|
Copy the value from the cell above the active cell into the cell or the formula bar. |
Ctrl+Shift+Straight quotation mark («) |
|
Create an embedded chart of the data in the current range. |
Alt+F1 |
|
Create a chart of the data in the current range in a separate Chart sheet. |
F11 |
|
Define a name to use in references. |
Alt+M, M, D |
|
Paste a name from the Paste Name dialog box (if names have been defined in the workbook). |
F3 |
|
Move to the first field in the next record of a data form. |
Enter |
|
Create, run, edit, or delete a macro. |
Alt+F8 |
|
Open the Microsoft Visual Basic For Applications Editor. |
Alt+F11 |
|
Open the Power Query Editor |
Alt+F12 |
Top of Page
Keyboard shortcuts for refreshing external data
Use the following keys to refresh data from external data sources.
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Stop a refresh operation. |
Esc |
|
Refresh data in the current worksheet. |
Ctrl+F5 |
|
Refresh all data in the workbook. |
Ctrl+Alt+F5 |
Top of Page
Power Pivot keyboard shortcuts
Use the following keyboard shortcuts with Power Pivot in Microsoft 365, Excel 2019, Excel 2016, and Excel 2013.
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Open the context menu for the selected cell, column, or row. |
Shift+F10 |
|
Select the entire table. |
Ctrl+A |
|
Copy selected data. |
Ctrl+C |
|
Delete the table. |
Ctrl+D |
|
Move the table. |
Ctrl+M |
|
Rename the table. |
Ctrl+R |
|
Save the file. |
Ctrl+S |
|
Redo the last action. |
Ctrl+Y |
|
Undo the last action. |
Ctrl+Z |
|
Select the current column. |
Ctrl+Spacebar |
|
Select the current row. |
Shift+Spacebar |
|
Select all cells from the current location to the last cell of the column. |
Shift+Page down |
|
Select all cells from the current location to the first cell of the column. |
Shift+Page up |
|
Select all cells from the current location to the last cell of the row. |
Shift+End |
|
Select all cells from the current location to the first cell of the row. |
Shift+Home |
|
Move to the previous table. |
Ctrl+Page up |
|
Move to the next table. |
Ctrl+Page down |
|
Move to the first cell in the upper-left corner of selected table. |
Ctrl+Home |
|
Move to the last cell in the lower-right corner of selected table. |
Ctrl+End |
|
Move to the first cell of the selected row. |
Ctrl+Left arrow key |
|
Move to the last cell of the selected row. |
Ctrl+Right arrow key |
|
Move to the first cell of the selected column. |
Ctrl+Up arrow key |
|
Move to the last cell of selected column. |
Ctrl+Down arrow key |
|
Close a dialog box or cancel a process, such as a paste operation. |
Ctrl+Esc |
|
Open the AutoFilter Menu dialog box. |
Alt+Down arrow key |
|
Open the Go To dialog box. |
F5 |
|
Recalculate all formulas in the Power Pivot window. For more information, see Recalculate Formulas in Power Pivot. |
F9 |
Top of Page
Function keys
|
Key |
Description |
|---|---|
|
F1 |
|
|
F2 |
|
|
F3 |
|
|
F4 |
|
|
F5 |
|
|
F6 |
|
|
F7 |
|
|
F8 |
|
|
F9 |
|
|
F10 |
|
|
F11 |
|
|
F12 |
|
Top of Page
Other useful shortcut keys
|
Key |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Alt |
For example,
|
|
Arrow keys |
|
|
Backspace |
|
|
Delete |
|
|
End |
|
|
Enter |
|
|
Esc |
|
|
Home |
|
|
Page down |
|
|
Page up |
|
|
Shift |
|
|
Spacebar |
|
|
Tab key |
|
Top of Page
See also
Excel help & learning
Basic tasks using a screen reader with Excel
Use a screen reader to explore and navigate Excel
Screen reader support for Excel
This article describes the keyboard shortcuts, function keys, and some other common shortcut keys in Excel for Mac.
Notes:
-
The settings in some versions of the Mac operating system (OS) and some utility applications might conflict with keyboard shortcuts and function key operations in Microsoft 365 for Mac.
-
If you don’t find a keyboard shortcut here that meets your needs, you can create a custom keyboard shortcut. For instructions, go to Create a custom keyboard shortcut for Office for Mac.
-
Many of the shortcuts that use the Ctrl key on a Windows keyboard also work with the Control key in Excel for Mac. However, not all do.
-
To quickly find a shortcut in this article, you can use the Search. Press
+F, and then type your search words.
-
Click-to-add is available but requires a setup. Select Excel> Preferences > Edit > Enable Click to Add Mode. To start a formula, type an equal sign ( = ), and then select cells to add them together. The plus sign (+) will be added automatically.
In this topic
-
Frequently used shortcuts
-
Shortcut conflicts
-
Change system preferences for keyboard shortcuts with the mouse
-
-
Work in windows and dialog boxes
-
Move and scroll in a sheet or workbook
-
Enter data on a sheet
-
Work in cells or the Formula bar
-
Format and edit data
-
Select cells, columns, or rows
-
Work with a selection
-
Use charts
-
Sort, filter, and use PivotTable reports
-
Outline data
-
Use function key shortcuts
-
Change function key preferences with the mouse
-
-
Drawing
Frequently used shortcuts
This table itemizes the most frequently used shortcuts in Excel for Mac.
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Paste selection. |
|
|
Copy selection. |
|
|
Clear selection. |
Delete |
|
Save workbook. |
|
|
Undo action. |
|
|
Redo action. |
|
|
Cut selection. |
|
|
Apply bold formatting. |
|
|
Print workbook. |
|
|
Open Visual Basic. |
Option+F11 |
|
Fill cells down. |
|
|
Fill cells right. |
|
|
Insert cells. |
Control+Shift+Equal sign ( = ) |
|
Delete cells. |
|
|
Calculate all open workbooks. |
|
|
Close window. |
|
|
Quit Excel. |
|
|
Display the Go To dialog box. |
Control+G |
|
Display the Format Cells dialog box. |
|
|
Display the Replace dialog box. |
Control+H |
|
Use Paste Special. |
|
|
Apply underline formatting. |
|
|
Apply italic formatting. |
|
|
Open a new blank workbook. |
|
|
Create a new workbook from template. |
|
|
Display the Save As dialog box. |
|
|
Display the Help window. |
F1 |
|
Select all. |
|
|
Add or remove a filter. |
|
|
Minimize or maximize the ribbon tabs. |
|
|
Display the Open dialog box. |
|
|
Check spelling. |
F7 |
|
Open the thesaurus. |
Shift+F7 |
|
Display the Formula Builder. |
Shift+F3 |
|
Open the Define Name dialog box. |
|
|
Insert or reply to a threaded comment. |
|
|
Open the Create names dialog box. |
|
|
Insert a new sheet. * |
Shift+F11 |
|
Print preview. |
|
Top of Page
Shortcut conflicts
Some Windows keyboard shortcuts conflict with the corresponding default macOS keyboard shortcuts. This topic flags such shortcuts with an asterisk (*). To use these shortcuts, you might have to change your Mac keyboard settings to change the Show Desktop shortcut for the key.
