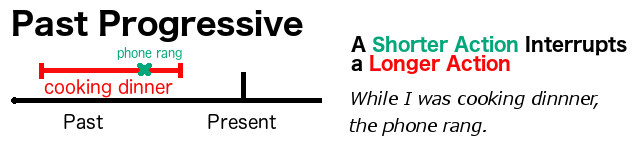[M] [T] I was going out, when the telephone rang. [M] [T] She got married when she was twenty-five. [M] [T] She surprised him when she arrived early. [M] [T] She was surprised when she saw the ghost.
Contents
- 1 What are 5 examples of simple sentences?
- 2 How can you use the word in a sentence?
- 3 What is 10 examples of sentences?
- 4 What are 10 examples of simple sentences?
- 5 What are sentence types?
- 6 What is a sentence for kids?
- 7 How do you write 5 sentences?
- 8 How many words is 5’7 sentences?
- 9 What are the 4 types of simple sentences?
- 10 What are 5 examples of complex sentences?
- 11 What are 5 compound sentences?
- 12 Can sentences example?
- 13 What are the 7 types of sentences?
- 14 What are the 7 sentence patterns?
- 15 How many sentences are in English?
- 16 What are the 12 types of sentences?
- 17 What is a sentence Grade 5?
- 18 What is good sentence?
- 19 What are some good sentences?
- 20 How do you make a simple sentence?
What are 5 examples of simple sentences?
Examples of simple sentences include the following:
- Joe waited for the train. “Joe” = subject, “waited” = verb.
- The train was late.
- Mary and Samantha took the bus.
- I looked for Mary and Samantha at the bus station.
- Mary and Samantha arrived at the bus station early but waited until noon for the bus.
How can you use the word in a sentence?
Used sentence example
- He used to be a pretty good mechanic.
- He is selling a used vehicle that is five years old.
- I’ll just have to get used to being idle.
- I used to trust Dad.
- We are so used to being with the big boys.
- Frank is a very nervous dog who isn’t used to being left alone.
- We used to be so close.
What is 10 examples of sentences?
Examples of Complete Sentences
- I ate dinner.
- We had a three-course meal.
- Brad came to dinner with us.
- He loves fish tacos.
- In the end, we all felt like we ate too much.
- We all agreed; it was a magnificent evening.
What are 10 examples of simple sentences?
50 examples of simple sentences
- She doesn’t study German on Monday.
- Does she live in Paris?
- He doesn’t teach math.
- Cats hate water.
- Every child likes an ice cream.
- 6.My brother takes out the trash.
- The course starts next Sunday.
- She swims every morning.
What are sentence types?
There are four types of sentences: simple, compound, complex, and compound-complex. Each sentence is defined by the use of independent and dependent clauses, conjunctions, and subordinators.Complex sentences: A complex sentence contains one independent clause and at least one dependent clause.
What is a sentence for kids?
A sentence is a set of words which makes up a complete thought. It achieves this by following a set of grammatical rules to convey a statement, question, exclamation, or command. A sentence starts with a capital letter and ends with a full stop, question mark or exclamation mark.
How do you write 5 sentences?
A five sentence paragraph consists of a main idea sentence, three sentences that explain the main idea with reasons, details or facts and a concluding sentence.
How many words is 5’7 sentences?
The word length for children novels is not set in stone, but even so, its likely to be around 20,000 to 40,000 words.
What are the 4 types of simple sentences?
There are four types of sentences: simple, compound, complex, and compound-complex.
What are 5 examples of complex sentences?
5 Examples of Complex Sentences
- When he handed in his homework, he forgot to hand the teacher the last stage.
- The human brain never stops working until you stand up to speak in public.
- Even though she suffered from arthritis, she studied hard because she wanted to go to medical school in London.
What are 5 compound sentences?
5 Examples of Compound Sentences
- I want to lose weight, yet I eat chocolate daily.
- Michael did not like to read. She was not very good at it.
- Dr. Mark said I could come to his office on Friday or Saturday of next week.
- My favorite sport is skiing. I am vacationing in Hawaii this winter.
Can sentences example?
Could sentence example
- I wish you could hear yourself talking.
- What could he do about it but lose more sleep?
- How could she blame him?
