способность,
inability
неспособность;
disability
нетрудоспособность
способный, умелый
unable
неспособный
disabled
искалеченный; инвалид
дать возможность
disable
делать неспособным, калечить
умело, искусно
абсурдность
абсурдный
приемлемость
приемлемый
unacceptable
неприемлемый
принимать, соглашаться
доступ
accessibility
доступность
доступный
доступно
случай, случайность
случайный
нечаянно, случайно
действие
actor
актер
actress
актриса
activity
активность
activities
деятельность
acting
представление
активный
acting
действующий, работающей
действовать
активно
достижение
достигать
привычка, приверженность, увлеченность
addict
увлеченный человек, имеющий стойкую привычку
способный вызывать привычку
увлекаться, предаваться
восхищение
восхитительный
восхищаться
восхитительно
совет
рекомендуемый
советовать
притворство, искусственность
affection
привязанность, любовь
притворный
affectionate
любящий
affective
эмоциональный
воздействовать, влиять; притворяться
соглашение, согласие
disagreement
разногласие, несогласие
соответствующий, приятный
соглашаться
disagree
не соглашаться
соответственно
агрессия
aggressor
агрессору зачинщик
агрессивный
нападать
агрессивно
цель
бесцельный
целиться, намереваться
бесцельно
то, что может быть позволено
unaffordable
то, что невозможно себе позволить
позволять себе
развлечение
приятно изумленный
amusing
забавный
развлекать, забавлять
изумленно
внешность; появление
disappearance
исчезновение
появляться
disappear
исчезать
назначение; деловая встреча
disappointment
разочарование, досада
назначенный
disappointed
огорченный
disappointing
разочаровывающий
назначать
disappoint
разочаровывать
одобрение
одобренный
approving
одобрительный
одобрять
одобрительно
соглашение; расположение
приведенный в порядок
приводить в порядок, организовывать
аргумент, довод
argumentation
аргументация
доказуемый (в споре)
argumentative
спорный, конфликтный
утверждать, спорить, ссориться
доказательно
присвоение; ассигнование
подходящий, соответствующий
inappropriate
несоответствущий, неуместный
присваивать, предназначать
соответственно, подходяще
прибытие
прибывать, приезжать
притяжение, привлекательность
привлеченный
attractive
привлекательный
привлекать
привлекательно
избежание, отмена
то, чего можно избежать
unavoidable
неизбежный
избегать
неизбежно
красота; красавица
красивый
украшать
красиво
роды
сносный, допустимый
unbearable
невыносимый
носить; терпеть
невыносимо
вера
вероятный, правдоподобный
unbelievable
невероятный
верить
выгода
выгодный
получать выгоду
зануда
boredom
скука
испытывающий скуку
boring
скучный, надоедливый
надоедать
скучно
дыхание, дуновение
breathing
дыхание
breather
короткая передышка
дышащий
breathless
бездыханный
дышать
затаив дыхание
дело
businessman
деловой мужчина
businesswoman
деловая женщина
занятой
businesslike
деловой, практичный
занимать делом
деловито, по-деловому
забота, уход
заботливый
careless
небрежный
заботиться, любить
заботливо
carelessly
небрежно
празднование
celebrity
знаменитость
знаменитый, прославленный
праздновать, прославлять
определенность
uncertainty
неопределенность, неуверенность
определенный
uncertain
неопределенный
определенно, уверенно
изменение; мелочь, сдача
изменчивый
changed
изменившийся
changeless
неизменный
unchanged
не изменившийся
менять; обменивать(ся)
неизменно
характер
характерный, типичный
характеризовать
выбор
разборчивый
выбирать
ребенок
children
дети
детский; ребяческий
очистка; устранение препятствий
четкий, ясный
очищать, расчищать
четко, ясно
облако
облачный
cloudless
безоблачный
собрание; коллекция
collector
сборщик
коллективный, совокупный
собирать; коллекционировать
колония
колониальный
колонизировать
цвет
цветной
colourless
бесцветный
multi-coloured
разноцветный
раскрашивать
комфорт; утешение
discomfort
беспокойство; неудобство
удобный, комфортабельный
uncomfortable
неудобный
утешать, успокаивать
удобно
uncomfortably
неудобно
община, общество
общественный, коллективный
сообщение
communicator
коммуникатор, переговорщик
использующийся в общении; коммуникативный
сообщать; общаться
сравнение
сравниваемый
comparative
сравнительный
сравнивать
сравнительно, относительно
соревнование; конкуренция
competitor
конкурент, соперник
соревновательный
соревноваться, конкурировать
в форме соревнования, конкуренции
завершение, окончание
законченный
complete
полный, завершенный
incomplete
неполный, назавершенный
заканчивать, завершать
полностью
поздравление
поздравлять
соединение, объединение
связанный, соединенный
соединять
disconnect
разъединять
внимание; рассмотрение, обсуждение
значительный
considerate
внимательный, деликатный, тактичный
inconsiderate
неосмотрительный; невнимательный к другим
считать, полагать; рассматривать
значительно
совесть
совестливый, добросовестный
conscientiousless
бессовестный
добросовестно
сознание
осознающий
unconscious
без сознания
сознательно, осознанно
консультация
consultant
консультант
консультирующий
консультировать
вместилище, контейнер
содержащий
содержать, вмещать
непрерывность
продолжающийся, длящийся
продолжать
непрерывно
управление, руководство
поддающийся управлению
uncontrollable
неподдающийся управлению
controlled
управляемый
uncontrolled
неуправляемый
управлять, регулировать
бесконтрольно
убеждение
убедительный
convinced
убежденный
убеждать
убедительно
повар
cooker
плита, духовка
переваренный
under-cooked
недоваренный
готовить еду
исправление
corrector
корректор
правильный
incorrect
неправильный
исправлять
правильно
прилавок
discount
скидка
accountant
бухгалтер
исчисляемый
uncountable
неисчисляемый
считать
немеряно, без счета
храбрость
храбрый
encouraged
воодушевленный
encouraging
подбадривающий
discouraged
обескураженный
приободрять, поддерживать
discourage
отговаривать, обескураживать
смело, храбро
создание
creativity
творчество
creator
творец, создатель
creature
творение; живое существо
творческий
создавать, творить
творчески
вера, доверие
вероятный, заслуживающий доверия
incredible
невероятный
вероятно
incredibly
невероятно
критик
criticism
критика
критический; переломный; рискованный
критиковать
критично, критически
культивация, обработка
культивированный, обработанный
обрабатывать
культура
культурный, воспитанный
cultural
культурный (как часть культуры)
культурно
лекарство; лечение
излечимый
incurable
неизлечимый
вылечивать, исцелять
неизлечимо
опасность
опасный
угрожать
опасно
день
ежедневный
ежедневно
обман, заблуждение
обманчивый
deceitful
обманчивый, лживый
обманывать
обманчиво, предательски
решение
определенный, явный
undecided
нерешительный, неясный
decisive
решительный, убежденный, убедительный
решать, принимать решение
решительно, определенно
определение
четкий, определенный
indefinite
неопределенный
определять, давать определение
определенно, ясно
indefinitely
нечетко, неопределенно
восторг, наслаждение
восхитительный
delighted
польщенный
восхищаться
с восторгом
доставка, поставка
доставленный
доставлять
зависимость
independence
независимость
зависимый
independent
независимый
зависеть
независимо
депрессия, подавленность
депрессивный, вызывающий депрессию
depressed
подавленный
подавлять
описание
описательный, наглядный
описывать
проект, дизайн
designer
дизайнер, проектировщик
проектировать
желание, стремление
желательный, желаемый
undesirable
нежелательный
желать, стремиться
желательно
разрушение
разрушенный
разрушать, уничтожать
решительность; определение
решительный
решать, определять
развитие
developer
разработчик
развитой
developing
развивающийся
undeveloped
неразвитый
развивать(ся)
умирающий
умирать
разница, различие
indifference
безразличие
другой, отличающийся
indifferent
безразличный
отличаться
по-другому
indifferently
с безразличием
тревога, беспокойство; нарушение тишины, порядка
обеспокоенный
disturbing
беспокоящий
беспокоить, мешать
сомнение
сомнительный
doubtless
несомненный
undoubted
бесспорный
сомневаться
с сомнением
doubtlessly
не сомневаясь
undoubtedly
без сомнения
легкость, свобода
disease
болезнь
легкий
uneasy
неловкий, тревожный
облегчать, ослаблять
легко
uneasily
неловко
хозяйство
экономический
economical
экономный
экономить
экономически; экономно
воспитатель, педагог
education
образование
образованный
uneducated
необразованный
educative
образовательный
воспитывать, давать образование
следствие, результат
effectiveness
эффективность
эффективный, действующий
производить, выполнять
эффективно, действенно
электричество
electrician
электрик