Change system preferences for keyboard shortcuts with the mouse
-
On the Apple menu, select System Settings.
-
Select Keyboard.
-
Select Keyboard Shortcuts.
-
Find the shortcut that you want to use in Excel and clear the checkbox for it.
Top of Page
Work in windows and dialog boxes
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Expand or minimize the ribbon. |
|
|
Switch to full screen view. |
|
|
Switch to the next application. |
|
|
Switch to the previous application. |
Shift+ |
|
Close the active workbook window. |
|
|
Take a screenshot and save it on your desktop. |
Shift+ |
|
Minimize the active window. |
Control+F9 |
|
Maximize or restore the active window. |
Control+F10 |
|
Hide Excel. |
|
|
Move to the next box, option, control, or command. |
Tab key |
|
Move to the previous box, option, control, or command. |
Shift+Tab |
|
Exit a dialog box or cancel an action. |
Esc |
|
Perform the action assigned to the default button (the button with the bold outline). |
Return |
|
Cancel the command and close the dialog box or menu. |
Esc |
Top of Page
Move and scroll in a sheet or workbook
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Move one cell up, down, left, or right. |
Arrow keys |
|
Move to the edge of the current data region. |
|
|
Move to the beginning of the row. |
Home |
|
Move to the beginning of the sheet. |
Control+Home |
|
Move to the last cell in use on the sheet. |
Control+End |
|
Move down one screen. |
Page down |
|
Move up one screen. |
Page up |
|
Move one screen to the right. |
Option+Page down |
|
Move one screen to the left. |
Option+Page up |
|
Move to the next sheet in the workbook. |
Control+Page down |
|
Move to the previous sheet in the workbook. |
Control+Page down |
|
Scroll to display the active cell. |
Control+Delete |
|
Display the Go To dialog box. |
Control+G |
|
Display the Find dialog box. |
Control+F |
|
Access search (when in a cell or when a cell is selected). |
|
|
Move between unlocked cells on a protected sheet. |
Tab key |
|
Scroll horizontally. |
Shift, then scroll the mouse wheel up for left, down for right |
Tip: To use the arrow keys to move between cells in Excel for Mac 2011, you must turn Scroll Lock off. To toggle Scroll Lock off or on, press Shift+F14. Depending on the type of your keyboard, you might need to use the Control, Option, or the Command key instead of the Shift key. If you are using a MacBook, you might need to plug in a USB keyboard to use the F14 key combination.
Top of Page
Enter data on a sheet
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Edit the selected cell. |
F2 |
|
Complete a cell entry and move forward in the selection. |
Return |
|
Start a new line in the same cell. |
Option+Return or Control+Option+Return |
|
Fill the selected cell range with the text that you type. |
|
|
Complete a cell entry and move up in the selection. |
Shift+Return |
|
Complete a cell entry and move to the right in the selection. |
Tab key |
|
Complete a cell entry and move to the left in the selection. |
Shift+Tab |
|
Cancel a cell entry. |
Esc |
|
Delete the character to the left of the insertion point or delete the selection. |
Delete |
|
Delete the character to the right of the insertion point or delete the selection. Note: Some smaller keyboards do not have this key. |
|
|
Delete text to the end of the line. Note: Some smaller keyboards do not have this key. |
Control+ |
|
Move one character up, down, left, or right. |
Arrow keys |
|
Move to the beginning of the line. |
Home |
|
Insert a note. |
Shift+F2 |
|
Open and edit a cell note. |
Shift+F2 |
|
Insert a threaded comment. |
|
|
Open and reply to a threaded comment. |
|
|
Fill down. |
Control+D |
|
Fill to the right. |
Control+R |
|
Invoke Flash Fill to automatically recognize patterns in adjacent columns and fill the current column. |
Control+E |
|
Define a name. |
Control+L |
Top of Page
Work in cells or the Formula bar
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Turn on or off tooltips for checking formulas directly in the formula bar. |
Control+Option+P |
|
Edit the selected cell. |
F2 |
|
Expand or collapse the formula bar. |
Control+Shift+U |
|
Edit the active cell and then clear it or delete the preceding character in the active cell as you edit the cell contents. |
Delete |
|
Complete a cell entry. |
Return |
|
Enter a formula as an array formula. |
Shift+ |
|
Cancel an entry in the cell or formula bar. |
Esc |
|
Display the Formula Builder after you type a valid function name in a formula |
Control+A |
|
Insert a hyperlink. |
|
|
Edit the active cell and position the insertion point at the end of the line. |
Control+U |
|
Open the Formula Builder. |
Shift+F3 |
|
Calculate the active sheet. |
Shift+F9 |
|
Display the context menu. |
Shift+F10 |
|
Start a formula. |
Equal sign ( = ) |
|
Toggle the formula reference style between absolute, relative, and mixed. |
|
|
Insert the AutoSum formula. |
Shift+ |
|
Enter the date. |
Control+Semicolon (;) |
|
Enter the time. |
|
|
Copy the value from the cell above the active cell into the cell or the formula bar. |
Control+Shift+Inch mark/Straight double quote («) |
|
Alternate between displaying cell values and displaying cell formulas. |
Control+Grave accent (`) |
|
Copy a formula from the cell above the active cell into the cell or the formula bar. |
Control+Apostrophe (‘) |
|
Display the AutoComplete list. |
Option+Down arrow key |
|
Define a name. |
Control+L |
|
Open the Smart Lookup pane. |
Control+Option+ |
Top of Page
Format and edit data
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Edit the selected cell. |
F2 |
|
Create a table. |
|
|
Insert a line break in a cell. |
|
|
Insert special characters like symbols, including emoji. |
Control+ |
|
Increase font size. |
Shift+ |
|
Decrease font size. |
Shift+ |
|
Align center. |
|
|
Align left. |
|
|
Display the Modify Cell Style dialog box. |
Shift+ |
|
Display the Format Cells dialog box. |
|
|
Apply the general number format. |
Control+Shift+Tilde (~) |
|
Apply the currency format with two decimal places (negative numbers appear in red with parentheses). |
Control+Shift+Dollar sign ($) |
|
Apply the percentage format with no decimal places. |
Control+Shift+Percent sign (%) |
|
Apply the exponential number format with two decimal places. |