- How could he find out?
- I never thought I could do it.
- I had let so much gas out of my balloon that I could not rise again, and in a few minutes the earth closed over my head.
What are the 7 types of sentences?
The other way is based on a sentence’s structure (simple, compound, complex, and compound-complex).
- Statements/Declarative Sentences. These are the most common type of sentence.
- Questions/Interrogative Sentences.
- Exclamations/Exclamatory Sentences.
- Commands/Imperative Sentences.
What are the 7 sentence patterns?
Sentence structure can be categorized into seven patterns: one simple, three compound, two complex, and one compound-complex.
How many sentences are in English?
There are four types of English sentence, classified by their purpose: declarative sentence (statement) interrogative sentence (question) imperative sentence (command)
What are the 12 types of sentences?
12 Types of Tenses With Examples Pdf
| Tense | Affirmative | Negative |
|---|---|---|
| Present simple | I have a car. | I don’t have a car. |
| Present continuous | You are playing football now. | You are not playing football now. |
| Present perfect | They have been there. | They haven’t been there. |
| Present perfect cont. | I have been living here. | I haven’t been living here. |
What is a sentence Grade 5?
A sentence is a group of words that conveys a complete idea.A sentence always starts with capital letter and end with a full stop, question mark or exclamation mark. 4. A sentence must have at least one doing word i.e. verb.
What is good sentence?
A good sentence is a complete sentence.
A complete sentence requires a subject and a verb and expresses a complete thought—also known as an independent clause. This element of sentence structure can stand on its own, expressing an idea without the need for additional information.
What are some good sentences?
Good sentence example
- It felt so good to be home. 790.
- You have a good family. 446.
- She is such a good seamstress. 485.
- It was a good thing they were going home tomorrow.
- It was all just good clean fun.
- It meant a good deal to him to secure a home like this.
- It would do no good to ask him why.
- He had done one good deed.
How do you make a simple sentence?
A simple sentence is typically made up of a subject, verb, and object, or SVO, and creates a complete thought; however, since a simple predicate is a verb or verb phrase only, a simple sentence can also be made up of only a subject and verb (SV).
Examples of how to use the word “when” in a sentence. How to connect “when” with other words to make correct English sentences.
when (adv, pron, conj): at what time; at the time at which; what/which time;considering the fact that
Use “when” in a sentence
| She was shocked when she heard my story. |
| I need absolute silence when I’m working. |
| When I hear that song, I remember my younger days. |
| She was very surprised when she heard the news. |
| My throat hurts when I swallow. |
| Do you know when they will arrive? |
| The thief ran away when he saw a policeman. |
| I used to be very thin when I was young. |
| She still sucks her thumb when she’s worried. |
| I’m training her to take over my job when I retire. |
| Do you know when he will come? |
| When did you buy it? |
| When will we arrive?
Back to “3000 Most Common Words in English” |
Adverb
When did the American Civil War begin?
The detective asked me when I last saw her.
When is the next performance?
It was a time when people didn’t have to lock their doors.
the happy days when we were together
We’re still waiting for the test results, when we’ll decide our next move.
Conjunction
When he finally showed up, he was drunk.
When I was in school, we didn’t have computers.
You can go when the bell rings.
Call me when you get home.
Things were better when he got a job.
When he watches television, he falls asleep.
She quit politics when she might have had a great career in it.
Pronoun
He retired in 1998, since when he has been devoting his time to gardening.
You need the report by when?
See More
Recent Examples on the Web
In the audience, Minority Leader Mitch McConnell (R., Ky.) beamed when Mr. Biden referred to him as the longest-serving Senate leader; that was an important personal milestone for Mr. McConnell.
—
What isn’t known for certain is when the family was killed.
—
Denis McCarville, 70, was arrested on Jan. 29 when the flight landed in Anchorage.
—
As when a little kid gets to run herself ragged to make her sleep better, there’s value in working the energy out.
—
The president is taking the House rostrum at a time when just a quarter of U.S. adults say things in the country are headed in the right direction, according to a new poll by The Associated Press-NORC Center for Public Affairs Research.
—
Russell and his Black teammates also took a stand when the Celtics journeyed South, sitting out a game in Kentucky after a Whites-only hotel denied them service.
