Импорт данных Excel в Project
Классический клиент Project Online Project профессиональный 2021 Project стандартный 2021 Project профессиональный 2019 Project стандартный 2019 Project профессиональный 2016 Project стандартный 2016 Project профессиональный 2013 Project стандартный 2013 Project 2010 Project стандартный 2010 Еще…Меньше
Если вы начали работу над проектом в Excel, но затем вам потребовались инструменты для управления более сложными расписаниями, общим доступом к ресурсам и отслеживанием, возможно, пора перенести данные в Project. Это можно сделать с помощью мастера импорта проекта. Просто выполните действия по импорту данных в новый или уже существующий проект, и мастер автоматически разместит их в соответствующие поля в Project.
-
В Project выберите команды Файл > Создать.
-
На странице Создать выберите команду Добавить из книги Excel.
-
В поле Открыть щелкните стрелку рядом с элементом Формат XML и выберите пункт Книга Excel или Книга Excel 97-2003 (если данные проект сохранены в формате более ранней версии приложения).
-
Найдите и выберите книгу, которую вы хотите импортировать, и нажмите кнопку Открыть.
-
В окне мастера импорта нажмите кнопку Далее, чтобы начать импорт, а затем следуйте указаниям, чтобы завершить операцию импорта.
-
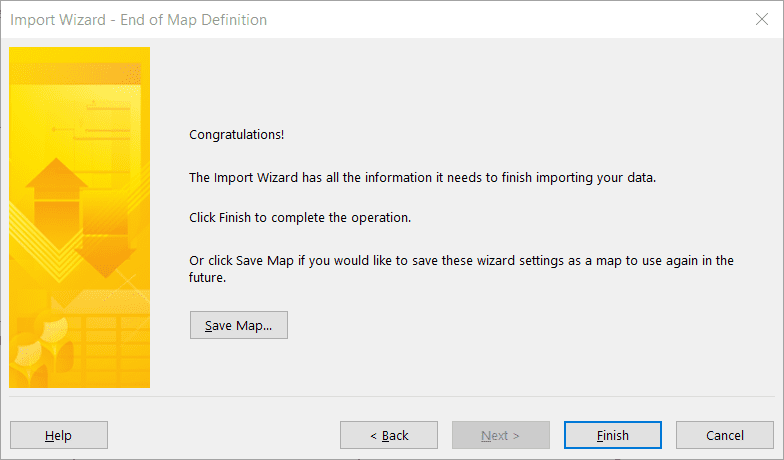
Действие 2. Создайте схему с нуля или выберите готовую схему, соответствующую имеющимся у вас данным, и нажмите кнопку Далее.
-
Действие 3. Импортируйте данные в новый или открытый проект и нажмите кнопку Далее.
-
Действие 4. Выберите тип сведений, которые вы импортируете, чтобы мастер мог правильно разместить данные из Excel в Project, и нажмите кнопку Далее.
-
Действие 5. Проверьте сопоставленные поля, внесите при необходимости изменения и нажмите кнопку Далее.
-
Последнее действие. Щелкните Сохранить схему, если вы хотите использовать ее повторно, и нажмите кнопку Готово.
-
Дополнительные сведения об импорте и экспорте данных проекта
-
Если вы часто начинаете создавать проекты в Excel, воспользуйтесь одним из имеющихся в приложении шаблонов проекта. Они разработаны с использованием соответствующих полей, что упрощает сопоставление данных при последующем экспорте проекта из Excel в Project. В Excel выберите команды Файл > Создать, а затем выберите нужный шаблон проекта, например, Список задач Microsoft Project.
-
Вы также можете экспортировать данные из Project в Excel для анализа данных и создания визуальных отчетов.
Нужна дополнительная помощь?
Introduction
This article discusses Microsoft Project and Excel integration points, specifically in the following areas:
- How to import data from Excel to Project
- Importing an initial last list
- How to export data from Project to Excel
- Exporting a to-do list for resources
- Exporting time-phased data for reporting
Why Bother with Excel?
First things first! My view is that Excel has become the default application used in most offices for producing lists, tabular data (i.e. lists with more than a single column), and graphs derived from the data. Excel has both advantages and disadvantages over Project, and there’s a definite tipping point between using Excel and using Project
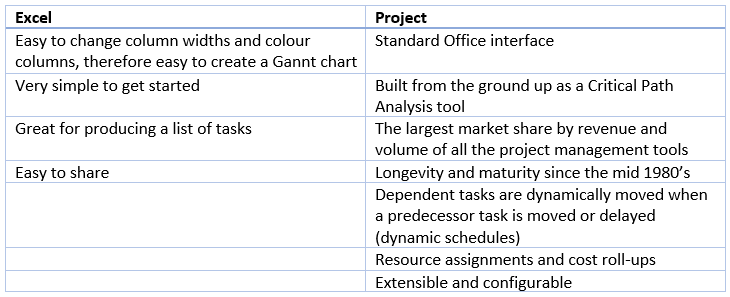
Speaking of tabular data, let’s review a small set of the pros and cons for using Excel and Project when managing a Gantt chart.
We’ll look at the pros first:
And now, the cons:
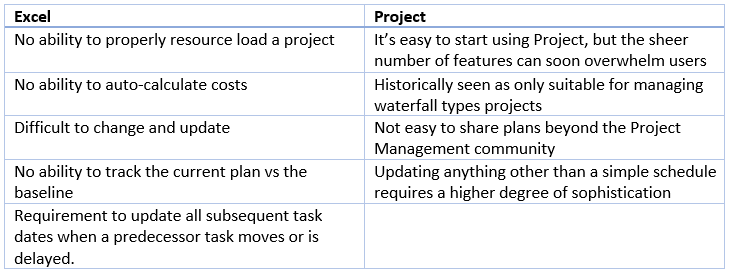
As you can see from my personal tables of pros and cons, Excel works well when we’re dealing with little more than a bunch of tasks and where we might want to draw a representation of a Gantt chart, but the point at which we’ll want to start using Project starts when we want to introduce any of the following:
- Dynamic Scheduling
- Resources
- Costs
- Critical Path
- Tracking
- Forecasting the future
- Reporting
When users need to get into any of the above, it’s a good idea to start using Project, so let’s think about how to import the data.
Import an Existing Excel file into Project
Copy and Paste
There are a couple of ways to import Excel data into Project, so let’s start with the easiest, which, of course, is copy and paste. In order to start this off, I’ve been using an Excel template call Project Planner, which matches my current needs of recording activities and durations. Note that one of the issues with this type of Excel file is the lack of fidelity in the durations. I’m limited to weeks in the Project Planner template.
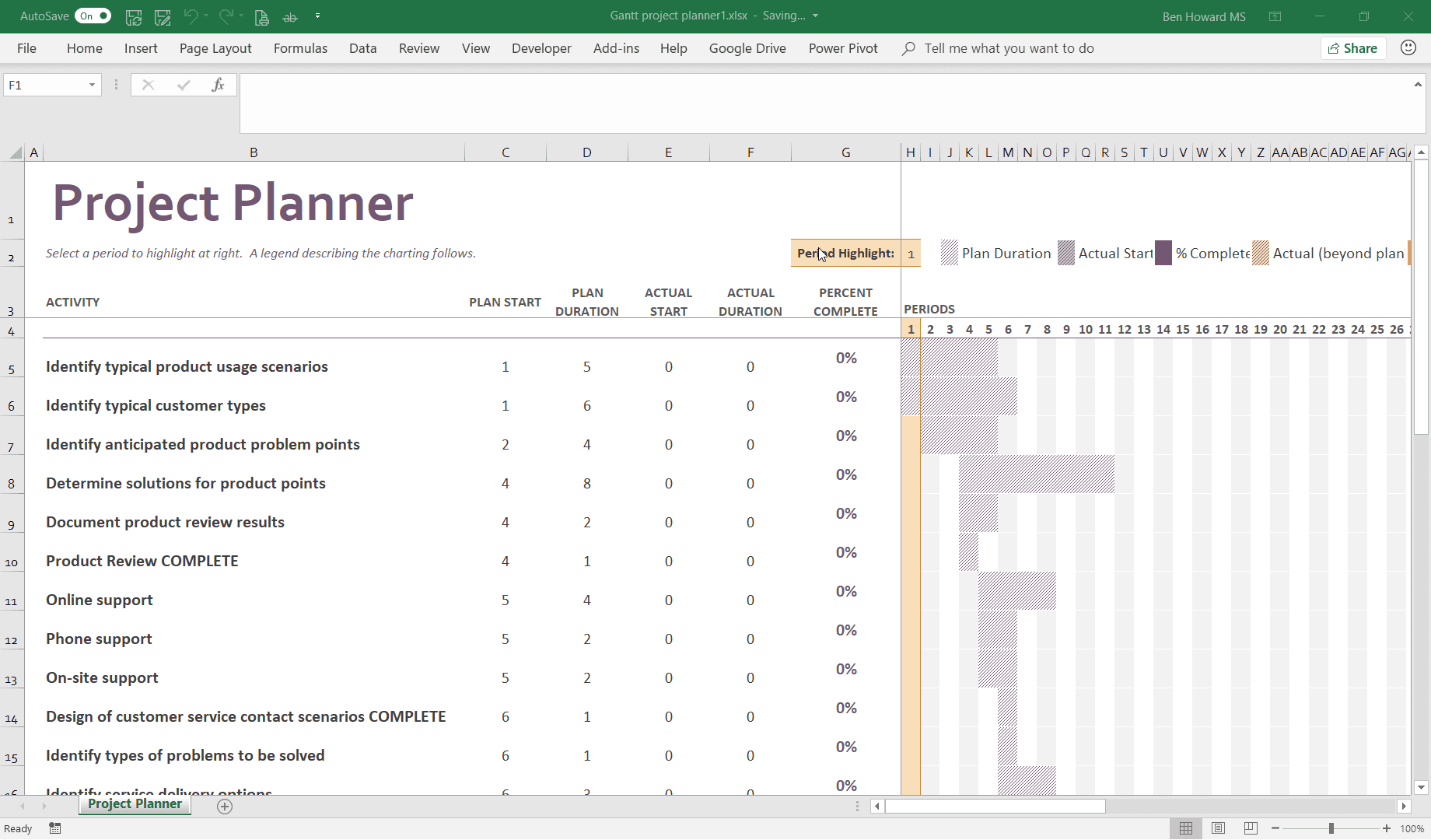
To import the tasks, I can perform a simple copy and paste of the activity name from Excel to the Task Name in Project.
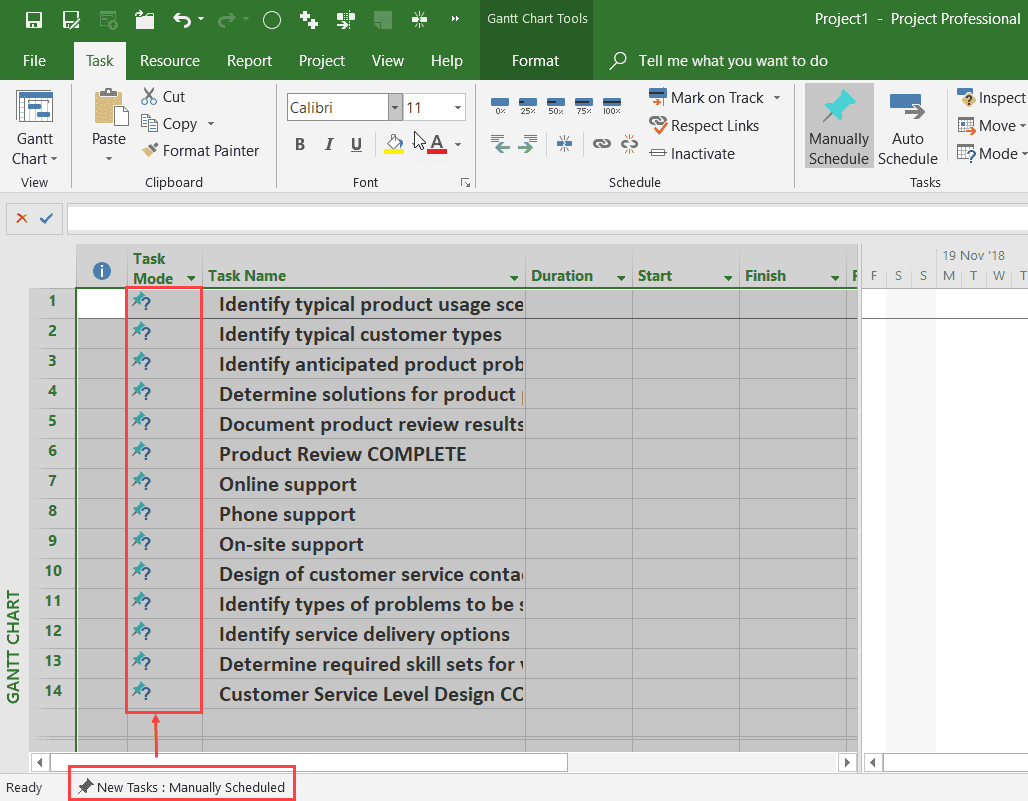
As you can see, the paste has created new tasks, but because the Task Scheduling mode for new tasks is set to Manually Scheduled, the tasks are created without any duration, start, or finish dates.
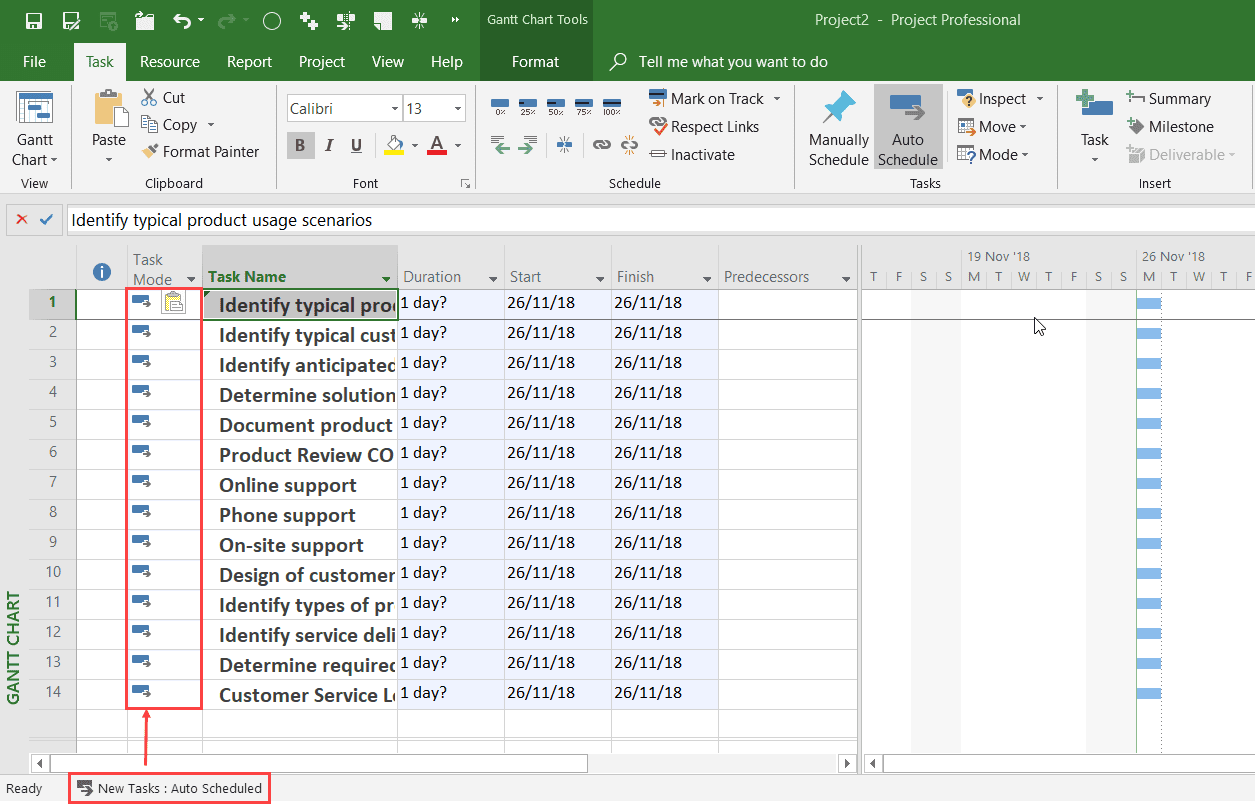
If I do that again, but with the Task Scheduling mode for new tasks set to Auto Scheduled, you will see that durations, start, and finish dates are created and Gantt bars can be displayed for each task.
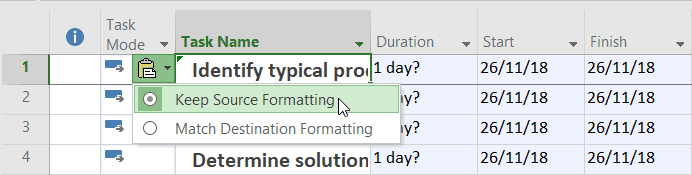
Note that any formatting applied to the text in Excel is preserved during the paste. If I wanted to reset the formatting back to default, I could either immediately use the smart tag and select Match Destination Formatting or use the Clear Formatting button from the ribbon.
