What Is Excel Bar Chart?
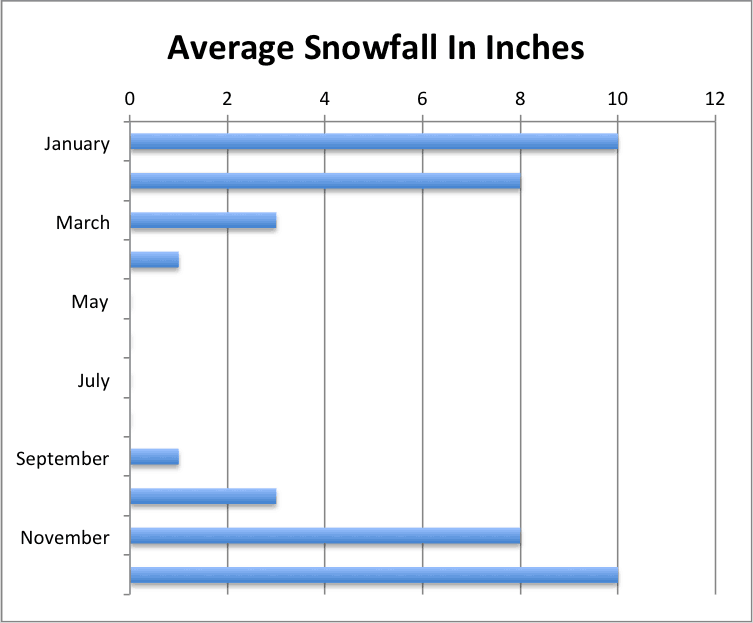
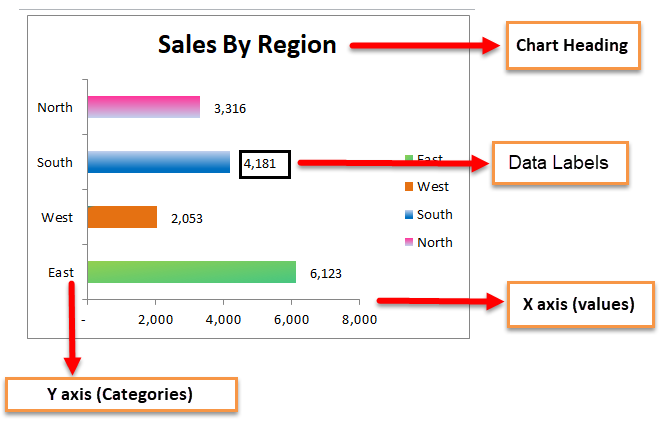
Bar charts in Excel are one of the options found in the Charts group used to display the values in the bar-chart format. They represent the values in horizontal bars. Categories are displayed on the Y-axis in these charts, and values are shown on the X-axis.
To create or make a bar chart, a user needs at least two variables, i.e., independent and dependent variables.
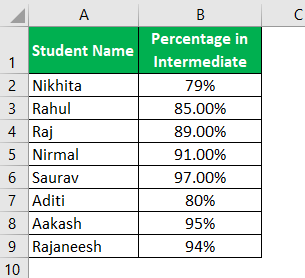
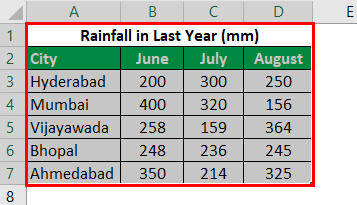
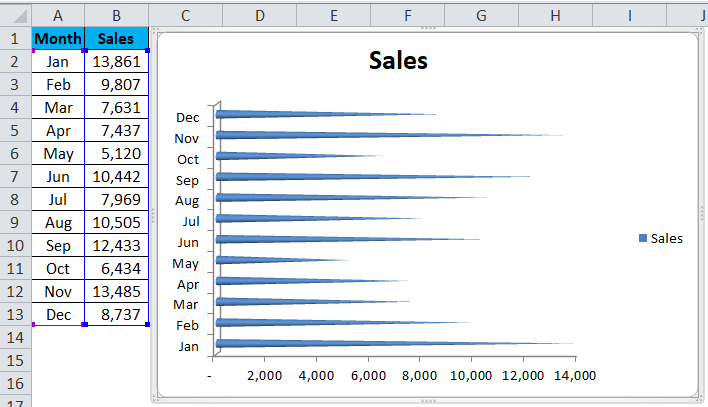
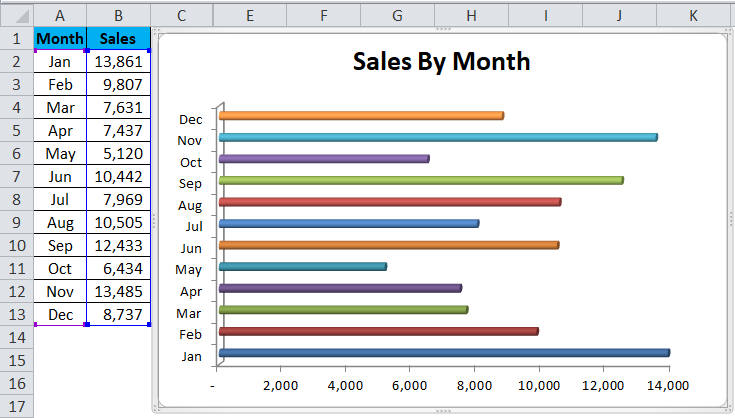
For example, consider the below table showing the marks obtained by students. Now, let us learn how to create bar chart in excel for the given data.
The steps used to create bar chart in excel are:
- Step 1: First, select the values in the table.
- Step 2: Next, go to Insert and click on Insert column or bar chart from the Charts group.
- Step 3: Choose the desired bar chart type.
As soon as we click on the chart type, Excel will display the values in the bar-chart type as shown in the image below.
Likewise, we can create bar chart in excel.
Explanation And Usage
Before using bar chart in excel, let us learn the three types of bar charts in Excel.
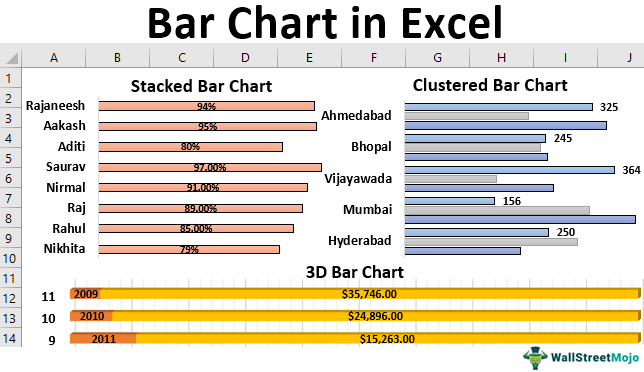
- Stacked Bar Chart: It is also referred the segmented chart. It represents all the dependent variables by stacking them together and on top of other variables.
- Clustered Bar Chart: This chart groups all the dependent variables to display in a graph format. A clustered chart with two dependent variables is the double graph.
- 3D Bar Chart: This chart represents all the dependent variables in 3D representation.
Table of contents
- What Is Excel Bar Chart?
- Explanation And Usage
- How To Create A Bar Chart in Excel?
- Examples
- Uses Of Bar Chart
- Important Things To Note
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Recommended Articles
- Bar Chart in excel is used to display the values in bar chart format.
- A bar chart is only useful for small sets of data.
- The bar chart ignores the data if it contains non-numerical values.
- It is hard to use the bar charts if data is not arranged properly in the Excel sheet.
- Bar charts and column charts have a lot of similarities except for the visual representation of the bars in horizontal and vertical format. These can be interchanged with each other.
How To Create A Bar Chart In Excel?
Creating bar chart in excel is easy. Let us see the steps used to create bar chart in excel;
- Step 1: Select the table.
- Step 2: Go to the Insert tab.
- Step 3: Click the drop-down button of the Insert Column or Bar Chart option from the Charts group.
- Step 4: Select the type of chart from the drop-down list.
Likewise, we can create bar chart in excel.
Examples
You can download this Bar Chart Excel Template here – Bar Chart Excel Template
Example #1 – Stacked Bar Chart
This example illustrates how to create a stacked bar graph in simple steps.
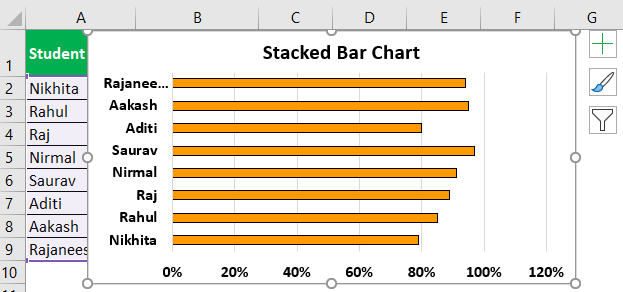
- First, we must enter the data into the Excel sheets in the table format, as shown in the figure.
- Then, select the entire table by clicking and dragging or placing the cursor anywhere in the table, and then, press CTRL+A to select the whole table.
