
58 example sentences with could have, couldn’t and could.
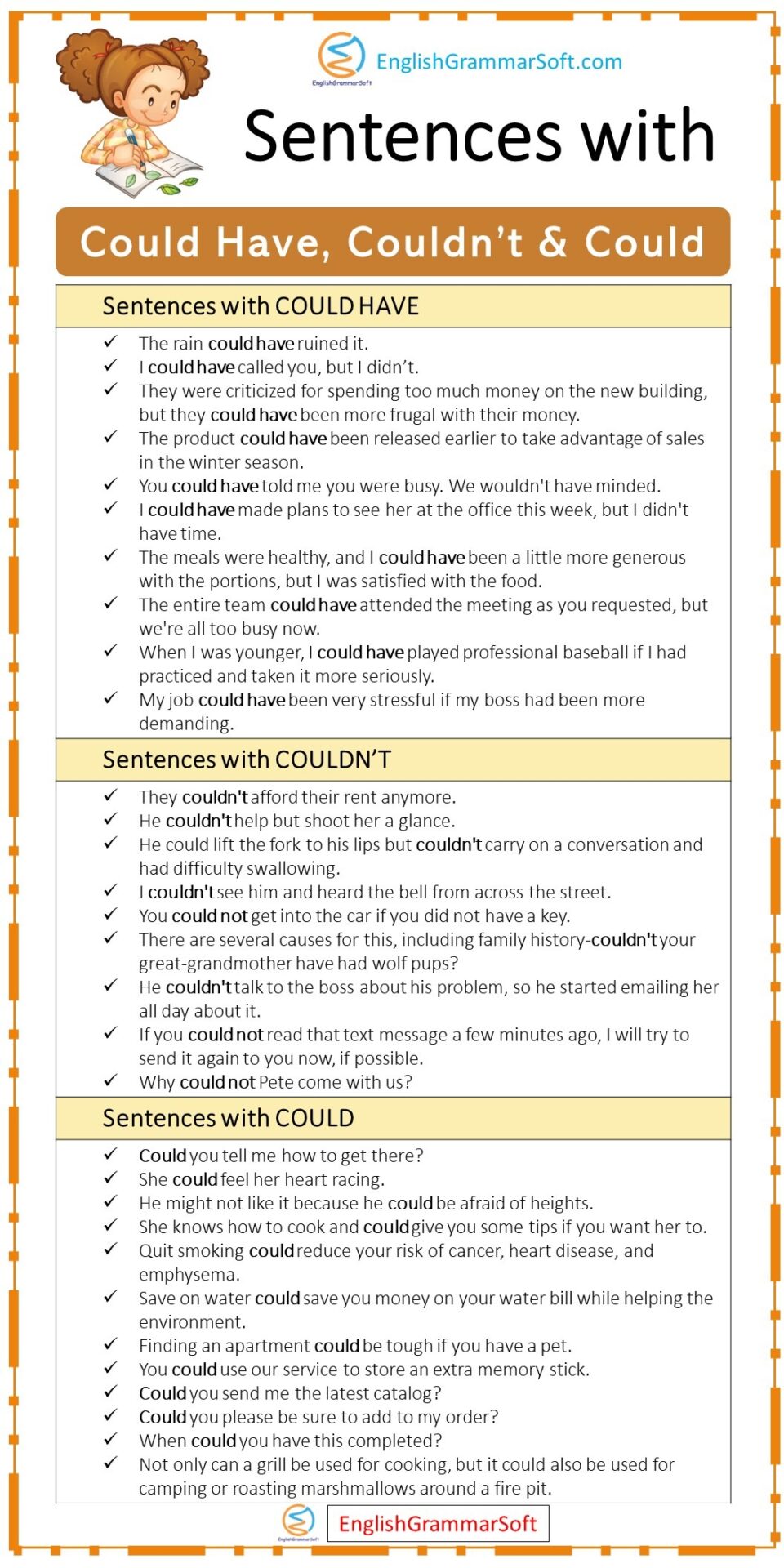
- The rain could have ruined it.
- I could have called you, but I didn’t.
- They were criticized for spending too much money on the new building, but they could have been more frugal with their money.
- The product could have been released earlier to take advantage of sales in the winter season.
- You could have told me you were busy. We wouldn’t have minded.
- I could have made plans to see her at the office this week, but I didn’t have time.
- The meals were healthy, and I could have been a little more generous with the portions, but I was satisfied with the food.
- The entire team could have attended the meeting as you requested, but we’re all too busy now.
- When I was younger, I could have played professional baseball if I had practiced and taken it more seriously.
- My job could have been very stressful if my boss had been more demanding.
- The committee’s decision could have had major implications for the project but didn’t, so we are relieved.
- Several major errors were discovered after the launch, which could have led to disaster if they had not been fixed in time.
- The delegation could have been handled better.
- You could have told me about the problem sooner.
- You could have had a better result if you had used another tester.
- You could have met all the customers’ requirements if you had accepted them.
- You could have improved your productivity if you hadn’t been so stressed out.
- The data that comes with the models could have been better presented.
- The parts of the model could have been easier to understand.
- If you could have run faster, you would have won the race.