электрический
электрифицировать
империя
empiror
император
имперский
empiric / empirical
исходящий из опыта, эмпирический
служба, работа
unemployment
безработица
employer
наниматель, работодатель
employee
работающий по найму
нанятый, занятый
unemployed
безработный
нанимать
конец, окончание
бесконечный
unending
нескончаемый
конец, окончание
бесконечно
окружающая среда
природный
развлечение
развлекательный
развлекать
энтузиазм, восторг
enthusiast
энтузиаст, восторженный человек
восторженный
с восторгом
оборудование
снаряженный, оборудованный
снаряжать
сущность
главный, основной
главным образом
экзамен; медосмотр
проэкзаменованный; осмотренный врачом
экзаменовать; осматривать
возбуждение, волнение
возбуждающий
excitable
возбудимый
excited
возбужденный, взволнованный
возбуждать, волновать
взволнованно, возбужденно
ожидание, предчувствие
ожидаемый
unexpected
неожиданный
ожидать, предчувствовать
расход(ы), затраты
дорогой
inexpensive
недорогой
тратить, расходовать
дорого
опыт, опытность
inexperience
неопытность
experiment
эксперимент
опытный
inexperienced
неопытный
experimental
эспериментальный
испытывать
взрыв
explosive
взрывчатое вещество
взрывчатый
взрываться
выражение
выразительный
выражать
выразительно
пространство, степень
длительный,обширный
extensive
обширный
простираться, тянуться
обширно, протяженно
крайняя степень, крайность
крайний, чрезвычайный
крайне
очарование, обаяние
чарующий
fascinated
очарованный
очаровывать
справедливость; порядочность
порядочный, справедливый
unfair
несправедливый
справедливо, честно; довольно-таки
финансы
финансовый
финансировать
финансово
твердость
твердый
утверждать
твердо
физическая форма, физическое состояние
находящийся в хорошей форме; подходящий
unfit
неподходящий
подгонять, подстраивать
следующий
следовать
глупыш, дурак
глупый
обманывать
глупо
забываемый
unforgettable
незабываемый
forgetful
забывчивый
forgotten
забытый
забывать
прощение
прощающий
forgivable
простительный
unforgivable
непростительный
прощать
с прощением
судьба, счастье; богатство, состояние
счастливый
unfortunate
несчастный
к счастью
unfortunately
к сожалению
свобода
свободный; бесплатный
свободно
частота
частый
часто посещать
часто
друг
friendship
дружба
friendliness
дружелюбие
дружеский, дружелюбный
unfriendly
недружеский
дружелюбно
страх, испуг
страшный
frightened
испуганный
frightening
пугающий
пугать, устрашать
страшно; испуганно
щедрость
щедрый
щедро
джентльмен
мягкий, нежный
мягко, нежно
привидение, призрак
похожий на привидение
трава
травяной
привычка, обычай
habitant
обитатель
habitat
естественная среда
habitation
жилище, обиталище
привычный
приучать
обычно
рука; рабочий
handful
горсть
удобный (для использования)
handmade
изготовленный вручную
вручать
счастье
unhappiness
несчастье
счастливый
unhappy
несчастный
счастливо
unhappily
несчастливо
вред
вредный
harmless
безвредный
повредить, навредить
вредно
здоровье
здоровый
unhealthy
нездоровый
дом, жилище
бездомный
честь
почетный
почитать, чтить
почетно
надежда
hopefulness
оптимизм, надежда
надеющийся
hopeless
безнадежный
надеяться
с надеждой
человечество
человеческий
humane
гуманный
inhuman
бесчеловечный
humanitarian
гуманитарный
юмор
юмористический
с юмором
спешка
торопливый, спешащий
hurried
торопливый
торопиться
торопливо
лед
ледяной
важность
важный
unimportant
незначительный
важно
впечатление
впечатленный
impressive
впечатляющий
unimpressed
безучастный
производить впечатление
впечатляюще
улучшение
улучшенный
улучшать
толчок, побуждение
импульсивный
импульсивно
несчастный случай; конфликт, инцидент
случайный
случайно
рост, увеличение
растущий
увеличивать(ся)
с ростом
промышленность
промышленный
industrious
трудолюбивый. усердный
индустриализовать
в промышленном отношении
сообщение, информация
informant
осведомитель
formality
формальность
осведомленный
well-informed
знающий, хорошо информированный
misinformed
неверно информированный
formal
формальный, официальный
informal
неофициальный
информировать
misinform
неверно сообщать; дезинформировать
информационно
интенсивность
интенсивный
интенсифицировать
интенсивно
интерес
заинтересованный
interesting
интересный
интересовать
изобретатель
invention
изобретение
изобретательный
изобретать
изобретательно
приглашение
приглашенный
приглашать
вдохновение
вдохновленный
inspiring
вдохновляющий
вдохновлять
знание
acknowledgement
признание; расписка
признанный
признавать, подтверждать
законность, легальность
юридический, законный
illegal
незаконный, подпольный
легализовать
законно
illegally
незаконно
сходство, подобие
приятный
unlike
непохожий
like
аналогичный
относиться хорошо
dislike
относиться отрицательно
вероятно
unlikely
невероятно
unlike
в отличие
жизнь
living
жизнь
оживленный, веселый
live
актуальный, реальный
жить
оживленно
литература
буквальный
literary
литературный
literate
грамотный
illiterate
неграмотный
буквально
место, поселение
местный
размещать
в определенном месте
одиночество
одинокий; один
удача
удачливый
unlucky
неудачливый, неудачный
к счастью
роскошь
шикарный
большинство
главный, основной
управляющий, руководитель
управленческий
управлять; справляться
женитьба
женатый / замужняя
unmarried
неженатый / незамужняя
жениться
встреча; собрание
встречать, знакомиться
память
memorial
мемориал
памятный
заучивать наизусть
нищета
нищенский, ничтожный
месяц
ежемесячный
ежемесячно
движение
неподвижный
показывать жестом
тайна, загадка
таинственный, загадочный
таинственно, загадочно
необходимость
необходимый
unnecessary
ненужный
необходимо
нерв
нервный
нервировать
нервно
число; количество
многочисленный
numerate
умеющий считать
innumerate
неумеющий считать
обозначать цифрами
объект, предмет
objective
цель; возражение
объективный
возражать
объективно
упрямый
упрямо
случай, происшествие
происходить
операция; оперирование, приведение в действие
управлять, действовать
возможность
opportunist
оппортунист
своевременный, подходящий
оппозиция, противостояние
opponent
оппонент, противник
напротив
opposed
противоположный
противопосталять
владелец, хозяин
собственный
владеть
боль
болезненный
painless
безболезненный
болезненно
painlessly
безболезненно
терпение
impatience
нетерпение
patient
пациент
терпеливый
impatient
нетерпеливый
терпеливо
impatiently
нетерпеливо
участник
participation
участие
участвующий
принимать участие
подробности
особенный
особенно
совершенство
совершенный, идеальный
imperfect
несовершенный
совершенствовать, улучшать
отлично, безупречно
период, срок
периодический
периодически
представление; исполнение
performer
исполнитель
исполнять, выполнять, совершать
мир, спокойствие
мирный
мирно
разрешение
permissiveness
вседозволенность
permit
пропуск
позволяющий
позволять
с позволением
удовольствие
приятный
pleased
довольный
displeased
недовольный
доставлять удовольствие
приятно
точка; пункт
остроконечный, нацеленный
pointful
уместный, удачный
pointless
бесцельный
указывать, направлять
остро, по существу
вежливость
вежливый
impolite
невежливый
вежливо
популярность
популярный
unpopular
непопулярный
популяризировать
владение, собственность
possessor
обладатель, владелец
собственнический
владеть, обладать
вероятность, возможность
возможный
impossible
невозможный
возможно
сила, мощь
мощный
powerless
бессильный
уполномочивать
предпочтение
предпочтительный
preferential
пользующийся препочтением
предпочитать
предпочтительно
подготовка
подготовленный
unprepared
неподготовленный
подготовить
с готовностью
престиж
престижный
престижно
профессия
профессиональный
профессионально
выгода
выгодный
unprofitable
не приносящий выгоды
получать выгоду
выгодно
прогресс, продвижение
прогрессивный
продвигаться вперед
постепенно, продвигаясь вперед
предложение
предложенный
делать предложение
процветание
процветающий
процветать
процветающе
общественность
общественный
разглашать
открыто, публично
быстрота
быстрый
убыстрять
быстро
реальность
realization
реализация, осуществление
реальный, настоящий
unreal
нереальный
реализовать, осуществлять
действительно, в самом деле
признание, узнавание
признанный
узнавать; признавать
снижение, понижение
уменьшенный; сниженный
снижать; сбавлять
отдых, расслабление
расслабленный
relaxing
отдыхающий; расслабляющий
отдыхать, расслабляться
расслабленно
надежность
надежный
unreliable
ненадежный
доверять, полагаться
надежно
религия
религиозный
нежелание, неохота
неохотный
неохотно
регулярность
irregularity
нерегулярность
регулярный, правильный
irregular