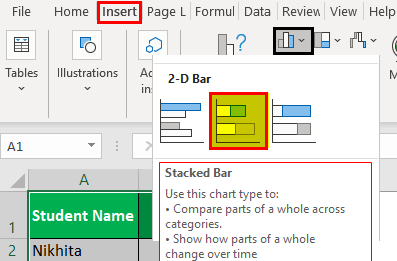
- Next, we will go to the Insert tab and move the cursor to the insert bar chart option.
- Under the 2D bar chart, we select the stacked bar chart, as shown in the figure below.
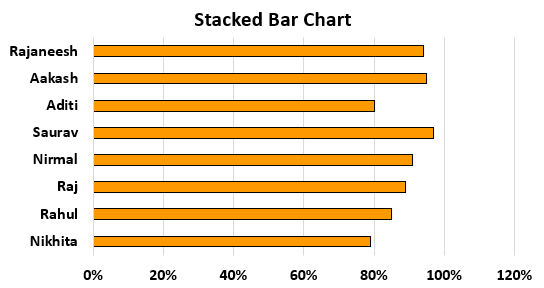
- We may see the stacked bar chart as shown below.
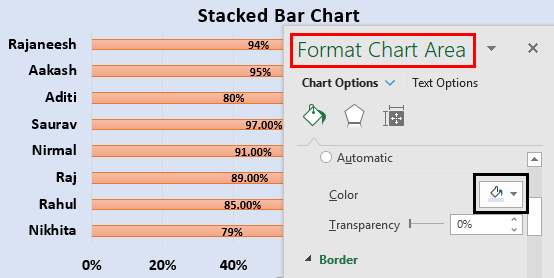
- We will add Data Labels to the data series in the plotted area.
We will click on the chart area to select the data series.
- Now, as shown in the screenshot, we will right-click on the data series and choose the add data labels to add the data label option.
- We can move the bar chart to the desired place in the worksheet. Then, we can click on the edge and drag it with the mouse.
- We can change the design of the bar chart utilizing the various options available, including changing color, changing the chart type, and moving the chart from one sheet to another sheet.
We get the following stacked bar chart.
We can use the Format Chart Area to change color, transparency, dash type, cap type, and join type.
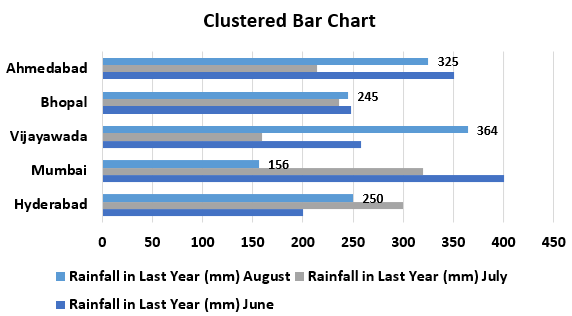
Example #2 – Clustered Bar Chart
This example illustrates how to create a clustered bar chart in simple steps.
- Step 1: As shown in the figure, we must enter the data into the Excel sheets in the Excel table format, as shown in the figure.
- Step 2: We must select the entire table by clicking and dragging or placing the cursor anywhere and pressing CTRL+A to choose the whole table.
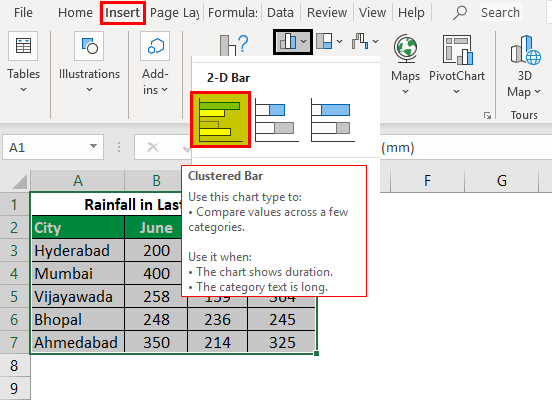
- Step 3: We will go to the Insert tab and move the cursor to the insert bar chart option. Then, under the 2D Bar Chart, select the clustered bar chart shown in the figure below.
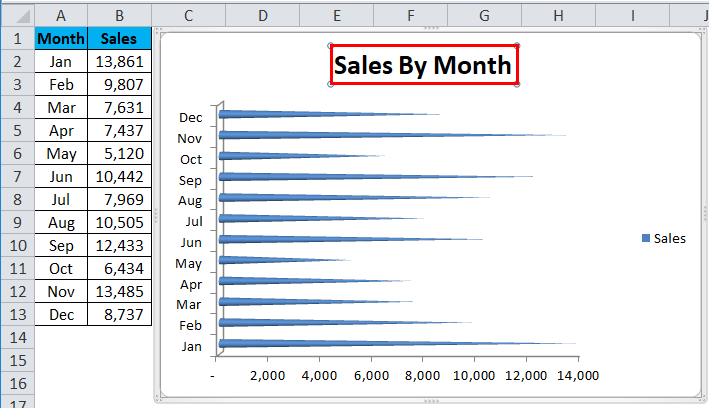
- Step 4: Next, we will add a suitable title to the chart, as shown in the figure.
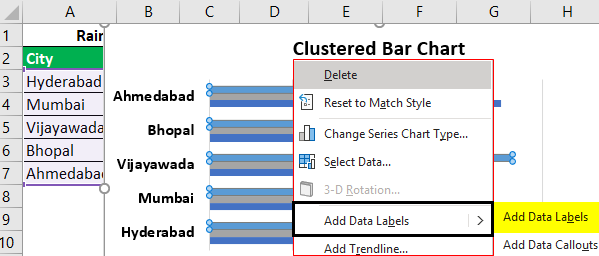
- Step 5: Now, we will right-click on the data series and choose the add data labels to add the data label option, as shown in the screenshot.
The data is added to the plotted chart, as shown in the figure.
- Step 6: We will now apply to format to change the charts’ design using the chart’s Design and Format tabs, as shown in the figure.
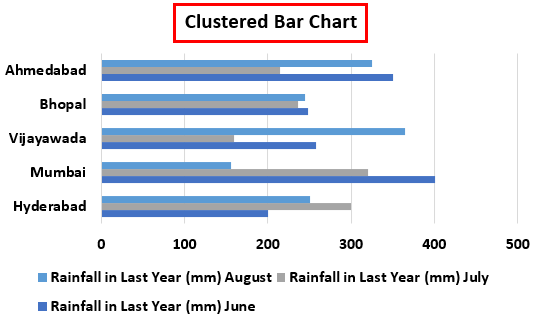
As a result, we can get the following chart.
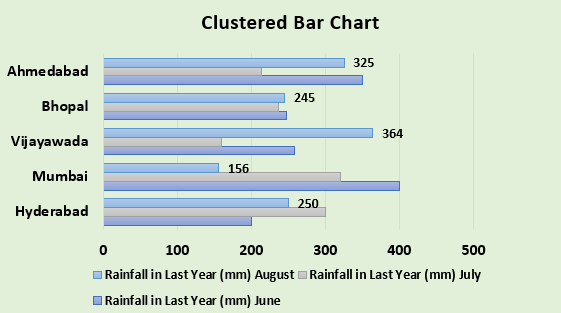
We can also change the chart’s layout using the Quick Layout feature.
Therefore, we will get the following clustered bar chart.
Example #3 – 3D Bar Chart
This example illustrates creating a 3D bar chart in Excel in simple steps.
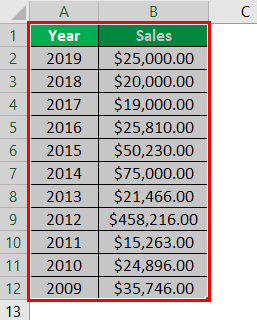
- Step 1: First, we must enter the data into the Excel sheets in the table format, as shown in the figure.
- Step 2: We will now select the whole table by clicking and dragging or placing the cursor anywhere and pressing CTRL+A to choose the table completely.
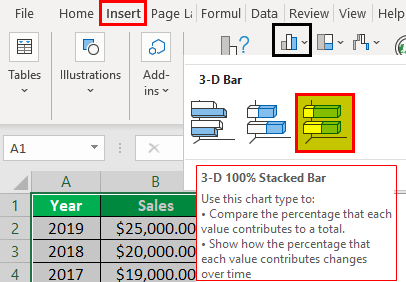
- Step 3: Next, we will go to the Insert tab and move the cursor to the insert bar chart option. Under the 3D Bar Chart, select the 100% stacked bar chart, as shown in the figure below.
