If the data you want to filter requires complex criteria (such as Type = «Produce» OR Salesperson = «Davolio»), you can use the Advanced Filter dialog box.
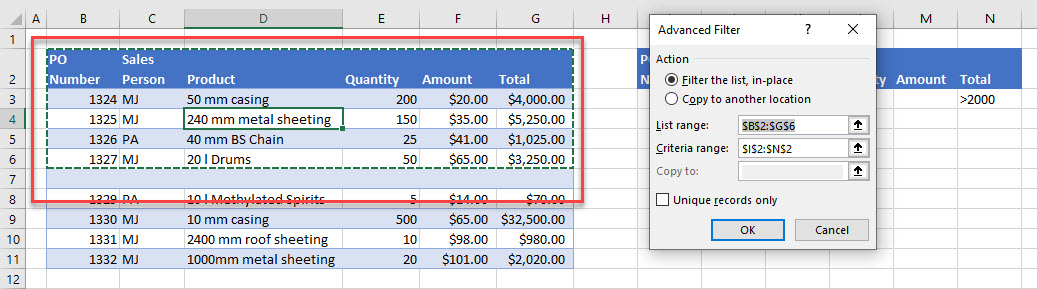
To open the Advanced Filter dialog box, click Data > Advanced.
|
Advanced Filter |
Example |
|---|---|
|
Overview of advanced filter criteria |
|
|
Multiple criteria, one column, any criteria true |
Salesperson = «Davolio» OR Salesperson = «Buchanan» |
|
Multiple criteria, multiple columns, all criteria true |
Type = «Produce» AND Sales > 1000 |
|
Multiple criteria, multiple columns, any criteria true |
Type = «Produce» OR Salesperson = «Buchanan» |
|
Multiple sets of criteria, one column in all sets |
(Sales > 6000 AND Sales < 6500 ) OR (Sales < 500) |
|
Multiple sets of criteria, multiple columns in each set |
(Salesperson = «Davolio» AND Sales >3000) OR |
|
Wildcard criteria |
Salesperson = a name with ‘u’ as the second letter |
Overview of advanced filter criteria
The Advanced command works differently from the Filter command in several important ways.
-
It displays the Advanced Filter dialog box instead of the AutoFilter menu.
-
You type the advanced criteria in a separate criteria range on the worksheet and above the range of cells or table that you want to filter. Microsoft Office Excel uses the separate criteria range in the Advanced Filter dialog box as the source for the advanced criteria.
Sample data
The following sample data is used for all procedures in this article.
The data includes four blank rows above the list range that will be used as a criteria range (A1:C4) and a list range (A6:C10). The criteria range has column labels and includes at least one blank row between the criteria values and the list range.
To work with this data, select it in the following table, copy it, and then paste it in cell A1 of a new Excel worksheet.
|
Type |
Salesperson |
Sales |
|
Type |
Salesperson |
Sales |
|
Beverages |
Suyama |
$5122 |
|
Meat |
Davolio |
$450 |
|
produce |
Buchanan |
$6328 |
|
Produce |
Davolio |
$6544 |
Comparison operators
You can compare two values by using the following operators. When two values are compared by using these operators, the result is a logical value—either TRUE or FALSE.
|
Comparison operator |
Meaning |
Example |
|---|---|---|
|
= (equal sign) |
Equal to |
A1=B1 |
|
> (greater than sign) |
Greater than |
A1>B1 |
|
< (less than sign) |
Less than |
A1<B1 |
|
>= (greater than or equal to sign) |
Greater than or equal to |
A1>=B1 |
|
<= (less than or equal to sign) |
Less than or equal to |
A1<=B1 |
|
<> (not equal to sign) |
Not equal to |
A1<>B1 |
Using the equal sign to type text or a value
Because the equal sign (=) is used to indicate a formula when you type text or a value in a cell, Excel evaluates what you type; however, this may cause unexpected filter results. To indicate an equality comparison operator for either text or a value, type the criteria as a string expression in the appropriate cell in the criteria range:
=»=
entry
»
Where entry is the text or value you want to find. For example:
|
What you type in the cell |
What Excel evaluates and displays |
|---|---|
|
=»=Davolio» |
=Davolio |
|
=»=3000″ |
=3000 |
Considering case-sensitivity
When filtering text data, Excel doesn’t distinguish between uppercase and lowercase characters. However, you can use a formula to perform a case-sensitive search. For an example, see the section Wildcard criteria.
Using pre-defined names
You can name a range Criteria, and the reference for the range will appear automatically in the Criteria range box. You can also define the name Database for the list range to be filtered and define the name Extract for the area where you want to paste the rows, and these ranges will appear automatically in the List range and Copy to boxes, respectively.
Creating criteria by using a formula
You can use a calculated value that is the result of a formula as your criterion. Remember the following important points:
-
The formula must evaluate to TRUE or FALSE.
-
Because you are using a formula, enter the formula as you normally would, and do not type the expression in the following way:
=»=
entry
» -
Do not use a column label for criteria labels; either keep the criteria labels blank or use a label that is not a column label in the list range (in the examples that follow, Calculated Average and Exact Match).
If you use a column label in the formula instead of a relative cell reference or a range name, Excel displays an error value such as #NAME? or #VALUE! in the cell that contains the criterion. You can ignore this error because it does not affect how the list range is filtered.
-
The formula that you use for criteria must use a relative reference to refer to the corresponding cell in the first row of data.
-
All other references in the formula must be absolute references.
Multiple criteria, one column, any criteria true
Boolean logic: (Salesperson = «Davolio» OR Salesperson = «Buchanan»)
-
Insert at least three blank rows above the list range that can be used as a criteria range. The criteria range must have column labels. Make sure that there is at least one blank row between the criteria values and the list range.
-
To find rows that meet multiple criteria for one column, type the criteria directly below each other in separate rows of the criteria range. Using the example, enter:
Type
Salesperson
Sales
=»=Davolio»
=»=Buchanan»
-
Click a cell in the list range. Using the example, click any cell in the range A6:C10.
-
On the Data tab, in the Sort & Filter group, click Advanced.
-
Do one of the following:
-
To filter the list range by hiding rows that don’t match your criteria, click Filter the list, in-place.
-
To filter the list range by copying rows that match your criteria to another area of the worksheet, click Copy to another location, click in the Copy to box, and then click the upper-left corner of the area where you want to paste the rows.
Tip When you copy filtered rows to another location, you can specify which columns to include in the copy operation. Before filtering, copy the column labels for the columns that you want to the first row of the area where you plan to paste the filtered rows. When you filter, enter a reference to the copied column labels in the Copy to box. The copied rows will then include only the columns for which you copied the labels.
-
-
In the Criteria range box, enter the reference for the criteria range, including the criteria labels. Using the example, enter $A$1:$C$3.
To move the Advanced Filter dialog box out of the way temporarily while you select the criteria range, click Collapse Dialog
.
-
Using the example, the filtered result for the list range is:
Type
Salesperson
Sales
Meat
Davolio
$450
produce
Buchanan
$6,328
Produce
Davolio
$6,544
Multiple criteria, multiple columns, all criteria true
Boolean logic: (Type = «Produce» AND Sales > 1000)
-
Insert at least three blank rows above the list range that can be used as a criteria range. The criteria range must have column labels. Make sure that there is at least one blank row between the criteria values and the list range.
-
To find rows that meet multiple criteria in multiple columns, type all the criteria in the same row of the criteria range. Using the example, enter:
Type
Salesperson
Sales
=»=Produce»
>1000
-
Click a cell in the list range. Using the example, click any cell in the range A6:C10.
-
On the Data tab, in the Sort & Filter group, click Advanced.
-
Do one of the following:
-
To filter the list range by hiding rows that don’t match your criteria, click Filter the list, in-place.
-
To filter the list range by copying rows that match your criteria to another area of the worksheet, click Copy to another location, click in the Copy to box, and then click the upper-left corner of the area where you want to paste the rows.
Tip When you copy filtered rows to another location, you can specify which columns to include in the copy operation. Before filtering, copy the column labels for the columns that you want to the first row of the area where you plan to paste the filtered rows. When you filter, enter a reference to the copied column labels in the Copy to box. The copied rows will then include only the columns for which you copied the labels.
-
-
In the Criteria range box, enter the reference for the criteria range, including the criteria labels. Using the example, enter $A$1:$C$2.
