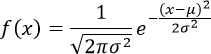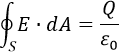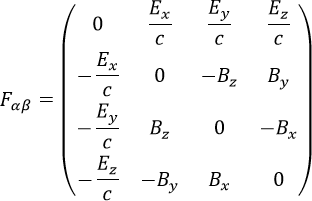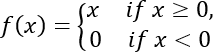Excel 2016 Word 2016 Outlook 2016 PowerPoint 2016 Excel 2013 Word 2013 Outlook 2013 PowerPoint 2013 Excel 2010 Word 2010 Outlook 2010 PowerPoint 2010 Excel 2007 Word 2007 Outlook 2007 PowerPoint 2007 More…Less
Equation Editor (Microsoft Equation 3.0) was included in earlier versions of Word, but was removed from all versions in the January 2018 Public Update (PU) and replaced with a new equation editor.
The content here describes this feature for users who have installed this update.
Important: Equation Editor 3.0 it was removed because of security issues with its implementation. Users who try to edit an equation created in Equation Editor 3.0 will receive the error message «Microsoft Equation is not available.» Equation Editor 3.0 objects will still display normally if you have MT Extra font installed (if you don’t have the font, you can download it). However, users can edit these equations only by downloading the MathType software tools that are provided by WIRIS. See MathType desktop for Equation Editor users.
Insert an equation with Equation Editor
-
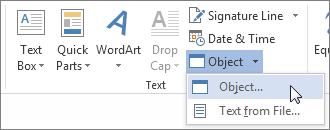
On the Insert tab, in the Text group, click Object.
-
In the Object dialog box, click the Create New tab.
-
In the Object type box, click Microsoft Equation 3.0, and then click OK.
-
Use the symbols, templates, or frameworks on the Equation toolbar to edit the equation.
-
In Word, Excel, or Outlook, to return to your document, click anywhere in the document.
In PowerPoint, to return to the presentation, in Equation Editor, on the File menu, click Exit and Return to Presentation.
Edit an equation in Equation Editor
If you used Equation Editor to insert an equation, you can also edit that equation in Equation Editor.
-
Double-click the equation object that you want to edit.
-
Use the symbols, templates, or frameworks on the Equation toolbar to edit the equation.
-
In Word, Excel, or Outlook, to return to your document, click anywhere in the document.
In PowerPoint, to return to the presentation, in Equation Editor, on the File menu, click Exit and Return to Presentation.
Insert an equation with Equation Editor
-
On the Insert tab, in the Text group, click Object.
-
In the Object dialog box, click the Create New tab.
-
In the Object type box, click Microsoft Equation 3.0.
If Equation Editor is not available, you might have to install it.
Install Equation Editor
-
Exit all programs.
-
Click Add or Remove Programs in Control Panel.
-
In the Currently installed programs box, click Microsoft Office <suite> 2007, and then click Change.
-
On the Change your installation of Microsoft Office <suite> 2007. screen, click Add or Remove Features, and then click Continue.
-
On the Installation Options tab, click the expand indicator (+) next to Office Tools.
-
Click the arrow next to Equation Editor, and then click Run from My Computer.
-
Click Continue.
-
After the Equation Editor installation is complete, restart the Office program that you were using.
-
-
In the Object dialog box, click OK.
-
Use the symbols, templates, or frameworks on the Equation toolbar to edit the equation.
-
In Word, Excel, or Outlook, to return to your document, click anywhere in the document.
In PowerPoint, to return to the presentation, in Equation Editor, on the File menu, click Exit and Return to Presentation.
Edit an equation in Equation Editor
If you used Equation Editor to insert an equation, you can edit that equation in Equation Editor.
-
Double-click the equation object that you want to edit.
-
Use the symbols, templates, or frameworks on the Equation toolbar to edit the equation.
-
In Word, Excel, or Outlook, to return to your document, click anywhere in the document.
In PowerPoint, to return to the presentation, in Equation Editor, on the File menu, click Exit and Return to Presentation.
To learn how to use built-in equations by using the Equation button, see Write an equation or formula.
See also
Linear format equations and Math AutoCorrect in Word
Write an equation or formula
Need more help?
Microsoft Equation helps you add fractions, exponents, integrals, and so on to Word documents.
You start building an equation by opening Microsoft Equation:
To insert an equation in your document, on the Insert tab, in the Symbols group,
click the arrow next to Equation:
You can use the vertical scroll bar in the Gallery to display additional equations
(how to add an equation into the Gallery, see
How to add your own equation to the Equation gallery).
If you see what you want, click it to insert it at the current insertion point in the document.
If you add it into an otherwise empty paragraph, the equation defaults to appearing in
Display mode. If the equation is on the same line as text, it appears in Inline mode:

To add your own equation, do one of the following:
- On the Insert tab, in the Symbols group, click the arrow next to Equation,
and then click Insert New Equation, - On the Insert tab, in the Symbols group, click the Equation button,
- Or simply press Alt+=.