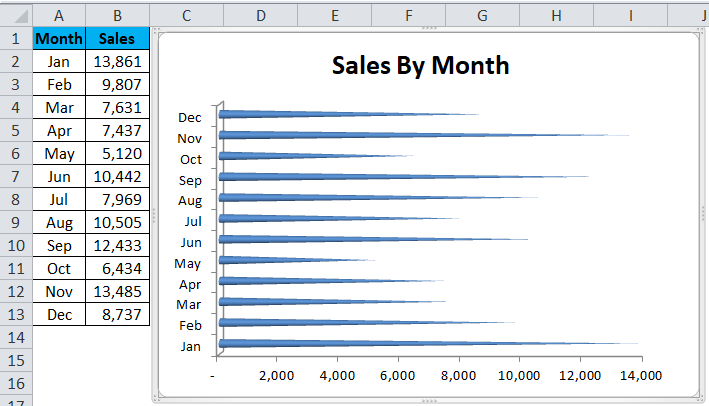
- Step 4: Now will add a suitable title to the chart, as shown in the figure.
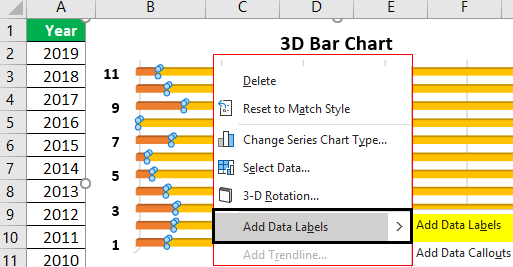
- Step 5: We will now right-click on the data series and choose Add Data Labels to add the data label option, as shown in the screenshot.
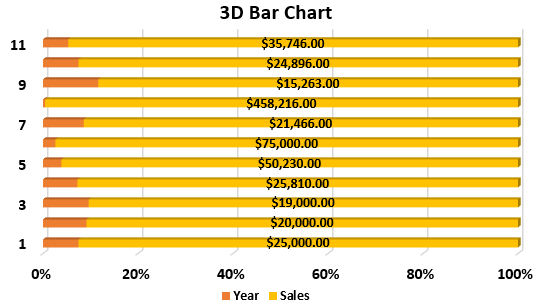
The data is added to the plotted chart, as shown in the figure.
Using the format chart area, we will apply the required formatting and design. As a result, we will get the following 3D bar chart.
Uses Of Bar Chart
Let us understand the uses of bar chart in Excel;
- Easier planning and making decisions based on the data analyzed.
- Determination of business decline or growth in a short time from the past data.
- Visual representation of the data and improved abilities in the communication of complex data.
- Comparing the different categories of data to enhance the proper understanding.
- Finally, summarize the data in the graphical format produced in the tables.
Important Things To Note
- We can turn any Excel data into a stacked bar graph that can display comparisons between categories of data, ranking, part-to-whole, deviation, or distribution.
- Bar Charts in excel compare parts of a whole with the ability to break down.
- We can also use the clustered bar chart to represent more than one data series in clustered horizontal columns when the data is complex and difficult to understand.
- In addition, we can also use a 3D bar chart to provide the chart’s title and define labels and values to make the chart more understandable.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is bar chart in excel?
Bar chart in excel is used to display small data into bar charts. There are bar charts, clustered bar charts, and 3D bar charts in excel.
2. What are independent and dependent variables?
• Independent Variable: This does not change concerning any other variable.
• Dependent Variable: This change concerns the independent variable.
3. How to create 2D bar chart in excel?
For example, consider the below table showing the price of various items. Now, let us learn how to create bar chart in excel.
The steps used to create bar chart in excel are:
• Step 1: First, select the values in the table.
• Step 2: Next, go to Insert and click on Insert column or bar chart from the Charts group.
• Step 3: Choose the desired bar chart type. In our example, we have selected 2D clustered bar.
As soon as we click on the chart type, Excel will display the values in the bar-chart type as shown in the image below.
Likewise, we can create bar chart in excel.
Recommended Articles
This article is a guide to Bar Chart in Excel. We discuss how to create different types of bar chart in Excel (stacked, clustered, and 3D), along with examples. You can have a look at other articles on Excel functions: –
- Stock Chart in Excel
- Create Control Charts in Excel
- Create Excel Combo Chart
- Make Dot Plots in Excel
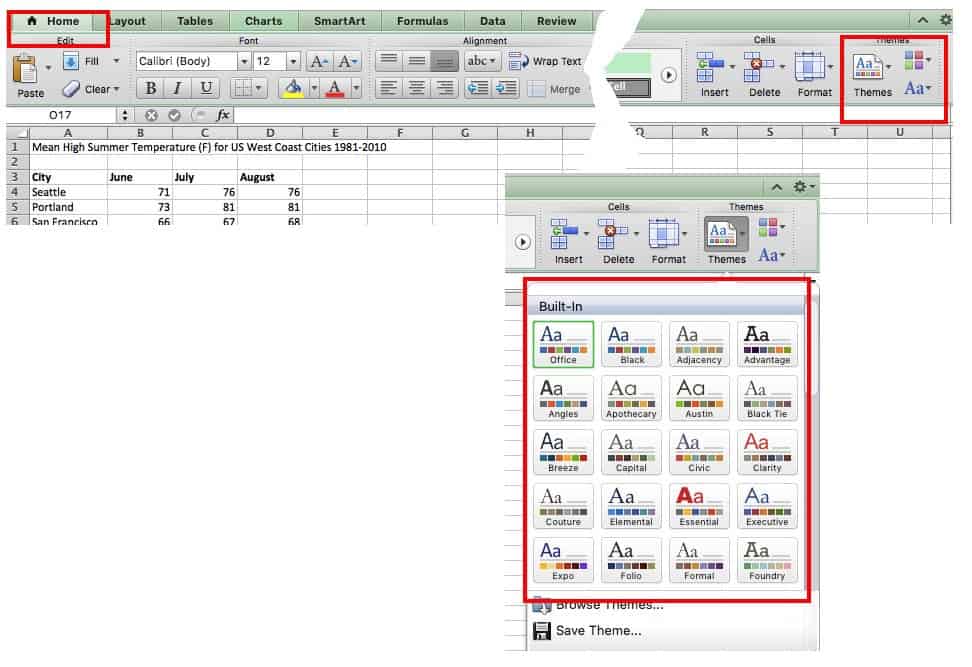
Once created, you can customize charts in many ways. Themes are preset color and shape combinations available in Excel. Changing the theme affects other options, as well as any other charts created in the future. If you only want to change the current chart, use the Chart Styles option.
To change the theme, click the Home tab, then click Themes, and make your choice.
Other versions of Excel: Click the Page Layout tab, click Themes, and then make your choice.
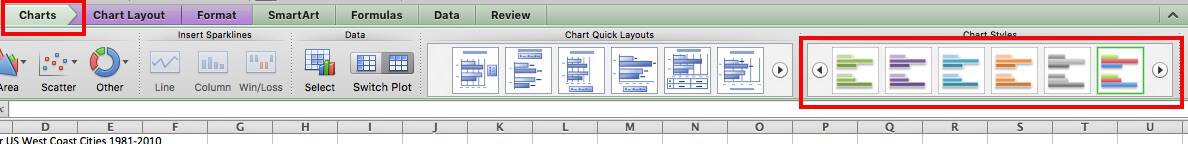
To change the style, click Charts, and scroll through the options under Chart Styles on the same ribbon.
Other versions of Excel: Click Chart Tools or Chart Design tab, and click Layout to scroll through the options under Chart Styles. If you have a Chart Design tab, the different layouts will appear in the ribbon, similar to the image above.
Adding Titles
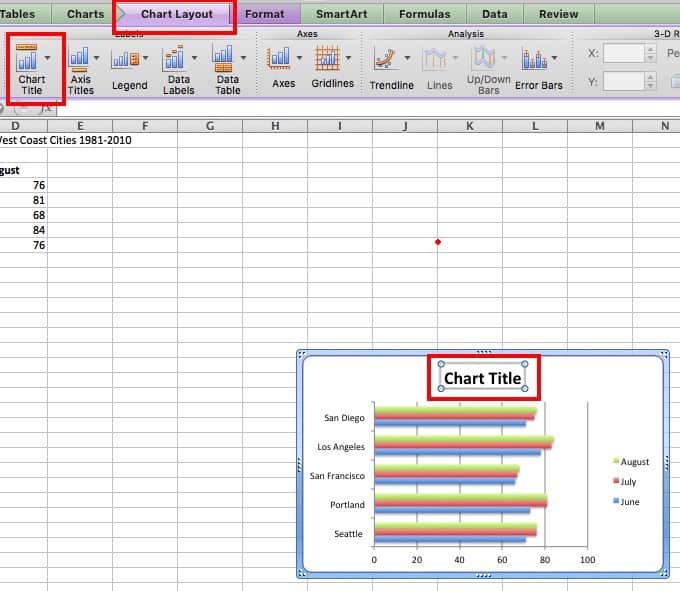
If the data presented in the chart isn’t quite clear, a title can help. Titles aren’t needed for charts with a single dependent variable.
Click on Chart Layout, click Chart Title, and click your option. Using the overlap/overlay option may cover part of the chart, so be sure the title doesn’t cover key information.
Other versions of Excel: Click Chart Tools tab, then click Layout, click Chart Title, and click your option.