To move the Advanced Filter dialog box out of the way temporarily while you select the criteria range, click Collapse Dialog
.
-
Using the example, the filtered result for the list range is:
Type
Salesperson
Sales
produce
Buchanan
$6,328
Produce
Davolio
$6,544
Multiple criteria, multiple columns, any criteria true
Boolean logic: (Type = «Produce» OR Salesperson = «Buchanan»)
-
Insert at least three blank rows above the list range that can be used as a criteria range. The criteria range must have column labels. Make sure that there is at least one blank row between the criteria values and the list range.
-
To find rows that meet multiple criteria in multiple columns where any criteria can be true, type the criteria in the different columns and rows of the criteria range. Using the example, enter:
Type
Salesperson
Sales
=»=Produce»
=»=Buchanan»
-
Click a cell in the list range. Using the example, click any cell in the list range A6:C10.
-
On the Data tab, in the Sort & Filter group, click Advanced.
-
Do one of the following:
-
To filter the list range by hiding rows that don’t match your criteria, click Filter the list, in-place.
-
To filter the list range by copying rows that match your criteria to another area of the worksheet, click Copy to another location, click in the Copy to box, and then click the upper-left corner of the area where you want to paste the rows.
Tip: When you copy filtered rows to another location, you can specify which columns to include in the copy operation. Before filtering, copy the column labels for the columns that you want to the first row of the area where you plan to paste the filtered rows. When you filter, enter a reference to the copied column labels in the Copy to box. The copied rows will then include only the columns for which you copied the labels.
-
-
In the Criteria range box, enter the reference for the criteria range, including the criteria labels. Using the example, enter $A$1:$B$3.
To move the Advanced Filter dialog box out of the way temporarily while you select the criteria range, click Collapse Dialog
.
-
Using the example, the filtered result for the list range is:
Type
Salesperson
Sales
produce
Buchanan
$6,328
Produce
Davolio
$6,544
Multiple sets of criteria, one column in all sets
Boolean logic: ( (Sales > 6000 AND Sales < 6500 ) OR (Sales < 500) )
-
Insert at least three blank rows above the list range that can be used as a criteria range. The criteria range must have column labels. Make sure that there is at least one blank row between the criteria values and the list range.
-
To find rows that meet multiple sets of criteria where each set includes criteria for one column, include multiple columns with the same column heading. Using the example, enter:
Type
Salesperson
Sales
Sales
>6000
<6500
<500
-
Click a cell in the list range. Using the example, click any cell in the list range A6:C10.
-
On the Data tab, in the Sort & Filter group, click Advanced.
-
Do one of the following:
-
To filter the list range by hiding rows that don’t match your criteria, click Filter the list, in-place.
-
To filter the list range by copying rows that match your criteria to another area of the worksheet, click Copy to another location, click in the Copy to box, and then click the upper-left corner of the area where you want to paste the rows.
Tip: When you copy filtered rows to another location, you can specify which columns to include in the copy operation. Before filtering, copy the column labels for the columns that you want to the first row of the area where you plan to paste the filtered rows. When you filter, enter a reference to the copied column labels in the Copy to box. The copied rows will then include only the columns for which you copied the labels.
-
-
In the Criteria range box, enter the reference for the criteria range, including the criteria labels. Using the example, enter $A$1:$D$3.
To move the Advanced Filter dialog box out of the way temporarily while you select the criteria range, click Collapse Dialog
.
-
Using the example, the filtered result for the list range is:
Type
Salesperson
Sales
Meat
Davolio
$450
produce
Buchanan
$6,328
Multiple sets of criteria, multiple columns in each set
Boolean logic: ( (Salesperson = «Davolio» AND Sales >3000) OR (Salesperson = «Buchanan» AND Sales > 1500) )
-
Insert at least three blank rows above the list range that can be used as a criteria range. The criteria range must have column labels. Make sure that there is at least one blank row between the criteria values and the list range.
-
To find rows that meet multiple sets of criteria, where each set includes criteria for multiple columns, type each set of criteria in separate columns and rows. Using the example, enter:
Type
Salesperson
Sales
=»=Davolio»
>3000
=»=Buchanan»
>1500
-
Click a cell in the list range. Using the example, click any cell in the list range A6:C10.
-
On the Data tab, in the Sort & Filter group, click Advanced.
-
Do one of the following:
-
To filter the list range by hiding rows that don’t match your criteria, click Filter the list, in-place.
-
To filter the list range by copying rows that match your criteria to another area of the worksheet, click Copy to another location, click in the Copy to box, and then click the upper-left corner of the area where you want to paste the rows.
Tip When you copy filtered rows to another location, you can specify which columns to include in the copy operation. Before filtering, copy the column labels for the columns that you want to the first row of the area where you plan to paste the filtered rows. When you filter, enter a reference to the copied column labels in the Copy to box. The copied rows will then include only the columns for which you copied the labels.
-
-
In the Criteria range box, enter the reference for the criteria range, including the criteria labels. Using the example, enter $A$1:$C$3.To move the Advanced Filter dialog box out of the way temporarily while you select the criteria range, click Collapse Dialog
.
-
Using the example, the filtered result for the list range would be:
Type
Salesperson
Sales
produce
Buchanan
$6,328
Produce
Davolio
$6,544
Wildcard criteria
Boolean logic: Salesperson = a name with ‘u’ as the second letter
-
To find text values that share some characters but not others, do one or more of the following:
-
Type one or more characters without an equal sign (=) to find rows with a text value in a column that begin with those characters. For example, if you type the text Dav as a criterion, Excel finds «Davolio,» «David,» and «Davis.»
-
Use a wildcard character.
Use
To find
? (question mark)
Any single character
For example, sm?th finds «smith» and «smyth»* (asterisk)
Any number of characters
For example, *east finds «Northeast» and «Southeast»~ (tilde) followed by ?, *, or ~
A question mark, asterisk, or tilde
For example, fy91~? finds «fy91?»
-
-
Insert at least three blank rows above the list range that can be used as a criteria range. The criteria range must have column labels. Make sure that there is at least one blank row between the criteria values and the list range.
-
In the rows below the column labels, type the criteria that you want to match. Using the example, enter:
Type
Salesperson
Sales
=»=Me*»
=»=?u*»
-
Click a cell in the list range. Using the example, click any cell in the list range A6:C10.
-
On the Data tab, in the Sort & Filter group, click Advanced.
-
Do one of the following:
-
To filter the list range by hiding rows that don’t match your criteria, click Filter the list, in-place
-
To filter the list range by copying rows that match your criteria to another area of the worksheet, click Copy to another location, click in the Copy to box, and then click the upper-left corner of the area where you want to paste the rows.
Tip: When you copy filtered rows to another location, you can specify which columns to include in the copy operation. Before filtering, copy the column labels for the columns that you want to the first row of the area where you plan to paste the filtered rows. When you filter, enter a reference to the copied column labels in the Copy to box. The copied rows will then include only the columns for which you copied the labels.
-
-
In the Criteria range box, enter the reference for the criteria range, including the criteria labels. Using the example, enter $A$1:$B$3.
To move the Advanced Filter dialog box out of the way temporarily while you select the criteria range, click Collapse Dialog
.
-
Using the example, the filtered result for the list range is:
Type
Salesperson
Sales
Beverages
Suyama
$5,122
Meat
Davolio
$450
produce
Buchanan
$6,328
Need more help?
You can always ask an expert in the Excel Tech Community or get support in the Answers community.
This tutorial shows some reasons an advanced filter might not work in Excel and how to avoid those issues.
Advanced Filter Not Working
Advanced filters in Excel extract data using more complex criteria than a standard filter. You are able to filter data to a different location from the original data, as well as setting a criteria range that enables you to filter on two or more columns of data using and/or scenarios. It’s also a great way to extract unique data from a list with duplicates.
If you find yourself in a situation where your filter isn’t working properly, it’s probably due to one or more of the reasons below.
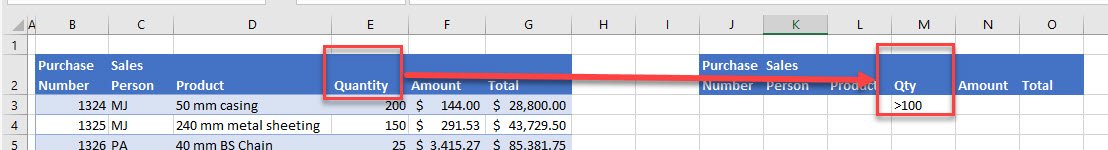
Column Headers Don’t Match
To use an advanced filter, the column headers in the data section need to match the column headers in the criteria section.