Word 2016 opens the Design tab under Equation Tools:
Word 2016 provides two formats of equations: Professional and Linear:
By default, uses the Professional present, but if you ever need Linear, select
the equation(s) you want to change, under Equation Tools, on the Design tab,
in the Conversions group, in the Convert drop-down list, choose the appropriate
option:
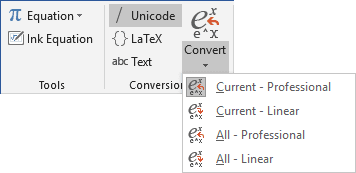
Equation Tools Design tab contains dozens of equation templates. Within each button on the
toolbar, there are several tools available. Simply click on a button to see the tools contained
in each. How to create an equation step-by-step, see:
- Normal or Gaussian distribution in the tip
How to insert an equation with fractions, square roots and exponents: - Gauss’s law, also known as Gauss’s flux theorem in the tip
How to insert an equation with integral: - Electromagnetic tensor in the tip
How to insert an equation with matrix: - One of De Morgan’s law in the tip
How to insert a Boolean algebra equation: - The formula of limit in the tip
How to insert an equation with a limit: - Euler’s formula in the tip
How to insert an equation with trigonometric functions: - A system of linear equations in the tip
How to insert an equation with a system of linear equations or linear system:
For more details about equations, see
Setting font size and styles in an equation
and
Adjusting spacing and alignment in an equation.
See also this tip in French:
Comment insérer des équations dans Microsoft Word.
In this article, you are going to learn, how to type and use Mathematical Equations in Microsoft Word 2016. Nowadays Writing Mathematical Formulas and Equations, and others Scientific Formulas in Ms. Word is very important. If you learn writing Formulas and Equations in Ms. Word, if you are a teacher you will be able to type your questions papers, your forms, and your books. If you are a student you will be able to type your homework and whatever you need to type you can easily type it and done your job. Now here you have many steps follow all of them carefully, and see the pictures. let’s get started on how to type & use mathematical equations in MS Word 2016.
-
- Select Insert Tab to Type and Use Mathematical Equations
- Click Equations Option to Open Design window
- Some Ready Formulas
- Write Your Formula without Using Keyboard
- Change the Type of your Equation
- Group Symbols Has All Scientific Symbols that You Need
- Structures are the Icons of our Main Group in This Article
- Conclusion
Select Insert Tab to Type and Use Mathematical Equations
To go to the first step, start opening your Ms. Word and click the Insert tab, then you see the corner of the page two options which you need them for your documents. One of them is Equations and the second one is Symbols. In this article, you are going to study the first option(Equation), and the next article you will go to learn about symbols.
Insert tab
Click Equations Option to Open Design window
In the Design Window, you have three Groups. This three group contains many icons which help you to complete your Document or Project, and also by opening this window, on Word page you see a new work board. On this working board, you can type your ideal Equations. These groups are:
-
-
- Tools
- Symbols
- Structures
-
Design Page
Some Ready Formulas
In this item, you have Five deferent options.
-
-
- Equations
- Ink Equations
- Professional
- linear
- Normal text
-
Equation option has some ready formulas and Equations which has already made and save there. You can select them and rewrite them according to your need and use them in your documents.
Use the ready Equations
Here you have the last option (Save selection to Equation Gallery). You can use this option to save your own and favorite Formulas in Equation Gallery, and then use them. To use this option first, you should make your equation ready then select them and save to Gallery. When you click the options in new page you should write information about your Formula to easily identify it from other formulas.
Save your Favorite Equations Here.
Write Your Formula without Using Keyboard
In this option, if you like to write your formulas using handwriting on your Tablet, smartphone or PC. you can use it easily write your Equations, then insert to the main page and continue your task.
Write your Formulas
Change the Type of your Equation
Here we have three others options that by using them you can change the type or shape of your Equations. Now here we have three formulas in three deferent types.
Deferent Type for Your Equations.
Group Symbols Has All Scientific Symbols that You Need
In this Group you have all symbols that you need in Math, Physics, Chemistry and other subjects, according to your need you can select and use them in your Equations and Formulas.
Second Group in Design Tab
Here you have some categories of Symbols that Microsoft Word 2016 already classified them to be easily recognized. The categories are:
-
-
- Basic Math
- Greek letters
- Letters Like Symbols
- Operators
- Arrows
- Negated Relations
- Scripts
- Geometry
-
Classified Symbols
Structures are the Icons of our Main Group in This Article
In this Group, we have some basics Categories that Help us to make our Equations, in these eleventh structures, we can make our Favorite Equations and Formulas. Here we have not any limit for our task because they work like a format that we are entering our Idea here to make our Formula.
Structures of Equations
Here we have various Equations, now as an example, i write a Formula. For writing your formula here, just you need to click on your favorite format then click on the square to fill in the blanks. In this example step by step, we are going on to reached the Sixth step.