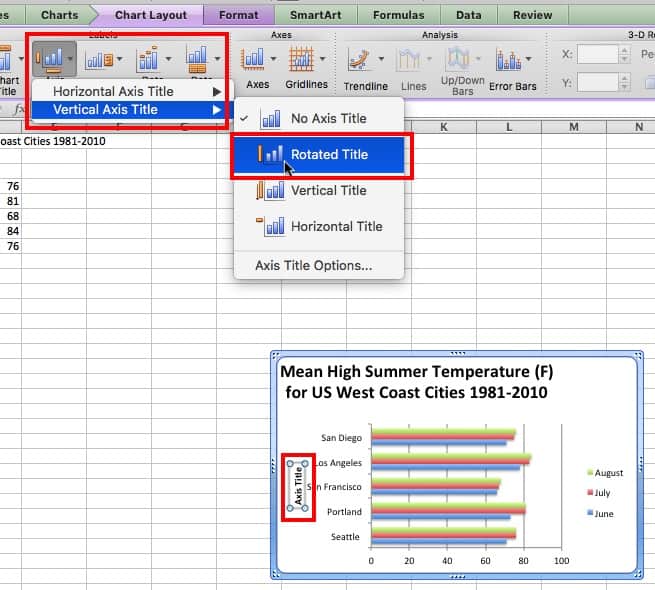
If the categories in the horizontal or vertical axis need a title, follow the steps above. However, select Axis Titles instead, and then choose the horizontal axis or vertical axis.
To change the font and appearance of titles, click Chart Title and then click More Title Options. Additionally, in some versions of Excel, you can click on the title in the chart and a side menu will appear with options to customize the text.
To reword a title, just click on it in the chart and retype.
Adjusting Axes
To adjust the horizontal or vertical axis, you can resize by clicking on a square in the corner and dragging an edge.
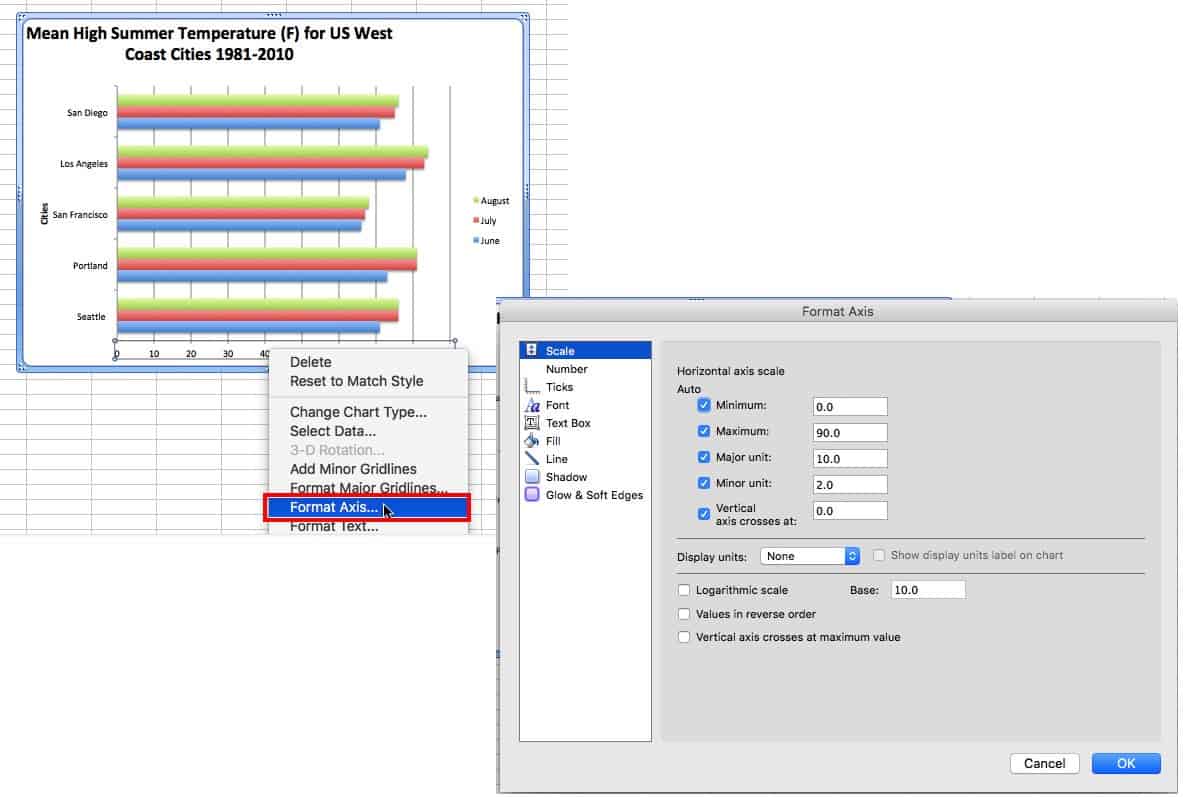
For finer adjustments, right click the axis and choose Format Axis…
For a numeric axis, you can change the the start and end points, as well as the units displayed. Simply change the numbers in the boxes to make the starting and ending point the minimum and maximum, respectively.
Formatting Text
To format the copy, right-click any text in the chart and click Format Text (or Format Title or Format Legend, etc. — depending on your version of Excel and the area of the chart you wish to change). From this menu, you can change the font style and color, and add shadows or other effects.
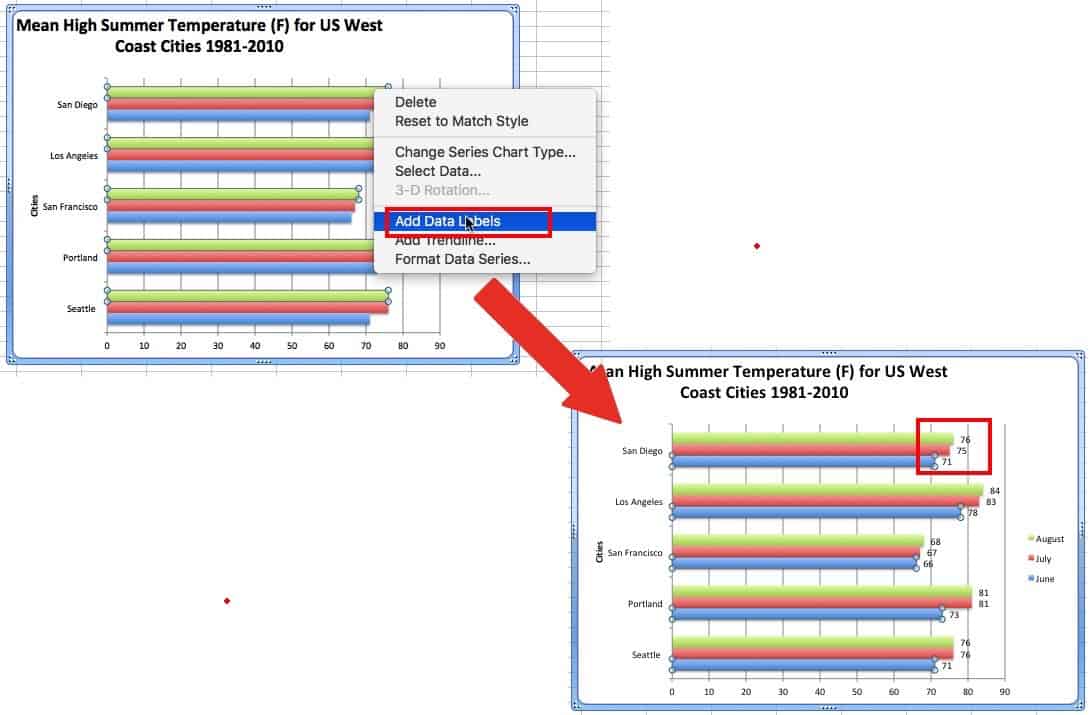
Adding Data Labels
Data labels show the value associated with the bars in the chart. This information can be useful if the values are close in range. To add data values, right-click on one of the bars in the chart, and click Add Data Labels. This will create a label for each bar in that series. For clustered charts, one of each color will have to be labeled.
Moving the Legend
Click and drag the legend to a new location on the chart, or click on it and press the delete button on your keyboard to remove it completely.
Data Order
The items will appear in reverse order from the spreadsheet. Rather than changing the order there, it’s easier to right-click the axis, click Format Axis…, and then click the box next to Categories in Reverse Order. This change will also affect the order of the data clusters, if that was the chart format chosen.
In some versions of Excel, you can also change the data order by selecting one of the bars and editing the formula bar.
Adjusting Axis Text
If the text on an axis is long, pivot it on an angle to occupy less space. Right-click the axis, click Format Axis, click Text Box, and enter an angle.
You can also opt to only show some of the axis labels. Right-click the axis, click Format Axis, then click Scale, and enter a value in the Interval between labels box. A value of 2 will show every other label; 3 will show every third.