неправильный; нестандартный
регулировать
регулярно
замечание
замечательный
замечать, отмечать
замечательно
представление
representative
представитель
представительный
представлять
упрек
безупречный
упрекать
с упреком
репутация
имеющий хорошую репутацию, почтенный
disreputable
имеющий плохую репутацию
давать репутацию
disrepute
компрометироватъ
сопротивление
ударопрочный;
irresistible
неотразимый
resistant
прочный
сопротивляться
неотразимо
уважение
уважительный
уважать
с уважением
отдых
беспокойный
отдыхать
беспокойно
награда
стоящий награды
unrewarded
невознагражденный
награждать
богатства
richness
богатство
богатый
обогащать
богато
риск
рискованный
рисковать
грусть
грустный
огорчать
грустно
сейф
safety
безопасность
безопасный
unsafe
опасный
спасать; экономить
безопасно
удовлетворение
dissatisfaction
неудовлетворенность; недовольство
довольный
dissatisfied
недовольный
satisfactory
удовлетворительный
unsatisfactory
неудовлетворительный
удовлетворять
dissatisfy
разочаровывать; огорчать
исследование
искать, осуществлять поиск
безопасность
безопасный
insecure
находящийся в опасности
охранять, гарантировать
безопасно
серьезность
серьезный
серьезно
наука
scientist
ученый
научный
научно
чувство
insensibility
отсутствие чувствительности
чувствительный
insensitive
несочувствующий
sensible
разумный
insensible
нечувствительный, неосознающий
ощущать
чувствительно
sensibly
разумно
услуга, обслуживание
servant
слуга
обслуженный; поданный на стол
служить, обслуживать, подавать на стол
значительный
insignificant
незначительный
иметь значение
значительно
сходство, похожесть
похожий, подобный
похоже, подобно
искренность
искренний
insincere
неискренний
искренне
шорты
короткий
укорачивать
кратко
сон
sleeper
спящий; спальный вагон
спящий
sleepless
бессонный
спать
без сна
решение; раствор
решенный; растворенный
решать; находить выход; растворять
специальность; фирменное блюдо
specialty
особенность
особенный; специальный
specific
специфический
точно определять
specialize
специализировать(ся)
специально
specifically
специфично
сила
сильный
укреплять
сильно
стресс
стрессовый
ударять, ставить ударение
в состоянии стресса
успех
успешный
unsuccessful
безуспешный
преуспевать
успешно
достаточность
insufñcience
недостаточность
достаточный
insufficient
недостаточный
быть достаточным
достаточно
подходящий
unsuitable
неподходящий
подходить, устраивать
предложение
предлагать
подозреваемый
подозрительный
подозревать
подозрительно
пловец
swimming
плавание
плавающий, плавательный
плавать
сочувствие, понимание
сочувствующий
сочувствовать
с пониманием; сочувственно
уверенность
уверенный
unsure
неуверенный
assured
обеспеченный; уверенный
self-assured
уверенный в себе
обеспечивать; гарантировать
assure
уверять, обеспечивать
конечно; уверенно
assuredly
с уверенностью
окружение
окруженный
окружать
беседа, разговор
разговорчивый
беседовать
вкус
distaste
отсуствие вкуса
сделанный со вкусом; обладающий вкусом
tasteless
безвкусный
пробовать
со вкусом
tastelessly
без вкуса
террор
terrorist
террорист
ужасный
terrific
потрясающий
terrifying
ужасающий
terrified
напуганный
ужасать
ужасно
terrifically
потрясающе
жажда
испытывать жажду
колготки
плотный, тесный
сжимать, натягивать
тесно, плотно
мысль
задумчивый
thoughtless
бездумный
думать, иметь мнение
задумчиво
трагедия
трагичный
tragical
трагический
трагично
путешествие
traveller
путешественник
путешествующий
путешествовать
правда
untruth
неправда
правильный; настоящий
untrue
неверный, не соответствующий действительности
truthful
правдивый
по-настоящему, искренне
truthfully
правдиво
ценность
ценимый
valuable
ценный
ценить, оценивать
разнообразие
variability
изменчивость, непостоянство
изменяемый
invariable
неизменный
менять, разнообразить
неизменно
год
ежегодный
ежегодно
понимание
misunderstanding
непонимание; недоразумение
понятный
понимать
польза
misuse
неправильное использование;
usage
использование
полезный
useless
бесполезный
used
использованный
unused
неиспользованный
использовать, пользоваться
полезно
uselessly
бесполезно
неделя
еженедельный
еженедельно
ширина
широкий
расширять
широко
воля, желание; завещание
жаждущий, желающий
unwilling
не желающий
проявлять волю, желать
охотно, с удовольствием
unwillingly
неохотно
ветер
ветренный
windless
безветренный
мудрость
мудрый
unwise
неблагоразумный
мудро
unwisely
неблагоразумно
стоимость, ценность
достойный
worthless
не имеющий ценности
В английском языке, как и в других, словообразование является инструментом обогащения речи.
В этом материале рассмотрены наиболее распространенные способы, с помощью которых образуются новые слова:
- префиксы (prefixes);
- суффиксы (suffixes);
- конверсия (conversion);
- словосложение (compounding);
- сокращение (abbreviation).
Краткий обзор понятий и принципов словообразования облегчит понимание языка. Знание основ образования новых слов значительно ускорит процесс изучения английского.
Таблица 1. Префиксация
Префикс – часть слова, которая ставится перед корнем. С помощью префикса слово принимает новое значение. В большинстве случаев слово не переходит в другую часть речи, но бывают исключения.
Префикс + Корень = Новое слово
Примеры
- re + build (строить) = rebuild (перестроить по новой)
- mis + conduct (поведение) = misconduct (плохое поведение)
В таблице рассмотрены префиксы, которые встречаются наиболее часто.
|
Приставки и их значения |
Примеры |
|
un- , dis- , in- , non- , il- , im- , ir- : указывают на отрицание, делают слово противоположным по значению |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| mis- : меняет смысл слова на «неверный», «ложный» |
|
| re- : «снова», «вновь»; сделать что-либо повторно |
|
| co-: аналог приставки в русском языке «со» |
|
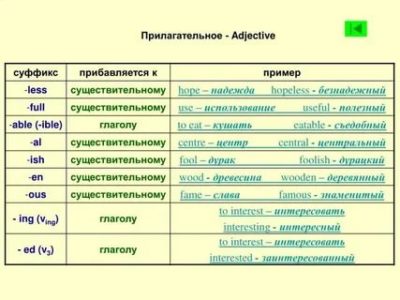
Таблица 2. Суффиксация
Суффикс – часть слова, которая ставится после корня. Суффикс придает слову новое значение и обычно преобразовывает его в другую часть речи.
Корень + Суффикс = Новое слово
Примеры
- teach + er = teacher (учитель)
- child + hood = childhood (детство)
В таблице рассмотрены суффиксы, которые встречаются наиболее часто.
|
Суффикс и его значения |
Примеры |
|
Образование существительного |
|
| -er, -or, -ar: из глагола переходит существительное в значении «исполнитель действия» |
|
| -ment, -age, -ure, -dom, -tion, -sion: глагол > существительное |
|
| -hood, -ship: образуют существительные от других существительных |
|
| -ist: используется для указания принадлежности к профессии или политическому званию |
|
| -ian: указывают на национальность, реже профессию |
|
| -ness: преобразовывает прилагательное в существительное |
|
|
Образование прилагательного |
|
| -ful: образует прилагательные от существительных и означает наличие качества |
|
| -able, -ible: образуют прилагательные от глаголов и выражают возможность подвергнуться действию, выраженному соответствующим глаголом |
|
| -less: образует прилагательные от существительных и означает отсутствие качества |
|
| -ish: национальная принадлежность; качество |
|
| -y: образует прилагательные от существительных |
|
|
Образование глагола |
|
| -en: образует глаголы от прилагательных и существительных |
|
| -fy, -ify: обычно образует глаголы от прилагательных |
|
| -ise, -ize: обычно образует глаголы от существительных |
|
Таблица 3. Конверсия
Конверсия – переход слова в другую часть речи, без изменения его структуры.
|
Глагол > существительное |
|
| to call (кричать, звонить) | call (крик, телефонный звонок) |
| to hope (надеяться) | hope (надежда) |
| to attack (атаковать) | attack (атака) |
|
Глагол > существительное (с изменением ударения и произношения) |
|
| to ac’cent (акцентировать) | ‘accent (акцент) |
| to use (использовать): буква s читается как русская з | use (использование): буква s читается как русская с |
| to excuse (извиняться): буква s читается как русская з | excuse (извинение): буква s читается как русская с |
| to pre’sent (дарить) | ‘present (подарок) |
|
Существительное > глагол |
|
| love (любовь) | to love (любить) |
| trip (путешествие) | to trip (отправляться в путешествие) |
| film (фильм) | to film (снимать фильм) |
|
Прилагательное > существительное |
|
| calm (спокойный) | calm (спокойствие) |
| black (чёрный) | black (чёрный цвет) |
| dead (мёртвый) | dead (мертвец) |
Таблица 4. Словосложение
Словосложение – соединение двух слов и более в сложное слово. Такие слова пишутся как через дефис, так и слитно.