For example, if your column headings are spelled differently in the data section from the criteria section, the advanced filter doesn’t work. Consider the filter setup below.
Although it’s pretty clear to any of us that Quantity and Qty are the same, Excel can’t recognize them as the same fields in an advanced filter. The headings need to match each other precisely.
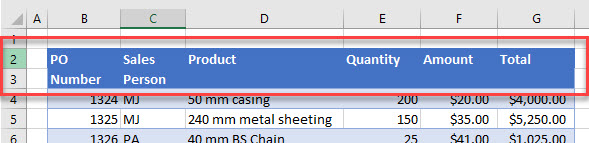
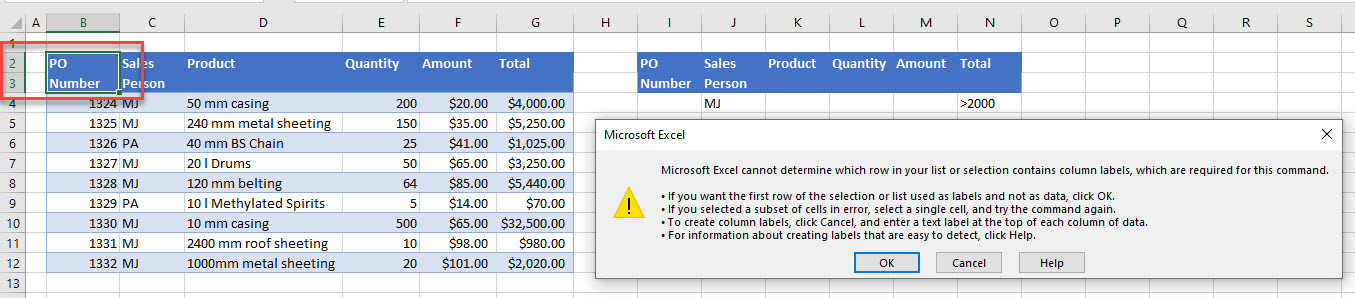
Headings Over Multiple Rows
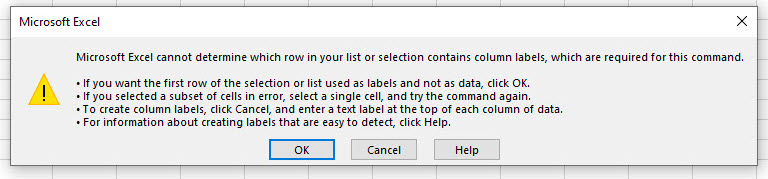
Another kind of mismatch occurs if any headings span multiple rows. You may get the error message:
Microsoft Excel cannot determine which row in your list or selection contains column labels, which are required for this command.
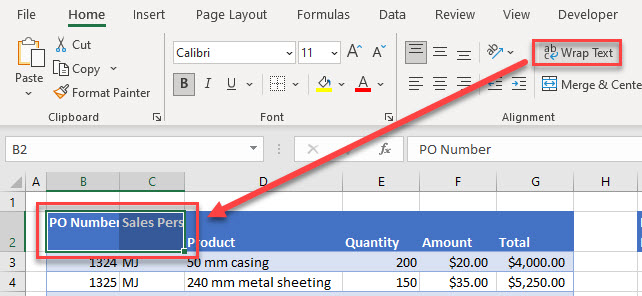
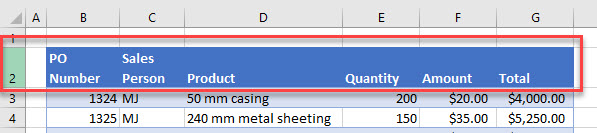
Consider the example below. Column headings need to be in a single row, but Columns B and C have one half of the heading in the first row, and the other half in the second row.
To solve this problem, make sure your headings are in a single row. Wrap the text if you still want to display the headings over two rows.
- Type headings in the first row only.
- Select the cells where you wish to wrap the text.
- In the Ribbon, go to Home > Alignment > Wrap Text.
Now, the headings can be displayed in the same way, with the same column width, and also be usable in an advanced filter.
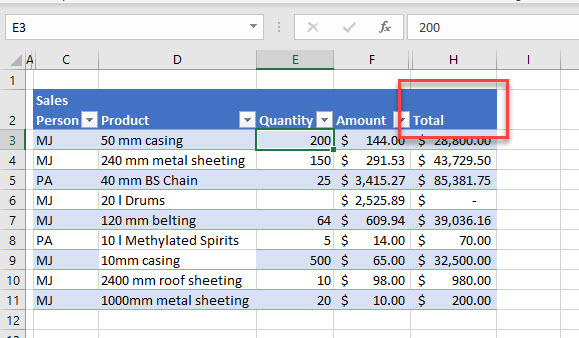
Dataset Error
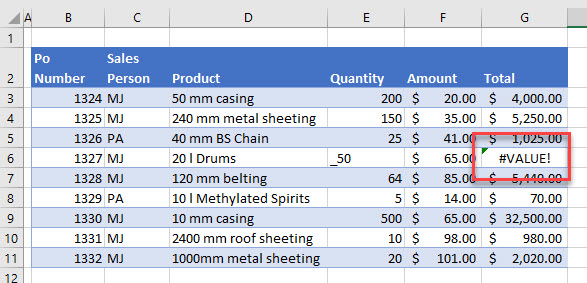
If your data contains error values, then the rows containing those errors aren’t included in the filtered result; your filter is not returning 100% correct data.
You need to ensure that your data does not contain any error values. You can use Excel’s error checking command to find your errors, or look for cells with green triangles. If an error is located, replace the error with valid data.
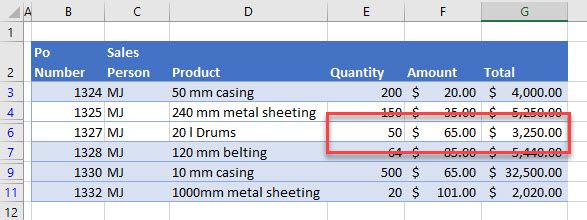
For example, in the graphic above, the value 50 has an underscore (_) in front of it resulting in the formula in the total column not calculating. If you remove the underscore, then the 50 becomes a value and the formula in the total column can calculate correctly.
Now, this data is ready to work accurately with an advanced filter.
General Filter Issues
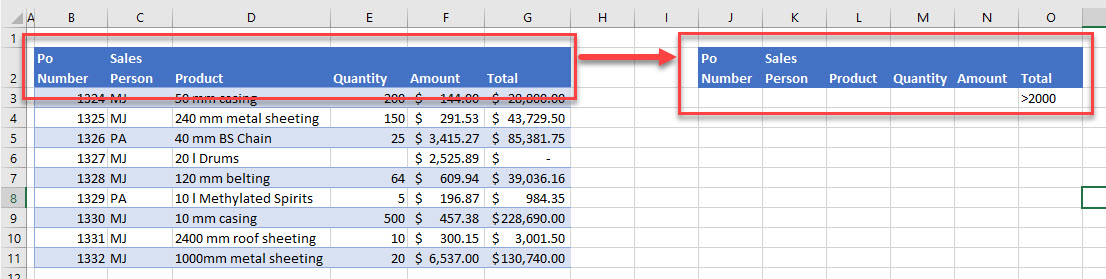
Incomplete Data Selection
If your data contains blank columns or rows, it can be easy to exclude some data from the filter. Excel doesn’t automatically recognize that the values below the blank row (or adjacent to a blank column) are part of the dataset.
It’s a good idea to select your data manually to ensure that you get all the data that you want to include. See our tutorials on deleting blank rows and blank columns.
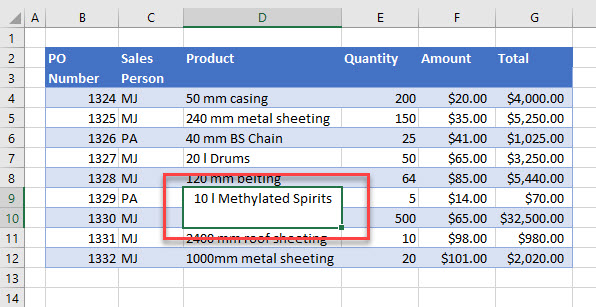
Merged Cells
If your column headings contain merged cells, the advanced filter won’t work.