If you want to create a cleaner, less cluttered chart, hiding some labels is a good option. But the context of the hidden text is still obvious.
Changing Chart Values
Update the spreadsheet and the values in the chart will update, too. But remember, if the chart has been copied to a non-Microsoft Office document, it won’t update — in this case, copy the updated version and replace it in the document.
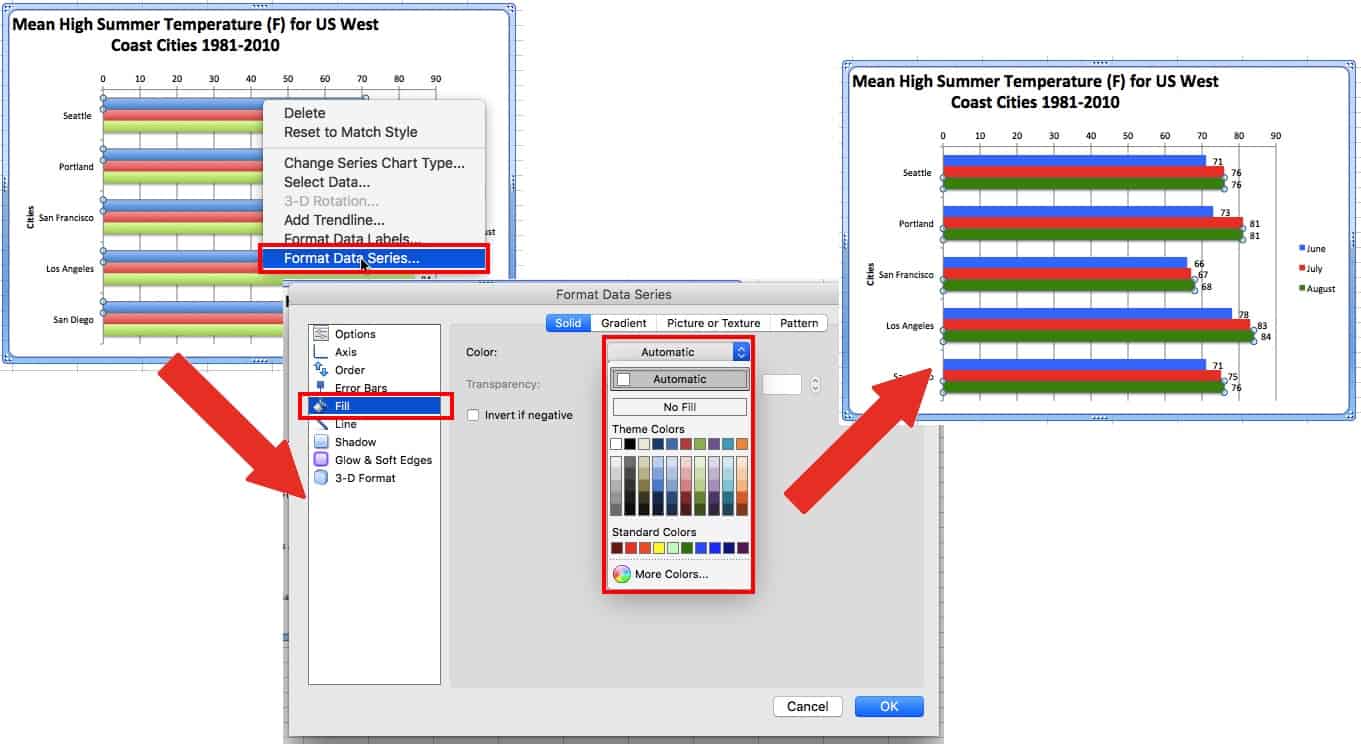
Changing the Look of the Bars
Right-click a bar, then click Format Data Series… and make adjustments. In addition to changing the color, you can also add a gradient or pattern, as well as many other effects.
For clustered bar charts, any changes will only affect the bars associated with the same dependant variable of the selected bar. Repeat to update all the bars in the chart.
If bars don’t look right, select the chart, right-click the chart and click Change Chart Type…. In addition to the 2D bars demonstrated in this tutorial, there are options for 3D bars/columns, cylinders, cones, and pyramids.
Changing the Background of the Chart and Plot Area
To change the background, right-click in a blank area of the chart and click Format Chart Area… or right-click the plot area and click Format Plot Area…. Like the bars, you can change the color, add a gradient or pattern, adjust the color and size of lines, as well as other effects.
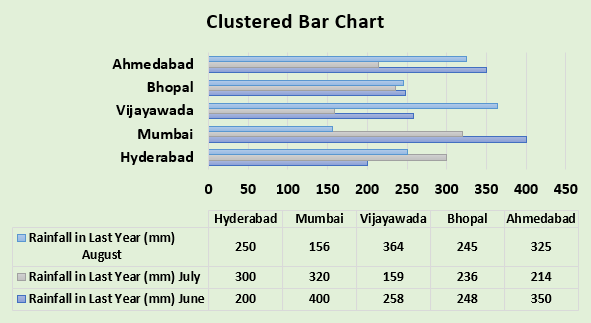
Adding a Data Table
A data table displays the spreadsheet data that was used to create the chart beneath the bar chart. This shows the same data as data labels, so use one or the other.
To add a data table, click the Chart Layout tab, click Data Table, and choose your option. If the legend key option is chosen, you can remove the legend as demonstrated in the image below.
Changing Chart Orientation
To swap the vertical and horizontal axes, right-click on the chart and click Change Chart Type. If you chose a column chart, chose bar chart instead, and vice versa. There are other ways to do this, but this is the simplest.
In this video, see how to create pie, bar, and line charts, depending on what type of data you start with.
Want more?
Copy an Excel chart to another Office program
Create a chart from start to finish
We created a clustered column chart in the previous video.
In this video, we are going to create pie, bar, and line charts.
Each type of chart highlights data differently.
And some charts can’t be used with some types of data.
We’ll go over this shortly.
To create a pie chart, select the cells you want to chart.
Click Quick Analysis and click CHARTS.
Excel displays recommended options based on the data in the cells you select, so the options won’t always be the same.
I’ll show you how to create a chart that isn’t a Quick Analysis option, shortly.
Click the Pie option, and your chart is created.
You can chart only one data series with a pie chart.
In this example, those are the Sales figures in cells B2 through B5.
I am going to move and resize the chart, so it displays without having to scroll, which will also make it easier to customize (something we’ll look at in the next video.)
I click the chart; hold down the left mouse button, and drag to move it.
I scroll down a little, click the bottom right-hand corner of the chart, and drag it up and to the left to make it smaller.
Different data displays better in different types of charts.
If you try to graph too much data in a pie chart it looks like this, not very useful.
Now, I am creating a bar chart using the same data we used to create the pie chart.
Charting the same data different ways can provide you with a different perspective that may help you discover different insights in the data.
We are creating some of the more common chart types, but there are many more options.
To create charts that aren’t Quick Analysis options, select the cells you want to chart, click the INSERT tab.
In the Charts group, we have a lot of options.
Click Recommended Charts to see the charts that will work best with the data you have selected; click All Charts for even more options.
These are all of the different types of charts you can create.
As I mentioned earlier, a pie chart is not a recommended option for the data we selected, because it can only display one data series.
We could make a Pie chart, but it would only show the first data series, the Average Precipitation for New York, and not the second data series, the Average Precipitation for Seattle.
Instead, let’s make a Line with Markers chart.
Click Line, click Line with Marker, point to an option and you get a preview of the chart.
Click OK, and we have created our line chart.
Up next, Customize charts.
Bar Chart in Excel (Table of Contents)
- Introduction to Bar Chart in Excel
- How to Create a Bar CHART in Excel?
Introduction to Bar Chart in Excel
Bar Chart in Excel is one of the easiest types of the chart to prepare by just selecting the parameters and values available against them. We must have at least one value for each parameter. Bar Chart is shown horizontally, keeping their base of the bars at Y-Axis. Bar Chart can be accessed from the insert menu tab from the Charts section, which has different types of Bar Charts such as Clustered Bar, Stacked Bar and 100% Stacked Bars available in 2D and 3D types.
In this article, I will take you through the process of creating Bar Charts.
How to Create Bar Chart in Excel?
Bar Chart in Excel is very simple and easy to create. Let us understand the working of the Bar Chart in Excel by Some Examples.
You can download this Bar Chart Excel Template here – Bar Chart Excel Template
Example #1
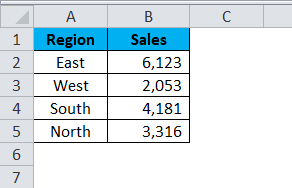
Take a simple piece of data to present the bar graph. I have sales data for 4 different regions East, West, South, and North.
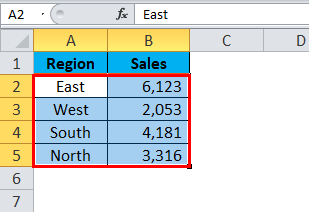
Step 1: Select the data.
