Содержание
- AddIn object (Excel)
- Remarks
- Example
- Properties
- See also
- Support and feedback
- Объект AddIns (Excel)
- Замечания
- Пример
- Методы
- Свойства
- См. также
- Поддержка и обратная связь
- How to automatically install and activate an Excel Addin using VBA code
- Объект AddIn (Excel)
- Замечания
- Пример
- Свойства
- См. также
- Поддержка и обратная связь
- Метод AddIns.Add (Excel)
- Синтаксис
- Параметры
- Возвращаемое значение
- Замечания
- Пример
- Поддержка и обратная связь
AddIn object (Excel)
Represents a single add-in, either installed or not installed.
The AddIn object is a member of the AddIns collection. The AddIns collection contains a list of all the add-ins available to Microsoft Excel, regardless of whether they’re installed. This list corresponds to the list of add-ins displayed in the Add-Ins dialog box.
Example
Use AddIns (index), where index is the add-in title or index number, to return a single AddIn object. The following example installs the Analysis Toolpak add-in.
Don’t confuse the add-in title, which appears in the Add-Ins dialog box, with the add-in name, which is the file name of the add-in. You must spell the add-in title exactly as it’s spelled in the Add-Ins dialog box, but the capitalization doesn’t have to match.
The index number represents the position of the add-in in the Add-ins available box in the Add-Ins dialog box. The following example creates a list that contains specified properties of the available add-ins.
The Add method adds an add-in to the list of available add-ins but doesn’t install the add-in. Set the Installed property of the add-in to True to install the add-in.
To install an add-in that doesn’t appear in the list of available add-ins, you must first use the Add method and then set the Installed property. This can be done in a single step, as shown in the following example (note that you use the name of the add-in, not its title, with the Add method).
Use Workbooks (index), where index is the add-in file name (not title) to return a reference to the workbook corresponding to a loaded add-in. You must use the file name because loaded add-ins don’t normally appear in the Workbooks collection. This example sets the wb variable to the workbook for Myaddin.xla.
The following example sets the wb variable to the workbook for the Analysis Toolpak add-in.
If the Installed property returns True, but the calls to functions in the add-in still fail, the add-in may not actually be loaded. This is because the Addin object represents the existence and installed state of the add-in but doesn’t represent the actual contents of the add-in workbook.To guarantee that an installed add-in is loaded, you should open the add-in workbook.
The following example opens the workbook for the add-in named «My Addin» if the add-in isn’t already present in the Workbooks collection.
Properties
See also
Support and feedback
Have questions or feedback about Office VBA or this documentation? Please see Office VBA support and feedback for guidance about the ways you can receive support and provide feedback.
Источник
Объект AddIns (Excel)
Коллекция объектов AddIn , представляющая все надстройки, доступные в Microsoft Excel, независимо от того, установлены ли они.
Замечания
Этот список соответствует списку надстроек, отображаемым в диалоговом окне Надстройки .
Пример
Используйте свойство Application , чтобы вернуть коллекцию AddIns . В следующем примере создается список, содержащий имена и установленные состояния всех доступных надстроек.
Используйте метод Add , чтобы добавить надстройку в список доступных надстроек. Метод Add добавляет надстройку в список, но не устанавливает ее. Установите для свойства Установленные надстройки значение True , чтобы установить надстройку.
Чтобы установить надстройку, которая не отображается в списке доступных надстроек, необходимо сначала использовать метод Add , а затем задать свойство Installed . Это можно сделать за один шаг, как показано в следующем примере (обратите внимание, что в методе Add используется имя надстройки, а не ее название).
Используйте AddIns (index), где index — это название или номер индекса надстройки, чтобы вернуть один объект AddIn . В следующем примере устанавливается надстройка «Инструмент анализа».
Не путайте заголовок надстройки, который отображается в диалоговом окне Надстройки , с именем надстройки, которое является именем файла надстройки. Заголовок надстройки должен быть написан точно так же, как в диалоговом окне Надстройки , но заглавная буква не должна совпадать.
Методы
Свойства
См. также
Поддержка и обратная связь
Есть вопросы или отзывы, касающиеся Office VBA или этой статьи? Руководство по другим способам получения поддержки и отправки отзывов см. в статье Поддержка Office VBA и обратная связь.