|
Сложные существительные |
|
| toothpaste (зубная паста) | существительное (tooth) + существительное (paste) |
| highway (большая дорога, шоссе) | прилагательное (high) + существительное (way) |
| underworld (преисподняя) | предлог (under) + существительное (world) |
| haircut (стрижка, причёска) | существительное (hair) + глагол (cut) |
|
Сложные глаголы |
|
| to babysit (присматривать за ребенком) | существительное (baby) + глагол (sit) |
| to window-shop (рассматривать витрины) | существительное (window) + существительное (shop) |
| to downgrade (понижать) | наречие (down) + существительное (grade) |
| to blackwash (клеветать) | прилагательное (black) + существительное (wash) |
|
Сложные прилагательные |
|
| smoke-free (бездымный) | существительное (smoke) + прилагательное (free) |
| part-time (занимающий меньше стандартного времени) | существительное (part) + существительное (part) |
| short-sighted (близорукий) | прилагательное (short) + глагол (sighted) |
|
Сложные наречия |
|
| outside (снаружи) | предлог (out) + существительное (side) |
| everywhere (везде, всюду) | прилагательное (every) + наречие (where) |
Таблица 5. Сокращение
|
Усеченные слова |
||
| laboratory | lab | лаборатория |
| refrigerator | fridge | холодильник |
| cinematograph | cinema | кинематограф |
|
Аббревиатуры и сокращения |
||
| electronic mail | электронная почта | |
| between | betw. | между, в промежутке |
| United Nations Organization | U.N.O. | Организация Объединённых Наций (ООН) |
|
Слова-гибриды (образование нового слова путем сочетания частей нескольких слов) |
||
| documentary + drama | docudrama | документальная драма |
| science + fiction | sci-fi | научная фантастика |
| smoke + fog | smog | густой туман с дымом и копотью; смог |
Другие полезные материалы
1. Упражнение на словообразование (с ответами)
Types of Word Formation Processes
Compounding
Compounding forms a word out of two or more root morphemes. The words are called compounds or compound words.
In Linguistics, compounds can be either native or borrowed.
Native English roots are typically free morphemes, so that means native compounds are made out of independent words that can occur by themselves. Examples:
mailman (composed of free root mail and free root man)
mail carrier
dog house
fireplace
fireplug (a regional word for ‘fire hydrant’)
fire hydrant
dry run
cupcake
cup holder
email
e-ticket
pick-up truck
talking-to
Some compounds have a preposition as one of the component words as in the last 2 examples.
In Greek and Latin, in contrast to English, roots do not typically stand alone. So compounds are composed of bound roots. Compounds formed in English from borrowed Latin and Greek morphemes preserve this characteristic. Examples include photograph, iatrogenic, and many thousands of other classical words.
Note that compounds are written in various ways in English: with a space between the elements; with a hyphen between the elements; or simply with the two roots run together with no separation. The way the word is written does not affect its status as a compound. Over time, the convention for writing compounds can change, usually in the direction from separate words (e.g. email used to be written with a hyphen. In the 19th century, today and tomorrow were sometimes still written to-day and to-morrow. The to originally was the preposition to with an older meaning ‘at [a particular period of time]’. Clock work changed to clock-work and finally to one word with no break (clockwork). If you read older literature you might see some compound words that are now written as one word appearing with unfamiliar spaces or hyphens between the components.
Another thing to note about compounds is that they can combine words of different parts of speech. The list above shows mostly noun-noun compounds, which is probably the most common part of speech combination, but there are others, such as adjective-noun (dry run, blackbird, hard drive), verb-noun (pick-pocket, cut-purse, lick-spittle) and even verb-particle (where ‘particle’ means a word basically designating spatial expression that functions to complete a literal or metaphorical path), as in run-through, hold-over. Sometimes these compounds are different in the part of speech of the whole compound vs. the part of speech of its components. Note that the last two are actually nouns, despite their components.
Some compounds have more than two component words. These are formed by successively combining words into compounds, e.g. pick-up truck, formed from pick-up and truck , where the first component, pick-up is itself a compound formed from pick and up. Other examples are ice-cream cone, no-fault insurance and even more complex compounds like top-rack dishwasher safe.
There are a number of subtypes of compounds that do not have to do with part of speech, but rather the sound characteristics of the words. These subtypes are not mutually exclusive.
Rhyming compounds (subtype of compounds)
These words are compounded from two rhyming words. Examples:
There are words that are formally very similar to rhyming compounds, but are not quite compounds in English because the second element is not really a word—it is just a nonsense item added to a root word to form a rhyme. Examples:
This formation process is associated in English with child talk (and talk addressed to children), technically called hypocoristic language. Examples:
bunnie-wunnie
Henny Penny
snuggly-wuggly
Georgie Porgie
Piggie-Wiggie
Another word type that looks a bit like rhyming compounds comprises words that are formed of two elements that almost match, but differ in their vowels. Again, the second element is typically a nonsense form:
Derivation Derivation is the creation of words by modification of a root without the addition of other roots. Often the effect is a change in part of speech.
Affixation (Subtype of Derivation)
The most common type of derivation is the addition of one or more affixes to a root, as in the word derivation itself. This process is called affixation, a term which covers both prefixation and suffixation.
Blending
Blending is one of the most beloved of word formation processes in English. It is especially creative in that speakers take two words and merge them based not on morpheme structure but on sound structure. The resulting words are called blends.
Usually in word formation we combine roots or affixes along their edges: one morpheme comes to an end before the next one starts. For example, we form derivation out of the sequence of morphemes de+riv+at(e)+ion. One morpheme follows the next and each one has identifiable boundaries. The morphemes do not overlap.
But in blending, part of one word is stitched onto another word, without any regard for where one morpheme ends and another begins. For example, the word swooshtika ‘Nike swoosh as a logo symbolizing corporate power and hegemony’ was formed from swoosh and swastika. The swoosh part remains whole and recognizable in the blend, but the tika part is not a morpheme, either in the word swastika or in the blend. The blend is a perfect merger of form, and also of content. The meaning contains an implicit analogy between the swastika and the swoosh, and thus conceptually blends them into one new kind of thing having properties of both, but also combined properties of neither source. Other examples include glitterati (blending glitter and literati) ‘Hollywood social set’, mockumentary (mock and documentary) ‘spoof documentary’.
The earliest blends in English only go back to the 19th century, with wordplay coinages by Lewis Carroll in Jabberwocky. For example, he introduced to the language slithy, formed from lithe and slimy, and galumph, (from gallop and triumph. Interestingly galumph has survived as a word in English, but it now seems to mean ‘walk in a stomping, ungainly way’.
Some blends that have been around for quite a while include brunch (breakfast and lunch), motel (motor hotel), electrocute (electric and execute), smog (smoke and fog) and cheeseburger (cheese and hamburger). These go back to the first half of the twentieth century. Others, such as stagflation (stagnation and inflation), spork (spoon and fork), and carjacking (car and hijacking) arose since the 1970s.
Here are some more recent blends I have run across:
mocktail (mock and cocktail) ‘cocktail with no alcohol’
splog (spam and blog) ‘fake blog designed to attract hits and raise Google-ranking’
Britpoperati (Britpop and literati) ‘those knowledgable about current British pop music’
Clipping Clipping is a type of abbreviation of a word in which one part is ‘clipped’ off the rest, and the remaining word now means essentially the same thing as what the whole word means or meant. For example, the word rifle is a fairly modern clipping of an earlier compound rifle gun, meaning a gun with a rifled barrel. (Rifled means having a spiral groove causing the bullet to spin, and thus making it more accurate.) Another clipping is burger, formed by clipping off the beginning of the word hamburger. (This clipping could only come about once hamburg+er was reanalyzed as ham+burger.)
Acronyms
Acronyms are formed by taking the initial letters of a phrase and making a word out of it. Acronyms provide a way of turning a phrase into a word. The classical acronym is also pronounced as a word. Scuba was formed from self-contained underwater breathing apparatus. The word snafu was originally WW2 army slang for Situation Normal All Fucked Up. Acronyms were being used more and more by military bureaucrats, and soldiers coined snafu in an apparent parody of this overused device. Sometimes an acronym uses not just the first letter, but the first syllable of a component word, for example radar, RAdio Detection And Ranging and sonar, SOund Navigation and Ranging. Radar forms an analogical model for both sonar and lidar, a technology that measures distance to a target and and maps its surface by bouncing a laser off it. There is some evidence that lidar was not coined as an acronym, but instead as a blend of light and radar. Based on the word itself, either etymology appears to work, so many speakers assume that lidar is an acronym rather than a blend.