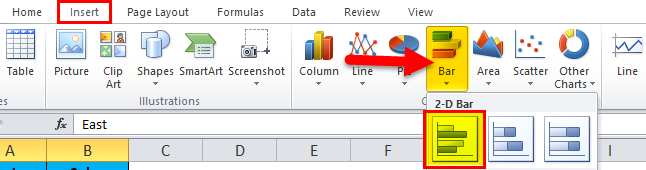
Step 2: Go to insert and click on Bar chart and select the first chart.
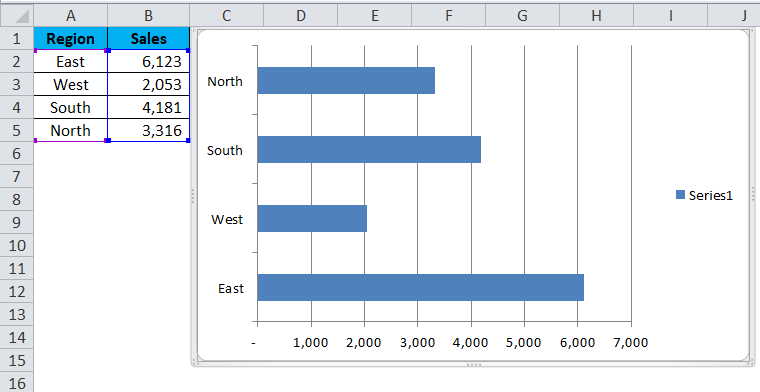
Step 3: once you click on the chart, it will insert the chart as shown in the below image.
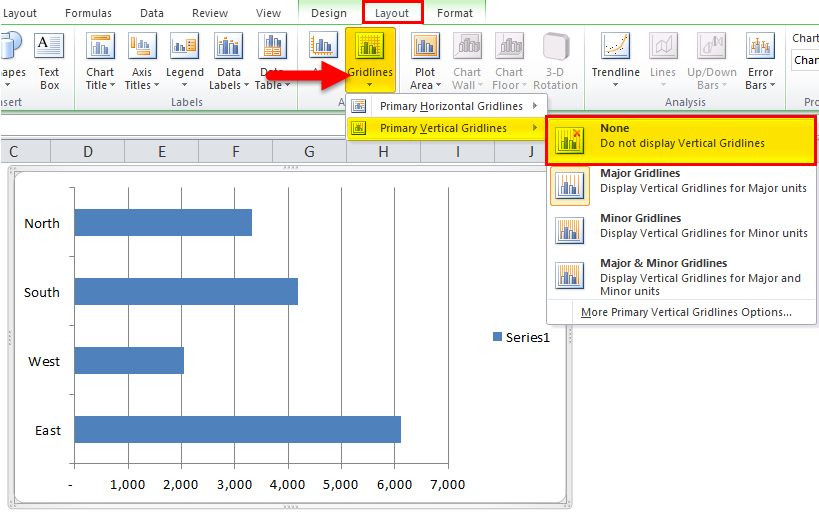
Step 4: Remove gridlines. Select the chart go to layout > gridlines > primary vertical gridlines > none.
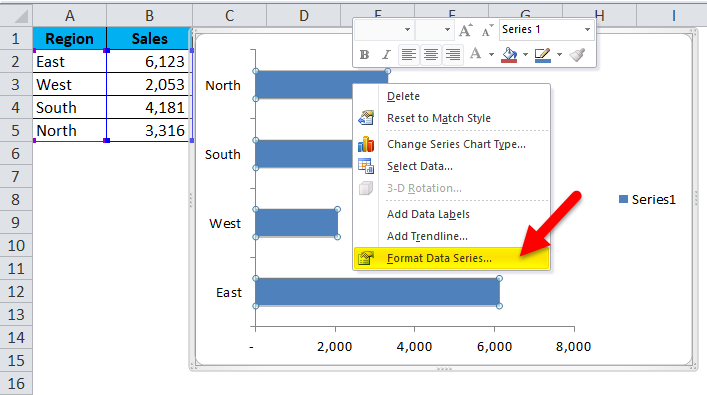
Step 5: select the bar, right-click on the bar, and select format data series.
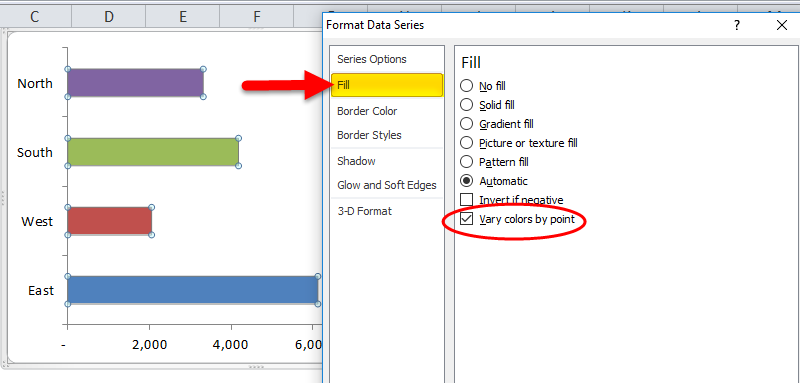
Step 6: Go to fill and select Vary Colours by Point.
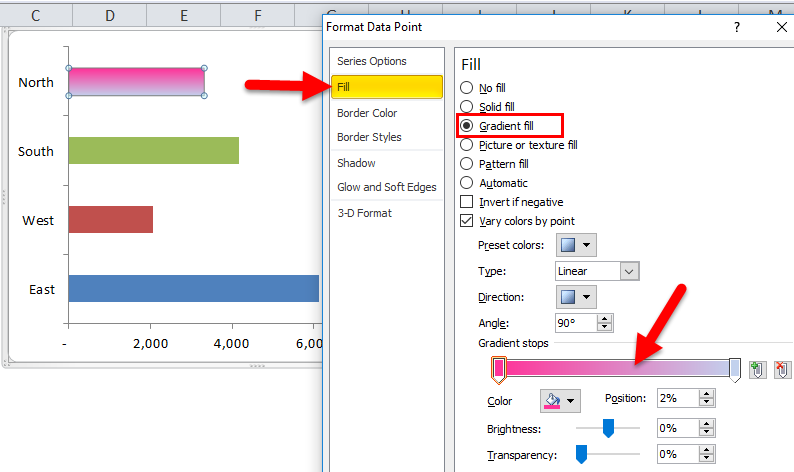
Step 7: Moreover, we can make the bar colors look attractive by right click on each bar separately.
Right, click on the first bar > go to Fill > Gradient Fill and apply the below format.
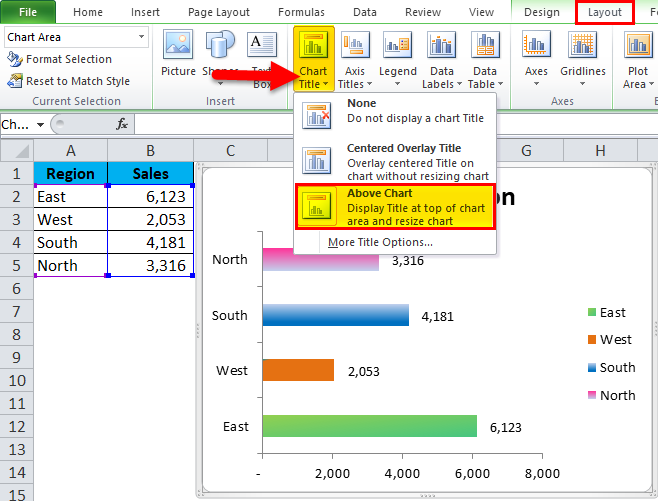
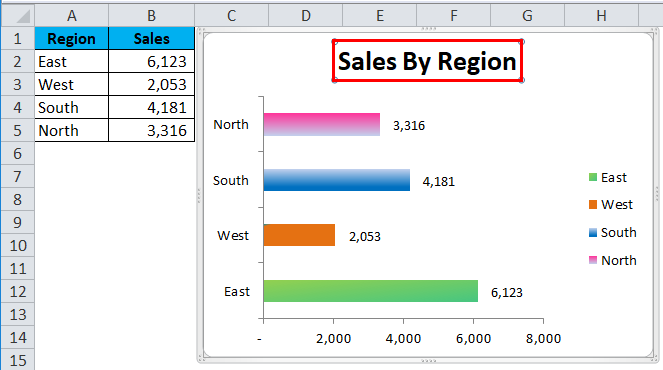
Step 8: To give the Chart Heading, go to layout>Chart Title > Select Above chart.
Chart Heading will be displayed as here it is Sales by Region.