Control+Shift+Caret (^) |
|
Apply the date format with the day, month, and year. |
Control+Shift+Number sign (#) |
|
Apply the time format with the hour and minute, and indicate AM or PM. |
Control+Shift+At symbol (@) |
|
Apply the number format with two decimal places, thousands separator, and minus sign (-) for negative values. |
Control+Shift+Exclamation point (!) |
|
Apply the outline border around the selected cells. |
|
|
Add an outline border to the right of the selection. |
|
|
Add an outline border to the left of the selection. |
|
|
Add an outline border to the top of the selection. |
|
|
Add an outline border to the bottom of the selection. |
|
|
Remove outline borders. |
|
|
Apply or remove bold formatting. |
|
|
Apply or remove italic formatting. |
|
|
Apply or remove underline formatting. |
|
|
Apply or remove strikethrough formatting. |
Shift+ |
|
Hide a column. |
|
|
Unhide a column. |
Shift+ |
|
Hide a row. |
|
|
Unhide a row. |
Shift+ |
|
Edit the active cell. |
Control+U |
|
Cancel an entry in the cell or the formula bar. |
Esc |
|
Edit the active cell and then clear it or delete the preceding character in the active cell as you edit the cell contents. |
Delete |
|
Paste text into the active cell. |
|
|
Complete a cell entry |
Return |
|
Give selected cells the current cell’s entry. |
|
|
Enter a formula as an array formula. |
Shift+ |
|
Display the Formula Builder after you type a valid function name in a formula. |
Control+A |
Top of Page
Select cells, columns, or rows
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Extend the selection by one cell. |
Shift+Arrow key |
|
Extend the selection to the last nonblank cell in the same column or row as the active cell. |
Shift+ |
|
Extend the selection to the beginning of the row. |
Shift+Home |
|
Extend the selection to the beginning of the sheet. |
Control+Shift+Home |
|
Extend the selection to the last cell used |
Control+Shift+End |
|
Select the entire column. * |
Control+Spacebar |
|
Select the entire row. |
Shift+Spacebar |
|
Select the current region or entire sheet. Press more than once to expand the selection. |
|
|
Select only visible cells. |
Shift+ |
|
Select only the active cell when multiple cells are selected. |
Shift+Delete |
|
Extend the selection down one screen. |
Shift+Page down |
|
Extend the selection up one screen |
Shift+Page up |
|
Alternate between hiding objects, displaying objects, |
Control+6 |
|
Turn on the capability to extend a selection |
F8 |
|
Add another range of cells to the selection. |
Shift+F8 |
|
Select the current array, which is the array that the |
Control+Forward slash (/) |
|
Select cells in a row that don’t match the value |
Control+Backward slash () |
|
Select only cells that are directly referred to by formulas in the selection. |
Control+Shift+Left bracket ([) |
|
Select all cells that are directly or indirectly referred to by formulas in the selection. |
Control+Shift+Left brace ({) |
|
Select only cells with formulas that refer directly to the active cell. |
Control+Right bracket (]) |
|
Select all cells with formulas that refer directly or indirectly to the active cell. |
Control+Shift+Right brace (}) |
Top of Page
Work with a selection
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Copy a selection. |
|
|
Paste a selection. |
|
|
Cut a selection. |
|
|
Clear a selection. |
Delete |
|
Delete the selection. |
Control+Hyphen |
|
Undo the last action. |
|
|
Hide a column. |
|
|
Unhide a column. |
|
|
Hide a row. |
|
|
Unhide a row. |
|
|
Move selected rows, columns, or cells. |
Hold the Shift key while you drag a selected row, column, or selected cells to move the selected cells and drop to insert them in a new location. If you don’t hold the Shift key while you drag and drop, the selected cells will be cut from the original location and pasted to the new location (not inserted). |
|
Move from top to bottom within the selection (down). * |
Return |
|
Move from bottom to top within the selection (up). * |
Shift+Return |
|
Move from left to right within the selection, |
Tab key |
|
Move from right to left within the selection, |
Shift+Tab |
|
Move clockwise to the next corner of the selection. |
Control+Period (.) |
|
Group selected cells. |
|
|
Ungroup selected cells. |
|
* These shortcuts might move in another direction other than down or up. If you’d like to change the direction of these shortcuts using the mouse, select Excel > Preferences > Edit, and then, in After pressing Return, move selection, select the direction you want to move to.
Top of Page
Use charts
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Insert a new chart sheet. * |
F11 |
|
Cycle through chart object selection. |
Arrow keys |
Top of Page
Sort, filter, and use PivotTable reports
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Open the Sort dialog box. |
|
|
Add or remove a filter. |
|
|
Display the Filter list or PivotTable page |
Option+Down arrow key |
Top of Page
Outline data
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Display or hide outline symbols. |
Control+8 |
|
Hide selected rows. |
Control+9 |
|
Unhide selected rows. |
Control+Shift+Left parenthesis (() |
|
Hide selected columns. |
Control+Zero (0) |
|
Unhide selected columns. |
Control+Shift+Right parenthesis ()) |
Top of Page
Use function key shortcuts
Excel for Mac uses the function keys for common commands, including Copy and Paste. For quick access to these shortcuts, you can change your Apple system preferences, so you don’t have to press the Fn key every time you use a function key shortcut.
Note: Changing system function key preferences affects how the function keys work for your Mac, not just Excel for Mac. After changing this setting, you can still perform the special features printed on a function key. Just press the Fn key. For example, to use the F12 key to change your volume, you would press Fn+F12.
If a function key doesn’t work as you expect it to, press the Fn key in addition to the function key. If you don’t want to press the Fn key each time, you can change your Apple system preferences. For instructions, go to Change function key preferences with the mouse.
The following table provides the function key shortcuts for Excel for Mac.