This also applies if there are any merged cells within the actual data. Make sure that any column headings and rows within the data do not contain merged cells.
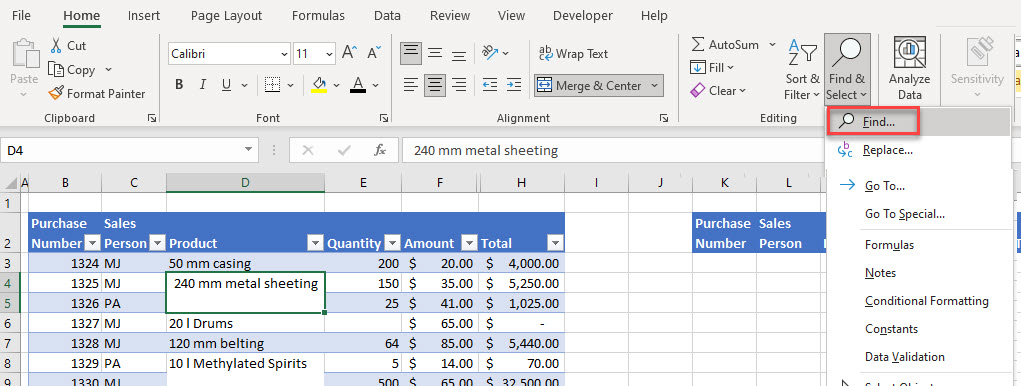
To find and unmerge any merged cells, follow these steps:
- Highlight your data.
- In the Ribbon, go to Home > Editing > Find & Select > Find…
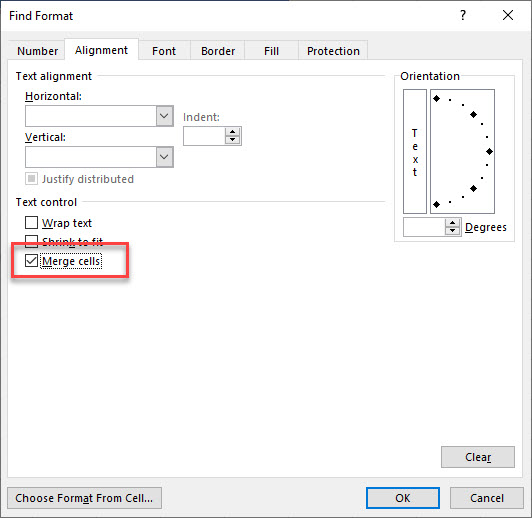
- In the Find and Replace dialog box, click Format…
- Tick Merge cells, and then click OK.
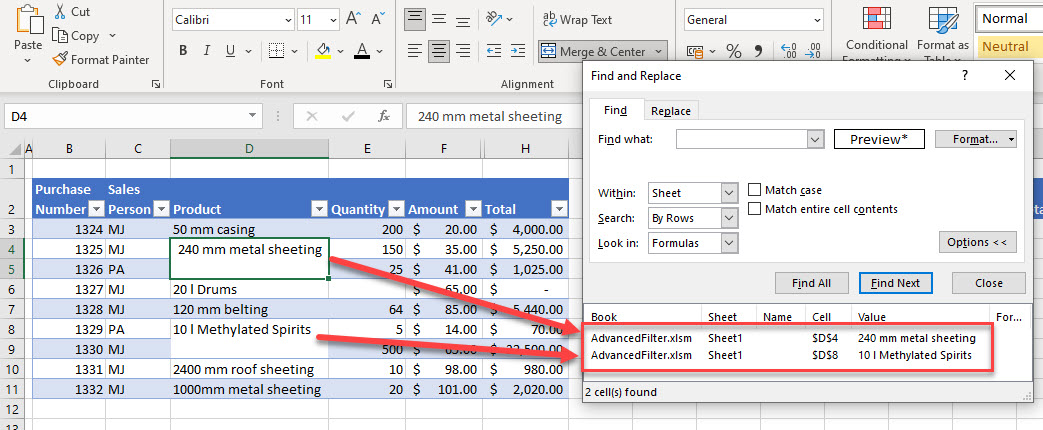
- Click Find All to identify the merged cells in the dataset.
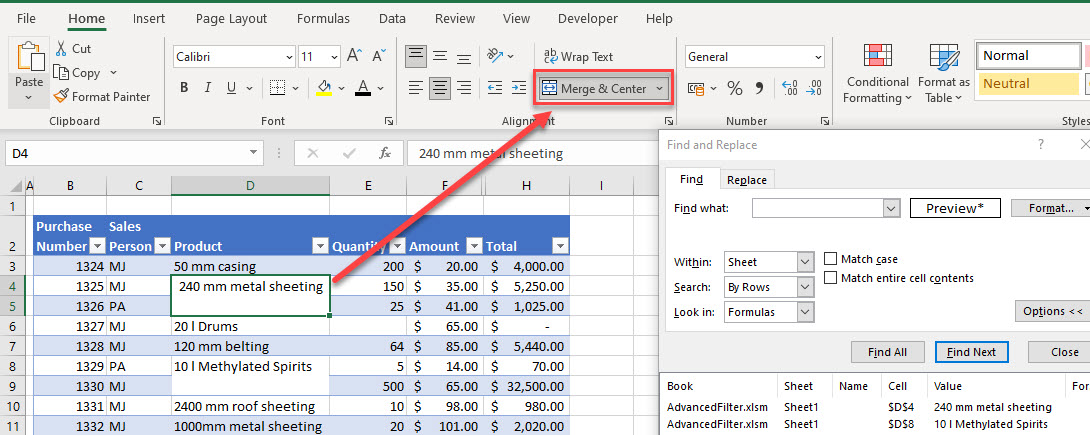
- To remove the merge, select the cell, and then, in the Ribbon, go to Home > Alignment > Merge & Center.
- You do not have to close the Find and Replace box while you do this which enables you to make sure that you unmerge all the necessary cells.
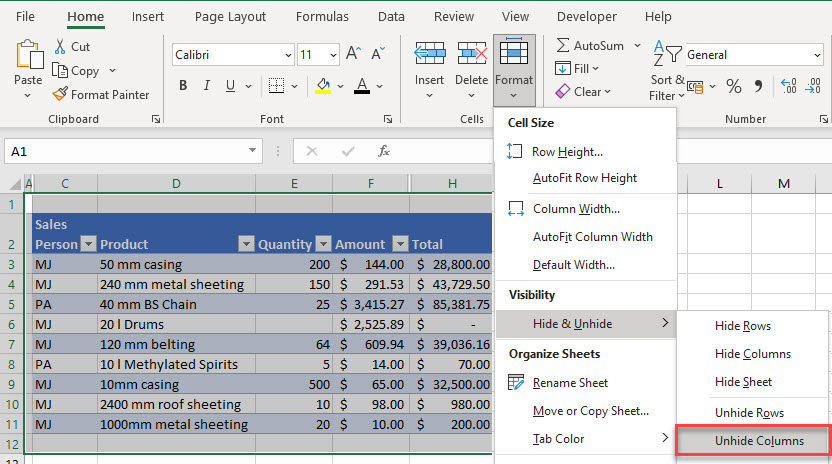
Hidden Columns
If you have hidden columns in your data, a filter may not work, depending on whether or not you have data in the hidden column(s).
If you click in a data table and apply a filter, you encounter the issue of incomplete data selection described above if the hidden columns are blank.
On the other hand, if the column is not blank but is hidden, then a filter is applied to the column but is unable to be used due to the column not being visible!
- To unhide any blank columns, select all the data – including the columns to the right and left of your data to include any hidden columns.
- Then in the Ribbon, go to Home > Cells > Format > Hide & Unhide > Unhide Columns.
All the columns in the data range should then be visible.