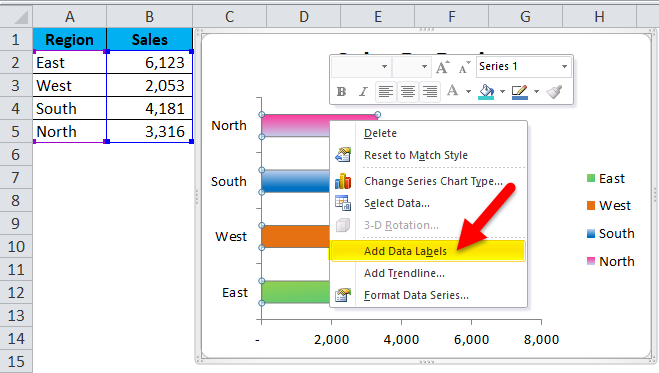
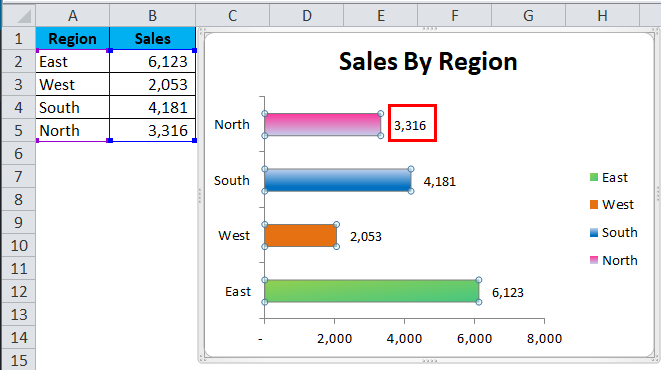
Step 9: To add Labels to the bar Right click on bar > Add Data Labels; click on it.
Data Label is added to each bar.
Similarly, you can choose different colors for each bar separately. I have chosen different colors, and my chart is looking like this.
Example #2
There are multiple bar graphs available. In this example, I am going to use the CONE type of bar chart.
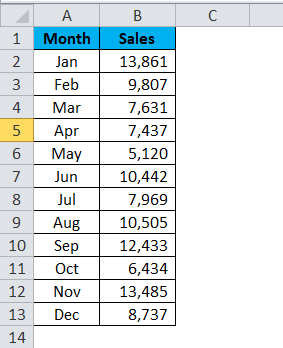
I have sales data from Jan to Dec. To present the data to the management to review the sales trend, I am applying a bar chart to visualize and present better.
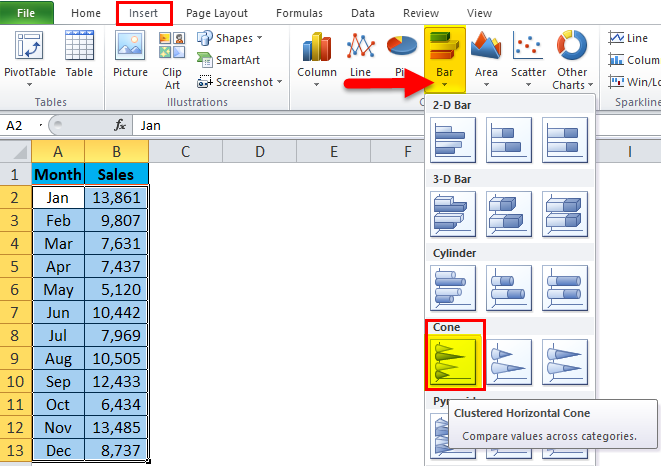
Step 1: Select the data > Go to Insert > Bar Chart > Cone Chart
Step 2: Click on the CONE chart, and it will insert the basic chart for you.
Step 3: Now, we need to modify the chart by changing its default settings.
Remove gridlines of the above Chart.
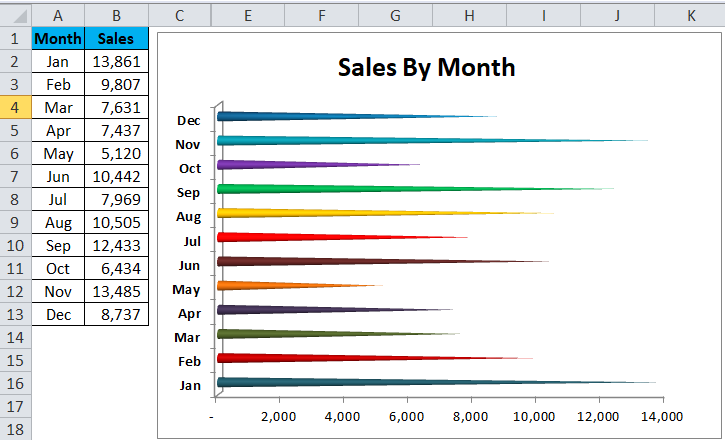
Change the chart title to Sales by month.
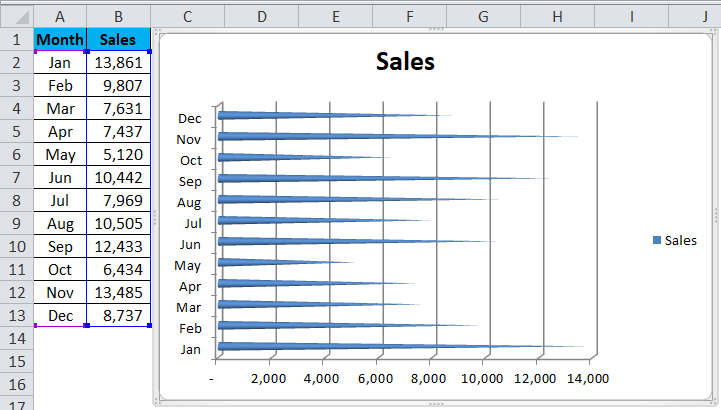
Remove Legends from the chart and enlarge to make visible all months vertically.
Step 4: Select each cone separately and filled with beautiful colors. After all the modifications, my chart looks likes this.
For the same data, I have applied different bar chat types.
Cylinder Chart:
Pyramid Chart:
Example #3
In this example, I am going to use a stacked bar chart. This chart tells the story of two series of data in a single bar.
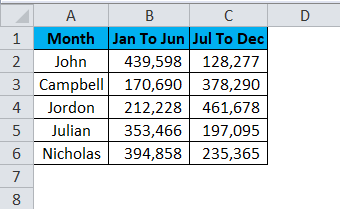
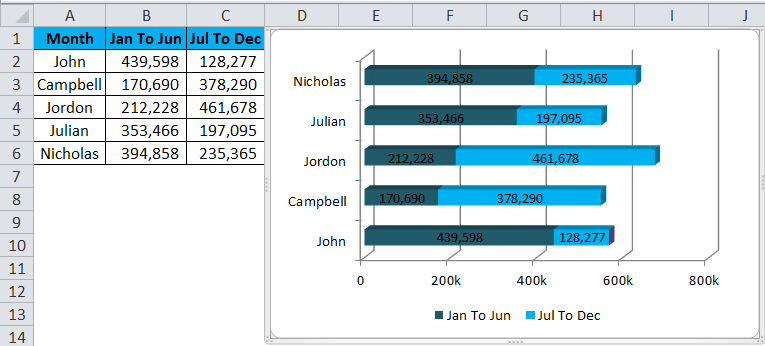
Step1: Set up the data first. I have the commission data for a sales team, which has been separated into two sections. One is for the first half-year, and another one is for the second half of the year.
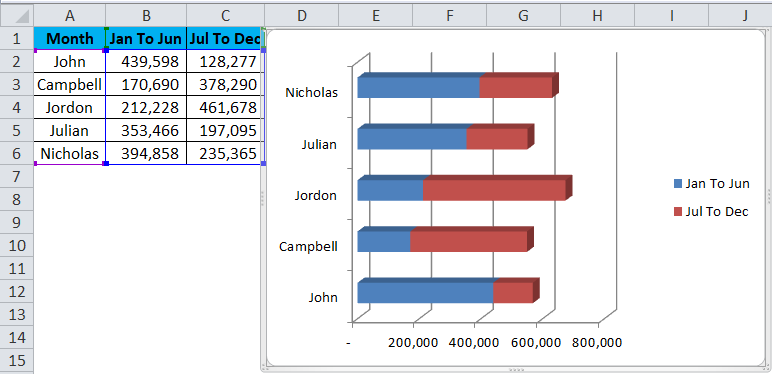
Step 2: Select the data > Go to Insert > Bar > Stacked bar in 3D.
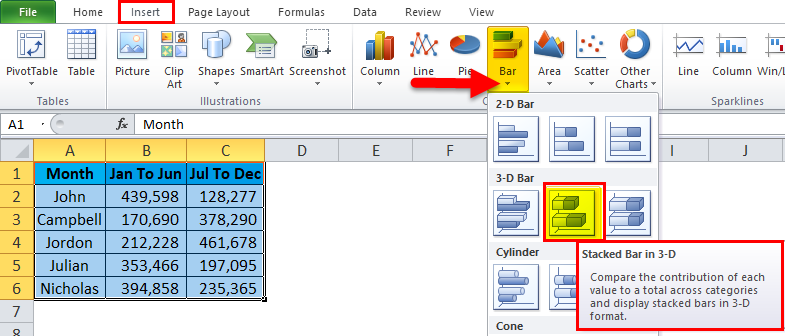
Step 3: Once you click on that chat type, it will instantly create a chart for you.