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Display the Help window. |
F1 |
|
Edit the selected cell. |
F2 |
|
Insert a note or open and edit a cell note. |
Shift+F2 |
|
Insert a threaded comment or open and reply to a threaded comment. |
|
|
Open the Save dialog box. |
Option+F2 |
|
Open the Formula Builder. |
Shift+F3 |
|
Open the Define Name dialog box. |
|
|
Close a window or a dialog box. |
|
|
Display the Go To dialog box. |
F5 |
|
Display the Find dialog box. |
Shift+F5 |
|
Move to the Search Sheet dialog box. |
Control+F5 |
|
Switch focus between the worksheet, ribbon, task pane, and status bar. |
F6 or Shift+F6 |
|
Check spelling. |
F7 |
|
Open the thesaurus. |
Shift+F7 |
|
Extend the selection. |
F8 |
|
Add to the selection. |
Shift+F8 |
|
Display the Macro dialog box. |
Option+F8 |
|
Calculate all open workbooks. |
F9 |
|
Calculate the active sheet. |
Shift+F9 |
|
Minimize the active window. |
Control+F9 |
|
Display the context menu, or «right click» menu. |
Shift+F10 |
|
Display a pop-up menu (on object button menu), such as by clicking the button after you paste into a sheet. |
Option+Shift+F10 |
|
Maximize or restore the active window. |
Control+F10 |
|
Insert a new chart sheet.* |
F11 |
|
Insert a new sheet.* |
Shift+F11 |
|
Insert an Excel 4.0 macro sheet. |
|
|
Open Visual Basic. |
Option+F11 |
|
Display the Save As dialog box. |
F12 |
|
Display the Open dialog box. |
|
|
Open the Power Query Editor |
Option+F12 |
Top of Page
Change function key preferences with the mouse
-
On the Apple menu, select System Preferences > Keyboard.
-
On the Keyboard tab, select the checkbox for Use all F1, F2, etc. keys as standard function keys.
Drawing
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Toggle Drawing mode on and off. |
|
Top of Page
See also
Excel help & learning
Use a screen reader to explore and navigate Excel
Basic tasks using a screen reader with Excel
Screen reader support for Excel
This article describes the keyboard shortcuts in Excel for iOS.
Notes:
-
If you’re familiar with keyboard shortcuts on your macOS computer, the same key combinations work with Excel for iOS using an external keyboard, too.
-
To quickly find a shortcut, you can use the Search. Press
+F and then type your search words.
In this topic
-
Navigate the worksheet
-
Format and edit data
-
Work in cells or the formula bar
Navigate the worksheet
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Move one cell to the right. |
Tab key |
|
Move one cell up, down, left, or right. |
Arrow keys |
|
Move to the next sheet in the workbook. |
Option+Right arrow key |
|
Move to the previous sheet in the workbook. |
Option+Left arrow key |
Top of Page
Format and edit data
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Apply outline border. |
|
|
Remove outline border. |
|
|
Hide column(s). |
|
|
Hide row(s). |
Control+9 |
|
Unhide column(s). |
Shift+ |
|
Unhide row(s). |
Shift+Control+9 or Shift+Control+Left parenthesis (() |
Top of Page
Work in cells or the formula bar
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Move to the cell on the right. |
Tab key |
|
Move within cell text. |
Arrow keys |
|
Copy a selection. |
|
|
Paste a selection. |
|
|
Cut a selection. |
|
|
Undo an action. |
|
|
Redo an action. |
|
|
Apply bold formatting to the selected text. |
|
|
Apply italic formatting to the selected text. |
|
|
Underline the selected text. |
|
|
Select all. |
|
|
Select a range of cells. |
Shift+Left or Right arrow key |
|
Insert a line break within a cell. |
|
|
Move the cursor to the beginning of the current line within a cell. |
|
|
Move the cursor to the end of the current line within a cell. |
|
|
Move the cursor to the beginning of the current cell. |
|
|
Move the cursor to the end of the current cell. |
|
|
Move the cursor up by one paragraph within a cell that contains a line break. |
Option+Up arrow key |
|
Move the cursor down by one paragraph within a cell that contains a line break. |
Option+Down arrow key |
|
Move the cursor right by one word. |
Option+Right arrow key |
|
Move the cursor left by one word. |
Option+Left arrow key |
|
Insert an AutoSum formula. |
Shift+ |
Top of Page
See also
Excel help & learning
Screen reader support for Excel
Basic tasks using a screen reader with Excel
Use a screen reader to explore and navigate Excel
This article describes the keyboard shortcuts in Excel for Android.
Notes:
-
If you’re familiar with keyboard shortcuts on your Windows computer, the same key combinations work with Excel for Android using an external keyboard, too.
-
To quickly find a shortcut, you can use the Search. Press Control+F and then type your search words.
In this topic
-
Navigate the worksheet
-
Work with cells
Navigate the worksheet
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Move one cell to the right. |
Tab key |
|
Move one cell up, down, left, or right. |
Up, Down, Left, or Right arrow key |
Top of Page
Work with cells
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Save a worksheet. |
Control+S |
|
Copy a selection. |
Control+C |
|
Paste a selection. |
Control+V |
|
Cut a selection. |
Control+X |
|
Undo an action. |
Control+Z |
|
Redo an action. |
Control+Y |
|
Apply bold formatting. |
Control+B |
|
Apply italic formatting. |
Control+I |
|
Apply underline formatting. |
Control+U |
|
Select all. |
Control+A |
|
Find. |
Control+F |
|
Insert a line break within a cell. |
Alt+Enter |
Top of Page
See also
Excel help & learning
Screen reader support for Excel
Basic tasks using a screen reader with Excel
Use a screen reader to explore and navigate Excel
This article describes the keyboard shortcuts in Excel for the web.
Notes:
-
If you use Narrator with the Windows 10 Fall Creators Update, you have to turn off scan mode in order to edit documents, spreadsheets, or presentations with Microsoft 365 for the web. For more information, refer to Turn off virtual or browse mode in screen readers in Windows 10 Fall Creators Update.
-
To quickly find a shortcut, you can use the Search. Press Ctrl+F and then type your search words.
-
When you use Excel for the web, we recommend that you use Microsoft Edge as your web browser. Because Excel for the web runs in your web browser, the keyboard shortcuts are different from those in the desktop program. For example, you’ll use Ctrl+F6 instead of F6 for jumping in and out of the commands. Also, common shortcuts like F1 (Help) and Ctrl+O (Open) apply to the web browser — not Excel for the web.
In this article
-
Quick tips for using keyboard shortcuts with Excel for the web
-
Frequently used shortcuts
-
Access keys: Shortcuts for using the ribbon
-
Keyboard shortcuts for editing cells
-
Keyboard shortcuts for entering data
-
Keyboard shortcuts for editing data within a cell
-
Keyboard shortcuts for formatting cells
-
Keyboard shortcuts for moving and scrolling within worksheets
-
Keyboard shortcuts for working with objects
-
Keyboard shortcuts for working with cells, rows, columns, and objects
-
Keyboard shortcuts for moving within a selected range
-
Keyboard shortcuts for calculating data
-
Accessibility Shortcuts Menu (Alt+Shift+A)
-
Control keyboard shortcuts in Excel for the web by overriding browser keyboard shortcuts
Quick tips for using keyboard shortcuts with Excel for the web
-
To find any command quickly, press Alt+Windows logo key, Q to jump to the Search or Tell Me text field. In Search or Tell Me, type a word or the name of a command you want (available only in Editing mode). Search or Tell Me searches for related options and provides a list. Use the Up and Down arrow keys to select a command, and then press Enter.