- The company could have quoted a lower price.
- We could have lost our money if my dad had not given us money.
- I could have taken that promotion; however, I decided to take a few years off before accepting another position at the company.
- I could have completed college, but I decided to explore other career options and missed out on the opportunity.
- We could have released it on time, but unfortunately, we didn’t
Sentences with Couldn’t (Could Not)
- They couldn’t afford their rent anymore.
- He couldn’t help but shoot her a glance.
- He could lift the fork to his lips but couldn’t carry on a conversation and had difficulty swallowing.
- I couldn’t see him and heard the bell from across the street.
- You could not get into the car if you did not have a key.
- There are several causes for this, including family history-couldn’t your great-grandmother have had wolf pups?
- He couldn’t talk to the boss about his problem, so he started emailing her all day about it.
- If you could not read that text message a few minutes ago, I will try to send it again to you now, if possible.
- Why could not Pete come with us?
- I couldn’t come to the phone because I was busy.
- I couldn’t eat the pudding because it had too much sugar.
- I couldn’t understand what the speaker was saying, so I asked for a video of the presentation.
- I couldn’t believe that Tom had eaten the whole cake alone, his friends had just arrived, and he could have offered them some of it!
- You could not drive a stick as I did as a kid.
- He couldn’t swim much farther, or he’d drown.
Sentences with the word Could
- Could you tell me how to get there?
- She could feel her heart racing.
- He might not like it because he could be afraid of heights.
- She knows how to cook and could give you some tips if you want her to.
- Quit smoking could reduce your risk of cancer, heart disease, and emphysema.
- Save on water could save you money on your water bill while helping the environment.
- Finding an apartment could be tough if you have a pet.
- You could use our service to store an extra memory stick.
- Could you send me the latest catalog?
- Could you please be sure to add to my order?
- When could you have this completed?
- Not only can a grill be used for cooking, but it could also be used for camping or roasting marshmallows around a fire pit.
- You could invest in a quality pair of shoes.
- If you could settle for a smaller house and fewer amenities, it would open up an area for others with bigger homes to move into.
- If you could choose the college or university for your children, would you?
- As a student, you could organize a food drive.
- You could collect canned goods and clothing to benefit the homeless.
- The manufacturing sector could experience Job loss due to increasing fuel costs..
Read also
- Sentences with Brevity
- Sentences with Semicolon
- Sentences with However
- Sentences with Used to
- Simple Sentences Examples
- What are Simple Sentences
- Imperative Sentences
- Simple, Compound and Complex Sentences
- 16 Tenses in English Grammar
could — перевод на русский
/kʊd/
Maybe you could help me solve a little problem I have.
Может ты мне поможешь с одним мелким дельцем?
He could fill like 50 balloons a day.
Он может наполнять наверно по пятьдесят шариков в день.
I was just thinking that we could have something…
Я просто думал, что у нас все же может быть что-то…
Could it be that he’s new?
Может он новенький?
With such a house how could there be no one?
Как в таком доме может никого не быть?
Показать ещё примеры для «может»…
I didn’t think I could do it.
Я не думал, что смогу.
Then the kids would turn against Frankie, and I could take over the peanut racket.
И когда детвора восстанет против Френки, я смогу захватить орехоторговлю. А-а-а!
«Now I knew I could win the Princess Dinarzade»
«Так я узнал, как смогу завоевать прекрасную Динарзаде»
Maybe I could help this Clara Wood of yours.
Возможно, я смогу помочь этой вашей Кларе Вуд.
I could never leave Jerry.
Я не смогу оставить Джерри.
Показать ещё примеры для «смогу»…
I was thinking that we could use your role as bridesmaid to really mess her up.
Я подумала, что можно использовать твою роль подружки, чтобы реально ей насолить.
One with nothing in his coat sleeves, the other one shuffling around on those little wooden feet, if you could call them that.
У одного рукава пальто совершенно пусты, другой суетится вокруг на этих деревянных ножках, если их вообще можно назвать ногами.
There was a window with a wire grating on it and through that window you could look out and see a lot of people out there who undestood a whole lot more what you’re going through than these doctors
¬ комнате присутствовало окно с решЄткой из проволоки, через которое можно было рассмотреть много подозрительных людей снаружи, и эти люди понимали, через что тебе придЄтс€ пройти, намного больше, чем персонал клиники.
Of course, I know we could find one, but maybe the people wouldn’t get out.
Конечно, я знаю, где можно его найти, но не уверен, что люди согласяться его покинуть.
You could go crazy staying here.
Можно сойти с ума оставаясь здесь.
Показать ещё примеры для «можно»…
So what I’m trying to say is that the remains could have been here long before this town is made.
что возможно останки были тут до основания города.
I could have induced him stay in a minute by offering to double his .. Thirty pieces of silver.
Возможно, он сразу согласился бы, если бы я удвоил его 30 серебренников.
— You probably could get some money out of him.
— Возможно, чтобы получить с него немного денег.
With such eyes, she could’ve been Turkish… or from Alexandria.
С такими глазами она, возможно, была турчанкой или из Александрии.
Could be, perhaps, but it isn’t very likely.