-
-
- Click on Script option to start Writing
- Inside your big square click on Brackets to have to smalls brackets, then write your numbers in squares
- Then writes equal and click on Large Operator and write your numbers or symbols
- Here also click on brackets and go down select the other option
- Now you completed your Equation without numbers and symbols
- It is your Equation now which is completed
-
Steps of Writing an Equation
Conclusion
It was all about that to Know how to type and use Mathematical Equations and Formulas in Microsoft Word 2016, as you all know that nowadays if we want to share our scientific knowledge with others through the Internet or books we must to use Ms Word and through the Ms Word we need to Know how to Write Equations and Formulas.
Here I explained all of them step by step very simple. If you have got any question regarding Word 2016, you may comment it. Thank you for being with us.
Download Article
A descriptive guide to inserting equations in Word
Download Article
Modern versions of Word include almost all the symbols and structures a math professor could need. These can either be quickly typed with shortcuts or found in the convenient Equation menu, depending on your preference. The process is a little different if you’re on a Mac, or using Word 2003 or older. Note that the old «Insert Object» method from Word 2003 is not included in modern versions. You can also write equations in Word using the mobile app. This wikiHow shows you how to insert equations in MS Word in all cases.
-
1
Press Alt and =. This will insert an equation at the position of your cursor and open the editor.
-
2
Insert symbols by typing “symbolname” and press the space bar. If you know the name of a symbol, simply type «» followed by the symbol name. For example, for the Greek letter theta, type theta and press the space bar to convert it. You can also look at https://www.rapidtables.com/math/symbols/Basic_Math_Symbols.html to preview symbol names.
Advertisement
-
3
Insert fractions using /. For example, typing «a/b» (and then pressing the space bar) puts a on top of b as a fraction.
-
4
Group expressions using parentheses (). Brackets, or parentheses, (), are used to group parts of the equation in the editor. For example, «(a+b)/c» will put the expression a+b on the top of the fraction but will not display the brackets.
-
5
Use _ and ^ to insert subscripts and superscripts. For example, «a_b» makes b the subscript of a, and likewise, «a^b» makes b the exponent of a. Subscripts and superscripts can be used simultaneously and are also how the equation editor adds limits to integrals, for example, typing «int_a^b» and pressing the space bar gives the integral from a to b.
-
6
Insert functions by pressing the space bar after the function name. Trigonometric functions such as sin and arctan are recognized, as well as other functions such as log and exp; however, you must press the space bar after typing the function name in order for the editor to recognize it as a function.
-
7
Make font changes. Font changes can be made as you are going along. To toggle bold and italic text use the normal shortcuts: Ctrl+B or Ctrl+I. To type text within an equation that looks ‘normal’, enclose it in quotation marks. To make a character into a script character use «script». For example, «scriptF» would change the F into a script character.
-
8
Look up other shortcuts. Typing equations is much faster than selecting symbols and structures from the menu but does require learning the shortcuts. Using the steps above, you can probably guess most of the shortcuts you will need.[1]
[2]
[3]
Advertisement
-
1
Open your Word document. Since the app works the same on every platform, this method will work for any mobile device.
- If you don’t have Microsoft Word, you can download it for free from the Google Play Store (Android) or App store (iOS).
-
2
Tap Home. When you tap Home, a list of options appears.[4]
- To see this option on a phone, you will need to tap the pencil icon above the text area to edit the document. Tap the up arrow on the right side of the menu that appears above your keyboard. If you’re using a tablet, the ribbon with Home, Insert, Draw, and Layout appears above the text area.
-
3
Tap Insert.
-
4
Tap Equation or Insert New Equation. You might have to scroll down the list to see this on phones.
-
5
Type your equation. For example, if you want to achieve a²+b²=c², type “a2+b2=c2.” If you can’t find the symbol you need on your keyboard, you can always copy and paste it into the document from other sources.
-
6
Double-tap your typed equation. A box will pop up above your equation.
-
7
Tap Math Options.
-
8
Tap Professional. Your symbols and numbers will change into an equation format.
Advertisement
-
1
Select the Insert tab on the ribbon. The ribbon is the horizontal menu between your document title and the document itself.
-
2
Find the Equation icon (π). You’ll see this on the far right, in the Symbols group.
-
3
Click the icon to insert an equation. A box will appear at the position of your text cursor. You can start typing immediately to start your equation or continue to the next step for more options.
-
4
Insert special formatting. When you clicked the Equations icon, the ribbon menu changed to display a large array of new options. Browse through them to find what you need, then type to complete the equation. Here’s a step by step example:[5]
- Click the Script icon to open a drop-down menu. Hover over each button and a tooltip will appear telling you what it is.
- Select the basic subscript option, and two squares will appear in your equation, one below the other: □□
- Click the first square and type in the value you’d like to display: 5□
- Click the second square and type in the subscript value: 53
-
5
Continue typing to complete the equation. If you do not need any special formatting, just continue typing to extend the equation. Word will automatically insert spaces and italicize variables.