—
However, the rumor was quickly put to rest when Lizzo shared a video on February 6 of the moment Harry won, including a shot of Adele cheering him on before realizing she was being recorded.
—
Seven of the final eight teams this year featured an offensive-minded head coach, and the one that didn’t was the Bills with Sean McDermott, whose offense fell off when Brian Daboll left for the Giants.
—
Ordinarily, sussing out the who-knows-what-and-when of damaging revelations is a Beltway parlor game.
—
Bumblefest and normalcy are not words that often appear in the same sentence, but the Sept. 17 return of Steve Rullman’s modern-rock hootenanny in downtown West Palm Beach now feels like a comforting symbol of back-when.
—
Frankly, the question was never an if, but a when and a how.
—
How about a streaming product versus a must-see-when-and-where-cable-event?
—
Williams, in short, paired all her how-to with a when-to wherewithal sometimes absent in her first two seasons.
—
Dan Marino lost his first game as a rookie starter way-back-when to Buffalo in overtime 38-35.
—
These squishable-when-they’re-not-spitting camelids hold antibodies that could hold the key to treating COVID-19, scientists suggested in a study published Tuesday in the journal Cell.
—
Saturday’s 38-31 win at Nebraska put to bed a lot of since-whens and last-times in Bloomington.
—
See More
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word ‘when.’ Any opinions expressed in the examples do not represent those of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback about these examples.
What’s the difference between the subordinate conjunctions when and while?
When & While: The Short Answer
In some sentences, you can use either without a great change in meaning. Generally, if you want to focus on an action that has a duration being in progress, use a while + a progressive tense.
While I was washing the dishes, my wife came home.* (Washing the dishes has a duration, e.g. 4 minutes.)
(*Note you can also use when here, but as a general rule, while is suitable.)
In other cases when you don’t need to emphasize that an action was in progress or the action is short and without a significant duration, use when and a simple tense.
When it started to rain, we went inside. (The action started is short; it is not something in progress).
When it started to rain, we went inside.
Here are some tips on the use of these two conjunctions.
Tip #1: Use a Progressive (Continuous) Tense with While to Show Focus
Progressive tenses use the BE verb + a verb in ~ing form.
While I was cooking dinner, the phone rang.
I will be sleeping at 11:00 p.m. tonight, so don’t phone me.
We use while to focus on an action happening at a specific time. Therefore, the most natural verb tense to use is a progressive tense, which shows that an action is in progress at a certain time.
It is common to use while with actions happening at a specific time (e.g. at 11 p.m.). Also, we use while to show that a shorter action (usually in the past simple, e.g. the phone rang) happened during as a longer action (usually in past progressive, e.g. I was cooking dinner). Often this shorter action interrupts the longer action.
A sensible rule is to use while with the progressive tenses and when with the simple tenses.
Tip #2: Use While with Actions that have a Limited Duration
- When I was a child, I played soccer. (Correct)
- While I was a child, I played soccer. (Not natural)
Why is #2 not natural? Well, when an action is too long (e.g. I was a child), we lose focus. The period of twelve years when you were a child is too long to use a progressive tense. We don’t use ‘while’ to talk about long periods of our lives. Instead, we use when and past simple. There’s another reason.
Tip #3: Use While with Action Verbs
Also, «While I was a child» is unnatural because the BE verb (was a child) is a state verb. State verbs are not action verbs (e.g. jump, kick, shower, drink). Instead, state verbs describe states or conditions (e.g. BE, live, understand, know, exist). We do not use progressive tenses with state verbs. As a result, we generally don’t use while with state verbs.
Compare:
While she was driving, I played with the radio. (Natural)
This is correct. Driving is an action verb and the action is limited in duration. In other words, driving is a short activity that has a clear start and end.
While When I lived in my hometown, my mother made me dinner. (While is not natural)
Live is a state verb, and also, the action of living in my hometown probably had a duration of 18 years. This is too long to focus on.
Exception: Focusing on a Verb in Progress
You could use while with a state verb like ‘live’ if you really want to focus on the fact that an action was in progress at a specific time. For example:
While I was living in India, there was a big earthquake.
Although it would probably be more common to use When I lived in India, this sentence is correct. The speaker chooses to use ‘While’ + present progressive’ to focus on an action being in progress (living) when another action happened.