Depending on the version of Microsoft 365 you are using, the Search text field at the top of the app window might be called Tell Me instead. Both offer a largely similar experience, but some options and search results can vary.
-
To jump to a particular cell in a workbook, use the Go To option: press Ctrl+G, type the cell reference (such as B14), and then press Enter.
-
If you use a screen reader, go to Accessibility Shortcuts Menu (Alt+Shift+A).
Frequently used shortcuts
These are the most frequently used shortcuts for Excel for the web.
Tip: To quickly create a new worksheet in Excel for the web, open your browser, type Excel.new in the address bar, and then press Enter.
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Go to a specific cell. |
Ctrl+G |
|
Move down. |
Page down or Down arrow key |
|
Move up. |
Page up or Up arrow key |
|
Print a workbook. |
Ctrl+P |
|
Copy selection. |
Ctrl+C |
|
Paste selection. |
Ctrl+V |
|
Cut selection. |
Ctrl+X |
|
Undo action. |
Ctrl+Z |
|
Open workbook. |
Ctrl+O |
|
Close workbook. |
Ctrl+W |
|
Open the Save As dialog box. |
Alt+F2 |
|
Use Find. |
Ctrl+F or Shift+F3 |
|
Apply bold formatting. |
Ctrl+B |
|
Open the context menu. |
|
|
Jump to Search or Tell me. |
Alt+Q |
|
Repeat Find downward. |
Shift+F4 |
|
Repeat Find upward. |
Ctrl+Shift+F4 |
|
Insert a chart. |
Alt+F1 |
|
Display the access keys (ribbon commands) on the classic ribbon when using Narrator. |
Alt+Period (.) |
Top of Page
Access keys: Shortcuts for using the ribbon
Excel for the web offers access keys, keyboard shortcuts to navigate the ribbon. If you’ve used access keys to save time on Excel for desktop computers, you’ll find access keys very similar in Excel for the web.
In Excel for the web, access keys all start with Alt+Windows logo key, then add a letter for the ribbon tab. For example, to go to the Review tab, press Alt+Windows logo key, R.
Note: To learn how to override the browser’s Alt-based ribbon shortcuts, go to Control keyboard shortcuts in Excel for the web by overriding browser keyboard shortcuts.
If you’re using Excel for the web on a Mac computer, press Control+Option to start.
-
To get to the ribbon, press Alt+Windows logo key, or press Ctrl+F6 until you reach the Home tab.
-
To move between tabs on the ribbon, press the Tab key.
-
To hide the ribbon so you have more room to work, press Ctrl+F1. To display the ribbon again, press Ctrl+F1.
Go to the access keys for the ribbon
To go directly to a tab on the ribbon, press one of the following access keys:
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Go to the Search or Tell Me field on the ribbon and type a search term. |
Alt+Windows logo key, Q |
|
Open the File menu. |
Alt+Windows logo key, F |
|
Open the Home tab and format text and numbers or use other tools such as Sort & Filter. |
Alt+Windows logo key, H |
|
Open the Insert tab and insert a function, table, chart, hyperlink, or threaded comment. |
Alt+Windows logo key, N |
|
Open the Data tab and refresh connections or use data tools. |
Alt+Windows logo key, A |
|
Open the Review tab and use the Accessibility Checker or work with threaded comments and notes. |
Alt+Windows logo key, R |
|
Open the View tab to choose a view, freeze rows or columns in your worksheet, or show gridlines and headers. |
Alt+Windows logo key, W |
Top of Page
Work in the ribbon tabs and menus
The shortcuts in this table can save time when you work with the ribbon tabs and ribbon menus.
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Select the active tab of the ribbon and activate the access keys. |
Alt+Windows logo key. To move to a different tab, use an access key or the Tab key. |
|
Move the focus to commands on the ribbon. |
Enter, then the Tab key or Shift+Tab |
|
Activate a selected button. |
Spacebar or Enter |
|
Open the list for a selected command. |
Spacebar or Enter |
|
Open the menu for a selected button. |
Alt+Down arrow key |
|
When a menu or submenu is open, move to the next command. |
Esc |
Top of Page
Keyboard shortcuts for editing cells
Tip: If a spreadsheet opens in the Viewing mode, editing commands won’t work. To switch to Editing mode, press Alt+Windows logo key, Z, M, E.
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Insert a row above the current row. |
Alt+Windows logo key, H, I, R |
|
Insert a column to the left of the current column. |
Alt+Windows logo key, H, I, C |
|
Cut selection. |
Ctrl+X |
|
Copy selection. |
Ctrl+C |
|
Paste selection. |
Ctrl+V |
|
Undo an action. |
Ctrl+Z |
|
Redo an action. |
Ctrl+Y |
|
Start a new line in the same cell. |
Alt+Enter |
|
Insert a hyperlink. |
Ctrl+K |
|
Insert a table. |
Ctrl+L |
|
Insert a function. |
Shift+F3 |
|
Increase font size. |
Ctrl+Shift+Right angle bracket (>) |
|
Decrease font size. |
Ctrl+Shift+Left angle bracket (<) |
|
Apply a filter. |
Alt+Windows logo key, A, T |
|
Re-apply a filter. |
Ctrl+Alt+L |
|
Toggle AutoFilter on and off. |
Ctrl+Shift+L |
Top of Page
Keyboard shortcuts for entering data
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Complete cell entry and select the cell below. |
Enter |
|
Complete cell entry and select the cell above. |
Shift+Enter |
|
Complete cell entry and select the next cell in the row. |
Tab key |
|
Complete cell entry and select the previous cell in the row. |
Shift+Tab |
|
Cancel cell entry. |
Esc |
Top of Page
Keyboard shortcuts for editing data within a cell
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Edit the selected cell. |
F2 |
|
Cycle through all the various combinations of absolute and relative references when a cell reference or range is selected in a formula. |
F4 |
|
Clear the selected cell. |
Delete |
|
Clear the selected cell and start editing. |
Backspace |
|
Go to beginning of cell line. |
Home |
|
Go to end of cell line. |
End |
|
Select right by one character. |
Shift+Right arrow key |
|
Select to the beginning of cell data. |
Shift+Home |
|
Select to the end of cell data. |
Shift+End |
|
Select left by one character. |
Shift+Left arrow key |
|
Extend selection to the last nonblank cell in the same column or row as the active cell, or if the next cell is blank, to the next nonblank cell. |
Ctrl+Shift+Right arrow key or Ctrl+Shift+Left arrow key |
|
Insert the current date. |
Ctrl+Semicolon (;) |
|
Insert the current time. |
Ctrl+Shift+Semicolon (;) |
|
Copy a formula from the cell above. |
Ctrl+Apostrophe (‘) |
|
Copy the value from the cell above. |
Ctrl+Shift+Apostrophe (‘) |
|
Insert a formula argument. |