-
6
Move the equation on the page. Select the entire equation text box, and you’ll see a tab with an arrow on the right-hand side. Click this arrow to reveal a list of visual options, including whether to center, left-justify, or right-justify the equation.
- You can also highlight the text in the equation and alter the font size and style as usual.
-
7
Write equations by hand (2016 only). If you have Word 2016, you can create an «equation» by drawing it with a mouse or touchscreen tool. Select Ink Equation from the drop-down Equations menu to get started.[6]
Advertisement
-
1
Select the Document Elements tab. This tab is on the ribbon menu, just below the highest row of icons.
-
2
Select the Equations icon on the far right. With Document Elements selected, Equation is the option farthest to the right, with a π icon. There are three options here:
- Click the arrow next to the Equations icon for a drop-down selection of common equations.
- Click the arrow, then click «Insert New Equation» to type your own.
- Click the icon itself to open up a larger menu of equation options on the ribbon.
-
3
Use the top menu instead. If you prefer to use the top menu, select «Insert,» then scroll all the way down to «Equation» in the drop-down menu.
- Your text cursor must be at a blank point in the document to access this command. (For example, if you have an existing object selected, this command is greyed out.)
-
4
Choose display options. Click the downward-facing arrow to the right of the equation box. A drop-down menu will appear with options to alter how your equation is displayed.
- This menu also includes the «save as new equation» command, useful for equations you plan to use frequently. This adds the selected equation to the drop-down menu when you click the arrow next to the Equations icon.
Advertisement
-
1
Know the limitations. Equations written in Word 2003 or earlier cannot be edited in later versions of Word. If you are collaborating with other Word users, it’s best to upgrade to a more recent version.[7]
-
2
Attempt to insert an equation. From the top menu, select Insert → Object → Create New. If you see «Microsoft Equation 3.0» or «Math Type» in the Objects list, select it to insert an equation. Otherwise, go to the next step.
- Once you’ve inserted an equation, a small window will open with various symbols. Click these buttons and select the symbol you need to add it to the equation.
- Word 2003 does not have the same formatting options as later versions. Some equations may look less professional than you’re used to.
-
3
Install the add-on if necessary. If your copy of Word 2003 does not have one of the add-ons you mentioned above, you’ll need to install one. It’s not easy to locate these anymore, but fortunately the install package may already be waiting on your computer:
- Close all Microsoft Office programs.
- Navigate to Start → Control Panel → Add or Remove Programs.
- Select Microsoft Office → Change → Add or Remove Features → Next.
- Click the + symbol next to Office Tools.
- Select Equation Editor and click Run, then Update.
- Follow the onscreen instructions. If you’re unlucky, you may need the Word 2003 install CD.
Advertisement
Add New Question
-
Question
How could I type the elements of a 6 x 2 matrix?
Insert Tab > Equation > Design Tab > Matrix. First select a 3 x 2 matrix, then in each element select a 2 x 1 matrix.
-
Question
How do I insert a square root?
Go to «Insert.» Click on «Equation.» On the top ribbon there is a list of various math symbols including various forms of the square roots. It has the word «Structures» as a grouping.
-
Question
How do I escape from the equation when I want to keep typing on the same line in MS Word?
Press the Tab key and start typing on the same line.
Ask a Question
200 characters left
Include your email address to get a message when this question is answered.
Submit
Advertisement
Video
-
To create the second line of an equation, press Shift + Enter.[8]
Enter will exit the equation or start a new equation paragraph, depending on your version of Word. -
If you are using Word 2007 or later and trying to edit a document created in Word 2003 or earlier, use the File → Convert command to unlock equations and other editing features.[9]
-
The Office 365 subscription service typically includes the latest version of Word. Follow the instructions for the most recent version that works on your operating system.
Thanks for submitting a tip for review!
Advertisement
-
If you save the document as a .docx file, people with Word 2003 and earlier will not be able to edit the equations.[10]
Advertisement
About This Article
Article SummaryX
1. Press Alt and = to insert an equation.
2. Add letters and numbers.
3. Insert symbols in the ″symbolname″ format.
4. Press the spacebar to convert a symbol.
5. Insert fractions with ″/″ key.
6. Group expressions between parentheses.
7. Use ″_″ for subscript and ″^″ for superscript.
8. Type a function and press the spacebar to insert.
Did this summary help you?
Thanks to all authors for creating a page that has been read 851,172 times.
Is this article up to date?
If you ever had to insert an equation as part of a Word document, you know manually entering formulae isn’t easy. The number of special characters involved and the complexity of proper formatting can make it really tough. Fortunately, Microsoft Office 2016 offers some tools to make life a little easier.
With Word, you can quickly insert stock equations, add specific equations and save them for future use, or draw them using your mouse or a touch interface. Additionally, you can copy and paste equations from other programs. So if you want to learn how to easily write math equations in Word, keep reading.
1. Inserting Stock Equations
There are certain mathematical equations that Office users will need time and time again, so Microsoft decided to save everyone some time and effort by offering several built-in staples.