Это возможно, но не очень вероятно.
Показать ещё примеры для «возможно»…
— Barney, you always could pick ’em. 9:00?
Ты всегда умел их подбирать.
— Wash sure could make ’em up, couldn’t he?
Уош умел рассказывать эти истории, да?
Well, at least he could dance, and he didn’t show me any sugarcane.
Он, хотя бы, умел танцевать, и не тащил меня на сахарные плантации.
I never could handle those fool things.
Никогда не умел курить как следует.
You never could.
Ты никогда не умел…
Показать ещё примеры для «умел»…
What could I know about it?
ј мне-то что может быть известно?
Children, if Dale and Jerry are drifting out to sea… don’t you think the best thing we could do is rescue them?
Мальчики, если Дейл и Джерри плывут в море, может быть, лучше помочь им?
Jerry, I admit as one man to another, that economically, I haven’t been of much value to you, but suppose you could put one on credit.
Джерри, могу сказать тебе, как мужчина мужчине, с экономической точки зрения, я был не очень ценным клиентом, но… может быть, ты мне нальёшь в кредит?
— That could stand for Greenway Park.
— Это может быть Гринуэй Парк.
And next he could say that this is his robe.
Может быть, он скажет, что я присвоил и этот халат.
Показать ещё примеры для «может быть»…
I wanted to die… so I could be with her.
Я хотела умереть… чтобы быть с ней.
But what if it could still be visited? What am I saying?
Тем не менее, этот исчезнувший мир должен быть найден.
I wish I were someone else. Then I could stay here with you forever.
Мне хотелось бы быть кем-то другим, чтобы остаться с тобой навсегда.
I only thought you should wait a little longer so you both could be sure.
Я только советую вам немного подождать. Чтобы быть уверенными.
You see, we could never in our whole lives be any happier than we are now.
Понимаешь, за всю оставшуюся жизнь нам уж не быть Такими счастливыми, как сейчас.
Показать ещё примеры для «быть»…
If you work hard, you could be a very good actress
Если будешь стараться, то из тебя получится очень хорошая актриса
You really think I could?
Ты правда думаешь, у меня получится?
Christian, with the help of Pierre and me maybe you could.
Кристиан, с помощью Пьера и меня может быть, у тебя получится.
You could do it if you wanted to.
У вас получится, если вы захотите.
I’m not a coward who wants to avoid unpleasantries, but you could do it better than I.
Я не трус и не боюсь этого, но у тебя лучше получится.
Показать ещё примеры для «получится»…
Frankie was up to something— — I could feel it-— And I needed to find out what.
Френки что-то затеял, я это чувствовал, и я должен был выяснить что.
I could feel how it should be, it was practically finished.
Я чувствовал, какой она должна была быть.
I could feel the ground under my feet again. And it looked like easy going from there on in.
Я снова чувствовал землю под ногами, и дальнейшее казалось делом решённым.
Yes, I could feel it.
Да, я это чувствовал.
I could almost hear them listening.
Я даже чувствовала его дыхание.
Показать ещё примеры для «чувствовал»…
He died in my arms five minutes ago, before he could finish his message to you, but I’m gonna finish it for him.
ќн умер у мен€ на руках п€ть минут назад, не успев закончить послание к вам, — … но € завершу начатое за него.
He must have been rather disappointed that you left before he could talk to you.
Наверное, он расстроился, не успев побеседовать с тобой.
And before you could count ten, the whole room was ablaze.
И не успели досчитать до десяти, как уже пылала вся комната.
Before he could yell or fight…
Прежде чем он успел крикнуть
We were going to be married on Tuesday, and then we postponed it, so my sister could get there from New Hampshire, remember?
Мы собирались пожениться во вторник, но потом отложили, чтобы моя сестра успела добраться из Нью-Гемпшира, помнишь?
Показать ещё примеры для «успев»…
Отправить комментарий
Could is a modal verb. Modal verbs are common in English.
Modals are used before other verbs to express ideas such as ability, possibility, certainty, necessity, or permission.
A modal verb is an auxiliary verb. It is a helping verb. It can’t be used by itself in sentence. It must be used before another verb.
It’s useless to try and remember what every modal verb means. One modal verb can have many different meanings. Instead, it’s easier to remember sentence structures.
“If you could go anywhere in the world, where would you go?”
This question form uses could with the 2nd conditional sentence structure to ask a hypothetical question. A hypothetical question is not a question about real events. A hypothetical question asks you to imagine a different reality.
In this question, the modal verb could is another way of saying if you were able to, or if you had the ability to, or if it were possible to.
Learn more: English Grammar: 2nd conditional sentence structure
These questions follow the same pattern:
if you could + verb, question word + would + verb?
If you could go anywhere in the world, where would you go?
You can change the order of the two parts:
Where would you go if you could go anywhere in the world?
Note that you don’t use a comma to separate the two parts of the sentence when the if-clause is in the second part of the sentence.
You can answer this by using part of the question:
I would …
I would go to Paris!
Or you can answer the question with one word:
Paris!
You can also answer the question by stating that this is someone that you have wanted to do for a long time:
I have always wanted to go to Paris!