Ctrl+Shift+A |
Top of Page
Keyboard shortcuts for formatting cells
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Apply bold formatting. |
Ctrl+B |
|
Apply italic formatting. |
Ctrl+I |
|
Apply underline formatting. |
Ctrl+U |
|
Paste formatting. |
Shift+Ctrl+V |
|
Apply the outline border to the selected cells. |
Ctrl+Shift+Ampersand (&) |
|
Apply the number format. |
Ctrl+Shift+1 |
|
Apply the time format. |
Ctrl+Shift+2 |
|
Apply the date format. |
Ctrl+Shift+3 |
|
Apply the currency format. |
Ctrl+Shift+4 |
|
Apply the percentage format. |
Ctrl+Shift+5 |
|
Apply the scientific format. |
Ctrl+Shift+6 |
|
Apply outside border. |
Ctrl+Shift+7 |
|
Open the Number Format dialog box. |
Ctrl+1 |
Top of Page
Keyboard shortcuts for moving and scrolling within worksheets
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Move up one cell. |
Up arrow key or Shift+Enter |
|
Move down one cell. |
Down arrow key or Enter |
|
Move right one cell. |
Right arrow key or Tab key |
|
Go to the beginning of the row. |
Home |
|
Go to cell A1. |
Ctrl+Home |
|
Go to the last cell of the used range. |
Ctrl+End |
|
Move down one screen (28 rows). |
Page down |
|
Move up one screen (28 rows). |
Page up |
|
Move to the edge of the current data region. |
Ctrl+Right arrow key or Ctrl+Left arrow key |
|
Move between ribbon and workbook content. |
Ctrl+F6 |
|
Move to a different ribbon tab. |
Tab key Press Enter to go to the ribbon for the tab. |
|
Insert a new sheet. |
Shift+F11 |
|
Switch to the next sheet. |
Alt+Ctrl+Page down |
|
Switch to the next sheet (when in Microsoft Teams or a browser other than Chrome). |
Ctrl+Page down |
|
Switch to the previous sheet. |
Alt+Ctrl+Page up |
|
Switch to previous sheet (when in Microsoft Teams or a browser other than Chrome). |
Ctrl+Page up |
Top of Page
Keyboard shortcuts for working with objects
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Open menu or drill down. |
Alt+Down arrow key |
|
Close menu or drill up. |
Alt+Up arrow key |
|
Follow hyperlink. |
Ctrl+Enter |
|
Open a note for editing. |
Shift+F2 |
|
Open and reply to a threaded comment. |
Ctrl+Shift+F2 |
|
Rotate an object left. |
Alt+Left arrow key |
|
Rotate an object right. |
Alt+Right arrow key |
Top of Page
Keyboard shortcuts for working with cells, rows, columns, and objects
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Select a range of cells. |
Shift+Arrow keys |
|
Select an entire column. |
Ctrl+Spacebar |
|
Select an entire row. |
Shift+Spacebar |
|
Extend selection to the last nonblank cell in the same column or row as the active cell, or if the next cell is blank, to the next nonblank cell. |
Ctrl+Shift+Right arrow key or Ctrl+Shift+Left arrow key |
|
Add a non-adjacent cell or range to a selection. |
Shift+F8 |
|
Insert cells, rows, or columns. |
Ctrl+Plus sign (+) |
|
Delete cells, rows, or columns. |
Ctrl+Minus sign (-) |
|
Hide rows. |
Ctrl+9 |
|
Unhide rows. |
Ctrl+Shift+9 |
|
Hide columns |
Ctrl+0 |
|
Unhide columns |
Ctrl+Shift+0 |
Top of Page
Keyboard shortcuts for moving within a selected range
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Move from top to bottom (or forward through the selection). |
Enter |
|
Move from bottom to top (or back through the selection). |
Shift+Enter |
|
Move forward through a row (or down through a single-column selection). |
Tab key |
|
Move back through a row (or up through a single-column selection). |
Shift+Tab |
|
Move to an active cell. |
Shift+Backspace |
|
Move to an active cell and keep the selection. |
Ctrl+Backspace |
|
Rotate the active cell through the corners of the selection. |
Ctrl+Period (.) |
|
Move to the next selected range. |
Ctrl+Alt+Right arrow key |
|
Move to the previous selected range. |
Ctrl+Alt+Left arrow key |
|
Extend selection to the last used cell in the sheet. |
Ctrl+Shift+End |
|
Extend selection to the first cell in the sheet. |
Ctrl+Shift+Home |
Top of Page
Keyboard shortcuts for calculating data
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Calculate workbook (refresh). |
F9 |
|
Perform full calculation. |
Ctrl+Shift+Alt+F9 |
|
Refresh external data. |
Alt+F5 |
|
Refresh all external data. |
Ctrl+Alt+F5 |
|
Apply Auto Sum. |
Alt+Equal sign ( = ) |
|
Apply Flash Fill. |
Ctrl+E |
Top of Page
Accessibility Shortcuts Menu (Alt+Shift+A)
Access the common features quickly by using the following shortcuts:
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Cycle between landmark regions. |
Ctrl+F6 or Ctrl+Shift+F6 |
|
Move within a landmark region. |
Tab key or Shift+Tab |
|
Go to the Search or Tell Me field to run any command. |
Alt+Q |
|
Display or hide Key Tips or access the ribbon. |
Alt+Windows logo key |
|
Edit the selected cell. |
F2 |
|
Go to a specific cell. |
Ctrl+G |
|
Move to another worksheet in the workbook. |
Ctrl+Alt+Page up or Ctrl+Alt+Page down |
|
Open the context menu. |
Shift+F10 or Windows Menu key |
|
Read row header. |
Ctrl+Alt+Shift+T |
|
Read row until an active cell. |
Ctrl+Alt+Shift+Home |
|
Read row from an active cell. |
Ctrl+Alt+Shift+End |
|
Read column header. |
Ctrl+Alt+Shift+H |
|
Read column until an active cell. |
Ctrl+Alt+Shift+Page up |
|
Read column from an active cell. |
Ctrl+Alt+Shift+Page down |
|
Open a list of moving options within a dialog box. |
Ctrl+Alt+Spacebar |
Top of Page
Control keyboard shortcuts in Excel for the web by overriding browser keyboard shortcuts
Excel for the web works in a browser. Browsers have keyboard shortcuts, some of which conflict with shortcuts that work in Excel on the desktop. You can control these shortcuts, so they work the same in both versions of Excel by changing the Keyboard Shortcuts settings. Overriding browser shortcuts also enables you to open the Excel for the web Help by pressing F1.
|
|
Top of Page
See also
Excel help & learning
Use a screen reader to explore and navigate Excel
Basic tasks using a screen reader with Excel
Screen reader support for Excel
Technical support for customers with disabilities
Microsoft wants to provide the best possible experience for all our customers. If you have a disability or questions related to accessibility, please contact the Microsoft Disability Answer Desk for technical assistance. The Disability Answer Desk support team is trained in using many popular assistive technologies and can offer assistance in English, Spanish, French, and American Sign Language. Please go to the Microsoft Disability Answer Desk site to find out the contact details for your region.