These equations can be accessed by heading to the Symbols section of the Insert tab. Click the Equation dropdown and choose one of the built-in examples to insert it into your document.
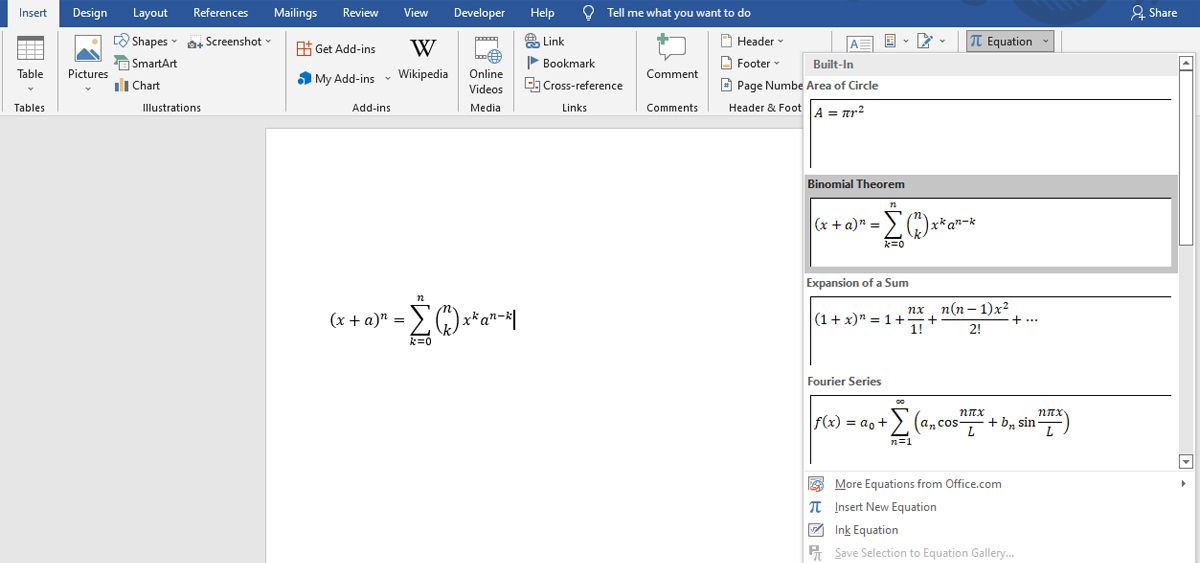
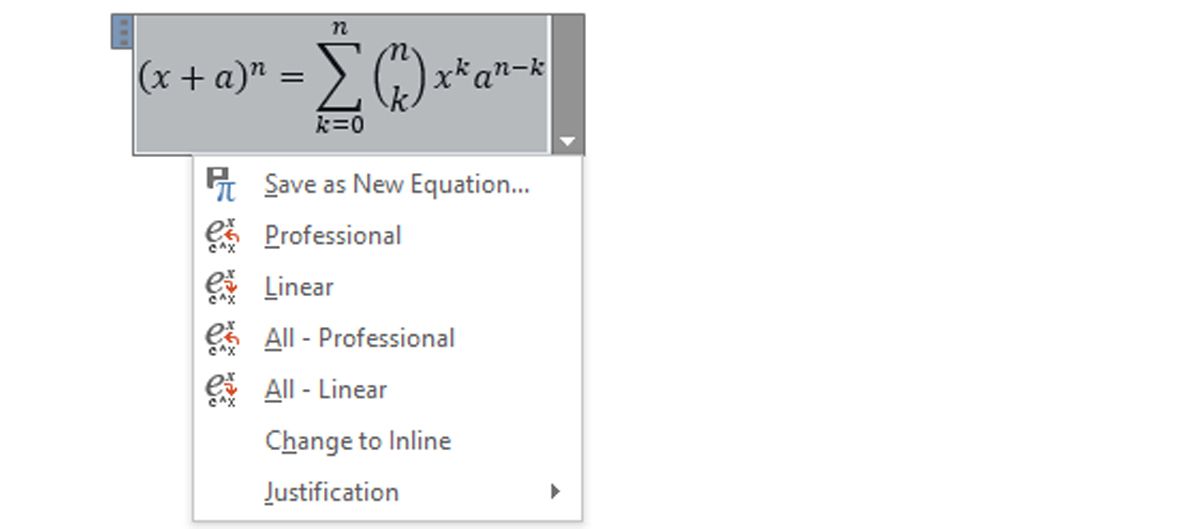
Once the equation is on the page, you can use the dropdown to its right to make tweaks, like switching between the Linear and Professional formatting styles. The box on the right-hand side of the equation is simply a «handle» to make it easier to drag the statement around your document without its contents being rearranged.
It’s worth noting that you can make edits to these built-in equations simply by highlighting individual values and typing in the desired replacement. Once you’ve done that, you can use the drop-down option Save as New Equation to store this formula for further usage.