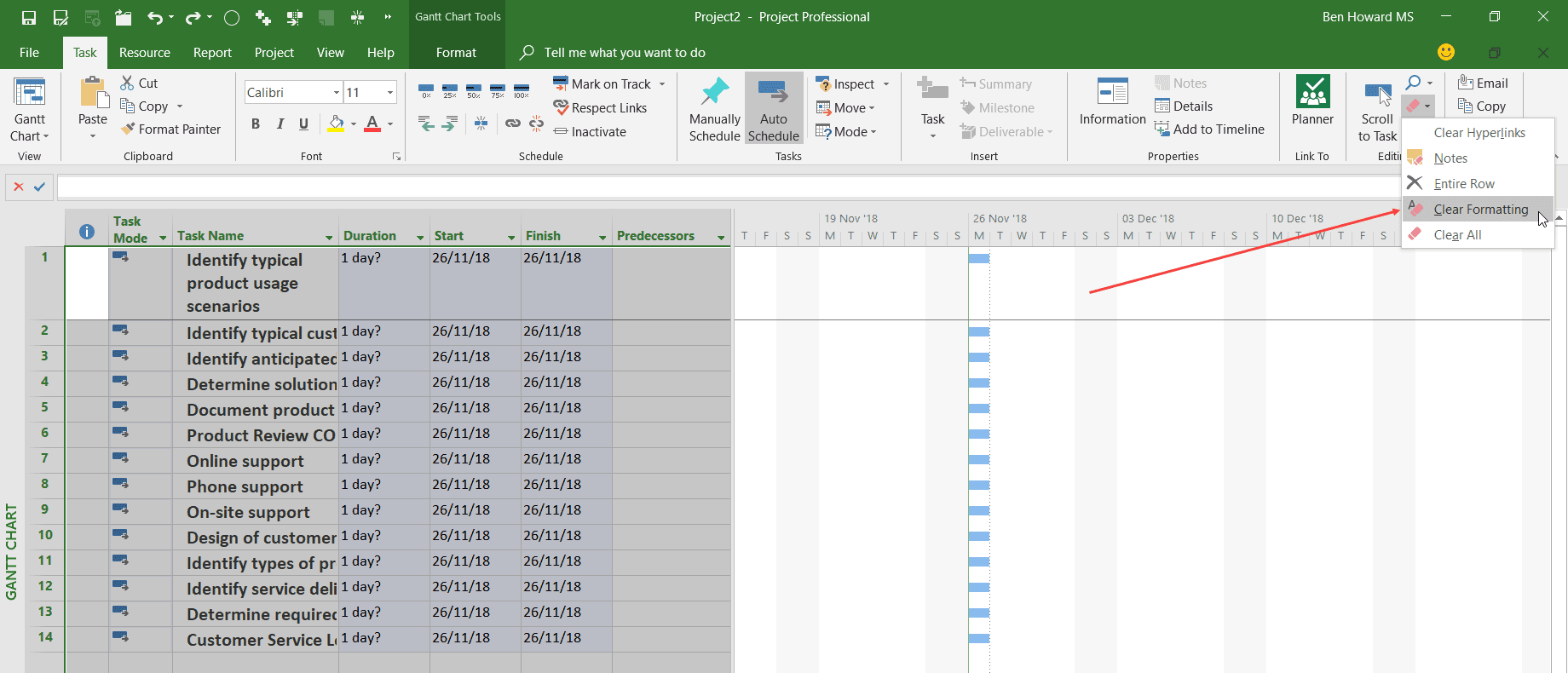
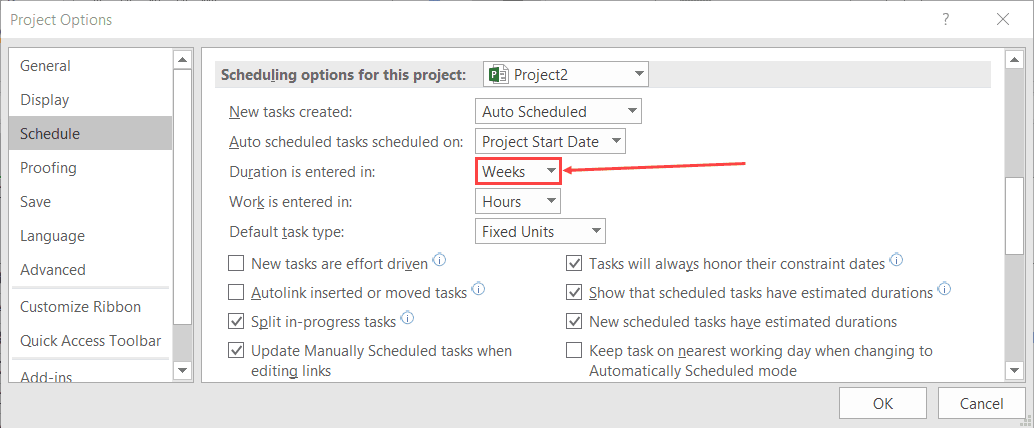
The next thing we can do is import the duration. After all, it is a field in the Excel file. The issue here is that the default duration value is set to “days,” and therefore when we import the duration value, it is expressed in days. As previously stated, the Excel file has the duration in weeks.
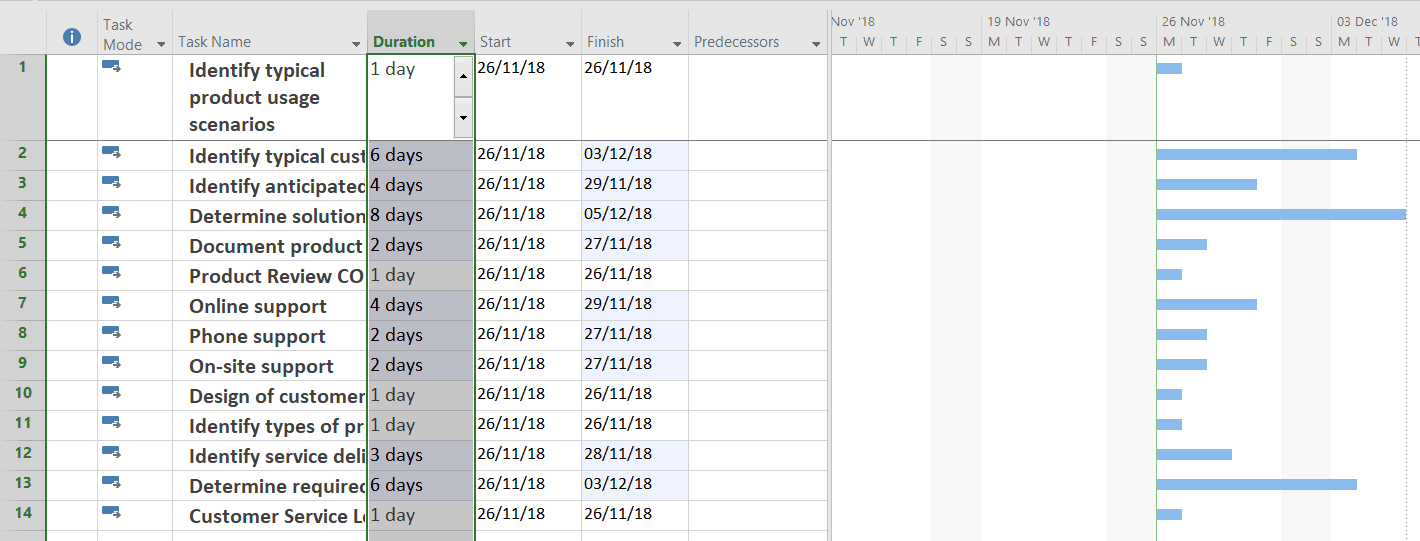
Using the Project | Options dialogue box, we can change the default duration to weeks and then re-paste the data. Note that you may have to reset the durations back to “1day ?” prior to re-pasting.
Creating a New Plan by Using the Import Wizard
We also have the option of importing an existing Excel workbook.
Before you import an Excel workbook, you need to do a little work on it because the Excel import expects a simple list with optional headers. It doesn’t really handle blank lines or merged cells very well, or at all. To get around this, you should copy and paste the relevant items into a new sheet.
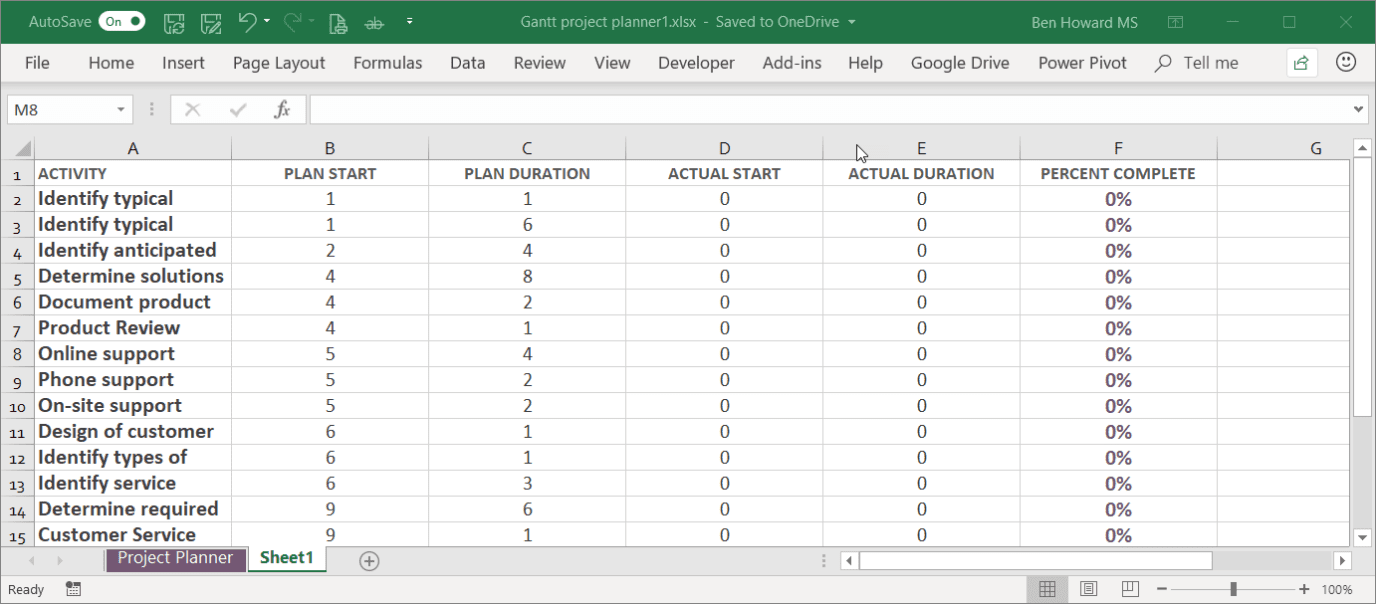
Now you’re ready to import the Excel file.
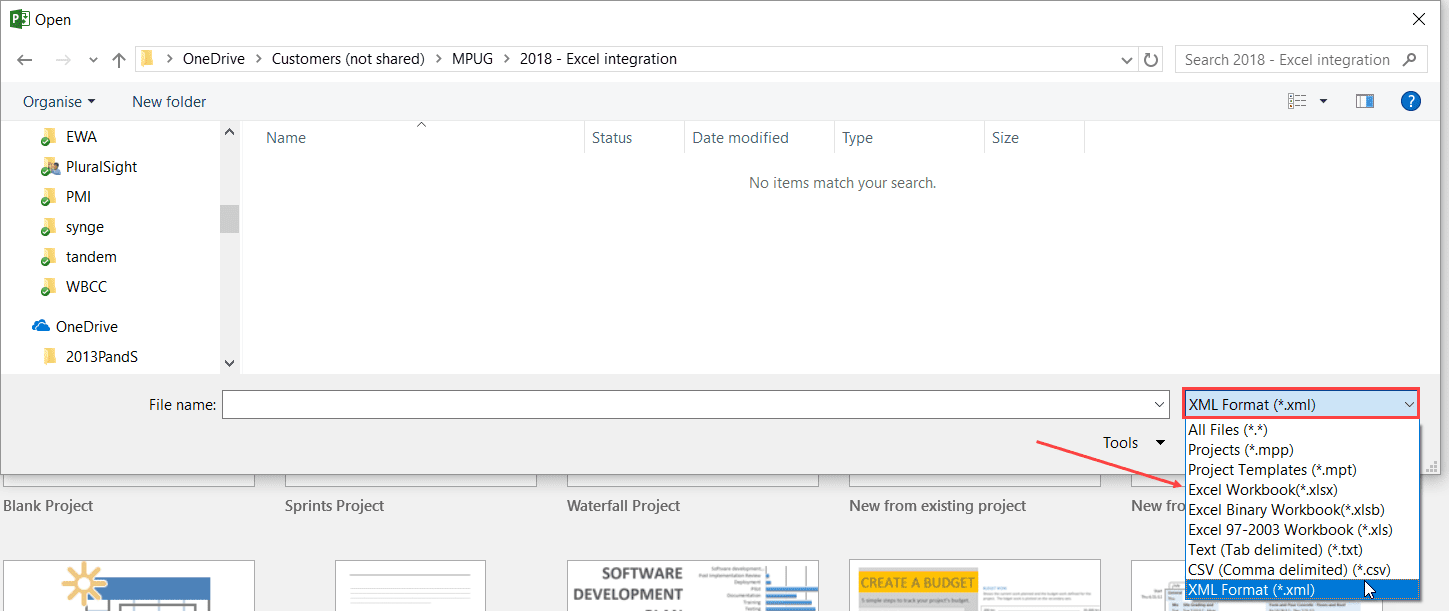
Remember to change the file type from .xml to .xlsx in the file open dialogue box.
You’ll be presented with a wizard, and it’s really just a question of walking though the various screens, as shown below.
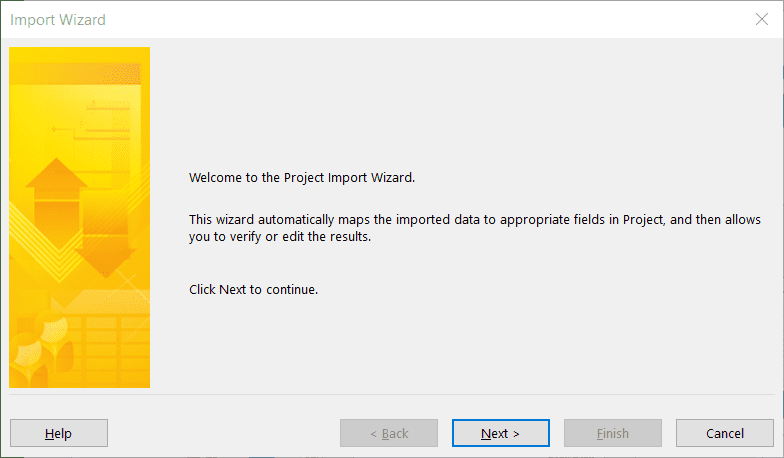
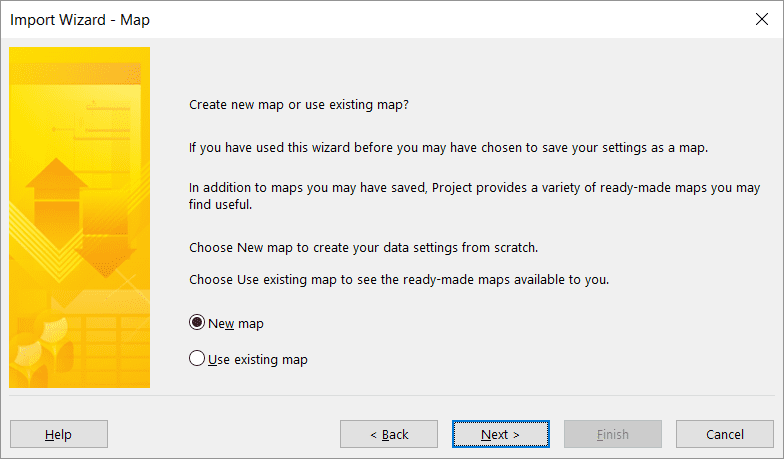
Choose whether to append to an existing project or create a new one.
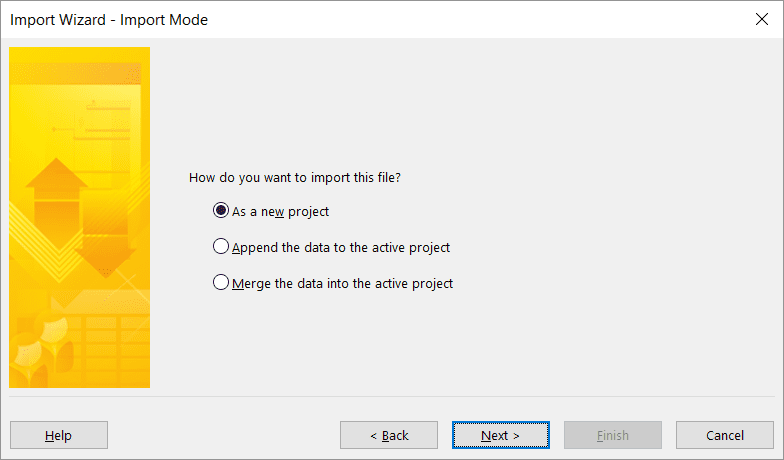
Then, choose what to import. The Excel file only contains tasks, and each column has a header, so you’ll need to select both items.
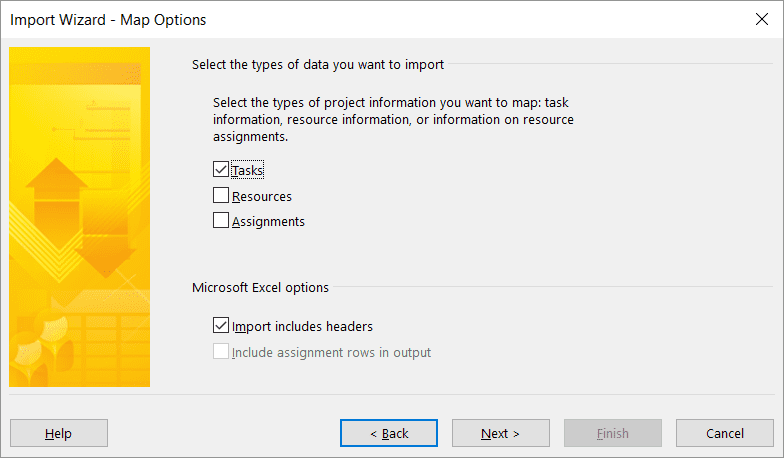
The next screen is where the mapping of Excel fields to Project fields happens.