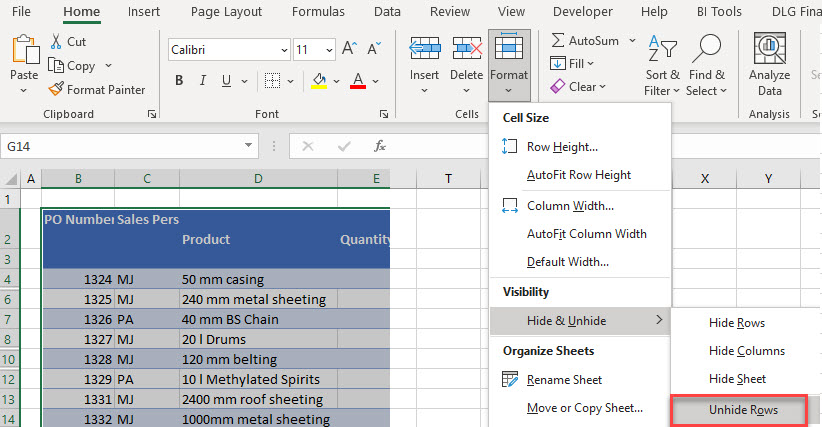
Hidden Rows
If you have hidden rows that are blank or do not contain the same kind/format of data as the range filtered on, you may get an error message or incorrectly filtered data. Filters work on rows that are initially hidden, but only if those rows are a part of a clean database.
To make sure all rows are unhidden in your data, select the data and then, in the Ribbon, go to Home > Cells > Format > Hide & Unhide > Unhide Rows.
I’m trying to filter a column based on values in another column. I click on the column that I want to filter (I click on «A» in sheet 1). The whole column is selected. I click on advanced filter. I click the button to select the second column. I go to sheet 2 and click on «A». That’s my column with the filter criteria. I click OK and nothing happens. All records are returned. How the heck does that thing work?
EDIT
I finally found out why. The column that you use as filter criteria has to have the same header name as the column that you want to filter … that’s so stupid -_- why wouldn’t you allow someone to filter a column based on a simple list of values without header name?
asked Sep 26, 2017 at 7:55
user3182532user3182532
1,0675 gold badges22 silver badges37 bronze badges
2
You can use filter based on a column B that will have formula:
=COUNTIF(Sheet2!A:A,A2)
Now just filter column B all values that are greater than 0.
As for your issue with advanced filter just select data without header row when applying advanced filter.
answered Sep 26, 2017 at 8:06
zipazipa
27.1k6 gold badges43 silver badges58 bronze badges
5
Расширенный фильтр и немного магии
У подавляющего большинства пользователей Excel при слове «фильтрация данных» в голове всплывает только обычный классический фильтр с вкладки Данные — Фильтр (Data — Filter):
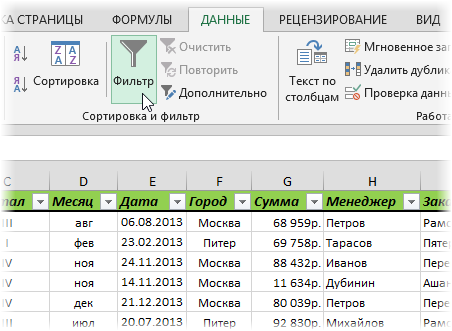
Такой фильтр — штука привычная, спору нет, и для большинства случаев вполне сойдет. Однако бывают ситуации, когда нужно проводить отбор по большому количеству сложных условий сразу по нескольким столбцам. Обычный фильтр тут не очень удобен и хочется чего-то помощнее. Таким инструментом может стать расширенный фильтр (advanced filter), особенно с небольшой «доработкой напильником» (по традиции).
Основа
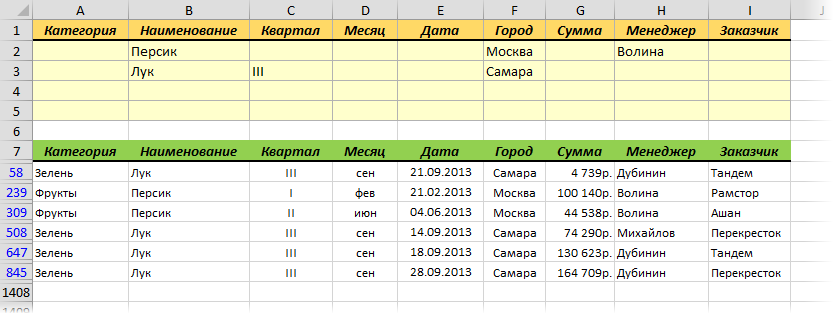
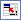
Для начала вставьте над вашей таблицей с данными несколько пустых строк и скопируйте туда шапку таблицы — это будет диапазон с условиями (выделен для наглядности желтым):
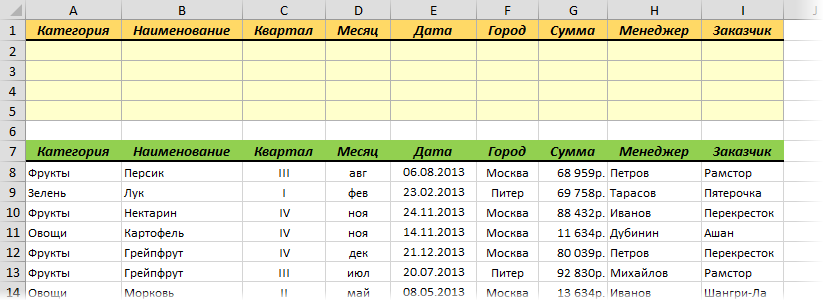
Между желтыми ячейками и исходной таблицей обязательно должна быть хотя бы одна пустая строка.
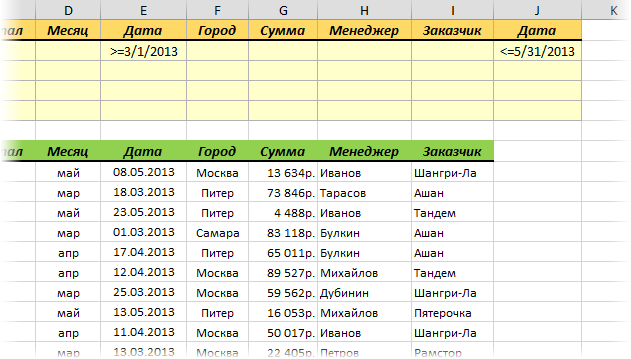
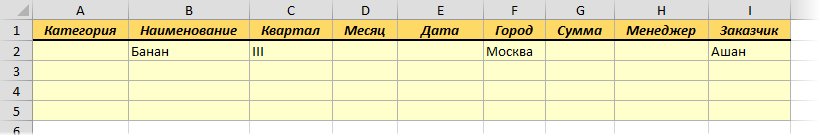
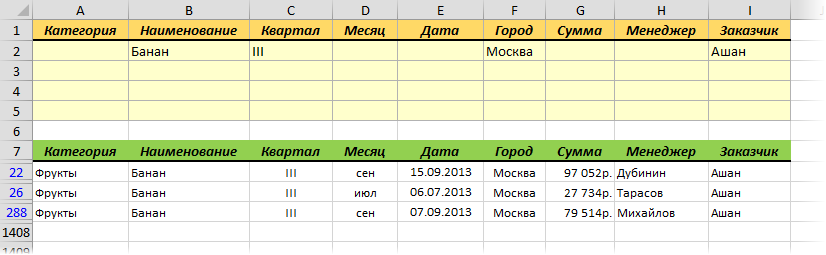
Именно в желтые ячейки нужно ввести критерии (условия), по которым потом будет произведена фильтрация. Например, если нужно отобрать бананы в московский «Ашан» в III квартале, то условия будут выглядеть так:
Чтобы выполнить фильтрацию выделите любую ячейку диапазона с исходными данными, откройте вкладку Данные и нажмите кнопку Дополнительно (Data — Advanced). В открывшемся окне должен быть уже автоматически введен диапазон с данными и нам останется только указать диапазон условий, т.е. A1:I2:
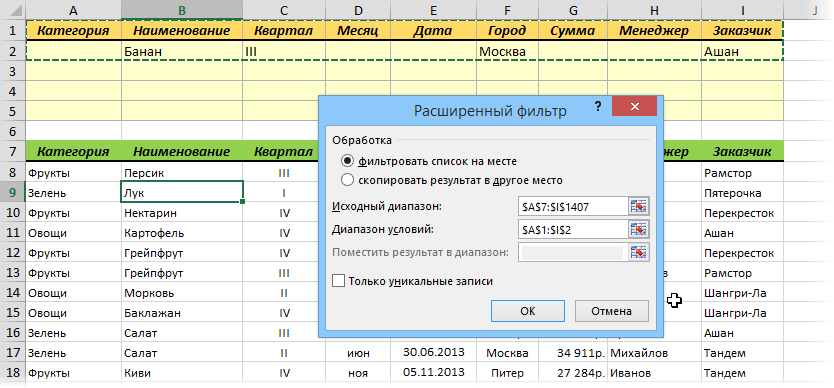
Обратите внимание, что диапазон условий нельзя выделять «с запасом», т.е. нельзя выделять лишние пустые желтые строки, т.к. пустая ячейка в диапазоне условий воспринимается Excel как отсутствие критерия, а целая пустая строка — как просьба вывести все данные без разбора.