Источник
How to automatically install and activate an Excel Addin using VBA code
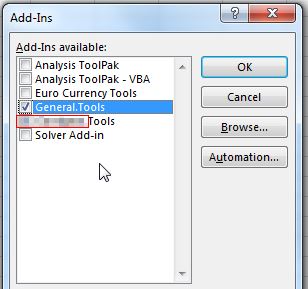
When you create Excel Addins and distribute them to a lot of users, normally the users must copy the Add-in files into the “Addins” folder from the path: “C:Usersuser_nameAppDataRoamingMicrosoftAddIns” and after that to activate the Addin from Excel:
Because these steps take time, the users must follow them everytime when you send a new version of the Addin and sometimes they forget what to do, I created a VBA code which installs and activates automatically a specified Addin file.
How it works ?
- Create a new folder with the INSTALL.xlsm file (which can be downloaded at the end of this post) and your Addin.xlam file. (the files must be in the same folder !):
- Open the INSTALL.xlsm file and in the VBA Developer- Module1, install_add_in() procedure change the fileName variable assignment with the name of your addin file:
- Save the file, create a *.zip/*.rar archive with the folder and send it to all users.
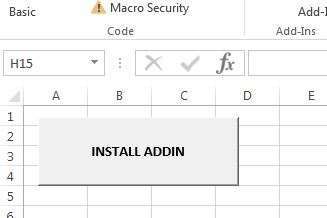
- The users will now Install and activate automatically the Addin by opening the INSTALL.xlsm file and just pressing the “INSTALL ADDIN” button.
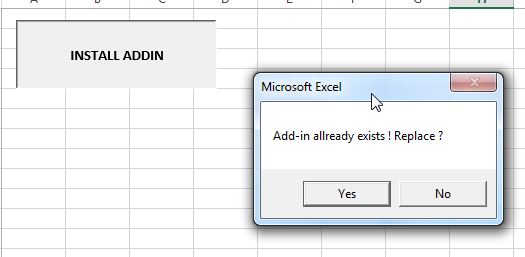
- If an old version of the Addin already exists in the Addins folder, the user will be asked to confirm if he wants to replace it with the new file.
–> Using this code the users will not have to remember where to copy the files and how to activate the Addins.
Источник
Объект AddIn (Excel)
Представляет одну надстройку, установленную или не установленную.
Замечания
Объект AddIn является членом коллекции AddIns . Коллекция AddIns содержит список всех надстроек, доступных для Microsoft Excel, независимо от того, установлены ли они. Этот список соответствует списку надстроек, отображаемым в диалоговом окне Надстройки .
Пример
Используйте AddIns (index), где index — это название или номер индекса надстройки, чтобы вернуть один объект AddIn . В следующем примере устанавливается надстройка «Инструмент анализа».
Не путайте заголовок надстройки, который отображается в диалоговом окне Надстройки , с именем надстройки, которое является именем файла надстройки. Заголовок надстройки должен быть написан точно так же, как в диалоговом окне Надстройки , но заглавная буква не должна совпадать.
Номер индекса представляет позицию надстройки в поле Доступные надстройки в диалоговом окне Надстройки . В следующем примере создается список, содержащий указанные свойства доступных надстроек.
Метод Add добавляет надстройку в список доступных надстроек, но не устанавливает ее. Установите для свойства Установленные надстройки значение True , чтобы установить надстройку.
Чтобы установить надстройку, которая не отображается в списке доступных надстроек, необходимо сначала использовать метод Add , а затем задать свойство Installed . Это можно сделать за один шаг, как показано в следующем примере (обратите внимание, что в методе Add используется имя надстройки, а не ее название).
Используйте книги (индекс), где index — это имя файла надстройки (а не название), чтобы вернуть ссылку на книгу, соответствующую загруженной надстройке. Необходимо использовать имя файла, так как загруженные надстройки обычно не отображаются в коллекции Книги . В этом примере переменная wb задает книгу для Myaddin.xla.
В следующем примере переменная wb задается в книге для надстройки «Инструмент анализа».