If you are a government, commercial, or enterprise user, please contact the enterprise Disability Answer Desk.
Is there a way to calculate entire workbook but not all open workbooks in VBA?
I know about
worksheet.Calculate
but it will only do 1 sheet. I also know about
Application.CalculateFull
But I think this recalculate all open workbooks at the same time.
Is it possible to do only 1 workbook?
Edit:
I get the approach:
For Each wks In ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets
wks.Calculate
Next
but this is very dangerous if sheets have links between them, then the order of calculation is important. I know I could find the exact sequence and apply it, problem is that on very large workbooks this can get somewhat tricky
TylerH
20.6k64 gold badges76 silver badges97 bronze badges
asked May 5, 2017 at 13:45
0
After some investigation and testing, selecting all sheets first and calculating afterward works :
Application.Calculation = xlManual
ThisWorkbook.Sheets.Select
ActiveSheet.Calculate
this calculate all selected sheet at the same time creating the right order of calculation
answered May 5, 2017 at 18:08
Steven GSteven G
15.9k7 gold badges51 silver badges76 bronze badges
2
The answer by Steven G doesn’t actually work, it just looks like it does.(I can’t reply to that post as I don’t have 50+ rep, which is annoying).
It still calculates the sheets in 1 directional order. I tested this by creating 5 sheets and having them all + 1 to another cell, on each sheet in different directions. Using the select sheets then calculate method will give the wrong result.
As it requires that the sheets are visible, elow is function I built to replace the calculate function using that method. (Requires dictionaries reference library). Do not use though.
EXAMPLE, METHOD DOES NOT WORK
Function Calculate_Workbook(Optional Wb As Workbook)
'Application.calculate will calculate all open books, which can be very slow.
'Looping through all sheets in workbook to calculate can be risky due to formula referencing a cell thats not yet calculated, calculation order may be important.
Dim DicShtVisible As New Dictionary
DicShtVisible.CompareMode = TextCompare
Dim Asht As Worksheet, AWkbk As Workbook 'Previously selected books
Dim Sht As Worksheet
Set Asht = ActiveSheet
Set AWkbk = ActiveWorkbook
If Wb Is Nothing Then Set Wb = ThisWorkbook
Wb.Activate
'Unhide all sheets as can't select very hidden stuff
For Each Sht In Wb.Sheets
DicShtVisible.Add Sht.Name, Sht.Visible
Sht.Visible = xlSheetVisible
Next Sht
'Select all sheets and calculate the lot
Wb.Sheets.Select
ActiveSheet.Calculate
'Reapply visibility settings
Dim Key As Variant
For Each Key In DicShtVisible.Keys
Wb.Sheets(Key).Visible = DicShtVisible.Item(Key)
Next Key
'Reset selections
AWkbk.Activate
Asht.Select
End Function
As far as I can see there is no solution, the only answer is to either know the calculation order of your workbook and manually calculate sheets in that order, or accept using Calculate and that it will calculate all open workbooks.
I would love to be proven wrong however. It’s such an annoying and stupid issue.
answered Jan 7, 2019 at 3:49
1
None that I know about, Steven.
You actually lose time doing Application.Worksheets(1).Calculate
I ran a timing test: 3 workbooks open in the same instance of Excel.
One with 8200 volatile functions, 8000 in one worksheet on 4 non-contiguous ranges, 200 in other worksheets.
Two other workbooks with a combined total of 100 functions. The results:
Application.Calculate— 4.41 msThisWorkbook.Worksheets(1).Calculate— 52.05 ms for each worksheetThisWorkbook.Worksheets(1).Range("R1").Calculate(repeated 4 times) — 84.64 ms
It’s counter-intuitive, but true.
You also lose time declaring Dim wks as Worksheet. Unless you do For … Each referring to it as ThisWorkbook.Worksheets(1) — is faster
Also, be careful referring to ActiveWorkbook — when you code runs your primary workbook might not be active one. ThisWorkbook (the one with code) is safer.
TylerH
20.6k64 gold badges76 silver badges97 bronze badges
answered Feb 23, 2018 at 18:11
ThisWorkbook will use only the workbook that the code resides in
For Each wks In ThisWorkbook.Worksheets
wks.Calculate
Next wks
answered May 25, 2017 at 7:08
Another option is to create a new instance of Excel, open the workbook is that instance and then calculate that. This will leave any workbooks in the original instance uncalculated, potentially saving you time if another workbook is very slow to calculated (100k+ formulas for instance).
Dim xlApp As Excel.Application
Dim wbTest As Workbook
Set xlApp = New Excel.Application
Set wbTest = xlApp.Workbooks.Open("c:temptest.xlsx")
' do a bunch of stuff in wbTest
xlApp.Calculate
Whether this is better depends on your circumstances. Opening a second instance of Excel involves a little extra time and probably more memory (although I haven’t tested this and it may not be a significant amount).
You may have to change more code to take account of the fact this workbook is in a different instance and there may be issues with some functions (for example if you check if a workbook is already open by spooling through all the workbooks in the original instance of Excel).
answered Aug 11, 2020 at 10:42
Eric NolanEric Nolan
1611 silver badge2 bronze badges
Just use Calculate
eg:
Sub Cal_()
Calculate
End Sub
TylerH
20.6k64 gold badges76 silver badges97 bronze badges
answered Jan 5, 2019 at 12:18
We can use
Application.CalculateBeforeSave = True
and then save the workbook? May be more finessed to trap the current value, set if not true, save, reset if was not true.
Bhargav Rao
49.1k28 gold badges124 silver badges139 bronze badges
answered Jul 11, 2019 at 17:51
jnm21jnm21
132 bronze badges
Try this:
Sub CalcBook()
Dim wks As Worksheet
Application.Calculation = xlManual
For Each wks In ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets
wks.Calculate
Next
Set wks = Nothing
End Sub
TylerH
20.6k64 gold badges76 silver badges97 bronze badges
answered May 5, 2017 at 15:23
William C.William C.