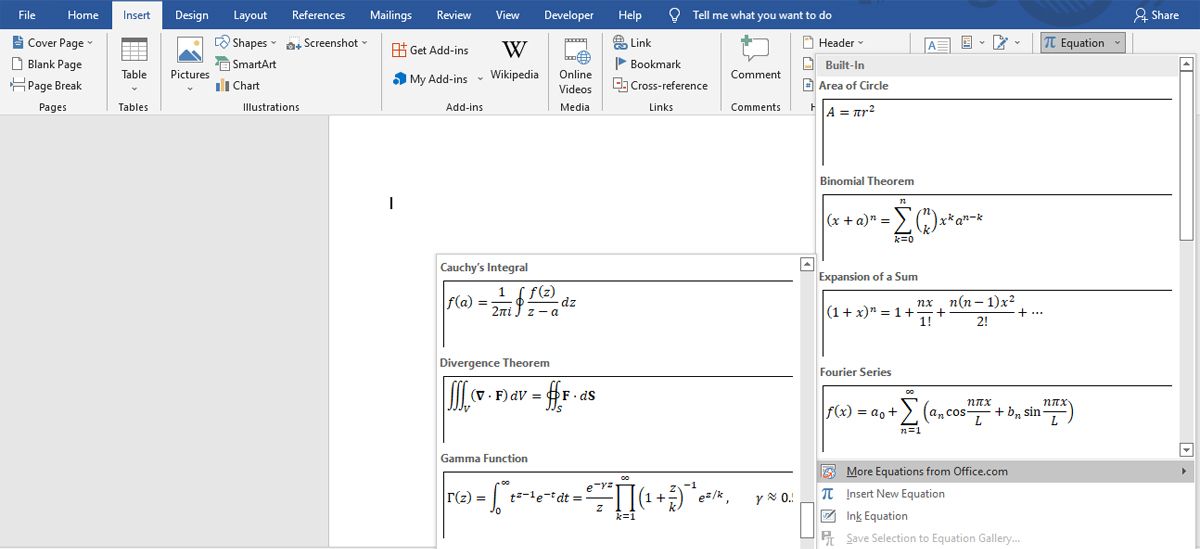
It’s well worth checking out the More Equations from Office.com option from the Equations drop-down in the Ribbon. As long as you’re connected to the Internet, this will offer up further pre-written equations sourced online, ranging from relatively simple stuff like a basic fraction multiplication template, to more in-depth formulas like the Gamma Function.
2. Writing Out Equations Manually
To start writing an equation manually, navigate to the Symbols section of the Insert tab and click the word Equation itself, rather than the accompanying drop-down button.
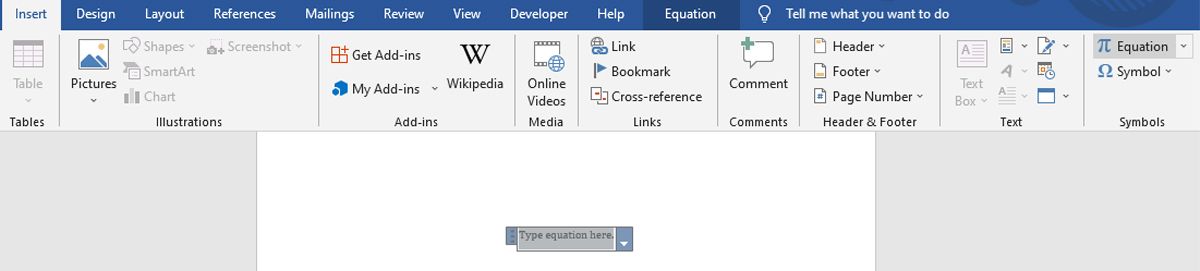
Microsoft Word comes with a lot of useful shortcuts, so if you want to start typing out an equation, press ALT + =. You’ll notice that when you start creating an equation manually, the Ribbon will relocate to the Equation Tools section of the Design tab to give you quick access to a number of symbols and structures.
It’s great to have these characters on hand, but you can of course also use the corresponding ASCII codes or even the Character Map. Note that while you’re in this mode, input from your keyboard will default to italicized math text when you’re in a math region. If you don’t want this to happen, use the Normal Text toggle in the Conversions section of the Ribbon.
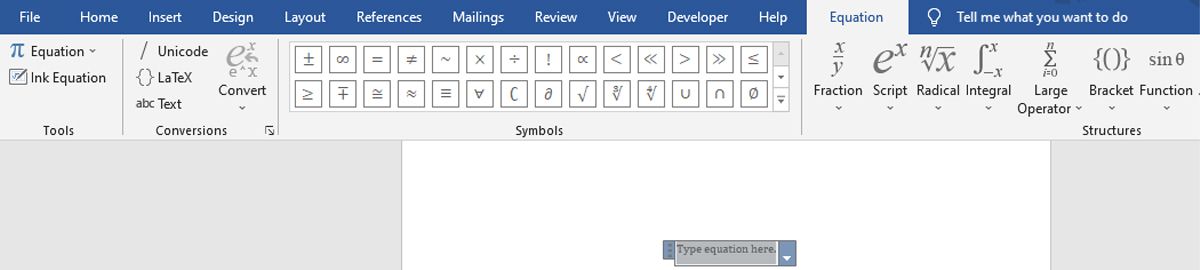
Once you’ve written up your equation, you can use the standard text formatting tools in Word to edit its visual appearance. However, changing the typeface likely won’t have much of an effect—only specialized math-friendly fonts tend to feature all the necessary characters. You can still amend the text size and color as normal.