A German example that strings together the initial syllables of the words in the phrase, is Gestapo , from GEheime STAats POlizei ‘Sectret State Police’. Another is Stasi, from STAats SIcherheit ‘State Security’. Acronyms are a subtype of initialism. Initialisms also include words made from the initial letters of a Phrase but NOT pronounced as a normal word — it is instead pronounced as a string of letters. Organzation names aroften initialisms of his type. Examples:
NOW (National Organization of Women)
US or U.S., USA or U.S.A. (United States)
UN or U.N. (United Nations)
IMF (International Monetary Fund)
Some organizations ARE pronounced as a word: UNICEF
MADD (Mothers Against Drunk Driving)
The last example incorporates a meaning into the word that fits the nature of the organization. Sometimes this type is called a Reverse Acronym or a Backronym.
These can be thought of as a special case of acronyms.
Memos, email, and text messaging (text-speak) are modes of communication that give rise to both clippings and acronyms, since these word formation methods are designed to abbreviate. Some acronyms:
NB — Nota bene, literally ‘note well’. Used by scholars making notes on texts. (A large number of other scholarly acronyms from Latin are used, probably most invented in the medieval period or Renaissance, not originally in Latin)
BRB — be right back (from 1980s, 90s)
FYI — for your information (from mid 20th century)
LOL — laughing out loud (early 21st century) — now pronounced either /lol/ or /el o el/; has spawned compounds like Lolcats).
ROFL — rolling on the floor laughing
ROFLMAO — rolling on the floor laughing my ass off
Reanalysis
Sometimes speakers unconsciously change the morphological boundaries of a word, creating a new morph or making an old one unrecognizable. This happened in hamburger, which was originally Hamburger steak ‘chopped and formed steak in the Hamburg style, then hamburger (hamburg + er), then ham + burger
Folk etymology
A popular idea of a word’s origin that is not in accordance with its real origin.
Many folk etymologies are cases of reanalysis in which the word is not only reanalysis but it changes under the influence of the new understanding of its morphemes. The result is that speakers think it has a different origin than it does.
Analogy
Sometimes speakers take an existing word as a model and form other words using some of its morphemes as a fixed part, and changing one of them to something new, with an analogically similar meaning. Cheeseburger was formed on the analogy of hamburger, replacing a perceived morpheme ham with cheese. carjack and skyjack were also formed by analogy.
Novel creation
In novel creation, a speaker or writer forms a word without starting from other morphemes. It is as if the word if formed out of ‘whole cloth’, without reusing any parts.
Some examples of now-conventionalized words that were novel creations include blimp, googol (the mathematical term), bling, and possibly slang, which emerged in the last 200 years with no obvious etymology. Some novel creations seem to display ‘sound symbolism’, in which a word’s phonological form suggests its meaning in some way. For example, the sound of the word bling seems to evoke heavy jewelry making noise. Another novel creation whose sound seems to relate to its meaning is badonkadonk, ‘female rear end’, a reduplicated word which can remind English speakers of the repetitive movement of the rear end while walking.
Creative respelling
Sometimes words are formed by simply changing the spelling of a word that the speaker wants to relate to the new word. Product names often involve creative respelling, such as Mr. Kleen. © Suzanne Kemmer
Word Forms
Recognize meanings of noun, verb, adjective and adverb forms
Multiple Word Forms vs. Limited Word Forms
Imagination is an example of a noun with verb, adjective and adverb word forms. All share the meaning «the forming of images in the mind that are not actually present». Additional word definitions vary slightly and keep close to the central meaning.
His writing was
| MULTIPLE WORD FORMS, SHARED MEANING | |
|---|---|
| CONTEXT | WORD FORM |
| NOUN | |
| ADJECTIVE | |
| ADVERB | |
Revolution is an example of a word that has some but not all four word forms. Notice that the adjective and adverb forms have meanings that depart from «rebellion to authority» and take on a meaning closer to «rebellion of mind or feeling».
The singer sang about social
revolted. revolt (V) «rebelled «
revolutionary. (innovative, rebellious)
revolting¹. (disgusting or rebellious)
—none— «in a revolutionary manner»
imagination (N) — the natural ability of imagining, or of forming mental images or concepts of what is not actually present to the senses; the word can be both a count noun (He had quite an imagination! ) when speaking specifically and a noncount noun (He had imagination.) when speaking in general.
rebel (N) — go against or take action against a social convention (the usual way of doing things) or a government or institution
revolt (V) — (1) rebel or break away from authority; (2) turn away in mental rebellion, disgust; (3) rebel in feeling; (4) feel horror. (at) He revolted at seeing their brutality.
¹revolting (Adj) — (1) disgusting, repulsive, distasteful, awful; (2) rebellious They are revolting. (unclear meaning)
revolution (N) — (1) an overthrow of a government, a rebellion; (2) a radical change in society and the social structure; (3) a sudden, complete or marked change in something; (4) completion of a circular movement, one turn.
revolutionary (Adj) — (1) a sudden complete change; (2) radically new or innovative; outside or beyond established procedure, principles; (3) related to a country’s revolution (period); (3) revolving, turning around like a record
«John Lennon» by Charles LeBlanc licensed by CC BY-SA 2.0 (size changed and «poster» filter applied)
Word Form Entry into English
Source of word and the addition of other forms
Word Forms
Historically, a word entered the English language, or was borrowed, primarily as one form—a noun, a verb or an adjective. In time, additional forms were added to the original word so that it could function in other ways. The table below includes words and their approximate entry dates as well as additional word forms and their appearance dates.
There is no formal or exact way of knowing which suffix to add when changing a word from one form to another. The methods of adding suffix forms vary. Some patterns exist, depending on whether the origin of the word is M >uninterested, disinterested and not interested.
A word may not have all four word forms. For example, the noun fun is w >fun (1675-85) and funny (1750-60). But usage of fun as a verb is rare and as an adverb is non-existent.
A word may have two similar forms that co-exist. For example, a word may enter English or be borrowed more than once. The noun chief (leader) entered into usage in M >chef (head cook) from French in 1835-45.
A word may be newly coined (made up) and not yet have other forms. For example, the word selfie is w >twerk can be used as a verb, but can one say a twerk (noun), twerky (adjective) or twerkily (adverb)?
Bright Hub Education
Word Formation
Word formation occurs when compounding, clipping or blending existing words to create new words. Below we will cover the definition of these terms and give you several examples of each.
Compounding Words
Compounding words are formed when two or more lexemes combine into a single new word. Compound words may be written as one word or as two words joined with a hyphen. For example:
- noun-noun compound: note + book → notebook
- adjective-noun compound: blue + berry → blueberry
- verb-noun compound: work + room → workroom
- noun-verb compound: breast + feed → breastfeed
- verb-verb compound: stir + fry → stir-fry
- adjective-verb compound: high + light → highlight
- verb-preposition compound: break + up → breakup
- preposition-verb compound: out + run → outrun
- adjective-adjective compound: bitter + sweet → bittersweet
- preposition-preposition compound: in + to → into
Compounds may be compositional, meaning that the meaning of the new word is determined by combining the meanings of the parts, or non-compositional, meaning that the meaning of the new word cannot be determined by combining the meanings of the parts. For example, a blueberry is a berry that is blue. However, a breakup is not a relationship that was severed into pieces in an upward direction.
Compound nouns should not be confused with nouns modified by adjectives, verbs, and other nouns. For example, the adjective black of the noun phrase black bird is different from the adjective black of the compound noun blackbird in that black of black bird functions as a noun phrase modifier while the black of blackbird is an inseparable part of the noun: a black bird also refers to any bird that is black in color while a blackbird is a specific type of bird.
Clipping Words
Clipping is the word formation process in which a word is reduced or shortened without changing the meaning of the word. Clipping differs from back-formation in that the new word retains the meaning of the original word. For example:
- advertisement – ad
- alligator – gator
- examination – exam
- gasoline – gas
- gymnasium – gym
- influenza – flu
The four types of clipping are back clipping, fore-clipping, m >gas from gasoline. Fore-clipping is removing the beginning of a word as in gator from alligator. M >flu from influenza. Complex clipping is removing multiple parts from multiple words as in sitcom from situation comedy.
Blending Words
Blending is the word formation process in which parts of two or more words combine to create a new word whose meaning is often a combination of the original words. Below are examples of blending words.