Если свойство Installed возвращает значение True, но вызовы функций в надстройке по-прежнему завершаются ошибкой, надстройка может не быть загружена. Это связано с тем, что объект Addin представляет существование и состояние установки надстройки, но не представляет фактическое содержимое книги надстройки. Чтобы гарантировать загрузку установленной надстройки, откройте книгу надстройки.
В следующем примере открывается книга для надстройки с именем «Моя надстройка», если надстройка еще не присутствует в коллекции Книги .
Свойства
См. также
Поддержка и обратная связь
Есть вопросы или отзывы, касающиеся Office VBA или этой статьи? Руководство по другим способам получения поддержки и отправки отзывов см. в статье Поддержка Office VBA и обратная связь.
Источник
Метод AddIns.Add (Excel)
Добавляет новый файл надстройки в список надстроек. Возвращает объект AddIn .
Синтаксис
expression. Add (FileName, CopyFile)
Выражение Переменная, представляющая объект AddIns .
Параметры
| Имя | Обязательный или необязательный | Тип данных | Описание |
|---|---|---|---|
| FileName | Обязательный | String | Имя файла, содержащего надстройку или ProgID надстройки автоматизации, которую вы хотите добавить в список в диспетчере надстроек. |
| CopyFile | Необязательный | Variant | Игнорируется, если файл надстройки находится на жестком диске. Значение true , чтобы скопировать надстройку на жесткий диск, если надстройка находится на съемном носителе (например, на компакт-диске). Значение false , чтобы надстройка оставалась на съемном носителе. Если этот аргумент опущен, Microsoft Excel отобразит диалоговое окно с запросом на выбор. |
Возвращаемое значение
Объект AddIn , представляющий новую надстройку.
Замечания
Этот метод не устанавливает новую надстройку. Чтобы установить надстройку, необходимо задать свойство Установленные .
Пример
В этом примере надстройка Myaddin.xla вставляется из диска A. При выполнении этого примера Microsoft Excel копирует файл A:Myaddin.xla в папку Library на жестком диске и добавляет заголовок надстройки в список в диалоговом окне Надстройки .
Поддержка и обратная связь
Есть вопросы или отзывы, касающиеся Office VBA или этой статьи? Руководство по другим способам получения поддержки и отправки отзывов см. в статье Поддержка Office VBA и обратная связь.
Источник
| title | keywords | f1_keywords | ms.prod | api_name | ms.assetid | ms.date | ms.localizationpriority |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
AddIn object (Excel) |
vbaxl10.chm184072 |
vbaxl10.chm184072 |
excel |
Excel.AddIn |
ad26800d-5342-fb4c-01f3-05b7eceb7ffd |
03/29/2019 |
medium |
AddIn object (Excel)
Represents a single add-in, either installed or not installed.
Remarks
The AddIn object is a member of the AddIns collection. The AddIns collection contains a list of all the add-ins available to Microsoft Excel, regardless of whether they’re installed. This list corresponds to the list of add-ins displayed in the Add-Ins dialog box.
Example
Use AddIns (index), where index is the add-in title or index number, to return a single AddIn object. The following example installs the Analysis Toolpak add-in.
AddIns("analysis toolpak").Installed = True
Don’t confuse the add-in title, which appears in the Add-Ins dialog box, with the add-in name, which is the file name of the add-in. You must spell the add-in title exactly as it’s spelled in the Add-Ins dialog box, but the capitalization doesn’t have to match.
The index number represents the position of the add-in in the Add-ins available box in the Add-Ins dialog box. The following example creates a list that contains specified properties of the available add-ins.
With Worksheets("sheet1") .Rows(1).Font.Bold = True .Range("a1:d1").Value = _ Array("Name", "Full Name", "Title", "Installed") For i = 1 To AddIns.Count .Cells(i + 1, 1) = AddIns(i).Name .Cells(i + 1, 2) = AddIns(i).FullName .Cells(i + 1, 3) = AddIns(i).Title .Cells(i + 1, 4) = AddIns(i).Installed Next .Range("a1").CurrentRegion.Columns.AutoFit End With
The Add method adds an add-in to the list of available add-ins but doesn’t install the add-in. Set the Installed property of the add-in to True to install the add-in.
To install an add-in that doesn’t appear in the list of available add-ins, you must first use the Add method and then set the Installed property. This can be done in a single step, as shown in the following example (note that you use the name of the add-in, not its title, with the Add method).