If your equation is one that you’re likely to reuse on a regular basis, it’s well worth saving it, so you don’t have to write out the formula manually each time. To do so, click the dropdown button on the right-hand side of your equation and select Save as New Equation.
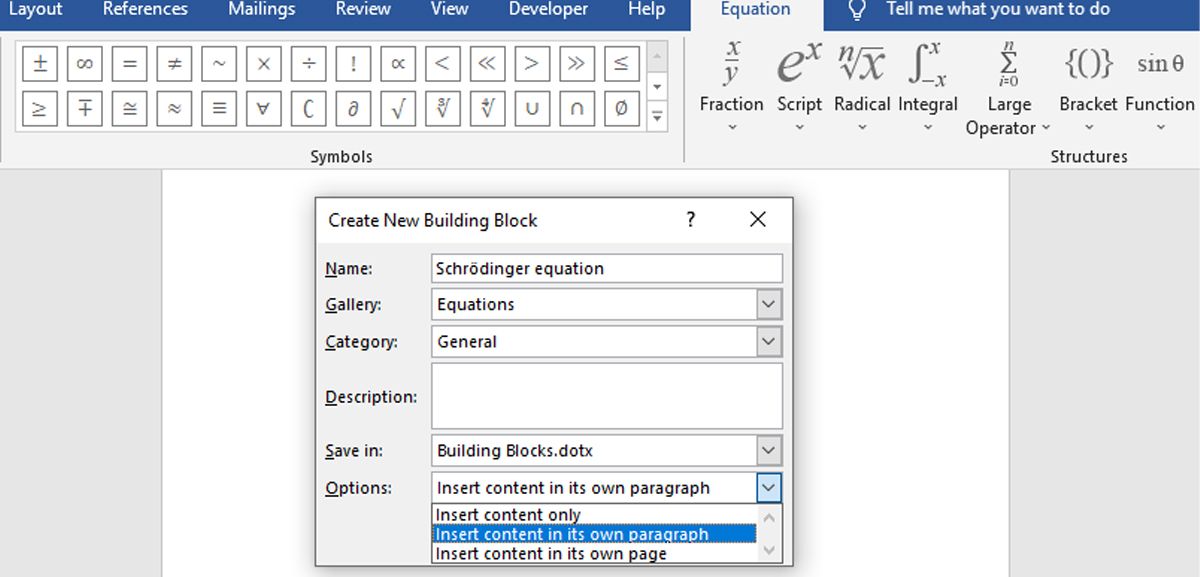
The save dialog that opens up as a result is largely self-explanatory, but do take a moment to consider the Options drop-down. This will allow you to stipulate whether your equation can be inserted directly into text, or whether it defaults to being added as a new paragraph or even a new page.
The latter two options won’t be appropriate for every single formula that you write, but they will save you time and effort when it comes to formatting in certain situations.
3. Drawing an Equation With Ink
Office 2016 also lets you write out equations freehand, either using your mouse or a touch interface. If you’re planning on working with the latter input method, make sure to familiarize yourself with Windows Ink beforehand.
Once you’re ready to get started, head to the Symbols section of the Insert tab and use the Equation drop-down. Select Ink Equation to open the drawing interface.