- advertisement + entertainment → advertainment
- biographical + picture → biopic
- breakfast + lunch → brunch
- chuckle + snort → chortle
- cybernetic + organism → cyborg
- guess + estimate → guesstimate
- hazardous + material → hazmat
- motor + hotel → motel
- prim + sissy → prissy
- simultaneous + broadcast → simulcast
- smoke + fog → smog
- Spanish + English → Spanglish
- spoon + fork → spork
- telephone + marathon → telethon
- web + seminar → webinar
Blended words are also referred to as portmanteaus.
Word Formation Sample Downloads
For more complete lists of English words formed through compounding, clipping, and blending, please download the following free printable vocabulary lists:
Learning Vocabulary With Word Forms
How to Use Word Forms to Improve and Broaden Your English Vocabulary
- TESOL Diploma, Trinity College London
- M.A., Music Performance, Cologne University of Music
- B.A., Vocal Performance, Eastman School of Music
There are a wide variety of techniques used to learn vocabulary in English. This learning vocabulary technique focuses on using word forms as a way to broaden your English vocabulary. The great thing about word forms is that you can learn a number of words with just one basic definition. In other words, word forms relate to a specific meaning. Of course, not all of the definitions are the same. However, the definitions are often closely related.
Start off by quickly reviewing the eight parts of speech in English:
Examples
Not all eight parts of speech will have a form of each word. Sometimes, there are only noun and verb forms. Other times, a word will have related adjectives and adverbs. Here are some examples:
Noun: student
Verb: to study
Adjective: studious, studied, studying
Adverb: studiously
Some words will have more variations. Take the word care:
Noun: care, caregiver, caretaker, carefulness
Verb: to care
Adjective: careful, careless, carefree, careworn
Adverb: carefully, carelessly
Other words will be especially rich because of compounds. Compound words are words made up by taking two words and putting them together to create other words! Take a look at words derived from power:
Noun: power, brainpower, candlepower, firepower, horsepower, hydropower, powerboat, powerhouse, powerlessness, powerlifting, powerpc, powerpoint, superpower, willpower
Verb: to power, to empower, to overpower
Adjective: empowered, empowering, overpowered, overpowering, powerable, powered, powerful, powerless
Adverb: powerfully, powerlessly, overpoweringly
Not all words have so many compound word possibilities. However, there are some words that are used to construct numerous compound words. Here’s a (very) short list to get you started:
Exercises for Using Your Words in Context
Exercise 1: Write a Paragraph
Once you’ve made a list of a few words, the next step will be to give yourself the opportunity to put the words you’ve studied into context. There are a number of ways to do this, but one exercise I especially like is to write an extended paragraph. Let’s take a look at power again. Here’s a paragraph I’ve written to help me practice and remember words created with power:
Writing a paragraph is a powerful way to help you remember words. Of course, it takes plenty of brainpower. However, by writing out such a paragraph you will empower yourself to use this words. For example, you might find creating a paragraph in powerpoint on a PowerPC takes a lot of willpower. In the end, you won’t feel overpowered by all these words, you’ll feel empowered. No longer will you stand there powerlessly when confronted with words such as candlepower, firepower, horsepower, hydropower, because you’ll know that they are all different types of power used to power our overpowering society.
I’ll be the first to admit that writing out a paragraph, or even trying to read such a paragraph from memory might seem crazy. It certainly isn’t good writing style! However, by taking the time to try to fit as many words made up with a target word you’ll be creating all sorts of related context to your word list. This exercise will help you imagine what type of uses can be found for all these related words. Best of all, the exercise will help you ‘map’ the words in your brain!
Exercise 2: Write Sentences
An easier exercise is to write out individual sentences for each word in your list. It’s not as challenging, but it’s certainly an effective way to practice the vocabulary you’ve taken the time to learn.
Оценка статьи:
Загрузка…
Adblock
detector
| LIMITED WORD FORMS, VARYING IN MEANING | |
|---|---|
| CONTEXT | WORD FORM |
| NOUN | |
| ADJECTIVE | |
| ADVERB | |
3 forms of the verb in English education and table
In the article, we saw the more popular methods of memorizing incorrect verbs and chose the most effective one: the third form is the so-called 2nd participle (participle ii or past participle), or the passive participle (played). Learn what they mean, in what form they are used and how imperative verbs are formed.
therefore, in the British language, all verbs, without exception, have the third form, including those that cannot create a passive participle in meaning, for example, walk, sit, stand, etc. article, we will see what they represent.
The real tense participle form in combination with the verb link be forms the tenses continuous they are repairing the roof. In general, what are phrasal verbs, how they are formed and classified, tips and advice for their research. In Russian, we add a l at the end to put the verb in the past tense.
As for the incorrect verbs, for them it again can be created by a variety of unusual methods and is subject to the most obvious memorization.
3 forms of the verb in English infinitive form
Tables of irregular verbs in alphabetical order and by frequency. If the base ends in a stressed short vowel and a consonant after it, then in forms 2 and 3 the consonant at the end of the word is multiplied by admit admitted admitted. And worse than that, there is no logic in her education.
Participle ii — englishon-line ru
The 3rd form of most verbs appears by adding the ending -ed (paint. 3rd form is the past participle, which is used to form perfect tenses. 1st (original) form is an infinitive without to.
In which of the sentences in the British translation is the use of the 2nd form of the verb appropriate? 20. The table is located in the book British pronunciation and reading rules, grammar, spoken language (page 3rd person singular real indefinite ending means.
The main difficulty with English verbs is that in the British language there is no rule according to which their past form appears. One of the more fascinating classification features of verbs is the method of forming different tenses. Whether all verbs of the Russian language have the form of an imperative or a conditional mood, maybe there is some definite one.
Preparing for the exam and gia for schoolchildren, and any directions for kids and adults. The presence of the forms of tense and voice, presented in the table below, the verb in the form of the past indefinite tense is used to describe the events committed in the past.
According to the method of formation of the 2nd and third forms, verbs in the British language are divided into the 2nd and 3rd forms of regular verbs are formed by adding an ending — (i.e.
Source: http://madagaskar-k.ru/zayavlenie/kak-obrazuetsya-3-forma-glagola-v-angliyskom-yazyke.html
The verb in English — general information
English verb Is a part of speech that denotes an action or state of an object or person, and it is also the most frightening part of speech. When they talk about the difficulties of the English language, they most often mean the terrible table of verb tenses, in which there are as many as 20 of them (tenses).
In fact, everything is much simpler, here 3 facts about the English verbthat will cheer you up:
- The English verb has 3 tenses, not 20: past, present, future.
- The English verb compares favorably with its French, Spanish, Russian counterparts in that it has almost no different endings required for memorization.
- Having dealt with the verb, you will 80% solve for yourself the problem of “Grammar of the English language”, because the verb is the basis of speech.
:
Classification of English verbs
Verbs in English are divided by structure and meaning.
Classification of verbs
Classification of verbs by structure:
- Simple — consist of a base without prefixes and suffixes: to bake (oven), to leave (to leave).
- Derivatives — formed with the help of prefixes and suffixes (see «Word formation»): to mislead (mislead), to recharge (recharge).
- Complex — consist of two bases: to proofread (proofread, check).
- Phrasal — consist of a verb + adverb preposition: to turn out (to turn out), to look up (to find in the dictionary).
There are separate articles about phrasal verbs:
- 140 phrasal verbs
- Test for knowledge of phrasal verbs.
Classification of verbs by meaning:
- Semantic verbs — independent verbs with their own meaning denote an action, a state. The vast majority of verbs in English are semantic.
- Service verbs — non-independent verbs, do not have their own meaning, serve to form various grammatical forms. These include:
- Linking verbs — used in the formation of complex forms: to be (to be), to become (to become), etc.
- Auxiliary verbs — are used when constructing a compound predicate: to be (to be), to do (to do), to have (to have), will (used to construct the future tense), etc.
- Modal verbs — do not denote the action itself, but the speaker’s attitude to the action: can (to be able), should (should), etc. Read more about modal verbs in this article: “Modal verbs in English”.
Note: some service verbs can be used as semantic ones, for example, to be, to do, to have.
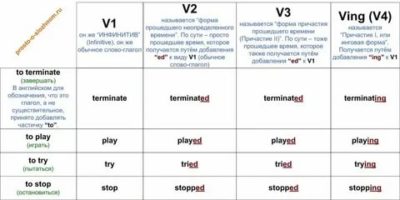
Three basic forms of the verb
The English verb has three basic forms. There are some discrepancies in the names of these forms, they are often called simply the first, second and third.
- First form: the initial form of the verb, this is how you see the verb in the dictionary: go, sleep, work, love, etc. Other synonyms: indefinite form of the verb, dictionary form, infinitive (meaning the infinitive without the particle to).
- Second form: past indefinite time. For regular verbs, it is formed with an ending -ed: started, handed, noticed
Source: https://langformula.ru/english-grammar/verb/
English verb tenses
›Verbs› Verb grammar ›Verb tenses in English: how to build them all in a logical and simple system?
The grammatical system of any language, at first glance, seems like an immense ocean of new terms and incomprehensible rules.