Select the drop down list to choose the fields to. Fields are mapped automatically if the names are the same between Excel and Project. Note I have chosen not to bring in the Actual Start, Duration values, or Percent Complete.
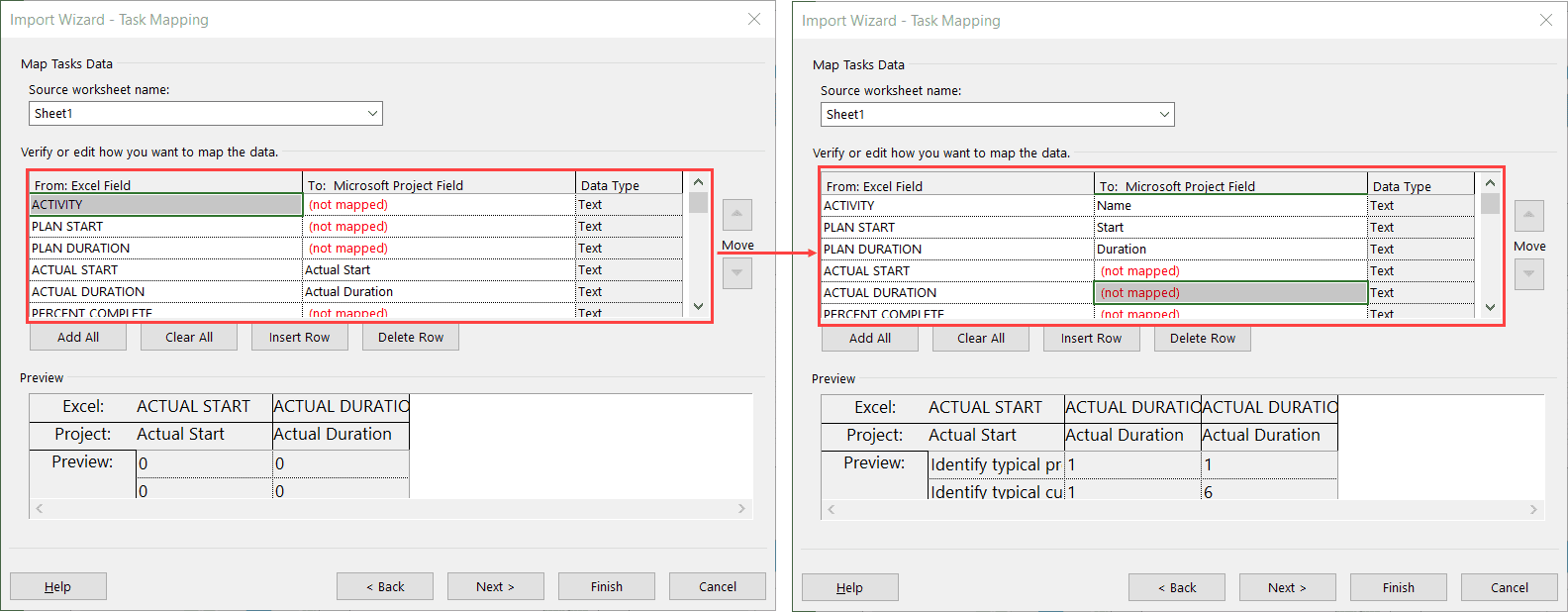
If this process is going to be repeated, then it is worth saving the fields in a new map.
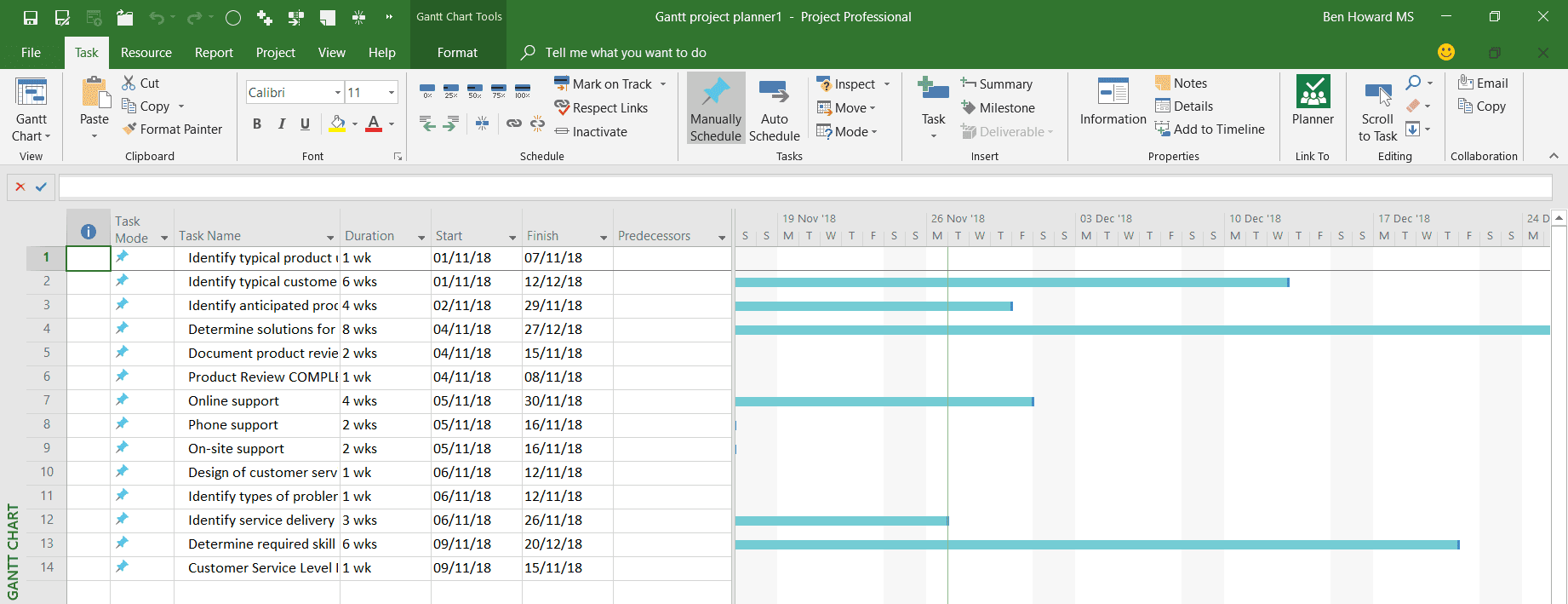
The mapped fields are imported into Project, using the default settings. Remember that the duration had already been set to weeks, and in this instance, because both the start and duration fields were mapped, Project could work out the finish date.
Finessing the Schedule
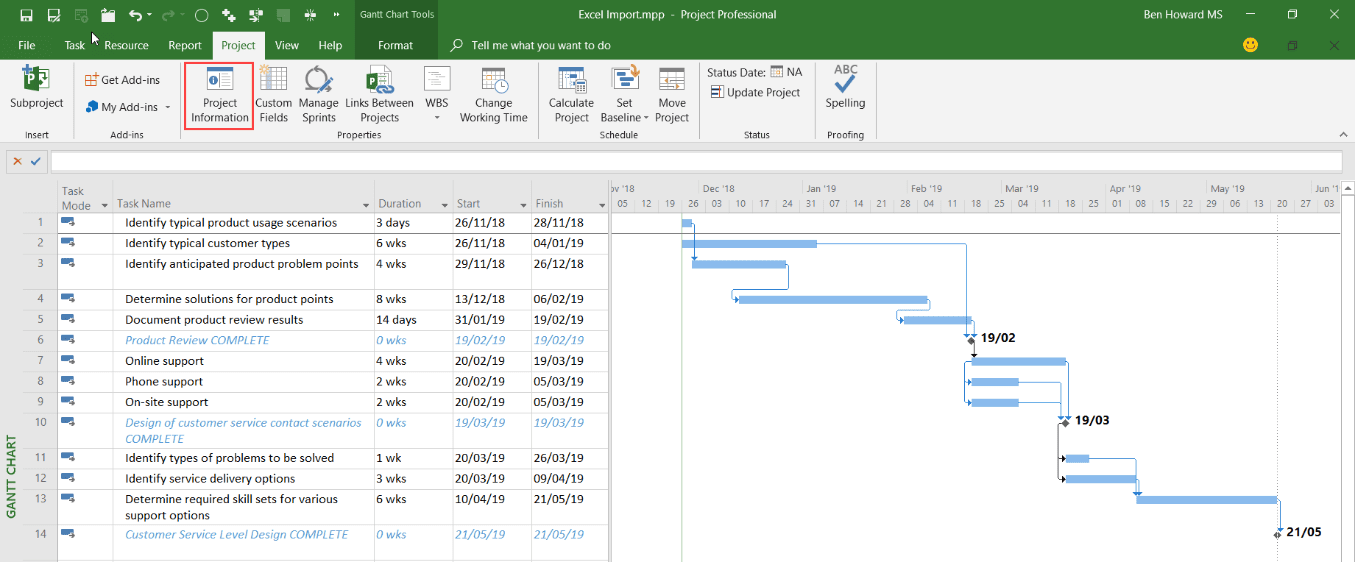
Now that the data is in Project we can begin to finesse it, change the task types, enter or modify start dates, or even better, create dependencies between the tasks (there is no way to easily convert the week number that the activity starts in the Excel file to a relative week number in the Project plan because Project works with real dates).
We’re going to finesse the schedule somewhat, changing the durations to better reflect reality, and adding in dependences and constraints where necessary.
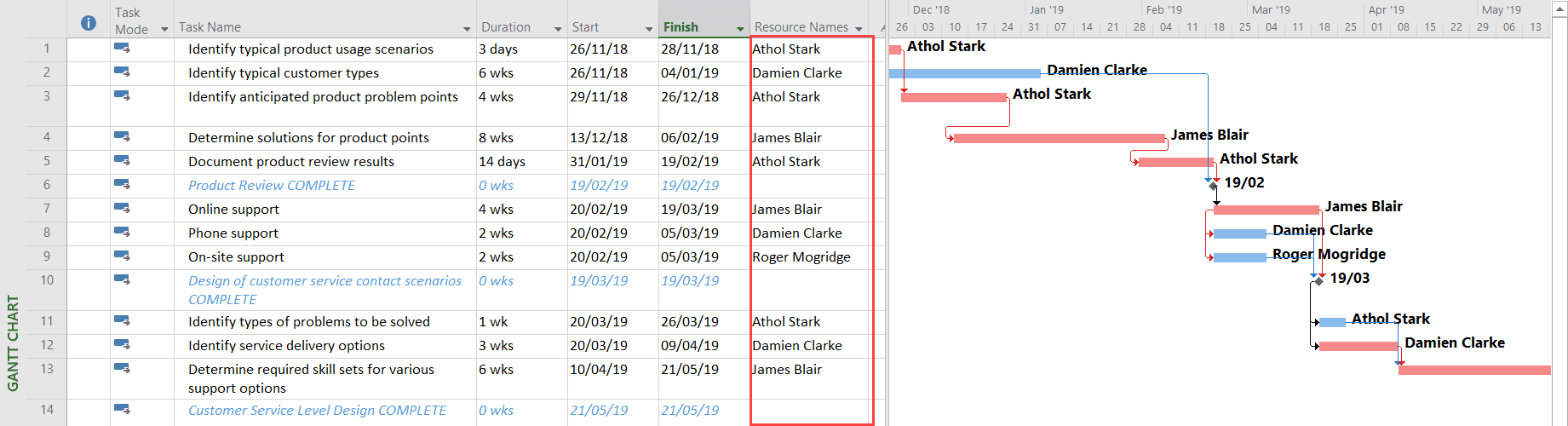
We can now easily visualize the different phases of the schedule, the milestones, and the interdependencies between tasks. Project even tells us when we’re due to finish (remember you can set the start date of the project via the Project tab, the Project Information button, or simply set the start date of the first two tasks). Already this Gantt chart is easier to read than its Excel equivalent, and it gets even better, as a quick selection of the checkbox to show critical tasks displays the critical path. That is, those tasks whose duration should not be delayed if I want to deliver the project in the shortest possible time.
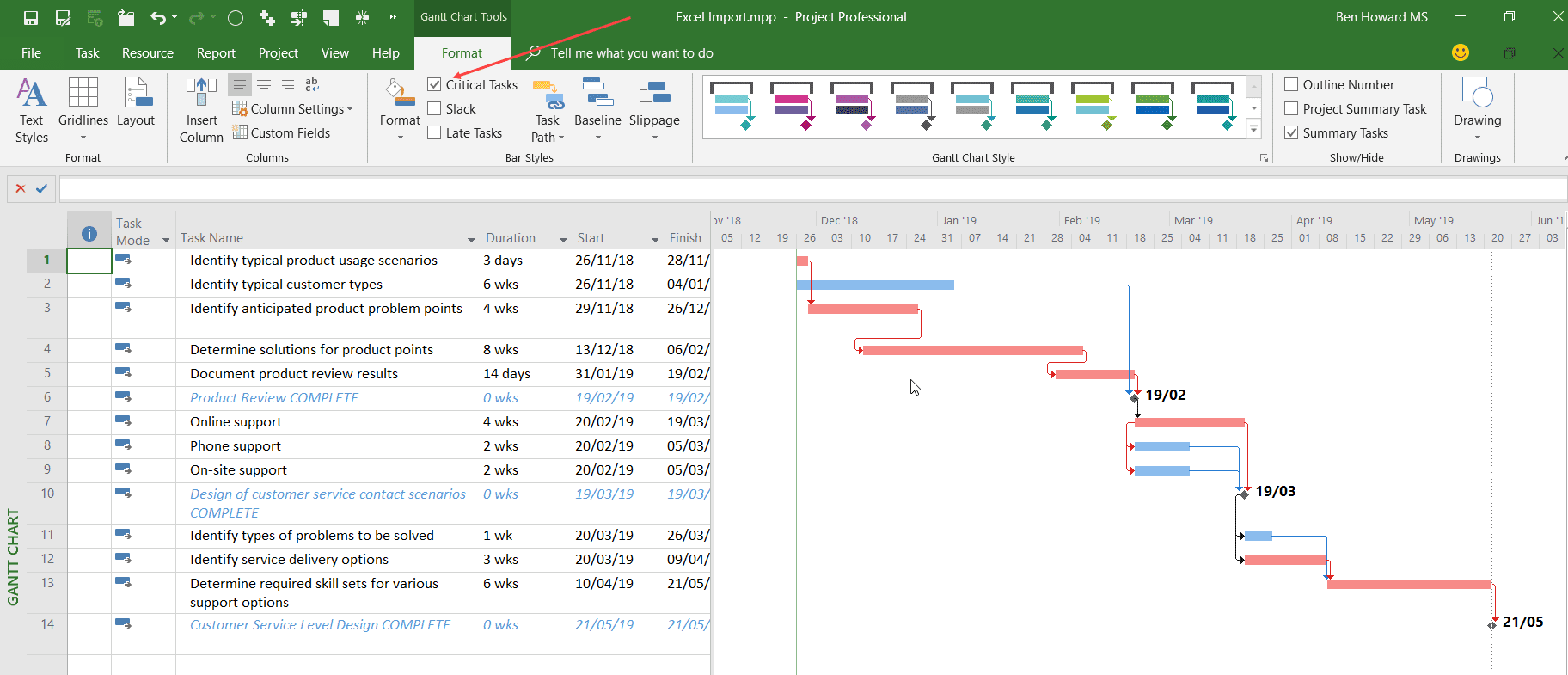
For those of us who have worked with Project for some time, this is not a revelation, but I have worked with customers who have experienced a “eureka” moment at seeing this.
We’re going to add some resources as assignments to the schedule.
Exporting Project Data to Excel
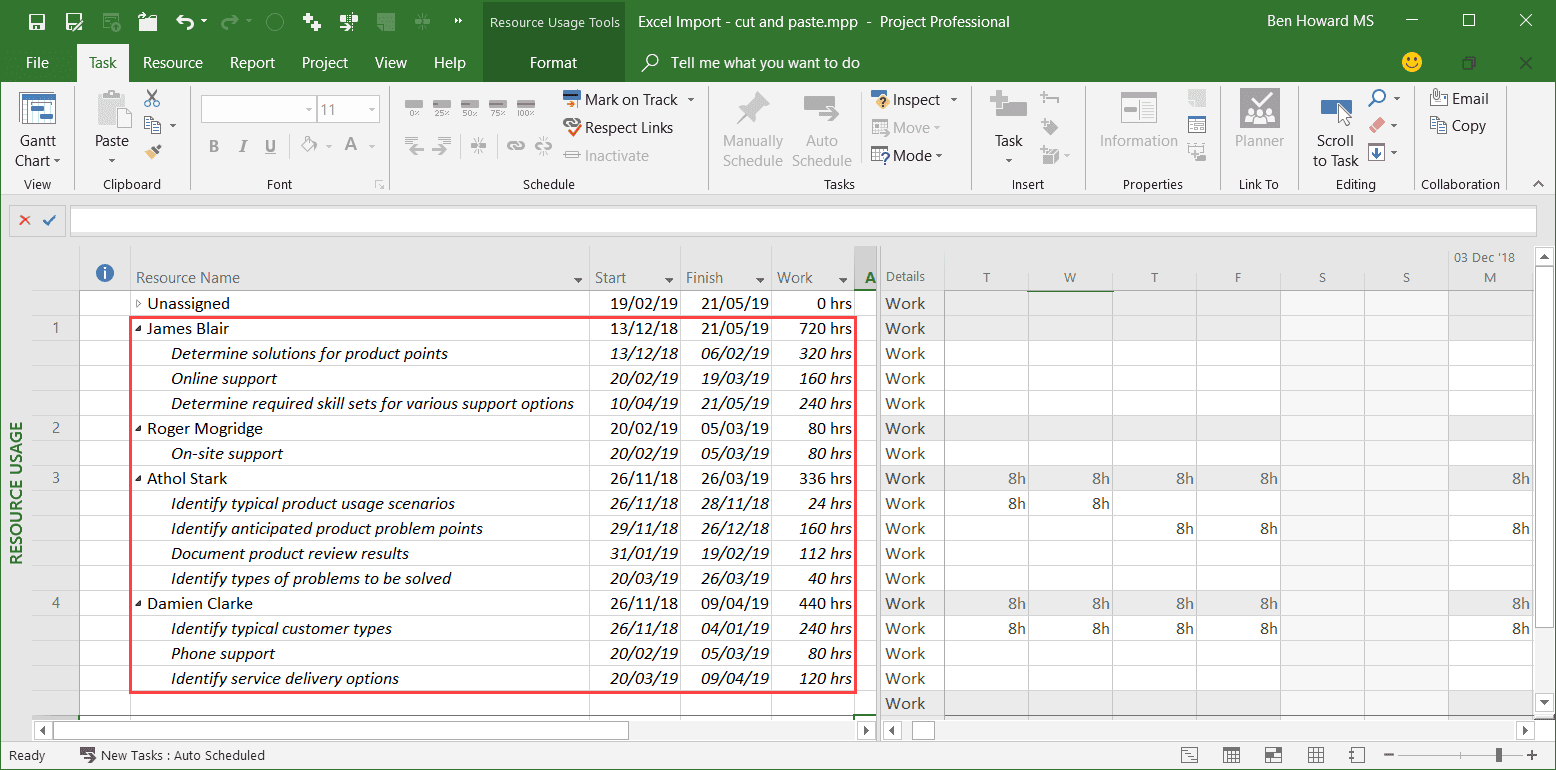
We’ve covered moving Excel data into Project, but it’s often useful to export Project data into Excel, especially from a communications and reporting perspective. In this example, we will produce a “who does what when” report, which used to be in Project, but was deprecated in the 2010 release.