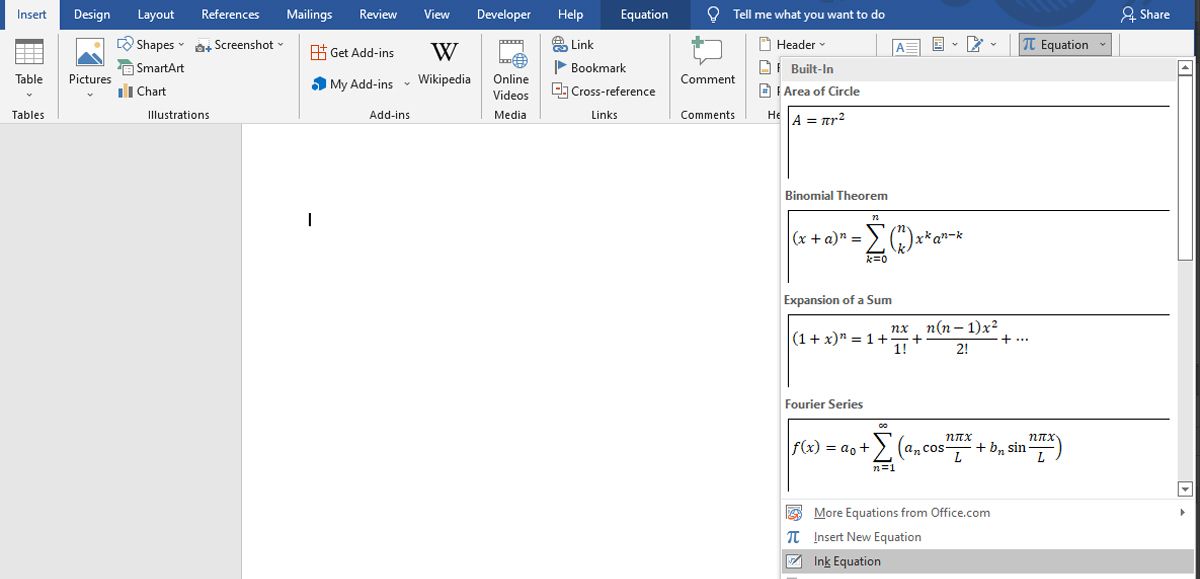
The drawing interface consists of a space for you to write, and a preview box that shows how the equation will look on the page. This gives you the opportunity to perfect your work before it’s inserted into the document—but you’ll likely find that Windows Ink is able to read your handwriting quite accurately.

Write out your equation in full before you go back to make any edits. Windows Ink is smart enough to take context into account, so even if it misunderstands certain characters as you’re writing them, it might auto-correct to the desired result after the entry is complete.
If you do need to fine-tune your equation, you have two tools at your disposal. The first is the Erase function, which deletes individual characters or symbols one by one and cannot be undone, so be careful as you’re using it.
You can also use Select and Correct to replace an element of your equation, rather than deleting it outright. To employ this tool, select it at the bottom of the window and use the cursor to draw around the character or symbol you want to amend until it turns red.
You’ll then be presented with a selection of replacements to pick from. If the character you’re looking for isn’t listed, you’ll just have to make another attempt at drawing it.
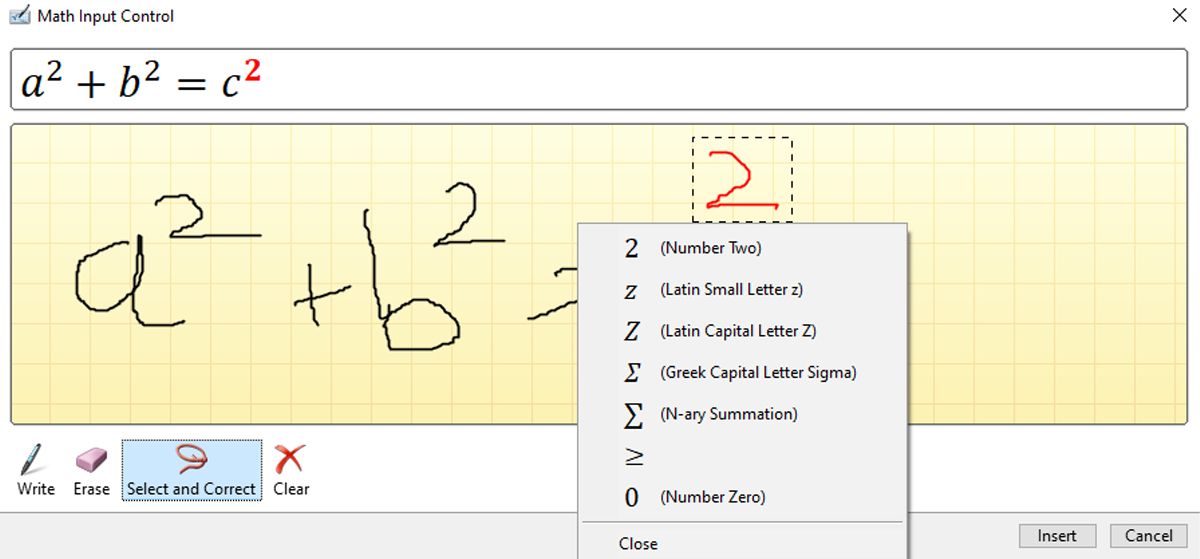
Once your equation is ready, just click Insert, and it will be added to your document.
4. Copy Equations From a Different App
While Office 2016 provides you with plenty of alternatives for writing math equations, it may not be good enough, especially if you’re working on a work or school assignment involving many equations and calculations. In this case, you’d have to do the math separately before adding it to your document.
In this case, a math software like Mathcad could be a better fit. You can copy and paste the equations and calculations as images. Set the same font and zoom percentage, so you’ll have a neat-looking document when you print it.
Write Math Equations With Ease
When writing math equations in Word, take some extra time to format them. Choose a font and size that makes them easier to read. Also, center aligning them might help.
If you’re working on a scientific assignment, there’s a chance you need to import a lot of data into your document. Fortunately, there are plenty of importing data methods that you can use.