Example questions
If you could play any musical instrument, which would you play?
If you could be any animal, what would you be?
If you could have one skill, what would it be?
If you could be someone else for a day, who would you like to be?
If you could relive one day of your life, which day would you relive?
Practice activity!
In the comments, answer one or all of the questions below. Then, ask your own question using “If you could … ?”
- If you could go anywhere in the world, where would you go?
- If you could be the president of your country for one day, what would you do?
- If you could have a superpower, what would you choose?
A superpower is a special power or ability to do something, like the ability to read someone’s mind. Usually only fictional characters like Superman or Wolverine have superpowers! - If you could travel back in time, where and when would you go?
- If you could have dinner with anyone, dead or alive, who would you choose?
image source
| CAN/COULD (AFFIRMATIVE) | CANNOT/COULD NOT (NEGATIVE) | BE ABLE TO (AFFIRMATIVE) | BE ABLE TO (NEGATIVE) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PAST ABILITY | He could run very fast when he was a child. | He couldn’t run very fast when he was a child. | He was able to run very fast when he was a child. | He wasn’t able to run very fast when he was a child. |
| PAST REPEATED ACTIONS | I could run marathons when I was younger. | I couldn’t run marathons when I was younger. | I was able to run marathons when I was younger. | I wasn’t able to run marathons when I was younger. |
| PAST SINGLE ACTION, STATIVE VERB | She could feel the wind on her face. | She couldn’t feel the wind on her face. | She was able to feel the wind on her face. | She wasn’t able to feel the wind on her face. |
| PAST SINGLE ACTION, ACTION VERB | NOT POSSIBLE! | I couldn’t get to the airport on time because of the traffic. | I was able to get to the airport on time, even though the traffic was bad. | I wasn’t able to get to the airport on time because of the traffic. |
| PRESENT ABILITY | He can speak Portuguese fluently. | He can’t speak Portuguese very well. | He is able to speak Portuguese fluently. | He isn’t able to speak Portuguese. |
| FUTURE ABILITY OR SKILL | NOT POSSIBLE! | NOT POSSIBLE! | When you pass your driving test, you will be able to drive your own car. | You will not be able to drive your own car if you don’t pass your driving test. |
| FUTURE DECISIONS AND ARRANGEMENTS | You can speak to the Director next week. | The Director cannot speak to you tomorrow. | The Director will be able to speak to you next week. | The Director won’t be able to speak to you tomorrow. |
Can and could are modal auxiliary verbs which express ability, permission, request, offer or possibility.
Could is originally the past form of can, but it also has certain functions which can does not, for example, it is used in hypothetical conditions.
Examples:
- She can speak English very well. (ability)
- I could ride a bike, but I couldn’t swim when I was seven years old. (ability)
- You can have a coffee break after you type these letters. (permission)
- Could I have some more salad with the meat? (request)
- Can I help you? Can I carry your bag? (offer)
- It could rain this afternoon. (possibility)
- This can’t be true. (negative possibility)
- We could get there in time if you were driving a bit faster. (hypothesis + ability/possibility)
Can and could are also used to express the progressive (continuous) aspect of verbs of perception (see, hear, feel, taste, smell, etc.) and verbs like understand, remember, etc:
Examples:
- Can you see the woman standing over there?
- We were so near the sea that I could hear the seagulls.
- When she entered the kitchen, she could smell something burning.
- I put my keys to a safe place before swimming, but now I can’t remember where.
- She couldn’t understand what the foreigner was saying.
As the past form of can, could is used for general ability in the past and in reported speech.
Examples:
-
- When she was younger, she could work for ten hours without stopping.
- He said he could get his wife to come to the football with us.
It is not used when only one occasion is implied, except for negative sentences:
Examples:
- How many goals were you able to score on Sunday?
- They managed to get to the station in ten minutes by taking a taxi.
- I was able to find all the words in the dictionary, still I couldn’t translate the text.
In requests, orders and suggestions, could is more polite than can:
Examples:
- Can I use your phone?
- Could you please do me a favour?
- Do you think you could help me for a few minutes?
- Do the washing first, then you can clean your room.
- When you’ve finished the letter, you could translate this article, if you like.
- If you haven’t got anything to do this afternoon, you could clean the car.
When we ask for permission, could is more polite than can. Could is not used to give or refuse permission:
Examples:
- Can/Could I ask you something? – Yes, of course you can.
- You can go now if you want to.
- Can I stay here for another hour? – No, I’m afraid you can’t.
This lesson includes:
- talking about ability in the present and future.
- talking about general ability in the past and ability on specific occasions in the past.
- the different uses of can, could and be able to
- the difference between could never and never could
- using the verbs manage and succeed for past ability
1. Ability in the present and future
Do the two exercises and then check the summary of rules.