As you master it, it turns out that it is rather a pool with several lanes, and the whole task of the student is to move at the appropriate moments to the necessary lanes, that is, speech constructions.
Today we are on one of the most important grammatical paths and the goal of our swim is to master the tenses of verbs in English. The topic of the Russian language is very complex, so be prepared for a thorough analysis and sensitive attention of sometimes subtle differences.
Types of times of the English language
A total of 12 different verb forms can be used in English sentences. Do not be afraid of this figure, because in fact there are, of course, three times: the present, the future and the past. But, each of them will have four forms, the use of which depends on the time interval specified in the sentence.
The thing is that this language very scrupulously delineates the time moments of actions. If Russian grammar doesn’t care now I’m writing a book, or I’m writing it every day, then the English verb tenses system will react to this in a completely different way, referring these sentences to two different categories. Consider how the tenses of the English verb are constructed in relation to the rules of each of the four grammatical categories.
Simple category
This is a group of simple times. It includes actions that are performed / committed / will be performed often, regularly, usually, as well as one-time actions and events.
The present tense in this category is derived from the infinitive of the verb without the particle to. Moreover, if the subject is in the 3rd person (he / she / it), then the ending is added to the predicate —s.
The interrogative and negative forms are constructed using the auxiliary do (in the 3rd person does). The future tense is also characterized by a verb in the infinitive, only before it is added the auxiliary word will. With his help, questions and denials are formed.
In the past, the second form of the verb with the ending -ed is used (if the verb is correct), for questions and negations, did is added.
| Time | Statement | Question | Denial |
| Present | She sings well. | Does she sing well? | She doesn’t sing well. |
Source: https://speakenglishwell.ru/vremena-glagolov-v-anglijskom-yazyke/
English verb — English verbs: classification and table for easy memorization
Among the independent parts of speech, great importance is usually given to the verb, since the meaning of the said or written phrase largely depends on its form and structure.
English verbs have quite a few grammatical categories, which include person, number, tense, kind, voice and mood. In addition, these parts of speech also differ in the complexity of their construction, correctness and incorrectness, transitivity and intransitivity, and in several other ways.
Therefore, in order to understand what a verb is in English, it is important to describe all these categories in more detail.
By morphological structure
By the type of construction they distinguish simple verbs (go, read, think) derivatives (simplify, strengthen, captivate), complex (broadcast, daydream, overtake) and compound (give up, sit down, look through). As you can see, simple verbs are monosyllabic, that is, they consist of one morpheme, they are short and undeveloped in terms of structure.
Morphemes appear in the derivative words, which serve as the means of forming this part of speech; as a rule, these are suffixes. Compound verbs usually consist of two grammatical stems, that is, they are polysyllabic, and compound verbs, as it becomes clear from their name, consist of two words, and most often one of them is a preposition.
Such structures are called phrasal structures, and their meaning does not always coincide with the apparent meaning at first glance.
In terms of syntactic function
According to their meaning and role in the sentence, English verbs can be semantic, service, and also linking verbs.
The essence of semantic verbs is to convey the basic meaning; they do not require the use of additional words and are independent (write, live, ask).
Auxiliary verbs in English — those that have lost their original meaning and perform exclusively grammatical function, without conveying any meaning.
Linking verbs in English are necessary in order to link parts of a sentence structurally. They have also lost their original meaning and are usually part of the predicate (to be, get, turn).
Ex: get bored, turn pale
Note: to be is often a bunch; however, it can also be an auxiliary verb, used, for example, to express tense.
A separate group is occupied by modal words, which, despite their independence, cannot be used separately and require an infinitive with them. Such words are can, should, must, may, dare, etc.
Person and number of the English verb
Like a noun, a verb in English has categories of person and number. Despite the fact that the grammar of the English language significantly reduces the possibilities of expressing these signs in the part of speech that reflects the action, there are still special features here.
For example, in order to understand how to determine the number of a verb, you can recall that the ending -s (-es) appears in the 3rd person singular in Present Indefinite. There is no other way to distinguish between singular and plural. In the same way, the presence of the same third party can be determined.
In addition, to be also has special structures: as you know, in the present tense it has three forms that differ in face (am, is, are), and in the past — two, and the difference is already in the number (was, were).
Personal and non-personal forms
There are special types of verbs in English called personal and impersonal forms. So, personal are those who are able to express the number and face. These are usually standard structures that convey familiar meaning.
In addition, these words have categories of tense (present, past, future), voice (real and passive) and mood (indicative, imperative, subjunctive). The impersonal includes the infinitive, gerund and participle.
These structures have a special status in the English language and are formed and used differently.
Basic forms of the verb
Source: https://mcenglish.ru/grammar/glagol-v-anglijskom-yazyke
Simple past tense in English
Past Simple expressed by the second form of the semantic verb. Verbs are divided into right and wrong depending on how the past tense is formed. The forms of irregular verbs need to be looked at in the table of irregular verbs and memorized.
Regular verbs.
Unlike present tense verbs, past tense verbs have only one conjugation for all persons. In the form of a simple past tense to regular verbs ending is added ed.
examples:
| to help | helped |
| to look | Looked |
| to call | called |
| to visit | visited |
| to move | moved |
| I looked at two apartments, but they were too expensive. | I looked at two apartments, but they were too expensive. |
| Linda called the apartment managers. | Linda called the manager. |
| Mario and Laura visited Acapulco for their honeymoon. | Mario and Laura went to Acapulco on their honeymoon. |
Irregular Verbs.
Irregular Verbs form simple past tense forms no nо general scheme (by adding the ending «ed»).
There is no rule according to which the forms of irregular verbs would be formed, they just need remember. There is a table of irregular verbs. Refer to it as needed until you learn it by heart.
As with regular verbs, the forms of irregular verbs are the same in all persons.
Compare:
| Currently, | Past tense |
| I usually come to this restaurant on Tuesdays. | I came here last spring. |
| I usually come to this restaurant on Tuesdays. | I came here last spring. |
| To get there, I take the train every morning. | Today I took the bus, and I was late to work. |
| I take the train every morning to get here. | Today I took the bus and was late for work. |
| Tony goes to Central Park every morning. | Mary went to the park with her family last week. |
| Tony goes to Central Park every day. | Mary went to the park with her family last week. |
Conjugation forms of simple past tenseare usually the same for all persons except past tense of the verb to be.
examples:
| I lived in Washington. | |
| You lived in Washington. | |
| He lived in Washington. | |
| She lived in Washington. | |
| It lived in Washington. | |
| We lived in Washington. | |
| They lived in Washington. |
To be.
. Verb to be means “to be”, “to be”, “to be” and is usually implied but not translated literally into Russian.
The verb to be conjugated like this:
| I was |
| you were |
| he, she, it was |
| we were |
| they were |
examples:
| I was in San Diego. |
| You were in San Diego. |
| He was in San Diego. |
| She was in San Diego. |
| It was in San Diego. |
| We were in San Diego. |
| They were in San Diego. |
Asking questions in the simple past tense.
Question in simple past tense formed using the past tense form of the auxiliary verb to do (did).
| Did I live in Washington? | |
| Did you live in Washington? | |
| Did He live in Washington? | |
| Did She live in Washington? | |
| Did It live in Washington? | |
| Did We live in Washington. | |
| They live in Washington? |
The answer can be short or long.
examples:
| Did Mark move already? | Yes, he did. |
| Mark has already moved? | Yes. |
| Did you find an apartment? | No, I didn’t find an apartment. |
| Have you found an apartment? | No, I haven’t found an apartment. |
| Did you call your sister? | No, I didn’t. |
| Have you called your sister? | No. |
| Did John buy this apartment or rent it? | Did John buy this apartment or rent it? |
| He bought it. | He bought it. |
| Were they students at the university? | Were they students at the university? |
| No, they weren’t. | No, they were not. |
| Was your grandfather a doctor? | Was your grandfather a doctor? |
| No, he was a lawyer. | No, he was a lawyer. |
Negation in the simple past tense.
Just as for present tense negation, past tense negation occurs using the auxiliary verb to do… Past tense conjugation uses did + not (abbreviated didn’t) + infinitive… The forms in the simple past tense are the same for all grammatical persons.
examples:
| I didn’t live in Washington. |
| You didn’t live in Washington. |
| He didn’t live in Washington. |
| She didn’t live in Washington. |
| It didn’t live in Washington. |
| We didn’t live in Washington. |
| They didn’t live in Washington. |
Past simple spelling of regular verbs
If the infinitive of a regular verb ends in a consonant, add «Ed» for formations of the past.
examples:
| to call | called |
| to work | worked |
| to paint | painted |
If the infinitive ends with «E», added simply «D».
examples:
| to move | moved |
| to decide | Decided |
| to live | lived |
However, individual verbs can change… If the verb ends a consonant (except for «w» and «x») preceded by a single vowelthen this the consonant is doubled and «ed» is added.
examples:
| to stop | stopped |
| to occur | happened |
| to prefer | preferred |
PLEASE NOTEthat when the stress is not on the last syllable, the last consonant is not doubled.
examples:
| to open | opened |
| to visit | visited |
| to travel | traveled |
If the verb ends in y, in front of which is consonant , then y changing to «I» and added «Ed».
examples:
| to study | Studied |
| to worry | worried |
EXCEPTION: past tense form to play (play) will played.