AddIns.Add("generic.xll").Installed = True
Use Workbooks (index), where index is the add-in file name (not title) to return a reference to the workbook corresponding to a loaded add-in. You must use the file name because loaded add-ins don’t normally appear in the Workbooks collection. This example sets the wb variable to the workbook for Myaddin.xla.
Set wb = Workbooks("myaddin.xla")
The following example sets the wb variable to the workbook for the Analysis Toolpak add-in.
Set wb = Workbooks(AddIns("analysis toolpak").Name)
If the Installed property returns True, but the calls to functions in the add-in still fail, the add-in may not actually be loaded. This is because the Addin object represents the existence and installed state of the add-in but doesn’t represent the actual contents of the add-in workbook.To guarantee that an installed add-in is loaded, you should open the add-in workbook.
The following example opens the workbook for the add-in named «My Addin» if the add-in isn’t already present in the Workbooks collection.
On Error Resume Next ' turn off error checking Set wbMyAddin = Workbooks(AddIns("My Addin").Name) lastError = Err On Error Goto 0 ' restore error checking If lastError <> 0 Then ' the add-in workbook isn't currently open. Manually open it. Set wbMyAddin = Workbooks.Open(AddIns("My Addin").FullName) End If
Properties
- Application
- CLSID
- Creator
- FullName
- Installed
- IsOpen
- Name
- Parent
- Path
- progID
See also
- Excel Object Model reference
[!includeSupport and feedback]
When you create Excel Addins and distribute them to a lot of users, normally the users must copy the Add-in files into the “Addins” folder from the path: “C:Usersuser_nameAppDataRoamingMicrosoftAddIns” and after that to activate the Addin from Excel:
Because these steps take time, the users must follow them everytime when you send a new version of the Addin and sometimes they forget what to do, I created a VBA code which installs and activates automatically a specified Addin file.
How it works ?
- Create a new folder with the INSTALL.xlsm file (which can be downloaded at the end of this post) and your Addin.xlam file. (the files must be in the same folder !):
- Open the INSTALL.xlsm file and in the VBA Developer- Module1, install_add_in() procedure change the fileName variable assignment with the name of your addin file:
Sub install_add_in() Dim mypath As String, strfile As String, fileName As String mypath = ActiveWorkbook.Path fileName = "General.Tools" 'replace General.Tools with the name of your Add-in !!! strfile = "" & fileName & ".xlam" file_to_copy = mypath & strfile folder_to_copy = Environ("Appdata") & "MicrosoftAddIns" copied_file = folder_to_copy & strfile 'Check if add-in is installed If Len(Dir(copied_file)) = 0 Then 'if add-in does not exist then copy the file FileCopy file_to_copy, copied_file AddIns(fileName).Installed = True MsgBox "Add-in installed" Else 'if add-in already exists then the user will decide if will replace it or not x = MsgBox("Add-in allready exists ! Replace ?", vbYesNo) If x = vbNo Then Exit Sub ElseIf x = vbYes Then 'deactivate the add-in if it is activated If AddIns(fileName).Installed = True Then AddIns(fileName).Installed = False End If 'delete the old file Kill copied_file 'copy the new file FileCopy file_to_copy, copied_file AddIns(fileName).Installed = True MsgBox "New Add-in Installed !" End If End If End Sub
- Save the file, create a *.zip/*.rar archive with the folder and send it to all users.
- The users will now Install and activate automatically the Addin by opening the INSTALL.xlsm file and just pressing the “INSTALL ADDIN” button.
- If an old version of the Addin already exists in the Addins folder, the user will be asked to confirm if he wants to replace it with the new file.
–> Using this code the users will not have to remember where to copy the files and how to activate the Addins.
Download the INSTALL.xlsm file:
INSTALL
An Excel Add-In is a file (usually with an .xla or .xll extension) that Excel can load when it starts up. The file contains code (VBA in the case of an .xla Add-In) that adds additional functionality to Excel, usually in the form of new functions.
Add-Ins provide an excellent way of increasing the power of Excel and they are the ideal vehicle for distributing your custom functions. Excel is shipped with a variety of Add-Ins ready for you to load and start using, and many third-party Add-Ins are available.