Переключатель Скопировать результат в другое место позволит фильтровать список не прямо тут же, на этом листе (как обычным фильтром), а выгрузить отобранные строки в другой диапазон, который тогда нужно будет указать в поле Поместить результат в диапазон. В данном случае мы эту функцию не используем, оставляем Фильтровать список на месте и жмем ОК. Отобранные строки отобразятся на листе:
Добавляем макрос
«Ну и где же тут удобство?» — спросите вы и будете правы. Мало того, что нужно руками вводить условия в желтые ячейки, так еще и открывать диалоговое окно, вводить туда диапазоны, жать ОК. Грустно, согласен! Но «все меняется, когда приходят они ©» — макросы!
Работу с расширенным фильтром можно в разы ускорить и упростить с помощью простого макроса, который будет автоматически запускать расширенный фильтр при вводе условий, т.е. изменении любой желтой ячейки. Щелкните правой кнопкой мыши по ярлычку текущего листа и выберите команду Исходный текст (Source Code). В открывшееся окно скопируйте и вставьте вот такой код:
Private Sub Worksheet_Change(ByVal Target As Range)
If Not Intersect(Target, Range("A2:I5")) Is Nothing Then
On Error Resume Next
ActiveSheet.ShowAllData
Range("A7").CurrentRegion.AdvancedFilter Action:=xlFilterInPlace, CriteriaRange:=Range("A1").CurrentRegion
End If
End Sub
Эта процедура будет автоматически запускаться при изменении любой ячейки на текущем листе. Если адрес измененной ячейки попадает в желтый диапазон (A2:I5), то данный макрос снимает все фильтры (если они были) и заново применяет расширенный фильтр к таблице исходных данных, начинающейся с А7, т.е. все будет фильтроваться мгновенно, сразу после ввода очередного условия:
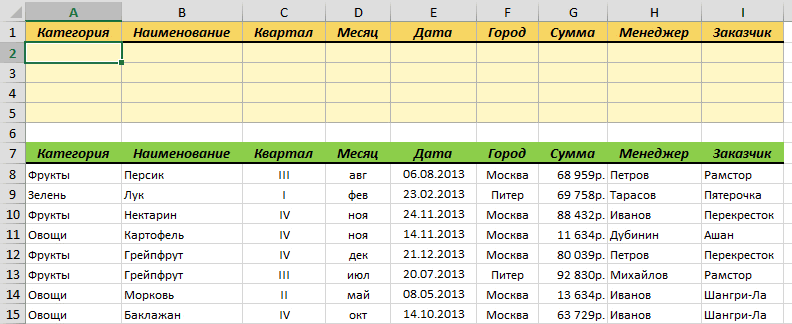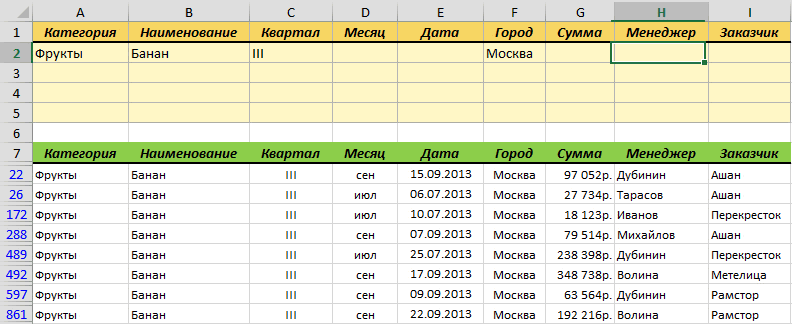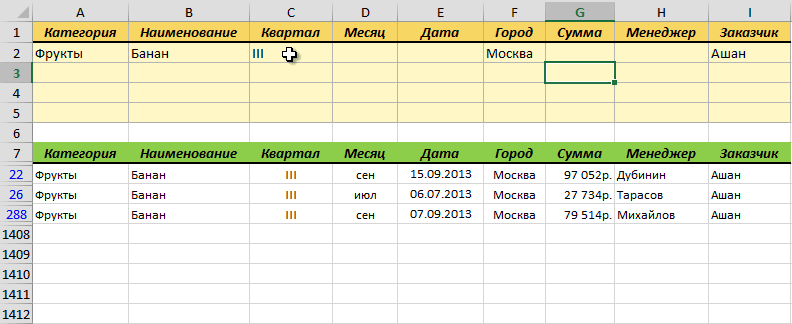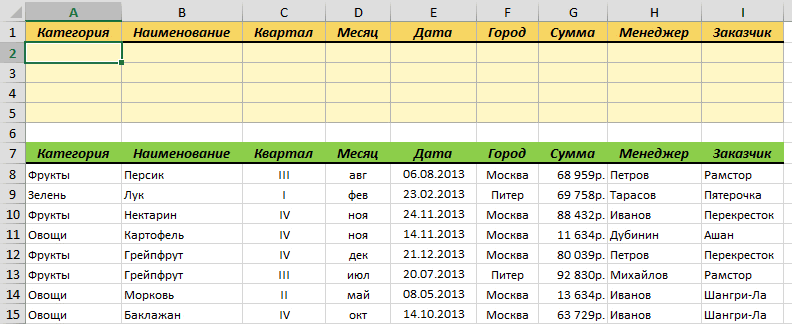
Так все гораздо лучше, правда? 
Реализация сложных запросов
Теперь, когда все фильтруется «на лету», можно немного углубиться в нюансы и разобрать механизмы более сложных запросов в расширенном фильтре. Помимо ввода точных совпадений, в диапазоне условий можно использовать различные символы подстановки (* и ?) и знаки математических неравенств для реализации приблизительного поиска. Регистр символов роли не играет. Для наглядности я свел все возможные варианты в таблицу:
| Критерий | Результат |
| гр* или гр | все ячейки начинающиеся с Гр, т.е. Груша, Грейпфрут, Гранат и т.д. |
| =лук | все ячейки именно и только со словом Лук, т.е. точное совпадение |
| *лив* или *лив | ячейки содержащие лив как подстроку, т.е. Оливки, Ливер, Залив и т.д. |
| =п*в | слова начинающиеся с П и заканчивающиеся на В т.е. Павлов, Петров и т.д. |
| а*с | слова начинающиеся с А и содержащие далее С, т.е. Апельсин, Ананас, Асаи и т.д. |
| =*с | слова оканчивающиеся на С |
| =???? | все ячейки с текстом из 4 символов (букв или цифр, включая пробелы) |
| =м??????н | все ячейки с текстом из 8 символов, начинающиеся на М и заканчивающиеся на Н, т.е. Мандарин, Мангостин и т.д. |
| =*н??а | все слова оканчивающиеся на А, где 4-я с конца буква Н, т.е. Брусника, Заноза и т.д. |
| >=э | все слова, начинающиеся с Э, Ю или Я |
| <>*о* | все слова, не содержащие букву О |
| <>*вич | все слова, кроме заканчивающихся на вич (например, фильтр женщин по отчеству) |
| = | все пустые ячейки |
| <> | все непустые ячейки |
| >=5000 | все ячейки со значением больше или равно 5000 |
| 5 или =5 | все ячейки со значением 5 |
| >=3/18/2013 | все ячейки с датой позже 18 марта 2013 (включительно) |
Тонкие моменты:
- Знак * подразумевает под собой любое количество любых символов, а ? — один любой символ.
- Логика в обработке текстовых и числовых запросов немного разная. Так, например, ячейка условия с числом 5 не означает поиск всех чисел, начинающихся с пяти, но ячейка условия с буквой Б равносильна Б*, т.е. будет искать любой текст, начинающийся с буквы Б.
- Если текстовый запрос не начинается со знака =, то в конце можно мысленно ставить *.
- Даты надо вводить в штатовском формате месяц-день-год и через дробь (даже если у вас русский Excel и региональные настройки).
Логические связки И-ИЛИ
Условия записанные в разных ячейках, но в одной строке — считаются связанными между собой логическим оператором И (AND):
Т.е. фильтруй мне бананы именно в третьем квартале, именно по Москве и при этом из «Ашана».