Ex 1a — Complete these sentences about present and future ability using the words in the box. ?
| 1. | She speak four foreign languages. | |
| 2. | The candidate should to speak fluent English. | |
| 3. | They’ve been come to an agreement at last. | |
| 4. | He’s run 100 metres in 10 seconds. | |
| 5. | He will to see you tomorrow afternoon. | |
| 6. | I do it tomorrow afternoon, if you like. | |
| 7. | We might not to do that. | |
| 8. | She make it to the wedding. | |
| 9. | She won’t to do it until next week. | |
| 10. | I’ve never been understand her. | |
| 11. | I’m afraid we are to fulfill your request. | |
| 12. | They do it before next Thursday. |
| Ex 1b — See instructions below | can | can’t | able to | not able to | ||
| 1. | present positive ability | |||||
| 2. | present negative ability | |||||
| 3. | ability after a modal (+ and -) | |||||
| 4. | ability with perfect aspect (+ and -) | |||||
| 5. | ability with a future tense (+ and -) | |||||
| 6. | a decision made now about the future (+ and -) |
Ex 1b — Look at the sentences in Ex 1a and decide which words or expressions you can use to express the functions above. There may be more than one answer to each usage.
Note — not able to can be expressed in several ways:
- not able to
- unable to
- no longer able to
Summary of the rules for ‘ability in the present’
- We use can / can’t (cannot) to speak about ability or possibility in the present.
She can speak four foreign languages.
She can’t make it to the wedding. - We can also use be able to / not be able to, but usually prefer can
He’s able to run 100 metres in 10 seconds. (He can run …)
I’m afraid we are not able to fulfill your request. (We can’t …) - But with Perfect tenses we have to use be able to and not can.
They’ve been able to come to an agreement at last.
I’ve never been able to understand her. - Similarly with other modal verbs (eg: should, might), we can’t use can but have to use be able to instead.
The candidate should be able to speak fluent English.
We might not be able to do that. - The same is true when we use will for the future.
He’ll be able to see you tomorrow afternoon.
She won’t be able to do it until next week. - But we use can (or be able to) when we decide now about something in the future.
I can do it tomorrow afternoon, if you like. (I’ll be able to do it …)
They can’t do it before next Thursday. (They won’t be able to do it …)
2. Ability in the past
Do the two exercises and read the notes that follow them, then check the summary of rules.
Ex 2a — Complete these sentences about past ability using the words in the box. ?
| 1. | At the age of eight she already speak three languages. | |
| 2. | And when she was ten she was speak another two languages. | |
| 3. | When I was 15 I ride a motorbike. | |
| 4. | Nor was I drive a car. | |
| 5. | Unfortunately I find my keys last night. | |
| 6. | But I was unlock the door with a spare key. | |
| 7. | Although I wasn’t find the original keys. | |
| 8. | They were contact the trapped miners several times. | |
| 9. | She smell gas coming from the cooker. | |
| 10. | But she distinctly remember turning off the gas. | |
| 11. | I understand a word of what he was saying. | |
| 12. | We see any food shops anywhere. |
| Ex 2b — See instructions below | could | couldn’t | able to | not able to | ||
| 1. | positive general ability in the past | |||||
| 2. | positive ability on a particular occasion | |||||
| 3. | negative general ability in the past | |||||
| 4. | negative ability on a particular occasion | |||||
| 5. | ability with the verbs remember, understand, see, hear, feel etc (+ and -) | |||||
| 6. | ability on more than one occasion (+ive) |
Ex 2b — Look at the sentences above and decide which words or expressions you can use to express the following. There may be more than one answer to each usage:
Note 1 — manage and succeed
When talking about being able to do something on a particular occasion in the past we sometimes use the verbs manage and succeed instead of be able to, especially if there was some difficulty involved.
Ex 2c — Complete the sentences using one small word plus the verb in brackets in the correct form.
| 1. | He managed from the burning vehicle. (escape) | |
| 2. | They succeeded the spread of the wildfires. (control) |
Note 2 — Adverbs of frequency
Look at this sentence
When I was young, I was never able to ride a bicycle ‘hands free’, at least not for more than a few seconds.
Are we talking here about a general ability, or an ability on a particular occasion?
Now look at this little story:
There was a particular computer game he used to play when he was a teenager. He always managed to get to Level 2, he was often able to get to Level 3, but only sometimes succeeded in getting to Level 4. However, he never managed to get to Level 5.
Adverbs of frequency describe how often or the number of occasions something happens. The sentence about riding a bicycle looks as though it’s about general ability, but the word never here really means: not once, on no occasion, so can take verb forms appropriate for ability on a specific occasion. So we could equally well say:
… I never managed to ride a bicycle ‘hands free’ …
or
… I never succeeded in riding a bicycle ‘hands free’ …
Note 3 — Restrictive expressions with could
These can be used in a similar way to couldn’t with ability on specific occasions.
Because of the strike, I could only get home last night by walking the whole way.
She could hardly walk, she was so drunk.
Note 4 — could have done
This refers to something that was possible in the past, but didn’t happen. It is perhaps therefore really more about possiblity than ability.
I could have walked, but I decided to take a taxi.
You could have phoned me!
Note 5 — could never and never could — what is the difference?
There are several songs with never could in the title
- Never could toe the mark — Waylon Jennings
- Never could have been worse — Trigun
- Never could believe — The Damned
I have seen suggestions in a couple of forums that could never is about the present / future, and never could is about the past. But it’s not quite that easy. It’s all about context. Look at these sentences, which are indeed about the present / future:
I could never do what you do.