Setup
Open VBA Editor
Step 1. Open any Excel file
Step 2. With your new template open in Excel, on the Developer tab, click Visual Basic
- Hot key —
Alt+F11 - If you cannot find your
Developertab, follow the instructions at this page.
Step 3. Now you can work on your VBA code
- For
SubasWorkbook_Open(),Workbook_BeforeClose(Cancel As Boolean), please add your code toThisWorkbook. - For other
SuborFunction, you can either write inThisWorkbookor create a module to write in.
Save your add-in
Save your workbook as Microsoft Excel Add-in (*.xla, *.xlam) to C:WINDOWSApplication DataMicrosoftAddIns.
Then this add-in would be automatically add to your add-in group.
Create Custom Buttons
Create your custom buttons whenever a workbook is opened.
Private Sub Workbook_Open()
Application.DisplayAlerts = False
Dim CmdBar As CommandBar
Dim CmdBarCtl As CommandBarControl
Dim cmdBarSubCtl As CommandBarControl
On Error GoTo Err_Handler
Set CmdBar = Application.CommandBars("Worksheet Menu Bar")
CmdBar.Visible = True
CmdBar.Protection = msoBarNoMove
Set CmdBarCtl = CmdBar.Controls.Add(Type:=msoControlButton)
With CmdBarCtl
.BeginGroup = True
.Caption = "Single Button"
.Style = msoButtonCaption
.OnAction = "NameOfASub"
End With
Application.DisplayAlerts = True
Exit Sub
Set CmdBarCtl = CmdBar.Controls.Add(Type:=msoControlPopup)
CmdBarCtl.Caption = "Drop Down Button"
Set cmdBarSubCtl = CmdBarCtl.Controls.Add(Type:=msoControlButton)
With cmdBarSubCtl
.Style = msoButtonIconAndCaption
.Caption = "option 1"
.FaceId = 317
.OnAction = "NameOfASub"
.Parameter = 1
.BeginGroup = True
End With
Set cmdBarSubCtl = CmdBarCtl.Controls.Add(Type:=msoControlButton)
With cmdBarSubCtl
.Style = msoButtonIconAndCaption
.Caption = "option 2"
.FaceId = 318
.OnAction = "NameOfASub"
.Parameter = 2
.BeginGroup = True
End With
Set cmdBarSubCtl = CmdBarCtl.Controls.Add(Type:=msoControlButton)
With cmdBarSubCtl
.Style = msoButtonIconAndCaption
.Caption = "option 3"
.FaceId = 224
.OnAction = "NameOfASub"
.Parameter = 3
.BeginGroup = True
End With
Err_Handler:
MsgBox "Error " & Err.Number & vbCr & Err.Description
Application.DisplayAlerts = True
Exit Sub
End Sub
Note that you can refer to this link to choose the icon you want to show in the button.
Define Actions
.OnAction = "NameOfASub" means that a subfunction named NameOfASub is being called as an action of a click on the certain button. That is, you need to self-defined these actions.
Public Sub NameOfASub()
MsgBox("Hello World!")
End Sub
Delete Custom Buttons Before Closed
Make sure you delete the button on closing Excel, otherwise an additional one will be added everytime you open a workbook.
Private Sub Workbook_BeforeClose(Cancel As Boolean)
Dim CmdBar As CommandBar
Set CmdBar = Application.CommandBars("Worksheet Menu Bar")
CmdBar.Controls("Single Button").Delete
CmdBar.Controls("Drop Down Button").Delete
End Sub
VBA Models
For detail information, please refer to Excel VBA official Webpage
Variable Declaration
Declare a variable
Dim cmd
Declare a variable with data type
Dim cmd As String
Declare a global variable
Public path As String
Assign value to a variable
Remember to add Set at the beginning.
Set path = "C:my_folder"
Range
Represents a cell, a row, a column, a selection of cells containing one or more contiguous blocks of cells, or a 3-D range.
Get a specific cell
Dim cell As Range
cell = ActiveSheet.Cells(1, 1)
Get a Range object that represents the used range on the specified worksheet. Read-only.