Если нужно связать условия логическим оператором ИЛИ (OR), то их надо просто вводить в разные строки. Например, если нам нужно найти все заказы менеджера Волиной по московским персикам и все заказы по луку в третьем квартале по Самаре, то это можно задать в диапазоне условий следующим образом:
Если же нужно наложить два или более условий на один столбец, то можно просто продублировать заголовок столбца в диапазоне критериев и вписать под него второе, третье и т.д. условия. Вот так, например, можно отобрать все сделки с марта по май:
В общем и целом, после «доработки напильником» из расширенного фильтра выходит вполне себе приличный инструмент, местами не хуже классического автофильтра.
Ссылки по теме
- Суперфильтр на макросах
- Что такое макросы, куда и как вставлять код макросов на Visual Basic
- Умные таблицы в Microsoft Excel
Advanced filter in Excel provides more opportunities for managing on data management spreadsheets. It is more complex in settings, but much more effective in action.
Using a standard filter, a Microsoft Excel user can solve not all of the tasks that are set. There is no visual display of the applied filtering conditions. It is not possible to apply more than two selection criteria. You can not filter the duplicate values to leave only unique records. And the criteria themselves are schematic and simple. The functionality of the extended filter is much richer. Let’s take a closer look at its possibilities.
How to make the advanced filter in Excel?
The advanced filter allows you to analysis data on an unlimited set of conditions. With this tool, the user can:
- to specify more than two selection criteria;
- to copy the result of filtering to another sheet;
- to set the condition of any complexity with the helping of formulas;
- to extract the unique values.
The algorithm for applying the extended filter is simple.
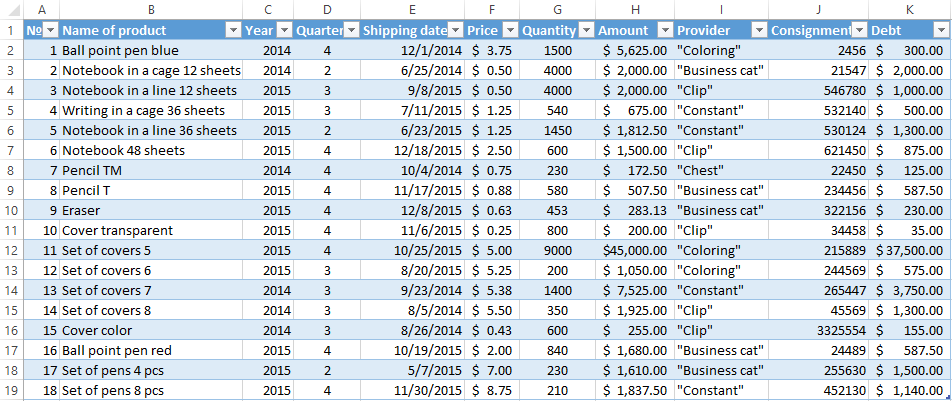
- To make the table with the original data or to open an existing one. Like so:
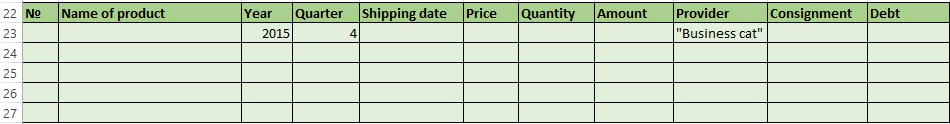
- To create the condition table. The features: the header line is the same with the «cap» of the filtered table. To avoid errors, need to copy the header line in the source table and paste it on the same sheet (side, top, underarm) or on another sheet. We enter the selection criteria into the condition table.
- Go to the «DATA» tab — «Sort and filter» — «Advanced». If the filtered information should be displayed on another sheet (NOT where the source table is), then you need to run the extended filter from another sheet.
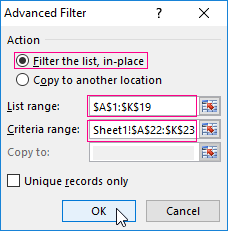
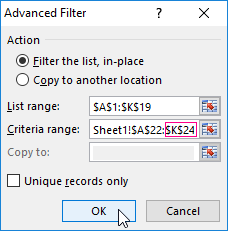
- In the «Advanced Filter» window that opens, to select the method of processing information (on the same sheet or on the other one), set the initial range (the table 1, example) and the range of conditions (the table 2, conditions). The header lines must be included in the ranges.
- To close the «Advanced Filter» window, click OK. We see the result.
The top table is the result of the filtering. The lower nameplate with the conditions is given for clarity near.
How to use the advanced filter in Excel?
To cancel the action of the advanced filter, we place the cursor anywhere in the table and press Ctrl + Shift + L or «DATA» — «Sort and Filter» — «Clear».
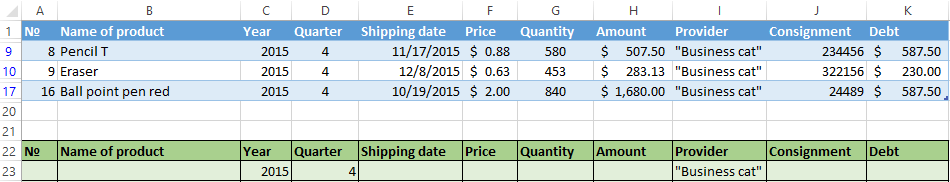
We will find using the «Advanced Filter» tool information on the values that contain the word «Set».
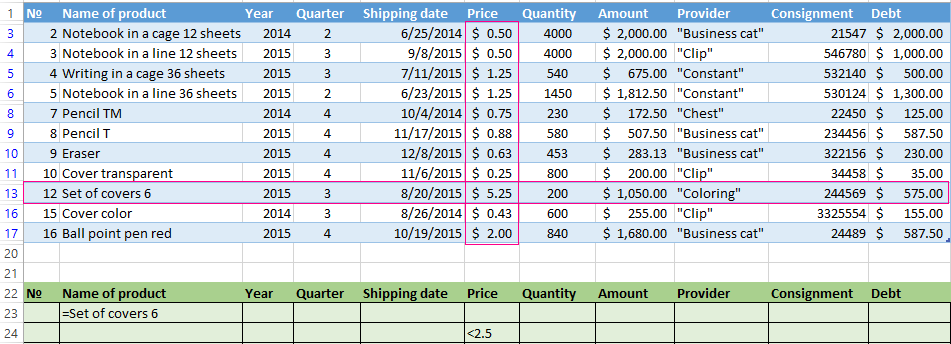
In the table of conditions we bring in the criteria. For example, these are:
The program in this case will search for all information on the goods, in the title of which there is the word «Set».
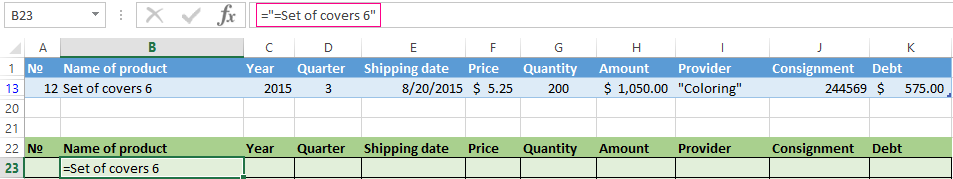
To search for the exact value, you can use the «=» sign. We enter the following criteria in the condition table:
Excel sees the «=» as a signal: the user will set the formula now. In order for the program to work correctly, the following should be written in the formula line: =»=Set of covers 6″.
After using the «Advanced Filter»:
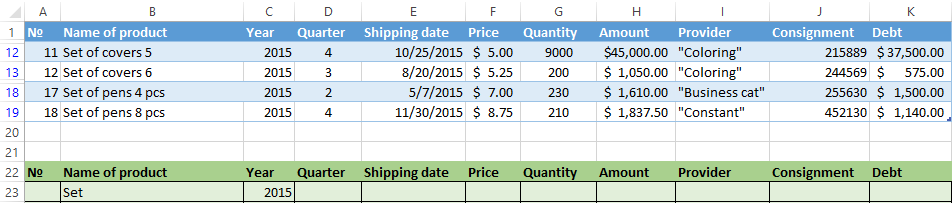
We filter the source table by the condition «OR» for different columns now. The operator «OR» is also in the tool «AutoFilter». But there it can be used within the single column.