Bungee jumping? I could never do that!
In fact could never in those sentences could be replaced by would never be able to. But now look at these sentences, which are all equally clearly about the past, and try saying them out loud. Which words would you stress?
I could never understand what she saw in him.
I never could understand what she saw in him.
We could never agree about anything.
We never could agree about anything.
The difference here is not one of time but one of emphasis. Look how the stress changes in these two sentences (make out = understand, getting at = trying to say):
I could never make out what she was getting at.
I never could make out what she was getting at.
The first uses normal word order and is almost a neutral statement of fact, whereas the second, by changing the expected word order and stress, really emphasises the fact that I was never able to understand her, and perhaps says something about my attitude. While this structure: never could do something is, I think, only used about the past, there is, however, at least one way we can use never could ( = never be able to) like this for the future:
Of course I don’t hate you. I never could (and I never would).
Summary of the rules for ‘ability in the past’
- We use could / could’t to speak about a general ability in the past or at a particular period in the past.
My aunt could speak four foreign languages. (She died a few years ago)
My wife, who’s Belgian, could speak four foreign languages by the time she was five.
He couldn’t drive until he was 35. - We can also use be able to / not be able to to describe general past ability.
She was able to speak four foreign languages by the time she was five.
He wasn’t able to drive until he was 35. - But for positive ability on a specific occasion (or occasions) in the past we use be able to and not could.
We were able to get a last minute deal on a holiday to Egypt.
- For negative ability on a specific occasion (or occasions), however, we can use couldn’t as well as not able to.
He couldn’t unlock the door that evening.
She wasn’t able to think up a suitable excuse for being late. - Sometimes we use manage to do or succeed in doing for ability on a particular past occasion, especially if there was some difficulty involved. These can be used in both positive and negative.
I finally managed to beat him at tennis last week.
She succeeded in finding a job straight after leaving university.
He didn’t manage to get his essay finished on time.
We never succeded in our attempts to catch him out. - We tend to use could rather than be able to (depending on context) after certain verbs, especially:
- Verbs of sensation: see, hear, smell, taste, feel
- Certain verbs of perception: remember, understand
I could see someone trying to get into the house next door.
She could clearly remember locking the door.but when it is more about ability than sensation or perception, we have a choice:
I could / was able to see the door of the house from where I was sitting.
She could / was able to remember every card that had been played.
If in doubt when talking about ability, present or past, use a suitable form of be able to. It will nearly always be correct. But if you want to sound more colloquial, try and practise the different forms.
3. Practice exercises
Ex 3a — Complete the sentences using can or can’t where possible (the context should tell you which). Where this is not possible use a suitable form of (not) be able to.
| 1. | He cook really well. | |
| 2. | As for me, I’ve never cook. | |
| 3. | Unfortunately I’m busy tomorrow, but I meet you on Wednesday. | |
| 4. | Have you asked David. He might help you. | |
| 5. | He’ll practise as a lawyer when he passes these exams. | |
| 6. | We deliver your new cooker tomorrow. | |
| 7. | Good news! I’ve get that book you were after. | |
| 8. | I’m afraid I do it tomorrow, I’m busy. | |
| 9. | She to get a job until she gets some experience. | |
| 10. | Pete sing for all the world, I think he’s tone deaf. |
Ex 3b — Complete the sentences using could or couldn’t where possible (the context should tell you which). Where this is not possible use a suitable form of (not) be able to.
| 1. | She ride a pony almost before she walk. | |
| 2. | Luckily we get tickets for the show. | |
| 3. | We went to the sales and find lots of bargains. | |
| 4. | We find a restaurant open anywhere. | |
| 5. | Jenny wasn’t at home but I contact her on her mobile. | |
| 6. | They hear footsteps behind them in the dark. | |
| 7. | I ski until I was in my twenties, when I took lessons. | |
| 8. | He distinctly remember asking for black coffee, not white. | |
| 9. | She didn’t want to come, but finally I persuade her. | |
| 10. | Even as a small child, David play the piano really well. |
Ex 3c — Complete the sentences using the word in brackets and a word from the box in a suitable form. You may also have to add a word or two.
everything remember dance make meet
pick get understand find open
| 1. | We up a real bargain in the sales. (manage) | |
| 2. | They only the problem worse. (succeed) | |
| 3. | He used to like Fred Astaire. (able) | |
| 4. | I couldn’t that attachment you sent me. (manage) | |
| 5. | She always she did. (succeed) | |
| 6. | He was busy and wasn’t me at the station. (able) | |
| 7. | We’ve finally just the right present for her. (manage) | |
| 8. | It was so embarrassing, I could his name. (never) | |
| 9. | I never the theory of relativity. (could ) | |
| 10. | Great news! She’s into Oxford after all. (succeed) |
Answers to the exercises.