Copy and Paste
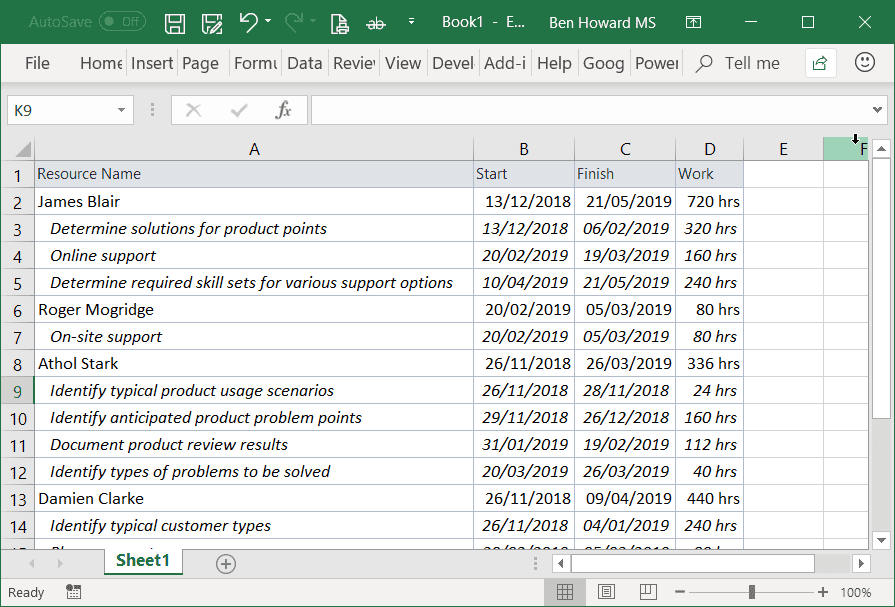
The simplest way to get at this data into Excel is to use the Resource Usage view, add in both the start and finish columns, highlight the data, and copy and paste it into Excel.
Visual Reports
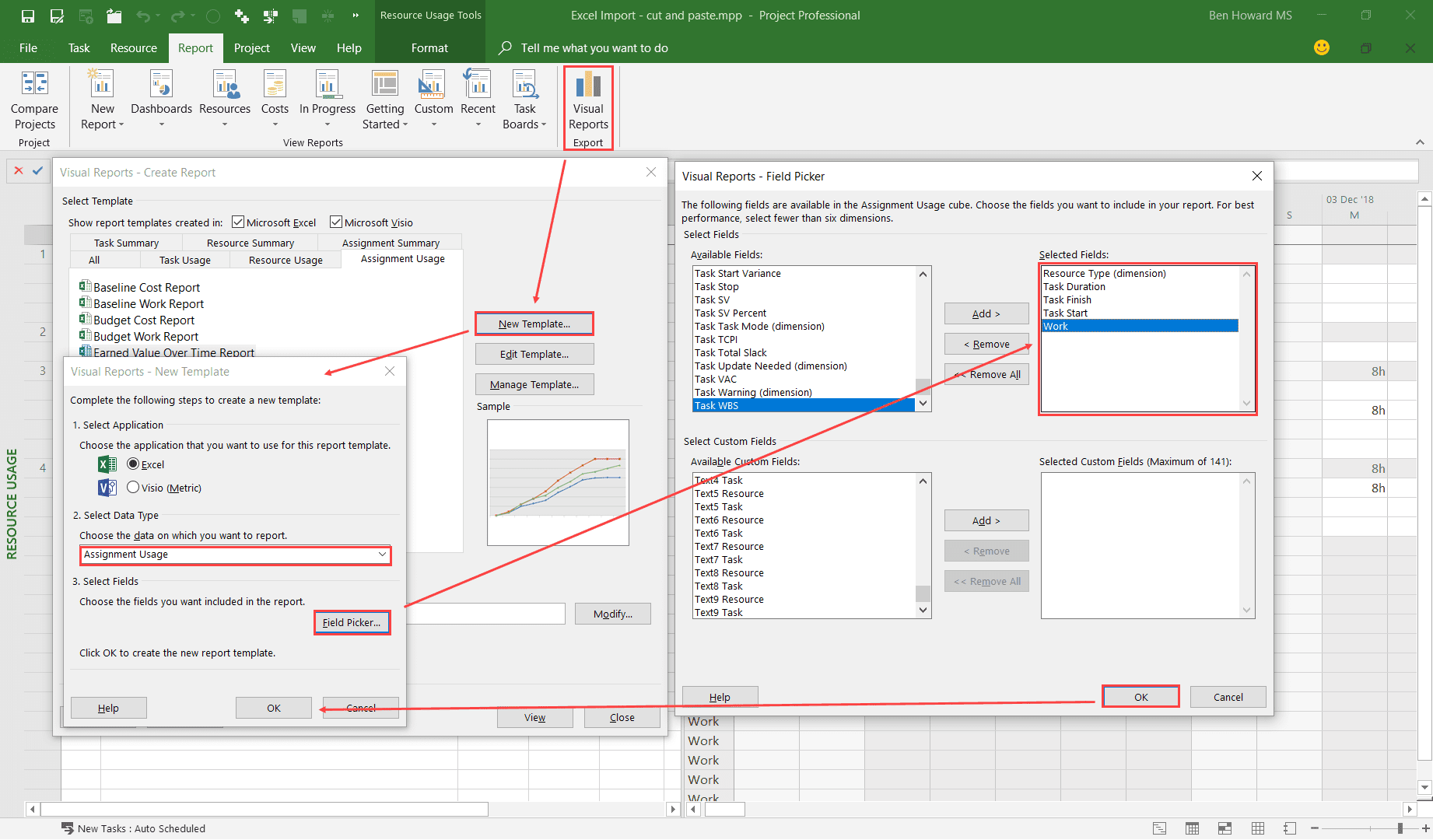
A more sophisticated and repeatable way to export data is to use the Visual Reports feature, which can export data to either Excel or Visio. There are many built in templates, but you can also build your own.
Using the New Template button, select the following fields:
- Resource Type
- Task Duration
- Task Finish
- Tasks Start
- Work
Project exports the data to Excel, and as long as you know about Pivot Tables, it’s easy to create your own reports and charts. Information on how to use Pivot Tables can be found in Excel’s help files.
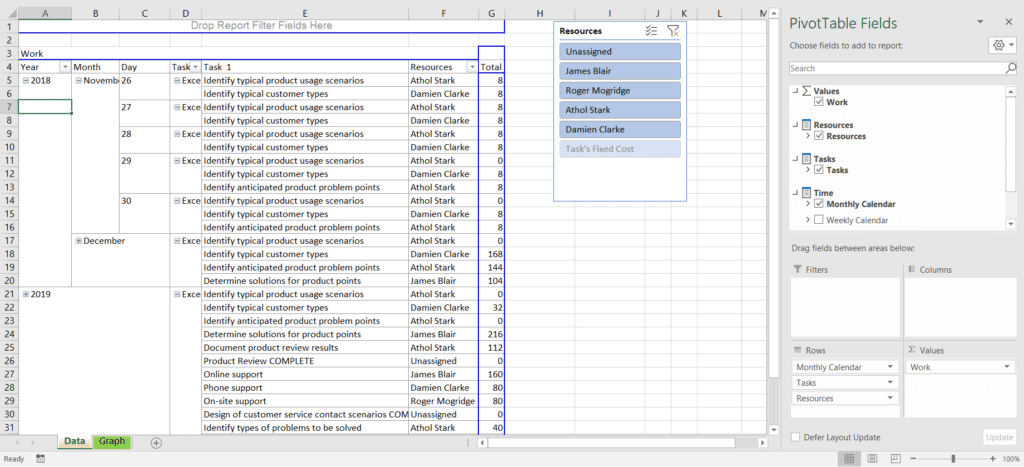
Save as Excel file
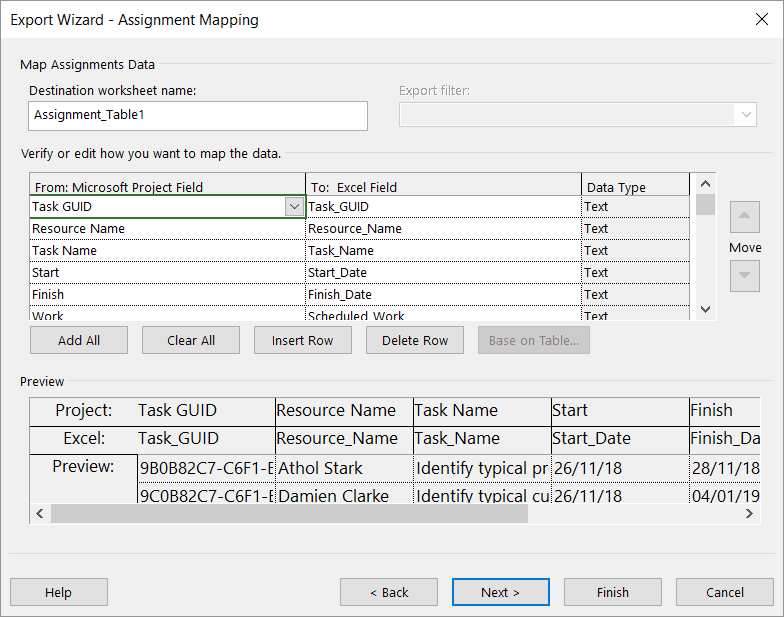
Saving as an Excel file brings up the Export wizard, which is very similar to the Import Wizard in functionality. The following options are available:

For a “who does what when report,” select Assignments during the mapping process and choose the fields to export. Note that the Task GUID is included in this report, but isn’t necessary.
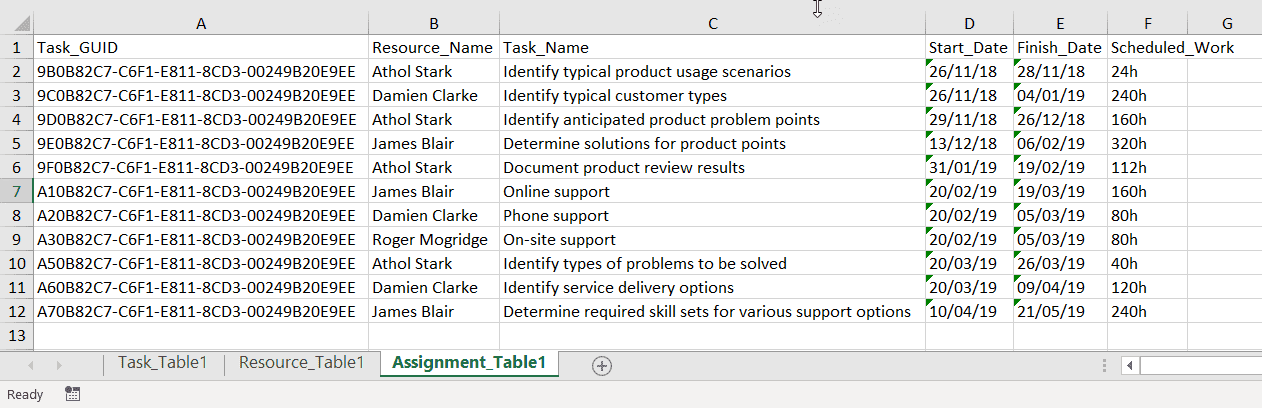
Each set of exported data (tasks, resources, and assignments) is placed in its own table in Excel, which can then be modified and handed out to resources, as required. A simple modification is to sort the data by Start Date.
Summary
In this article, I’ve discussed importing data from Excel to Project (typically done when users reach a limitation with Excel in terms of managing a Gantt Chart). Importing can be as simple as copy and paste or more sophisticatedly by using the Import Wizard.
It is also possible to take data the other way, from Project to Excel. Sometimes this can be as simple as a copy and paste, but we can also be a little more sophisticated by using Visual Reports or the Export to Excel wizard. All three methods produce great results, and you should experiment with each one and settle on using the one, which works best for you and meets your organization’s requirements.
If you want to check out the plan that I used to create the article and the other associated files they are available for download here.
Good luck!
Related Content
Microsoft Project Training
- All Microsoft Project Training Webinars
Microsoft Project Courses :
- Microsoft Project Practitioner Course
- Advanced Microsoft Project Course
Microsoft Project Tutorial: Learn how to import an Excel into Microsoft Project
If you’ve worked with external vendors for any length of time, I’m sure you’ve noticed the variety of formats vendors use for a project schedule. In some cases, it is a formal MS Project schedule. In other cases, it is a set of dates described in an email or it is developed in every non-MS Project user’s favorite tool – Excel or a spreadsheet variant.
The following is a brief tutorial on how to import an Excel spreadsheet project schedule into Microsoft Project.
For the past four years, I’ve worked for companies that outsource the majority of their IT work to external vendors using fixed-price contracts. One challenge in jointly delivering a project with an external vendor is obtaining the vendor project schedule in a format that can be integrated with Microsoft Project.
The obvious solution is to have the vendor provide its Microsoft Project schedule; the reality is some vendors are reluctant to hand over their detailed schedule because it contains cost data, notes, custom macros, and other private data. If you’ve worked with outsourcing vendors, then you’re familiar with some vendors who don’t consistently use Microsoft Project as a scheduling tool.
In my case, I typically receive an Excel file with tasks and start and finish dates. Ironically, my vendor extracts this information from his Microsoft Project schedule and provides an Excel file that I can scroll through to find key milestones and due dates. Faced with the poor usability in scanning hundreds of tasks using Excel, I developed an import map that will properly import the Excel sheet that builds the task hierarchy in Microsoft Project.
When you export data from Microsoft Project into Excel, the data file doesn’t maintain the hierarchy. Creating the hierarchy in Excel usually involves grouping and indenting in Excel or using a custom macro to build the hierarchy. When you import an Excel file into Microsoft Project, it also lacks any of the indenting (Figure 1) and summary tasks that make Microsoft Project a valuable roll-up tool.
Figure 1 – Schedule in Excel
Build the Excel to Project import map
My solution was to develop an import map that includes the key fields in the table below
| Field Name | Description |
| ID | The Task ID for the Microsoft Project task |
| Outline Level | Determines the Outline Level in a project’s hierarchy. An Outline Level of 1 is at the highest level in the hierarchy, and an Outline Level of 5 has four summary level tasks above it. |
| Name | Task Name |
| Start | Forecasted Start date |
| Finish | Forecasted Finish date |
| % Complete | Task completion percentage |
| Baseline Start | Original Baseline Start date |
| Baseline Finish | Original Baseline Finish date |
| Actual Start | Actual task Start date |
| Actual Finish | Actual task Finish date |
| Predecessors | Identifies the Task ID of a predecessor task |
| Resource Name | Assigned Resource |
To build this map in Microsoft Project:
- Open a sample Microsoft Project schedule. (It helps if you have a completed project schedule so the final export will have meaningful data.)
- Go to File | Save As.
- Select the Microsoft Excel Workbook (*.xls) as the Save as Type and click Save.
- Click Next and leave Selected Data as the option.
- Click New Map.
- Select the Tasks checkbox (Figure 2).
Figure 2 – Task Mapping
- Click the Microsoft Office Project field and select the fields in table above.
- Click the Next button.
- Click Save Map and Save It as Excel MPP Map.
- Click the Finish button.
The Excel extract will now contain the key fields needed to build the project hierarchy.
In this case, I had to build the export map for the vendor so they could simply export their Microsoft Project data into a format that I could use to import the file. Once the vendor had this map in their Microsoft Project file, the vendor could easily save an Excel file using this extract. It ensured the vendor’s confidential data was kept confidential, while the critical data that I needed to understand milestones and start and finish dates for key tasks could be imported into my Microsoft Project schedule.
Import Excel Into Microsoft Project Wizard
Once the vendor provided a file using this format, their schedule could easily be imported into Microsoft Project by following these steps:
- Start Microsoft Project with a blank project schedule.
- In Microsoft Project, go to File | Open.
- Change the Files of Type combo box to Microsoft Excel (*.xls).
- Select the extract file and click Open.
- Click the Next button.
- Select Use Existing Map.
- Select the Excel MPP map.
- Select Append the Data to the Active Project (Figure 3).
Figure 3 – Import Wizard
- Click the Next button.
- Click the Next button.
- Click the Finish button.