In the condition label we introduce the selection criteria: =»=Set of covers 6″. (In the column «Name of product») and = «<2.5$» (in the column «Price»). That is, the program must select those values that contain the EXACTLY information about the good «Set of covers 6 ». OR to the information about the goods, which price is <2.5.
Please note: the criteria must be written under the corresponding headings in the DIFFERENT lines.
The result of selection:
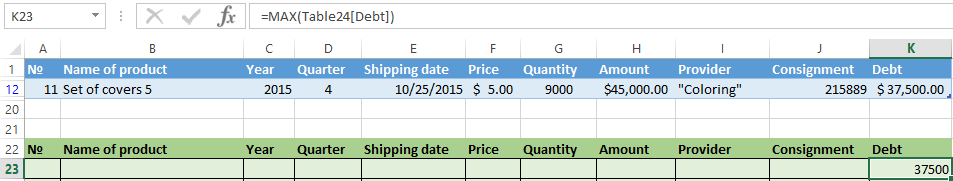
The advanced filter allows you to use as a criterion of a formula. Let’s consider the example.
Selection of the line with the maximum indebtedness: =MAX(Table1[Debt]).
So we get the results as after running several filters on the one Excel sheet.
How to make few filters in Excel?
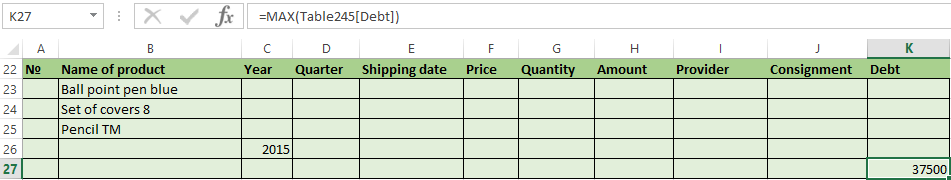
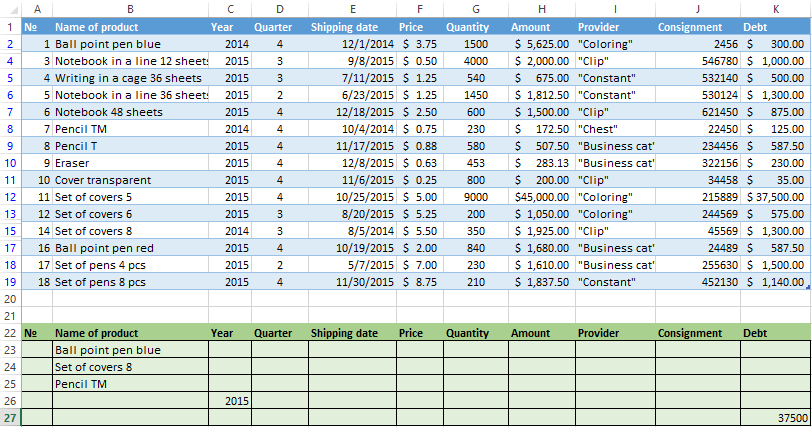
Let’s create the filter by several values. To do this, we enter in the table of conditions several criteria for selecting data:
Apply the tool «Advanced Filter»:
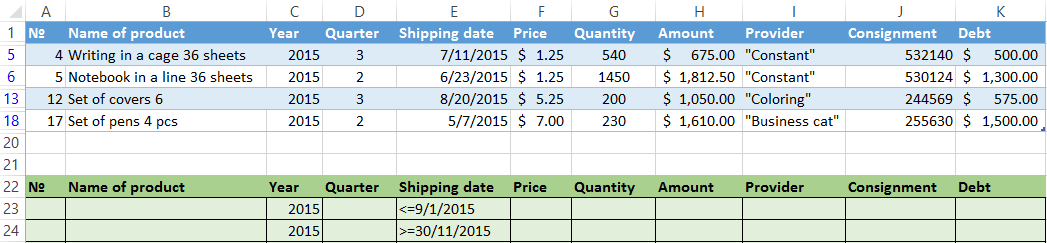
Now from the table with the selected data we will extract new information, which was selected according to other criteria. There are only shipping date for autumn 2015 (from September to November). Example:
We introduce a new criterion in the condition table and apply the filtering tool. The initial range — is the table with data selected according to the previous criterion. This is how the filter is performed across on several columns.
To use few filters, you can create several condition tables on the new sheets. The method of implementation depends from the task which was set by user.
How to make the filter in Excel by lines?
By standard methods — you may not do it by any ways. Microsoft Excel selects data only in columns. Therefore, we need to look for other solutions.
Here are some examples of string criteria for the extended filter in Excel:
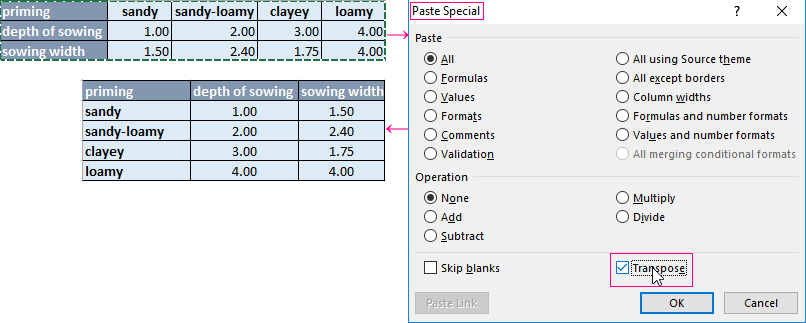
- Convert to the table. For example, from three rows make a list of three columns and apply the filtering to the transformed version.
- Use formulas to display exactly the data in the string that are needed. For example, make some indicator drop-down list. And in the next cell, enter the formula using the IF function. When a certain value is selected from the drop-down list, its parameter appears next to it.
To give an example of how the filter works by rows in Excel, we are creating the label:
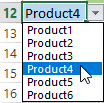
For the list of products, we create the drop-down list:
If necessary, learn how to create a drop-down list in Excel.
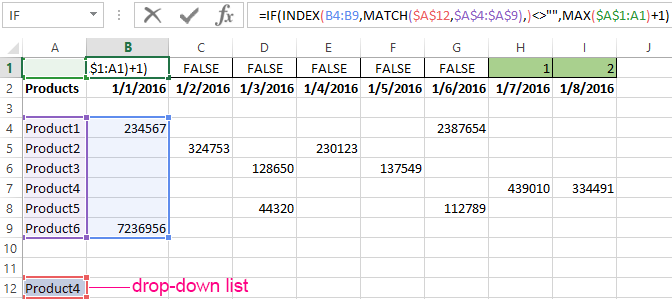
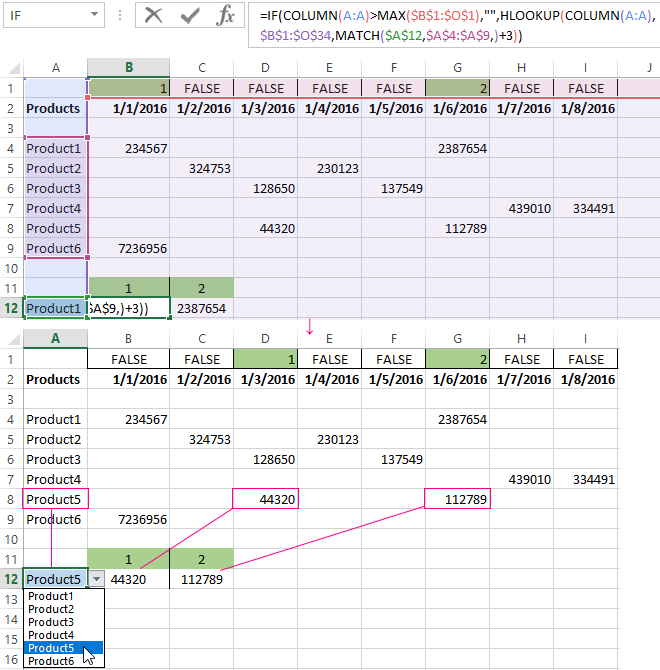
Above the table with the original data, we insert an empty line. In the cells, we introduce the formula that will show which columns the information is taken from.
Next to the drop-down list box, we enter the following formula:
Its task is select from the table those values, that correspond to a certain good.
Download examples of advanced filtering
Thus, using the tool «Drop-down list» and built-in functions Excel selects data in rows according to a certain criterion.

 .
.