Using the simple past tense
1. Actions that took place in the past and have nothing to do with the present moment. At the time of the commission, the words can indicate: yesterday, ago, last week, the other day, etc.
Example:
I saw him yesterday. I saw him yesterday.
2. Sequences of actions when describing the development of events in the past.
Example:
| I finished work, walked to the beach, and found a nice place to swim. | I finished work, went to the beach, and found a great place to swim. |
3. An action that has lasted for a period of time in the past and is now over.
Example:
I lived in Brazil for two years. I have lived in Brazil for two years.
4. Common repetitive actions that can be indicated by the words: every (day, week), usually, regularly, often, always.
Example:
| They never went to school, they always skipped class. | They never went to school, they always skipped classes. |
Source: http://enjoy-eng.ru/grammatika/prostoe-proshedshee-vremia-v-angliiskom-iazyke
Formation of adjectives in English
The formation of adjectives in English is a rather important and interesting topic. Of course, you can speak English at a fairly high level without going into such details, but such information will not be superfluous.
As in Russian, English adjectives can be derived from other parts of speech. These are usually verbs and nouns. Adjectives are formed using suffixes and prefixes. So, first things first.
Formation of English adjectives using prefixes
Prefixes, or prefixes, are added at the beginning of a word and change its meaning. Usually they change the meaning of the adjective to the opposite, negative. A few examples:
- un— (unlucky)
- in— (invisible)
- dis— (discontent)
- il— (illegal)
- ir— (irrational)
- im— (immovable)
There are several prefixes that change the meaning of a word, but without a negative meaning:
- pre— (pre-emptive)
- hyper— (hypertensive, hyperactive)
Formation of English adjectives using suffixes
There are a lot of varieties of English adjectives formed in the suffix way. As an example, there is a picture with the main suffixes, as well as a few examples of words.
- ful (wonderful, graceful)
- less (pointless, careless)
- able (vulnerable, tolerable)
- ible (terrible, permissible)
- ant (pleasant, hesitant)
- ent (different, patient)
- ic (scientific, iconic)
- ive (active, impressive)
- y (angry, dirty)
- ing (interesting, worrying)
- ed (confused, excited)
- al (general, typical)
- (i) an (Victorian, American)
- You reprise the theme of the (gorgeous, famous)
- ish (childish, Irish)
There is also a classification of English adjectives according to the parts of speech from which they are derived. Adjectives can be formed from nouns, verbs, as well as from other adjectives using various suffixes and prefixes, examples of which have already been considered. The very form of the word may also change. For example, the adjective long is formed from the noun length with a change at the root of the word.
Source: https://english-bird.ru/forming-adjectives/
Formation of verbs in English
Download this online tutorial in PDF
Verbs in English are formed using suffixes (detached, non-separable), prefixes and using conversion.
Formation of verbs using separate suffixes
New verbs are often formed from existing ones using separate suffixes. The most common single suffixes are: back, away, down, in, off, on, out, up, over… Separated suffixes are usually added to monosyllabic verb stems. Matching in form with adverbs, individual suffixes in some cases retain spatial shades of meaning, slightly changing the meaning of the original stem:
to go (to go) — to go away (to leave),
to come (to come) — to come back (to return),
to look (look) — to look up (look up)
In other cases, adding a separate suffix creates a verb with a completely new meaning:
to give (to give) — to give up (to give up some activity), to get (to receive) — to get off (get off the vehicle), to go (to go) — to go on (to continue doing something).
Examples of verbs with separate suffixes:
away: to go away to leave; to run away escape; to throw away to throw; to do away with smth. destroy, liquidate something; to take away
back: to come / go back — return
down: to sit down to sit down; to settle down to settle; to come down to go down; to climb down to get down, get off; to slow down to slow down (The vehicle slowed down at the next turn) to write down to write
in: to come in to enter (Come in, please!) to get in to enter the transport; to hand in hand in, hand over (Hand in your papers!) to run in to run in; to drop in visit
off: to bite off bite off; to cut off cut off, chop off; to take off take off (Take off your cap and boots) to switch off off (Switch off the lights, it isn’t dark.) to get off off the vehicle (This is where I usually get off).
on: to call on to attend (He often called on Helen when she was ill.) to go on to continue (Go on writing!) to carry on to continue some work; to put on put on, put on; to switch on turn on, turn on the light (Switch on the lights, it’s getting dark.) to get on live (How is Mike getting on?)
out: to get out to go out (Get out! Go away!) to run out to run out; to take out take out; to find out find out; to carry out execute (We should carry out our research.) to cut out cut; to make out understand, understand (I can’t make anything out).
over: to come over to come (Hey, Kate, come over to my place!) to talk over to discuss; to think over to think (We should think it over).
up: to come up to come; to drive up to drive up by car; to cheer up to cheer up, to cheer up (Cheer up, Jack! Don’t be sad, Jack!) to get up to get out of bed; to look up to look up; to shut up to shut up (Shut up, Terry!) to make up invent, compose; to wake up wake up
Formation of verbs using inseparable suffixes
Of the suffixes of the usual type for the formation of verbs, the suffix -ize is often used, which forms verbs with an abstract meaning: to realize, to privatize, to mobilize, to organize.
There are also verbs formed from adjectives using the -en suffix: broad (wide) — to broaden (expand) to lengthen, to widen, to redden, to darken.
Forming verbs using prefixes
With the help of prefixes, verbs are usually formed from the verbs themselves. Frequent verb prefixes are as follows:
The prefix ge-, which means repeated action:
reread
rebuild
rewrite (write again, rewrite)
Verbs with other meanings also have this prefix: to remember, to respect, to recover, etc.
The prefix dis-, which means an action opposite to that expressed by the derivative verb stem:
to disagree, to disappear, to disapprove, to discover, to dis.
The prefix mis-, which means an action performed by an error: to misunderstand (misunderstand), to mispronounce (mispronounce), to misbehave (misbehave), to mistake (make a mistake, mistakenly consider someone else).
Formation of verbs using conversion
Thus, verbs are formed mainly from nouns:
dust — to dust
a bomb (bomb) — to bomb (bomb)
water — to water
a hand (hand) — to hand (hand)
a head — to head
a finger (finger) — to finger (press with a finger)
winter (winter) — to winter (winter)
The number of verbs formed from nouns by conversion is very large.
Source: http://englishgu.ru/obrazovanie-glagolov-v-angliyskom-yazyike/
Word formation. Noun suffixes in English (grade 9)
This is a lesson from the cycle «Word formation in English» and in it we will consider the common noun suffixes: -er / or, -tion, -ing, -ness, -ence / ance (5). Exercises on word formation of a noun will help you understand how nouns are formed in English using suffixes, as well as prepare for English exams in the form of the OGE and USE.
for posting on other Internet resources is prohibited. EnglishInn.ru.
Basic noun suffixes in English (grade 9)
Remember 5 main noun suffixes.
- er / or (worker)
- tion (informaproduction)
- ing (reading)
- ness (happyness)
- ence / ance (difference)
Next, let’s dwell in more detail on each of them.
1. Suffixes of nouns formed from a verb
- -er / or (doer suffix) dance — dancer work — workercollect — collector
invent — inventor
- -tion (process suffix) collect — collection
invent — invention
- -ingsuffer — suffering warn — warning
mean — meaning
Remember three suffixes -er (-or), -tion, -ing, with the help of which nouns are formed from the verb.
2. Suffixes of nouns formed from an adjective
- -nessill — illness
kind — kindness
- -ance / -ence (corresponding adjectives have suffixes: -ant / -ent) important — importance
different — difference
Remember two suffixes: -ness, -ence (ance), with the help of which nouns are formed from an adjective.
Suffixes of nouns in English. Exercises
Suffixes -ness & -tion Are the most common noun suffixes.
Exercise 1. Suffix -ness. Translate these nouns and indicate the adjectives from which they are derived.
foolishness, happiness, seriousness, illness, readiness, richness, strangeness, carelessness, whiteness, cleverness, greatness, brightness
Note.
Source: http://englishinn.ru/slovoobrazovanie-suffiksyi-sushhestvitelnyih-v-angliy.html
Suffixes in English: 40 Most Common
Hey.
Source: https://corp.lingualeo.com/ru/2016/11/16/suffiksyi-v-angliyskom-yazyike/


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-691905009-58daa0043df78c5162b0bfe8.jpg)