The end result is a properly formatted Microsoft Project file that contains the vendor’s project schedule. Once the schedules are converted, I insert them as subprojects in the master project schedule.
Before I came up with this solution, I would import the schedule as a new project; I ran into calculation issues because the % Complete field is a calculated field and didn’t consistently convert.
Applying imports to other project schedules
You can apply these same map concepts to other schedules that lack the Outline Level, but you’ll need to build the Outline Level manually. Depending on the level of granularity required, you might just want the vendor’s key tasks and milestones instead of the entire project schedule. The main benefit is that once you have the vendor and your project activities defined in one integrated view, you can easily identify late tasks and analyze the critical path.
In fixed-price outsourcing projects, you may outsource the work to another supplier and establish penalties for failing to meet milestones. From a financial viewpoint, it makes sense because a fixed-price contract puts all the risk on the vendor; however, effective project managers collaborate with all their team members (vendors, customers, and internal team members) to deliver their projects. A key to being a successful PM is tracking to an integrated project schedule so the team can collectively understand progress.
If the vendor can’t provide all their schedule data, this Excel MPP map will help integrate the data you need.
For more tutorials on how to use Microsoft Project, check out our list of Microsoft Project tutorials.
Список курсов/Материалы темы «Управление интеграцией»
Видео материала «Установка связей между MS Excel и MS Project Pro»
Ниже приведенная информация является справочным материалом. Подробнее о данном материале и его практическом применении вы можете узнать, просмотрев видео.
Содержание:
- Использование фиксированных таблиц в MS Power BI
Использование фиксированных таблиц в MS Power BI
В MS Project Pro Вы можете обновлять данные на основании справочников что храниться в файле MS Excel. Для этого необходимо:
- Создайте файл MS Excel, где будет храниться справочная информация.
- Выделите ячейку значения, которой должен быть передан в MS Project Pro.
- Открываем проект в MS Project Pro и становимся на ячейку в которую хотим передать данные.
- Нажимаем контекстное меню и выбираем пункт «Специальная вставка«.
- В открывшемся окне «Специальная вставка» устанавливаем пункт «Связать:» и выбираем пункт «Текстовые данные«.
- Нажимаем кнопку «Ок«.
При изменении данных в таблице MS Excel будут меняться связанные поля в плане-графике MS Project Pro. При установке значений полей справочника учитывайте тип поля который будет передаваться в план-график MS Project Pro.
Есть ряд особенности работы со ссылками:
- При редактировании значений в поле со связью в MS Project Pro связь будет удалена.
- При перепланировании связанных полей в плане-графике значения будут меняться. В результате значения в плане-графике и в справочнике будут отличатся.
- При открытии плана-графика со связями MS Project Pro предлагается запрос на обновление связей.
- Файл справочника в MS Excel необходимо разместить на дисках со свободным доступом пользователя плана-графика в MS Project Pro.
Вас могут заинтересовать следующие материалы
 |
Календарь проекта в MS Project Pro | |
|---|---|---|
| Установка и настройка календарей проектов и календарей системы. | ||
|
01.11.2022 |
15765 |
 |
Корпоративные календари в MS Project Online | |
|---|---|---|
| Установка и настройка календарей проектов и календарей системы | ||
|
20.05.2020 |
1748 |
 |
Дополнительные параметры сервера MS Project Online | |
|---|---|---|
| Описание особенностей настройки системы управления проектами MS Project Online | ||
|
20.05.2020 |
1294 |
Learn how to import Microsoft Excel XLS and XLSX Data File into Microsoft Project. Many folks use Microsoft Excel as a tool used for organizing project data. Microsoft Project has several features that support importing this Excel project data into a Project schedule file.
Manual entry of project data into Microsoft Project from Microsoft Excel can be cumbersome. Importing the project data directly from Microsoft Excel is a much more efficient way. And, of course, Microsoft Project has several data types that support importing Microsoft Excel spreadsheet data.
Here we look at how to import Microsoft Excel XLS and XLSX files into Microsoft Project 2013.
In Figure 1 we have our demonstration project data.
 Figure 1
Figure 1
This data is simply of list of project tasks and associated task information. The Microsoft Project import wizard defaults to importing Sheet1. All our project data is contained in Sheet1. For proper importing the Excel datasheet names, column headers, must be one word, or two words separated by the underline special character.
We want to create some custom fields, select the project tab, properties ribbon group, and custom fields, Figure 2.
 Figure 2
Figure 2
In Figure 3 we define our first data type.
 Figure 3
Figure 3
This is a unique task code that we plan to read in as text. In Figure 3 we choose the Text1 data field and select rename. We rename our Text1 data field Task_Name, Figure 3. We also add another data type in Text2 named Cost_Code. We continue and add a third data type. This data type we plan to make a list of skill trades. After renaming Text3 Trade, select lookup, Figure 4.
 Figure 4
Figure 4
Select insert to add a new value. A list of our schedule trades is displayed in Figure 5.
 Figure 5
Figure 5
Great! We have competed the definition of our text fields.
Continue in the custom field dialog and select cost from the type drop down menu, Figure 6.
 Figure 6
Figure 6
Rename Cost1 Expense, Figure 7.
 Figure 7
Figure 7
Proceed and select number from the type drop down menu, Figure 8.
 Figure 8
Figure 8
Finally, we rename Number1, Value_Factor, Figure 9.
 Figure 9
Figure 9
Now with all our data types defined we set up the schedule columns, as per Figure 10.
 Figure 10
Figure 10
We are now ready to import our project data spreadsheet.
Select File and Open, Figure 11.
 Figure 11
Figure 11
In the File system we find and open the file ‘project data.xlsx’. We could have also imported from an xls file, Figure 12.
 Figure 12
Figure 12
When we select the xlsx file type the import wizard – map dialog pops up on the screen, Figure 13.
 Figure 13
Figure 13
Toggle new map and select next. Map refers to the direct mapping between Excel data and Microsoft Project data. In the next screen select ‘append the data to the active project’ and click next, Figure 14.
 Figure 14
Figure 14
In Figure 15, we select the task information to import along with the column headers.
 Figure 15
Figure 15
Click next. Change the source work sheet name to Sheet1, Figure 16.
 Figure 16
Figure 16
In Figure 17 we see our mapping, everything looks good.
 Figure 17
Figure 17
When we finally select Finish, and the project data imports as per Figure 18.
 Figure 18
Figure 18
Summary
It is possible to import an Excel XLS or XLSX files directly into Microsoft Project 2013. Microsoft Project supports several data types including: text, text including lookup attributes, costs, and numbers. Make sure the Excel spreadsheet column headings have no spaces.
The import procedure is to open a Microsoft Project file. Set up the customized fields and then column headings. Import the project data by appending to the open project. If fields were not properly mapped, the import wizard provides the option to edit how you want to map the data. So, you can import Microsoft Excel XLS and XLSX data files into Microsoft Project.
Связь с другими программами
При
работе с планом проекта может оказаться,
что средств программы Microsoft
Project
вам недостаточно. Например, вам потребуется
произвести вычисления с данными проекта
и построить различные графики. С другой
стороны, может возникнуть
ситуация, когда у заказчика или участника
проекта отсутствует Microsoft
Project.
В
этой главе вы узнаете о связи Microsoft
Project
с другими программами. Обмениваясь
данными с программой Microsoft
Excel
[Майкрософт Эксел], вы можете выполнить
сложные расчеты с данными проекта,
создать разнообразные диаграммы, а
также включить электронную таблицу в
план проекта.
Если
ваш план проекта получился достаточно
большим, может оказаться удобней
работать с данными проекта, используя
базу данных программы Microsoft
Access
[Майкрософт Эксес]. Эту программу также
удобно использовать для пополнения
существующей базы данных информацией
из проекта и, наоборот, для включения
базы данных в план.
Импортировав
план проекта в программу Microsoft
Outlook
[Майкрософт Аутлук], можно
создать механизм напоминания сотрудникам
о необходимости выполнения
определенной работы в заданное время.
Если вы создали в Microsoft
Outlook
список
людей, его можно включить в проект как
дополнительные ресурсы.
Если
экспортировать план проекта в Web-формат
и разместить его на сайте, то с
планом сразу могут познакомиться другие
участники и заказчик, что существенно
повысит эффективность совместной работы
над проектом.
Если
вы экспортируете диаграмму из плана
проекта в изображение, то потом в
графическом редакторе будет возможность
внести изменения или просмотреть
рисунок.
Интеграция с программой Microsoft Excel
При
создании проекта может оказаться, что
у некоторых участников проекта установлена
только программа Microsoft
Excel.
В этом случае следует воспользоваться
возможностью интеграции программ
Microsoft
Project
и Microsoft
Excel.
Кроме того, Microsoft
Excel
полезно использовать для выполнения
сложных расчетов
с данными проекта, создания разнообразных
диаграмм. В этом разделе вы рассмотрите
интеграцию с программой Microsoft
Office
Excel
2003, т.е. узнаем, как
копировать электронную таблицу в план
проекта, перемещать диаграмму Ганта
в документ Microsoft
Excel,
импортировать и экспортировать план
проекта.
Сначала
скопируем ячейки электронной таблицы
в план проекта.
-
Нажмите
кнопку Пуск
(Start)
на Панели
задач (Taskbar)
операционной системы
Windows.
На экране появится основное меню. -
Выберите
команду Все
программы ♦ Microsoft
Office
♦ Microsoft
Office
Excel
2003 (All
Programs
♦ Microsoft
Office
♦ Microsoft
Office
Excel
2003) из основного
меню. На экране появится рабочее окно
программы Microsoft
Excel
(Рис.
7.1).
Рис.
7.1. Рабочее окно программы Microsoft
Excel
-
Нажмите
комбинацию клавиш Alt+F1.
чтобы закрыть Область
задач (Task
Рапе)
в правой части рабочего окна программы
Microsoft
Excel
(Рис. 7.2). -
В
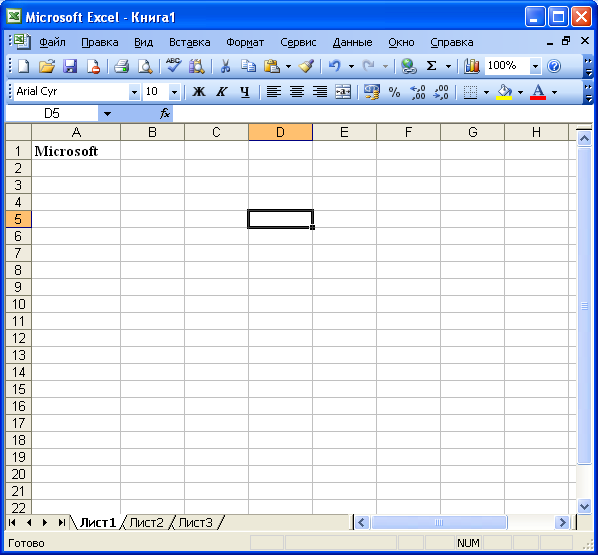
ячейку А1 введите слово Microsoft.
Рис.
7.2. Область задач (Task
Pane)
скрыта
-
В
ячейку А2 введите слово Project
(Рис. 7.3).
Рис.
7.3. Заполненные ячейки
-
Установите
указатель мыши на ячейку А1. -
Нажмите
и удерживайте левую кнопку мыши. -
Не
отпуская левую кнопку мыши, переместите
мышь к ячейке А2. -
Отпустите
левую кнопку мыши. Диапазон ячеек А1
:А2 будет выделен. -
Нажмите
кнопку копировать
на панели инструментов Стандартная
(Standard).
Выделенный
диапазон ячеек будет скопирован в буфер
обмена. -
Щелкните
мышью на кнопке с программой Microsoft
Project
на Панели
задач (Taskbar)
для перехода к данной программе. -
Нажмите
кнопку создания нового документа на
панели инструментов Стандартная
(Standard),
чтобы открыть
новый документ. -
Щелкните
мышью на первой ячейке столбца Название
задачи (Task
Name). -
Нажмите
кнопку вставить
на панели инструментов Стандартная
(Standard).
В окне программы
Microsoft
Project
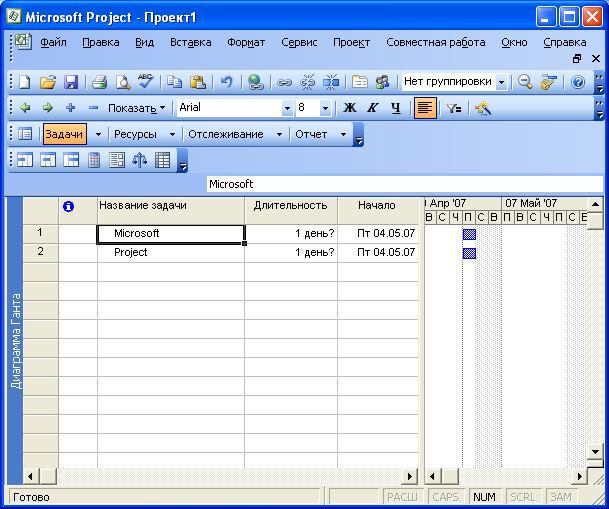
появится список задач (Рис. 7.4).
Рис.
7.4. Вставленные данные из электронной
таблицы
Иными
словами, программа Microsoft
Project
интерпретировала вставленные из
электронной
таблицы данные как список задач.
-
Выберите
команду меню Файл
♦ Закрыть (File
♦ Close).
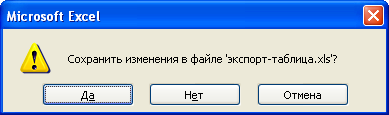
На экране появится диалог
с вопросом о сохранении документа (Рис.
7.5).
Рис.
7.5. Диалог с вопросом о сохранении
документа
-
Нажмите
кнопку Нет
(No),
чтобы закрыть диалог и не сохранять
документ.
Теперь
скопируем диаграмму Ганта в программу
Microsoft
Excel.
-
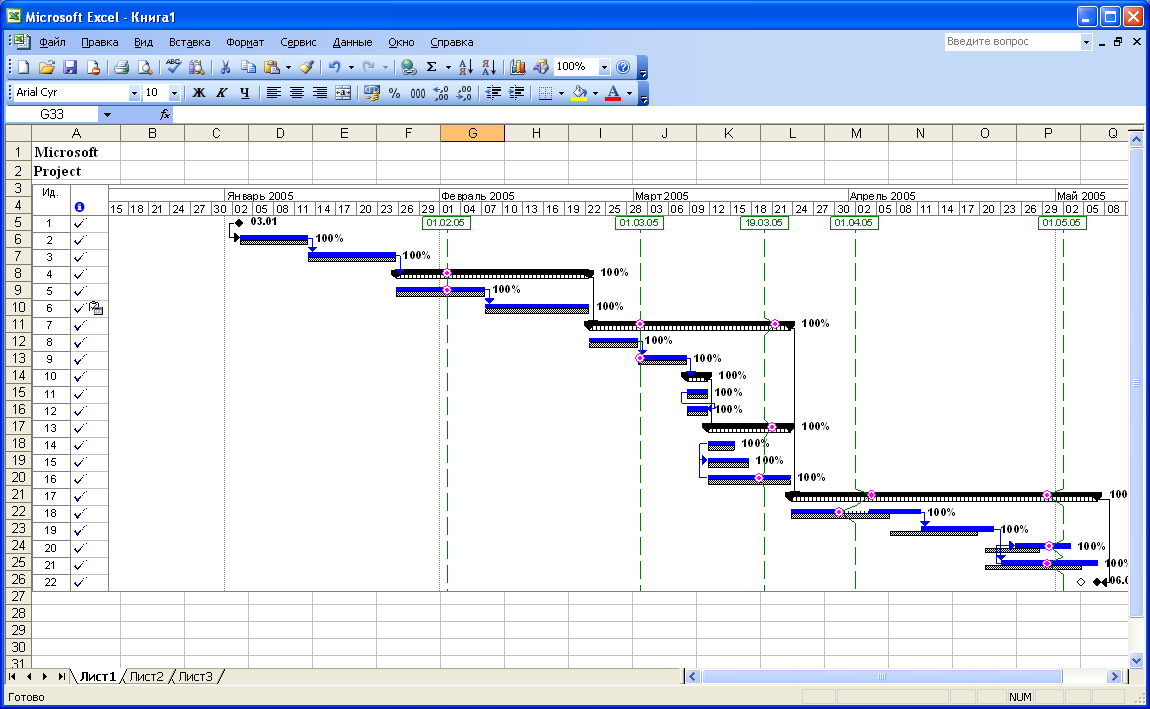
Выберите
команду меню Вид
♦ Диаграмма Ганта (View
♦ Gantt
Chart)
для перехода
к диаграмме Ганта в нашем плане проекта. -
Перетащите
мышью полоску, разделяющую список задач
и диаграмму Ганта, в крайнее левое
положение, чтобы весь экран занимала
диаграмма (Рис. 7.6).
Рис.
7.6. Диаграмма Ганта
-
Выберите
команду меню Правка
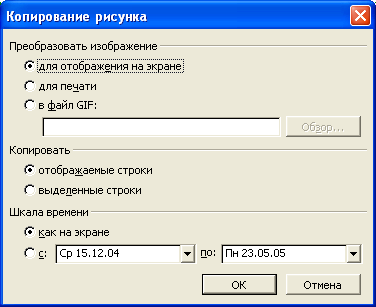
♦ Копировать рисунок (Edit
♦
Сору
Picture).
На экране появится диалог Копирование
рисунка (Copy
Picture)
(Рис.
7.7).
Рис.
7.7. Диалог Копирование
рисунка (Copy
Picture)
-
Если
в группе элементов управления
Преобразовать
изображение (Render
image)
не установлен переключатель для
отображения на экране (For
screen),
то установите его, чтобы скопировать
рисунок в буфер обмена. -
Убедитесь,
что в группе Копировать
(Сору)
установлен переключатель отображаемые
строки (Rows
on
screen)
для копирования всего содержимого
рабочего
окна программы. -
Если
в группе Шкала
времени (Timescale)
не установлен переключатель как
на
экране (As
shown
on
screen),
то установите его, чтобы при копировании
сохранить
шкалу времени неизменной. -
Нажмите
кнопку ОК, чтобы закрыть диалог
Копирование
рисунка (Сору
Picture).