Dim range As Range
range = ActiveSheet.UsedRange
'OR
range = ActiveSheet.Range("A1").CurrentRegion
Set value/formula of a Range object
ActiveSheet.Cells(1, 1).Value = 24
ActiveSheet.Cells(2, 1).Formula = "=Sum(B1:B5)"
Get the number of rows used
Dim uTotalRows As Integer
uTotalRows = ActiveSheet.UsedRange.Rows.Count
MsgBox (uTotalRows)
Define/Call a Function
Define a function.
[Modifiers] Function FunctionName [(ParameterList)] As ReturnType
….Statements….
End Function
Function hypotenuse(ByVal side1 As Single, ByVal side2 As Single) As Single
Return Math.Sqrt((side1 ^ 2) + (side2 ^ 2))
End Function
Call your defined function.
Dim testLength, testHypotenuse As Single
testHypotenuse = hypotenuse(testLength, 10.7)
String Concatenation
To concat string str1 with string str2, you can use the operator &.
Dim str1 As String
Dim str2 As String
...
Dim concat_str As String
concat_str = str1 & str2
Save the current workbook
ActiveWorkbook.Save
Get path and name of current workbook/sheet
Get path of current workbook
Dim path As String
path = Application.ActiveWorkbook.path
Get full path of current workbook (include workbook name)
Dim fullpath As String
fullpath = Application.ActiveWorkbook.FullName
Get name of current workbook
Dim bookname As String
bookname = ActiveWorkbook.Name
Get name of current sheet
Dim sheetname As String
sheetname = ActiveSheet.Name
Run an executable with parameters
Method 1. Use Shell
cmd = "myApp.exe" & " " & "myParameter"
retval = Shell(cmd, vbNormalFocus)
Method 2. Use WScript
(This method allows you to wait until the execution completes and returns.)
Set wsh = VBA.CreateObject("WScript.Shell")
Dim waitOnReturn As Boolean: waitOnReturn = True
Dim windowStyle As Integer: windowStyle = 1
cmd = "myApp.exe" & " " & "myParameter"
wsh.Run cmd, windowStyle, waitOnReturn
Open up an existing workbook
Open an existing workbook (pop-up)
Dim objXLApp, objXLWb
Set objXLApp = CreateObject("Excel.Application")
objXLApp.Visible = True
Set objXLWb = objXLApp.Workbooks.Open(report)
objXLWb.Sheets(sheetname).Activate
Open an existing workbook (invisible) in read-only mode
Dim wb As Workbook
Set wb = Workbooks.Open(Path_to_WB, True, True)
Flow Control
If Else
If condition [ Then ]
[ statements ]
[ ElseIf elseifcondition [ Then ]
[ elseifstatements ] ]
[ Else
[ elsestatements ] ]
End If
For more details, please refer to VBA condition syntax
Loop
For Loop simple example:
For i = 1 To 10
Total = Total + iArray(i)
Next i
For Loop example with Step:
For d = 0 To 10 Step 0.1
dTotal = dTotal + d
Next d
To break the for loop, use Exit For:
For i = 1 To 100
If dValues(i) = dVal Then
indexVal = i
Exit For
End If
Next i
For Each simple example:
For Each wSheet in Worksheets
MsgBox "Found Worksheet: " & wSheet.Name
Next wSheet
For more information, please refer to Excel VBA — For Loop, For Each, and Do Loop and Excel VBA Tutorial Part 6 — VBA Loops.
References
- Build an Excel Add-In
- 如何:在功能區顯示開發人員索引標籤
- Creating VBA Add-ins to Extend and Automate Microsoft Office Documents
- Excel VBA 參考
- face ID Table
- VBA condition syntax
- how to create an Excel VBA Userform
- Excel VBA Tutorial Part 6 — VBA Loops
- Excel VBA — For Loop, For Each, and Do Loop
I’ll give it a try. Please see comments in code.