2121 silver badge14 bronze badges
5
Have you ever had to sum the same cell across multiple sheets? This often occurs where information is held in numerous sheets in a consistent format. For example, it could be a monthly report with a tab for each month (see screenshot below as an example).
Watch the video
Watch the video on YouTube.
I see many examples where the user has clicked the same cell on each sheet, putting a “+” symbol between each reference. If there are a lot of worksheets, it takes a while to click on them all. Also, if the sheet names are long, the formula starts to look quite unreadable. The screenshot below shows an example of this type of approach.
The formula in cell C5 is:
=Jan!C5+Feb!C5+Mar!C5+Apr!C5+May!C5+Jun!C5+ Jul!C5+Aug!C5+Sep!C5+Oct!C5+Nov!C5+Dec!C5
How do you know if you’ve clicked on every worksheet? What if you happened to miss one by accident? There is only one way to know – you’ve got to check it!
The chances are that you don’t need to do all that clicking. And just think about the time you will waste if there is a new tab to be added.
The good news is that there is another approach we can take that will enable us to sum across different sheets easily. I still remember the first time a work colleague showed me this trick; my jaw hit the ground in amazement. I thought he was an Excel genius. That’s why I’m sharing it here; by using this approach, you can look like an Excel genius to your work colleagues too 🙂
To sum the same cell across multiple sheets of a workbook, we can use the following formula structure:
=SUM('FirstSheet:LastSheet'!A1)
- Replace FirstSheet and LastSheet with the worksheet names you wish to sum between. If your worksheet names contain spaces, or are the name of a range (e.g., Q1 could be the name of a sheet or a cell reference ), then single quotes ( ‘ ) are required around the sheet names. If not, the single quotes can be left out.
- Replace A1 with the cell reference you wish to use
With this beautiful little formula, we can see all the worksheets included in the calculation just by looking at the tabs at the bottom. Take a look at the screenshot below. All the tabs from Jan to Dec are included in the calculation.
The formula in cell C5 is:
=SUM(Jan:Dec!C5)
SUM across multiple sheets – dynamic
We can change this to be more dynamic, making it even easier to use. Instead of using the names of the first and last tabs, we can create two blank sheets to act as bookends for our calculation.
Take a look at the screenshot below. The Start and End sheets are blank. By dragging sheets in and out of the Start and End bookends, we can sum almost anything we want.
The formula in cell C5 is
=SUM(Start:End!C5)
We can also create sub-calculations. For example, we could add quarters as interim bookends too. There is the added advantage that the tabs also serve as helpful presentation dividers. The example below shows the calculation of just Jan, Feb, and Mar sheets.
The formula in cell C5 is:
=SUM('Q1:Q2'!C5)
Excel could mistake Q1 and Q2 as cell references; therefore, adding single quotes around the sheet names is essential.
Which other formulas does this work for?
This approach doesn’t just work for the SUM function. Here is a list of all the functions for which this trick works.
| Basic Calculations
SUM AVERAGE AVERAGEA PRODUCT |
Counting
COUNT COUNTA |
Min & Max
MAX MAXA MIN MINA |
Standard deviation
STDEV STDEVA STDEVP STDEVPA |
Variance
VAR VARA VARP VARPA |
The drawbacks
There are a few things to be aware of:
- All the sheets must be in a consistent layout and must stay that way. If one worksheet changes, the formula many not sum the correct cells.
- Usually, formula cell references move automatically when new rows or columns are inserted. This formula does not work like that. It will only move if you select all the sheets and then insert a row or column into all of those sheets at the same time.
- Any sheets which are between the two tabs are included within the calculation. Therefore, even though we cannot see them, hidden sheets are also included in the result.
About the author
Hey, I’m Mark, and I run Excel Off The Grid.
My parents tell me that at the age of 7 I declared I was going to become a qualified accountant. I was either psychic or had no imagination, as that is exactly what happened. However, it wasn’t until I was 35 that my journey really began.
In 2015, I started a new job, for which I was regularly working after 10pm. As a result, I rarely saw my children during the week. So, I started searching for the secrets to automating Excel. I discovered that by building a small number of simple tools, I could combine them together in different ways to automate nearly all my regular tasks. This meant I could work less hours (and I got pay raises!). Today, I teach these techniques to other professionals in our training program so they too can spend less time at work (and more time with their children and doing the things they love).
Do you need help adapting this post to your needs?
I’m guessing the examples in this post don’t exactly match your situation. We all use Excel differently, so it’s impossible to write a post that will meet everybody’s needs. By taking the time to understand the techniques and principles in this post (and elsewhere on this site), you should be able to adapt it to your needs.
But, if you’re still struggling you should:
- Read other blogs, or watch YouTube videos on the same topic. You will benefit much more by discovering your own solutions.
- Ask the ‘Excel Ninja’ in your office. It’s amazing what things other people know.
- Ask a question in a forum like Mr Excel, or the Microsoft Answers Community. Remember, the people on these forums are generally giving their time for free. So take care to craft your question, make sure it’s clear and concise. List all the things you’ve tried, and provide screenshots, code segments and example workbooks.
- Use Excel Rescue, who are my consultancy partner. They help by providing solutions to smaller Excel problems.
What next?
Don’t go yet, there is plenty more to learn on Excel Off The Grid. Check out the latest posts:
In this article, you will learn how to Force Calculate All Worksheets with a shortcut in Microsoft Excel. You will also get to know the shortcut to Force Calculate All Worksheets on Mac. The easy key combinations will make you operate Microsoft Excel
Force Calculate All Worksheets With Shortcut in Microsoft Excel
Here we will show you how to force calculate all worksheets in Microsoft Excel. Like many other programs Microsoft Excel also uses similar key combinations while using shortcuts.
You can use the key combinations given below to force calculate all worksheets using the shortcut. This shortcut is used for the force calculation for all the worksheets open in all the workbooks even when cells have not been changed. For Mac users, there is not any shortcut available for this till now, if you know any please inform us. So, here we go:
How to Force Calculate All Worksheets With Shortcut in Microsoft Excel?
It is used to force calculate all worksheets in Microsoft Excel. This shortcut is used for the force calculation for all the worksheets open in all the workbooks even when cells have not been changed. For Mac users, there is not any shortcut available for this till now, if you know any please inform us. This way you can easily force calculate all worksheets using this shortcut.
Did this page help you?
|




 +F, and then type your search words.
+F, and then type your search words.