Диаграмма Ганта будет скопирована в
буфер обмена. -
С
помощью мыши верните полоску, разделяющую
список задач и диаграмму Ганта,
в прежнее центральное положение. -
Щелкните
мышью на кнопке с программой Microsoft
Excel
на Панели
задач (Taskbar)
для перехода к данной программе. -
Щелкните
мышью на ячейке A3. -
Выберите
команду меню Правка
♦ Вставить (Edit
♦ Insert).
В электронную таблицу
будет вставлена диаграмма Ганта (Рис.
7.8).
Рис.
7.8.
Диаграмма
Ганта в Excel
Сейчас
импортируем план проекта из Microsoft
Excel
в Microsoft
Project.
-
Нажмите
кнопку создания нового документа на
панели инструментов Стандартная
(Standard),
чтобы открыть новый документ в Microsoft
Excel. -
Если
в рабочем окне программы Microsoft
Excel
отсутствует панель Область
задач
(Task
Pane),
то выберите команду меню Вид
♦ Панели инструментов ♦ Область
задач (View
♦ Toolbars
♦ Task
Pane).
В правой части рабочего окна программы
Microsoft
Excel
появится панель Область
задач (Task
Pane)
(Рис. 7.1). -
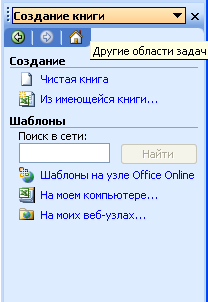
Из
открывающегося списка в верхней части
Области
задач (Task
Pane)
выберите
Создание
книги (New
Workbook).
Вид панели Область
задач (Task
Pane)
изменится (Рис. 7.9).
Рис.
7.9. Панель Создание
книги (New
Workbook)
-
В
разделе Шаблоны
(Templates)
на панели Создание
книги (New
Workbook)
щелкните
мышью на ссылке На
моем компьютере (On
my
computer),
чтобы открыть
диалог Шаблоны
(Templates). -
Выберите
вкладку Решения
(Spreadsheet
Solutions) (Рис.
7.10).
Р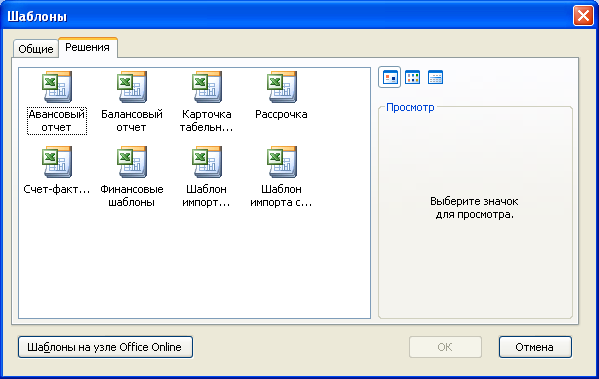
7.10. Вкладка
Решения
(Spreadsheet
Solutions) диалога
Шаблоны
(Templates)
-
Щелкните
мышью на значке с надписью Шаблон
импорта
списка
задач
Microsoft
Project (Microsoft
Project Task List Import Template). -
Нажмите
кнопку OK,
чтобы закрыть диалог Шаблоны
(Templates). -
В
окне программы Microsoft
Excel
выберите лист Таблица_задач
(TaskJTable)
(Рис. 7.11).
Р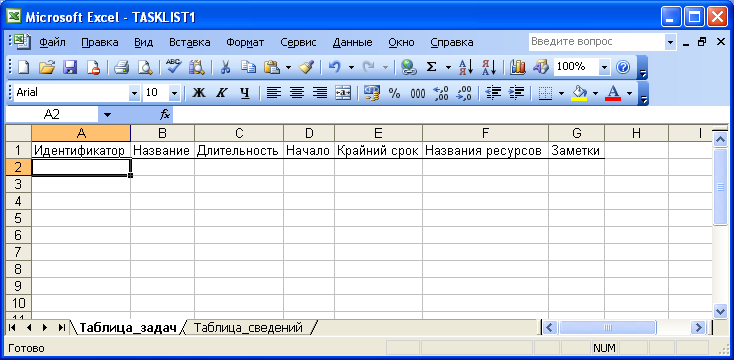
7.11. Шаблон для списка задач
Обратите
внимание, что названия столбцов шаблона
практически совпадают с названиями
полей списка задач Microsoft
Project.
-
В
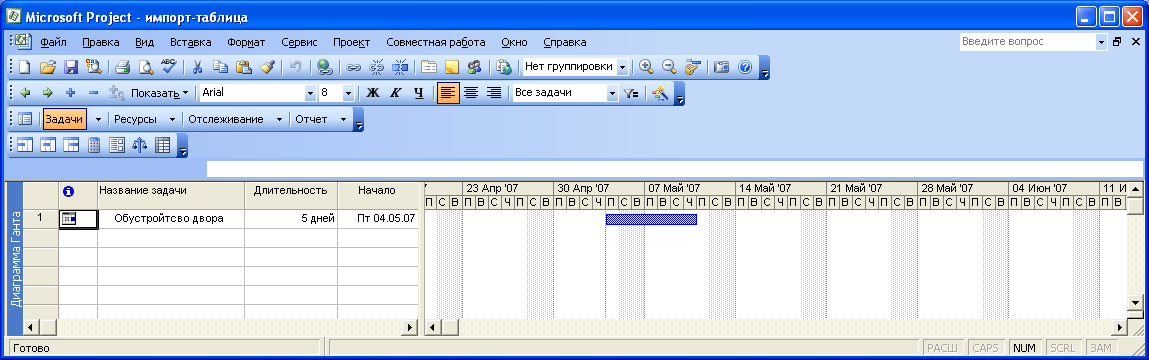
ячейку А2 введите номер задачи 1.
-
В
ячейку В2 введите название работы
Обустройство
двора. -
В
ячейку С2 введите длительность задачи
5
дней (5
days). -
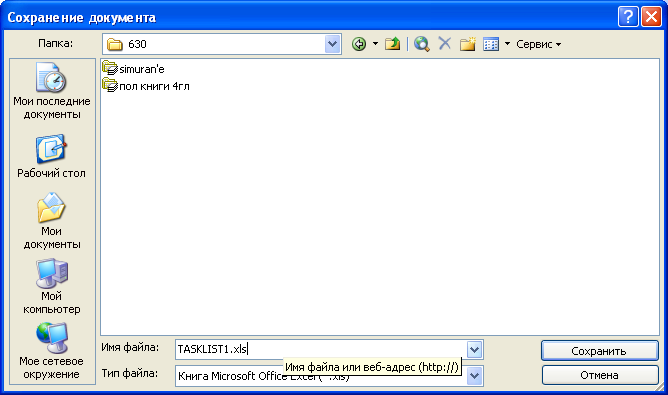
Выберите
команду меню Файл
♦ Сохранить как (File
♦ Save
As).
На экране появится
диалог Сохранение
документа (Save
As)
(Рис. 7.12).
Рис.
7.12. Диалог Сохранение
документа
(Save
As)
-
В
открывающемся списке Папка
(Save
in)
выберите диск для документа. -
В
списке файлов и каталогов выберите
папку, в которой будет сохранен документ. -
Убедитесь,
что в открывающемся списке Тип
файла (Save
as
type)
выбрана строка
Книга
Microsoft
Office
Excel
(Microsoft
Office
Excel
Workbook)
для сохранения
документа в виде электронной таблицы. -
В
поле ввода Имя
файла (File
name)
введите имя создаваемого файла
Импорт-таблица.
Расширение
.xls
будет
присвоено имени файла автоматически. -
Нажмите
кнопку Сохранить
(Save),
чтобы закрыть диалог Сохранение
документа
(Save
As).
Документ будет сохранен на диске. -
Щелкните
мышью на кнопке с программой Microsoft
Project
на Панели
задач (Taskbar)
для перехода к данной программе. -
Нажмите
кнопку Открыть на панели инструментов
Стандартная
(Standard).
На экране
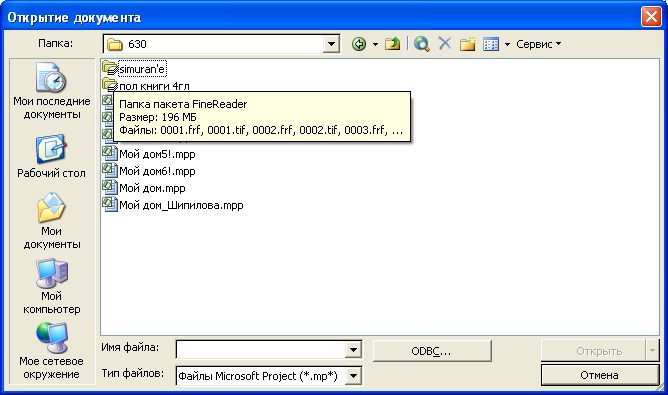
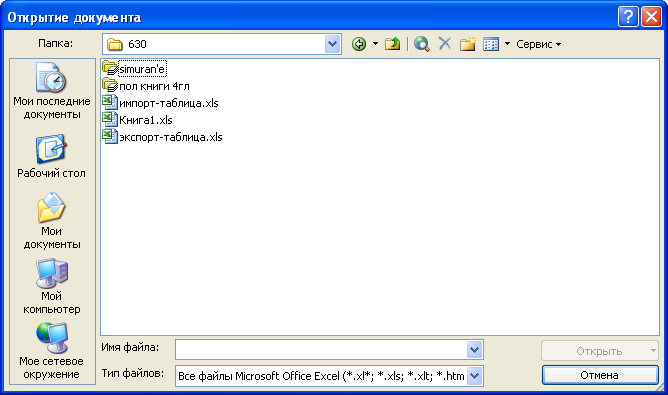
появится диалог Открытие
документа (Open)
(Рис. 7.13).
Рис.
7.13. Диалог Открытие
документа (Open)
-
В
открывающемся списке Папка
(Look
in)
выберите диск, на котором хранится
документ Импорт-таблица. -
В
списке файлов и каталогов выберите
папку с документом. -
В
открывающемся списке Тип
файла (File
of
type)
выберите строку Книги
Microsoft
Excel
(Microsoft
Excel
Workbooks)
для загрузки электронной таблицы. -
Щелкните
мышью на имени файла Импорт-таблица
в
списке каталогов. -
Нажмите
кнопку Открыть
(Open).
Диалог Открытие
документа (Open)
будет закрыт,
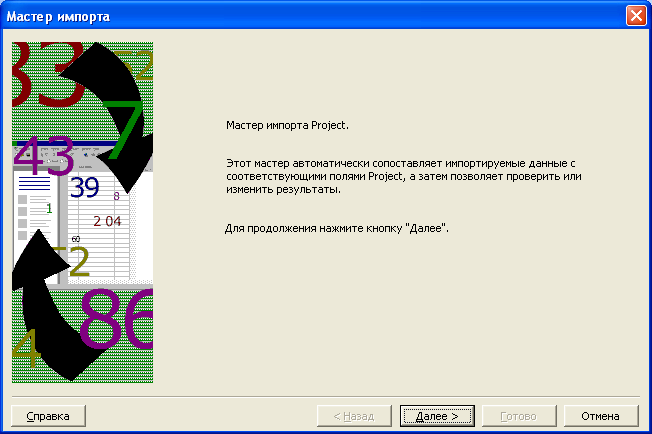
а на экране появится первый диалог
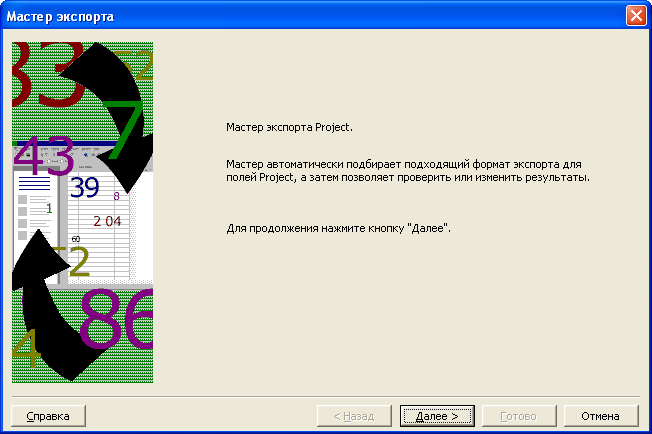
мастера импорта (Рис. 7.14).
Рис.
7.14. Первый диалог мастера импорта
-
Нажмите
кнопку Далее
(Next).
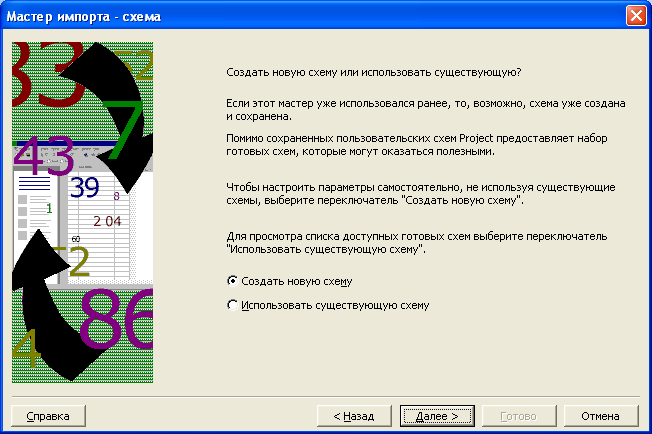
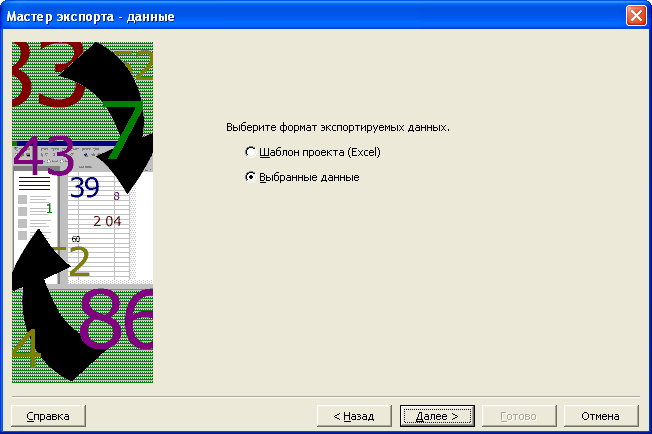
На экране появится второй диалог мастера
импорта
(Рис. 7.15). В английской версии программы
этому диалогу предшествует диалог
выбора формата данных.
Рис.
7.15. Второй диалог мастера импорта
-
Установите
переключатель Создать
новую схему (New
map)
для создания новой
схемы импорта. -
Нажмите
кнопку Далее
(Next).
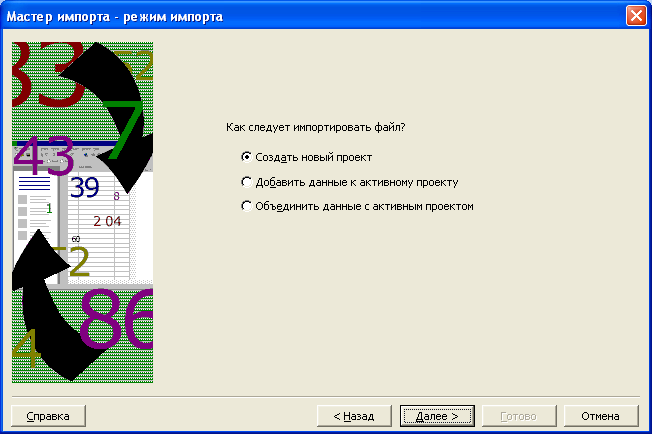
На экране появится третий диалог мастера
импорта
(Рис. 7.16).
Рис.
7.16. Третий диалог мастера импорта
-
Если
не установлен переключатель Создать
новый проект (As
a
new
project),
то установите его, чтобы при импорте
документа был создан новый проект. -
Нажмите
кнопку Далее
(Next).
На экране появится четвертый диалог
мастера импорта (Рис. 7.17).
Рис.
7.17. Четвертый диалог мастера импорта
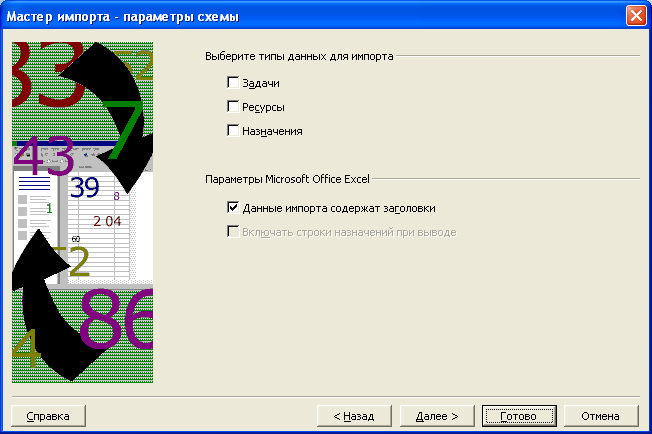
-
В
группе элементов управления Выберите
тип данных для импорта (Select
the
types
of
data
you
want
to
import)
установите флажок Задачи
(Tasks)
для импорта
задач. -
Нажмите
кнопку Далее
(Next).
На экране появится пятый диалог мастера
импорта (Рис. 7.18).
Рис.
7.18. Пятый диалог мастера импорта
В
столбцах Из:
поле Excel
(From:
Excel
Fields)
и В:
поле Microsoft
Project
(To:
Microsoft
Office
Project
Field)
центральной таблицы диалога отображаются
названия
полей программ Microsoft
Excel
и Microsoft
Project,
которые будут соответствовать
друг другу при импорте. Эти поля можно
изменить, но предлагаемый
по умолчанию вариант является приемлемым.