ThisWorkbook
Option Explicit
'
'---------------------------------------------------------------------
' Purpose : Call for installation as an addin if not installed
'---------------------------------------------------------------------
'
Private Sub Workbook_Open()
Dim AddinTitle As String, AddinName As String
Dim XlsName As String
AddinTitle = Left(ThisWorkbook.Name, Len(ThisWorkbook.Name) - 4)
XlsName = AddinTitle & ".xlsm"
AddinName = AddinTitle & ".xla"
'check the addin's not already installed in UserLibraryPath
If Dir(Application.UserLibraryPath & AddinName) = Empty Then
'ask if user wants to install now
If MsgBox("Install " & AddinTitle & _
" as an add-in?", vbYesNo, _
"Install?") = vbYes _
Then
Run "InstallAddIn"
End If
Else
If ThisWorkbook.Name = XlsName Then
Run "ReInstall"
End If
End If
End Sub
'
'---------------------------------------------------------------------
' Purpose : Actuate the addin, add custom controls
'---------------------------------------------------------------------
'
Private Sub Workbook_AddinInstall()
Run "AddButtons"
End Sub
'
'---------------------------------------------------------------------
' Purpose : Deactivate the addin, remove custom controls
'---------------------------------------------------------------------
'
Private Sub Workbook_AddinUninstall()
Run "RemoveButtons"
End Sub
Module
Option Explicit
'
'---------------------------------------------------------------------
' Purpose : Convert .xls file to .xla, move it to
' addins folder, and install as addin
'---------------------------------------------------------------------
'
Private Sub InstallAddIn()
Dim AddinTitle As String, AddinName As String
Dim XlsVersion As String, MessageBody As String
With ThisWorkbook
AddinTitle = Left(.Name, Len(.Name) - 4)
AddinName = AddinTitle & ".xlam"
XlsVersion = .FullName '< could be anywhere
'check the addin's not installed in
'UserLibraryPath (error handling)
If Dir(Application.UserLibraryPath & AddinName) = Empty Then
.IsAddin = True '< hide workbook window
'move & save as .xla file
.SaveAs Application.UserLibraryPath & AddinName, 55
'go thru the add-ins collection to see if it's listed
If Listed Then
'check this addins checkbox in the addin dialog box
AddIns(AddinTitle).Installed = True '<--Error happening if .xlam format
Else
'it's not listed (not previously installed)
'add it to the addins collection
'and check this addins checkbox
AddIns.Add(ThisWorkbook.FullName, True) _
.Installed = True
End If
'inform user...
MessageBody = AddinTitle & " has been installed - " & _
"to access the tools available in" & _
vbNewLine & _
"this addin, you will find a button in the 'Tools' " & _
"menu for your use"
If BooksAreOpen Then '< quit if no other books are open
.Save
MsgBox MessageBody & "...", , AddinTitle & _
" Installation Status..."
Else
If MsgBox(MessageBody & " the" & vbNewLine & _
"next time you open Excel." & _
"" & vbNewLine & vbNewLine & _
"Quit Excel?...", vbYesNo, _
AddinTitle & " Installation Status...") = vbYes Then
Application.Quit
Else
.Save
End If
End If
End If
End With
End Sub
'---------------------------------------------------------------------
' Purpose : Checks if this addin is in the addin collection
'---------------------------------------------------------------------
'
Private Function Listed() As Boolean
Dim Addin As Addin, AddinTitle As String
Listed = False
With ThisWorkbook
AddinTitle = Left(.Name, Len(.Name) - 4)
For Each Addin In AddIns
If Addin.Title = AddinTitle Then
Listed = True
Exit For
End If
Next
End With
End Function
'---------------------------------------------------------------------
' Purpose : Check if any workbooks are open
' (this workbook & startups excepted)
'---------------------------------------------------------------------
'
Private Function BooksAreOpen() As Boolean
'
Dim Wb As Workbook, OpenBooks As String
'get a list of open books
For Each Wb In Workbooks
With Wb
If Not (.Name = ThisWorkbook.Name _
Or .Path = Application.StartupPath) Then
OpenBooks = OpenBooks & .Name
End If
End With
Next
If OpenBooks = Empty Then
BooksAreOpen = False
Else
BooksAreOpen = True
End If
End Function
'---------------------------------------------------------------------
' Purpose : Replace addin with another version if installed
'---------------------------------------------------------------------