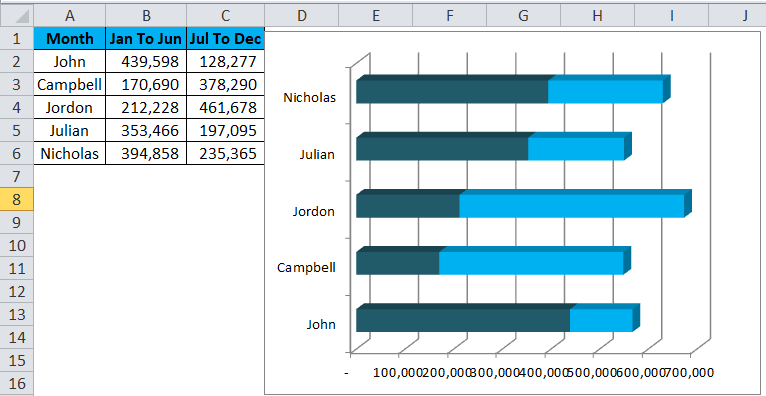
Step 4: Modify each bar color by following the previous example steps.
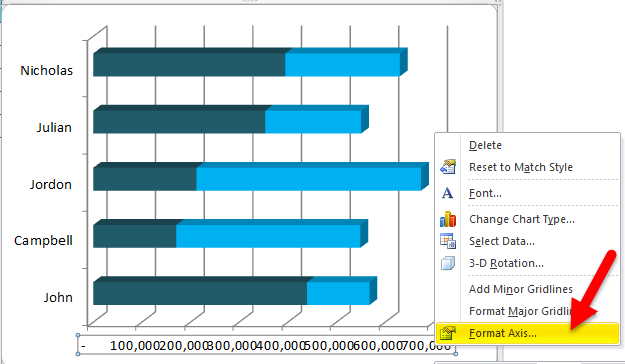
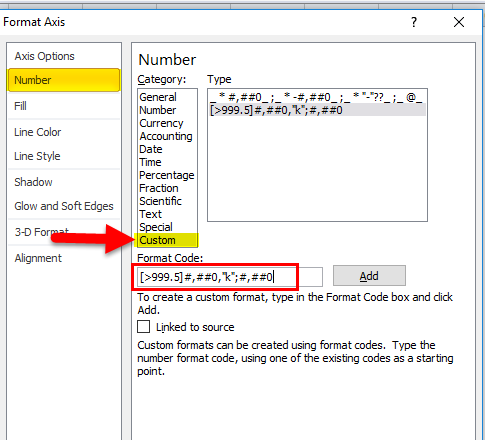
Step 5: Change the number format to adjust the spacing. Select the X-Axis and right-click > Format Axis.
Step 6: Go to Number > Custom > Apply this code [>999.5]#,##0,”k”;#,##0.
This will format the lakhs into thousands. For example, format the 1, 00,000 as 100K.
Step 7: Finally, my chart looks like this.
Advantages of Bar Chart in Excel:
- Easy comparison with better understanding.
- Quickly find the growth or decline.
- Summarize of the table data into visuals.
- Make quick planning and take decisions.
Disadvantages of Bar Chart in Excel:
- Not suitable for a large amount of data.
- Do not tell many assumptions associated with the data.
Things to Remember
- Data arrangement is very important here. IF the data is not in a suitable format, then we cannot apply a bar chart.
- Choose a bar chart for a small amount of data.
- Any non-numerical value is ignored by the bar chart.
- Column and bar charts are similar in terms of presenting the visuals, but the vertical and horizontal axis is interchanged.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to a BAR chart in Excel. Here we discuss its uses and how to create Bar Chart in Excel with excel examples and downloadable excel templates. You may also look at these useful functions in excel –
- Grouped Bar Chart
- Excel Stacked Bar Chart
- Excel Clustered Bar Chart
- Free Excel Template
A bar chart (or a bar graph) is one of the easiest ways to present your data in Excel, where horizontal bars are used to compare data values. Here’s how to make and format bar charts in Microsoft Excel.
Inserting Bar Charts in Microsoft Excel
While you can potentially turn any set of Excel data into a bar chart, It makes more sense to do this with data when straight comparisons are possible, such as comparing the sales data for a number of products. You can also create combo charts in Excel, where bar charts can be combined with other chart types to show two types of data together.
RELATED: How to Create a Combo Chart in Excel
We’ll be using fictional sales data as our example data set to help you visualize how this data could be converted into a bar chart in Excel. For more complex comparisons, alternative chart types like histograms might be better options.
To insert a bar chart in Microsoft Excel, open your Excel workbook and select your data. You can do this manually using your mouse, or you can select a cell in your range and press Ctrl+A to select the data automatically.
Once your data is selected, click Insert > Insert Column or Bar Chart.
Various column charts are available, but to insert a standard bar chart, click the “Clustered Chart” option. This chart is the first icon listed under the “2-D Column” section.
Excel will automatically take the data from your data set to create the chart on the same worksheet, using your column labels to set axis and chart titles. You can move or resize the chart to another position on the same worksheet, or cut or copy the chart to another worksheet or workbook file.
For our example, the sales data has been converted into a bar chart showing a comparison of the number of sales for each electronic product.
For this set of data, mice were bought the least with 9 sales, while headphones were bought the most with 55 sales. This comparison is visually obvious from the chart as presented.
Formatting Bar Charts in Microsoft Excel
By default, a bar chart in Excel is created using a set style, with a title for the chart extrapolated from one of the column labels (if available).
You can make many formatting changes to your chart, should you wish to. You can change the color and style of your chart, change the chart title, as well as add or edit axis labels on both sides.
It’s also possible to add trendlines to your Excel chart, allowing you to see greater patterns (trends) in your data. This would be especially important for sales data, where a trendline could visualize decreasing or increasing number of sales over time.
RELATED: How to Work with Trendlines in Microsoft Excel Charts
Changing Chart Title Text
To change the title text for a bar chart, double-click the title text box above the chart itself. You’ll then be able to edit or format the text as required.
If you want to remove the chart title completely, select your chart and click the “Chart Elements” icon on the right, shown visually as a green, “+” symbol.
From here, click the checkbox next to the “Chart Title” option to deselect it.
Your chart title will be removed once the checkbox has been removed.
Adding and Editing Axis Labels
To add axis labels to your bar chart, select your chart and click the green “Chart Elements” icon (the “+” icon).
From the “Chart Elements” menu, enable the “Axis Titles” checkbox.
Axis labels should appear for both the x axis (at the bottom) and the y axis (on the left). These will appear as text boxes.
To edit the labels, double-click the text boxes next to each axis. Edit the text in each text box accordingly, then select outside of the text box once you’ve finished making changes.
If you want to remove the labels, follow the same steps to remove the checkbox from the “Chart Elements” menu by pressing the green, “+” icon. Removing the checkbox next to the “Axis Titles” option will immediately remove the labels from view.
Changing Chart Style and Colors
Microsoft Excel offers a number of chart themes (named styles) that you can apply to your bar chart. To apply these, select your chart and then click the “Chart Styles” icon on the right that looks like a paint brush.
A list of style options will become visible in a drop-down menu under the “Style” section.
Select one of these styles to change the visual appearance of your chart, including changing the bar layout and background.
You can access the same chart styles by clicking the “Design” tab, under the “Chart Tools” section on the ribbon bar.
The same chart styles will be visible under the “Chart Styles” section—clicking any of the options shown will change your chart style in the same way as the method above.
You can also make changes to the colors used in your chart in the “Color” section of the Chart Styles menu.
Color options are grouped, so select one of the color palette groupings to apply those colors to your chart.
You can test each color style by hovering over them with your mouse first. Your chart will change to show how the chart will look with those colors applied.
Further Bar Chart Formatting Options
You can make further formatting changes to your bar chart by right-clicking the chart and selecting the “Format Chart Area” option.
This will bring up the “Format Chart Area” menu on the right. From here, you can change the fill, border, and other chart formatting options for your chart under the “Chart Options” section.
You can also change how text is displayed on your chart under the “Text Options” section, allowing you to add colors, effects, and patterns to your title and axis labels, as well as change how your text is aligned on the chart.
If you want to make further text formatting changes, you can do this using the standard text formatting options under the “Home” tab while you’re editing a label.
You can also use the pop-up formatting menu that appears above the chart title or axis label text boxes as you edit them.
READ NEXT
- › How to Find Links to Other Workbooks in Microsoft Excel
- › How to Create a Chart Template in Microsoft Excel
- › How to Rename a Data Series in Microsoft Excel
- › How to Add and Customize Data Labels in Microsoft Excel Charts
- › How to Make a Bar Graph in Google Sheets
- › How to Create a Geographical Map Chart in Microsoft Excel
- › How to Create and Customize a People Graph in Microsoft Excel
- › HoloLens Now Has Windows 11 and Incredible 3D Ink Features