-
Нажмите
кнопку Далее
(Next).
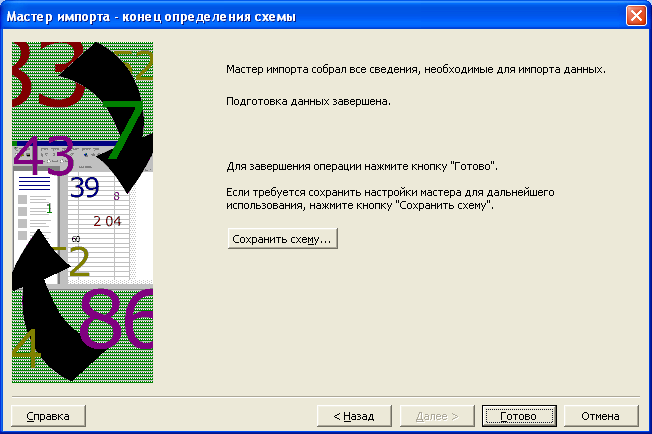
На экране появится последний диалог
мастера импорта (Рис. 7.19).
Рис.
7.19. Последний диалог мастера импорта
-
Нажмите
кнопку Готово
(Finish),
чтобы завершить работу мастера импорта.
В
окне программы Microsoft
Project
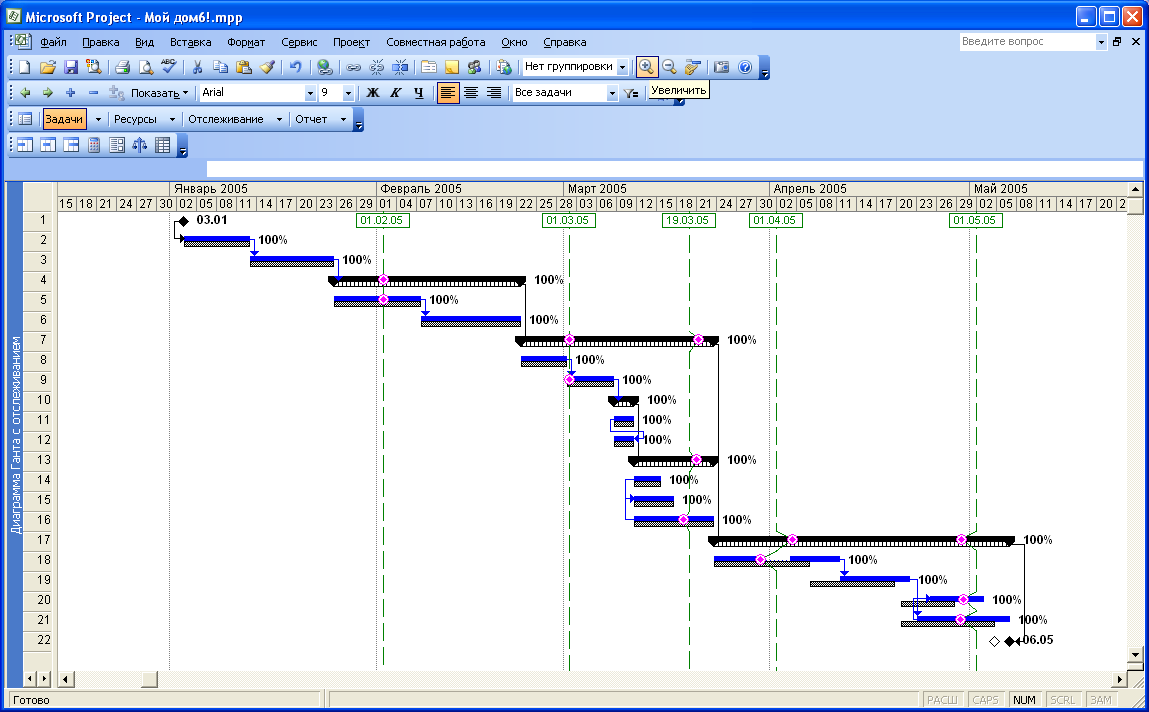
появится импортированный план проекта
(Рис. 7.20).
Рис.
7.20. Импортированный план проекта
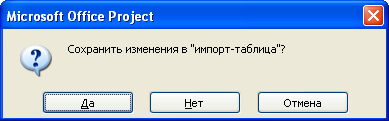
-
Выберите
команду меню Файл
♦ Закрыть (File
♦ Close).
На экране появится диалог с предложением
сохранить документ (Рис. 7.21).
Рис.
7.21. Диалог с предложением сохранить
документ
-
Нажмите
кнопку Нет
(No),
чтобы отказаться от сохранения
импортированного документа на диске.
Диалог закроется, а в окне программы
снова появится план
проекта строительства дома.
Давайте
экспортируем план проекта из программы
Microsoft
Project
в Microsoft
Excel.
-
В
Microsoft
Project
выберите команду меню Файл
♦ Сохранить как (File
♦Save
As).
На экране появится диалог Сохранение
документа (Save
As)
(Рис.
7.22).
Рис.
7.22.
Диалог
Сохранение
документа (Save
As)
-
В
открывающемся списке Папка
(Save
in)
выберите диск для документа. -
В
списке файлов и каталогов выберите
папку, в которой будет сохранен документ. -
В
открывающемся списке Тип
файла (Save
as
type)
выберите строку Книга
Microsoft
Excel
(Microsoft
Excel
Workbook)
для экспорта документа в электронную
таблицу. -
В
поле ввода Имя
файла (File
name)
введите имя создаваемого файла
Экспорт-
таблица.
Расширение
.xls
будет
присвоено имени файла автоматически. -
Нажмите
кнопку Сохранить
(Save),
чтобы закрыть диалог Сохранение
документа
(Save
As).
На экране появится первый диалог мастера
экспорта (Рис. 7.23).
Рис.
7.23.Первый диалог мастера экспорта
-
Нажмите
кнопку Далее
(Next).
На экране появится второй диалог мастера
экспорта
(Рис. 7.24).
Рис.
7.24. Второй диалог мастера экспорта
-
Установите
переключатель Шаблон
проекта (Excel)
(Project
Excel
Template),
чтобы
использовать шаблон проекта программы
Microsoft
Excel
при экспорте. -
Нажмите
кнопку Готово
(Finish)
для завершения работы мастера экспорта. -
Щелкните
мышью на кнопке с программой Microsoft
Excel
на Панели
задач (Taskbar)
для перехода к данной программе. -
Нажмите
кнопку Открыть
на панели инструментов Стандартная
(Standard).
На
экране появится диалог Открытие
документа (Open)
(Рис. 7.25).
Рис.
7.25. Диалог Открытие
документа (Open)
-
В
открывающемся списке Папка
(Look
in)
выберите диск, на котором хранится
документ Экпорт-таблица. -
В
списке файлов и каталогов выберите
папку с документом. -
Щелкните
мышью на имени файла Экпорт-таблица
в
списке файлов и каталогов. -
Нажмите
кнопку Открыть
(Open).
Диалог Открытие
документа (Open)
будет закрыт,
а в окне программы Microsoft
Excel
на листе Таблица_задач
(Task_Table)
появится экспортированный из Microsoft
Project
список задач плана
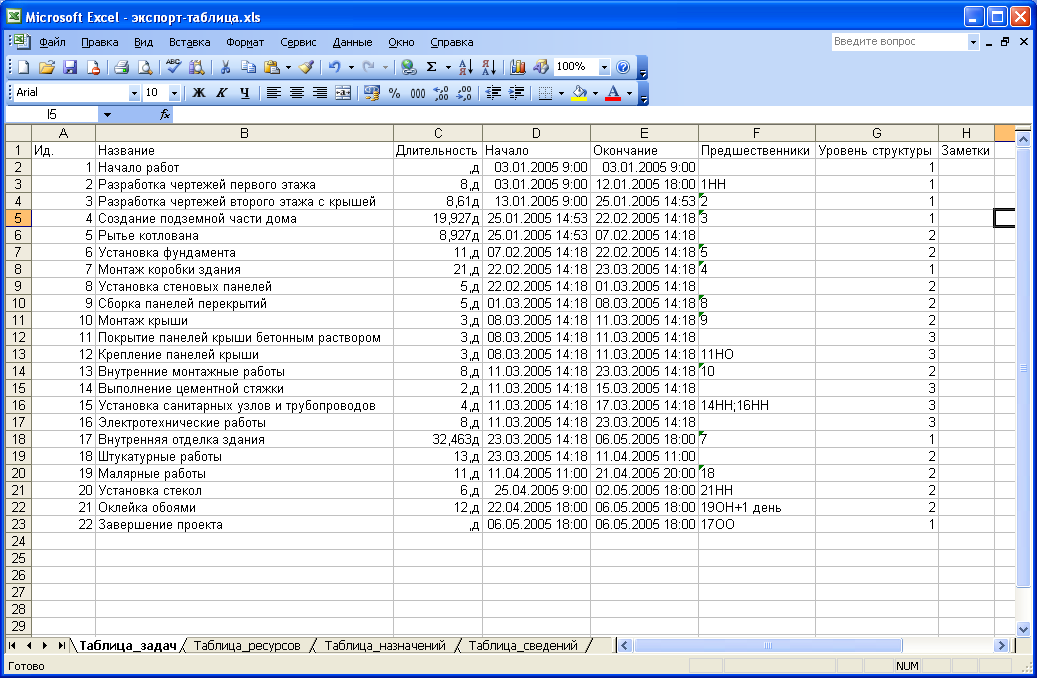
проекта (Рис. 7.26).
Обратите
внимание, что формат представления
экспортированного плана проекта похож
на исходный вариант плана в Microsoft
Project.
Рис.
7.26. Экспортированный в Microsoft
Excel
список задач
-
Щелкните
мышью на ярлыке листа Таблица_ресурсов
(Resource_Table).
В
окне программы появится экспортированный
из Microsoft
Project
список ресурсов
плана проекта (Рис. 7.27).
Рис.
7.27. Экспортированный в Microsoft
Excel
список ресурсов
-
В
Microsoft
Excel
выберите команду меню Файл
♦ Выход (File
♦ Exit).
На экране
появится диалог с предложением сохранить
документ (Рис. 7.28).
Рис.
7.28. Диалог с предложением сохранить
документ
-
Нажмите
кнопку Нет
(No),
чтобы отказаться от сохранения
экспортированного
документа на диске. Диалог закроется,
и работа программы Microsoft
Excel
будет завершена.
Следует
отметить, что вы можете экспортировать
в Microsoft
Excel
часть
созданного плана, а также использовать
импортированные из Excel
данные для добавления в существующий
план.
Соседние файлы в папке лабы Project
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #

Almost everyone, at some point in time, have managed or attempted to manage a project using Microsoft Excel. Since its release in 1987, this spreadsheet program is being used by millions of users today around the world for various purposes. It is an excellent software for spreadsheet creation, calculation, and data visualization.
Some of the reasons why people use Excel for project management is because Office is a popular application and is widely used by companies, institutions, and many other organizations. Therefore, people are familiar with it. And since it is flexible, managers try to make it work for project management, at the same time trying to save on spending for additional software.
Disadvantages of using Excel
Here are some of the disadvantages of using Excel as a project management tool:
1. Excel is not designed for project collaboration.
Excel may be flexible enough to allow a single user to manage a simple project, but most business cases are far from simple and solitary. The projects that companies initiate, plan, execute and deliver usually involve teams of multiple members, sometimes even involve multiple teams across the enterprise. Excel simply does not have the tools or features to automatically handle the coordination and updating of the status of different tasks being performed by multiple people.
2. Excel is limited as a data repository
As teams start to work on projects one after the other, and sometimes more than one simultaneously, the amount of project data can grow very fast. Since Excel as a standalone program can only hold certain types of data and information, teams will have to use other applications or solutions to manage their other project documentation. It can be difficult and confusing to find and update these documents separate from the other project information inside the spreadsheet.
3. Excel lacks the needed transparency in project management
Most of the time, the project manager will be in charge to update the Excel project spreadsheet regarding the completion of tasks, the progress of the project, the actual hours spent by each team member, and other important information. This can be time-consuming for the project manager. It can also be stressful for the team members who are constantly being asked for updates. And this process is prone to error. Furthermore, by the time the project manager consolidates the data, it is probably outdated and does not reflect the true status of the project.
4. Excel is not an ideal project reporting tool
Although Excel has data visualization tools, not everyone in the team would know how to use it. If there is a capable person, the rest may have to rely on him or her, and this can be burdensome for just one person. When senior management needs a presentation of the project, this would require extra effort to create additional views. And different persons need different views to analyze the project, which will require additional tabs in the spreadsheet until it is stretched to its limits.
5. Excel lacks essential project management capabilities
Creating a project schedule in Excel can be a lot of work simply because you will have to enter every bit of data. If you need to update a schedule, you will have to manually change everything, too. Furthermore, a Gantt chart is not automatically created in Excel, but Gantt charts are essential for project planning and scheduling. Another important feature is creating dependencies. This will have to be done manually to make sure tasks are done in the right sequence and order.
The Microsoft Project Solution
All these disadvantages in using Excel as a project management tool can be disregarded by switching to Microsoft Project. As a cloud-based solution, project team members can update the status of their tasks, share documents, and communicate with one another just using their web browser or mobile app.
Team members can easily submit timesheets, and project managers do not have to spend extra time asking for updates, collecting data, and updating documents for reporting purposes. The cloud-based solution includes the platform to capture and update in real-time information for payroll, billing, invoicing, and other purposes.
Microsoft Project includes built-in tools to plan projects, such as Gantt charts and other customizable templates. This helps in starting the project quickly instead of building from scratch. Furthermore, it has the reporting tools that can easily show the health of the project without having to ask a specialist to create the needed views. And all these information are visible for all members with the right access and privilege.
Benefits of using Microsoft Project
Like many other cloud-based project management software, Project Online is a more suitable application than Excel for managing projects. Aside from having a collaboration-ready tool, Project Online has features designed to support project management best practices that help ensure project success:
- Portfolio Management – provides a portfolio view of projects
- Project Management – manage projects from waterfall to agile
- Resource Management – provides advanced resource planning tools
- Roadmapping – build ready-to-present roadmaps with high-level view of projects and programs
- Project Collaboration – collaborate with integrated tools such as Planner, Teams, Skype, SharePoint, and others
- Strong Reporting – track and report on project performance with out-of-the-box reports and Power BI solutions, and
- 24/7 Accessibility – work from anywhere using a web browser, desktop, and mobile devices.
Transitioning from Excel to Microsoft Project requires an investment in time, money, and resources. However, it is a good investment that can make a strong impact in the long run. Project information will be more transparent, processes can be more efficient, and people will be more effective with their time. All these productivities can mean more successful projects and also a happier project team.
Trending Project Management Software
If you’re interested in learning more about top-rated project management software, project-management.com actively recommends the following:
1
Prommpt

Visit website
Prommpt is a project management platform which at its core enables true collaboration between all project members and stake holders, whether in-house or external. Available as Web-App and iPad App Prommpt.com suits any project environment.