'
Private Sub ReInstall()
Dim AddinName As String
With ThisWorkbook
AddinName = Left(.Name, Len(.Name) - 4) & ".xla"
'check if 'addin' is already installed
'in UserLibraryPath (error handling)
If Dir(Application.UserLibraryPath & AddinName) = Empty Then
'install if no previous version exists
Call InstallAddIn
Else
'delete installed version & replace with this one if ok
If MsgBox(" The target folder already contains " & _
"a file with the same name... " & _
vbNewLine & vbNewLine & _
" (That file was last modified on: " & _
Workbooks(AddinName) _
.BuiltinDocumentProperties("Last Save Time") & ")" & _
vbNewLine & vbNewLine & vbNewLine & _
" Would you like to replace the existing file with " & _
"this one? " & _
vbNewLine & vbNewLine & _
" (This file was last modified on: " & _
.BuiltinDocumentProperties("Last Save Time") & ")", _
vbYesNo, "Add-in Is In Place - " & _
"Confirm File Replacemant...") = vbYes Then
Workbooks(AddinName).Close False
Kill Application.UserLibraryPath & AddinName
Call InstallAddIn
End If
End If
End With
End Sub
'---------------------------------------------------------------------
' Purpose : Convert .xla file to .xls format
' and move it to default file path
'---------------------------------------------------------------------
'
Private Sub RemoveAddIn()
Dim AddinTitle As String, AddinName As String
Dim XlaVersion As String
Application.ScreenUpdating = False
With ThisWorkbook
AddinTitle = Left(.Name, Len(.Name) - 4)
AddinName = AddinTitle & ".xla"
XlaVersion = .FullName
'check the 'addin' is not already removed
'from UserLibraryPath (error handling)
If Not Dir(Application.UserLibraryPath & AddinName) = Empty _
Then
.Sheets(1).Cells.ClearContents '< cleanup
Call RemoveButtons
'move & save as .xls file
.SaveAs Application.DefaultFilePath & _
"" & AddinTitle & ".xls"
Kill XlaVersion '< delete .xla version
'uncheck checkbox in the addin dialog box
AddIns(AddinTitle).Installed = False
.IsAddin = False '< show workbook window
.Save
'inform user and close
MsgBox "The addin '" & AddinTitle & "' has been " & _
"removed and converted to an .xls file." & _
vbNewLine & vbNewLine & _
"Should you later wish to re-install this as " & _
"an addin, open the .xls file which" & _
vbNewLine & "can now be found in " & _
Application.DefaultFilePath & _
" as: '" & .Name & "'"
.Close
End If
End With
Application.ScreenUpdating = True
End Sub
'---------------------------------------------------------------------
' Purpose : Add addin control buttons
'---------------------------------------------------------------------
'
Private Sub AddButtons()
'change 'Startups...' to suit
Const MyControl As String = "Startups..."
'change 'Manage Startups' to suit
Const MyControlCaption As String = "Manage Startups"
Dim AddinTitle As String, Mybar As Object
AddinTitle = Left(ThisWorkbook.Name, Len(ThisWorkbook.Name) - 4)
Call RemoveButtons
On Error GoTo ErrHandler
Set Mybar = Application.CommandBars("Worksheet Menu Bar") _
.Controls("Tools").Controls _
.Add(Type:=msoControlPopup, before:=13)
'
With Mybar
.BeginGroup = True
.Caption = MyControl
'-------------------------------------------------------------
.Controls.Add.Caption = MyControlCaption
.Controls(MyControlCaption).OnAction = "ShowStartupForm"
'-------------------------------------------------------------
With .Controls.Add
.BeginGroup = True
.Caption = "Case " & AddinTitle
End With
.Controls("Case change " & AddinTitle).OnAction = "ULCase.UpperMacro"
'-------------------------------------------------------------
.Controls.Add.Caption = "Remove " & AddinTitle
.Controls("Remove " & AddinTitle).OnAction = "Module1.RemoveAddIn"
'-------------------------------------------------------------
End With
Exit Sub
ErrHandler:
Set Mybar = Nothing
Set Mybar = Application.CommandBars("Tools") _
.Controls.Add(Type:=msoControlPopup, before:=13)
Resume Next
End Sub
'
'---------------------------------------------------------------------
' Purpose : Remove addin control buttons
'---------------------------------------------------------------------
'
Private Sub RemoveButtons()
'
'change 'Startups...' to suit
Const MyControl As String = "Startups..."
On Error Resume Next
With Application
.CommandBars("Tools").Controls(MyControl).Delete
.CommandBars("Worksheet Menu Bar") _
.Controls("Tools").Controls(MyControl).Delete
End With
End Sub