Remember: While Means an Action Had a Start and an End (a Duration)
If a sentence uses while, it suggests that the action happened over a period of time. Here’s are two better examples to show what I mean:
When the phone rang, I was making lunch.
The longer action (making lunch) was happening when a shorter action happened (phone rang).
Key question: How many times did the phone ring? Because we’re using when, we don’t know. The use of when doesn’t suggest it was an ongoing action. The phone may have rang once and stopped.
While the phone was ringing, I was making lunch.
How many times did the phone ring here? More than once. Because we are using While + present progressive, we are focusing on duration. This means that the action (ring) happened over a period of time that had a start and end. When we say ‘the phone was ringing’ in the progressive, we are saying that this happened for some time. (Thanks to Clive at Englishforums for this point.)
While vs. When: In Conclusion
We can conclude the following:
- To emphasize (focus) that an action was in progress at a specific time, use while + a progressive tense ( = While I was eating, …)
- Otherwise, use when + a simple tense. (= When I ate, …)
- Verbs with while have a duration. The period of the verb cannot be too long or we lose focus. (= While I was a child = When I was a child)
- Progressive tenses use action verbs, so use while with an action verb (While I was dancing) and not a state verb (While I was hungry)
I hope these ideas have been useful. Remember, these are general tips (not fixed rules). There will be exceptions depending on what the speaker wants to emphasize. If you have any questions or comments, please leave them below.
— Matthew Barton / Creator of Englishcurrent.com
When is a wh-word. We use when to ask questions, as a conjunction and to introduce relative clauses.
When as a question word
We can use when to ask for information about what time something happens:
When did you leave?
When are you going on holiday?
When will you know the result of the exam?
We can use when in indirect questions:
She asked me when I would be ready to start the job.
I wonder when the new computers will arrive.
When as a conjunction
We use when as a conjunction meaning ‘at the time that’. The clause with when is a subordinate clause (sc) and needs a main clause (mc) to complete its meaning. If the when-clause comes before the main clause, we use a comma.
Talking about the past
[SC]When I was young, [MC]there were no houses here.
[MC]Nobody spoke [SC]when she came into the room.
Talking about the present
When you start the engine, there’s a strange noise.
Talking about the future
In references to the future with when, we use the present simple or the present perfect in the when-clause, not the future with shall and will:
When the new park opens, I’ll go there every day.
Not: When the new park will open, I’ll go there every day.
When I’ve finished my homework, I’m going to phone Marita.
Not: When I’ll finish my homework, I’m going to phone Marita.
We can use when as a conjunction to mean ‘considering that’:
What’s the point in going out when we have to be home by eleven o’clock?
When as a relative pronoun
We can use when as a relative pronoun in relative clauses:
That was the week when we booked our holiday.
The parcel arrived in the post at 11 am, when I was still at work.
Since when?
We can use since when to ask at what time something began. We often use it as a response when we are surprised that something has begun:
A:
Hilary’s working at the Art Museum now.
A:
Oh, she’s been there about three months.
Warning:
Using Since when at the start of a question can express anger or sarcasm:
[talking about children watching television]
A:
Maybe you should try not to let them watch so much television.
B:
Since when are you an expert on childcare? (This is very direct.)
When or if?
We use when to refer to a future situation or condition that we are certain of, whereas we use if to introduce a possible or unreal situation.
Compare
|
I will definitely see Gary. |
|
I may see Gary but I am not certain. |
When or since?
We use when to mean ‘(at) the time that’. We use since to refer to a particular time in the past until another time or until now:
I had a great time when I went to the coast.
I have been having a boring time since I came back home.
Not: I have been having a boring time when I came back home.
When: typical errors
-
Be careful not to use when instead of if:
If you arrive too late, you are not allowed to take the examination because they don’t accept late enrolment.
Not: When you arrive too late, …
-
Be careful not to use when instead of since:
I was very surprised to see him because it’s been a long time since I last saw him.
Not: … it’s been a long time when I last saw him.
-
We don’t use will after when to mean ‘at that time’:
When I start college, I’ll miss my old school friends.
Not: When I’ll start college, I’ll miss my old school friends.