По правилам «классического» английского языка, глагол
may
должен был употребляться для выражения возможности
вследствие разрешения
, а глагол can выражал физическую возможность (употреблять его для выражения возможности в результате разрешения считалось неправильным). В современном языке это правило практически не соблюдается и can употребляется для выражения возможности как вследствие физической способности, так и вследствие разрешения. Глагол
may
сейчас выражает разрешение в основном в формальном стиле. Глагол
may
также выражал и физическую возможность (в определенной степени и это значение сейчас немного устарело и часто характерно для формальной речи, но в ряде случаев вполне сохранилось и в разговорной речи, в первую очередь в отношении формы
might
). Кроме того
may/might
и can/could употребляются для выражения предположений.
I. CAN: ВОЗМОЖНОСТЬ СОВЕРШИТЬ ДЕЙСТВИЕ
4.87
Глагол can выражает возможность совершить действие, как вследствие физической способности, так и вследствие разрешения (здесь значение «пересекается» со значением глагола may).
1.
Физическая
способность совершить действие
a) способность, полученная в результате знаний, умения, физической силы и т.п. (= I am able to = I have the ability to):
I can use a typewriter perfectly now.
He’s over eighty but can still read without glasses.
She can make all her own dresses.
He can speak English.
Can you speak Swedish?
Dogs can’t climb trees.
Can you lift this box?
Henry can lift 100 kilos.
My car can do 180 kph.
I can read Italian, but I can’t speak it.
I can’t visit you every day.
Can you translate this book?
The child is ten years old but can’t read yet.
These roses can grow anywhere.
Can gases freeze?
b) возможность в связи со
сложившимися обстоятельствами
(=I am able to=I have the chance to и =I am able to=I am free to):
We can go to Paris this weekend, because I don’t have to work.
There are three possibilities: we can go to the police, we can talk to a lawyer, or we can forget all about it.
We can sit at home and watch football matches in comfort, thanks to television.
Come when you like. I can see you at any time.
Anybody who wants to can join the club.
I can’t come out this evening: I have to see my brother.
3. Can может употребляться с глаголами физического восприятия (see, hear, feel, smell, taste) и некоторыми другими глаголами для выражения происходящего в настоящий момент:
I (саn) hear a dog barking somewhere.
I (can) see Susan coming.
What did you put in the stew? I (can) taste something funny.
I can’t/don’t understand what she’s talking about.
Do/Can you follow what he’s saying?
I (can) remember your grandfather.
4. Can часто опускается, когда речь идет о способности говорить на каком-либо языке или играть на музыкальных инструментах:
She speaks Greek. / She can speak Greek.
Do/Can you play the piano?
5. Can употребляется в просьбах, а также в значении «могу ли…» при предложении чем-то помочь (здесь «примешивается» и желание получить разрешение):
Can you wait a moment, please?
Dan, can you help me, please?
Can I have these shoes, please? (в магазине)
Can you come to the meeting tomorrow?
Саn you lend me three shillings?
Can I get you lemonade? – That’s very nice of you.
Can I help you, sir? – No thank you. I’m being served.
Can I carry your bag? – Oh, thank you.
6. С помощью предложений с вопросительными наречиями можно выразить неудовольствие:
What can he mean?
(Похожим образом звучат предложения с ever, on earth, in the world, the devil: What ever does he mean? What on earth does he mean? What in the world does he want?)
7. Когда употребление can
грамматически невозможно
(за неимением у всех модальных глаголов инфинитива и причастий) можно употреблять be able to:
What have you been able to find out? (не ‘What have you could… ?’)
I might be able to help you. (не ‘I might can… ’)
He hasn’t been able to work recently.
She might not be able to fly to London.
He used to be able to speak German well.
Не seems (to be) quite unable to give up his bad habits.
Не seemed (to be) unable to give up his bad habits.
8. Be able to может употребляться и просто как замена can. Can предпочтительнее, чем be able to
a) когда говорится о чем-то, что происходит
в момент речи
:
Watch me, Mum; I can stand on one leg. (не ‘…I’m able to stand on one leg’.)
I can see a ship. (более естественно, чем I am able to see a ship.)
b) с глаголами в форме
пассивного залога
:
CDs can now be copied easily (лучше, чем ‘CDs are now able to be copied…’)
He can’t be understood. (лучше, чем ‘He’s not able to be understood’.)
c) со значением
«знать/уметь как…»
:
Can you cook? (более естественно, чем ‘Are you able to cook?’)
ПРОШЛОЕ
4.88
1. Could употребляется для выражения способности что-то делать в прошлом, только если из контекста (например, есть другой глагол в форме прошедшего времени) очевидно, что речь идет именно о прошлом:
She could read Latin when she was twelve!
Не could speak German well when he was young, but he has forgotten most of his German now.
It could be quite frightening if you were alone in our big old house.
She could read when she was four.
My grandmother could sing like an angel (можно догадаться, что это было в прошлом).
My last car could do 200 kph (слово ‘last’ указывает на прошлое).
In those days everybody could find a job (обстоятельство ‘in those days’ указывает на прошлое).
Можно употреблять was/were able to:
She was able to read when she was four.
2. Could употребляется в придаточных предложениях и косвенной речи:
Can you help me? – What did you say? – I asked if you could help me.
Can you give me a hand? – What? – I asked if you could give me a hand.
You could get a better job if you spoke a foreign language.
I told you I could use a typewriter.
I told him I could help him.