Learn more about Prommpt

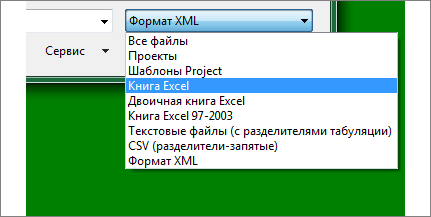
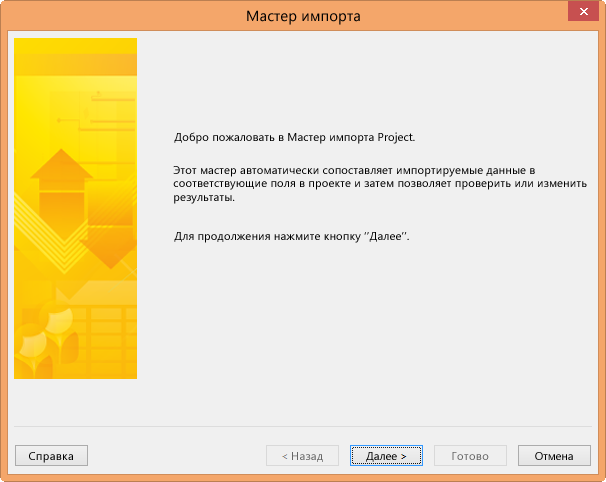







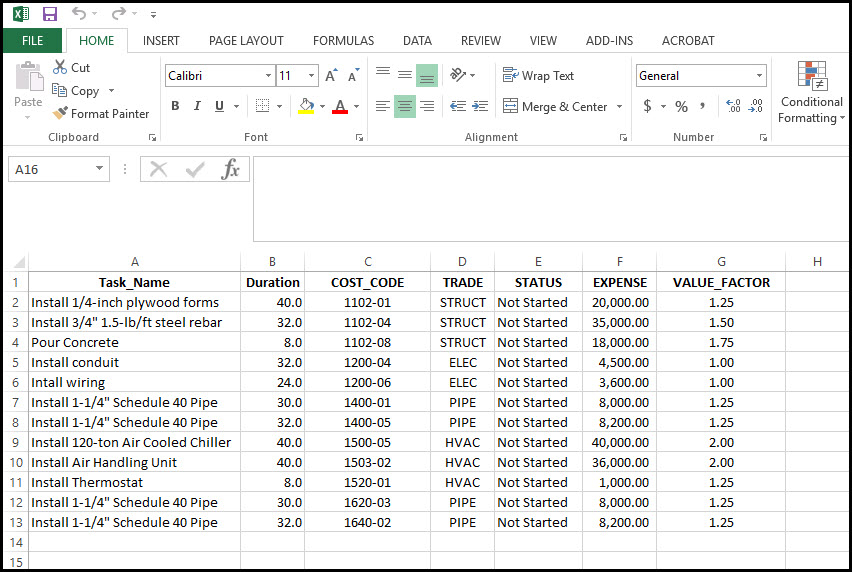 Figure 1
Figure 1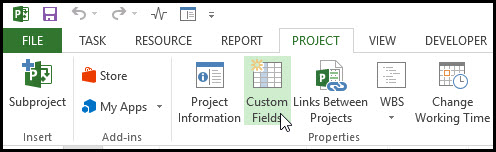 Figure 2
Figure 2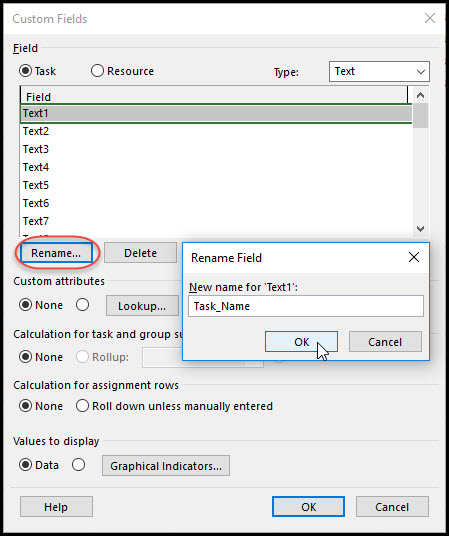 Figure 3
Figure 3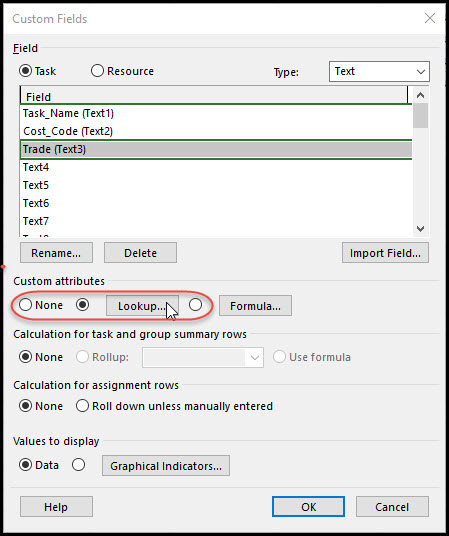 Figure 4
Figure 4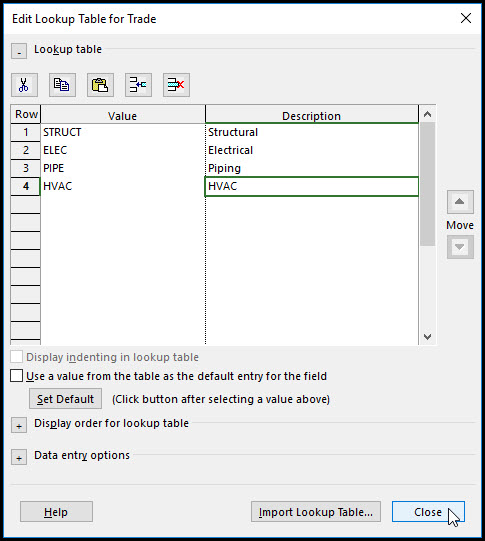 Figure 5
Figure 5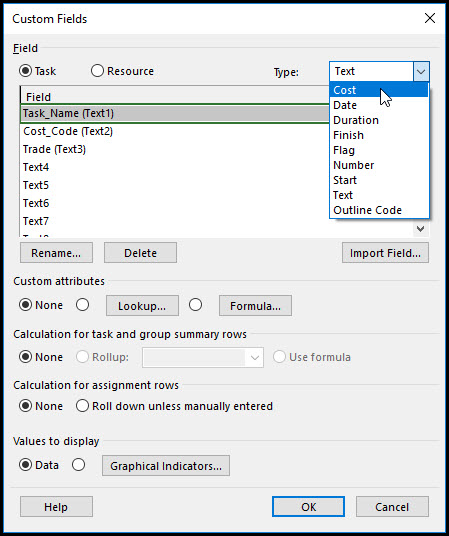 Figure 6
Figure 6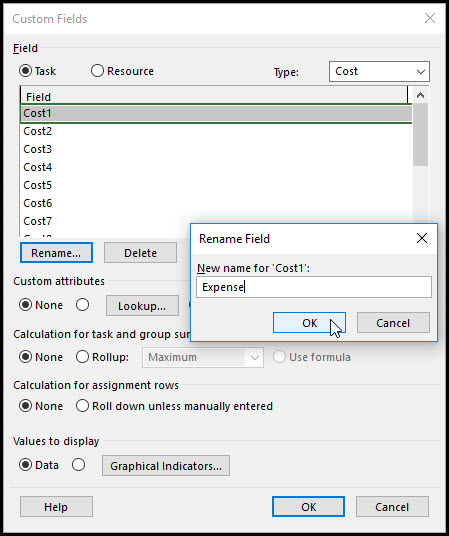 Figure 7
Figure 7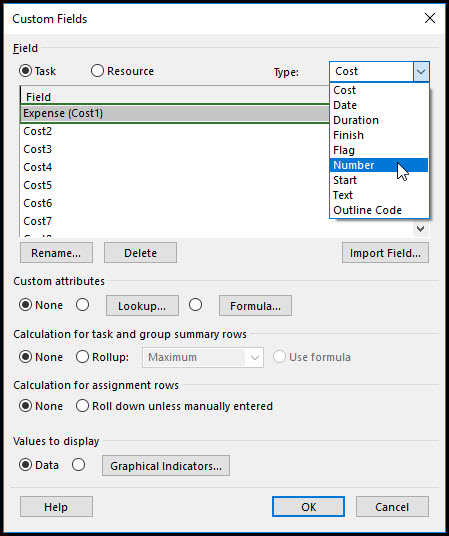 Figure 8
Figure 8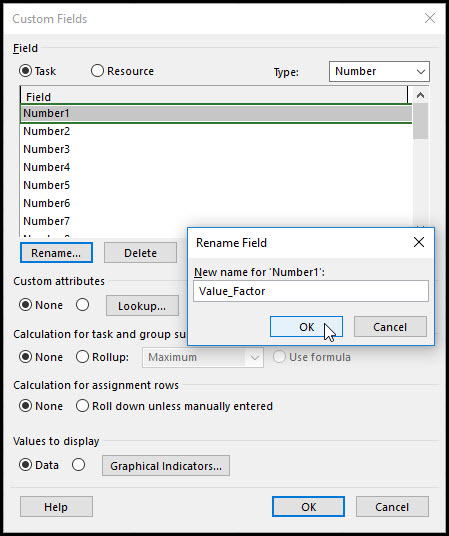 Figure 9
Figure 9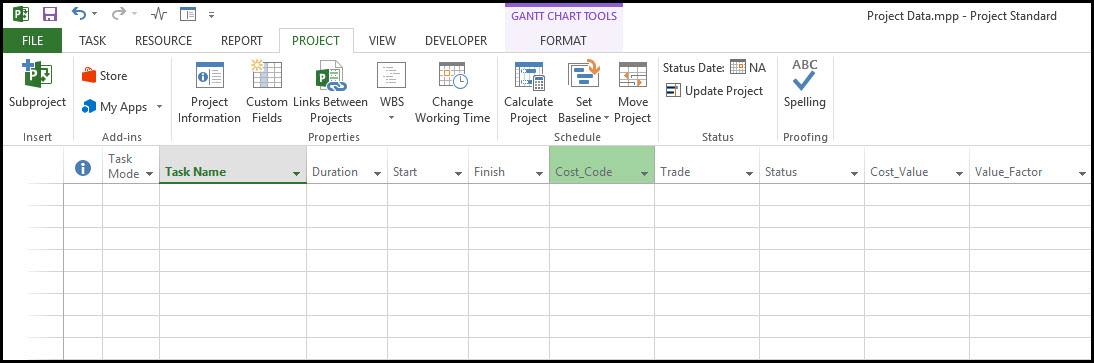 Figure 10
Figure 10 Figure 11
Figure 11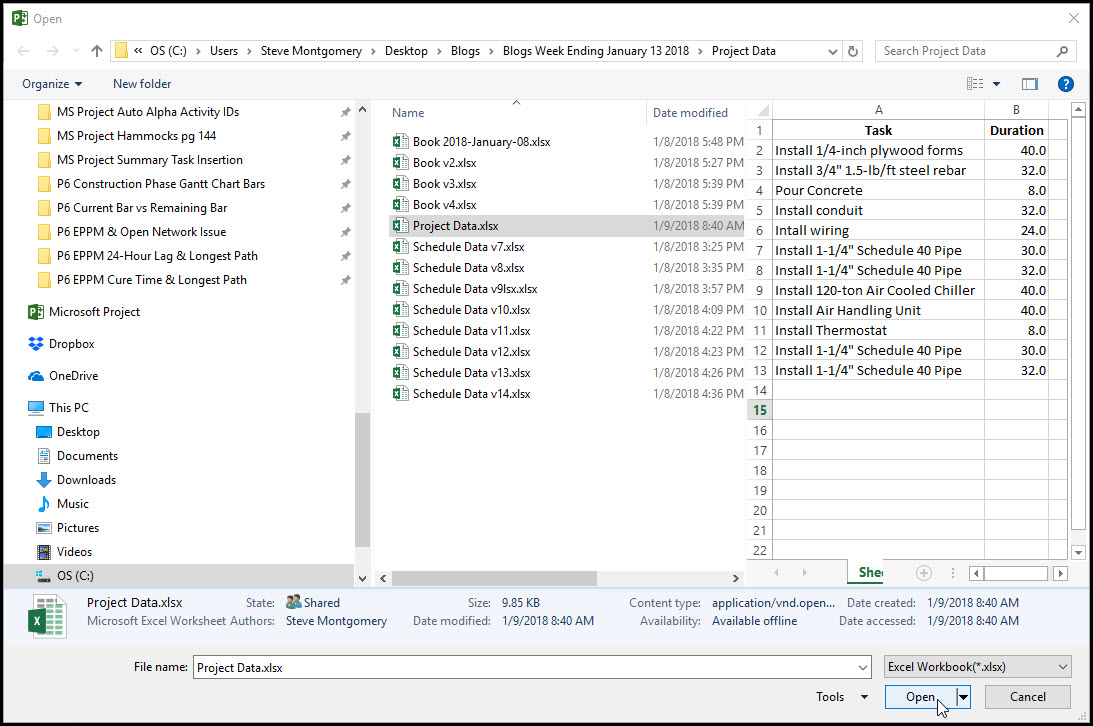 Figure 12
Figure 12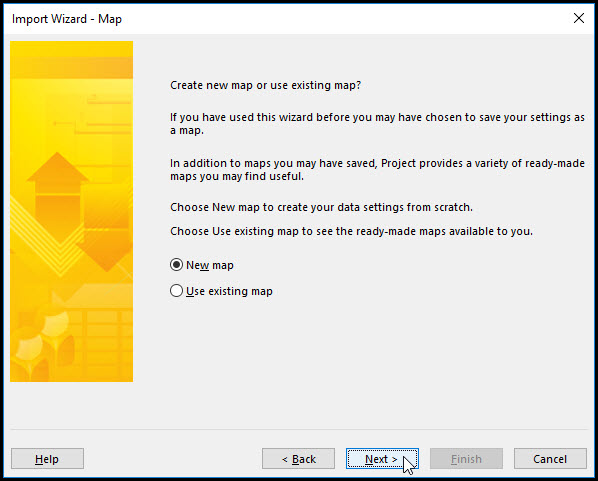 Figure 13
Figure 13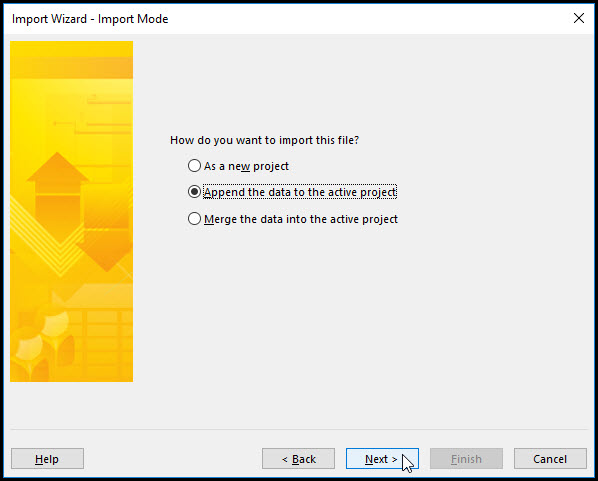 Figure 14
Figure 14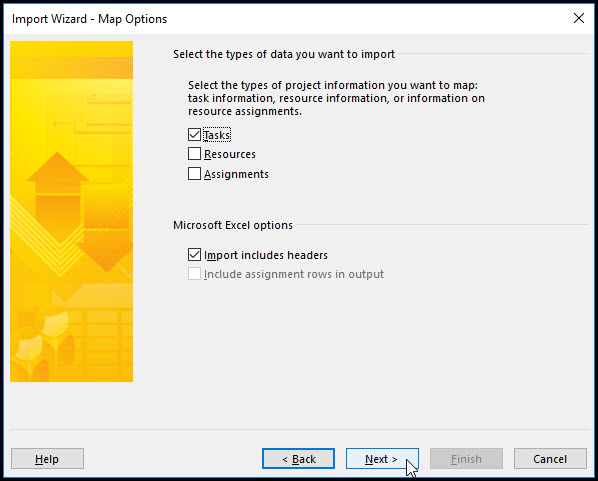 Figure 15
Figure 15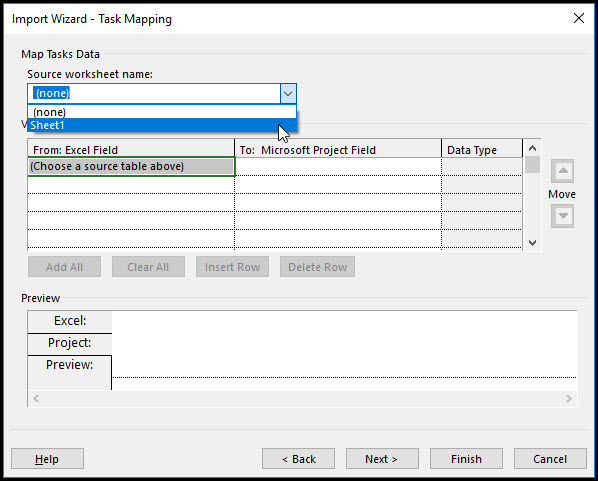 Figure 16
Figure 16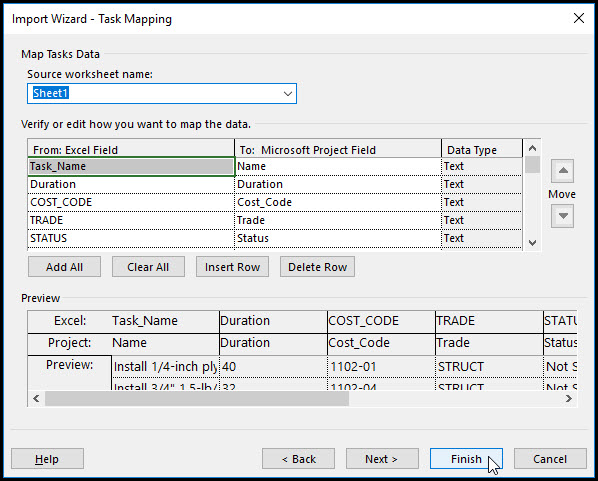 Figure 17
Figure 17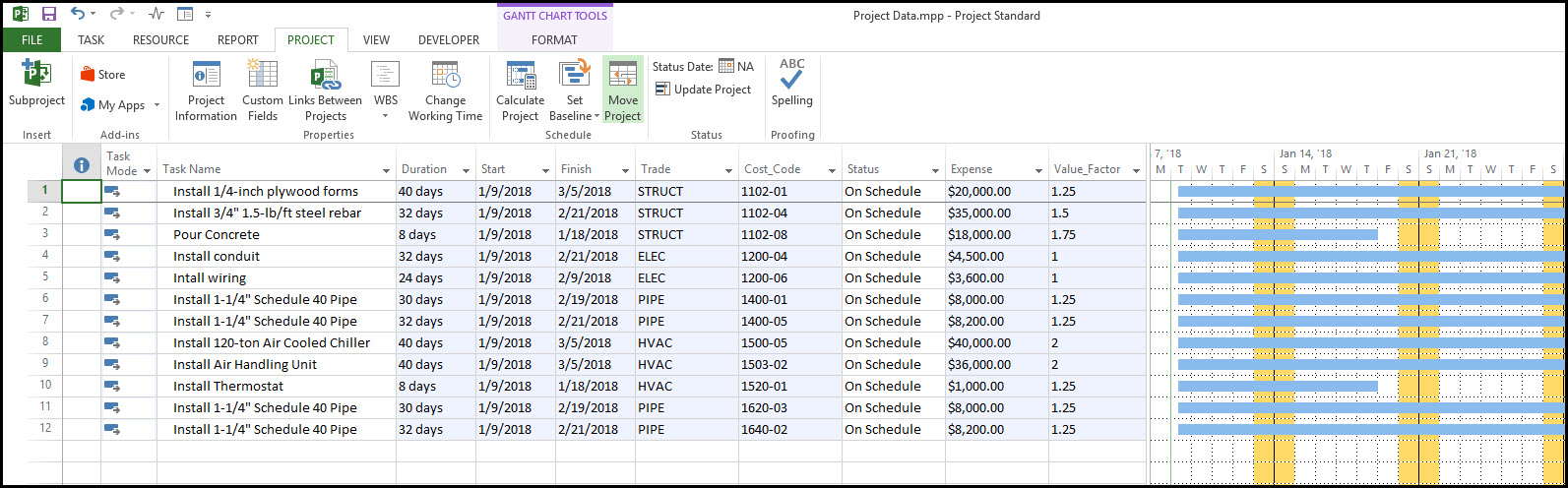 Figure 18
Figure 18