3. Can/could выражает именно
возможность
что-либо совершить, поэтому, как правило, не употребляется для выражениях законченных в прошлом отдельных действий. В отношении таких действий could выражает сослагательность:
Тоm could pass the examination, we all were sure of that (Том мог сдать и мы были в этом уверены, но предложение не означает, что он его действительно сдал).
Tom could pass the examination (Том мог бы сдать экзамен, но тоже не значит, что он его сдал).
Для выражения законченных действий в прошлом можно употреблять
a) просто Past Simple:
I found a really nice dress in the sale. (не ‘I could find… ’)
Torn passed the examination.
Harry swam across the river.
Аnn didn’t catch her train.
(could в таких предложениях не употребляется)
b) manage (предполагает трудности, которые пришлось преодолеть) и succeed:
I managed to run 10 km yesterday. (не ‘I could run 10 km
yesterday… ’ )
I managed to buy a really nice coat yesterday. (не ‘I could buy a really nice
coat yesterday’.)
After six hours’ climbing, we succeeded in getting to the top of the mountain. (не ’… we could get to the top… ’ )
Torn succeeded in passing the examination.
Harry managed to swim across the river.
Anne didn’t manage to catch the train.
Did you manage to get to the top of the mountain?
How did you manage to get here in time?
I managed to get /succeeded in getting all my clothes into the suitcase.
c) обороты с get
Не got it done. (‘Не could get it done’ означает, что он мог бы это сделать).
d) оборот be able to:
I was able to pass the examination.
How many eggs were you able to get? (не ‘…could you get?’)
4. Но could можно употреблять, выражая, что что-то не случилось в конкретном случае в прошлом
a) с глаголами see, hear, smell, taste, feel, understand, remember:
I could smell something burning.
I could understand everything she said.
Не could smell something burning.
Suddenly she realised she could smell something burning.
He spoke so quickly that I couldn’t understand him at all.
Though I was sitting in the last row, I could see the film well.
I could not hear him.
b) в отношении единичного случая в придаточном предложении:
I’m so glad that you could come.
c) при употреблении отрицательной формы couldn’t:
I managed to find the street, but I couldn’t find her house.
Не said he couldn’t come to the meeting.
The box was so heavy that I couldn’t lift it.
I tried to lift the box but couldn’t.
Не said he was sorry he couldn’t lend me the money.
d) с наречиями hardly и only (так как они также имеют негативный оттенок).
She could hardly believe her eyes. I could only get six eggs.
5. Употребляется can’t, а не couldn’t, когда речь идет о том, что невозможно:
There can’t be many people in the world who haven’t watched television.
The doctor can’t see you this morning; he’s busy at the hospital.
6. Could+have+past participle указывает на
неосуществленную
в прошлом возможность:
The President was always available. We could see him at any time (мы могли его видеть)
You never came to see me. Why not? You could have seen me at any time (ты мог, но не делал).
Не could easily have done it.
You could have caught the train if you had hurried.
I could have married anybody I wanted to.
I was so angry I could have killed her!
Why did you jump out of the window? You could have hurt yourself.
I could have won the race if I hadn’t fallen.
I could have kissed her if I’d wanted to.
Так можно выразить
неудовольствие
:
You could have helped me — why did you just sit and watch?
You could have told me you were getting married.
Отрицательное предложение показывает, что возможности что-то сделать не было вообще:
I couldn’t have won, so I didn’t go in for the race.
I couldn’t have enjoyed myself more — it was a perfect day.
Такая конструкция иногда может выражать и
предположение
:
Who sent those flowers? – I’m not sure. It could have been your mother.
Предложение может относиться к
настоящему времени
:
He could have been Prime Minister now if he hadn’t decided to leave politics.
We could have spent today at the seaside, but we thought it was going to
rain, so we decided not to.
□ Иногда употребляется can+have+past participle:
I don’t know where she can have gone.
7. Was/were able to предпочтительнее, когда речь идет о единичном достижении в прошлом, а не способности вообще (в этом случае можно употреблять и could и was/were able to):
She swam strongly and was able to cross the river easily, even though it was swollen by the heavy rain (не‘ She swam strongly and could cross… ’)
He didn’t want to buy a new suit but at last we were able to persuade him.
She wasn’t able to pass the exam.
Sue could play the flute quite well/ Sue was able to play… (способность вообще)
Отрицательную форму couldn’t можно употреблять в обоих случаях:
He couldn’t play tennis.
We couldn’t persuade him to buy a new suit.
8. Could звучит естественнее
a) в отрицательных предложениях:
I tried to get up but I couldn’t move (естественнее, чем ‘…I wasn’t able to move’.)
b) с глаголами физического восприятия (feel, hear, see, smell, taste) и выражающими умственную деятельность (believe, decide, remember, understand и т.п.):
I could remember the crash, but nothing after that (естественнее, чем ‘I was able to remember…’)
c) после the only thing/place/time и all, со значением ‘the only thing’:
All we could see were his feet. (естественнее, чем ‘All we were able to…’)
d) выражая идею что что-то чуть не случилось, особенно с наречиями almost, hardly, just, nearly:
I could nearly touch the ceiling (естественнее, чем ‘I was nearly able to…’)

